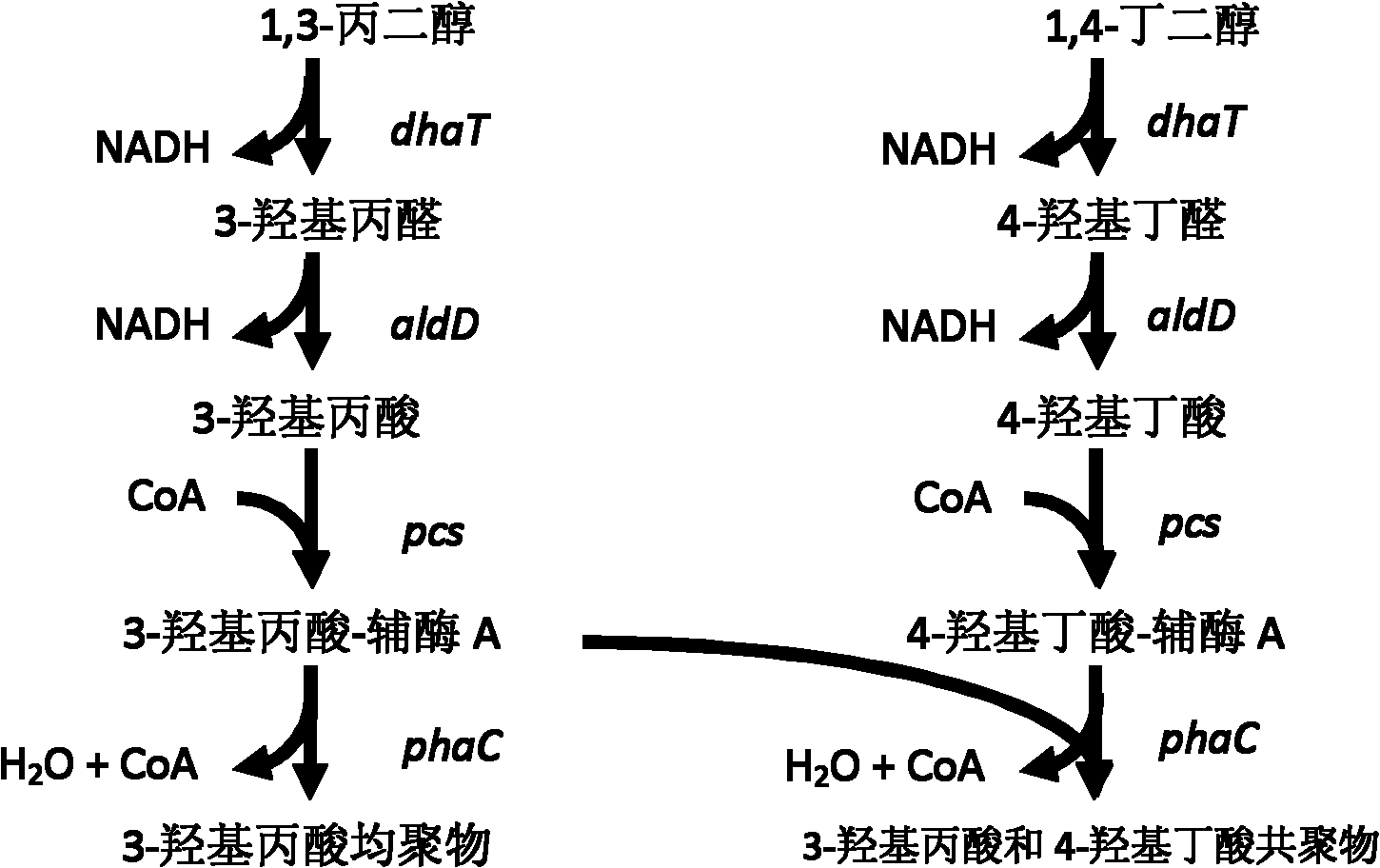
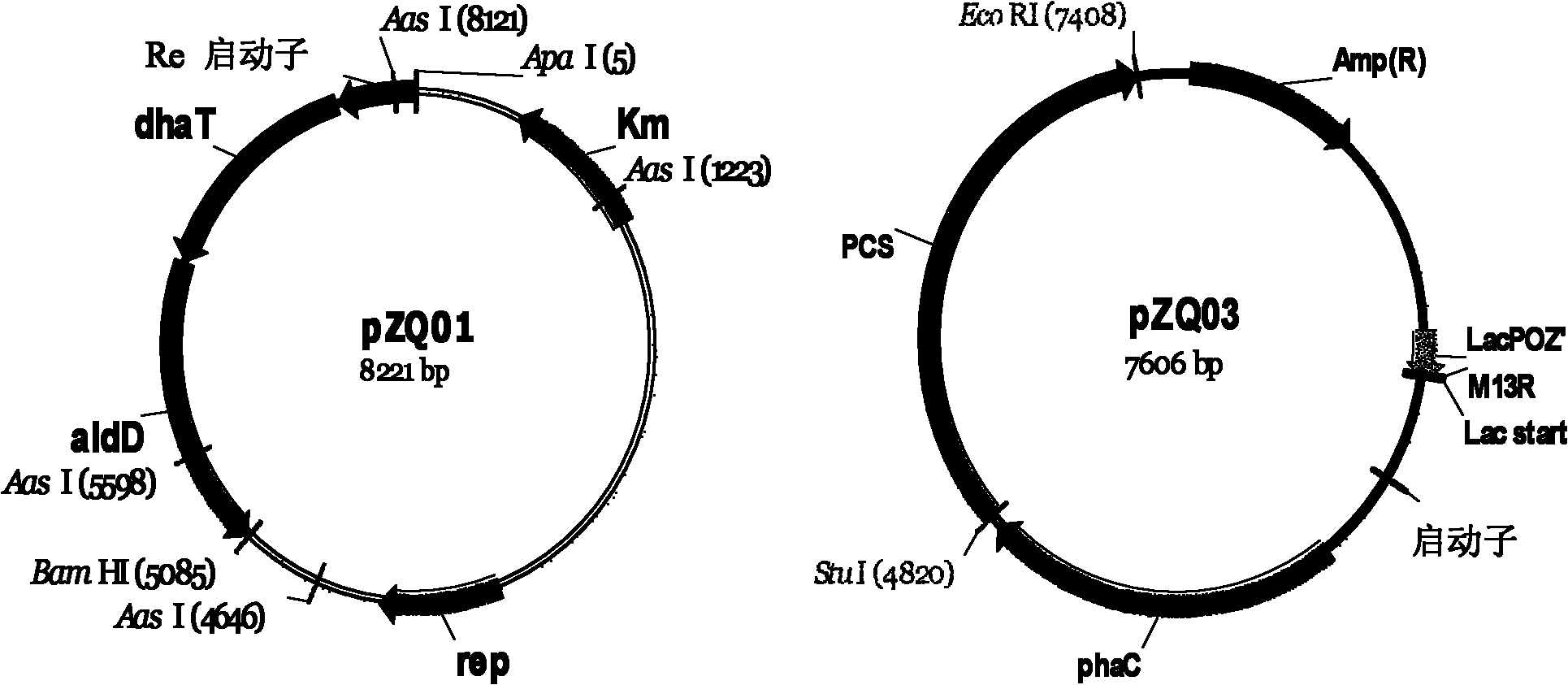
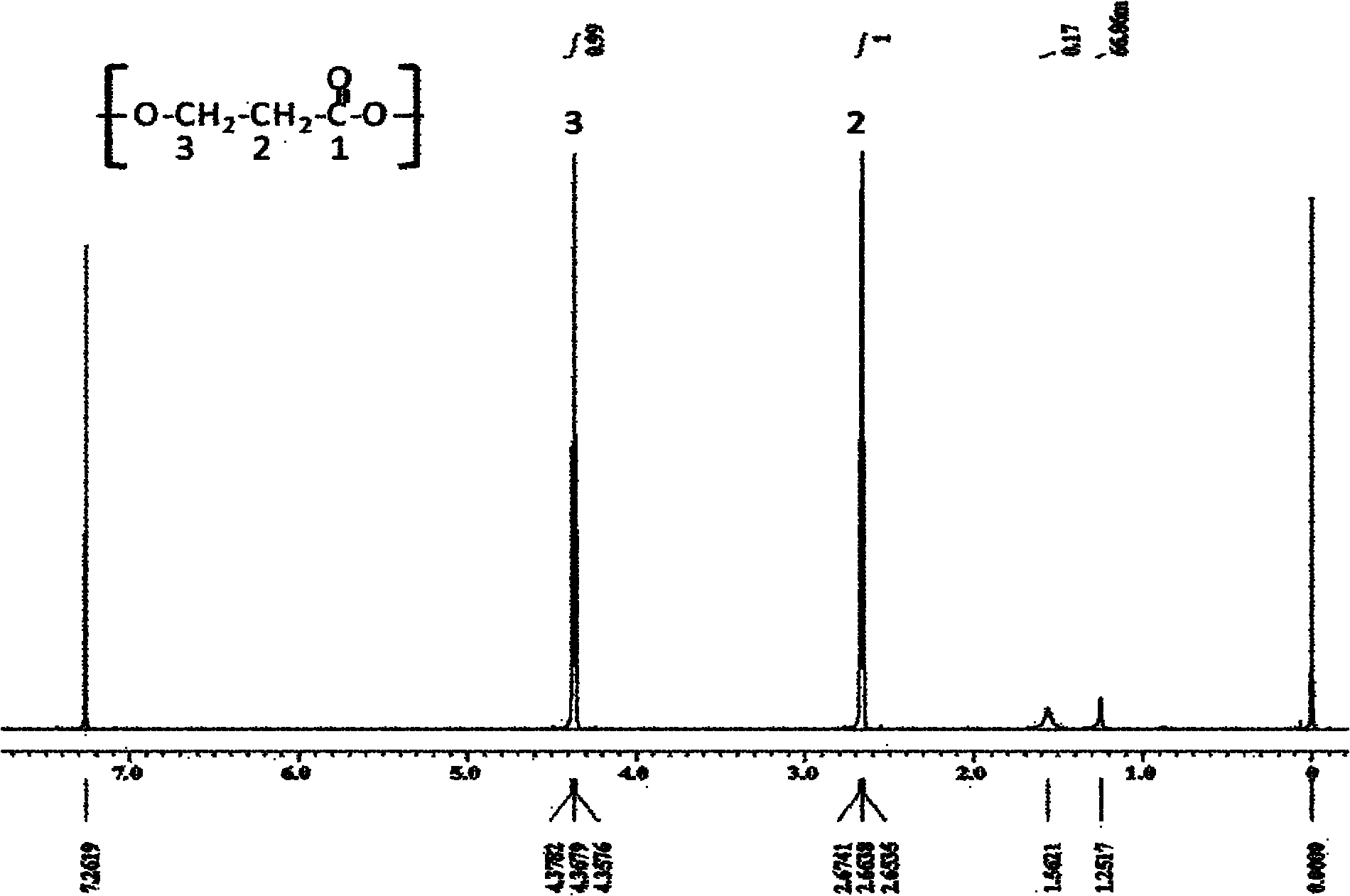
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
A hydroxypropionic acid copolymer and hydroxypropionic acid technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering bacteria, can solve problems such as complex production process, and achieve the effects of simple production process, low cost and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Example 1. Construction of expression engineering bacteria
[0059] 1. Construction of expression vector pZQ03
[0060] 1) Extract the genome of Ralstonia eutropha H16 (ATCC number: 17699, available from the American Type Culture Collection), using the R.eutrophaH16 genome as a template, and using P Re Sense and P Re Antisense is the primer, PCR reaction is carried out with pfu enzyme to amplify the target promoter P Re , And design and introduce restriction sites at both ends of the fragment.
[0061] P Re Sense: 5’ATAA GTCGAC CTCCTATTTGATTGTCTCTCTGCCGTC 3’ (sequence 6)
[0062] SalI
[0063] P Re Antisense: 5’TTAA GGGCCC GATGCGAGCGCTGCATACCGTC 3’ (sequence 7)
[0064] ApaI
[0065] PCR reaction conditions:
[0066] First denature at 94°C for 8min; then denature at 94°C for 30sec, anneal at 60°C for 30sec, extend at 72°C for 1min24sec, 29 cycles; then extend at 72°C for 10min.
[0067] PCR amplification target fragment (20μL system)
[0068] Template DNA 0.4μL
[0069] Primer 1...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2. Experiments for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid homopolymer P(3HP) with expression engineering bacteria
[0114] 1. Shake flask culture exploration test
[0115] 1. Use LB as a medium to produce 3-hydroxypropionic acid homopolymer P(3HP)
[0116] Expression engineered bacteria E.coliTrans1-T1 (pZQ01, pZQ03), E.coliTrans5α (pZQ01, pZQ03) and E.coliS17-1 (pZQ01, pZQ03) were cultured in LB medium at 37℃, 200rpm overnight; then press 5 % Inoculum amount (v / v), respectively inoculate to 100mL LB medium containing 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PDO) (containing: 5g / L yeast extract, 10g / L peptone, 10g / L NaCl, 10g / L 1,3-PDO, the rest is water, pH 7.0-7.2), 37°C, 200 rpm, shake flask culture for 48 hours to obtain a bacterial solution. Each strain is set in three parallel groups. Use nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer NMR (JEOL, ECA-600SCC) and gas chromatograph (GC, Hewlett-Packard model 6890) to verify the accumulation of homopolymers in cells; use gas chromatograph to qua...
Embodiment 3
[0171] Example 3. Shaking flask experiment for producing P(3HP-co-4HB) copolymer with expression engineering strain E.coli S17-1 (pZQ01, pZQ03)
[0172] Expression engineered bacteria E.coliS17-1 (pZQ01, pZQ03) were cultured in LB, LB' and TB medium at 37°C and 200 rpm overnight; then inoculated to 100 mL at 5% inoculum (v / v) Culture of LB, LB' and TB with different concentrations of 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PDO, see Table 4) and / or different concentrations of 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD, see Table 4) Base, 37 ℃, 200 rpm, shake flask culture for 48 hours, each strain set three groups in parallel.
[0173] Using the conditions in the above gas phase detection method, the standard samples are prepared as follows:
[0174] Preparation of the standard sample of the copolymer of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and 4-hydroxybutyric acid: Take about 30ul of 30% (volume concentration) 3HP (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (TCI), catalog number H0297) aqueous solution in the ester Add 2ml of chloroform and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com