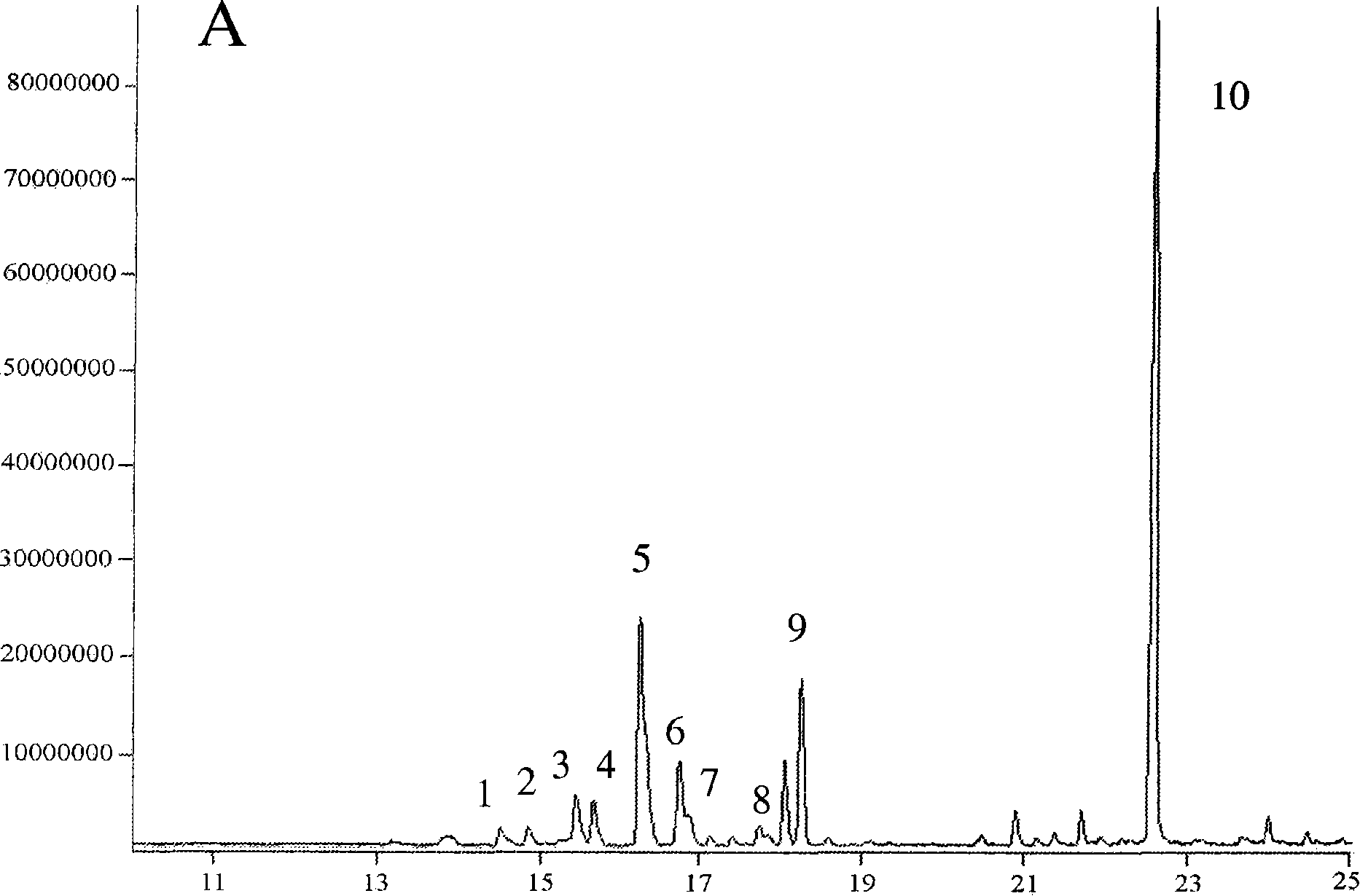
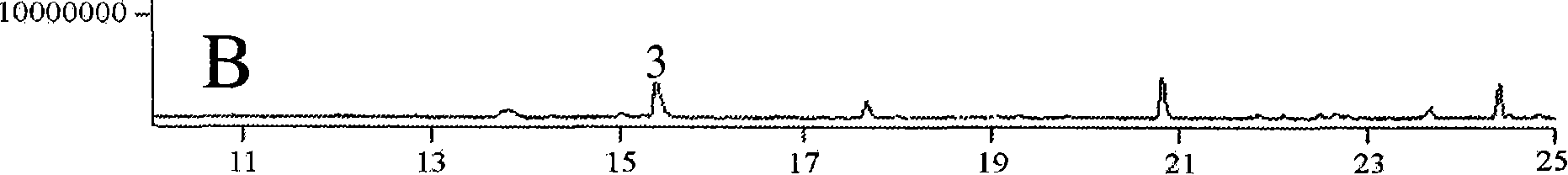
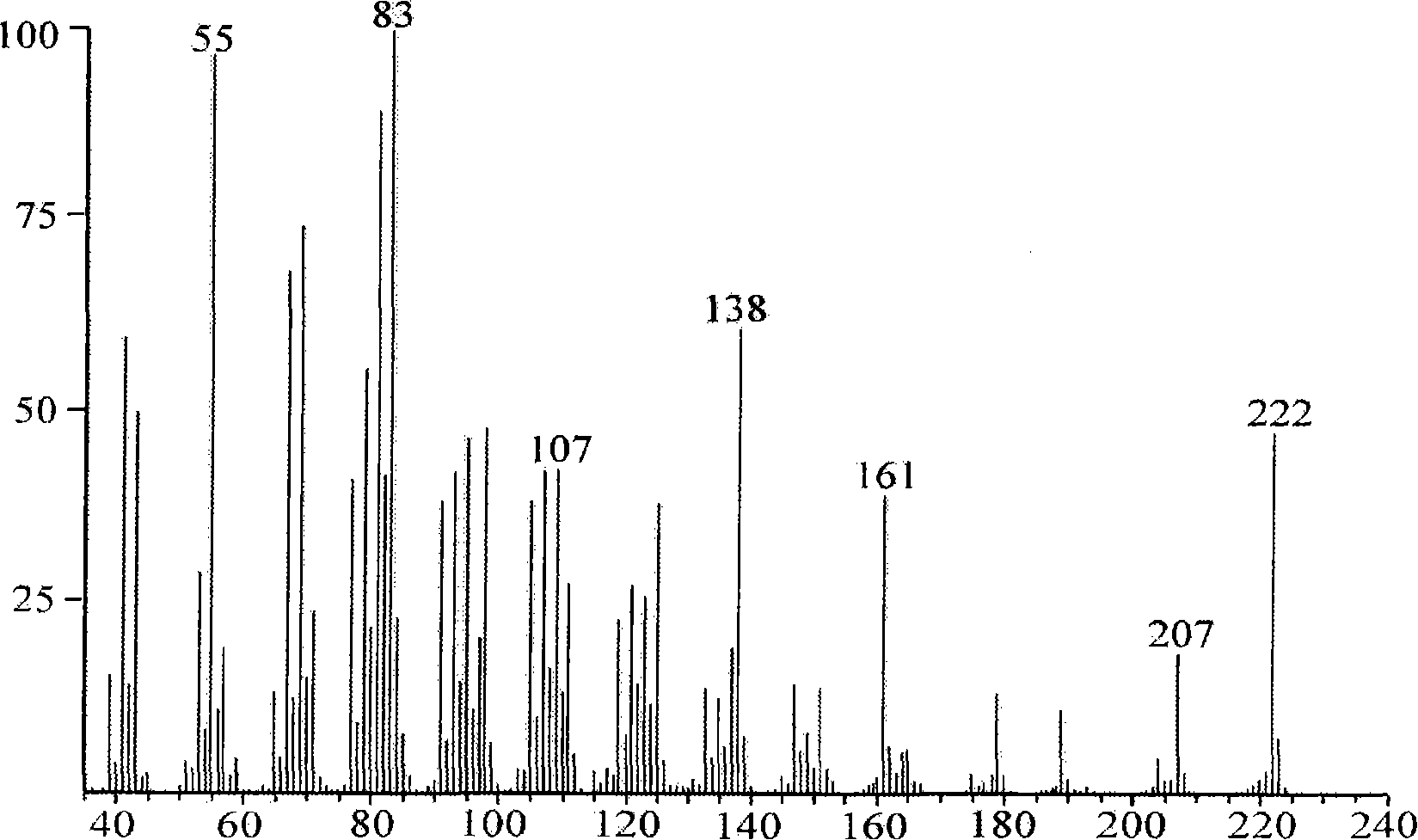
Transformed plants accumulating mono- and/or sesquiterpenes
A technology of plants and plant materials, applied in the fields of plant products, plant genetic improvement, plant equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] Example 1: Selection of plant material
[0105] Homozygous lines of the "Shanxi" tobacco line containing a truncated hamster hydroxymethyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase gene were bred according to the method described in Chappell et al. (hereinafter referred to as 14-8) and an F2 segregating sibling line lacking the transgene (hereinafter referred to as 14-2). In summary, the hamster gene first characterized by Chin et al. (1984) was modified by removing nucleotides 28-1023 to obtain a truncated form of the gene, referred to as delta-227HMGR. The BamH1 / Sst1 fragment of the truncated HMGR cDNA was isolated and inserted into the intermediate plastid vector pKYLX 61, and the EcoR1 / Cla1 fragment of this construct was subsequently inserted into the corresponding pKYLX71 site to generate the pKYLX71-truncated HMGR gene construct. Schardl et al. (1987) developed the Ti-plasmid series pKYLX61 and pKYLX71.
[0106] The pKYLX71-HMGR plasmid was transferred into Agrobacterium tumefac...
Embodiment 2-5
[0110] Embodiment 2-5: Construction of recombinant and plant transformation vector
[0111] Selection The hygromycin selection marker (Hajdukiewicz et al., 1994) was used to generate the selection marker for transformed plants. New vectors were designed with appropriate recombinant cloning sites as described by Hartley et al. (2000).
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2: Formation of pBDON vector
[0113] Figure 8 , the pBI101 vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was digested with restriction enzymes Sph1 and Sst1 and purified by agarose gel (Sambrook et al., 1989) to isolate the DNA corresponding to the plasmid vector (excluding the RB border and NPTII gene cassette) Fragment (1). Simultaneously, the attp recombinant cassette including the ccdb gene and the chloramphenicol resistance gene was amplified from the pDON221 vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) with primers Attp1-SstI-FW and Attp2-SphI-RV using standard PCR conditions ( 2). The PCR-amplified DNA fragment was digested with Sph1 / Sst1, gel purified and ligated into the corresponding sites of the similarly digested pBI101 vector described above to produce the intermediate pBattp vector (3).
[0114] The hygromycin gene cassette was prepared using a two-step method. First use PCR primers HPT-NotI-FD and HPT-Xba1-RV that hygromycin gene (HPT) and CaUTR (termination seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com