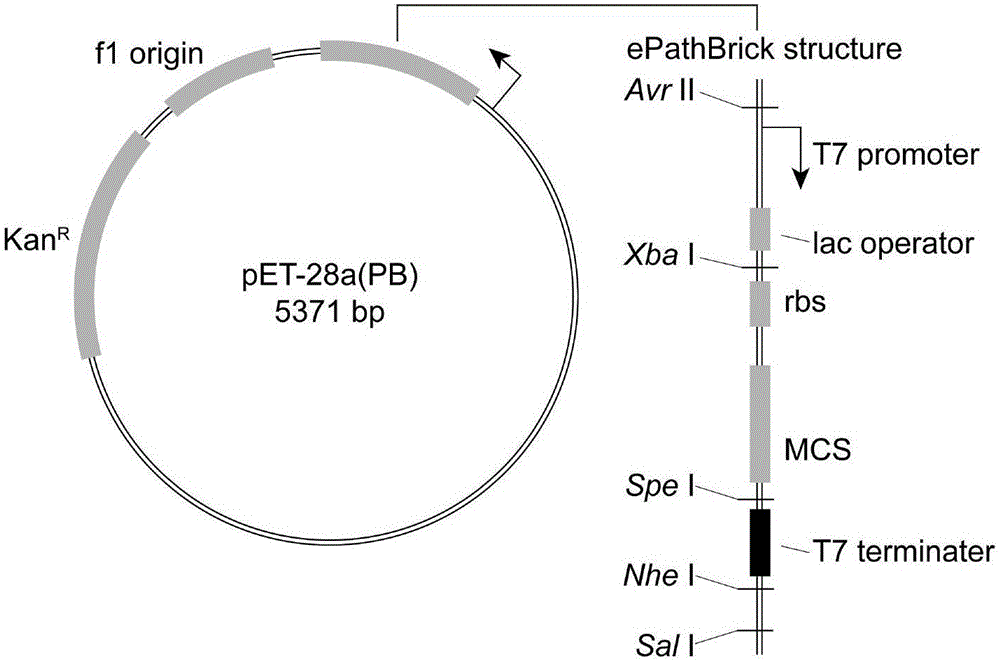
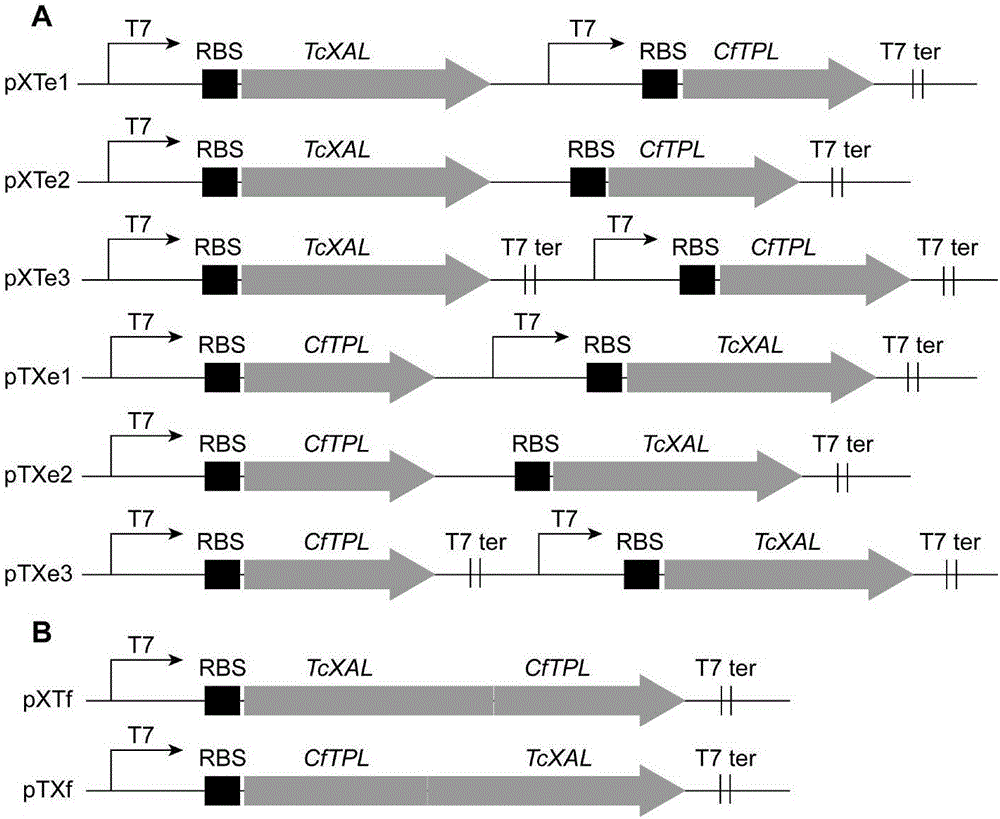
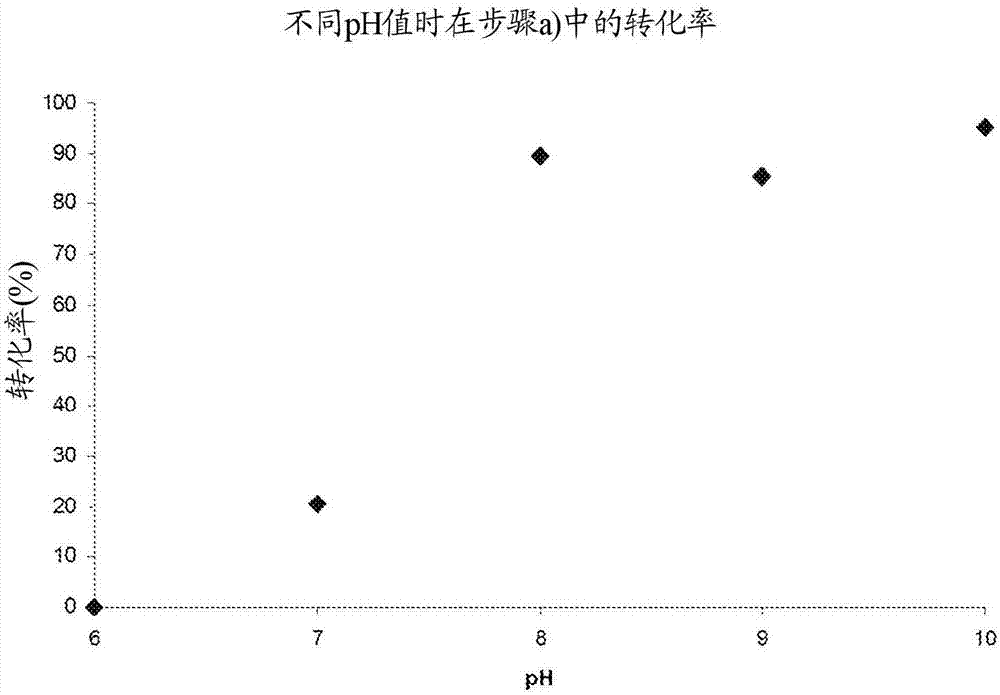
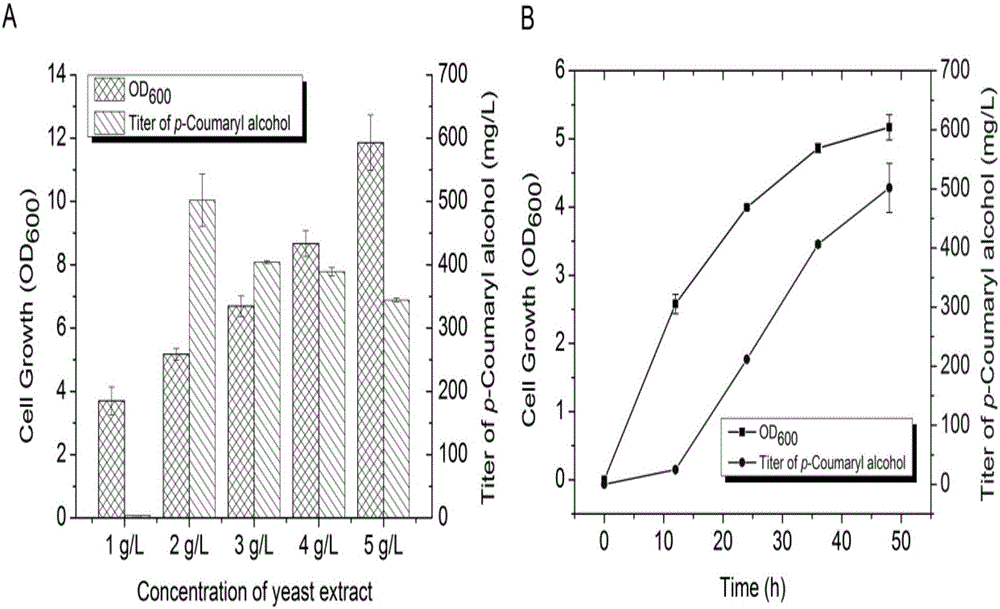
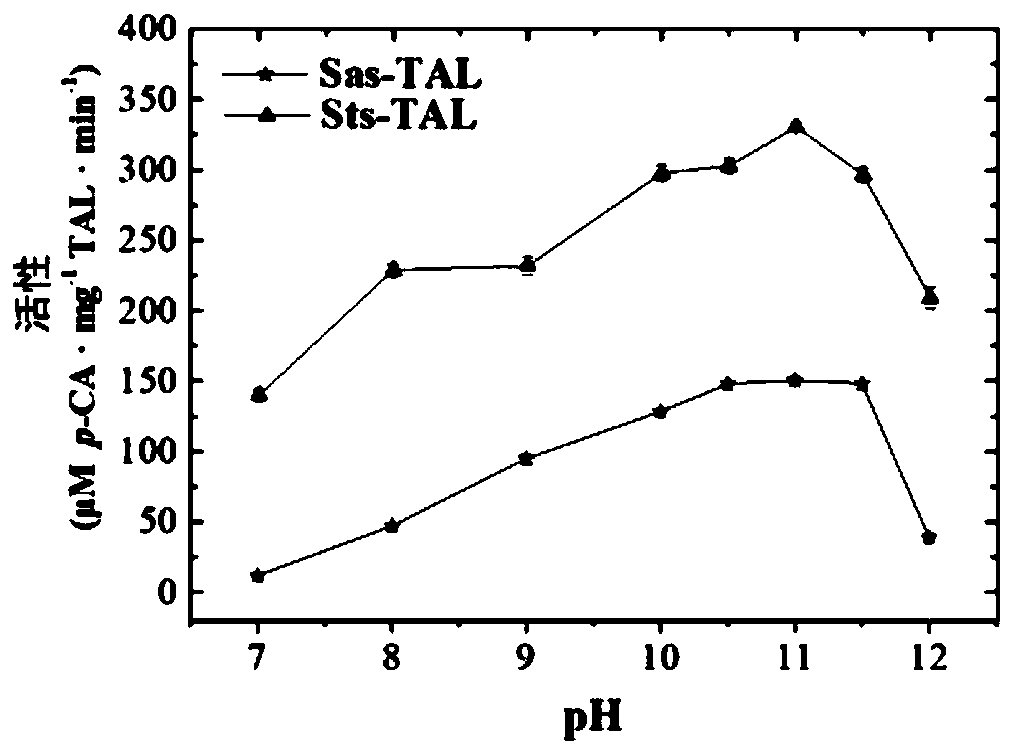
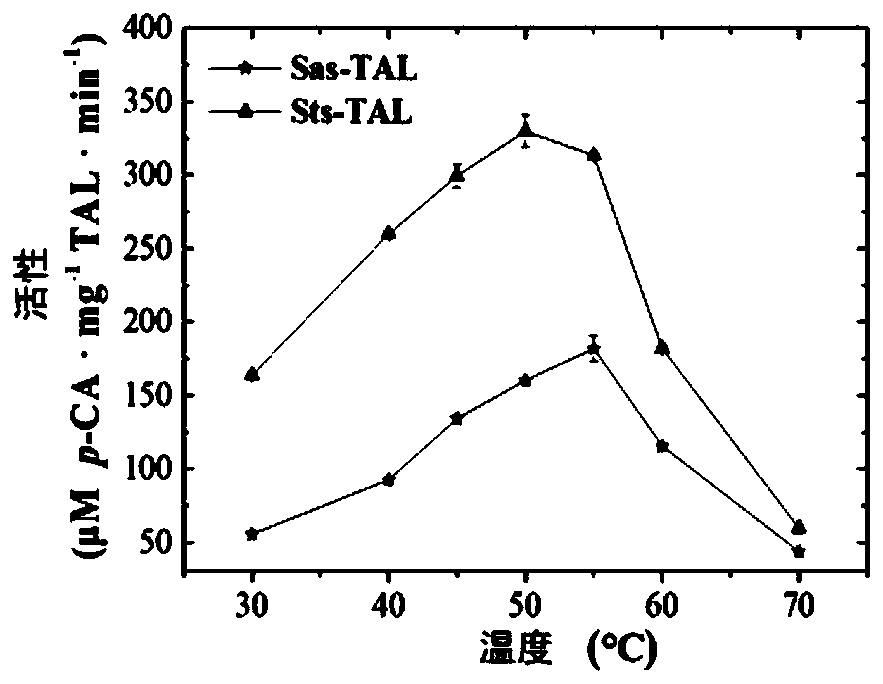
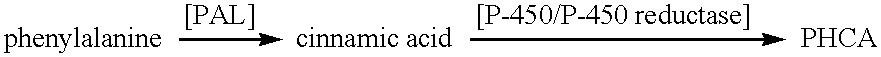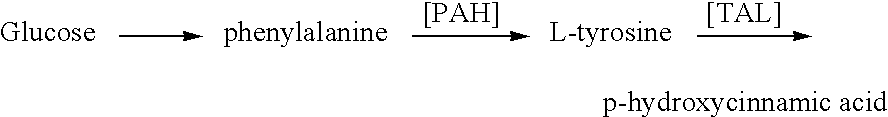Patents
Literature
35 results about "Tyrosine ammonia-lyase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
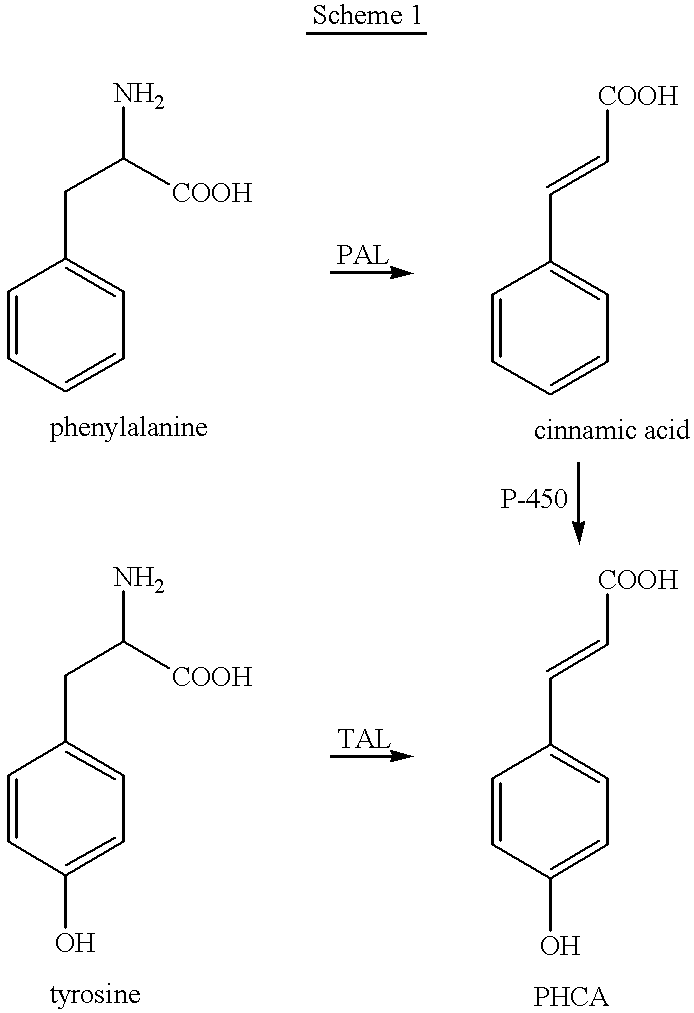
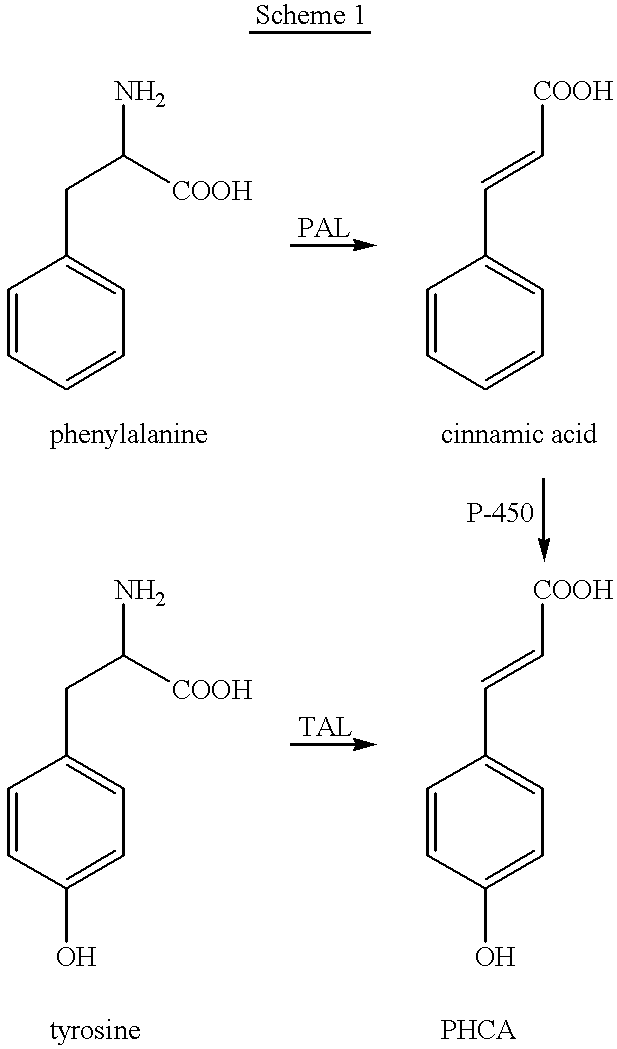
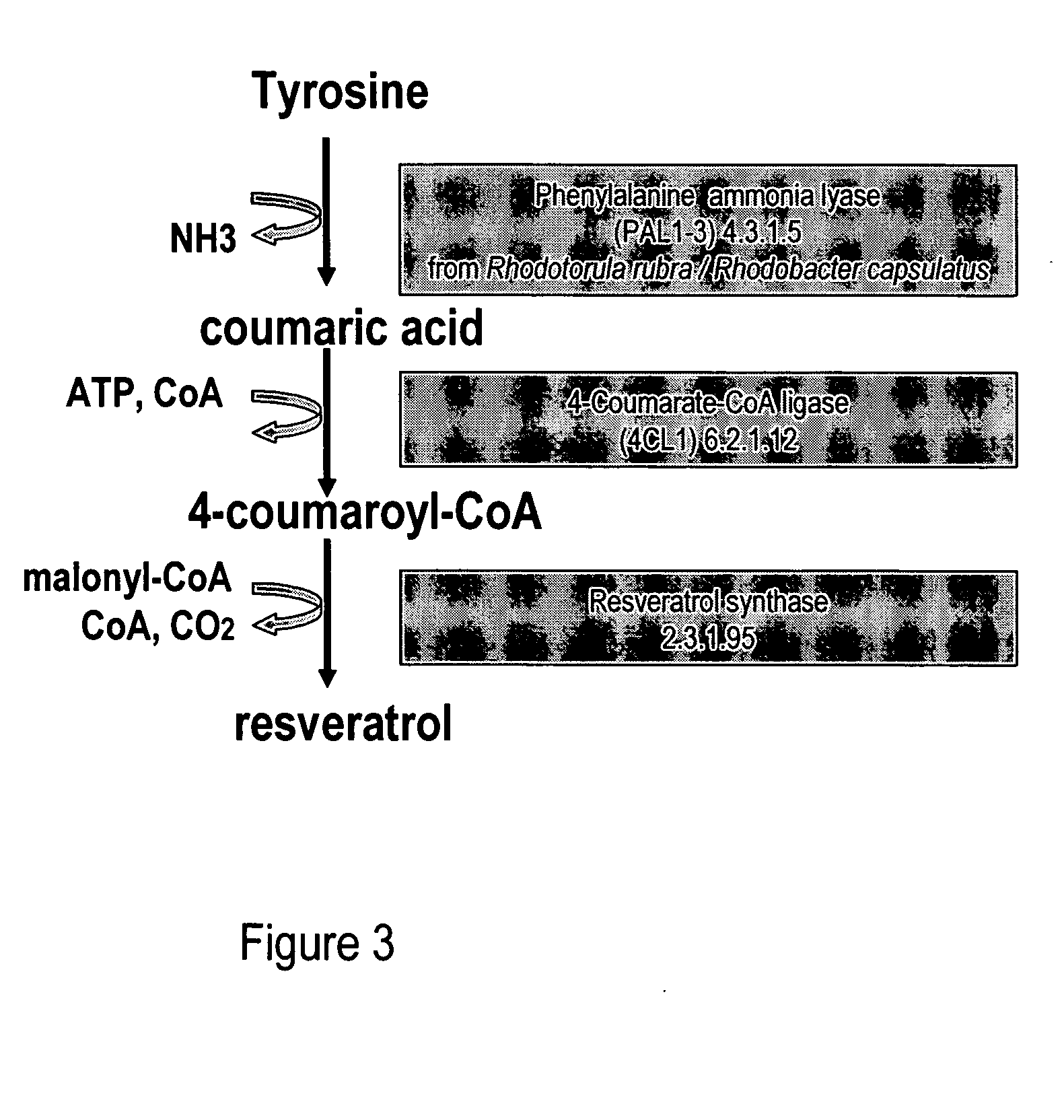
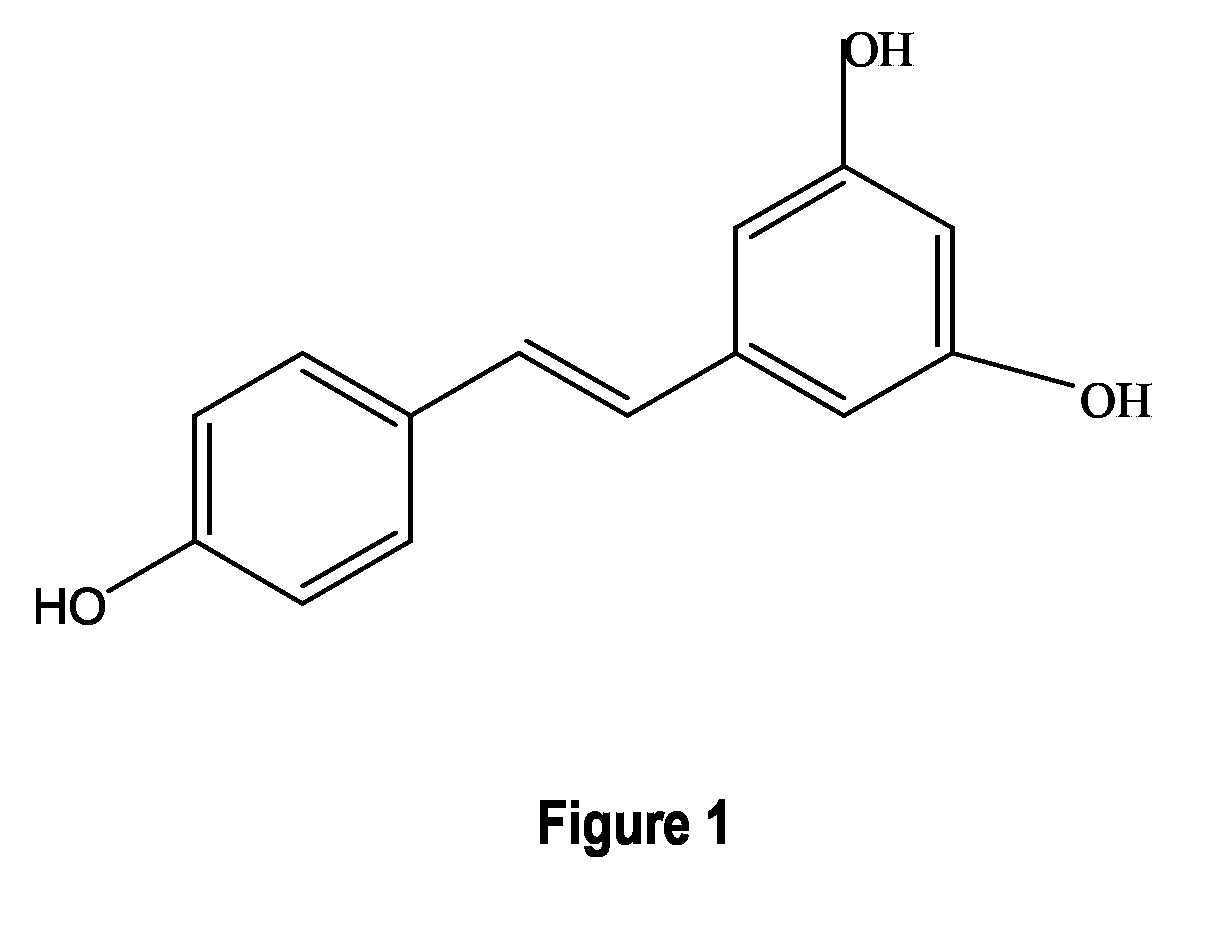
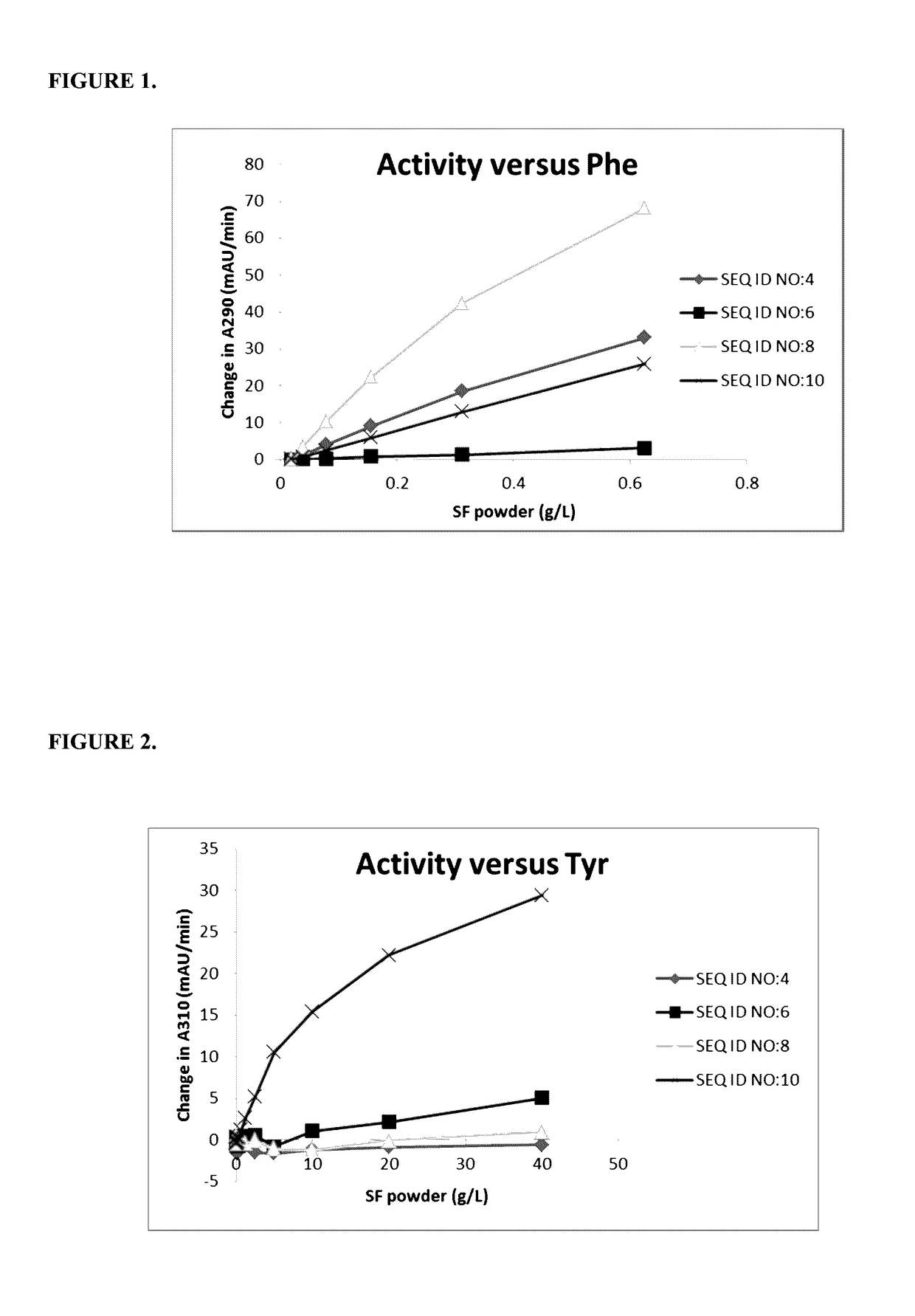
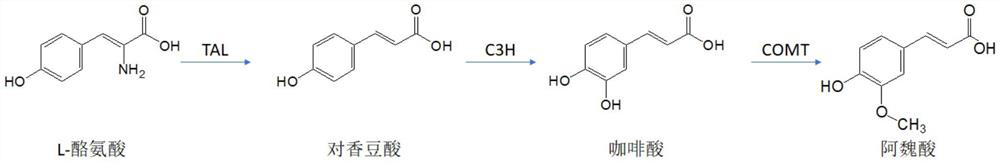
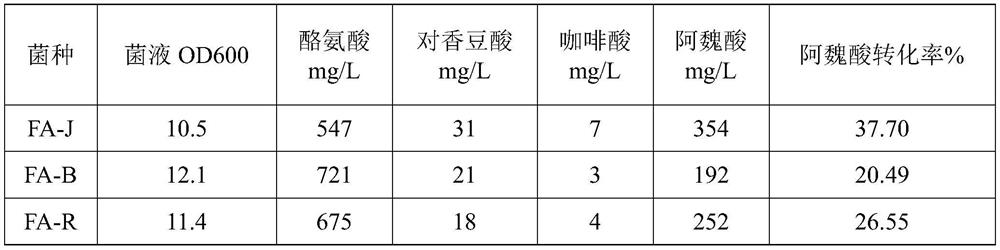
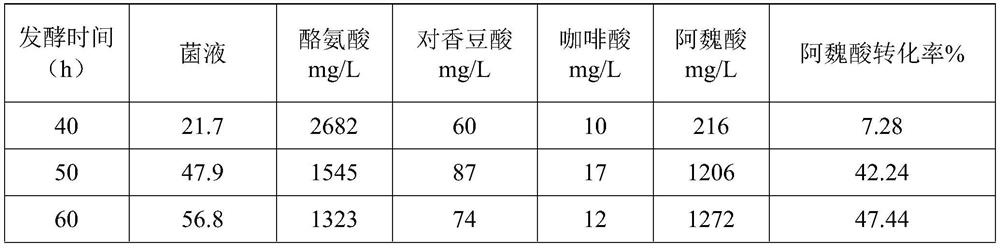
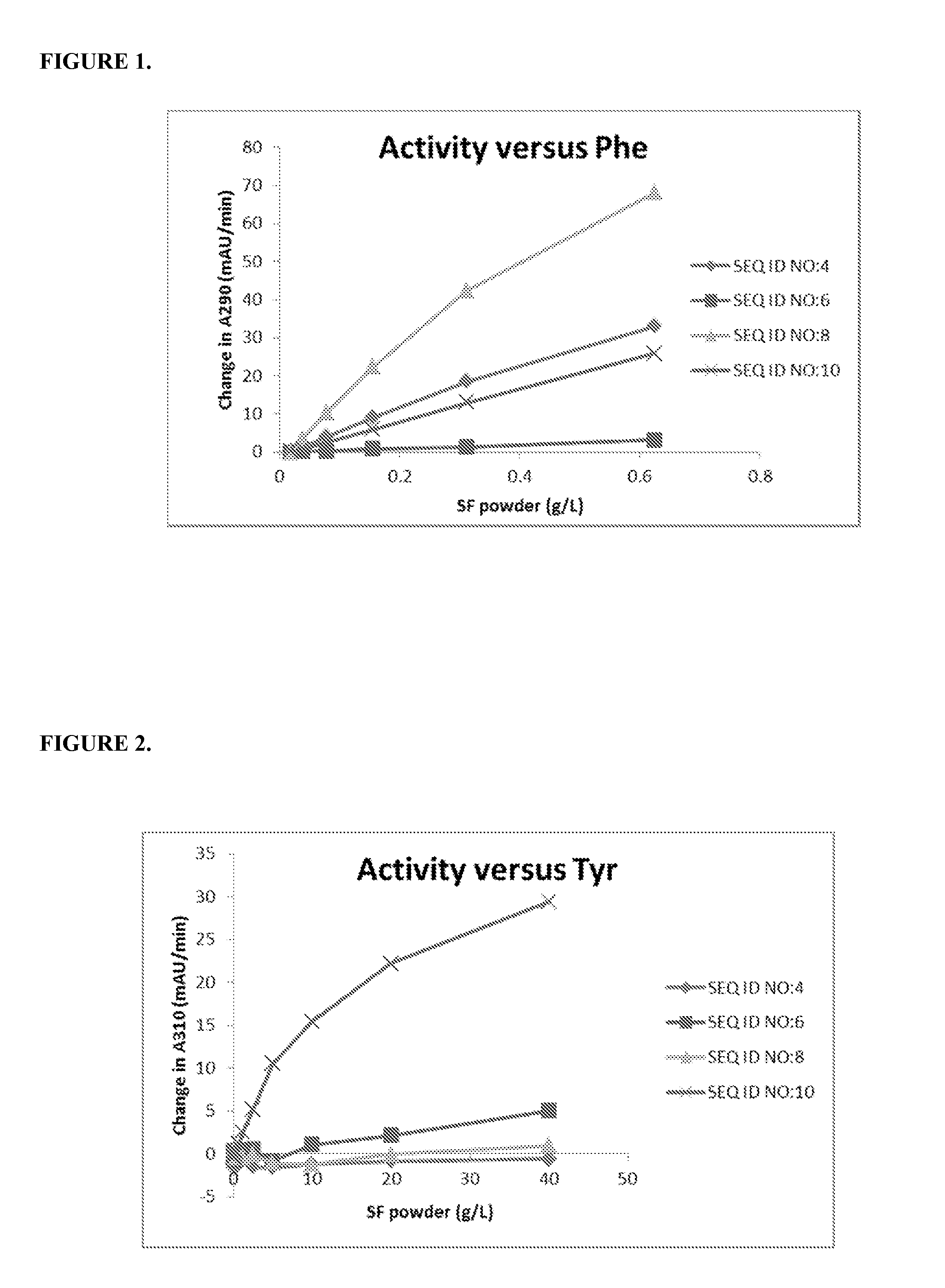
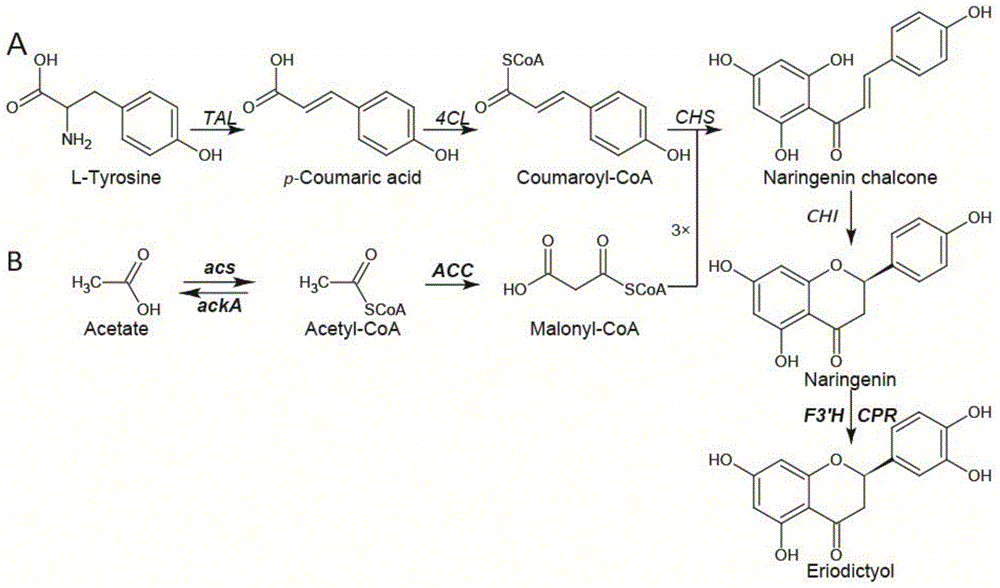
Tyrosine ammonia lyase (L-tyrosine ammonia-lyase, TAL or Tyrase) is an enzyme in the natural phenols biosynthesis pathway. It transforms L-tyrosine into p-coumaric acid. ⟶TAL + Ammonia + H⁺
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
InactiveUS6368837B1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliTyrosine
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Polynucleotide encoding a mutant Rhodotorula glutinis tyrosine ammonia lyase polypeptide
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biological method for producing resveratrol
InactiveCN102605006ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhenylalanine hydroxylase
The invention discloses a biological method for producing resveratrol, which comprises the following steps: ligating target genes obtained by restriction enzyme digestion to an expression vector, wherein the target genes include the sequences of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and resveratrol synthase (RS); transforming the constructed expression vector into a strain to obtain a recombinant engineered strain; and fermenting the recombined engineered strain. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention uses the genetically engineered strain for fermentation to produce resveratrol, so as to realize denovo synthesis of resveratrol with no need of adding substrates. The method disclosed by the invention solves the source problem of resveratrol, and at the same time, reduces the production cost in a maximum extent, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
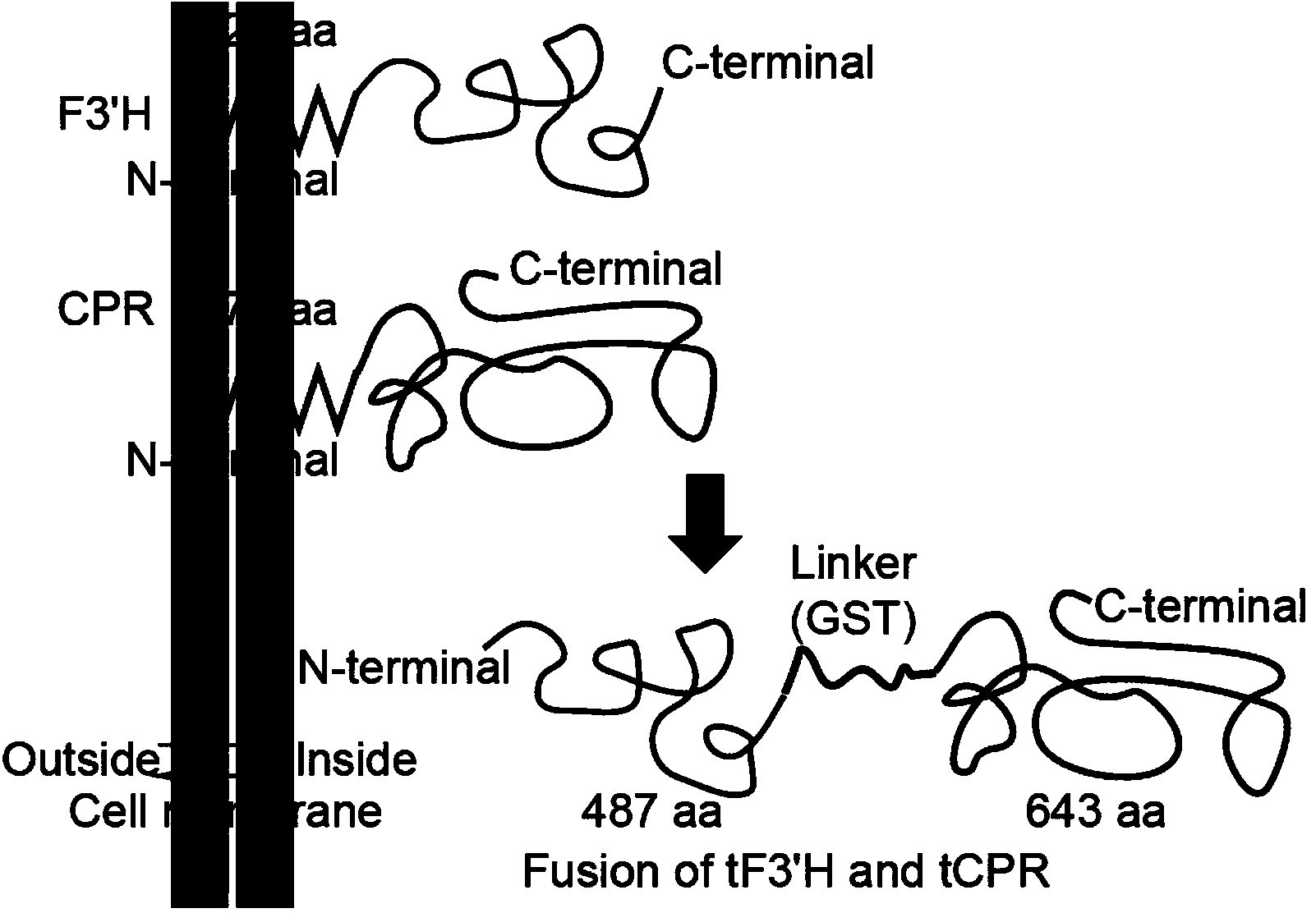
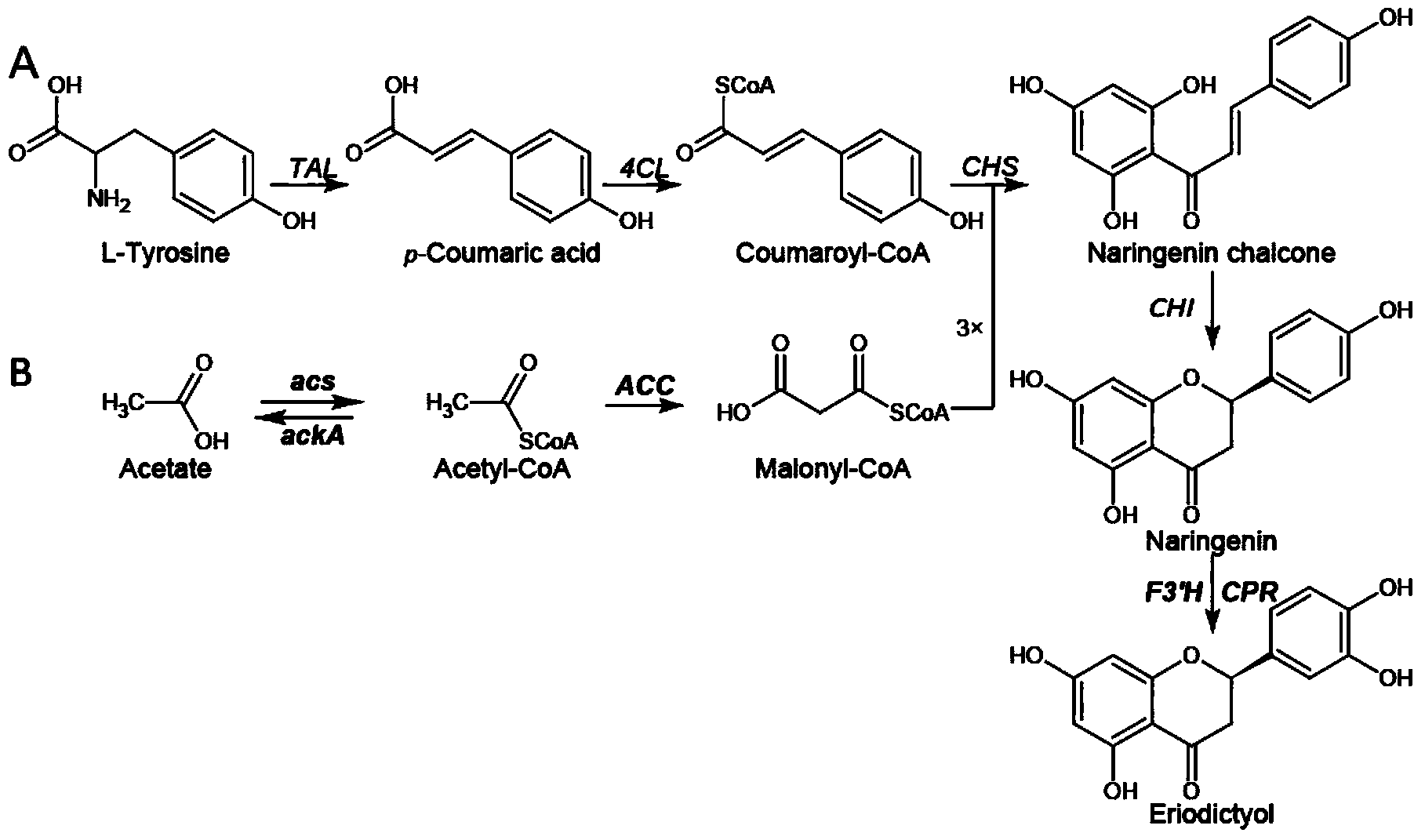
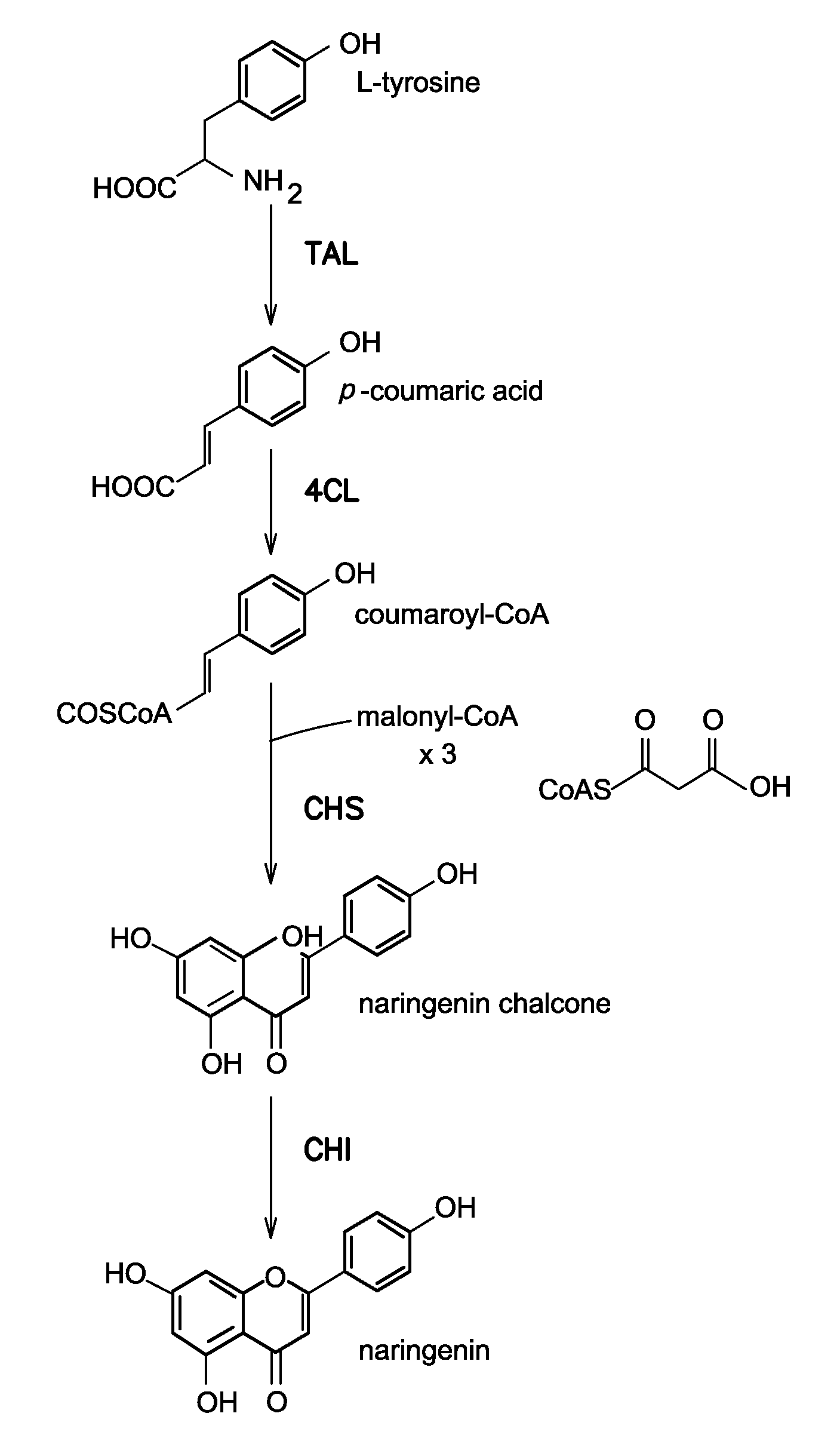
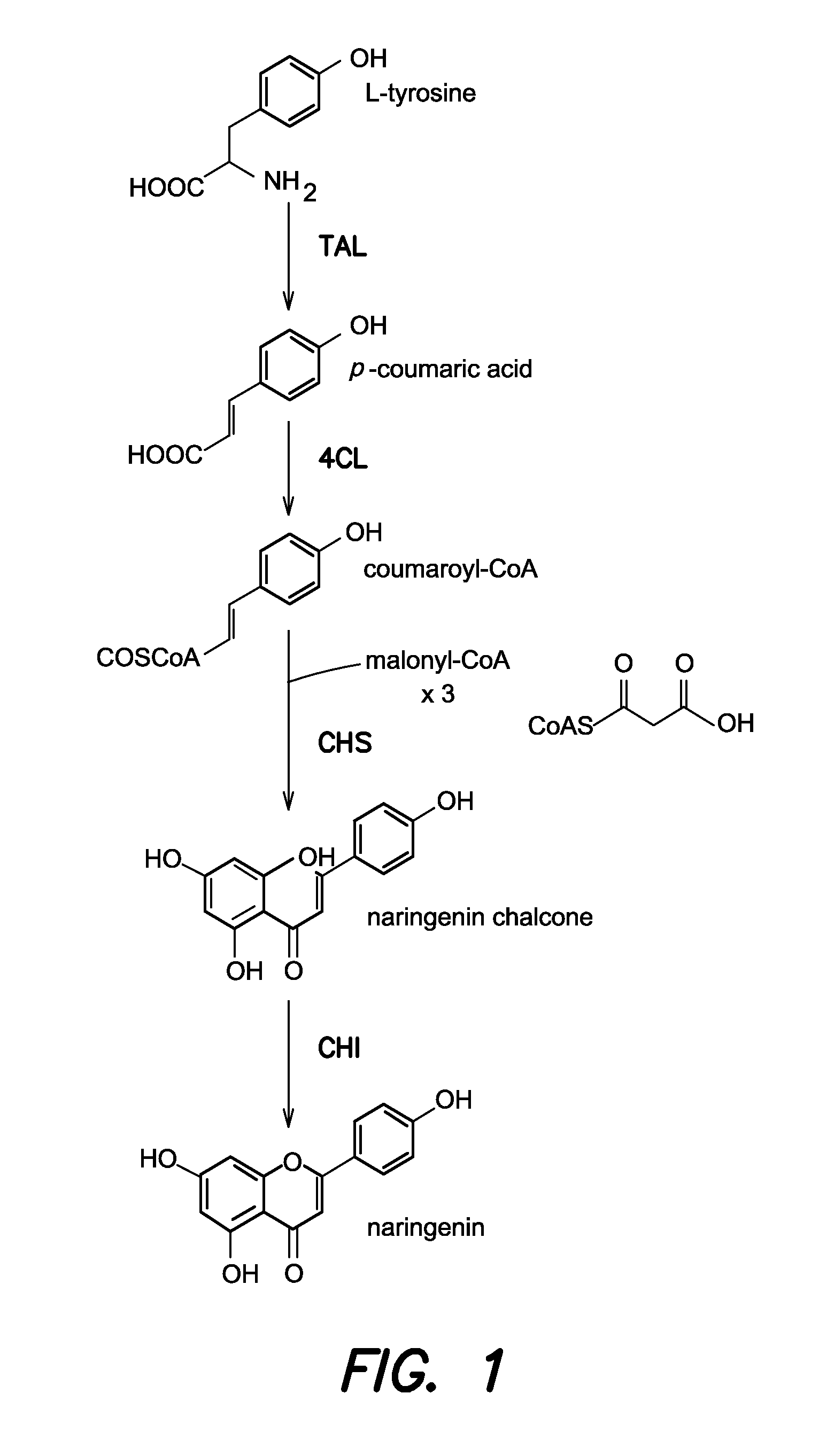
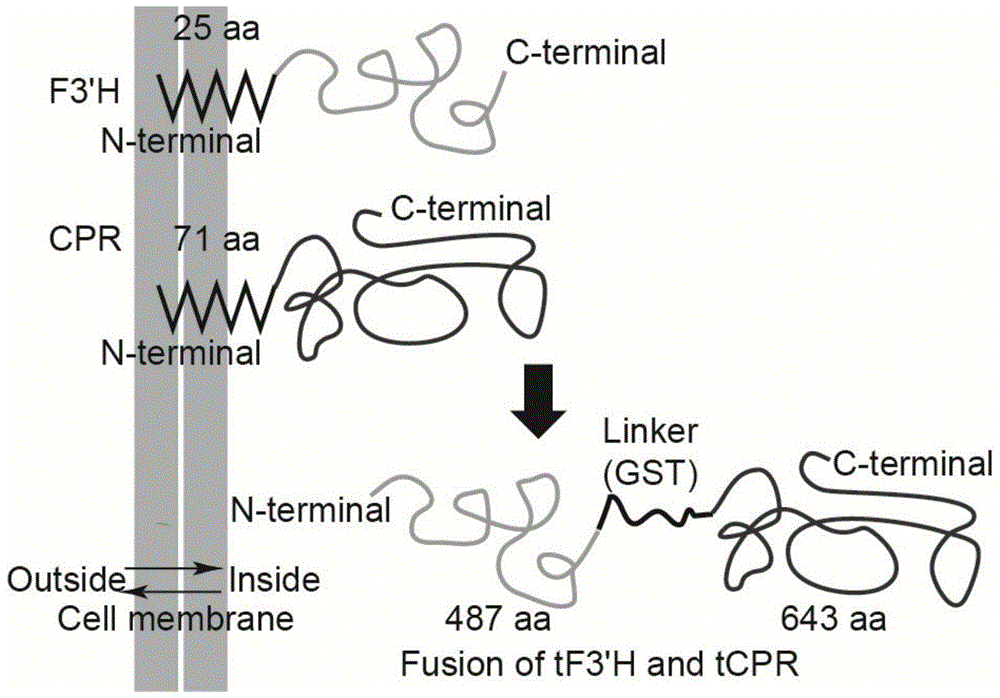
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
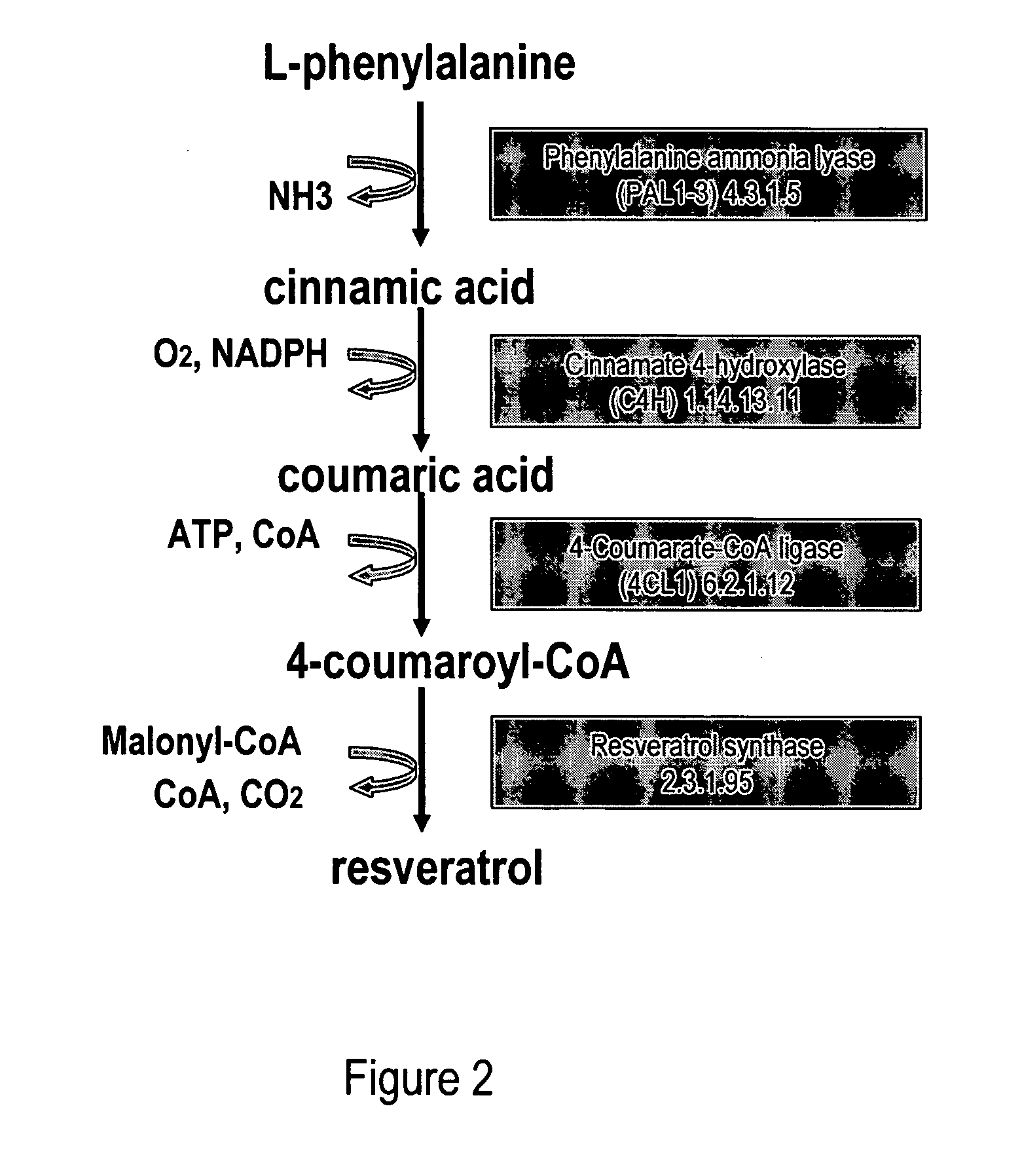
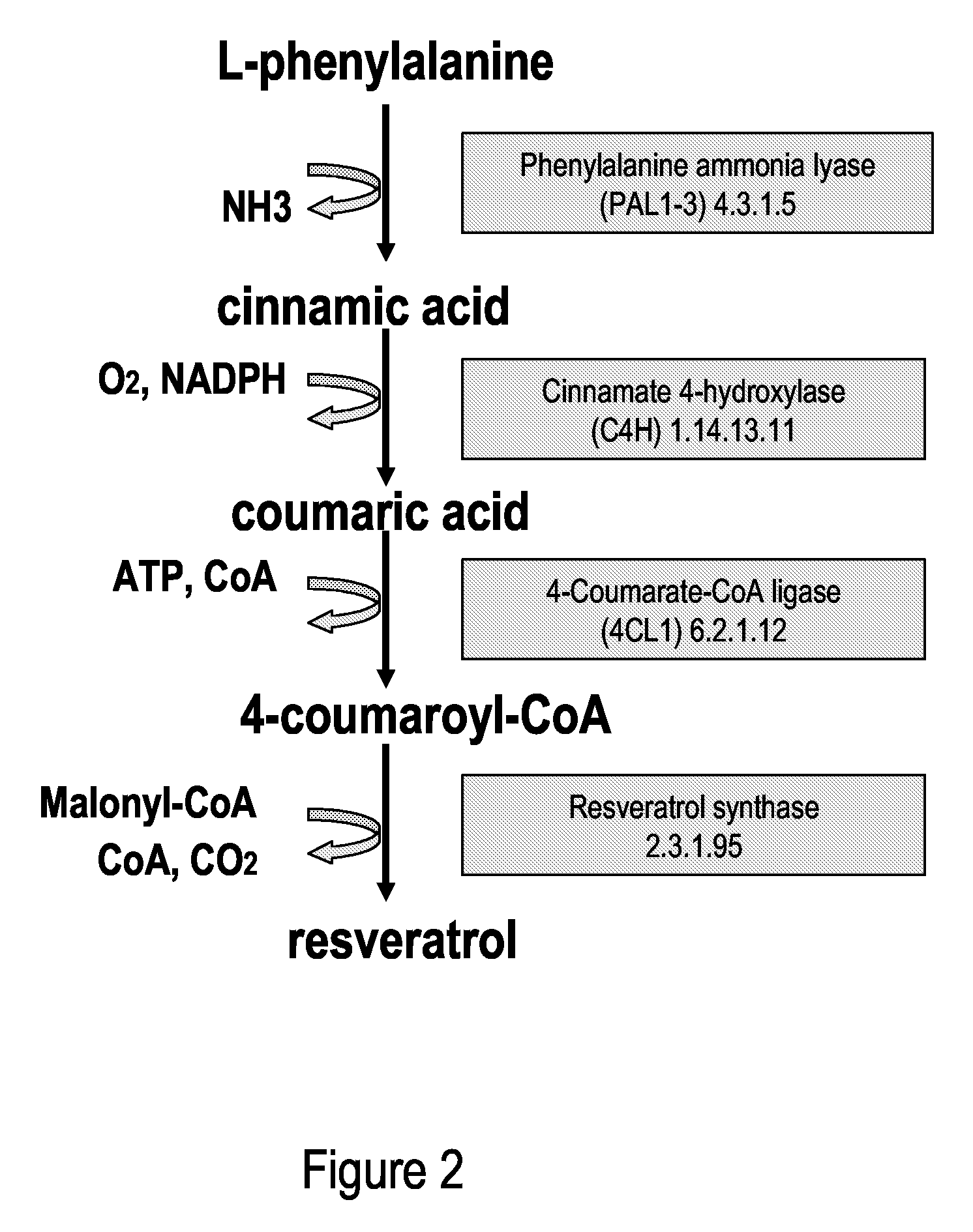
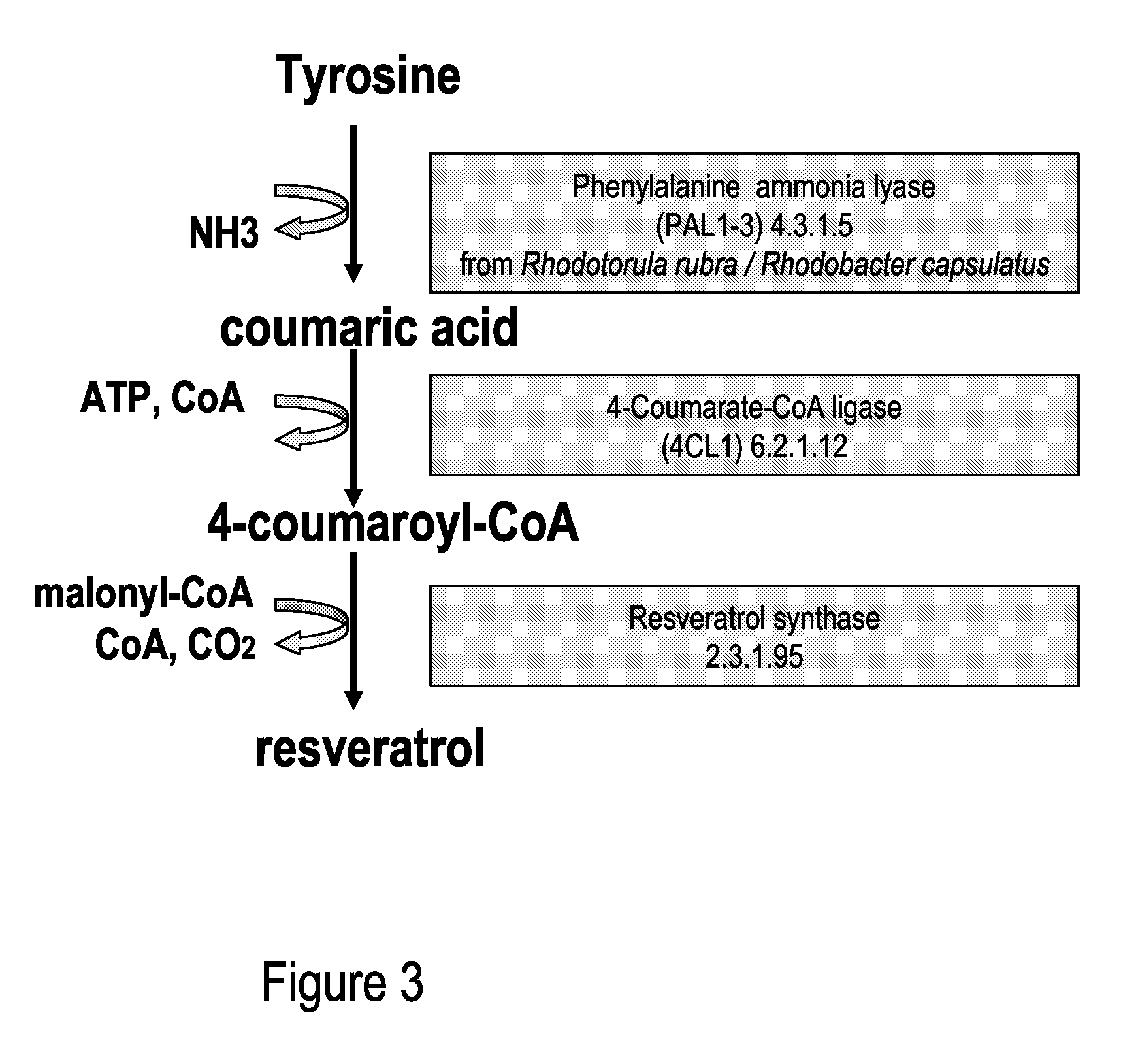
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Strains for the production of flavonoids from glucose
ActiveUS20120034661A1Simple and economical processIncrease productionFungiBacteriaGlucose polymersD-Glucose
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
High efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as substrate
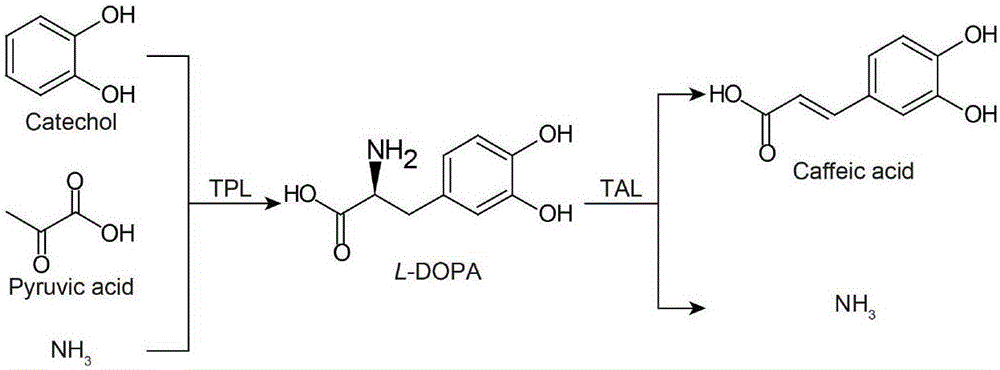
InactiveCN106701843AEase of mass productionEfficient synthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisCaffeic acid
Belonging to the field of biochemical engineering, the invention discloses a high efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as the substrate. According to the invention, tyrosine phenol-lyase takes catechol, pyruvic acid and ammonia as the substrate to synthesize levodopa, tyrosine ammonia-lyase converts levodopa into trans-caffeic acid and NH3. Catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride are relatively cheap compounds, therefore the caffeic acid biosynthesis method provided by the invention has large potential. Compared with the previous conversion methods taking L-tyrosine as the substrate, the substrate used by the method are cheaper and easier for large-scale production. Compared with chemical synthesis methods, the product of the method provided by the invention is single trans-caffeic acid, and further separation of an isomer is unnecessary.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods for the production of tyrosine, cinnamic acid and para-hydroxycinnamics acid
Genes encoding phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) and phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) have been introduced into a host organism for the production of Para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The introduction of these genes results in the redirection of carbon flow in the host, optimizing the flow of carbon from glucose to PHCA. The intermediates, tyrosine and cinnamic acid are also produced.
Owner:ORMON CORP +1
Method for producing p-vinylphenols
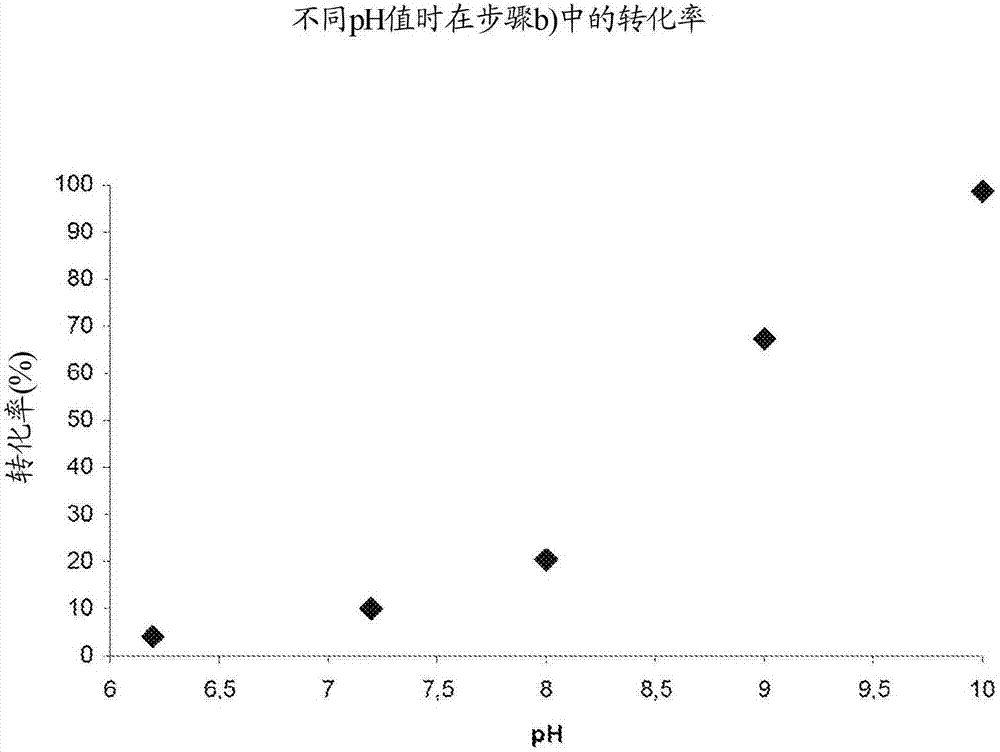
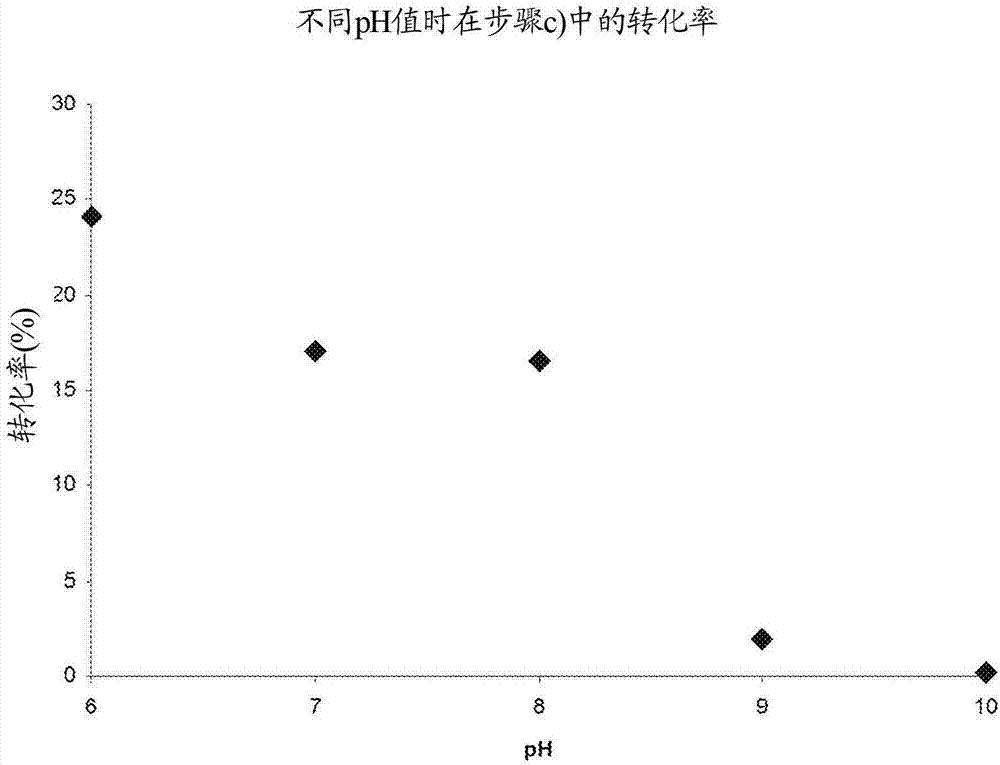
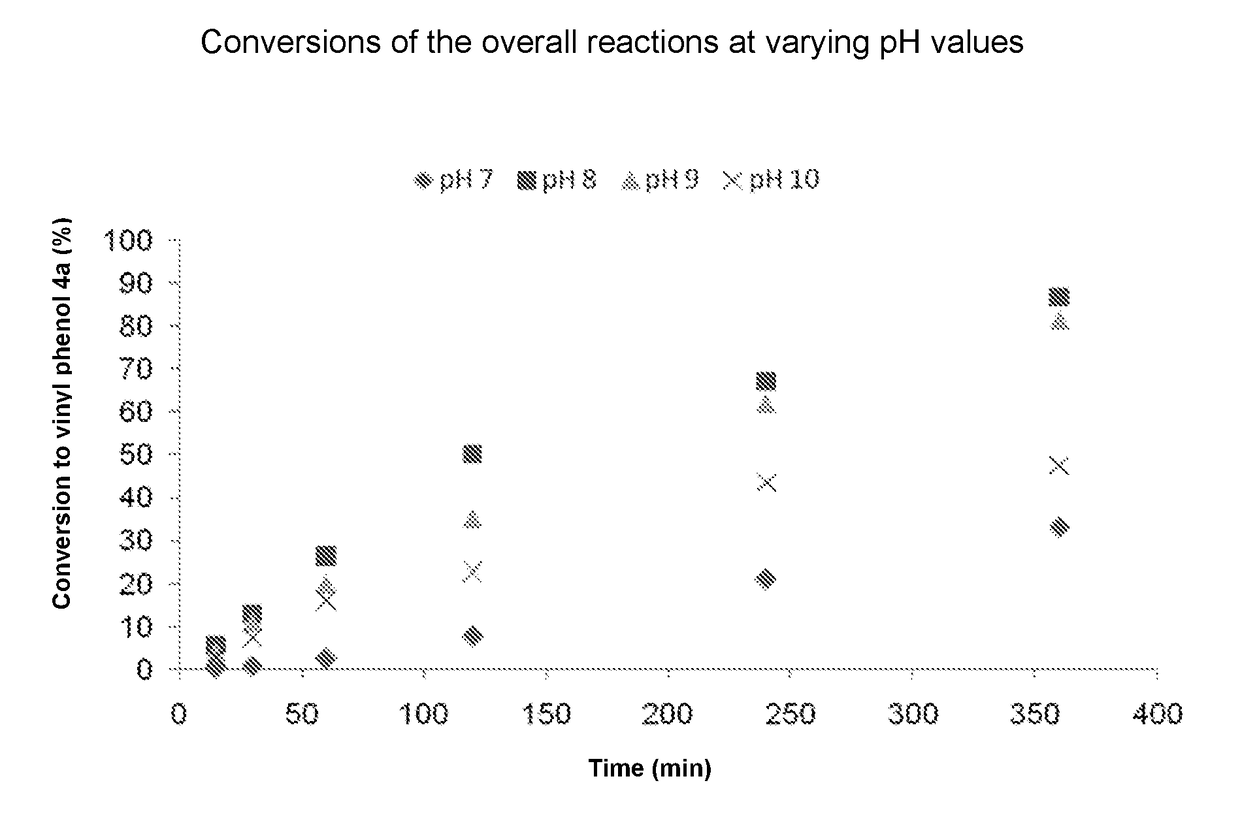
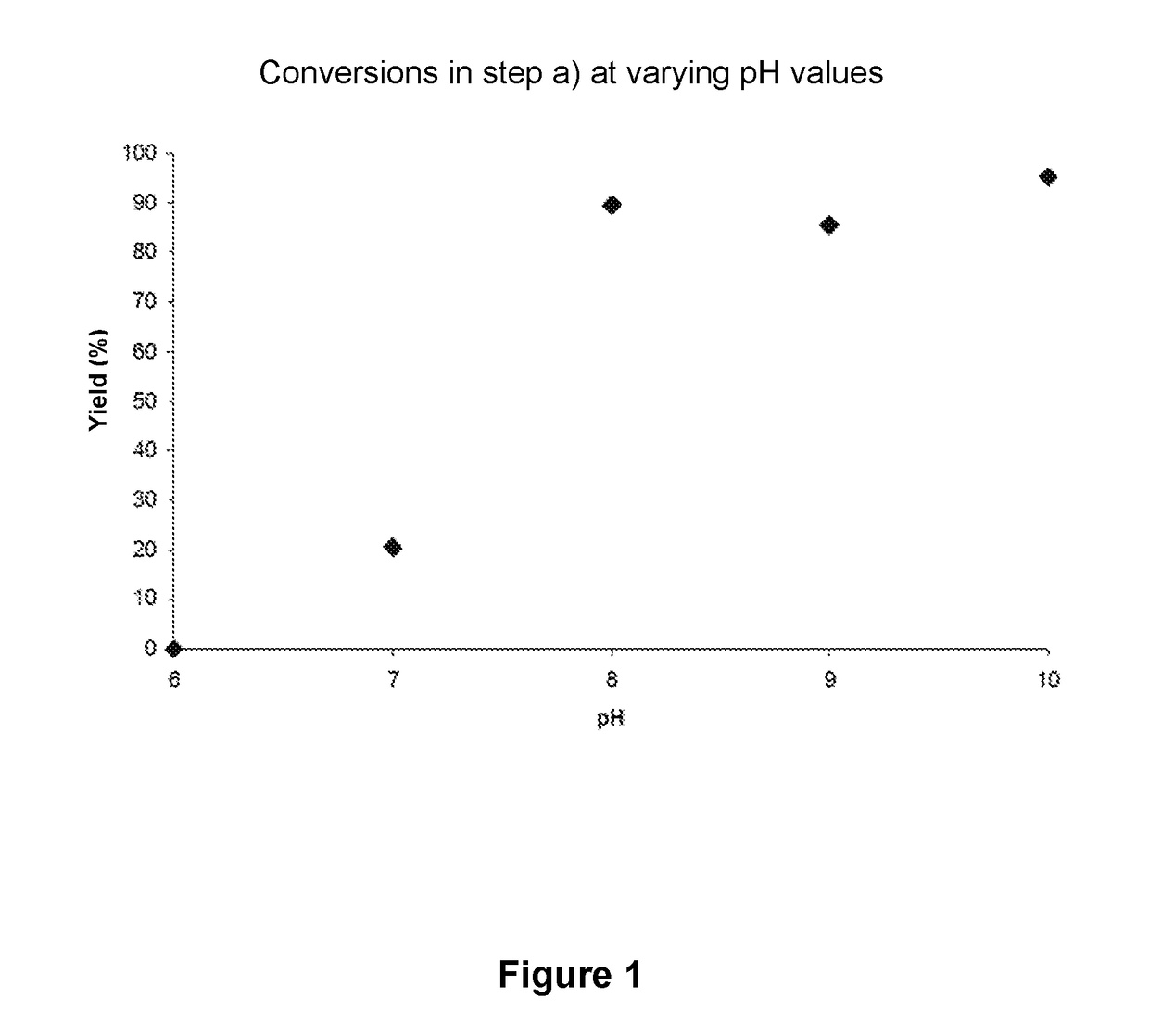
The invention relates to a biocatalytic method for producing p-vinylphenols, comprising a three-stage one-pot reaction according to the following reaction scheme: (A) wherein a) an optionally substituted phenol (1) is bound to pyruvic acid (BTS) to form the optionally substituted tyrosine (2) by means of catalytic action of a tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) and in the presence of ammonium ions, b) ammonia is eliminated from the tyrosine (2) by means of catalytic action of a tyrosine-ammonia-lyase (TAL) or phenyl-ammonia-lyase (PAL), in order to produce an optionally substituted p-coumaric acid (3), and c) the p-coumaric acid (3) undergoes a decarboxylation by means of catalytic action of a phenolic acid decarboxylase (PAD), in order to produce the desired, optionally substituted p-vinyl phenol(4); d) wherein the resultant CO2 is removed from the reaction system, in order to move the chemical equilibrium of all three reaction steps in the direction of the products.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GRAZ
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
ActiveCN108949652AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
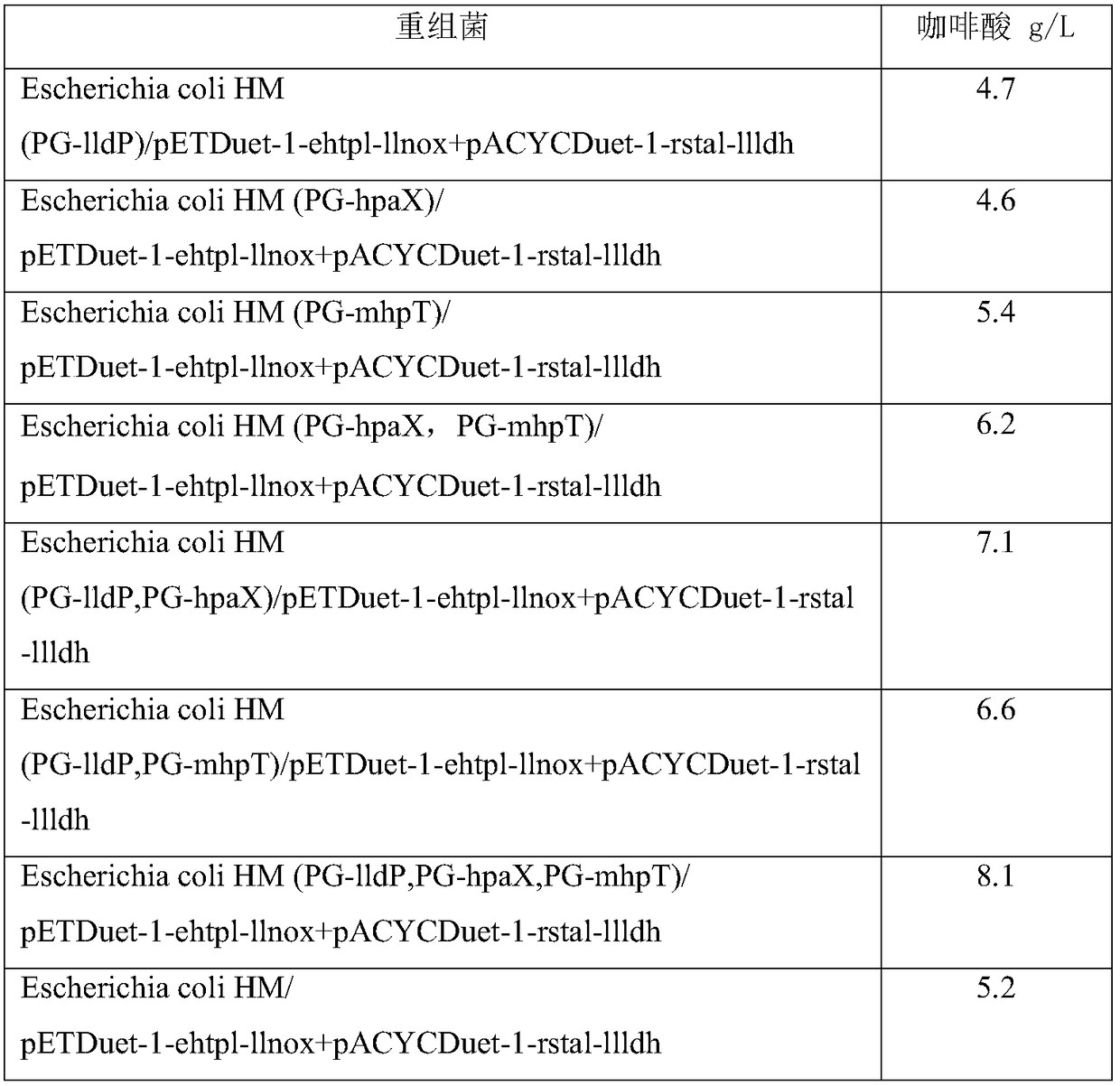
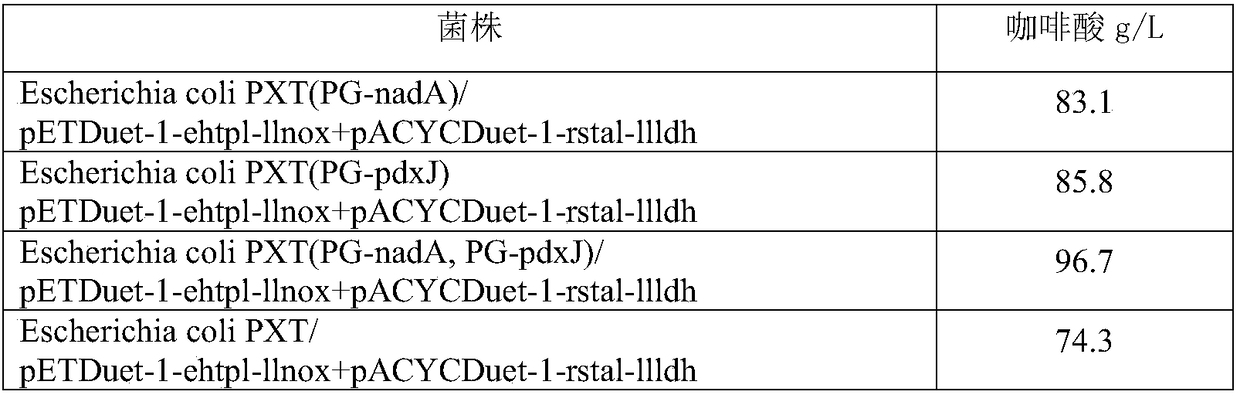
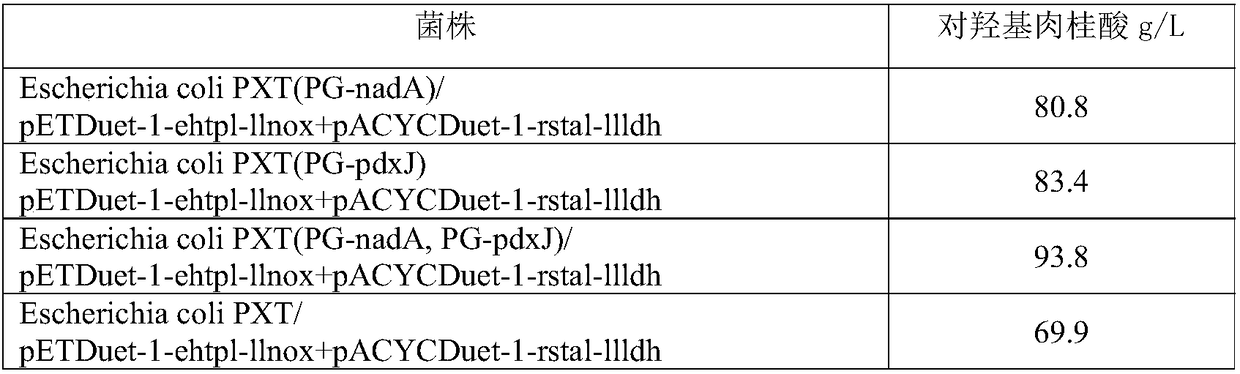
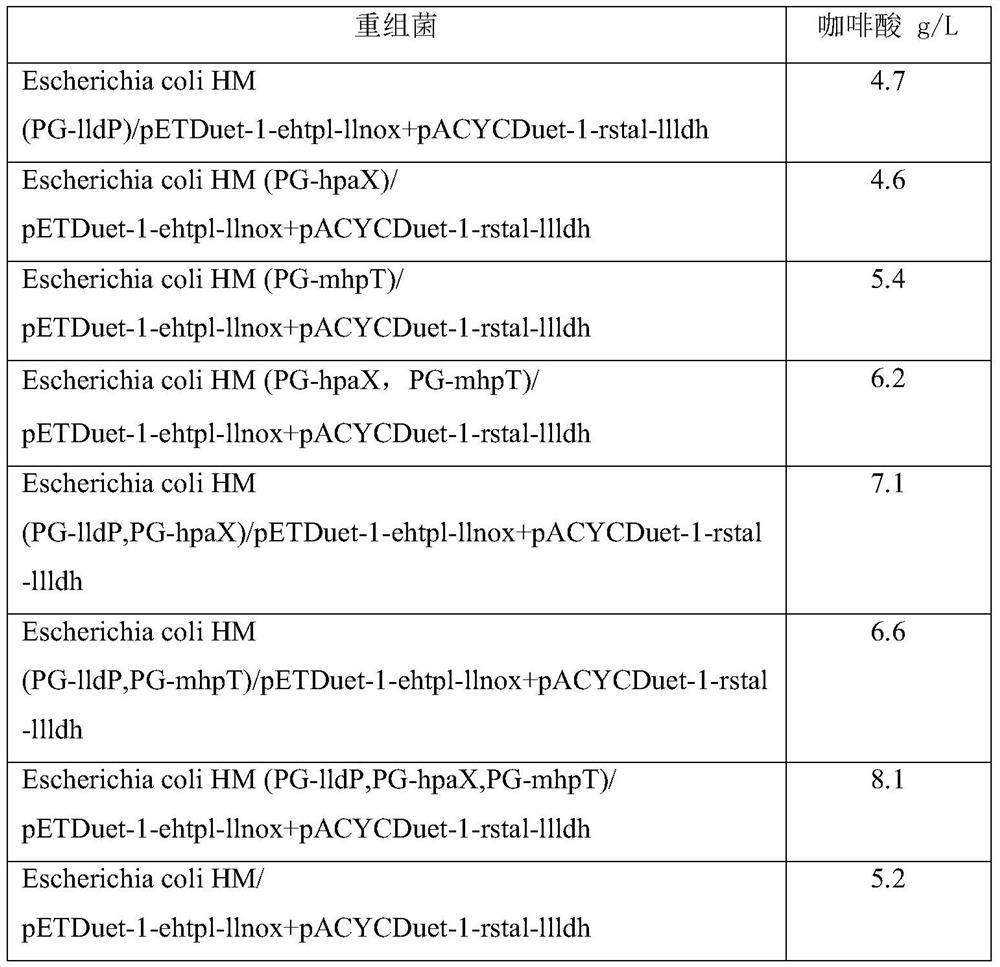
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium providedby the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing caffeic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages of realization of the efficient production ofcaffeic acid, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
DNA and amino acid sequences of a tyrosine-inducible tyrosine ammonia lyase enzyme from the yeast Trichosporon cutaneum
A novel tyrosine-inducible tyrosine ammonia lyase enzyme was isolated from the yeast Trichosporon cutaneum. This enzyme has a higher activity for tyrosine than for phenylalanine and is useful for the production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid directly from tyrosine. The gene encoding this enzyme was sequenced using 3′ and 5′ RACE cloning of the TAL cDNA and the gene was expressed in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in the bacterium Escherichia coli.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol
InactiveCN105907804AEfficient productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCinnamoyl-CoA reductaseCoumaric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and discloses a method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol. The metabolic pathway for production of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol is added into hosts. More precisely, tyrosine ammonia lyase, cinnamoyl-coA reductase, alcohol dehydrogenase and coumaric acid coA ligase are efficiently expressed in the host for producing tonquinol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid3-monooxygenase is added to produce caffeol, coffee acyl coenzyme AO-methyl transferase or caffeic acid O-methyl transferase is added to produce ferulenol. Genes coded by the enzyme are guided into the host, and the production host of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol can be generated by means of glucose. The invention further discloses a method for co-culture of different hosts, and the caffeol and the ferulenol are produced more efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Tyrosine ammonia lyase recombinant bacterium and construction method and application thereof, and tyrosine ammonia lyase and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110938579AEfficient catalysisEasy to operateCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaNucleotideTyrosine
The invention provides a tyrosine ammonia lyase recombinant bacterium and a construction method and application thereof, and tyrosine ammonia lyase and a preparation method and application thereof. The construction method of the tyrosine ammonia lyase recombinant bacterium comprises the following steps: extracting a target gene with a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2; connecting the target gene to a plasmid to obtain a recombinant plasmid; introducing the recombinant plasmids into a thallus to obtain a tyrosine ammonia lyase recombinant bacterium. The invention aims at providing a tyrosine ammonia lyase recombinant bacterium and a construction method and application thereof, and tyrosine ammonia lyase and a preparation method and application thereof. The tyrosine ammonia lyase is high in conversion efficiency and high in stability.
Owner:杭州唯铂莱生物科技有限公司
Engineered tyrosine ammonia lyase
The present invention provides engineered tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) polypeptides and compositions thereof. In some embodiments, the engineered TAL polypeptides have been optimized to provide enhanced catalytic activity while reducing sensitivity to proteolysis and increasing tolerance to acidic pH levels. The invention also provides methods for utilization of the compositions comprising the engineered TAL polypeptides for therapeutic and industrial purposes.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing ferulic acid and biosynthesis method of ferulic acid
InactiveCN111705031APromote biotransformationImprove conversion rateCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaHeterologousCoumaric acid
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing ferulic acid and a biosynthesis method of the ferulic acid, and belongs to the technical field of biological application. Thegenetically engineered bacterium for producing the ferulic acid can produce the ferulic acid by using tyrosine and methionine as raw materials. According to the biosynthesis way of the ferulic acid inplants, the recombinant genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by a genetic engineering method, and the genetically engineered bacterium can heterologously express tyrosine ammonia lyase, coumaric acid-3-hydroxylase and caffeic acid-3-O-methyltransferase, so that tyrosine biotransformation is promoted, the ferulic acid is produced by one-pot fermentation, the conversion rate is high, the purity of the obtained ferulic acid is high, the process is simple and clean, the cost is low, and the genetically engineered bacterium for producing the ferulic acid and the biosynthesis method of theferulic acid can be used for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
Engineered tyrosine ammonia lyase
ActiveUS20150299689A1High catalytic activityReduce sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaIncreased toleranceTyrosine ammonia-lyase
The present invention provides engineered tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) polypeptides and compositions thereof. In some embodiments, the engineered TAL polypeptides have been optimized to provide enhanced catalytic activity while reducing sensitivity to proteolysis and increasing tolerance to acidic pH levels. The invention also provides methods for utilization of the compositions comprising the engineered TAL polypeptides for therapeutic and industrial purposes.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Method for synthesizing D(+)beta -(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid by enzymic method
ActiveCN108424937AOriginalHigh molar conversionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisSynthesis methods
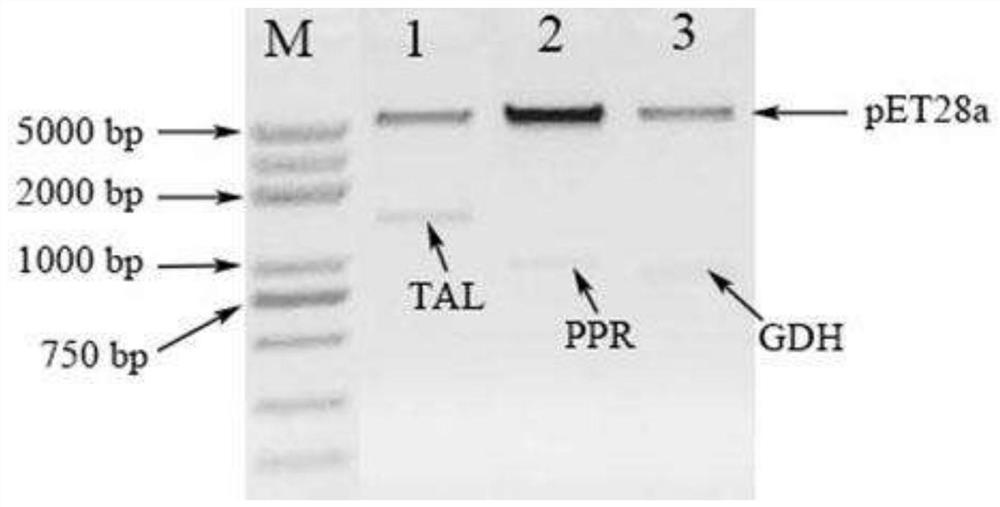
The invention discloses a novel synthesis method for D(+)beta -(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid. The method is characterized in that the beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) lacticacid is produced by catalyzing levodopa through tyrosine ammonia-lyase, phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase and specifically comprises the following steps: putting 0.5 to 1.5 mol of the levodopa (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl alanine), 10 to 30 g / L of tyrosine ammonia-lyase wet cell mass, 10 to 30 g / L of phenylpyruvate reductase wet cell mass and 10 to 30 g / L of glucose dehydrogenase wet cell mass into a reactor for uniformly mixing; and adjusting the pH value to be 7.0, and carrying out catalytic reaction at the temperature of 30 DEG C for 16 to 20 hours to obtain the beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) lacticacid. Accordingto the method, the D(+)beta -(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid is produced by utilizing the tyrosine ammonia-lyase, the phenylpyruvate reductase and the glucose dehydrogenase for the first time and taking the levodopa as a substrate through an enzymic method; and raw materials are saved and the pollution of chemical synthesis is avoided.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Combinatorial biosynthesis method of resveratrol
InactiveCN106191137AEase of industrial productionReduce manufacturing costCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
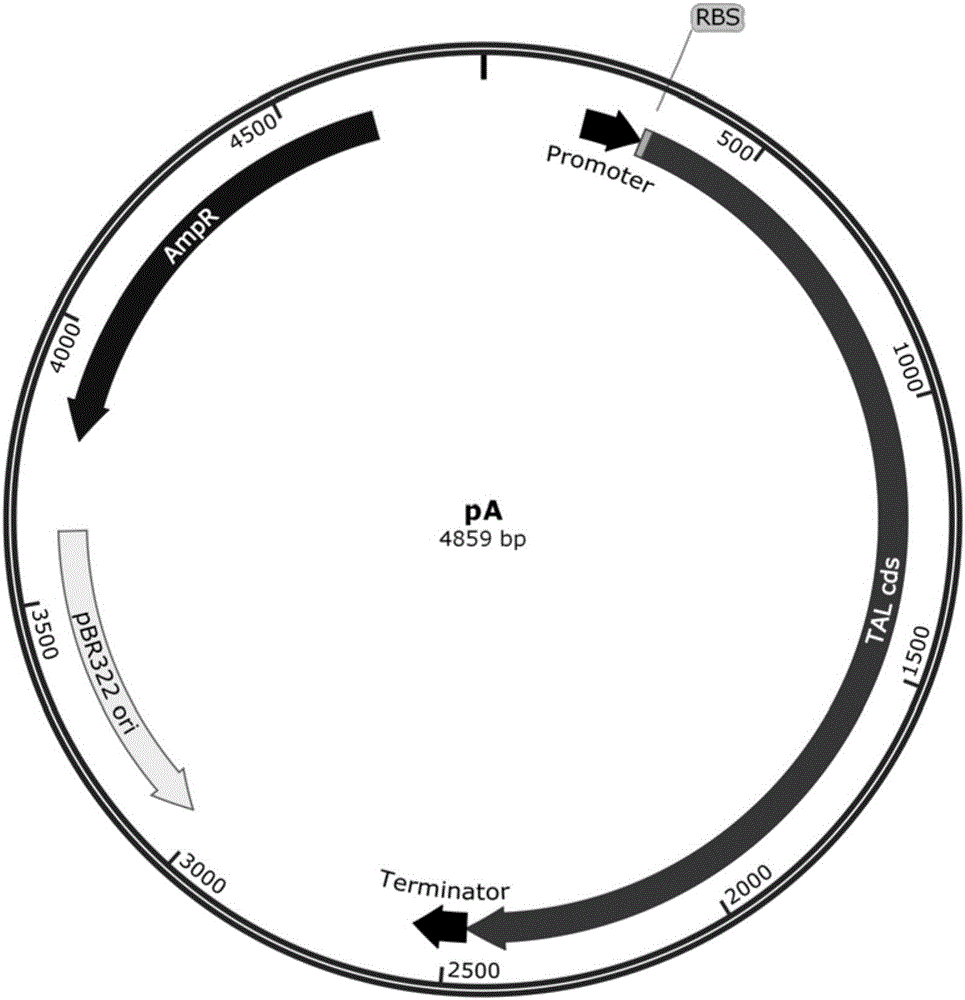
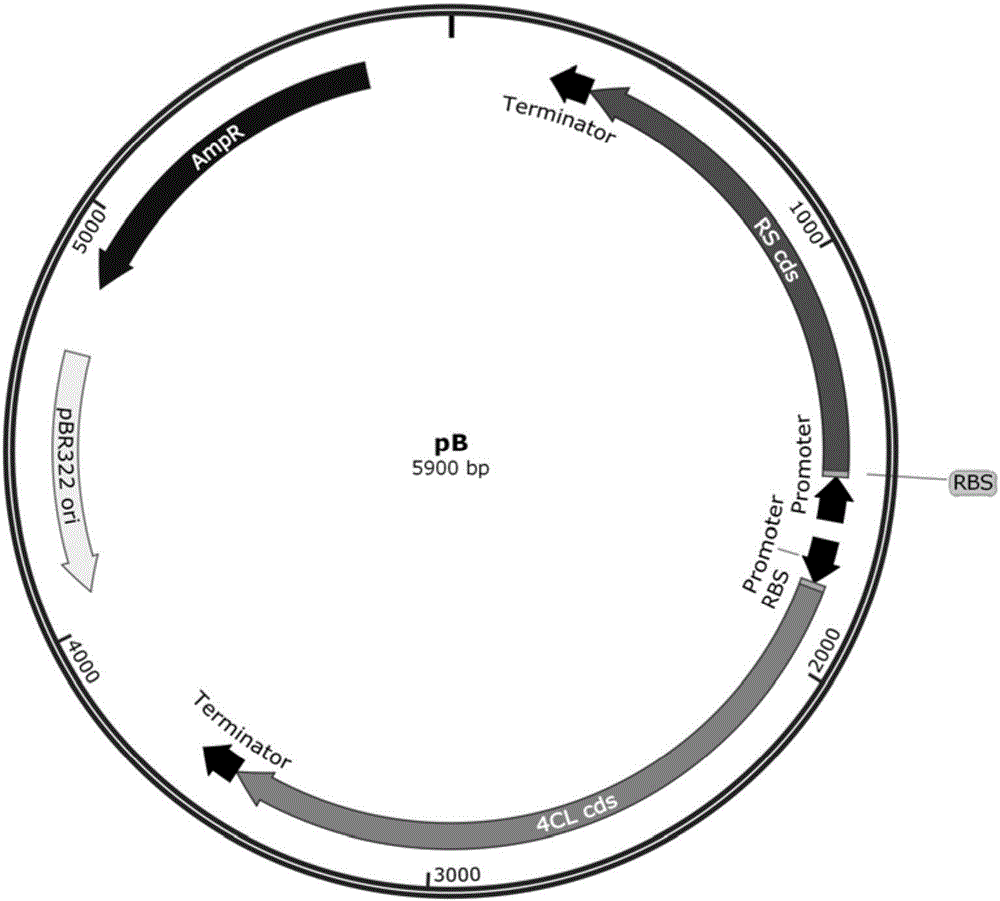
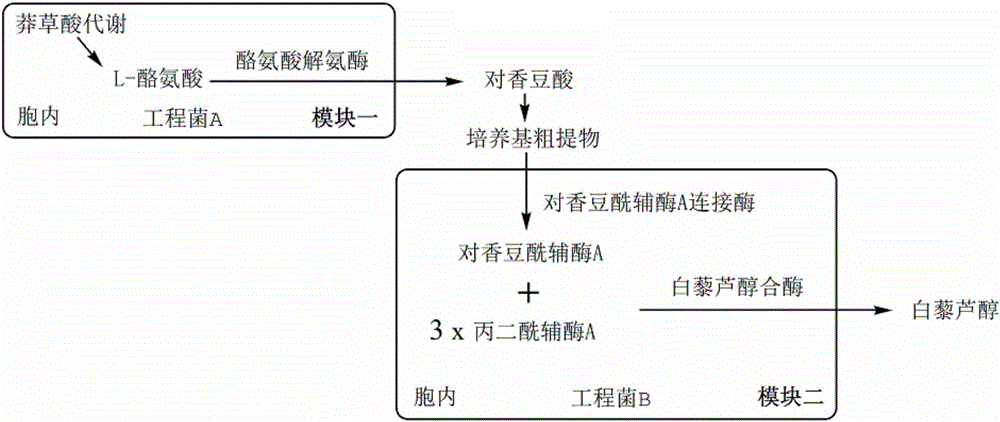
The invention discloses a combinatorial biosynthesis method of resveratrol, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Two production modules are constructed; in the first production module, recombinant escherichia coli can express tyrosine ammonia lyase through a constructed constitutive expression system and achieve denovo synthesis of p-coumaric acid; in the second production module, the recombinant escherichia coli can express p-coumaric acyl coenzyme A ligase and resveratrol synthase through the constructed constitutive expression system and synthesize resveratrol through p-coumaric acid produced by the first module. According to the method, the advantages that the two production modules can conduct regulation separately and can better achieve the maximum production value theoretically are achieved through step-by-step culture; the constitutive expression system which does not need an inducer and is efficient is provided, and therefore usage of a toxic inducer is avoided; through denovo synthesis of resveratrol, the production cost is reduced, and industrial production is better promoted.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce eriodictyol
ActiveCN103865864BReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
DNA and amino acid sequence of a tyrosine ammonia lyase enzyme from the bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides
A novel tyrosine ammonia lyase enzyme was identified in the bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. This enzyme has a higher activity for tyrosine than for phenylalanine and is useful for the production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid directly from tyrosine. The gene encoding this enzyme was cloned by direct amplification using the genomic DNA and was expressed in E. coli.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid
ActiveCN108949840AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBio engineering
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing p-hydroxycinnamic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a phenol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium can realize the efficient production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and a method for producing the p-hydroxycinnamic acid has the advantages of simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Strain for producing tyrosine ammonia lyase and application of strain
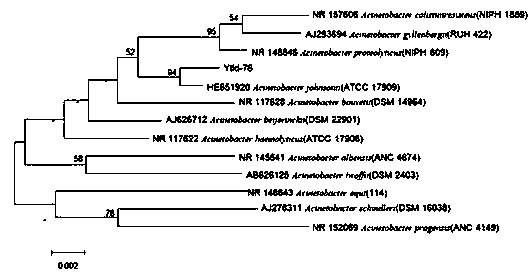
ActiveCN111424005ABroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActive agentTyrosine
The invention relates to a strain for producing tyrosine ammonia lyase and an application of the strain, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is classified and named as Acinetobacterjohnsonii, is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 15, 2020, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19831. The strain provided by the invention has good hereditary stability and low culture cost, the generated tyrosine ammonia lyase has high enzyme activity, and the strain has a wide applicable substrate spectrum and can be directly used for direct conversion and synthesis of p-hydroxycinnamic acid and p-hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. During catalytic synthesis, addition of a surfactant, an organic solvent and other membrane penetrating agents is not needed, introduction of exogenous impurities is avoided, extraction and separation operation is facilitated, and advantages are achieved for industrial application.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
A kind of biological preparation method of caffeic acid
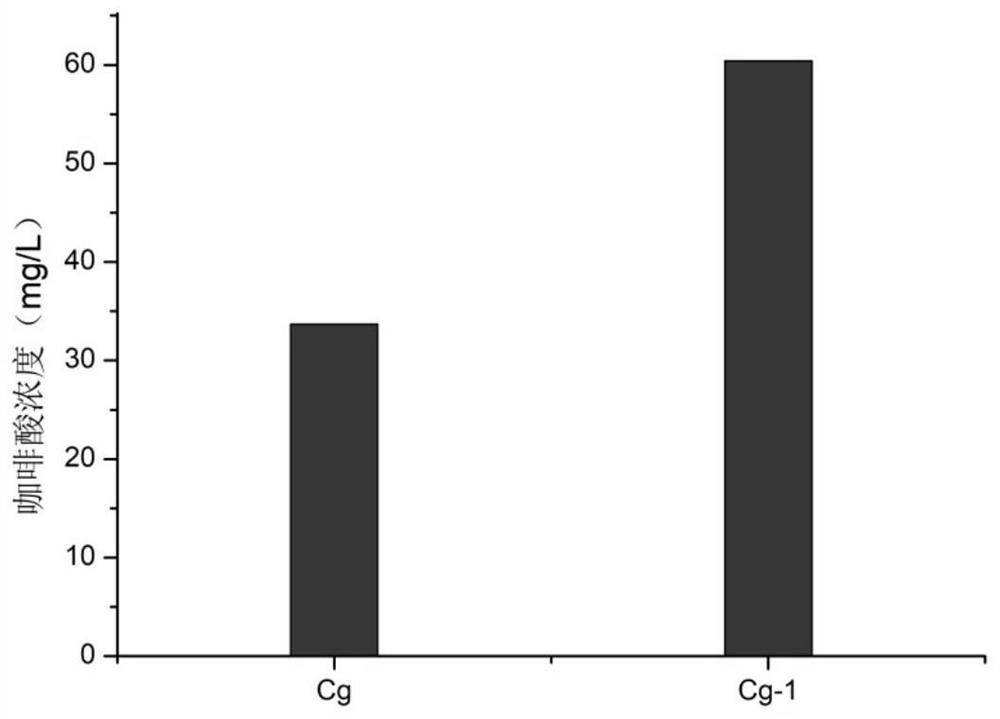
ActiveCN112553098BIncrease productionImprove conversion rateCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiFlavin reductaseEnzyme Gene
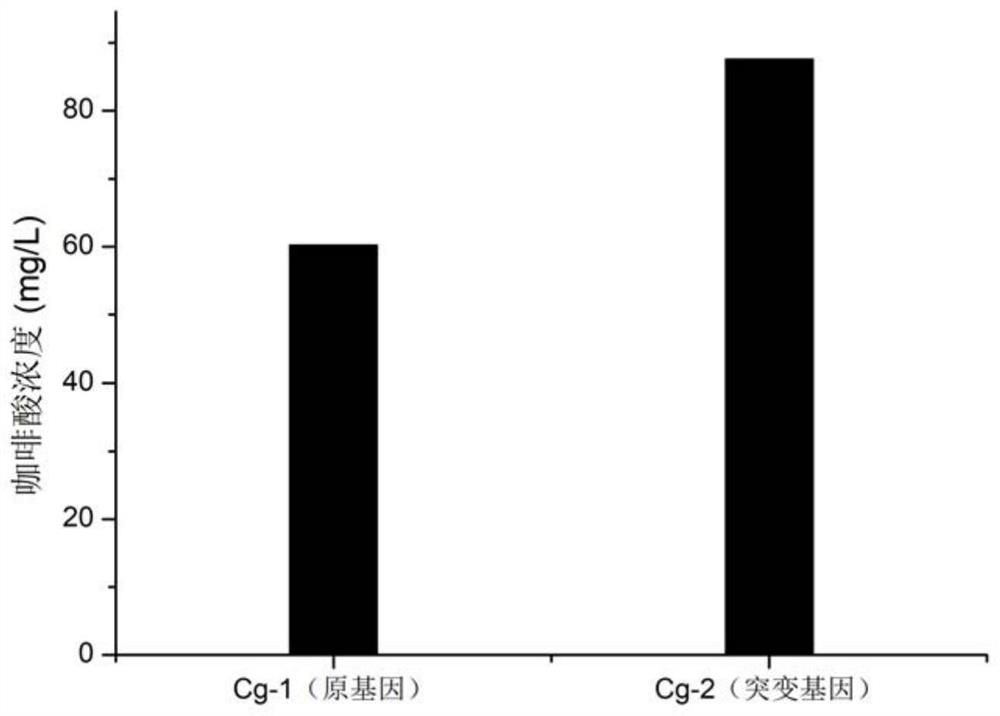
The invention discloses a biological preparation method of caffeic acid, which belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The present invention selects high osmotic pressure Candida glycerol producing yeast CCTCC M93018 to construct engineering bacteria, knocks out L-tryptophan synthesis gene trp1 and L-phenylalanine synthesis gene pheA, and overexpresses 3-deoxy-D-arabinan Keto-7-phosphate synthase gene aro4 and bifunctional choroidate synthase and flavin reductase gene aro7, and tyrosine ammonia lyase, and 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid-3-monooxygenase Mutation, in the yeast to achieve de novo synthesis of caffeic acid with glucose as carbon source, caffeic acid production reached 87.6mg / L. The preparation method of the invention has the characteristics of convenient operation, high conversion efficiency, low production cost, wide industrial application prospect and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of engineering bacteria and its application in producing caffeic acid
ActiveCN108949652BEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium and its application for producing caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention provides a recombinant bacteria capable of producing caffeic acid at low cost; the recombinant bacteria simultaneously expresses four enzymes, namely tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and NADH oxidase; Further, the recombinant bacteria of the present invention also knocks out the phenolic substance decomposition gene, and strengthens the expression of any one or more of the lactic acid transport gene, the catechol transport gene, and the coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The invention realizes the efficient production of caffeic acid, and has the advantages of simple process and few impurities, and has important industrial application value.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
A method for enzymatically synthesizing Danshensu
ActiveCN108424937BOriginalHigh molar conversionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisDihydroxyphenylalanine
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing danshensu. The method uses tyrosine ammonia lyase, phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase to catalyze levodopa to produce danshensu. Specifically, 0.5-1.5mol of levodopa (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine), 10-30g / L of wet bacterium of tyrosine ammonia lyase, and 10-30g of wet bacterium of phenylpyruvate reductase / L, 10-30g / L of wet cells of glucose dehydrogenase were placed in a reactor and mixed evenly, the pH value was adjusted to 7.0, the temperature was 30°C, and the catalytic reaction was carried out for 16-20h to obtain Danshensu. For the first time, the method uses tyrosine ammonia lyase, phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase to produce danshensu enzymatically with levodopa as a substrate, saving raw materials and avoiding the pollution of chemical synthesis.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
A tyrosine ammonia lyase-producing strain and its application
ActiveCN111424005BBroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActive agentTyrosine
The invention relates to a strain producing tyrosine ammonia-lyase and its application, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is classified and named as Acinetobacter johnsonii, and has been preserved in China's microbial strains on May 15, 2020 General Microbiology Center of the Preservation Management Committee, deposit number: CGMCC No.19831. The bacterial strain provided by the present invention has good genetic stability, low cultivation cost, high enzymatic activity of tyrosine ammonia-lyase, and wide applicable substrate spectrum. There is no need to add membrane-permeable agents such as surfactants and organic solvents during synthesis, avoiding the introduction of foreign impurities, which is conducive to extraction and separation operations, and has advantages in industrial applications.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Biological method for producing resveratrol
InactiveCN102605006BDe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a biological method for producing resveratrol, which comprises the following steps: ligating target genes obtained by restriction enzyme digestion to an expression vector, wherein the target genes include the sequences of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and resveratrol synthase (RS); transforming the constructed expression vector into a strain to obtain a recombinant engineered strain; and fermenting the recombined engineered strain. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention uses the genetically engineered strain for fermentation to produce resveratrol, so as to realize denovo synthesis of resveratrol with no need of adding substrates. The method disclosed by the invention solves the source problem of resveratrol, and at the same time, reduces the production cost in a maximum extent, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
METHOD FOR PREPARING p-VINYL PHENOLS
InactiveUS20180057845A1High reaction yieldFast and almost completeOrganic chemistryFermentationTyrosine ammonia-lyaseReaction step
A biocatalytic method is provided for preparing p-vinyl phenols by a three-step, one-pot reaction according to the following reaction scheme:wherein the three steps include: (a) optionally substituted phenol (1) is bound to pyruvic acid (BTS) to form optionally substituted tyrosine (2) by the catalytic action of a tyrosine phenol-lyase (TPL) and in the presence of ammonium ions, (b) ammonia is eliminated from tyrosine (2) by the catalytic action of a tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) or a phenyl ammonia-lyase (PAL) to produce optionally substituted p-coumaric acid (3), and (c) p-coumaric acid (3) is subjected to a decarboxylation reaction by the catalytic action of a phenolic acid decarboxylase (PAD), to produce the desired, optionally substituted p-vinyl phenol (4); and (d) wherein the generated CO2 is removed from the reaction system to shift the chemical equilibrium of all three reaction steps (a), (b) and (c) towards the product side.
Owner:UNIV GRAZ
Rosev analogs and genetically engineered bacteria producing the rosavi analogs and applications thereof
ActiveCN111943996BIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesSugar derivativesUdp glucosyltransferaseTyrosine
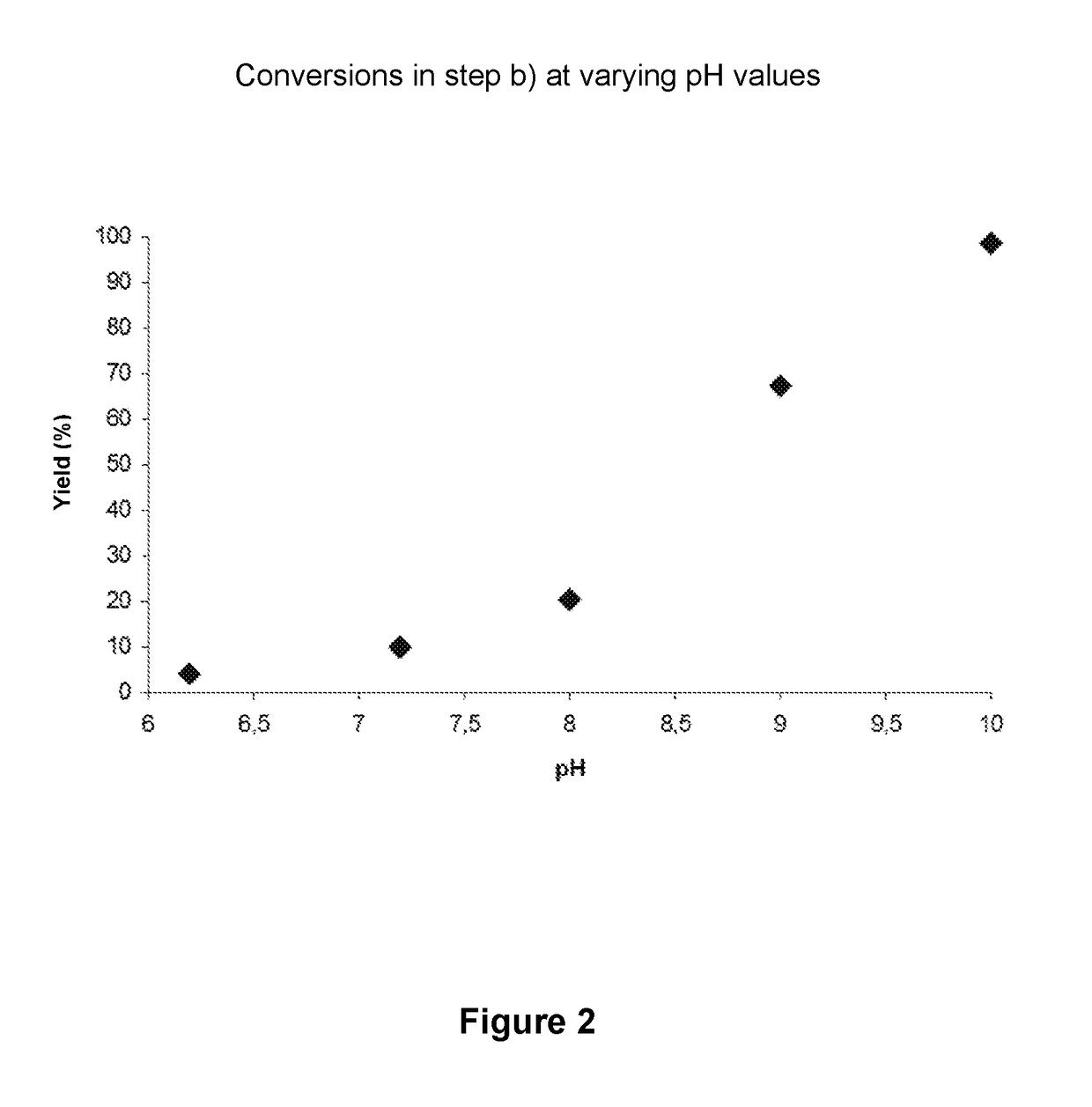
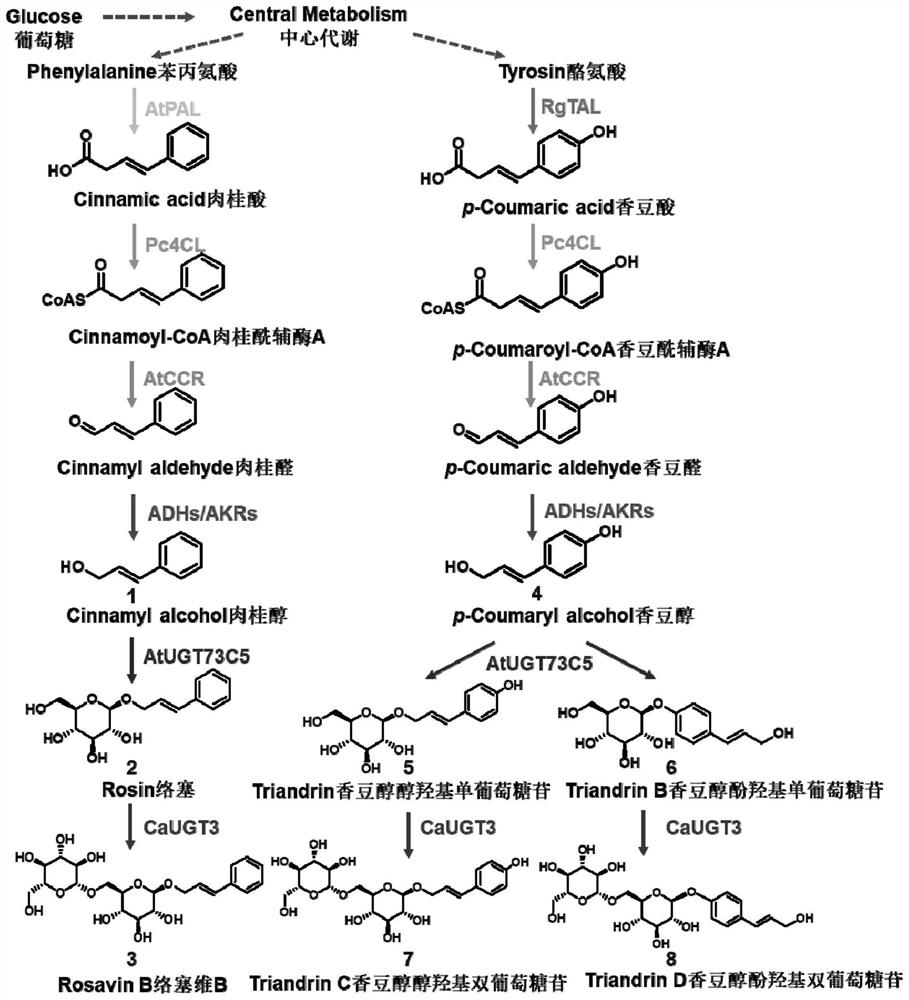
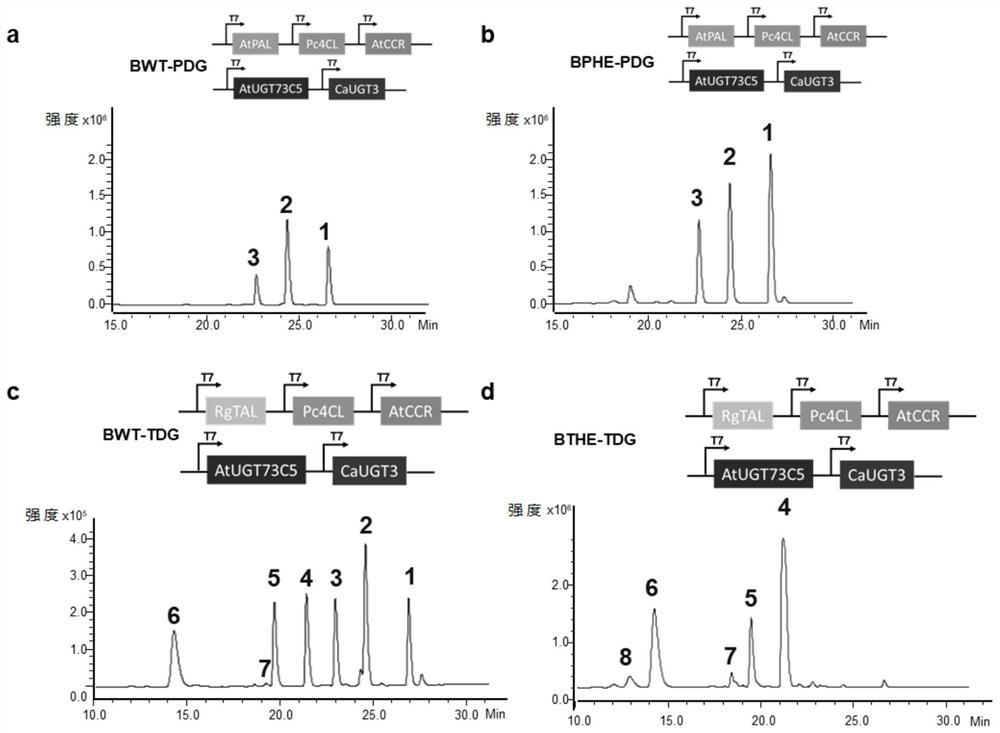
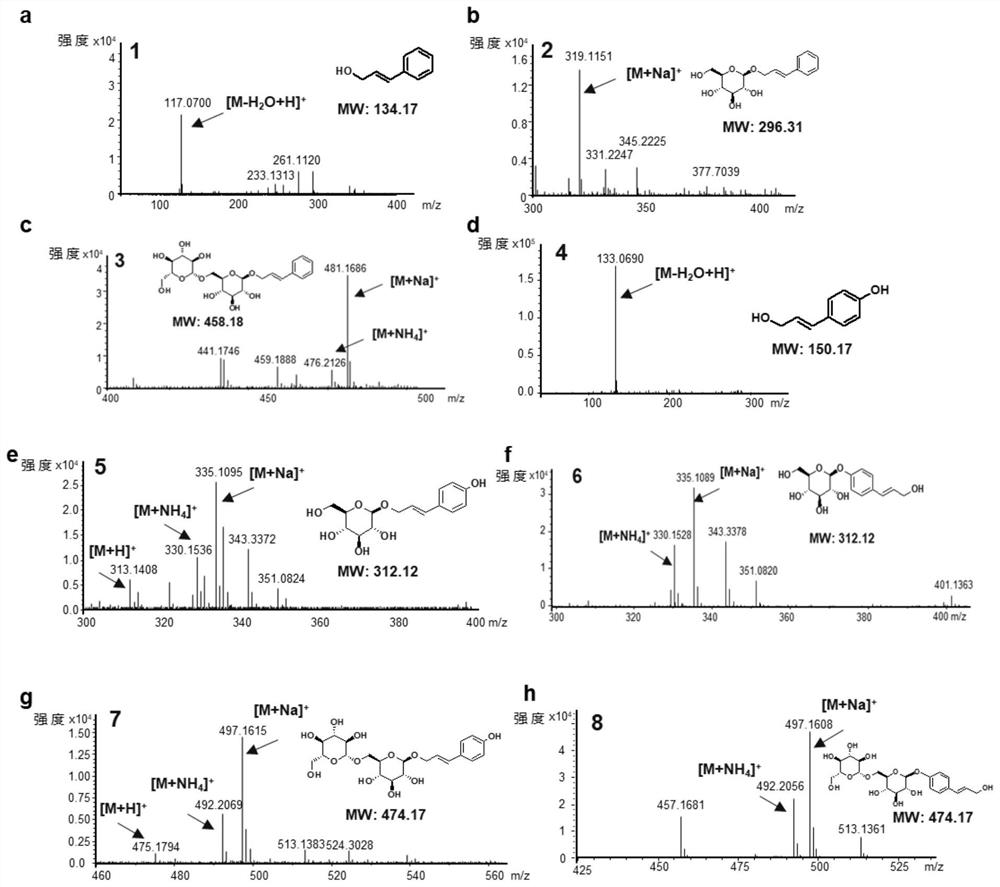
The present invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a rosavir analog, a genetically engineered bacterium producing the rosavir analog, and an application thereof. The rosevin analog has a structure shown in formula I, formula II, formula III or formula IV, and the genetically engineered bacterium contains phenylalanine ammonia lyase or tyrosine ammonia lyase, 4-coumaric acid coenzyme A Genes for ligase 4CL, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase CCR, and UDP glucosyltransferase UGT. The genetically engineered bacteria can ferment and produce Triandrin and Triandrin B (Formula IV); or Triandrin, Triandrin B, Triandrin C (Formula II) and Triandrin D (Formula III), and the yield of Triandrin and Triandrin B can reach up to 1.7g / L and 1.6g / L; or Luosaiwei B (formula I), the highest output can reach 1.6g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com