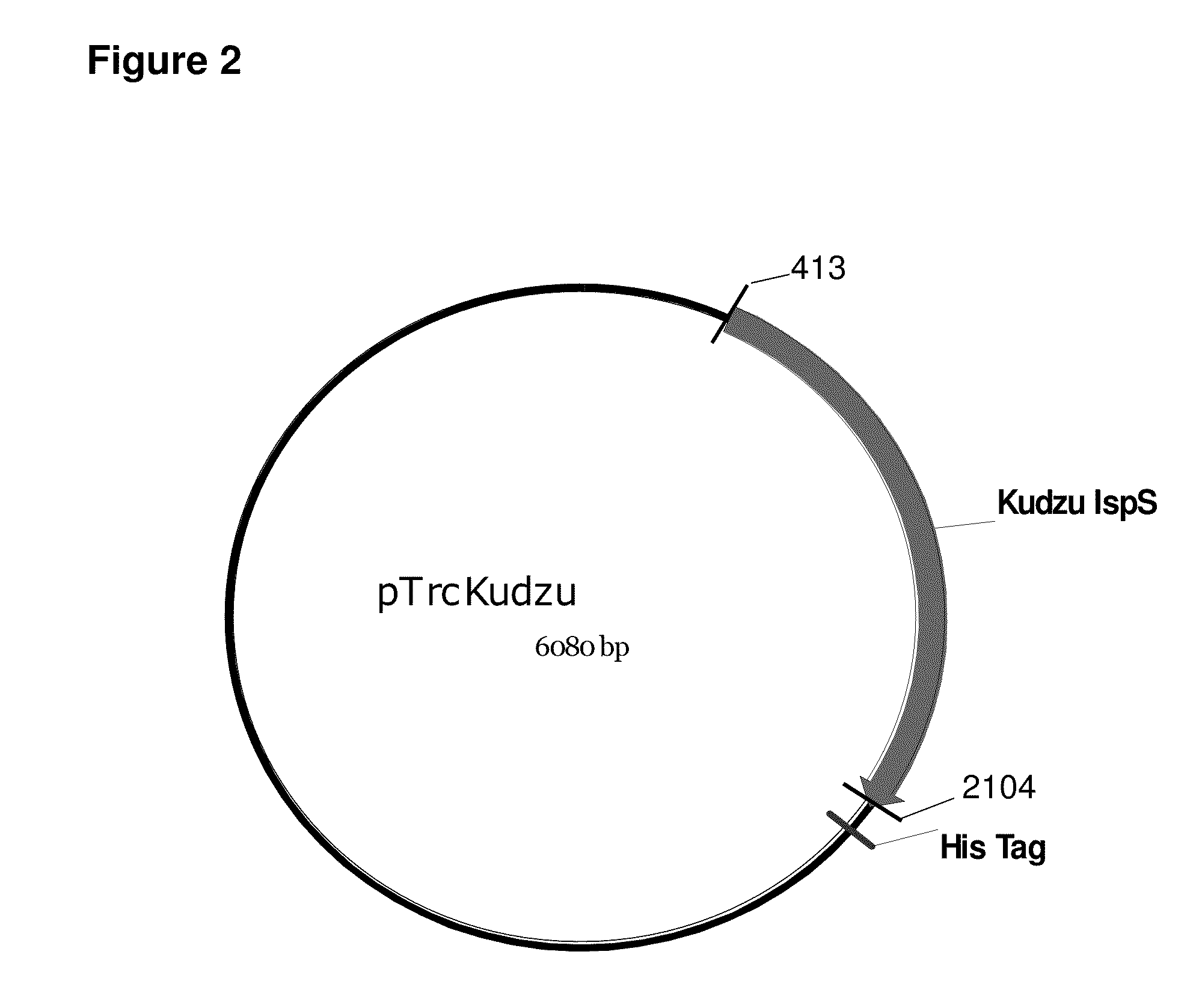
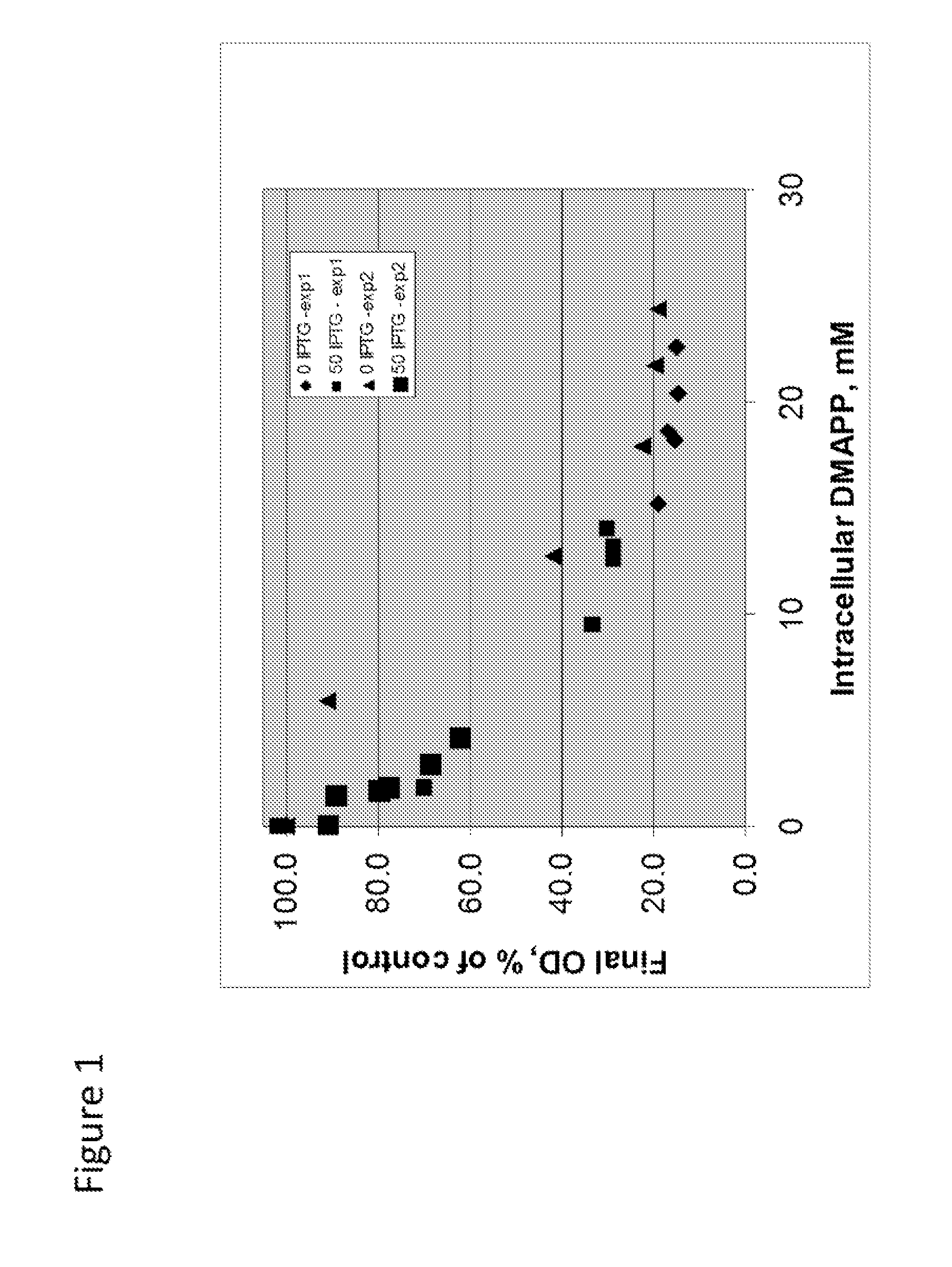
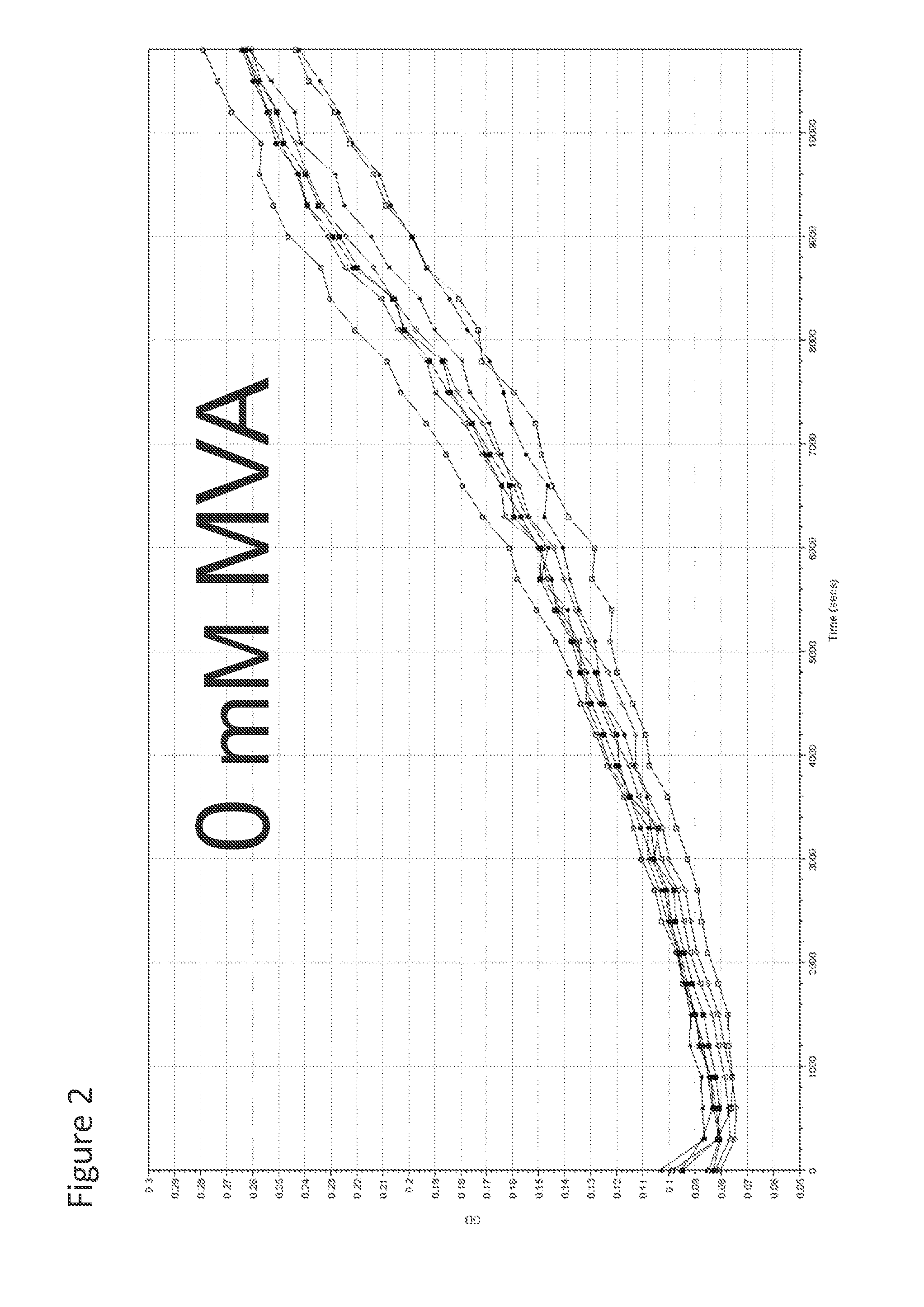
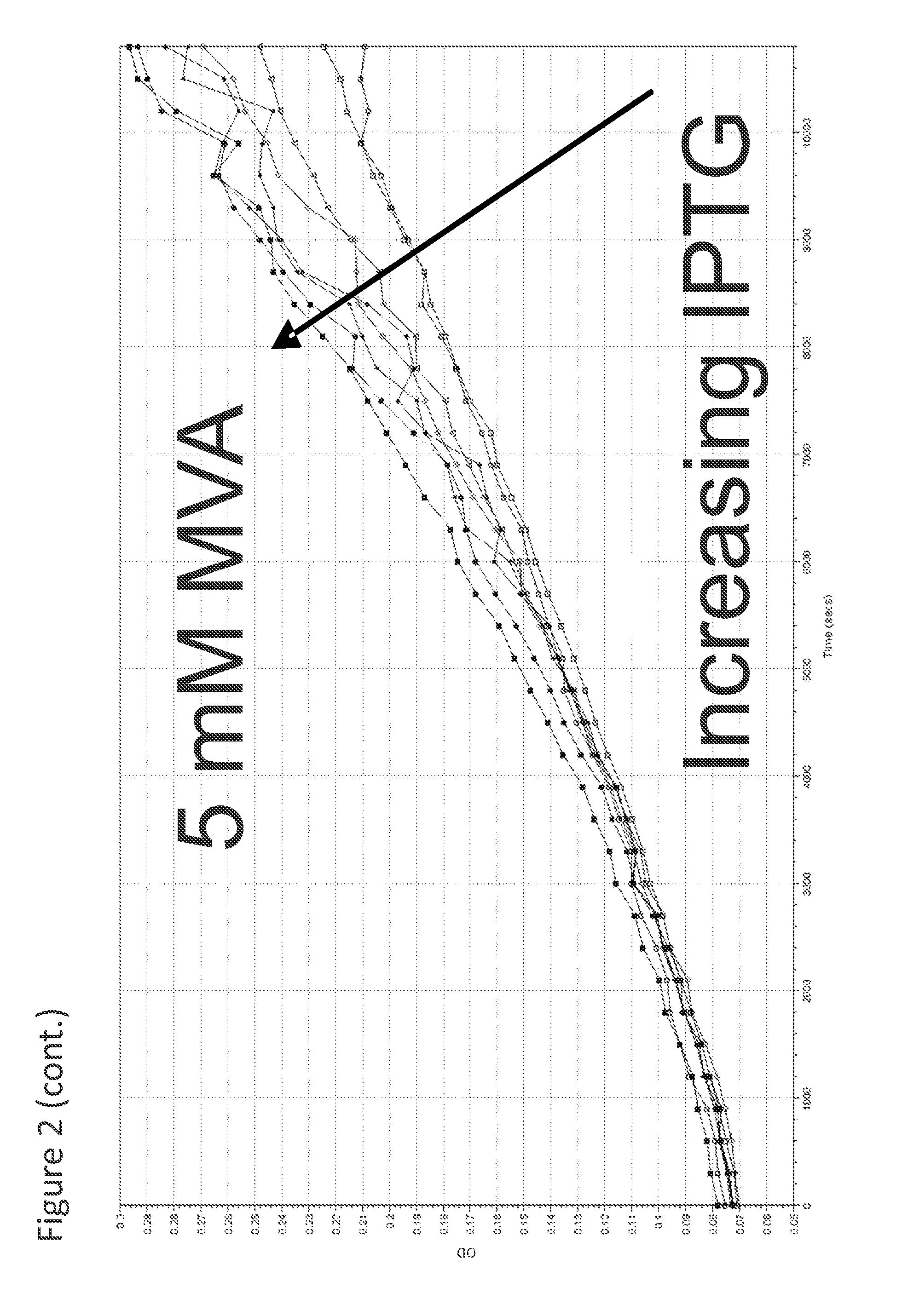
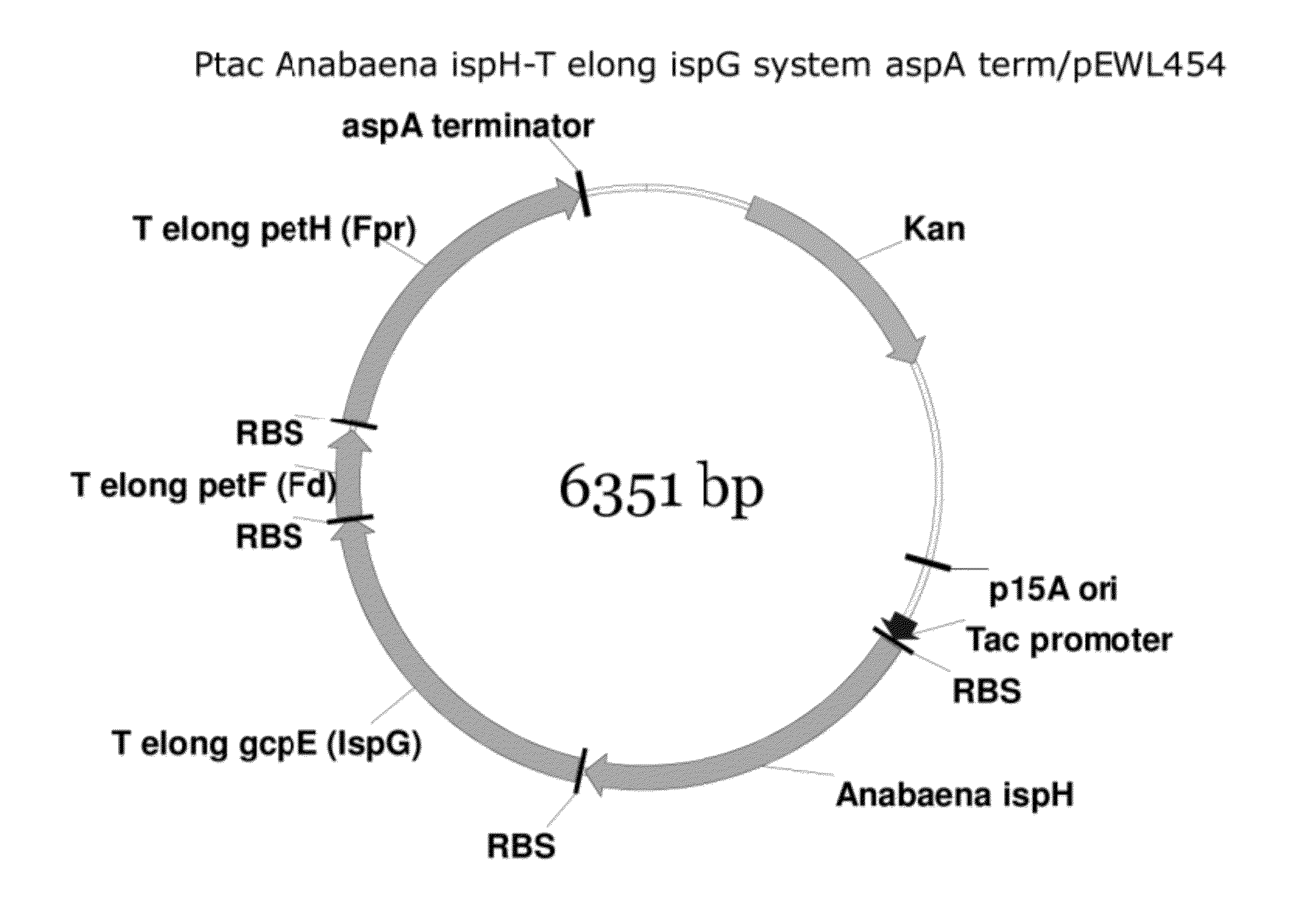
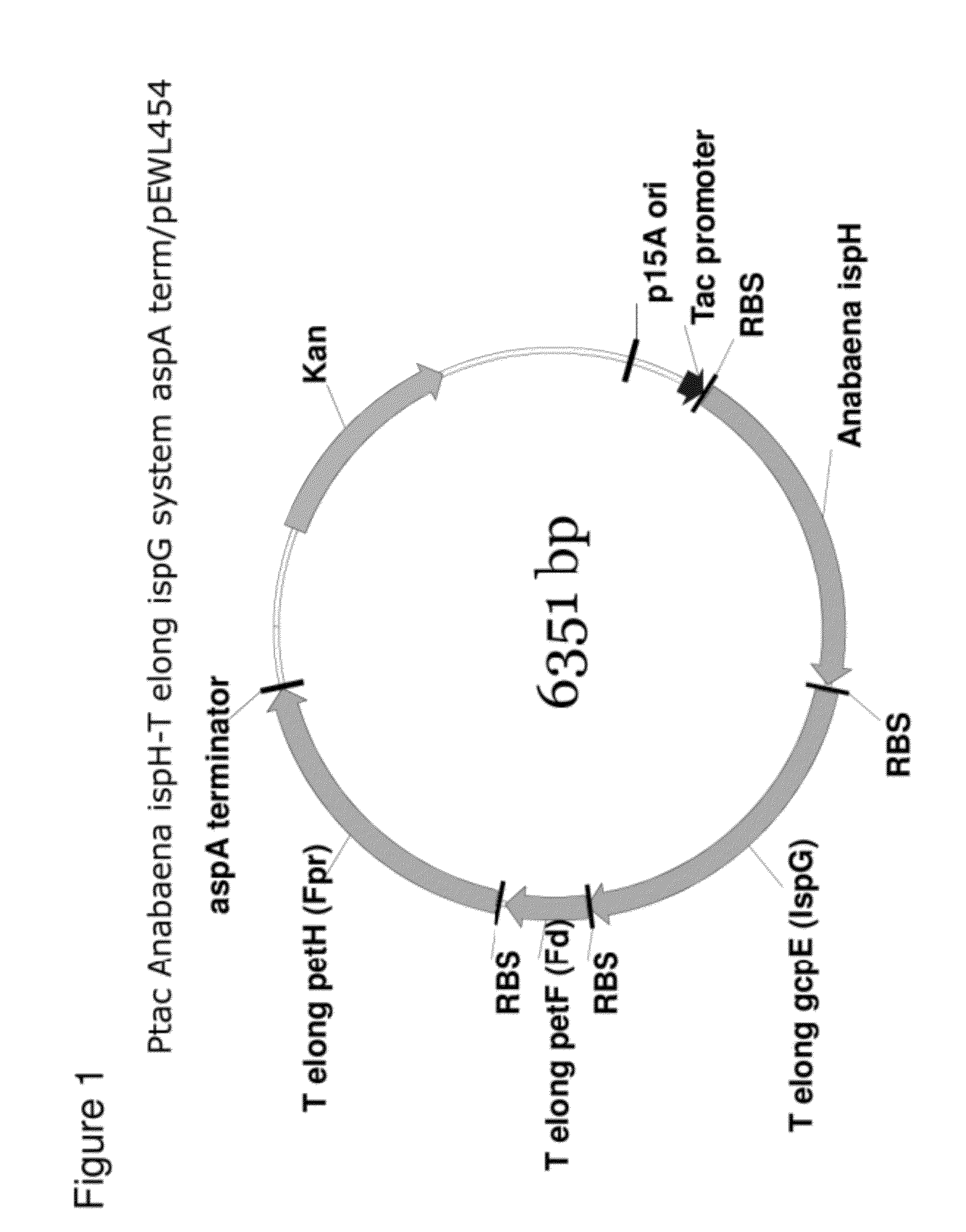
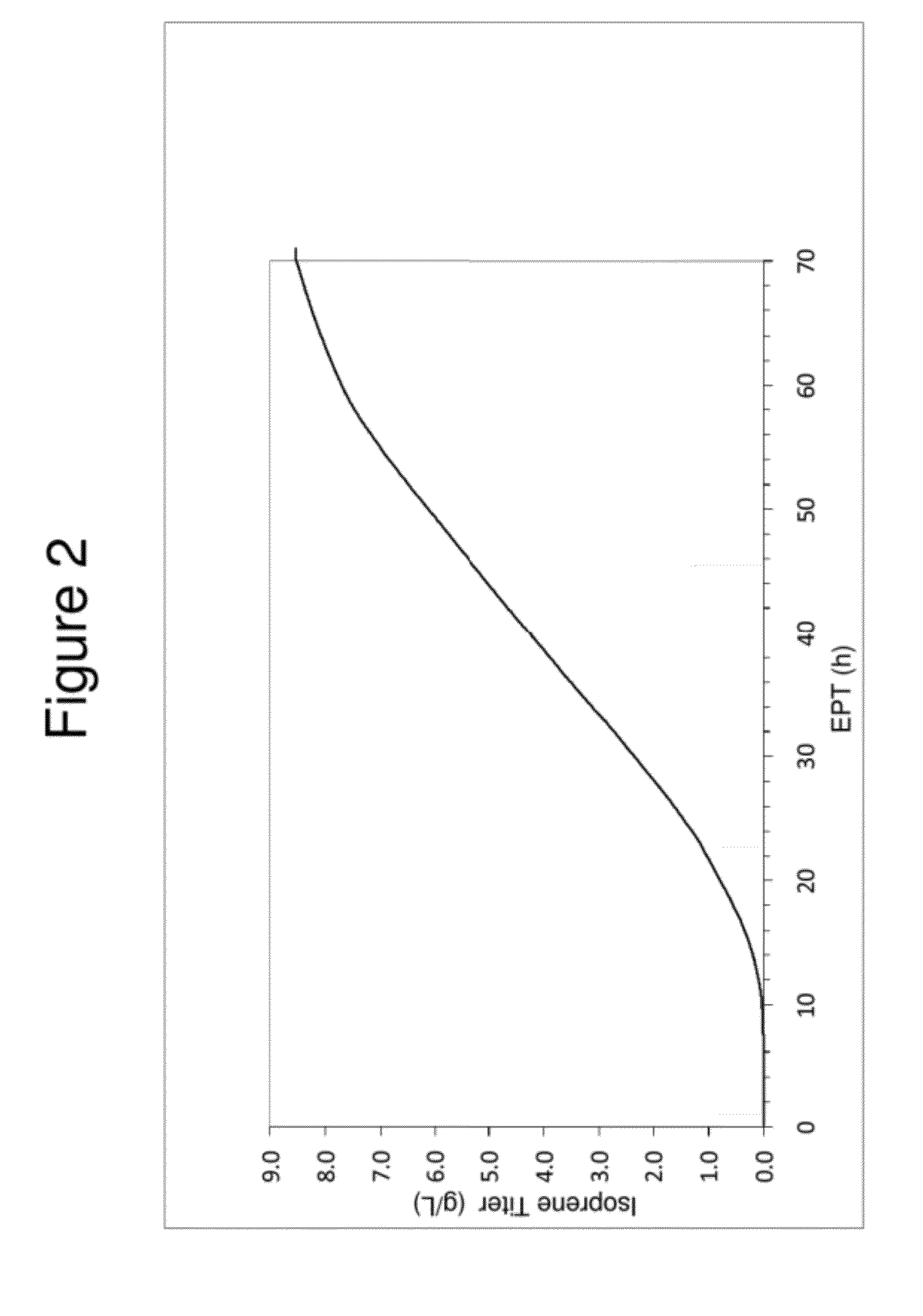
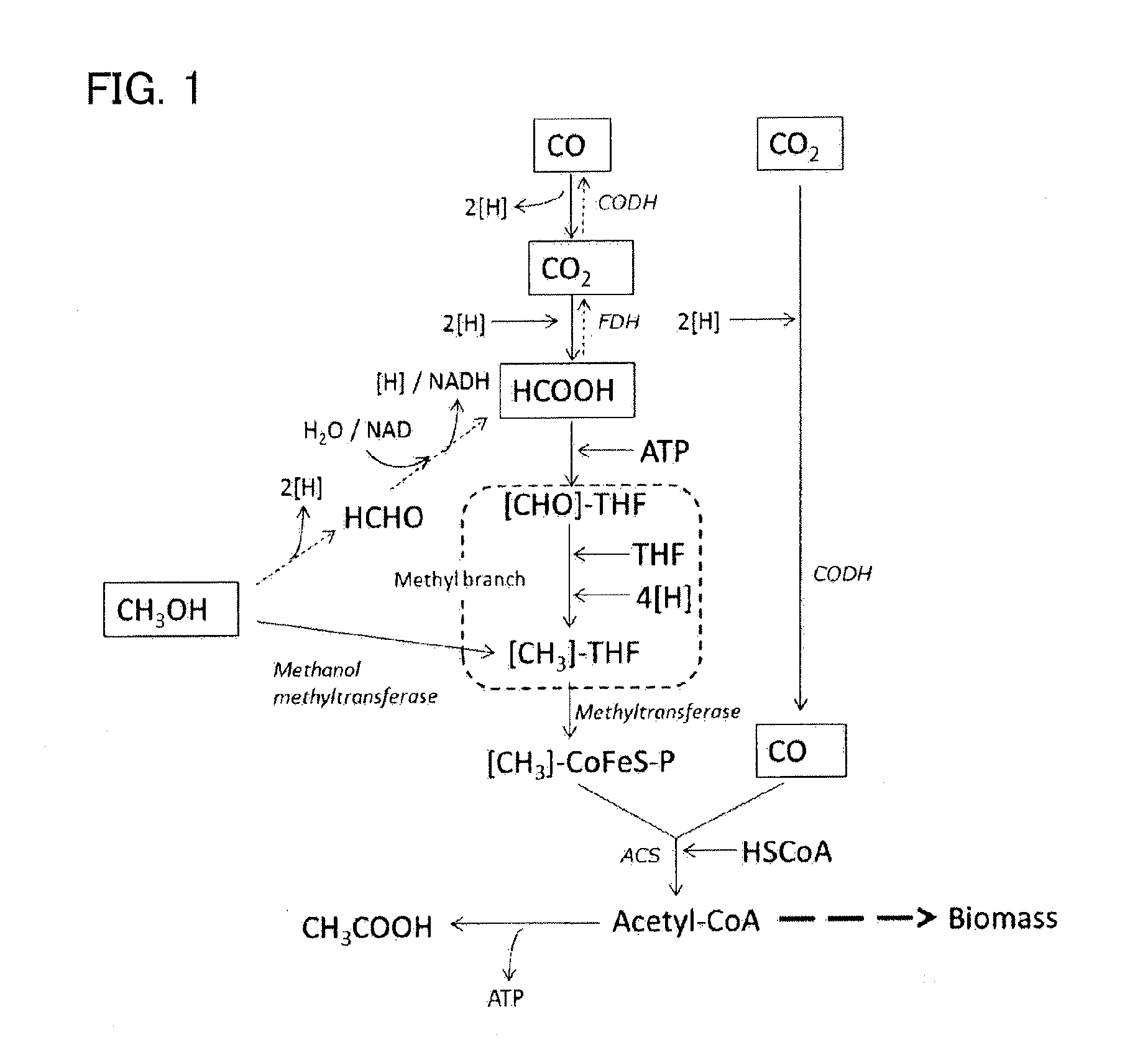
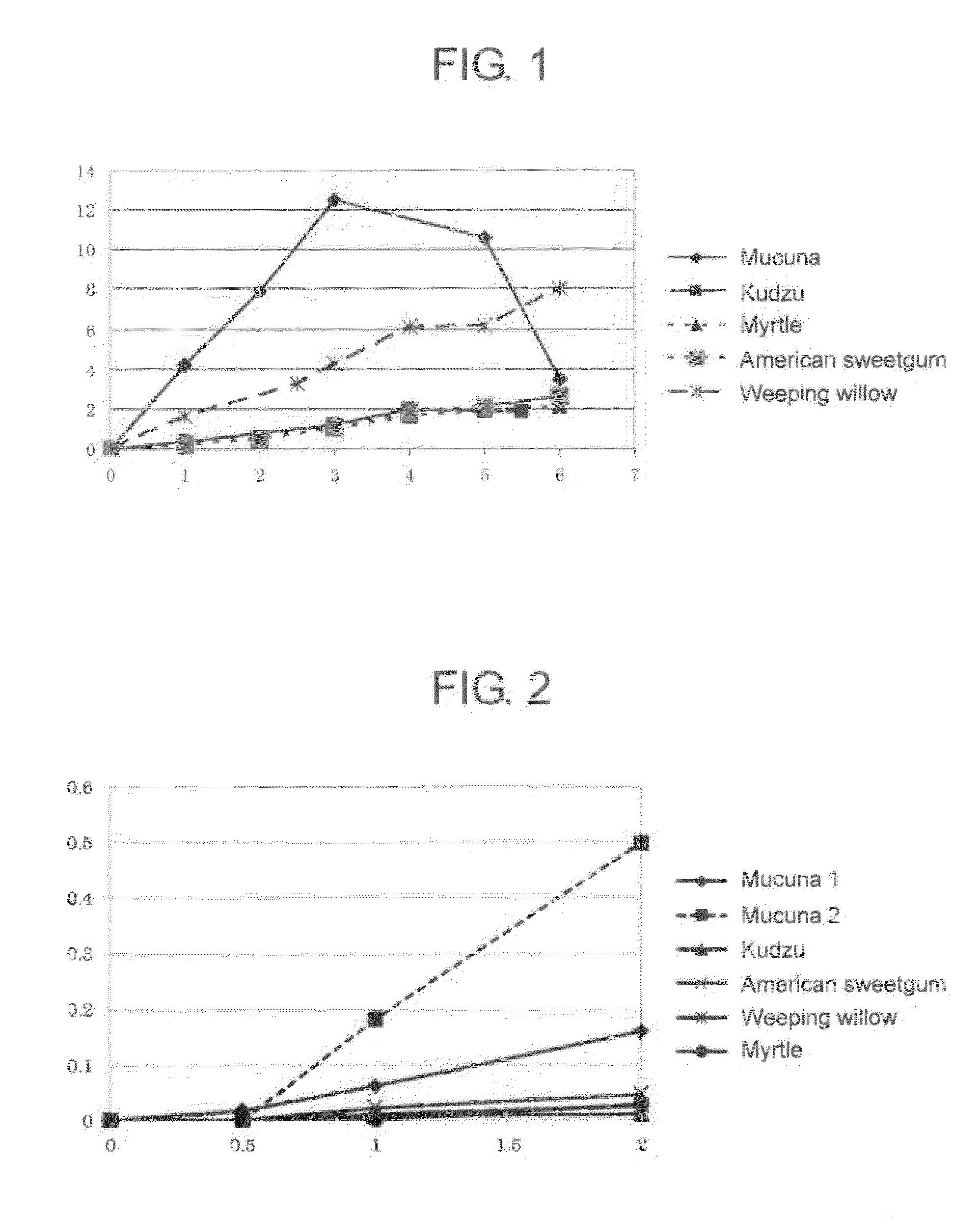
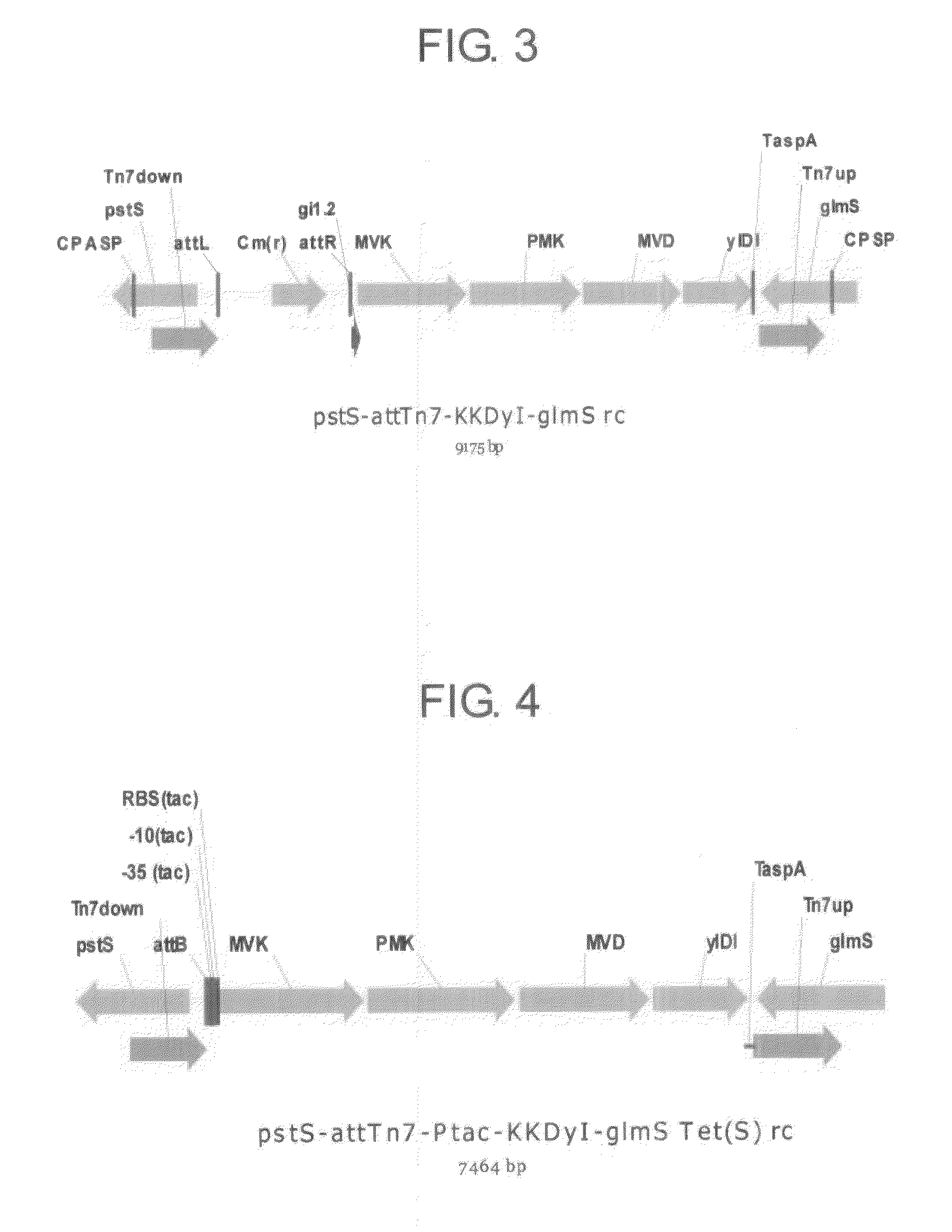
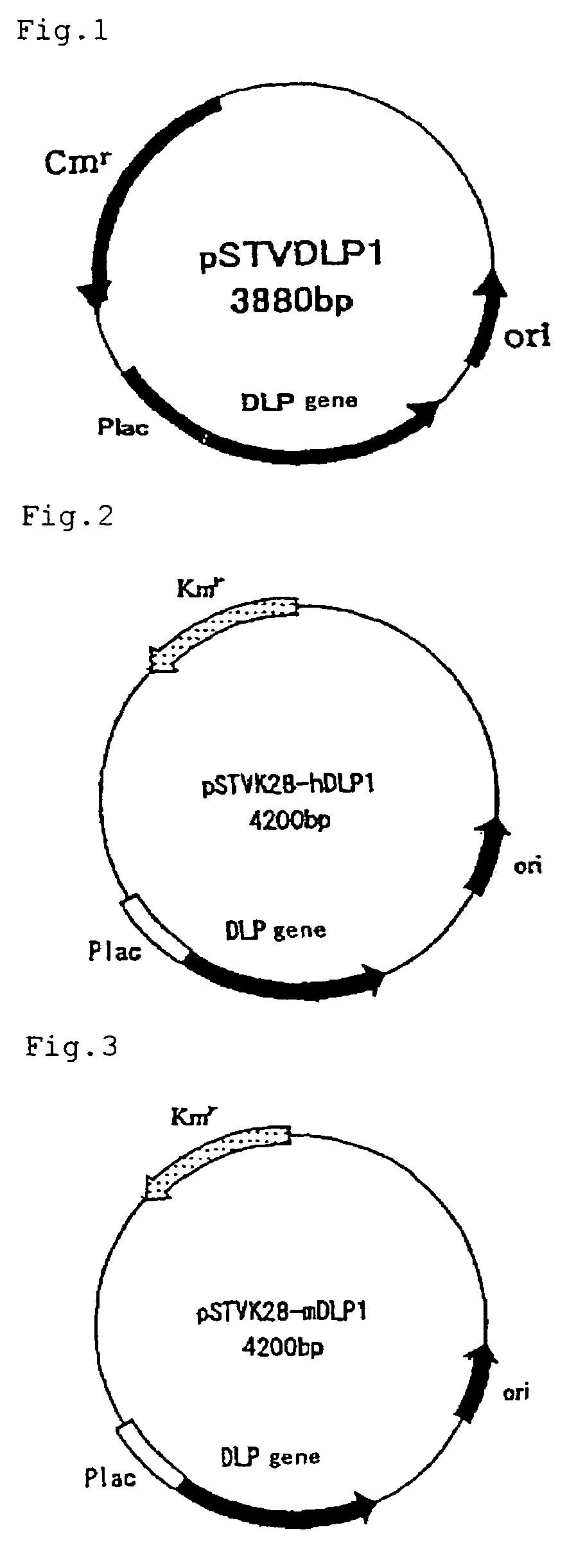
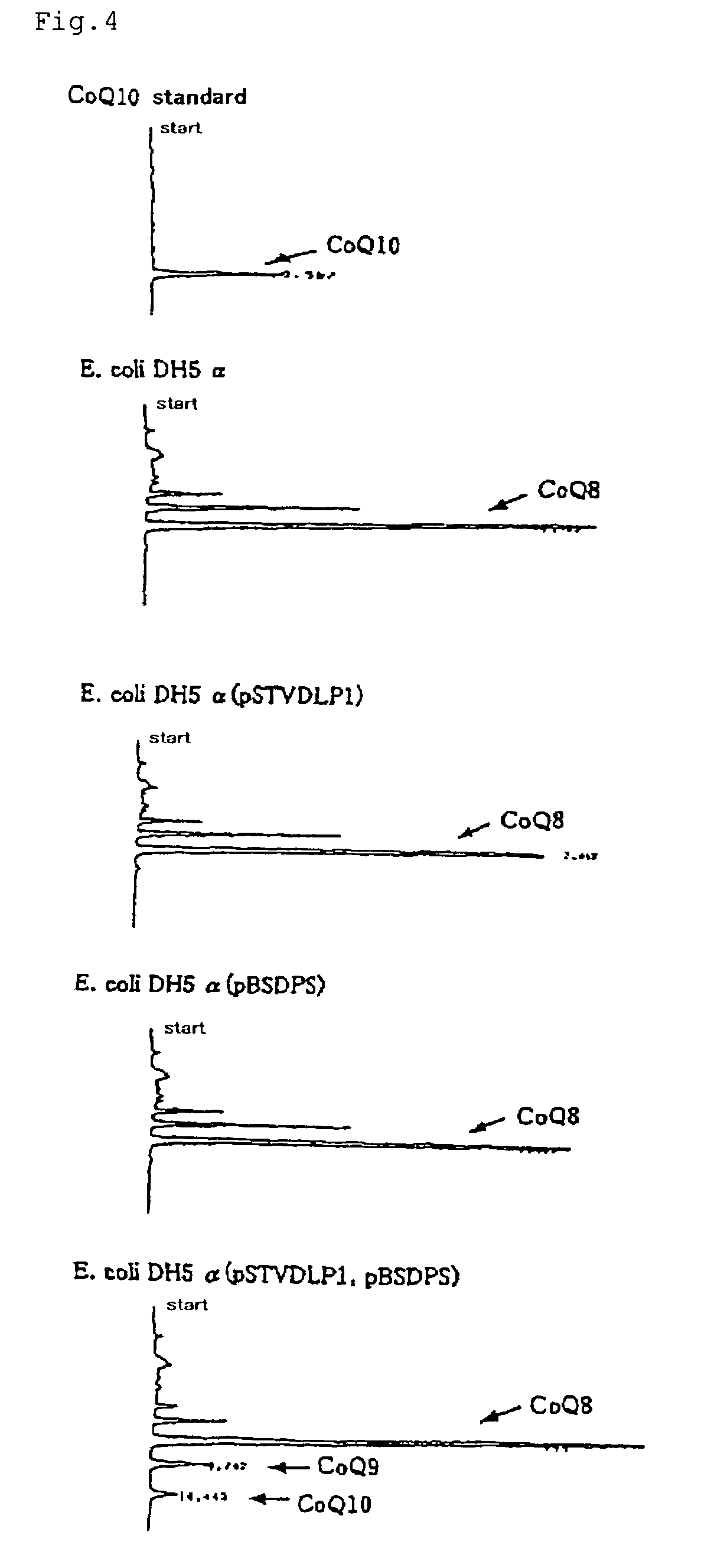
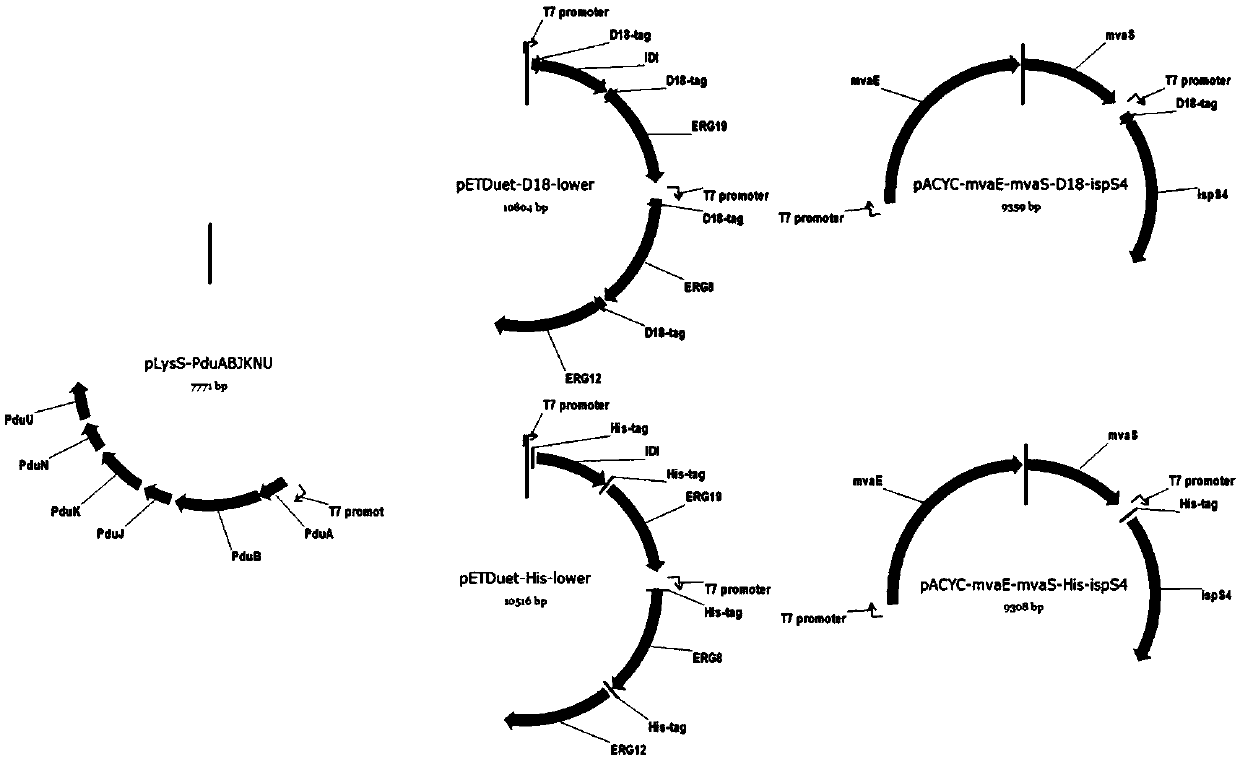
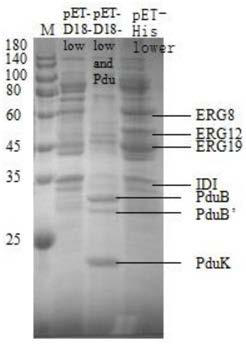
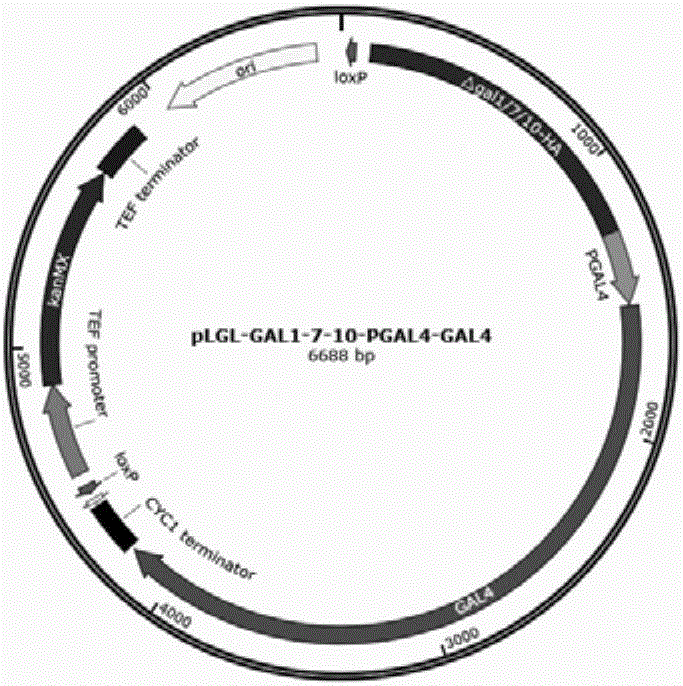
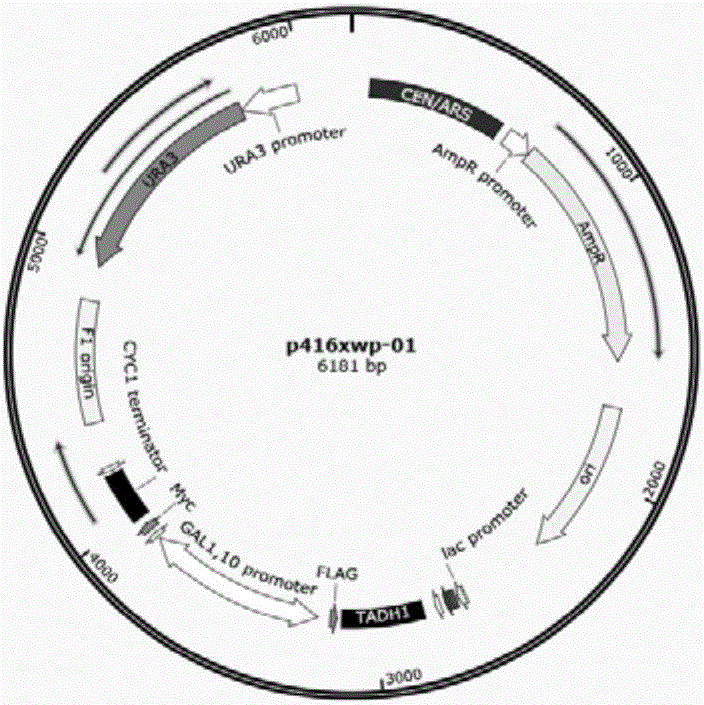
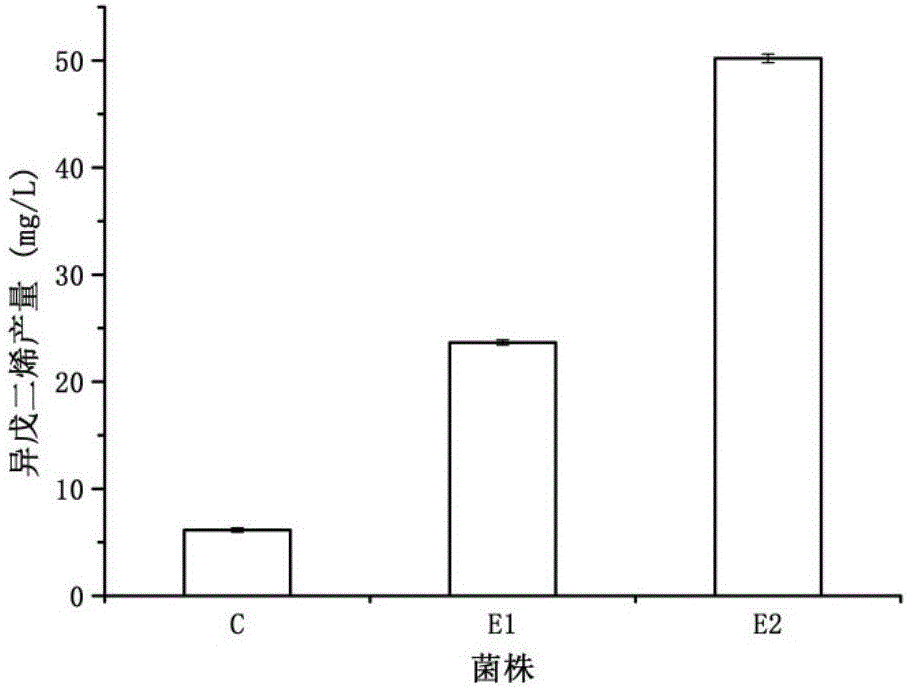
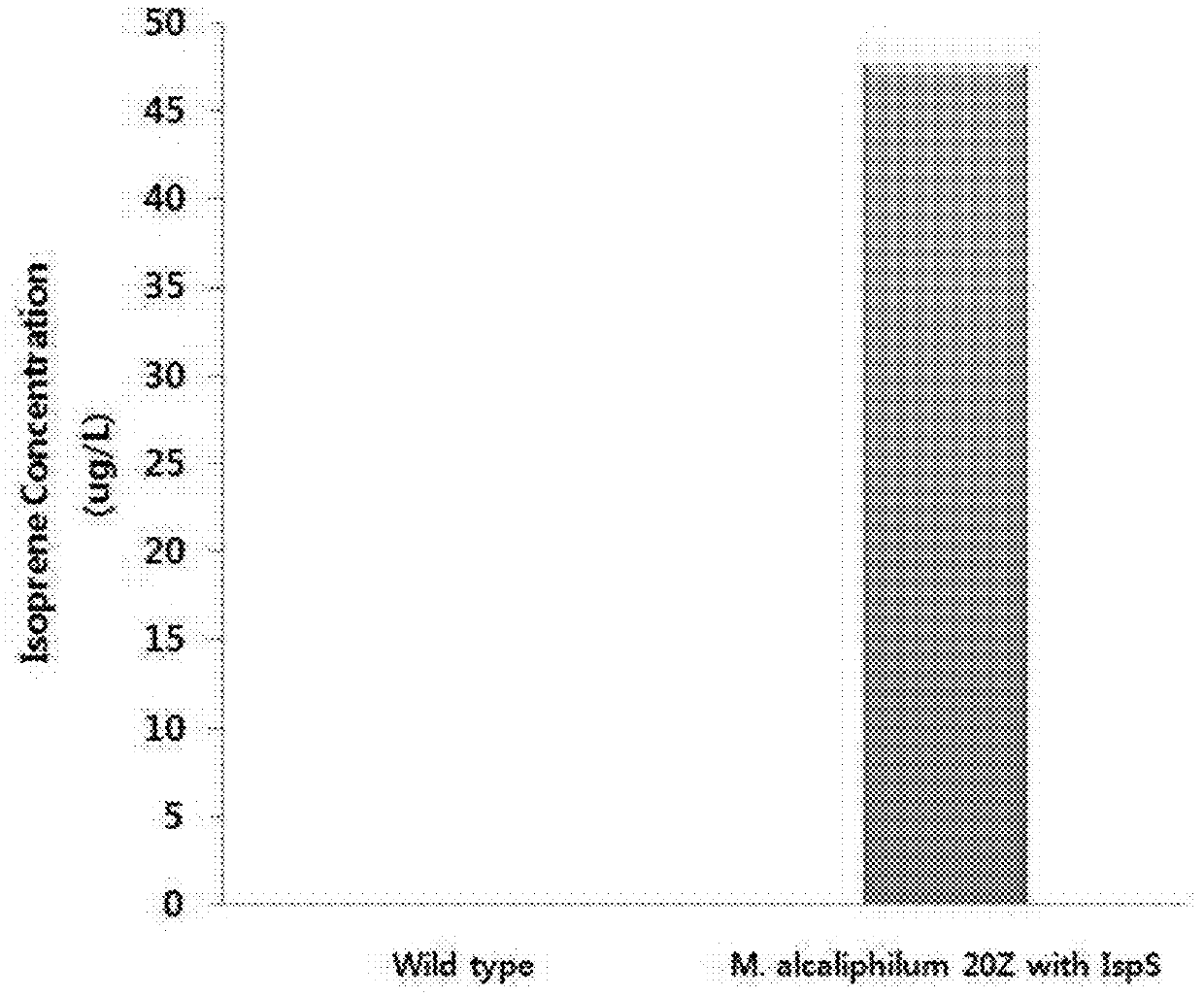
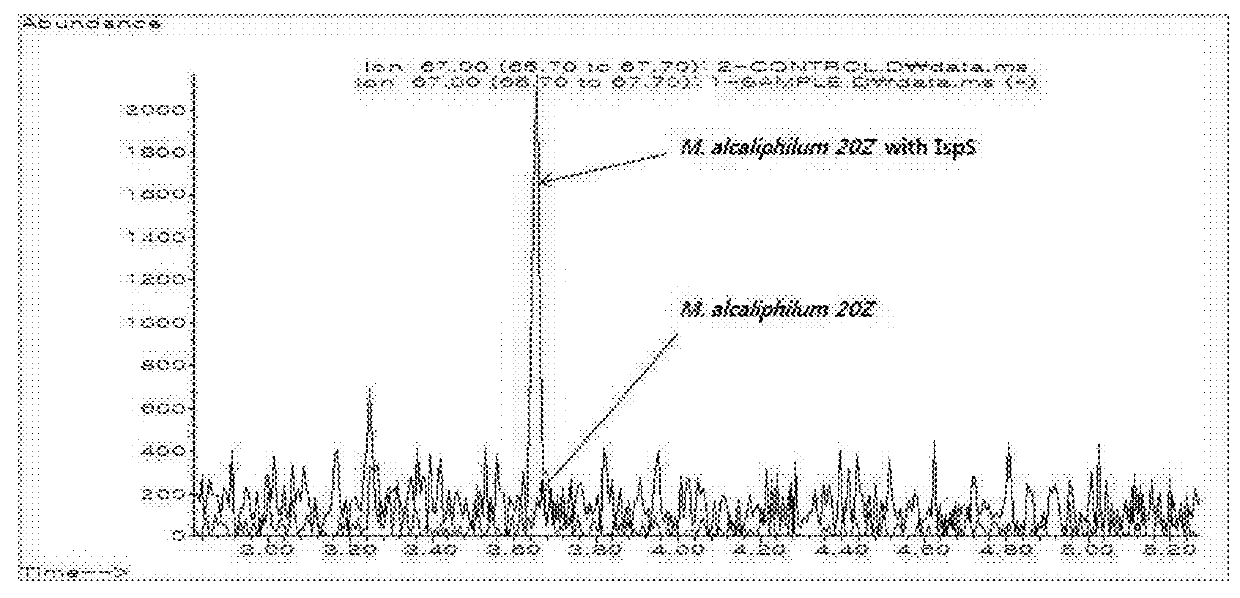
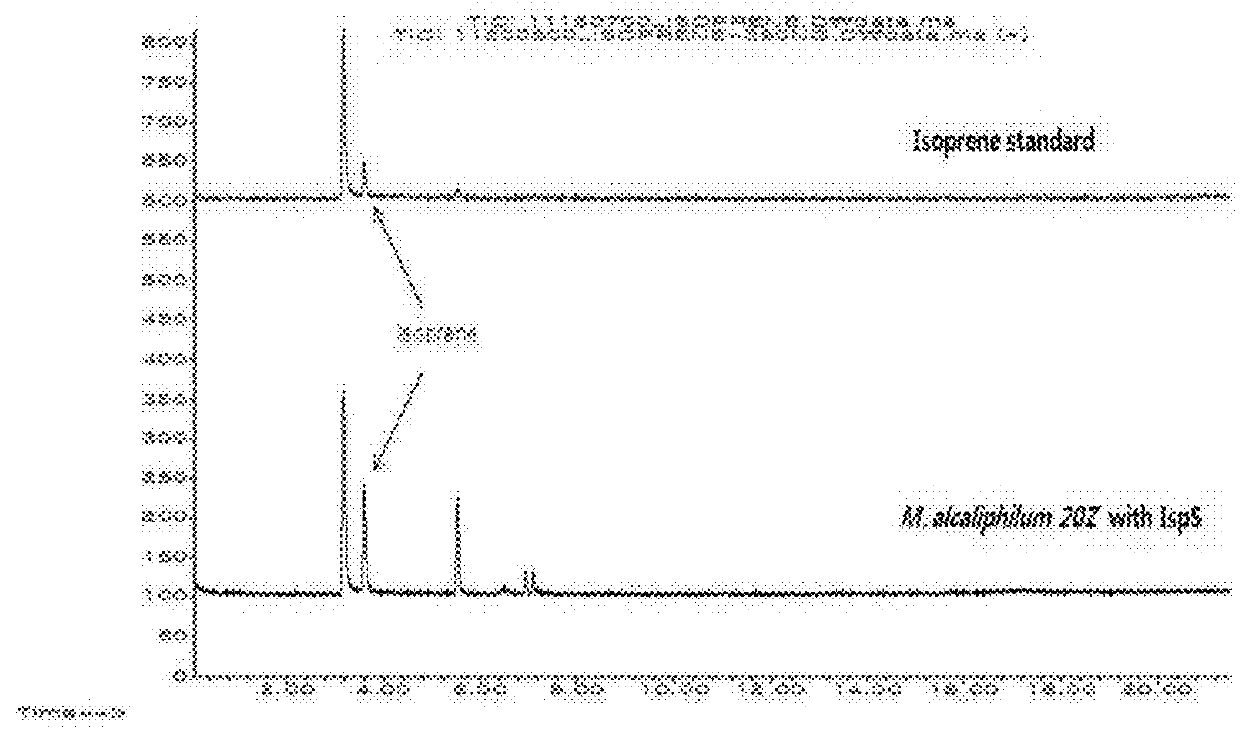
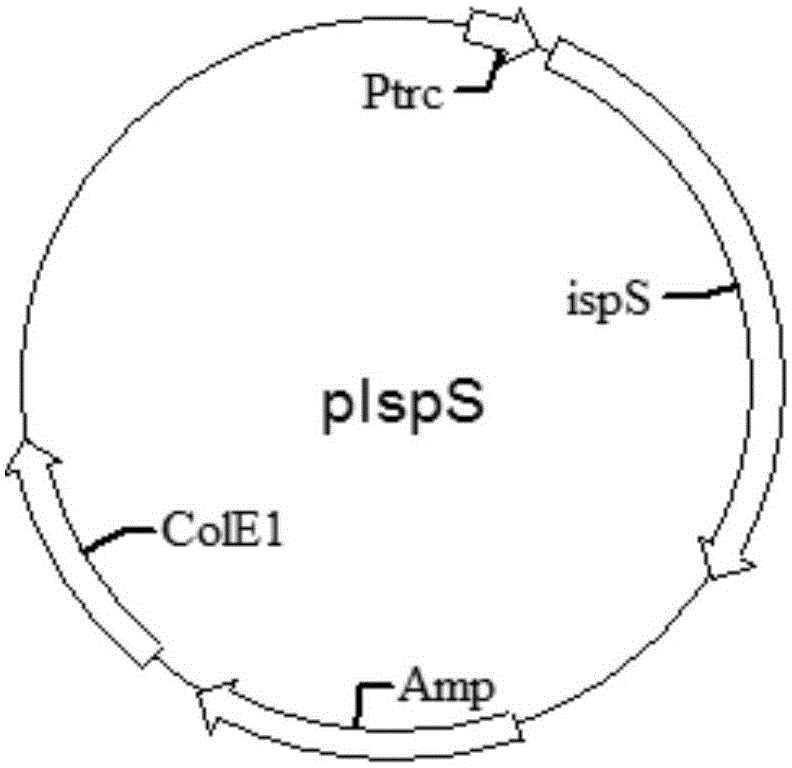
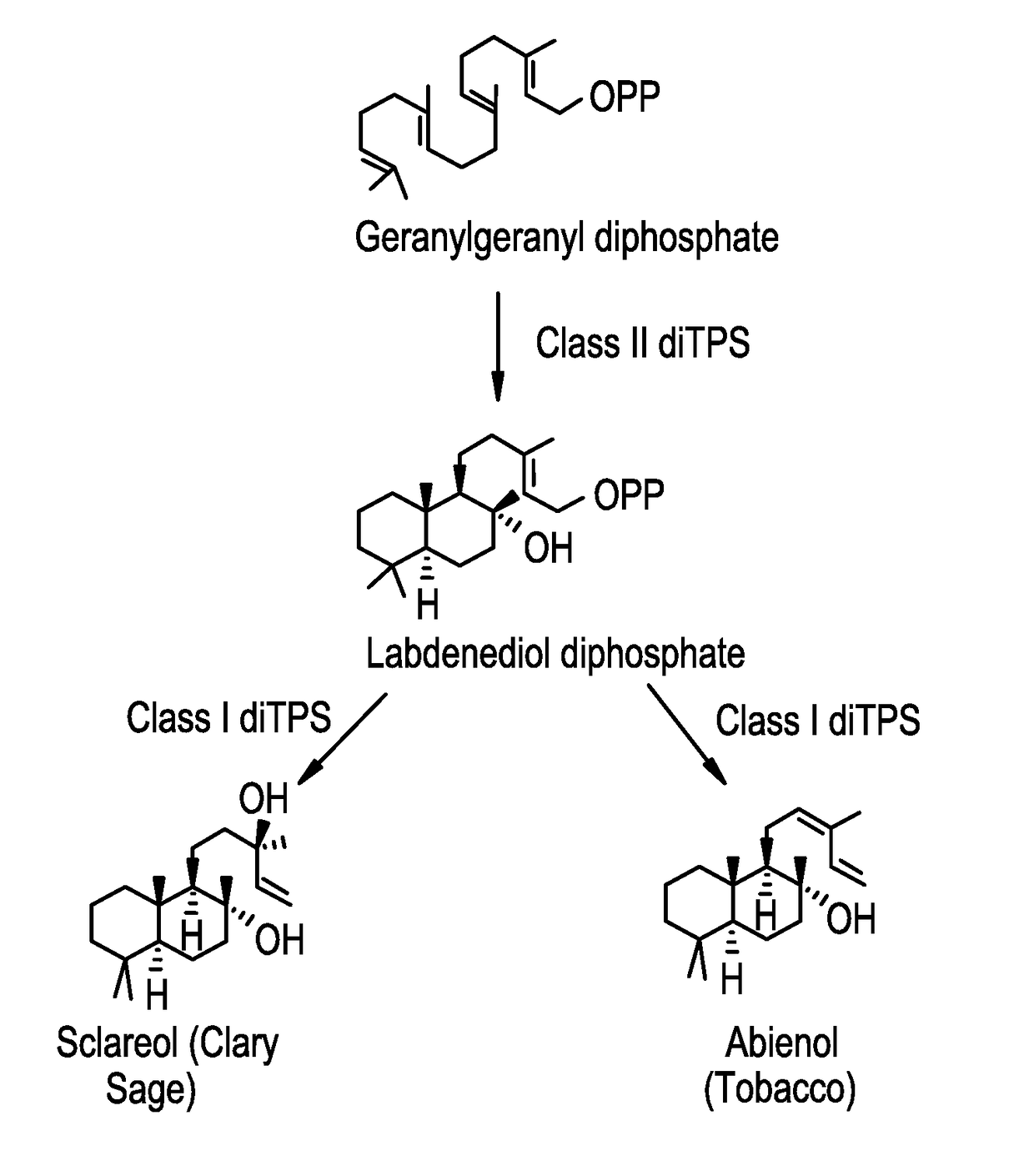
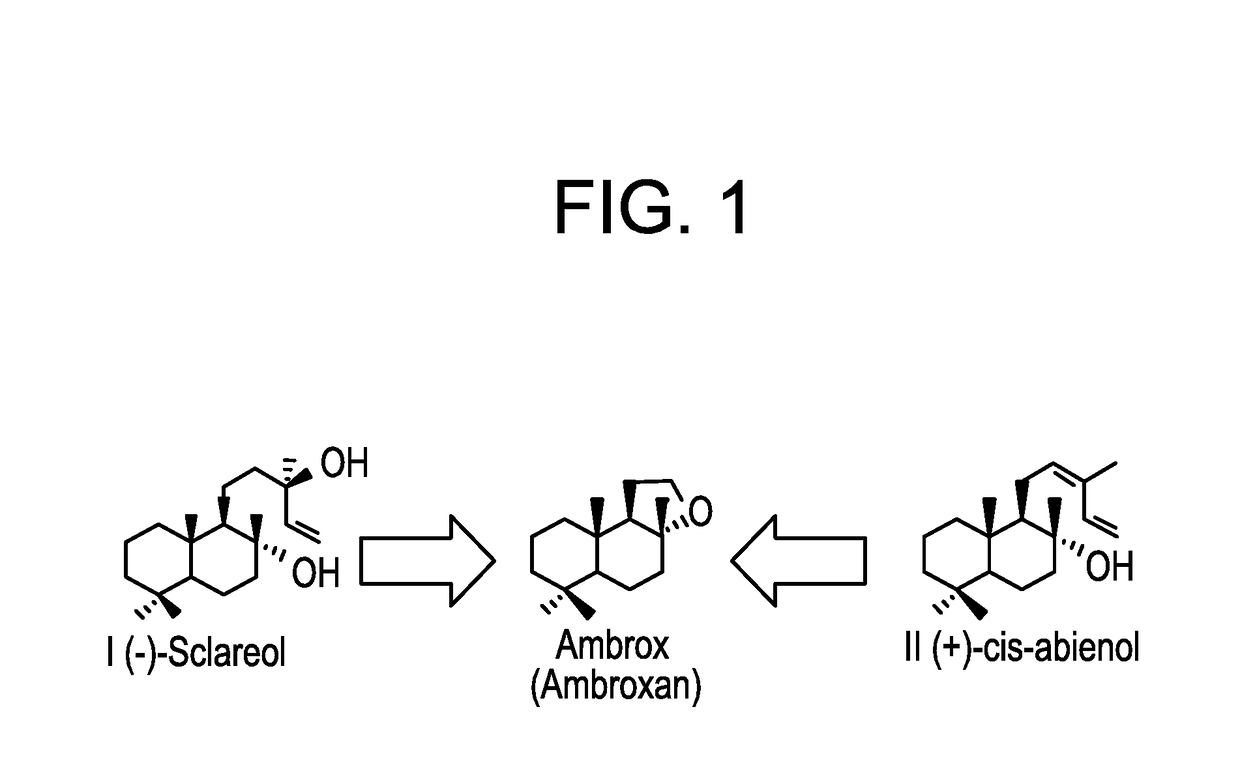
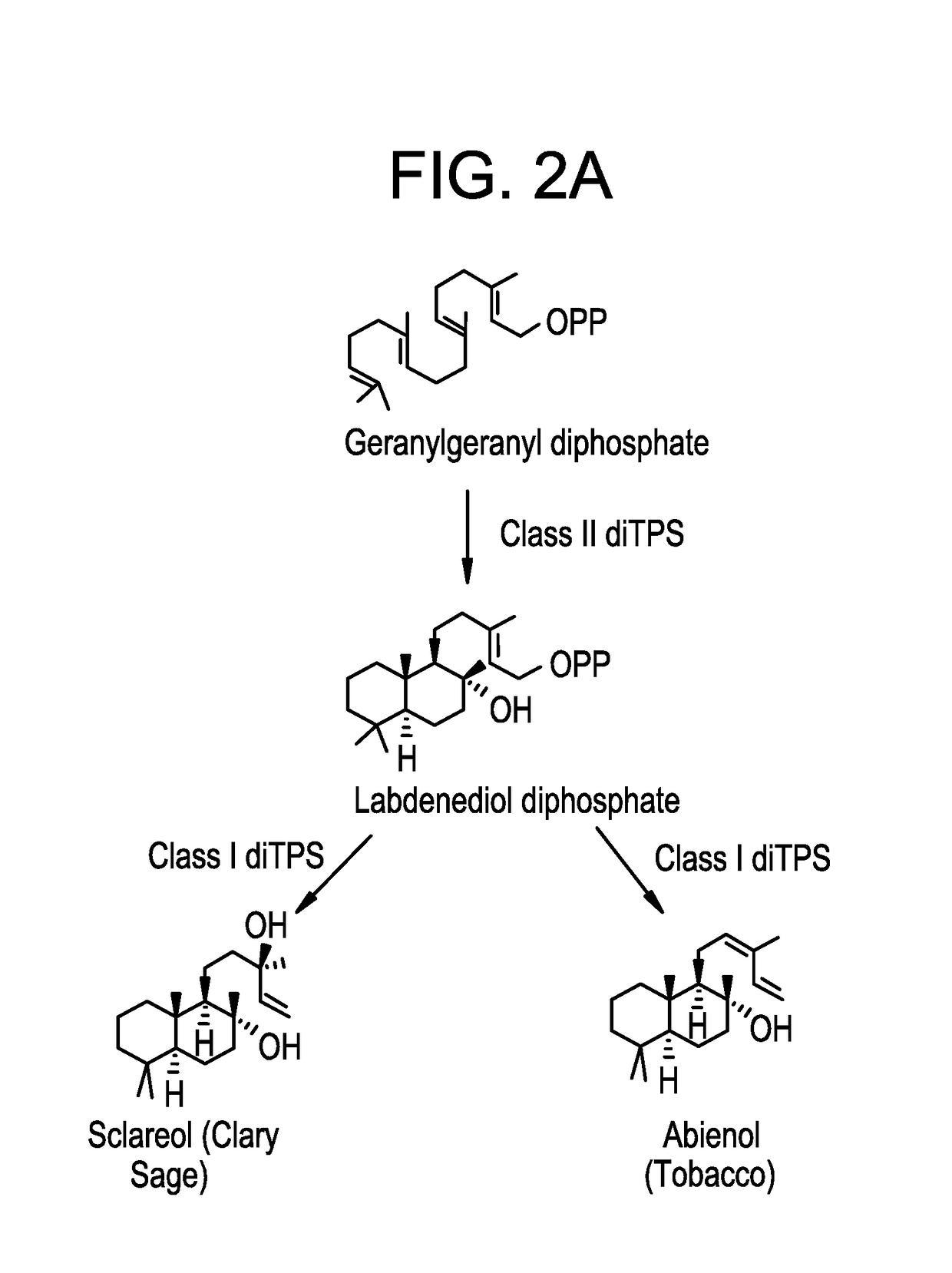
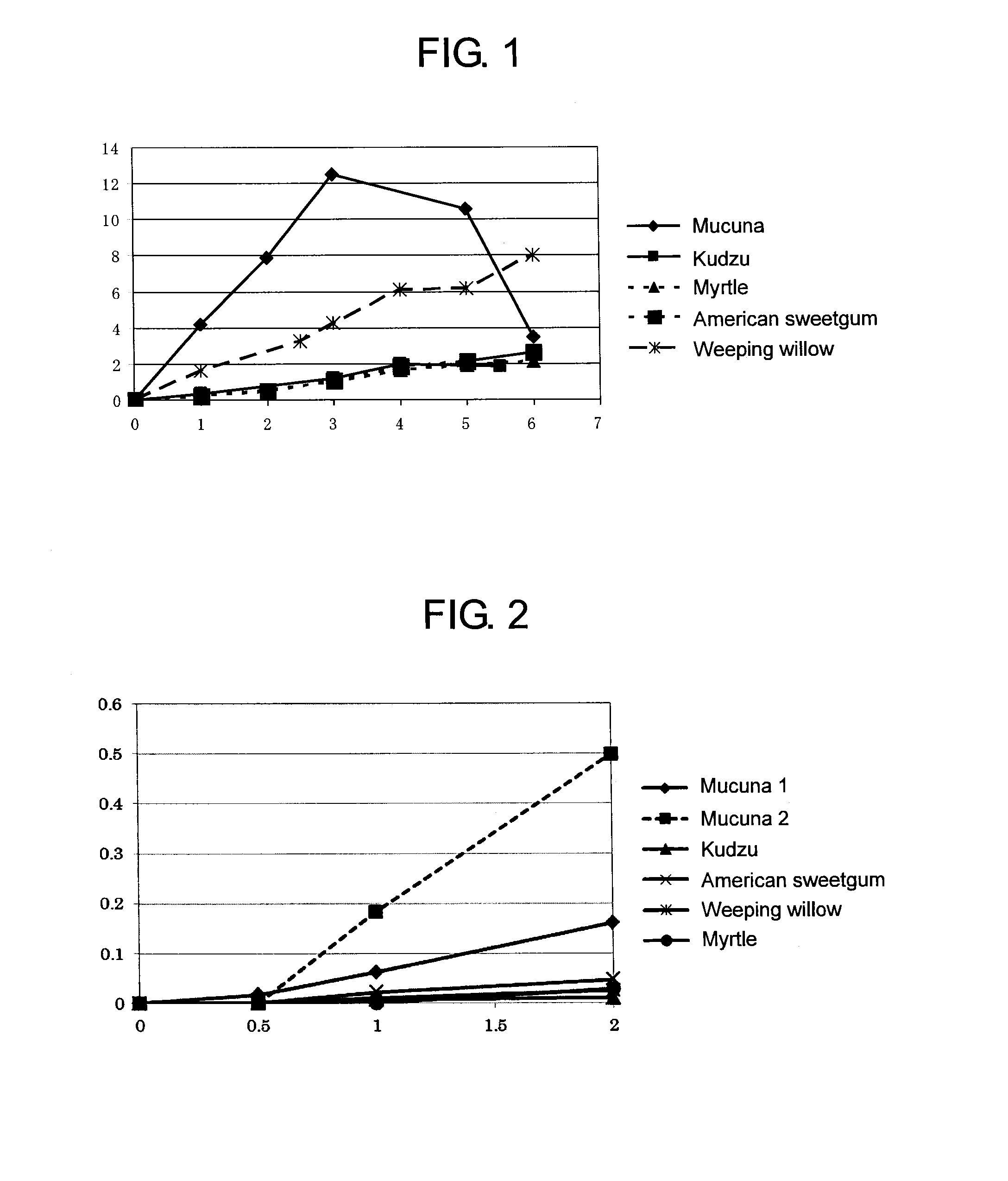
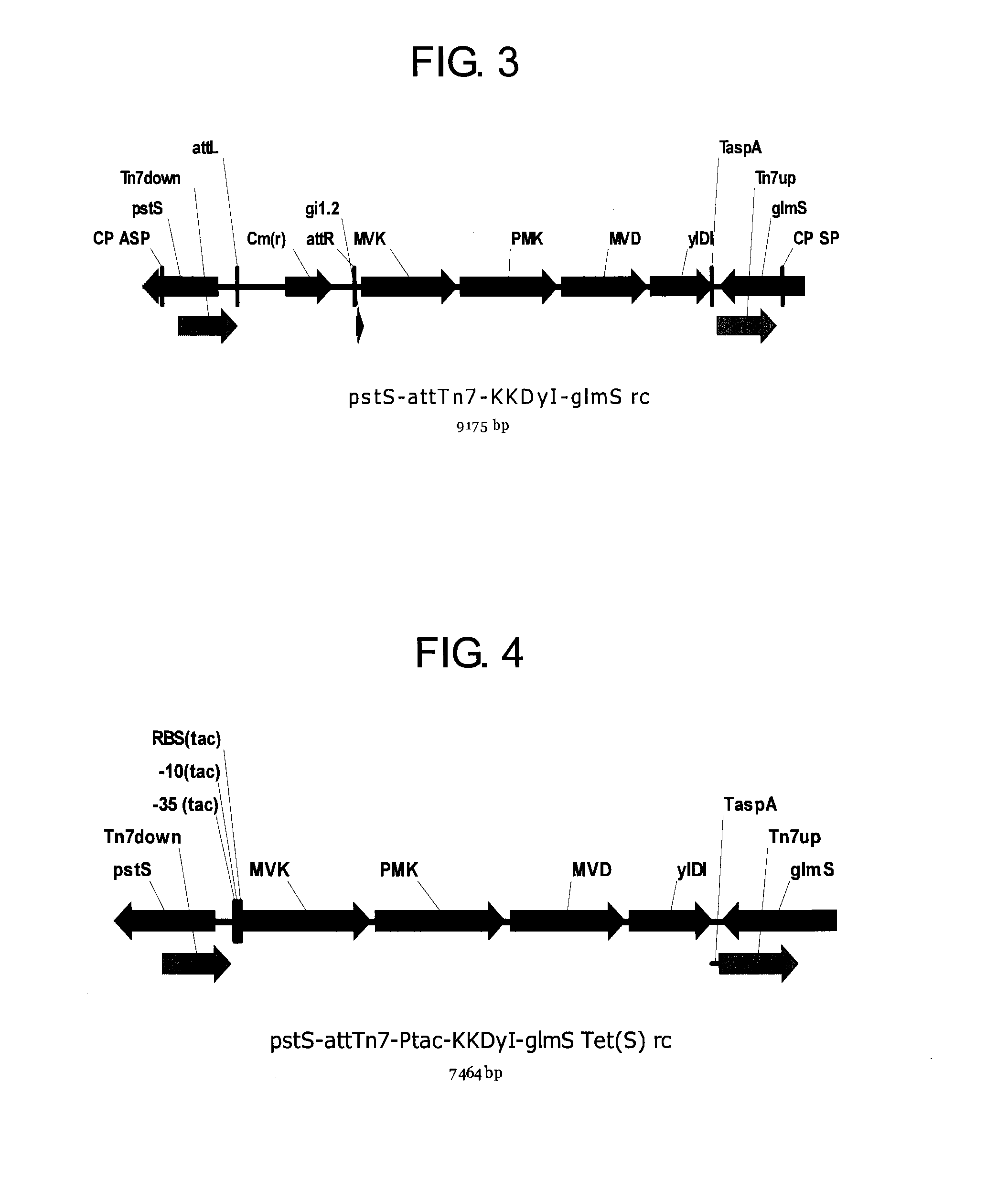
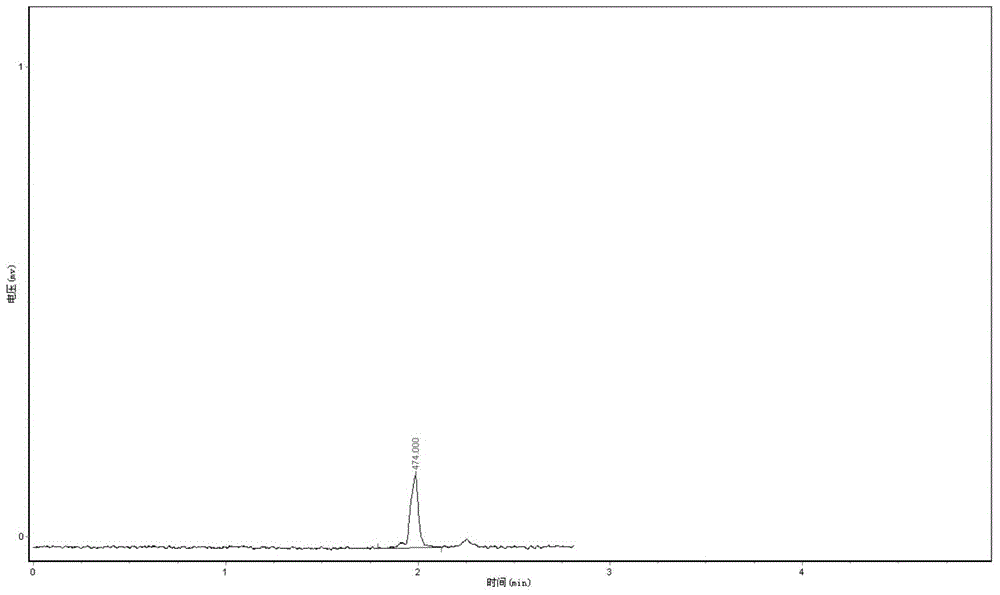
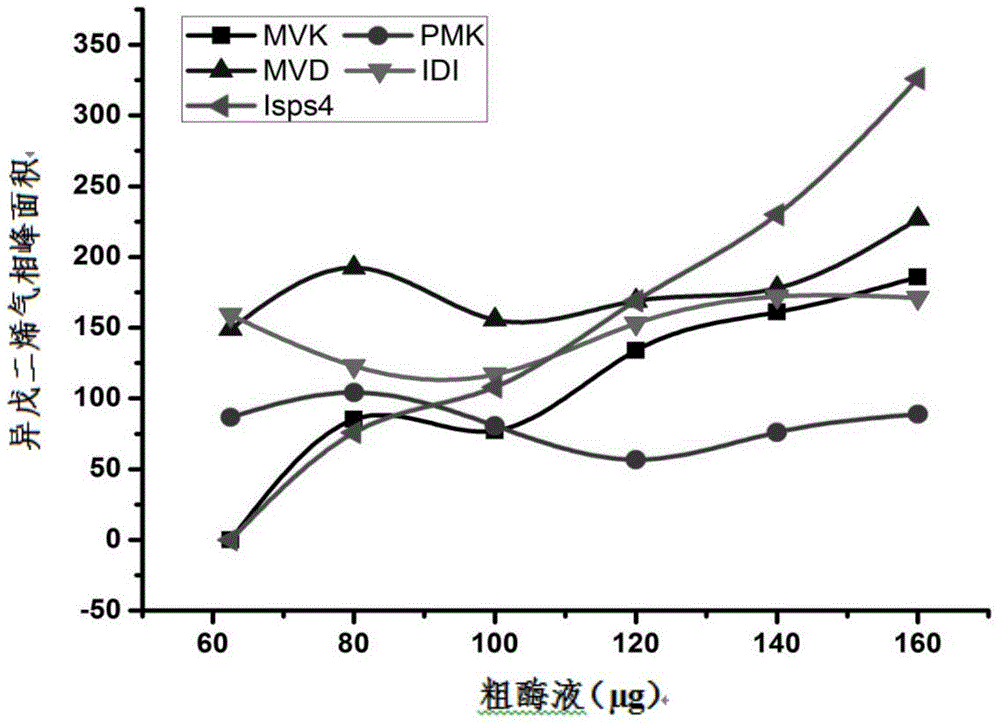
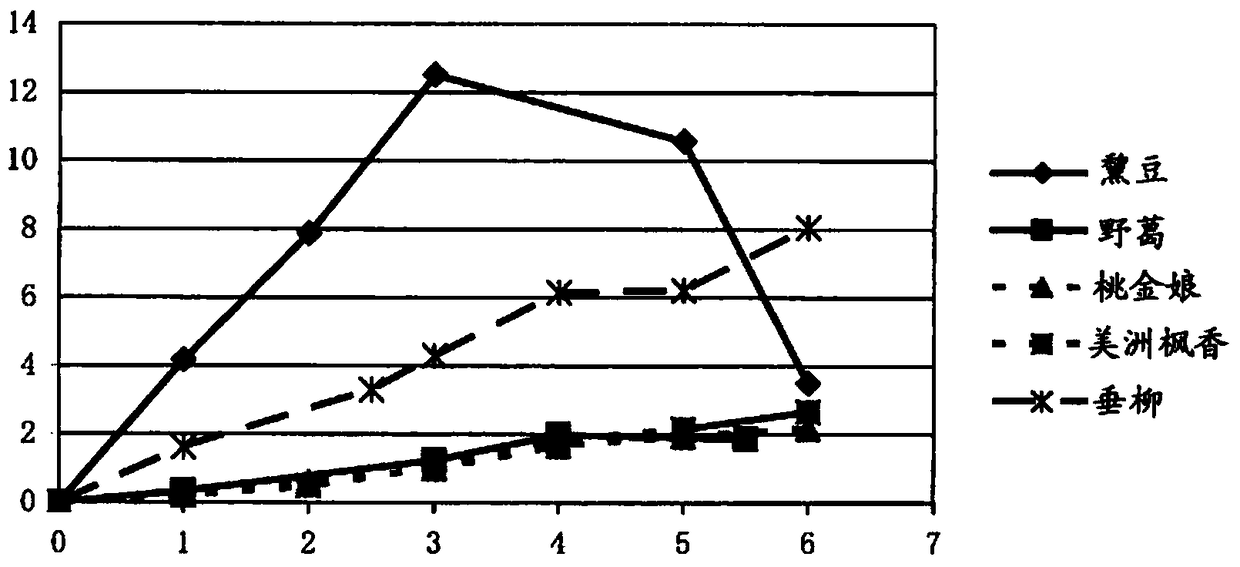
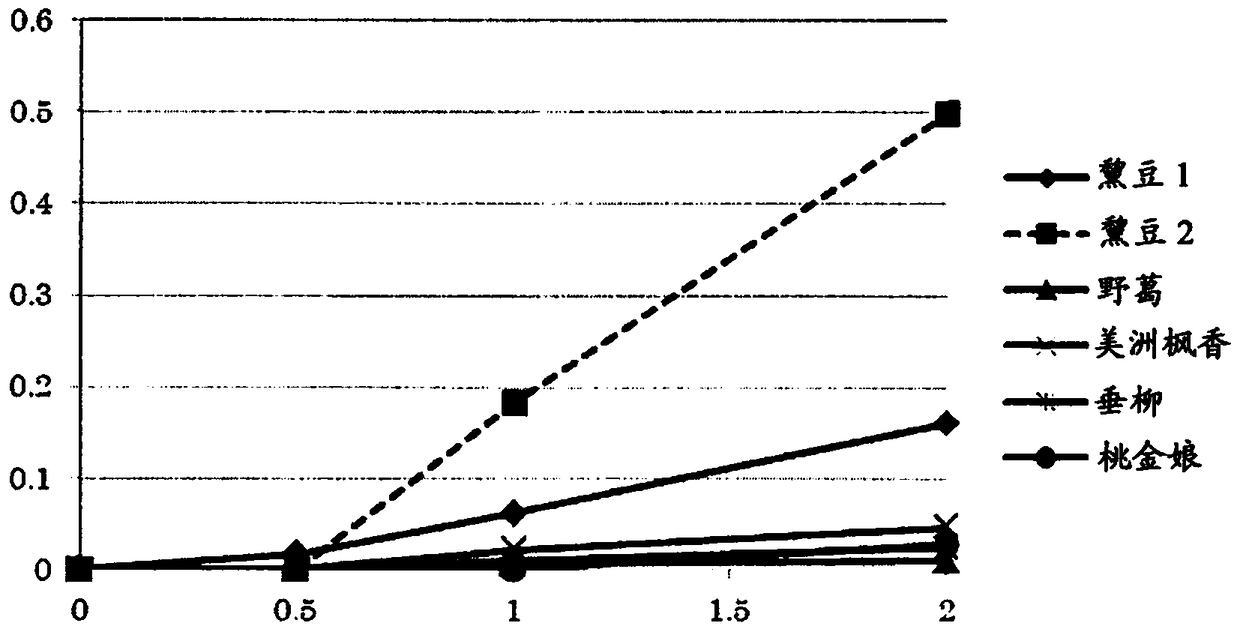
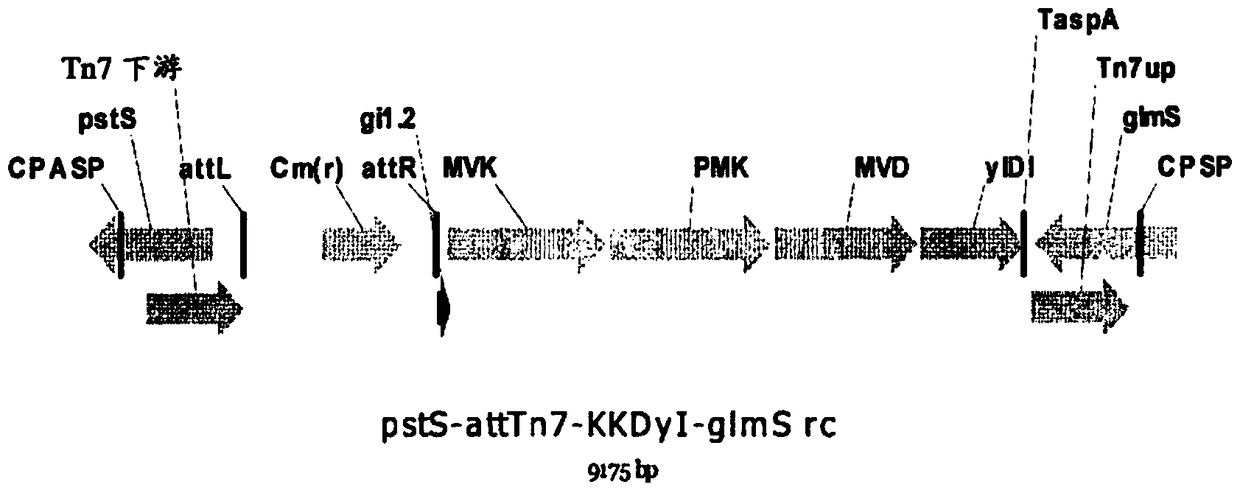
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Isoprene synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
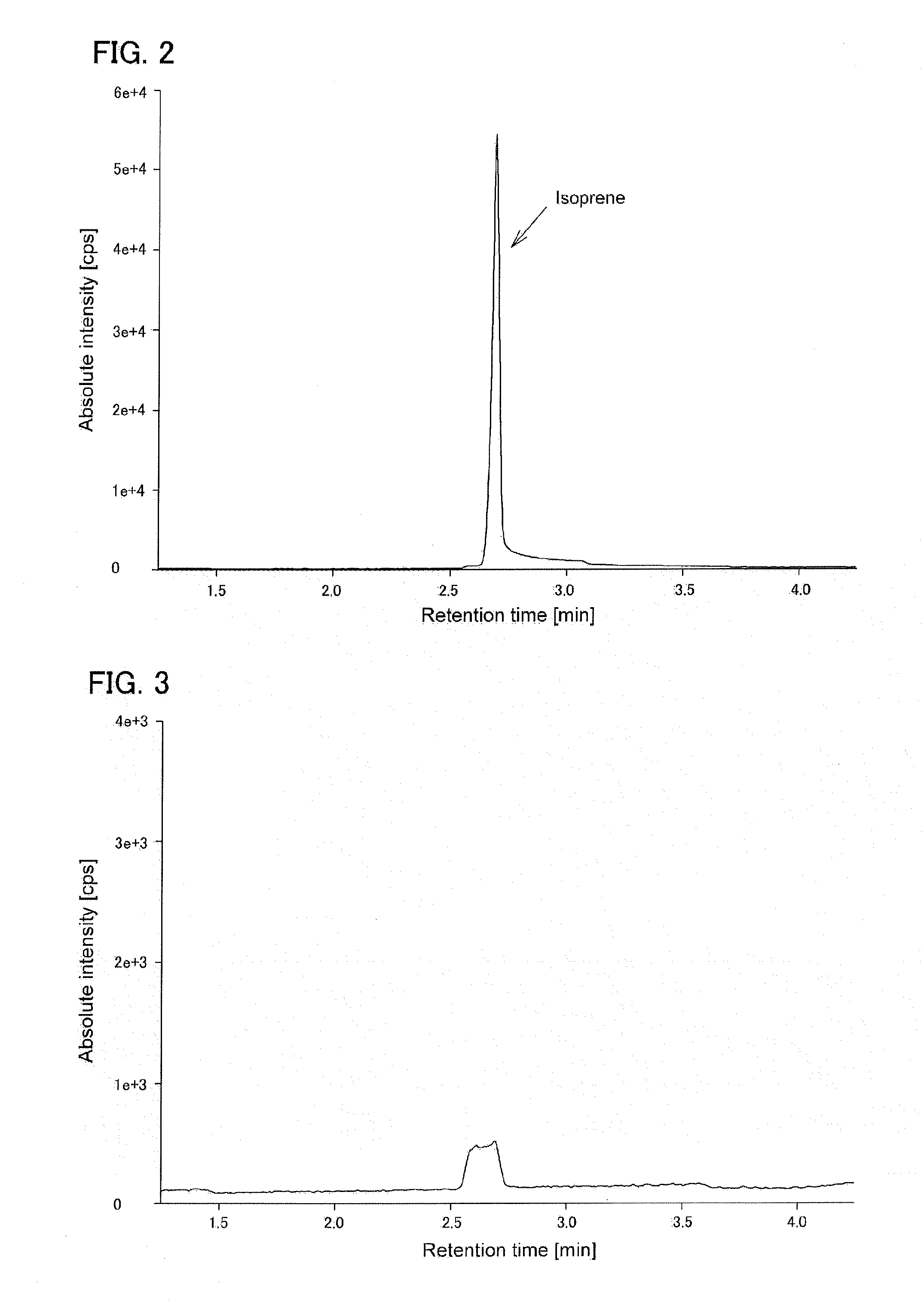
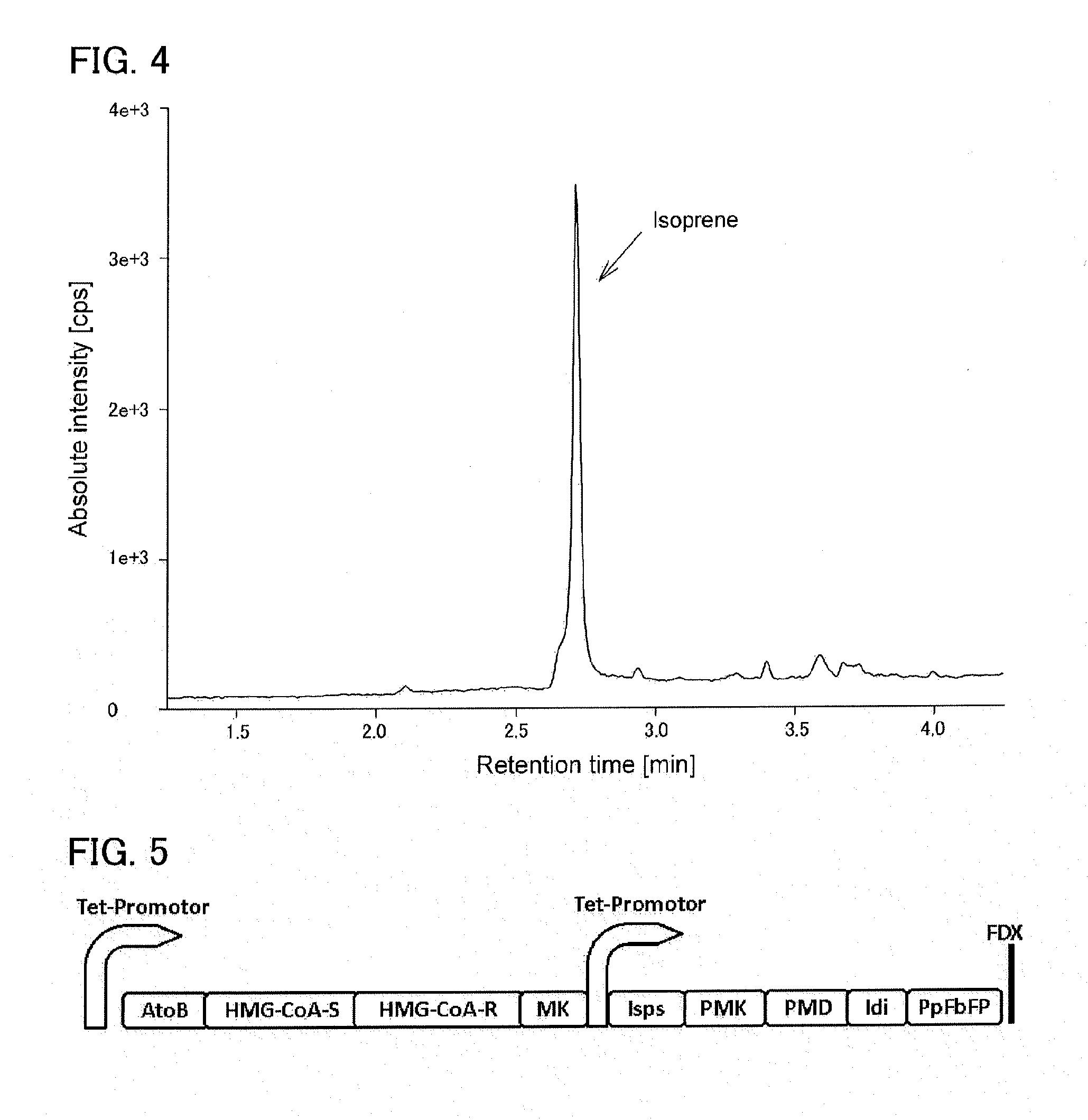
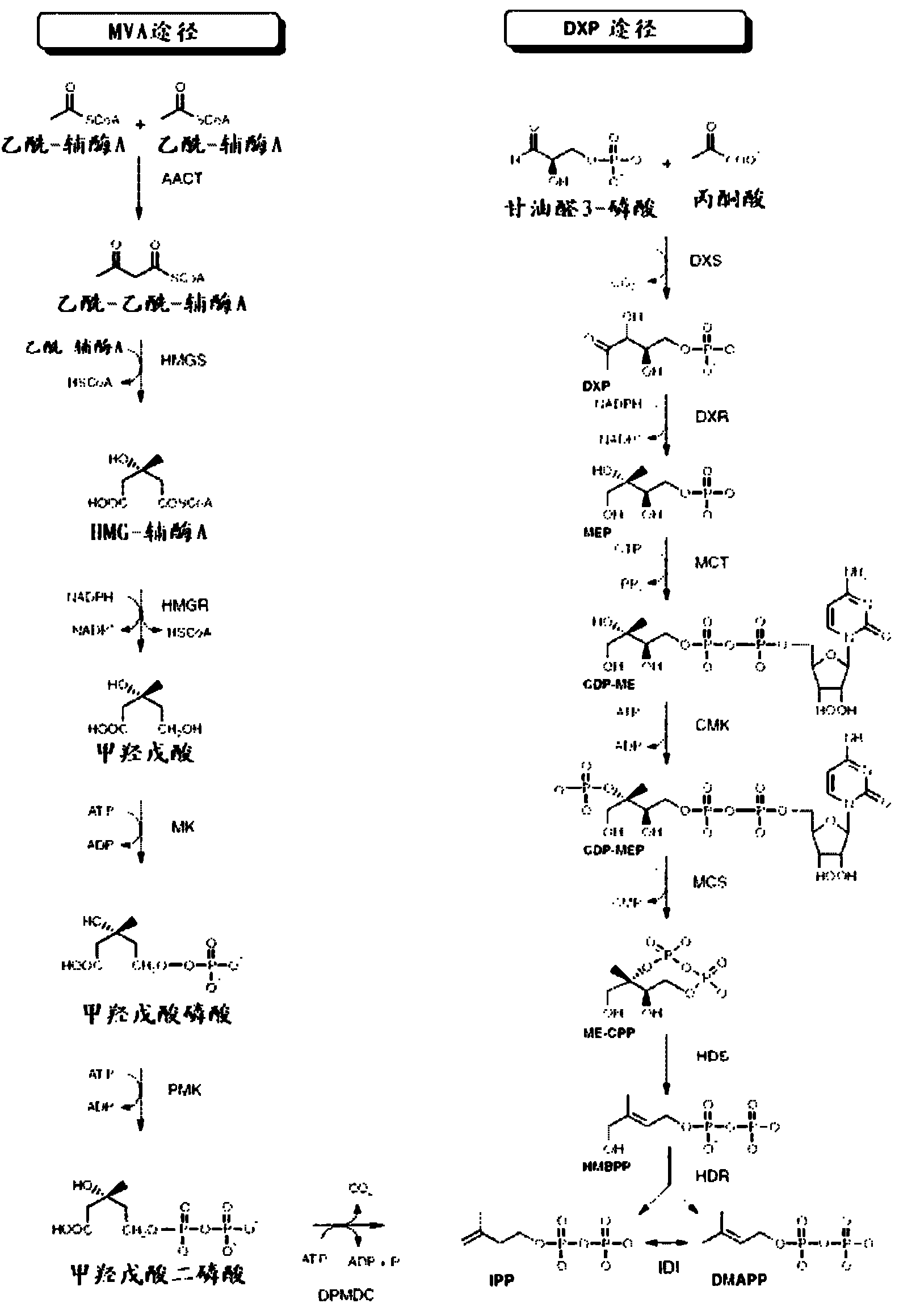
In enzymology, an isoprene synthase (EC 4.2.3.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction dimethylallyl pyrophosphate ⇌ isoprene + diphosphate Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, and two products, isoprene and pyrophosphate. This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically those carbon-oxygen lyases acting on phosphates. The systematic name of this enzyme class is dimethylallyl-pyrophosphate pyrophosphate-lyase (isoprene-forming).
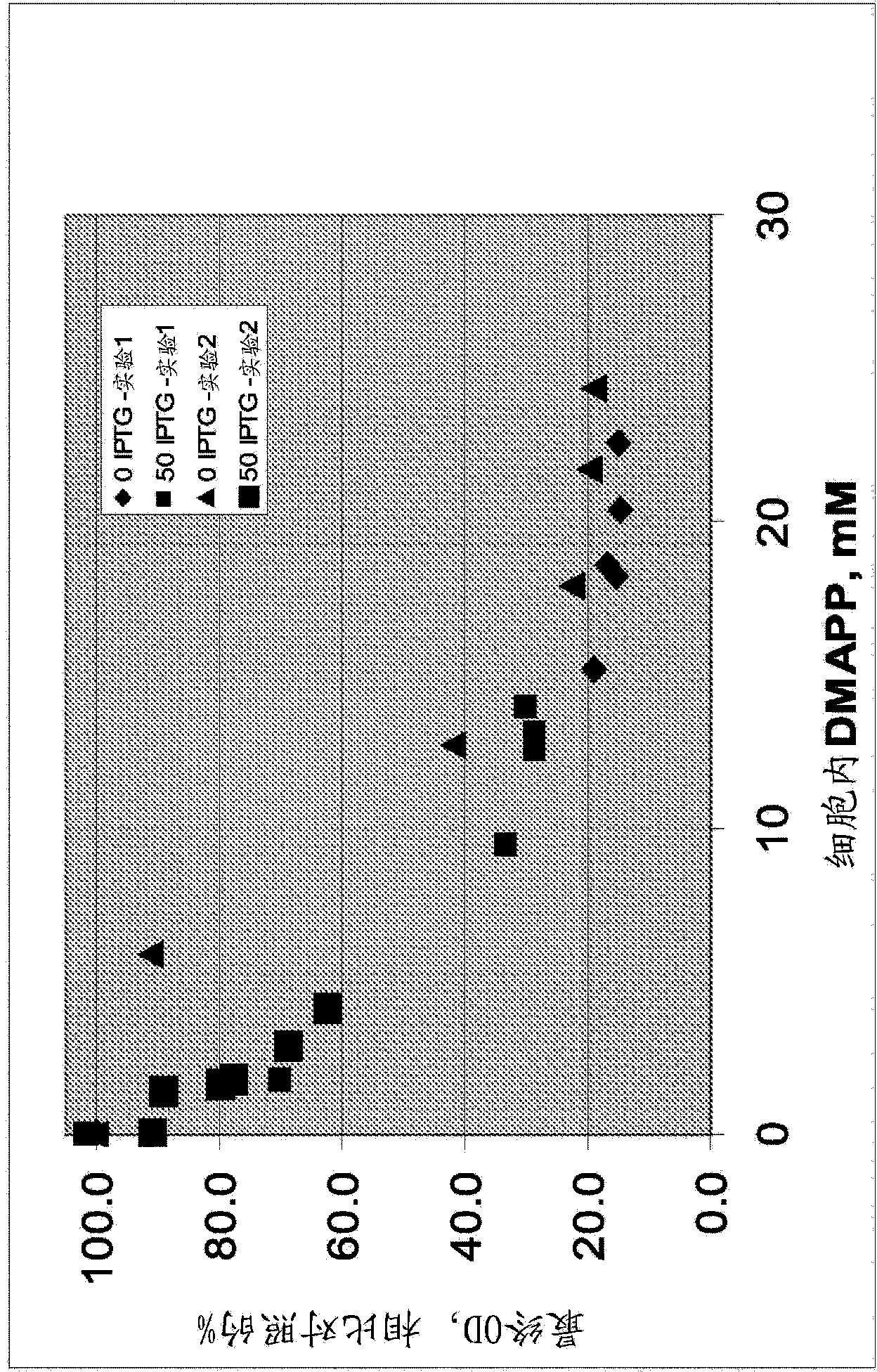
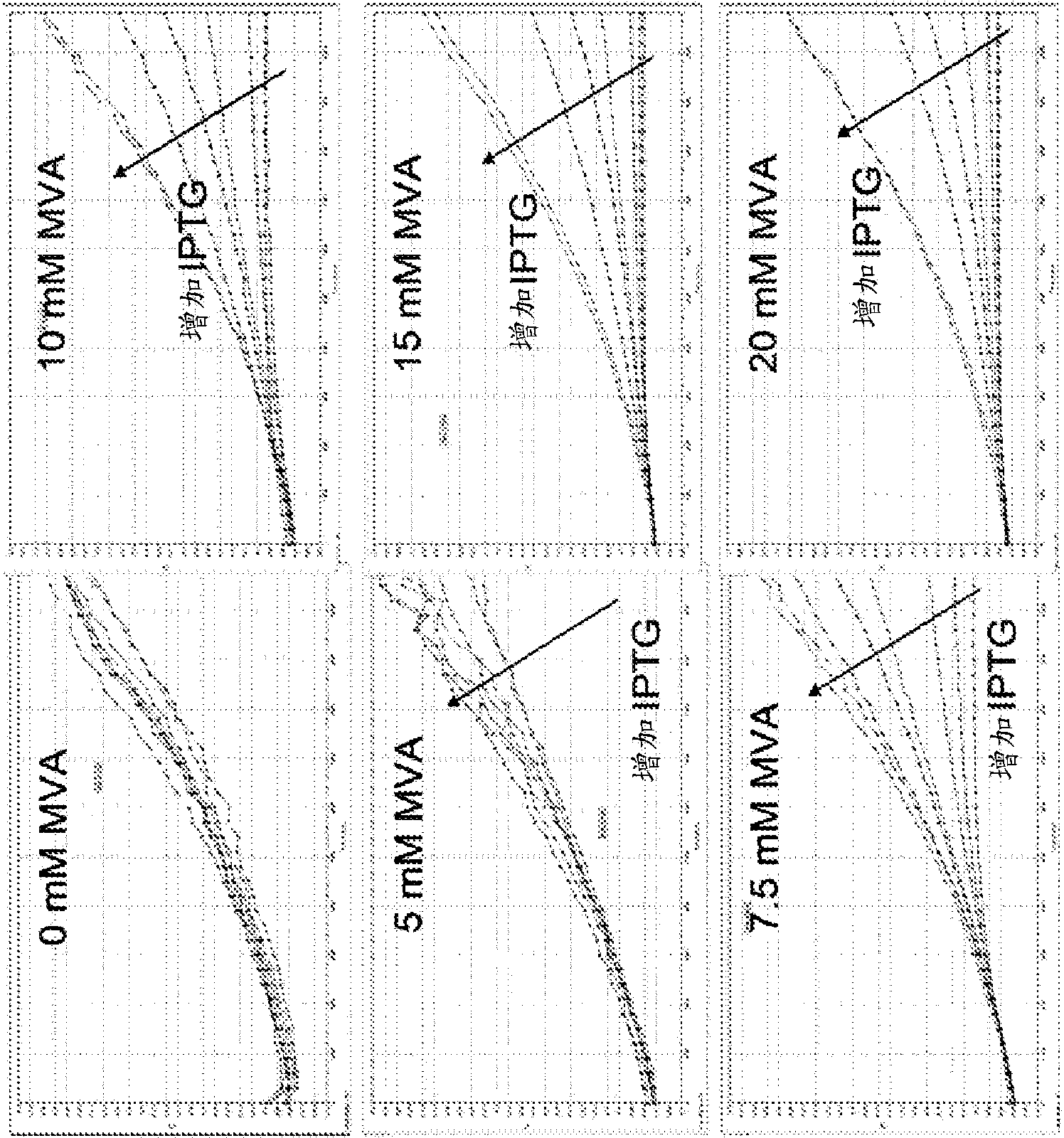
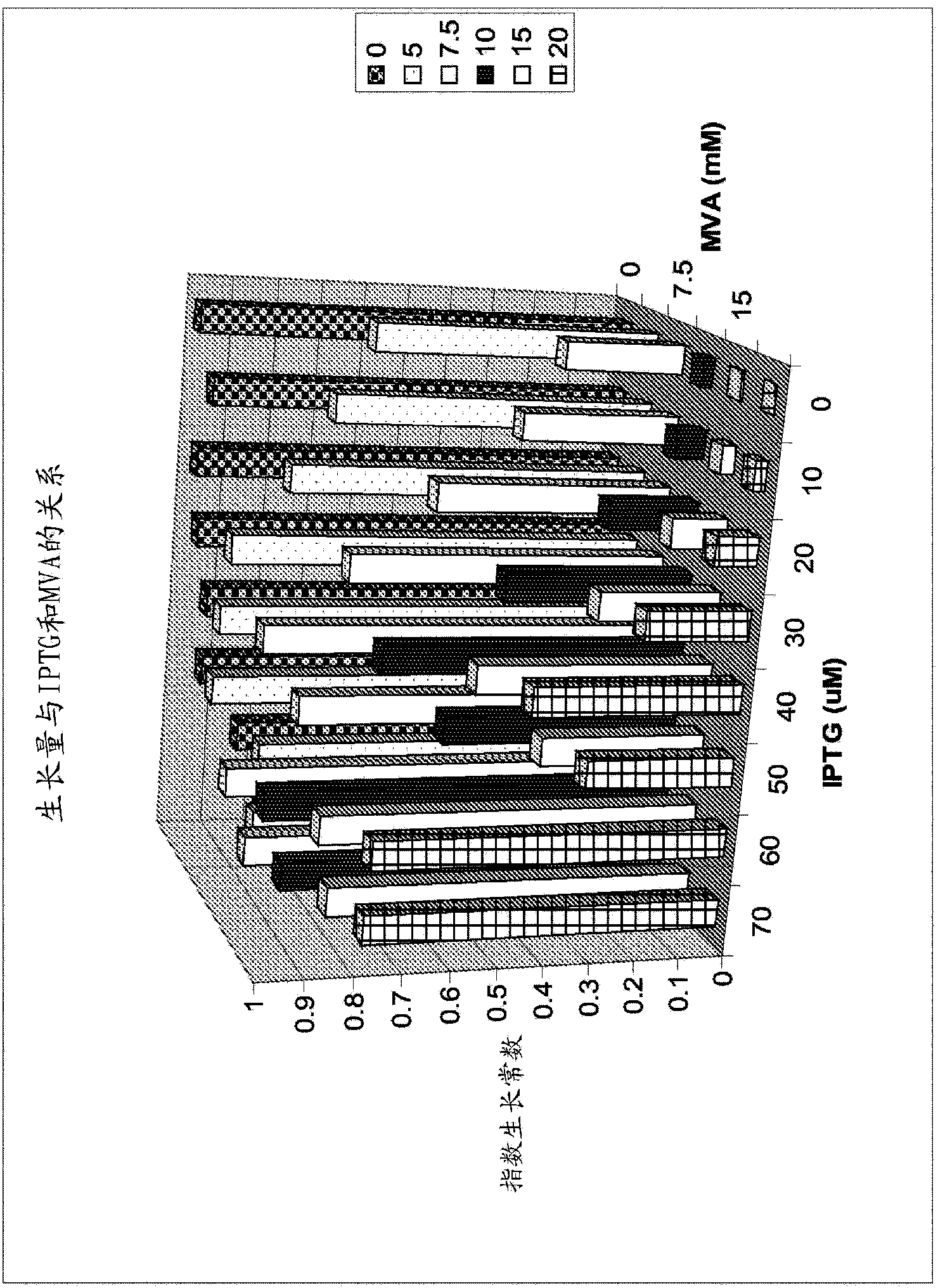
Increased isoprene production using mevalonate kinase and isoprene synthase
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Identification of isoprene synthase variants with improved properties for the production of isoprene
InactiveUS20130330796A1Increased production of isopreneImprove propertiesBacteriaUnicellular algaeIsoprene synthaseMedicinal chemistry
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
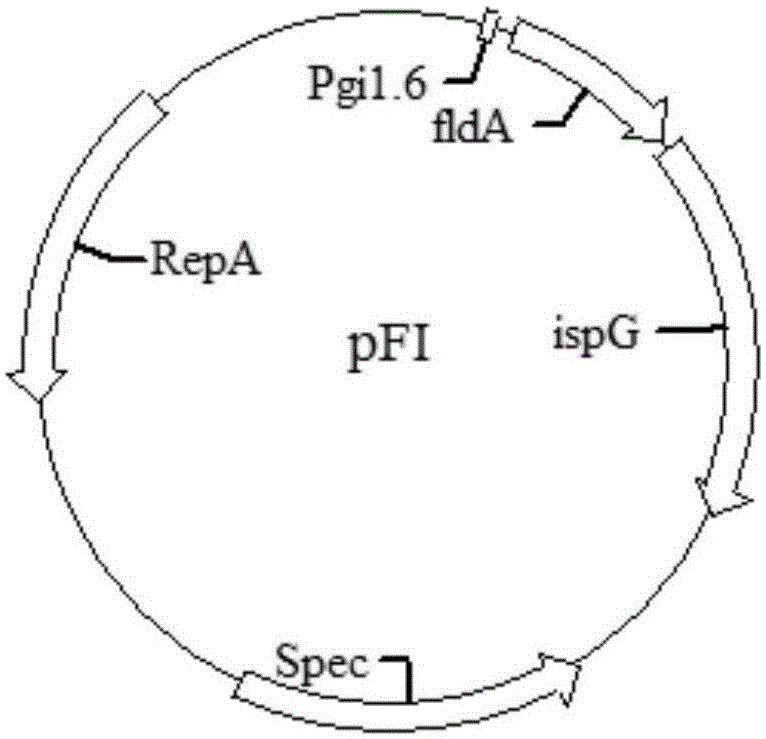
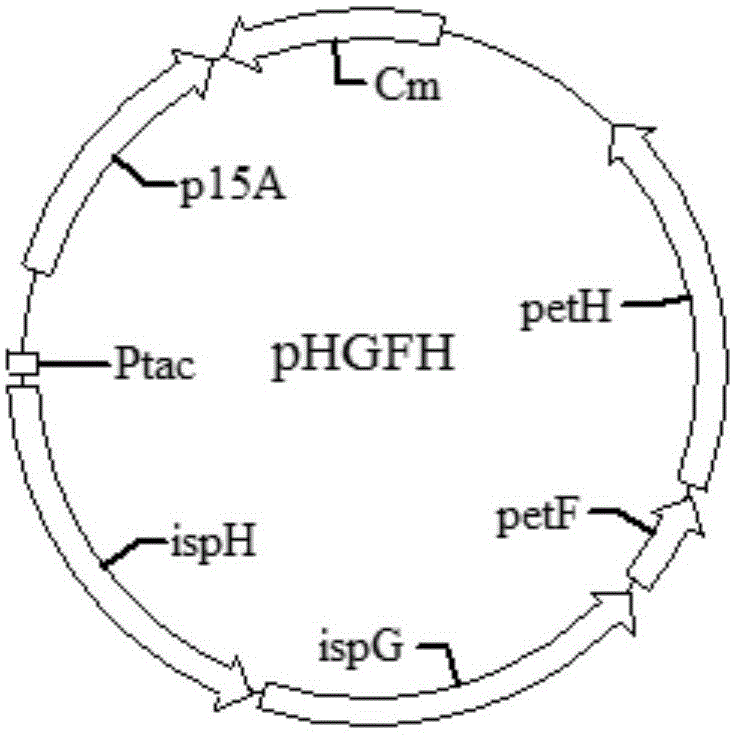
Compositions and methods for improved isoprene production using two types of ispg enzymes
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Recombinant cell, and method for producing isoprene
InactiveUS20150284742A1Efficient supplyImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaWaste based fuelIsoprene synthaseIsopentadiene
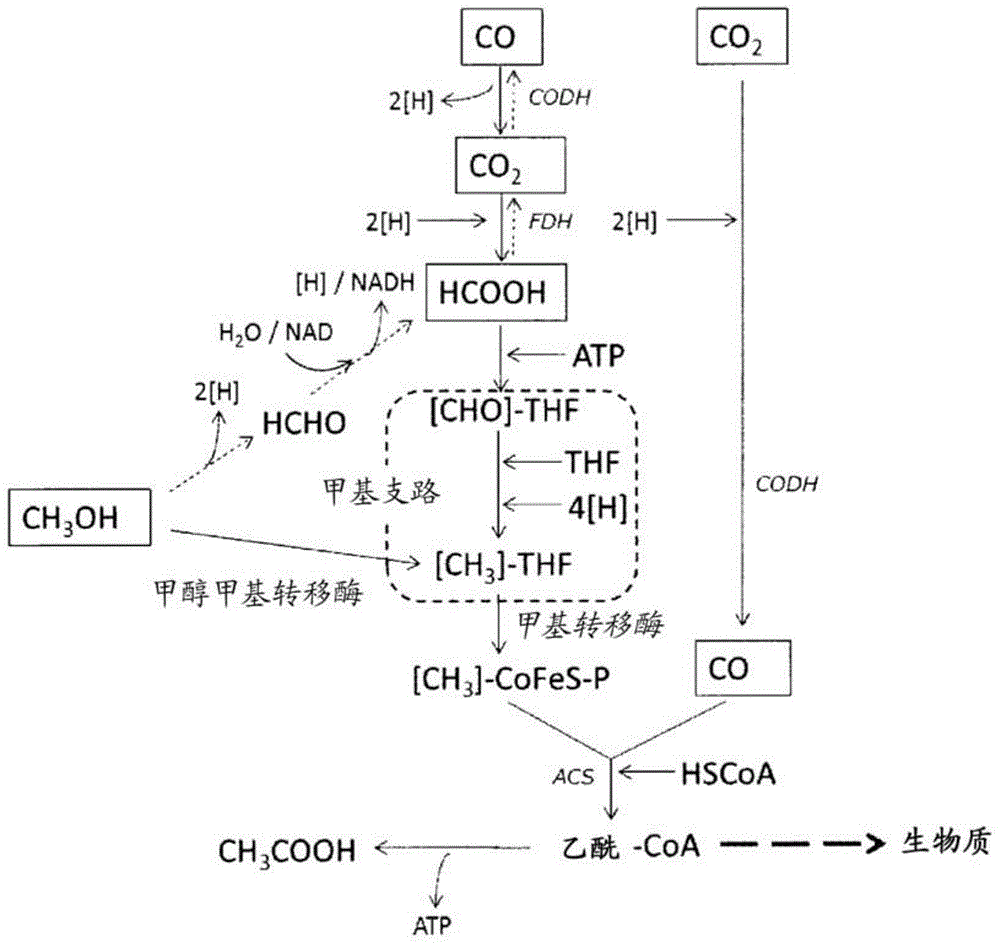
To provide a series of techniques capable of producing isoprene from syngas or the like.Provided is a recombinant cell prepared by introducing a nucleic acid encoding isoprene synthase into a host cell having an isopentenyl diphosphate synthesis ability by a non-mevalonate pathway, wherein the nucleic acid is expressed in the host cell, and the recombinant cell is capable of producing isoprene from at least one C1 compound selected from the group consisting of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, formic acid, and methanol. As the host cell, a Clostridium bacterium or a Moorella bacterium is exemplified. Also provided is a method for producing isoprene using the recombinant cell.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Isoprene synthase variants for improved production of isoprene
InactiveCN103443271AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProduction rateIsoprene synthase
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Isoprene synthase and gene encoding the same, and method for producing isoprene monomer
ActiveUS20140113344A1Easy to optimizeEasy to produceBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
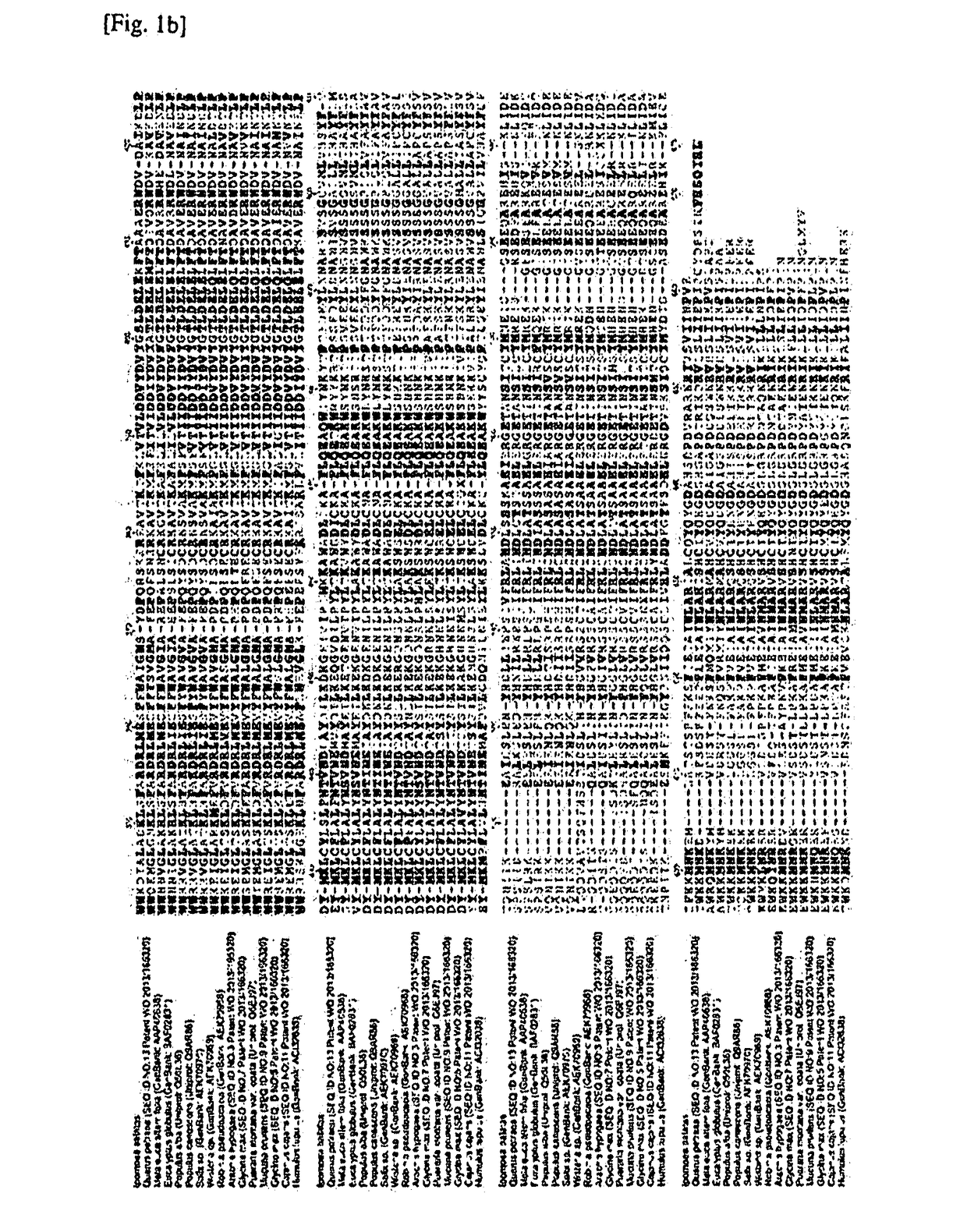
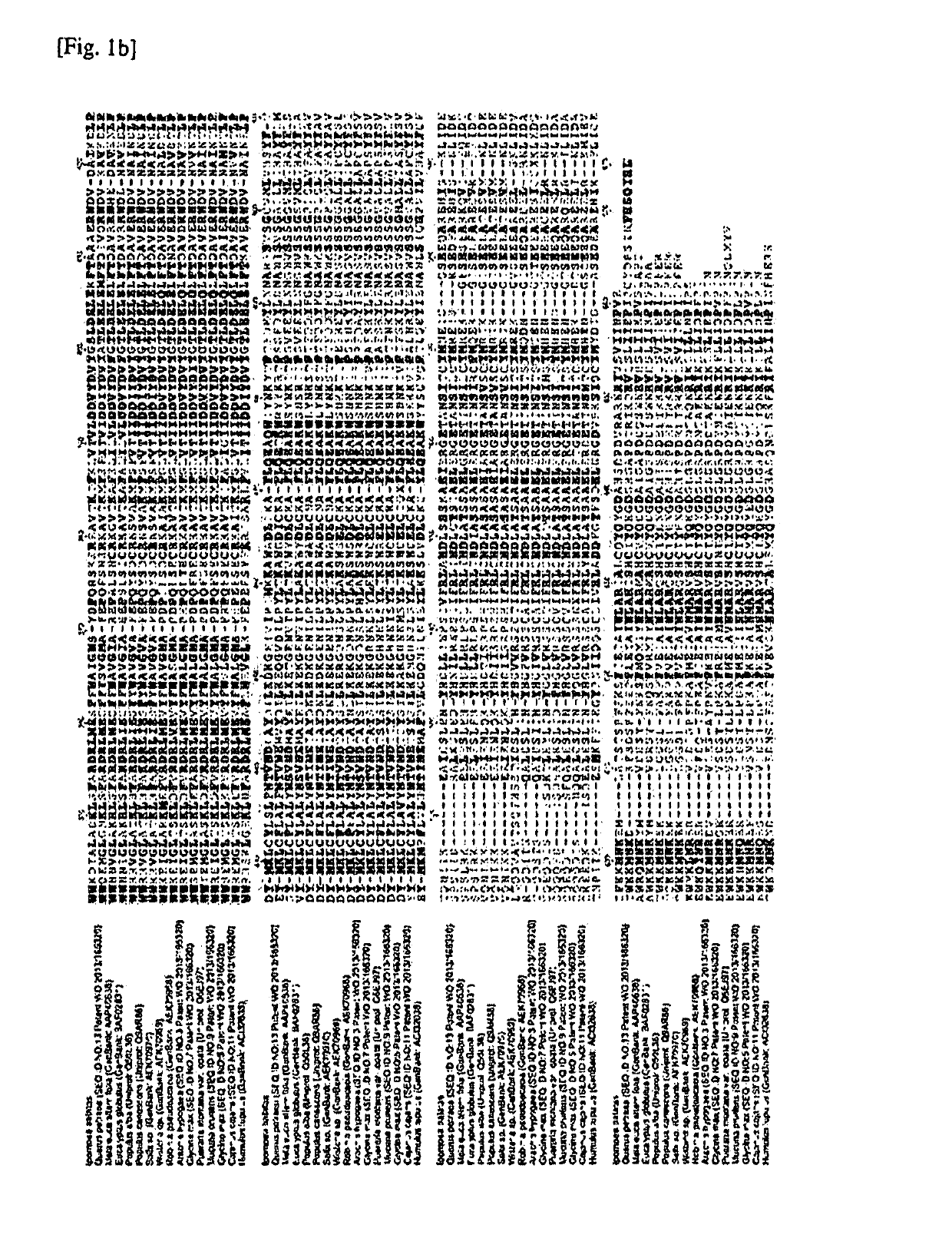
The present invention provides means useful for establishing an excellent isoprene monomer production system. Specifically, the present invention provides a polynucleotide of the following (a), (b), or (c):(a) a polynucleotide comprising (i) the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, or (ii) the nucleotide sequence consisting of the nucleotide residues at positions 133 to 1785 in the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1;(b) a polynucleotide that comprises a nucleotide sequence having 90% or more identity to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and encodes a protein having an isoprene synthase activity; or(c) a polynucleotide that hybridizes under a stringent condition with a polynucleotide consisting of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and encodes a protein having an isoprene synthase activity; and the like.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Recombinant cell and production method for isoprene
To provide a series of techniques capable of producing isoprene from syngas or the like. Provided is a recombinant cell prepared by introducing a nucleic acid encoding isoprene synthase into a host cell having an isopentenyl diphosphate synthesis ability by a non-mevalonate pathway, wherein the nucleic acid is expressed in the host cell, and the recombinant cell is capable of producing isoprene from at least one C1 compound selected from the group consisting of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, formic acid, and methanol. As the host cell, a Clostridium bacterium or a Moorella bacterium is exemplified. Also provided is a method for producing isoprene using the recombinant cell.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
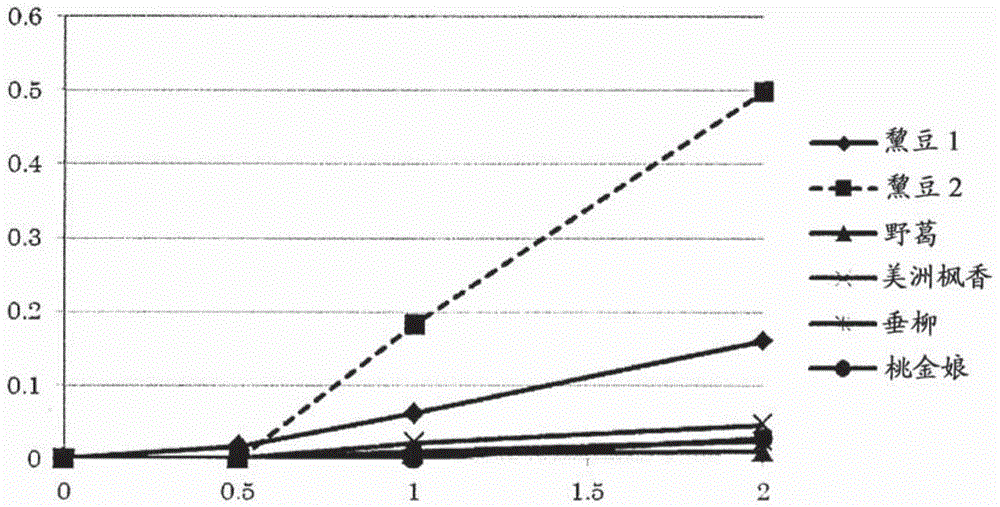
Legume isoprene synthase for production of isoprene
The present invention provides methods and compositions of polypeptides having isoprene synthase activity with improved performance characteristics. In particular, the present invention provides legume isoprene synthases for increased isoprene production in recombinant host cells.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Isoprene synthase variants for improved microbial production of isoprene
The present invention provides methods and compositions comprising at least one isoprene synthase enzyme with improved catalytic activity and / or solubility. In particular, the present invention provides variant plant isoprene synthases for increased isoprene production in microbial host cells. Biosynthetically produced isoprene of the present invention finds use in the manufacture of rubber and elastomers.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
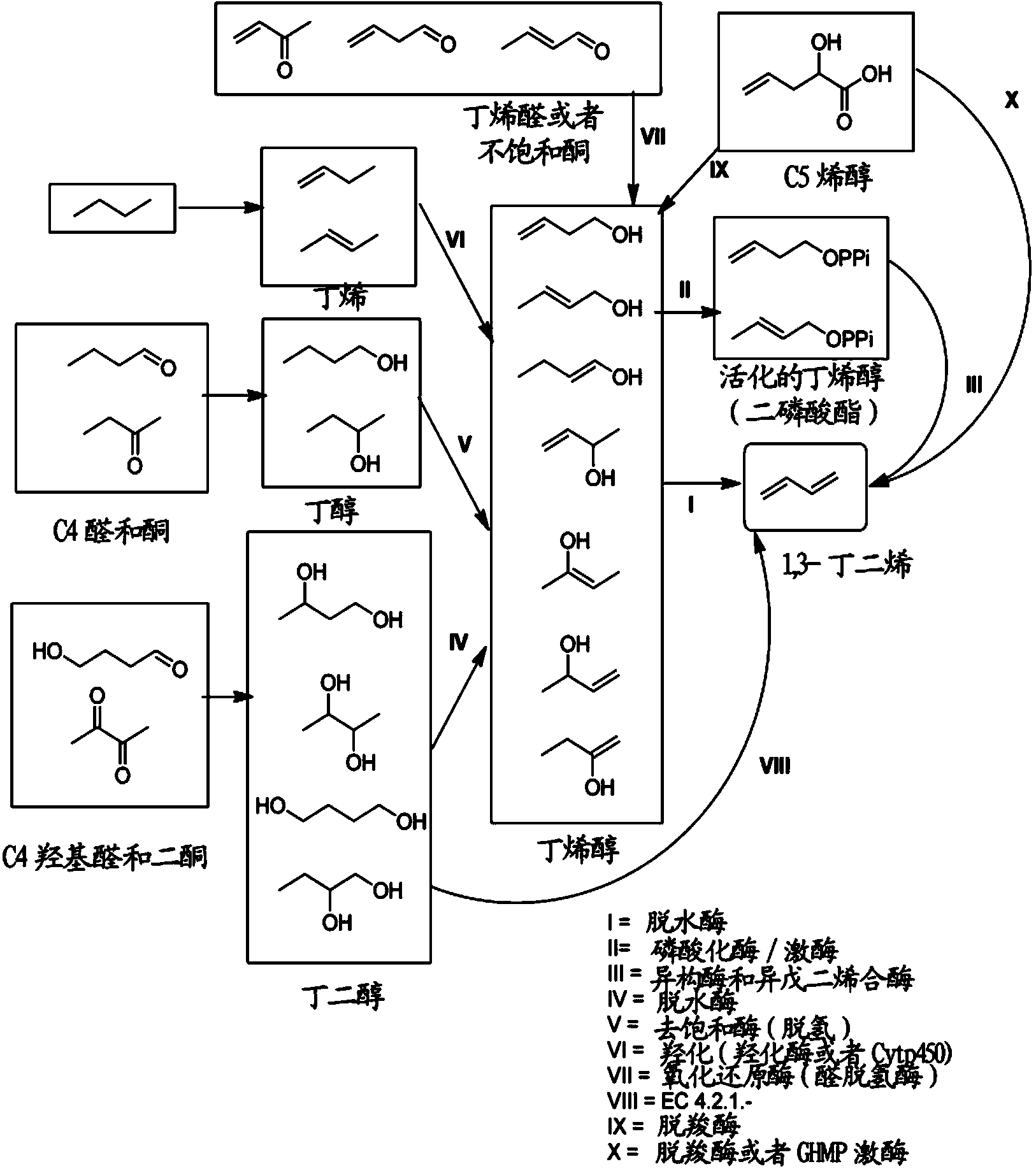
Methods for biosynthesizing 1,3butadiene
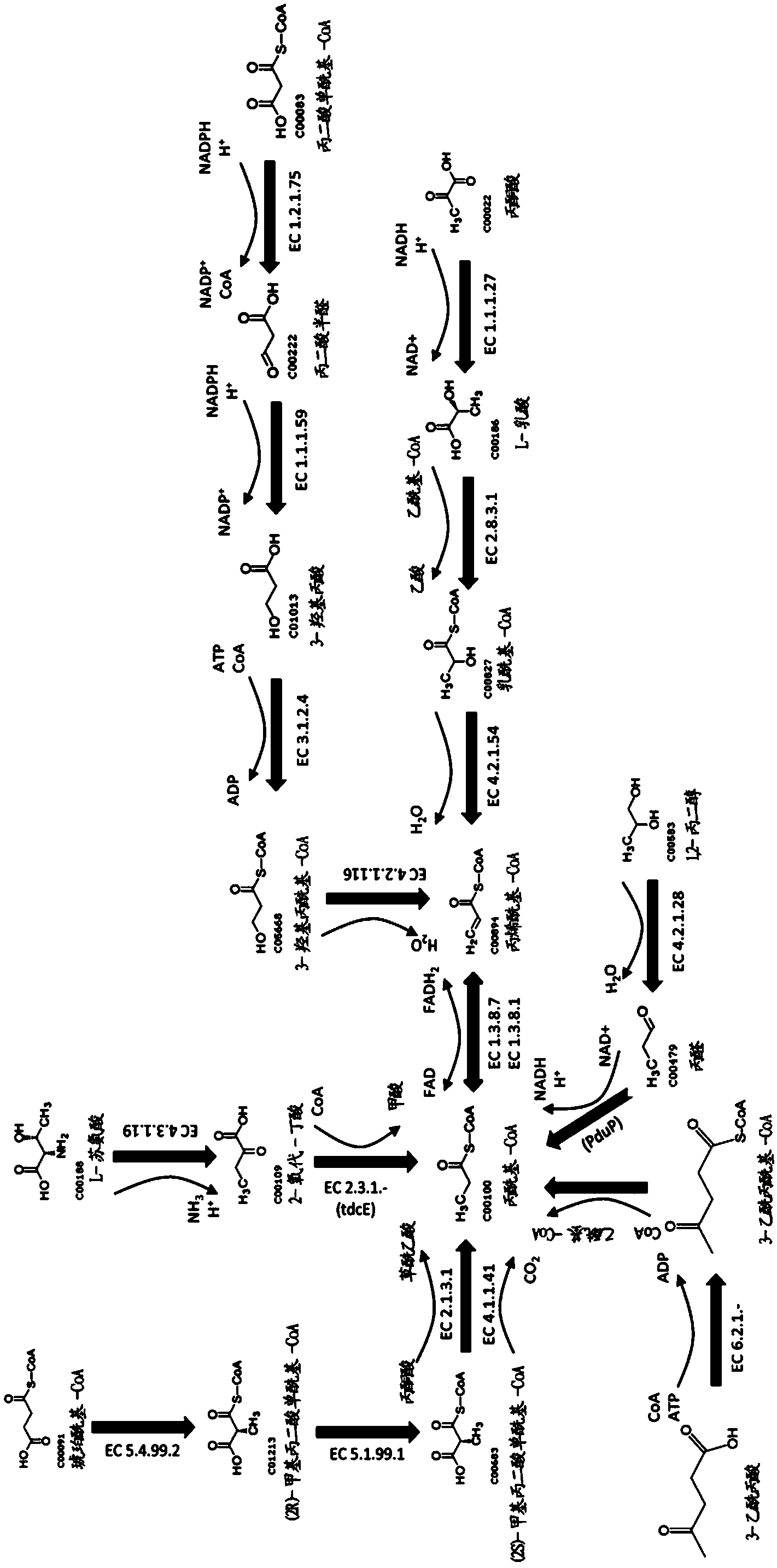
This document describes biochemical pathways for producing butadiene by forming two vinyl groups in a butadiene synthesis substrate. These pathways described herein rely on enzymes such as mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase, isoprene synthase, and dehydratases for the final enzymatic step.
Owner:INVISTA TEXTILES (U K) LTD
Novel Isoprene Synthase and Method of Preparing Isoprene Using Thereof
ActiveUS20170211056A1Excellent isoprene productivityIncrease productivityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGene conversionIsoprene synthase
Provided are a novel isoprene synthase derived from sweet potato and a method of preparing isoprene using the same, and more specifically, a novel isoprene synthase derived from sweet potato, a gene encoding the isoprene synthase, a host cell transformed with the gene, and a method of preparing isoprene using the same. The isoprene synthase of the present invention may have higher isoprene productivity as compared to isoprene synthases known in the related art to thereby be effectively used in isoprene biosynthesis and preparation of an isoprene polymer using the same.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Isoprene synthase and coding gene thereof, expression vector, engineering bacteria and method for producing isoprene and application
ActiveCN109097378AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
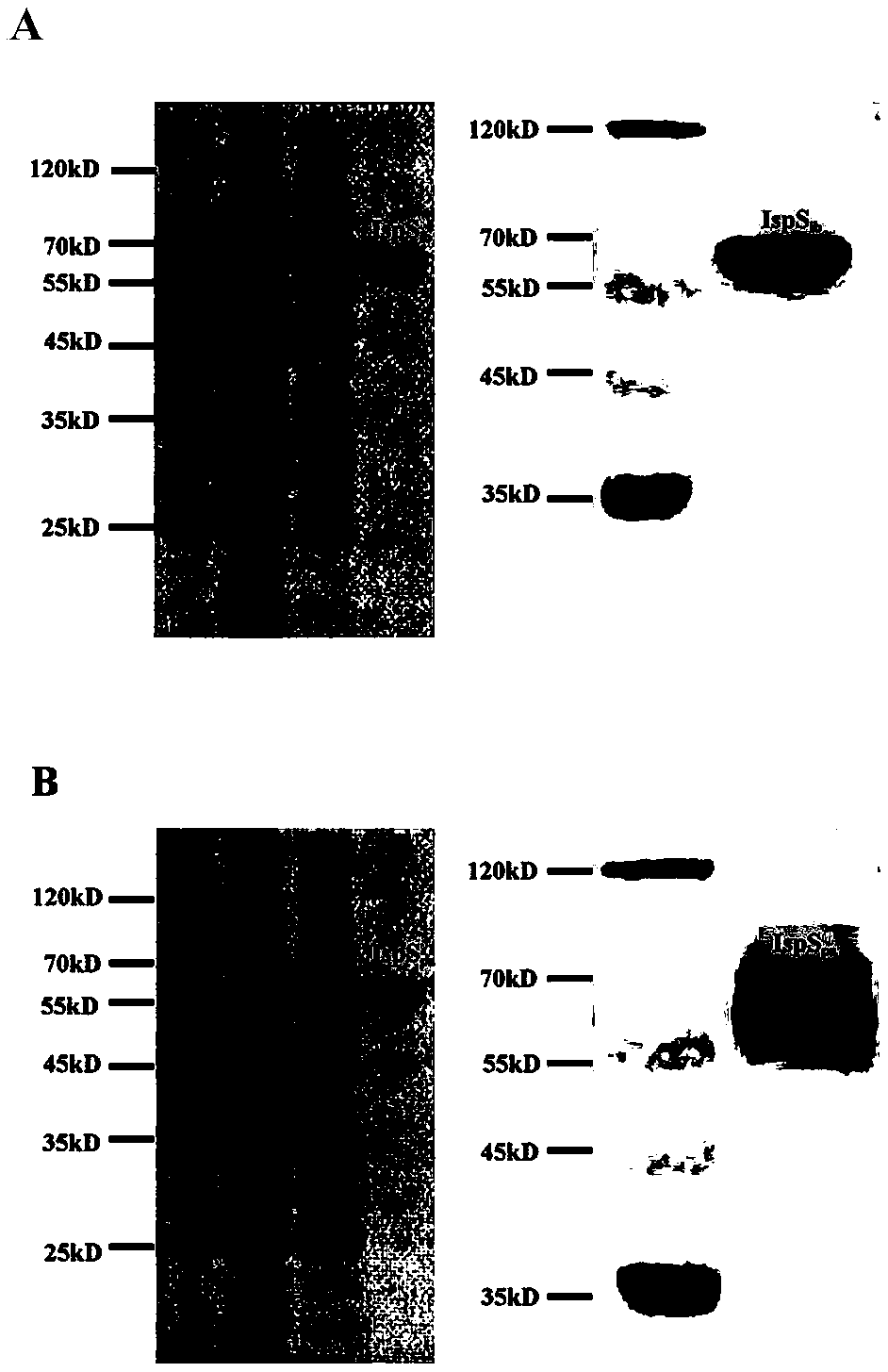
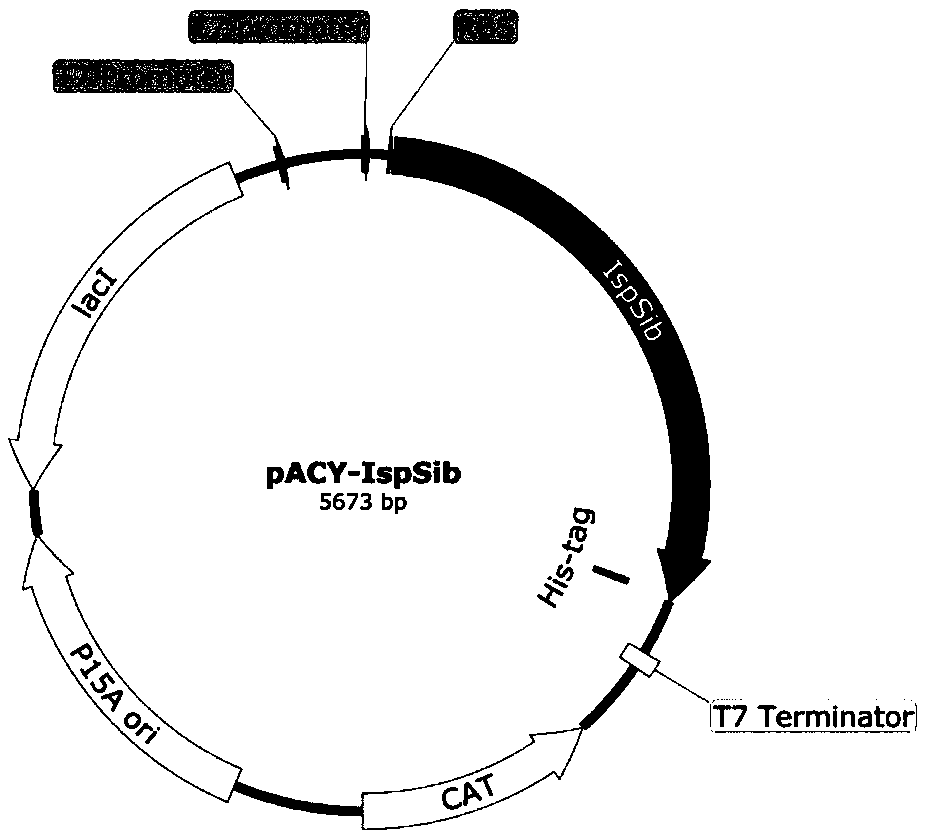
The invention discloses an isoprene synthase and a coding gene thereof, an expression vector, engineering bacteria and a method for producing isoprene and application, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the isoprene synthase gene IspSib is as shown in SEQ ID NO 2, and the amino acid sequence of the isoprene synthase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention also provides a prokaryotic expression vector containing the isoprene synthase gene and co-transformation of the prokaryotic expression vector and a downstream expression vector of mevalonate pathway to obtain an isoprene-producing fungus The present invention also provides a method for fermentative production of isoprene and the above-mentioned isoprene synthase gene, isoprene synthase, enzyme having isoprene synthase activity, prokaryotic expression vector thereof and The application of engineering bacteria in the production of isoprene. The isoprene synthase enzyme activity provided by the present invention is high and has high affinity for the substrate DMAPP.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant cells and method for producing isoprene or terpene
InactiveCN109689857AEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLycopersenePhytoene synthesis
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Isoprene synthase and gene encoding the same, and method for producing isoprene monomer
The present invention provides means useful for establishing an excellent isoprene monomer production system. Specifically, the present invention provides a polynucleotide of the following (a), (b), or (c):(a) a polynucleotide comprising (i) the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, or (ii) the nucleotide sequence consisting of the nucleotide residues at positions 133 to 1785 in the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1;(b) a polynucleotide that comprises a nucleotide sequence having 90% or more identity to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and encodes a protein having an isoprene synthase activity; or(c) a polynucleotide that hybridizes under a stringent condition with a polynucleotide consisting of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and encodes a protein having an isoprene synthase activity; and the like.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Method of expressing long-chain prenyl diphosphate synthase
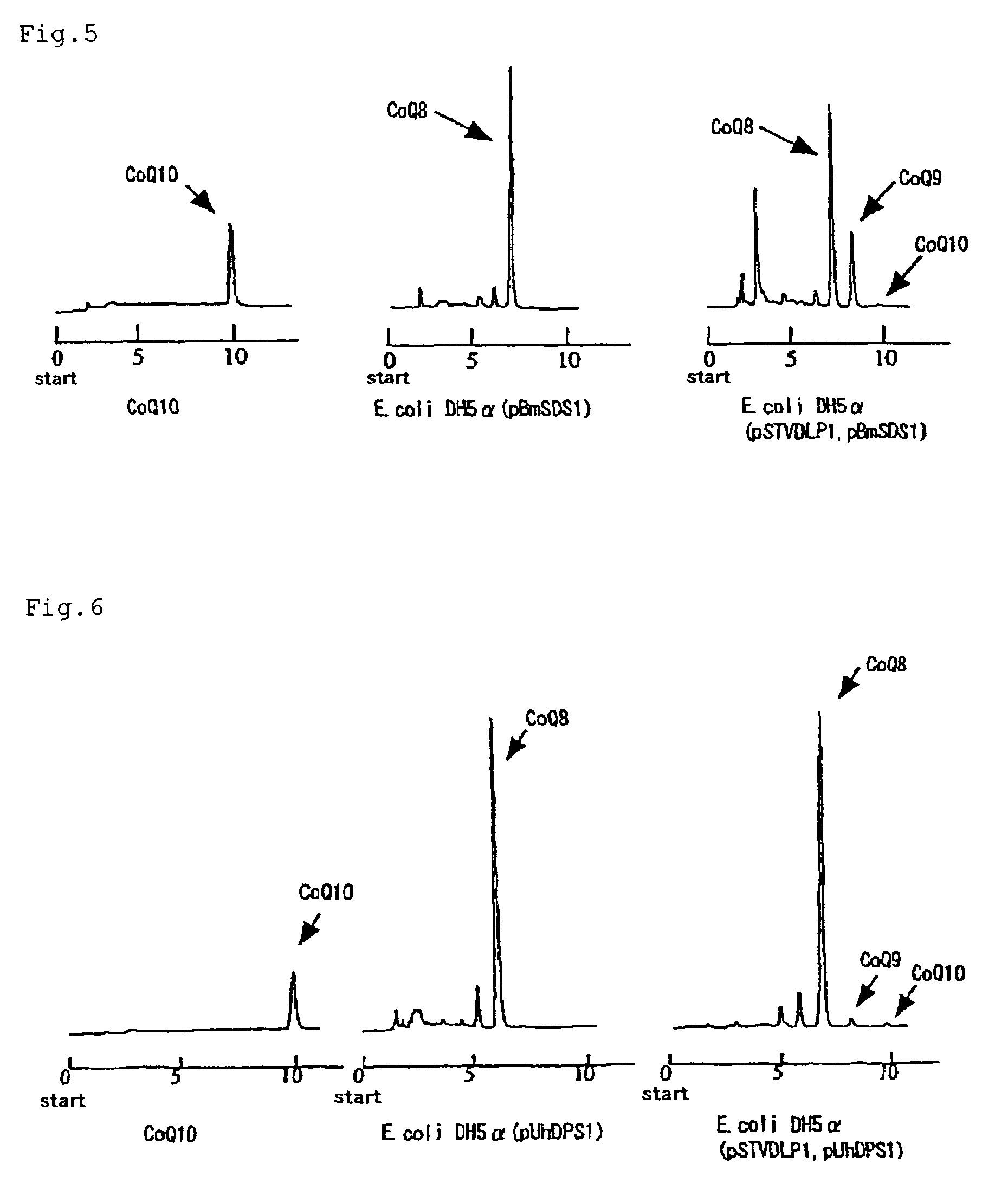
InactiveUS7402413B2Easy to getIncreases coenzyme Q productionSugar derivativesBacteriaSide chainA-DNA
The present invention provides a method of producing a long-chain prenyl diphosphate synthase (in particular decaprenyl diphosphate synthase and solanesyl diphosphate synthase) using a gene and a protein which are required for enabling or enhancing the activity expression of a eukaryote-derived long-chain prenyl diphosphate synthase as well as a method of efficiently producing a coenzyme Q having a long-chain isoprenoid in its side chain (in particular coenzyme Q9 or coenzyme Q10) using a microorganism. The present invention relates to a DNA having a base sequence shown under SEQ ID NO:1, 3 or 5 and a DNA sequence derived from the above base sequence by deletion, addition, insertion and / or substitution of one to several bases thereof, and coding for a protein enabling (functioning) or enhancing the activity expression of a eukaryote-derived long-chain prenyl diphosphate synthase in a host microorganism.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Compositions and methods for improved isoprene production using two types of ISPG enzymes
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
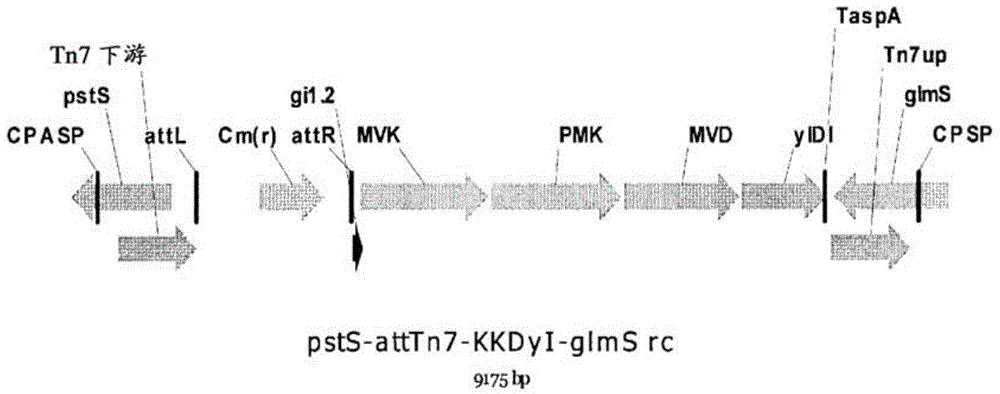
Genetic engineering stain for improving yield of isoprene and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111363709AReduce growth impactHave selective permeabilityBacteriaTransferasesEnzyme GeneGenetic engineering
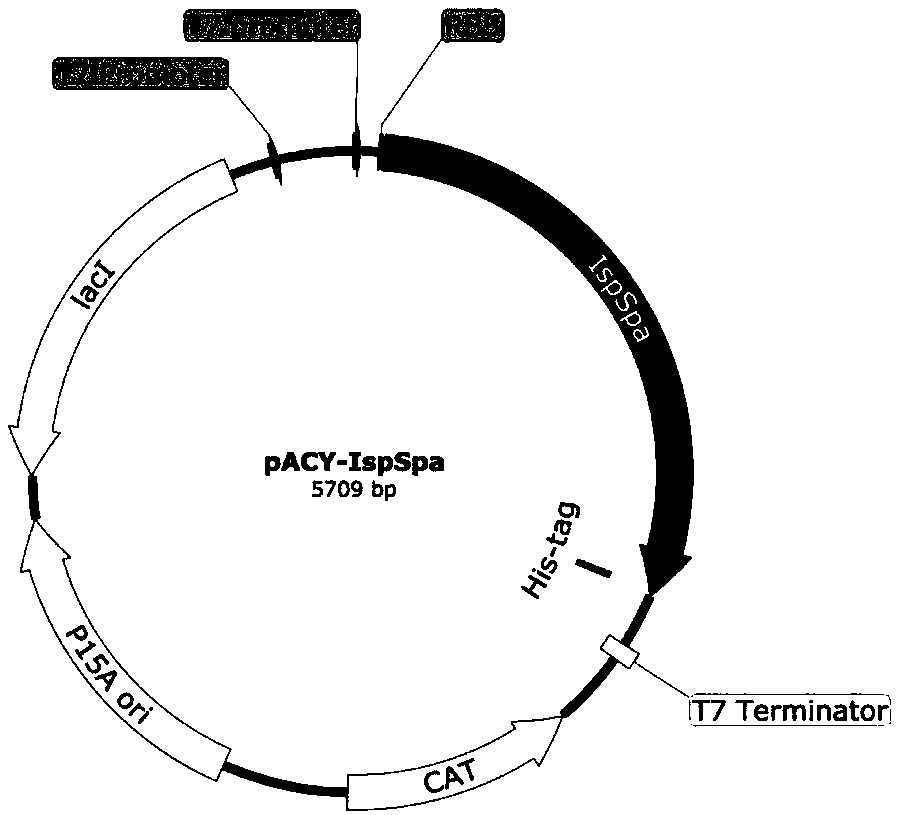
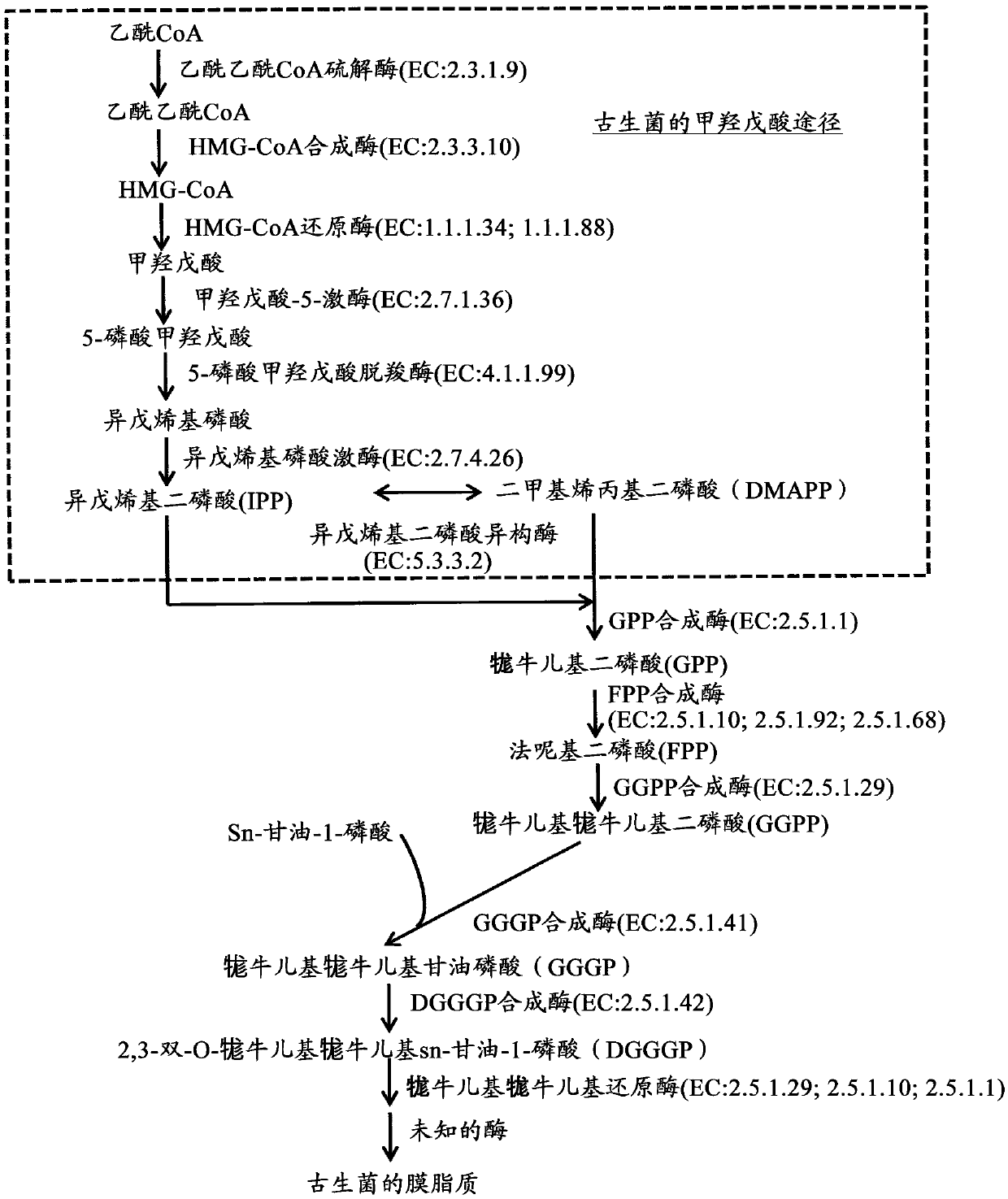
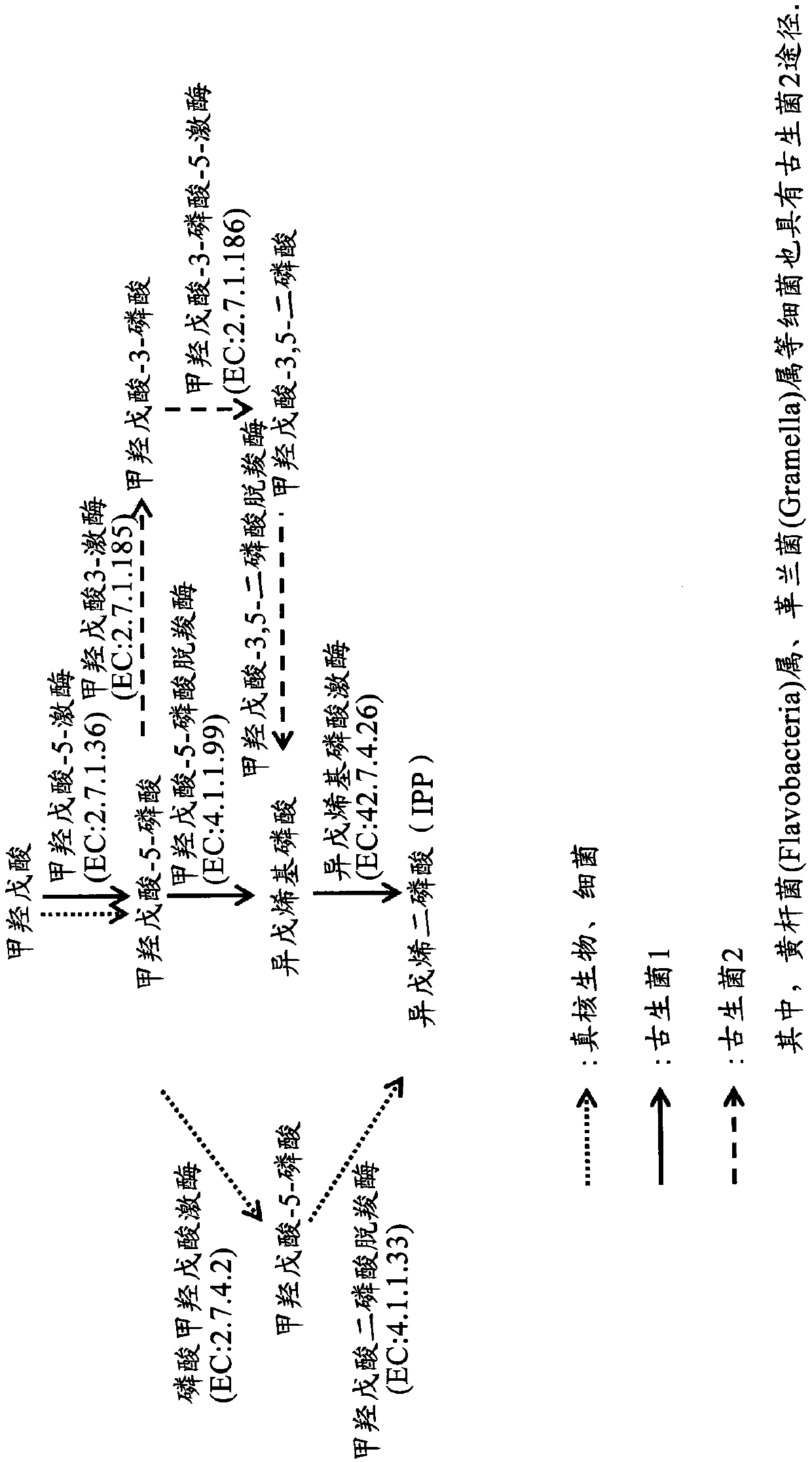
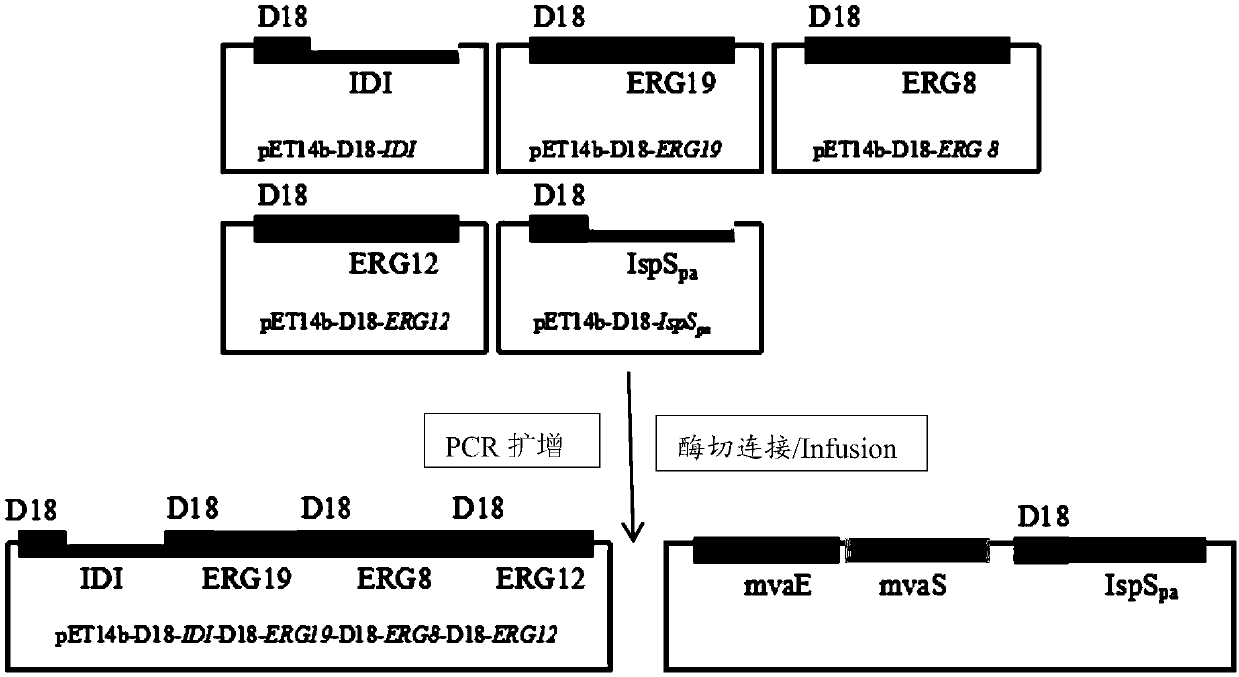
The invention provides a genetic engineering stain for improving yield of isoprene and a construction method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. In orderto improve the yield of the isoprene synthesized by a biological method and to reduce the toxicity of an intermediate product on bacteria, the invention provides the genetic engineering stain for improving the yield of the isoprene. The genetic engineering stain over-expresses a mevalonate kinase gene ERG12 containing a D18 encapsulated signal peptide sequence, a phosphomevalonate kinase gene ERG8 containing the D18 encapsulated signal peptide sequence, a mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase gene ERG19 containing the D18 encapsulated signal peptide sequence, an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene IDI1 containing the D18 encapsulated signal peptide sequence, an isoprene synthase gene IspSpa containing the D18 encapsulated signal peptide sequence, and recombinant plasmids containing PduA, PduB, PduJ, PduK, PduN and PduU gene clusters, and a starting strain is escherichia coli. The genetic engineering stain can be used for producing the isoprene through fermentation.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for improving isoprene synthesis capability of saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN106399139AImprove synthesis abilityIncreased transcript levelsFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionIsoprene synthase
The invention provides a method for improving an isoprene synthesis capability of saccharomyces cerevisiae. An IspS (isoprene synthase) gene sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 from a white poplar is cloned to a plasmid through enzyme digestion and connection and is converted into a saccharomyces cerevisiae parent body, so that isoprene is synthesized in the saccharomyces cerevisiae; a transcriptional level of IspS gene is enhanced through GAL4 over-expression; the catalytic activity of IspS is improved through orthogenesis. The saccharomyces cerevisiae and the isoprene synthase are combined together, so that the yield of isoprene is improved to be 8.2 times as much as the original yield.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing isoprene using recombinant halophilic methanotroph
The present invention relates to a recombinant methanotroph having an ability to produce isoprene and a method for producing isoprene using the same, and more particularly to a recombinant methanotroph having an ability to produce isoprene wherein a gene encoding an isoprene synthase having a homology of at least 70% to the amino acid sequence of Ipomoea batatas isoprene synthase is introduced into the recombinant methanotroph, and a method for producing isoprene using the recombinant methanotroph. The use of a recombinant methanotroph according to the present invention enables isoprene to be produced in high yield by using methane gas or methanol which is obtained from waste such as natural gas, biomass, municipal waste or the like as a carbon source.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
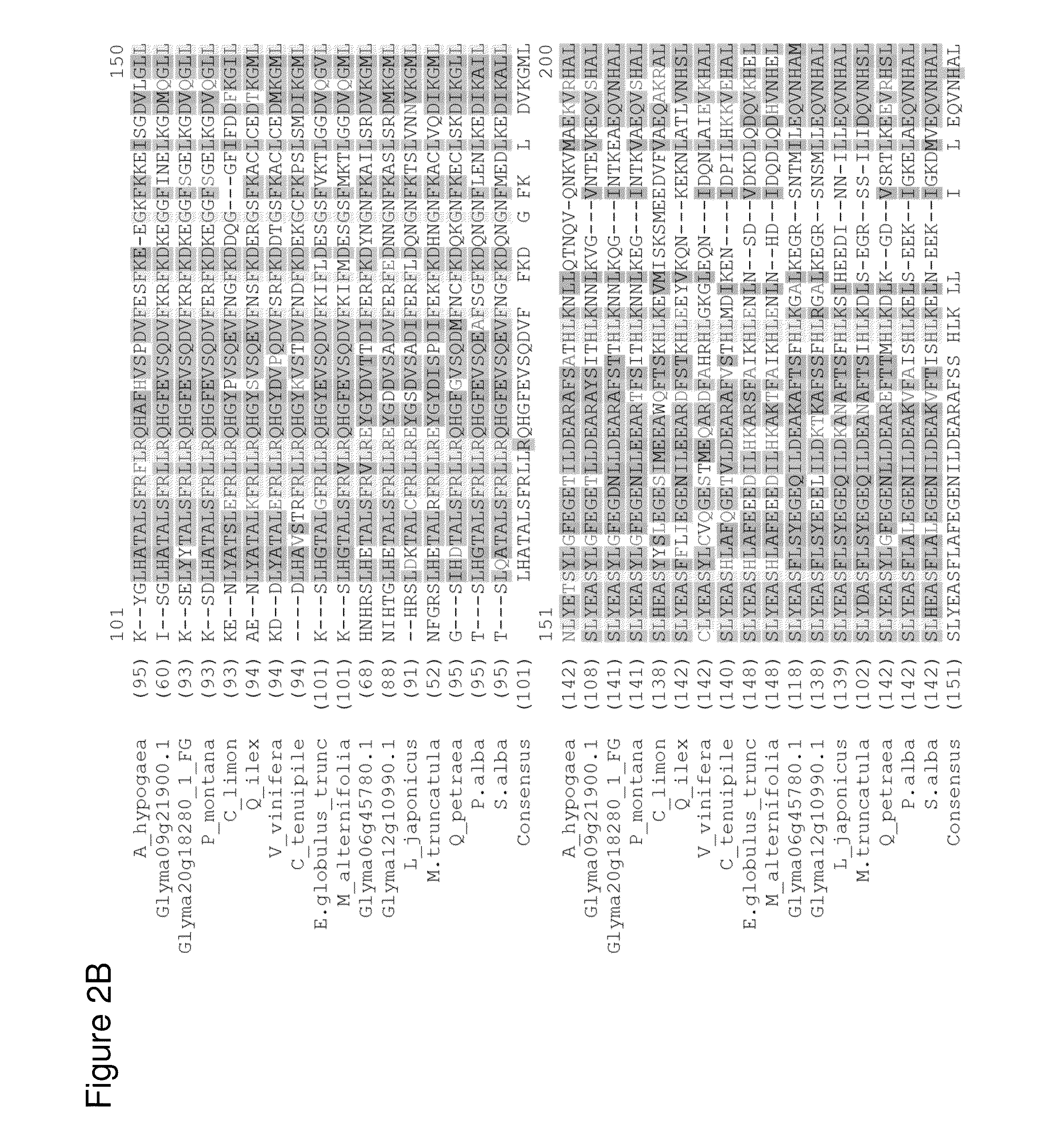
Three-dimensional structure of isoprene synthase and its use thereof for generating variants
The present invention provides a three-dimensional structures of P. tremuloides isoprene synthase and P. alba isoprene synthase. The invention also provides methods of using the three dimensional structure to design isoprene synthases with improved activity for increased isoprene production in microbial host cells. Biosynthetically produced isoprene of the present invention finds use in the manufacture of rubber and elastomers.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Isoprene synthase and polynucleotide encoding same, and method for producing isoprene monomer
The invention provides a useful means for establishing an excellent isoprene monomer production system. Specifically, the invention provides polynucleotides and the like of (a), (b), or (c) below: (a) polynucleotide containing (i) a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or (ii) a base sequence comprising nucleotide residue numbers 133-1785 in the base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1; (b) polynucleotide containing a base sequence having 90% or greater identity with the base sequences (i) or (ii) above, and encoding a protein having isoprene synthase activity; or (c) a polynucleotide that hybridizes with a polynucleotide comprising a base sequence complementary to the base sequences (i) or (ii) above, under stringent conditions, and encodes a protein having isoprene synthase activity.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Isoprene genetic engineering producing strain and application thereof
The invention relates to an isoprene genetic engineering producing strain and anapplication thereof. By introducing an exogenous mevalonic acid path in a hot cell and overexpressing isoprene synthase, more preferably enhancing a methyl erythritol phosphate in the host cell, isoprene is efficiently produced by applying a prokaryotic cell.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for producing abienol
ActiveUS20170362583A1Improve productivityOrganic chemistryTransferasesIsoprene synthaseGeranylgeranyl diphosphate
The present disclosure relates to a novel method, expression vectors, and host cells for producing abienol by converting geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) to abienol in the presence of a combination of a class II diterpene synthase and a bifunctional class I / II abienol synthase.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Modified isoprene synthase
InactiveUS20160257944A1Excellent isoprene monomer production systemImprove productivityFermentationCarbon-oxygen lyasesAmino acid substitutionIsoprene synthase
Modified isoprene synthases that have one or more mutations of a given amino acid residue(s) in any amino acid sequence of(a) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:4,(b) an amino acid sequence having one or several amino acid substitutions, deletions, insertions or additions in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:4, or(c) an amino acid sequence having 90% or more identity to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:4,and has an isoprene synthetic activity are useful for preparing isoprene monomer in improved yields.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing isoprene by in vitro enzymatic reaction and application of isoprene
InactiveCN104480146APrecise control of dosageAccurately control the dosageMicroorganism based processesFermentationIsopentenyl pyrophosphateMetabolic enzymes
The invention discloses a method for producing isoprene by in vitro enzymatic reaction and an application of isoprene and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of respectively introducing an obtained mevalonate kinase gene, a phosphomevalonate kinase gene, a mevalonate-pyrophosphate decarboxylase gene, an isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene and an isoprene synthase into host bacteria, carrying out fermental cultivation to obtain five recombinant bacteria, respectively carrying out ultrasonic disruption on each thallus to obtain a crude enzyme solution, mixing five crude enzyme solutions to obtain a reaction enzyme solution and adding a reaction substrate solution into the reaction enzyme solution to in vitro synthesize isoprene. By the method disclosed by the invention, the in-vitro synthesis of isoprene from mevalonic acid by virtue of enzymatic reaction is achieved and the synthesis of isoprene by precisely in vitro controlling the content of metabolic enzyme is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Isoprene synthase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105985975ACapable of producing isopreneBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProkaryotic expressionIsoprene synthase
The invention relates to an isoprene synthase gene and an application thereof, in order to solve the technical problem that the synthesis of isoprene, with the adoption of engineering bacteria, is not high in efficiency. The invention provides the isoprene synthase gene, protein expressed by the isoprene synthase gene, a prokaryotic expression vector and an engineering bacterium containing the isoprene synthase gene as well as a preparation method for producing the isoprene engineering bacterium and an application of the isoprene engineering bacterium. The isoprene synthase gene disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the field of preparing the isoprene.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Isoprene synthase gene and application thereof
The invention relates to an isoprene synthase gene and an application thereof, in order to solve the technical problem that the synthesis of isoprene, with the adoption of engineering bacteria, is not high in efficiency. The invention provides the isoprene synthase gene, protein expressed by the isoprene synthase gene, a prokaryotic expression vector and an engineering bacterium containing the isoprene synthase gene as well as a preparation method for producing the isoprene engineering bacterium and an application of the isoprene engineering bacterium. The isoprene synthase gene disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the field of preparing the isoprene.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Isoprene synthase and gene encoding same and method for producing isoprene monomer
The present invention provides methods for establishing superior isoprene monomer production systems. Specifically, the present invention provides polynucleotides and analogs thereof of the following (a), (b) or (c): (a) polynucleotides comprising (i) nucleosides represented by SEQ ID NO:1 acid sequence, or (ii) a nucleotide sequence consisting of the 133rd to 1785th nucleotide residues in the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1; (b) a polynucleotide comprising A nucleotide sequence having 90% or more identity to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and the polynucleotide encodes a protein having isoprene synthase activity; or (c) A polynucleotide that hybridizes under stringent conditions to a polynucleotide consisting of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of (i) or (ii) above, and the polynucleotide encodes a polynucleotide having isoprene synthesis Enzymatically active protein.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Isoprene synthase and method of preparing isoprene using thereof
Provided are a novel isoprene synthase derived from sweet potato and a method of preparing isoprene using the same, and more specifically, a novel isoprene synthase derived from sweet potato, a gene encoding the isoprene synthase, a host cell transformed with the gene, and a method of preparing isoprene using the same. The isoprene synthase of the present invention may have higher isoprene productivity as compared to isoprene synthases known in the related art to thereby be effectively used in isoprene biosynthesis and preparation of an isoprene polymer using the same.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Isoprene synthase gene and its application
The invention relates to an isoprene synthetase gene and applications of the isoprene synthetase gene, for solving the technical problem that the efficiency for synthesizing isoprene by adopting engineering bacteria is not high. The invention provides the isoprene synthetase gene, protein expressed by the isoprene synthetase gene, a prokaryotic expression vector containing the isoprene synthetase gene, engineering bacteria, as well as preparation method and applications of the engineering bacteria capable of producing isoprene. The isoprene synthetase gene can be widely applied to the preparation field of isoprene.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com