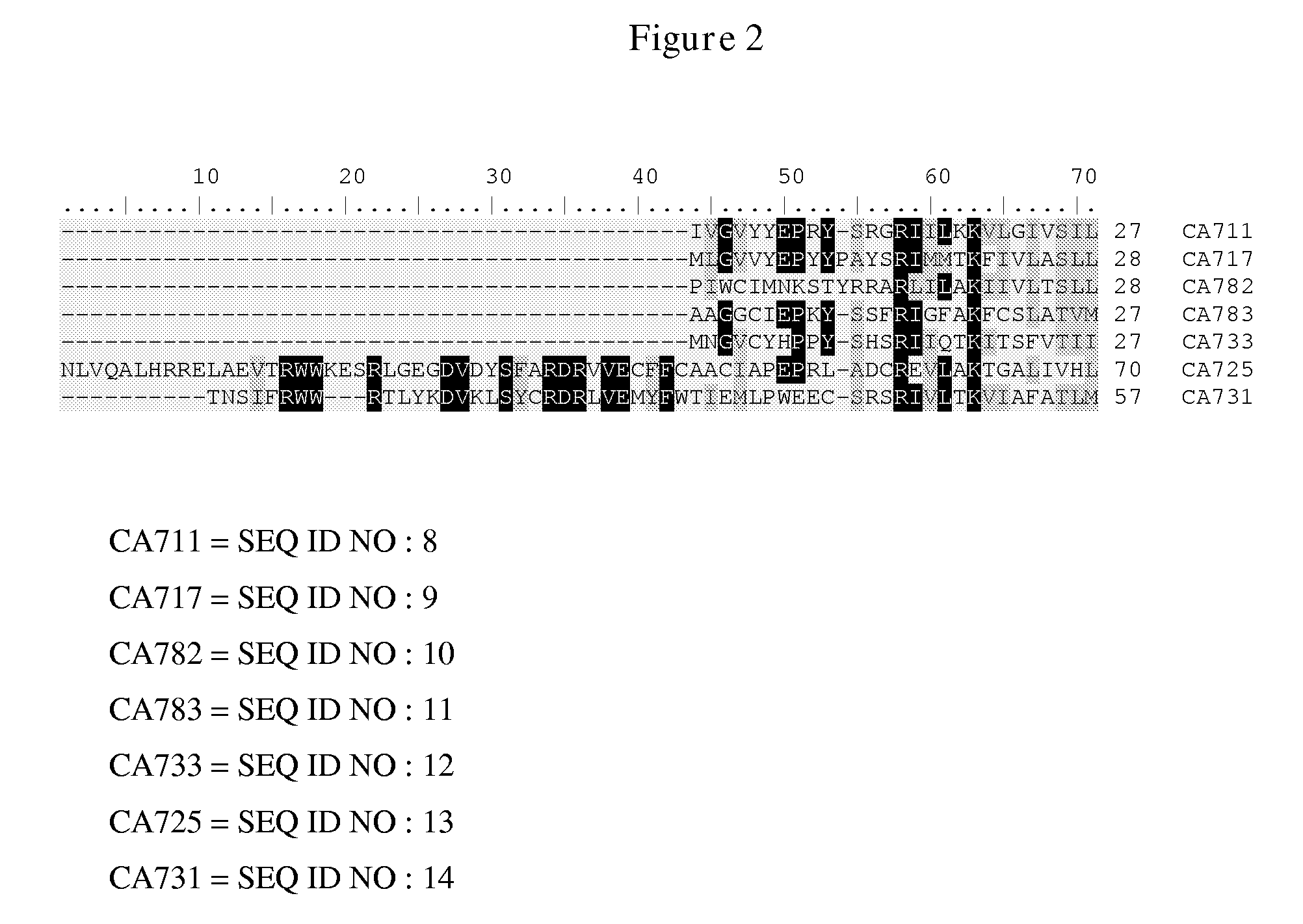
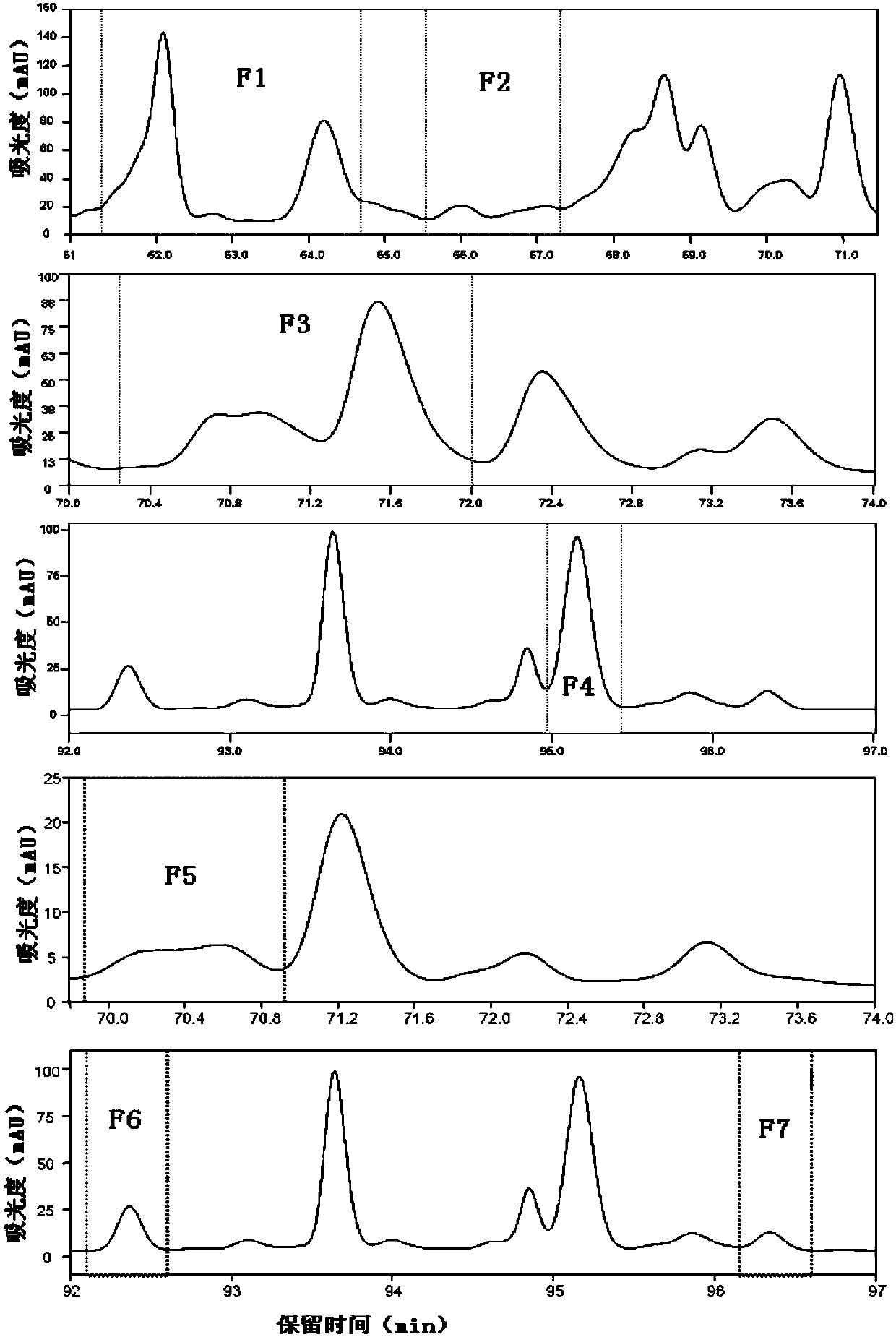
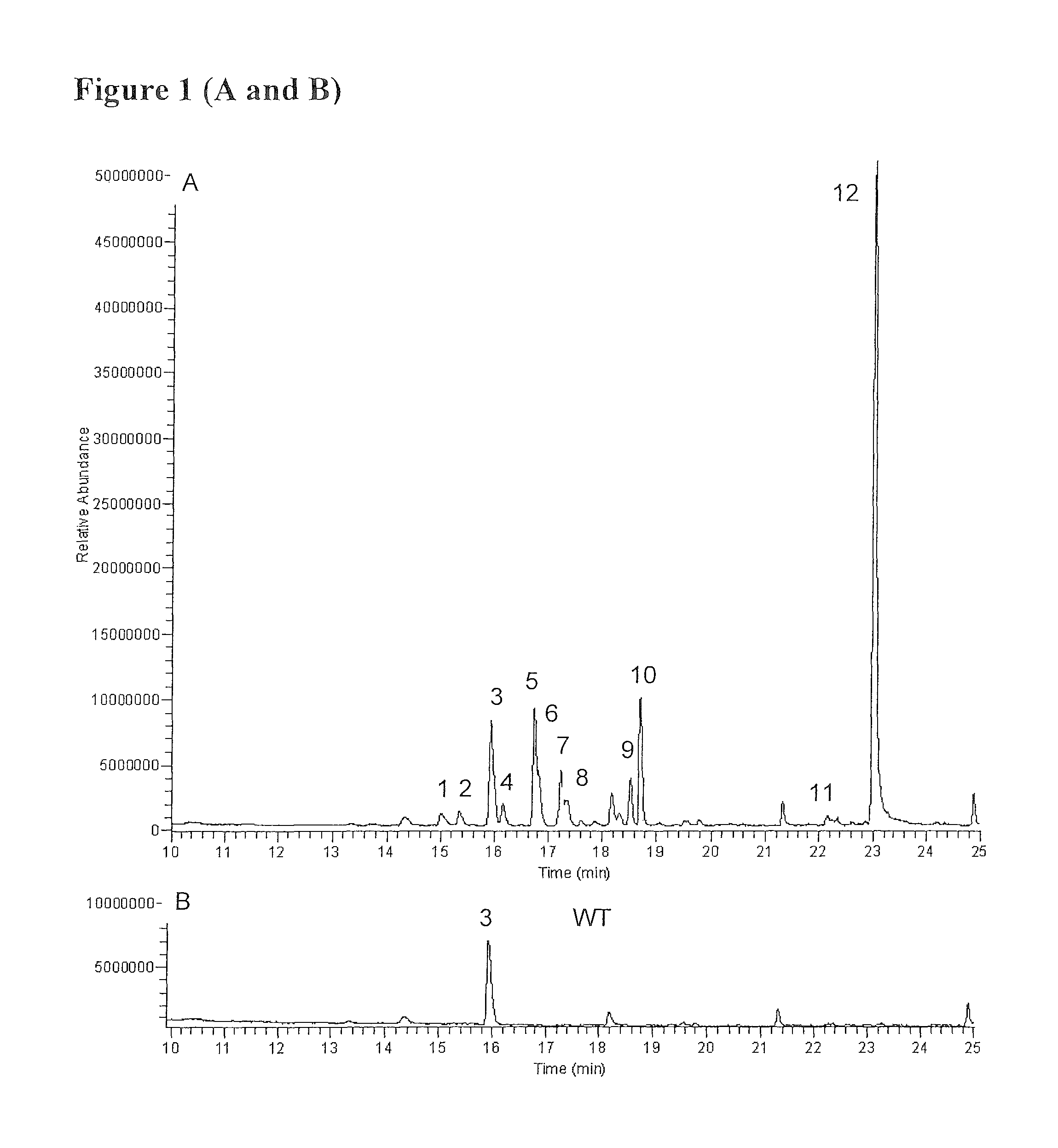
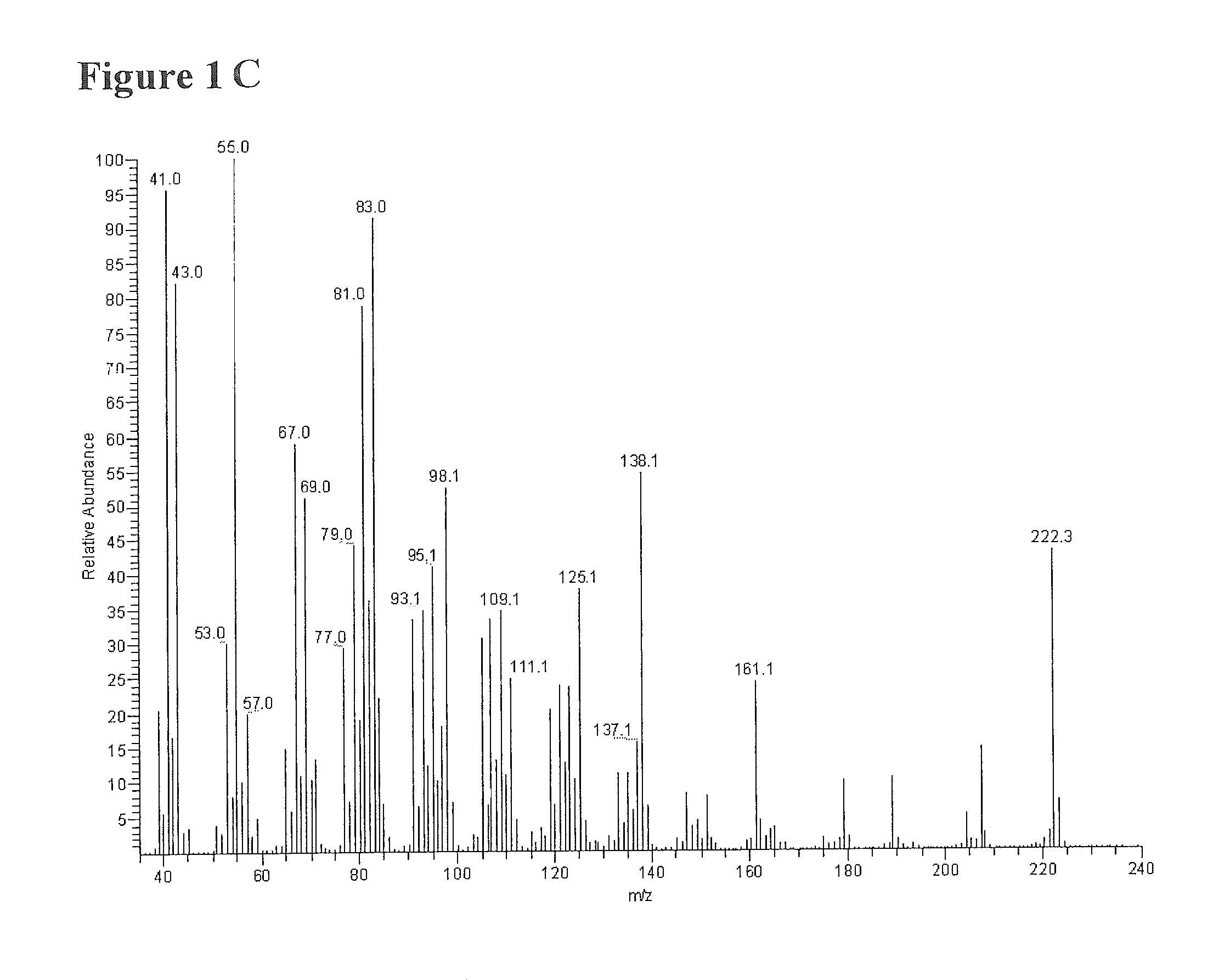
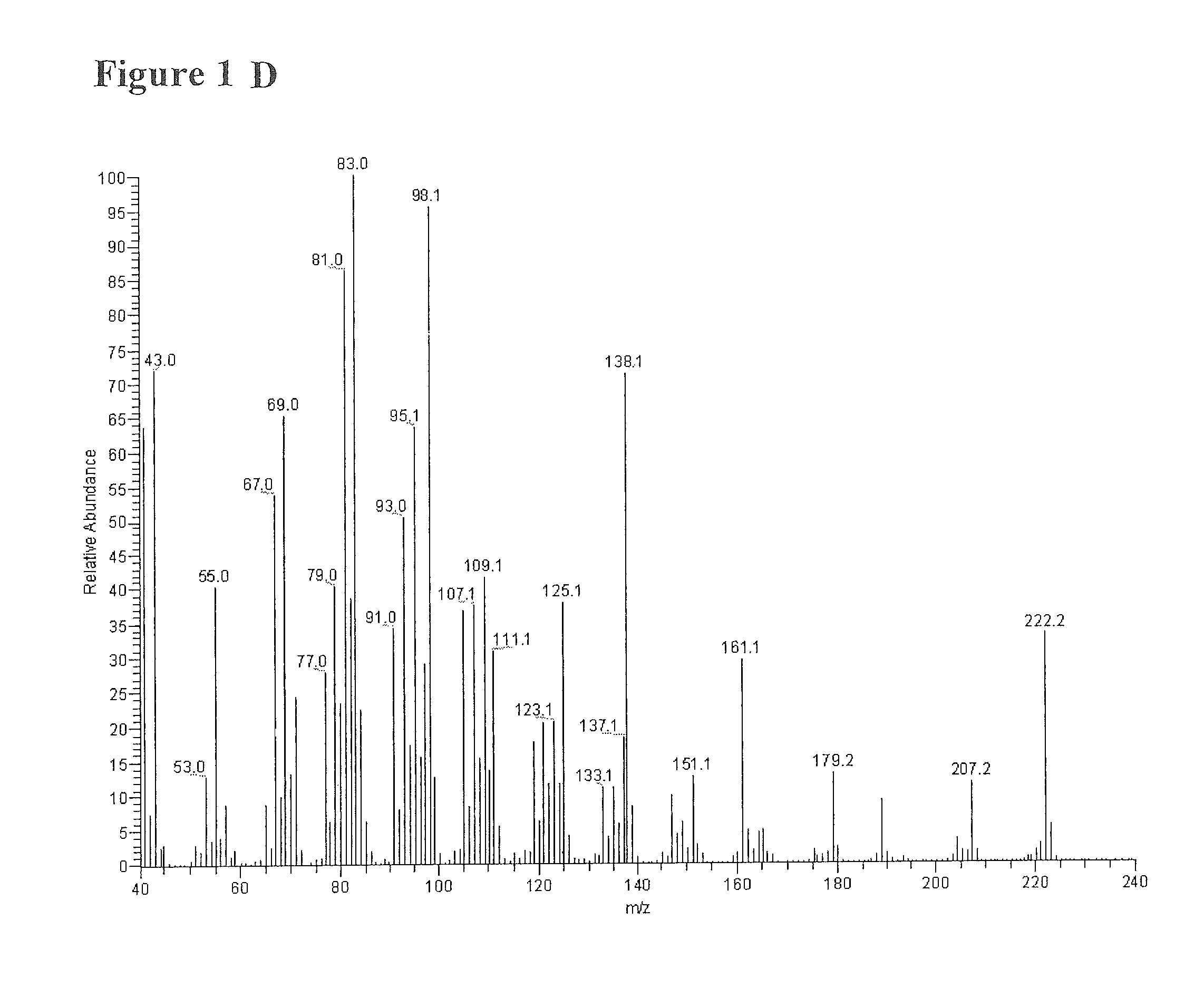
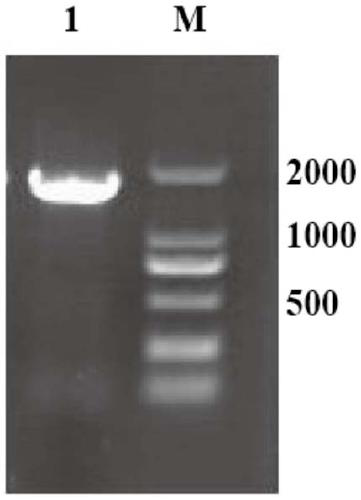
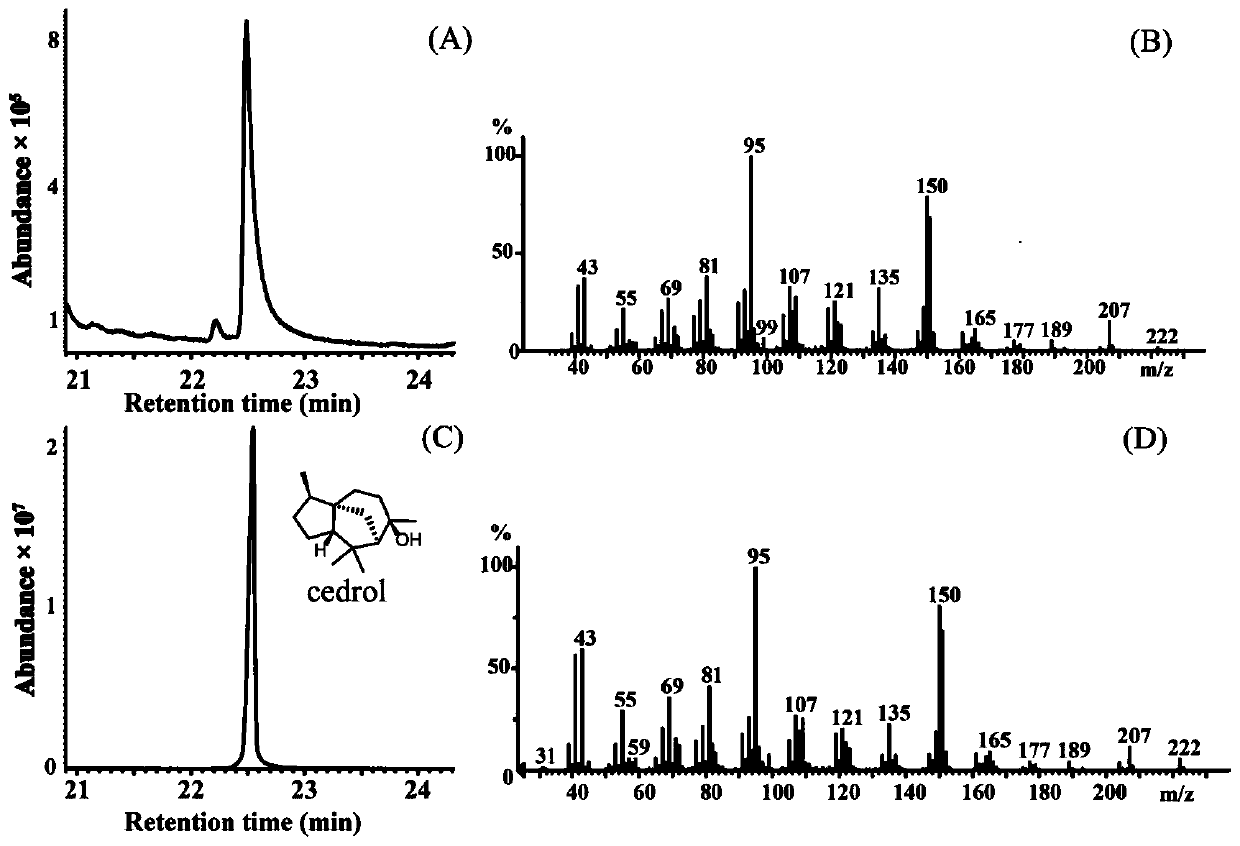
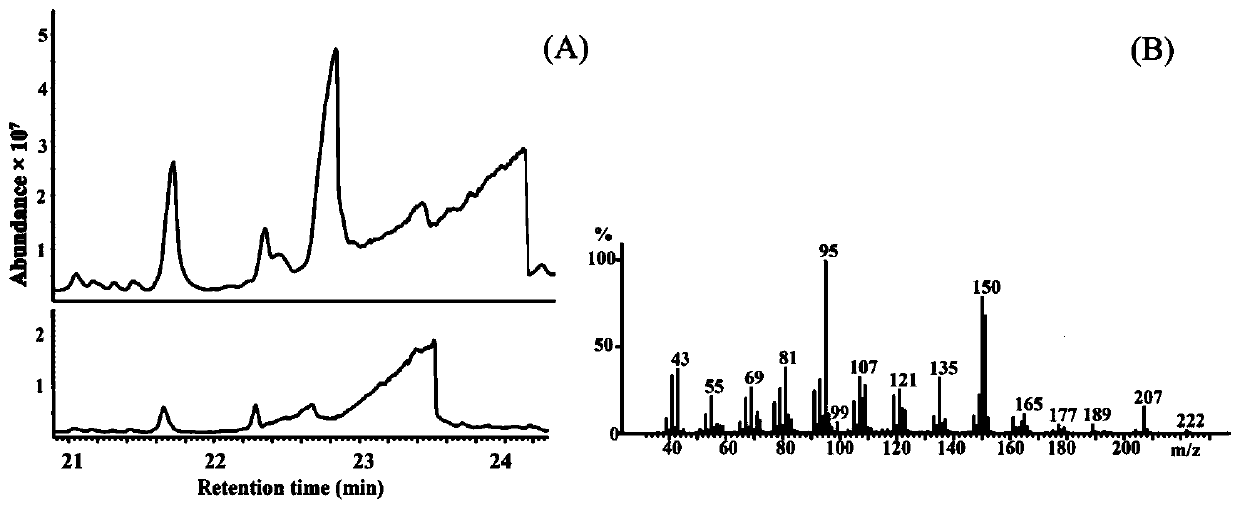
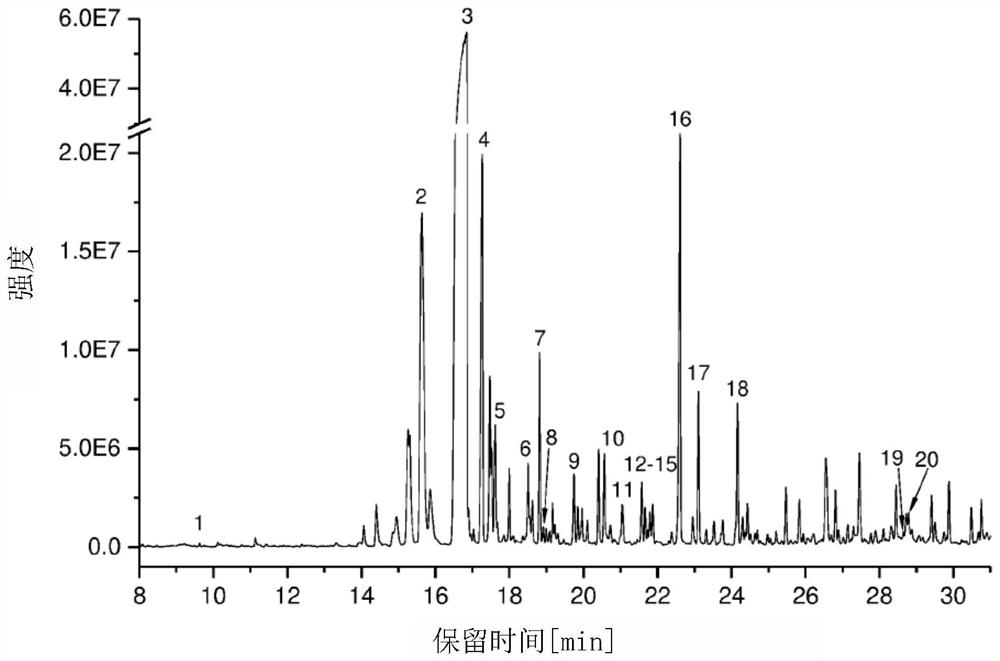
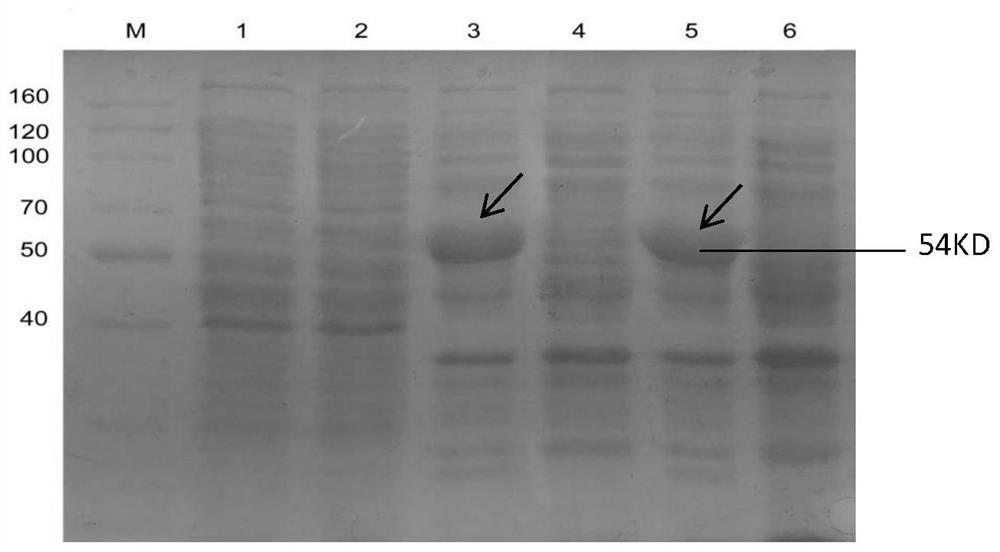
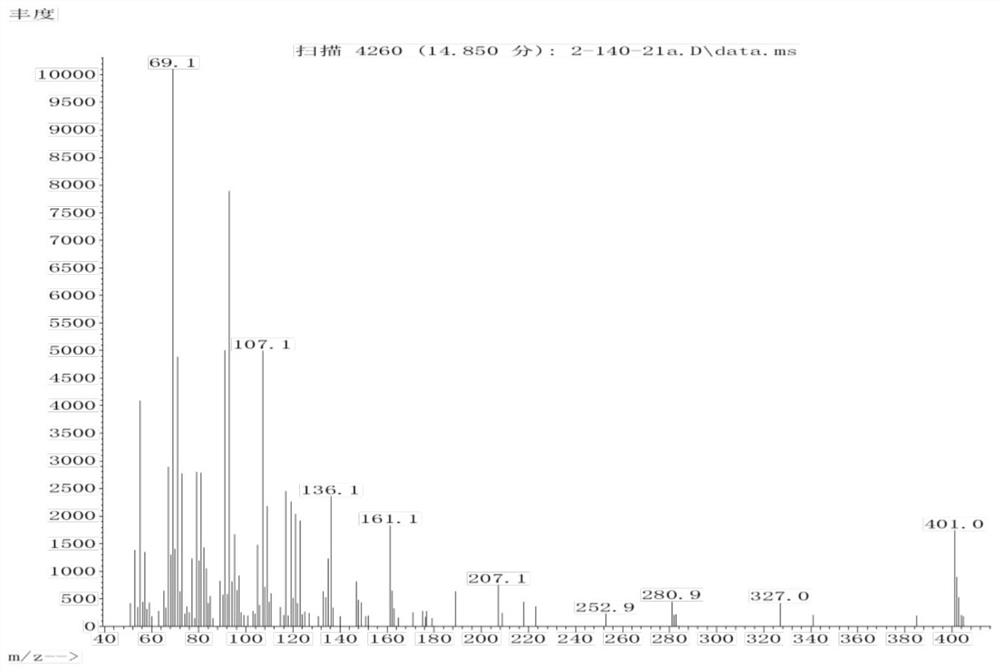
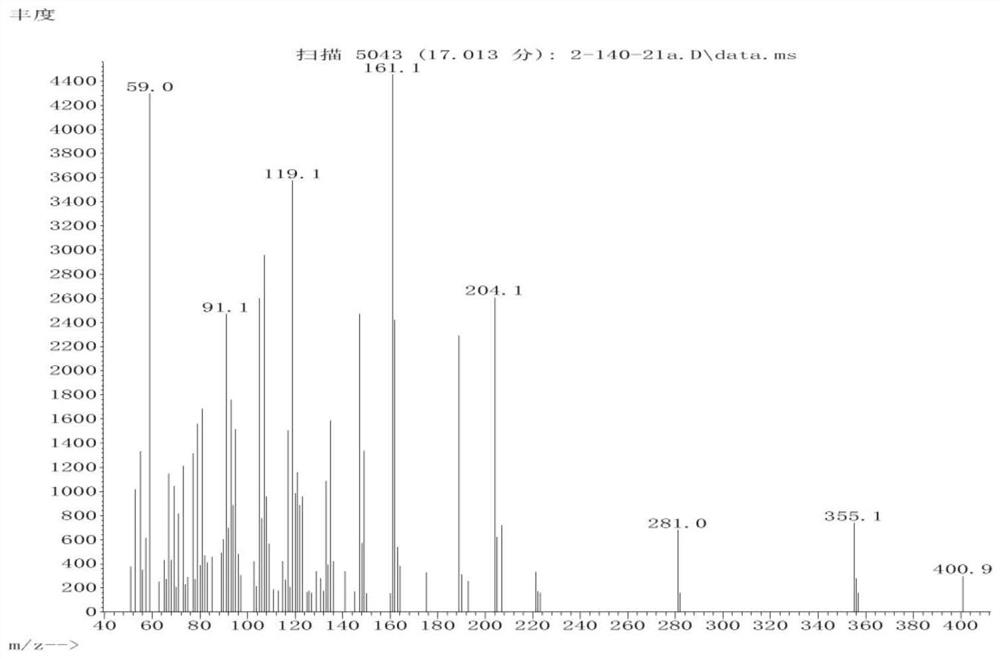
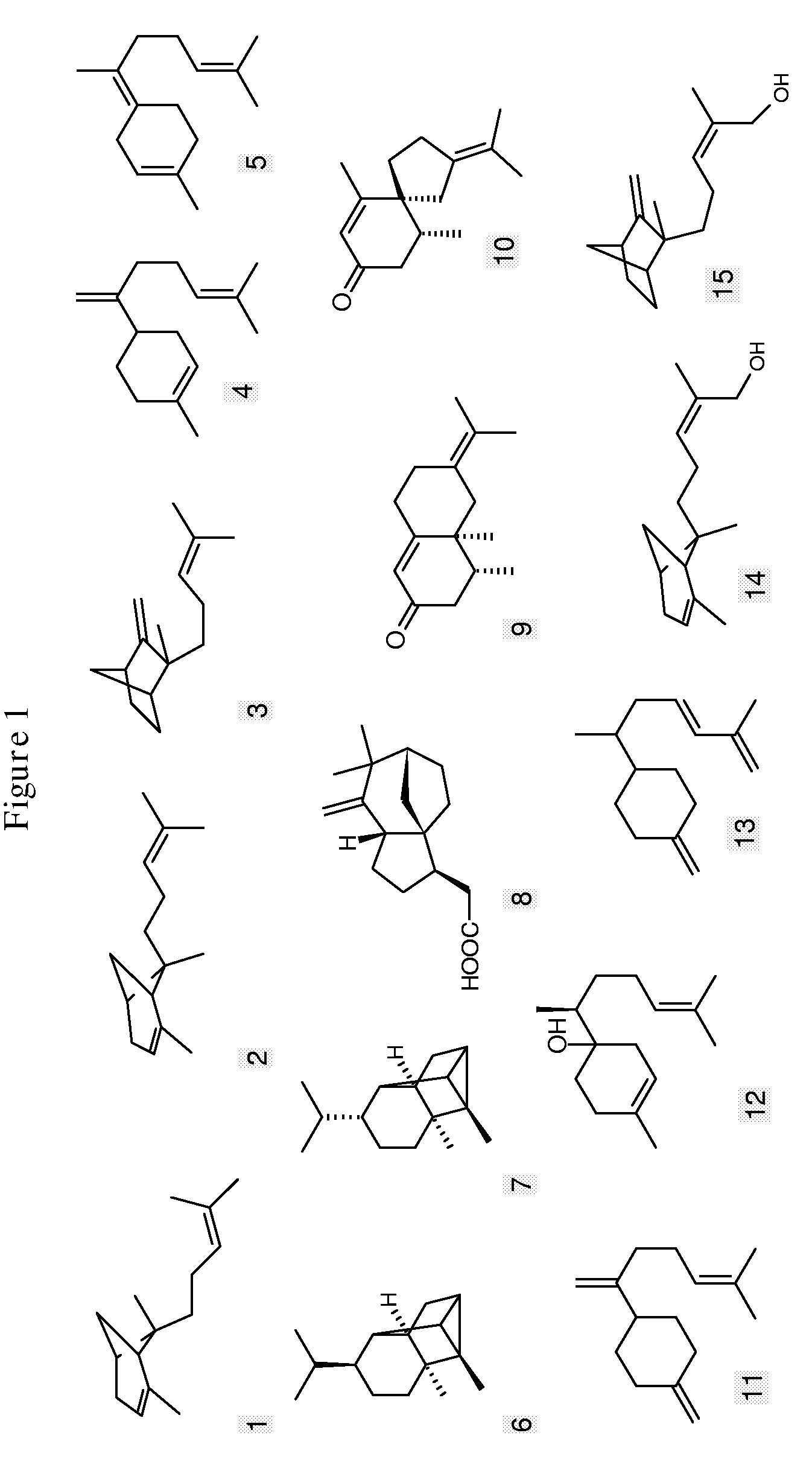
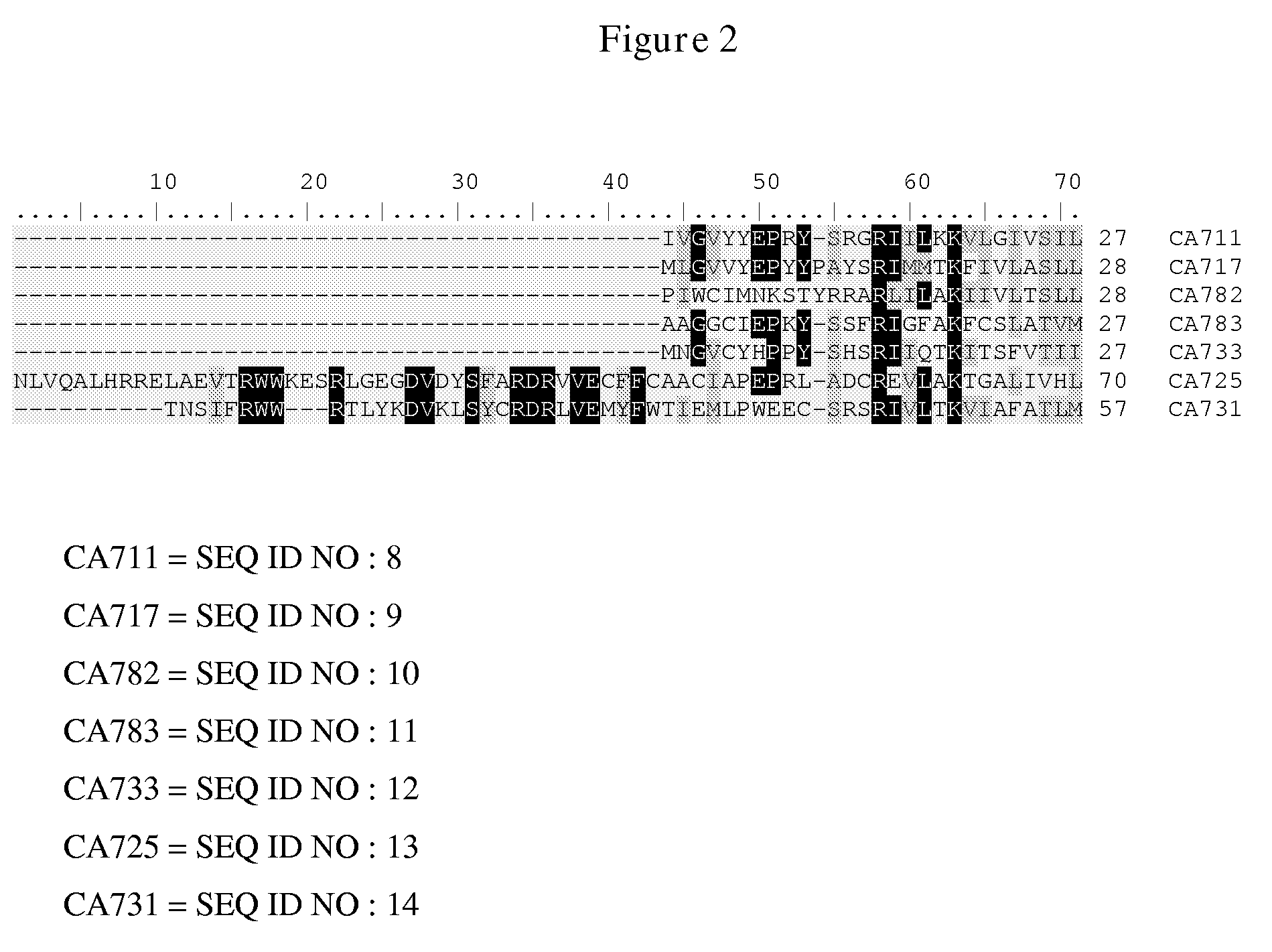
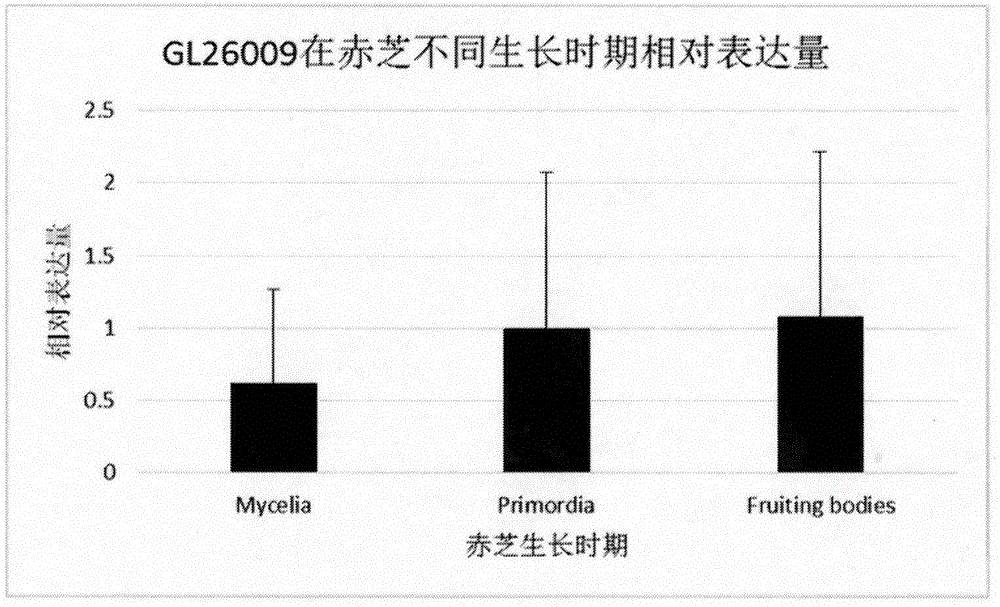
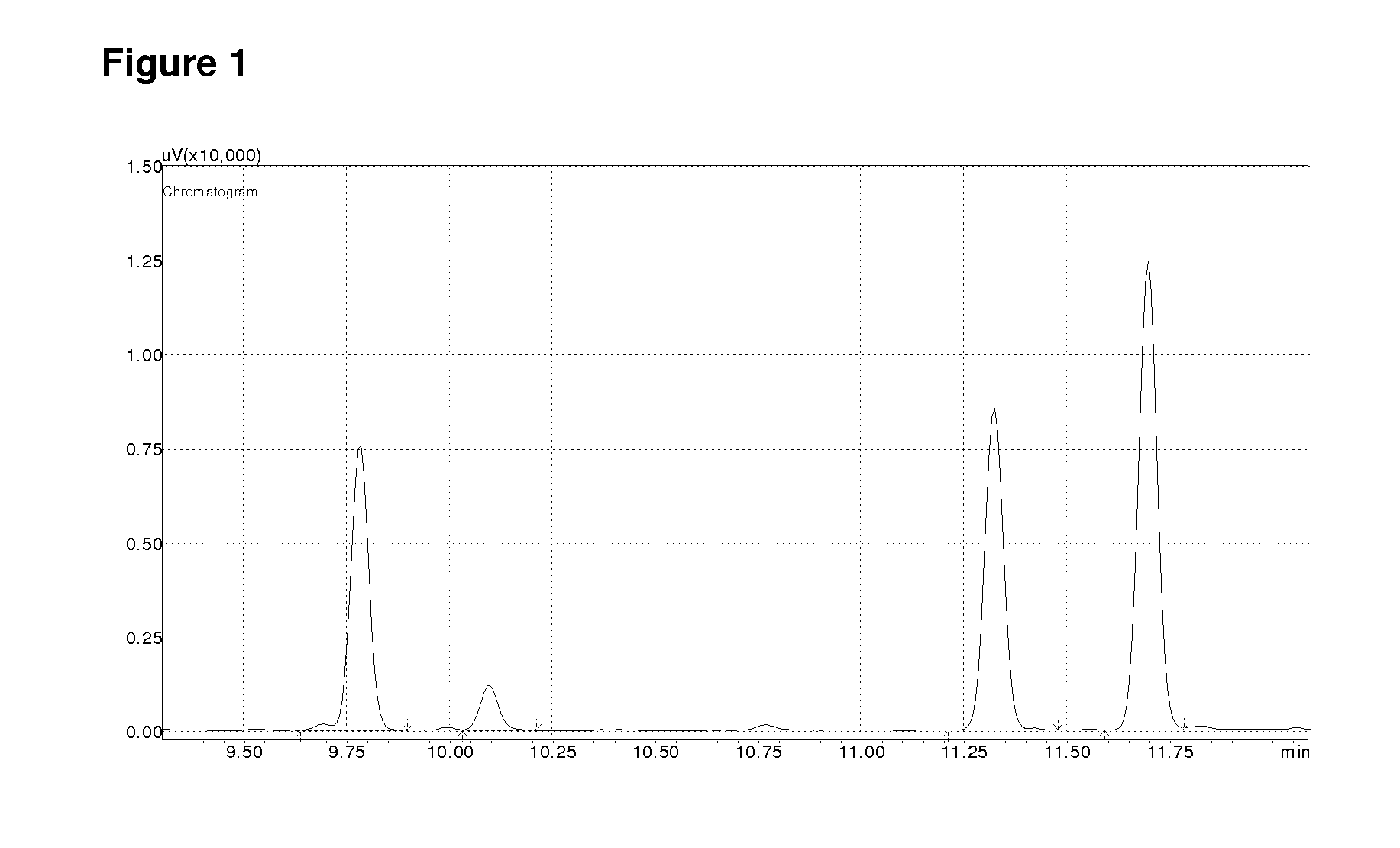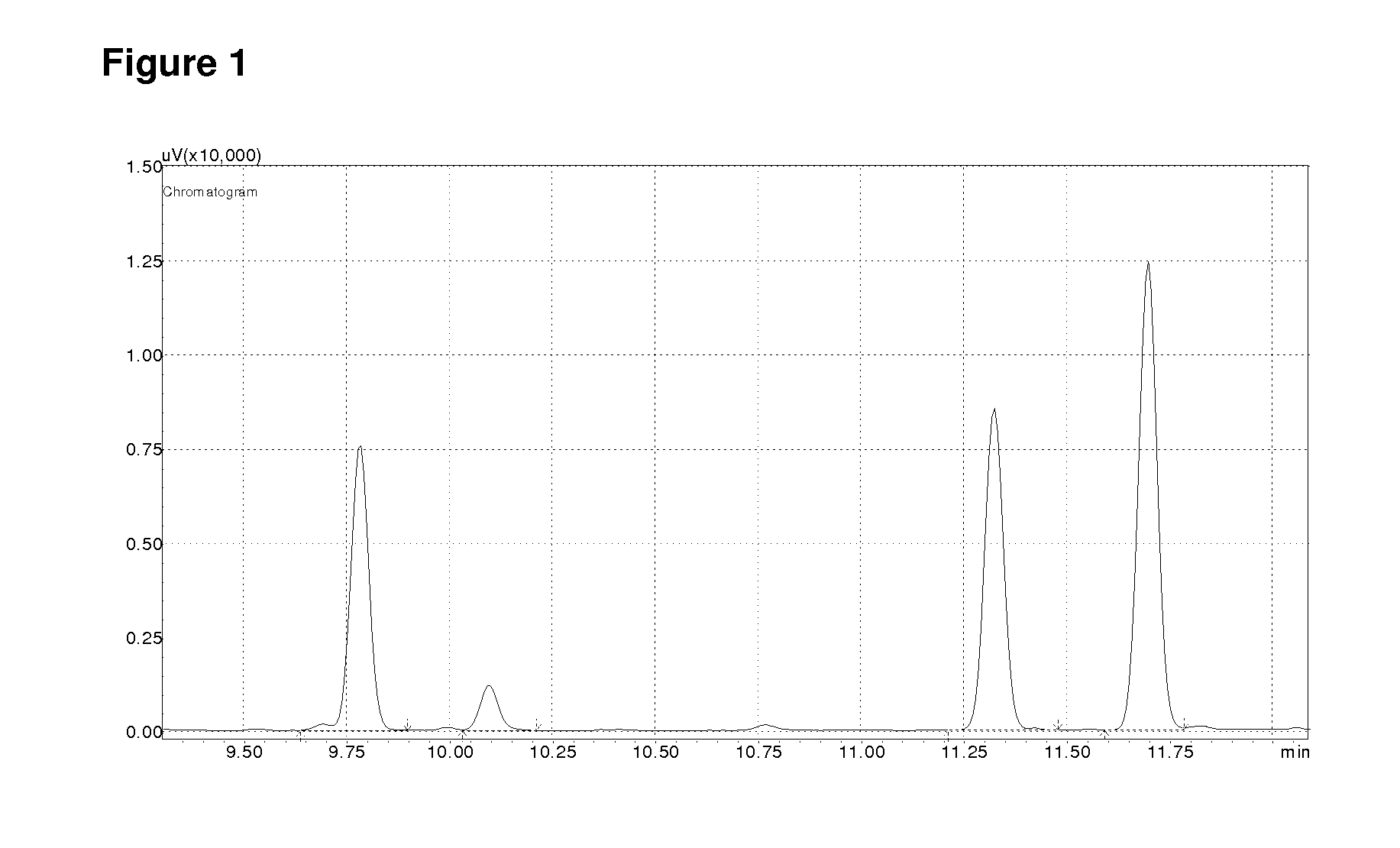Patents
Literature
70 results about "Terpene synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
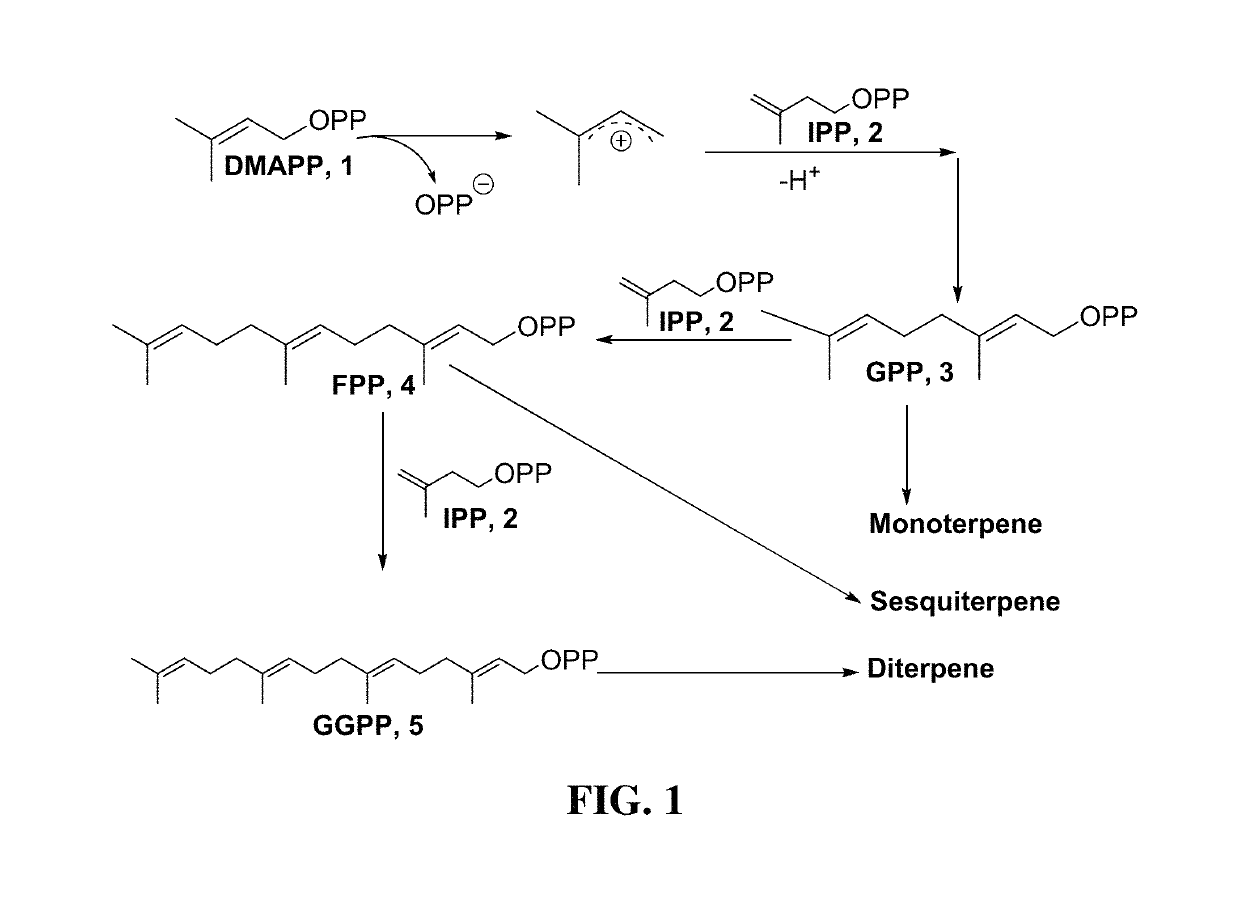
In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene and also part of the secondary metabolism.
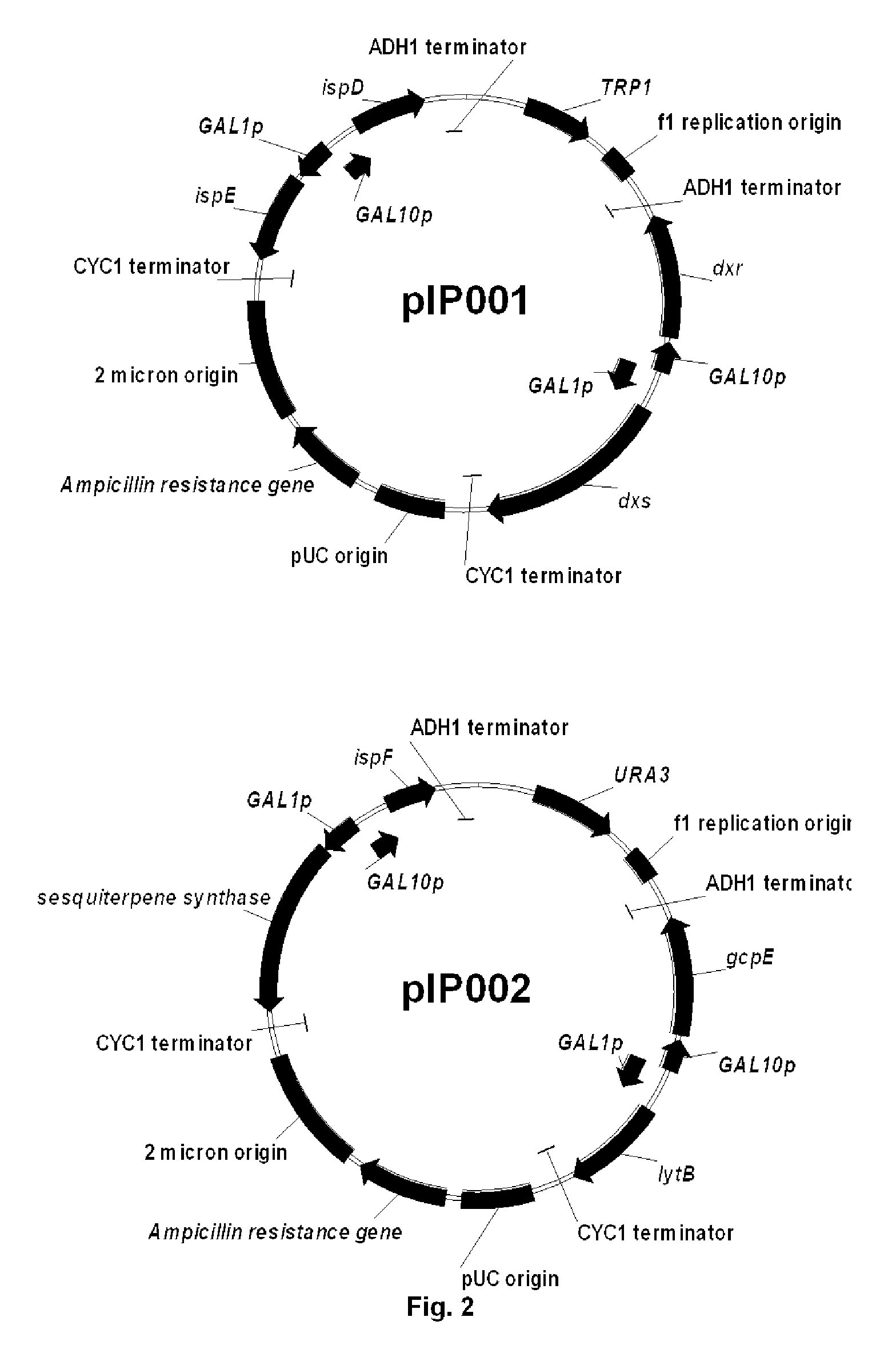
System For Producing Terpenoids In Plants
InactiveUS20080281135A1Increase productionOther foreign material introduction processesLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTerpene synthaseHeterologous
The invention concerns a method for producing terpenes of interest in plants having glandular trichomes, as well as plants useful for producing said terpenes of interest. Said plants comprise a sequence encoding a heterologous terpene synthase under the control of a promoter enabling it to be specifically expressed in the trichomes. Moreover, the pathway for producing endogenous diterpenes is preferably blocked in the trichomes of the plants, to increase the flow in the heterologous pathway. The secretion of heterologous terpenes is spontaneous resulting in easy collection. The present invention also concerns plants exhibiting a blocked production of a compound having antibiotic properties at the surface of leaves exhibiting enhanced efficiency of transformation by a bacterium.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Transformed plants accumulating terpenes
InactiveUS20090123984A1Increase contentHigh yieldTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesTerpene synthaseGene conversion
The present invention relates to transformed plants with an altered terpene content, preferably over-accumulating a mono- or sesqui-terpene. By transformation of plants with genes encoding terpene synthases (TS), and prenyl transferases (PRT), plants accumulating at least 1000 ng / per g of fresh leaf of a specific terpene were obtained. The present invention provides an advantageous system for production of terpenes in that any desired mono- or sesqui-terpene at the choice of the skilled person can be produced in plants. Preferably, the transformed plants contain at least one recombinant plastid targeted TS and PRT.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Method for producing terpenes and mep-transformed microorganisms therefore
InactiveUS20090155874A1High of compoundIncrease volumeHydrocarbon by isomerisationFungiTerpene synthaseHeterologous
The present invention relates to a microorganism capable of producing a terpene of choice. The microorganism expresses a heterologous pathway for the formation of isoprene units and, preferably, a heterologous terpene synthase. In this way, high amounts of terpene can be isolated from the medium of the microorganism.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Expression constructs and uses thereof in the production of terpenoids in yeast
InactiveUS20130302861A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesBiotechnologyTerpene synthase
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Terpene synthases from santalum
An isolated nucleic acid molecule that encodes a terpene synthase and is selected from among: a) a nucleic acid molecule comprising the sequence of nucleotides set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 5; b) a nucleic acid molecule that is a fragment of (a); c) a nucleic acid molecule comprising a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to (a)- or (b); and d) a nucleic acid molecule that encodes a terpene synthase having at least or at least about or at least about 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99% identity to any one of (a)-(c); wherein the nucleic acid molecule encodes a terpene synthase.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA +2
Terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof
ActiveCN106906201ASpecificEfficientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSynthetic biology
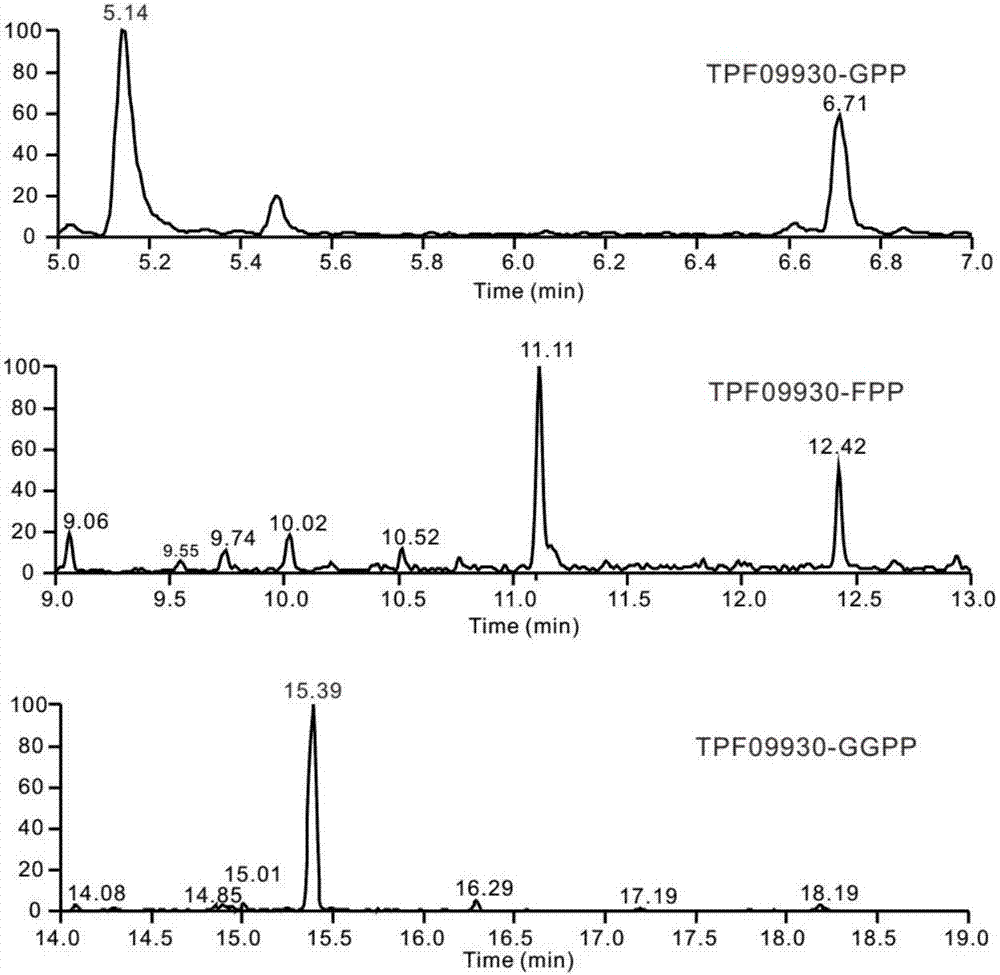
The invention discloses a terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. Terpene synthase TPF09930 for producing the nerolidol is provided, a nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase TPF09930 is as shown in SEQIDNO:2, the terpene synthase TPF09930 is combined with mevalonic acid pathway related genes to construct a strain for producing the nerolidol. By overexpression of Escherichia coli XL1 blue-derived atoB gene or idi gene of mevalonic acid pathway, catalytic substrate Farnesyl pyrophosphate can be synthesized in large scale, and producing of the nerolidol can be further promoted. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency, can improve the nerolidol yield, greatly overcomes the defects of a large amount of raw materials and a low nerolidol yield, reduces study cost, and ensures greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods of developing terpene synthase variants
ActiveUS8236512B1Improve performanceReduced viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTerpene synthaseIn vivo
The present disclosure relates to methods of developing terpene synthase variants through engineered host cells. Particularly, the disclosure provides methods of developing terpene synthase variants with improved in vivo performance that are useful in the commercial production of terpene products. Further encompassed in the present disclosure are superior terpene synthase variants and host cells comprising such terpene synthase variants.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Methods of developing terpene synthase variants
ActiveUS20120196315A1Improved in vivo performanceImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTerpene synthaseIn vivo
The present disclosure relates to methods of developing terpene synthase variants through engineered host cells. Particularly, the disclosure provides methods of developing terpene synthase variants with improved in vivo performance that are useful in the commercial production of terpene products. Further encompassed in the present disclosure are superior terpene synthase variants and host cells comprising such terpene synthase variants.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Novel Sesquiterpene Synthases and Methods of their Use
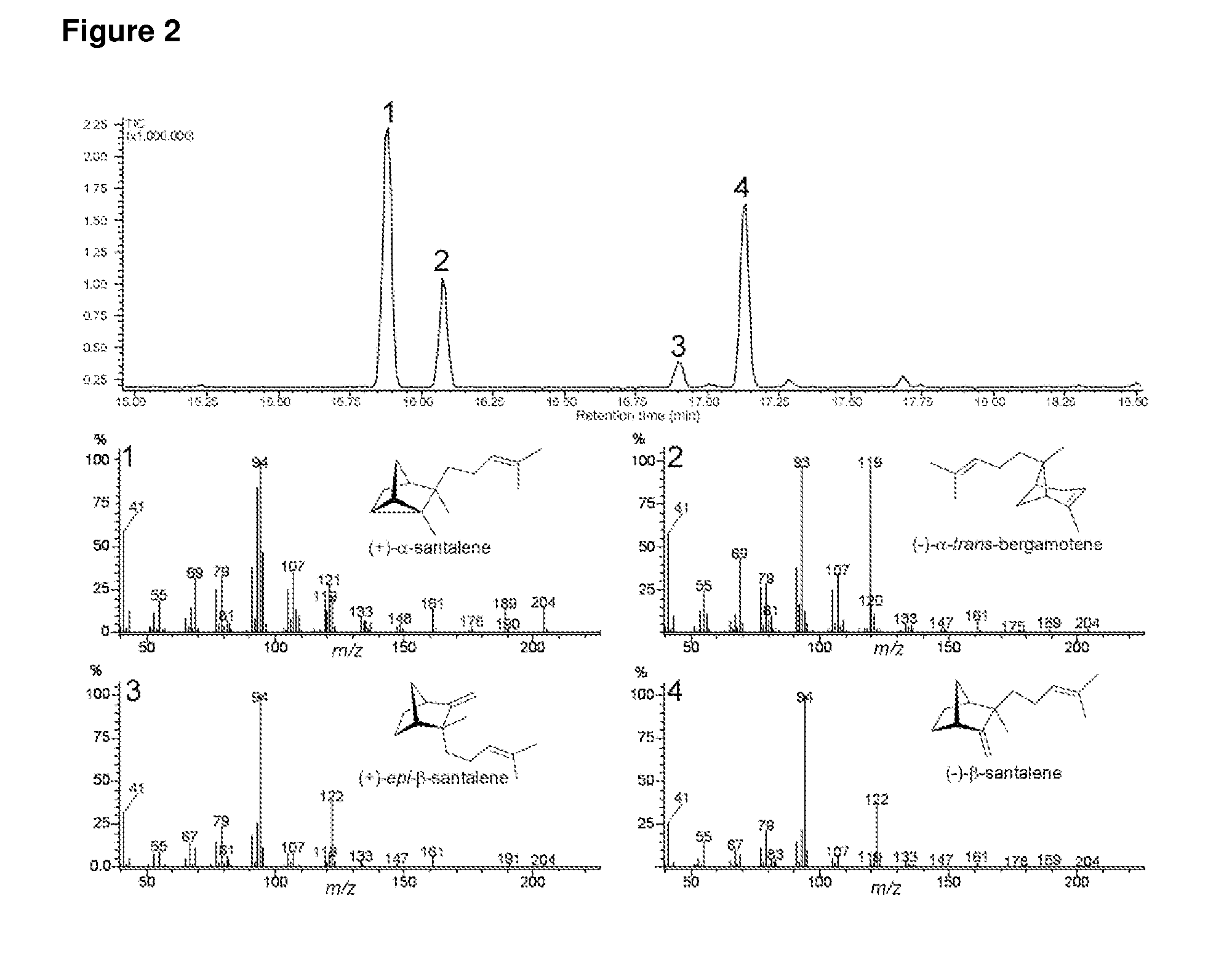
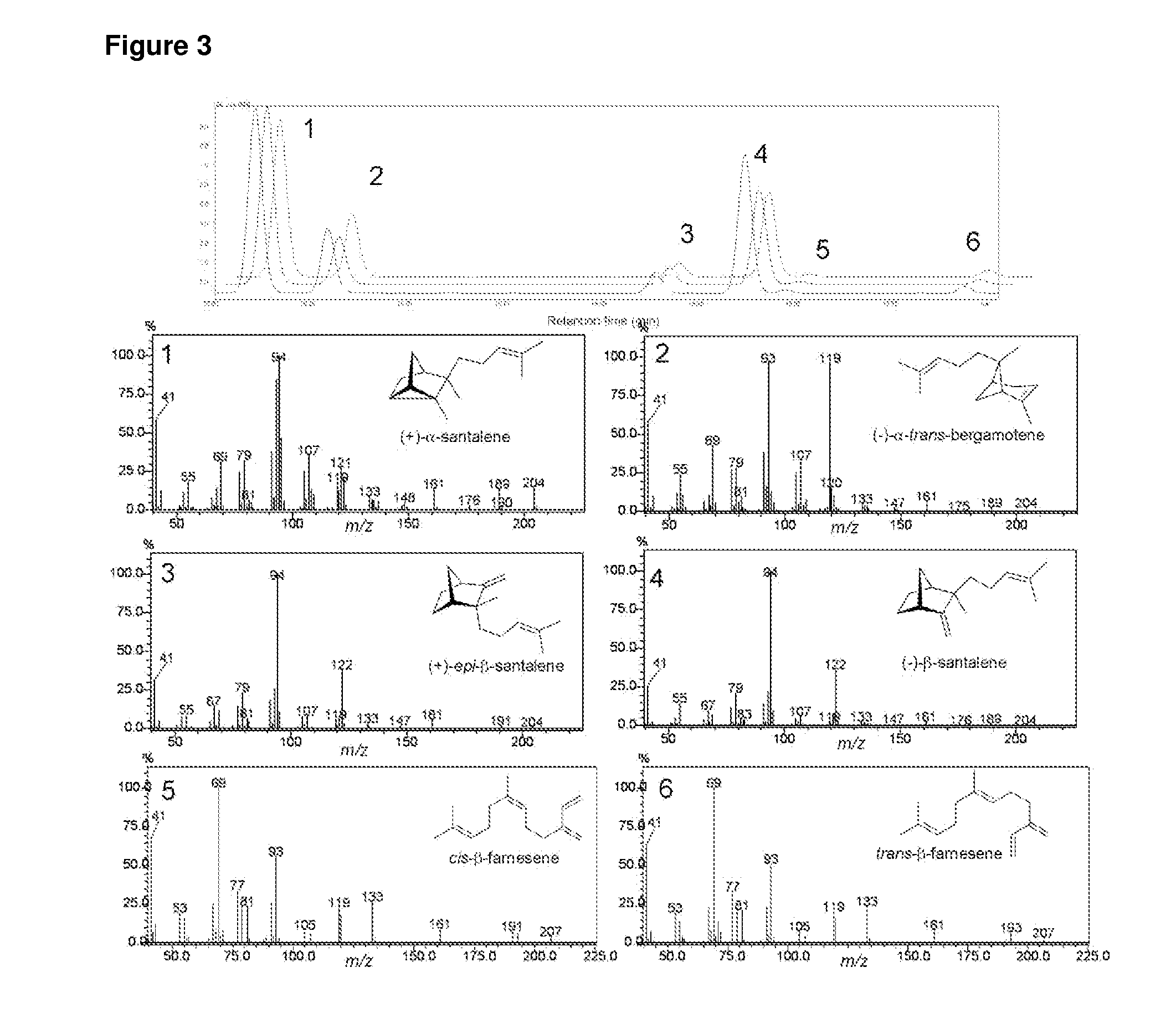
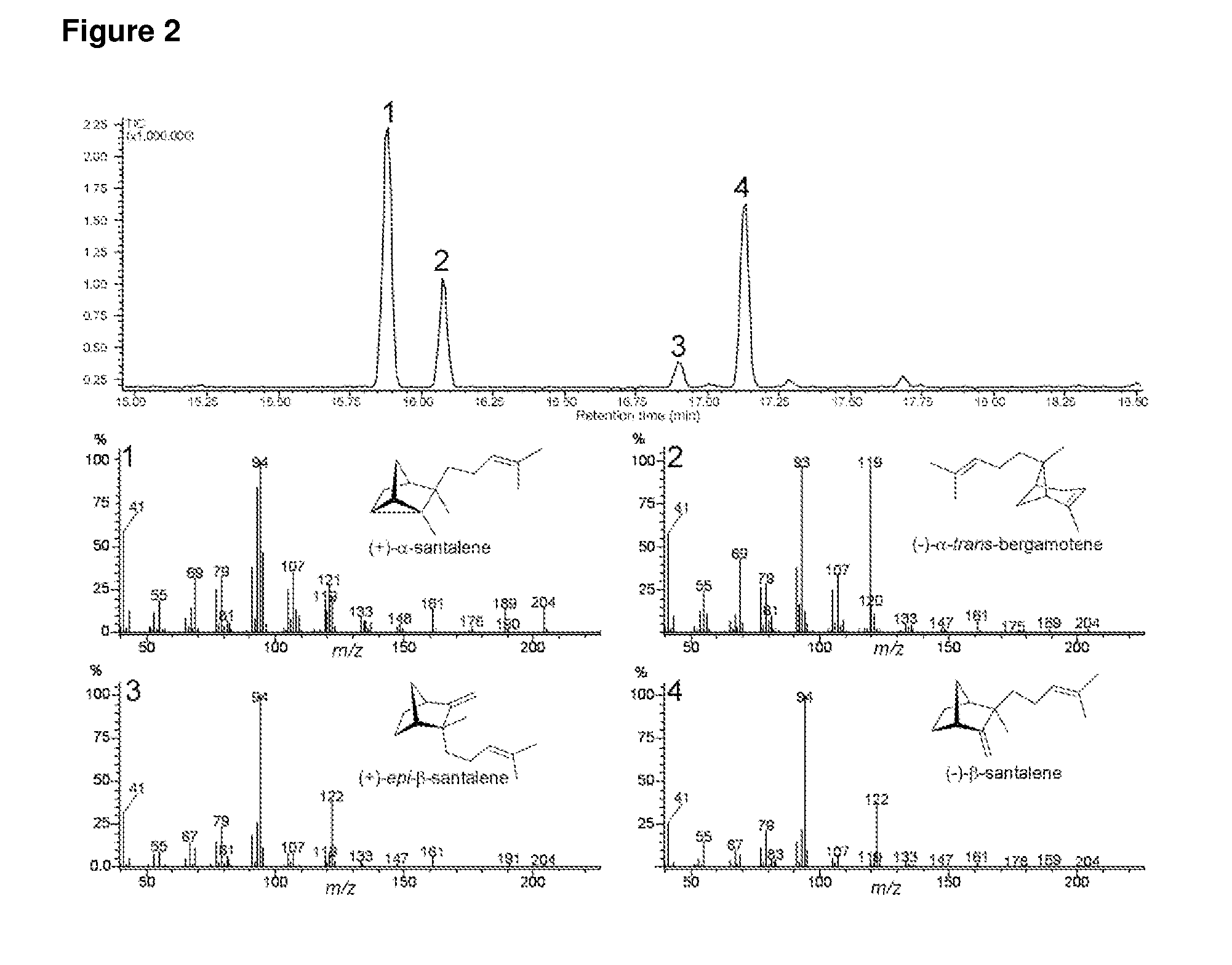
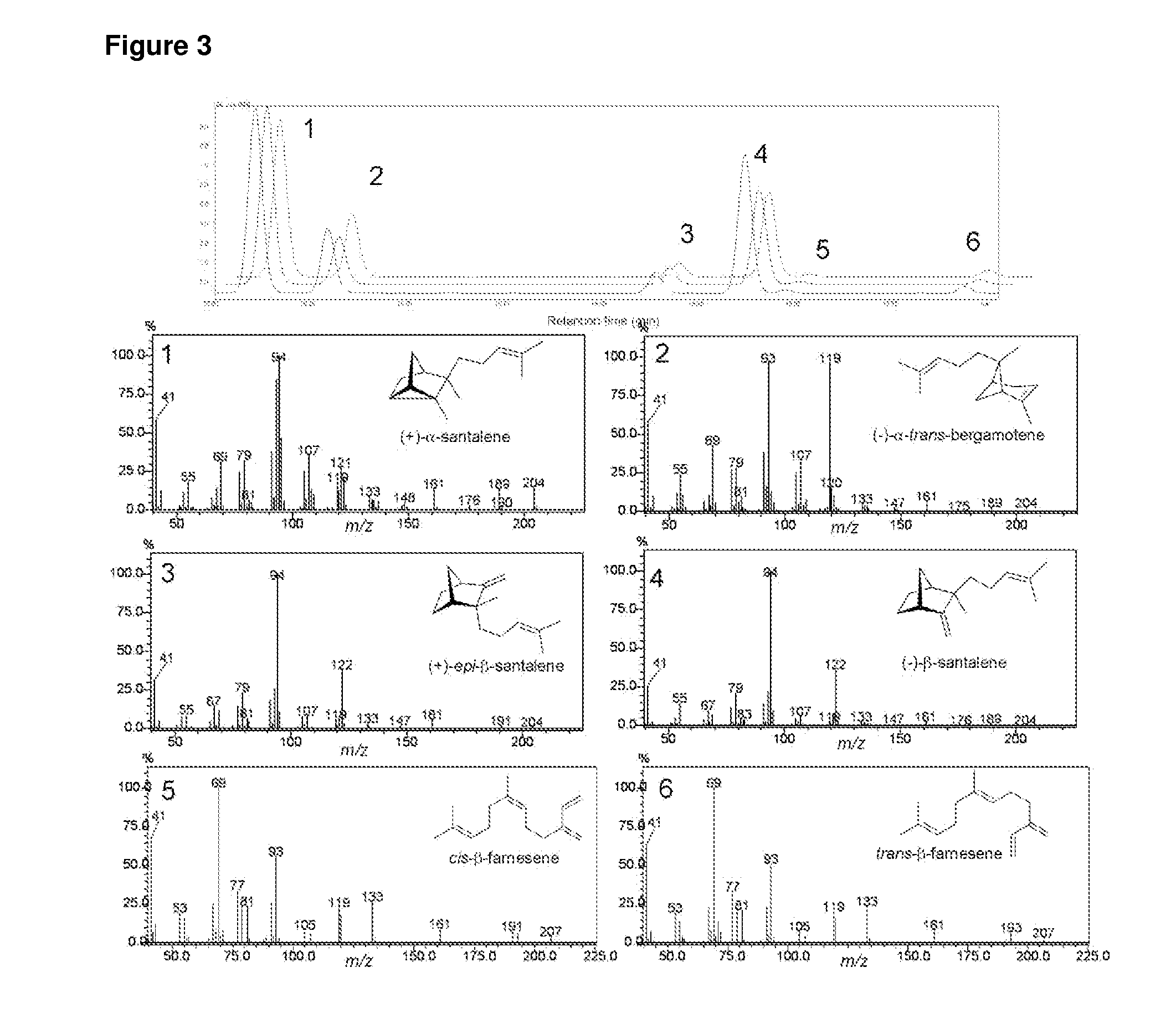
The present invention relates to novel terpene synthases. The terpene synthases are capable of synthesising mono-, bi- and / or tri-cyclic sesquiterpenes having a C2-C7 or a C3-C7 bond, starting from an acyclic pyrophosphate terpene precursor, farnesyl-pyrophosphate. Accordingly, for the first time, sesquiterpene synthases catalyzing the cyclisation to the santalene and bergamotene carbon skeleton are disclosed. The present invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the sesquiterpene synthases and to methods for making terpenoids.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
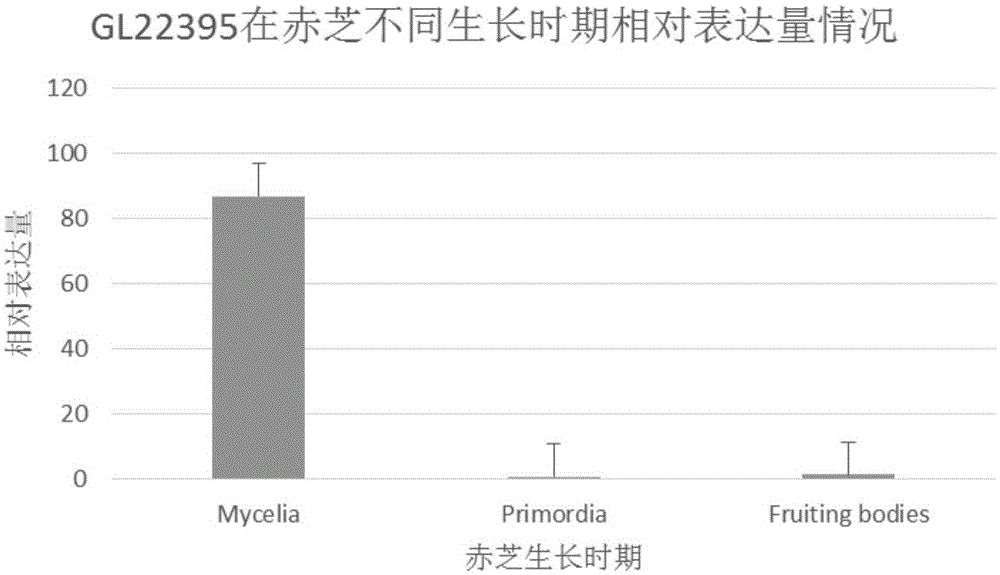
CDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene and application of cDNA sequence
The invention relates to a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of a ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene and an application of the cDNA sequence. The cDNA sequence of the ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL22395 encoding gene is represented as Seq ID No.2, and 419 amino acids are encoded. The ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase gene GL22395 is adopted to transform escherichia coli, and endogenous FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) is taken as a substrate, so that terpenoid is synthesized in an internal heterogeneous source of escherichia coli.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Terpene synthases from santalum
An isolated nucleic acid molecule that encodes a terpene synthase and is selected from among: a) a nucleic acid molecule comprising the sequence of nucleotides set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 5; b) a nucleic acid molecule that is a fragment of (a); c) a nucleic acid molecule comprising a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to (a)- or (b); and d) a nucleic acid molecule that encodes a terpene synthase having at least or at least about or at least about 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99% identity to any one of (a)-(c); wherein the nucleic acid molecule encodes a terpene synthase.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA +2
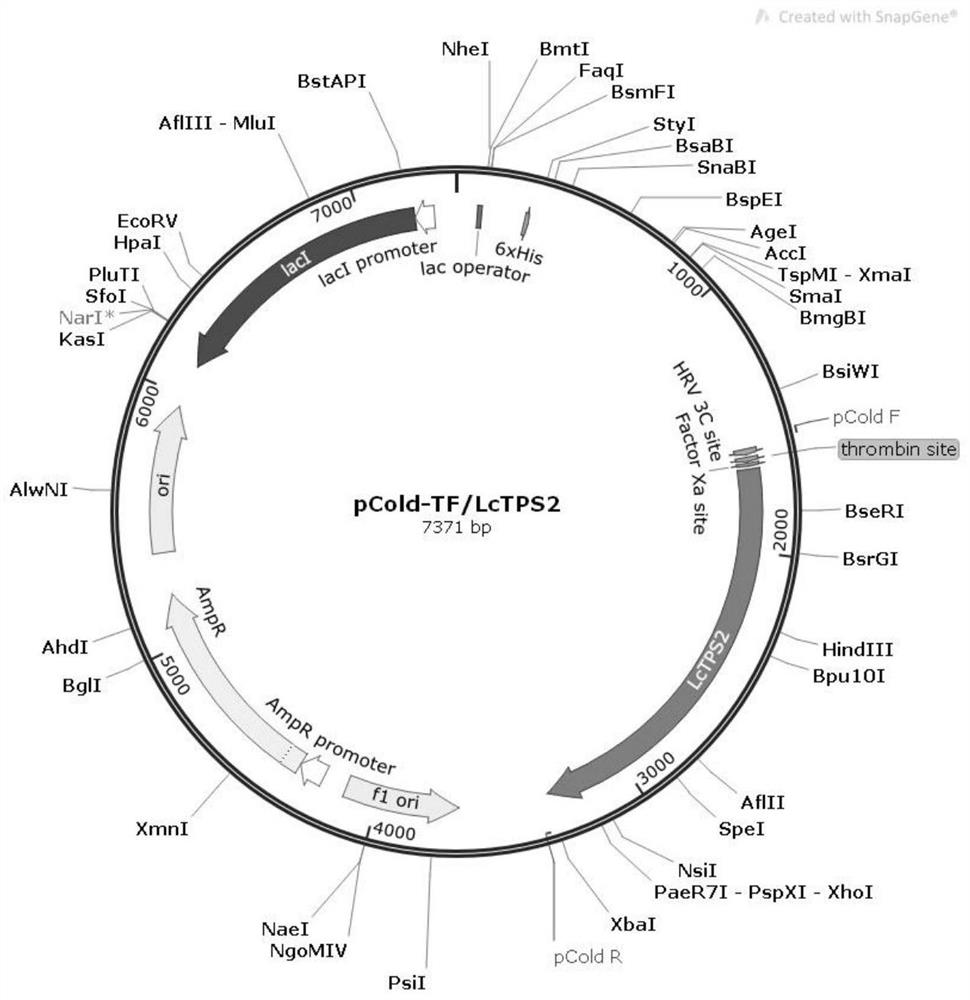
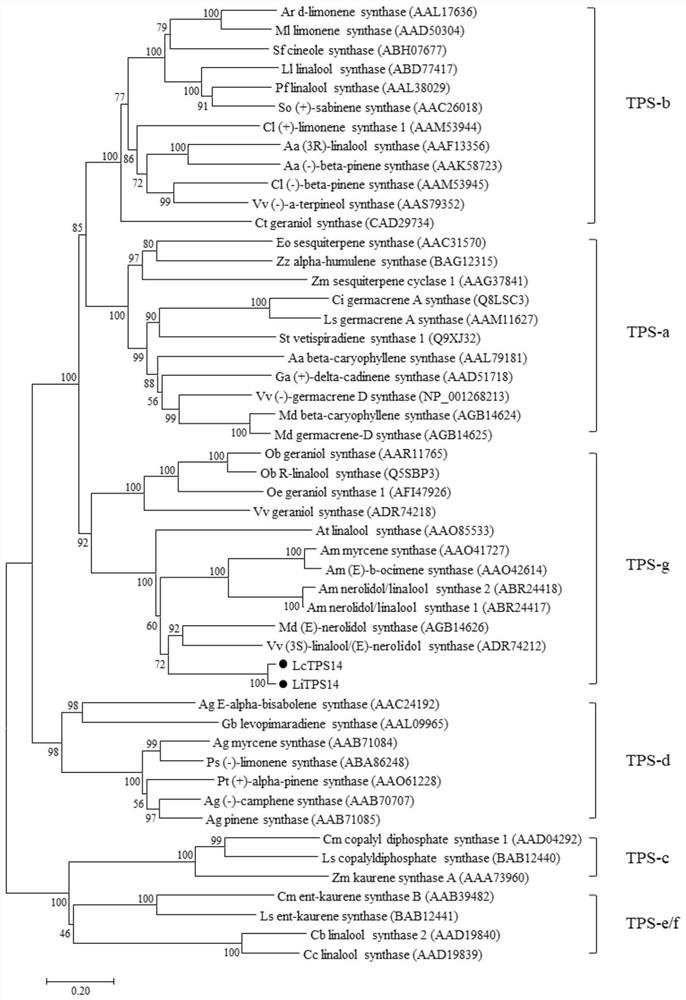
Difunctional sesterterpene/diterpene synthase LcTPS2, coding gene, product thereof and application of difunctional sesterterpene/diterpene synthase LcTPS2
ActiveCN113186183AShorten the production cycleHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntipyreticNucleotideEngineered genetic
The invention provides a difunctional sesterterpene / diterpene synthase LcTPS2, a coding gene and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of synthetic biology and natural pharmaceutical chemistry. According to the invention, a terpene synthase LcTPS2 coding gene for synthesizing a 14- / 18-membered ring terpene compound is cloned and functionally identified from labiatae plant Ipomoea cairica, and the nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase LcTPS2 coding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The genetically engineered cell constructed by the invention is safe and stable and short in production cycle, and the synthesized macrocyclic sesterterpene product has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activity, and has an obvious inhibiting effect on inducing a Jurkat cell line to secrete IL-2 by combining phytohemagglutinin with 12-phorboester-13-acetate and stimulating mouse T cells to generate cell factors IFN-gamma by CD3 and CD28 monoclonal antibodies. However, the compound has no obvious cytotoxicity to Jurkat and splenocytes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
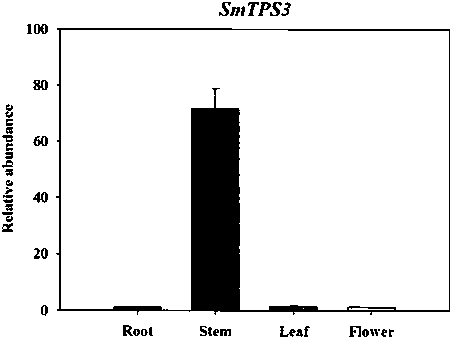
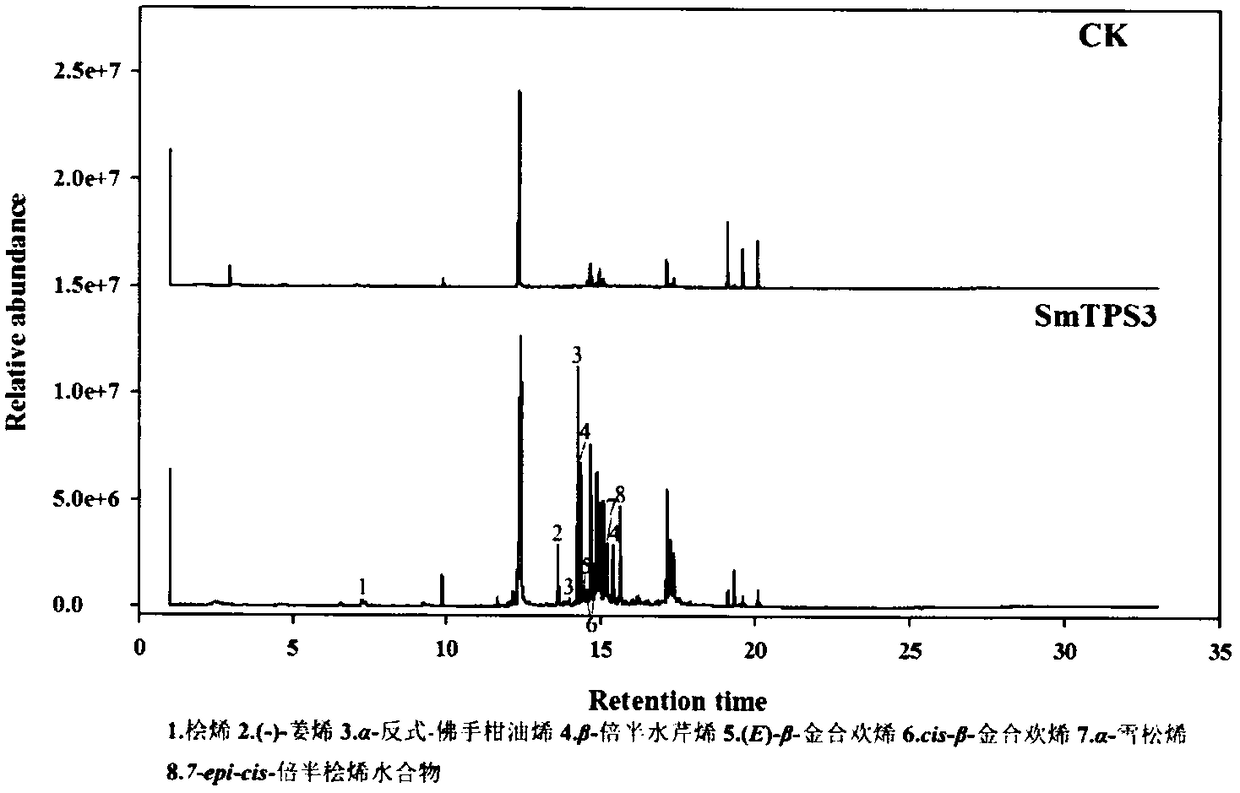
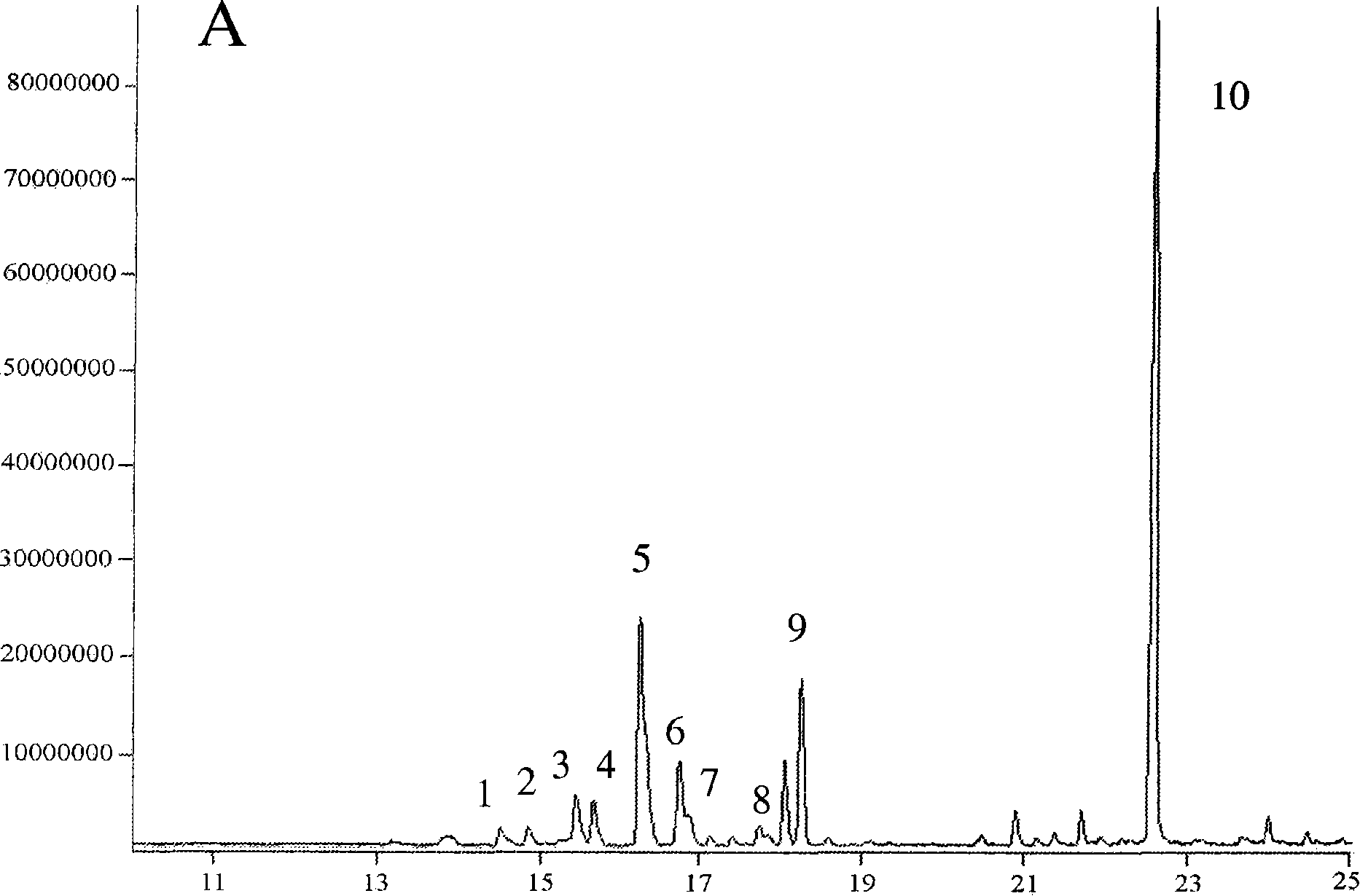
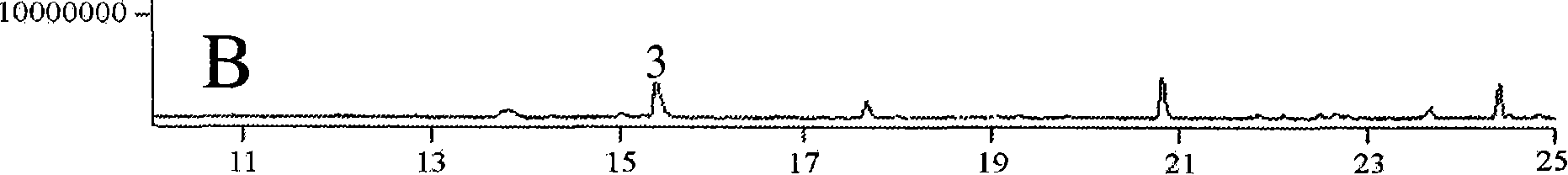
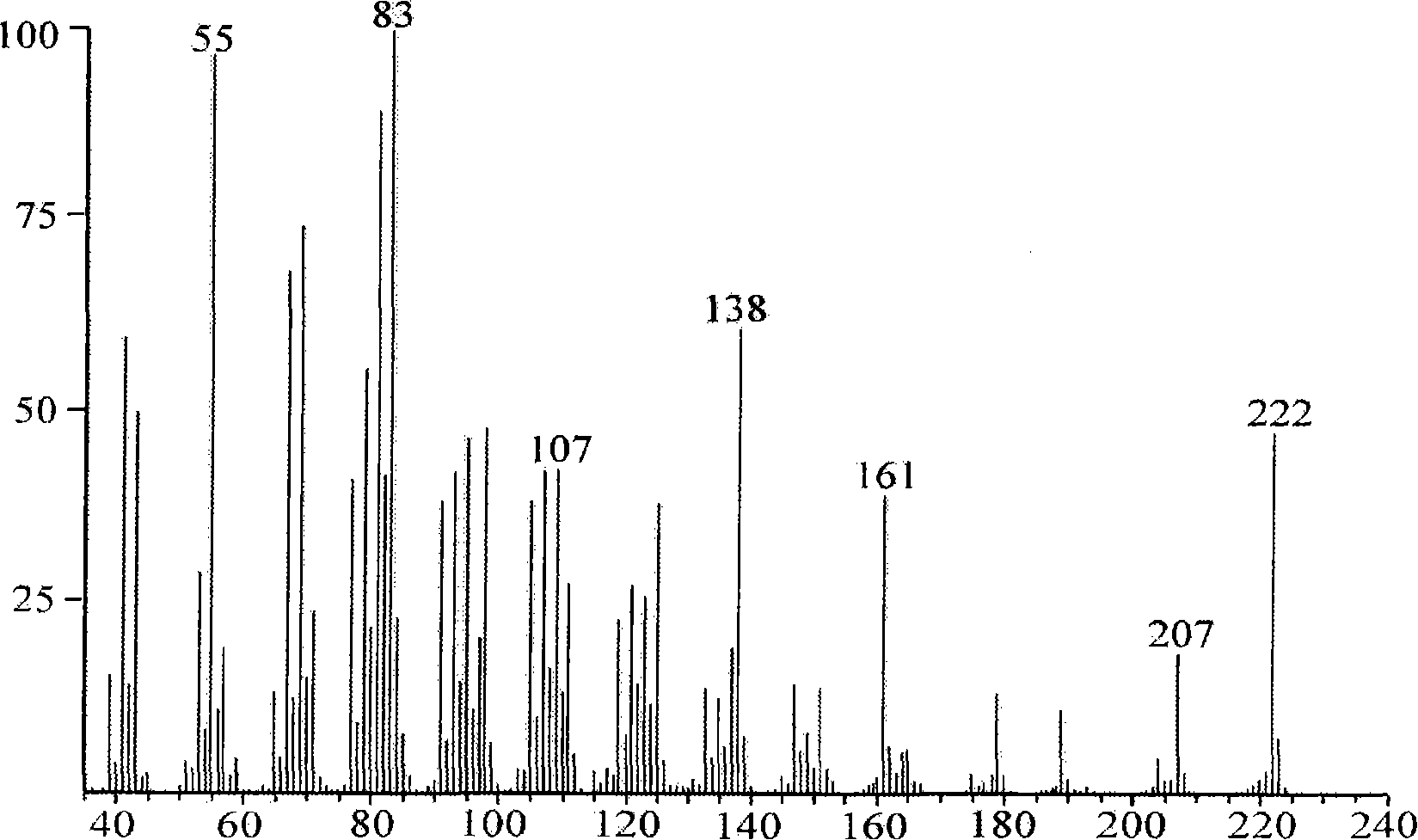
Method used for synthesizing plurality of sesquiterpenoid compounds using salviae miltiorrhizae SmTPS3 gene
ActiveCN108795960AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPhellandrene
The invention discloses a terpene synthases gene sequence (SmTPS3) mainly participating in synthesis of a plurality of salviae miltiorrhizae secondary metabolites sesquiterpenoids such as zingiberene.The SmTPS3 gene possesses a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1, and the protein encoded by the gene possesses an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No.2. The SmTPS3 gene sequence is obtained based on salviae miltiorrhizae genome and transcriptome data, a pET28a-SmTPS3 prokaryotic expression vector is constructed, the catalysis products of SmTPS3 are detected in Escherichia coli, so that the gene functions of SmTPS3 are verified. It is shown by research results that: SmTPS3 is capable of catalyzing synthesis of a plurality of sesquiterpenoid components including zingiberene,alpha-bergamot oil alkene, beta- sesquiphellandrene; zingiberene possesses anti-virus activity, anti-fertility activity, and antiulcer activity, and can be taken as food flavoring agent and cosmeticraw material; bergamot essential oil possesses excellent curative effects in alleviating anxiety and depression. The method is capable of providing salviae miltiorrhizae terpene synthases gene synthesis of sesquiterpenoid compounds with foundation, and promoting medicine development and industry development of sesquiterpenoid compounds, such as zingiberene and alpha-bergamot oil alkene, based onSmTPS3 catalysis synthesis.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Transformed plants accumulating mono- and/or sesquiterpenes
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Terpene synthases for biofuel production and methods thereof
The present invention relates to terpene synthases capable of degrading precursors into biofuel compounds, such as terpenoid compounds. In one instance, a transformed organism can include such terpene synthases, as well as vectors encoding such synthases. Methods of employing such synthases and organisms are also described herein.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for producing terpenes and MEP-transformed microorganisms therefore
InactiveUS8048658B2High productIncrease volumeFungiHydrocarbon by isomerisationMicroorganismHeterologous
The present invention relates to a microorganism capable of producing a terpene of choice. The microorganism expresses a heterologous pathway for the formation of isoprene units and, preferably, a heterologous terpene synthase. In this way, high amounts of terpene can be isolated from the medium of the microorganism.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
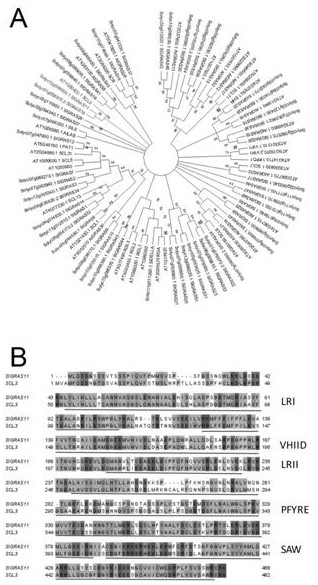
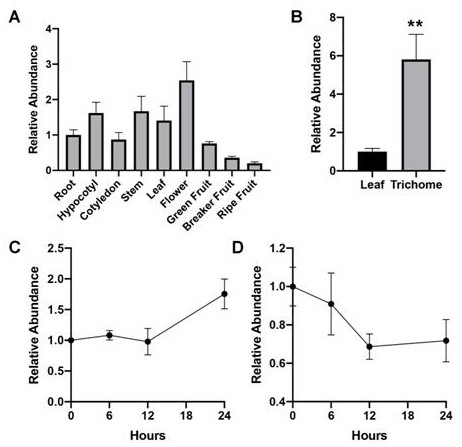
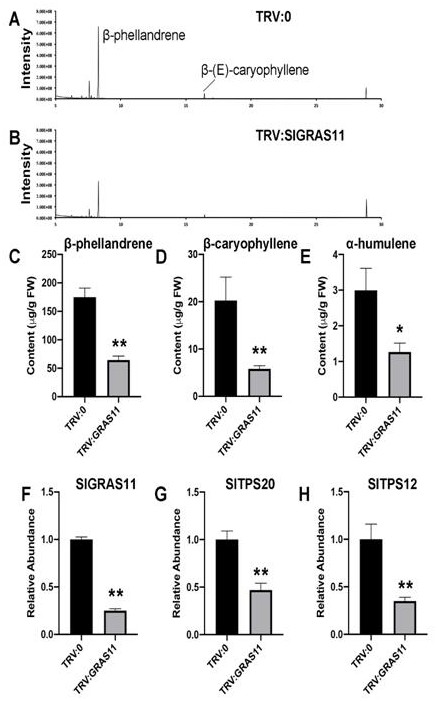
Application of GRAS11 to regulation of synthesis of plant terpenoids and/or development of glandular hairs
PendingCN113215171AImprove developmentIncrease in sizePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyTerpene synthase
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to an application of GRAS11 to regulation of synthesis of plant terpenoids and / or development of glandular hairs. According to the invention, firstly, amplification is performed in Solanumlycopersicum L. to obtain a transcription factor GRAS11, and the transcription factor GRAS11 is specifically expressed in glandular hairs of leaves and stems. The overexpression of GRAS11 can significantly enhance the expression level of terpene synthase and upstream precursor synthetic pathway genes in tissues such as leaves, thereby improving the yield of terpenoids and increasing the volume of glandular hairs. The invention provides beneficial values for research and application in aspects of improving crop nutritional quality, improving crop insect resistance and disease resistance and the like in genetic engineering.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Eucalyptus TPS gene, RNA interference vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105002194AReduce the content of allelochemicalsReduce allelopathyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTerpene synthaseMolecular breeding
According to the invention, terpene synthase (TPS) gene is obtained through PCR and RACE technologies and sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.15. Sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO. 23 and SEQ ID NO.26 are respectively selected as a forward fragment and a reverse fragment to construct a RNA interference vector Part27-TPS-RNAi for reducing content of eucalyptus allelochemicals. The vector is transferred into eucalyptus so as to successfully obtain a plant with low content of allelochemicals. The invention relates to gene engineering for reducing content of eucalyptus allelochemicals and provides an important allelochemical synthase gene, the RNA interference expression vector and its application. Thus, a new idea is provided for applying RNA interference and transgenic technology to forest tree molecular breeding. The expected goal of obtaining a new eucalyptus material with low content of allelochemicals by the RNA interference principle is achieved; successful living examples are provided for the RNA interference-mediated eucalyptus molecular breeding and gene engineering; and the blank of RNA interference-mediated allelochemicals reduction in the field of study is filled.
Owner:CHINA EUCALYPT RES CENT
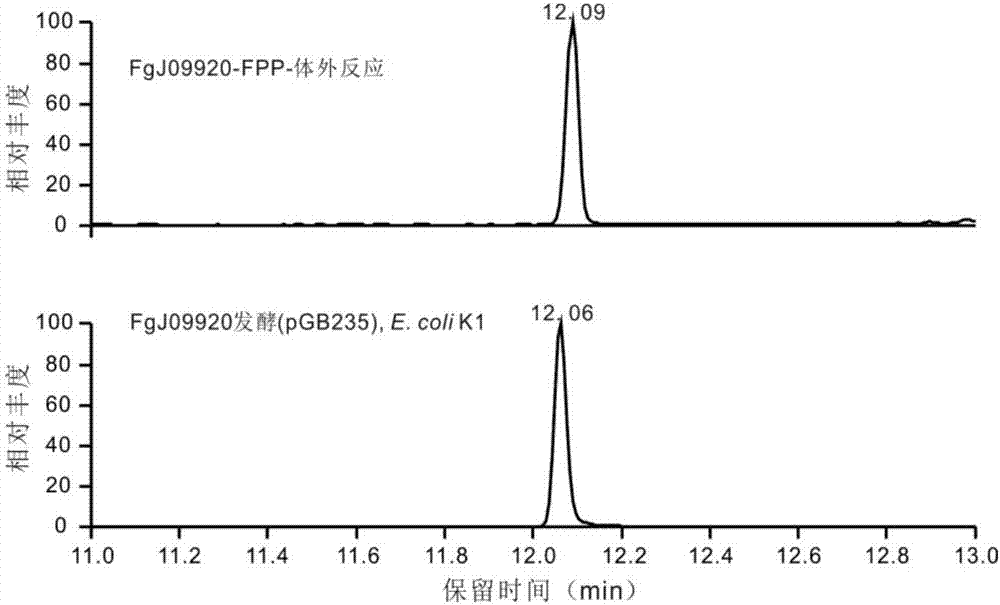
Terpene synthase for producing koraiol and application of terpene synthase
The invention discloses terpene synthase for producing koraiol and an application of the terpene synthase, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The terpene synthase FGJ09920 for synthesizing the koraiol is provided, the nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, the terpene synthase and related genes containing mevalonic acid pathways establish strains for producing the koraiol, atoB genes or idi genes of the mevalonic acid pathways derived from Escherichia coli XL1-blue are over-expressed, a large number of catalytic substrate FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) is synthesized, and production of the koraiol can be further facilitated. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency and overcomes the shortcomings that input quantity of raw materials is high, and the yield of the koraiol is low, the yield of the koraiol can be improved, research cost is reduced, and green and environment-friendly production is ensured.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Transcription factor modulating terpene biosynthesis
InactiveUS20140173771A1Increase productionIncrease secretionBacteriaImmunoglobulinsTerpene synthasePolynucleotide
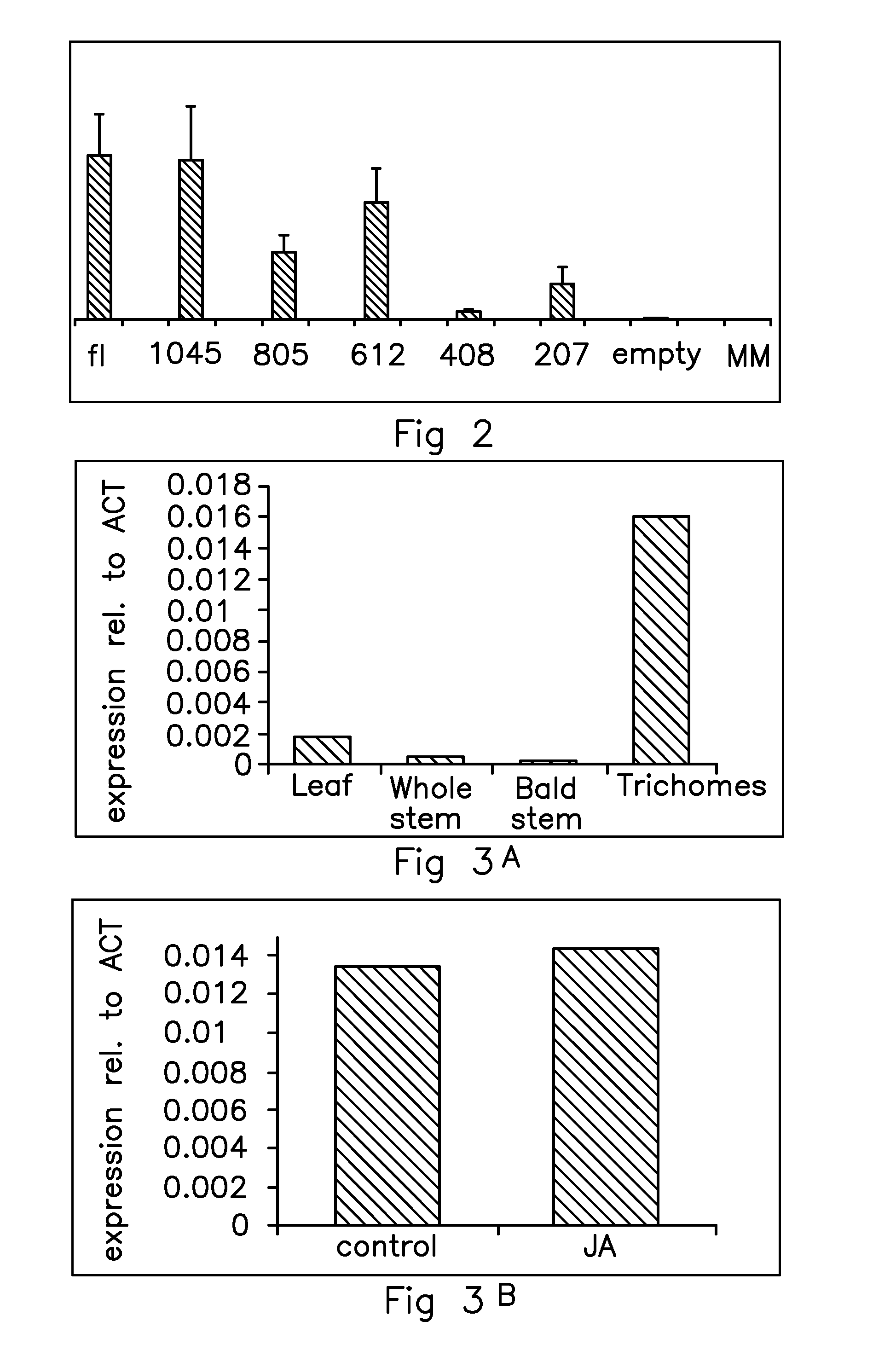
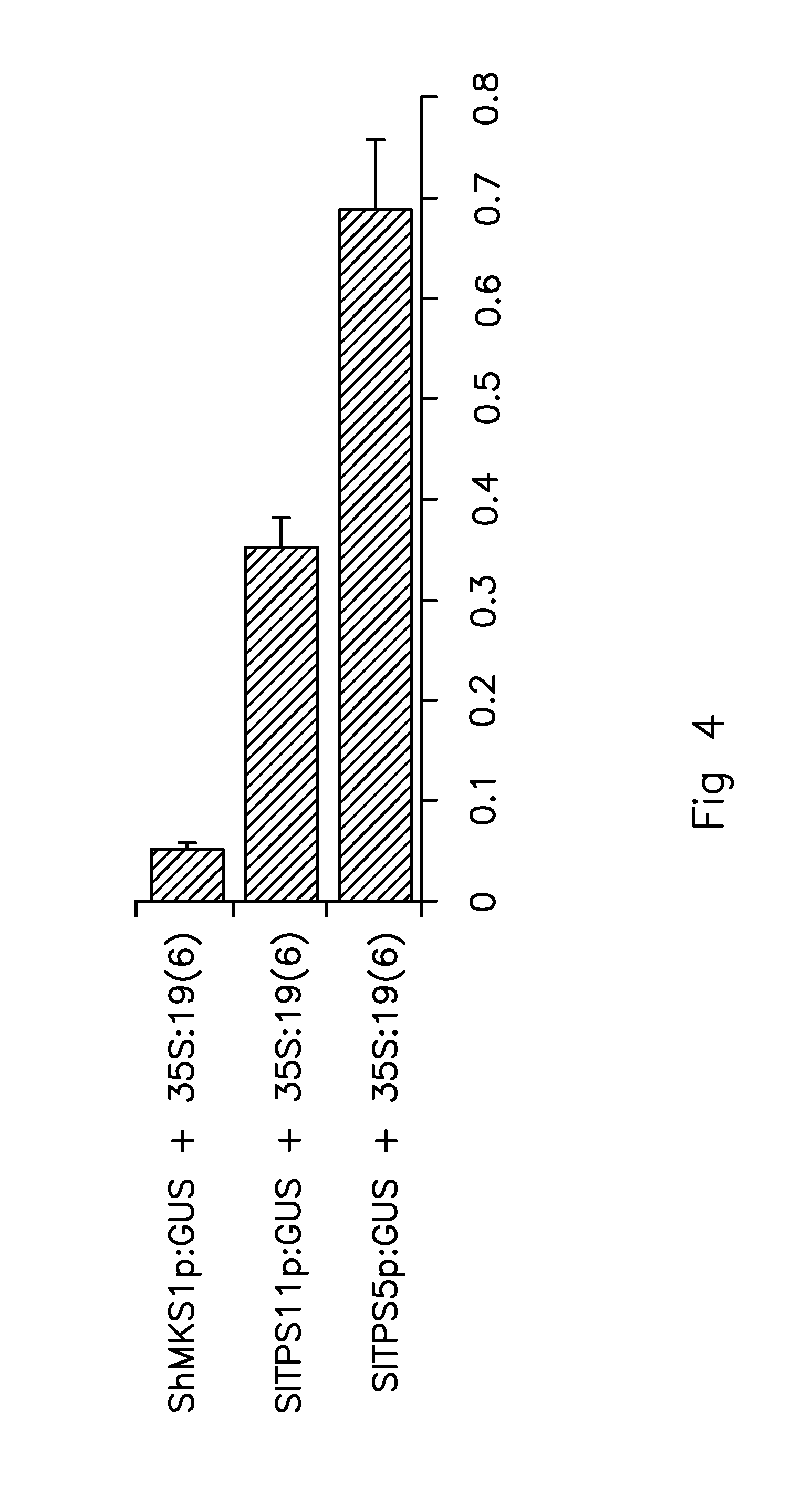
The present invention relates to identification and isolation of zinc finger transcription factor in tomato that specifically expresses in glandular trichomes of Solanum lycopersicum cultivar Moneymaker and binds to the promoters of the genes encoding Terpene Synthase 5 (also known as Monoterpene Synthase 1) and Terpene Synthase 11 (also known as Sesquiterpene Synthase 1). The invention provides the isolated, recombinant or synthetic polynucleotides encoding the polypeptide sequences of SEQ ID NO:2 and variants and fragments thereof. The invention also provides constructs, vectors, host cells and plants genetically modified to contain the polynucleotides of the invention. The methods for producing plants with altered levels of terpenes, including transformed and mutant plants, are also provided.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Indole synthase and its application
ActiveCN110093329ASpecific and efficient synthesisAntibacterial and anti-inflammatoryTransferasesChemical recyclingTerpene synthaseMedicinal chemistry
The invention discloses a terpene synthase and its application. Specifically, the invention provides use of the terpene synthase and a plasmid and a vector expressing the terpene synthase for catalyzing the synthesis of terpenes or preparing a catalyst for a reaction for catalyzing the synthesis of hydrazines, and also provides a method for the preparation of terpenes. The terpene synthase can specifically and efficiently synthesize a plurality of sesquiterpene compounds by using a terpenoid precursor material as a substrate.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACTION TECH CO LTD
Transformed plants accumulating terpenes
InactiveUS8017835B2High yieldIncrease volumeTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesTerpene synthaseGene conversion
The present invention relates to transformed plants with an altered terpene content, preferably over-accumulating a mono- or sesqui-terpene. By transformation of plants with genes encoding terpene synthases (TS), and prenyl transferases (PRT), plants accumulating at least 1000 ng / per g of fresh leaf of a specific terpene were obtained. The present invention provides an advantageous system for production of terpenes in that any desired mono- or sesqui-terpene at the choice of the skilled person can be produced in plants. Preferably, the transformed plants contain at least one recombinant plastid targeted TS and PRT.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Cedar synthase Lc-CedS encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109735523ARich diversitySolve the sourceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a cedar synthase Lc-CedS for producing cedar camphor, an encoding gene of the cedar synthase Lc-CedS and application of the cedar synthase Lc-CedS. Starting from Leucosceptrumcanum, cloning and functional authenticating are conducted on an encoding gene of a terpene synthase Lc-CedS for synthesizing the cedar campho, the encoding gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in Seq ID No.2 and is connected with different expression carriers to construct recombinant plasmids capable of being expressed in escherichia coli and tobacco, the recombinant plasmids are transferred into the escherichia coli and tobacco to construct an engineering cell, and the cedar camphor is heterogeneously synthesized from the escherichia coli and tobacco. The cedar camphor has important application value. The constructed gene engineering cell is safe, stable and short in production cycle and has great value in application and development.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for terpenoid production
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Lagerstroemia terpene synthase gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a lagerstroemia terpene synthase gene and application thereof. According to the invention, the terpene synthase gene is cloned and separated from lagerstroemia plants for the first time, the catalytic function of the terpene synthase gene is explored through in-vitro expression, the molecular mechanism of biosynthesis of floral substances of the lagerstroemia plants is preliminarily understood, and a basis is provided for further research on floral biosynthesis and regulation of the lagerstroemia plants.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Terpene Synthases for Biofuel Production and Methods Thereof
The present invention relates to terpene synthases capable of degrading precursors into biofuel compounds, such as terpenoid compounds. In one instance, a transformed organism can include such terpene synthases, as well as vectors encoding such synthases. Methods of employing such synthases and organisms are also described herein.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Aquilaria sinensis terpene synthase
ActiveCN113234740AImprove solubilityIncrease productionFermentationGenetic engineeringTerpene synthaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to an aquilaria sinensis terpene synthase, and provides a modified sesquiterpene synthase gene, which enables common host microorganisms to be efficiently expressed through a gene engineering technology: a synthase of a sesquiterpene compound with high catalytic synthesis efficiency of a target product and good solubility is provided; therefore, progress and development of a biological enzyme catalytic synthesis technology of the sesquiterpenoids are promoted.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Leaf fertilizer for increasing yield and quality of blumea balsamifera
ActiveCN106316636AImprove photosynthetic activityIncreased biomassOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesSolubilityTerpene synthase
The invention provides a blumea-balsamifera leaf fertilizer. The blumea-balsamifera leaf fertilizer is prepared from, by mass, 17%-70% of marine-organism active polysaccharides, 9%-60% of humic acid, 1%-15% of vitamins, 1%-15% of inositol and 0.05%-3% of gibberellin. By means of the marine-organism active polysaccharides, the humic acid and the vitamins, nutrient components required by blumea-balsamifera growing can be supplemented in time, the photosynthetic activity of blumea balsamifera can also be improved, and the activity of terpene synthase such as L-borneol is promoted; by means of the inositol and the gibberellin, synthesis of endogenous hormones in the blumea balsamifera can be promoted, falling off is reduced, accumulation of the L-borneol is promoted, and the resistance of the blumea balsamifera to the extreme weather such as diseases and pests, cold and the high temperature is increased; leaf spraying is carried out in the blumea-balsamifera growing period and before harvesting, the biological yield of the blumea balsamifera is increased by 60% or above, and the yield of the blumea balsamifera is increased by 20% or above. A preparing method of the blumea-balsamifera leaf fertilizer has the advantages of being easy and convenient to operate, mild in technology condition, good in water solubility, convenient to spray, remarkable in economical benefit and the like.
Owner:海南艾纳香生物科技发展股份有限公司
Sesquiterpene synthases and methods of their use
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL-TS2 coding gene cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence and application of ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL-TS2 coding gene cDNA sequence
The invention relates to a ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL-TS2 coding gene cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence and application of the ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL-TS2 coding gene cDNA sequence. The ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase GL-TS3 coding gene cDNA sequence is shown as Seq ID No.2, and 346 amino acids are coded. Escherichia coli is converted through ganoderma lucidum terpene synthase gene GL-TS2; endogenous FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) is used as a substrate, and the goal of heterologous synthesis of terpenoid in the escherichia coli is achieved.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com