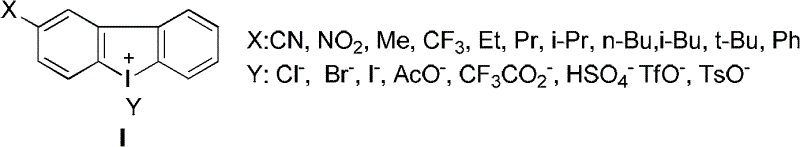Patents
Literature
80 results about "NADH oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
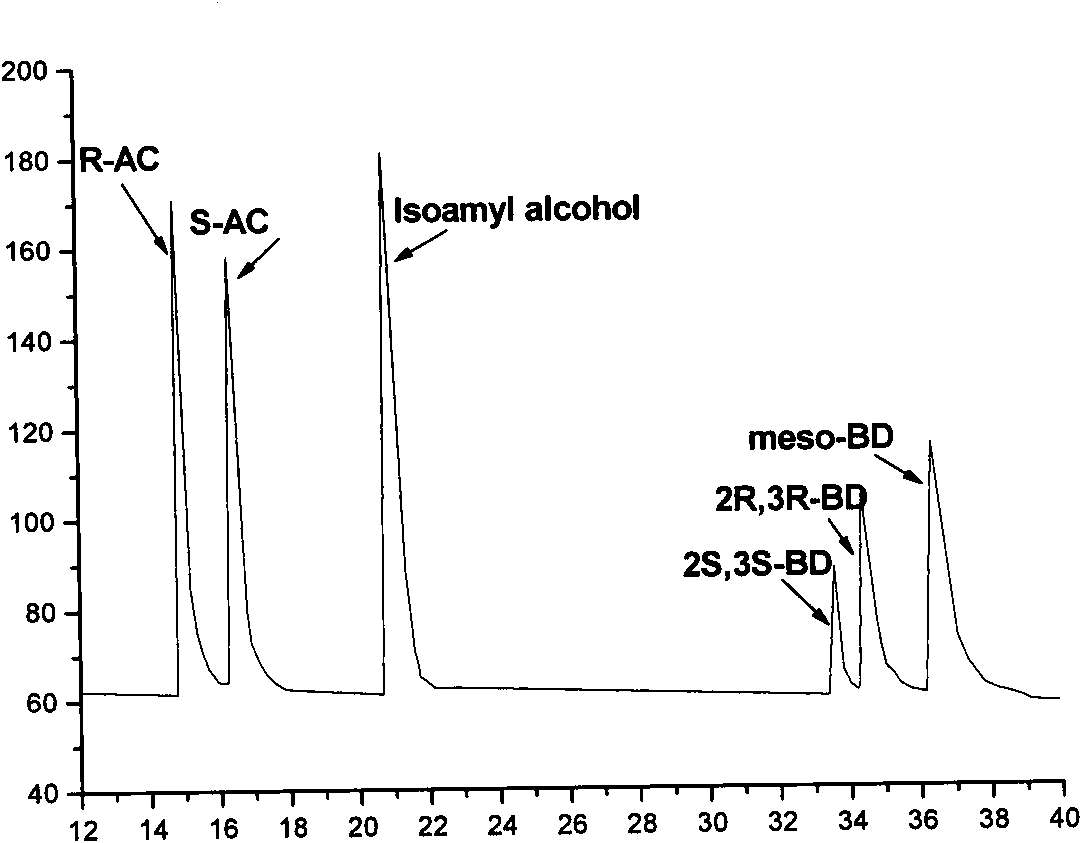
Gene recombination bacterium and application thereof in preparing chiral pure acetoin and 2,3-butanediol
InactiveCN101565685AEasy to operateAchieve productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGram
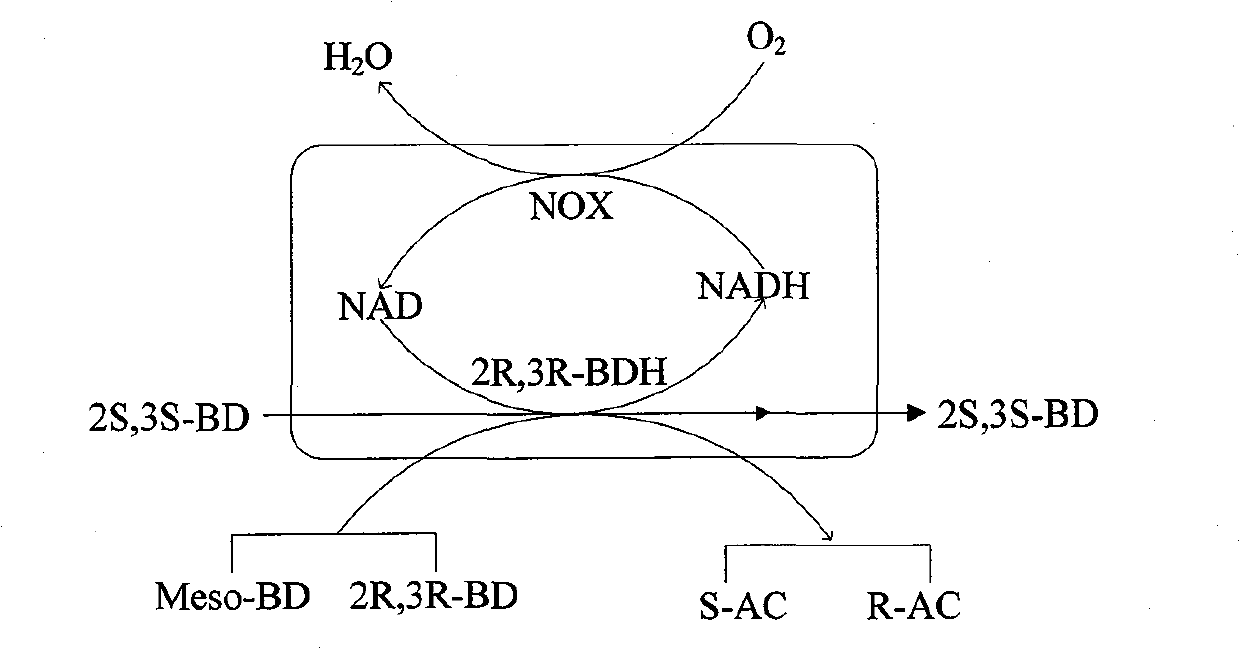
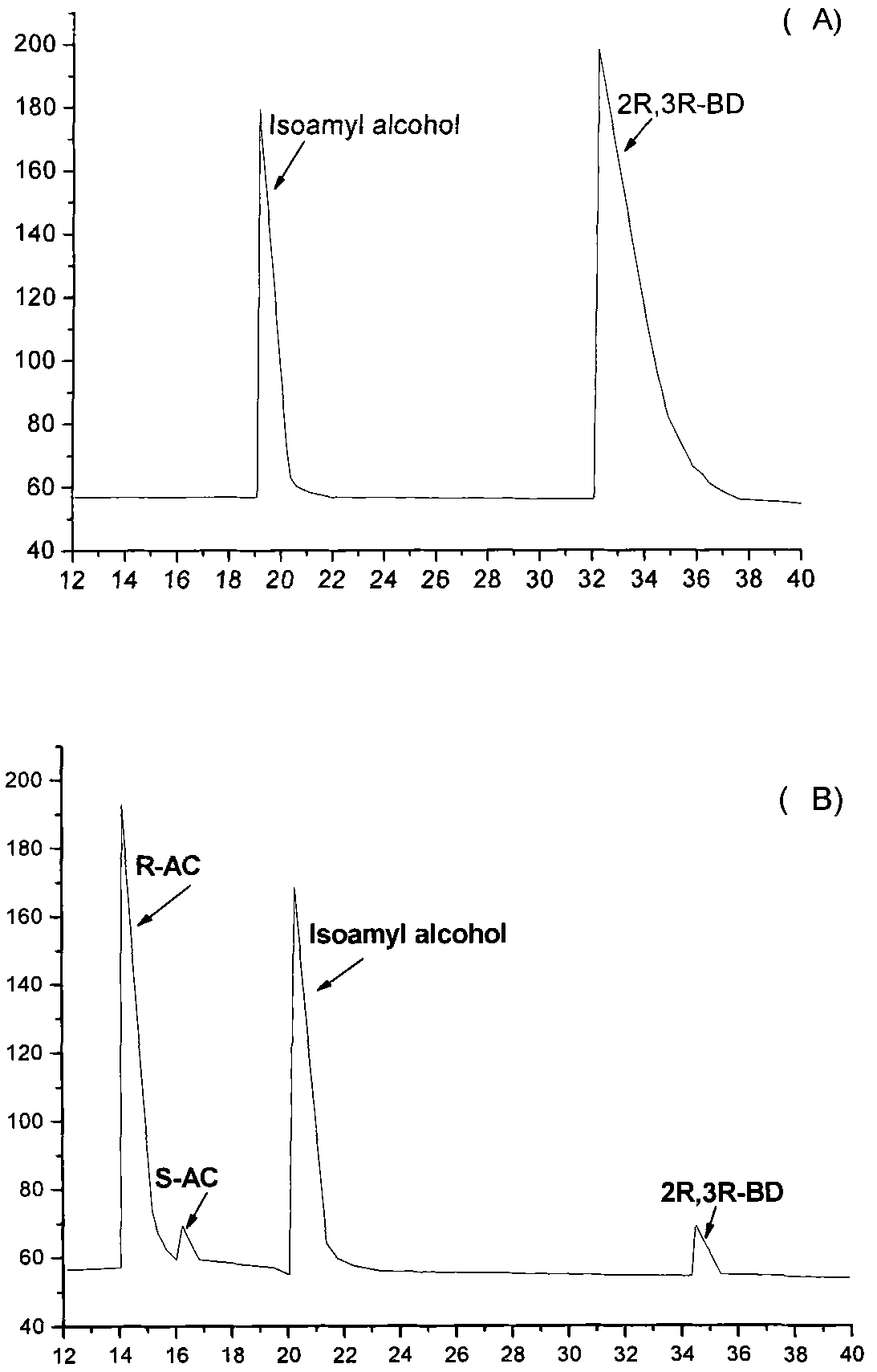
The invention discloses an E. coli BL21(pETDuet-ydjLnox) containing a 2R,3R-butanediol dehydrogenase gene ydjL and an NADH oxidase gene nox, wherein the strain is preserved in the 'China Center for Type Culture Collection' on December 23 in 2008, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 208259. The invention also discloses application of a gene recombination bacterium in producing chiral S-AC by catalyzing meso-BD, producing chiral R-AC by catalyzing 2R,3R-BD and producing chiral pure 2S,3S-BD by splitting a 2,3-BD mixture. The concentration of a chiral AC prepared from the recombinant E. coli can reach over 6 grams per liter (the ee value is more than or equal to 96 percent); and the ee value of the chiral pure 2S,3S-BD is more than or equal to 98 percent, and the regeneration of a cofactor is achieved, thus the gene recombination bacterium has great industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Agents for sequestering serum aging factors and uses therefore
InactiveUS20050226947A1Prevent and ameliorate and conditionPrevent and ameliorate skin damageBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseCell damage
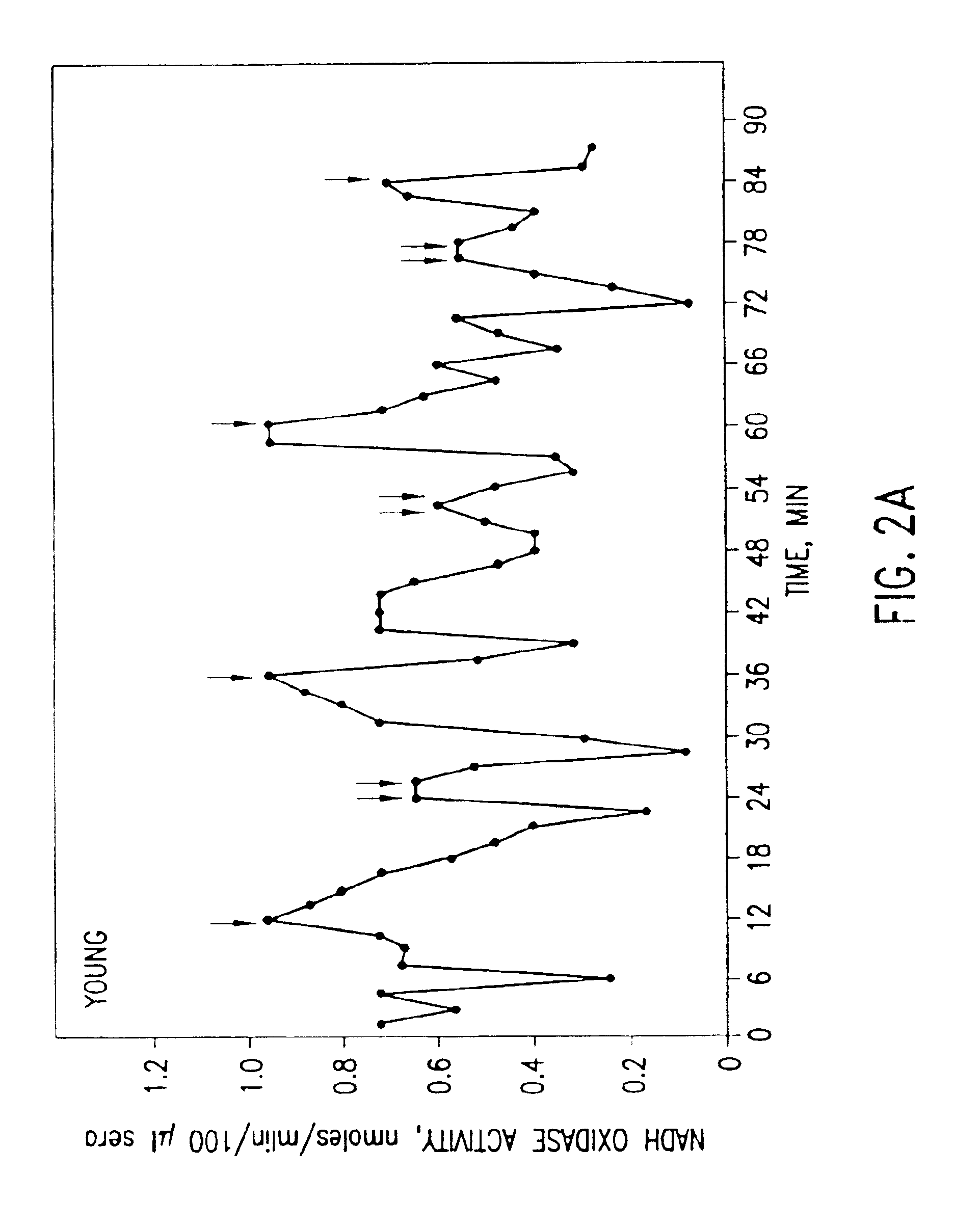
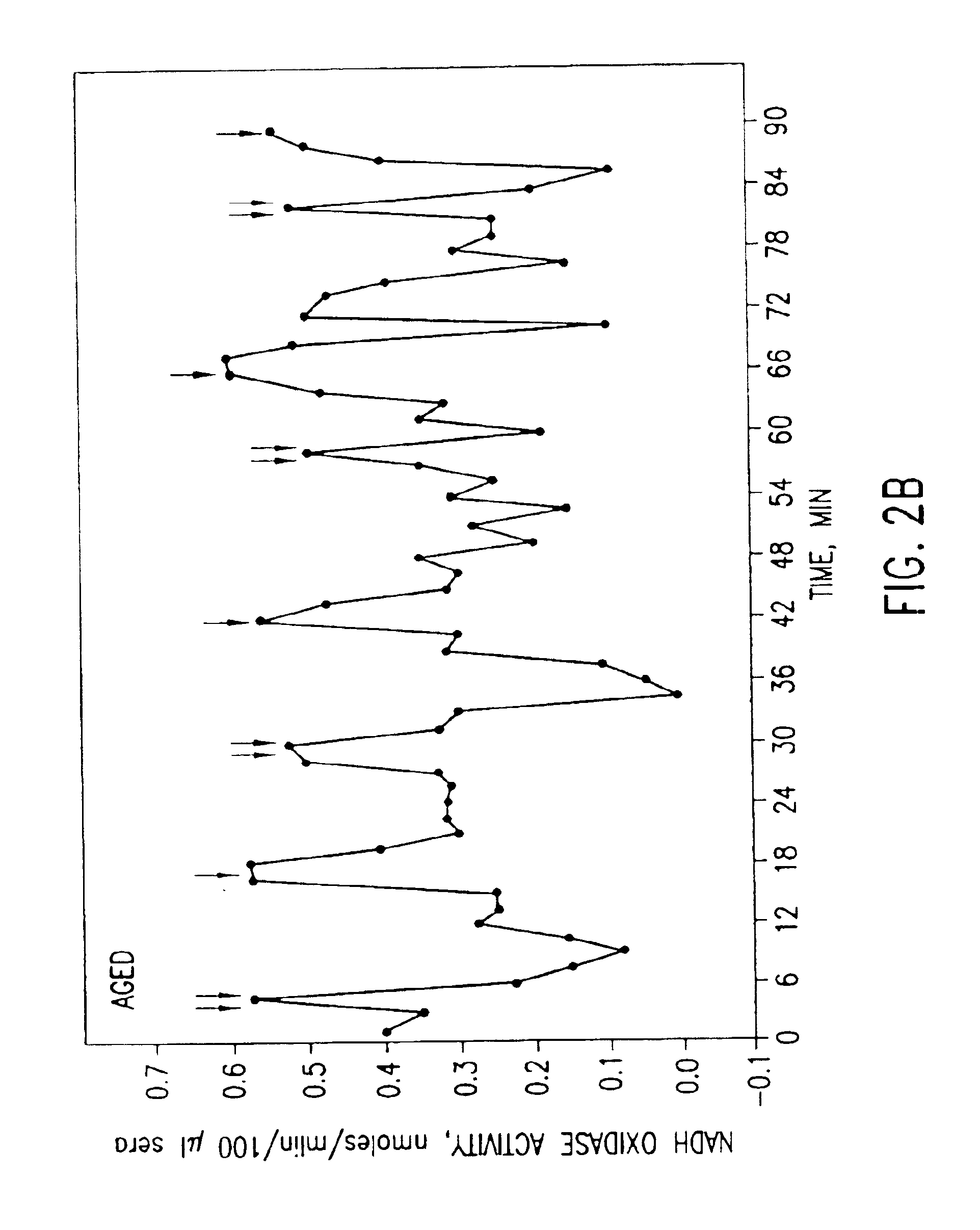
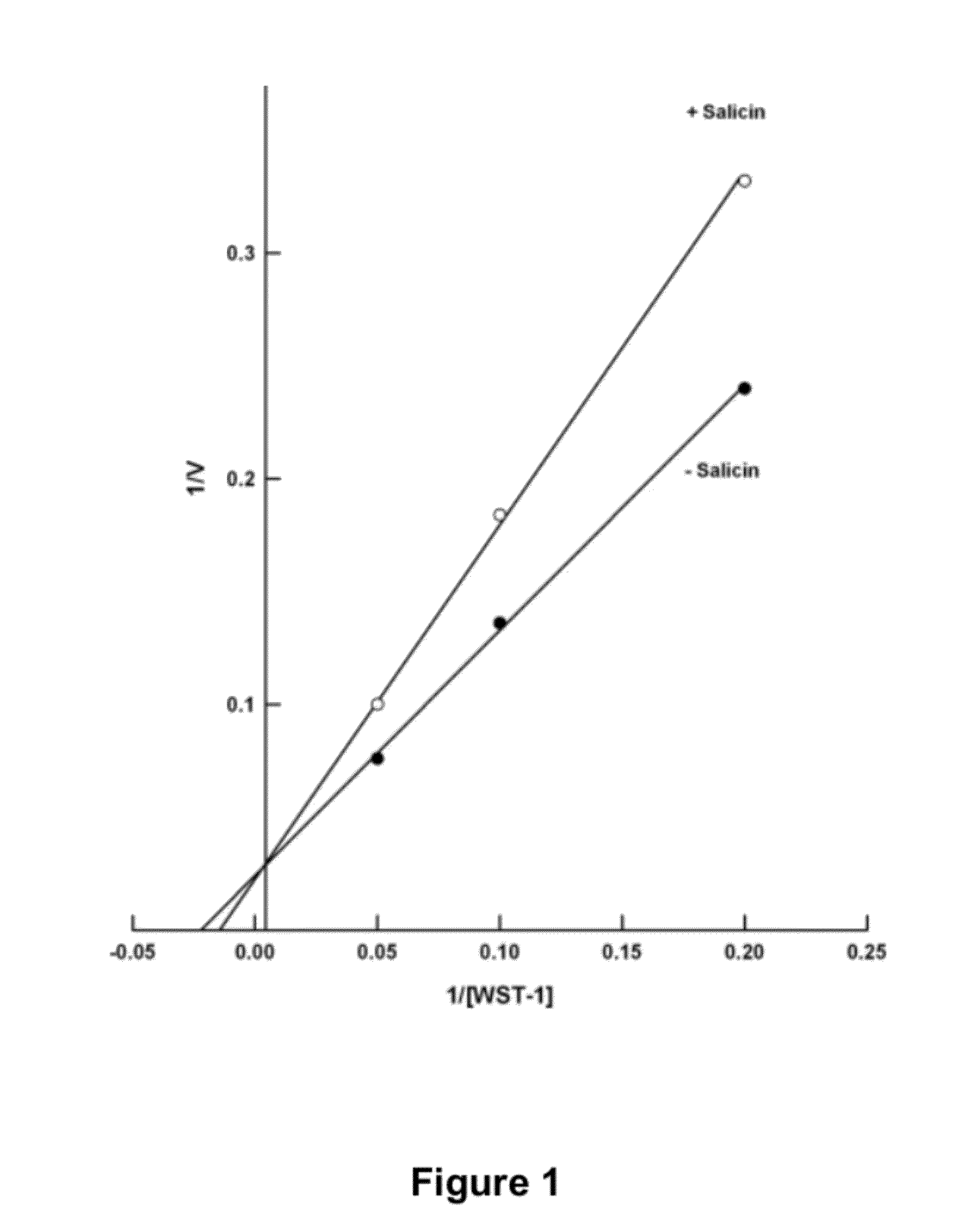
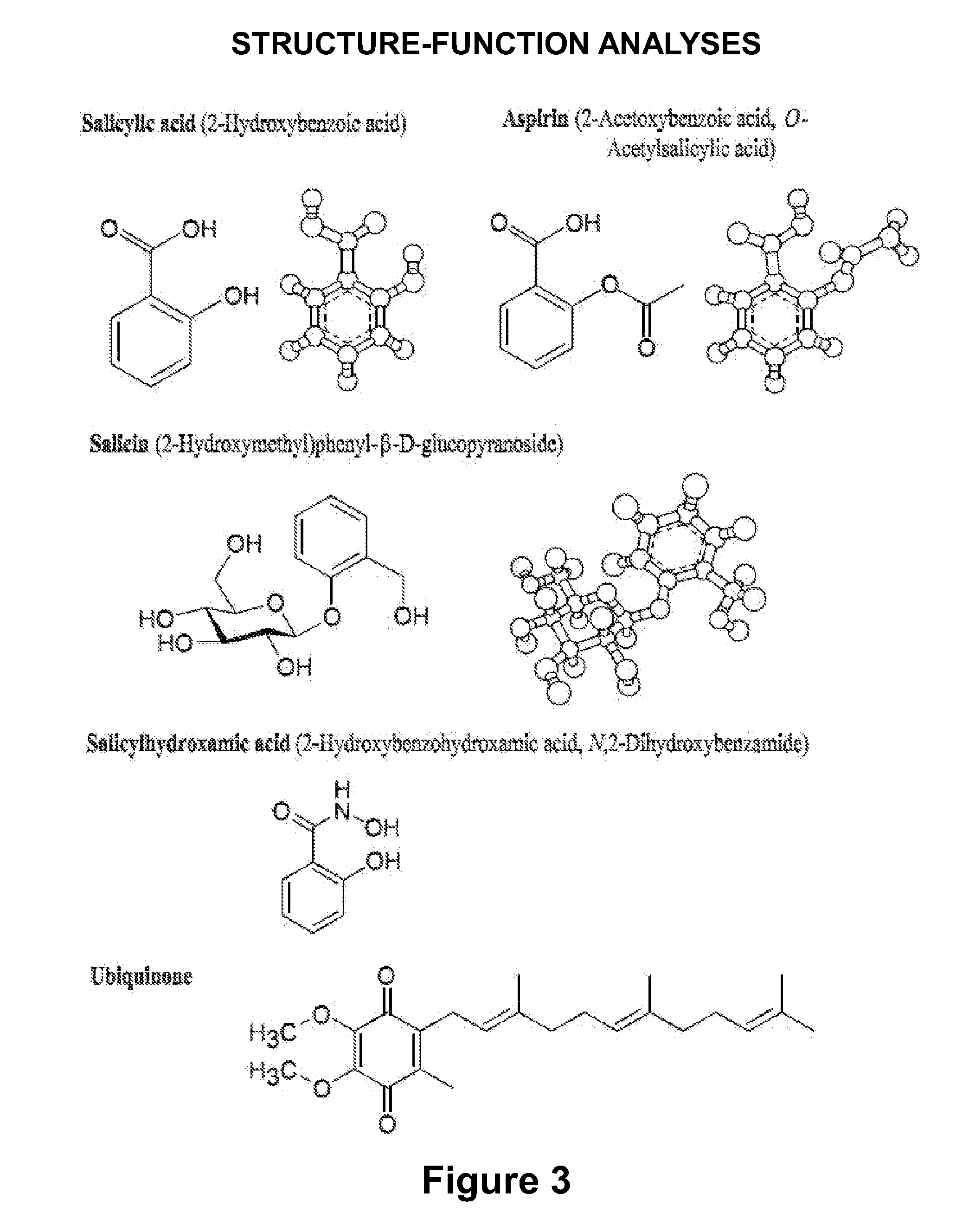
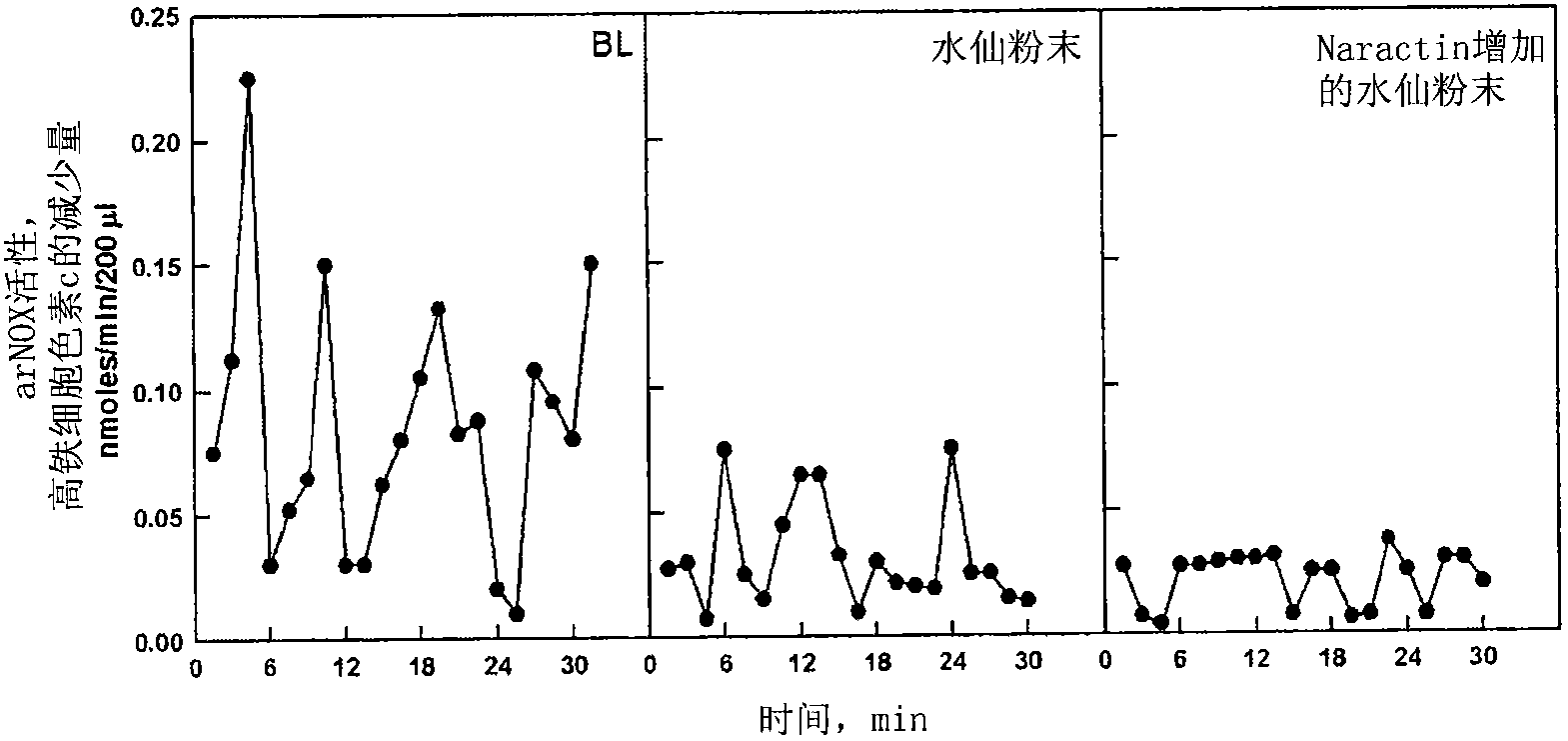
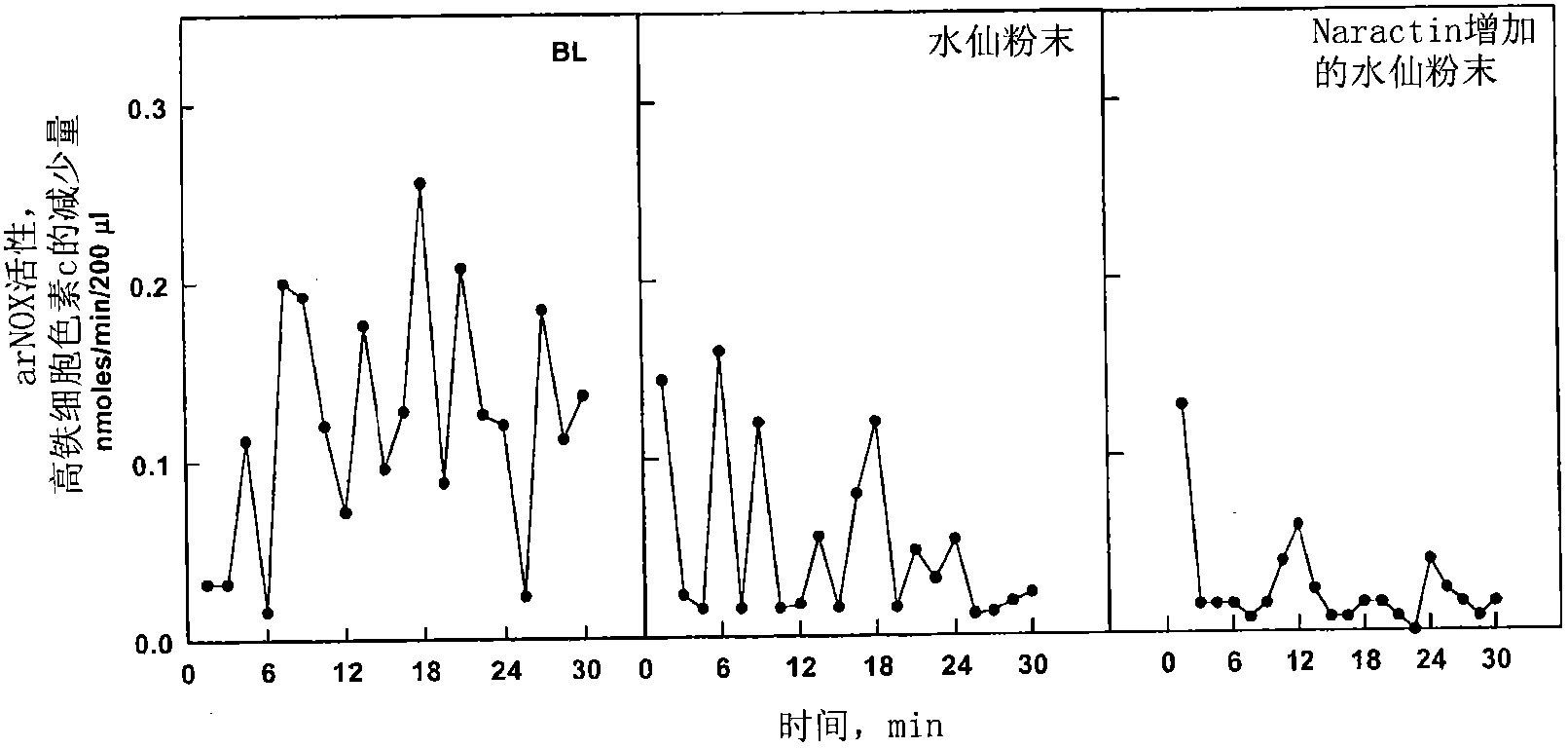
Methods for the prevention or treatment of disorders and complications of disorders resulting from cell damage caused by an aging-related isoform of NADH oxidase (arNOX) are described. The agent for such inhibition comprises processed various Narcissus tazzeta extracts, preferably IBR-DORMIN®, both alone and in combination with other inhibition agents, including ubiquinones like coenzyme Q. These agents bind arNOX and inhibit the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species, thereby decreasing the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species. Such agents, and their methods of administration, as extremely effective as part of anti-aging treatments.
Owner:NU SKIN INT
Agents for sequestering aging factors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070104810A1Prevent and improve healthReduce appearance problemsBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseCell damage
Methods for the prevention or treatment of disorders and complications of disorders resulting from cell damage caused by an aging-related isoform of NADH oxidase (arNOX) are described. The agent for such inhibition comprises processed various Narcissus tazetta extracts, preferably IBR-DORMIN®, both alone and in combination with other inhibition agents, including ubiquinones like coenzyme Q. These agents bind arNOX and inhibit the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species, thereby decreasing the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species. Such agents, and their methods of administration, as extremely effective as part of anti-aging treatments.
Owner:KERN DALE
Method to Treat Skin Conditions with Narcissus Tazetta Bulb Extract
InactiveUS20080175935A1Prevent and improve healthReduce appearance problemsBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseCell damage
Methods for the prevention or treatment of disorders and complications of disorders resulting from cell damage caused by an aging-related isoform of NADH oxidase (arNOX) are described. The agent for such inhibition comprises processed various Narcissus tazetta extracts, preferably IBR-DORMIN®Narcissus tazetta bulb extract, both alone and in combination with other inhibition agents, including ubiquinones like coenzyme Q. These agents bind arNOX and inhibit the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species, thereby decreasing the ability of arNOX to generate reactive oxygen species. Such agents, and their methods of administration, as extremely effective as part of anti-aging treatments.
Owner:NU SKIN INT
Methods for identifying agents that inhibit serum aging factors and uses and compositions thereof
InactiveUS6878514B1Reduced responseInhibits ability of AR-NOX to generateOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseSerum ige
The invention described herein encompasses methods of preventing or treating disorders caused by oxidative damage by an aging-specific isoform of NADH oxidase (AR-NOX). The invention encompasses methods of assaying, screening, and identifying agents that inhibit AR-NOX, as well as methods using ubiquinone to inhibit the ability of AR-NOX to generate reactive oxygen species. These agents may be formulated into pharmaceutical compositions in the prevention and treatment of disorders caused by oxidative damage.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method of improving the efficacy of lactic acid bacterial starter cultures and improved starter culture compositions
InactiveUS20020081712A1Enhancement of acid productionIncreased biomass productionMilk preparationBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseBacteroides
Methods of enhancing the growth rate and / or controlling the metabolic activity of lactic acid bacteria and of improving the shelf life and / or the quality of an edible product using lactic acid bacterial organisms which are defective in their pyruvate metabolism. There is also provided starter culture compositions comprising such defective lactic acid bacteria as helper organisms and lactic acid bacterial starter culture strains. Useful helper organisms are Lactococcus strains which are defective with respect to pyruvate formate lyase (Pfl) and / or lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) activity. The helper organisms may overexpress a gene coding for an NAD+ regenerating enzyme such as NADH oxidase encoded by nox gene.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
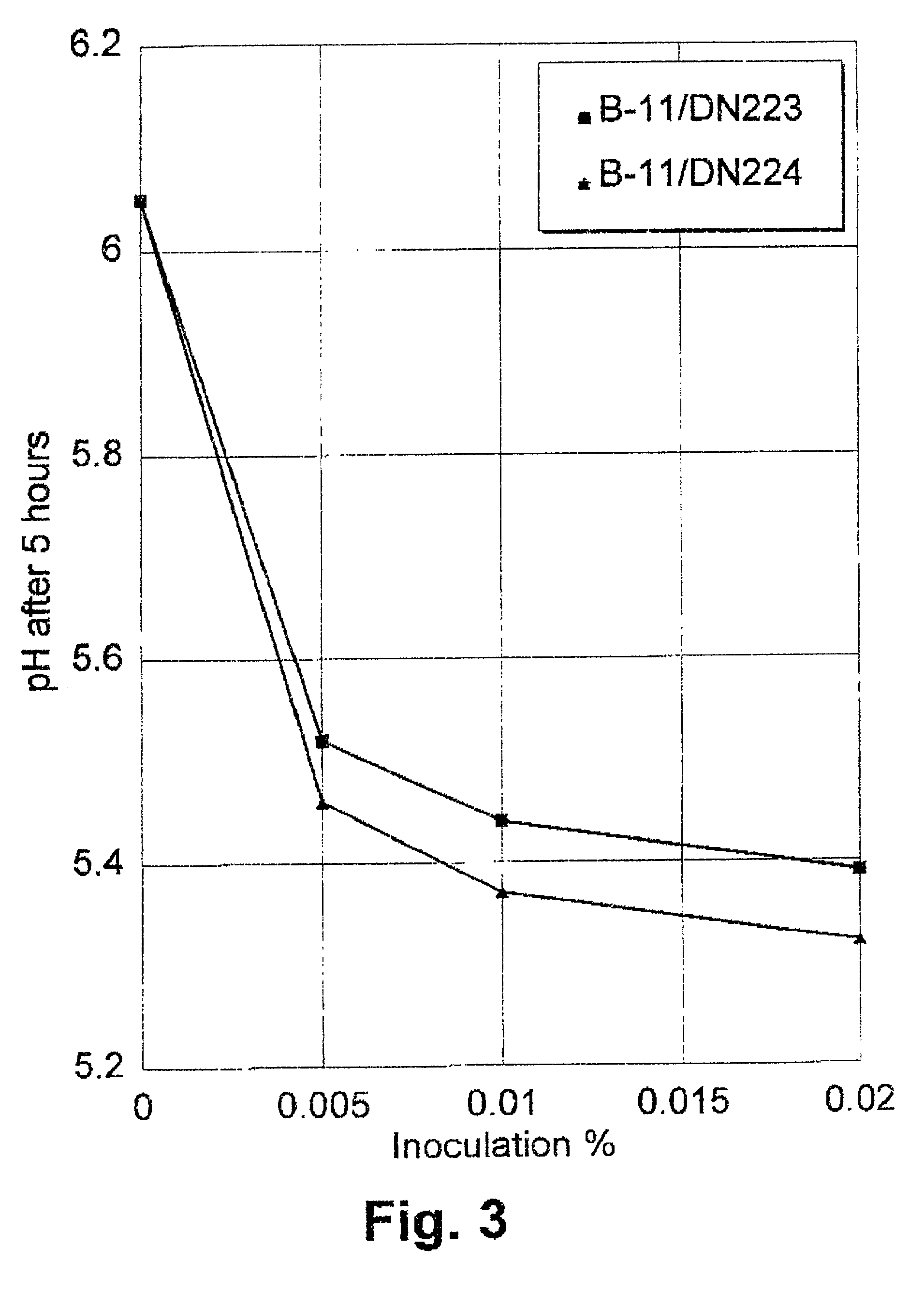
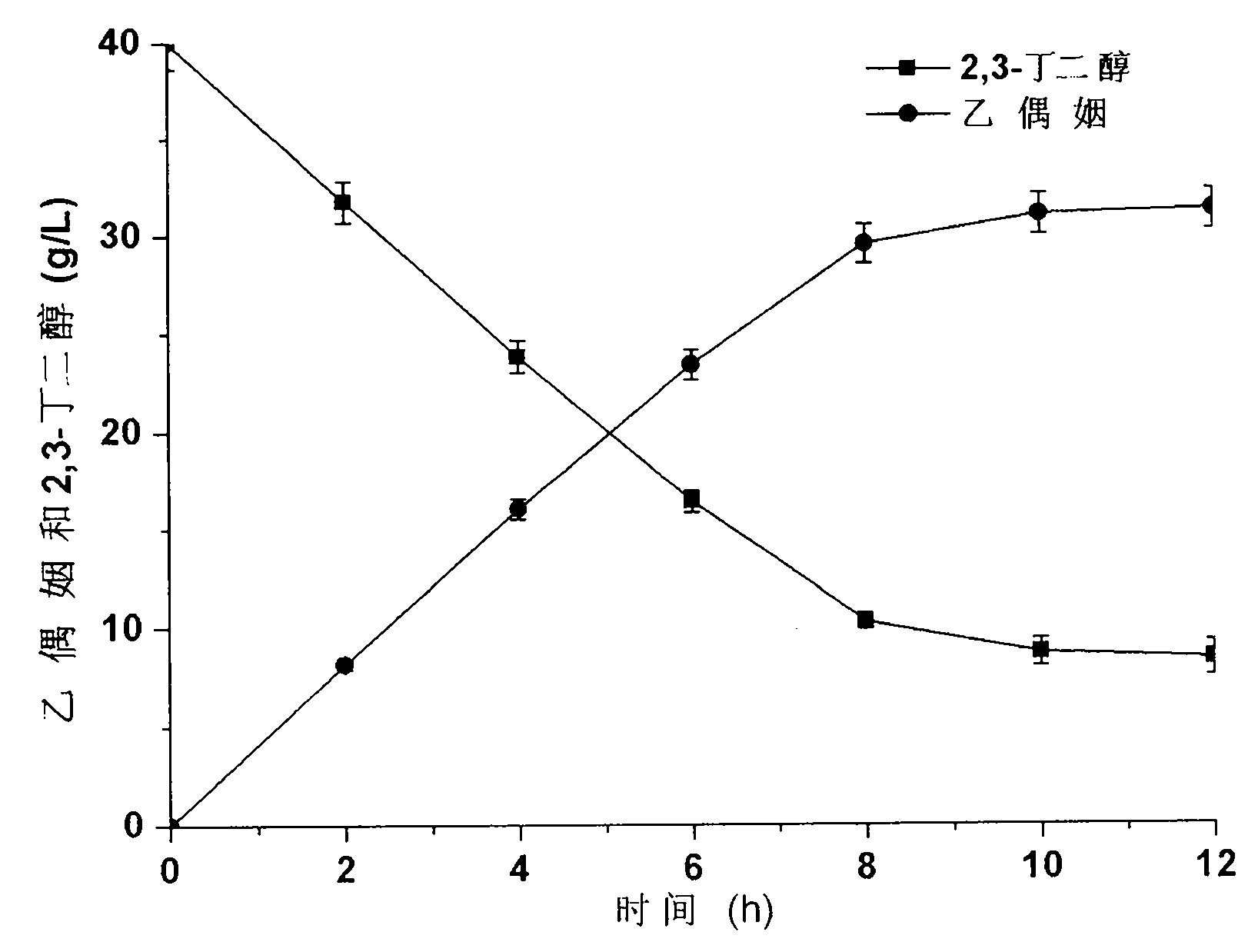
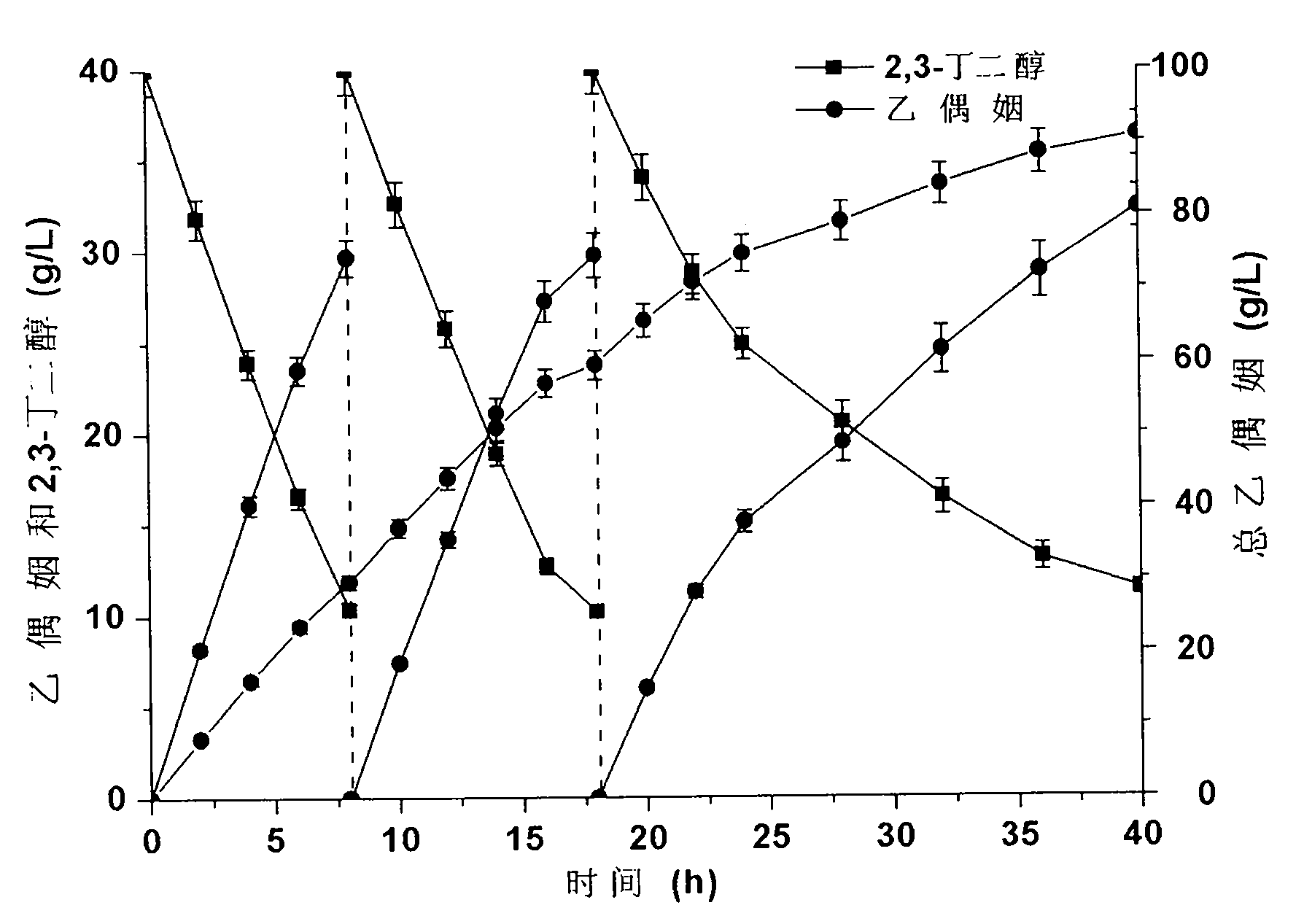
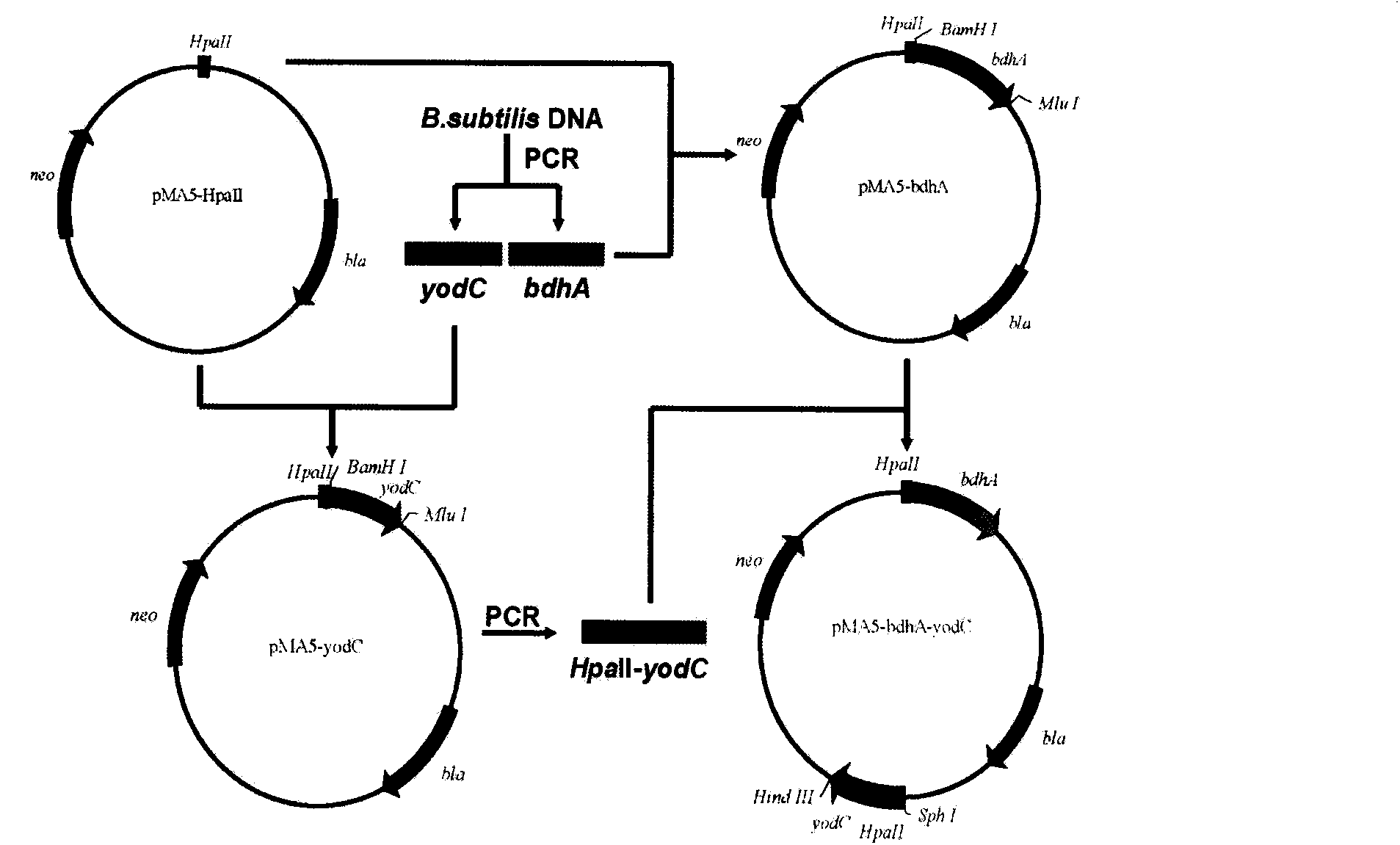
Method for producing acetoin by efficient bioconversion of 2,3-butanediol by using Bacillus subtilis nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)<+> regeneration system
InactiveCN104017764AEasy to separateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeButanediol
The invention discloses a method for producing acetoin by efficient bioconversion of 2,3-butanediol by using a Bacillus subtilis nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)<+> regeneration system, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Acetoin reductase and educed form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NADH) oxidase in a high-yield acetoin strain B.subtilis JNA with independent intellectual property rights, which are autonomously screened from a laboratory are cloned by the method disclosed by the invention, and excessive coexpression of the acetoin reductase and NADH oxidase in B.subtilis JNA is carried out, so that the production of acetoin by effective conversion of the 2,3-butanediol in the wild-type high-yield acetoin bacillus subtilis by virtue of the NAD<+> regeneration system is realized for the first time at home and abroad. The enzyme activity determination and intracellular coenzyme level research on the built gene engineering strain prove that the 2,3-butanediol can be lastingly and effectively converted by B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-bdhA-yodC to produce the acetoin. 120g / L of 2,3-butanediol can be finally converted into about 92.5g / L of acetoin by the B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-bdhA-yodC when the temperature is 40 DEG C and the pH is 8.0 under the optimal whole-cell conversion condition of adding 5mM of MnC12, the acetoin yield can be up to 2.31g / (L.h), and is the highest lever for producing the acetoin from the bacillus subtilis in the current report, and a foundation is provided for industrial production of the acetoin from microorganisms.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
ORAL INHIBITORS OF AGE-RELATED NADH OXIDASE (arNOX), COMPOSITIONS AND NATURAL SOURCES
InactiveUS20120207862A1Reduce arNOX-mediated damageReduce severityBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseNatural source
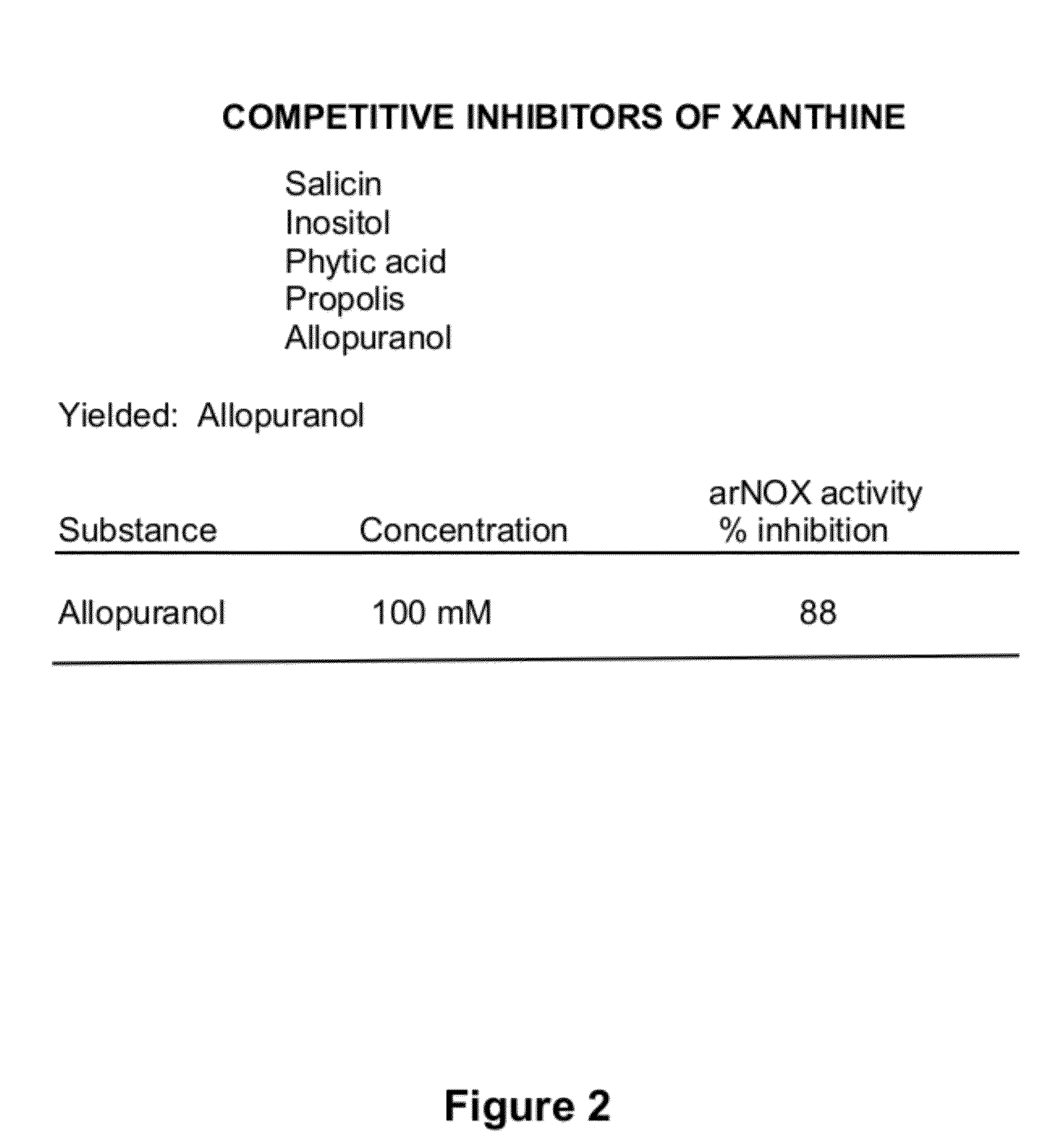
Described are compositions and agents for blocking serum and other aging factors, especially arNOX in serum, skin or other body fluid or tissue and / or on the cell surface, and methods for using the same. More particularly, the invention relates to agents comprising any one of several naturally-occurring arNOX inhibitors capable of reducing occurrence or severity of or treating disorders and complications of disorders resulting from cell damage caused by aging-related isoforms of NADH oxidase (arNOX). In one exemplary embodiment, nutraceutical, cosmeceutical or pharmaceutical compositions comprise at least one naturally occurring arNOX inhibitor or inhibitor source. Such naturally occurring inhibitors also are capable of augmenting the anti-arNOX effect of other naturally occurring arNOX inhibitory agents. The discovery of multiple inhibitors with significantly different kinetics of inhibition that when combined provide long term arNOX inhibition is one of the unique and non-obvious features of the present methods and compositions.
Owner:NOX TECH
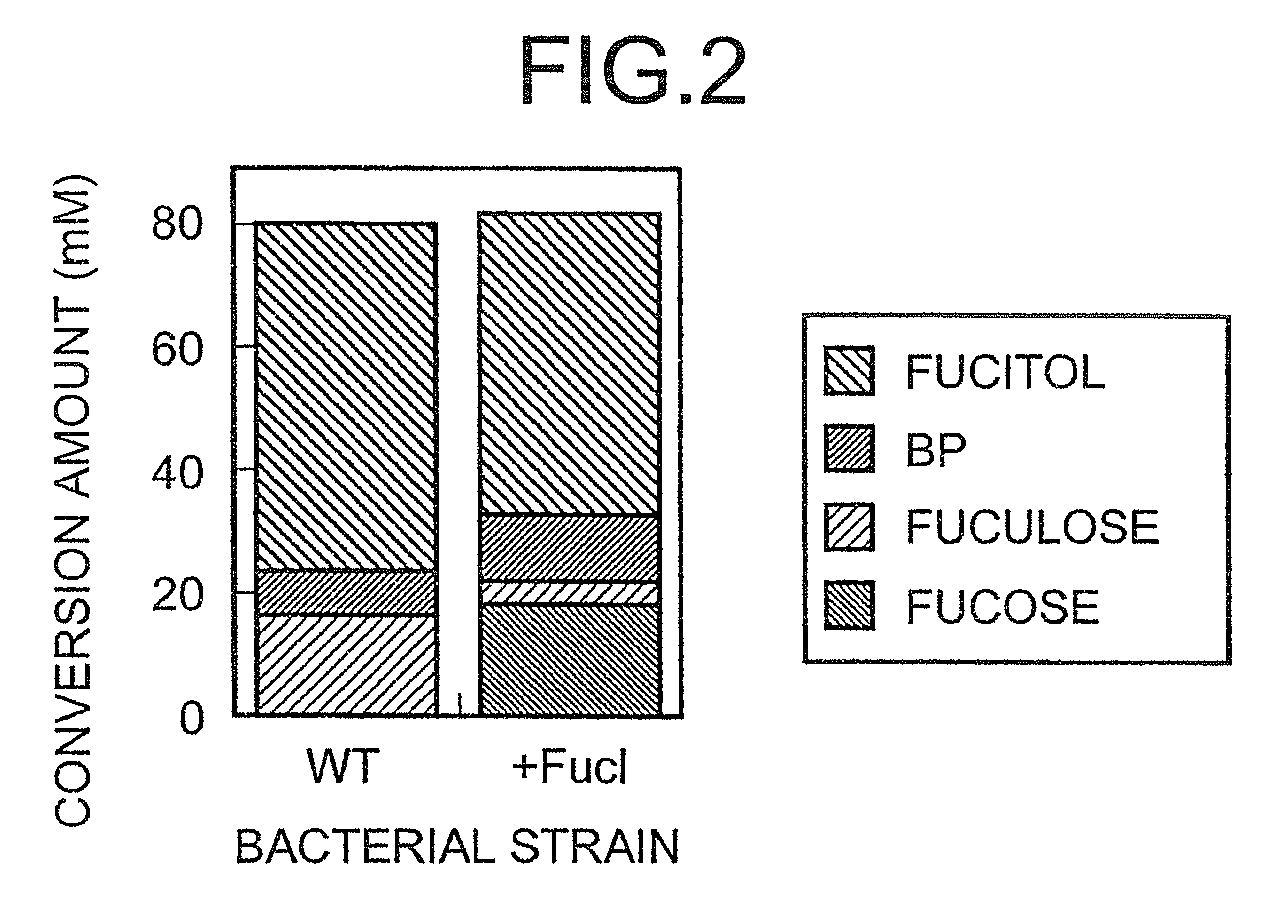
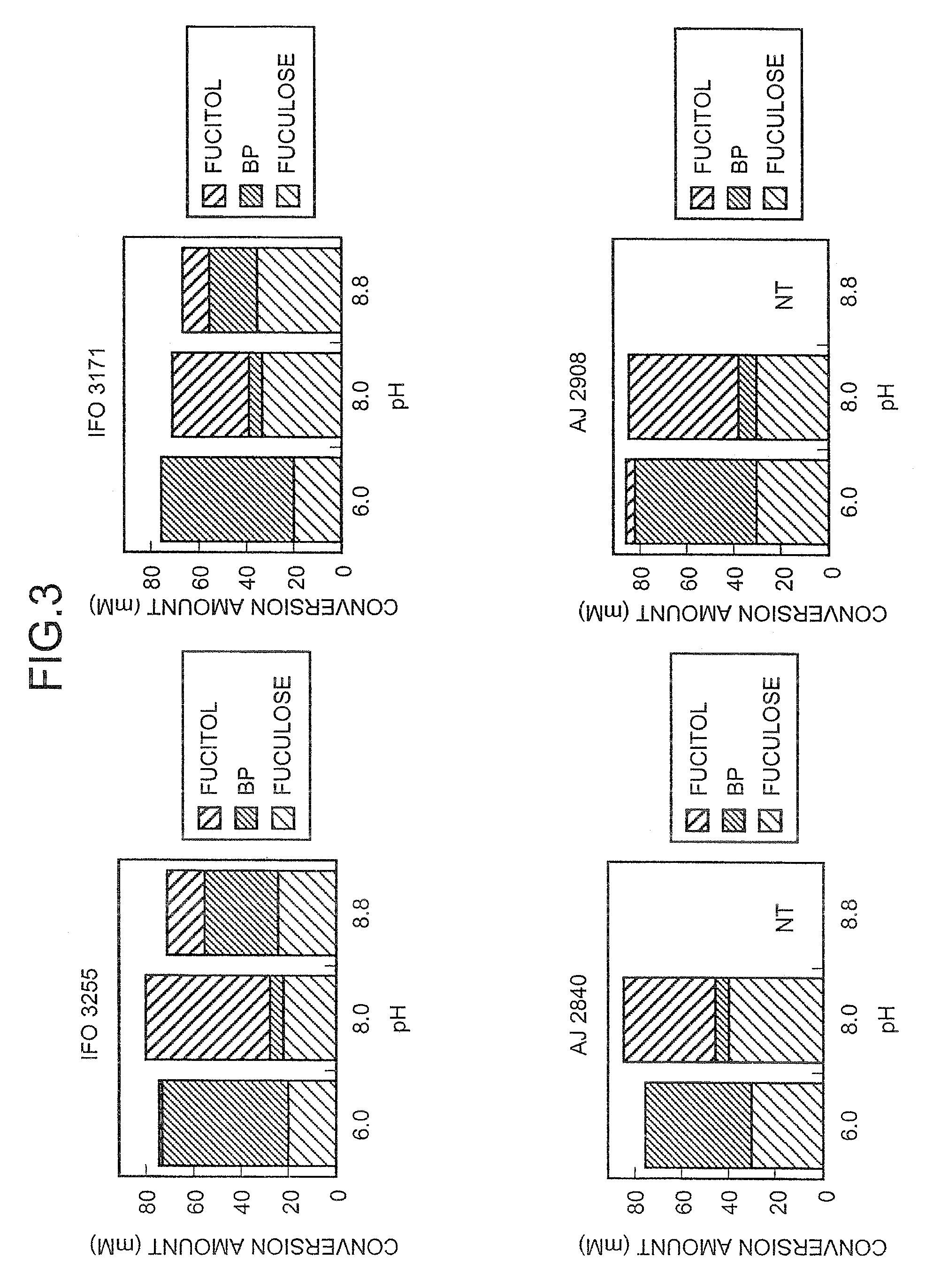
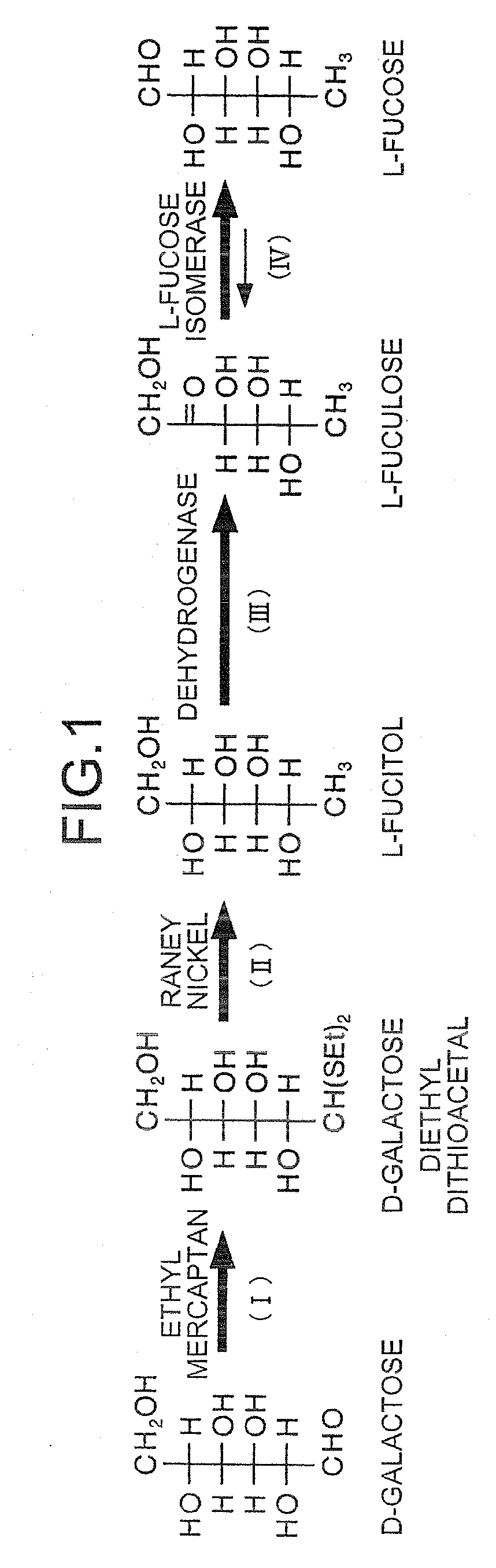
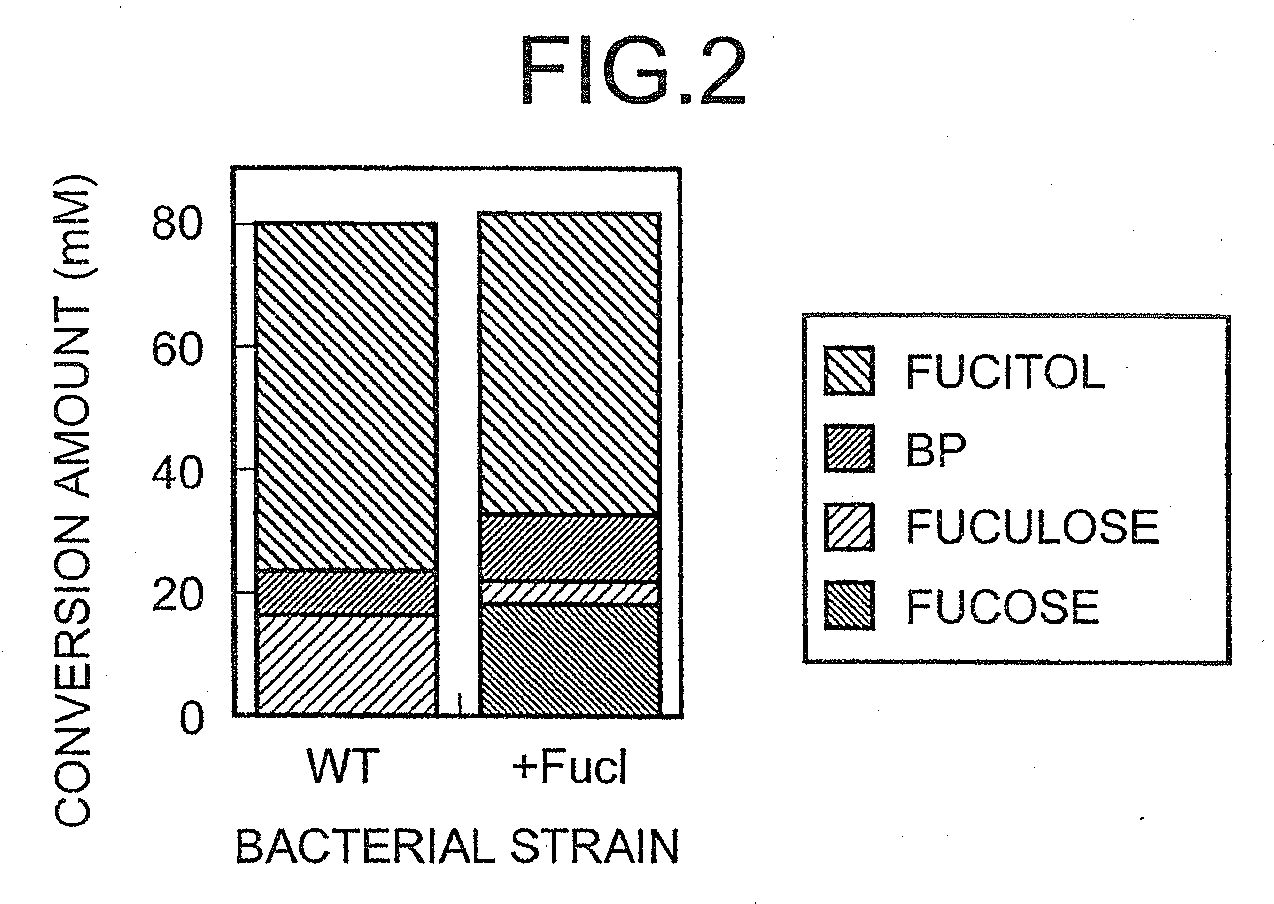
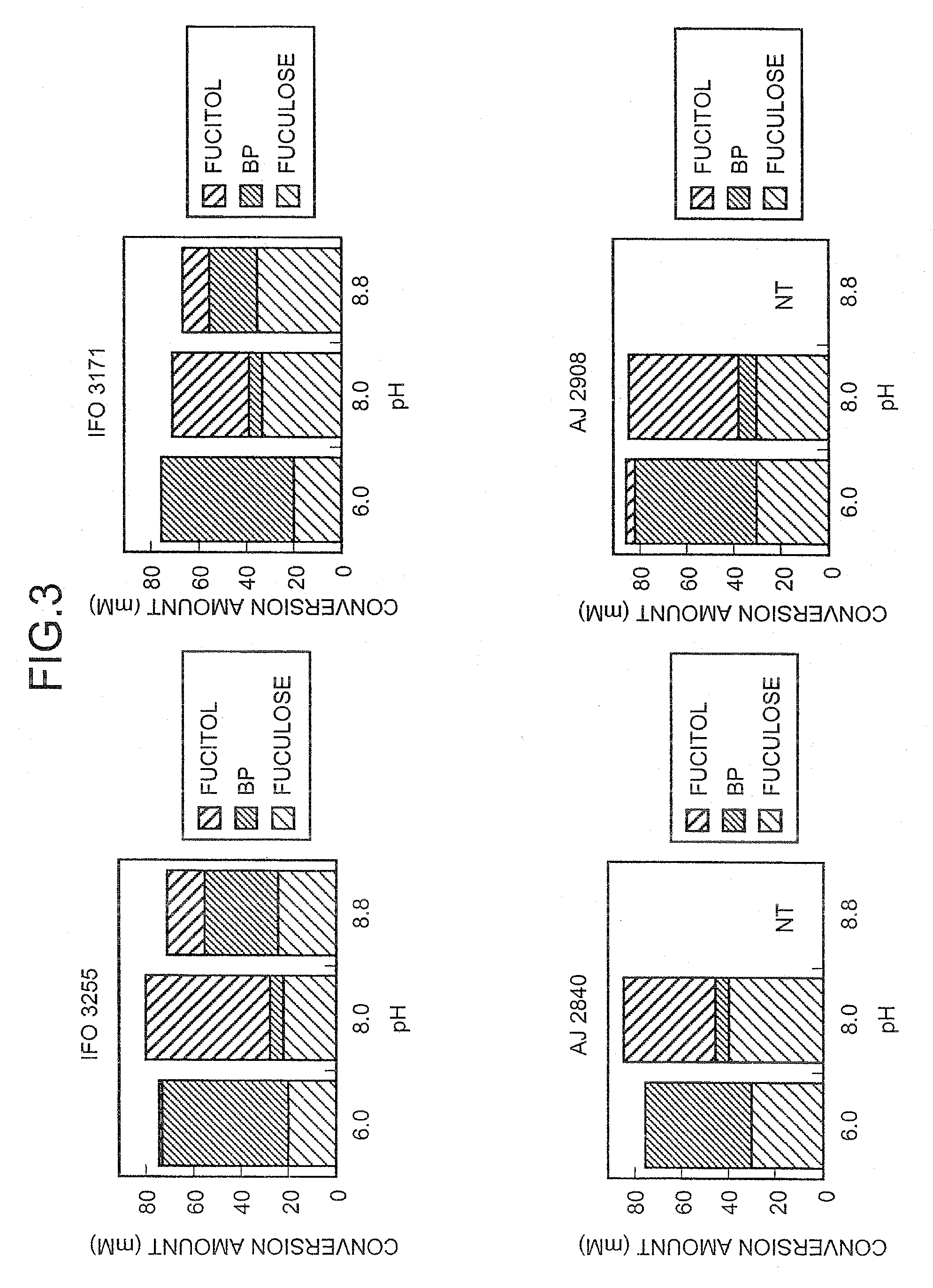
Method for producing L-fuculose and method for producing L-fucose
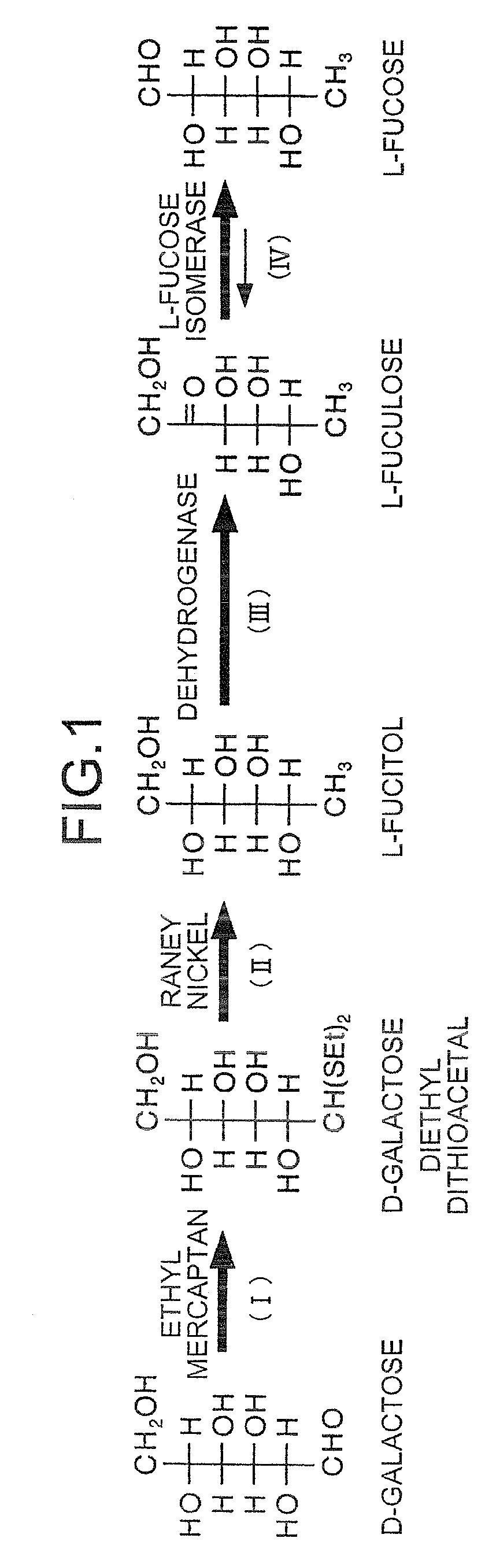
The present invention provides a method for producing L-fuculose and L-fucose which is suitable as an industrial method. L-Fuculose is synthesized from L-fucitol in the presence of a microorganism-derived protein having a dehydrogenase activity which results in production of L-fuculose from L-fucitol. The reaction system preferably contains NADH oxidase. L-Fuculose thus synthesized is then converted into L-fucose.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
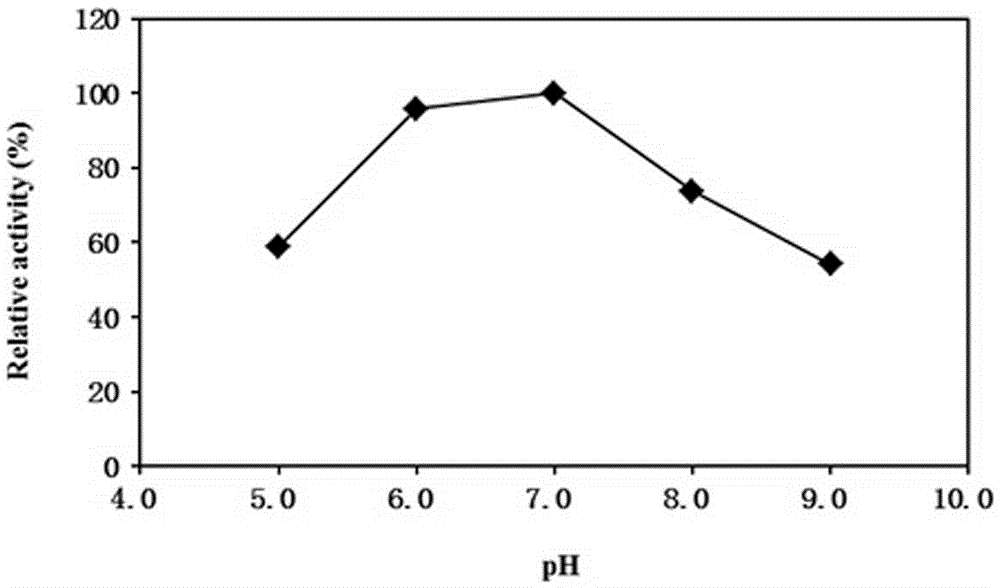
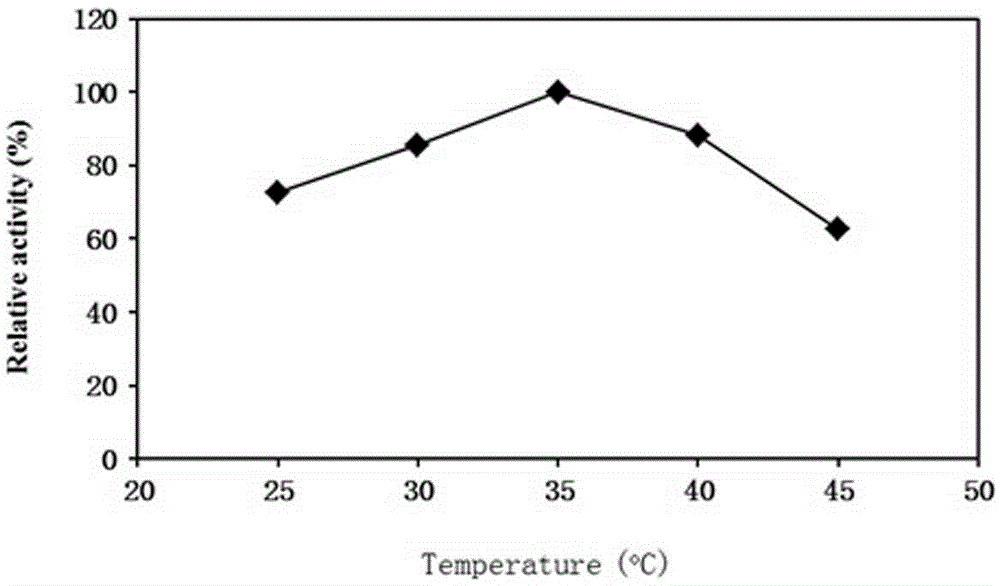
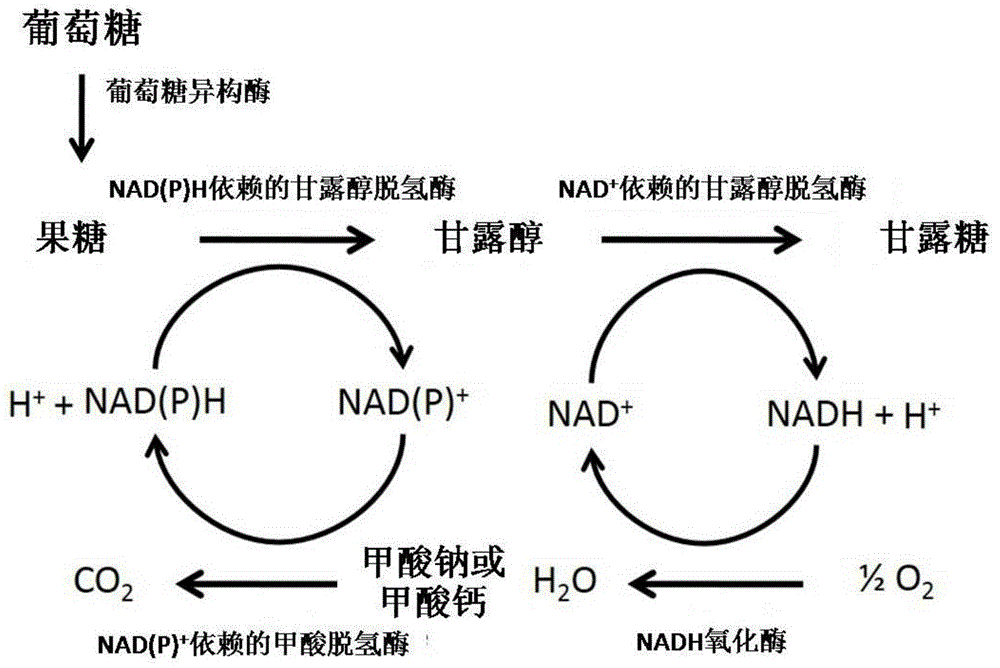
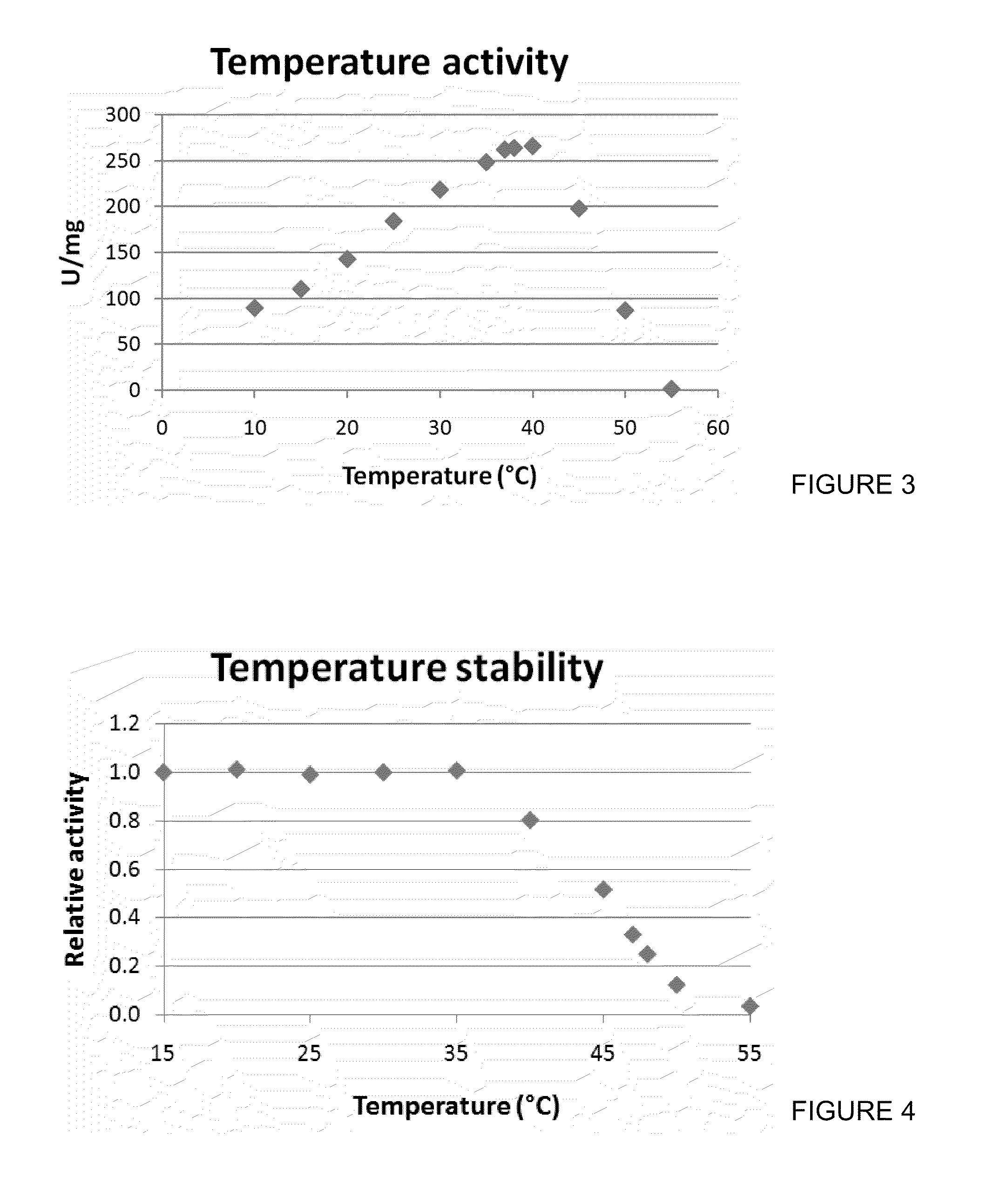
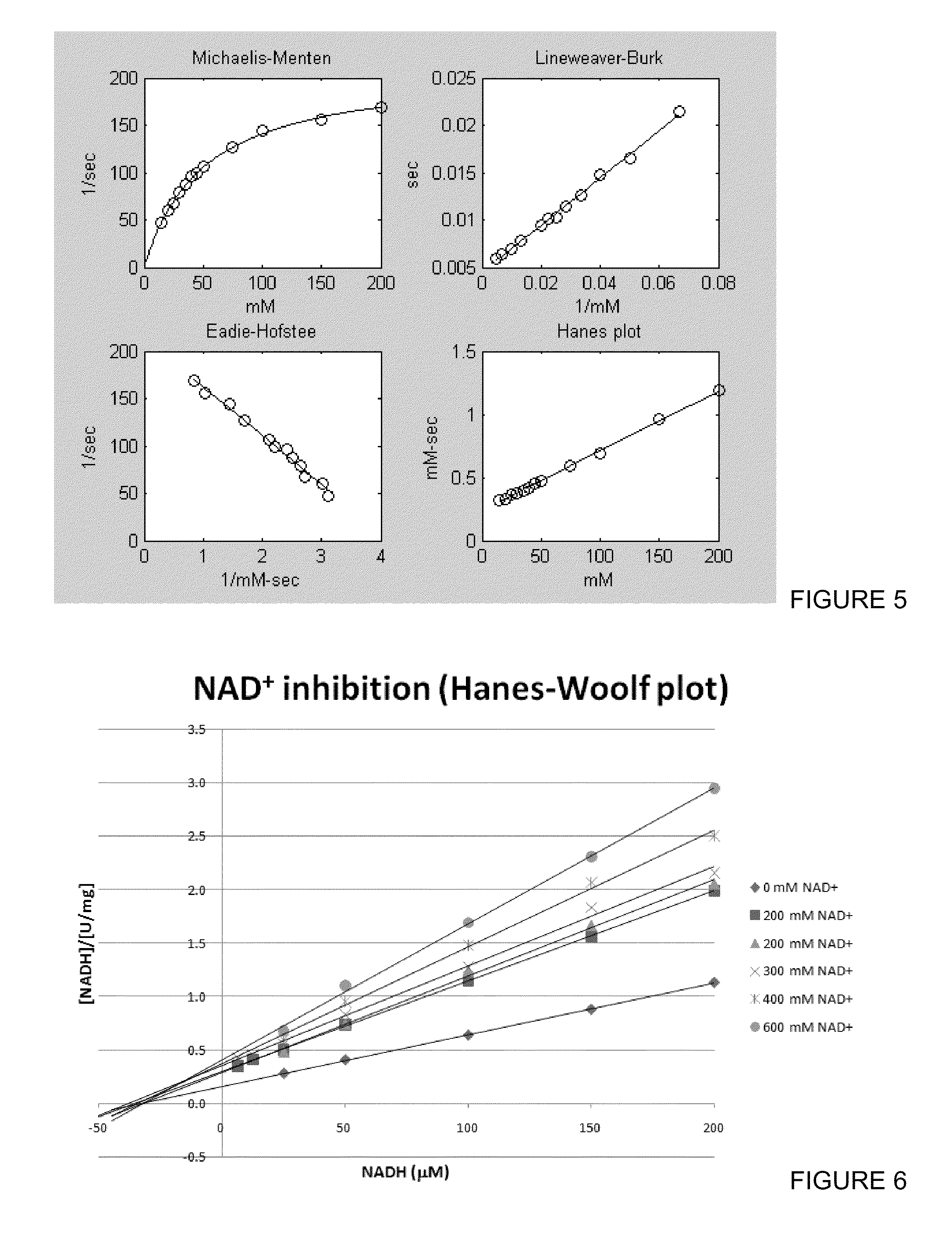
NADH oxidase mutant having improved stability and use thereof
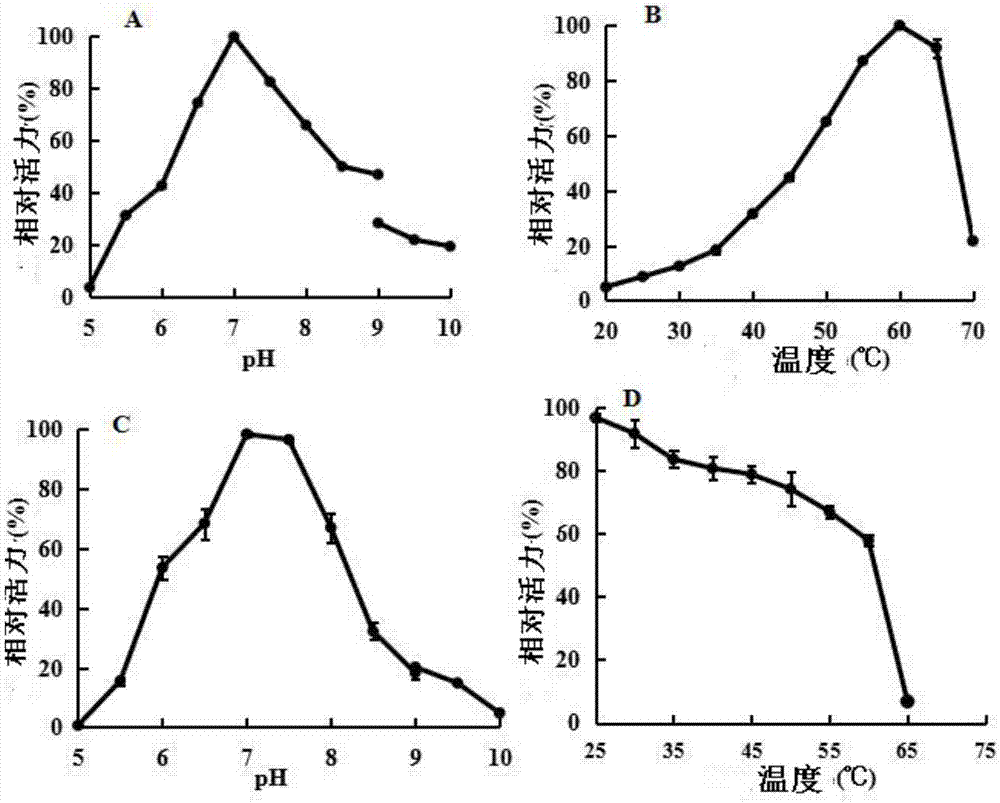
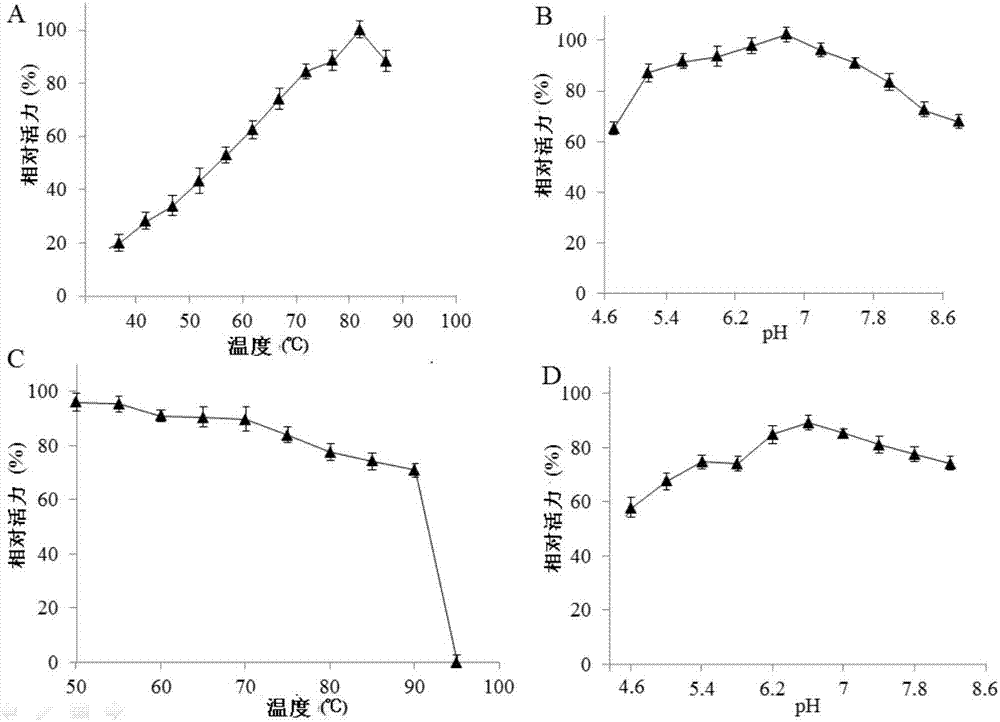
Water-forming NADH oxidase derived from Streptococcus mutans should be further improved in terms of stability for practical use in industrial production. An object of the present invention is to provide an enzyme that is obtained through modification of a water-forming NADH oxidase, which is useful as an NAD+ regeneration system for stereoselective oxidation catalyzed by an oxidoreductase, by protein engineering techniques so that the enzyme can withstand long-term use without exhibiting a reduction of its activity for the regeneration of NAD+, that is, an enzyme having improved stability, and to provide a method for efficiently producing a useful substance such as an optically active alcohol or amino acid. The present invention relates to an enzyme modification method that can improve the stability of water-forming NADH oxidase derived from Streptococcus mutans by appropriately introducing mutation.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for producing l-fuculose and method for producing l-fucose
The present invention provides a method for producing L-fuculose and L-fucose which is suitable as an industrial method. L-Fuculose is synthesized from L-fucitol in the presence of a microorganism-derived protein having a dehydrogenase activity which results in production of L-fuculose from L-fucitol. The reaction system preferably contains NADH oxidase. L-Fuculose thus synthesized is then converted into L-fucose.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Water type NADH oxidase of reproducible coenzyme NAD+ and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105331589AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationDihydroxyacetoneGlycerol dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to NADH oxidase in the field of biotechnology and particularly provides water type NADH oxidase of reproducible coenzyme NAD+ and an encoding gene and application thereof. The oxidase is represented by an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. By the adoption of the water type NADH oxidase, 1,3-dihydroxyacetone can be produced through in-vitro serial connection and glycerin conversion of the oxidase and glycerol dehydrogenase. Compared with a chemical method for preparing the 1,3-dihydroxyacetone, the method has the advantages of being moderate in reaction condition, friendly to environment, simple in operation, easy to amplify and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
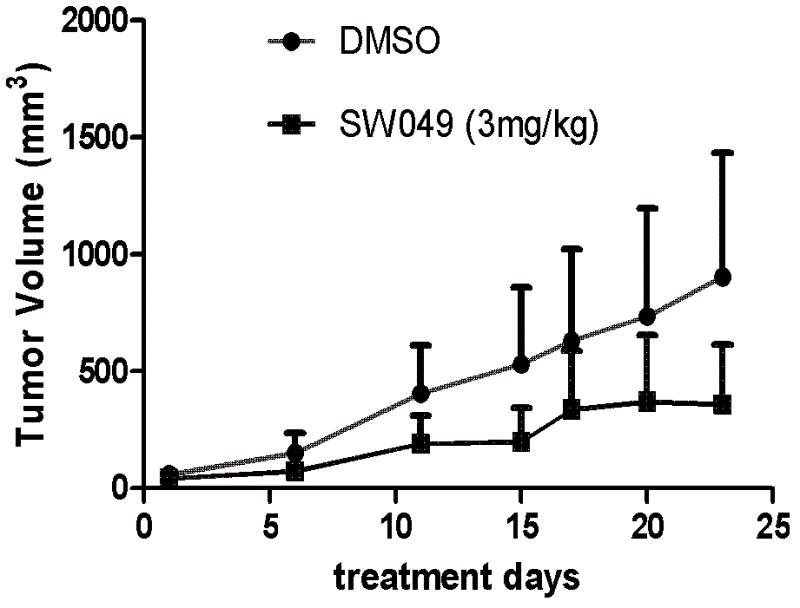
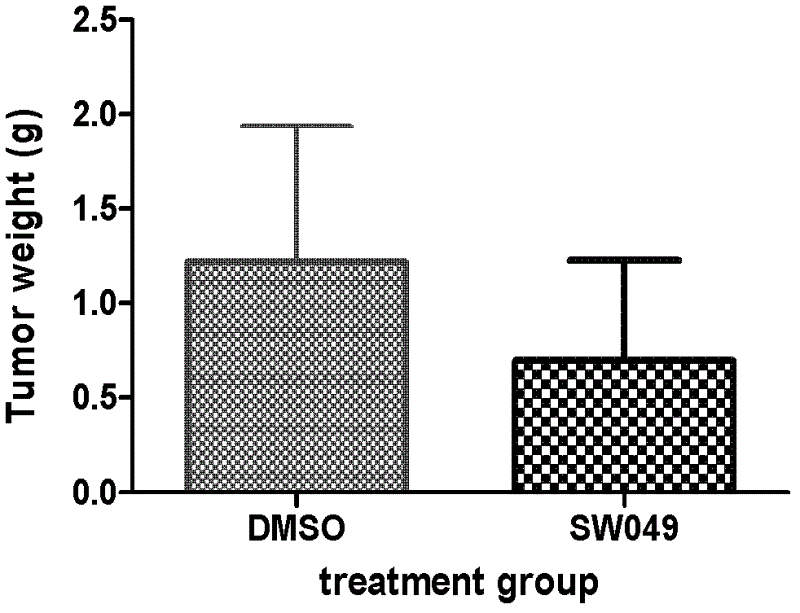
Aromatic iodonium salts as NADH oxidase inhibitors and anti-tumor application thereof
The invention provides a series of novel aromatic iodonium salt compounds that are used as NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide) oxidase inhibitors, and discovers the new anti-cancer application of the novel aromatic iodonium salt compounds and a few of other known NADH oxidase inhibitors. The iodonium salts can inhibit the activity of NADH oxidases in in-vitro assays, and can obviously inhibit the growth of malignant cells of humanized pancreatic cancer, multiple myeloma, esophageal carcinoma, intestinal cancer and the like. To aim at new anti-cancer targets, the development of novel anti-tumor drugs can be carried forward.
Owner:文石军 +2
Method for preparing mannose through biological process
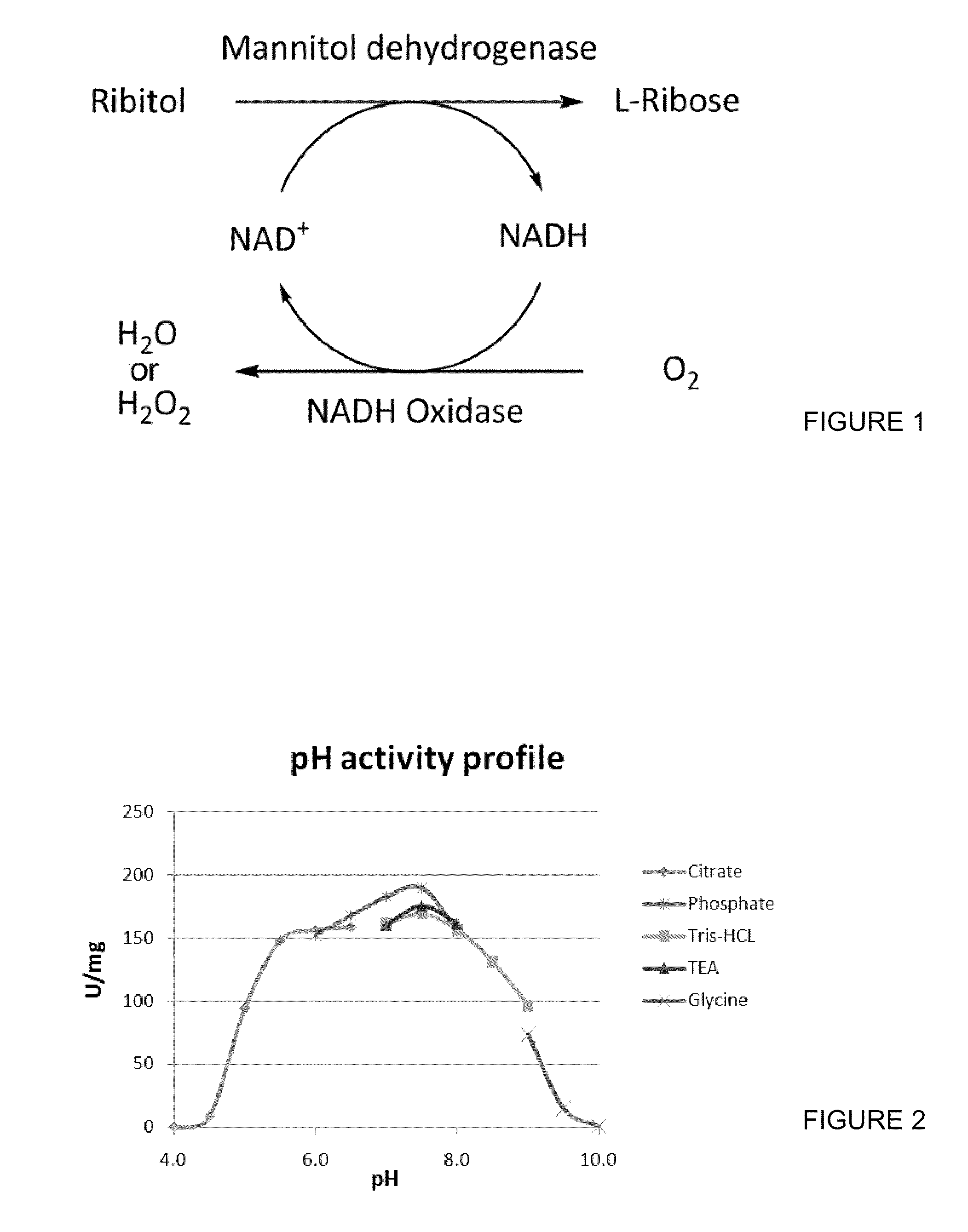
The invention discloses a method for preparing mannose through a biological process. According to the method, one or two of sodium formate and calcium formate, and one or two of glucose and fructose are taken as the raw materials, under the condition that glucose isomerase is available or not available, a biological catalysis system composed of an NAD (P)H-dependent mannitol dehydrogenase, an NAD(P)<+>-dependent formate dehydrogenase, an NAD<+>-dependent mannitol dehydrogenase, an NADH oxidase and a coenzyme is adopted for catalyzing, so that the mannose is prepared. The method for preparing the mannose provided by the invention has the characteristics that the raw materials are cheap, the reaction selectivity is high, etc, and the method belongs to a novel preparation reaction route of the mannose.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
NADH oxidase from lactobacillus
The present invention is directed to a new NADH oxidase from Lactobacillus, nucleic acids encoding the NADH oxidase, methods of producing the NADH oxidase, as well as there use in producing improved NADH oxidase enzymes and for producing chrial enantiomer-enriched organic compounds, such as alcohols and / or amino acids.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
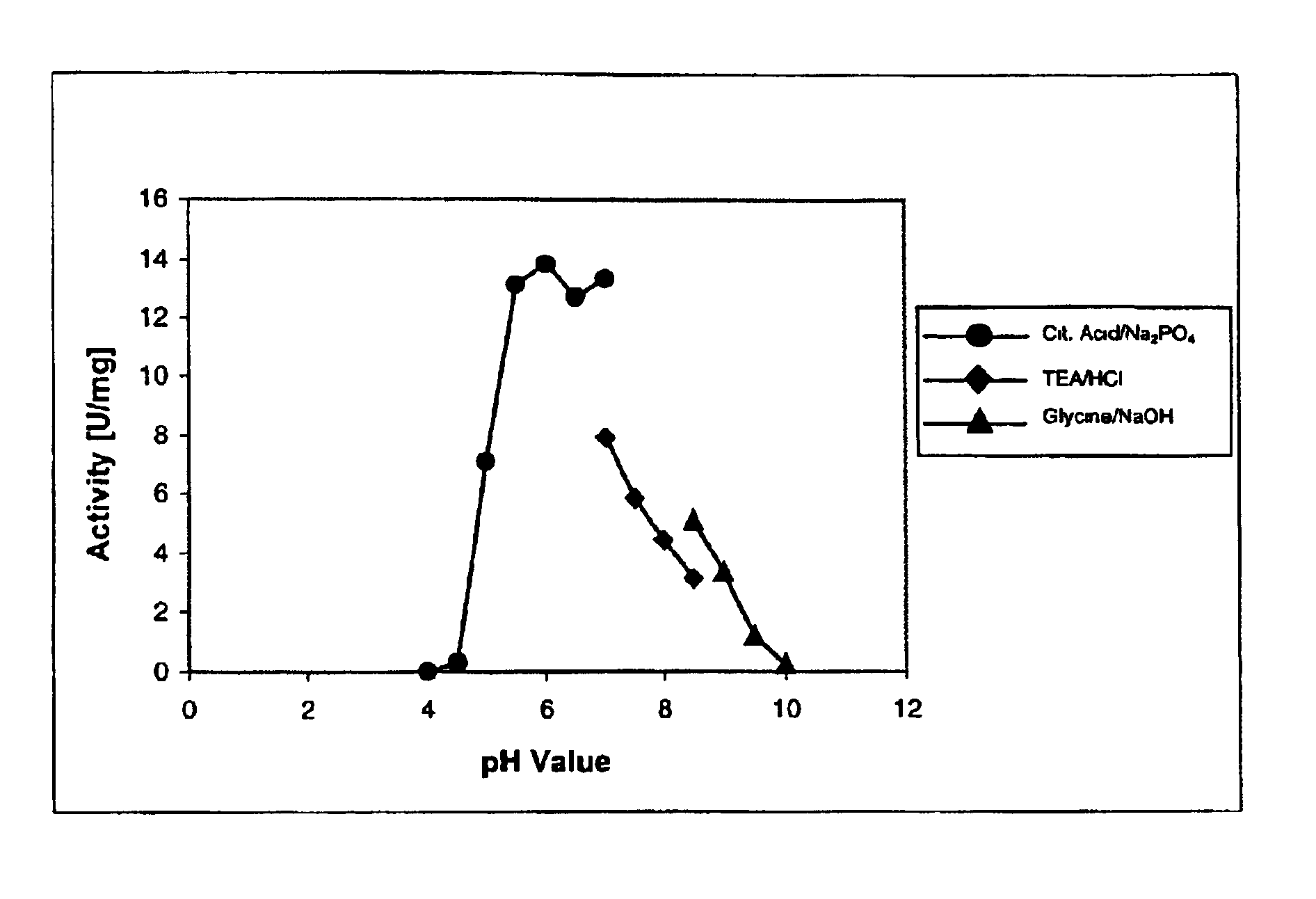
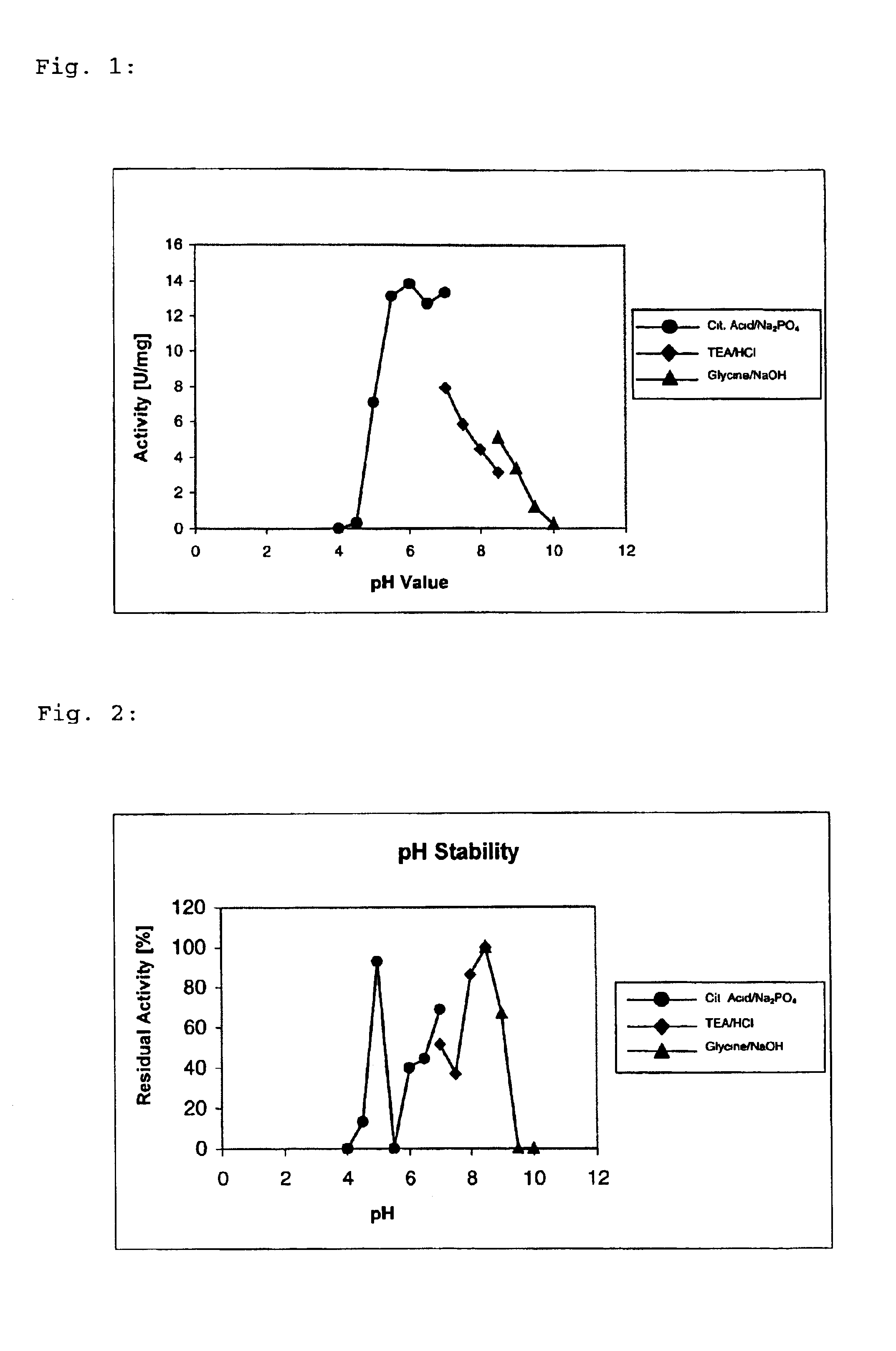
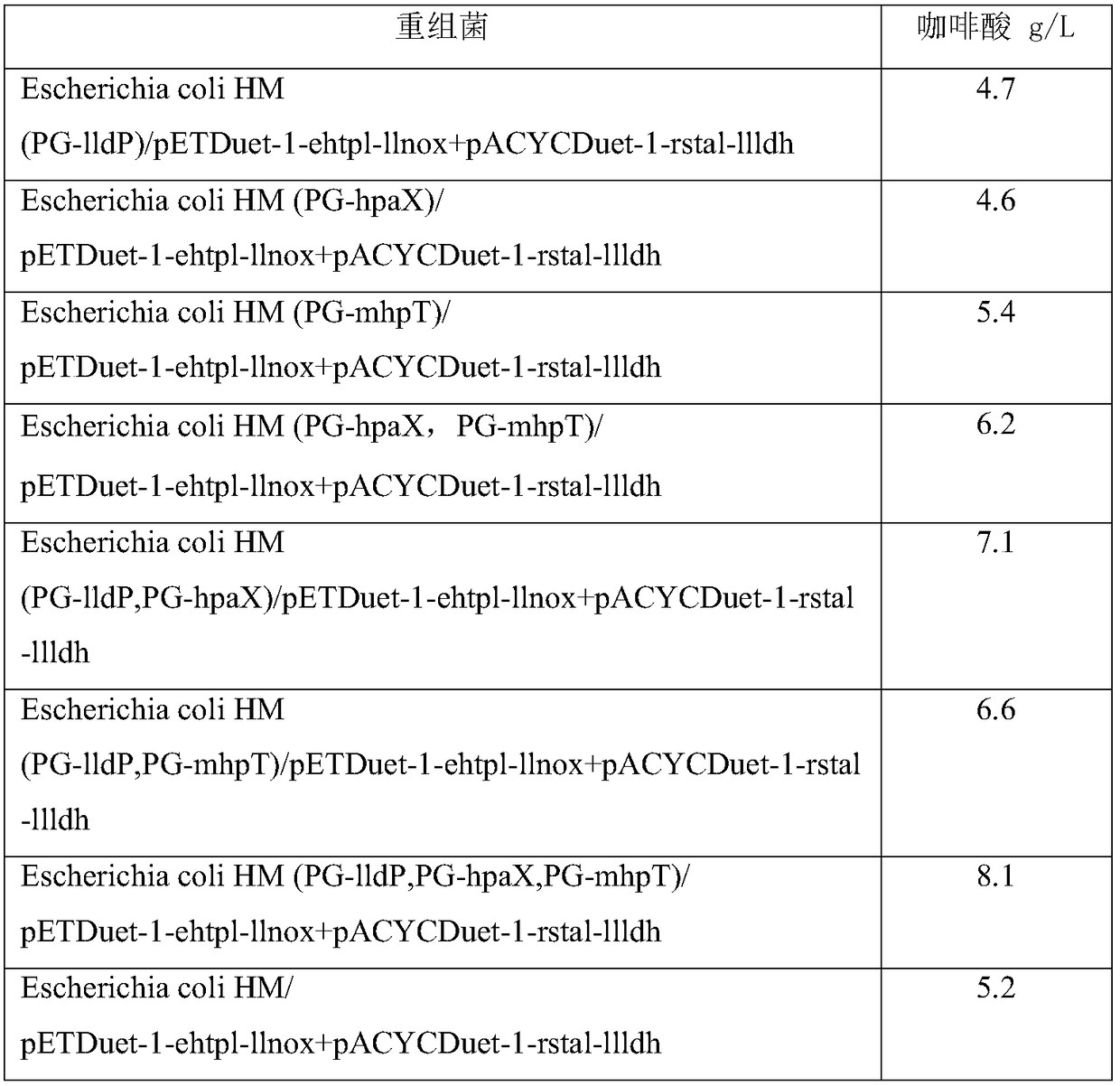
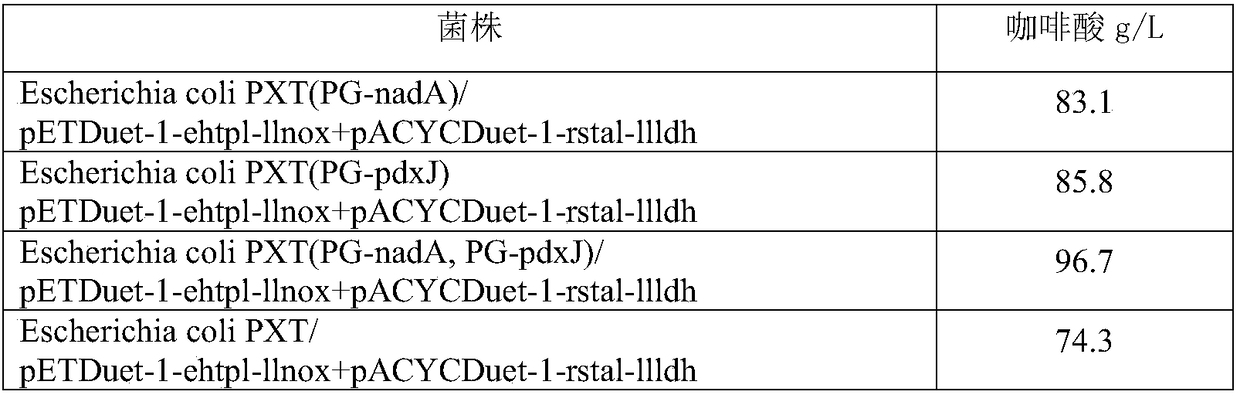
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
ActiveCN108949652AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium providedby the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing caffeic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages of realization of the efficient production ofcaffeic acid, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
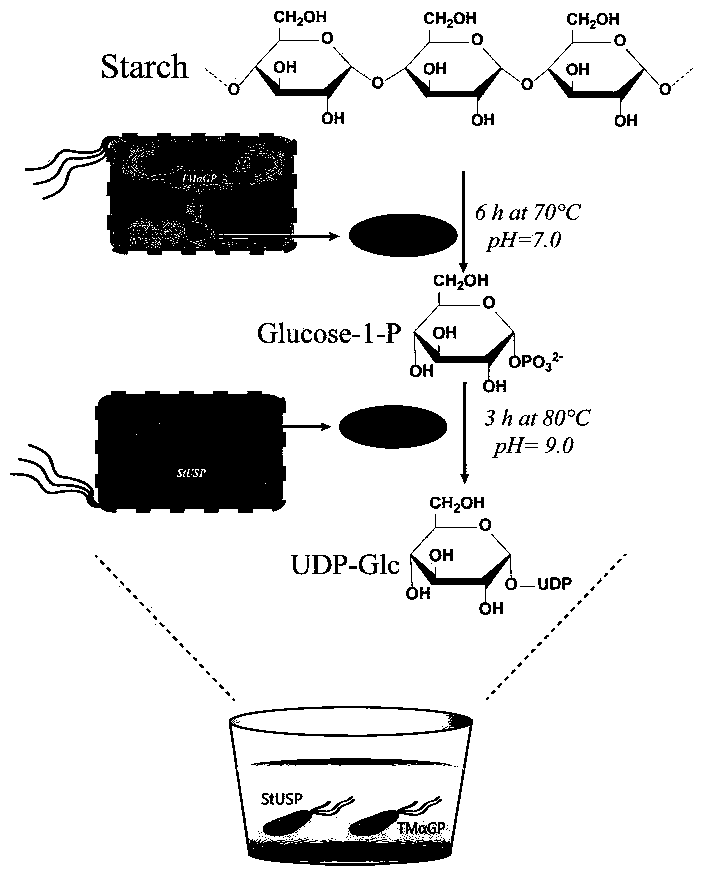
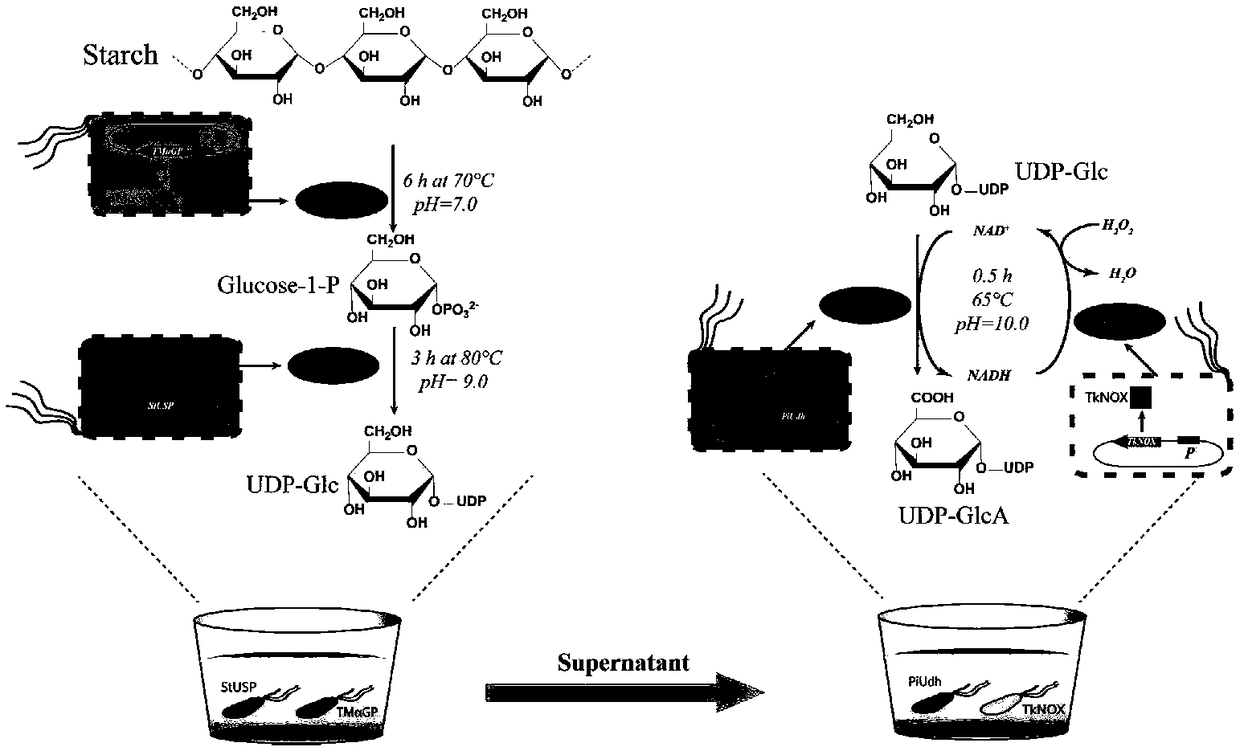
Biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
ActiveCN109371079AEasy to transformSynthetic interferenceMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliUridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. The method includes adopting soluble starch as a main initial raw material, conducting recombinant expression on high-temperature alpha-glucan phosphorylase and high-temperature sugar-1-nucloside phosphorylase in escherichia coli respectively, and utilizing high-temperature whole cell catalysis of expressed bacteria to synthesize uridine diphosphate glucose; on this basis, conducting recombinant expression on high temperature uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase in the escherichia coli, coupling a synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucose to conduct high temperature whole cell catalysis to synthesize the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and introducing awhole cell catalysis system of high temperature NADH oxidase into the synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid to form a high temperature NAD+ / NADH circulating system to reduce theuse of coenzyme NAD+. The high temperature whole cell catalysis method is utilized to successfully avoid the interference of various metabolic pathways of the bacteria in the synthesis process and reduce the purification difficulty.
Owner:安徽禾庚生物技术有限公司
Compositions and methods for using nadh oxidases
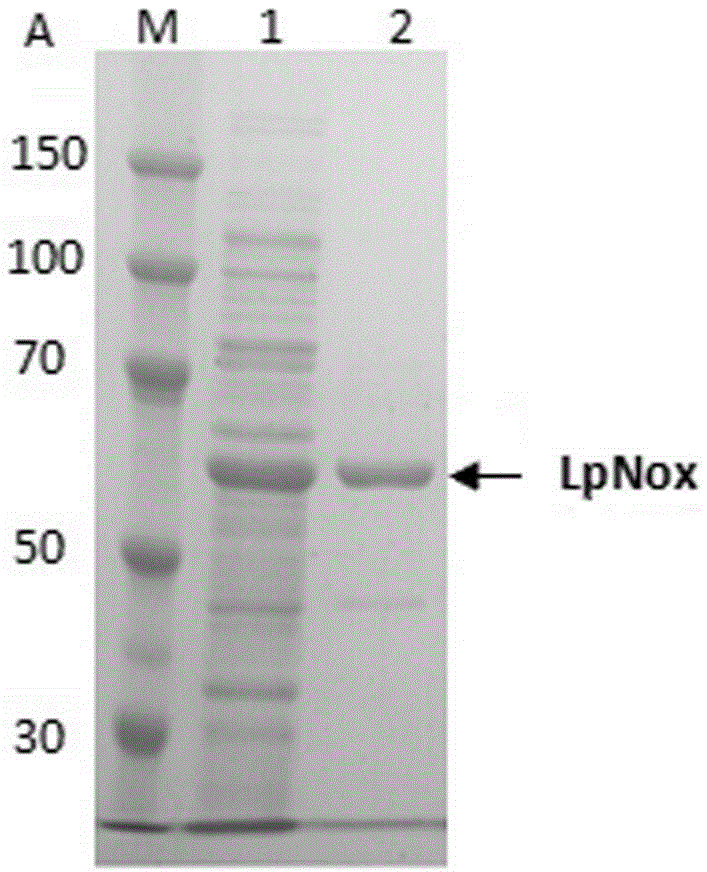
The present disclosure relates generally to bacterial NADH oxidases and, more particularly, to novel NADH oxidases obtained from Lactobacillus plantarum, and derivatives thereof that demonstrate enzymatic activity for NADH, NADPH, or both NADH and NADPH. The compositions comprising an NADH oxidase obtained from L. plantarum or derivatives thereof include: isolated enzymes; recombinantly produced enzymes and derivatives thereof, as well as catalytically active portions thereof; nucleic acids encoding an NADH oxidase obtained from L. plantarum, derivatives thereof, and portions thereof. The methods of the present invention include isolation of NADH oxidases obtained from L. plantarum, derivatives thereof, and portions thereof, and methods for enzymatic reactions comprising NADH oxidase obtained from L. plantarum, including the production of enantiomer-enriched organic compounds.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
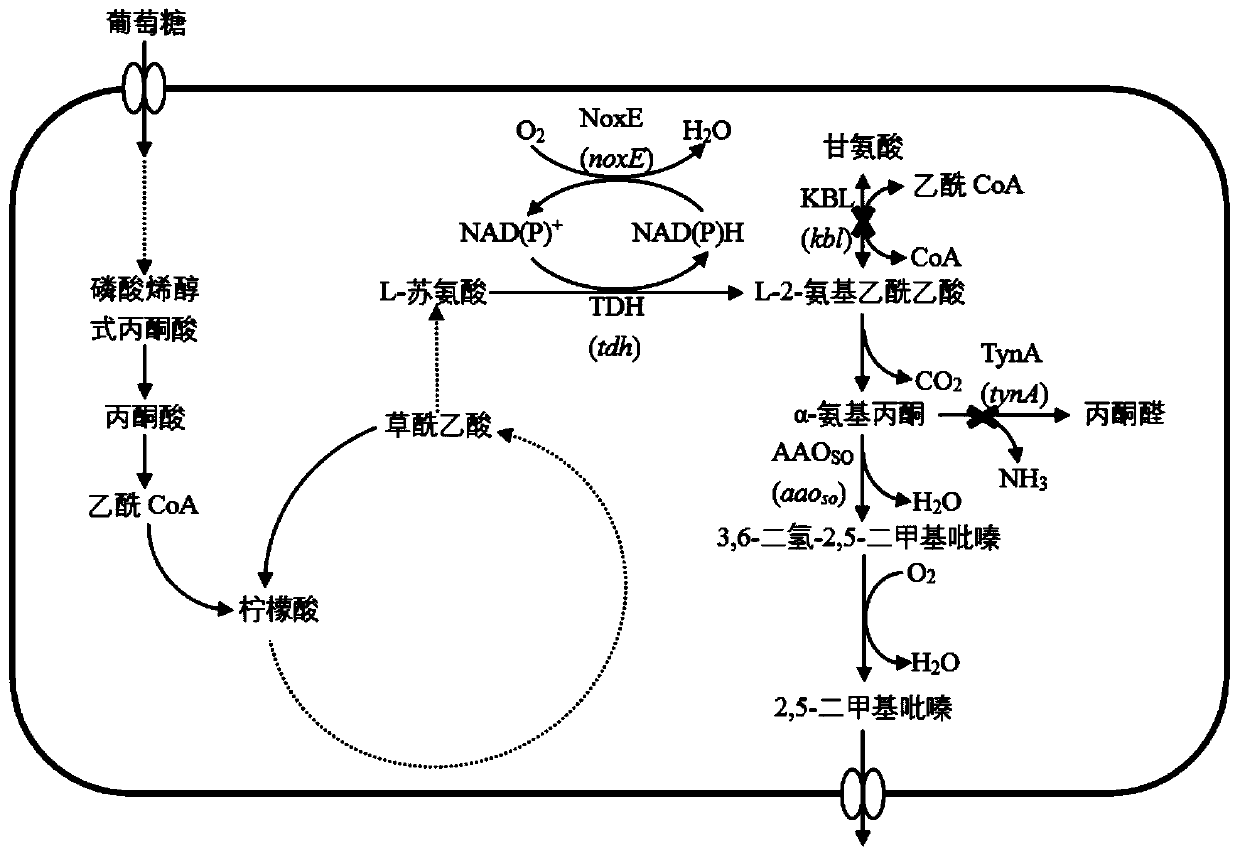
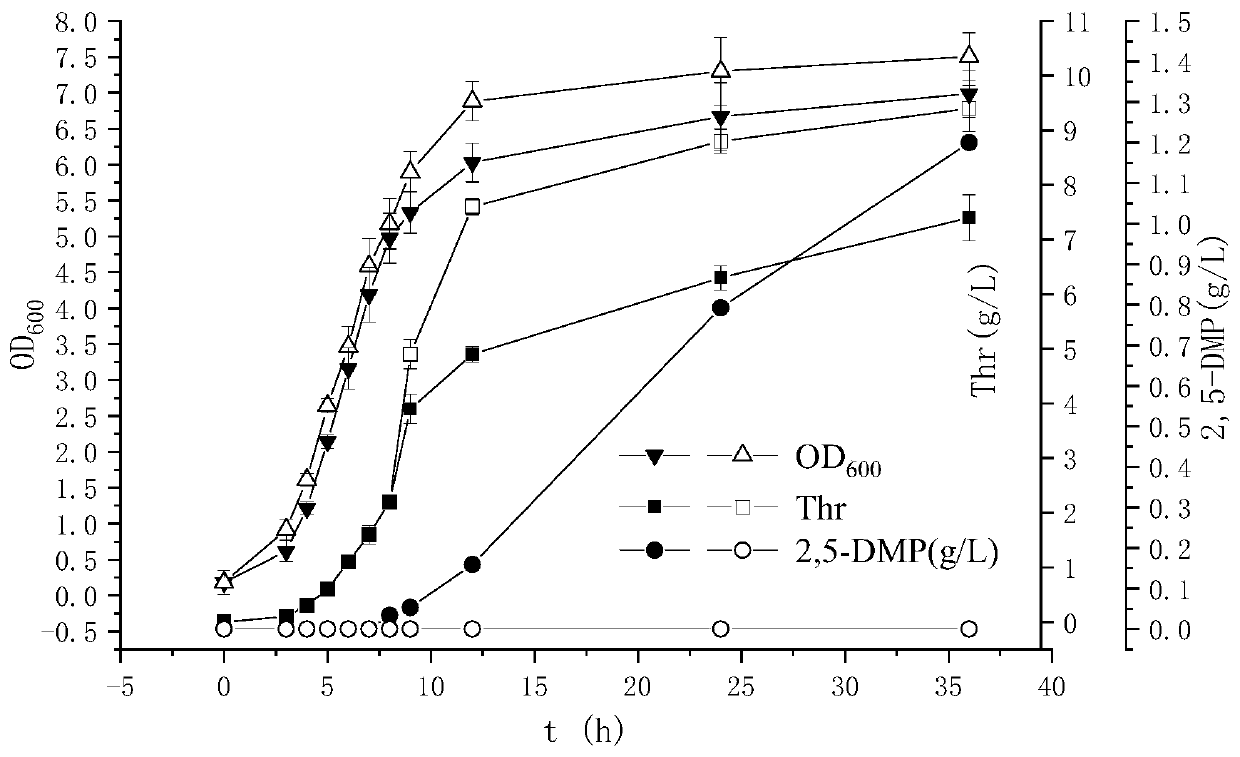
Escherichia coli recombinant bacteria capable of high-producing 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine and construction method of escherichia coli recombinant bacteria
InactiveCN111411067AImprove unbalanced shortcomingsProlonged metabolic pathwayBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
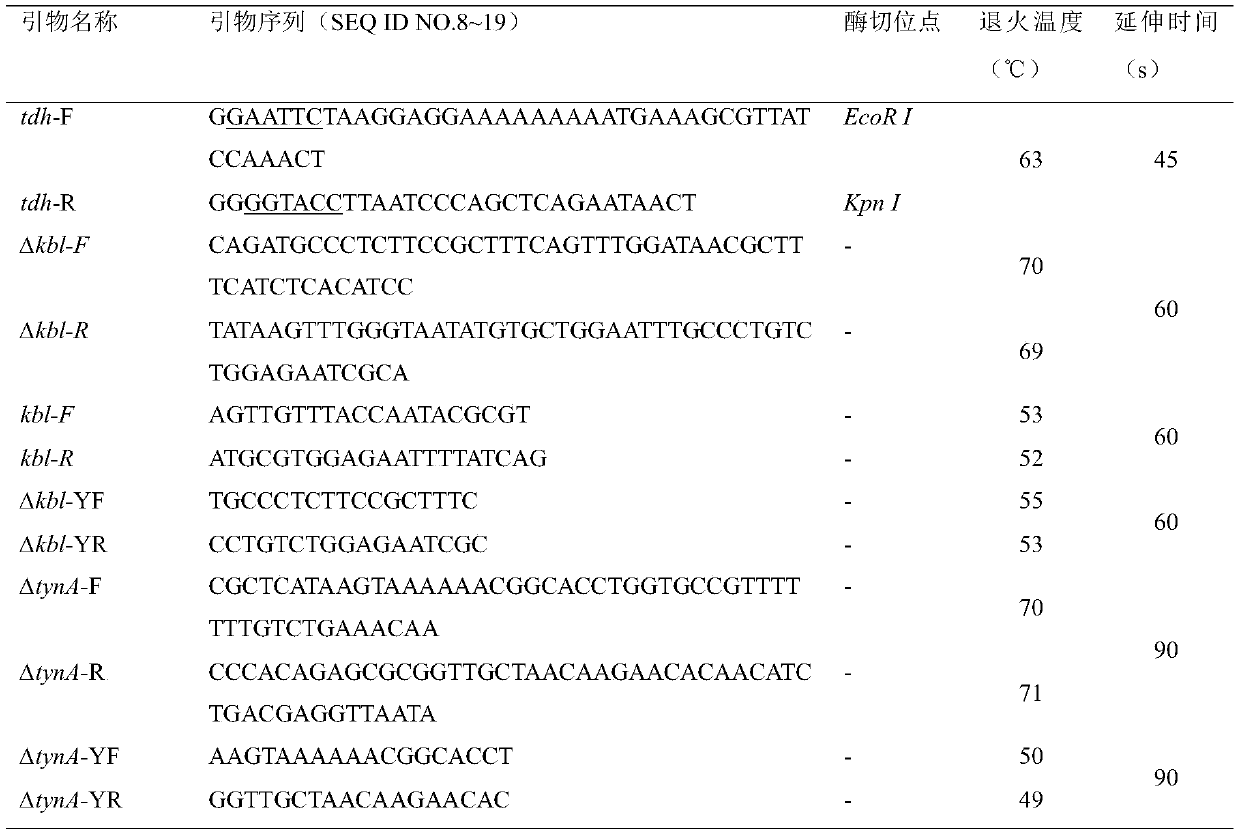
The invention discloses escherichia coli recombinant bacteria capable of high-producing 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine and a construction method of the escherichia coli recombinant bacteria, and belongs to thetechnical field of gene engineering. According to the escherichia coli recombinant bacteria and the construction method thereof, a genetic engineering method is applied, L-threonine dehydrogenase TDHis overexpressed in escherichia coli K-12 capable of high-producing L-threonine, and NADH oxidase NoxE derived from lactococcus microorganisms and aminoacetone oxidase AAOSO derived from streptococcus microorganisms are expressed in a heterologous manner, and meanwhile 2-amino-3-ketobutyric acid CoA ligase KBL and primary amine oxidase TynA are knocked out, so that a novel and efficient 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine synthetic route is constructed, and the problem of unbalance of cofactors in the recombinant bacteria is solved. By taking escherichia coli E. coli THR as an example, the accumulation amount of 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine reaches 1.2 + / -0.2 g / L through a 36h shaking flask fermentation experiment of the recombinant bacteria. According to the method, L-threonine high-producing strains are used as starting strains, the synthetic route of 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine in escherichia coli is successfully reconstructed, the defect of unbalanced intracellular cofactors is improved, and a new idea is provided for breeding 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of hyrogen peroxide producting enzyme for treatment of otitis media
InactiveUS20050238635A1Improve antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsBiocideNasal Cavity EpitheliumMiddle ear
The present invention relates to the use of hydrogen peroxide producing enzyme for manufacturing of a medicament for treatment and / or prevention of otitis media (inflammation in the middle ear), preferably in children. This enzyme is preferably NADH oxidase. The medicament is intended to be administered with lactoperoxidase into the nasal cavity.
Owner:TANO KRISTER
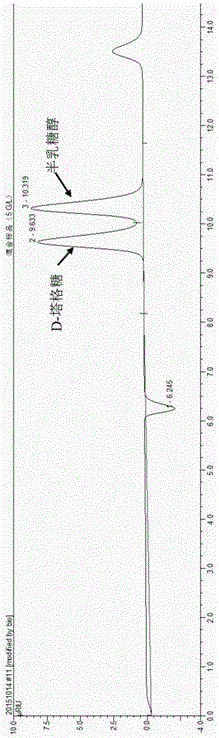
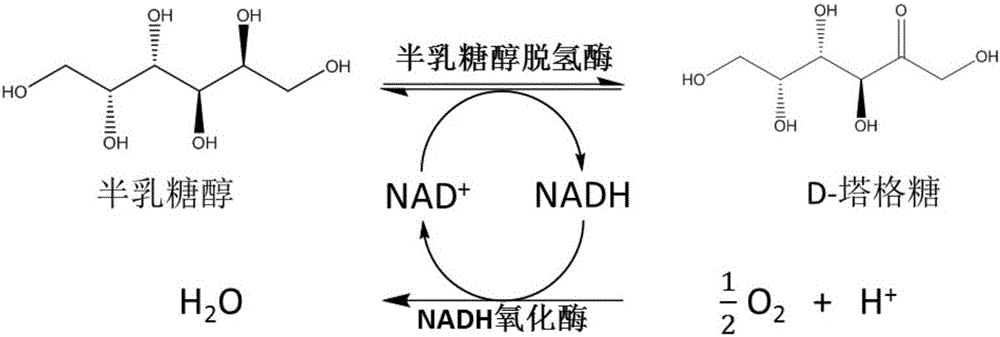
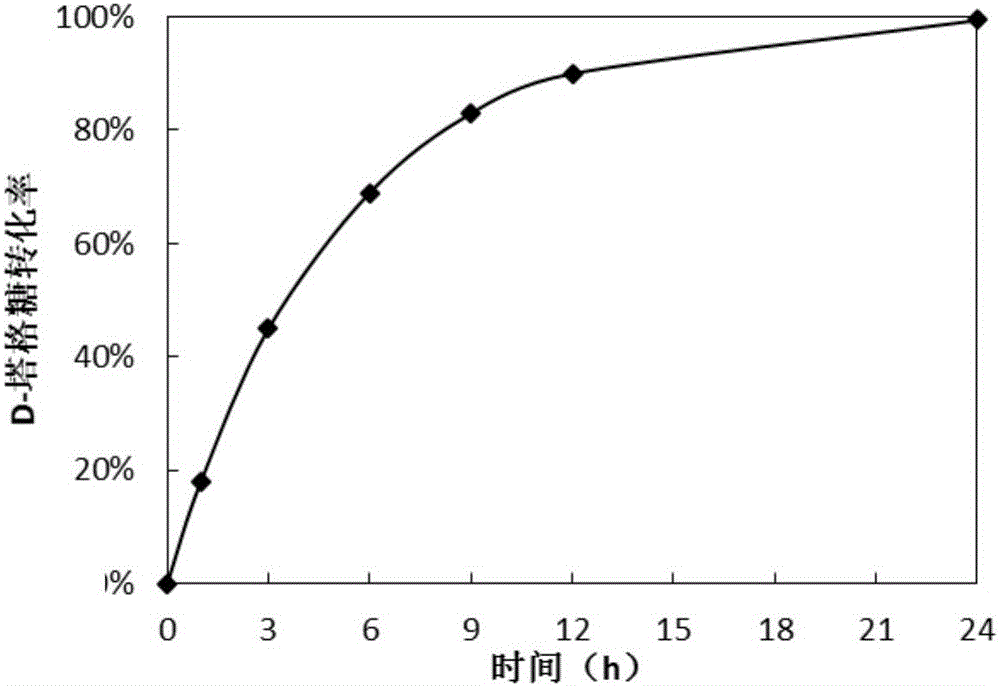
Method for preparing D-tagatose by enzyme process
ActiveCN105734092AReduced downstream operationsReduce manufacturing costNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesHydrogenArabinose isomerase
The invention discloses a method for preparing D-tagatose by an enzyme process. The method comprises the following steps: 1) separately establishing engineering bacteria containing galactitol dehydrogenase gene and engineering bacteria containing NADH oxidase gene or establishing coexpression engineering bacteria containing galactitol dehydrogenase gene and NADH oxidase gene; 2) fermenting the established engineering bacteria to obtain a whole cell containing galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase; and 3) with the whole cell containing galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase or the free enzyme of galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase as a catalyst, catalyzing the galactitol by taking NAD+ as a hydrogen acceptor in a weakly alkaline condition to obtain D-tagatose. Compared with traditional production method depending on L-arabinose isomerase, in the invention, the substrate conversion rate is high (>99.0%) and the product is easy to separate; and moreover, the co-product of a coenzyme circulation system adopted in the method is water which does not influence the separation and purification of the principal product.
Owner:江苏中酶生物科技有限公司
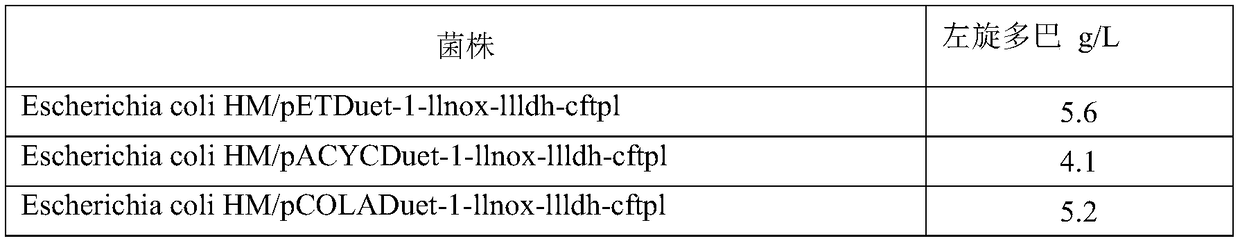
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of levodopa
ActiveCN108949649ANot easy to decomposeHigh NAD contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of levodopa, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium is a recombinant Escherichia coli capable of producing pure levodopa at low cost; the recombinant Escherichia coli simultaneously expresses exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase, NADH oxidase and tyrosine phenol lyase, and is obtained by knocking out an aromatic compound-degrading gene from host Escherichia coli; and the recombinant Escherichia coli can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, an ammonia ion transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene, an NAD synthesis gene and a pyridoxal phosphate synthesis gene. A bacterium can be applied to the production of levodopa, and a method for producing the levodopa has the advantages of simple production process, few impurities, easily available raw materials and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Compositions comprising ARNOX-inhibitors for the inhibition of reactive oxygen species
The invention relates to agents for sequestering serum aging factors, and methods for using the same. More particularly, the invention relates to agents termed herein 'Naractin' to denote any one of several naturally-occurring arNOX inhibitors either present in N. tazetta powder or capable of augmenting N. tazetta powder to an inhibitory level comparable to that of the fresh N. tazetta extracts, and to methods for using 'Naractins' to prevent or treat disorders and complications of disorders resulting from cell damage caused by an aging-related isoform of NADH oxidase (arNOX). In one exemplary embodiment the agents of the invention comprise at least one naturally occurring Naractin. Such naturally occurring naratins are also capable of augmenting the anti-arNOX effect of other naturally occurring arNOX inhibitory agents.
Owner:NU SKIN INT +1
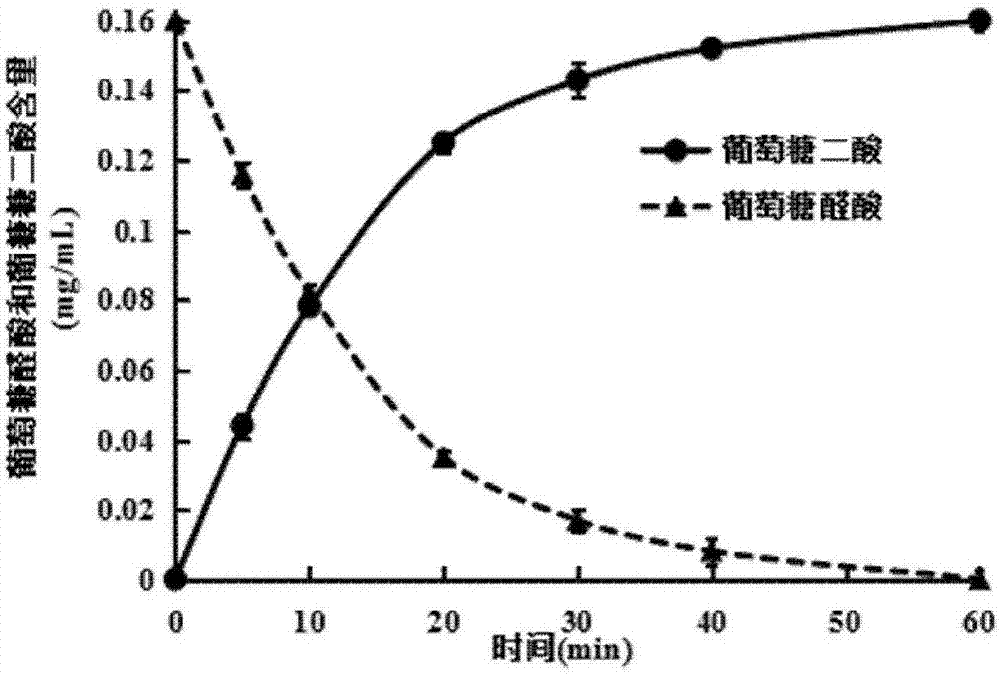
Preparation method of glucaric acid and uronic acid dehydrogenase-NADH oxidase and application thereof in preparation
ActiveCN107365806ASolve pollutionMild reaction conditionsOxidoreductasesFermentationFiberAlpha-glucuronidase
The invention discloses a preparation method of glucaric acid and uronic acid dehydrogenase-NADH oxidase and an application thereof in preparation. The preparation method includes: taking xylan extracted in wood fiber plants as a raw material; preparing glucuronic acid by adopting a high-temperature xylanase and alpha-glucuronidase hydrolyzing technology; preparing the glucaric acid by oxidizing the glucuronic acid generated through the double-functional uronic acid dehydrogenase-NADH oxidase. With the method, use amount of NAD can be effectively saved, the NAD is regenerated in situ by taking the NADN oxidase as uronic acid dehydrogenase to promote circulation of coenzyme, the uronic acid dehydrogenase continuously catalyzes the glucuronic acid to be converted into the glucaric acid, catalytic efficiency is improved, and conversion rate can be up to 100%; meanwhile, the preparation method has the advantages of high efficiency, rapidness, specificity and moderate reaction conditions, and chemical substances of acid, alkali and the like are not involved in the entire preparation process; the preparation method is low in energy consumption and small in pollution, and operation is simple and easy to control.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing tetramethylpyrazine from cheap raw materials
ActiveCN107177620AIncrease productionIncrease productivityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for producing tetramethylpyrazine from cheap raw materials. The method comprises steps as follows: nucleotide sequences of an alpha-acetolactate synthase gene, an alpha-acetolacetate decearboxylase gene and an NADH oxidase gene are subjected to codon optimization; a gene cluster containing the three genes is obtained through splicing; the gene cluster is inserted into an expression vector, and polycistron recombinant plasmid is obtained; the polycistron recombinant plasmid is introduced into a host strain E.coli, and a gene engineering strain producing acetylmethylcarbinol is obtained; a fermentation medium containing the cheap raw materials is inoculated with the activated strain for fermentation culture, and fermentation broth containing acetylmethylcarbinol is obtained; the fermentation broth is subjected to centrifugal treatment, a supernatant is taken, diammonium hydrogen phosphate is added, acetylmethylcarbinol produced through fermentation reacts with NH4<+>, and tetramethylpyrazine is synthesized. The widely sourced and low-cost raw materials can be effectively utilized by the strain for producing a high-concentration precursor substance, namely, acetylmethylcarbinol, oxidative coenzyme NAD<+> can be regenerated effectively, yield and production efficiency of acetylmethylcarbinol can be increased, so that the production cost of acetylmethylcarbinol is effectively reduced, and production period is shortened.
Owner:南宁中诺生物工程有限责任公司 +1
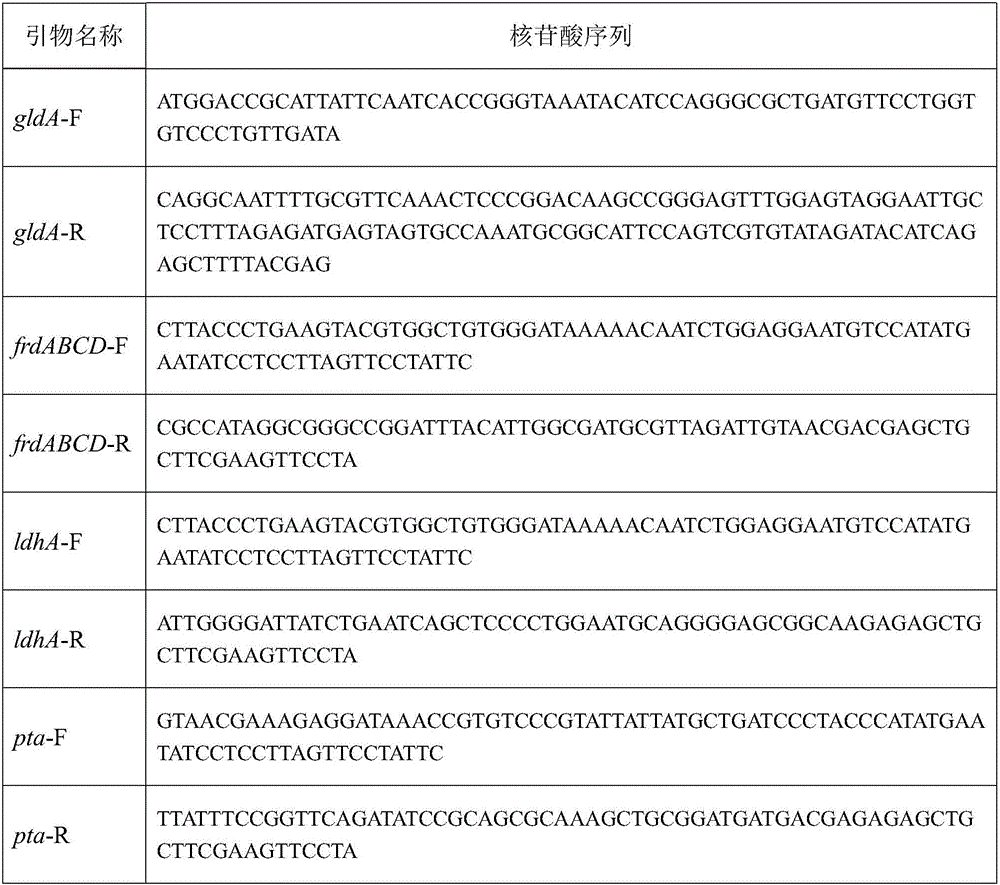
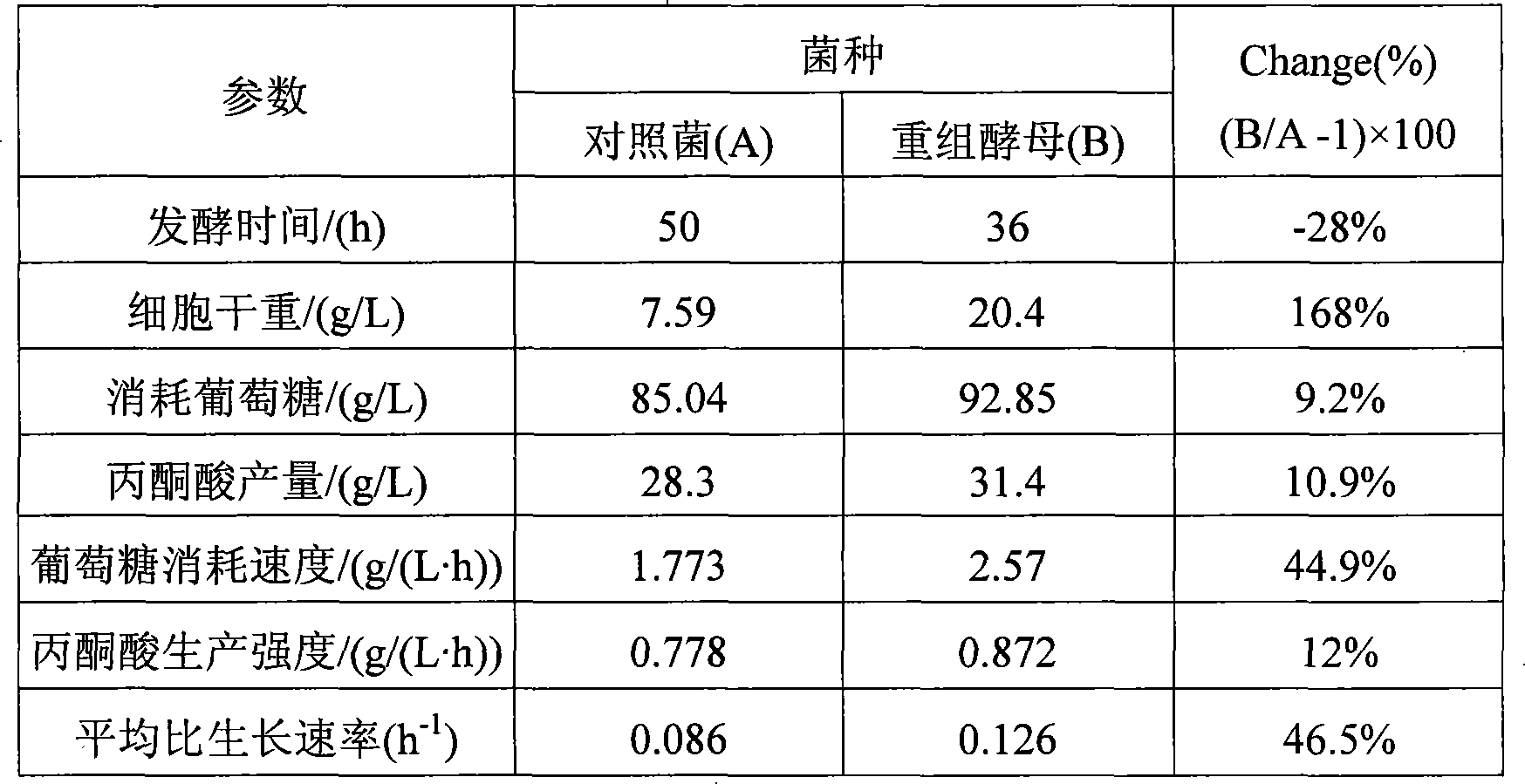
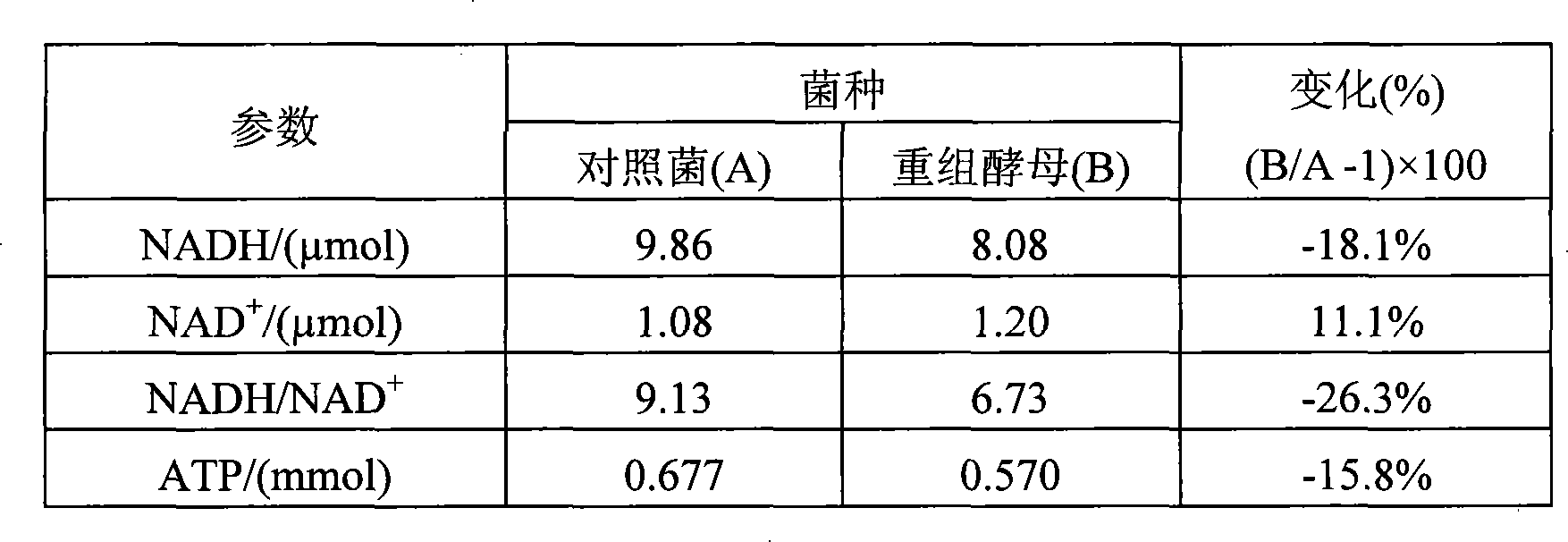
Construction of bacterial strain producing pyruvic acid recombination and method for improving production strength of pyruvic acid
InactiveCN101245322AIncrease production intensityIncrease concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesDry weightBacterial strain
The invention relates to a construction of a recombinant bacterium for producing pyruvate and a method for improving the production strength of pyruvate by using the recombinant bacterium, which pertains to the technical filed of auxiliary factor metabolic regulation and control strategic optimized fermentation process. The method regulates and controls the carbon metabolic flow to strengthen the production strength of the pyruvate by changing an auxiliary factor NADH and adopts molecular approach to allow the NADH oxidase noxE gene which is coded into water and is derived from L. lactis to be over expressed in an industrial bacterial strain Torulosis glabrata CCTCC NO: M 202019 for producing the pyruvate by the fermentation method, so as to obtain an NADH oxidase over expressed recombinant bacterium PdnoxE CCTCC NO: M 208022; compared with the starting bacterial strain, the bacterial dry weight, the glucose consumption rate and the pyruvate production strength thereof are respectively improved by 168 percent, 44.9 percent and 12 percent. The method has universally applicable significance for the improvement of a plurality of important fermentation products (such as, organic acids and amino acids etc.).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of pyruvic acid
ActiveCN108949656ANot easy to decomposeHigh NAD contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of pyruvic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium simultaneously expresses exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase, is obtained by knocking out a pyruvic acid absorption gene from host Escherichia coli, and can achieve enhanced expression of a lactic acid transporter gene, a pyruvic acid transporter gene and an NAD synthesis gene. The double-enzyme co-expression engineering bacterium is constructed on the basis of reconstructing Escherichia coli transportation and a coenzyme synthesis system in order to realize efficient production of pyruvic acid and reduce the generation of impurities.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
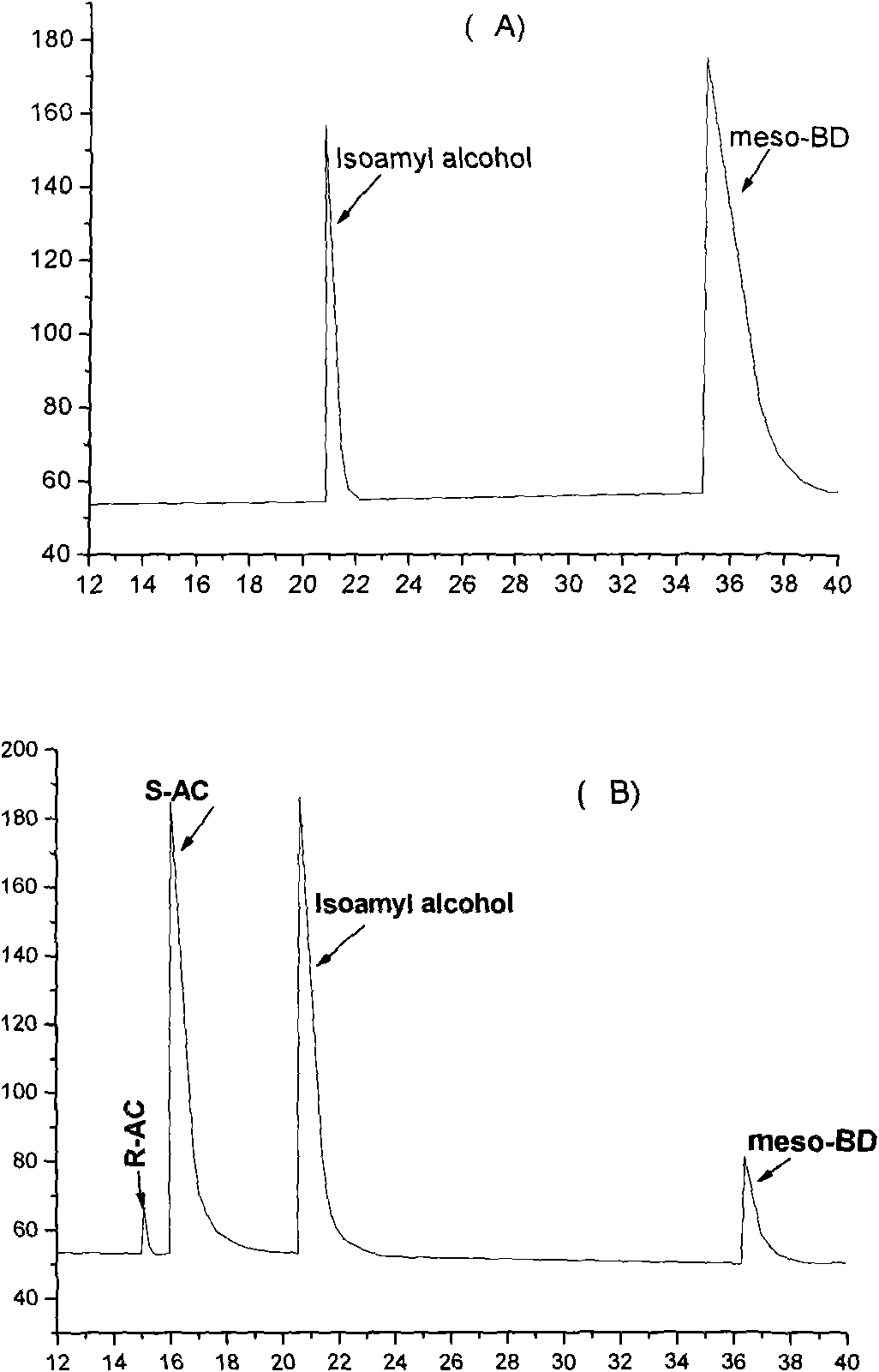
Gene recombination bacterium and application thereof in preparing chiral pure acetoin and 2,3-butanediol
InactiveCN101565685BLow costEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses an E. coli BL21(pETDuet-ydjLnox) containing a 2R,3R-butanediol dehydrogenase gene ydjL and an NADH oxidase gene nox, wherein the strain is preserved in the 'China Center for Type Culture Collection' on December 23 in 2008, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 208259. The invention also discloses application of a gene recombination bacterium in producing chiral S-AC bycatalyzing meso-BD, producing chiral R-AC by catalyzing 2R,3R-BD and producing chiral pure 2S,3S-BD by splitting a 2,3-BD mixture. The concentration of a chiral AC prepared from the recombinant E. coli can reach over 6 grams per liter (the ee value is more than or equal to 96 percent); and the ee value of the chiral pure 2S,3S-BD is more than or equal to 98 percent, and the regeneration of a cofactor is achieved, thus the gene recombination bacterium has great industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method for L-type rare ketohexose
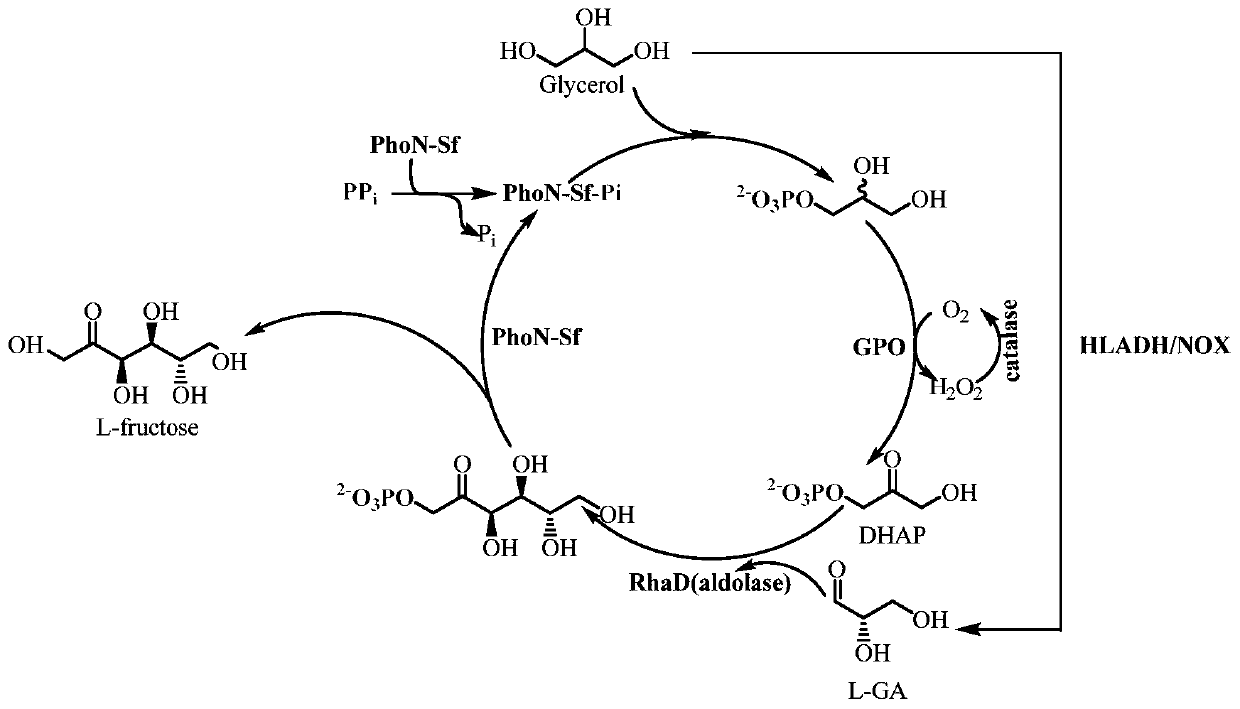
The invention discloses a preparation method for L-type rare ketohexose. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with glycerol and pyrophosphoric acid as substrates, adding aldolase containing L-rhamnose-1-phosphate, glycerophosphate oxidase, catalase, acid phosphatase, equine dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase into the glycerol and pyrophosphoric acid so as to establish a multi-enzyme reaction system, and carrying out enzyme catalytic reaction; and separating an enzyme catalytic reaction product, and carrying out purifying. According to the invention, raw materials are low in price;glycerol triphosphate is produced without glycerol kinase and ATP for substrate phosphorylation; the cost of producing the L-type rare ketohexose is greatly reduced; equine dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase are combined to produce L-glyceraldehyde; and use of NAD+ is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
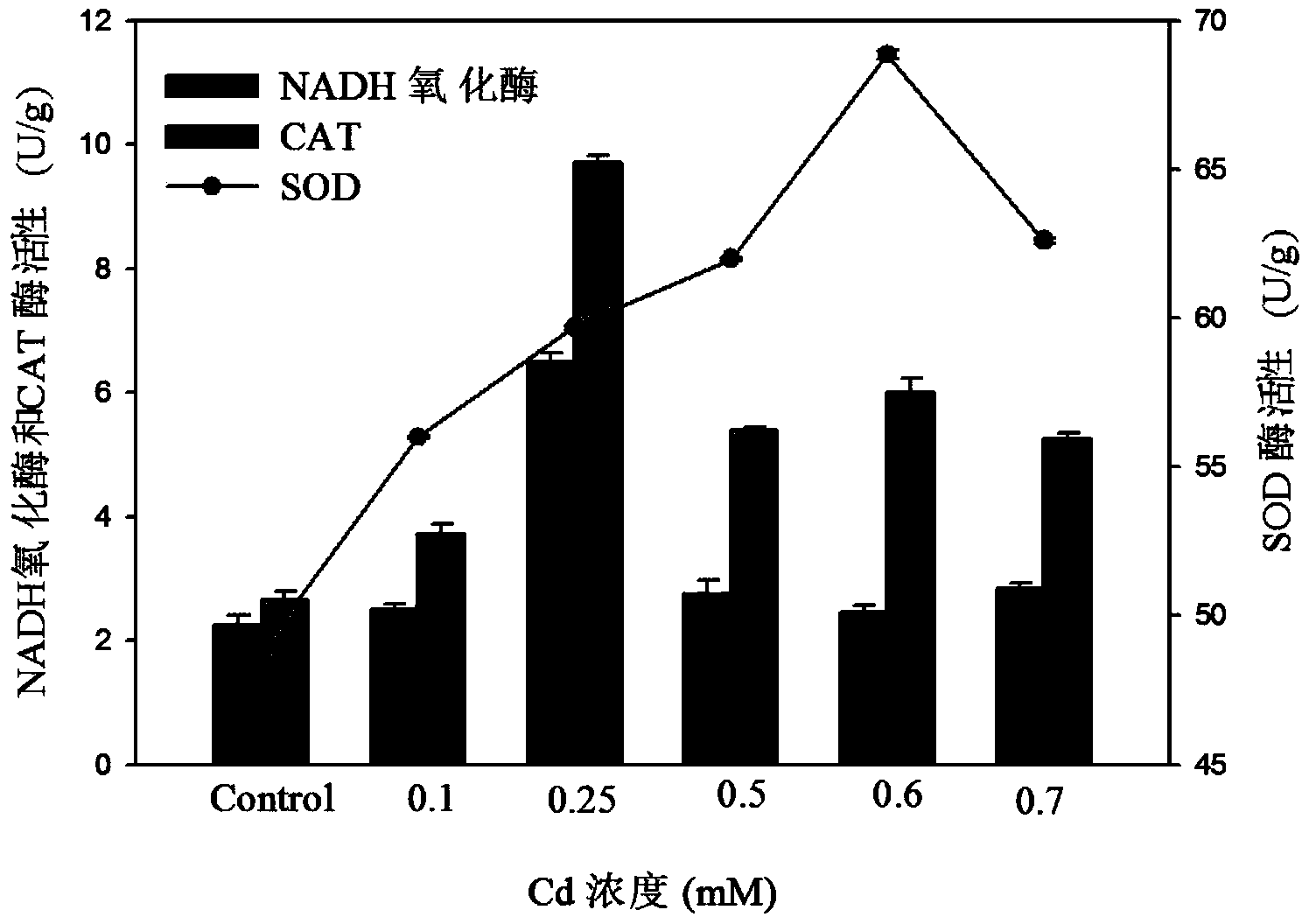
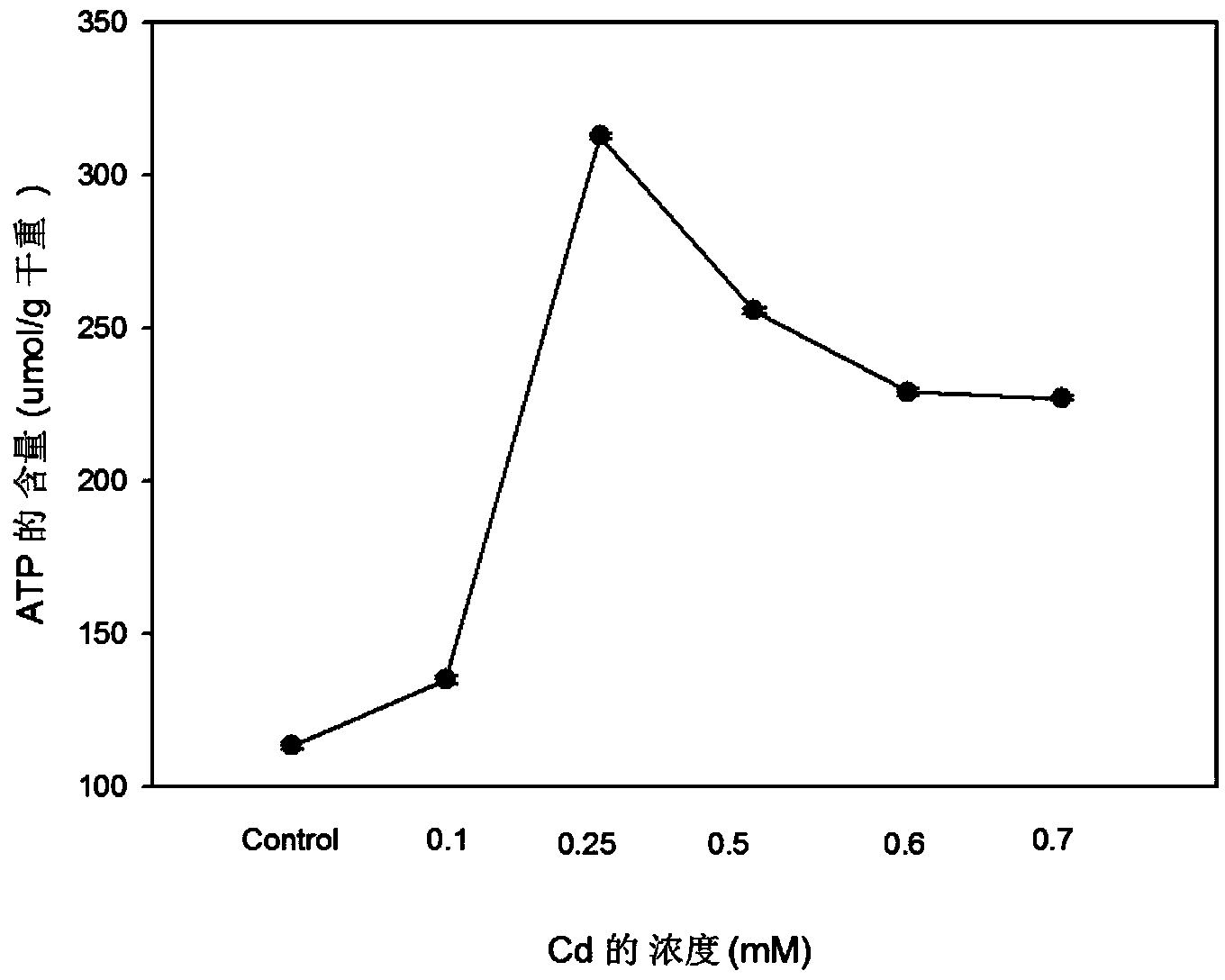
Method for extracting SOD, CAT, NADH oxidase and ATP in white-rot fungi composite adsorbent simultaneously
InactiveCN104293742AImprove crushing effectGrinding speed is fastSugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesAtp contentWhite rot
The invention discloses a method for extracting SOD, CAT, NADH oxidase and ATP in a white-rot fungi composite adsorbent simultaneously. The method for extracting SOD, CAT, NADH oxidase and ATP in the white-rot fungi composite adsorbent simultaneously comprises the following steps: adding the white-rot fungi composite adsorbent into a CaCl2 solution to prepare small balls with white-rot fungi being embedded, and carrying out constant temperature shaking culture on the small balls with the white-rot fungi being embedded to obtain a culture solution; adding Cd<2+> into the culture solution for carrying out stress culture, then taking out the small balls with the white-rot fungi being embedded, and carrying out liquid nitrogen grinding to obtain a grinding sample; and adding phosphate buffer into the grinding sample, carrying out ultrasonic treatment in an ice bath, centrifuging to obtain a compound of SOD, CAT, NADH oxidase and ATP. The method for extracting SOD, CAT, NADH oxidase and ATP in the white-rot fungi composite adsorbent simultaneously has the advantages that heavy metal stress is adopted for improving enzyme activity of SOD, CAT and NADH oxidase and increasing ATP content, a cell breakage effect is good and extraction efficiency is high.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com