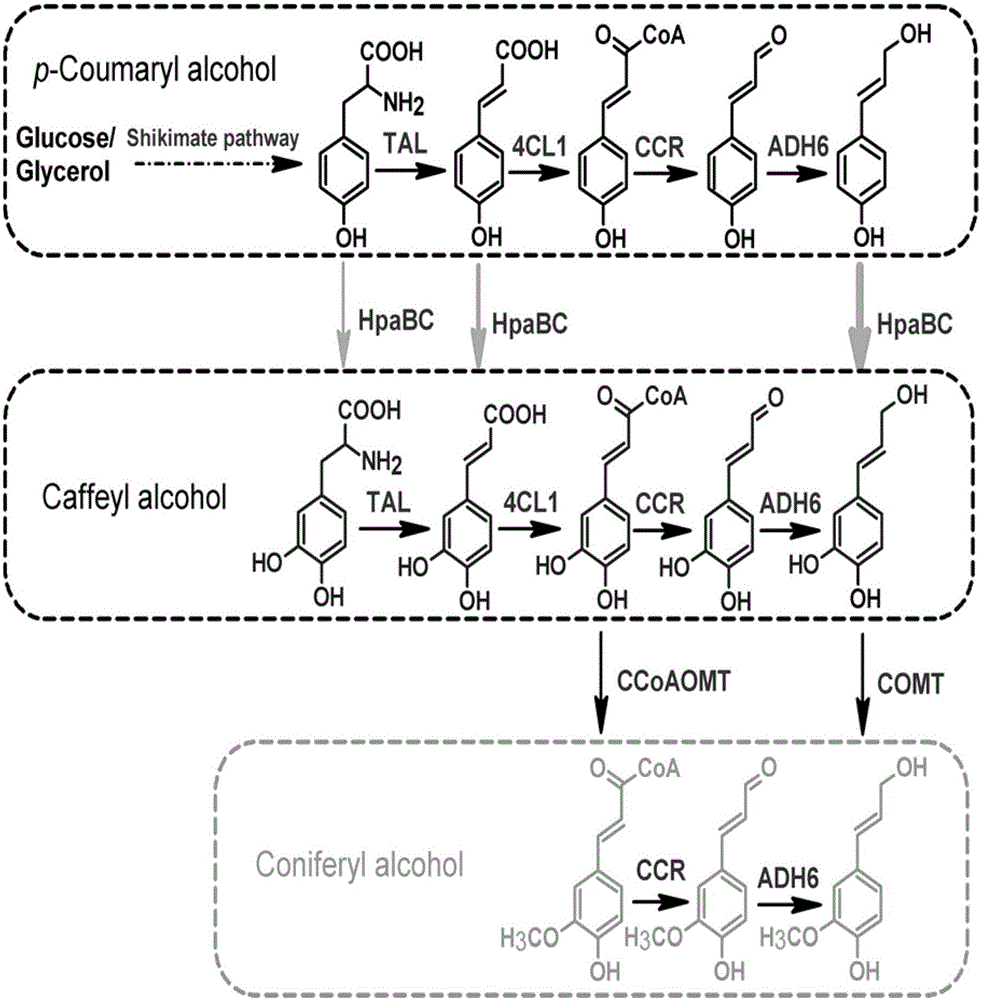
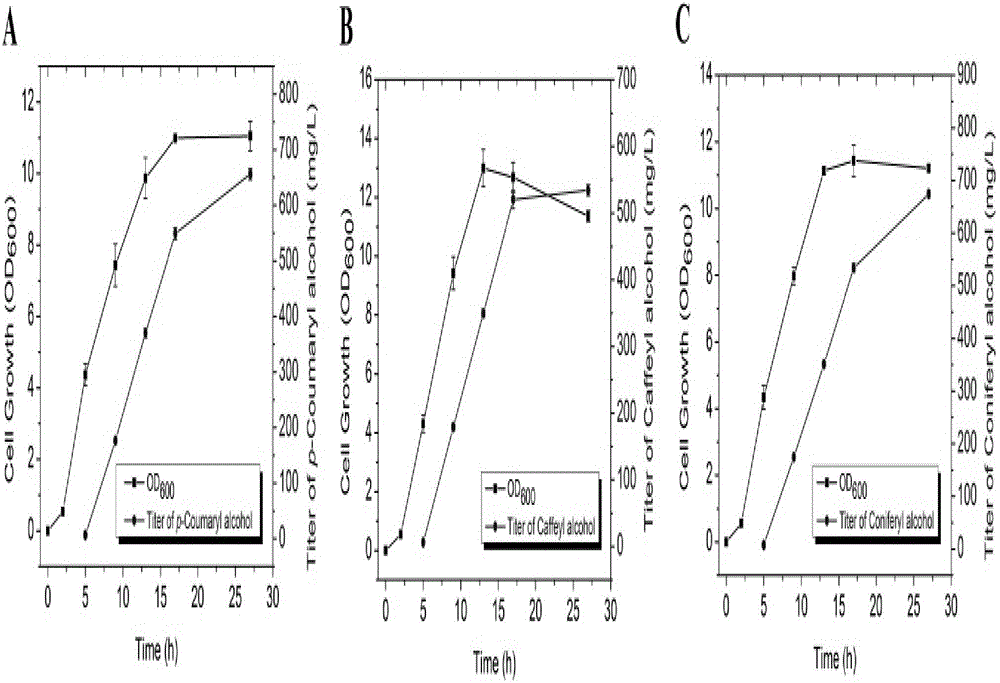
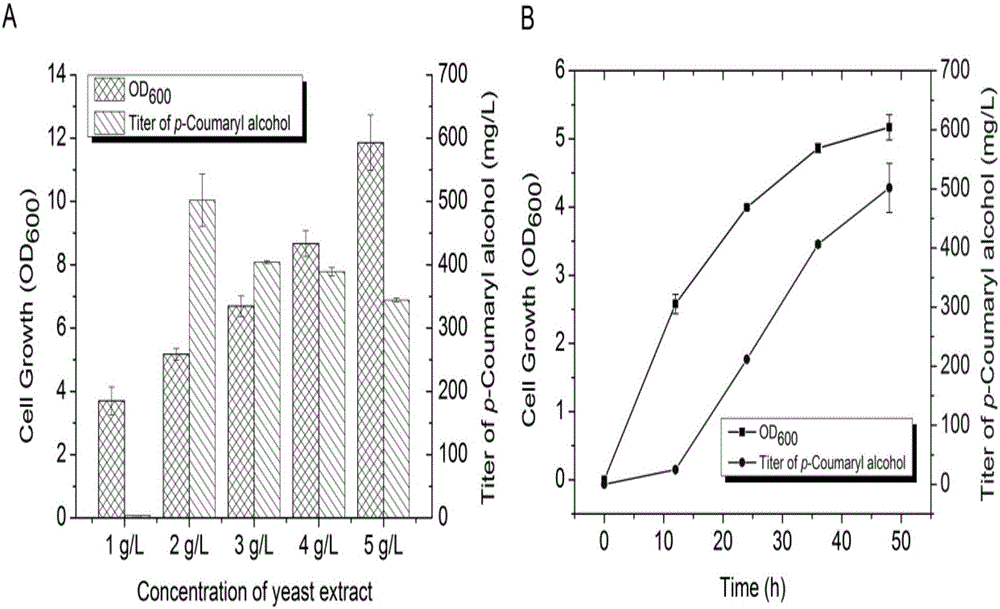
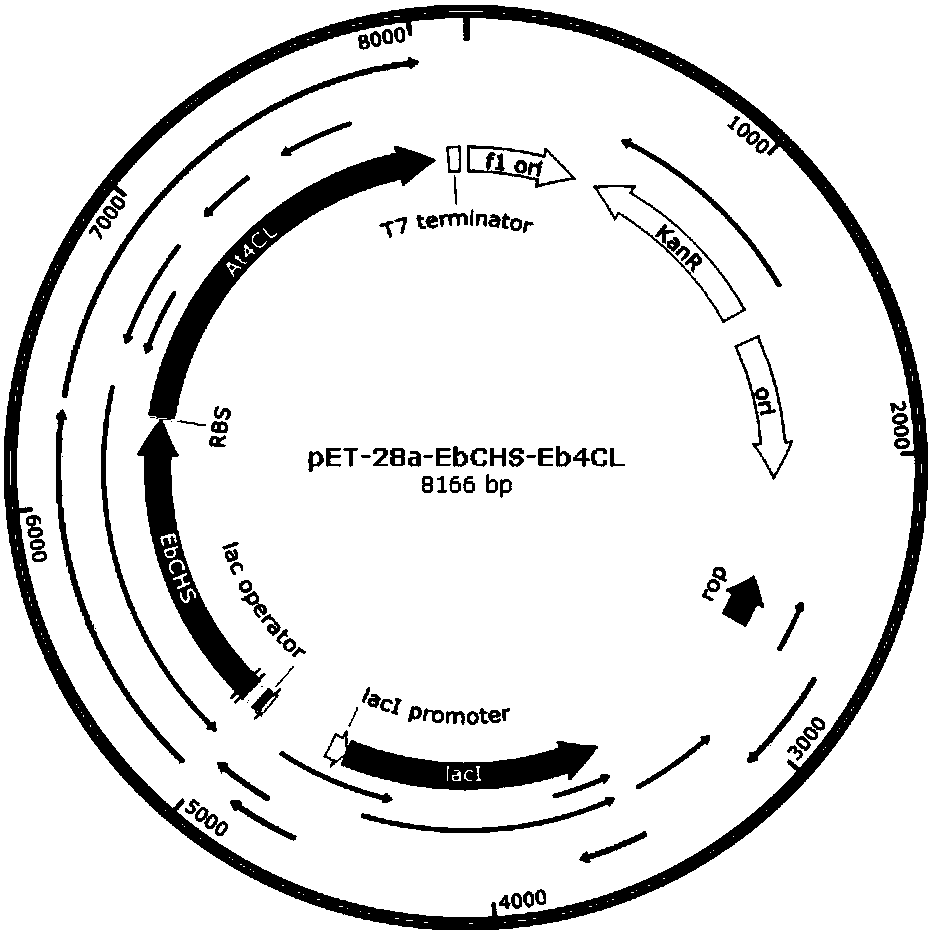
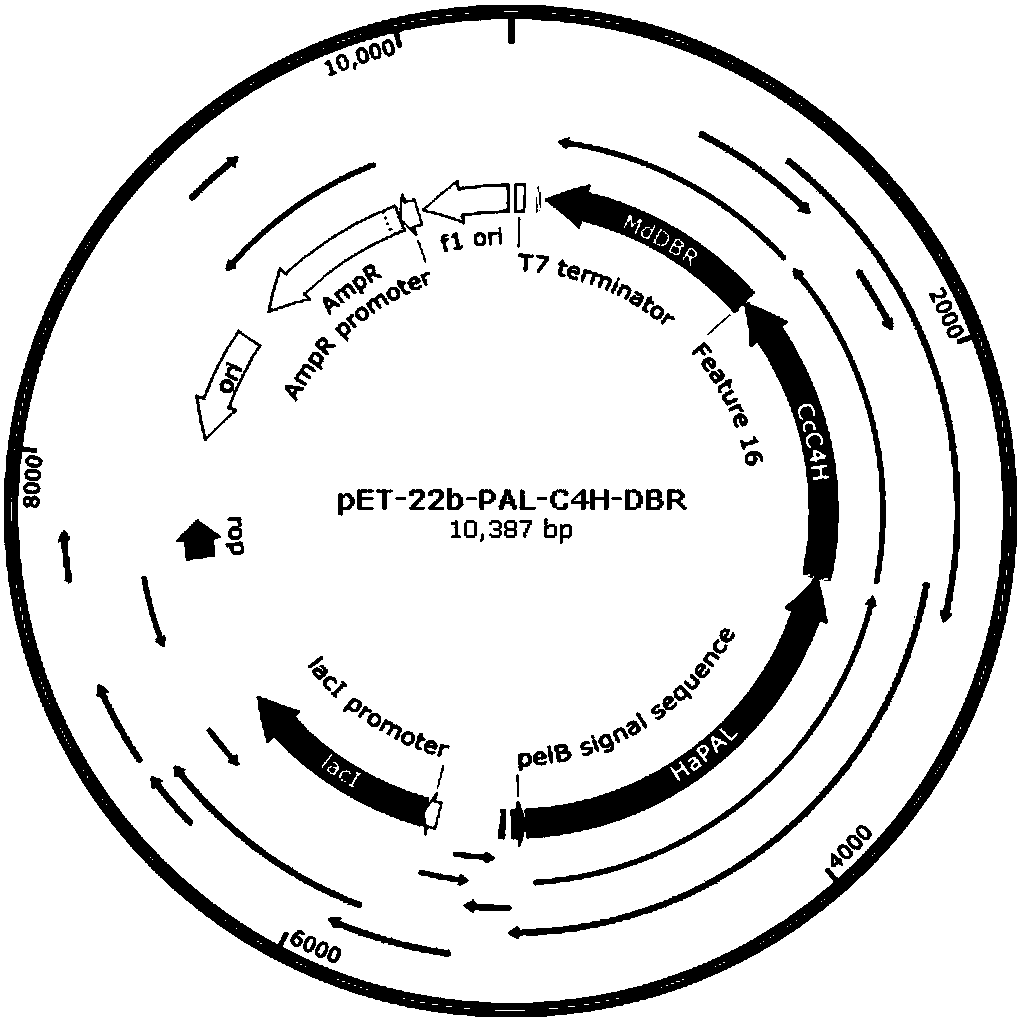
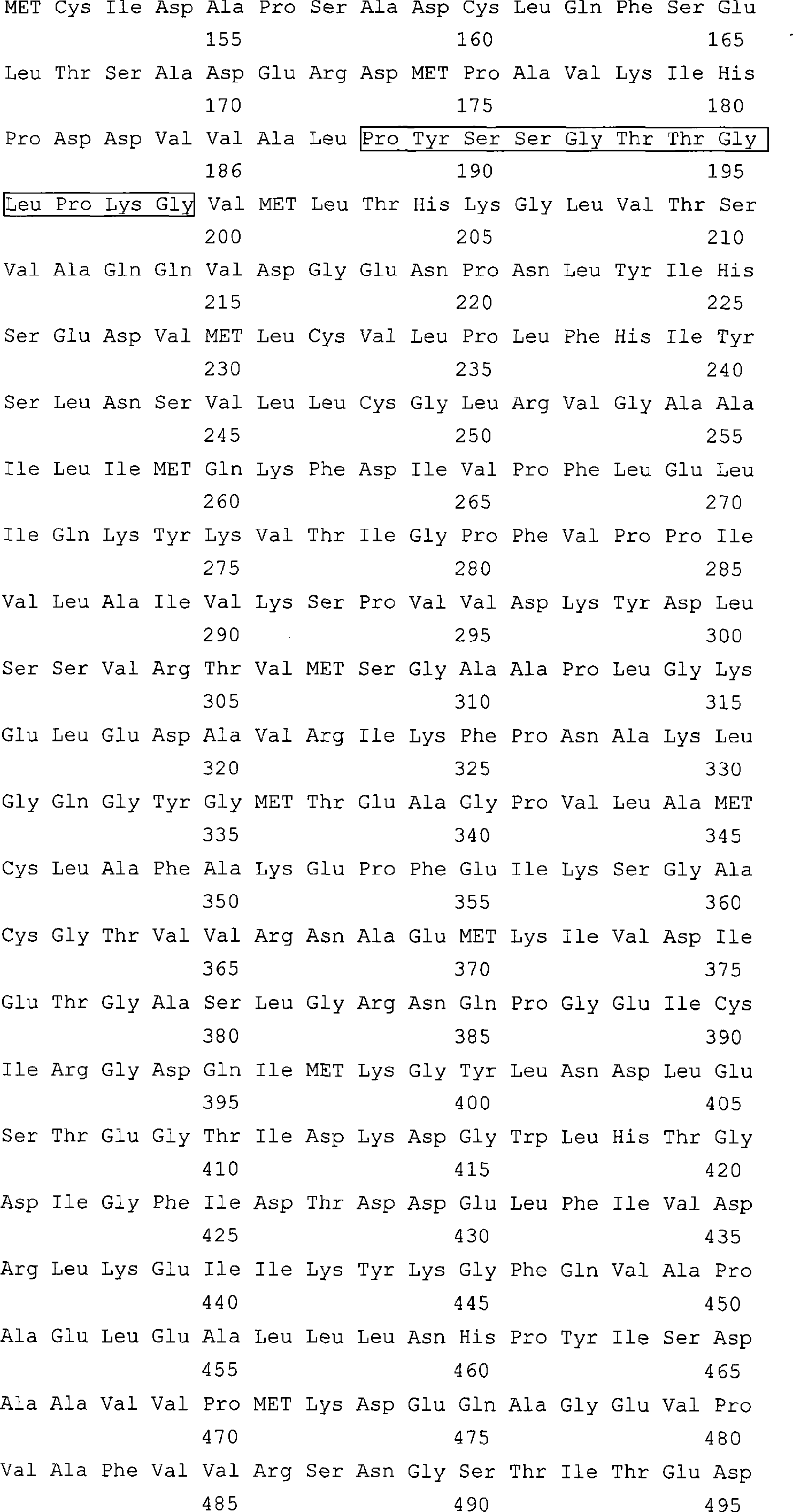Patents
Literature
66 results about "Coenzyme A Ligases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes that catalyze the formation of acyl-CoA derivatives. EC 6.2.1.
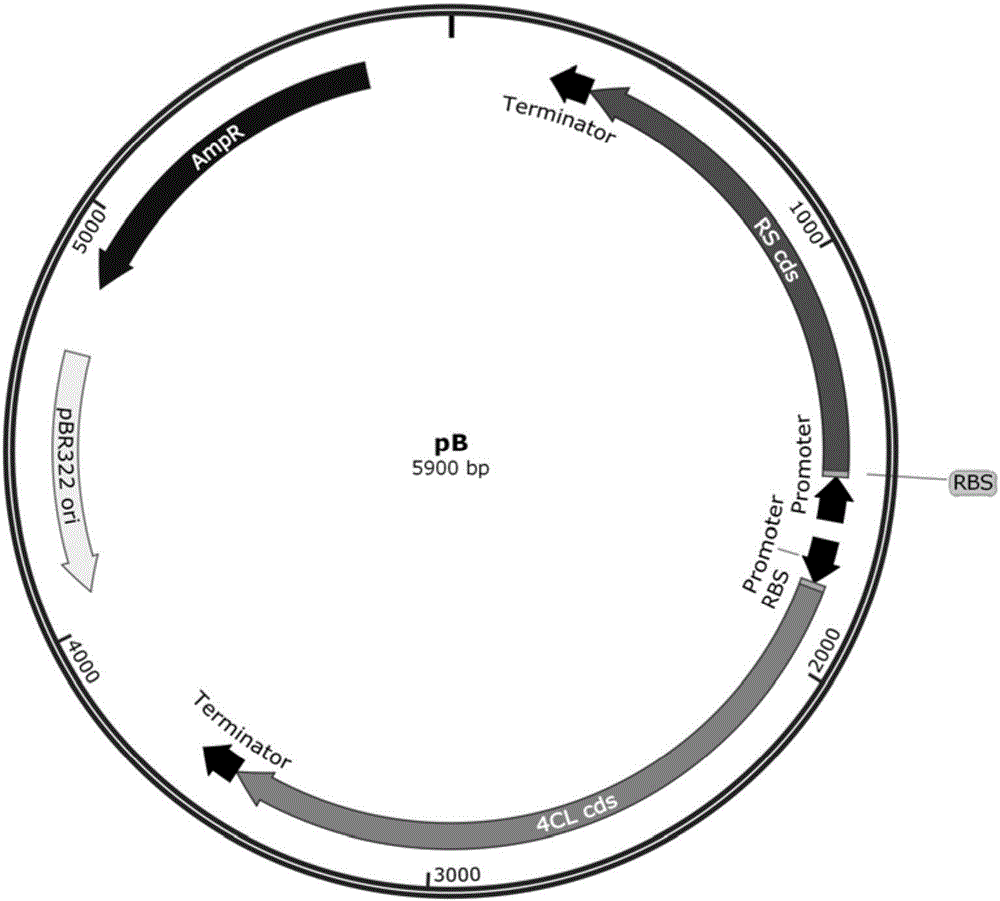
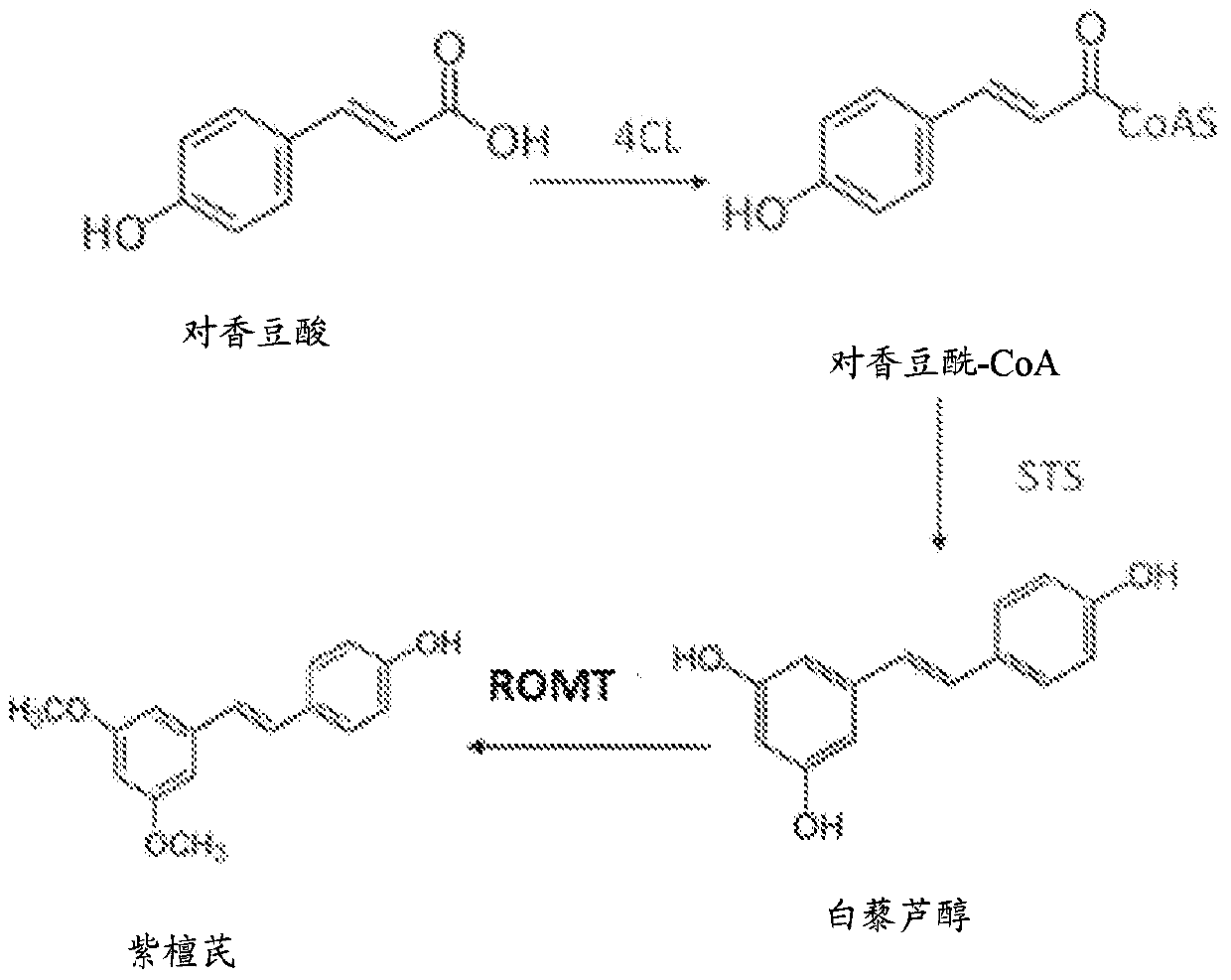
Biological method for producing resveratrol
InactiveCN102605006ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhenylalanine hydroxylase
The invention discloses a biological method for producing resveratrol, which comprises the following steps: ligating target genes obtained by restriction enzyme digestion to an expression vector, wherein the target genes include the sequences of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and resveratrol synthase (RS); transforming the constructed expression vector into a strain to obtain a recombinant engineered strain; and fermenting the recombined engineered strain. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention uses the genetically engineered strain for fermentation to produce resveratrol, so as to realize denovo synthesis of resveratrol with no need of adding substrates. The method disclosed by the invention solves the source problem of resveratrol, and at the same time, reduces the production cost in a maximum extent, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
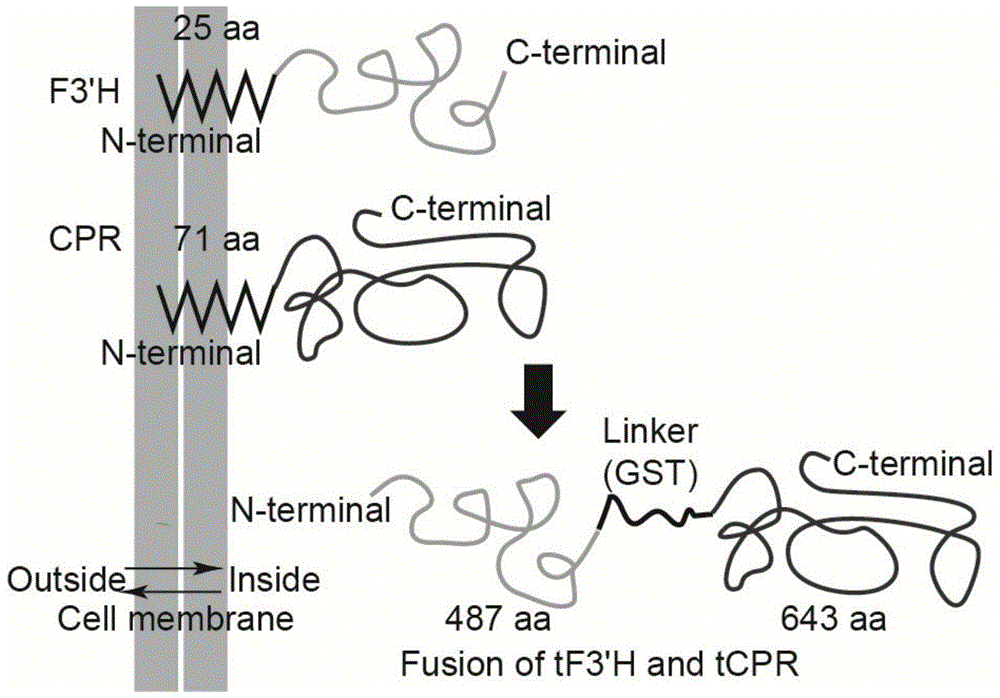
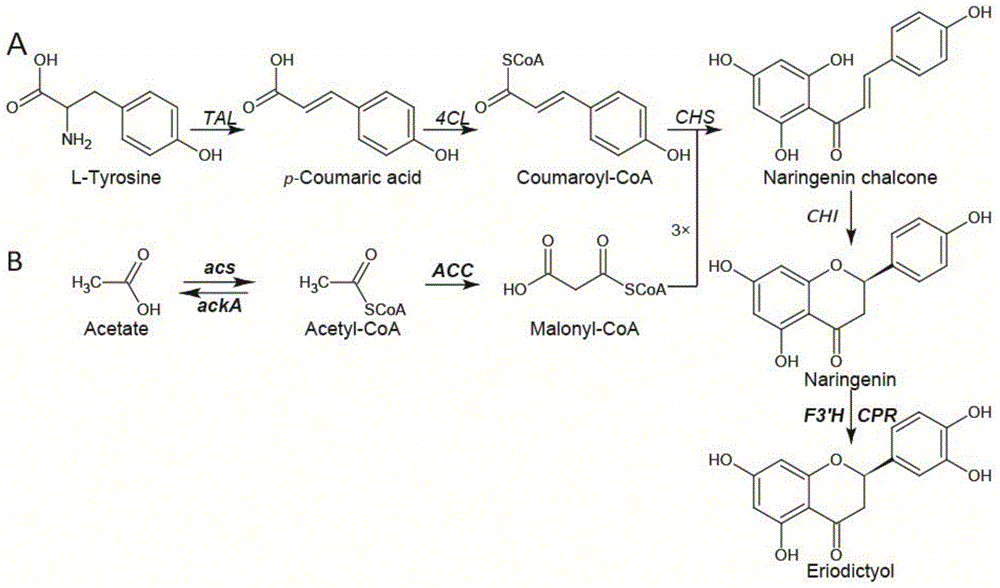
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
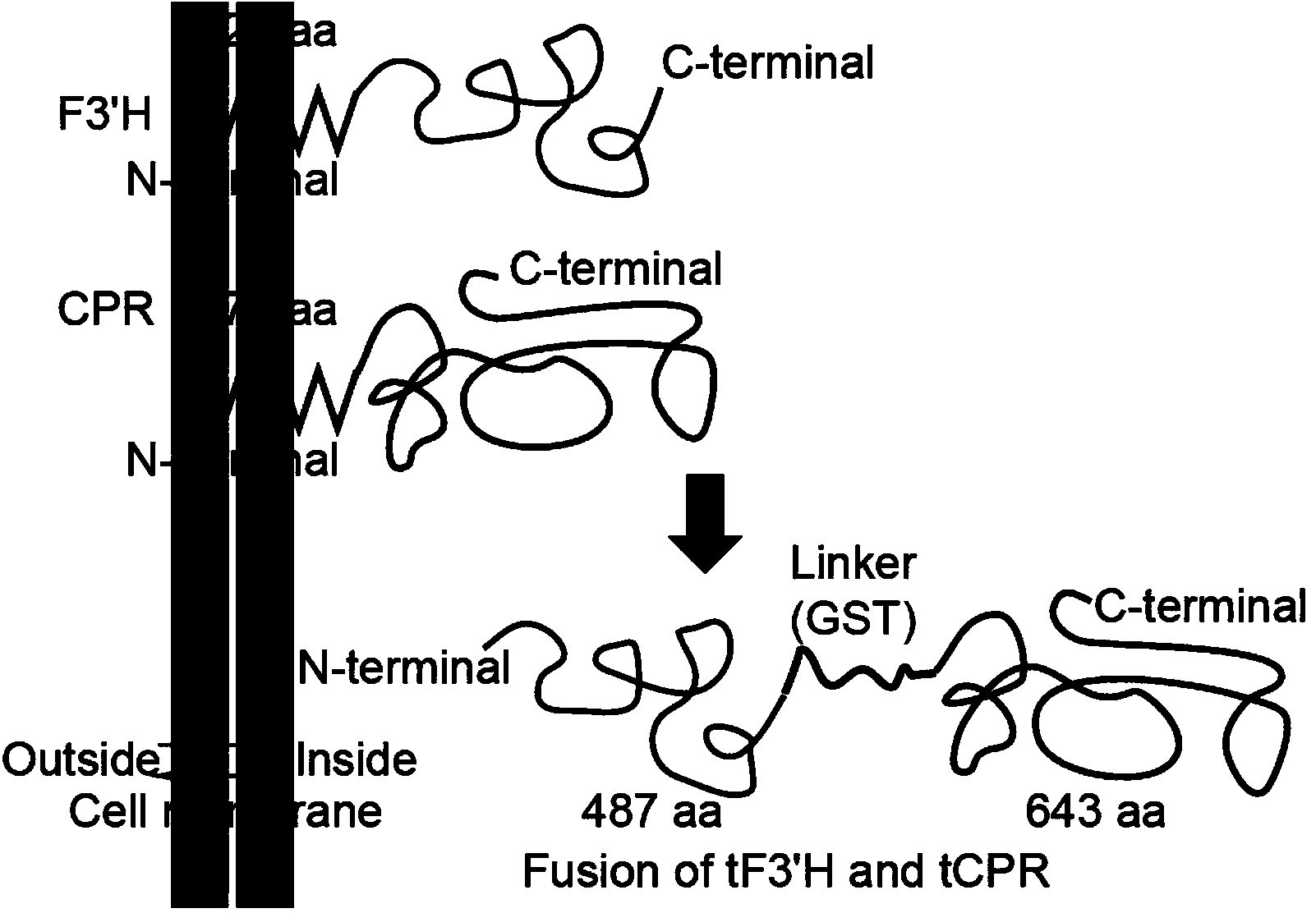
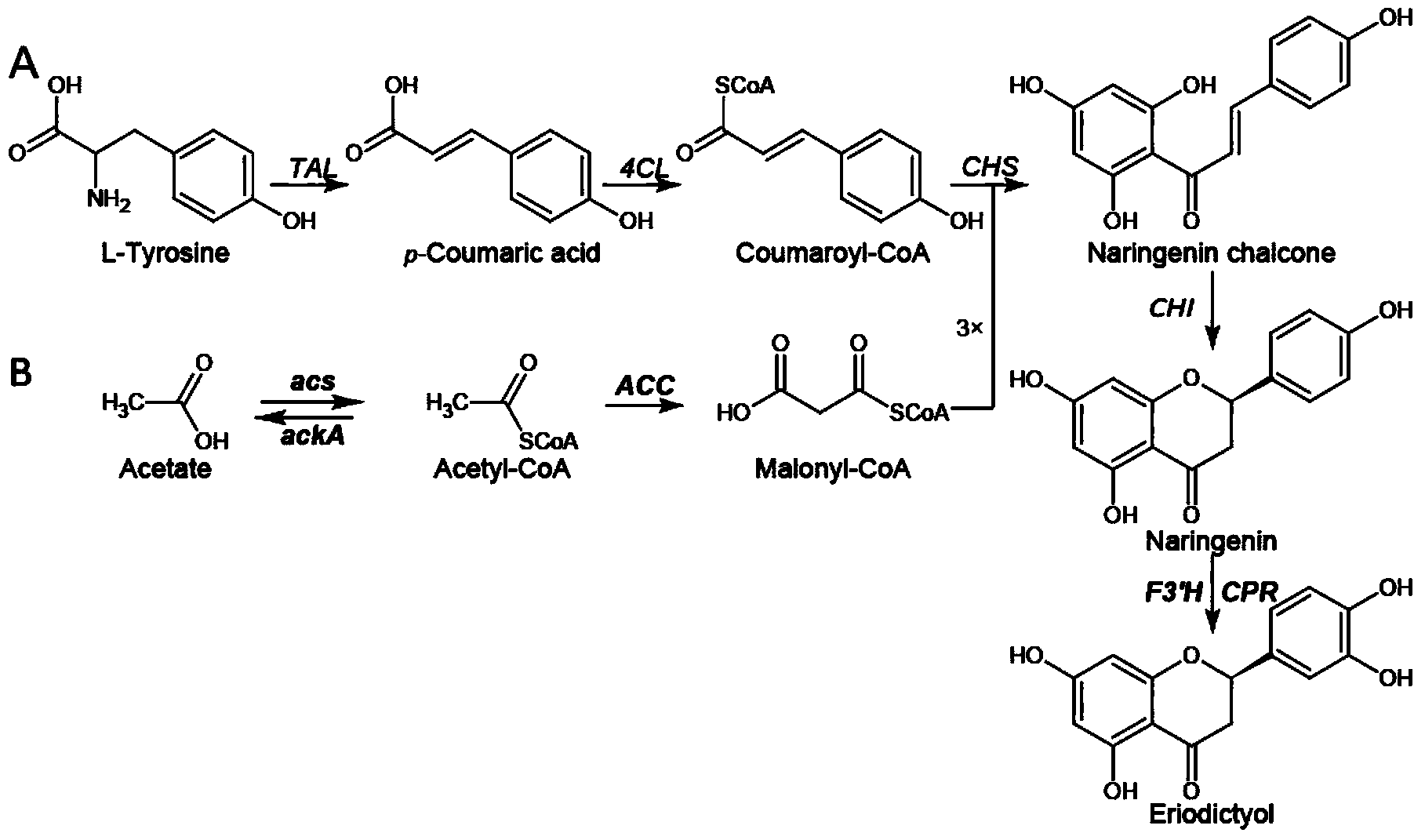
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering strain taking tyrosine as substrate to synthesize naringenin and construction method thereof
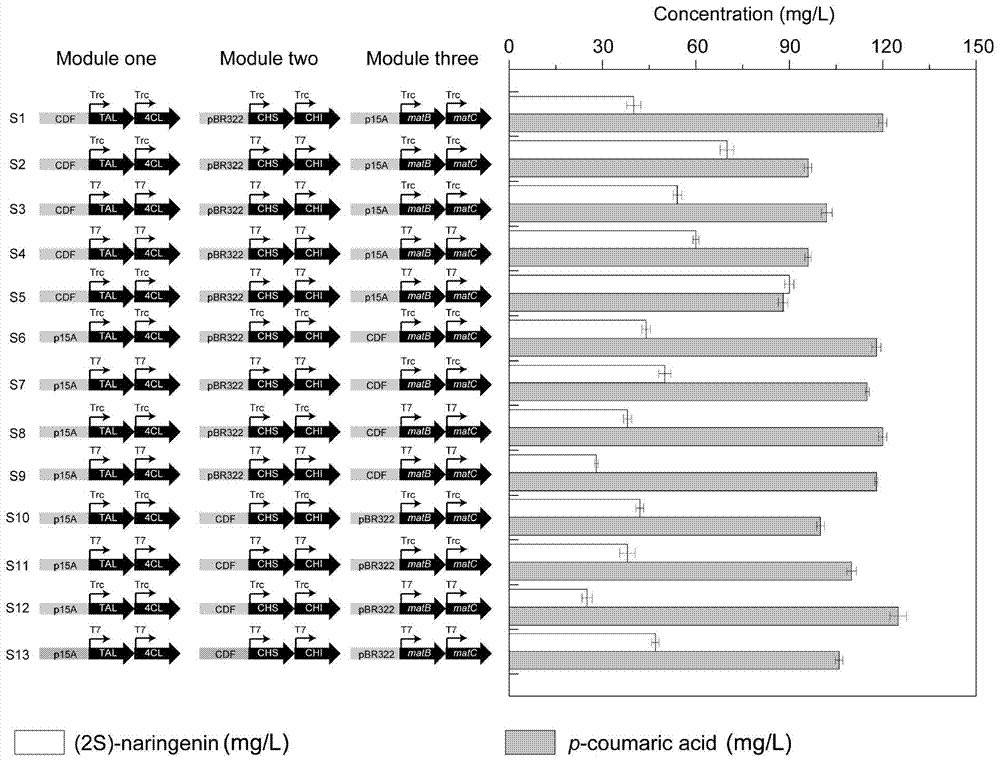
The invention discloses a genetic engineering stain taking tyrosine as a substrate to synthesize naringenin and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of synthetic biology or metabolic engineering. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, a synthesis route constituted by six genes, namely a gene matB encoding a malonic acid transporting enzyme, a gene matC encoding a malonic acid absorption route, a gene encoding a tyrosine ammonialyase (TAL), the gene encoding a 4-cinnamic acid: coenzyme A ligase (4CL), the gene encoding a chalcone synthase (CHS) and the gene encoding a chalcone isomerase (CHI) is introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 to obtain a recombinant strain capable of taking the tyrosine as the substrate to synthesize the naringenin, the synthesis route is further optimized through a modular transformation theory, the strain is finally fermented in a shaking flask for 72 hours by taking the tyrosine as the substrate, and the yield of the naringenin achieves 90mg / L. A strategy adopted by the construction method disclosed by the invention provides certain reference significance for future production of natural small molecular substances by a microbiological method.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
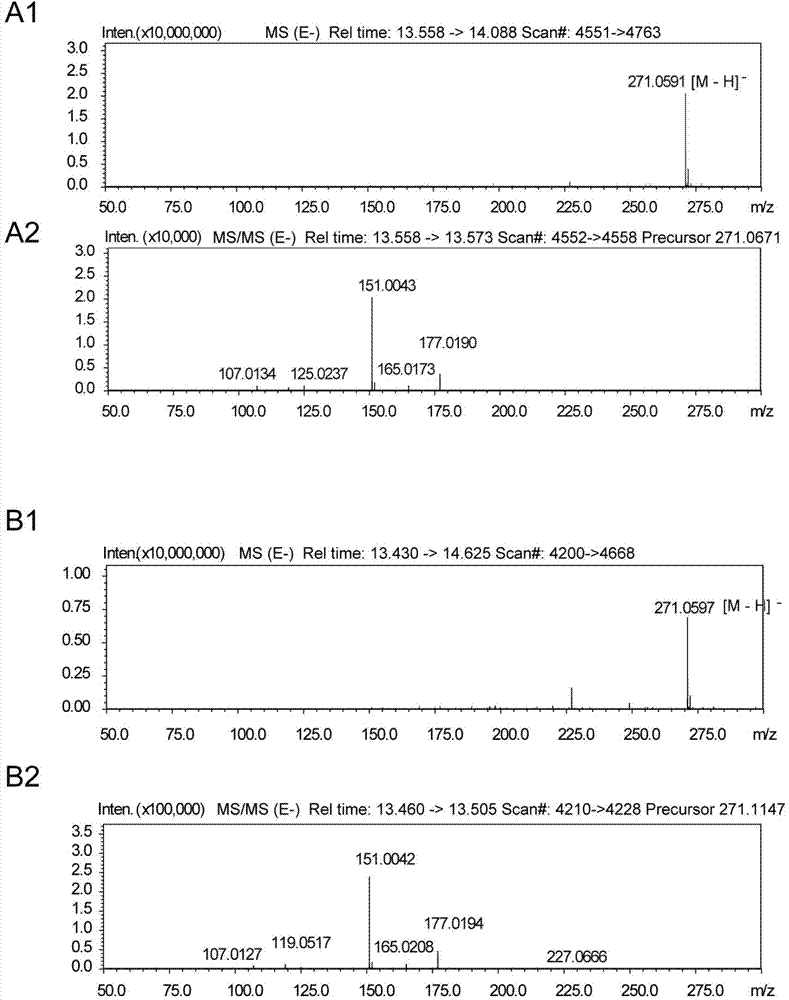
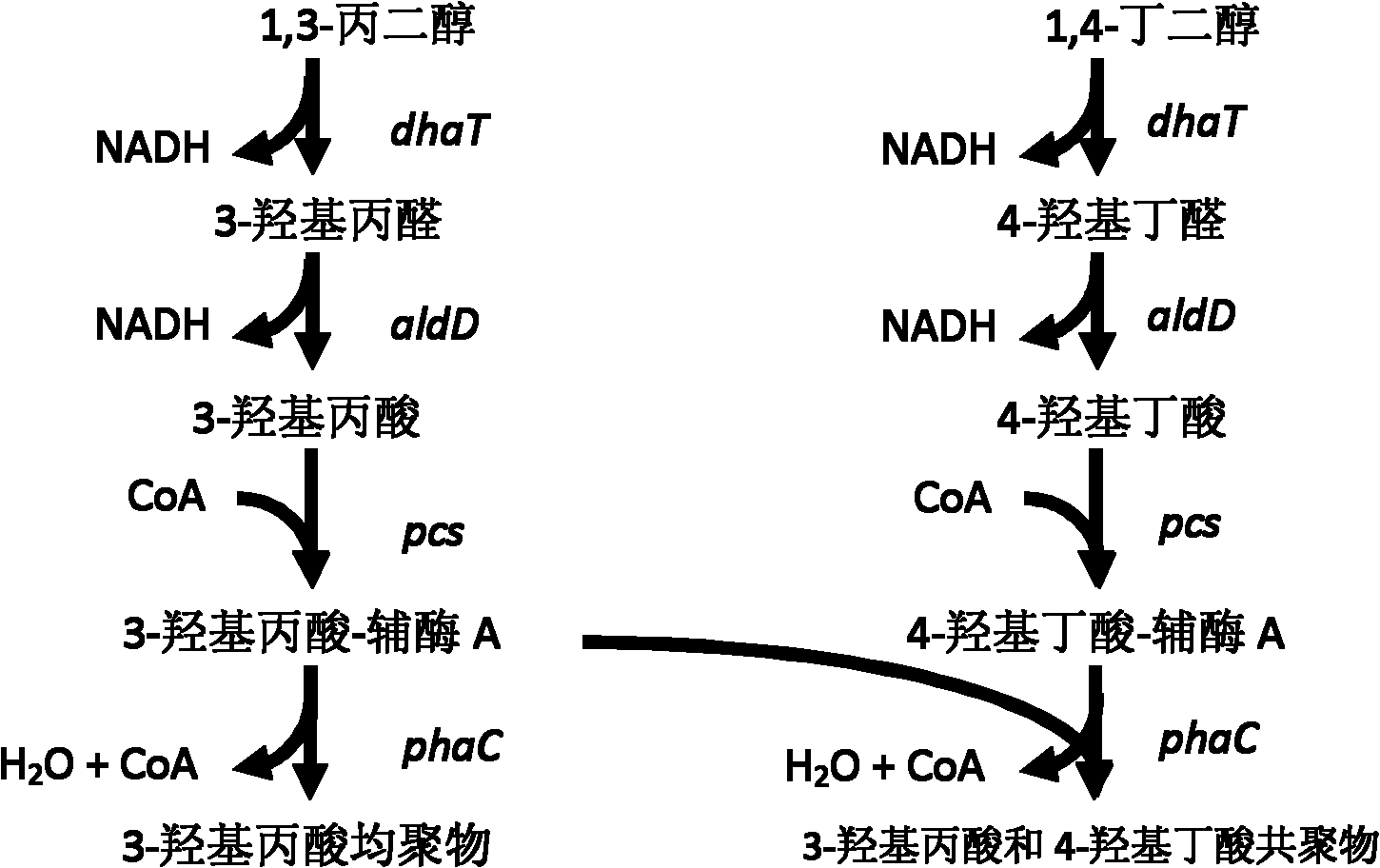
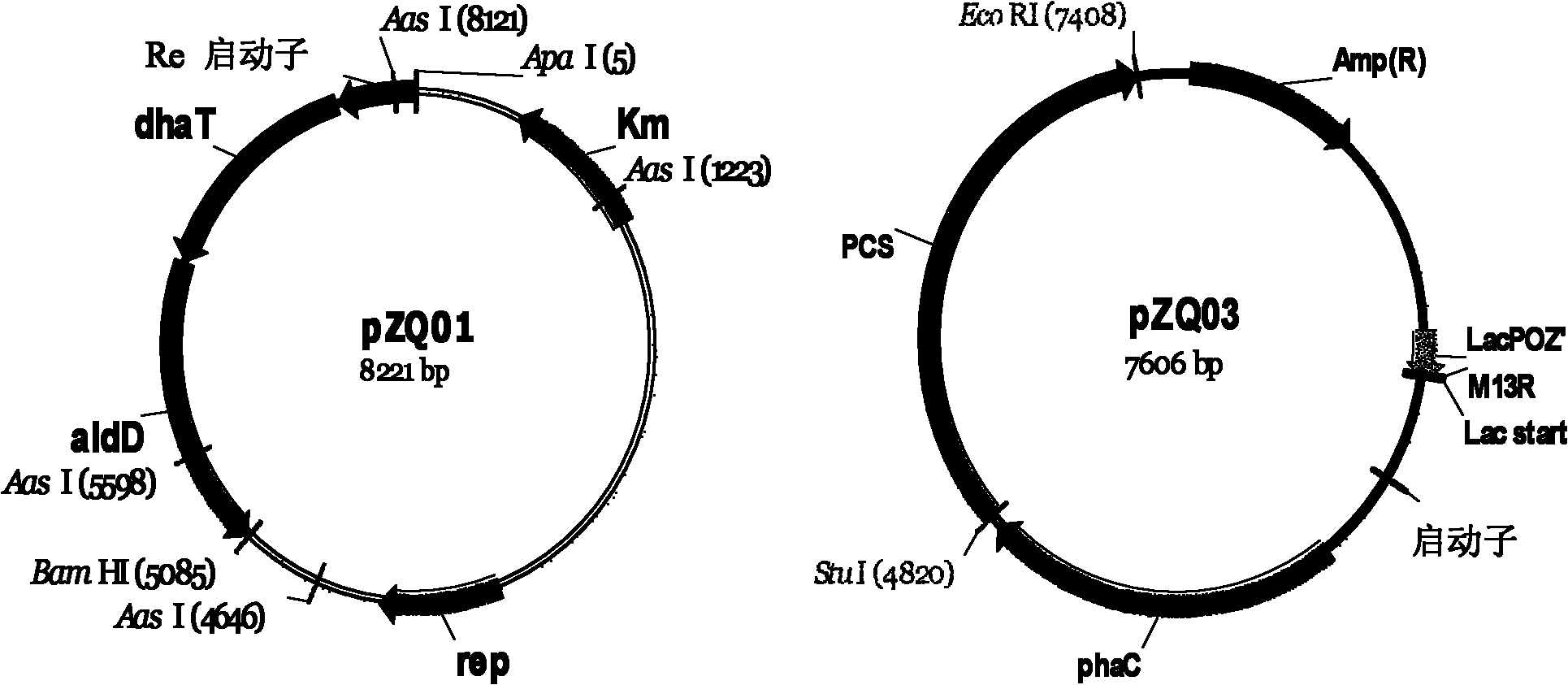
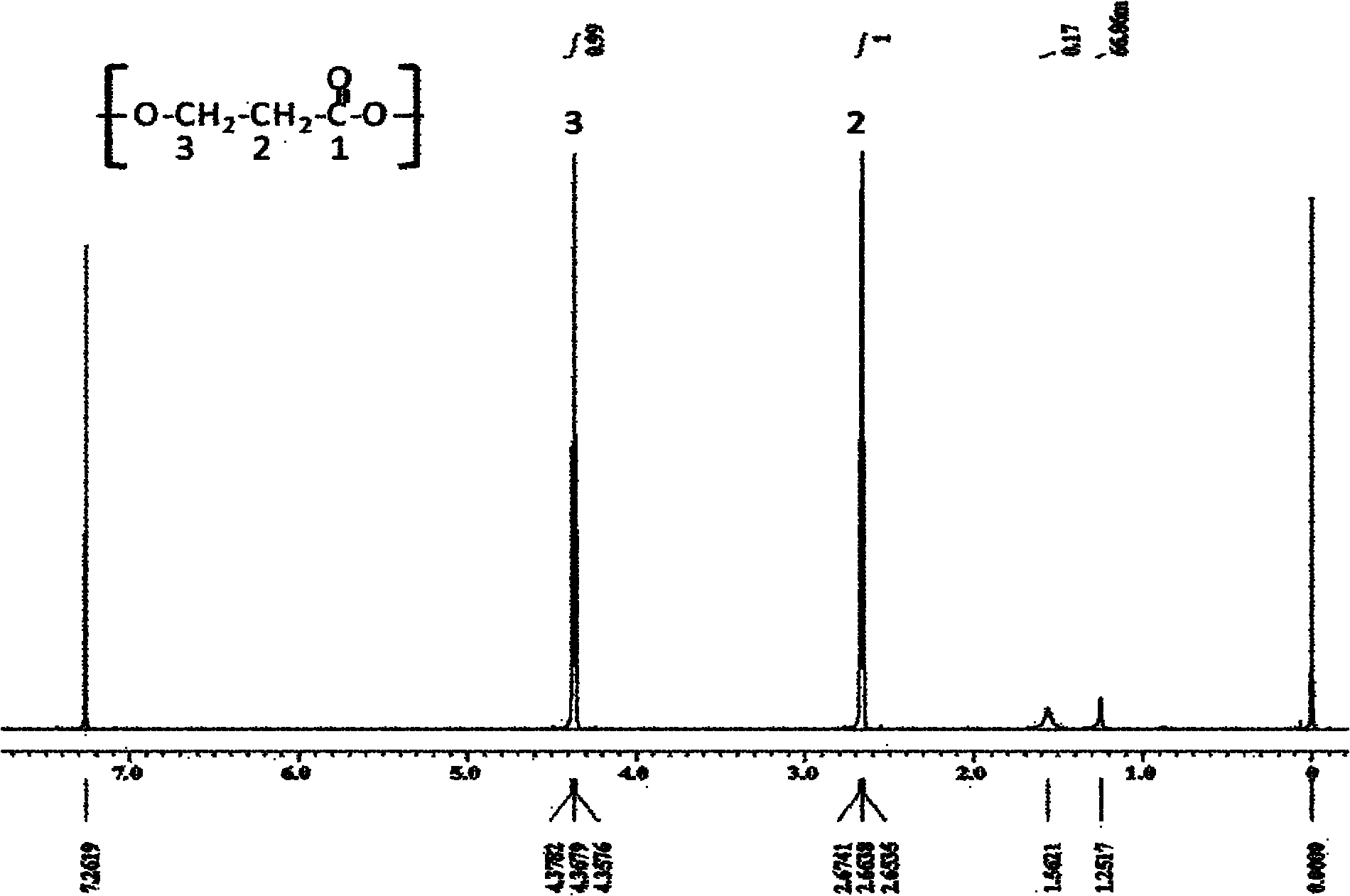
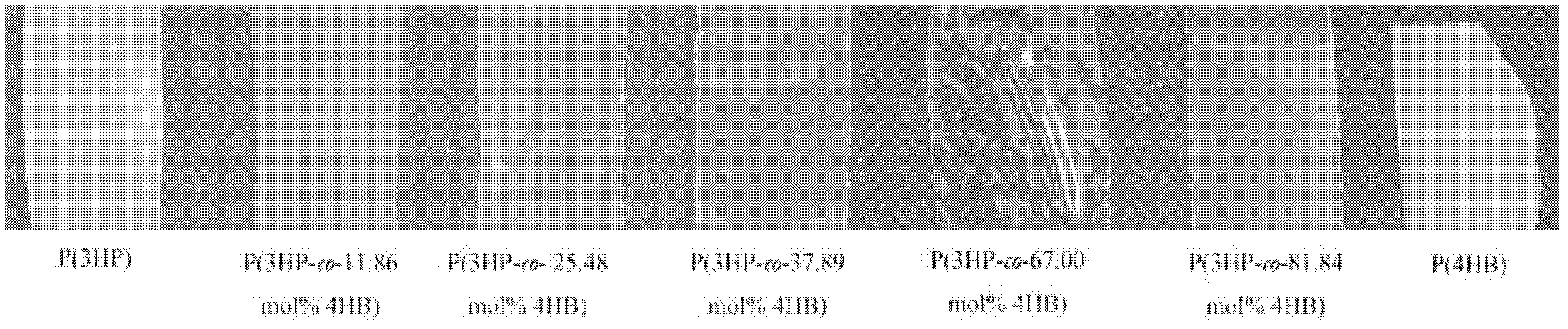
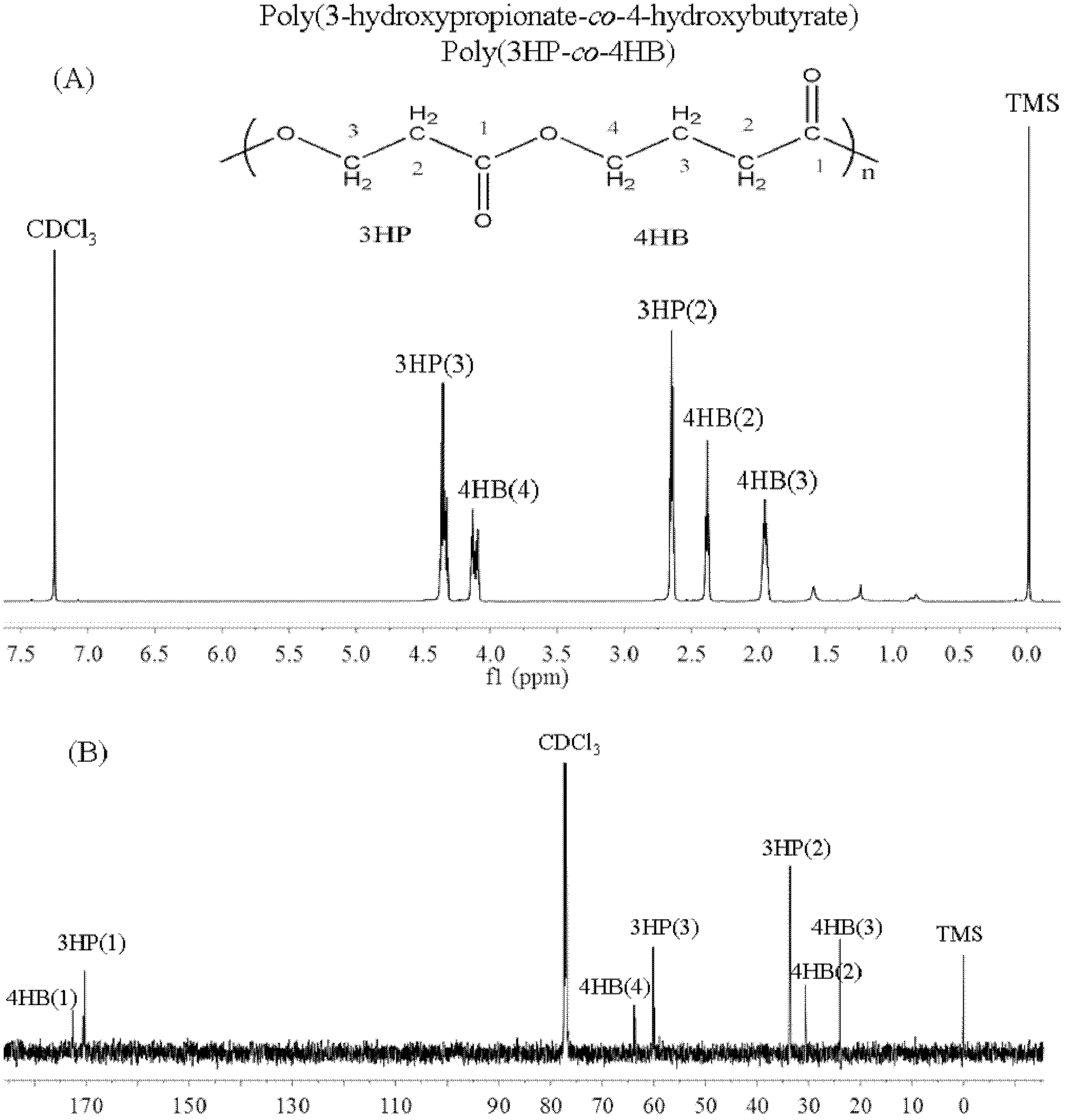
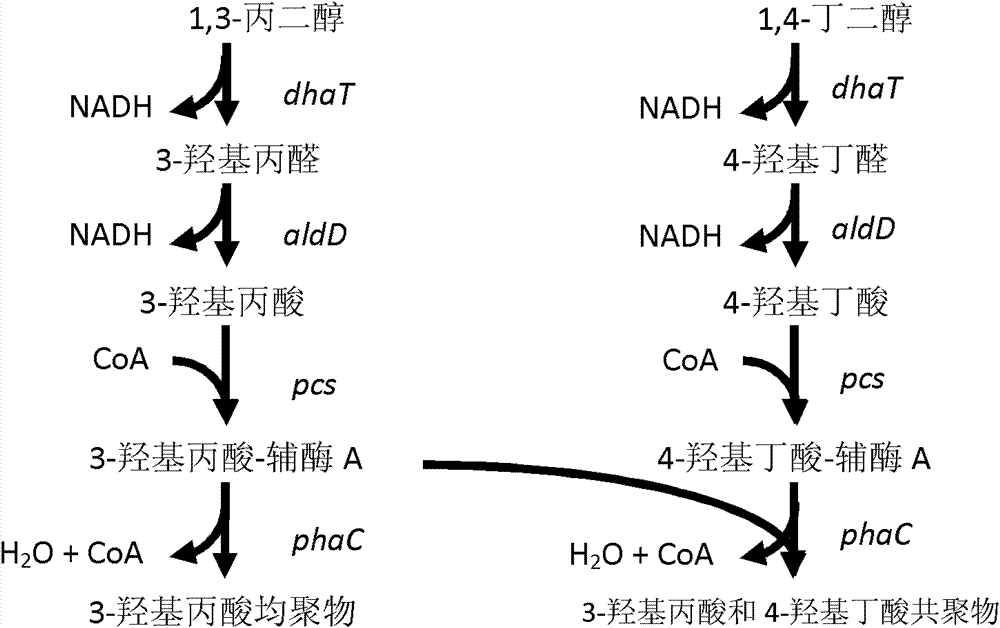
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPolymerase L
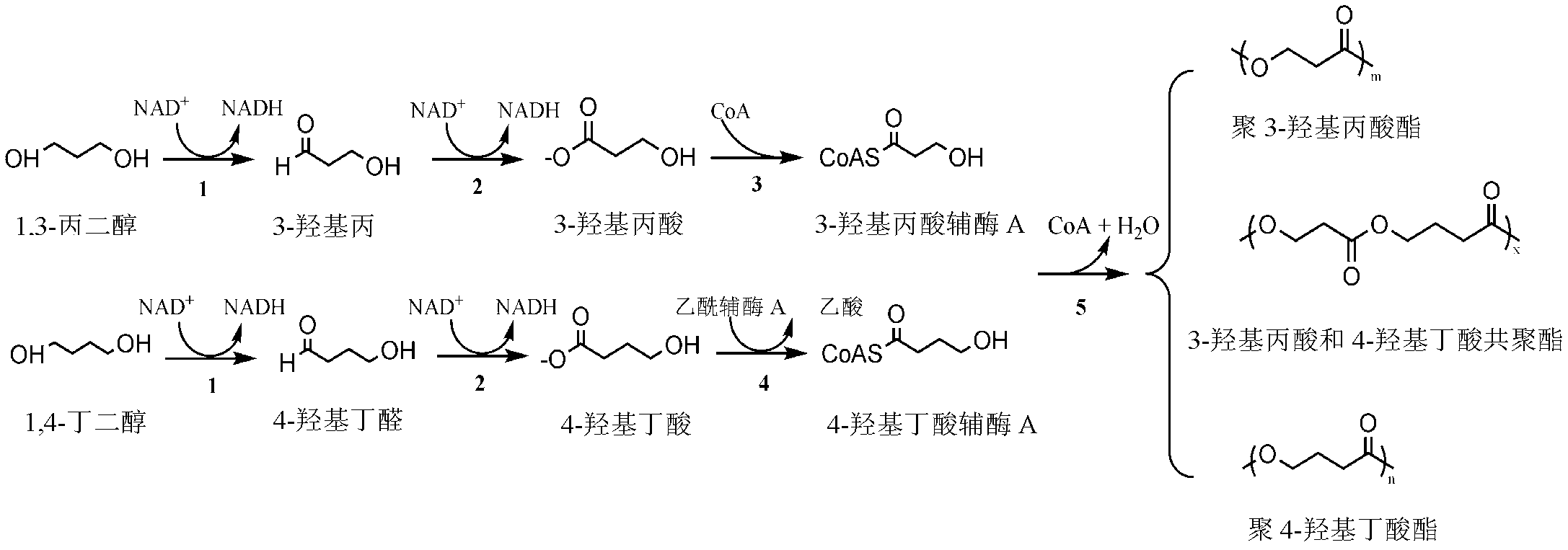
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108203713AClear backgroundGrow fastCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliUdp glucosyltransferase
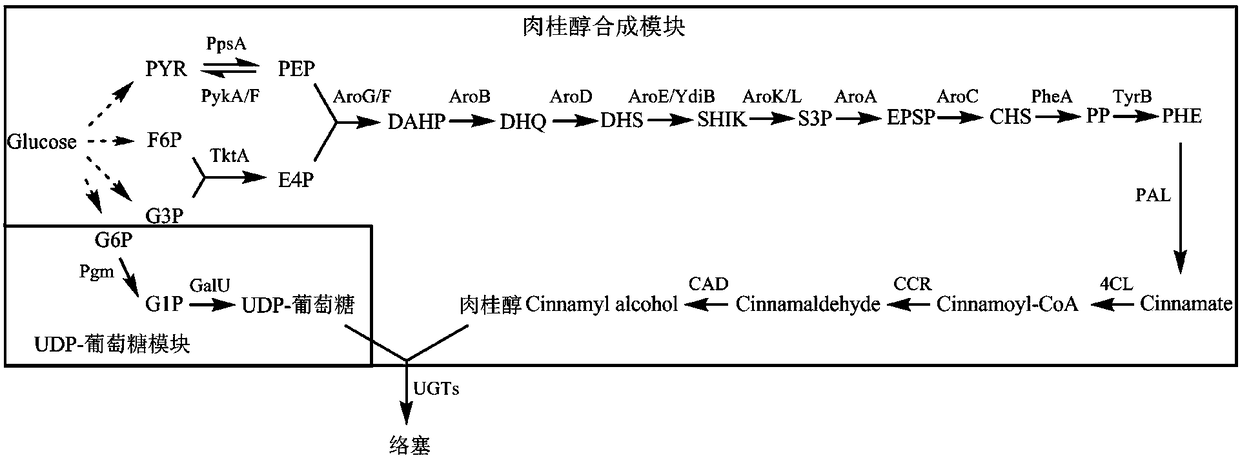
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and a construction method and applications thereof. The construction method comprises followingsteps: phenylalnine ammonialyase PAL, p-hydroxycinnamic acid coenzyme A ligase 4CL, and cinnamamide coenzyme A reductase CCR are introduced into Escherichia coli so as to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol. In the construction method, Escherichia coli is taken as a model organism, the background is clear, growth speed is high, large scale fermentation culture is convenient to realize, and cost is low. The recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin is obtained via construction of a cinnamic alcohol synthesis pathway, the cinnamic alcohol yield is 300mg / L; UDP glucosyltransferase is introduced into Escherichia coli further, so that organic combination of biological synthesis pathways of rosin and cinnamic alcohol isrealized, the highest rosin yield is 280mg / L. The construction method is capable of providing large scale industrialized production of cinnamic alcohol and / or rosin with foundation.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant bacteria for producing copolymer of 3-hydracrylic acid and 4-hydroxybutyric acid and application thereof
InactiveCN102676567AExcellent thermodynamic propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acid3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for producing a copolymer of 3-hydracrylic acid and 4-hydroxybutyric acid and application thereof. According to a method for constructing the recombinant bacteria, a 1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase encoding gene, an aldehyde dehydrogenase encoding gene, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase encoding gene, 4-hydroxybutyric acid coenzyme A transferase encoding gene and a polyhydroxyalkanoate polymerase encoding gene are imported into starting bacteria to obtain the recombinant bacteria. After engineering bacteria are produced in a 500-mL shake flask, the yield of P(3HP-co-4HB) can reach 6.2 g / L, and the maximum P(3HP-co-4HB) reaches 63 percent of the dry weight of cells. According to the recombinant bacteria, a production process is simple, and the thermodynamic property of the produced polymer can be changed by regulating the ratio of 3HP and 4HB, so the recombinant bacteria has bright application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
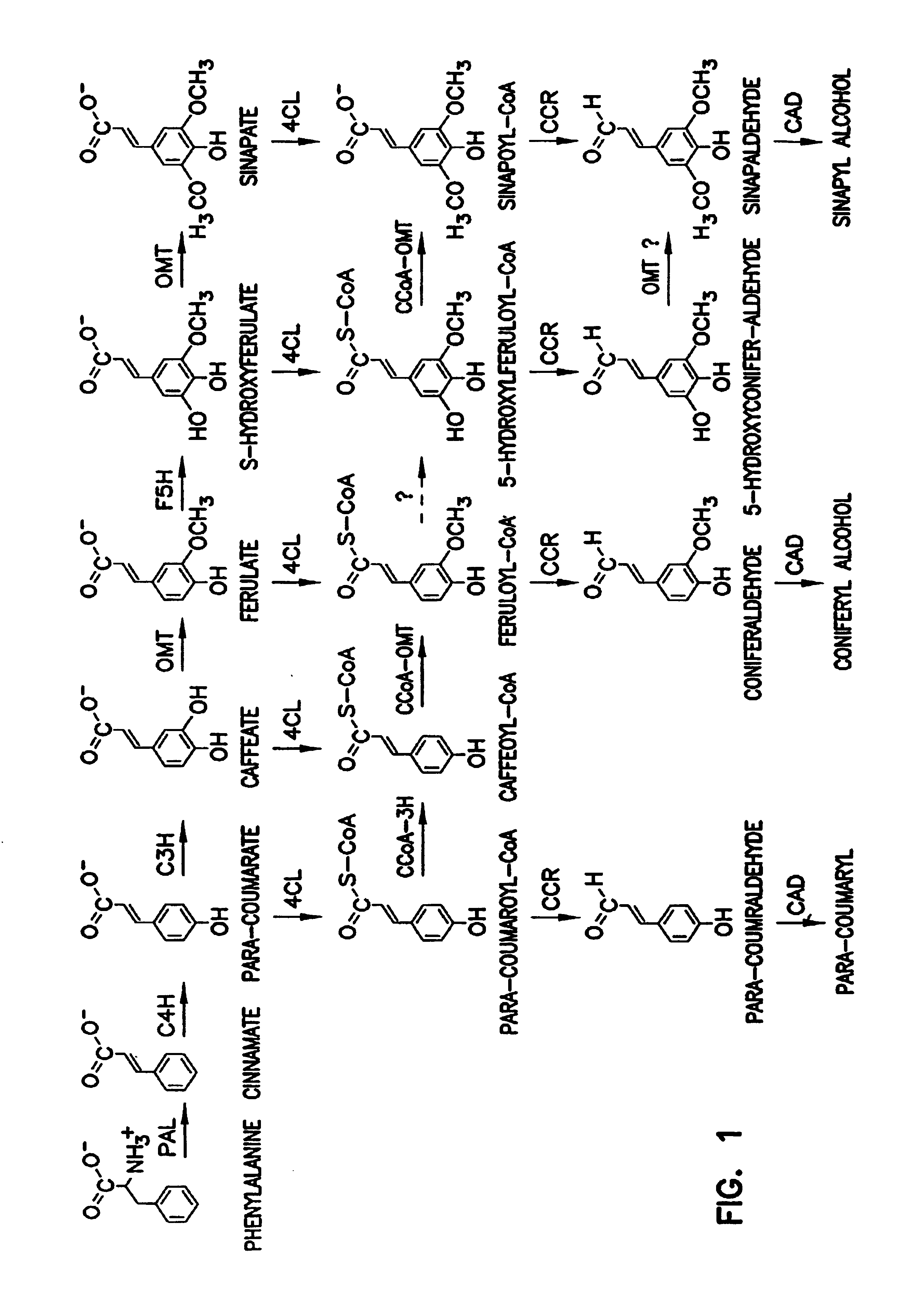
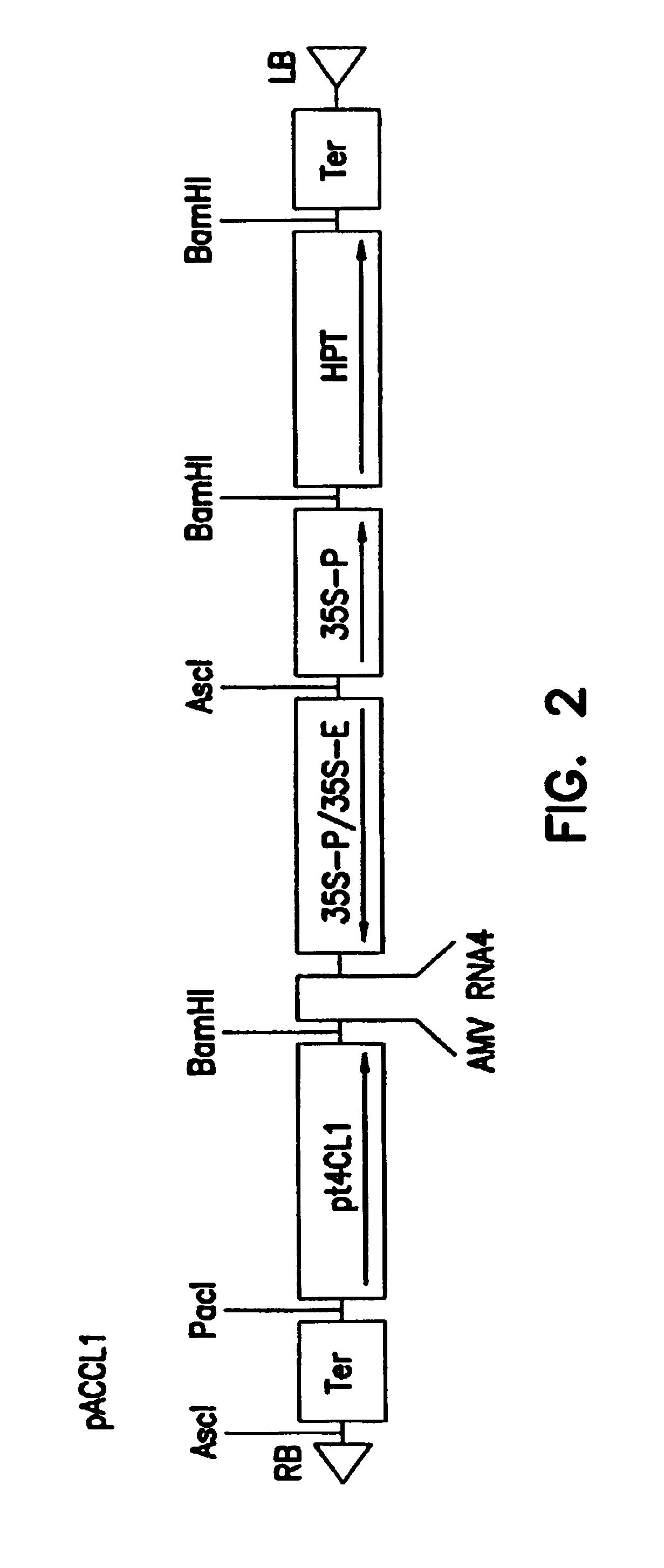
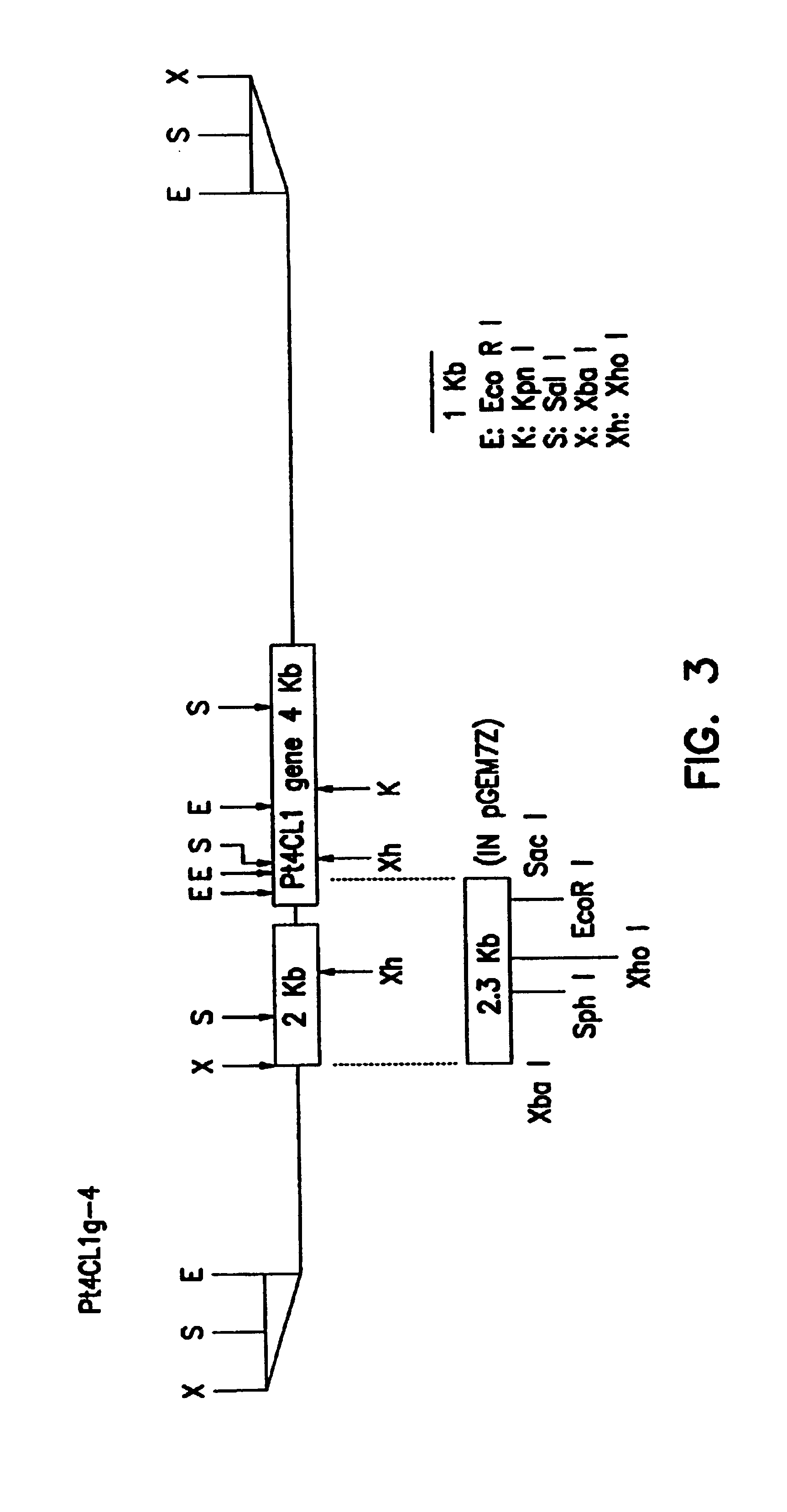
Genetic engineering of plants through manipulation of lignin biosynthesis
InactiveUS6969784B2Quick upgradeLow lignin contentSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGenetic engineeringCoenzyme A Ligases
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHCAL UNIV BOARD OF CONTROL +1
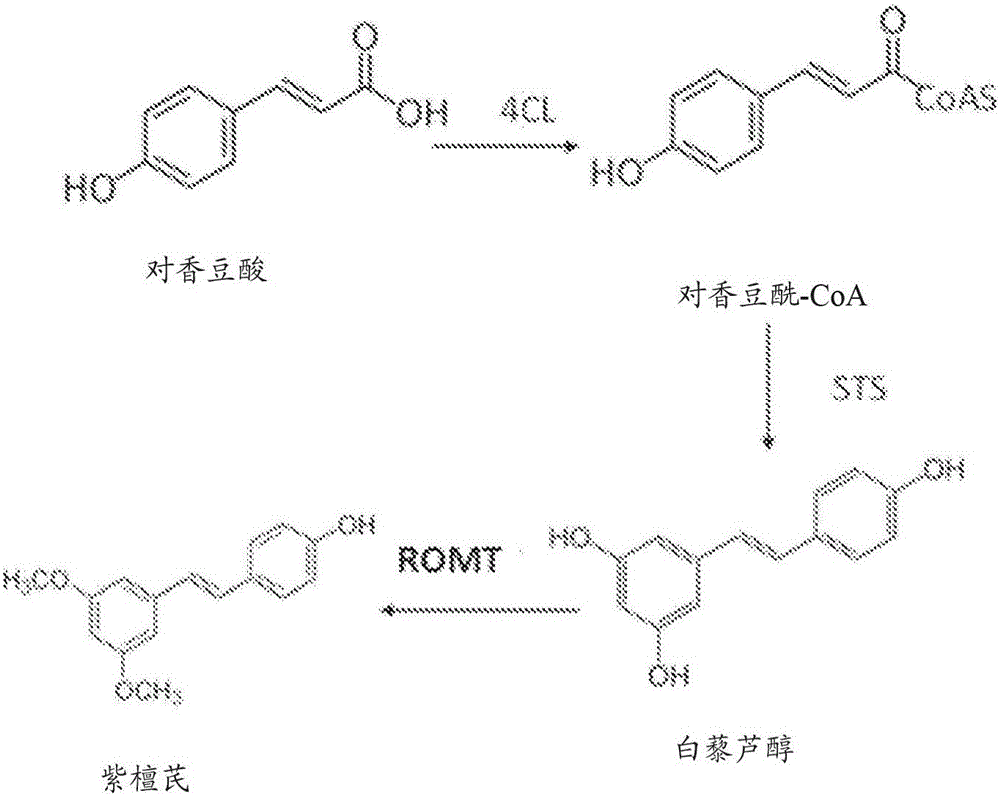
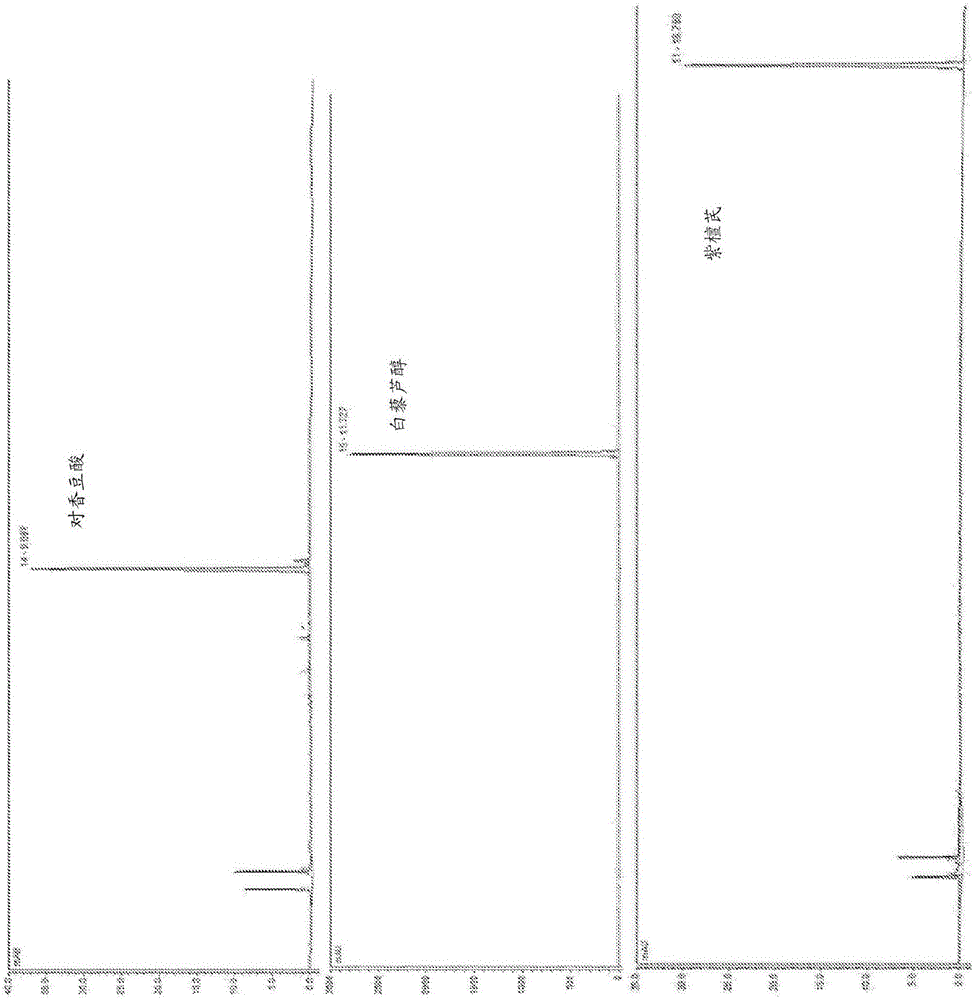
Methods of using O-methyltransferase for biosynthetic production of pterostilbene
ActiveCN106102454ASolve the technical problem of generating pterostilbenePromote generationBryophytesNervous disorderStilbene synthaseP-Coumaric acid
A biosynthetic method of making pterostilbene including expressing a 4- coumaratexoenzyme A ligase (4CL) in a cellular system, expressing a stilbene synthase (STS) in the cellular system, expressing a resveratrol O-methyltransferase (ROMT) in the cellular system, feeding p-coumaric acid to the cellular system, growing the cellular system in a medium, and producing pterostilbene.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Paulownia 4-coumaric acid: coenzyme A ligase gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101434937AChange compositionChange physical and chemical propertiesFungiBacteriaPaulowniaCoumaric acid
The invention discloses a paulownia 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, encoding genes and application thereof. Amino acid residue sequence of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase is shown in SEQ ID No. of 1. The information can be used for constructing genes of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, or antisense genes and RNA disturbing mass of the genes, which can be used for improving plant materials and constructing new materials with higher or lower lignin content.
Owner:河南省绿士达林业新技术研究所
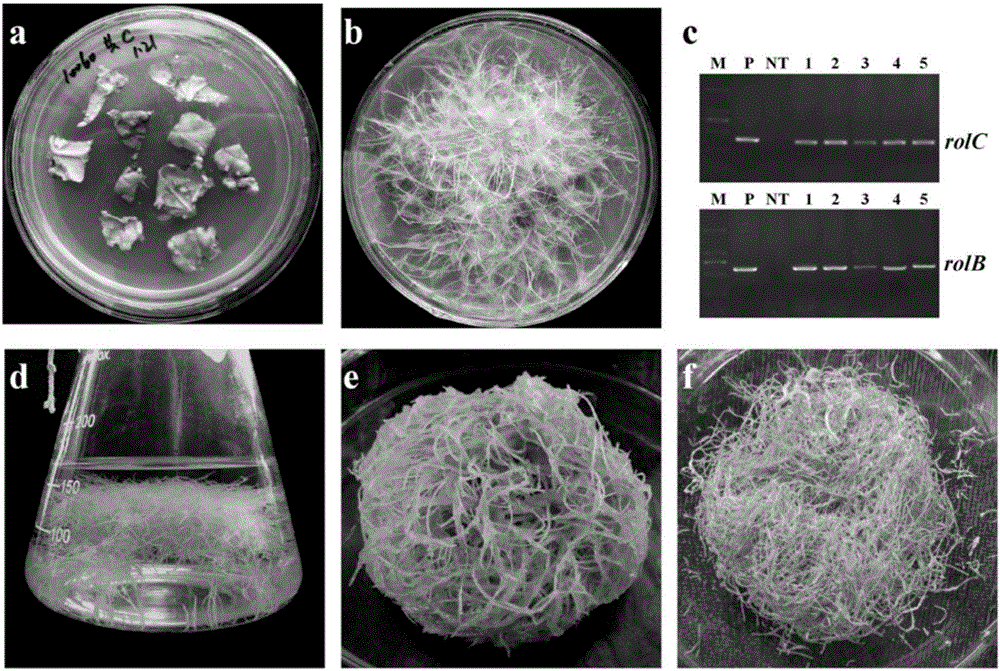
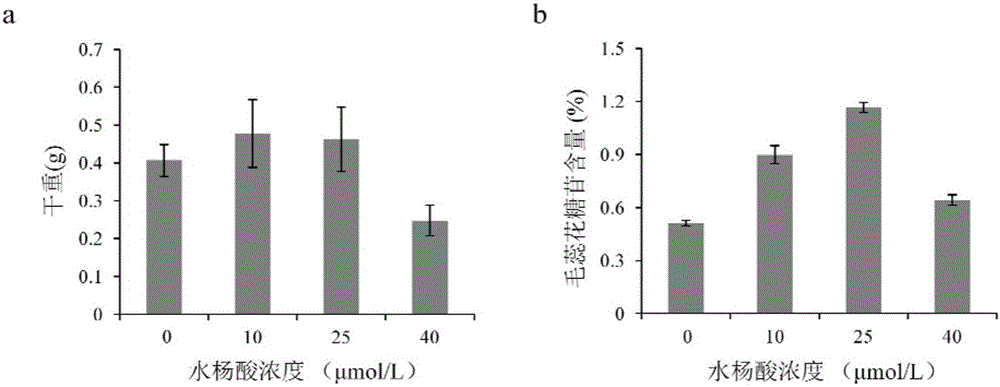
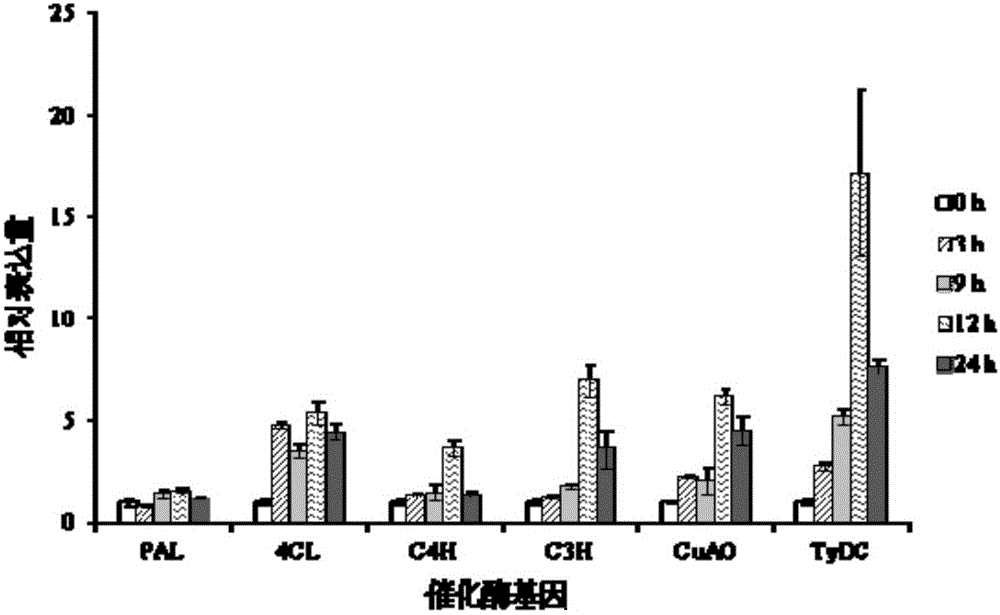
Method for producing verbascoside by using hairy roots of rehmannia
ActiveCN106148453AIncrease productionShort training periodMicroorganism based processesFermentationCoumaric acidSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing verbascoside by using hairy roots of rehmannia, and belongs to the technical field of bio-culture. The method comprises the following step: putting the hairy roots of the rehmannia into a salicylic acid-containing culture solution for inducing culture to obtain the verbascoside. The theory of the method is that the hairy roots, which are treated by salicylic acid, of the rehmannia can enhance the expression of key biosynthetic enzymes, such as phenylalnine ammonialyase (PAL), 4-coumaroyl-co-A ligase (4CL), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), coumaric acid hydroxylase (C3H), copper amine oxidase (CuAO) and tyrosine carboxy-lyase (TyDC), for the verbascoside within a short time period (12 to 24 h) so as to complete gathering of the verbascoside and further increase the yield of the verbascoside. The method is easy and convenient to operate, short in culture period, convenient for industrial, large-scale and standardized implementation, and has a great significance for promotion of large-scale production of the verbascoside.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing resveratrol and a constructing method thereof
InactiveCN106032525AIncrease productionAchieve truly industrial outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTyrosine
A genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing resveratrol is disclosed. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by knocking tyrR and trpED which are genes limiting tyrosine synthesis from glucose out of E.coli BW25113, and the chromosome is recombined with a tyrosine deaminase gene tal of rhodotorula glutinis, a petroselinum crispum p-coumaric acid: coenzyme A ligase gene 4cl and a stilbene synthase gene sts of grapes. The genetically engineered bacterium adopts glucose as a substrate to synthesize the resveratrol.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol
InactiveCN105907804AEfficient productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCinnamoyl-CoA reductaseCoumaric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and discloses a method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol. The metabolic pathway for production of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol is added into hosts. More precisely, tyrosine ammonia lyase, cinnamoyl-coA reductase, alcohol dehydrogenase and coumaric acid coA ligase are efficiently expressed in the host for producing tonquinol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid3-monooxygenase is added to produce caffeol, coffee acyl coenzyme AO-methyl transferase or caffeic acid O-methyl transferase is added to produce ferulenol. Genes coded by the enzyme are guided into the host, and the production host of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol can be generated by means of glucose. The invention further discloses a method for co-culture of different hosts, and the caffeol and the ferulenol are produced more efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for Escherichia coli whole cell catalyzed production of phloretin
InactiveCN107805646ALow costPrevent extractionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a method for Escherichia coli whole cell catalyzed production of phloretin. The synthesis method is characterized in that the production of the phloretin is completed by adopting phenylalanine as a raw material and an Escherichia coli engineering bacterium as a host bacterium through catalysis of multiple enzymes in the host bacterium; and the host bacterium at least can express phenylalnine ammonialyase, cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase, 4-coumaric acid coenzyme A ligase, double-bond reductase and chalcone synthetase. The method has the following advantages: 1, the phenylalanine is used as the raw material, so the raw material cost of the method is low; 2, catalytic synthesis of biological enzymes in microorganisms is carried out based on microorganism modification, solarge-scale extraction, separation and purification processes are avoided, and the production cost and the environmental protection are easy to control; 3, the size and the quantity of production devices used in the method are less than those of other methods, so the method can be easily industrially converted; and 4, only the final step in the production of the method contains separation and purification processes, so the product purifying process is simple, and the product has better quality and higher content than the product obtained through general methods.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
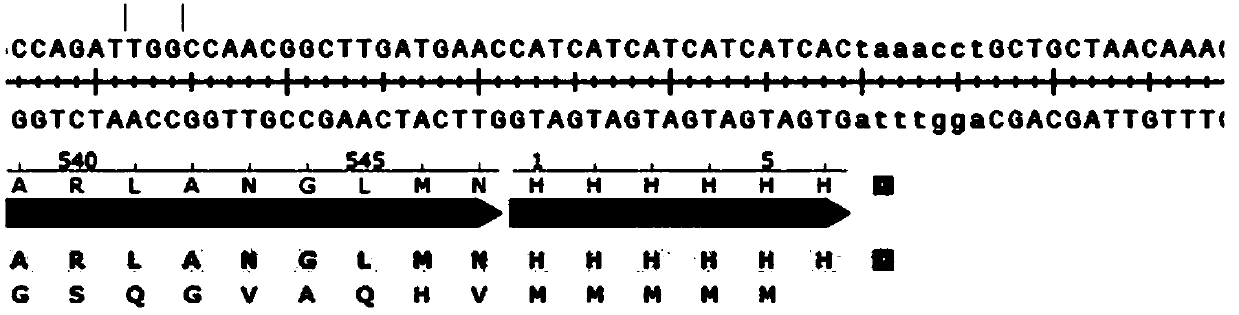
Coding sequences and applications of 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase protein family of isatis indigotica fortune
InactiveCN104805096AAltered biosynthetic applicationsEnzymesAngiosperms/flowering plantsCoenzyme A biosynthesisCoenzyme A Ligases
The present invention provides three sections of coding sequences of 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase protein family of isatis indigotica fortune, wherein the coding sequences are respectively represented by SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, and SEQ ID NO.3. The present invention further provides amino acid sequences of the 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase protein family of the isatis indigotica fortune, wherein the amino acid sequences are characterized in that the amino acid sequences are represented by SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6. The present invention further provides applications for changing biosynthesis of lariciresinol by regulating the expression of the 4-coumarate coenzyme A family protein of the isatis indigotica fortune. According to the present invention, the important application values are provided in the fields of breeding and biological energy sources.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
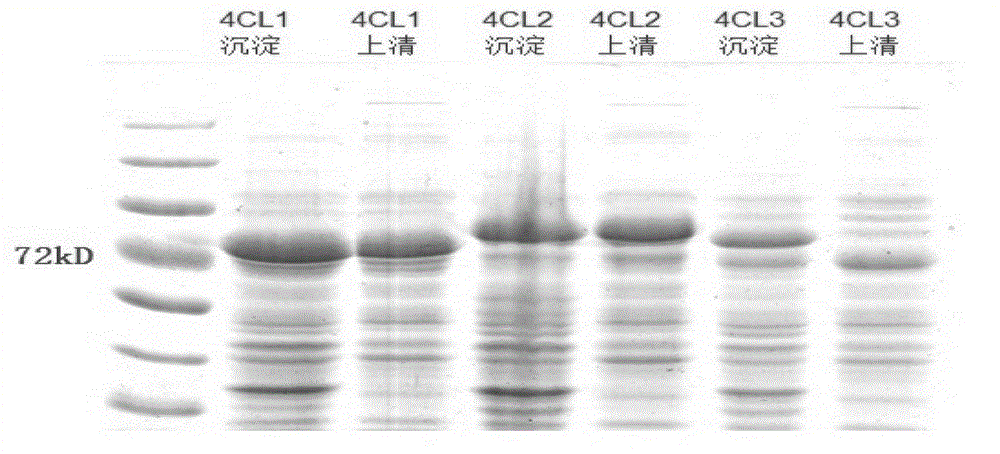
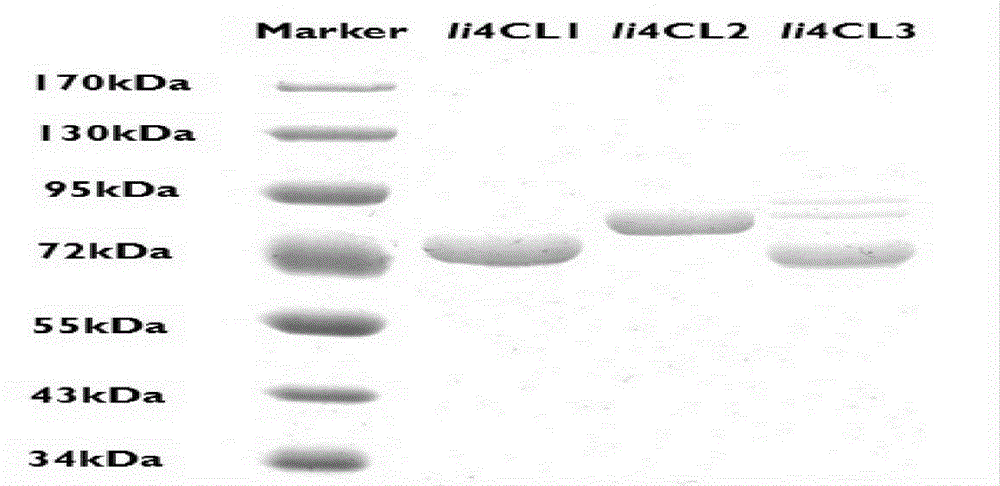
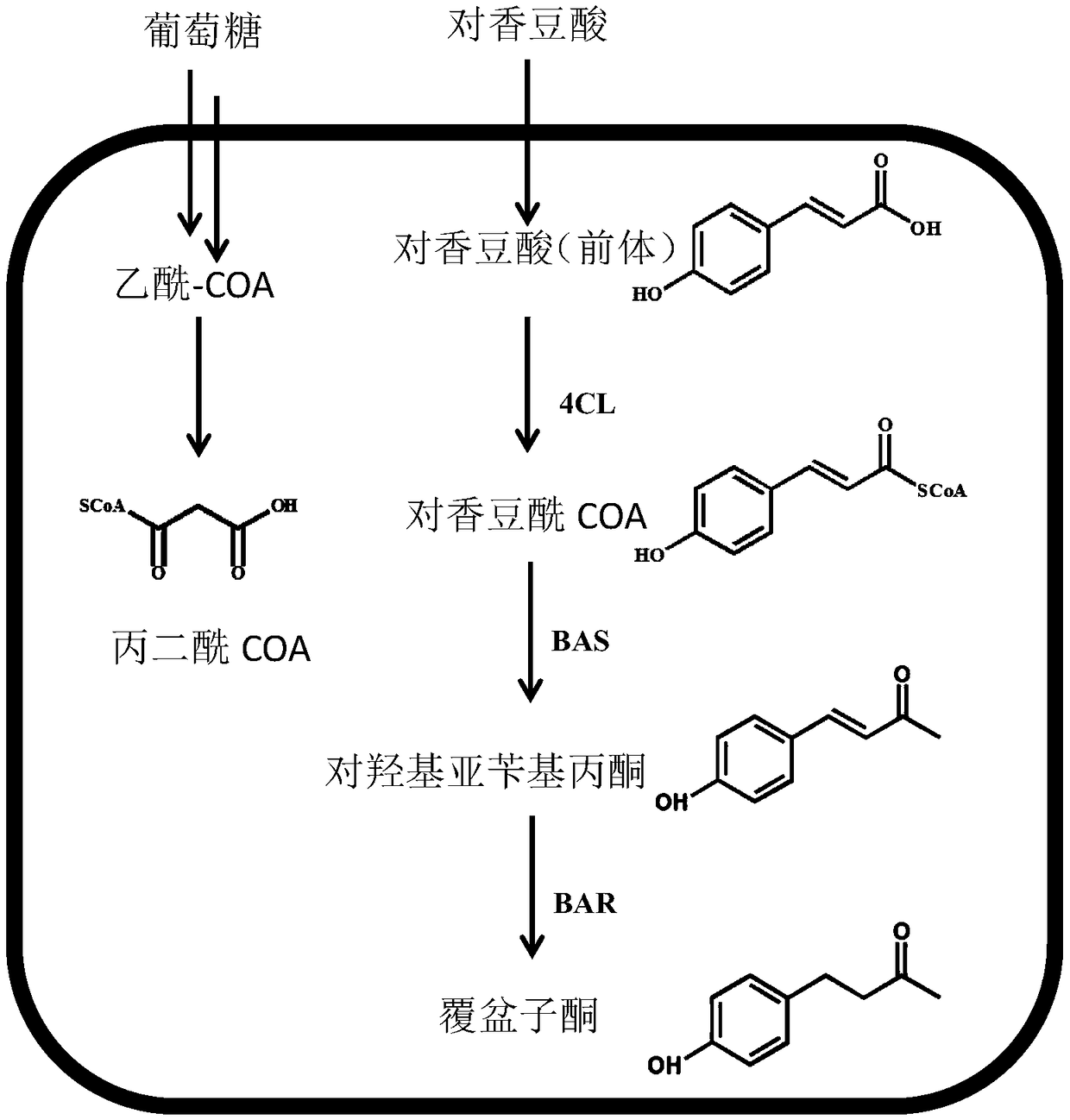
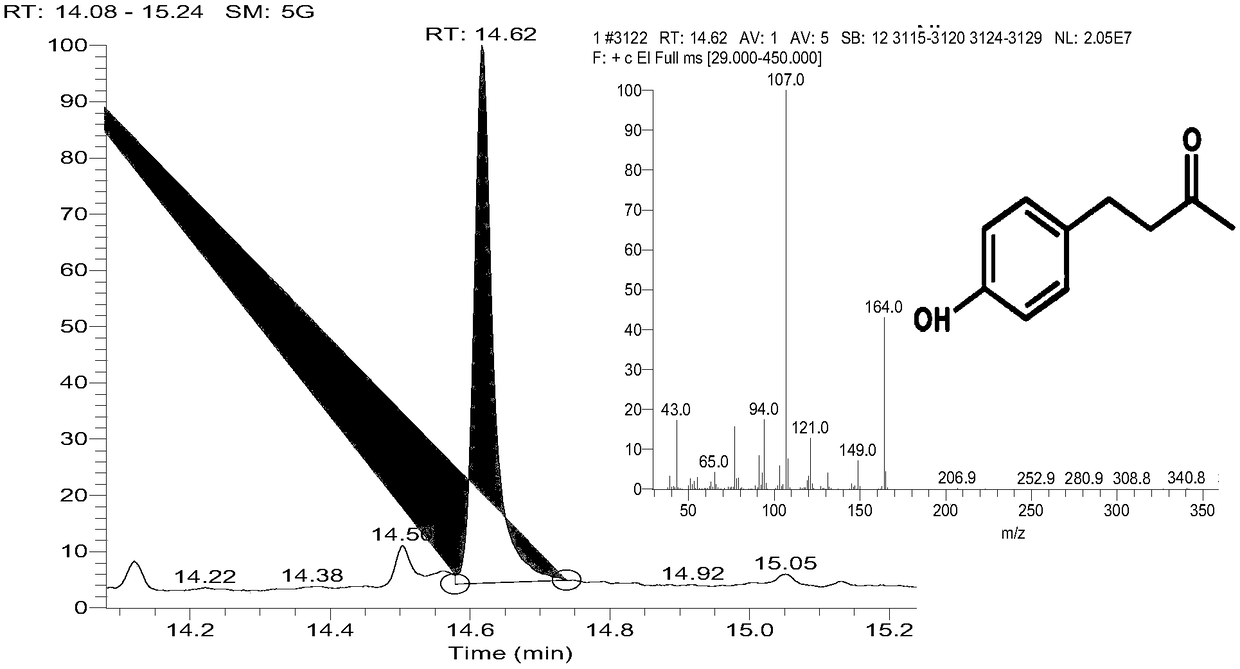
Method using biological method to prepare raspberry ketone
ActiveCN108753852AIncrease productionImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a method using a biological method to prepare raspberry ketone. The method includes: simultaneously expressing plant-source 4-coumaryl coenzyme A ligase, benzyl acetone synthase and benzyl acetone reductase in Escherichia coli in an induced manner. The method has the advantages that the benzyl acetone reductase (RiRZS1) is added to the metabolic pathway of biological raspberry ketone synthesis, so that the conversion efficiency of the intermediate product 4-hydroxybenzal acetone is increased; in addition, the yield of the shaking-flask-fermentation raspberry ketone reaches 70.62mg / L, and the yield of the raspberry ketone is evidently increased by the biological synthesis method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
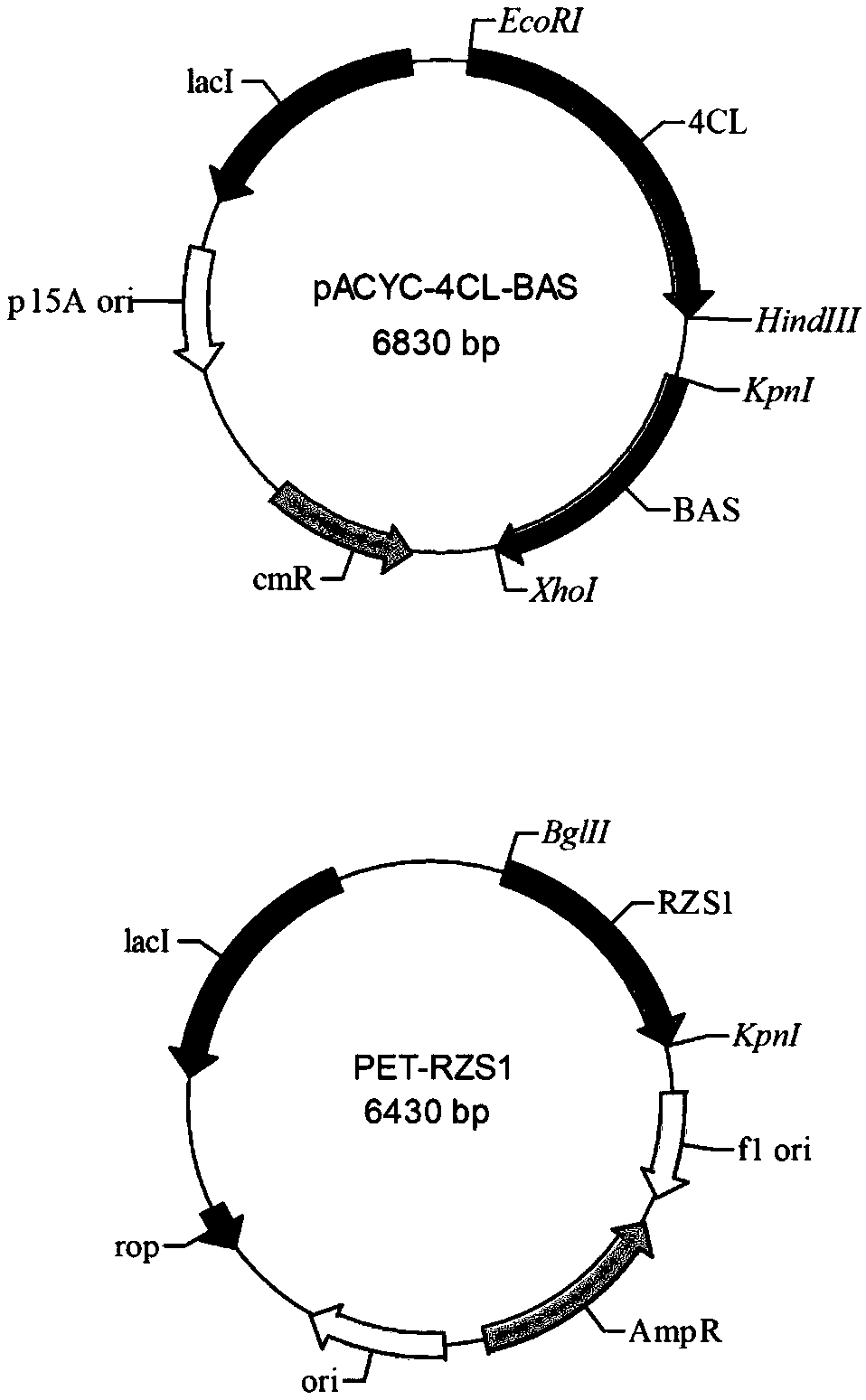
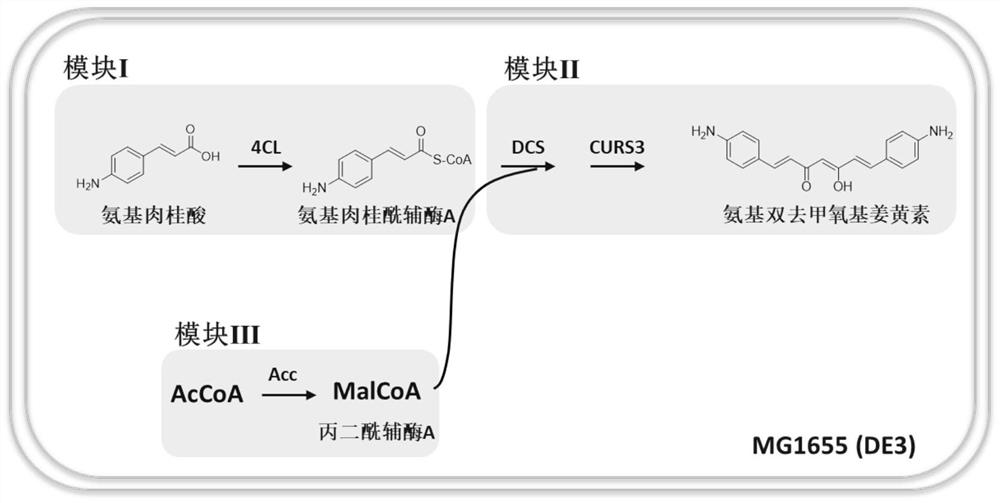
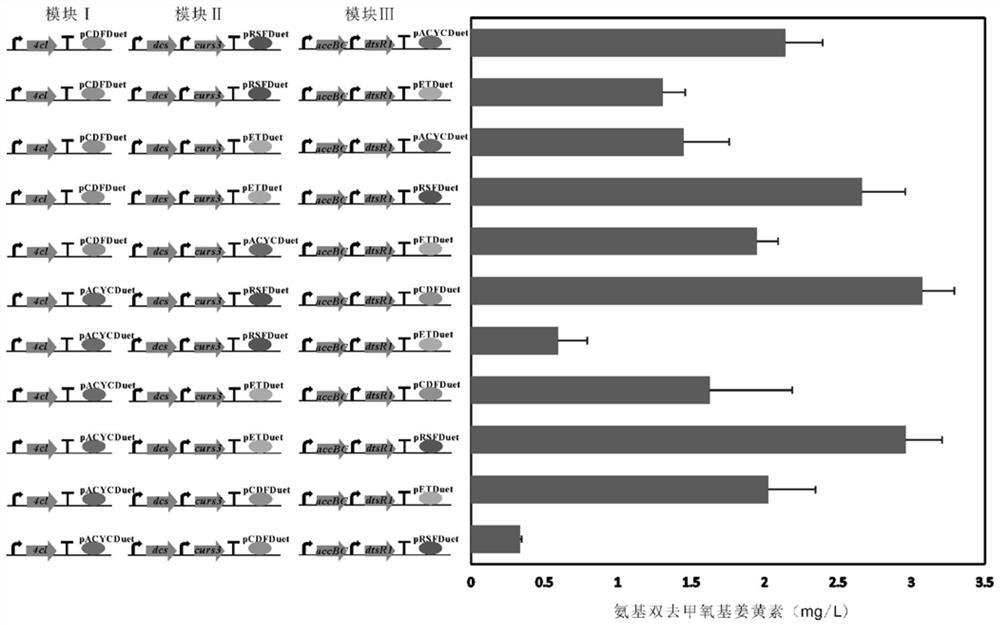
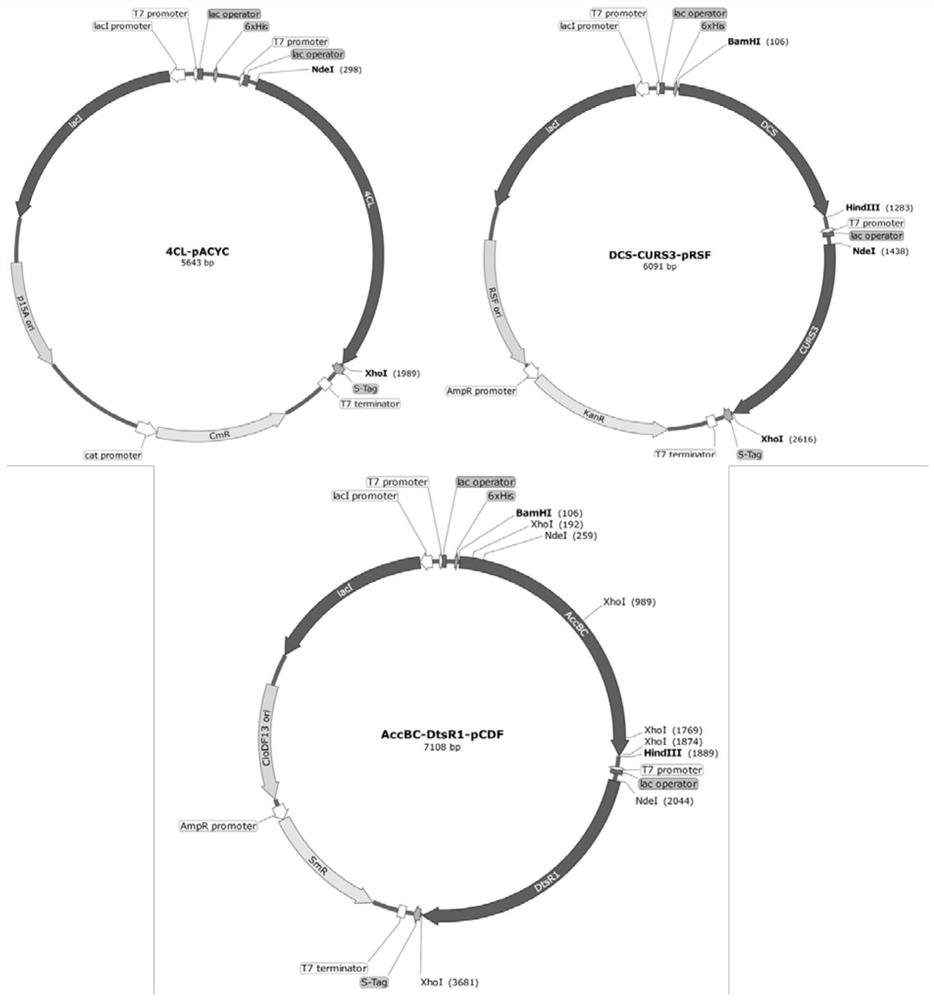
Construction and fermentation optimization method of amino-bis-demethoxycurcumin high-yield strain
The invention relates to construction and fermentation optimization methods of an amino-bis-demethoxycurcumin high-yield strain. The invention discloses an escherichia coli engineering strain for synthesizing aminodidemethoxycurcumin by taking p-aminocinnamic acid as a substrate, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology or metabolic engineering. A synthetic route composed of a 4-coumaroyl coenzyme A ligase gene 4cl, a dimer ketone synthase gene dcs, a curcumin synthase gene curs3 and acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes accBC and dtsR1 is transferred into Escherichia coli MG1655 (DE3), andthe synthetic route is subjected to modular division and optimization to obtain an engineering bacterium with optimal yield. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of amino didemethoxycurcumin reaches 33mg / L after the strain is fermented for 48h by taking p-aminocinnamic acid as a substrate. The invention lays a foundation for industrial production and application of the high-activity amino didemethoxycurcumin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
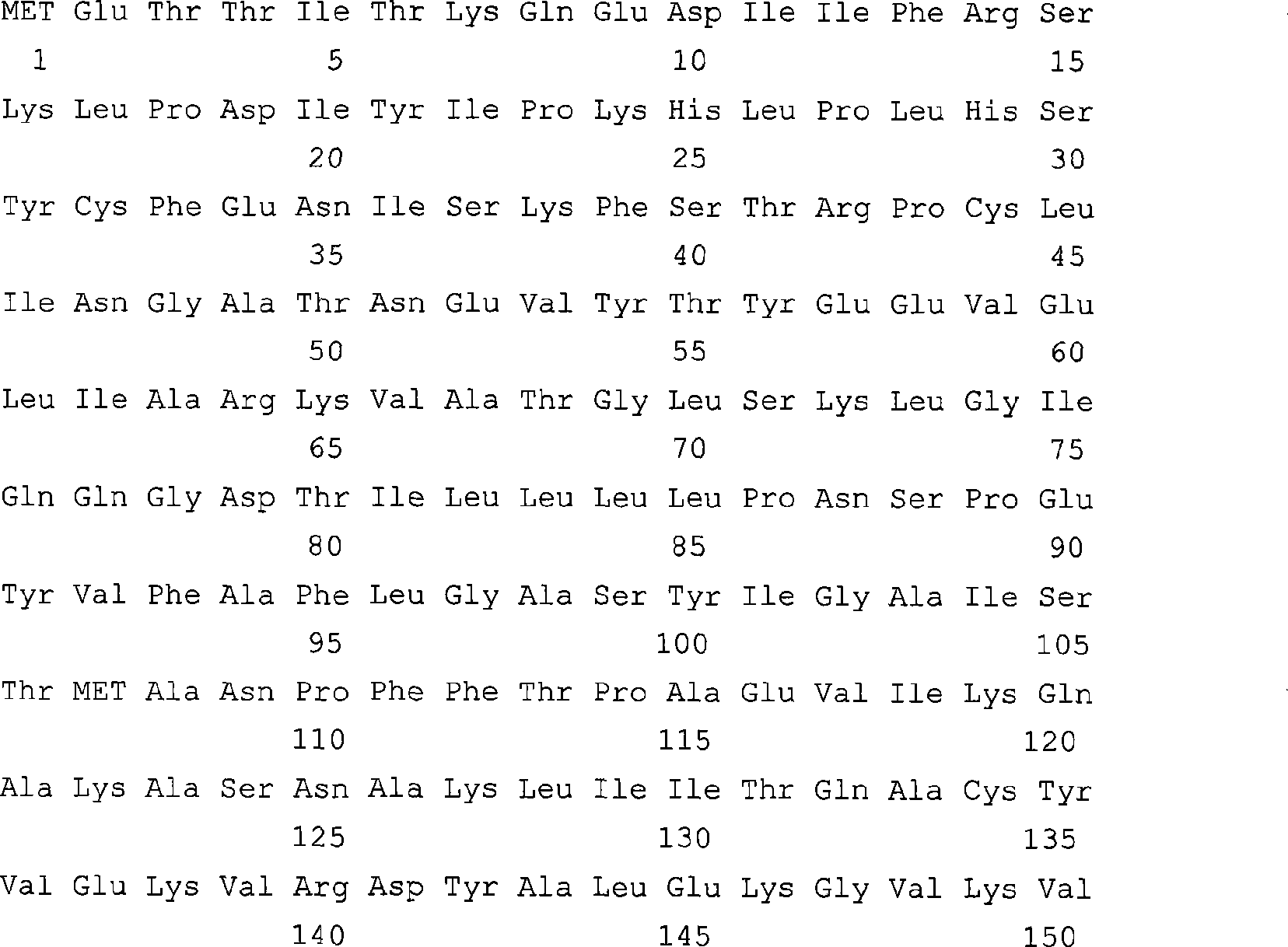
4-coumarate coenzyme a ligase originated from ornithogalum caudatum, nucleotide sequence, and applications thereof
The invention provides a 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase originated from ornithogalum caudatum, and the amino acid sequence of the ligase is represented by the SEQ ID No.1. The invention further provides a nucleotide sequence, which encodes the gene of the 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase and is represented by the SEQ ID No.2, a carrier containing the nucleotide sequence and a host cell. The invention also provides an application of 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase or cells containing 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase on catalyzing substrates such as p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, cinnamic acid, and the like into corresponding thioester compounds.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method using blue algae to synthesize phloretin
PendingCN109913508AEasy to buildReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidChalcone synthase
The invention provides a technical method using 'photosynthetic bacteria', namely blue algae as the substrate organism to synthesize phloretin. The method mainly includes: exogenously expressing 4 coumarate Coenzyme A Ligase (4CL) and Chalcone synthase (CHS) which are two key enzymes for phloretin synthesis in the blue algae so as to use p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid (also called phloretic acid)as the substrate to catalytically synthesize the phloretin, the 4CL catalyzes single-molecule p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid to generate p-hydroxybenzene propionyl coenzyme A, the CHS catalyzes three-molecule malonyl coA and the single-molecule p-hydroxybenzene propionyl coenzyme A to synthesize the single-molecule phloretin. The method has the advantages that the phloretin is produced by usingone microorganism which can perform photosynthesis, the phloretin biological synthesizing approach which is cheap in raw material, simple in equipment, low in environment pollution and high in yield is created, and the method conforms to the direction of green production.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
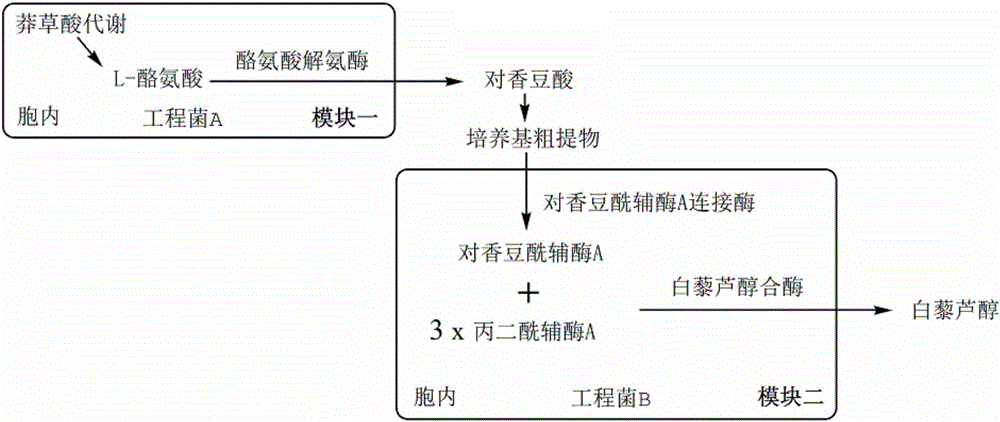
Combinatorial biosynthesis method of resveratrol
InactiveCN106191137AEase of industrial productionReduce manufacturing costCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a combinatorial biosynthesis method of resveratrol, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Two production modules are constructed; in the first production module, recombinant escherichia coli can express tyrosine ammonia lyase through a constructed constitutive expression system and achieve denovo synthesis of p-coumaric acid; in the second production module, the recombinant escherichia coli can express p-coumaric acyl coenzyme A ligase and resveratrol synthase through the constructed constitutive expression system and synthesize resveratrol through p-coumaric acid produced by the first module. According to the method, the advantages that the two production modules can conduct regulation separately and can better achieve the maximum production value theoretically are achieved through step-by-step culture; the constitutive expression system which does not need an inducer and is efficient is provided, and therefore usage of a toxic inducer is avoided; through denovo synthesis of resveratrol, the production cost is reduced, and industrial production is better promoted.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce eriodictyol
ActiveCN103865864BReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
Method for constructing stably inherited genetic engineering strain for efficient biosynthesis of beta-arbutin and application thereof
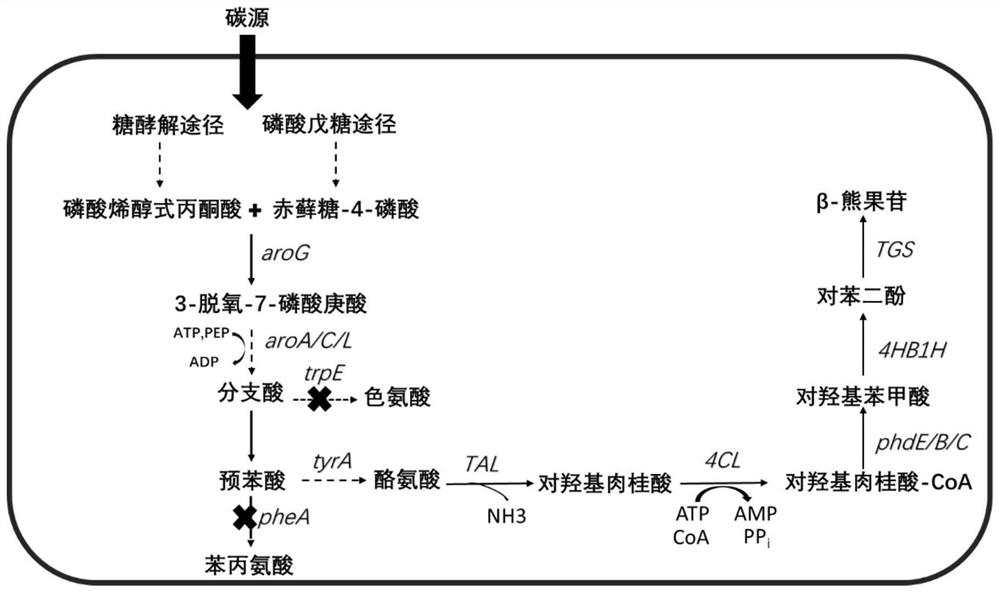
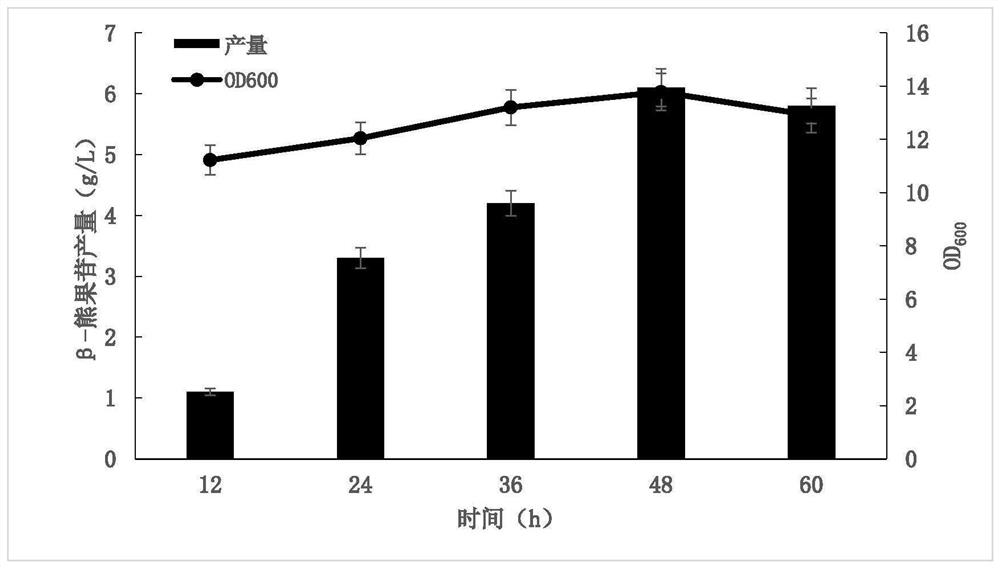
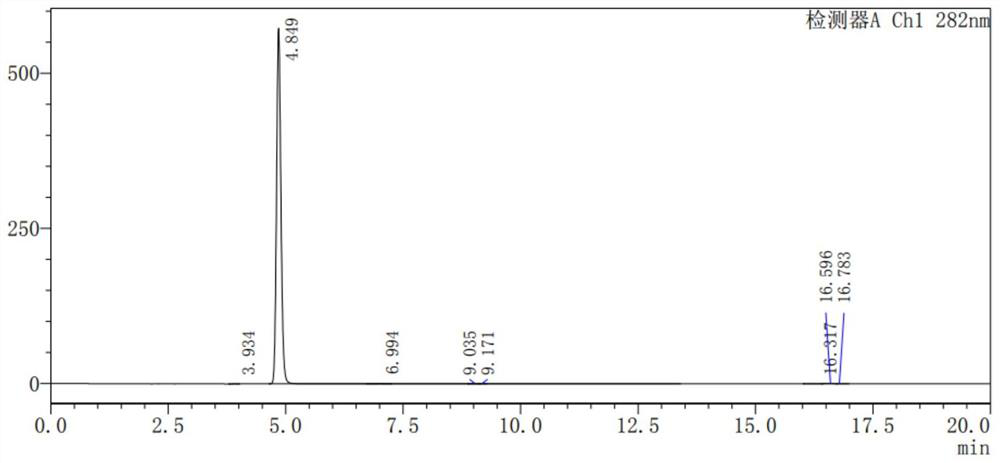
PendingCN114107354AStable productionEfficient biosynthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaTyrosineOxidative enzyme
The invention provides a method for constructing a stably inherited genetic engineering strain for efficient biosynthesis of beta-arbutin and application of the genetic engineering strain. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, integrating genes for coding tyrosine lytic enzyme, coumaric acid coenzyme A ligase, beta-cinnamyl hydroxylase, beta-cinnamyl oxidase and beta-cinnamyl deacylase (phdC) in a host, and constructing a host strain capable of realizing high yield of p-hydroxybenzoic acid; secondly, genes for coding 4-hydroxybenzoic acid hydroxylase and glucosyltransferase are integrated in the host, and a strain capable of producing beta-arbutin is constructed. And finally, integrating a gene of a coding core pathway and a gene of a shikimic acid pathway onto a genome of the engineering bacterium, and knocking out a gene of a competitive pathway to construct a stably inherited beta-arbutin efficient biosynthesis gene engineering strain, so that the influence of unstable engineering bacterium production caused by application of plasmids is avoided; the method has an application prospect in industrial production of beta-arbutin.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542BImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCoenzyme A Ligases
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
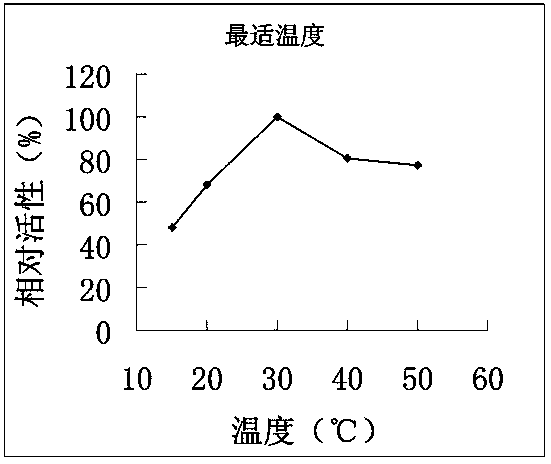
Aureobasidium pullulans malate-CoA ligase as well as recombinant expression vector and application thereof
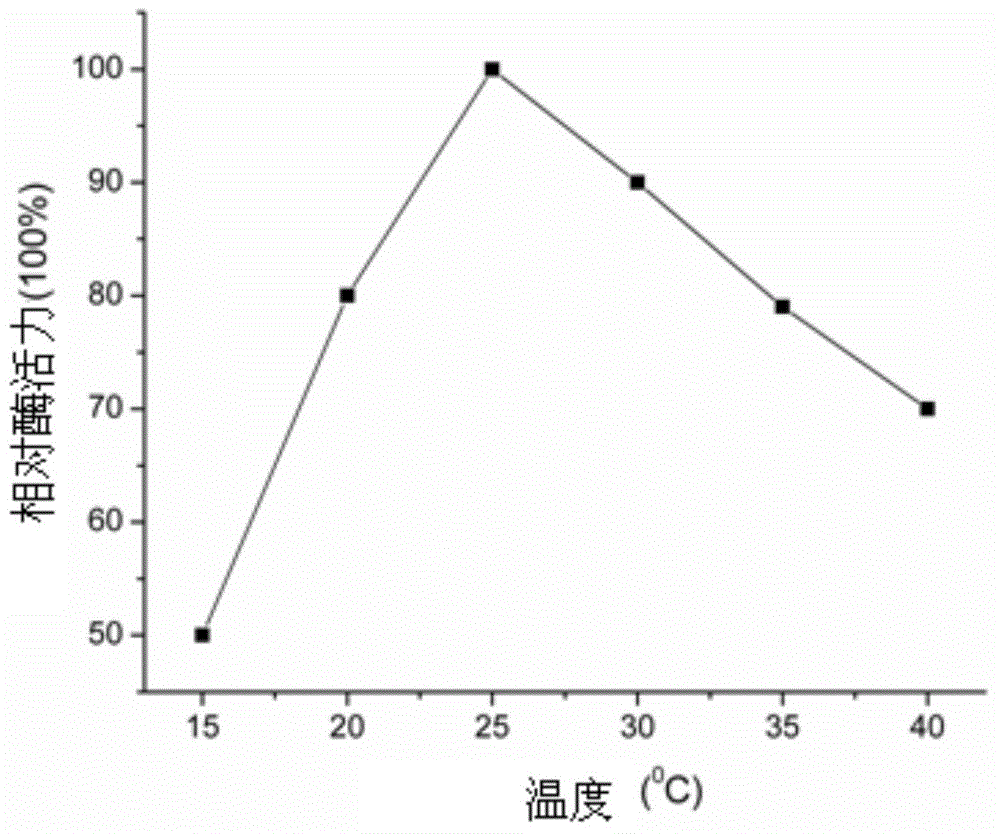
The invention discloses aureobasidium pullulans malate-CoA ligase. An amino acid sequence of aureobasidium pullulans malate-CoA ligase is represented as SEQ ID NO.10, and aureobasidium pullulans malate-CoA ligase comprises 439 amino acids; a cDNA (complementary desoxyribonucleic acid) sequence is represented as SEQ ID NO.9; a genomic sequence is s represented as SEQ ID NO.8; and after the cDNA sequence is subjected to recombinant expression, recombinant protein with molecular weight of about 68 kDa can be obtained. The enzymatic property detection shows that the activity of malate-CoA ligase subjected to the recombinant expression is 0.176 U, the optimal reaction temperature is 25 DEG C, the optimal pH is 8.0, and the optical ATP (adenosine triphosphate) substrate concentration is 0.2 mM; and further, the malate-CoA ligase has wider substrate selectivity and can catalyzing different monomers such as malic acid, oxalic acid, oxaloacetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, butyric acid or malonic acid for reaction, and the malic acid yield is increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
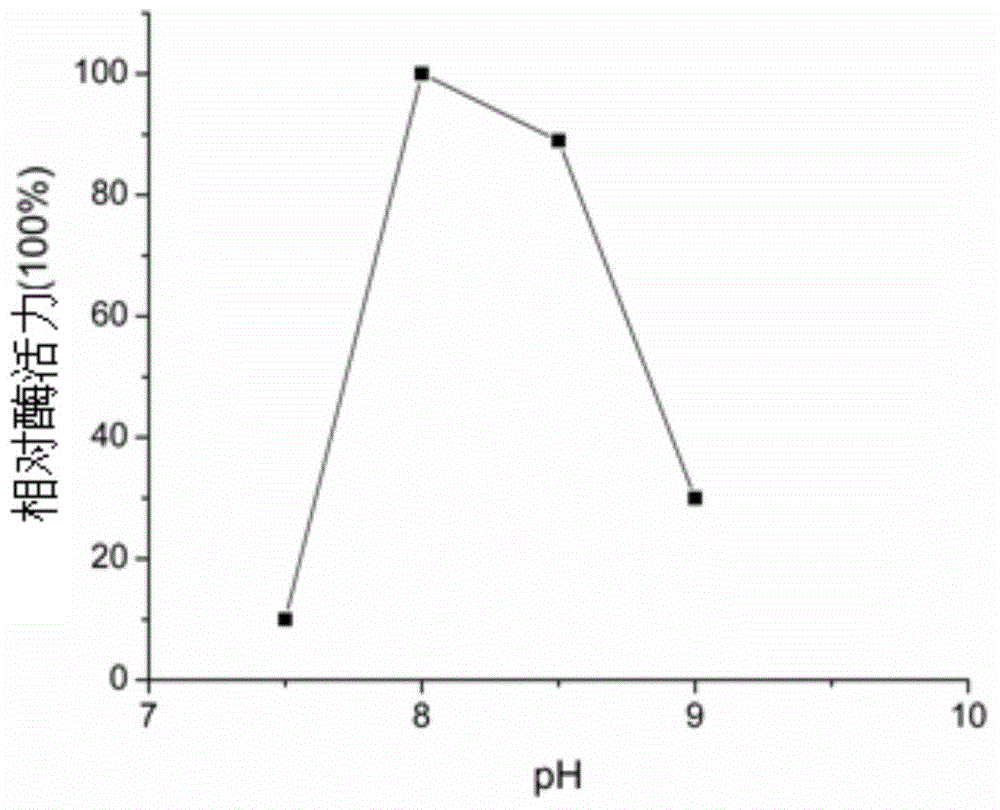
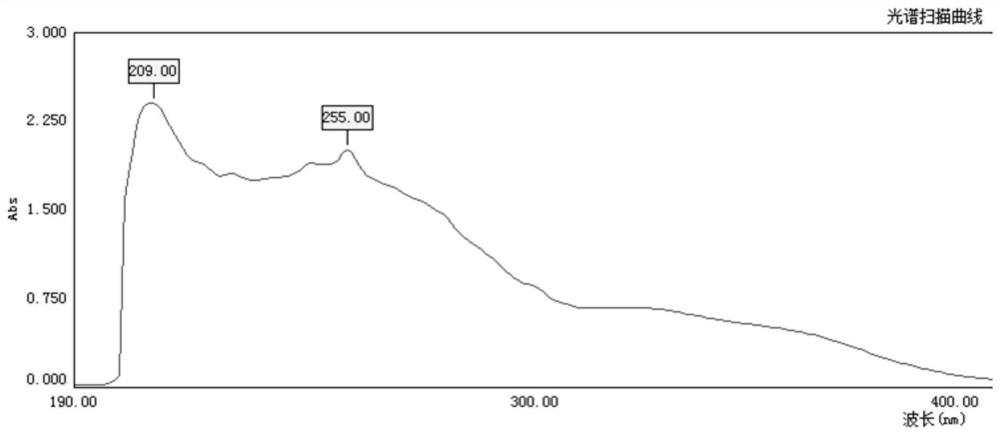
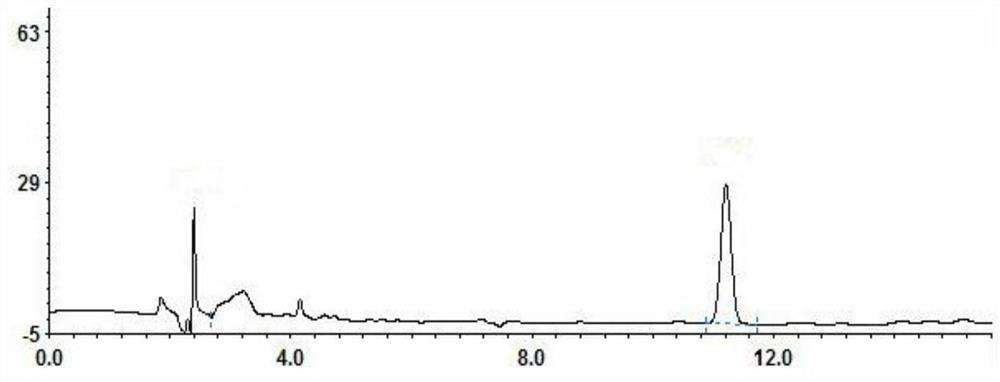
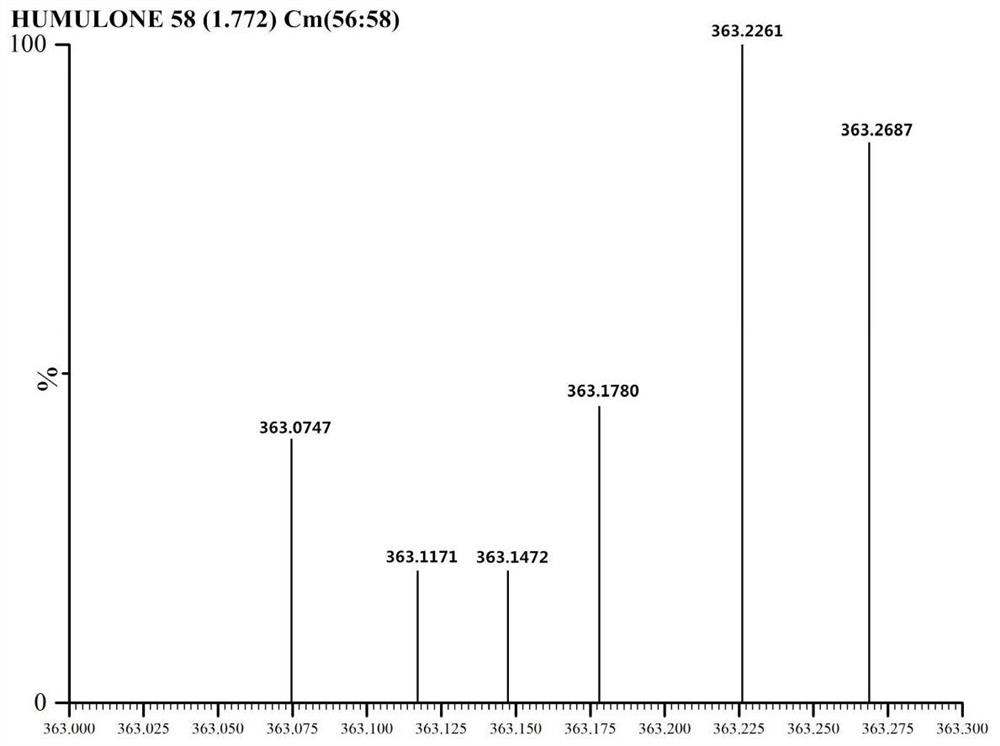
Construction method and application of engineering escherichia coli for producing humulone
ActiveCN111662919AThere will be no large fluctuations in concentrationAvoid restrictionsBacteriaOrganic compound preparationEscherichia coliIsomerase
The invention provides a construction method and application of engineering escherichia coli for producing humulone. The construction method comprises the following steps: taking engineering escherichia coli as an original strain, constructing a gene obtained after evolution of prenyl pyrophosphate isomerase derived from the engineering escherichia coli, a gene obtained after evolution of prenyl transferase derived from humulus lupulus and a monooxygenase gene into a vector plasmid to obtain a first expression vector; constructing a gene obtained after evolution of pentanedione synthase derived from humulus lupulus, a gene obtained after evolution of cytoplasmic coenzyme A ligase and an gene segment obtained after evolution of prenyl transferase into another vector plasmid to obtain a second expression vector; transferring the expression vectors into engineering escherichia coli to obtain engineering escherichia coli for producing humulone. The invention also provides a method for synthesizing humulone by using the engineering escherichia coli biological method. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of few steps, high purity and stable quality, gets ridof dependence on humulus lupulus raw materials, and avoids massive consumption of solvents.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Traneverine analogue, genetically engineered bacterium for producing same and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN111943996AIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaUdp glucosyltransferaseCoumaric acid
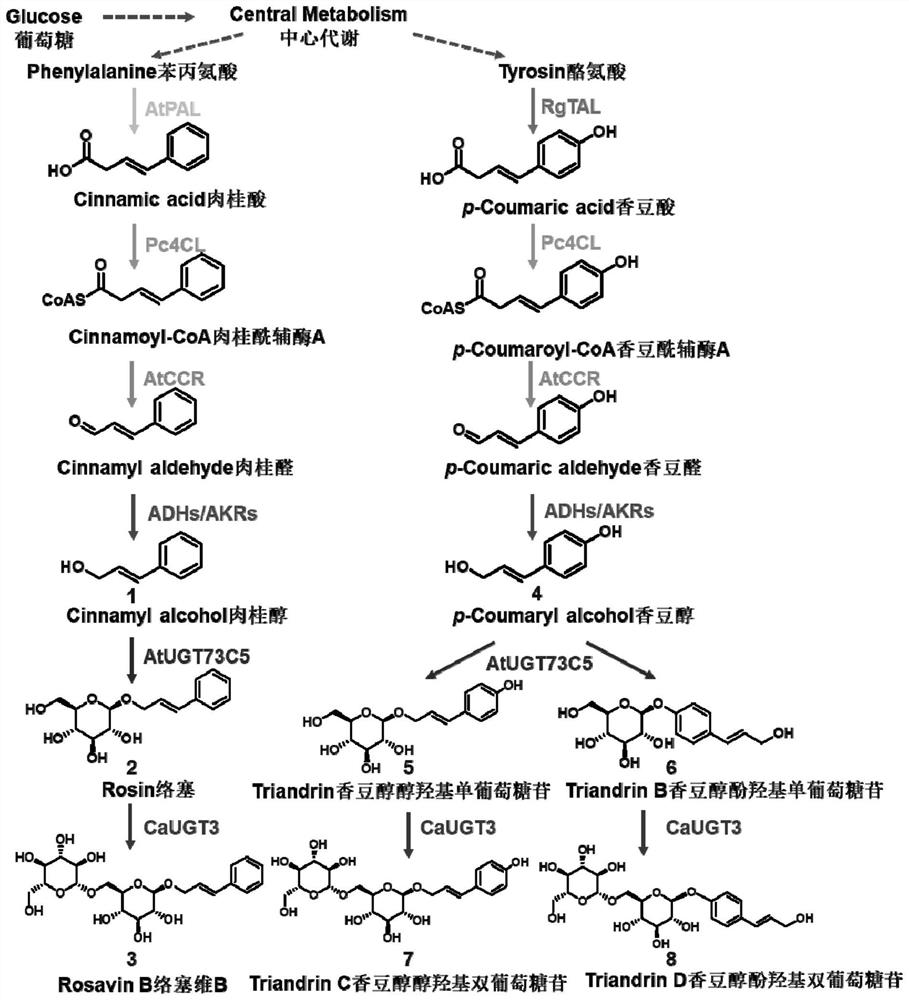
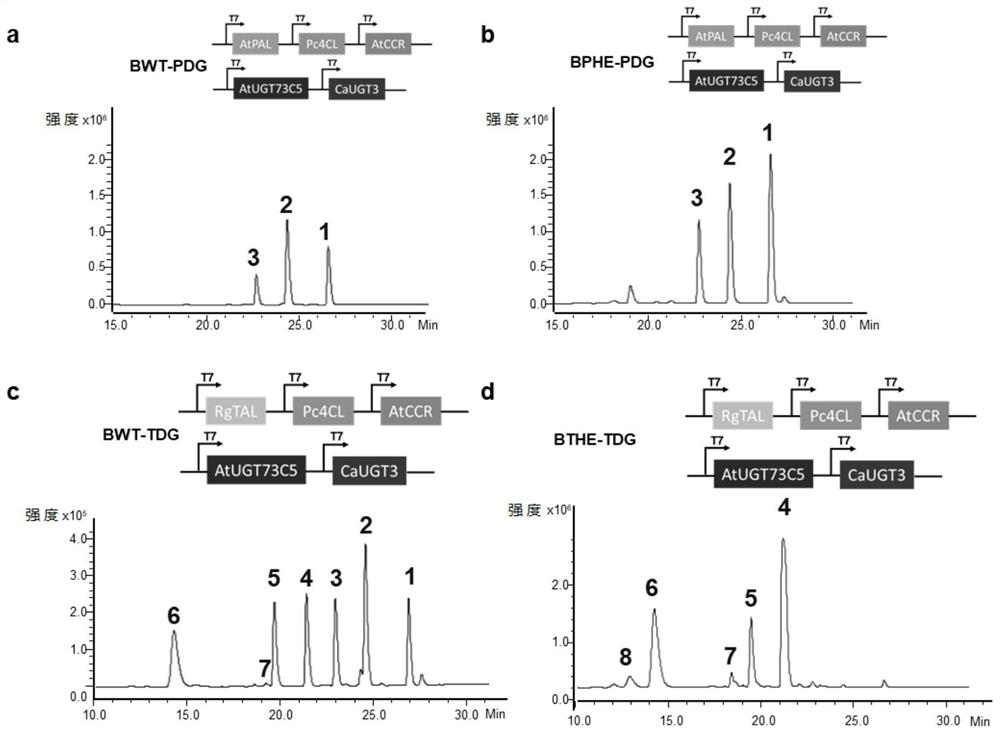
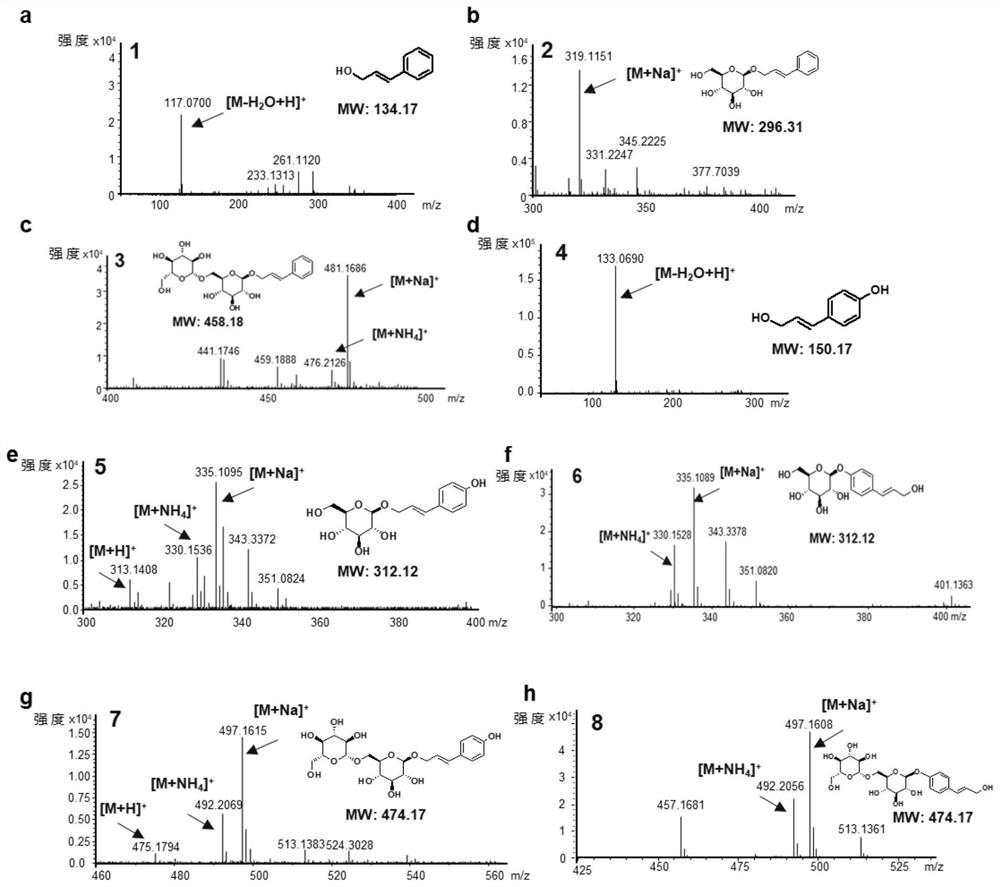
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a Traneverine analogue, a genetically engineered bacterium for producing the same and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The Traneverine analogue has a structure shown as a formula I, a formula II, a formula III or a formula IV. The genetically engineered bacterium contains genes for coding phenylalanine ammonialyase or tyrosine ammonialyase, 4-coumaric acid coenzyme A ligase 4CL, cinnamoyl coenzyme A reductase CCR and UDP glucosyltransferase UGT. The genetically engineered bacterium can beused for producing Triandrin and Triandrin B (formula IV) or Triandrin, Triandrin B, Triandrin C (formula II) and Triandrin D (formula III) by fermentation, and the highest yield of Triandrin and Triandrin B can reach 1.7g / L and 1.6g / L; or the highest yield of Traneverine B (formula I) can reach 1.6g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
SUCLA2 gene mutant and its application
ActiveCN103571854ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutantSuccinate-coenzyme A ligase
The invention relates to a separated nucleic acid of an encoded succinate coenzyme A ligase beta subunit mutant, a separated polypeptide, a method for screening a biological sample susceptible to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes, a system for screening the biological sample susceptible to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes, and a kit for screening the biological sample susceptible to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes. Specifically, compared with the SEQ ID NO:1, the separated nucleic acid of the encoded succinate coenzyme A ligase beta subunit mutant has c.C308A mutation. By detecting whether the mutant exists in the biological sample, whether the biological sample is susceptible to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes can be effectively detected.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Method of producing a tripeptide gamma-glu-val-gly using enterobacteriaceae
A method for producing γ-Glu-Val-Gly is described, wherein the method includes the steps of cultivating a γ-Glu-Val-Gly-producing bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae in a culture medium so that the γ-Glu-Val-Gly accumulates in the culture medium or the cells of the bacterium, or both, and collecting the γ-Glu-Val-Gly from the culture medium or the cells of the bacterium, or both. The bacterium has been modified to overexpress a gene encoding a protein having L-threonine 3-dehydrogenase activity and a gene encoding a protein having 2-amino-3-oxobutanoate coenzyme A ligase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Engineering bacterium for microbial synthesis of piceatannol by taking glucose as substrate as well as construction and application of engineering bacterium
PendingCN114395497AIncrease contentIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiBiotechnologyTyrosine
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for microbial synthesis of piceatannol by taking glucose as a substrate as well as construction and application of the engineering bacterium. According to the invention, L-tyrosine ammonolysis enzyme, p-coumaroyl-coenzyme A ligase, resveratrol synthetase, DAHP synthetase, chorismate mutase and hydroxylase complex genes are over-expressed in the engineering strain, so that the de novo synthesis strategy of piceatannol is realized, and the content of the product piceatannol is remarkably increased; and a simple and effective implementation method is provided for safe biotransformation. The yield of the engineering bacterium for synthesizing piceatannol by using the glucose as the substrate microorganism disclosed by the invention can reach 7-8g / L.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
Engineering bacterium for synthesizing dencichine and application
PendingCN114517174AImprove the ability to synthesize notoginsengKnockout or inhibition of competing pathwaysBacteriaHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlyoxylate dehydrogenase
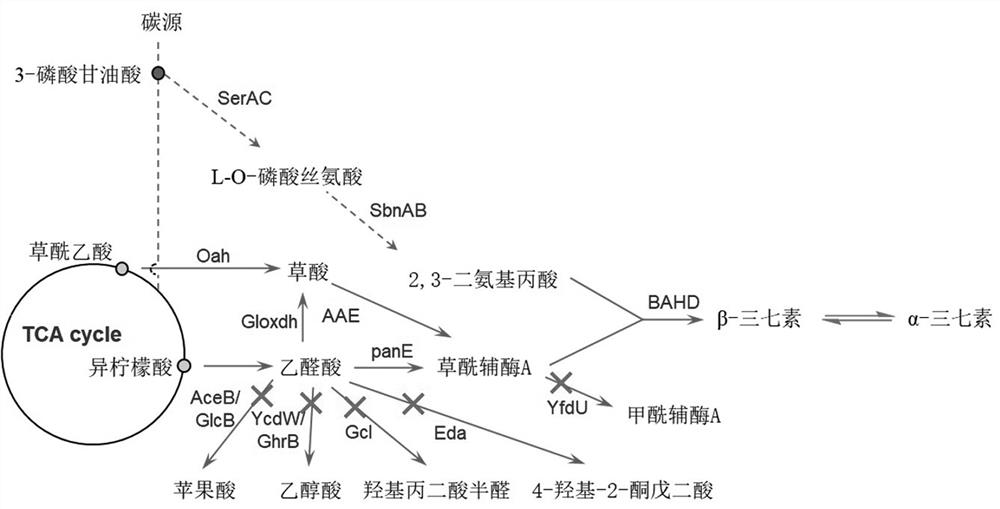
The invention provides an engineering bacterium for synthesizing dencichine, the engineering bacterium comprises a host bacterium and a plasmid vector transferred into the host bacterium, and an enzyme for coding and synthesizing oxalyl coenzyme A and a gene of 2, 3-diamino propionic acid N-oxalyltransferase BAHD are introduced into the plasmid vector at the same time. Three ways for synthesizing the oxalyl-coenzyme A enzyme are as follows: acylation glyoxylate dehydrogenase panE, glyoxylate dehydrogenase Gloxdh and oxalyl-coenzyme A ligase AAE, and oxaloacetic acid hydrolase Oah and oxalyl-coenzyme A ligase AAE. And a gene for coding and synthesizing the 2, 3-diaminopropionic acid biosynthase is also introduced into the plasmid vector. The engineering bacteria are optimized in manners of enhancing an upstream path, inhibiting competition and the like so as to improve the production capacity of dencichine. Therefore, the dencichine produced by using the engineering bacteria has the advantages of simple method, low cost, high conversion rate and the like, and is beneficial to industrial production and cost reduction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for producing pterostilbene biosynthetically using o-methyltransferase
ActiveCN106102454BSolve the technical problem of generating pterostilbenePromote generationBryophytesNervous disorderCoumaric acidStilbene synthase
A biosynthetic method for preparing pterostilbene, comprising expressing 4-coumaric acid in a cell system: Coenzyme A ligase (4CL), expressing stilbene synthase (STS) in a cell system, expressing resveratrol in a cell system Reveritol O‑methyltransferase (ROMT), supplying p-coumaric acid to the cell system, growing the cell system in culture, and producing pterostilbene.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com