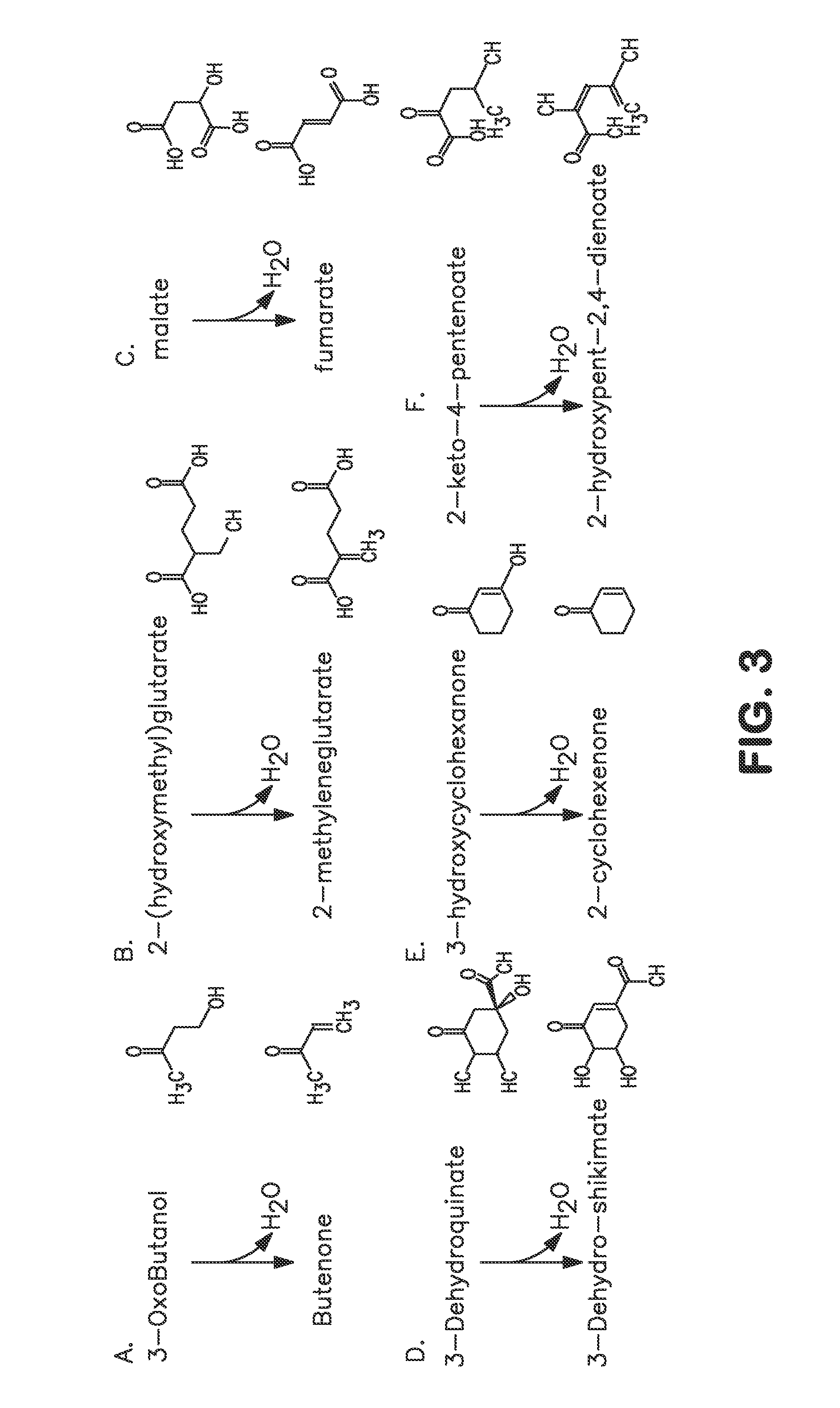
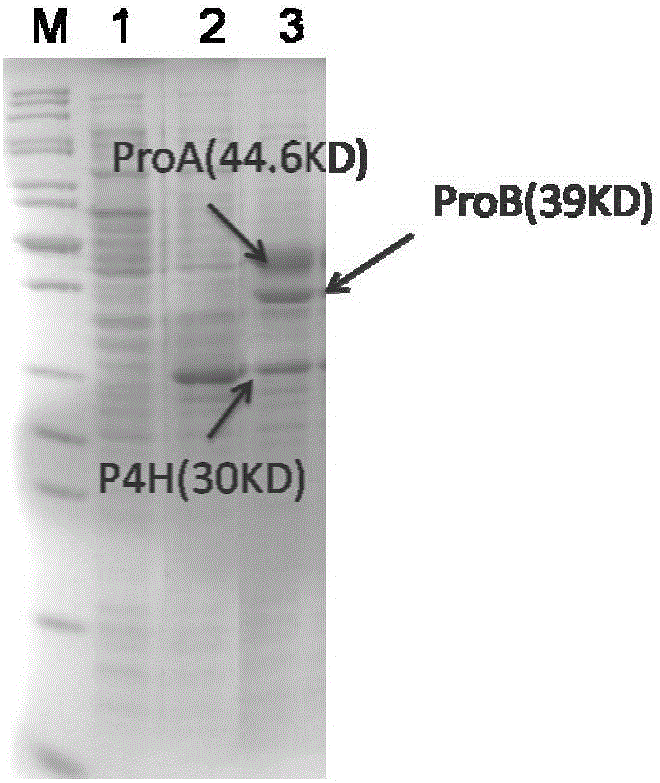
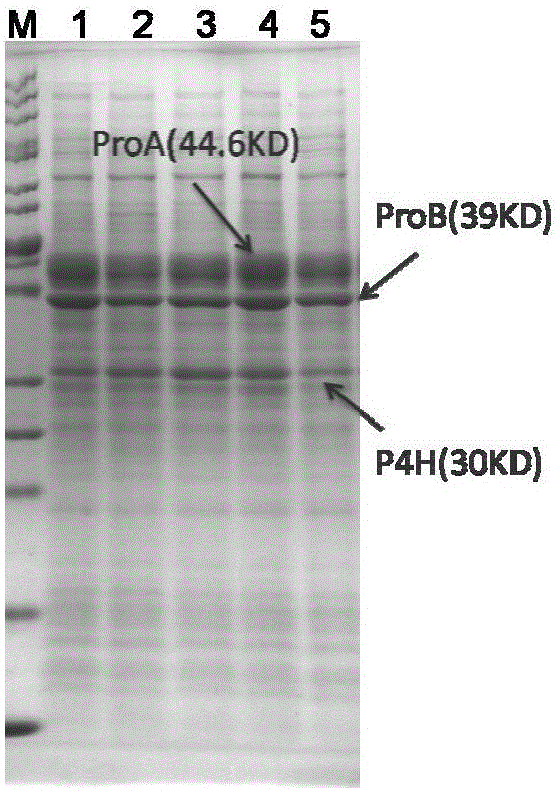
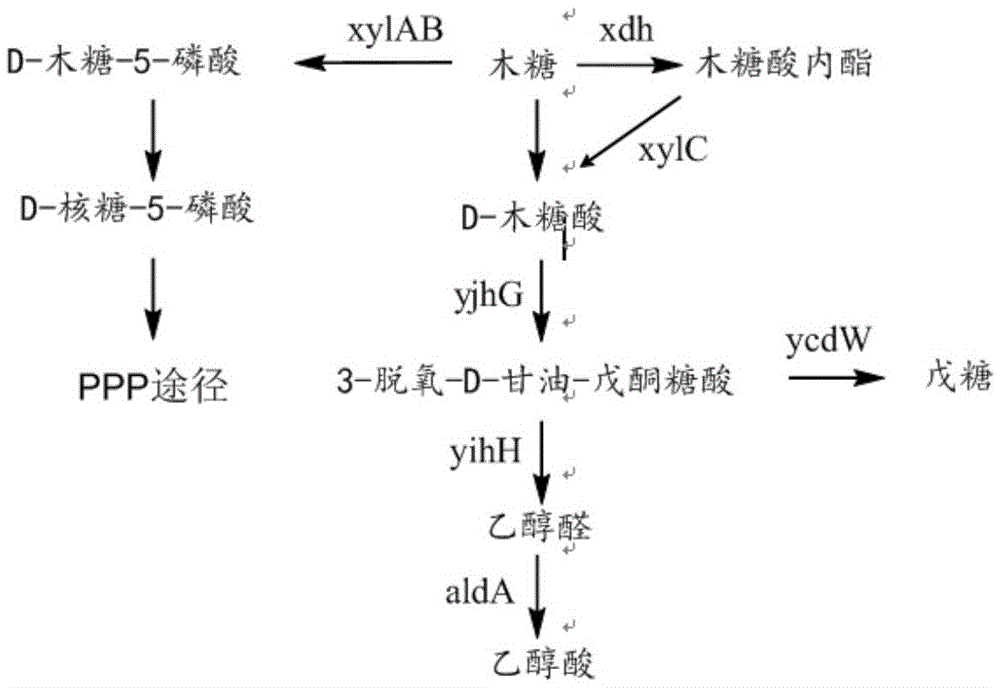
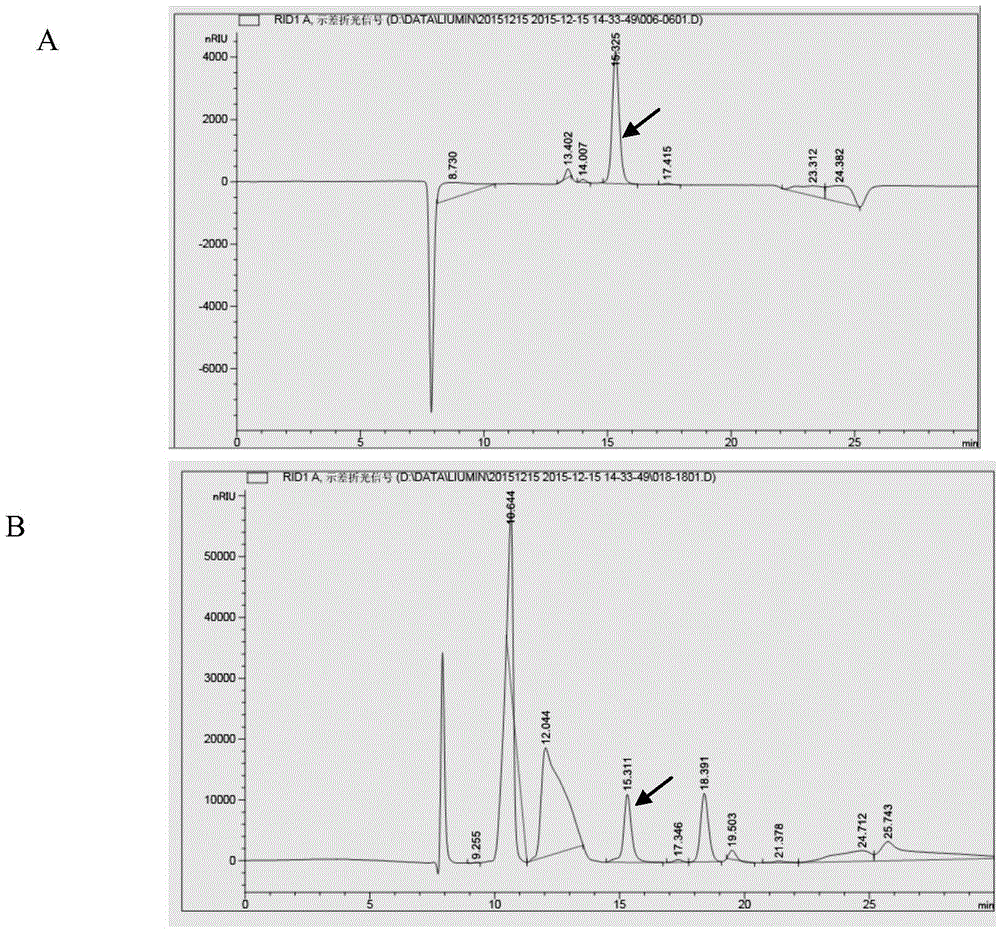
Patents
Literature
352 results about "Aldehyde dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (EC 1.2.1.3) are a group of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of aldehydes. They convert aldehydes (R–C(=O)–H) to carboxylic acids (R–C(=O)–O–H). The oxygen comes from a water molecule. To date, nineteen ALDH genes have been identified within the human genome. These genes participate in a wide variety of biological processes including the detoxification of exogenously and endogenously generated aldehydes.
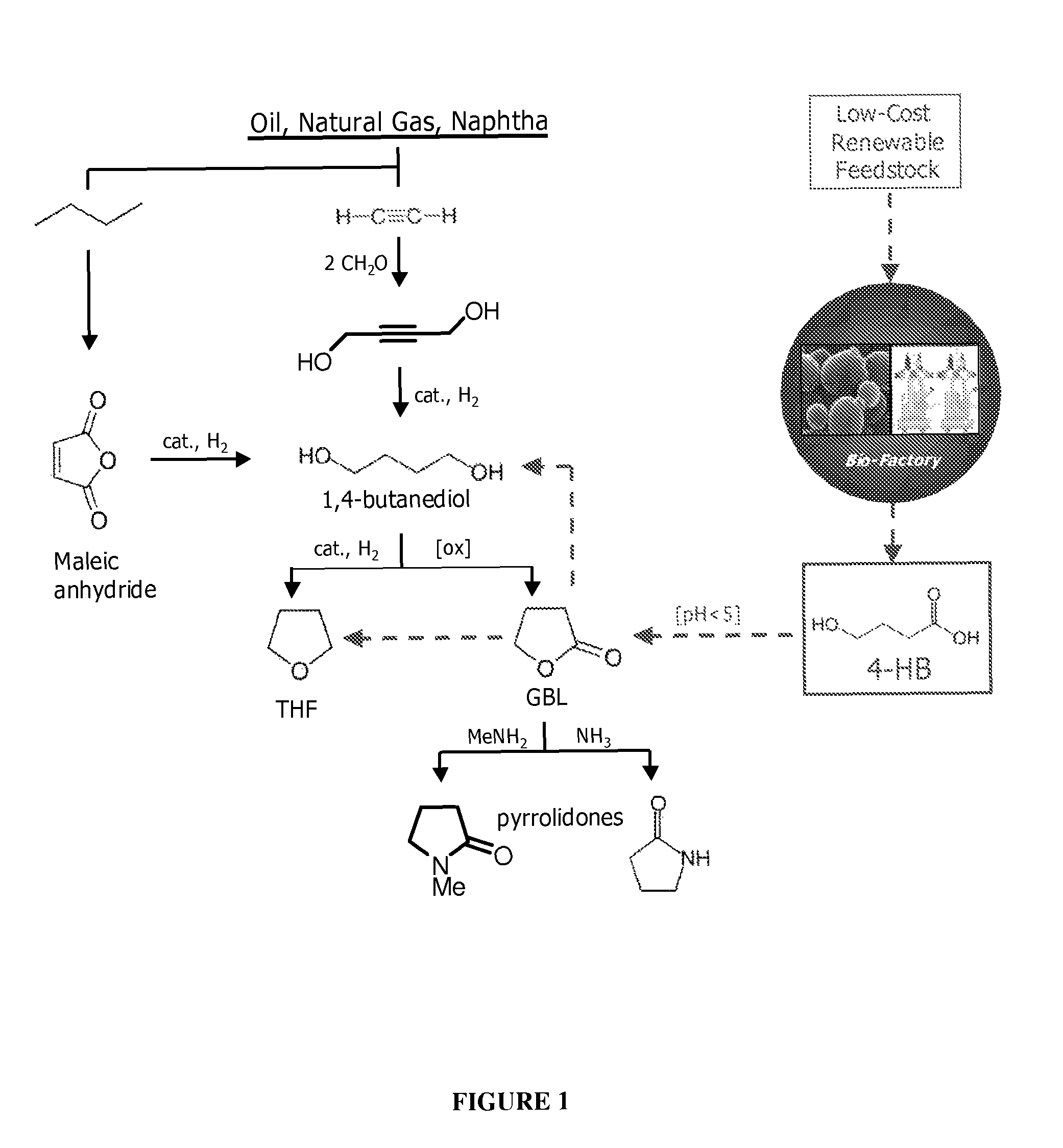
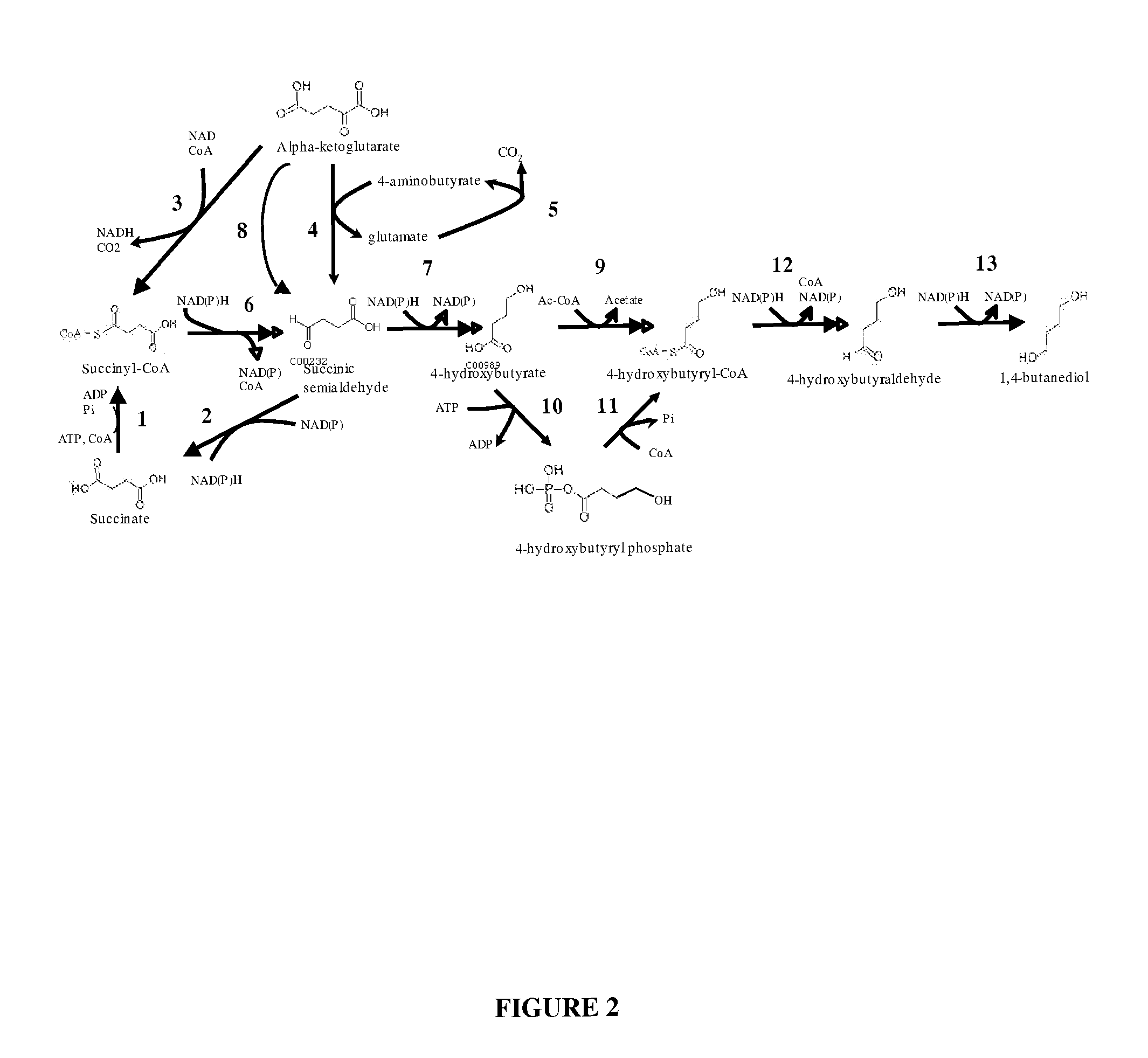
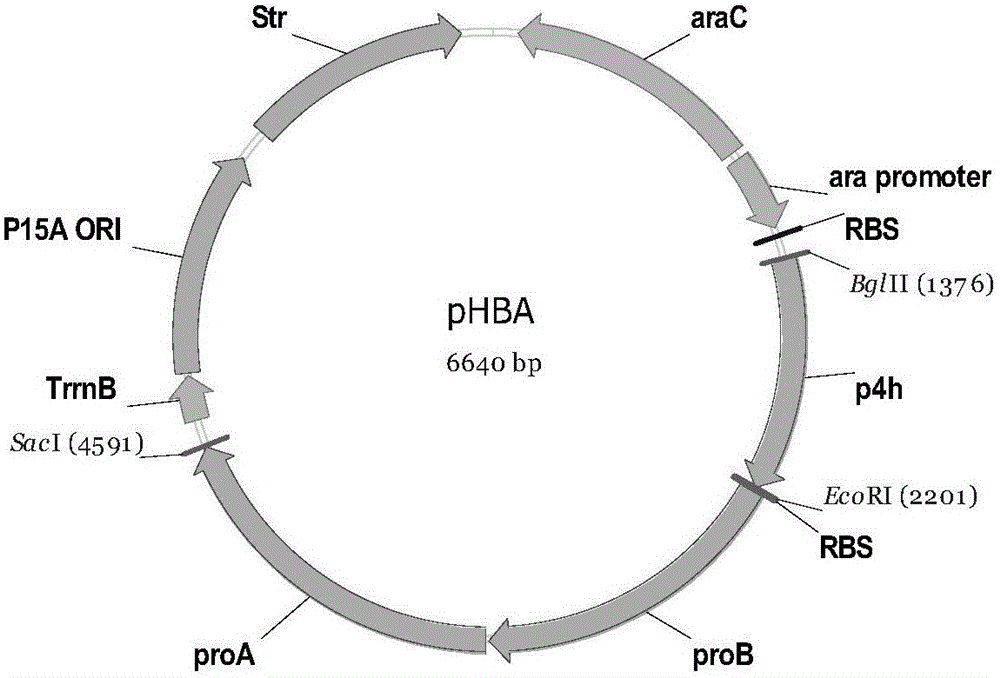
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of 1,4-butanediol and its precursors
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-hydroxybutanoic acid (4-HB) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) biosynthetic pathways. The pathways include exogenous nucleic acids encoding a) an α-ketoglutarate decarboxylase; b) a 4-hydroxybutanoate dehydrogenase; c) a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA:acetyl-CoA transferase or a butyrate kinase and a phosphotransbutyrylase; d) an aldehyde dehydrogenase, and e) an alcohol dehydrogenase, wherein the exogenous nucleic acids are expressed in sufficient amounts to produce 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO). Also provide is a method for the production of 1,4-BDO. The method includes culturing the non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-HB and 1,4-BDO biosynthetic pathways substantially anaerobic conditions for a sufficient period of time to produce 1,4-BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Compositions and methods for silencing aldehyde dehydrogenase
InactiveUS8999950B2Increasing the amount of acetaldehydeIntensifying the adverse effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcoholismsLipid formation
The present invention provides compositions comprising therapeutic nucleic acids such as interfering RNA (e.g., dsRNA such as siRNA) that target aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene expression, lipid particles comprising one or more (e.g., a cocktail) of the therapeutic nucleic acids, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles (e.g., for treating alcoholism in humans).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Novel alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenases
The present invention is directed to a recombinant enzymes having alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity which comprises one or more recombinant polypeptides selected from the group consisting of polypeptides which are identified by SEQ ID NO 5, SEQ ID NO 6, SEQ ID NO 7, SEQ ID NO 8 and chimeric recombinant polypeptides that are a chimeric combination of at least two of the following amino acid sequences identified by SEQ ID NO 5, SEQ ID NO 6, SEQ ID NO 7, SEQ ID NO 8 and functional derivatives of the polypeptides identified above which contain addition, insertion, deletion and / or substitution of one or more amino acid residues, wherein said enzymatic polypeptides have said alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. DNA molecules encoding the recombinant polypeptides, vectors comprising such DNA molecules, host cells transformed by such vectors and processes for the production of such recombinant enzymes are provided. Furthermore, the recombinant enzymes having alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity are used for obtaining aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids, and specifically, 2-keto-L-gulonic acid an intermediate for the production of L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
Owner:ROCHE VITAMINS INC
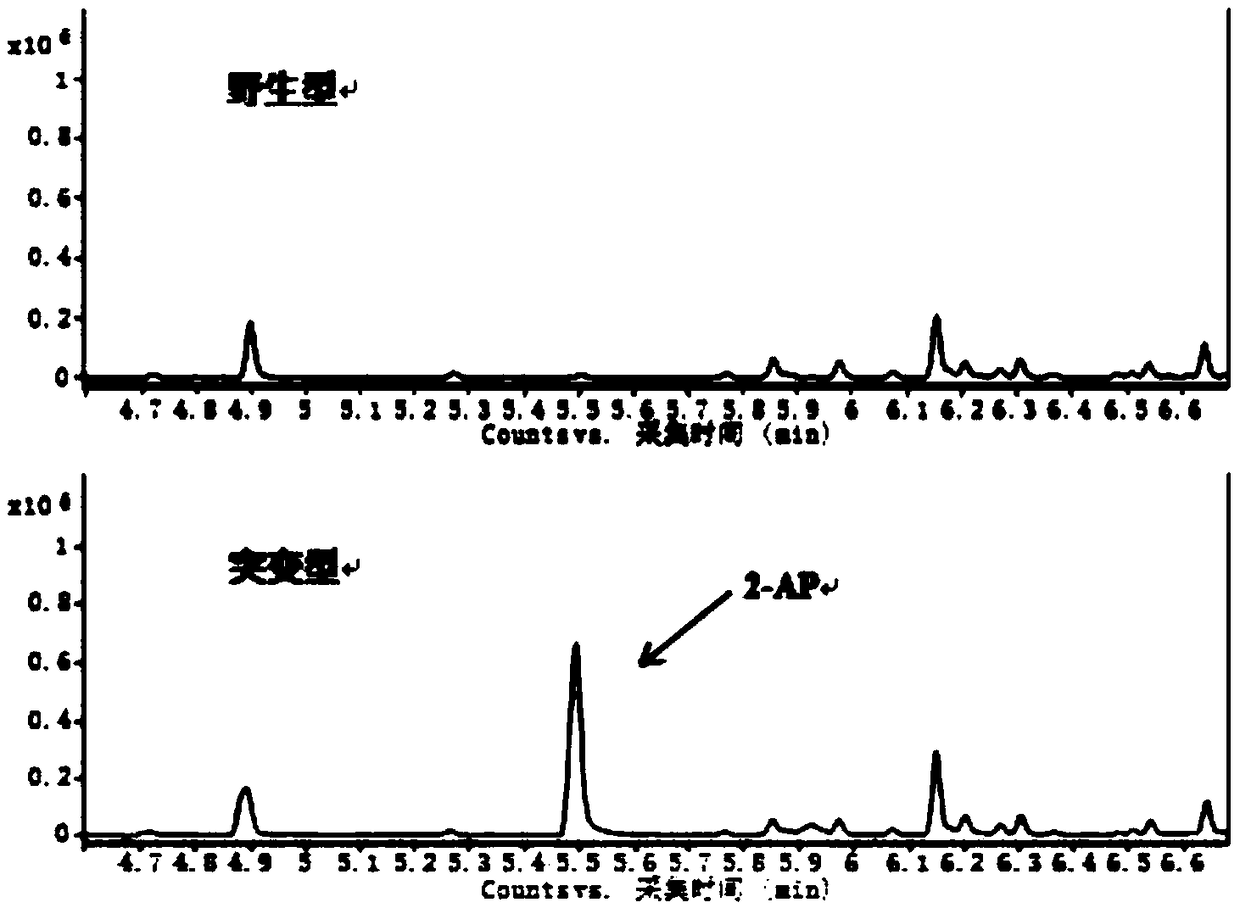
Method for creating fragrant rice by knocking out BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene by utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 system
InactiveCN108913714ASuccessful knockoutRapid creationVectorsPlant peptidesBetaine2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline
The invention discloses a method for creating fragrant rice by knocking out a BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 system, belongs to the technical field of rice breeding, and relates to a method for creating fragrant rice by applying the rice betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH2) gene. According to the method, in the fragrant rice, the function of the BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene is lost, so that a chemical substance of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline(2-AP) is accumulated so as to generate the fragrance, and a sgRNA guide sequence adopted by the CRISPR / Cas9 system is any one of the sequences which are as as shown in the SEQ ID NO.2 or the SEQ ID NO.3 in the figure 1 in the specification. The method has the advantages that the BADH2 (betaine aldehydedehydrogenase) gene can be successfully knocked out, so that the fragrant rice can be quickly created; and the operation is simple, time and labor are saved, and the breeding life of the fragrant riceis shortened.
Owner:江西省超级水稻研究发展中心
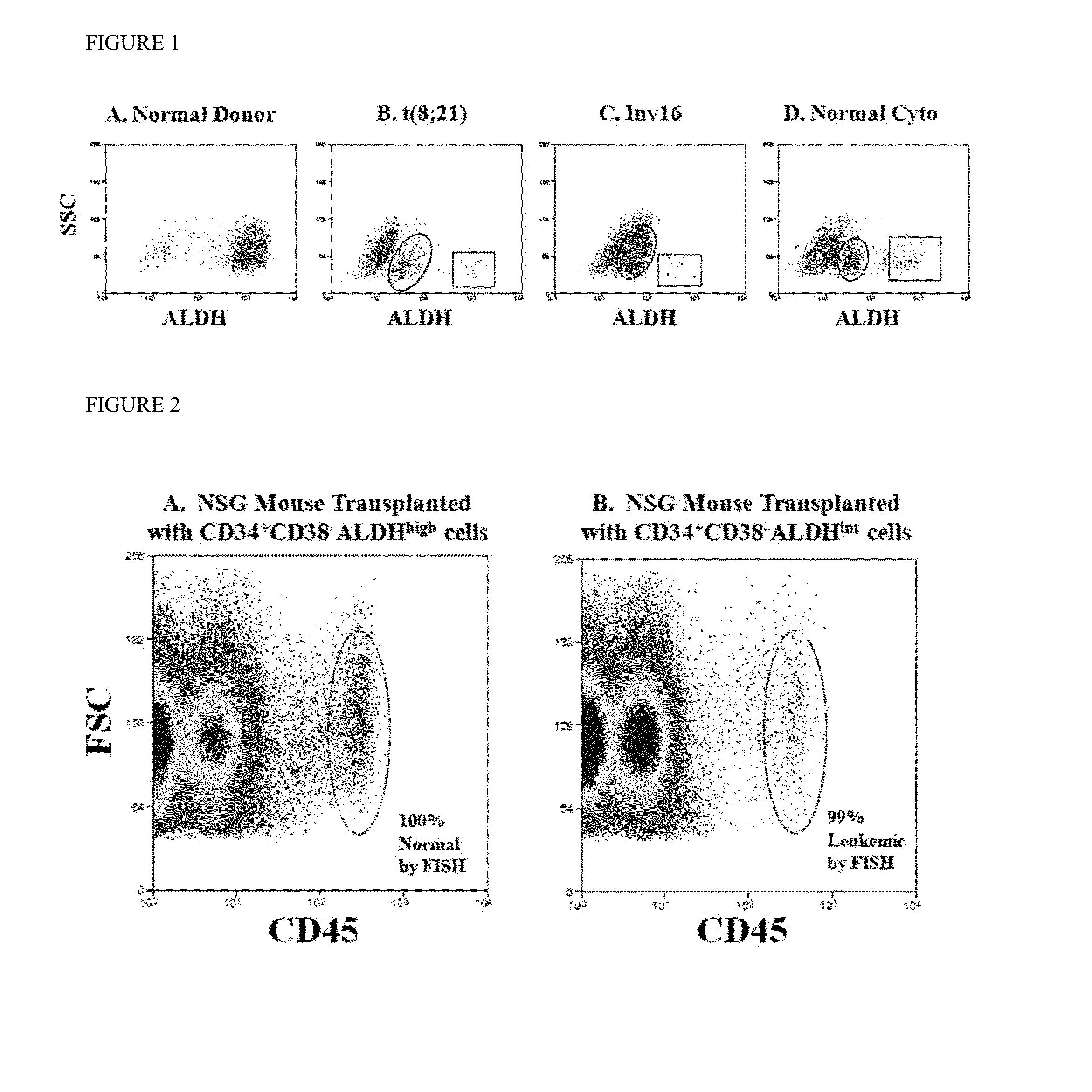
Methods for identifying leukemia stem cells and distinguishing them from normal hematopietic stem cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: uses in diagnosis, treatment, and research
ActiveUS20130079424A1Increase relapse riskIncrease riskBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCD34Minimal residual disease
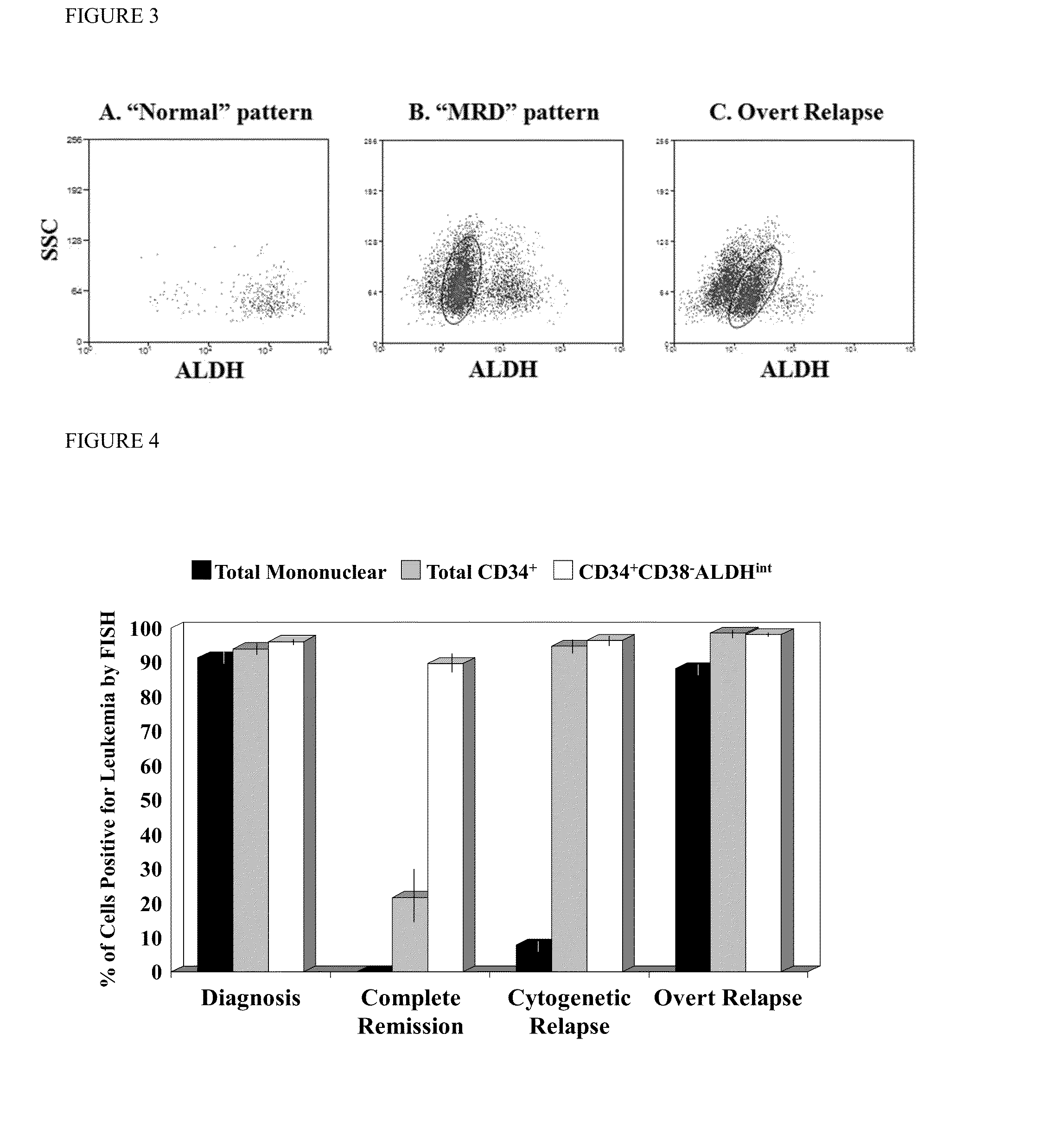
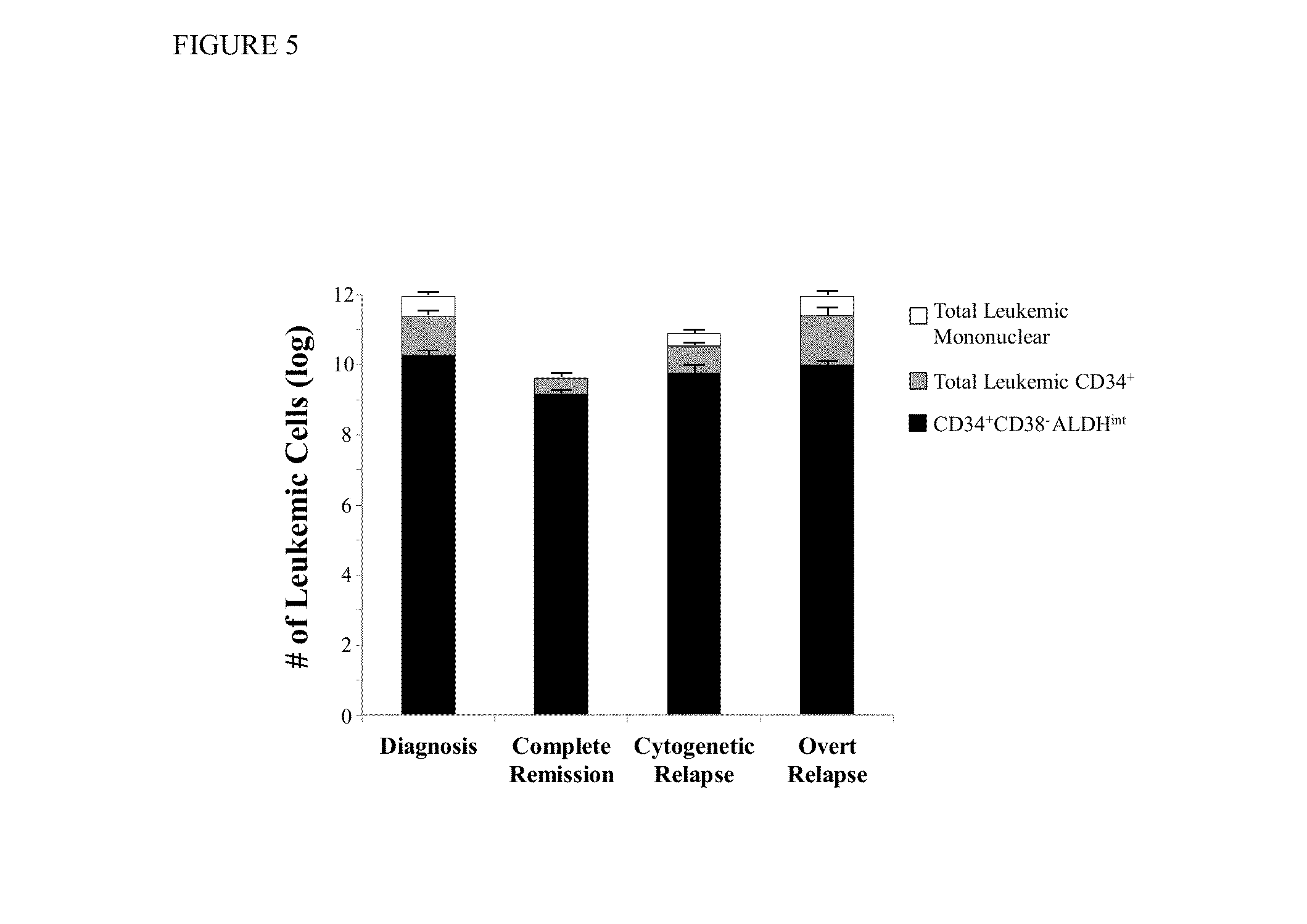
Using the methods of the present invention, intermediate (int) levels of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity reliably distinguished leukemic CD34+CD38− cells capable of engrafting immunodeficient mice, from residual normal hematopoietic stem cells that exhibited relatively higher ALDH activity. Minimal residual disease (MRD) detected during complete remission was enriched for the CD34+CD38−ALDHint leukemic cells, and the presence of these cells after therapy highly correlated with subsequent clinical relapse. The methods of the present invention can distinguish normal from leukemic CD34+CD38− cells, and identifies those AML cells associated with relapse. Methods of prediction of relapse of AML patients and methods of treatment are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Stem Cell Populations and Methods of Use
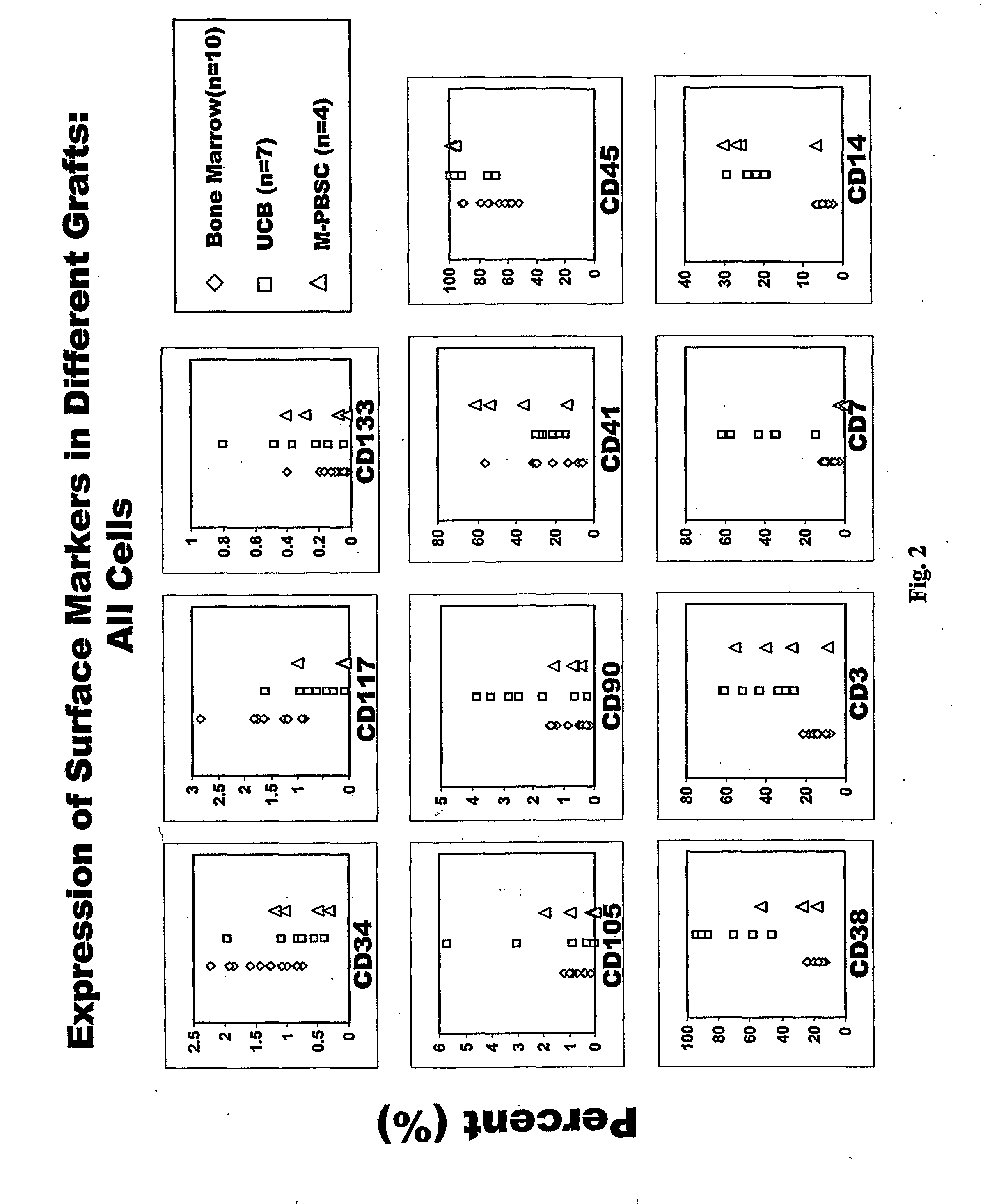
Populations of stem cells and methods for their isolation and use are provided. These stem cell populations comprise aldehyde dehydrogenase positive (ALDHbr) cells isolated from bone marrow, and ALDHbr CD105+ cells derived from any stem cell source. These populations may also comprise cells expressing such surface markers as CD34, CD38, CD41, CD45, CD105, CD133, CD135, CD117, and HLA-DR, and / or are substantially free from such cell surface markers as CD3, CD7, CD 10, CD 13, CD 14, C1319, CD33, CD35, CD56, CD 127, CD 138, and glycophorin A. The population may also comprise cells expressing CD90. The stem cell populations of the invention are isolated from a stem cell source such as bone marrow, peripheral blood, umbilical cord blood, and fetal liver. Methods of the invention comprise isolating and purifying stem cell populations from stem cell sources, and methods of using these cells to reconstitute, repair, and regenerate tissues.
Owner:ALDAGEN
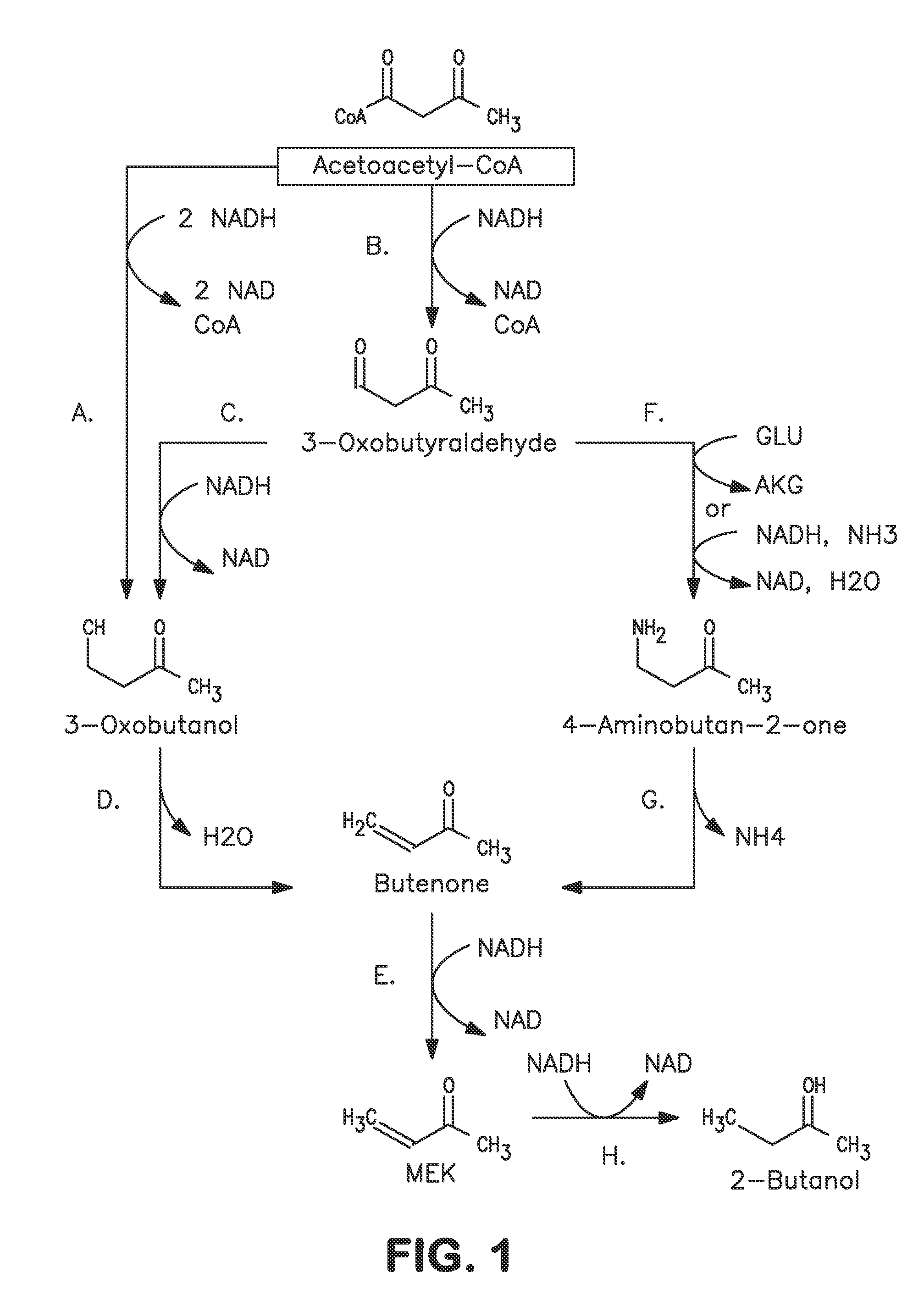
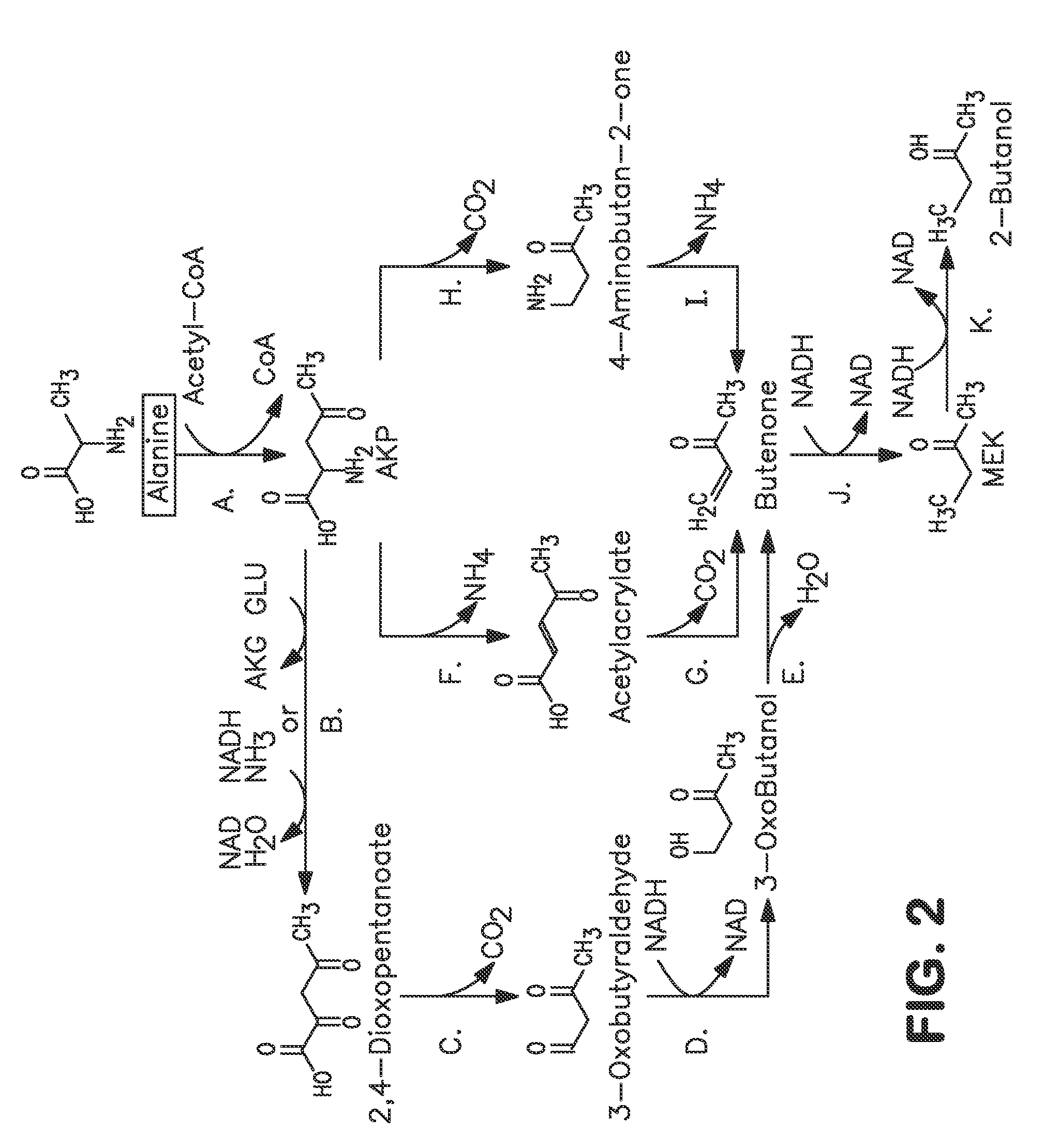
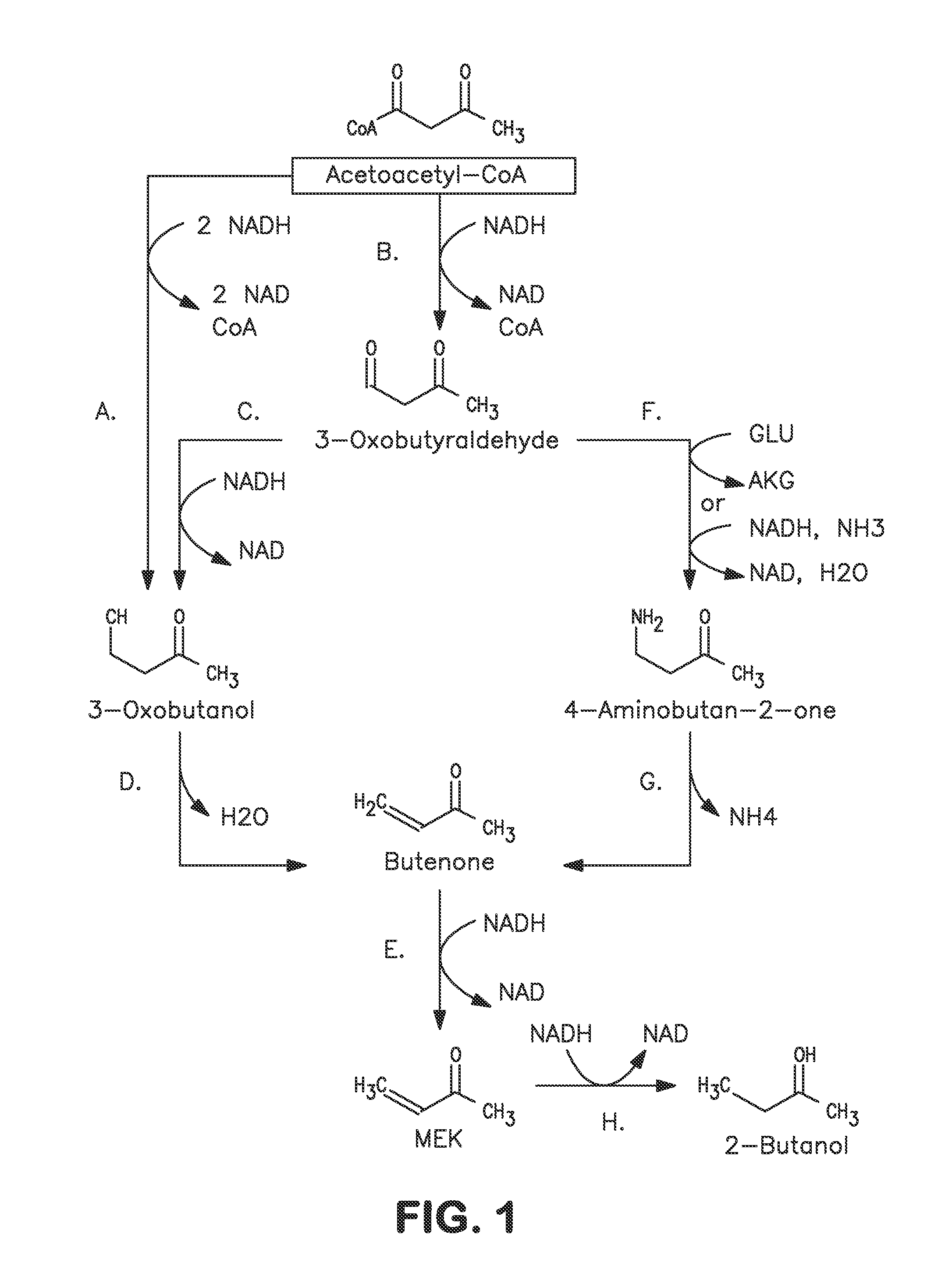
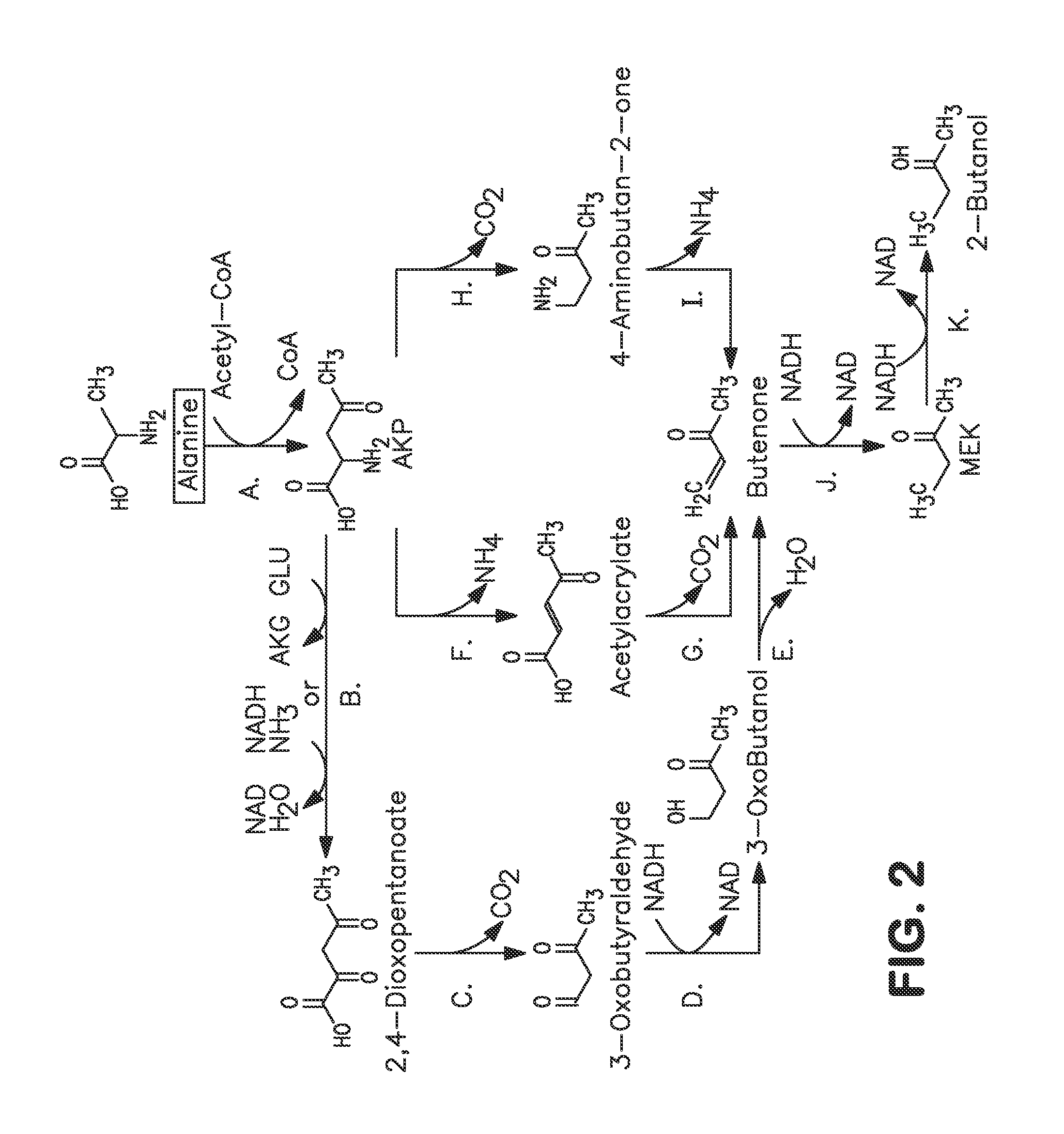
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
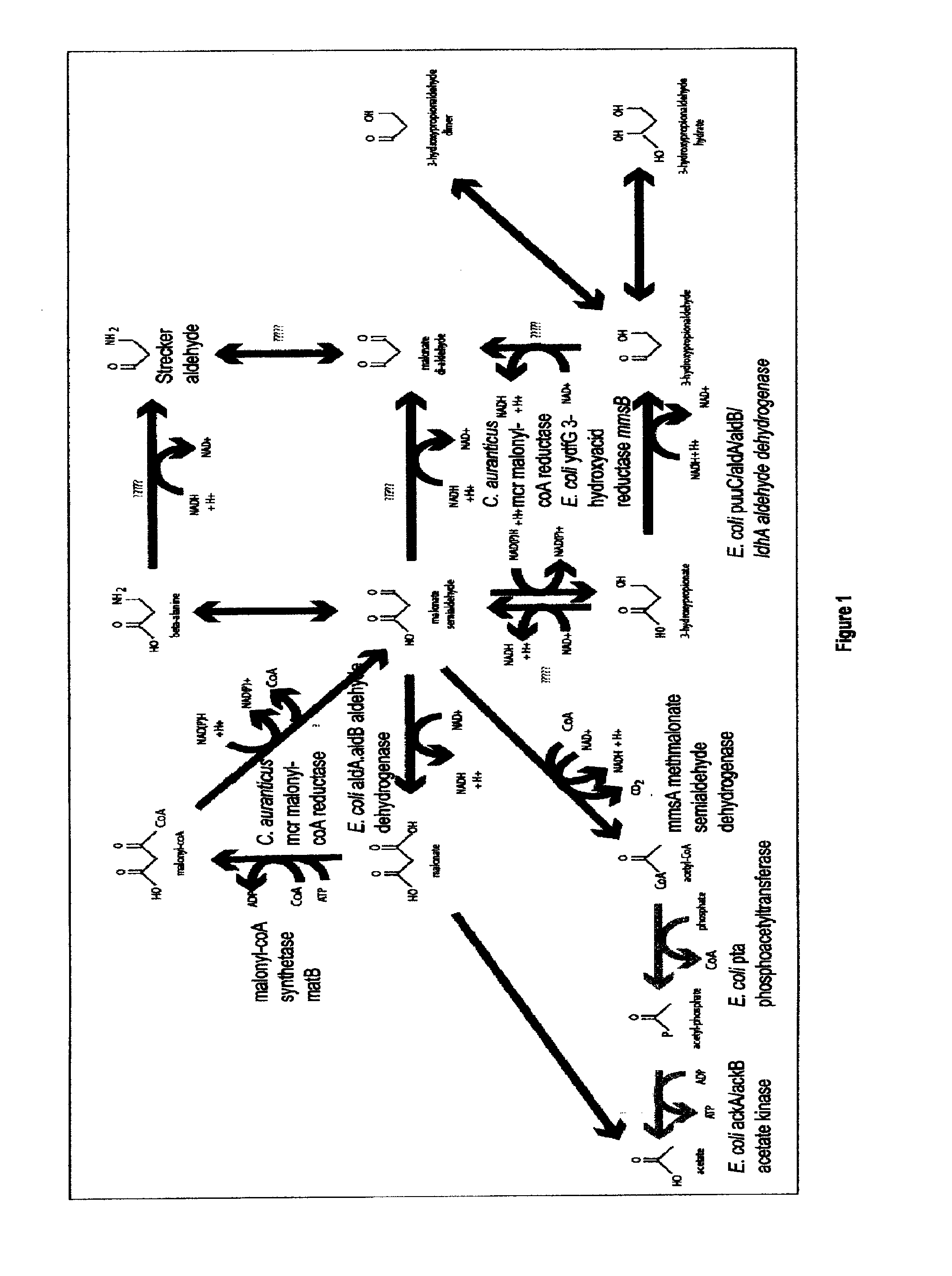
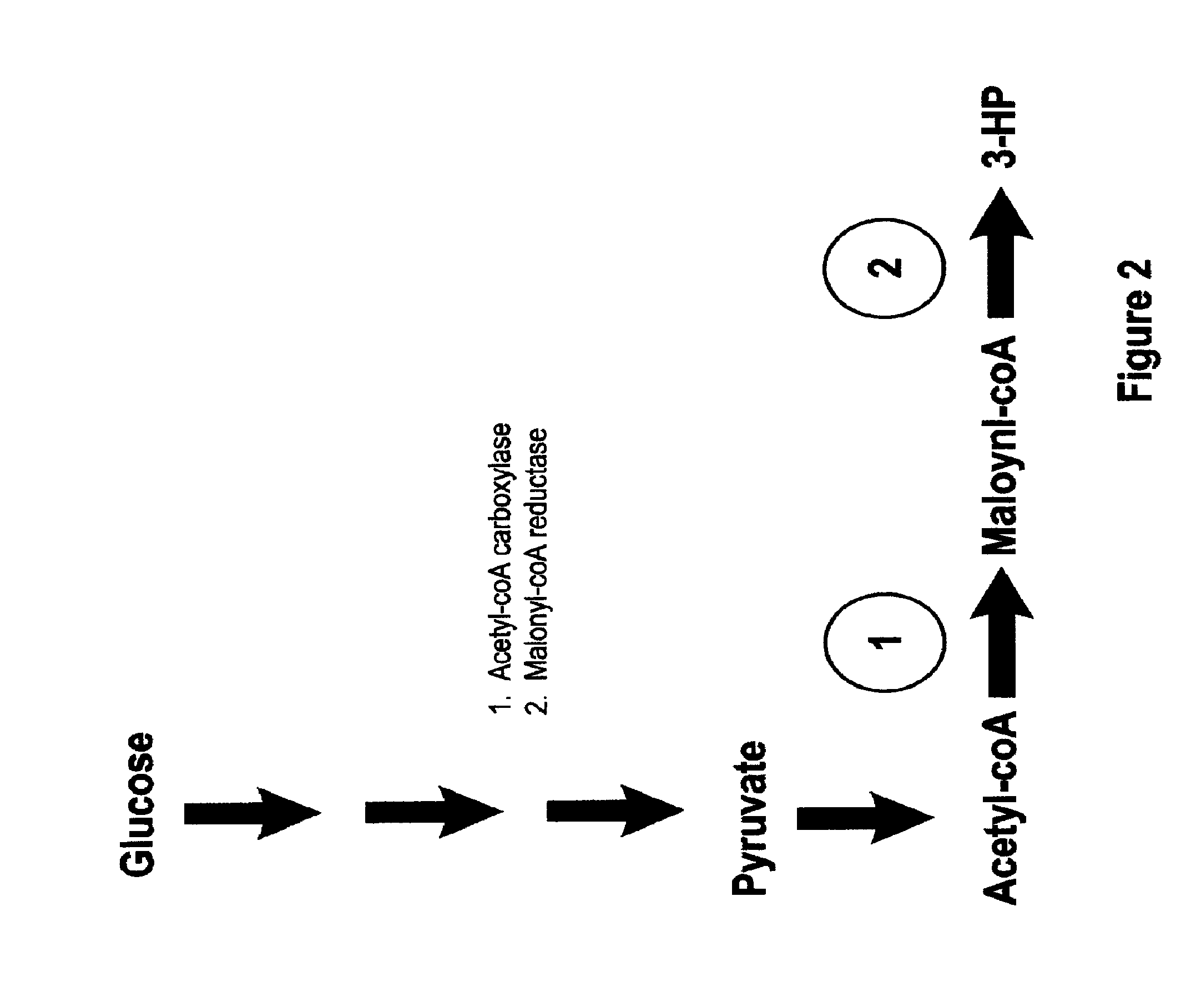
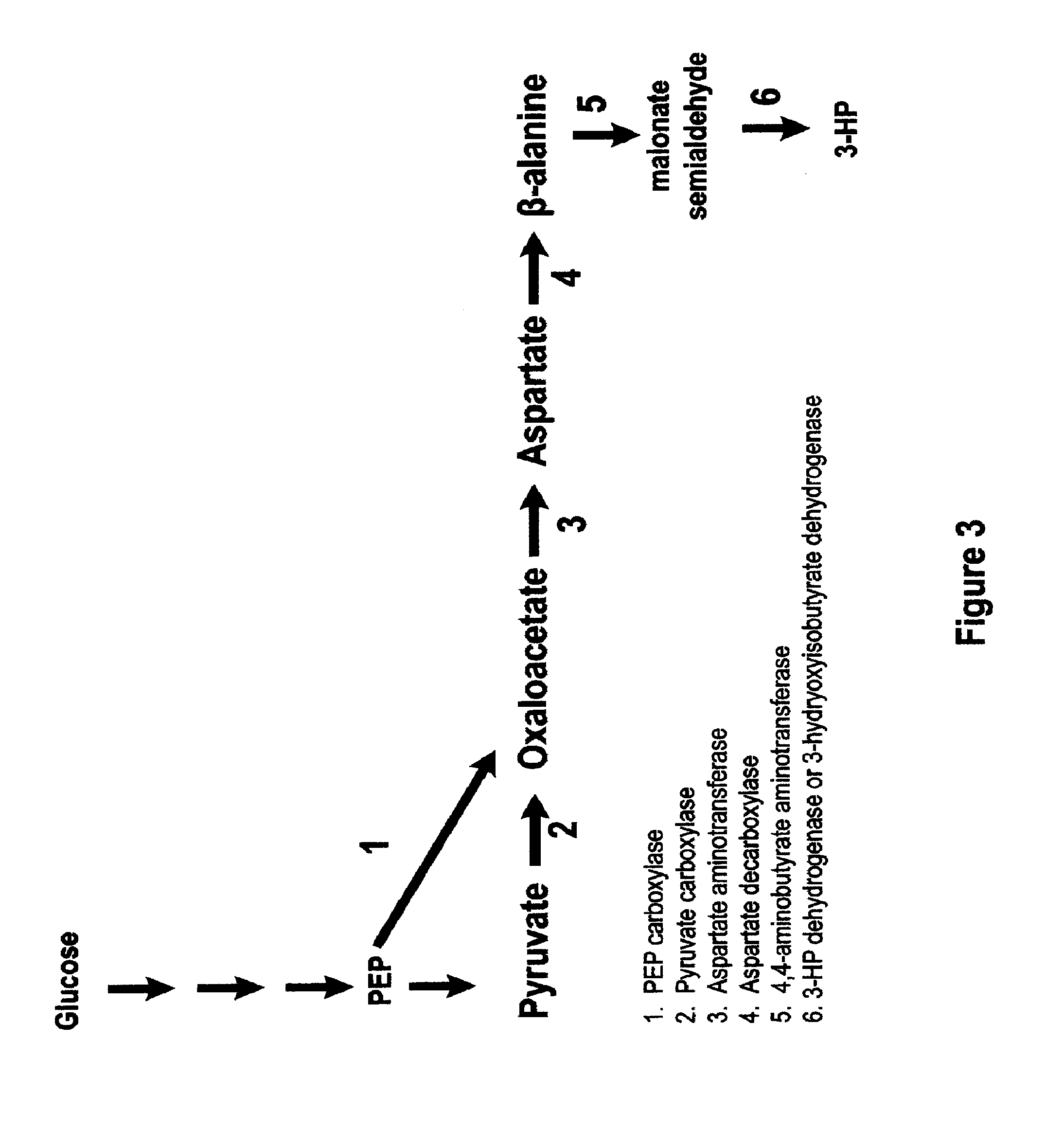
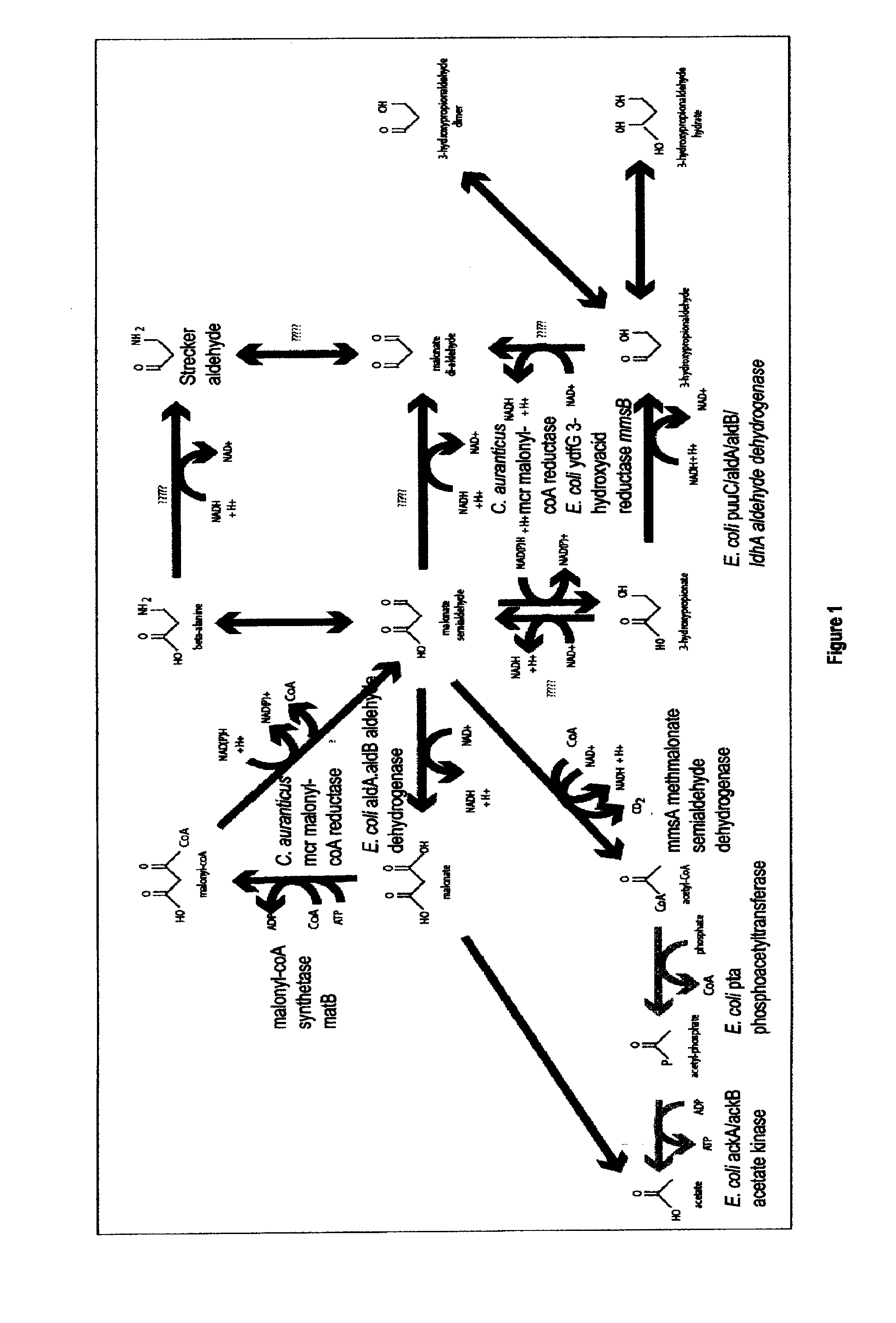
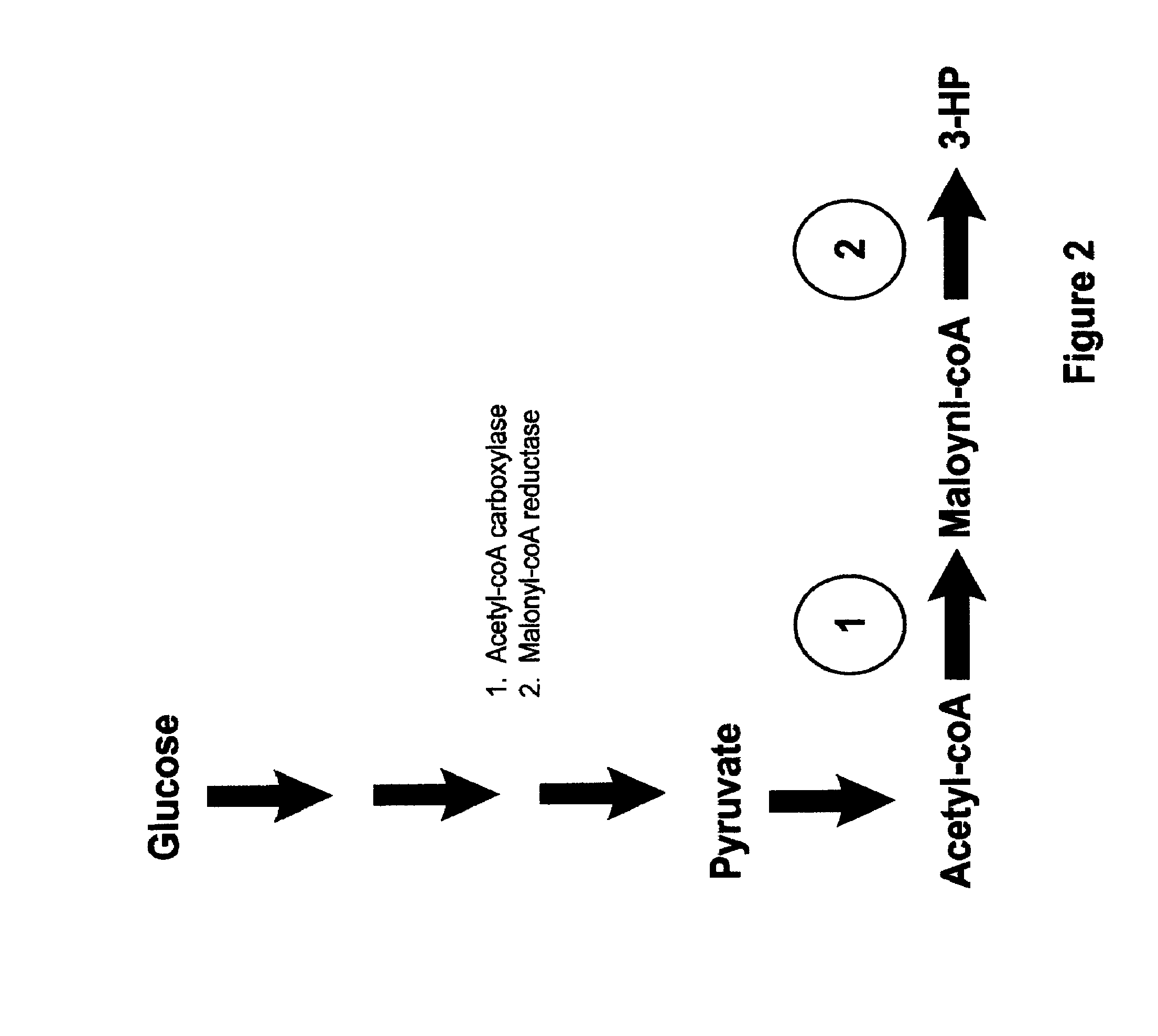
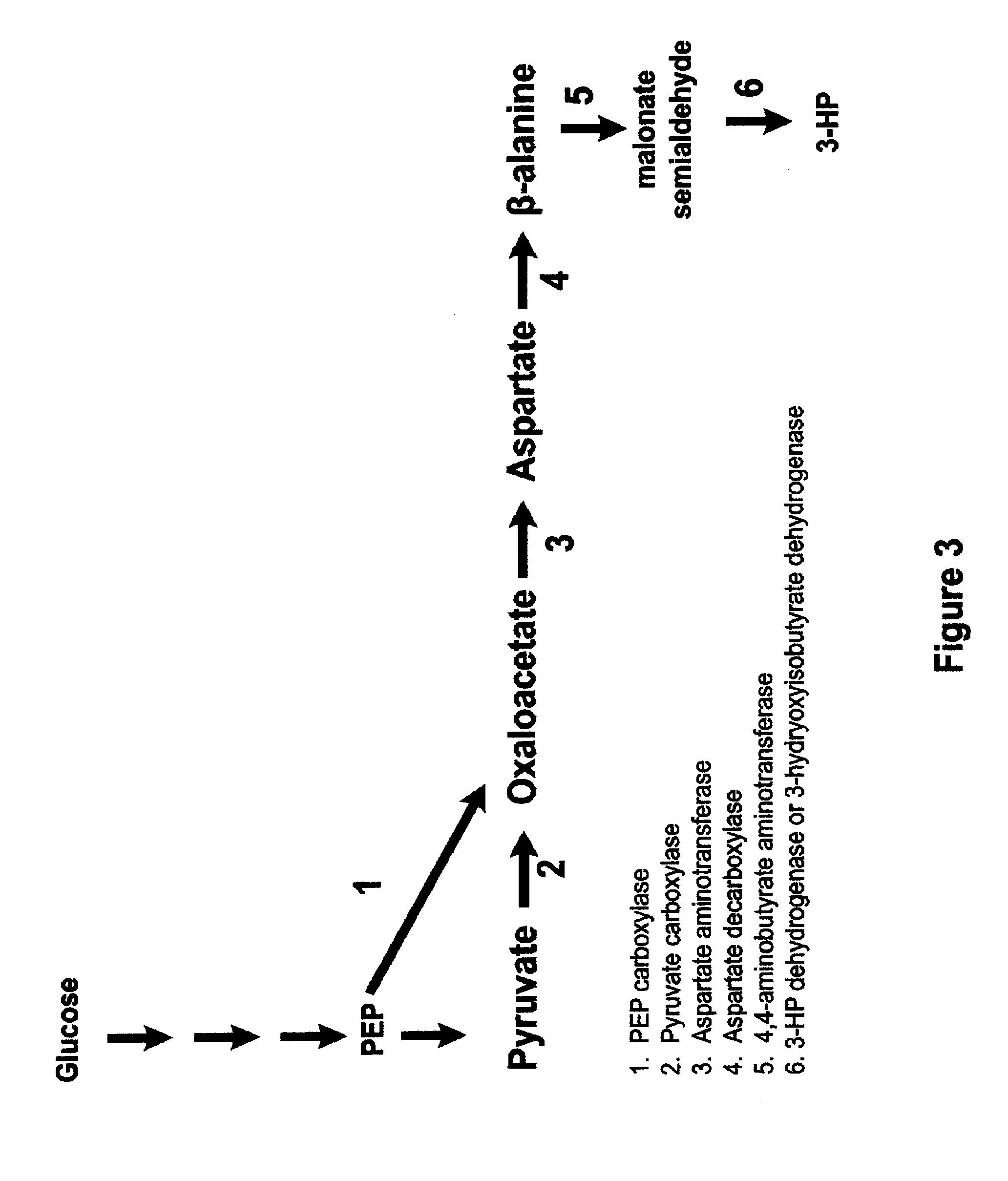
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method for detecting blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1749756AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAdenosinePeroxidase
The present invention belongs to the field of medical detection technology. The reagent kit for blood ammonia diagnosis includes buffering solution, adenosine triphophate, glutamic acid, pyruvic acid, alcohol, oxidized coenzyme, glutamine synthetase, pyruvate oxidase, hydrogen peroxidase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Through mixing the sample and reagent in certain volume ratio to produce enzyme coupling reaction, and detecting in biochemical analyzer the main wavelength absorbency change speed, the blood ammonia content is measured. The present invention can obtain the measurement result in biochemical analyzer in high sensitivity, high precision and no contamination of various foreign and internal matters.
Owner:王尔中
Microorganism producing o-acetyl-homoserine and the method of producing o-acetyl-homoserine using the microorganism
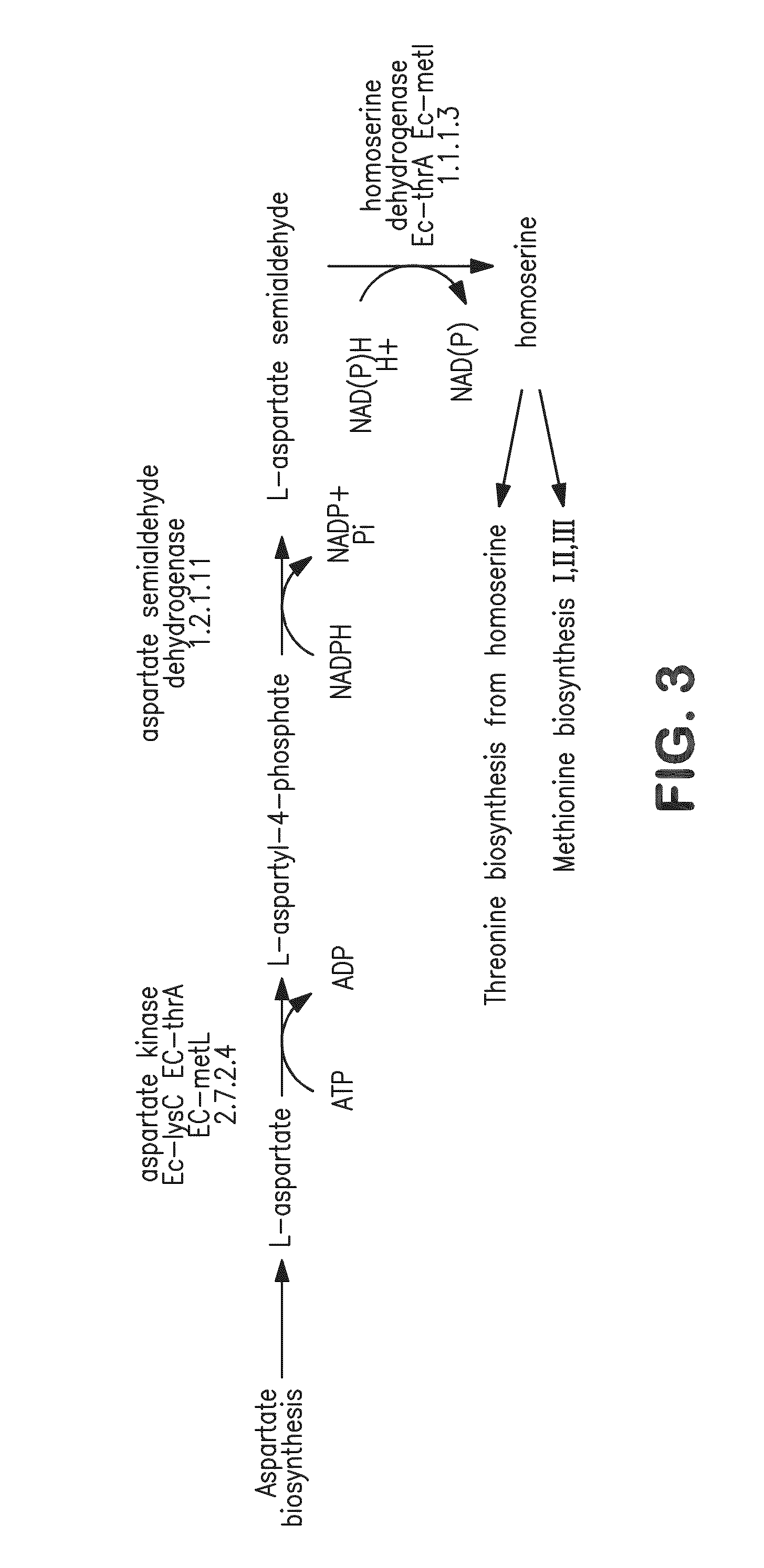
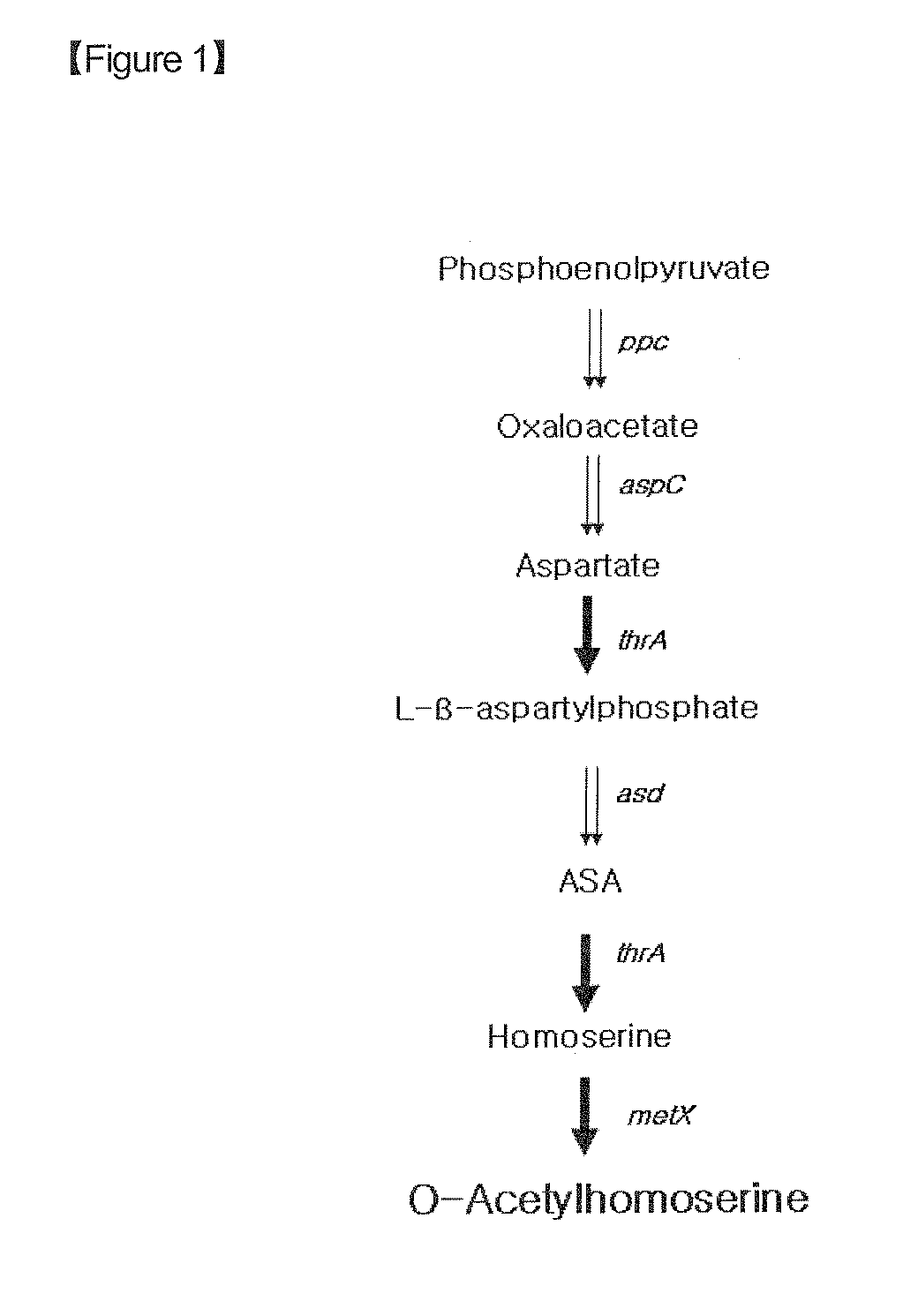
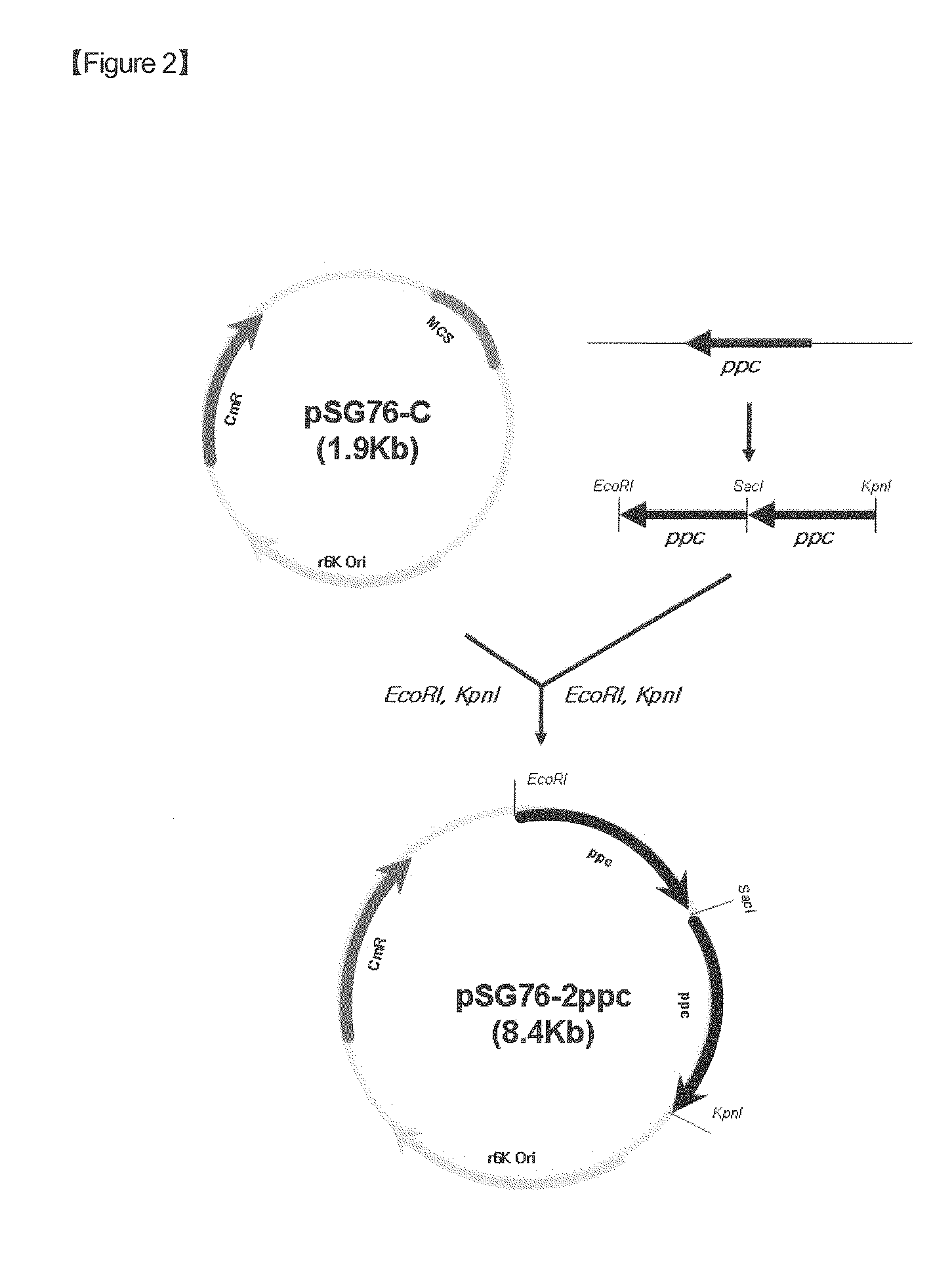
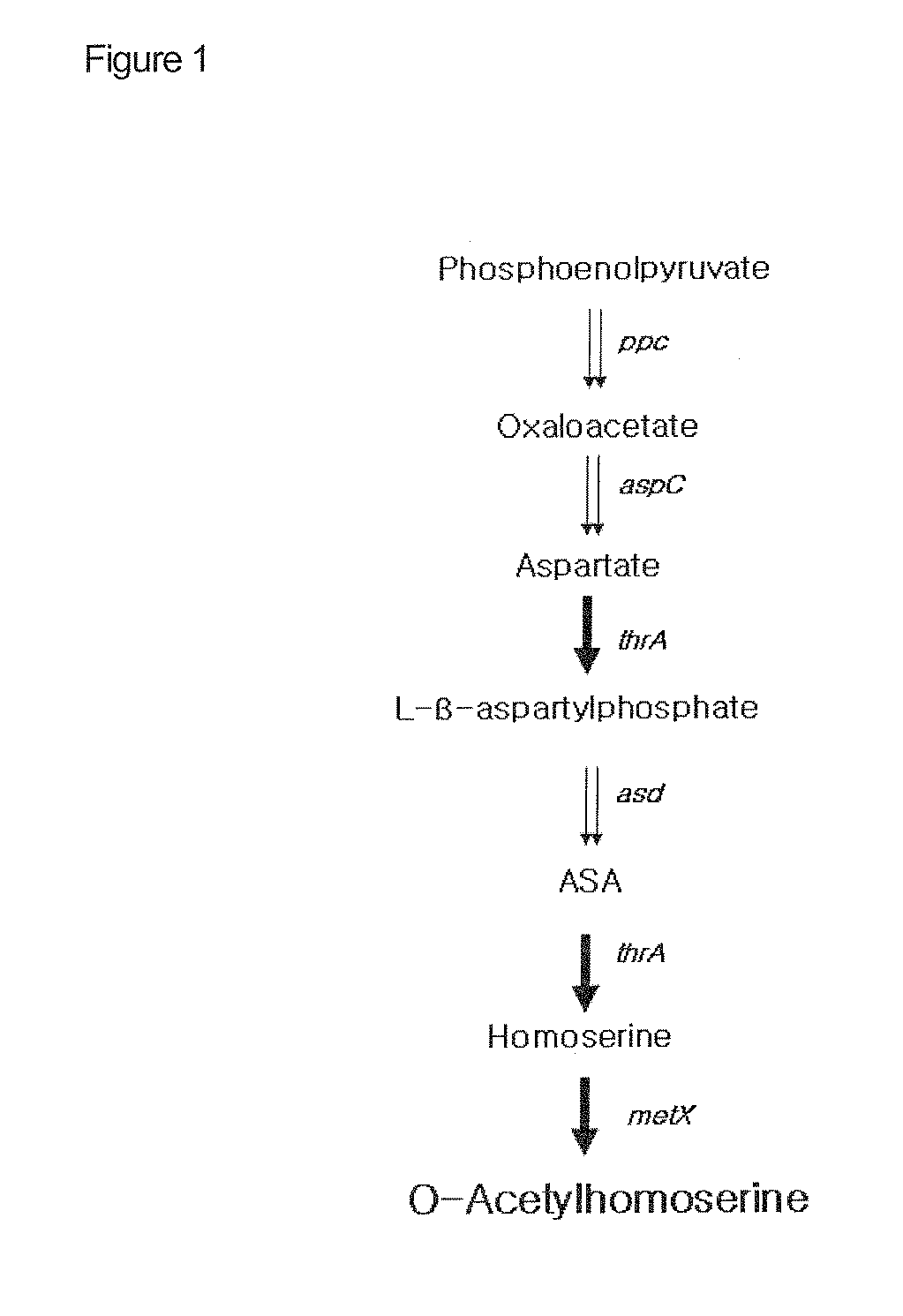
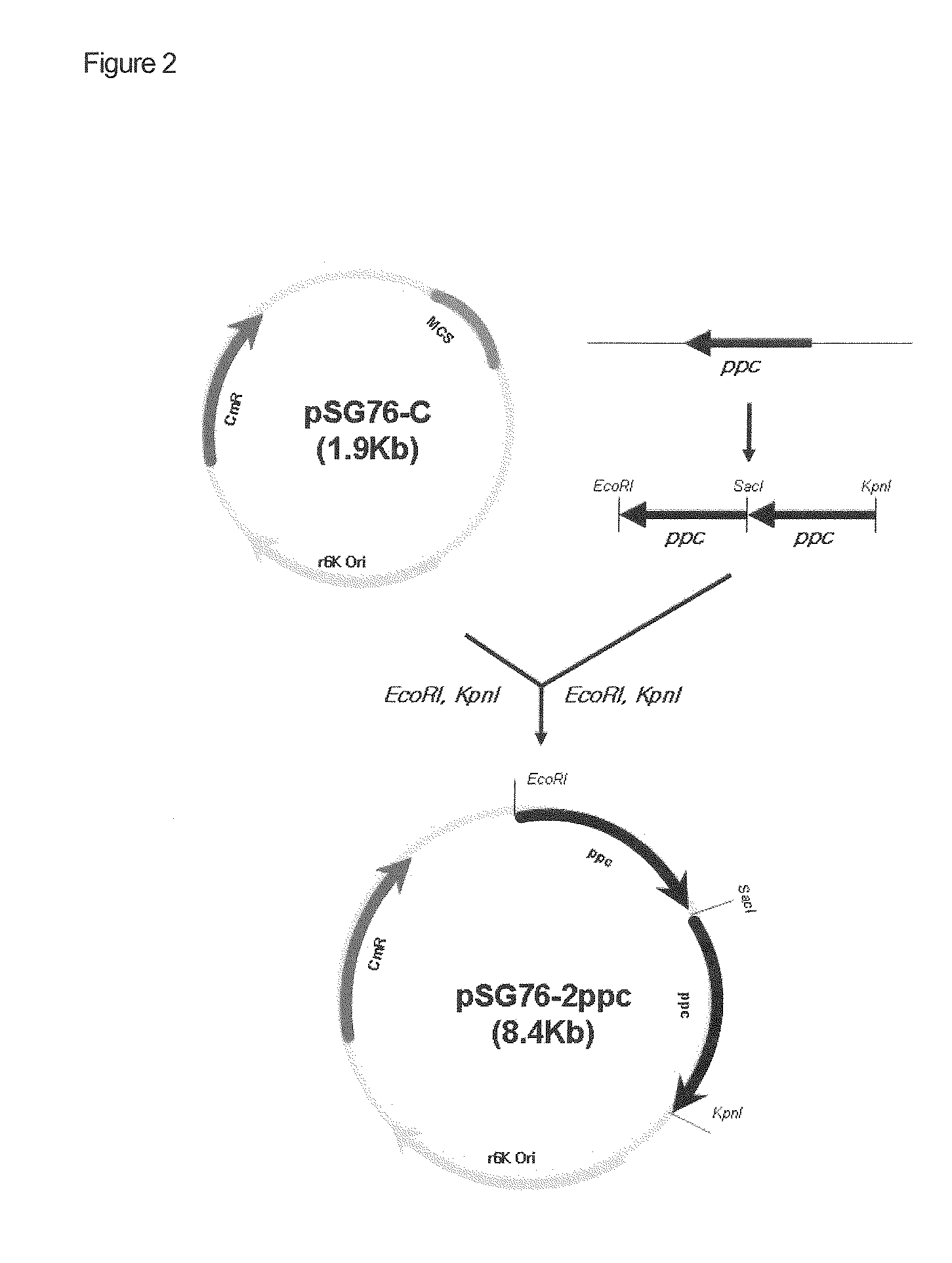
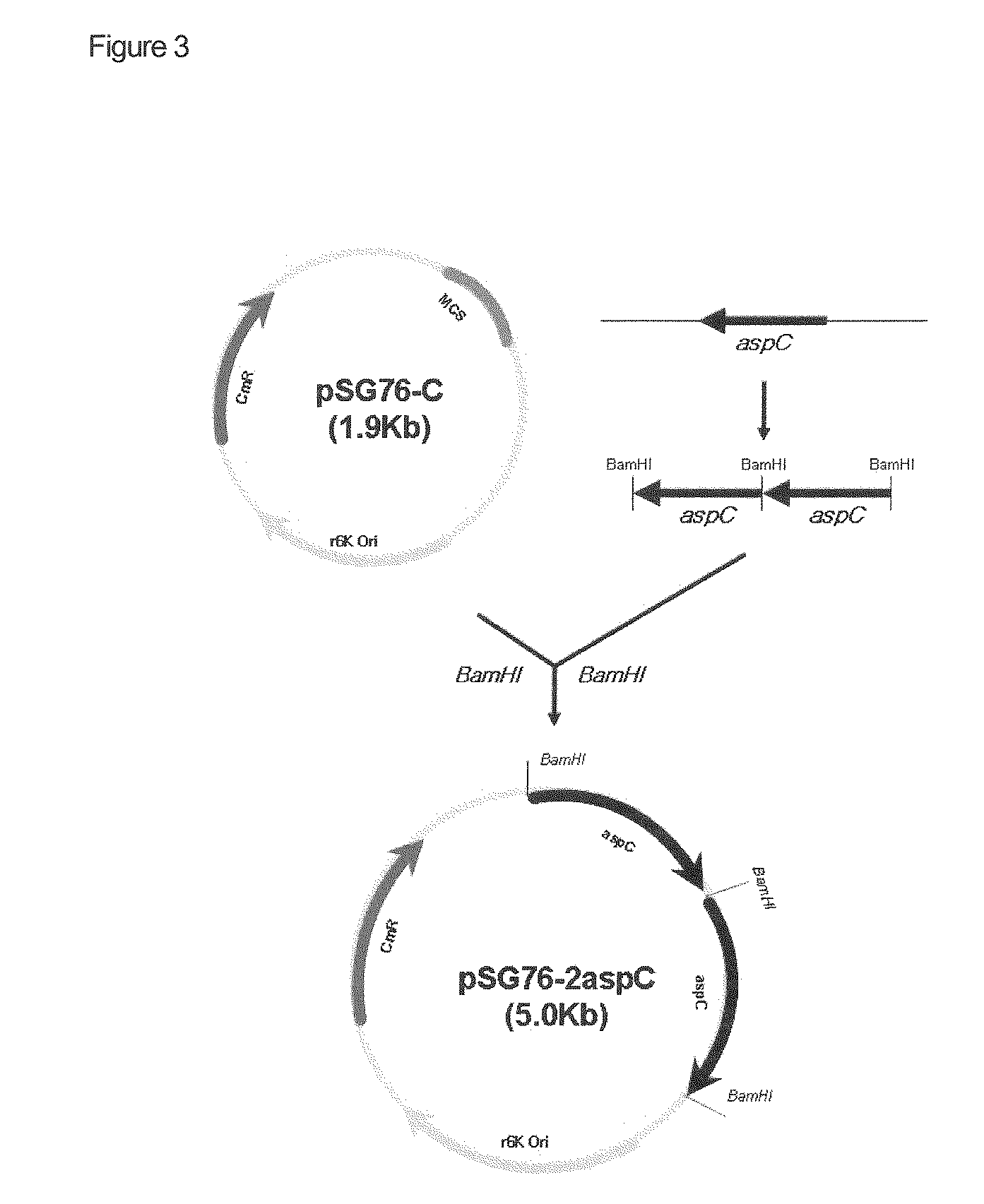
Disclosed is a strain of Escherichia sp., capable of producing O-acetyl homoserine in high yield, with the introduction and enhancement therein of the activity of: homoserine acetyl transferase, aspartokinase and homoserine dehydrogenase; and at least one enzyme selected from a group consisting of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, aspartate aminotransferase and aspartate semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase. Also, a method of producing O-acetyl homoserine using the strain is provided.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxyproplonic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
InactiveUS20130189787A1Lower metabolismDecrease microbial enzymatic conversionBacteriaUnicellular algaeEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, directed to achieve decreased microbial conversion of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) to aldehydes of 3-HP. In various embodiments this is achieved by disruption of particular aldehyde dehydrogenase genes, including multiple gene deletions. Among the specific nucleic acids that are deleted whereby the desired decreased conversion is achieved are aldA, aldB, puuC), and usg of E. coli. Genetically modified microorganisms so modified are adapted to produce 3-HP, such as by approaches described herein.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
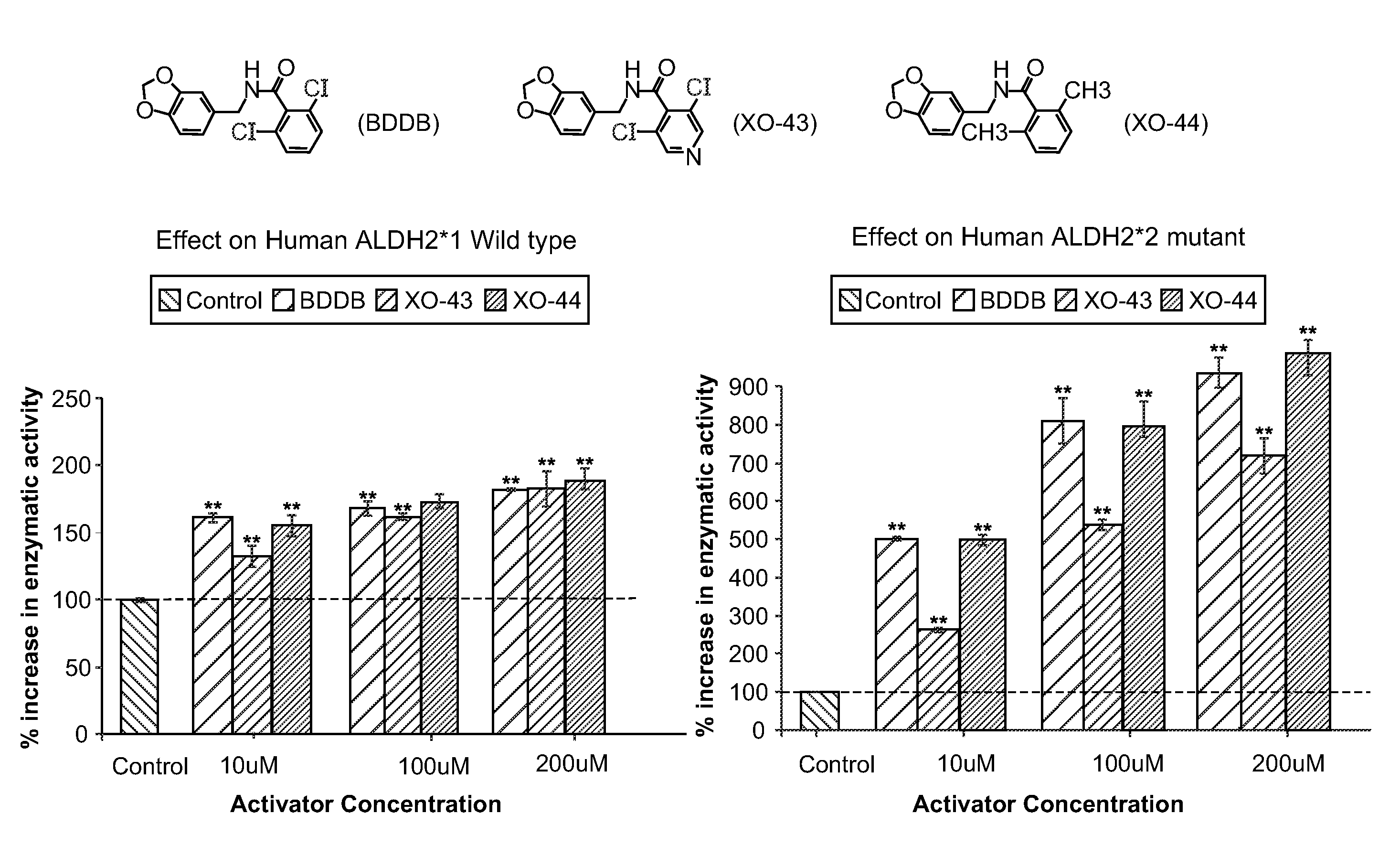
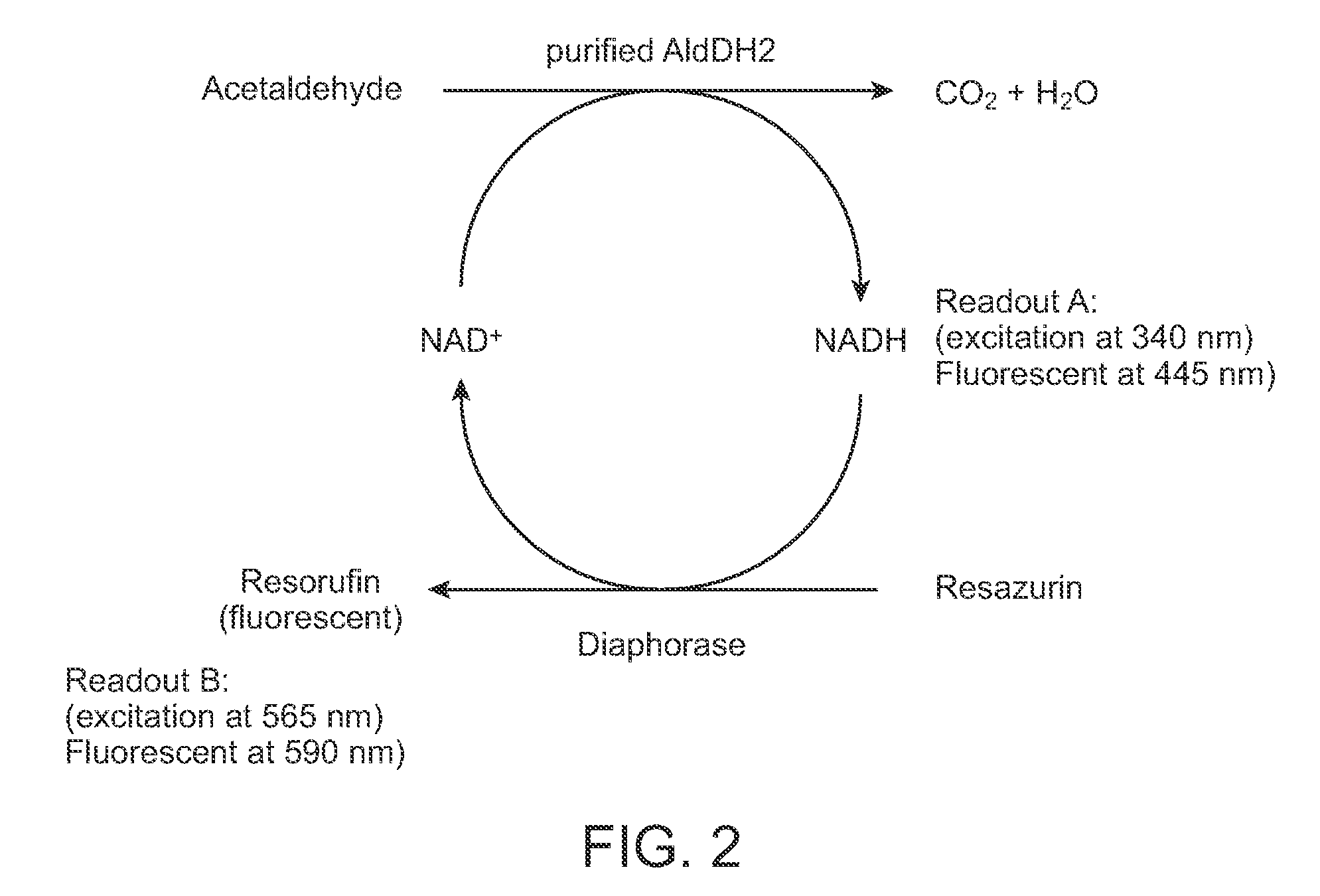
Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 modulators and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides compounds that function as modulators of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) activity; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds. The present invention provides therapeutic methods involving administering a subject compound, or a subject pharmaceutical composition. The present invention further provides assays for identifying agonists of ALDH2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
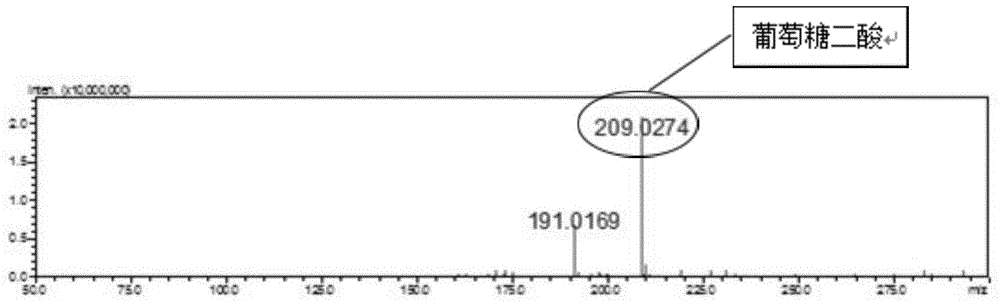
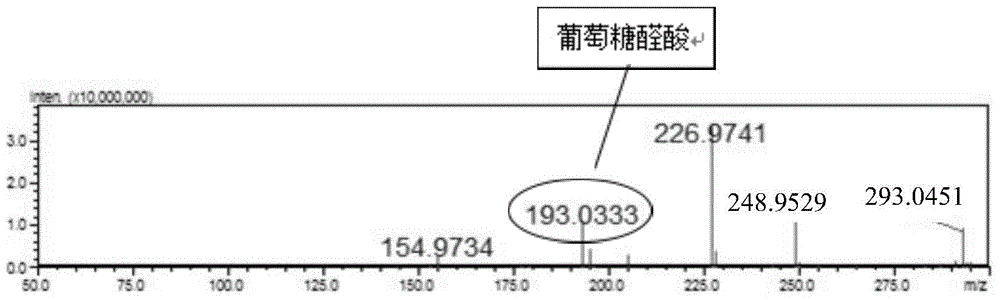
Biosynthesis method of glucuronic acid and glucuric acid
ActiveCN104312987AEfficient yieldEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of glucuronic acid and glucuric acid, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The biosynthesis method is characterized by expressing myo inositol oxygenase (MIOX) from pichia pastoris in Escherichia coli to convert myo inositol into glucuronic acid, and expressing aldehyde acid dehydrogenase (Udh) from pseudomonas putida to convert produced glucuronic acid into glucuric acid, thereby successfully establishing a synthesis path from myo inositol to glucuric acid. Recombinant Escherichia coli established by the method has very great application prospect, and a new idea is provided for generating glucuronic acid and glucuric acid through conversion by the biological method.
Owner:江苏弘康未来营养科技有限公司
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of mek and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
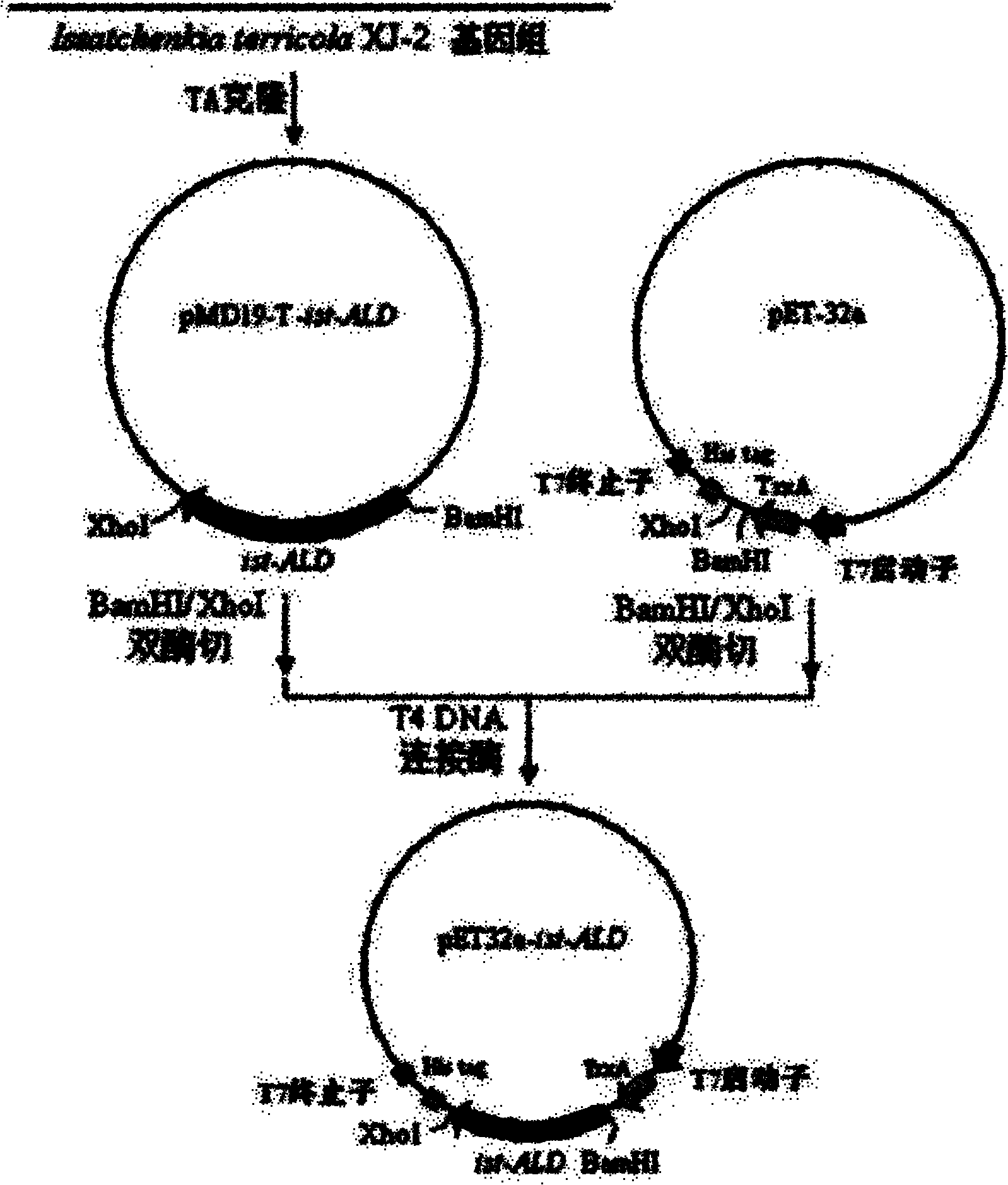
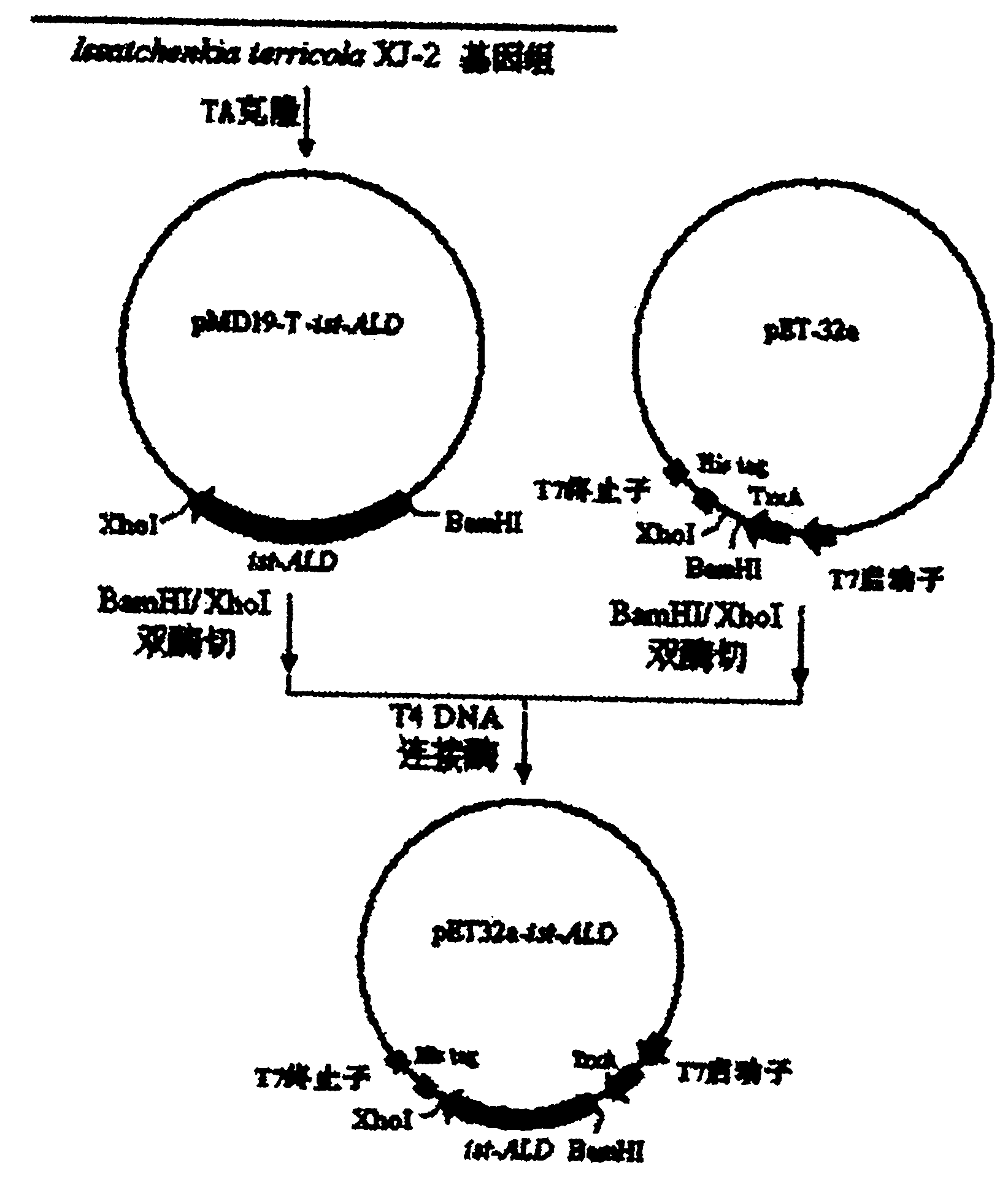
Issatchenkia terricola acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene and expression vector thereof
InactiveCN101985625AHigh activityAchieve heterologous expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsEscherichia coliOpen reading frame
The invention belongs to the technical field of food industry biology, and relates to an issatchenkia terricola acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene and an expression vector thereof. The sequence of the gene is SEQ ID No. 16, the open reading frame sequence of the gene is SEQ ID No. 17, and the amino acid sequence coded by the gene is SEQ ID No. 18. The gene is inserted into the expression vector to transform escherichia coli for IPTG (isopropyl beta-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside) inducible expression. The expressed recombinant enzyme can catalyze acetaldehyde oxidation to generate acetic acid. The invention provides a novel high-activity acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene; and the gene realizes recombinant expression in the escherichia coli, overcomes the defect of low yield of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase produced by fermenting the issatchenkia terricola XJ-2, can provide a large amount of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase for researching alcohol relieving products, and lays a foundation for constructing safe acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene engineering bacteria.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mutations in nucleic acid molecules encoding 11-CIS retinol dehydrogenase, the mutated proteins, and uses thereof
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Method for composite acetic acid bacterium culture and solid-state acetic acid fermentation
InactiveCN101875908AMild tasteIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteFruit juice
The invention relates to the table vinegar production field, in particular to a method for composite acetic acid bacterium culture and solid-state acetic acid fermentation, which solves the problems that the acetic acid bacterium is simplex in strain, the acetic acid conversion rate is low, the traditional acetic acid bacterium culture method causes instability of table vinegar quality and the like in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing Huniang 1.01, As1.41, bacterium gluconicum, acetobacter separated from a Shanxi mature vinegar grains and high-yield acetaldehyde dehydrogenase acetobacter to form the composite acetic acid bacteria, and then carrying out continuous culture in a composite culture medium comprising grape fruit juice, multi-strain nutrition-enhancing yeast, yeast extract, ethanol and distilled water to obtain a composite acetic acid bacteria culture solution; and finally carrying out solid-state acetic acid fermentation, wherein the inoculation process adopts operating techniques of mixing the grains at a pan bottom, drawing fire, burying in fire and rubbing the grains. The invention uses the advantages of multiple strains, raises the yield of gluconic acid in metabolite, produces a final product which is moderately sour and has unique flavor, improves the conversion rate of acetic acid, and shortens the fermentation period, thereby having profound significance in the progress of the table vinegar brewage technology.
Owner:山西三盟实业发展有限公司
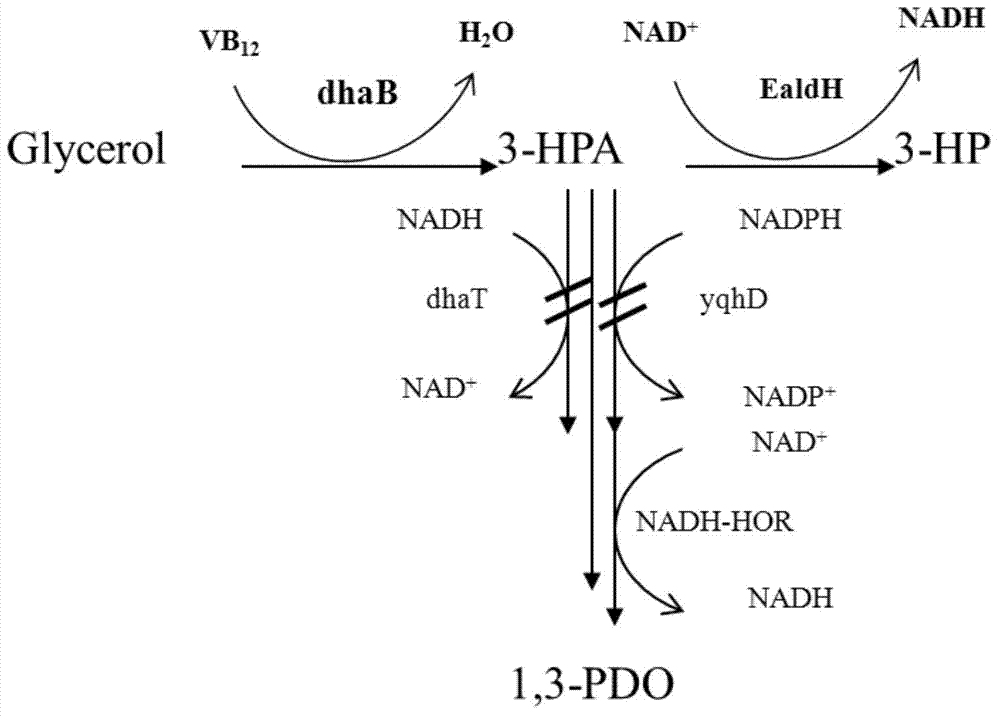
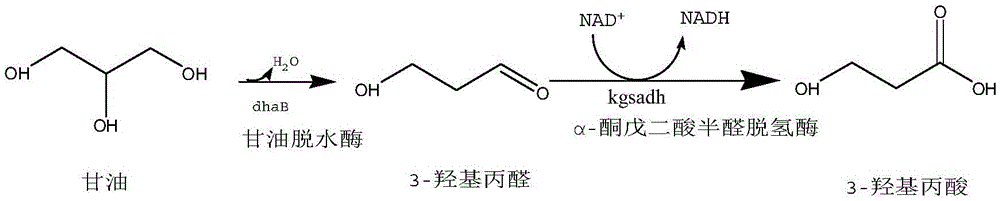
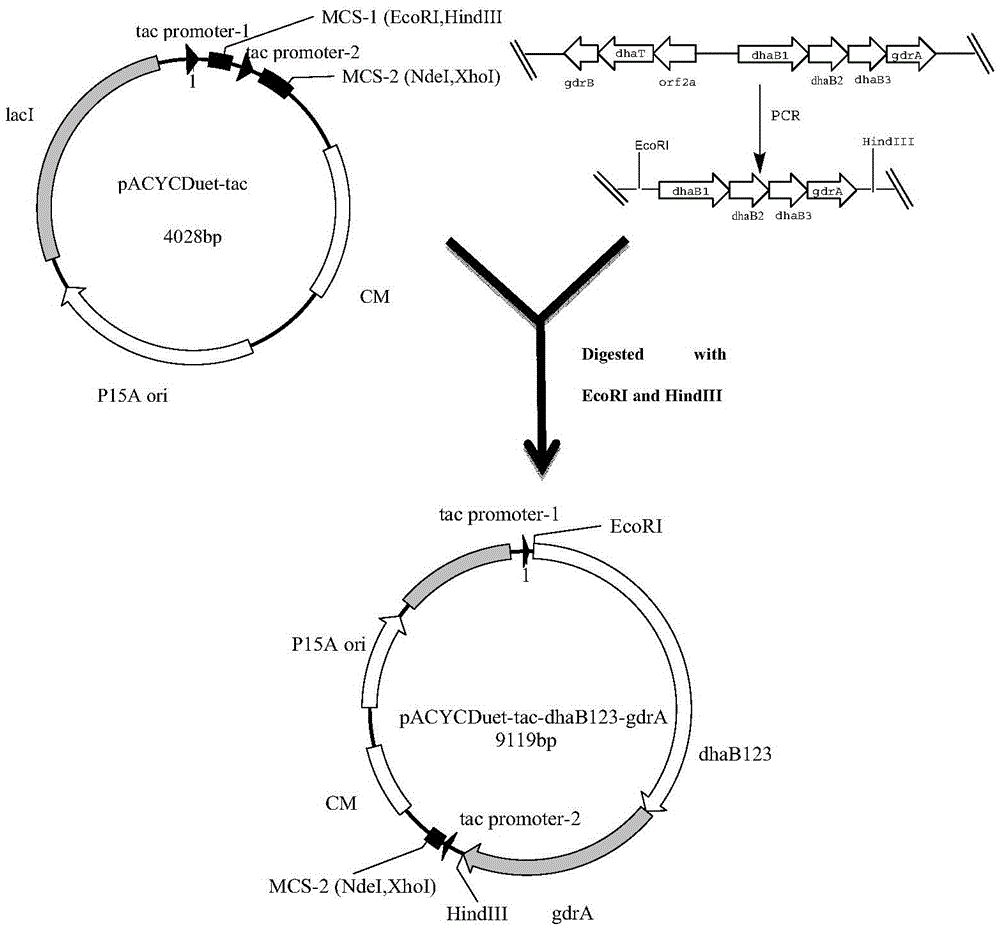
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922AReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidK pneumoniae
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microorganism producing O-acetyl-homoserine and the method of producing O-acetyl-homoserine using the microorganism
Disclosed is a strain of Escherichia sp., capable of producing O-acetyl homoserine in high yield, with the introduction and enhancement therein of the activity of: homoserine acetyl transferase, aspartokinase and homoserine dehydrogenase; and at least one enzyme selected from a group consisting of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, aspartate aminotransferase and aspartate semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase. Also, a method of producing O-acetyl homoserine using the strain is provided.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
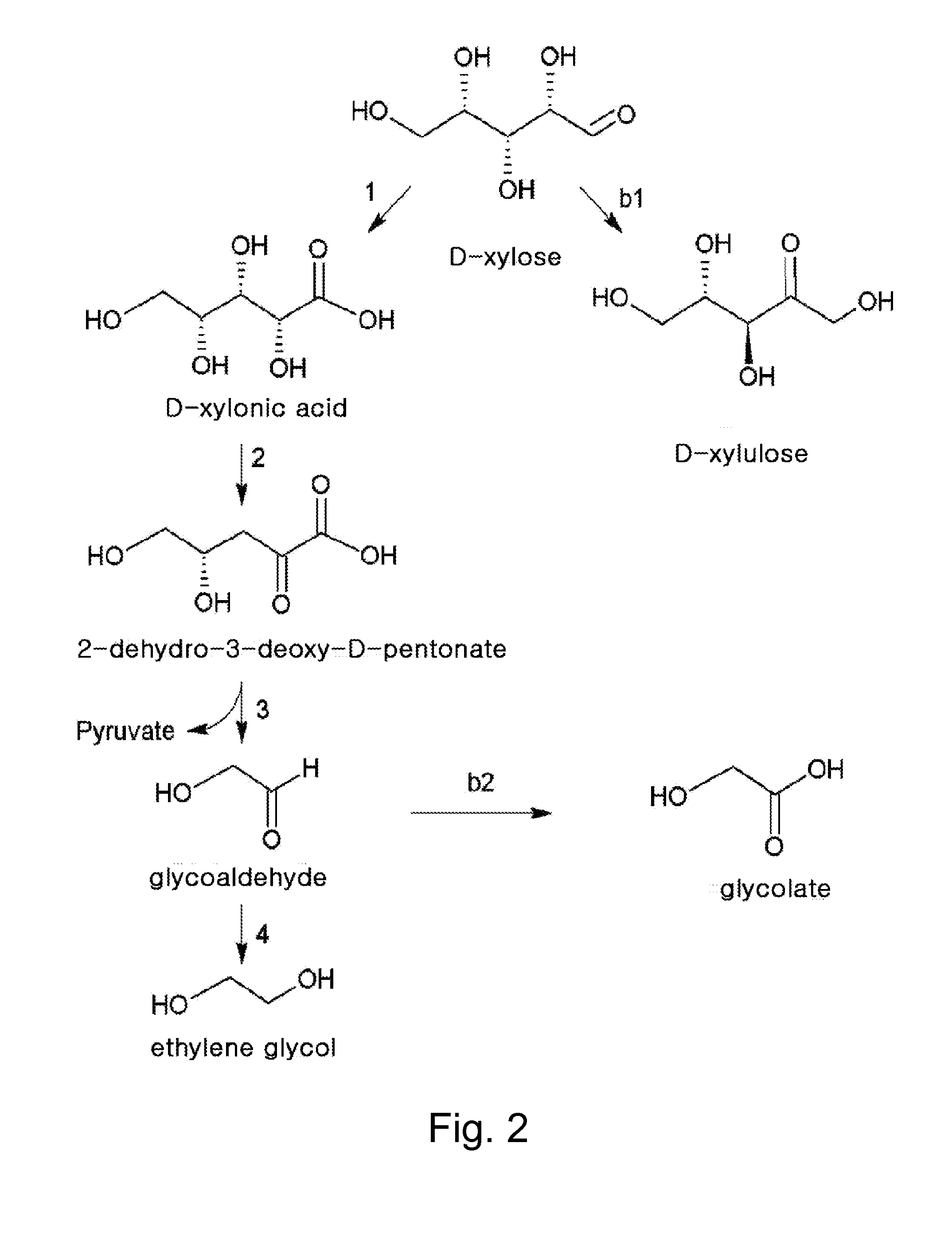
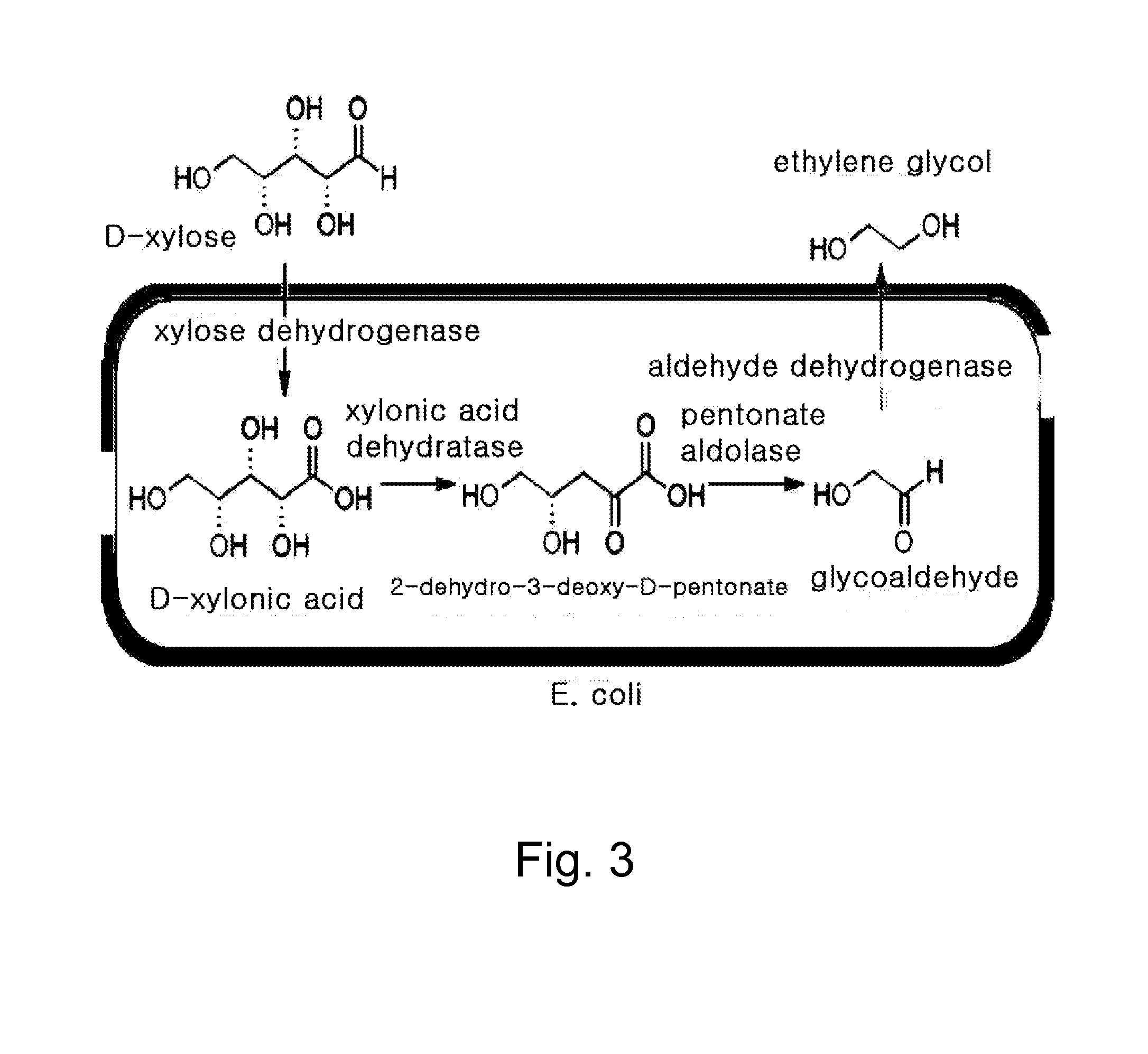
Ethane-1,2-diol producing microorganism and a method for producing ethane-1,2-diol from d-xylose using the same
Disclosed herein is a microorganism capable of producing ethane-1,2-diol from D-xylose, and a method for producing ethane-1,2-diol using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to an engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) prepared by knocking out a D-xylose isomerase gene and / or an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene within the genomic DNA of E. coli and transforming an expression vector including a D-xylose dehydrogenase gene into the E. coli, and an efficient method for producing ethane-1,2-diol from D-xylose using the engineered E. coli.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
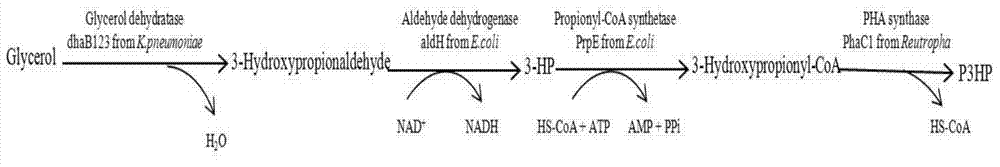
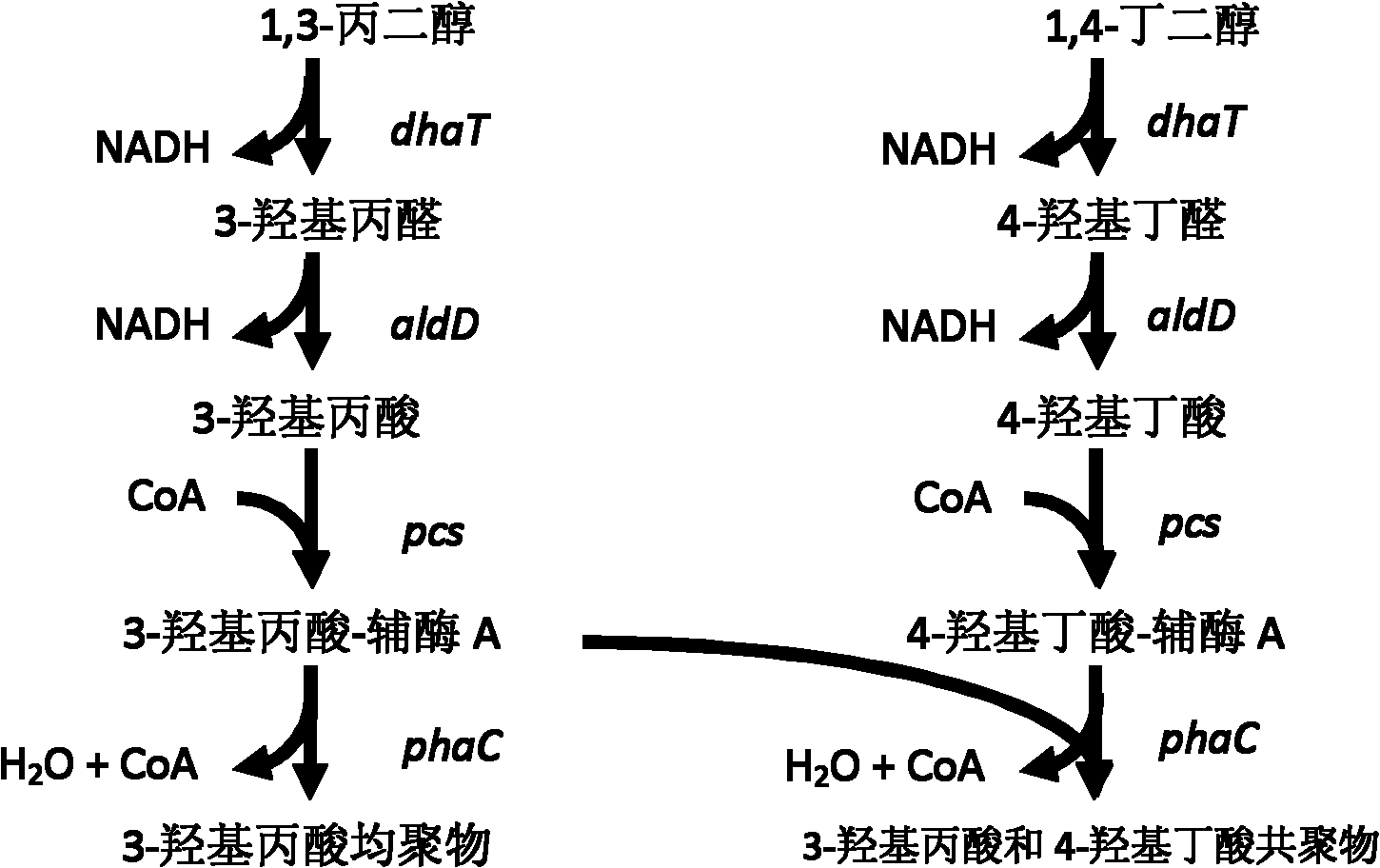
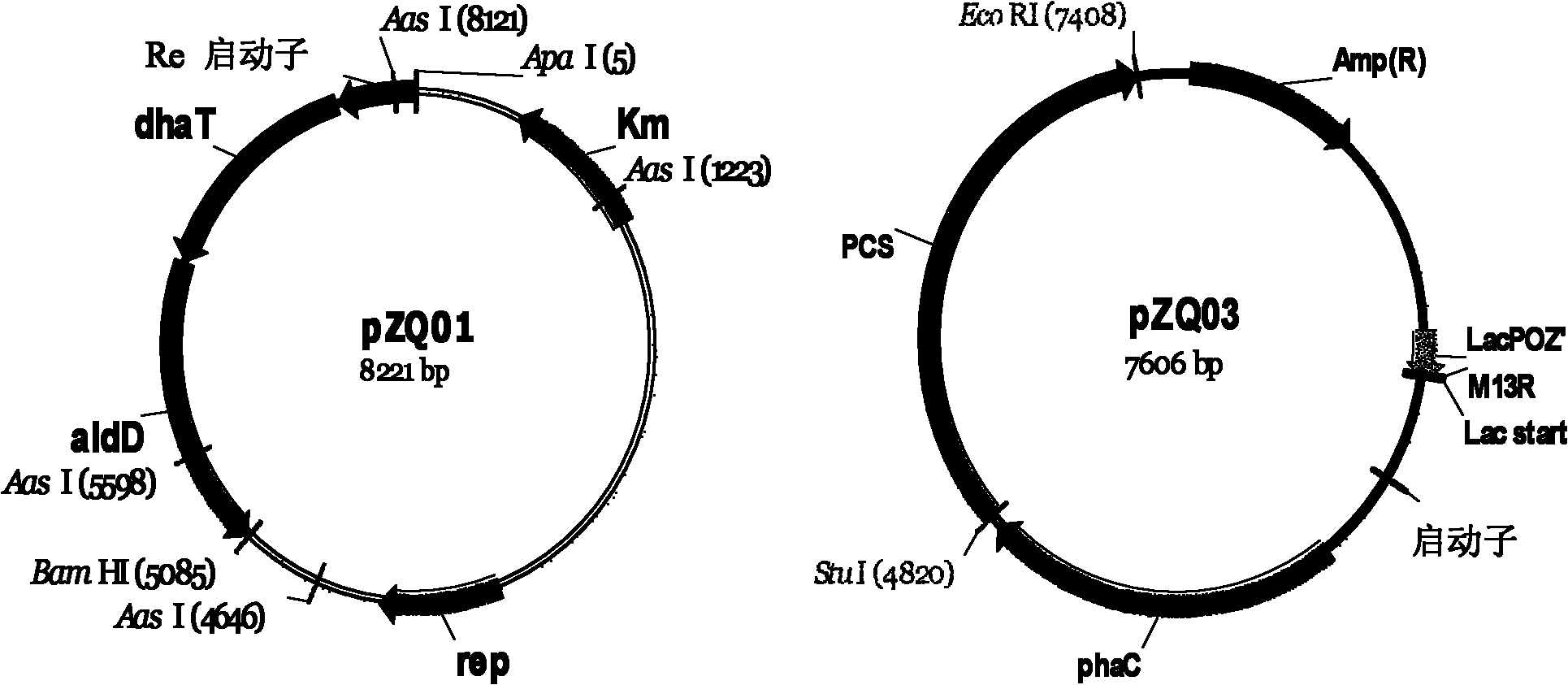
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPolymerase L
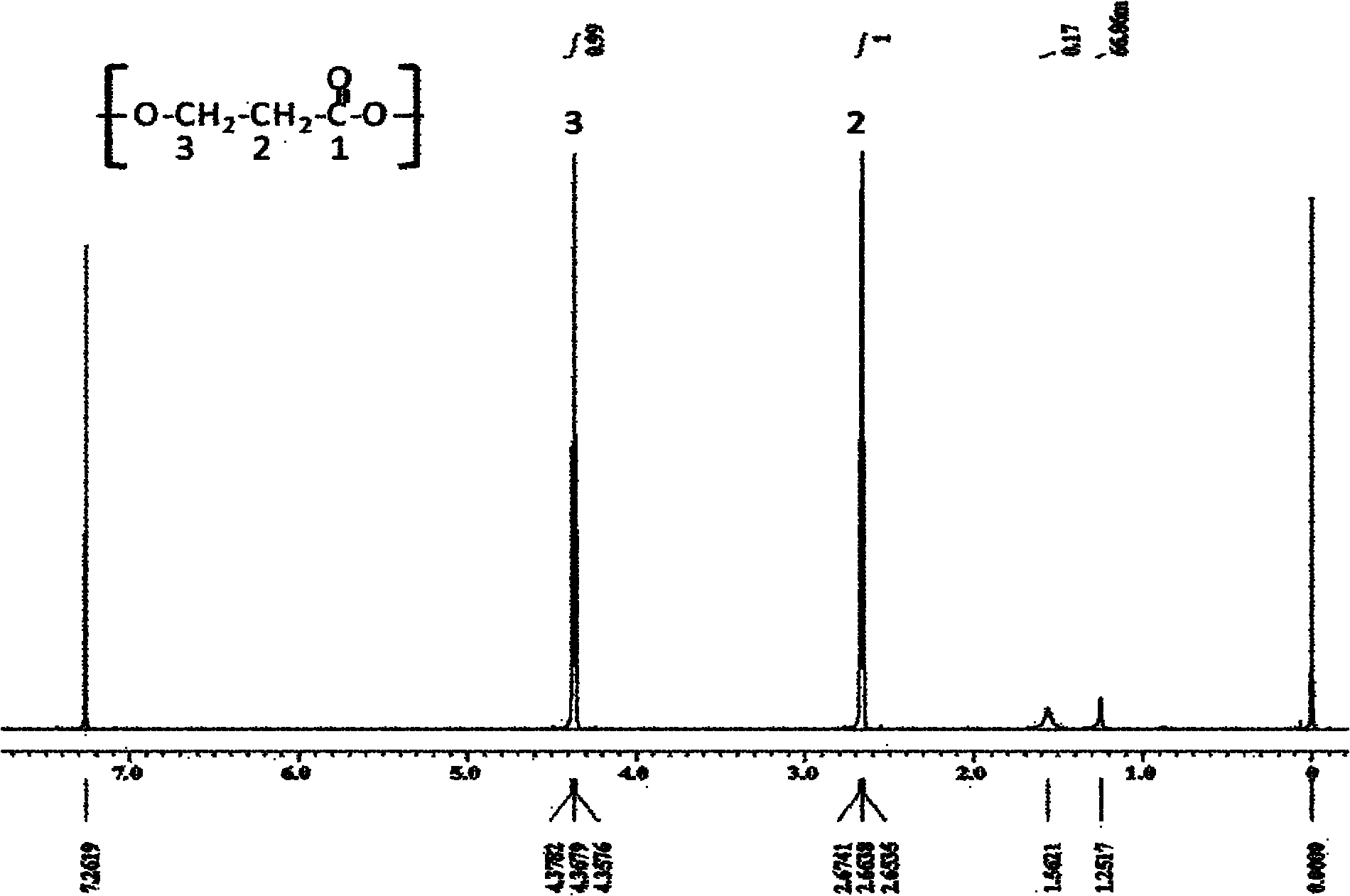
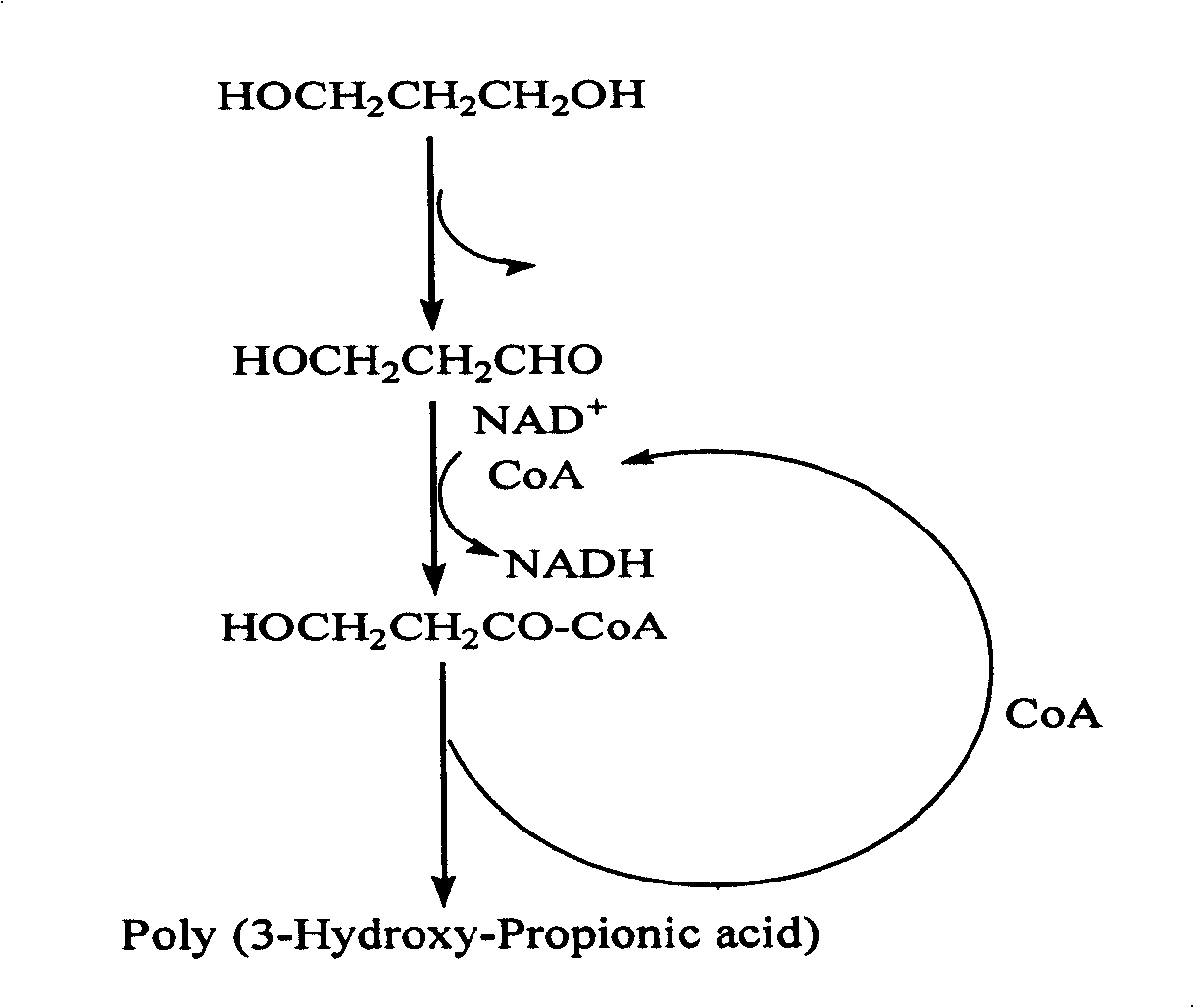
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
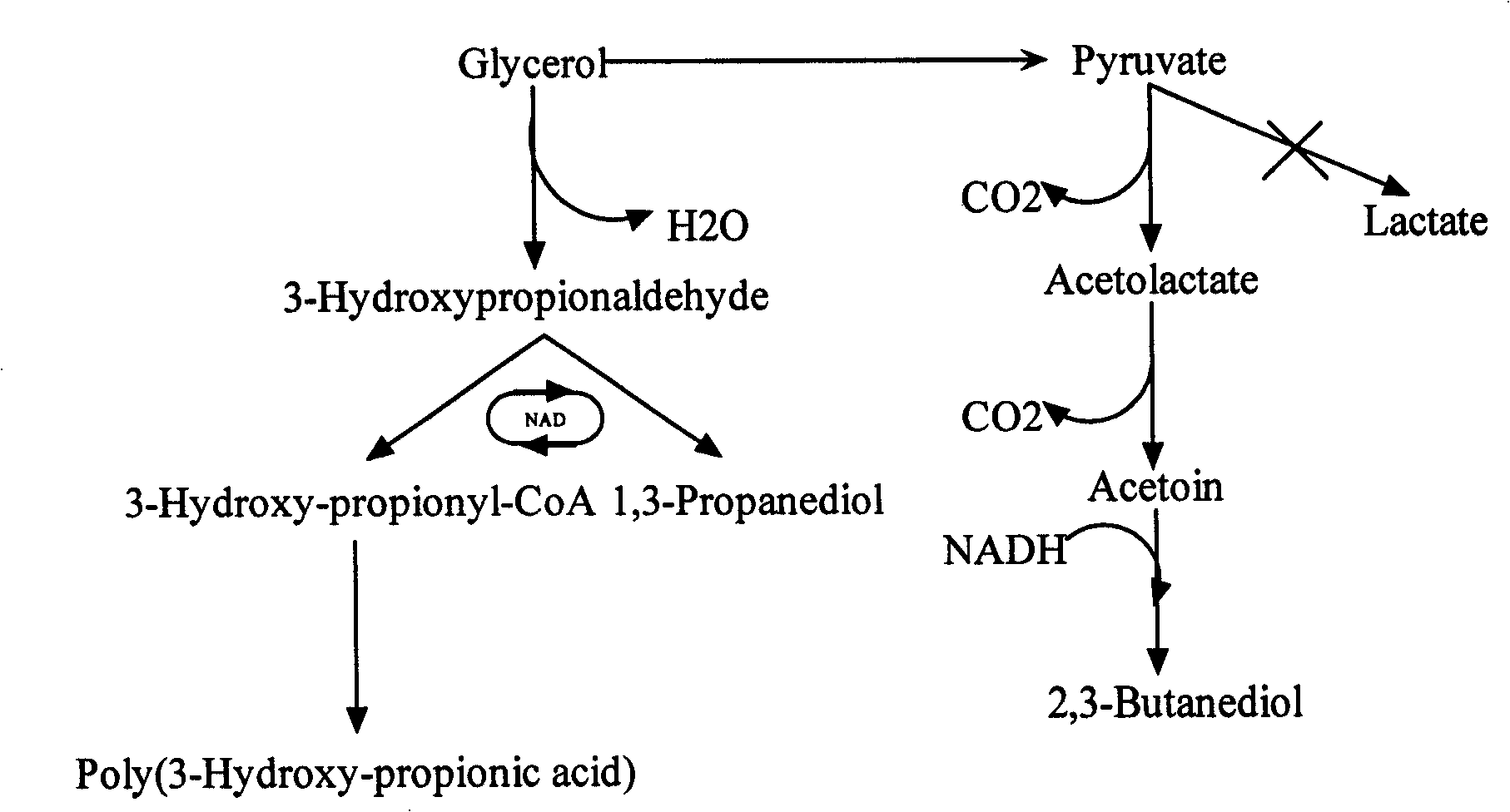
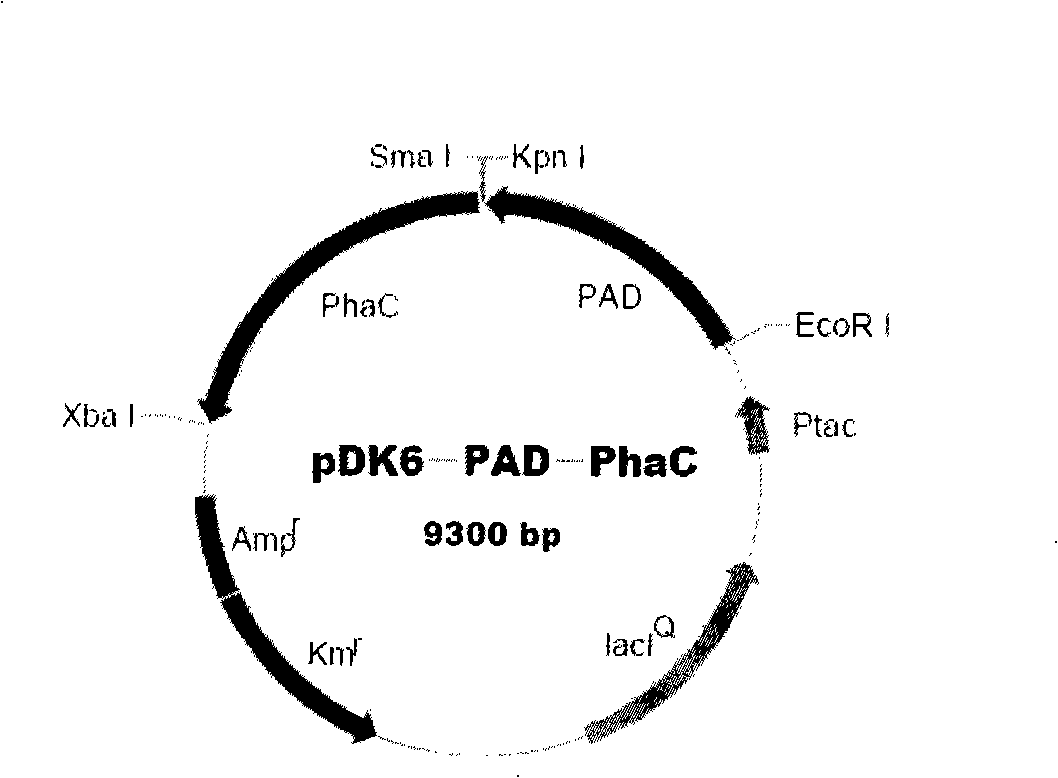
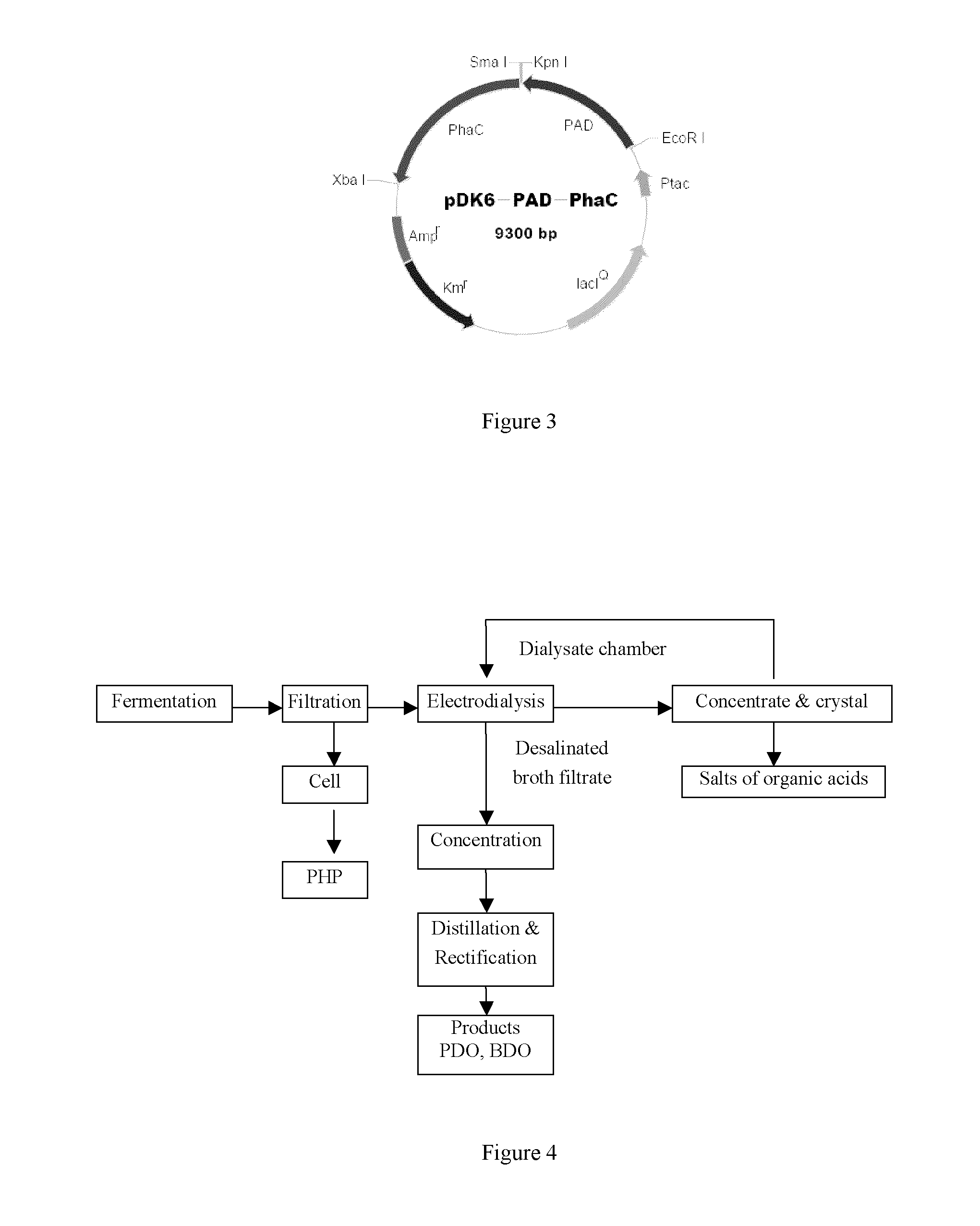
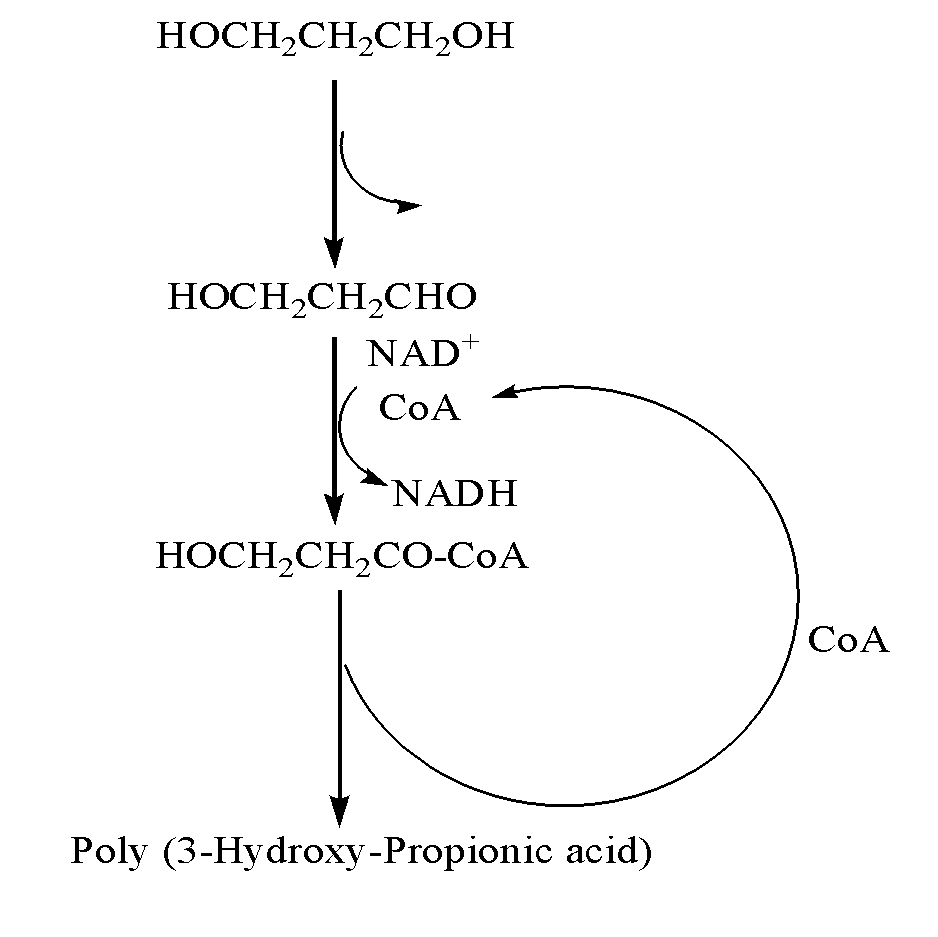
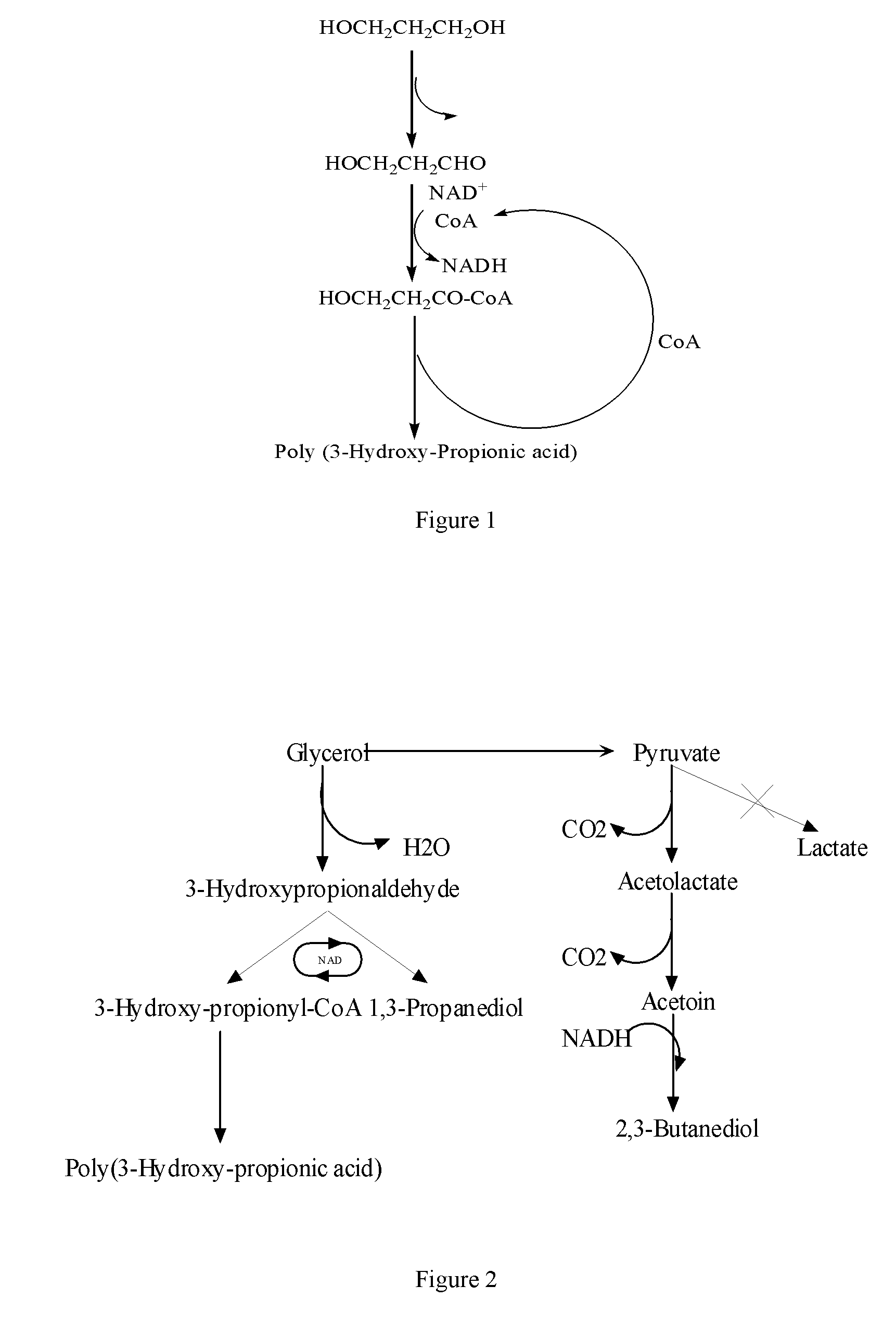
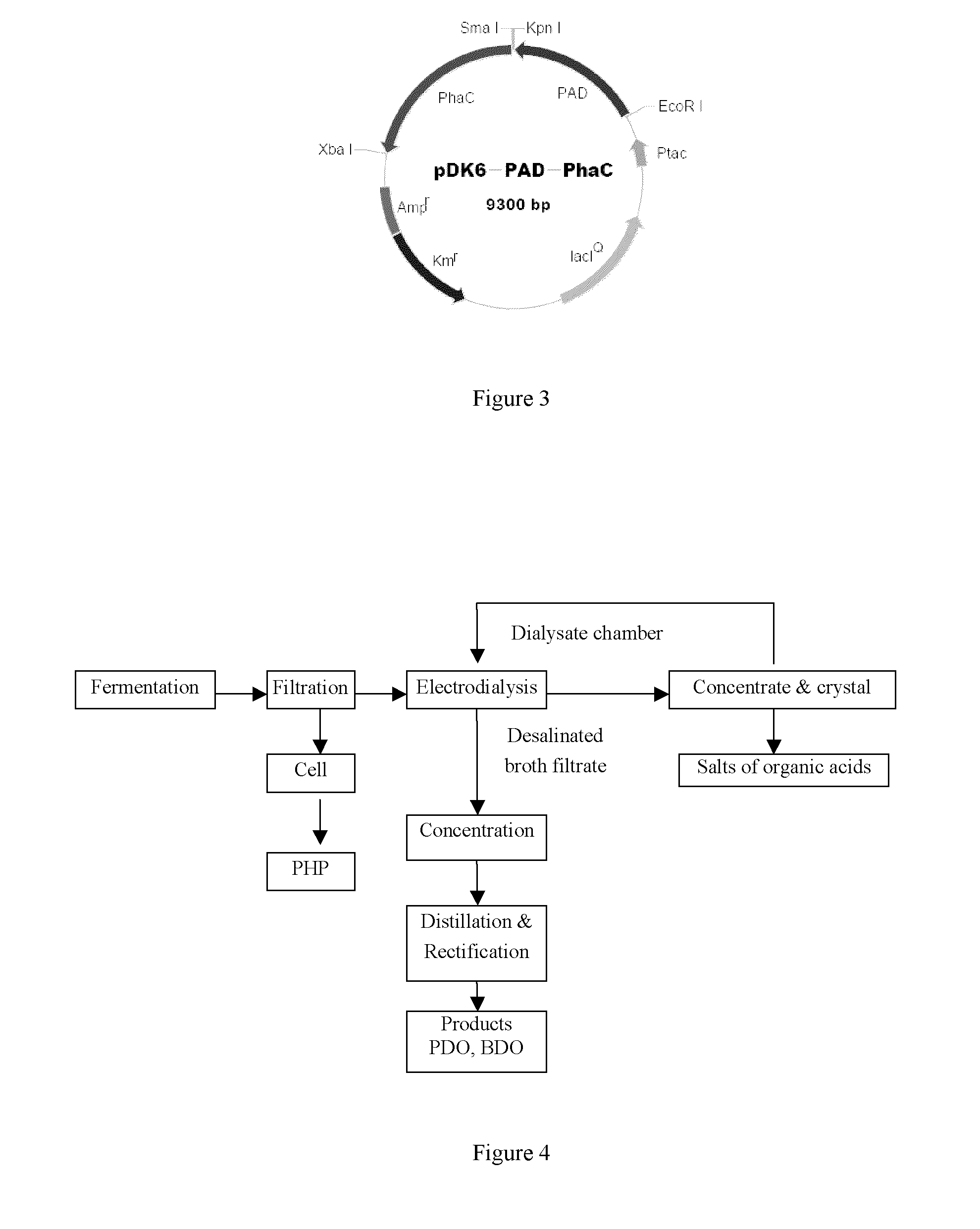
Method for fermentation co-production of PDO,BDO and PHP by constructing gene engineering strain
A method for constructing genetic engineering bacteria used in the fermentation and the coproduction of PDO, BDO and PHP belongs to the biochemical technical field. The process of the method comprises the following steps that: D-type lactate dehydrogenase gene is removed from wild fungus used for generating PDO, and coenzyme A dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase and polyhydroxy fatty acid synthase gene are introduced so as to construct genetic engineering bacteria used in the fermentation and the coproduction of PDO, BDO and PHP; aerobic fermentation and a fermentation adjust and control mode according to which glycerol and an alkali solution undergo mixing fed batch are adopted; and a product extraction flow during which fermentation broth undergoes membrane filtration, electrodialysis, concentration and rectification steps so as to separate the products of PDO, BDO and PHP. The method has the advantages that: the constructed genetic engineering bacteria can produce PDO, BDO and PHP at the same time, thereby increasing the utilization rate of raw materials and reducing production cost; meanwhile, the synthesis of byproduct lactic acid is reduced, and an after-extraction process is simplified so as to reduce extraction cost; moreover, the method increases the synthesis of thalli NADH2 while introducing PHP.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
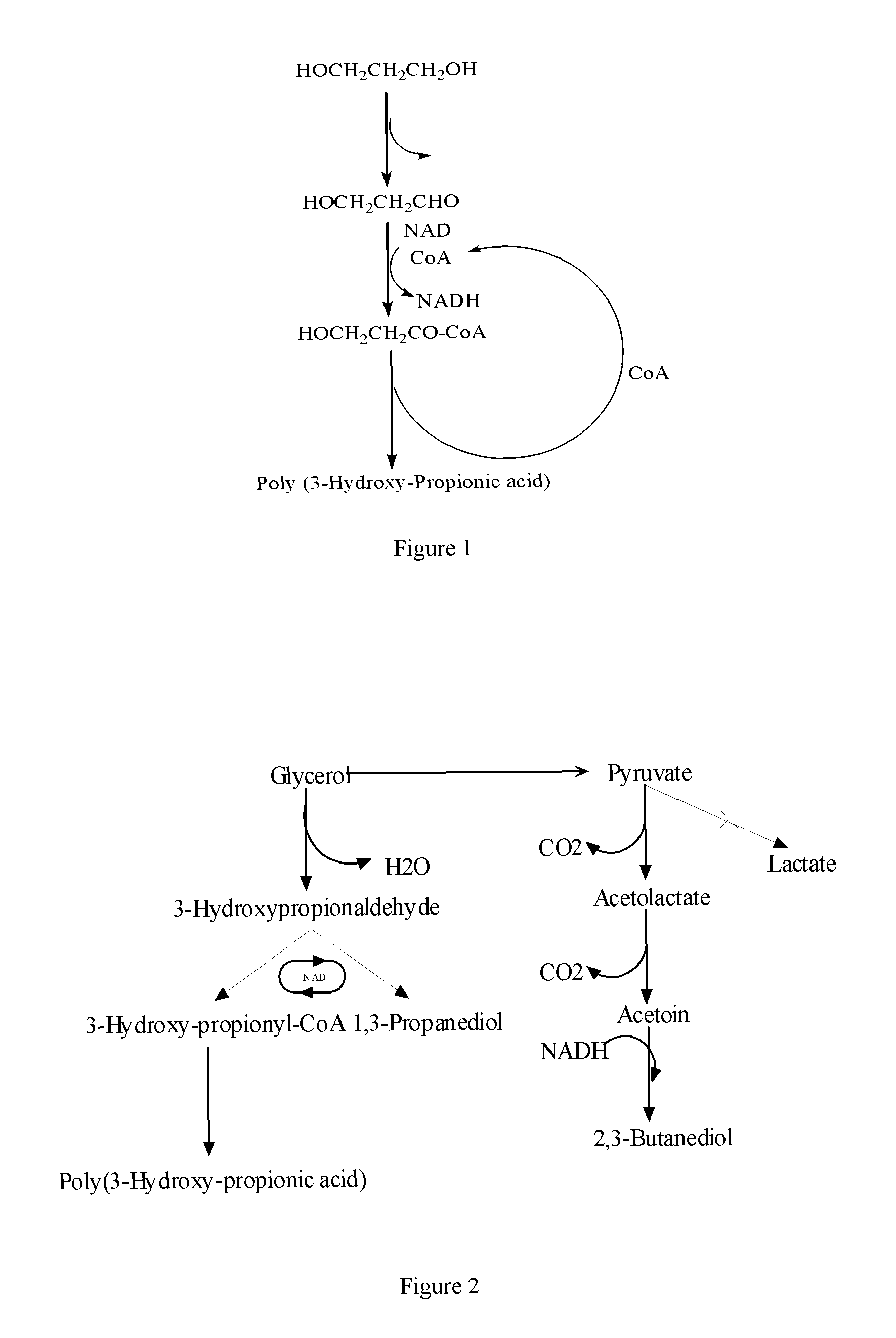
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation
The present invention relates to genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of 1,3-propanediol (PDO), 2,3-butanediol (BDO), and polyhydroxypropionic acid (PHP) by fermentation. In particular, the invention relates to a genetically engineered micro-organism suitable for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation, characterized in that: compared with corresponding wild-type starting micro-organism, the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene in the genetically engineered micro-organism is deleted or functionally inactivated, and the genetically engineered micro-organism comprises a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms, and methods for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation of a genetically engineered bacterium are also taught.
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
Preparation of health-care product for relieving alcohol and preventing getting drunk
InactiveCN102132869APrevent drunkennessProlonged drunk timeFood preparationAcetic acidEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention relates to preparation of a health-care product for relieving alcohol and preventing getting drunk, which prepares capsules for oral taking by using mixture of high-activity alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase as a main ingredient, adding an enzyme stabilizer such as ferric ions, freeze-drying and adding conventional auxiliary materials. The health-care product has remarkable effects of relieving alcohol and preventing getting drunk. After a drinker takes the product before drinking, alcohol can metabolize quickly in the gastrointestinal tract into acetic acid to beabsorbed or excreted, so the damage of the alcohol to the human body is lowered.
Owner:快醒生物科技(北京)有限公司
Method for Producing a Target Substance by Fermentation
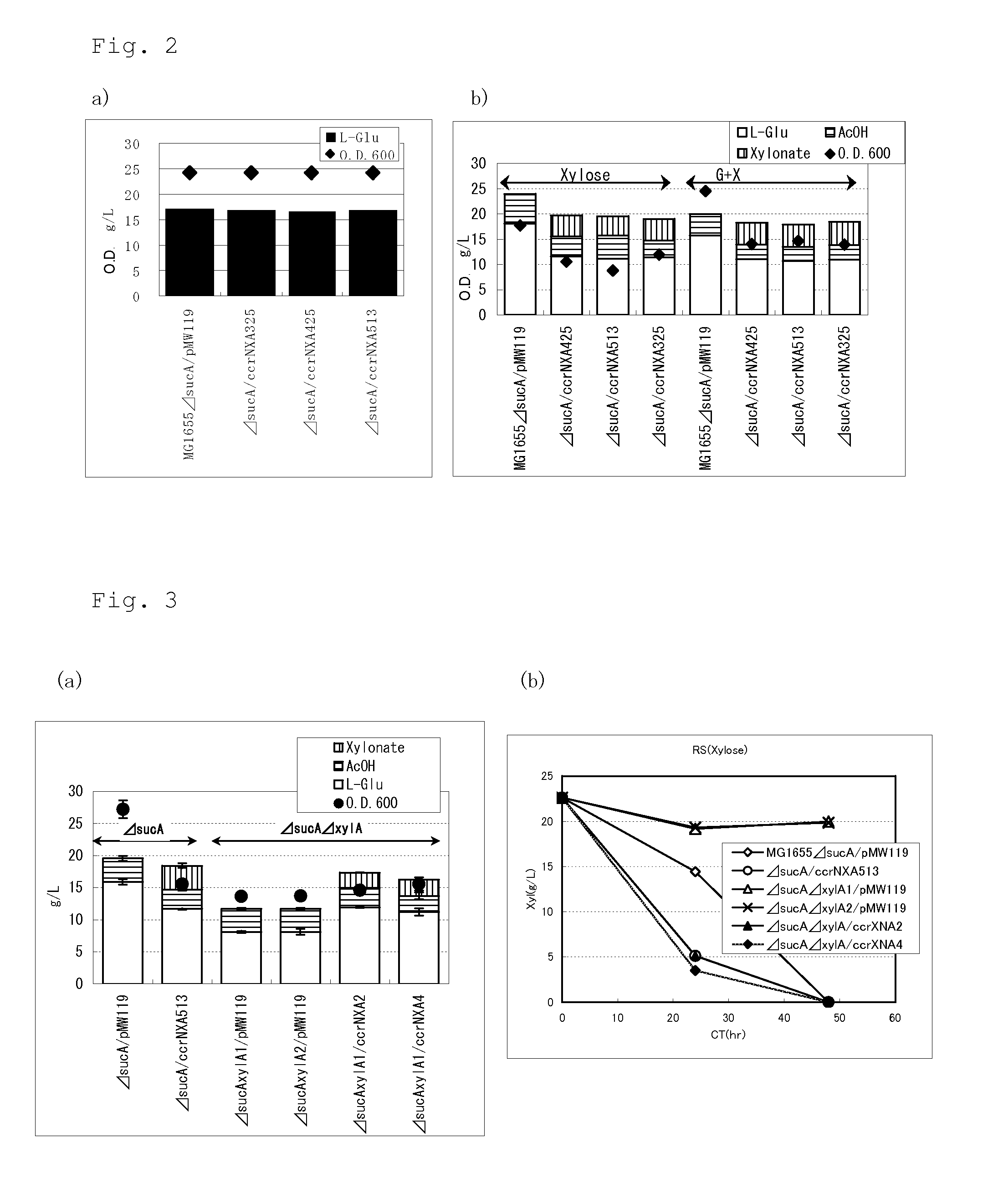
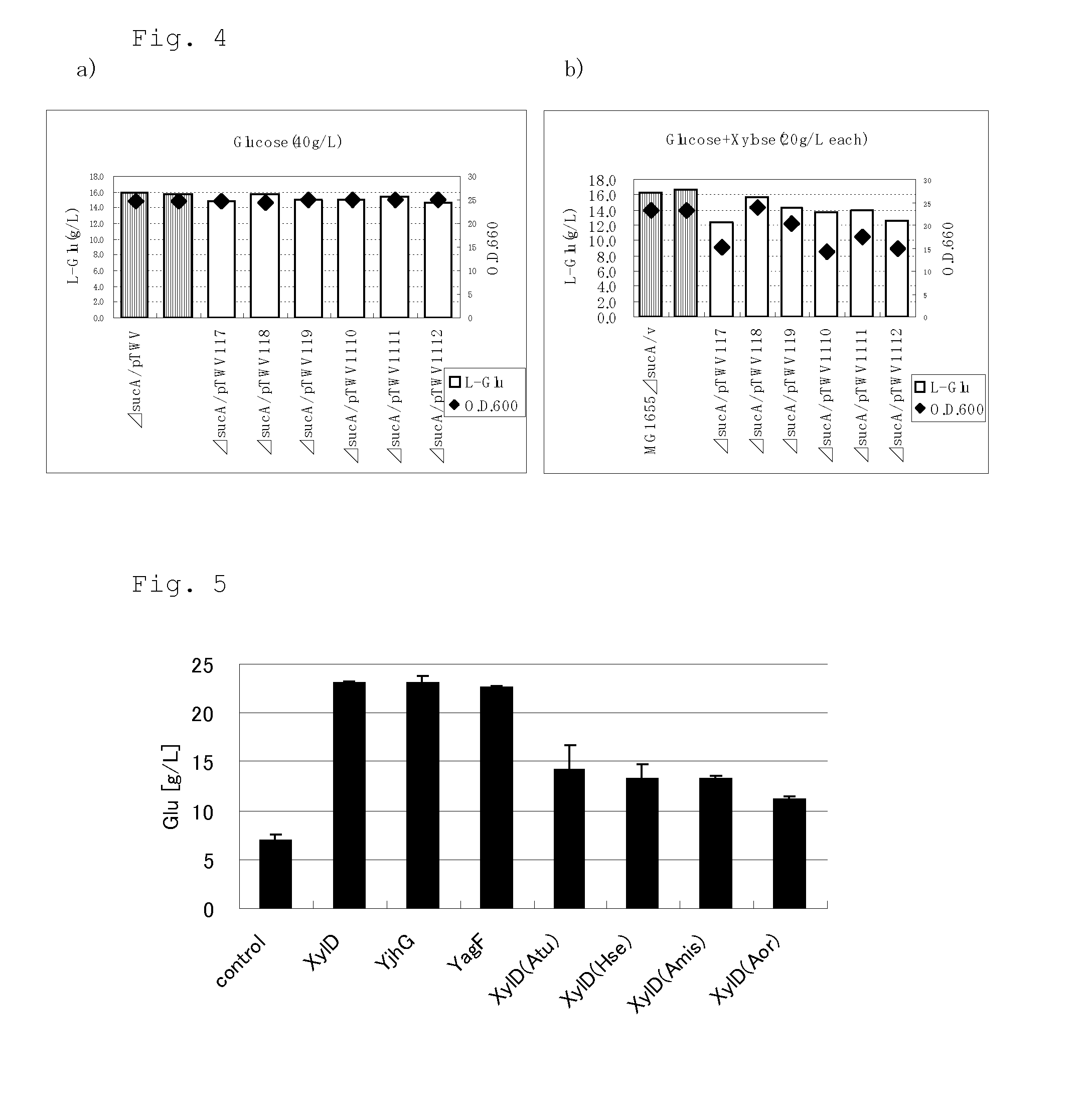
ActiveUS20130295621A1Efficient productionEfficiently assimilateHydrolasesOxidoreductases2-ketoglutaric acidXylonic acid
A target substance can be produced by culturing a bacterium having an ability to produce 2-ketoglutaric acid or a derivative thereof, and an ability to produce xylonic acid from xylose, which is imparted with xylonate dehydratase activity, 2-keto-3-deoxyxylonate dehydratase activity and 2-ketoglutaric semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity, or in which these activities are enhanced, in a medium containing xylose as a carbon source to produce and accumulate the target substance in the medium, and collecting the target substance from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
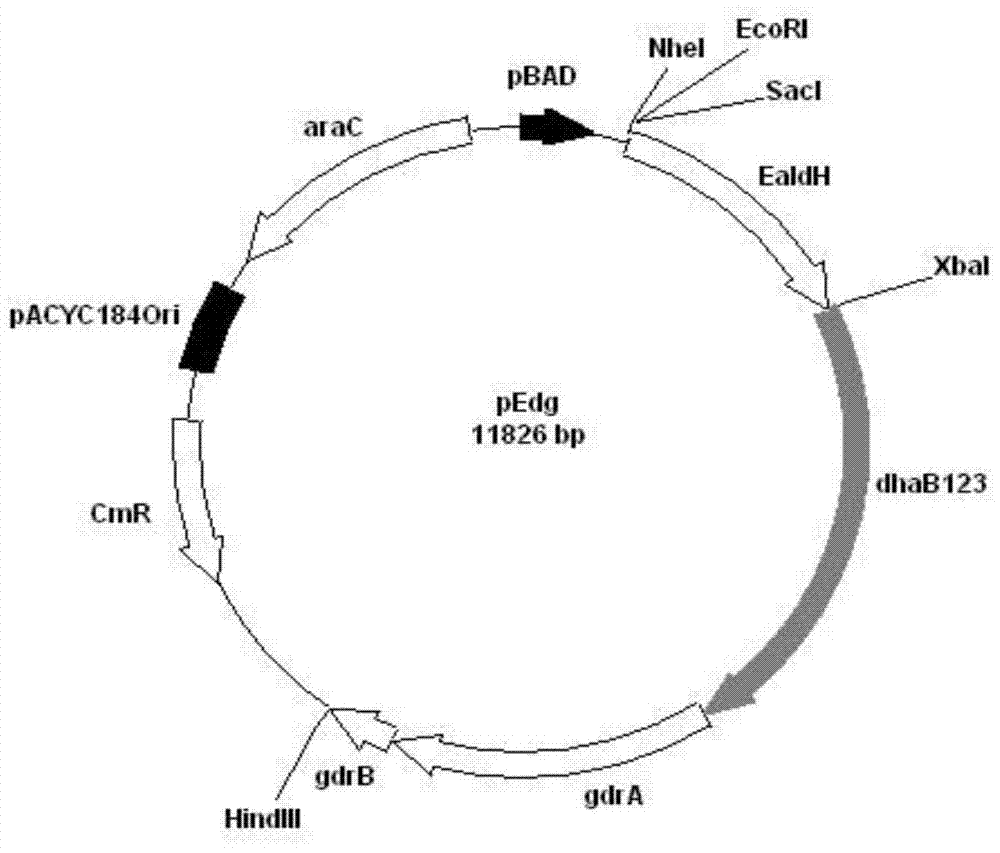
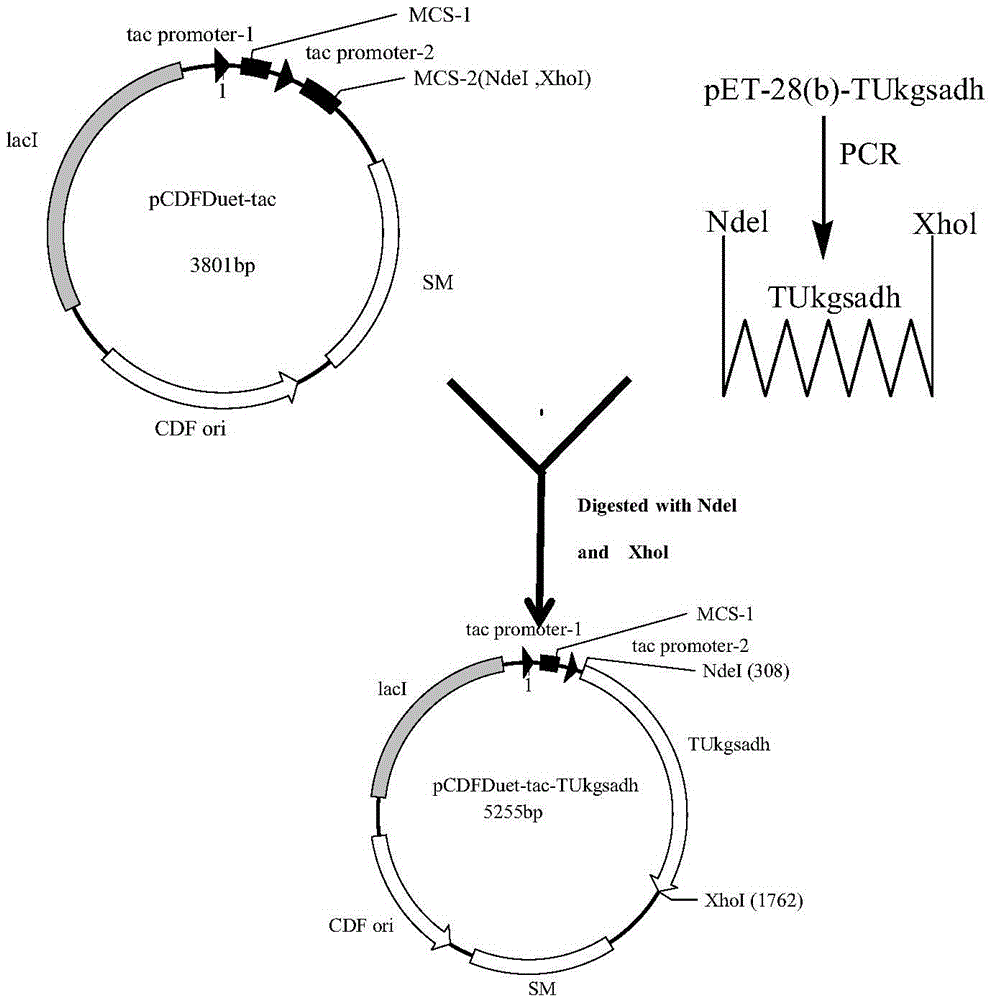
Recombinant Escherichia coli and application of recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid
ActiveCN105567622AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli and application of the recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The recombinant Escherichia coli is formed by glycerol dehydratase genes dhaB123, glycerol dehydratase reactivating factor genes gdrA, alpha-oxoglutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase mutant coding genes TUkgsadh and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase coding genes gpdl which are guided into host bacteria. By means of the gene knockout technique, the yield of byproduct 1,3-propylene glycol is reduced, and meanwhile, cofactors NAD+ of aldehyde dehydrogenase are regenerated. Thus, the yield of the 3-hydroxypropionic acid is improved by 1.5 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
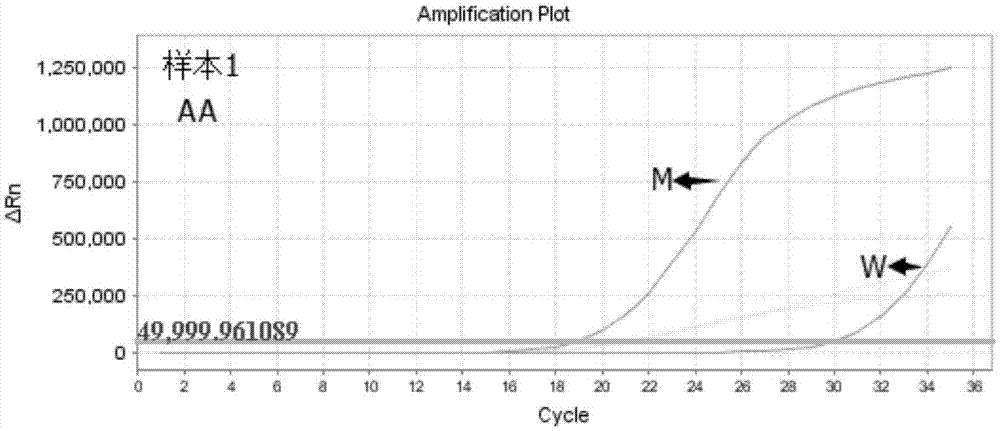
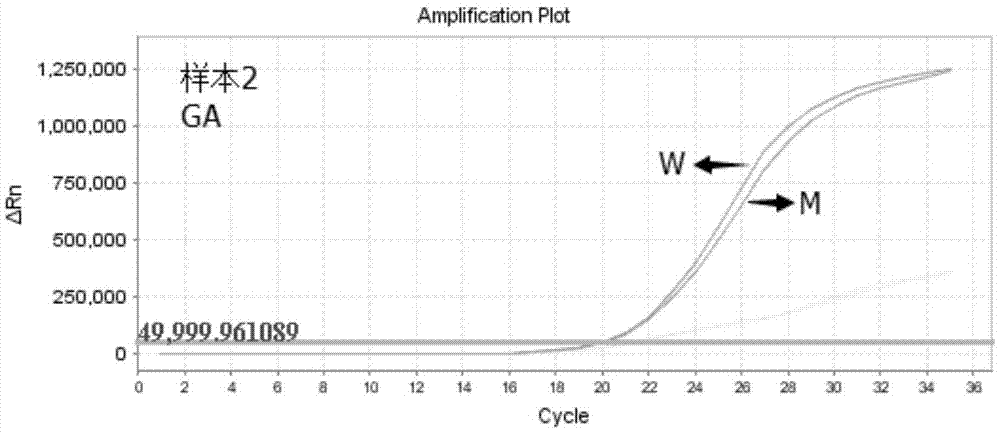
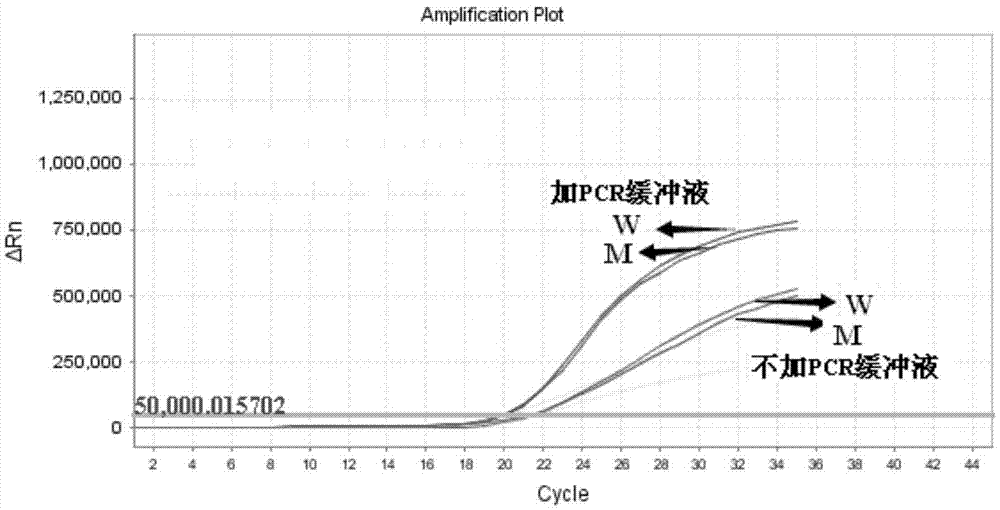
Primers, probe and kit for detecting ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase gene2) gene polymorphism
InactiveCN105441439AAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAldehyde dehydrogenaseNon toxicity
The invention discloses primers, a probe and a kit for detecting ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase gene2) gene polymorphism and belongs to the technical field of gene polymorphism site detection. Nucleotide sequences of the primers comprise a mutant type ARMS upstream primer represented as SEQ ID NO:1, a wild type ARMS upstream primer represented as SEQ ID NO:2 and a common downstream primer represented as SEQ ID NO:3, and the probe adopts a common Taqman probe. The kit comprises an amplification primer of an internal control gene and the Taqman probe. The primers and the probe as well as the kit comprising the primers and the probe can be used clinically for detecting various types of samples and have the remarkable advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, short experimental period, simplicity in operation, safety, non-toxicity, low cost and the like.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
Engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106086102AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseGlutamate 5-kinase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and building method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and a building method and application of the recombinant bacteria and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The xylose dehydrogenase gene, xylonic acid lactonase gene, xylonic acid dehydratase gene, 3-deoxygenation-D-glycerin ketopentose acid aldolase gene and glycolic aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in the recombinant bacteria using the xylose to produce the glycollic acid are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant bacteria and a method using the recombinant bacteria to produce the glycollic acid. By the recombinant bacteria, the biological synthesizing path using D-xylose as the carbon source to form the glycollic acid through glycolic aldehyde conversion is achieved for the first time.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of pdo, bdo and php by fermentation
ActiveUS20110117617A1Less producedImprove isolationBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The present invention relates to methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO, and PHP by fermentation. The micro-organism is characterized in that its D-lactate dehydrogenase gene has been deleted or functionally inactivated, and it comprises heterogenous polynucleotides encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms are also disclosed
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com