Patents
Literature
84 results about "Farnesyl pyrophosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
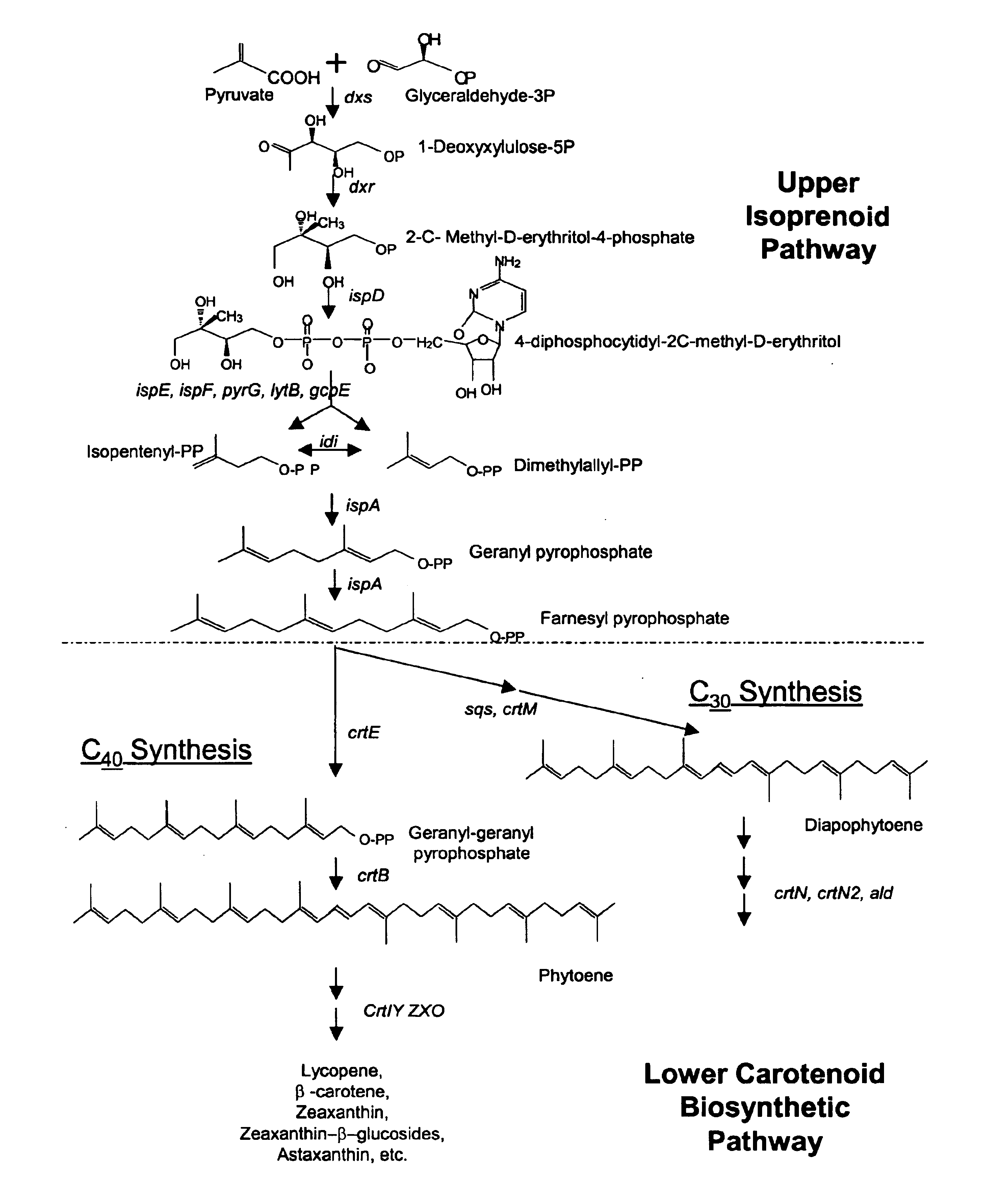
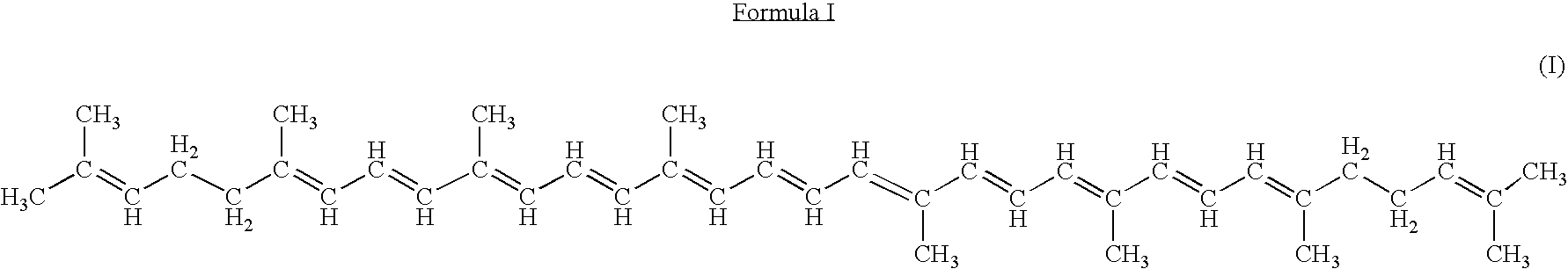
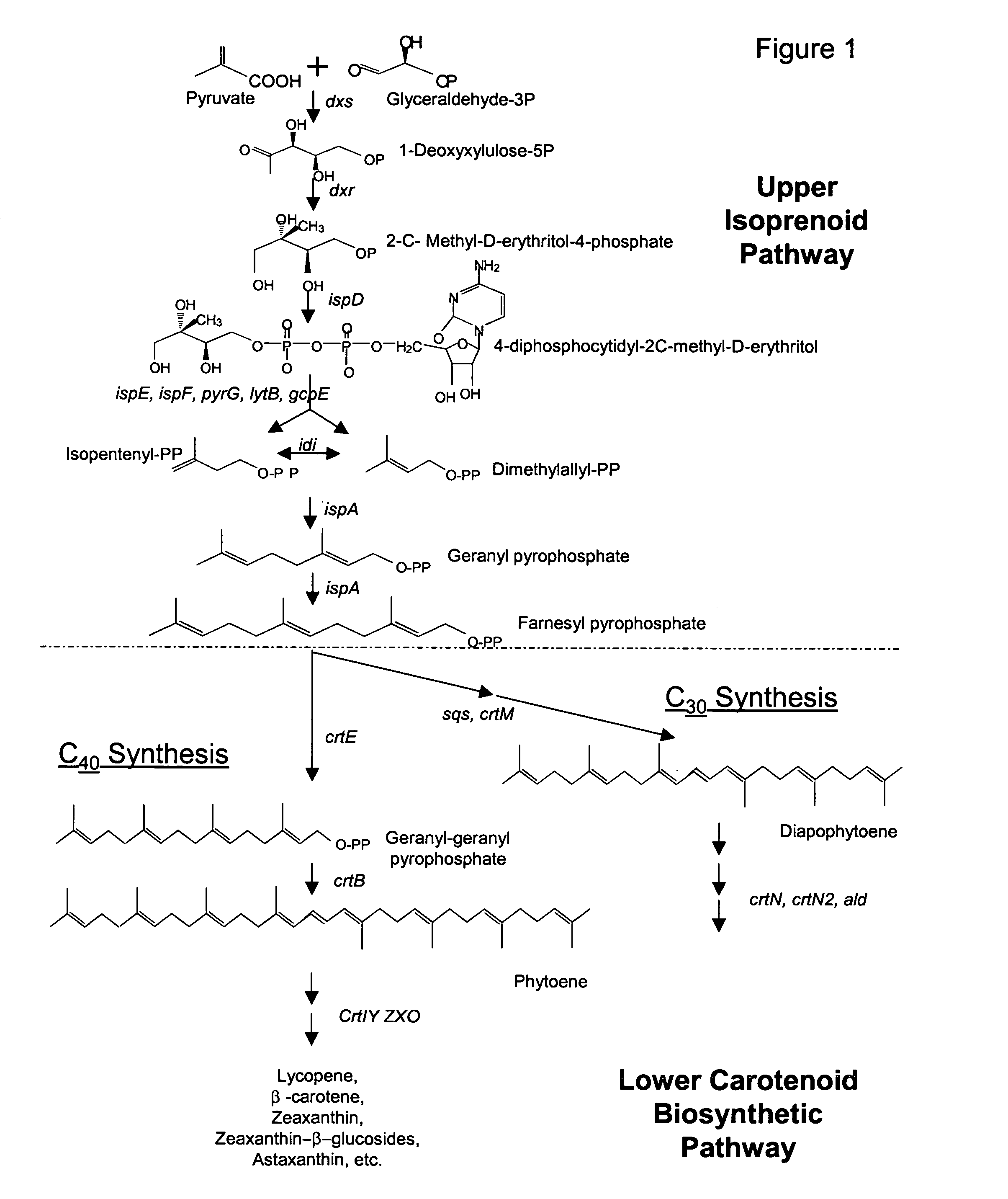
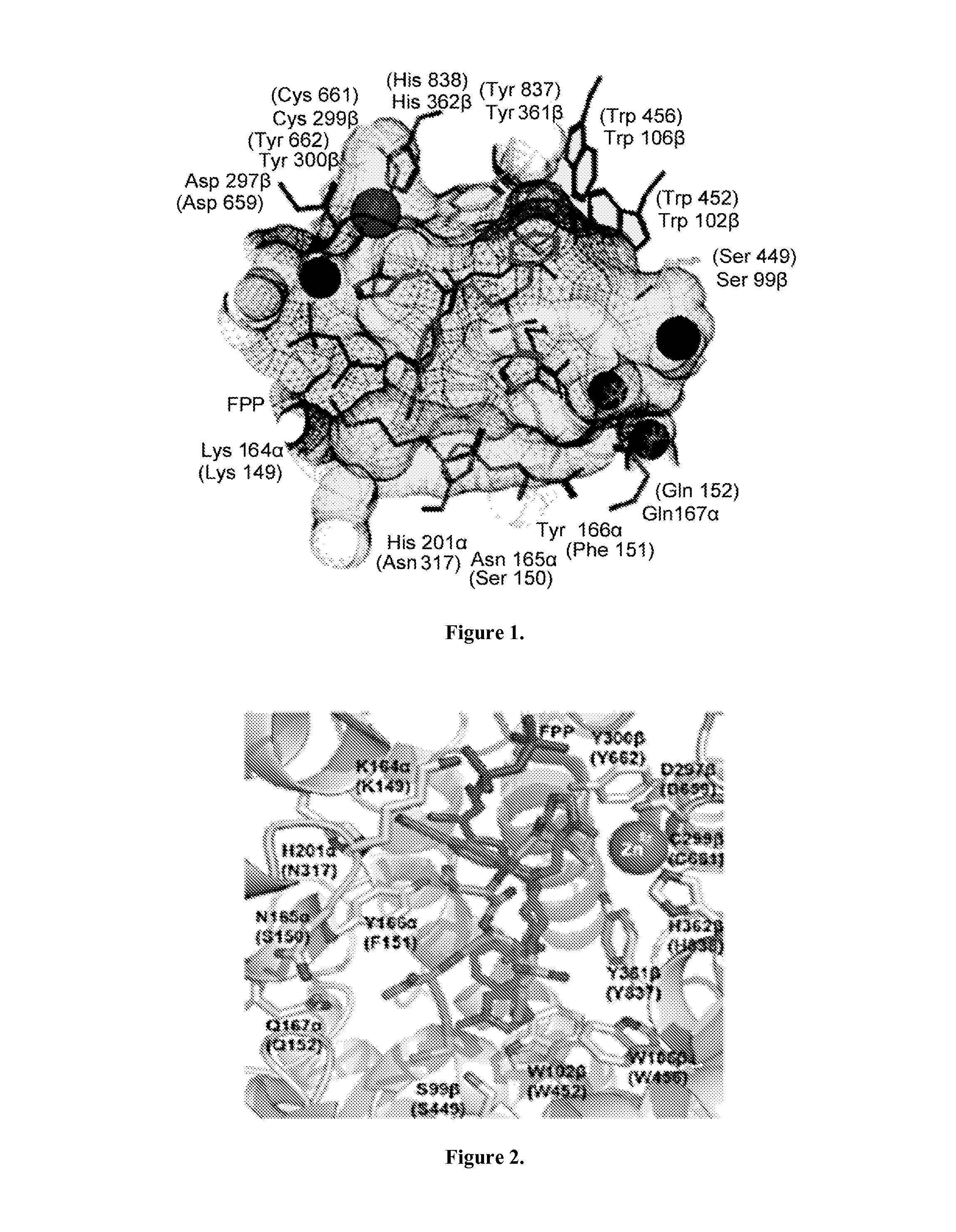
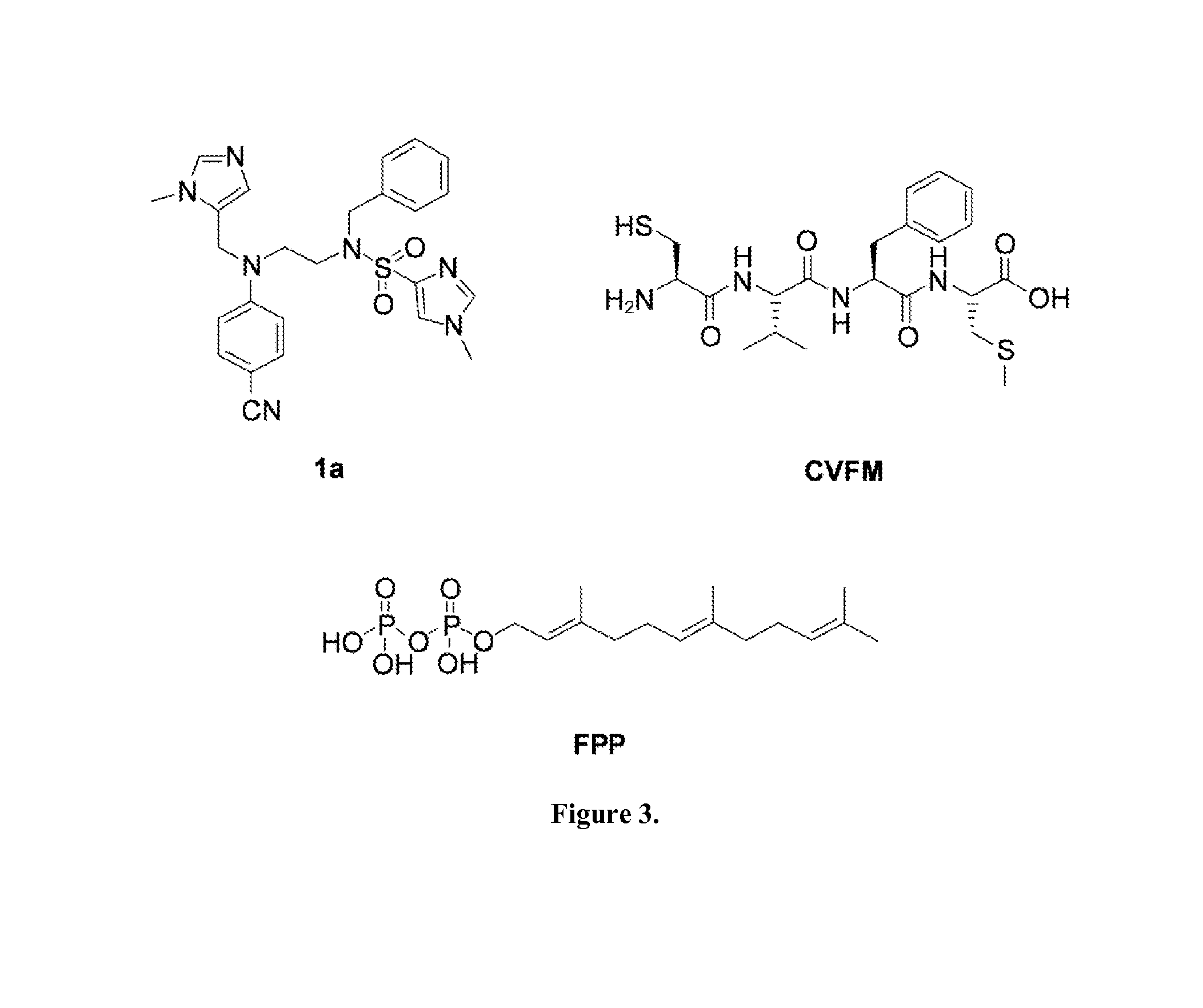
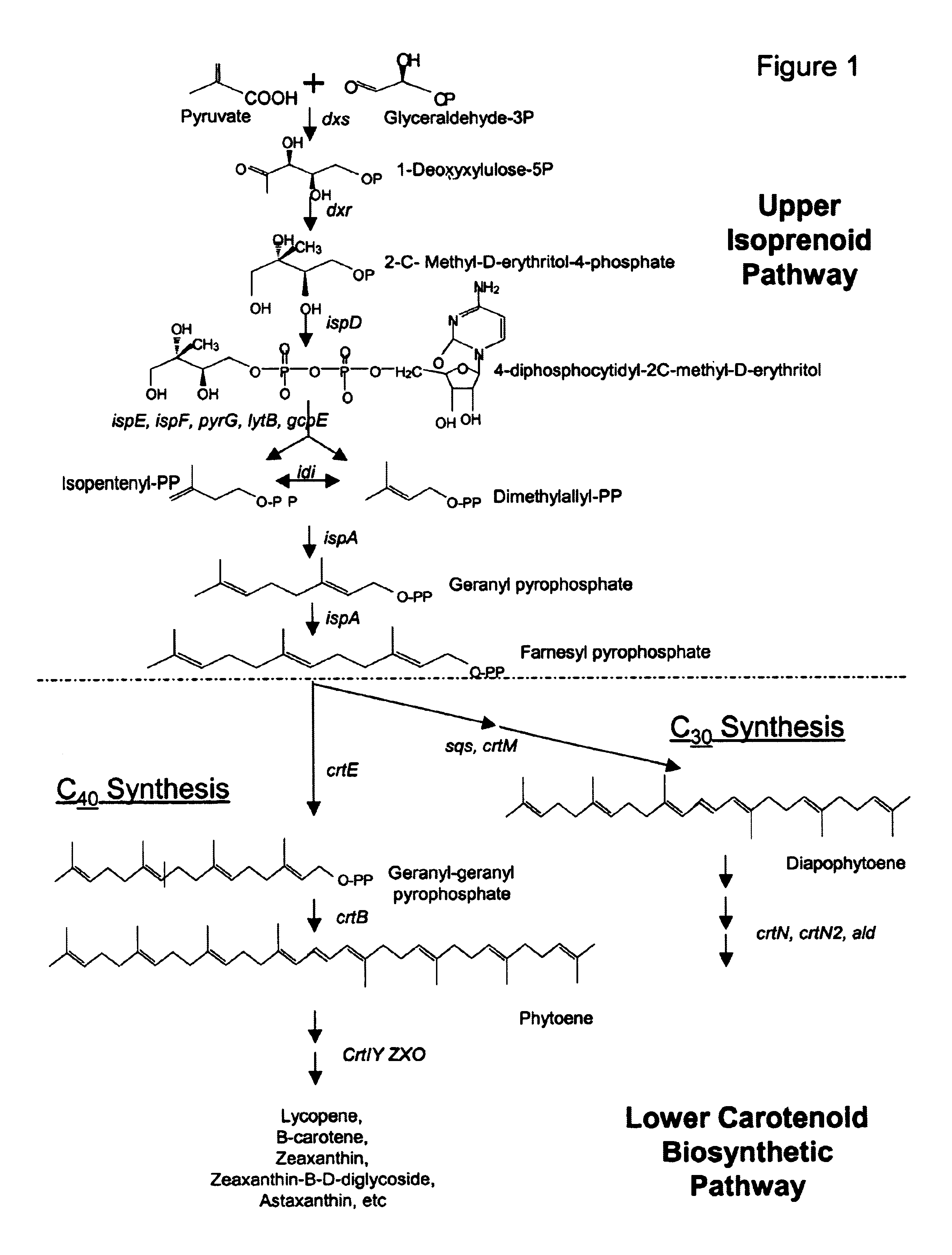
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is an intermediate in both the mevalonate and non-mevalonate pathways used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes, terpenoids, and sterols.
Methods for suppressing the induction of nitric oxide synthase in a cell
InactiveUS7049058B2Increase ratingsIncrease volumeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAntioxidantSuppressor
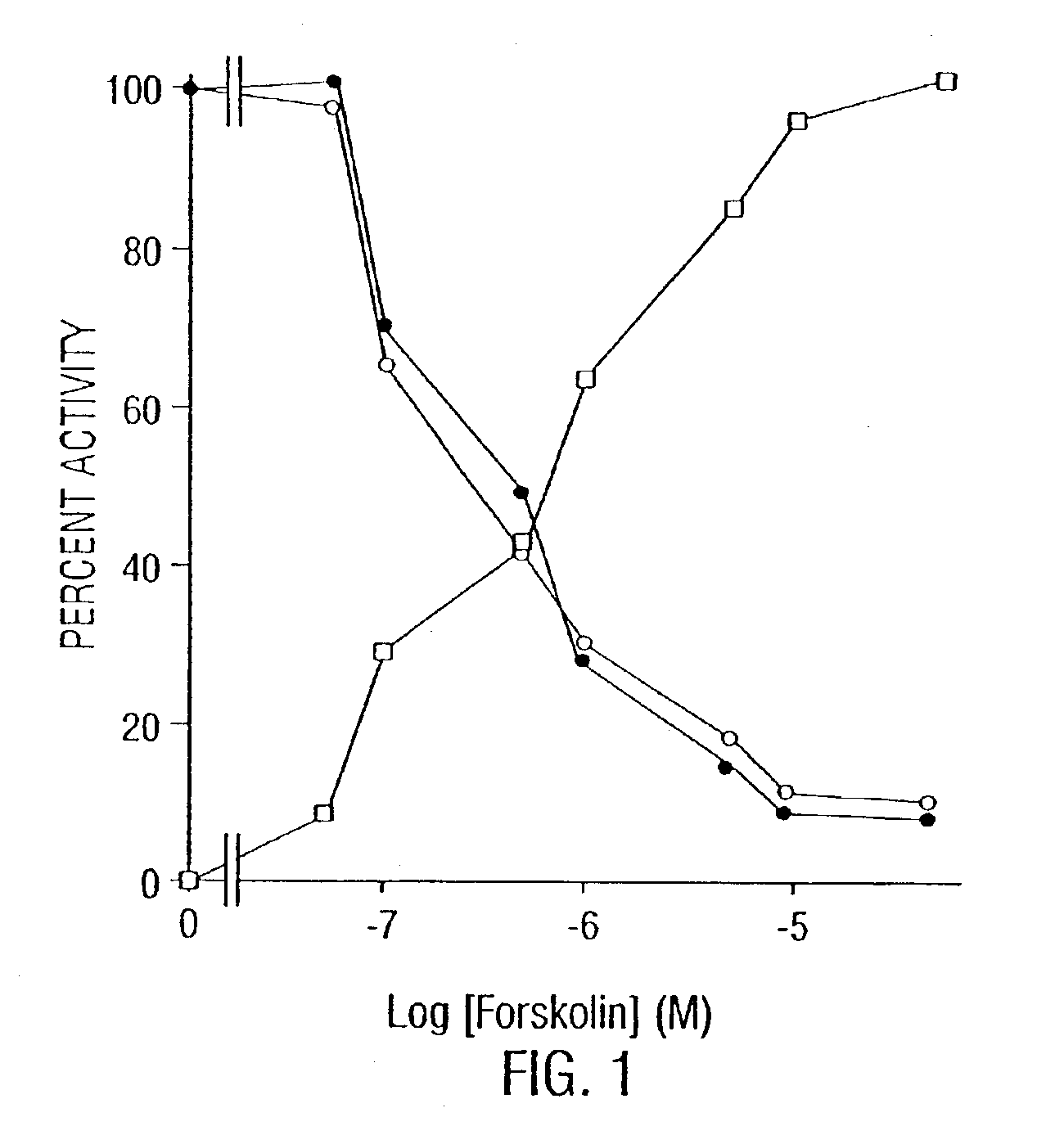
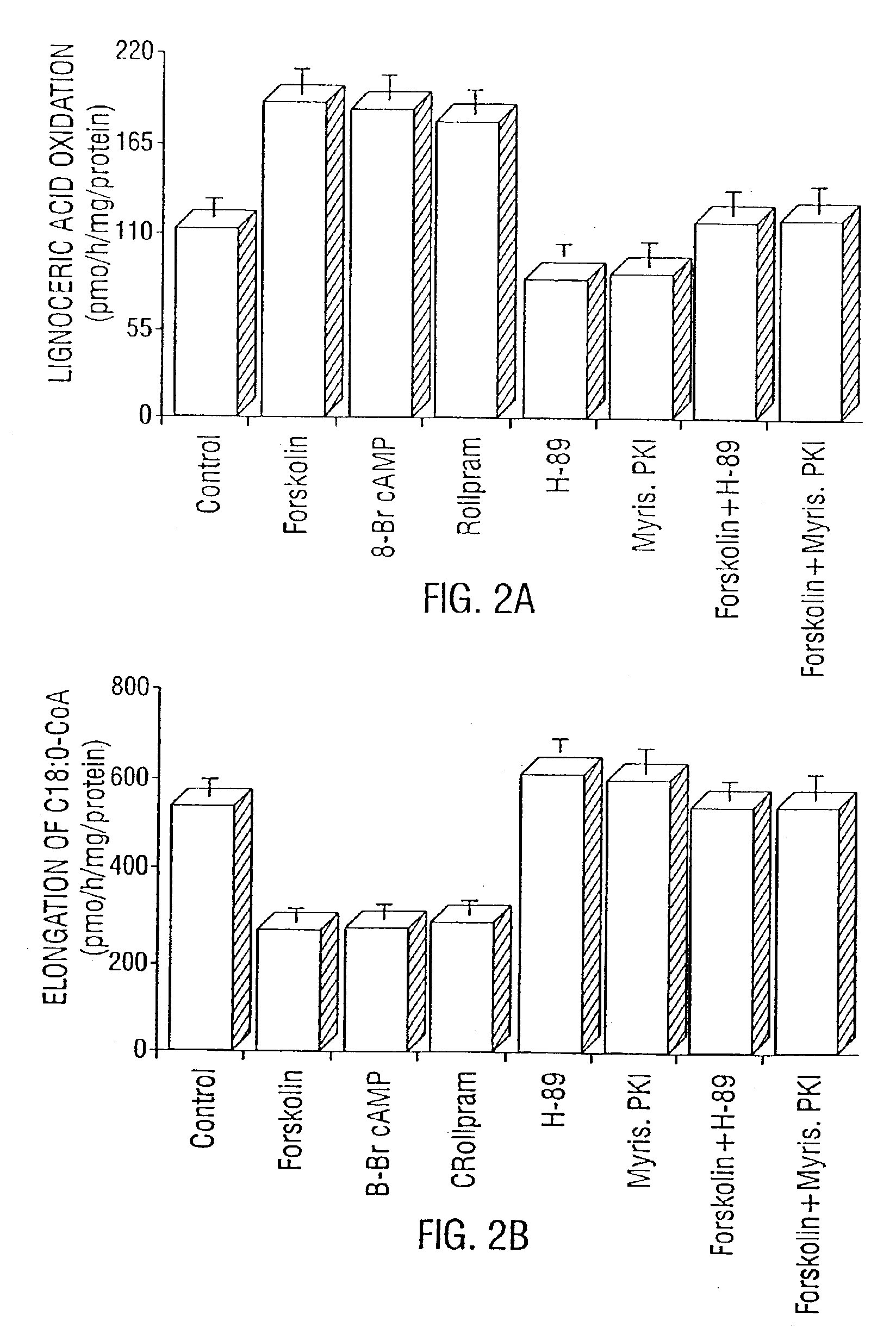
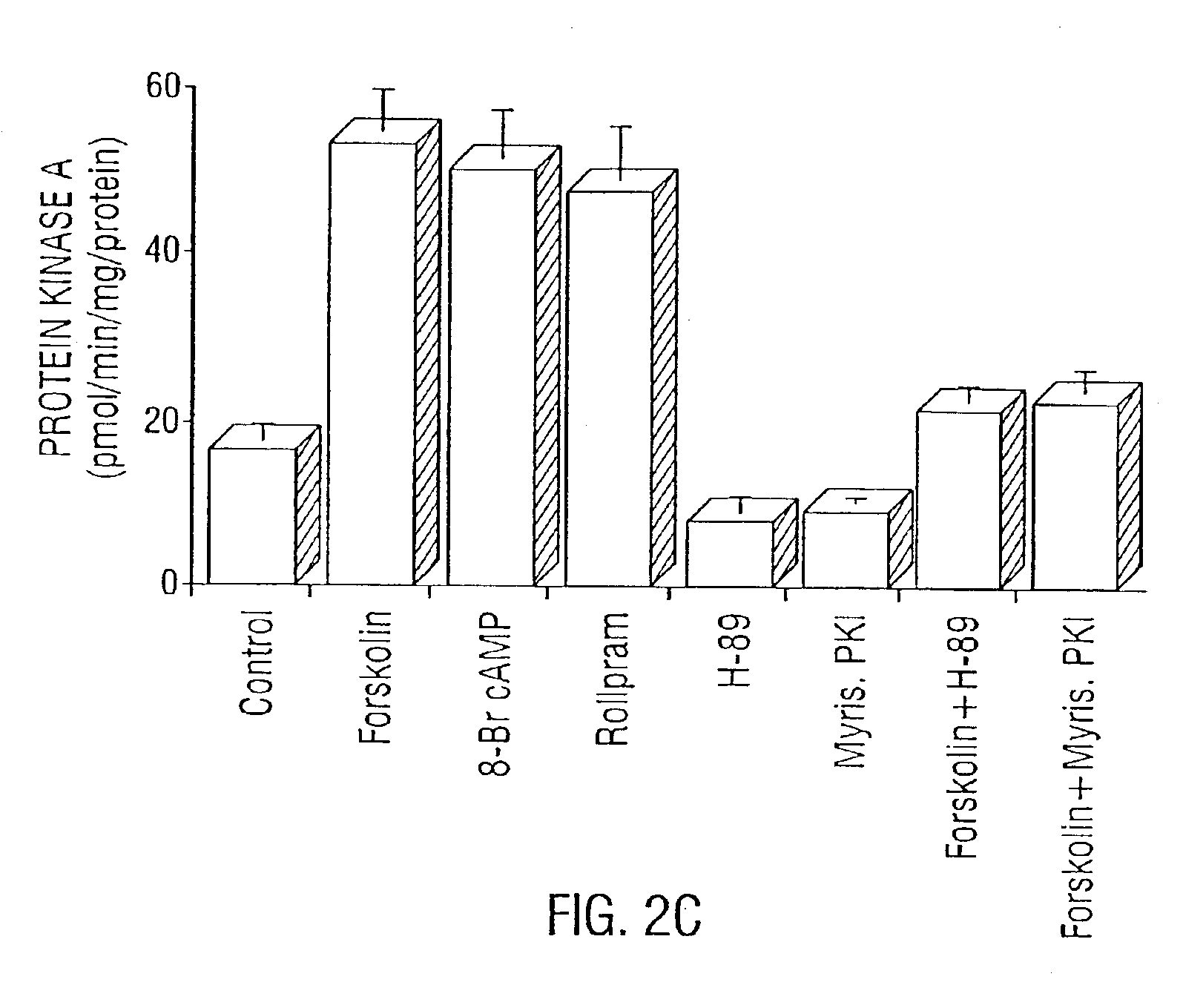
Disclosed are methods for suppressing the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase in a cell comprising contacting said cell with an effective amount of at least one induction suppressor of inducible nitric oxide synthase or a cytokine are disclosed. The induction suppressor can be an inhibitor of mevalonate synthesis, an inhibitor of the farnesylation of Ras, an antioxidant, an enhancer of intracellular cAMP, an enhancer of protein kinase A (PKA), an inhibitor of NF-kβ activation, an inhibitor of Ras / Raf / MAP kinase pathway, an inhibitor of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase or an inhibitor of farnesyl pyrophosphate.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Increased isoprene production using mevalonate kinase and isoprene synthase
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method for production of isoprenoids
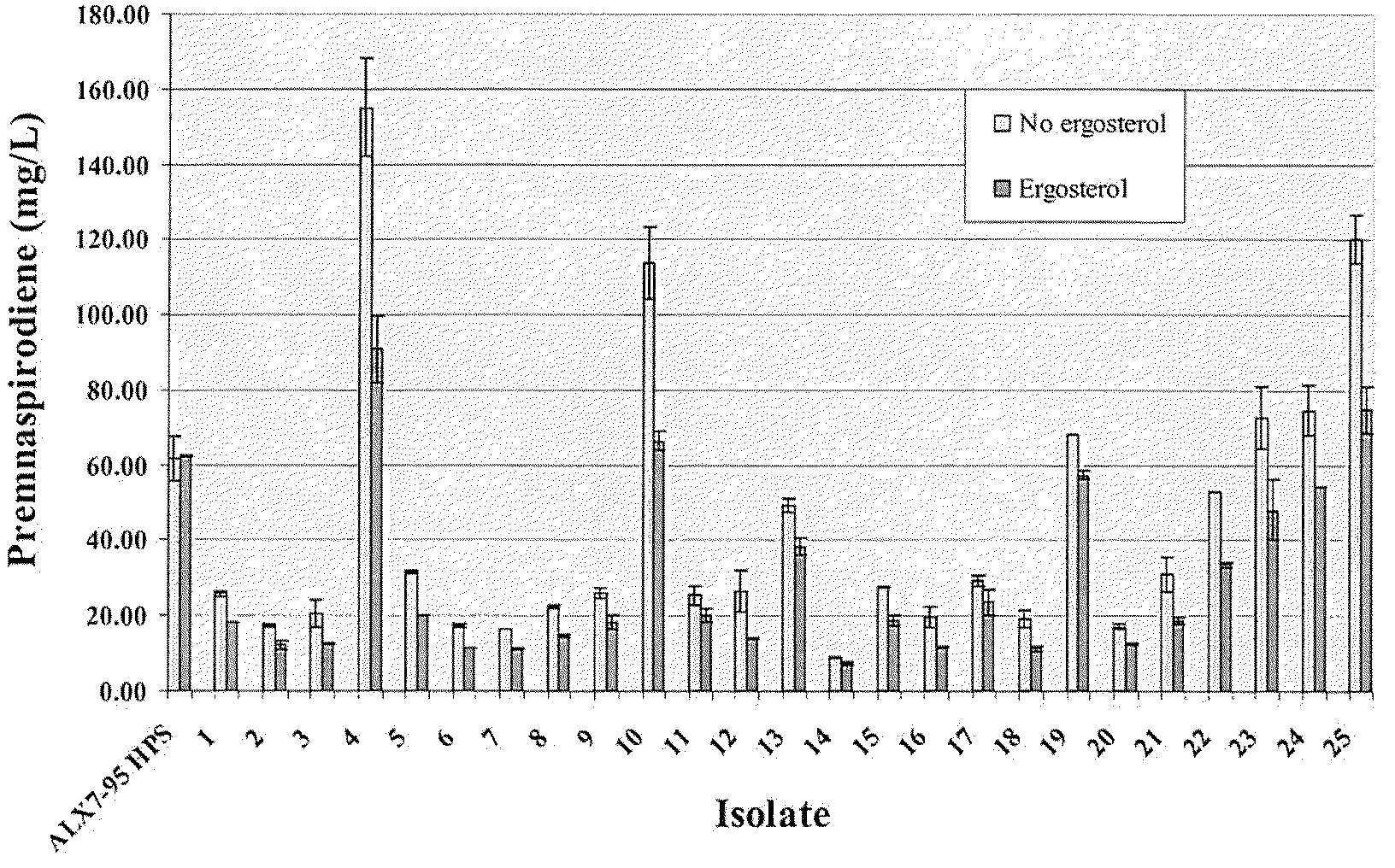
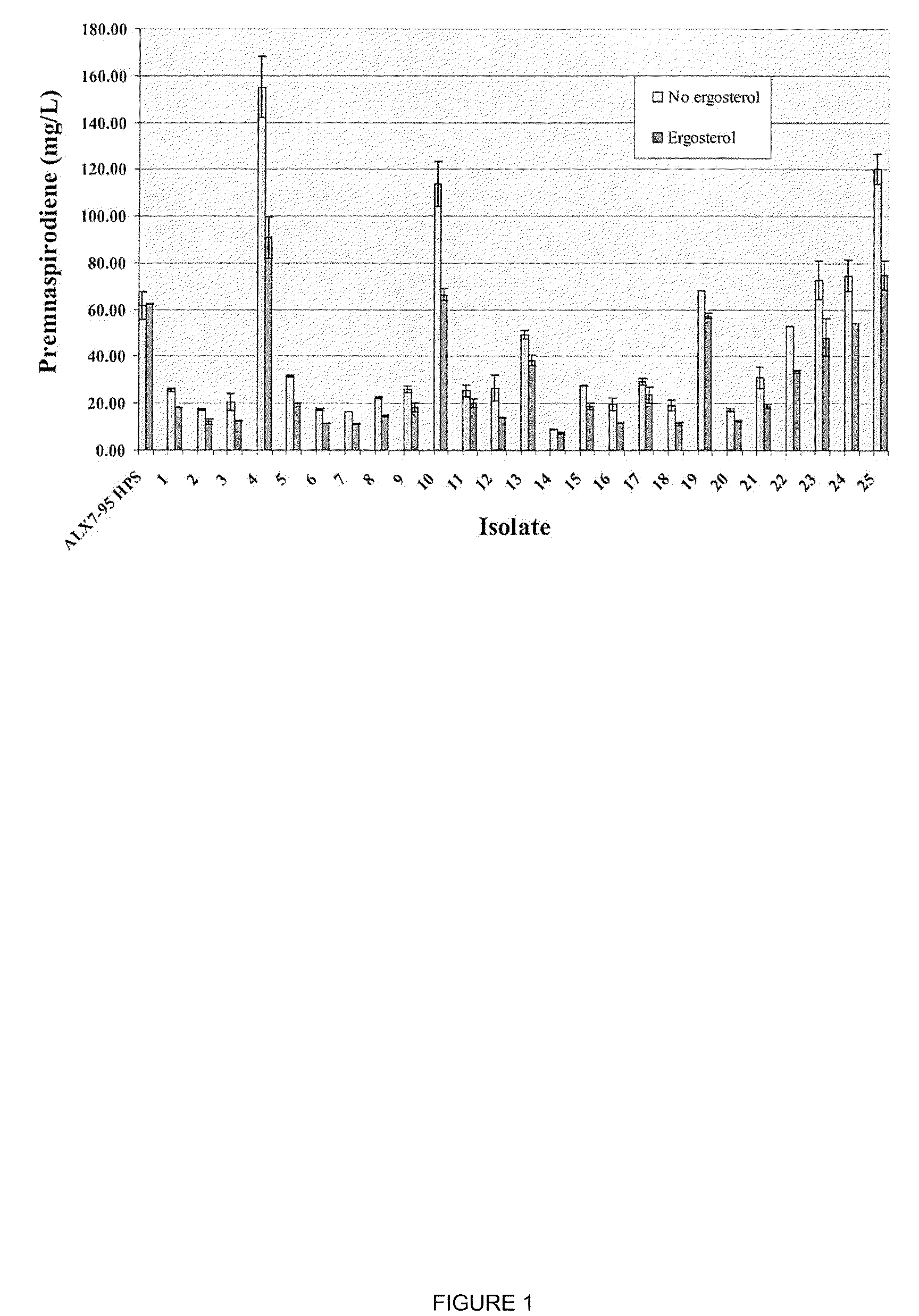
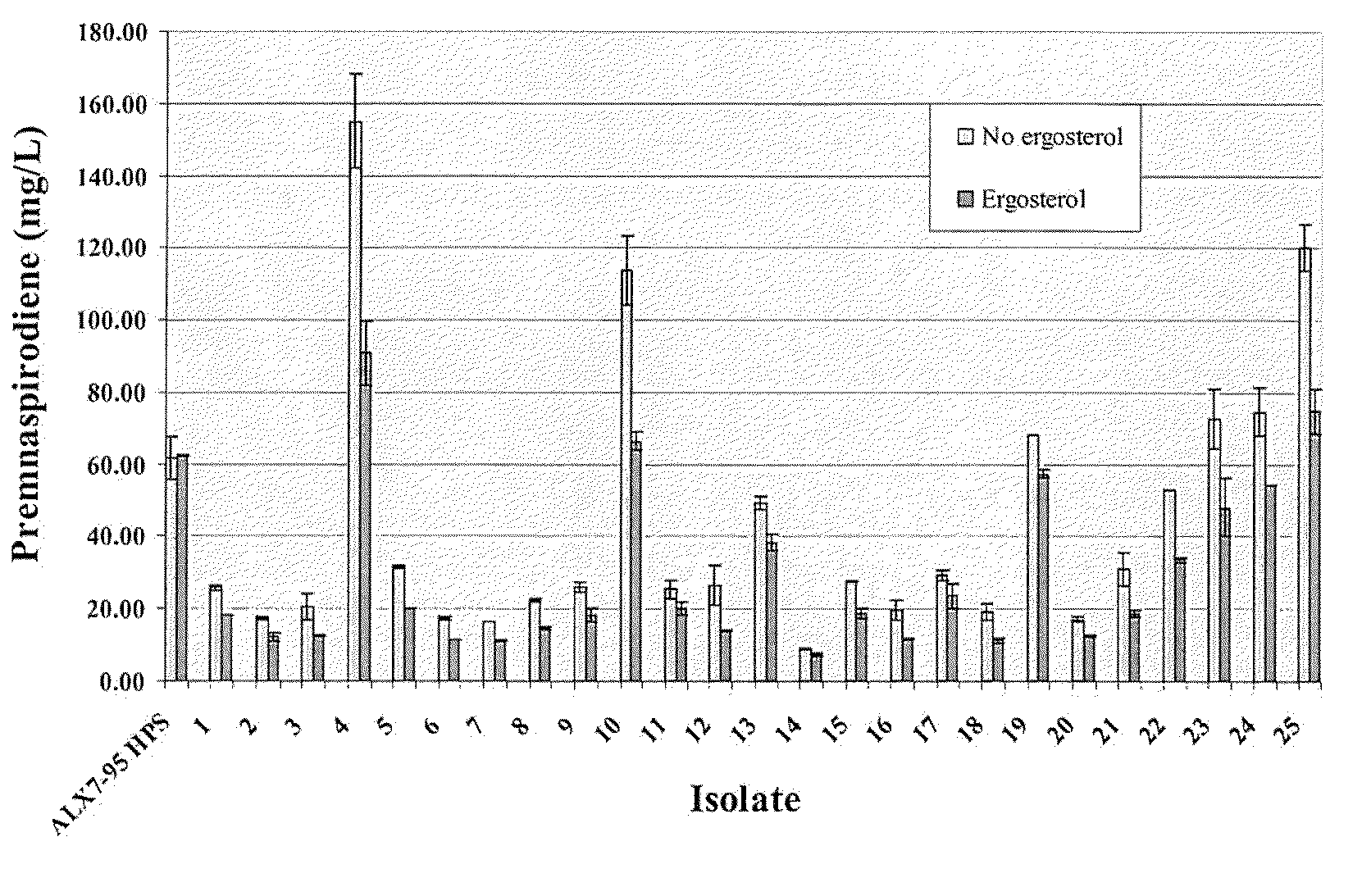
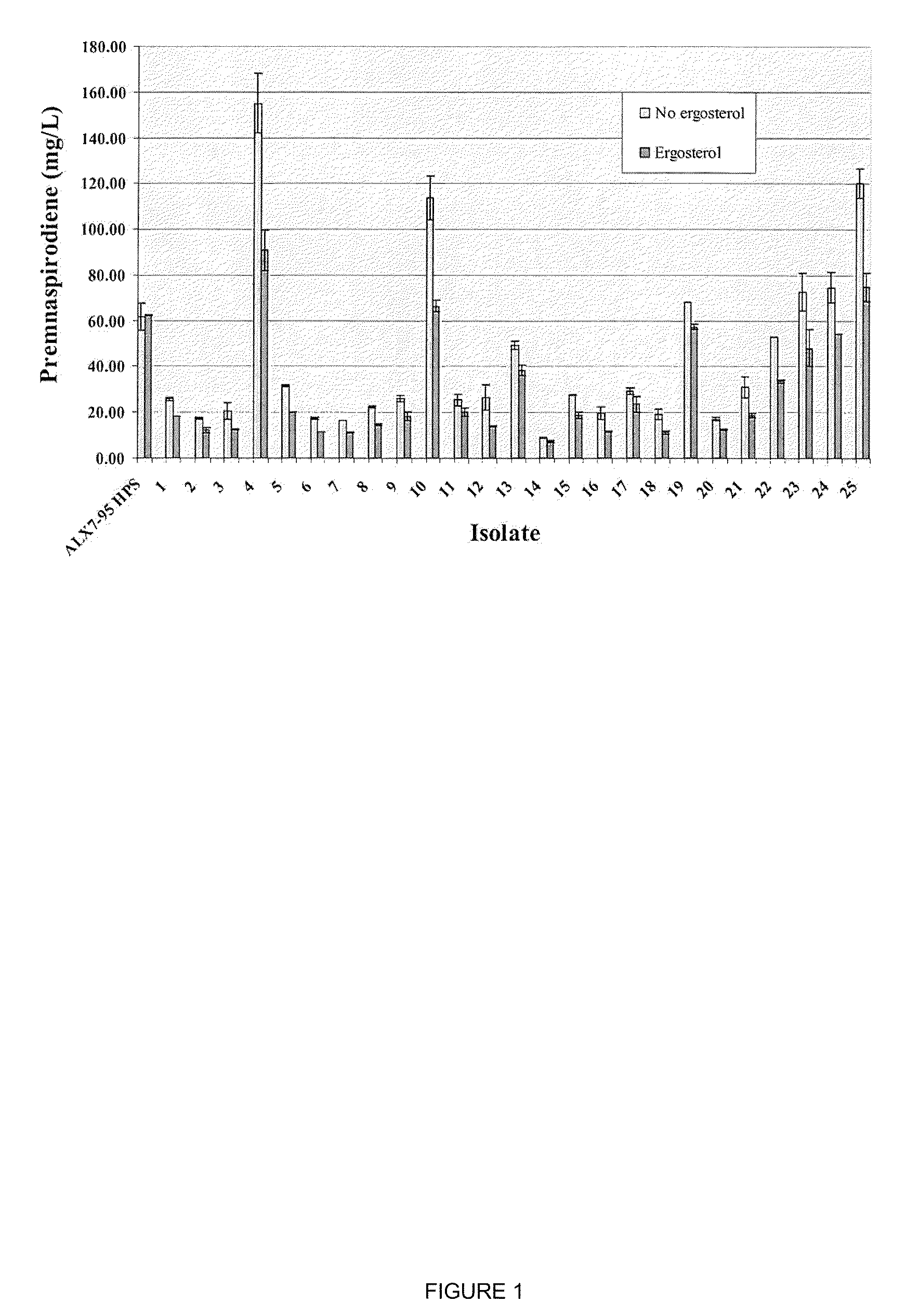
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Isoprenoid compounds
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
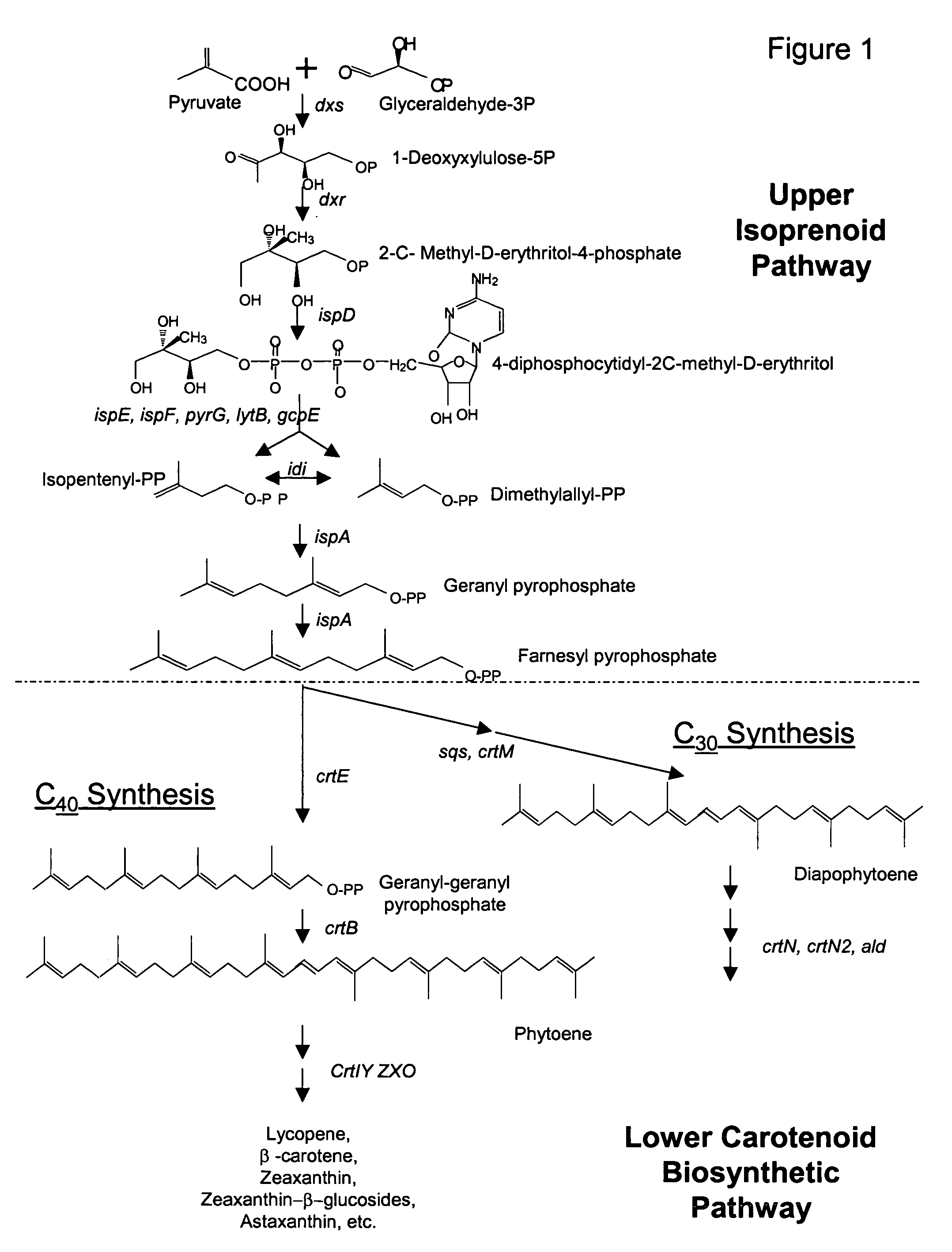
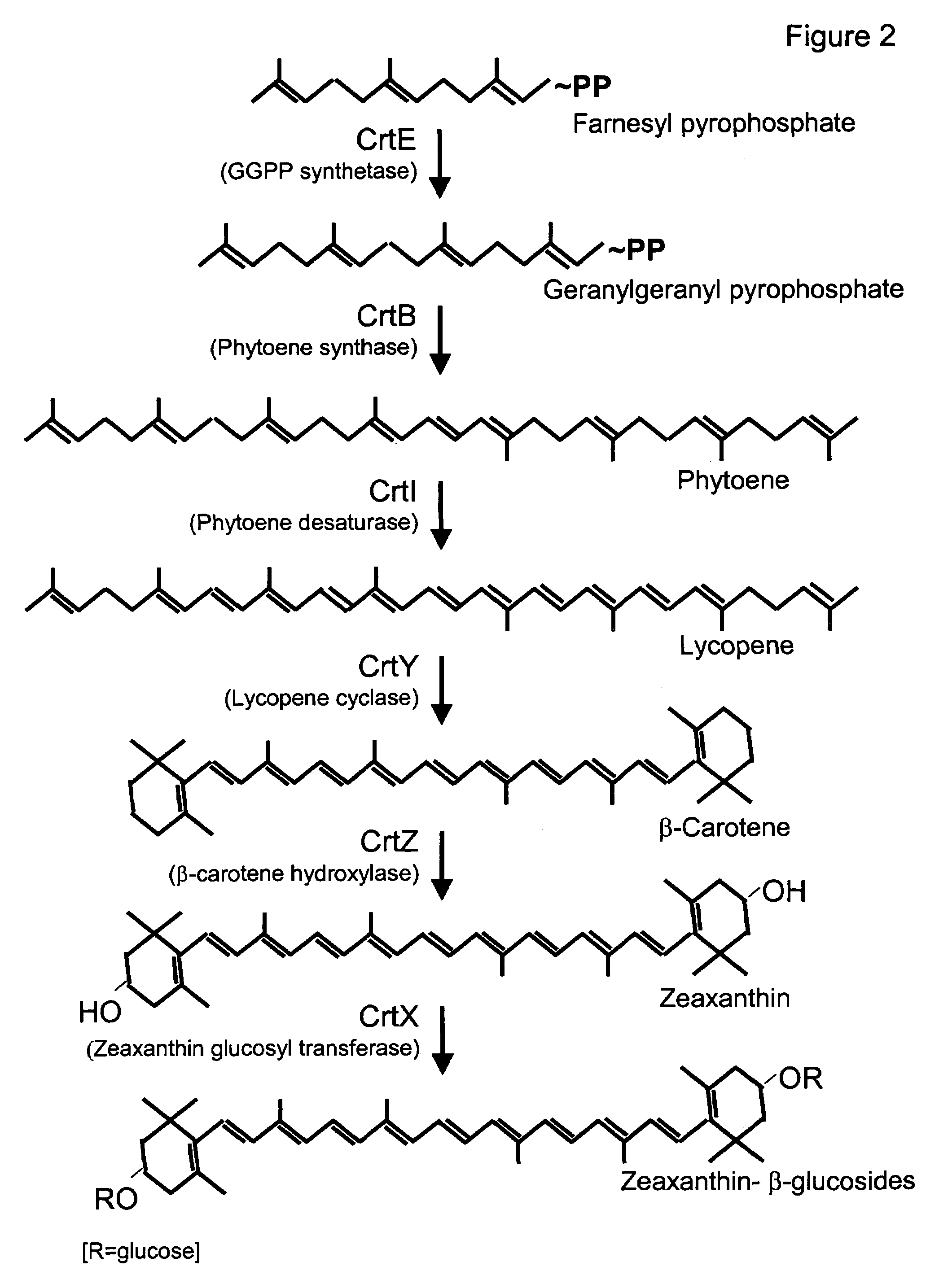
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for production of isoprenoid compounds
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (IPI) and/or prenyl transferase inhibitors
Methods of treatment and prophylaxis of various diseases and disorders, and in particular diseases and disorders of lipid and bone metabolism, involving the administration of prenyl transferase (farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase) and / or isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase inhibitor compounds are disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
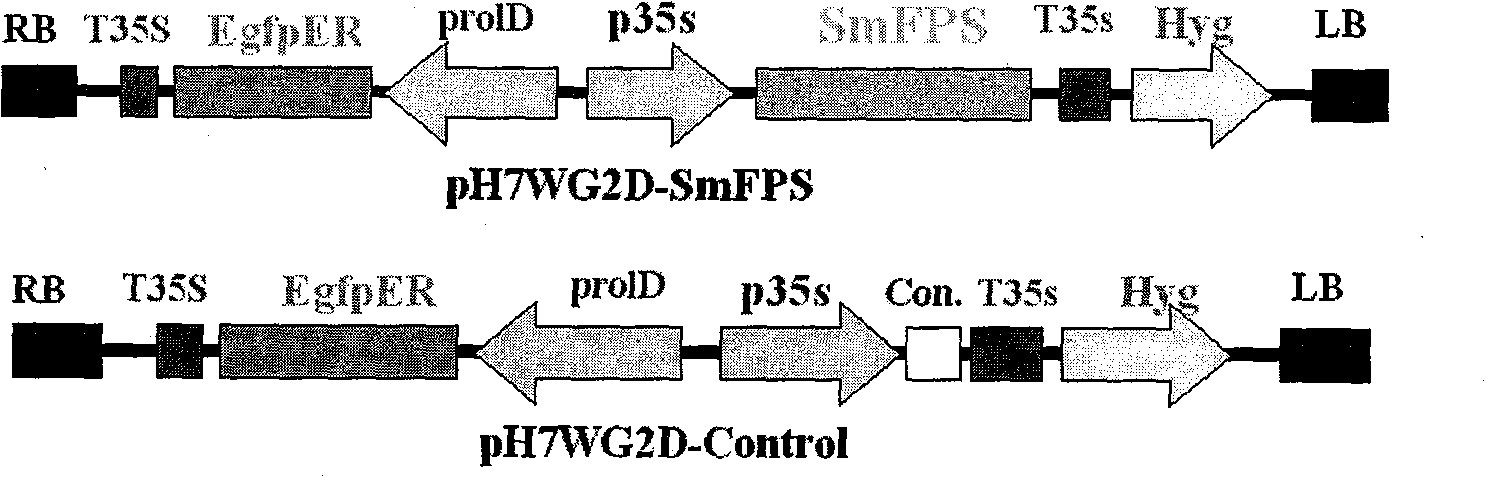
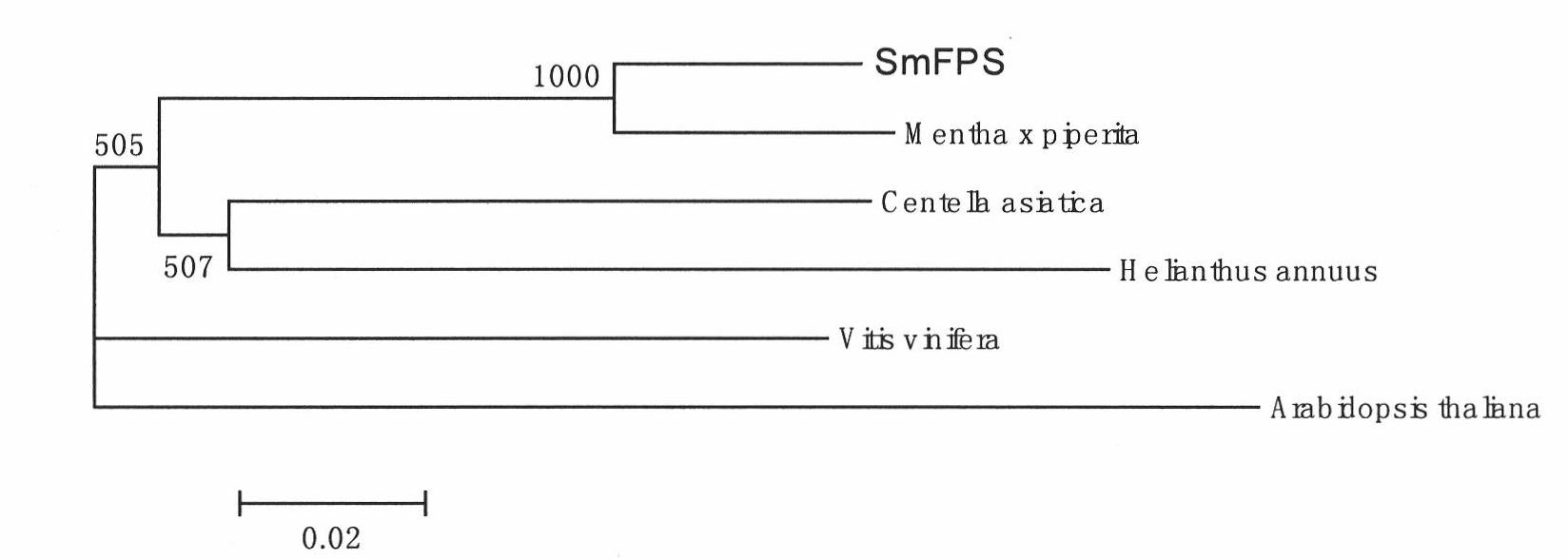
SmFPS (Salviamiltiorrhizabge Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase) gene as well as coded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101928716AIncrease contentRelieve severe plaque deficiencyTransferasesFermentationSalvia miltiorrhizaNucleotide
The invention discloses a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene as well as a coded protease and application thereof. The gene is obtained by clone from salviamiltiorrhizabge by utilizing a cDNA chip technology, which fills the blank of separating and cloning the farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from a rare traditional Chinese medicine of salviamiltiorrhizabge. The farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more nucleotides or allelic genes and derived nucleotide sequence thereof. The protein coded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more amino acids. The farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene can improve the content of tanshinone which is diterpene active element in the salviamiltiorrhizabge by the biotechnology, is beneficial to the quality improvement of the salviamiltiorrhizabge medicine, can be used for the breeding selection and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
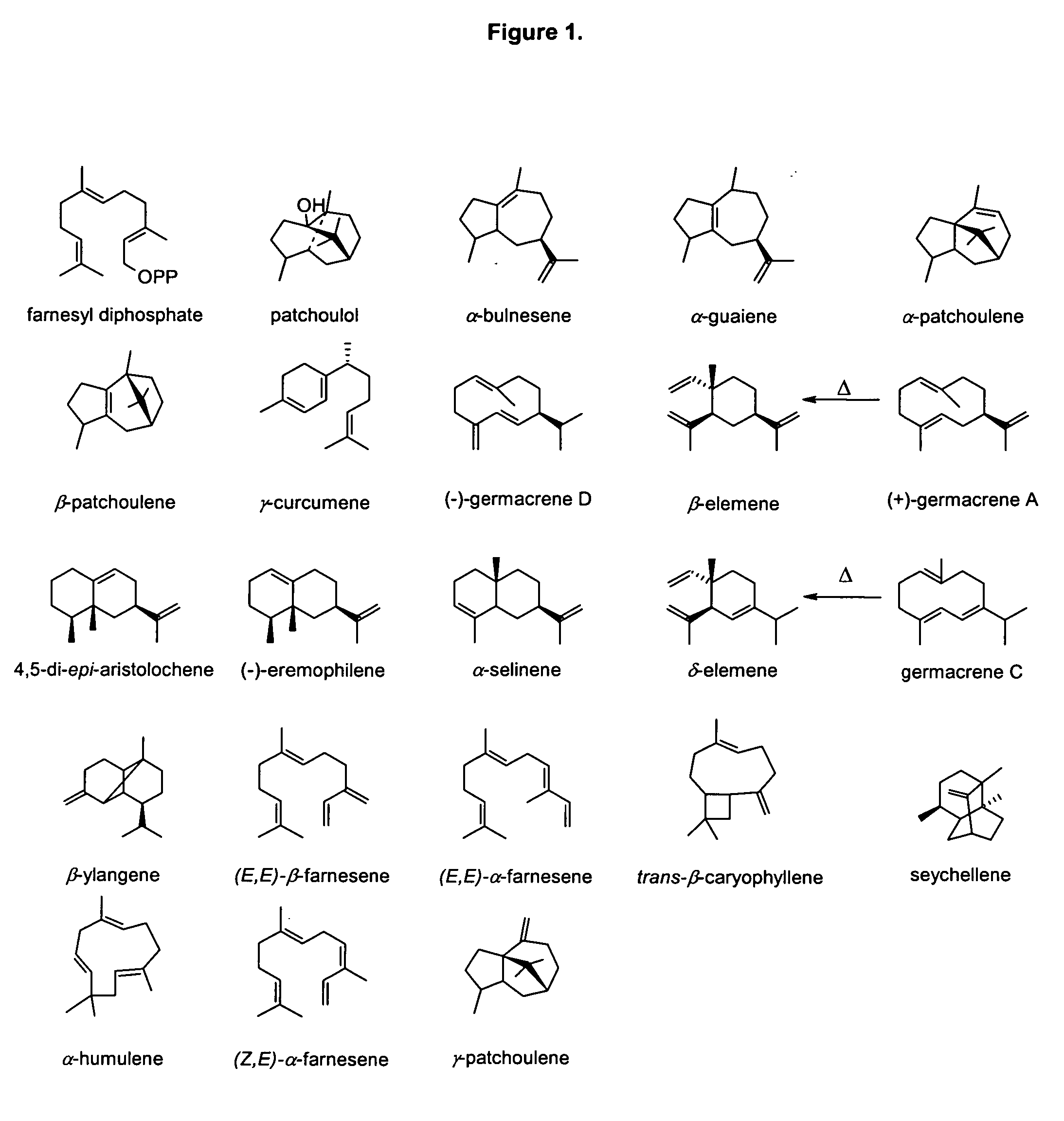
Sesquiterpene synthases from Patchouli
The invention relates to sesquiterpene synthases from Patchouli plants (Pogostemon cablin), and methods of their production and use. In one embodiment, the invention provides nucleic acids comprising a nucleotide sequence as described herein that encodes for at least one sesquiterpene synthase. In a further embodiment, the invention also provides for sesquiterpene synthases and methods of making and using these enzymes. For example, sesquiterpene synthases of the invention may be used to convert farnesyl-pyrophosphate to various sesquiterpenes including patchoulol, γ-curcumene and other germacrane-type sesquiterpenes.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
Genes have been isolated from strain DC260, a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family, encoding geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), phytoene synthase (CrtB), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ), and zeaxanthin glucosyl transferase (CrtX) activity. The genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Novel sesquiterpene synthetase and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel sesquiterpene synthetase and an application thereof. The novel sesquiterpene synthetase is obtained by separation and can cyclize farnesyl pyrophosphate to produce alpha-bisabol. Product specific sites of the sesquiterpene synthetase are obtained by structural domain replacement and point mutation experiments. The sesquiterpene synthetase has good enzymatic activity and can be applied in industrial production of the alpha-bisabol.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Construction method for high-yield sclareol strain
InactiveCN103387944AEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for constructing a high-yield sclareol engineering strain by a synthetic biology methdo, and an application thereof. The construction method for the strain relates to express plant sourced key enzymes for synthesizing sclareol, wherein the key enzymes comprise a pyrophosphoric acid ladanum enediol ester synthase and a sclareol synthase; and overexpress a combination of one or more yeast endogenous enzyme-based genes, wherein the enzyme-based genes comprise a key enzyme of a mevalonic acid approach-(hydroxymethyl) coenzyme A reductase, and two enzymes of an isopentenylpyrophosphate approach-a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and a geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. The method can efficiently produce sclareol, with a shake flask fermentation level reaches 9 mg / l, and has industrial application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof
ActiveCN106906201ASpecificEfficientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSynthetic biology
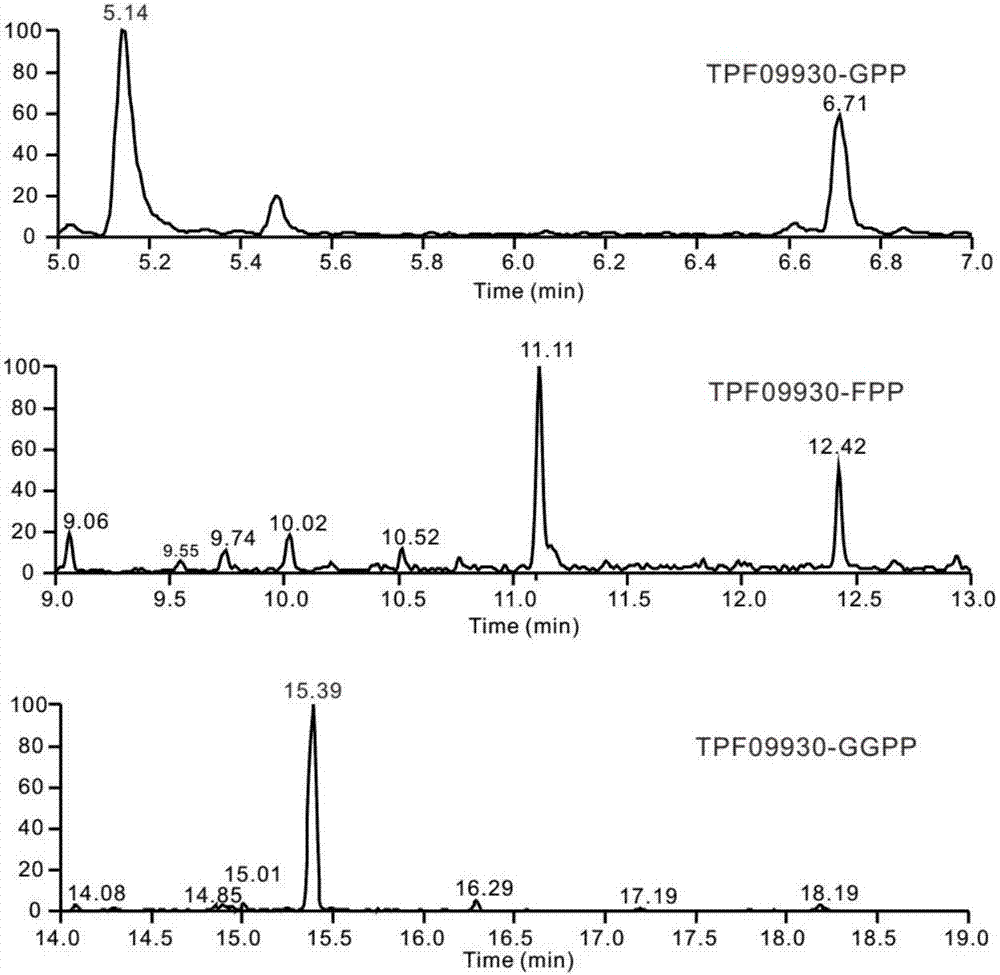
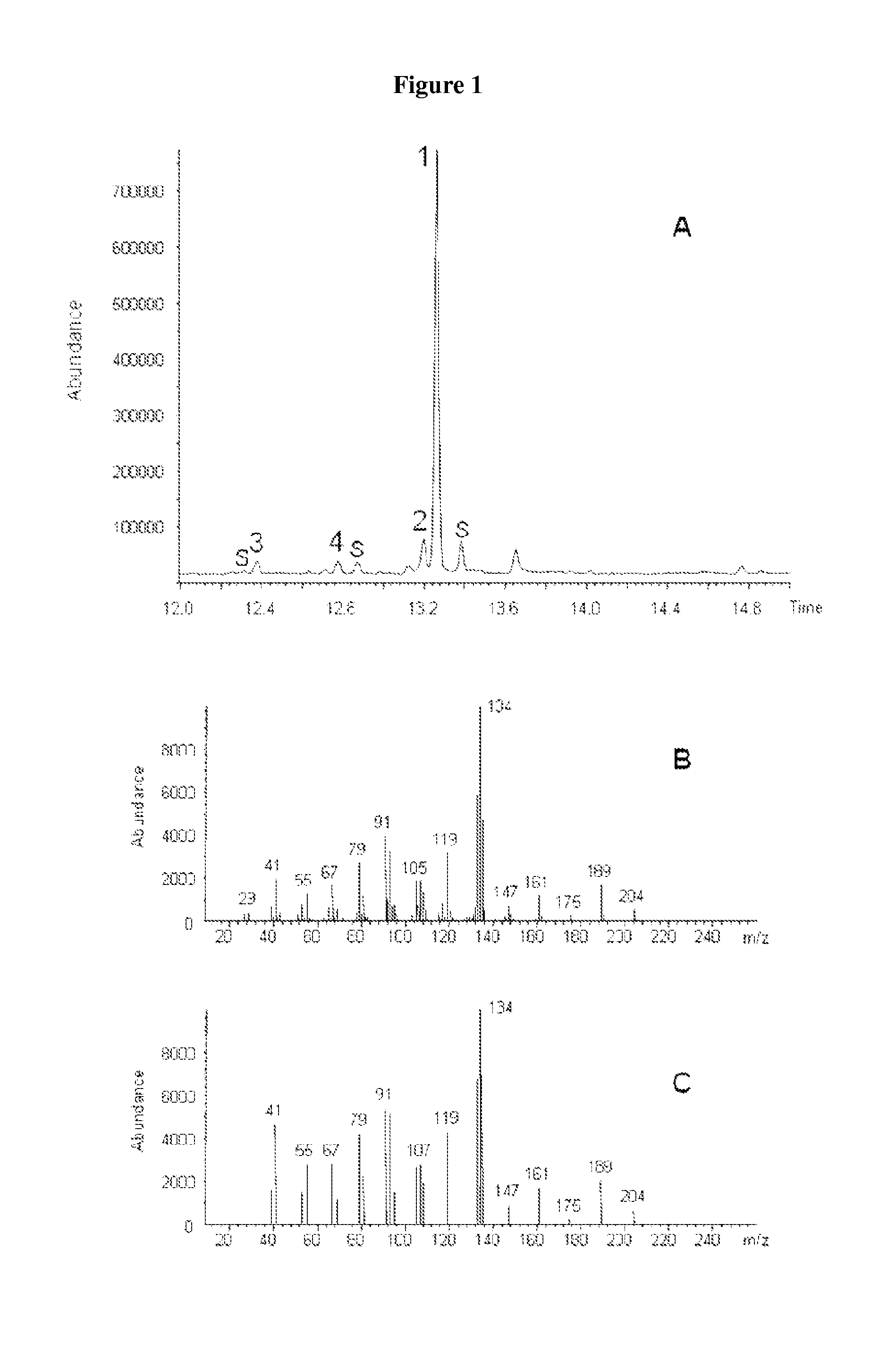
The invention discloses a terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. Terpene synthase TPF09930 for producing the nerolidol is provided, a nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase TPF09930 is as shown in SEQIDNO:2, the terpene synthase TPF09930 is combined with mevalonic acid pathway related genes to construct a strain for producing the nerolidol. By overexpression of Escherichia coli XL1 blue-derived atoB gene or idi gene of mevalonic acid pathway, catalytic substrate Farnesyl pyrophosphate can be synthesized in large scale, and producing of the nerolidol can be further promoted. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency, can improve the nerolidol yield, greatly overcomes the defects of a large amount of raw materials and a low nerolidol yield, reduces study cost, and ensures greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
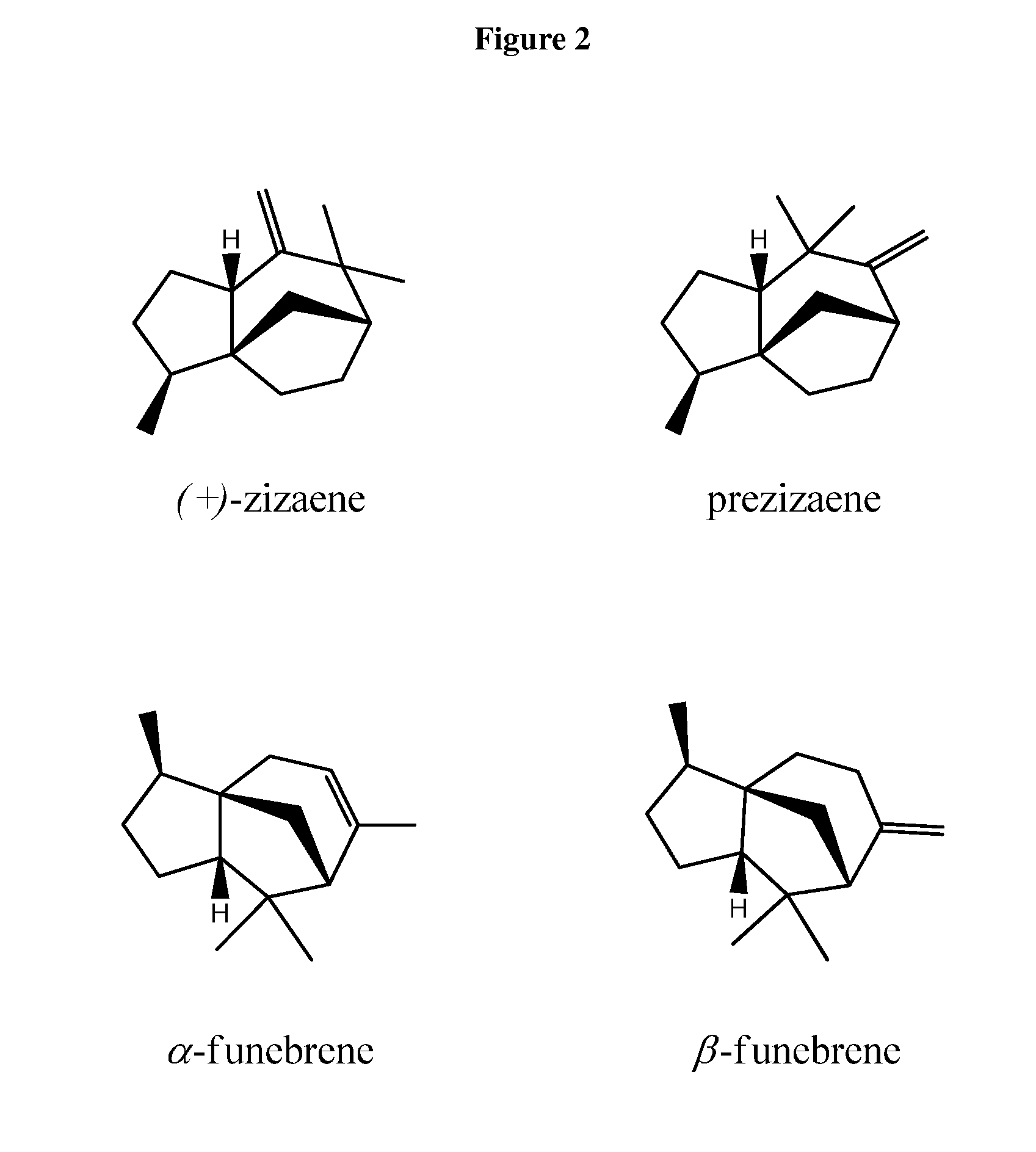
Method for producing (+)-zizaene
ActiveUS8703454B2Enhanced and reduced enzymatic activityAltered substrate utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaPyrophosphateIn vivo
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Sesquiterpene synthase from eupatorium adenophorum spreng, gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application of sesquiterpene synthase
The invention discloses sesquiterpene synthase from eupatorium adenophorum spreng, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacterium and application of the sesquiterpene synthase. Amino acid sequences of the sesquiterpene synthase are shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The sesquiterpene synthase, the gene, the vector, the engineering bacterium and the application have the advantages that catalysts come from the eupatorium adenophorum spreng which is a high-yield medicinal plant for beta-elemene, as proved by in-vitro activity, substrates FPP (Farnesyl pyrophosphate) can be catalyzed by the catalysts to generate the beta-elemene, and the final yield of the beta-elemene can ultimately reach 7.499 micro-grams / mL.
Owner:JINGANG PHARMA DALIAN
Dual inhibitors of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I
ActiveUS9040563B2Easy to derivatizeExtensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) studyBiocideOrganic chemistryEthylenediamineAnticarcinogen
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
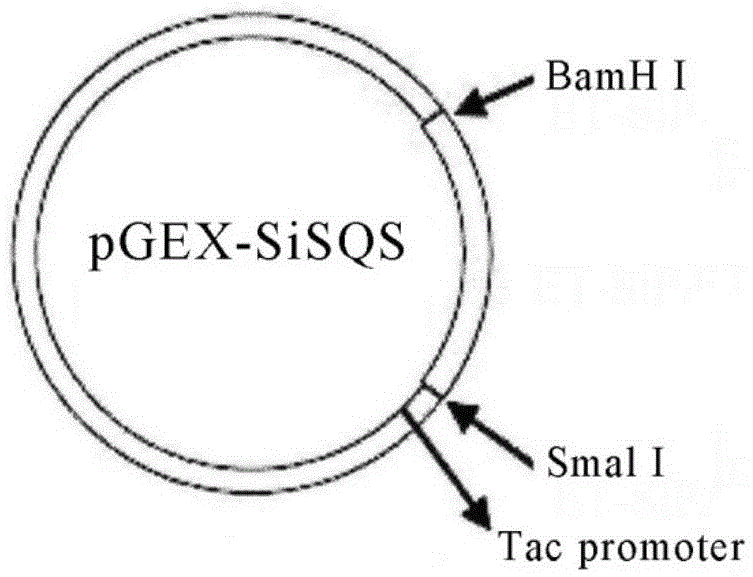
Saussurea involucrata cell squalene synthase (SiSQS) gene as well as products coded by same and application thereof
The invention provides saussurea involucrata cell squalene synthase (SiSQS) gene as well as products coded by same and application thereof. The complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) length of the SiSQS gene is 1846bp. A SiSQS recombinant expression vector is obtained by connecting the SiSQS gene and a prokaryotic expression vector, and SiSQS is prepared by the SiSQS recombinant expression vector; the SiSQS can be applied to squalene preparation taking farnesyl pyrophosphate as substrate. The SiSQS gene provided by the invention can be used for increasing the content of chemical component beta-sitosterol of saussurea involucrata cells by a genetic engineering technology, and is especially applied to the culture field of saussurea involucrata and cells and / or tissues of plants which belong to the species similar to the saussurea involucrata.
Owner:DALIAN PRACTICAL BIOTECH +1
Genes of strain DC413 encoding enzymes involved in biosynthesis of carotenoid compounds
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Novel Sesquiterpene Synthases and Methods of their Use
The present invention relates to novel terpene synthases. The terpene synthases are capable of synthesising mono-, bi- and / or tri-cyclic sesquiterpenes having a C2-C7 or a C3-C7 bond, starting from an acyclic pyrophosphate terpene precursor, farnesyl-pyrophosphate. Accordingly, for the first time, sesquiterpene synthases catalyzing the cyclisation to the santalene and bergamotene carbon skeleton are disclosed. The present invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the sesquiterpene synthases and to methods for making terpenoids.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
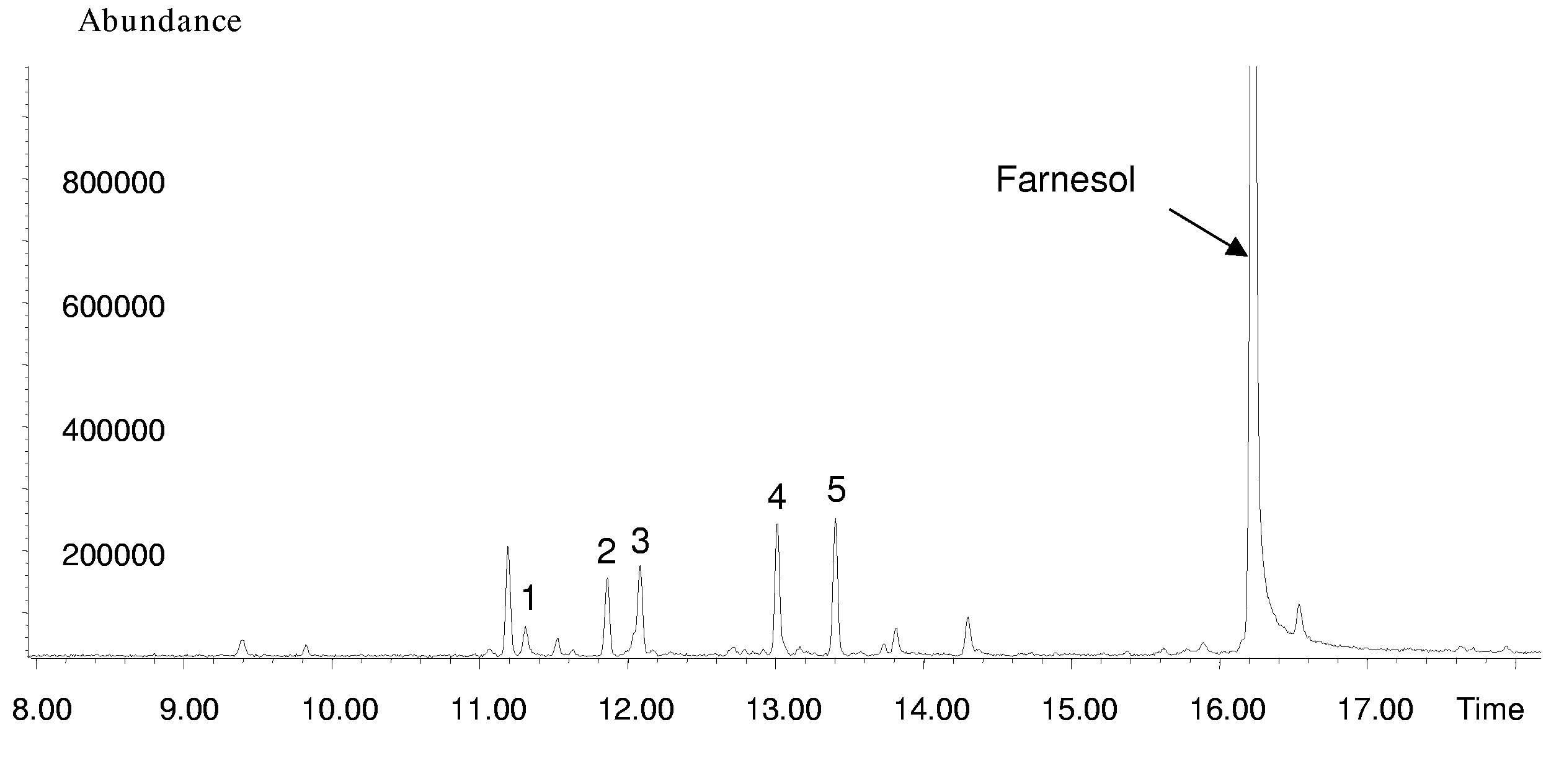
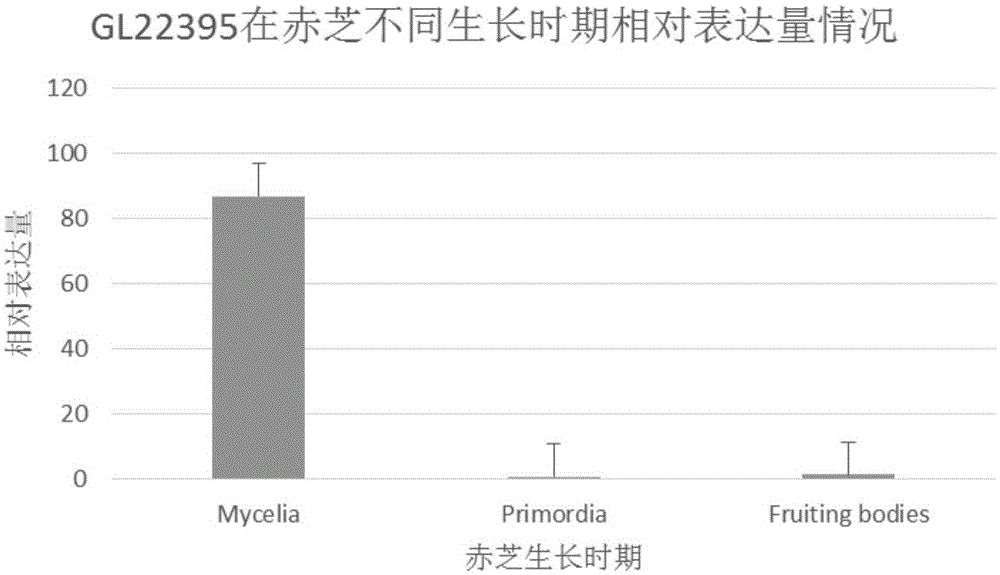
CDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene and application of cDNA sequence
The invention relates to a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of a ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene and an application of the cDNA sequence. The cDNA sequence of the ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene is represented as Seq ID No.2, and 419 amino acids are encoded. The ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase gene GL22395 is adopted to transform escherichia coli, and endogenous FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) is taken as a substrate, so that terpenoid is synthesized in an internal heterogeneous source of escherichia coli.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
Genes have been isolated from Pectobacterium cypripedii encoding geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthase (CrtE), phytoene synthase (CrtB), phytoene desaturase (Crtl), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ), and zeaxanthin glucosyl transferase (CrtX) activity. The genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Sesquiterpene cyclase, preparation and application thereof, and synthesis method of 2Z,4E-alpha-ionylideneehane
ActiveCN108753744AHas the function of sesquiterpene cyclaseWith laboratoryOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringAbscisic acidSynthesis methods
The invention discloses sesquiterpene cyclase, preparation and application thereof, and a synthesis method of 2Z,4E-alpha-ionylideneehane. At first, the amino acid sequence of provided sesquiterpene cyclase BcABA3 is represented by the sequence 2, and a derived polypeptide is also provided. The sesquiterpene cyclase can catalyze farnesyl pyrophosphate cyclization to synthesize 2Z,4E-alpha-ionylideneehane. At the same time, gene sequence that encodes the amino acid sequence of sesquiterpene cyclase is provided. A recombinant protein containing the amino acid sequence is also provided. The invention further provides a method of using the sesquiterpene cyclase, the recombinant protein, and farnesyl pyrophosphate taken as the substrate to synthesize 2Z,4E-alpha-ionylideneehane and abscisic acid. The invention further provides a recombinant expression carrier containing a sesquiterpene cyclase coding gene, a converter, and applications thereof. A synthesis method of 2Z,4E-alpha-ionylideneehane is also provided; according to the synthesis method, farnesyl pyrophosphate is taken as the substrate, and the synthesis is catalyzed by sesquiterpene cyclase or recombinant sesquiterpene cyclase.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Fermentative carotenoid production
Novel proteins of microorganism E-396 (FERM BP-4283) and the DNA sequences which encode these proteins have been discovered to provide an improved biosynthetic pathway from farnesyl pyrophosphate and isopentyl pyrophosphate to various carotenoids, especially zeaxanthin, astaxanthin, adonixanthin and canthaxanthin.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Composition and methods used during Anti-hiv treatment
InactiveUS20110046091A1Restoration of the normal phenotypeSymptoms improvedBiocideMetabolism disorderPremature agingSide effect
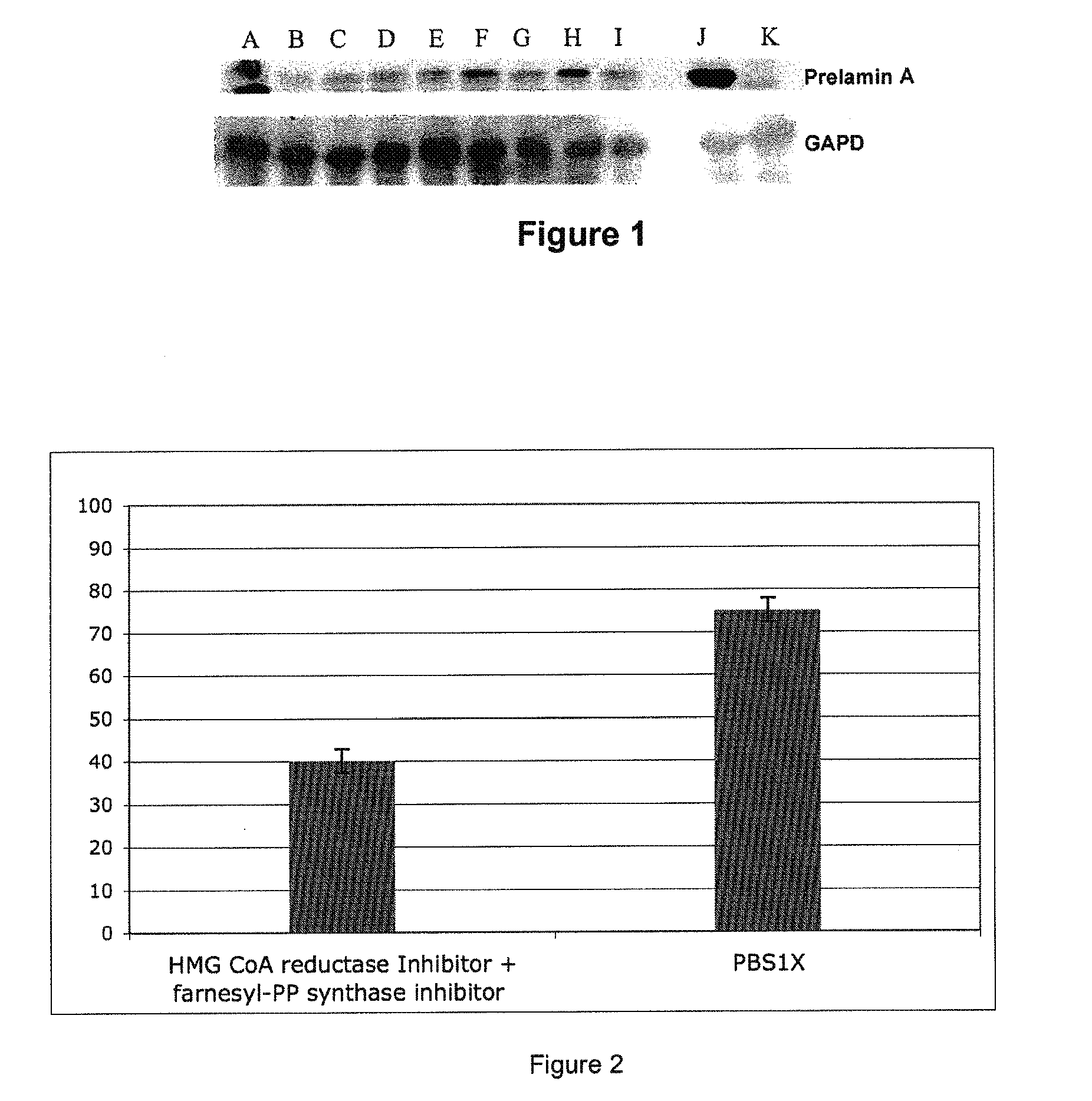
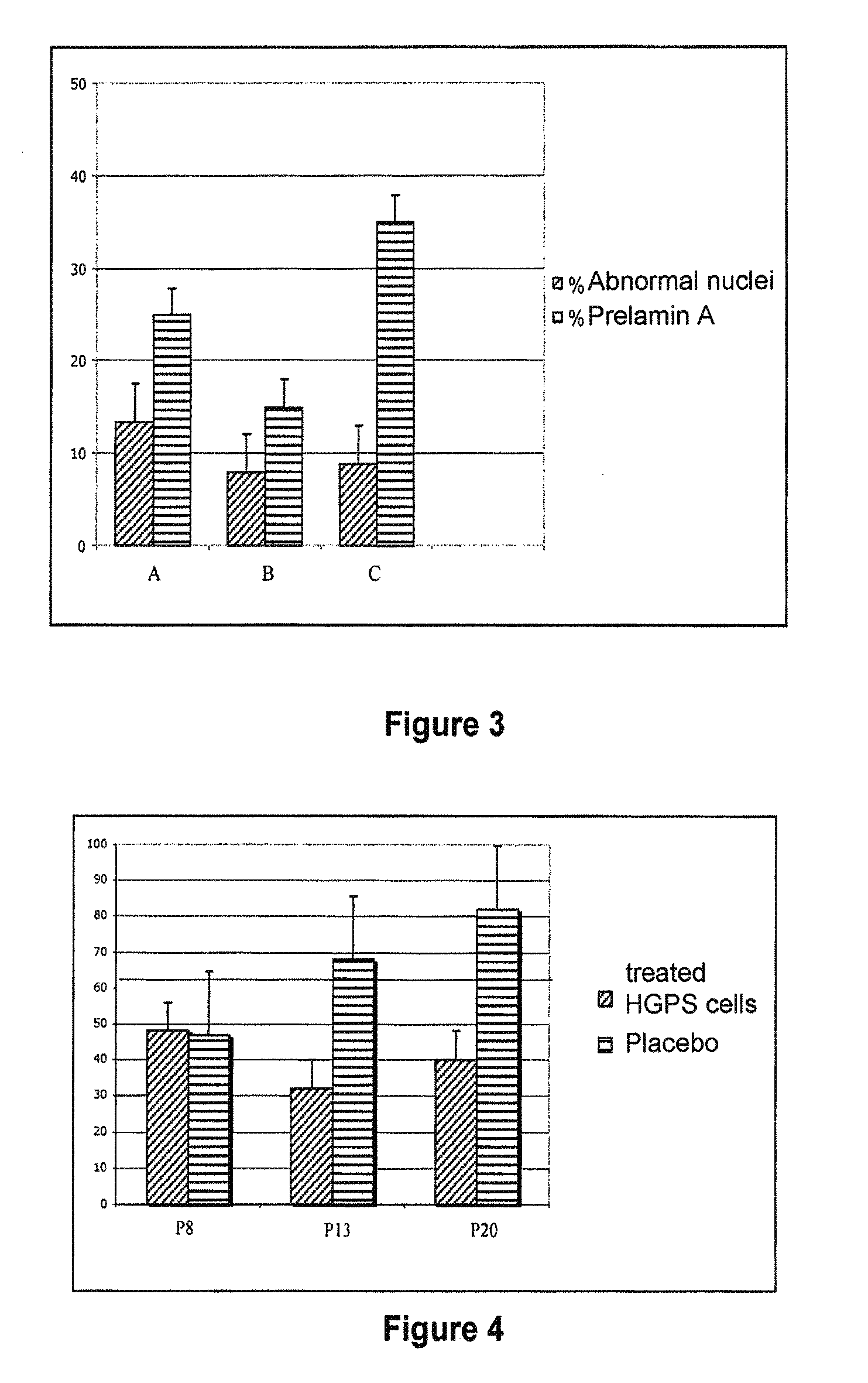
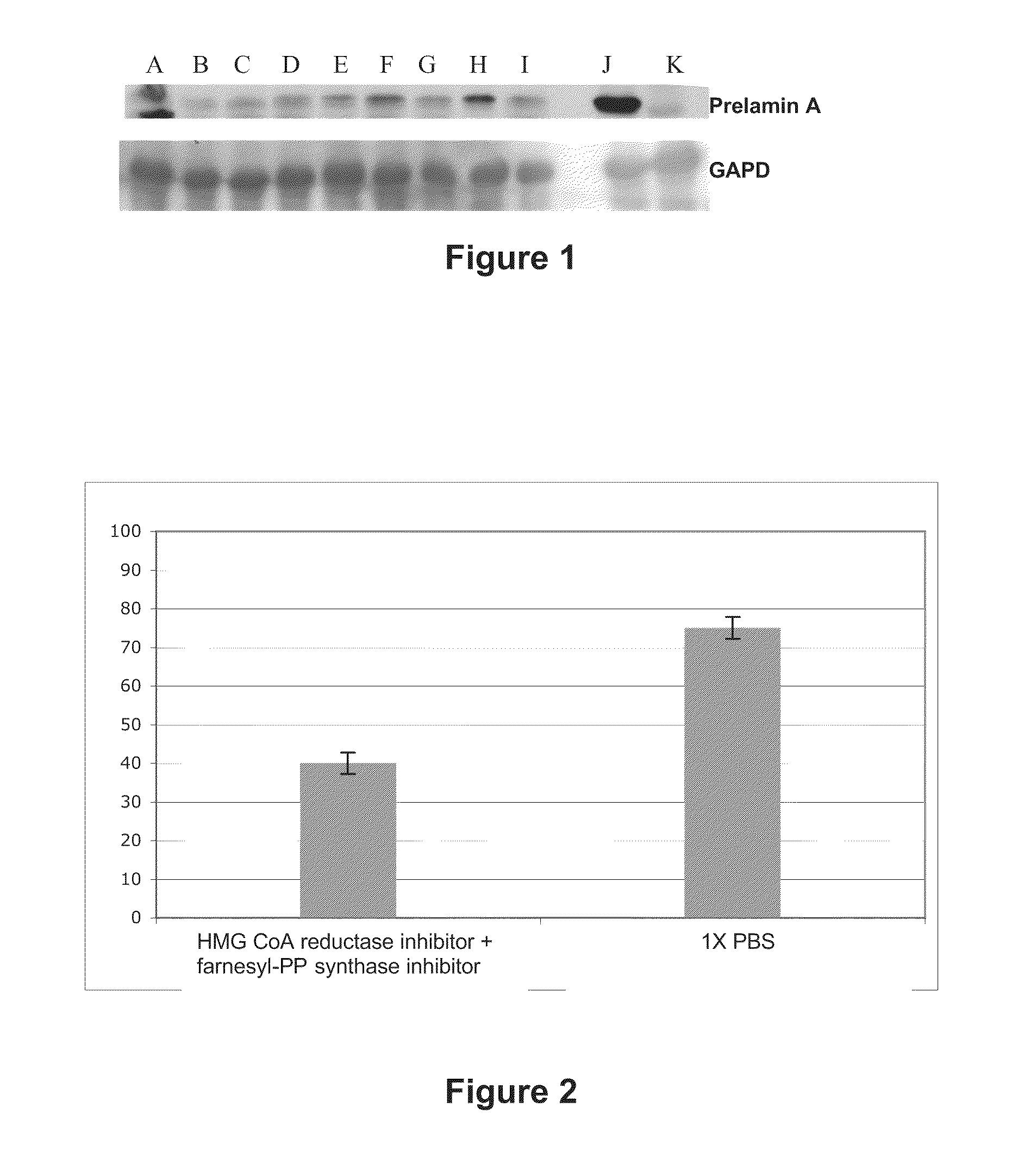
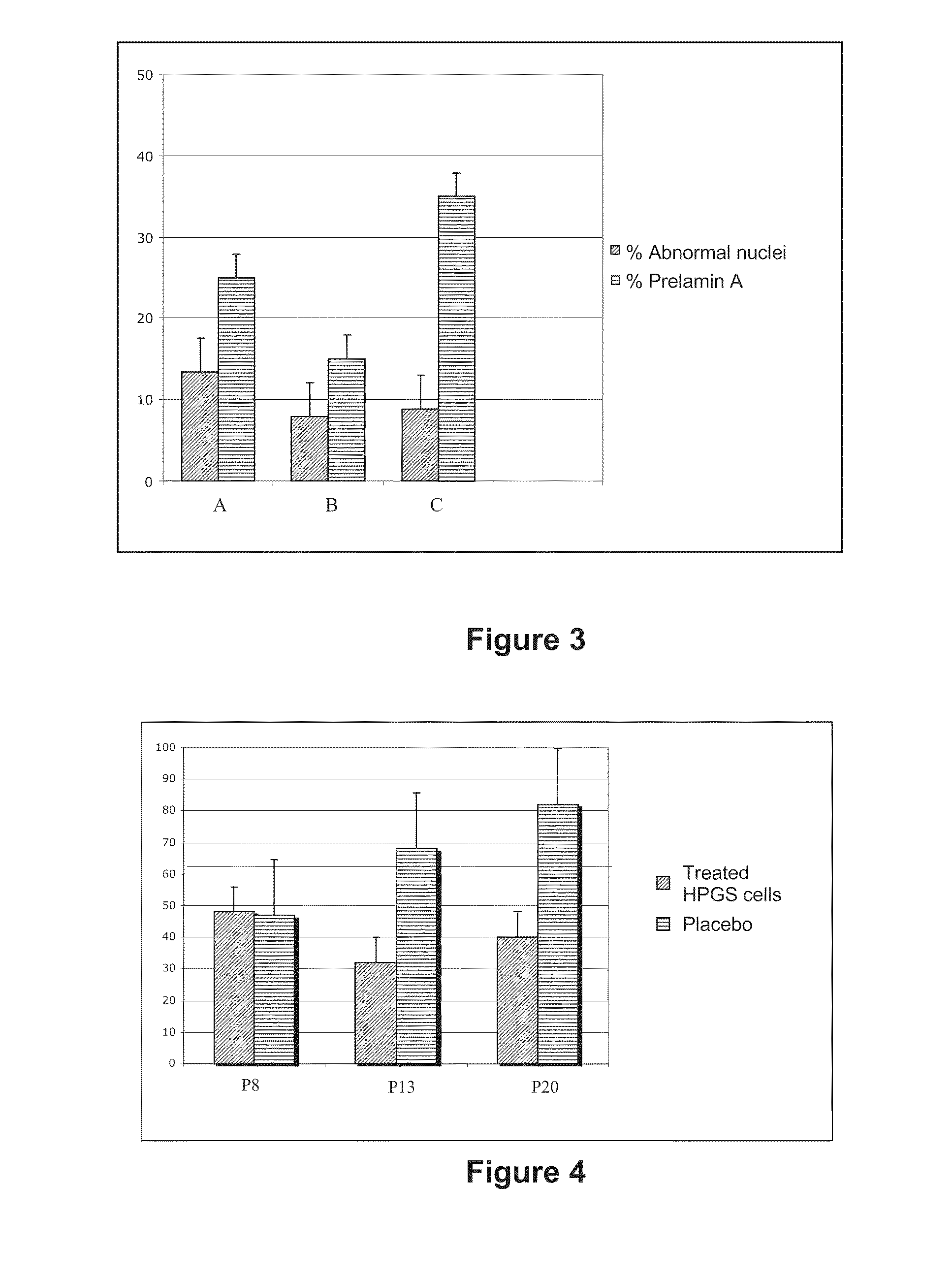
This invention relates to a composition comprising an anti-HIV treatment and a treatment for side effects of said anti-HIV treatment in an HIV-infected patient. This invention is, for example, very useful in the treatment of side effects caused by certain anti-HIV treatments, for example premature aging and lipodystrophy, which can be caused by protease inhibitors or reverse transcriptase inhibitors. The composition of this invention includes at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor, at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor, and at least one anti-HIV agent. One of the processes for treating an HIV-infected patient includes, in any order, the following steps: (i) administration of a mixture including at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor and at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor and (ii) administration of an anti-HIV agent, in which the administrations are concomitant, successive or alternative.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE
Cosmetic and/or dermatological composition
InactiveUS20110165092A1Effective treatmentRestoration of the normal phenotypeBiocideCosmetic preparationsAgeingSubject matter
The subject matter of the invention is a cosmetic and / or dermatological composition for use in the treatment of skin and / or hair disorders. More particularly, the invention relates to a cosmetic and / or dermatological composition comprising an inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, an inhibitor of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, or an inhibitor of one of the physiologically acceptable salts thereof and a cosmetic and / or dermatological product. The present invention finds, for example, a very advantageous use in the treatment of the effects of early ageing, in particular in terms of the skin and the hair system.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I
Saffron, saffron endophytic fungi GGPPS (geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase) gene, gene cloning method and application
The invention relates to a saffron, a saffron endophytic fungi GGPPS (geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase) gene, a gene cloning method and application, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The invention discloses two genes including the saffron and GGPPS in metabolic pathway of the saffron endophytic fungi; the two genes have nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.3, have the identical open reading frames shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and code amino acid sequences shown as code SEQ ID NO.2. The color genetic complementary reaction verifies that the GGPPS gene coding protein has a typical GGPPS enzyme function; FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) and IPP (isopentenyl pyrophosphate) can be catalyzed to be synthesized into the GGPPS (C<20>).
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacterium for producing beta-caryophyllene, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111004763AIncrease productionWith scale developmentBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for producing beta-caryophyllene, and a construction method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides the engineering bacterium for producing beta-caryophyllene, and the construction method and the application thereof in order to improve the biosynthesis efficiency of beta-caryophyllene. The construction method comprises the following steps: introducing an encoding gene of beta-caryophyllene synthetase cloned from tobacco into a receptor strain capable of generating farnesyl pyrophosphate to obtain a recombinant bacterium; and obtaining the engineering bacterium for producing the beta-caryophyllene from the recombinant bacterium. Heterologous reconstruction of a beta-caryophyllene biosynthetic pathway and coproduction of products are successfully realized by using a bioengineering technology, and the yield of beta-caryophyllene reaches 25.06 mg / L by using a shake flask fermentation method; and the yield of beta-caryophyllene is increased by about 85 times through a high-density fermentation technology of a recombinant strain in a fermentation tank.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Construction and transformation of chamomile farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPS) gene eukaryotic expression vector
InactiveCN102816784AIncrease productionGreat contributionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a construction and transformation method of a chamomile farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPS) gene eukaryotic expression vector, comprising the steps of: extracting an RNA (ribonucleic acid) from chamomile petals, and inversely transcribing the RNA into cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) with total chamomile RNAs as a template; carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification using a cDNA as a template to obtain a target fragment; connecting the target fragment with a T4 ligase; transforming a connection product to an escherichia coli DH5 alpha competent cell to obtain an eukaryotic expression vector PBI121 / FPS; then introducing a recombinant expression vector to agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105; and infecting the plant Yunyan85 by using the agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 to finally obtain a resistant tobacco plant. An FPS gene is cloned by using a gene engineering technology, the callus tissues of the plant are infected by virtue of the agrobacterium tumefaciens, and the construction and transformation method lays a foundation for improvement of chamazulene yields through expression of the FPS gene in a plant frond.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
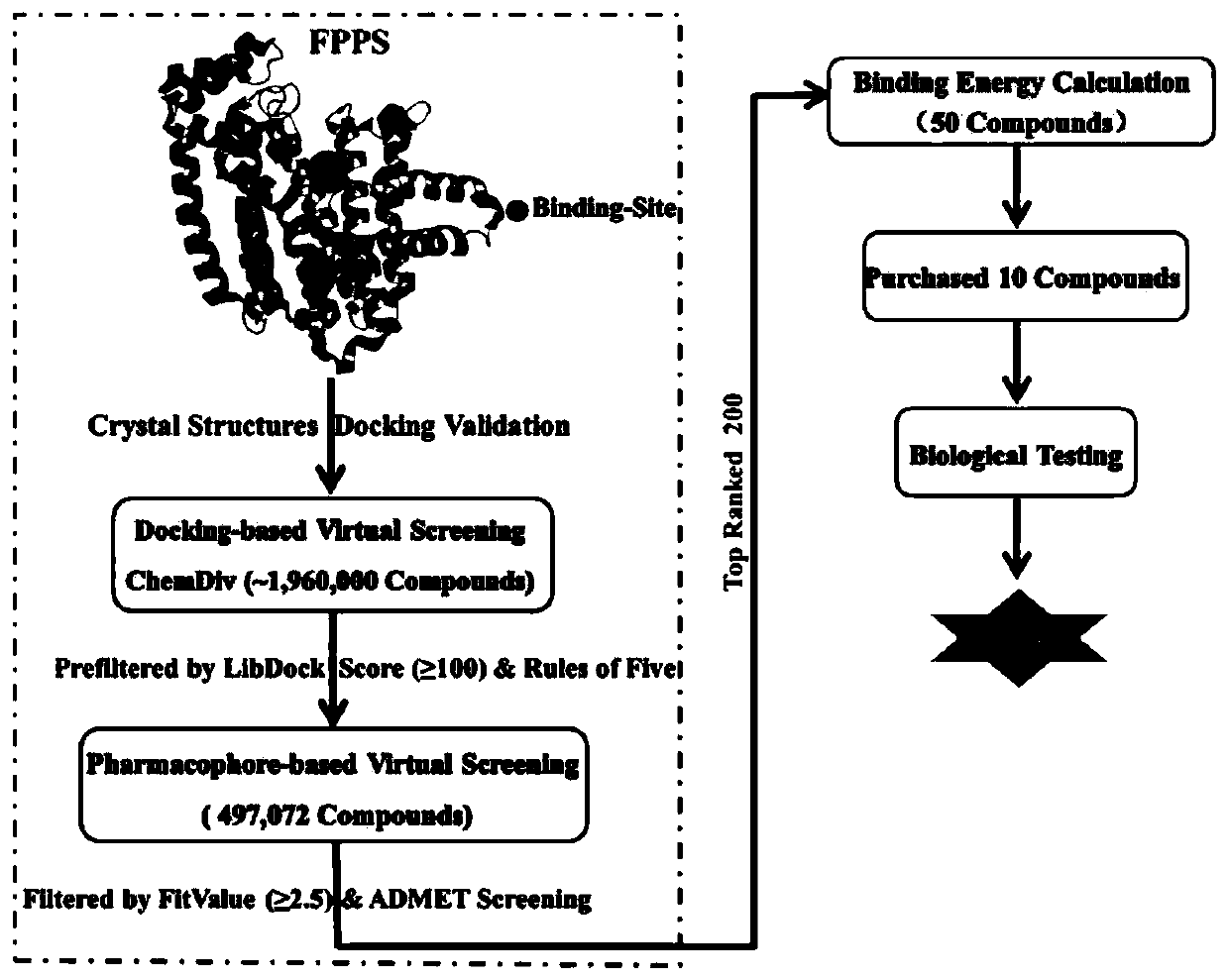
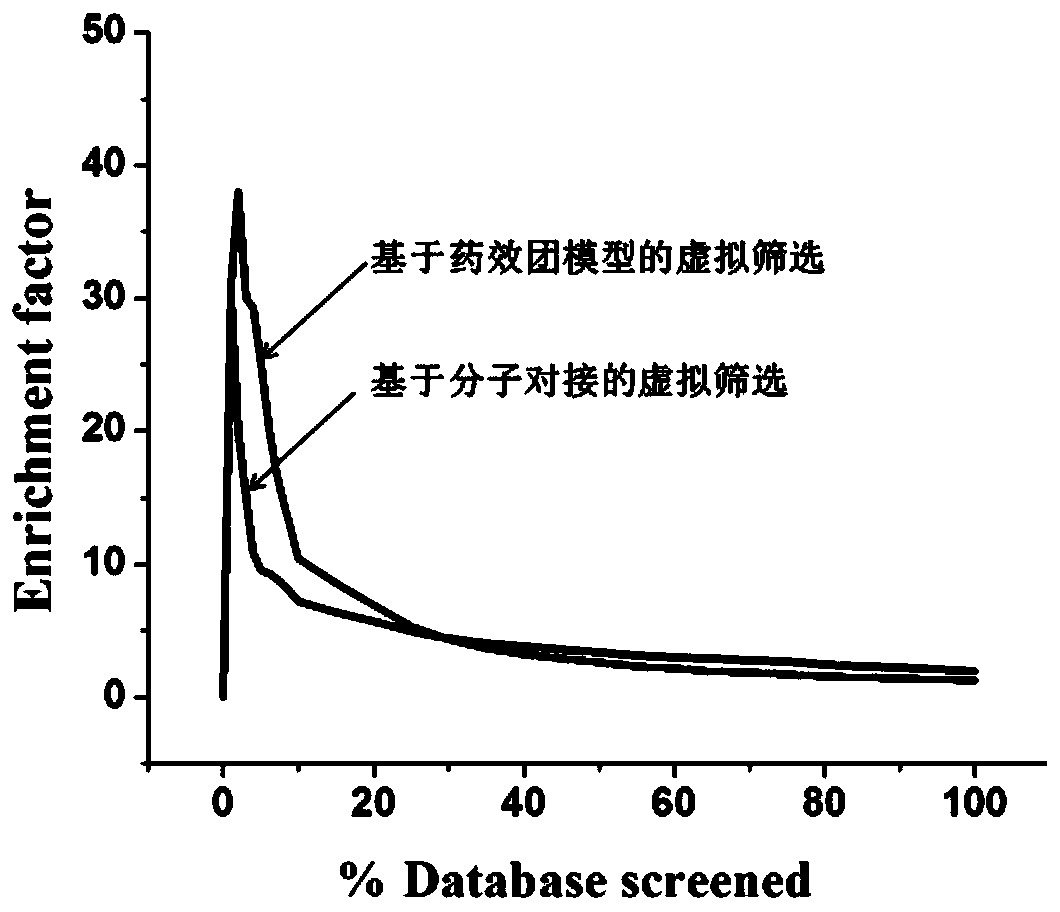
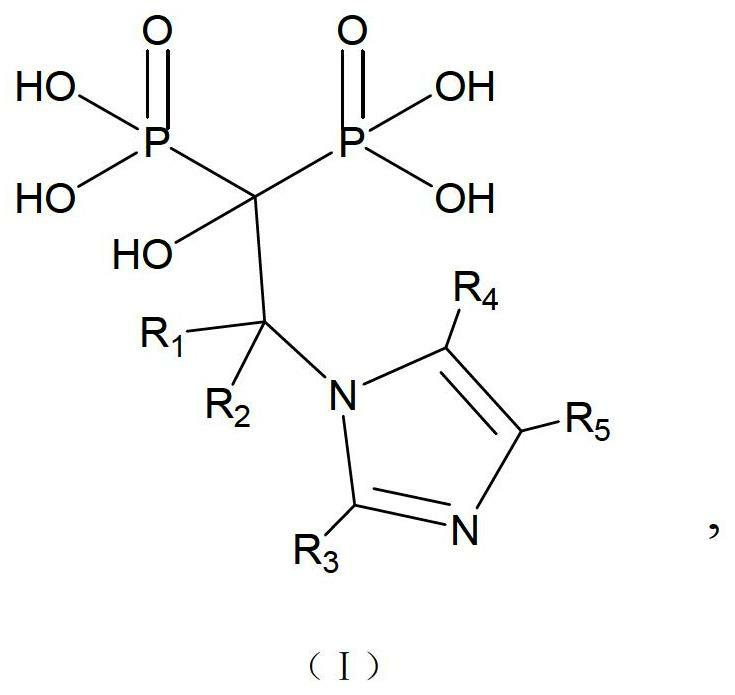
Screening method and application of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase FPPS inhibitor
ActiveCN110289054AReduce blindnessImprove hit rateChemical property predictionMolecular designData setScreening method
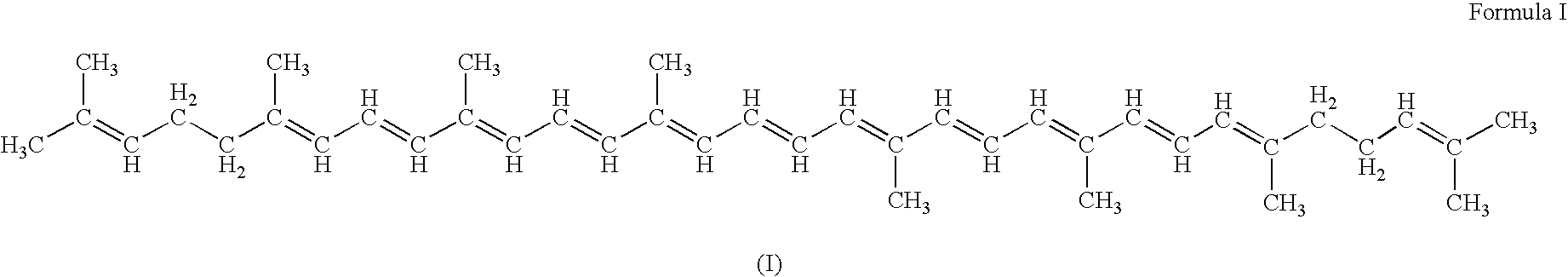
The invention provides a screening method of a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) inhibitor. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an FPPS template; (2) preparing a data set; 3) performing virtual screening based on molecular docking; 4) performing virtual screening based on the pharmacophore model; 5) calculating binding energy; 6) integrating the docking scores in the steps 3), 4) and 5), the pharmacophore model FitValue value and the binding energy to obtain the FPPS inhibitor; and 7) carrying out FPPS enzyme activity inhibition experiment on the FPPS inhibitor obtained by virtual screening, and determining the FPPS inhibitor with the structure shown in the formula I. The method gives full play to the advantages of theoretical screening, reduces the blindness of drug synthesis, effectively improves the hit rate of positive drugs, saves manpower, material resources and financial resources, and realizes the new use value of old drugs. The invention further provides application of the FPPS inhibitor obtained through screening in preparation of drugs for treating colon cancer.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
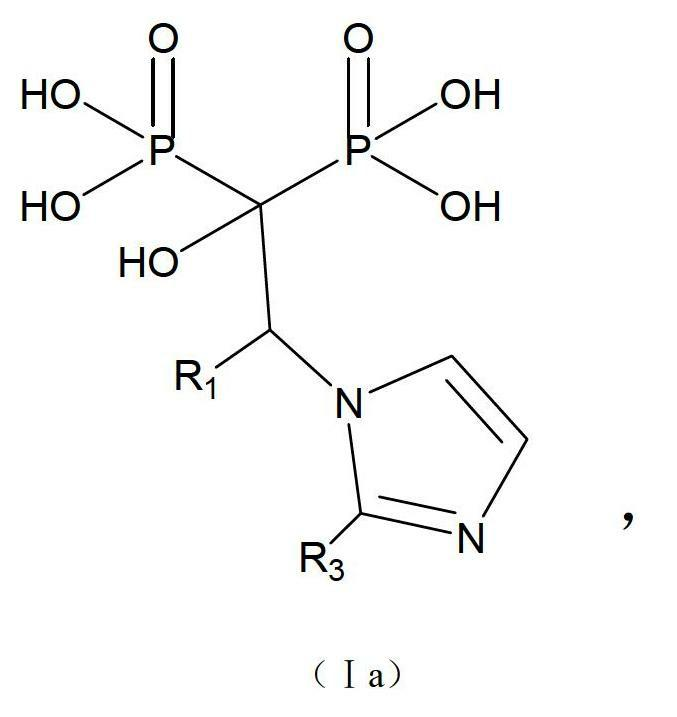
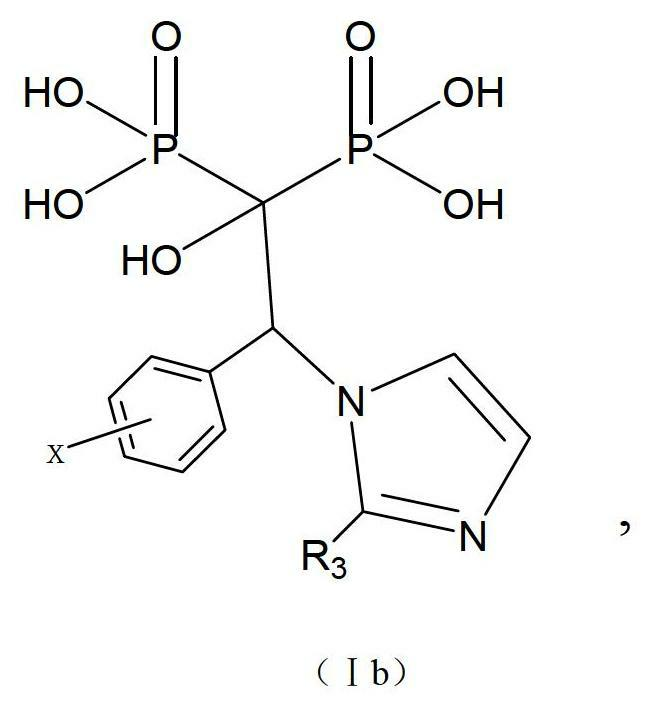
Imidazole diphosphonie acid compound and pharmaceutically-acceptable salt and medicinal application thereof
ActiveCN102659840ABlock signalingInhibit growthOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhosphanilic acidImmunotherapy
The invention relates to a novel imidazole diphosphonie acid compound and a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt thereof. The diphosphonie acid compound disclosed by the invention, farnesylpyrophosphate synthetase is treated, and lipotropy is enhanced. The type of compound can be used for treating diseases including osteoporosis, hypercalcinemia and the like, and can be applied to cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy and the like.
Owner:北京清辉联诺生物科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com