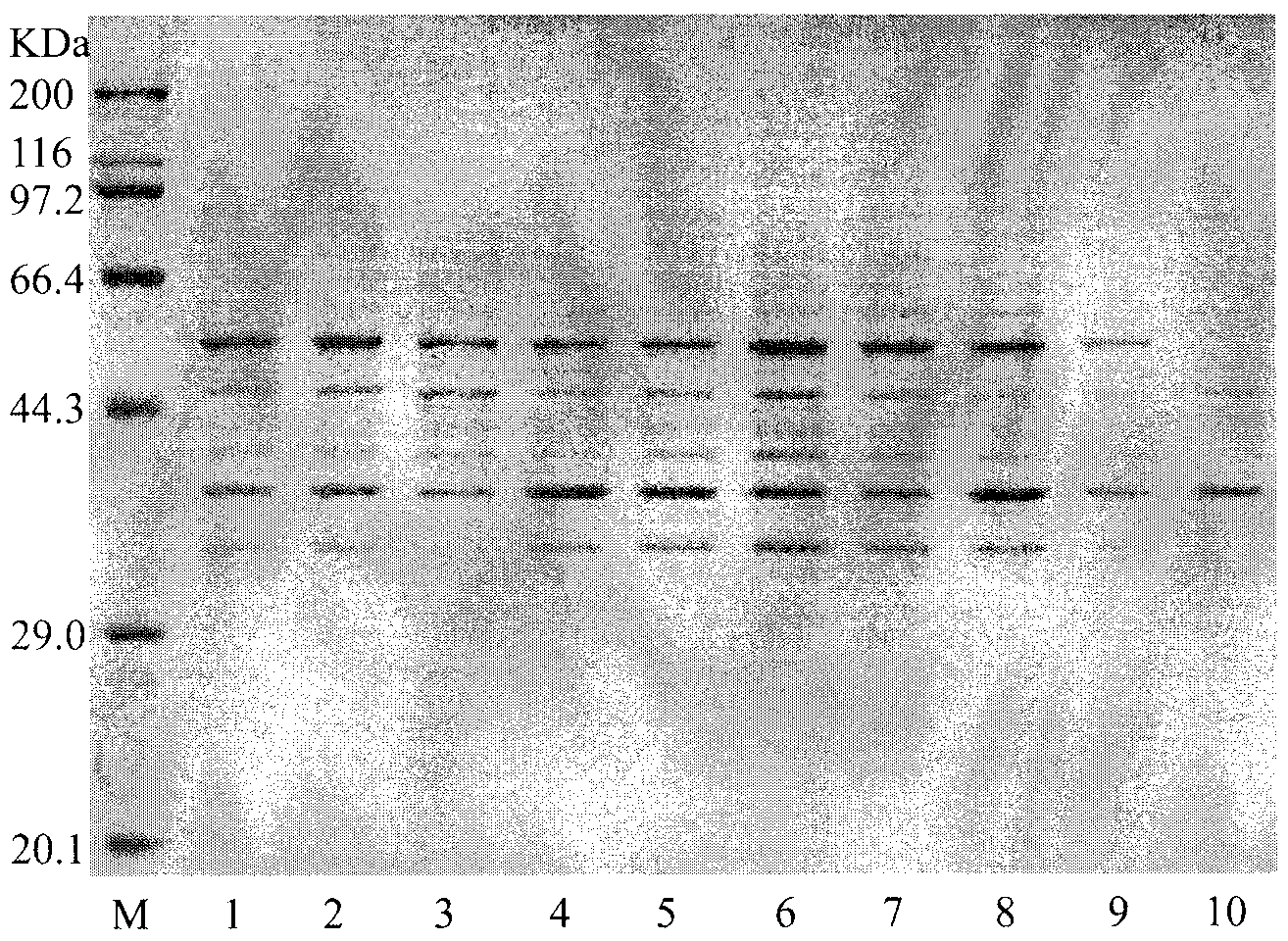
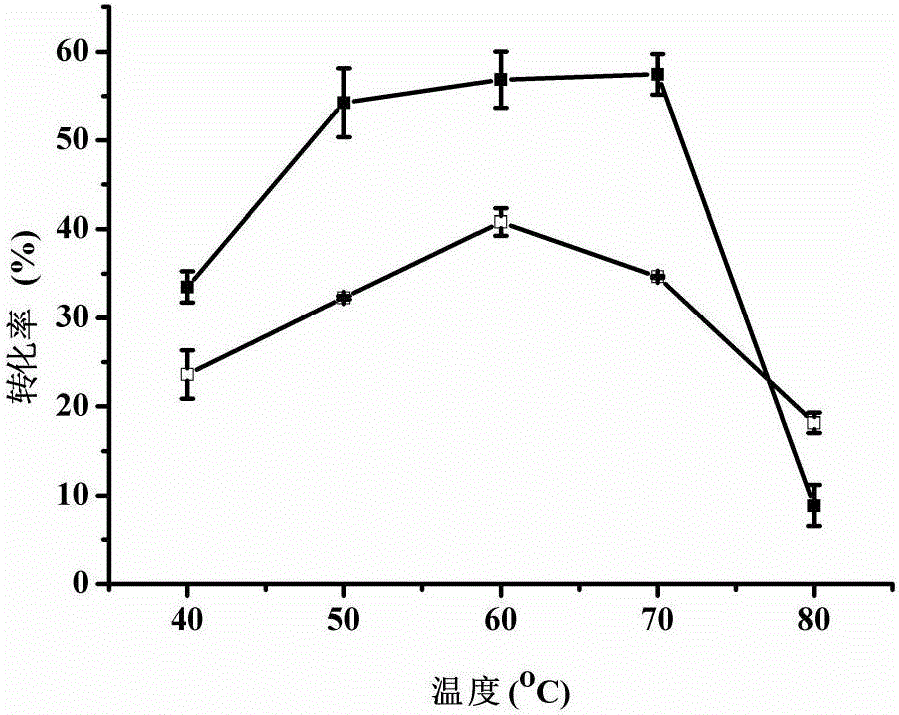
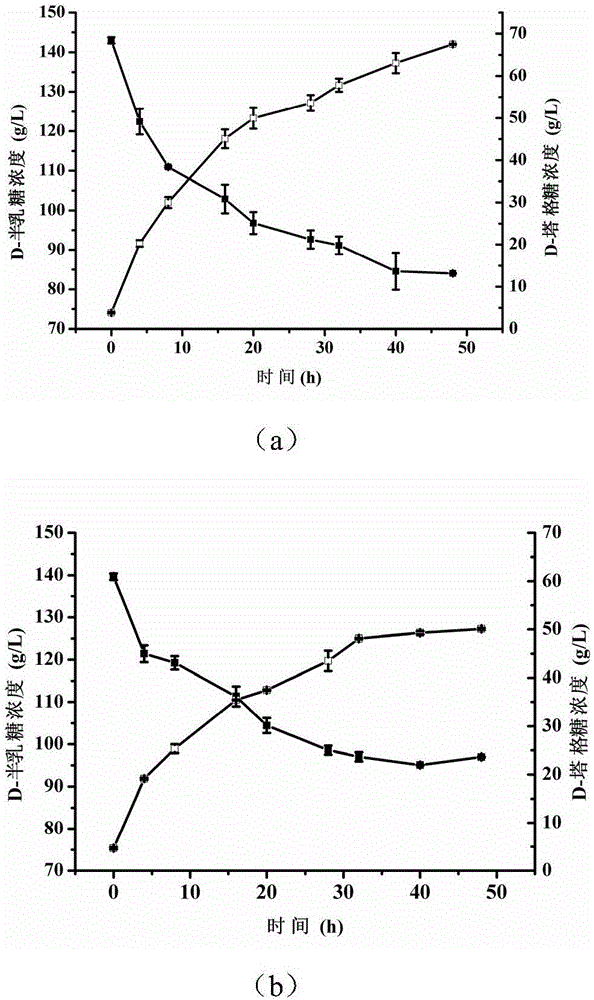
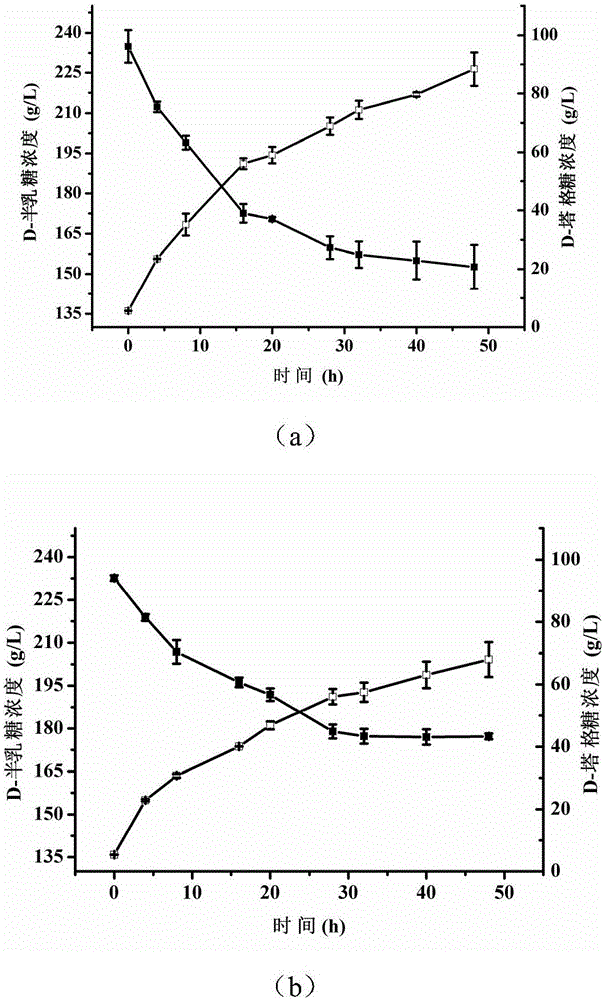
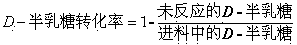Patents
Literature
61 results about "Arabinose isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
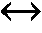
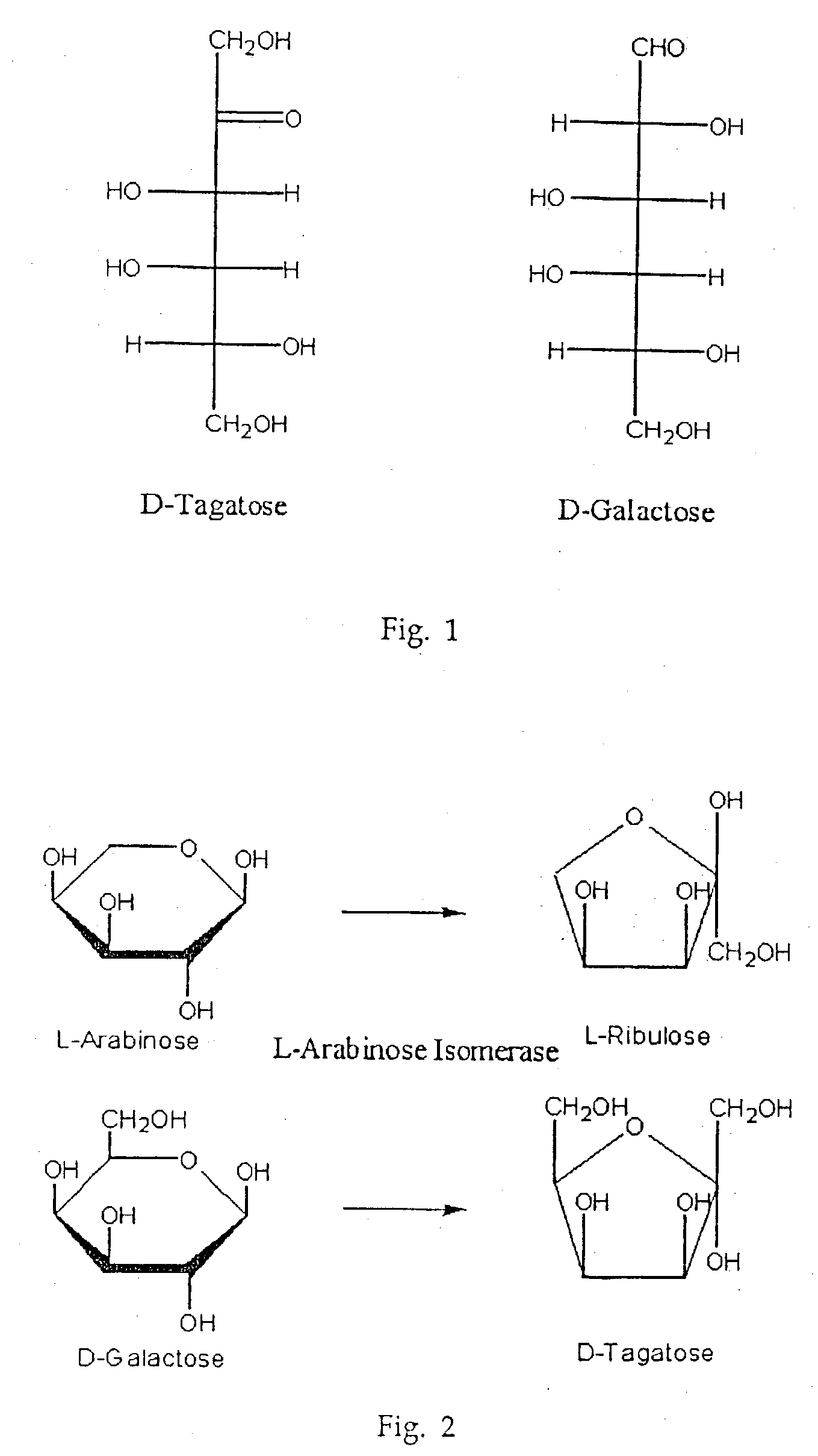
In enzymology, an arabinose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction D-arabinose ⇌ D-ribulose Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, D-arabinose, and one product, D-ribulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-arabinose aldose-ketose-isomerase.
Novel arabinose-fermenting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20100304454A1Improve stabilityAvoid recombinationFungiHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlucose repression
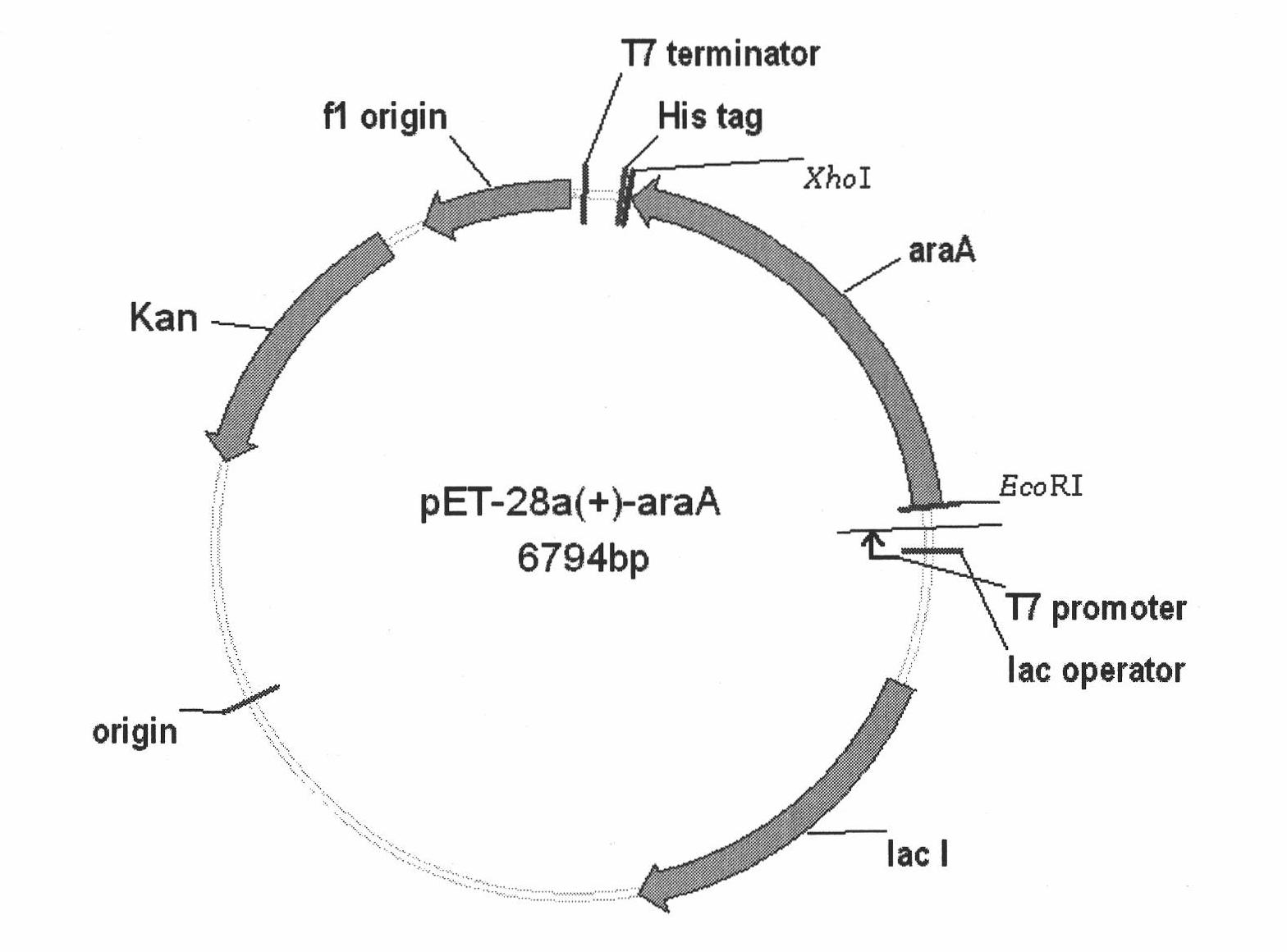
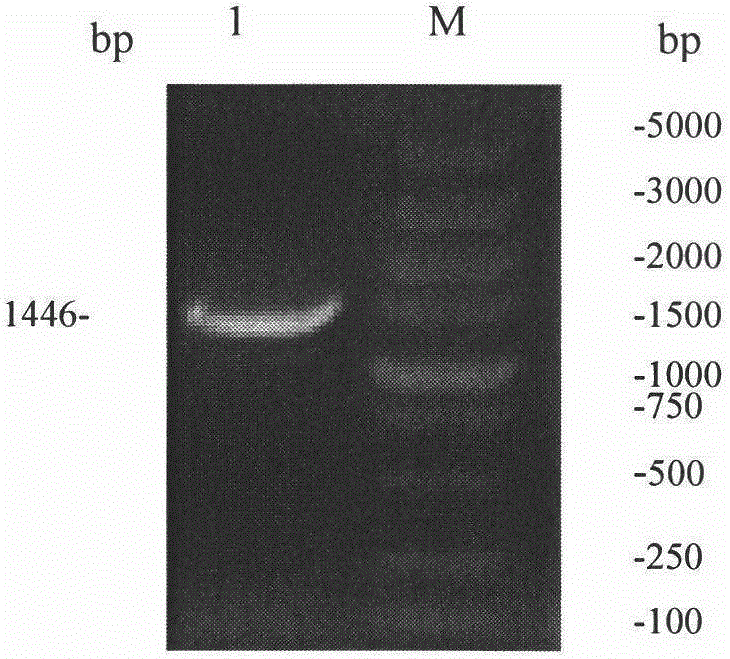
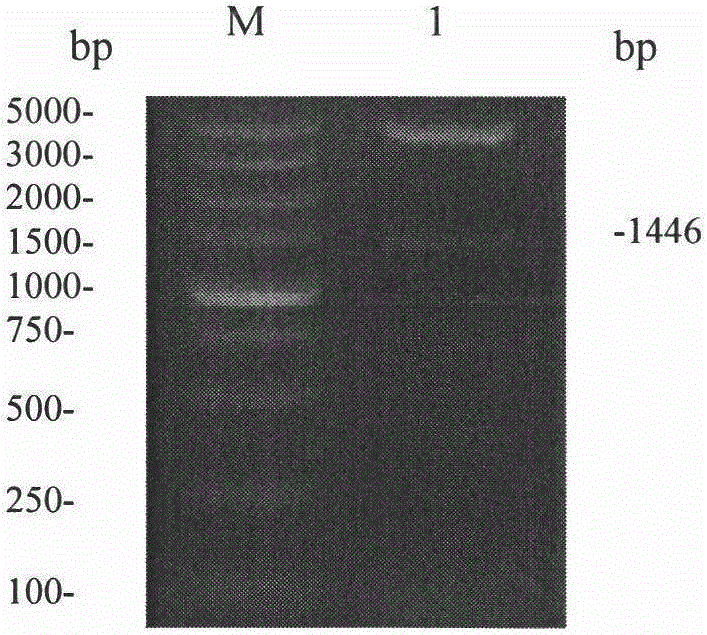
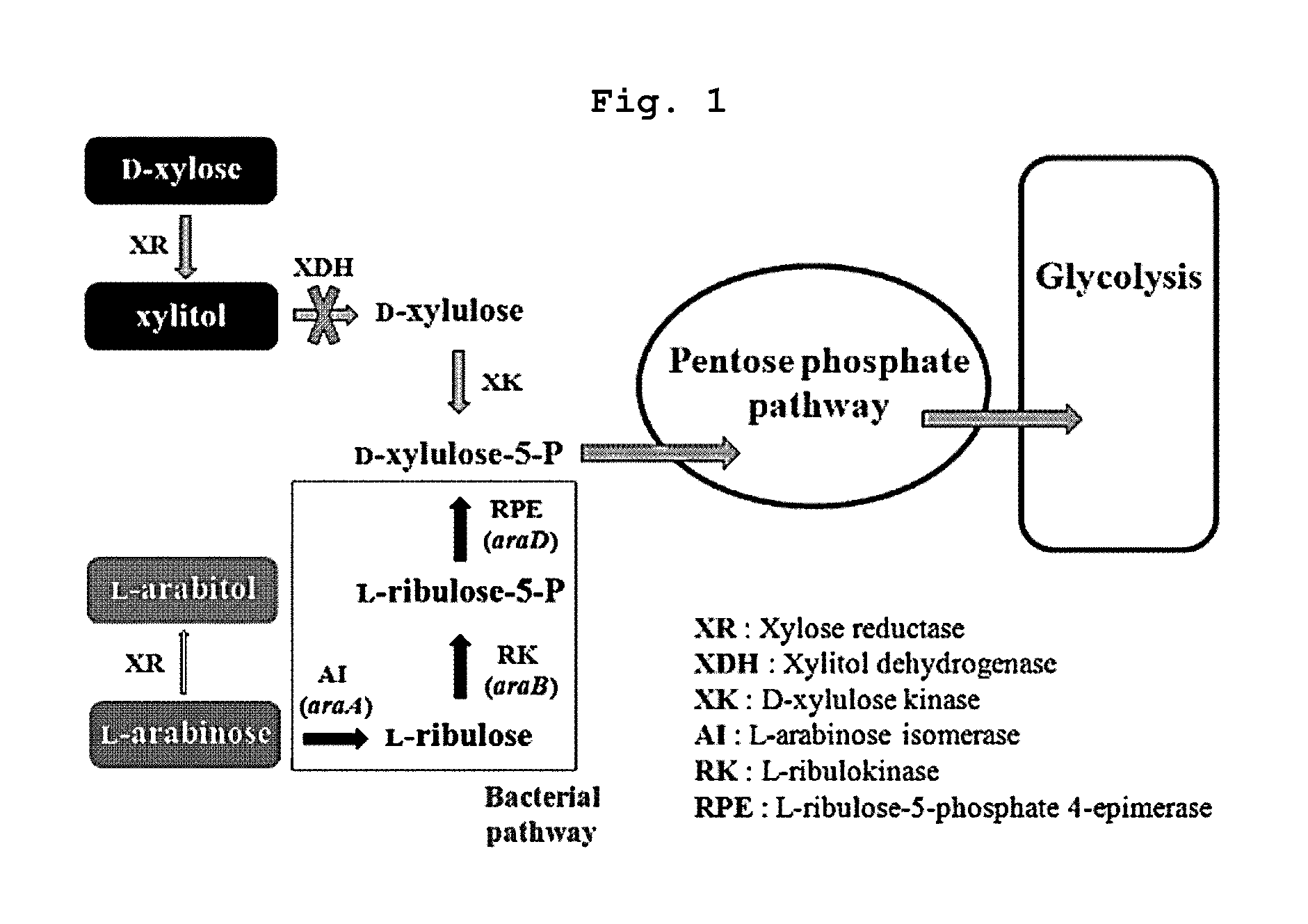
The present invention relates to eukaryotic cells which have the ability to convert L-arabinose into D-xylulose 5-phosphate. The cells have acquired this ability by transformation with nucleotide sequences coding for an arabinose isomerase, a ribulokinase, and a ribulose-5-P-4-epimerase from a bacterium that belongs to a Clavibacter, Arthrobacter or Gramella genus. The cell preferably is a yeast or a filamentous fungus, more preferably a yeast is capable of anaerobic alcoholic fermentation. The may further comprise one or more genetic modifications that increase the flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, reduce unspecific aldose reductase activity, confer to the cell the ability to directly isomerise xylose into xylulose, increase the specific xylulose kinase activity, increase transport of at least one of xylose and arabinose into the host cell, decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression, increase tolerance to ethanol, osmolarity or organic acids; and / or reduce production of by-products. The cell preferably is a cell that has the ability to produce a fermentation product such as ethanol, lactic acid, 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, acrylic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, amino acids, 1,3-propane-diol, ethylene, glycerol, -lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins. The invention further relates to processes for producing these fermentation products wherein a cell of the invention is used to ferment arabinose into the fermentation products.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TAL1 (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Method for microbial production of xylitol from arabinose
Recombinant microorganisms are useful for producing xylitol by fermentation of arabinose. The recombinant microorganisms are produced by transformation of host microorganisms with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding for each of L-xylulose reductase, D-tagatose 3-epimerase, and L-arabinose isomerase, which transformants express the heterologous polynucleotides at a sufficient functional level to be effective to produce xylitol from arabinose. Production of xylitol is effected by contacting these recombinant microorganisms with a substrate comprising arabinose under conditions effective to produce xylitol from arabinose.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
High temperature resistant L-arabinose isomerase and application thereof
InactiveCN101845429AImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeat stability
The invention discloses a high temperature resistant L-arabinose isomerase which has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses a gene sequence for encoding the high temperature resistant L-arabinose isomerase, a gene engineering bacterium and construction method thereof, an expression method for the L-arabinose isomerase, and application of the L-arabinose isomerase and the gene engineering bacterium in preparing D-tagatose. The reaction temperature of the high temperature resistant L-arabinose isomerase is 40 to 70 DEG C, and the reaction pH is 5.5 to 7.5. The recombinase shows good heat stability and pH tolerance; the added low-concentration Mn2+, Co2+ ions can greatly improve enzyme activity and heat stability; and the high temperature resistant L-arabinose isomerase has wide application prospect and economic significance for industrial production of the novel functional sweetener D-tagatose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Arabinose Isomerase Expressed From Corynebacterium Genus and Tagatose Manufacturing Method By Using It
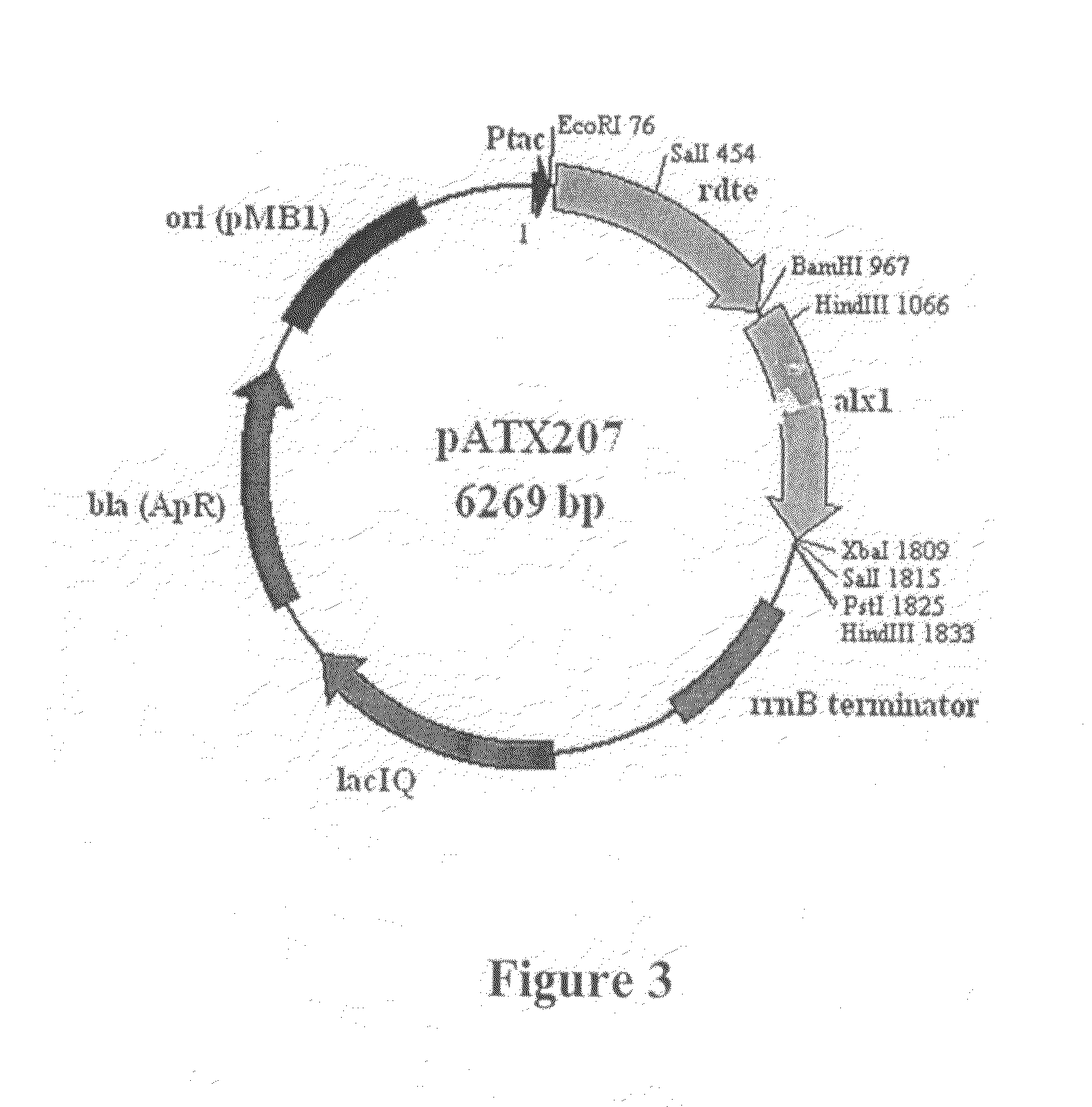
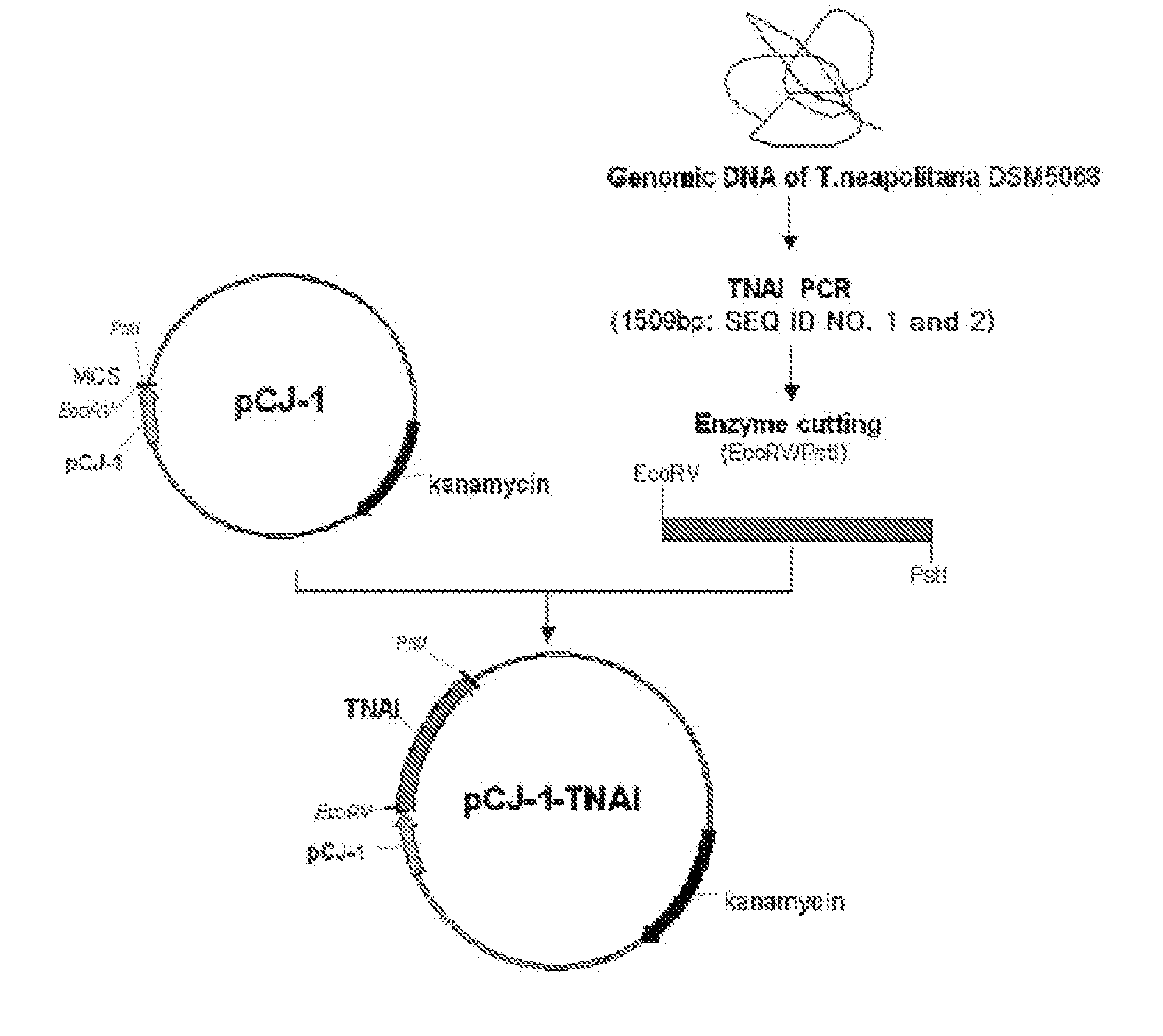
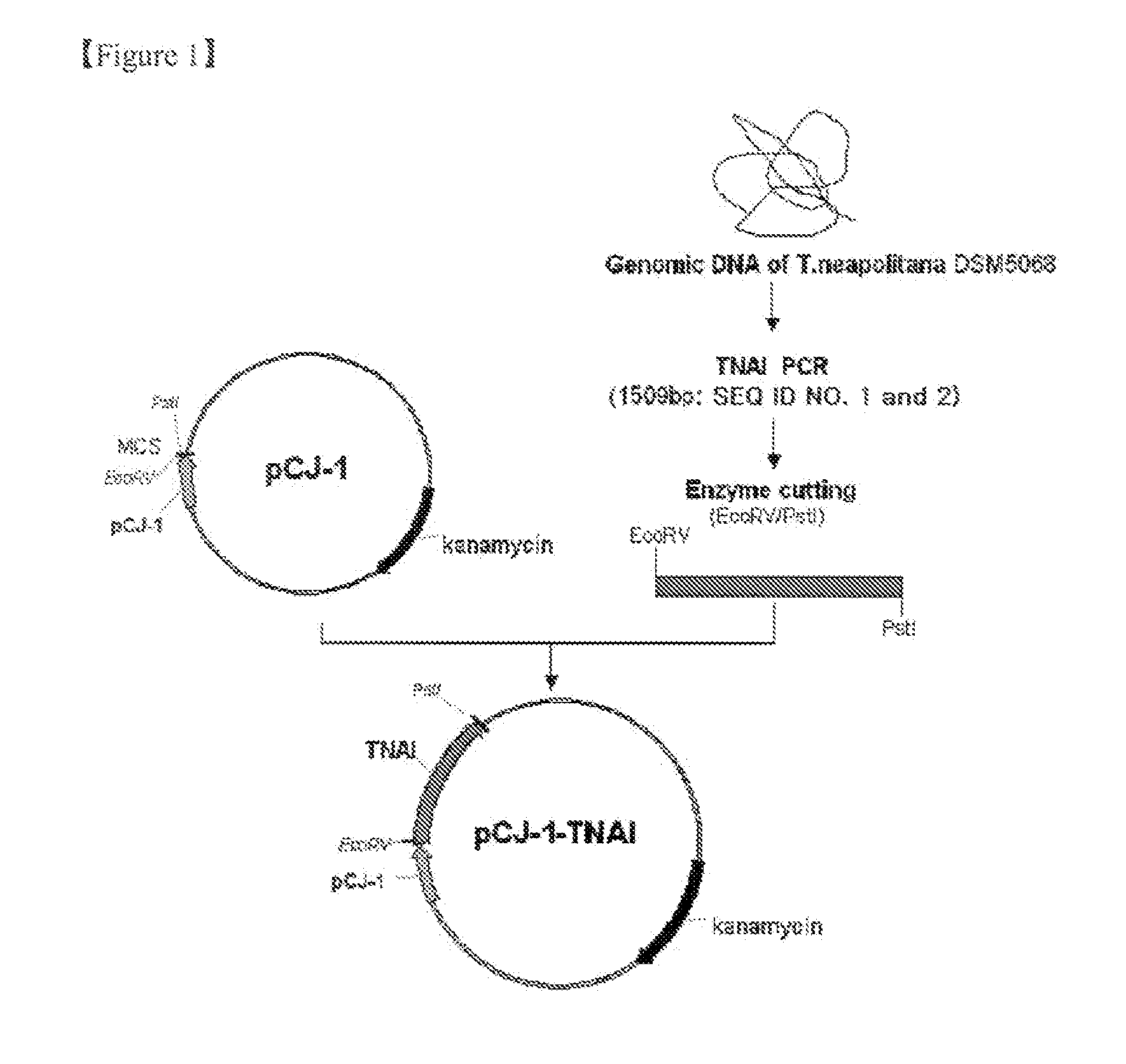
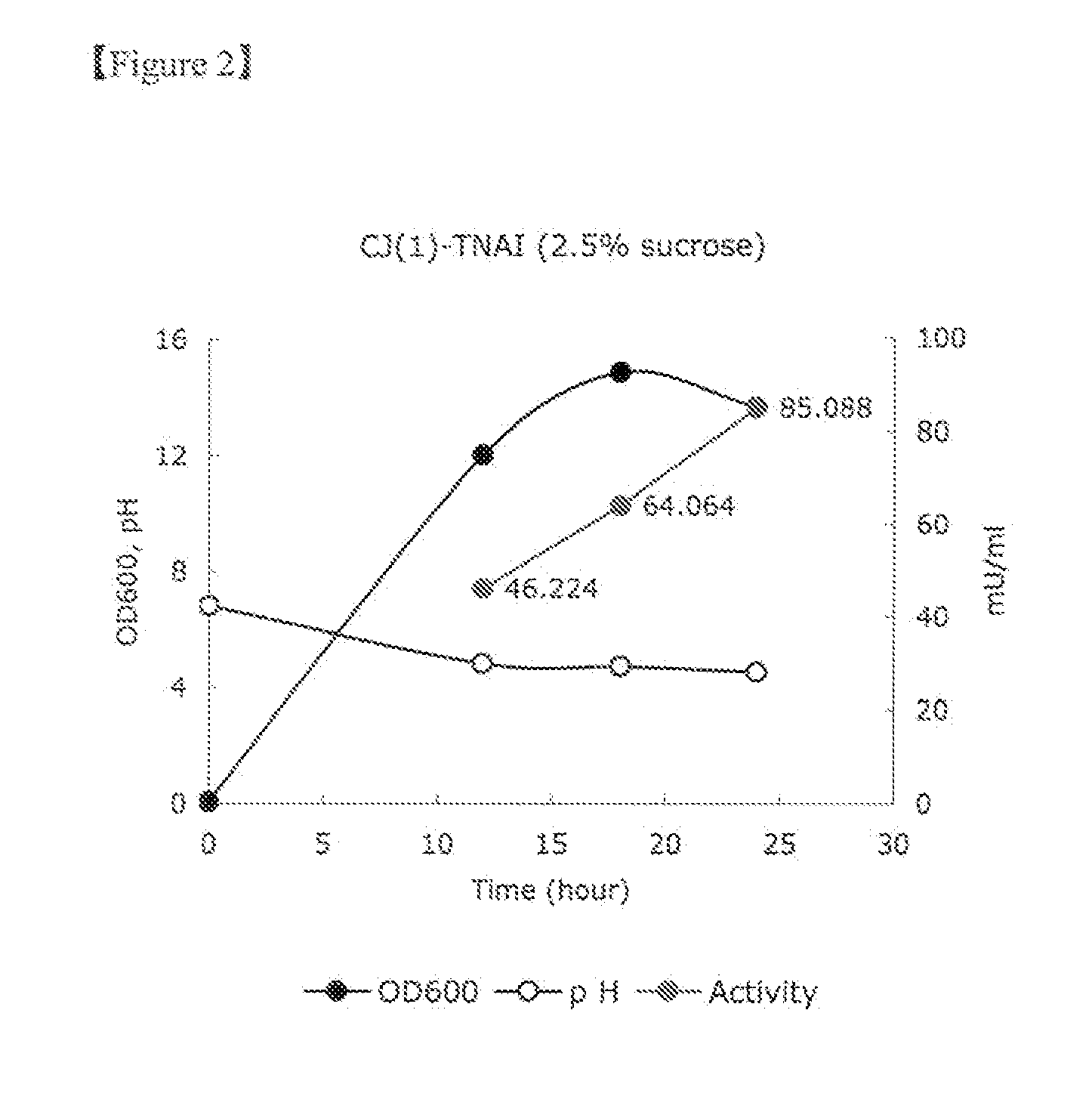
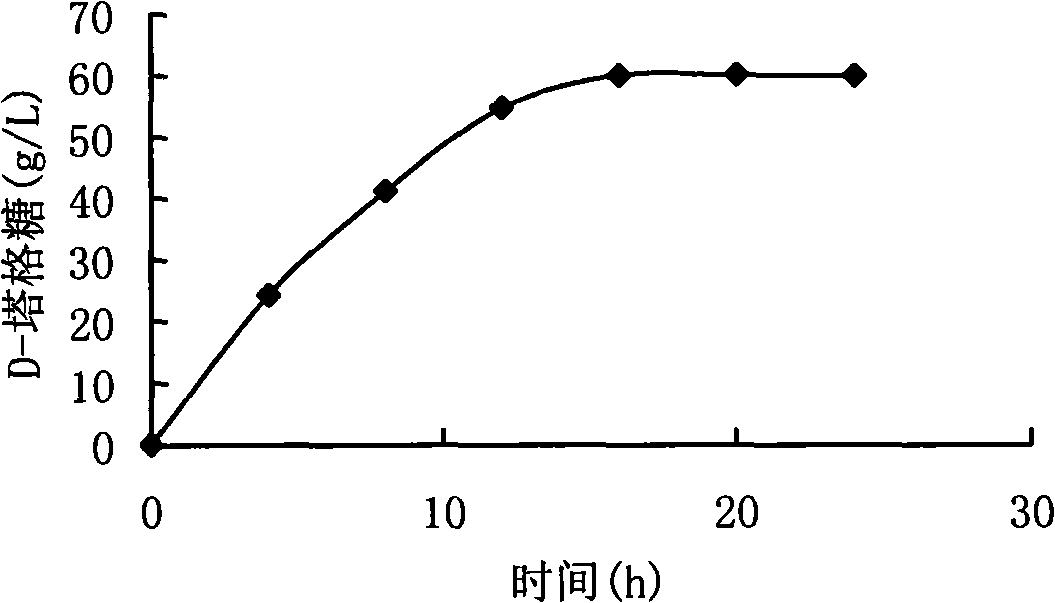
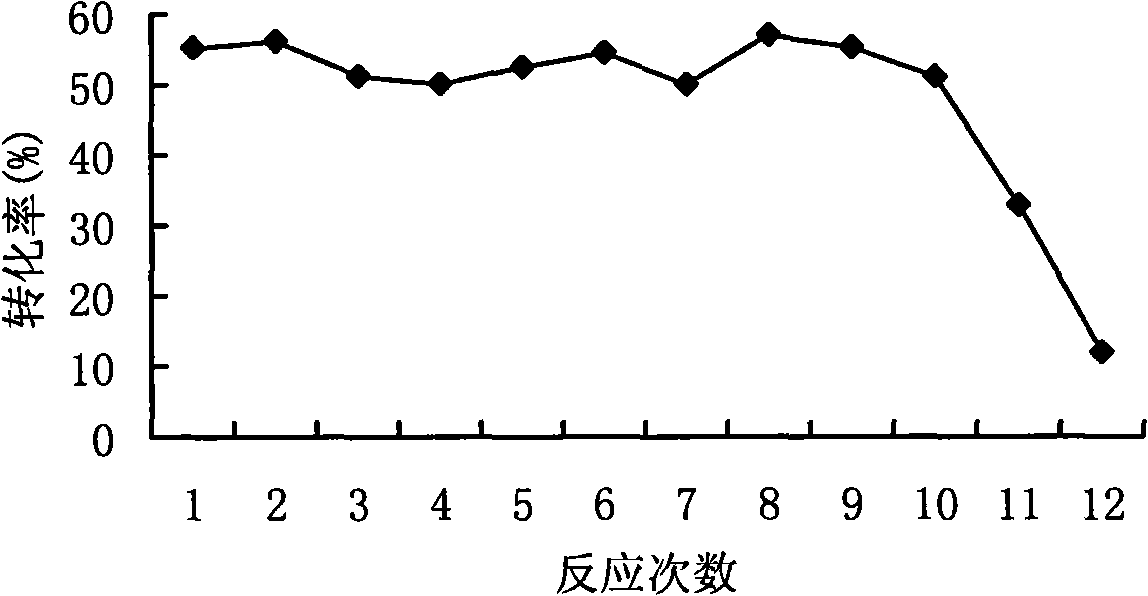
The present invention relates to a thermophilic arabinose isomerase and a method of manufacturing tagatose using the same, and more precisely, a gene encoding arabinose isomerase originating from the thermophilic Thermotoga neapolitana DSM 5068, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a method of preparing a food grade thermophilic arabinose isomerase from the recombinant GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) strain transformed with the said expression vector, and a method of preparing tagatose from galactose using the said enzyme.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Colibacillus for recombining L-arabinose isomerase and method for preparing tagatose
InactiveCN101265460ASuitable for industrial productionLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field, and relates particularly to genetically engineered bacteria by using recombinant DNA technology to construct high expressing L-arabinose isomerase, and a method for synthesizing tagatose by using the L-arabinose isomerase produced by genetically engineered bacteria. The genetically engineered bacteria can efficiently express the L-arabinose isomerase, the L-arabinose isomerase produced by the genetically engineered bacteria can be uses enzyme source to synthesize D-tagatose in the presence of the catalysis of D-galactose. The method has the advantages of simpleness, high efficiency, short period, etc, and the immobilized L- arabinose isomerase can be repeatedly used for more than ten times, thus being suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:上海斯贝生物科技有限公司
Recombinant gras strains expressing thermophilic arabinose isomerase as an active form and method of preparing food grade tagatose by using the same
ActiveUS20100041106A1Easy to useHigh glucose concentrationSugar derivativesIsomerasesBiotechnologyGeobacillus thermodenitrificans
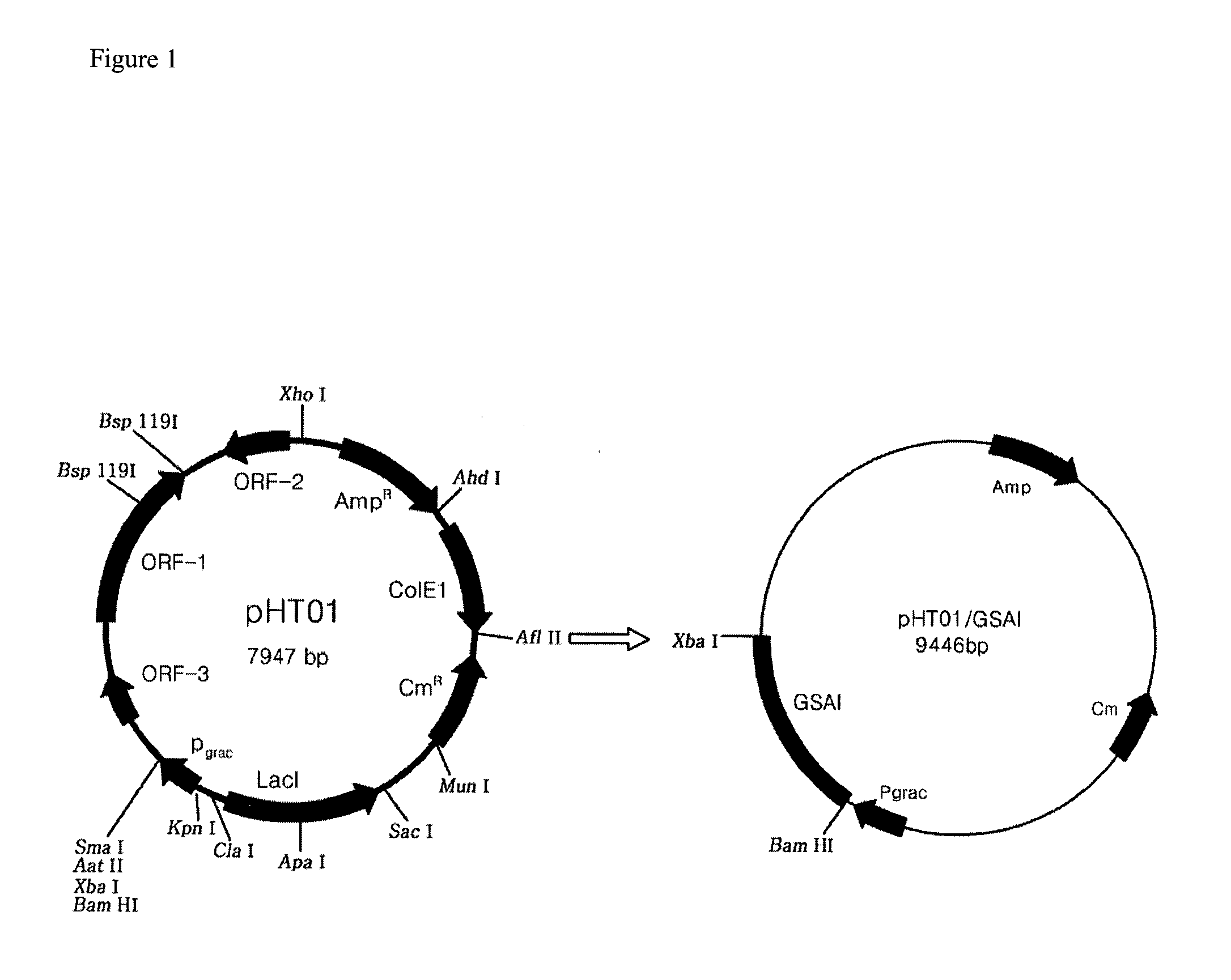
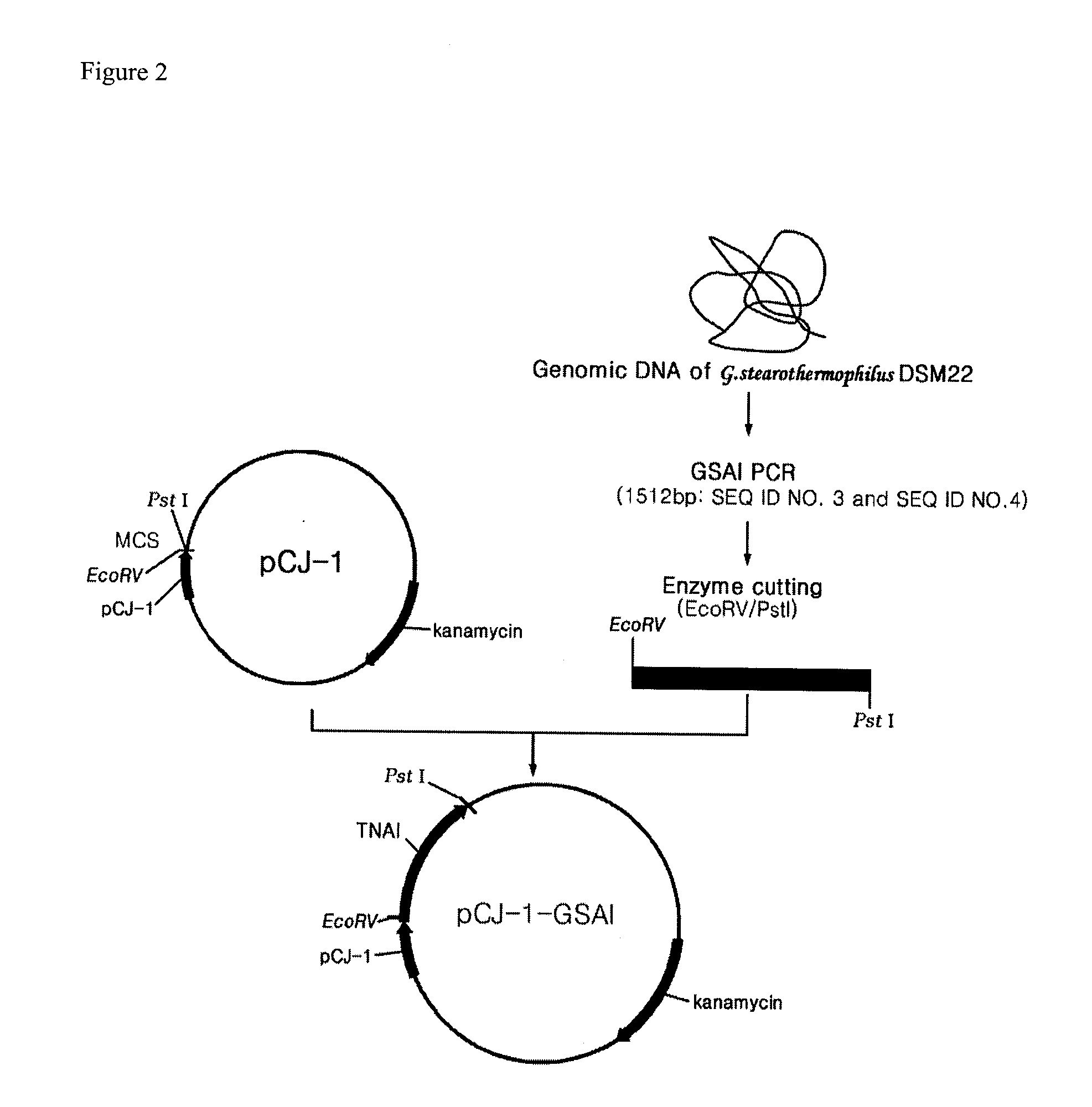
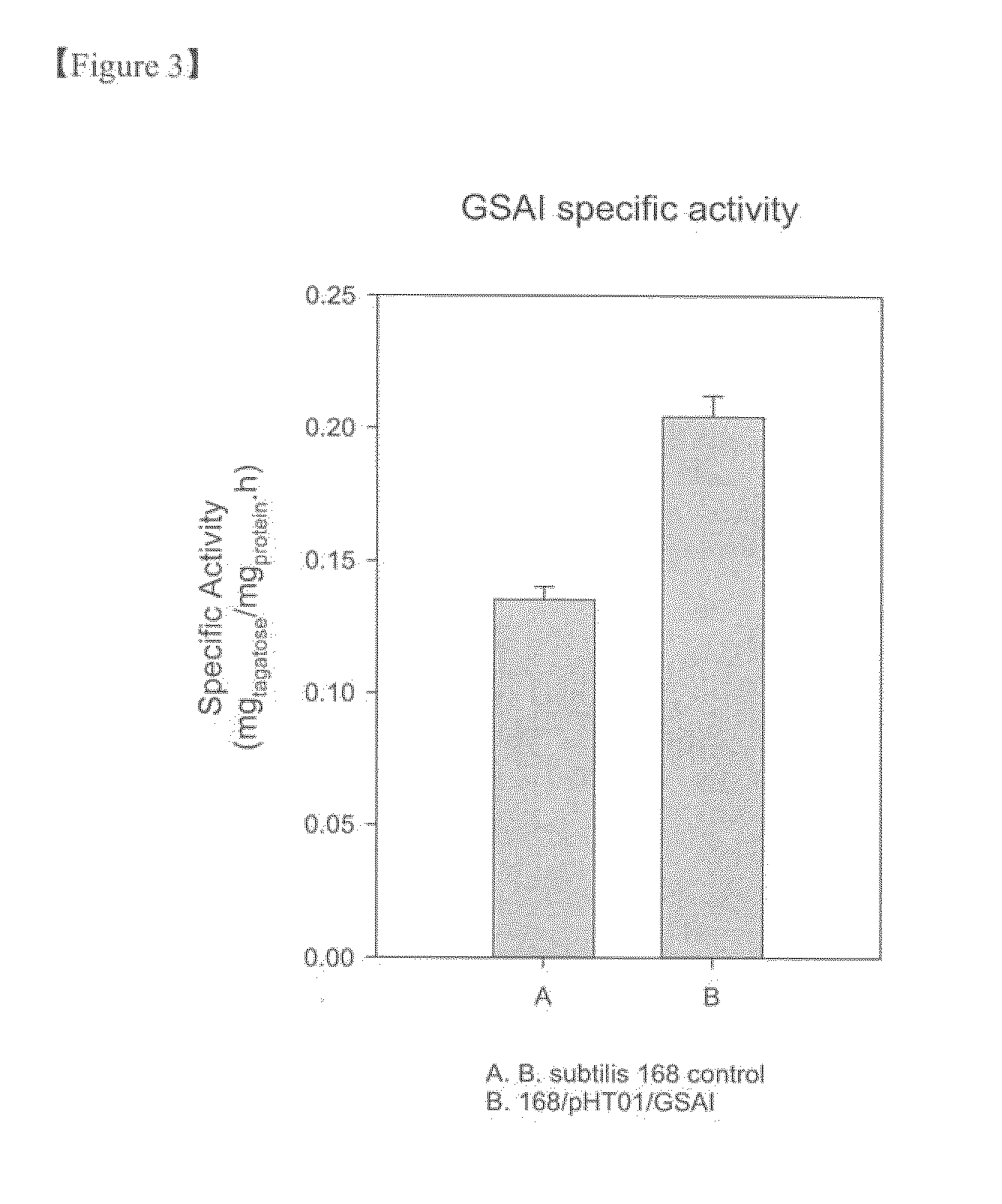
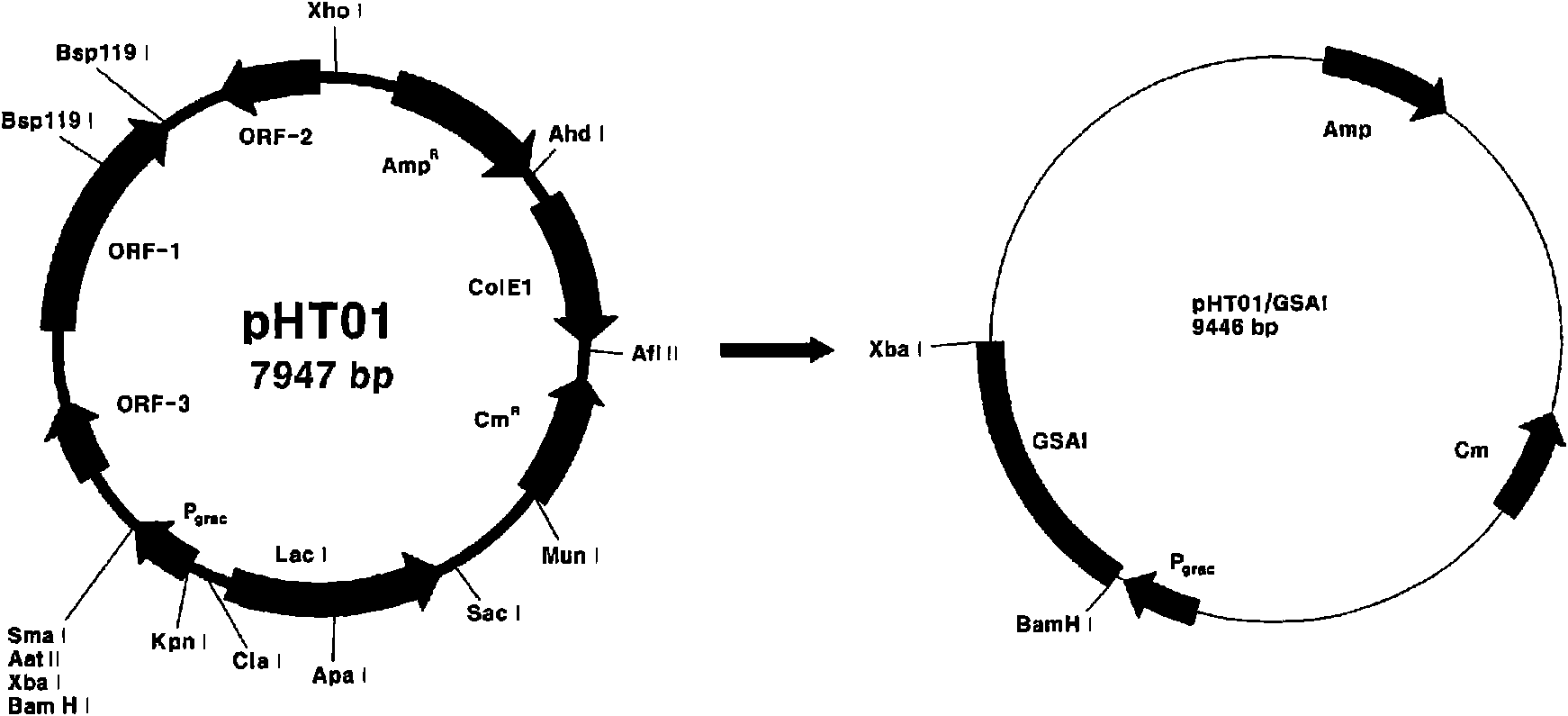
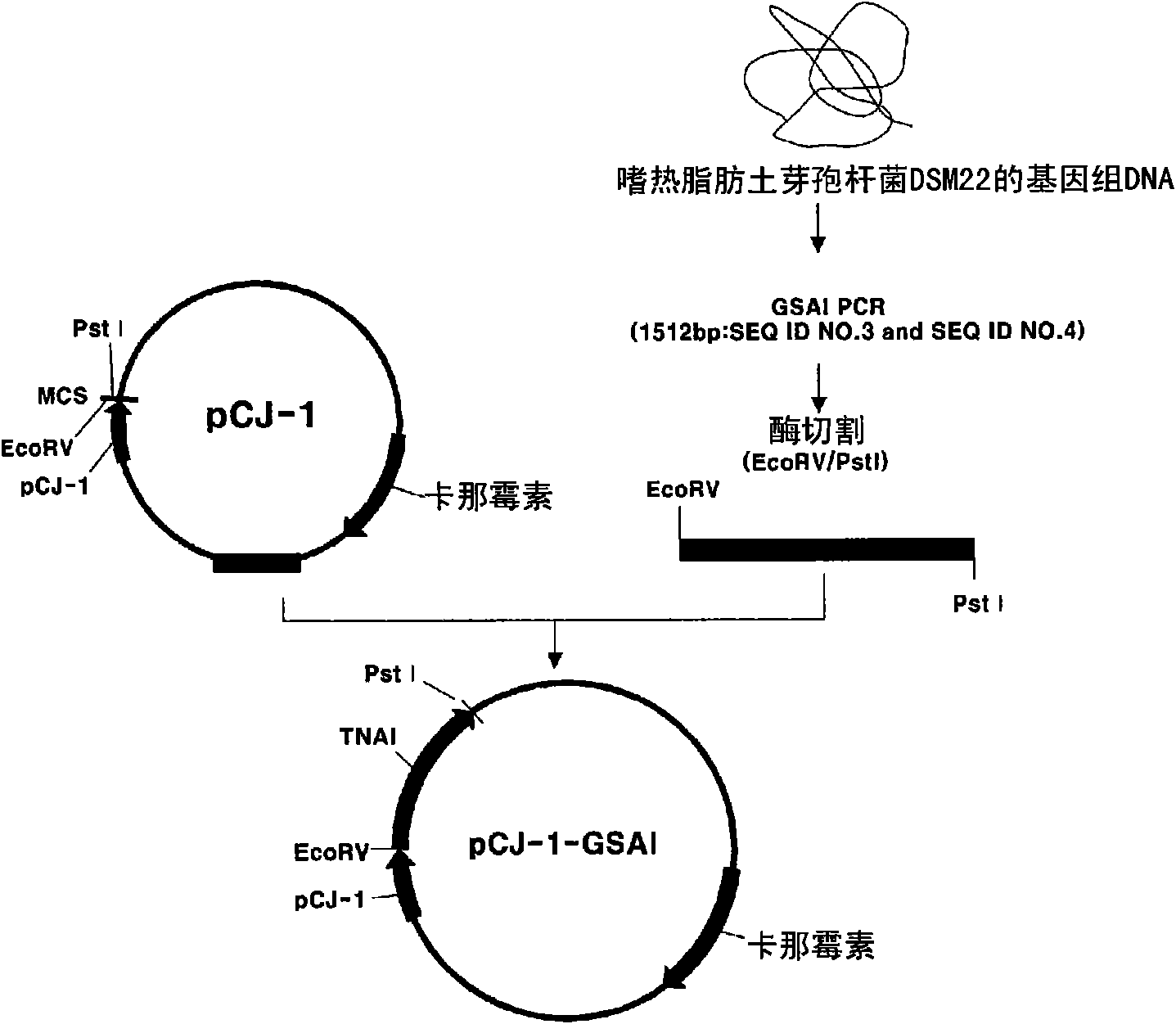
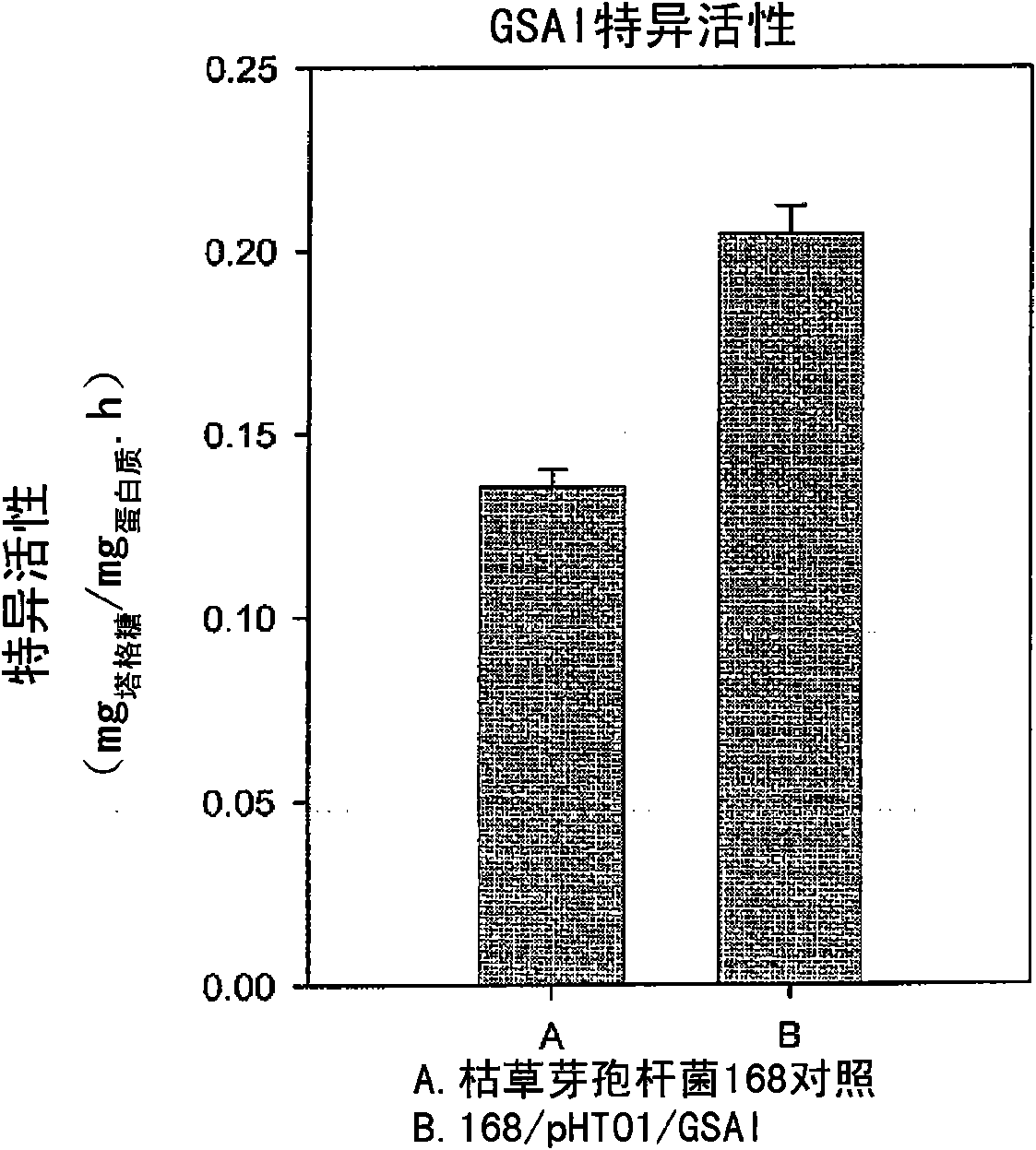
The present invention relates to a recombinant GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) strains expressing thermophilic arabinose isomerase as an active form and method of food grade tagatose by using the same, and more precisely, a gene encoding arabinose isomerase originating from the thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus DSM22 and Geobacillus thermodenitrificans, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a recombinant GRAS strains expressing the thermophilic arabinose isomerase as an active form by transformed with the expression vector, and a method of preparing food grade tagatose from galactose by using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Polypeptides Having L-Arabinose Isomerase Activity Exhibiting Minimum Dependence on Metal Ions for Its Activity and for Thermostability and Nucleic Acids Encoding the Same
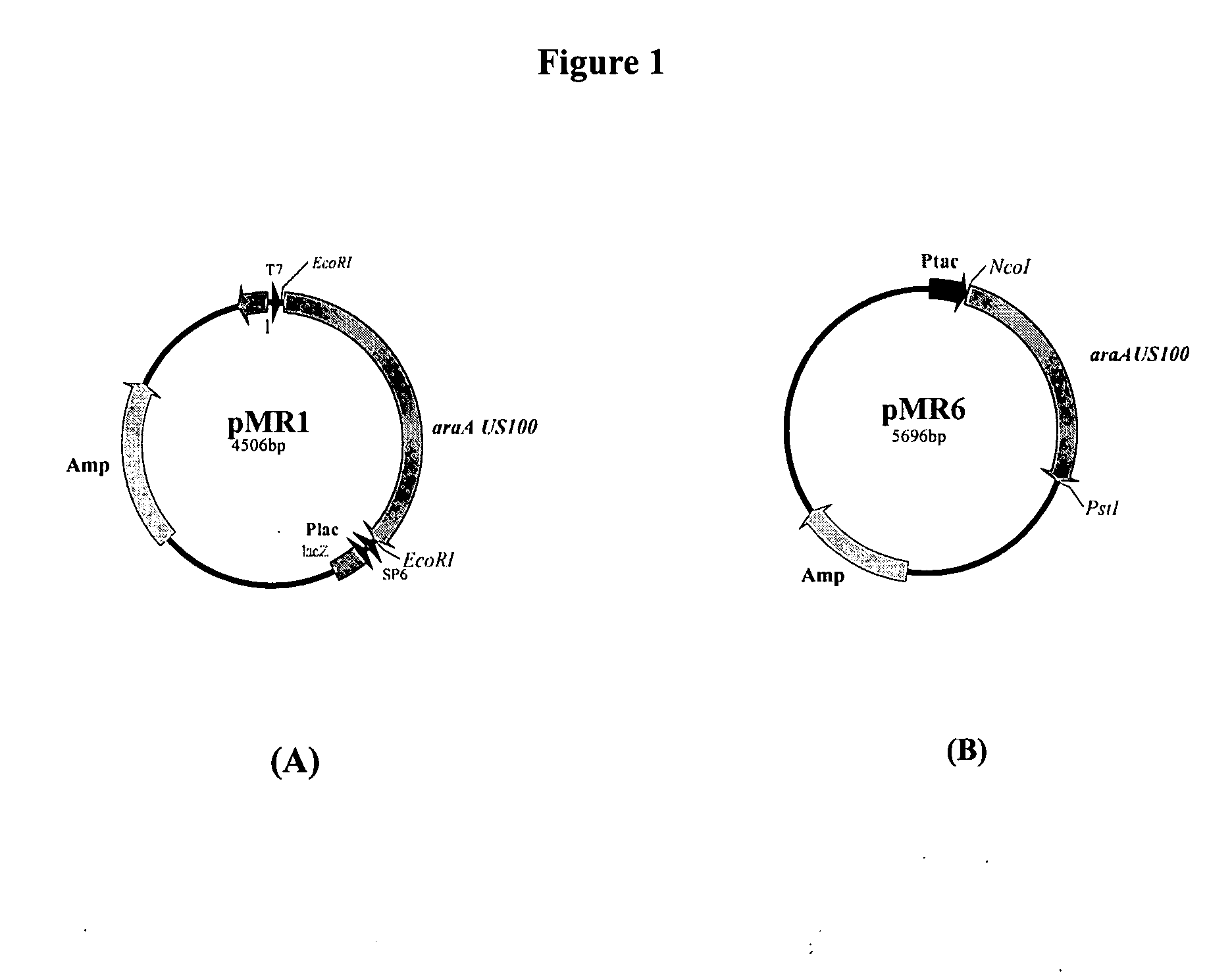
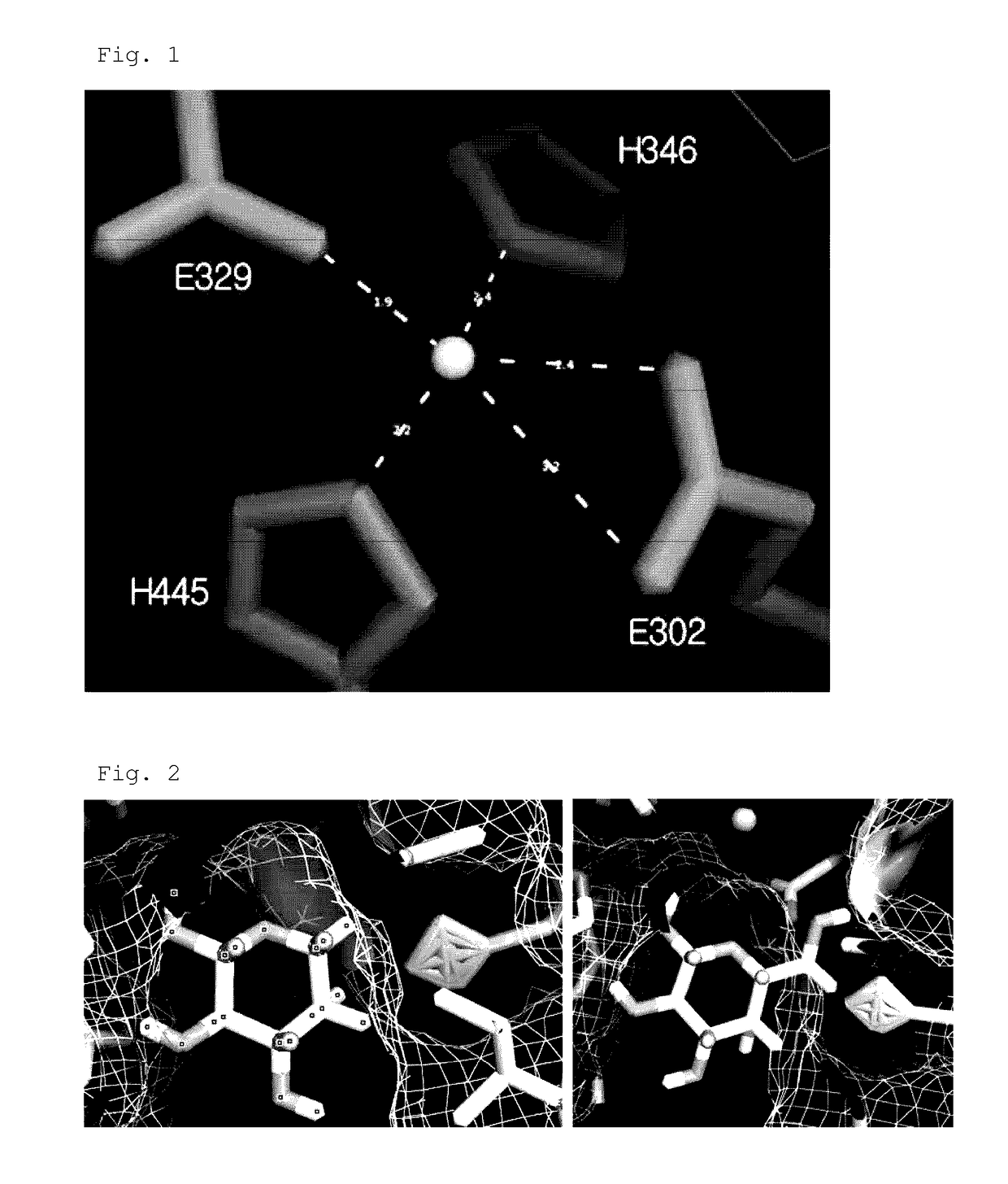
The invention concerns identification of a gene encoding a novel L-arabinose isomerase of the Bacillus stearothernivphilus strain US 100 (L-AI US 100), a L-arabinose isomerase expressed from said gene, recombinant vectors harbouring said gene, microorganisms transformed with said vector, a protocol for preparing and purifying said recombinant protein, biochemical and kinetic characterization of said recombinant enzyme and a method for bioconversion of a D-galactose solution into a solution rich in D-tagatose using said polypeptide. This novel protein has original characteristics, in particular its independence from metal ions for its activity and its low need for such ions for its thermostability, as well as its potential for isomerizing D-galactose into D-tagatose with great efficacy of about 48% after 7 hours at 70° C.
Owner:CENT DE BIOTECH DE SFAX - CBS
Gene engineering bacterium for coexpressing L-arabinose isomerase gene and mannitose-6-phosphoric acid isomerase
ActiveCN103555646AIncrease enzyme activityShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotidePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterium for coexpressing L-arabinose isomerase gene and mannitose-6-phosphoric acid isomerase. The strain comprises nucleotide sequences disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. The gene engineering bacterium can be used for producing L-ribose by catalyzing L-arabinose, and has the advantages of one-step conversion, simple technique and high conversion rate; by using the gene engineering bacterium, the conversion rate of L-ribose is up to 25-50%; and thus, the gene engineering bacterium has favorable industrialization prospects.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Biological tagatose production by recombinant Escherichia coli
This invention relates to a recombinant Escherichia coli and a process for producing D-tagatose. In detail, it includes the construction of recombinant E.coli harboring L-arabinose isomerase, whole-cell conversion of D-galactose into D-tagatose by recombinant E.coli expressing L-arabinose isomerase, enzymatic production of D-tagatose by the extract of recombinant E.coli expressing L-arabinose isomerase, and bioconversion by immobilized L-arabinose isomerase.
Owner:TONGYANG CONFECTIONER
Recombinant L-arabinose isomerase as well as gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103045575AEase of industrial productionSimple methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus subtilisArabinose isomerase
The invention discloses a recombinant L-arabinose isomerase (L-AI) as well as a gene and preparation method thereof and a method for preparing D-tagatose by utilizing the L-AI. Especially bacillus subtilis is used for expressing L-arabinose isomerase, the recombinant L-arabinose isomerase with biological activity is obtained, and the L-AI is more beneficial to industrial production of D-tagatose. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of simplicity, high efficiency and short cycle.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
L-AI (L-arabinose isomerase) and application thereof
ActiveCN106480006ANotable featuresRemarkable effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
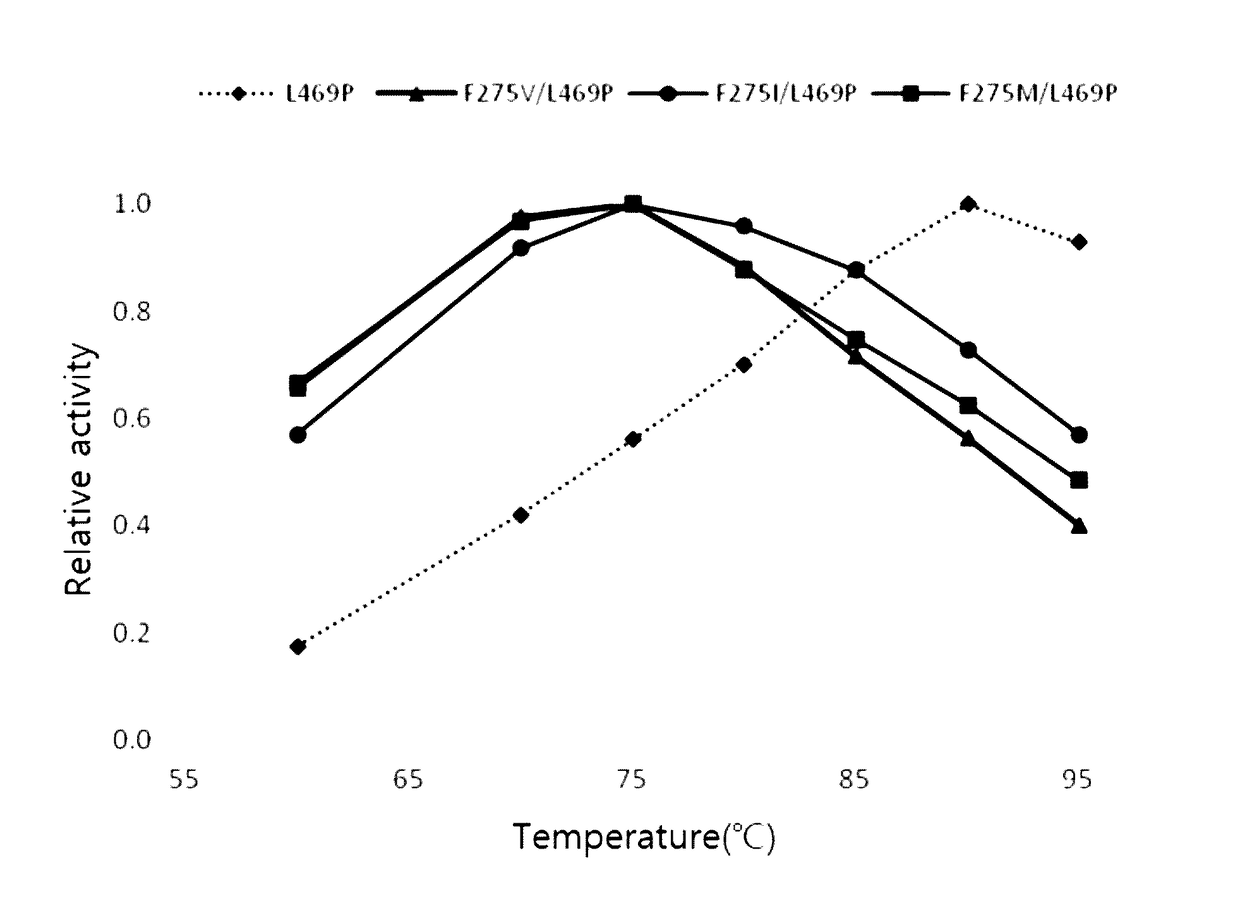
The invention discloses L-AI (L-arabinose isomerase). The L-AI is prepared through the step as follows: 279th phenylalanine of L-AI of Bacillus coagulans NL01 is mutated into isoleucine, and the L-AI is obtained, wherein the GenBank registration number of a nucleotide sequence of an L-AI gene araA is KX356659. The invention further discloses escherichia coli containing the L-AI as well as a construction method and an application of the escherichia coli. According to the constructed recombinant escherichia coli, F279I expressed by the escherichia coli has high catalytic efficiency on D-galactose. The optimal reaction temperature of a whole-cell catalysis reaction system is mild, a browning reaction can be avoided, and the L-AI better facilitates industrial production of D-tagatose when compared with wild type L-AI and other common L-AI from thermophilic bacteria and thermoacidophiles. Meanwhile, the whole-cell catalysis reaction system adopts simple components and has greater industrial production and application potential and economic value.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for preparing D-tagatose by enzyme process
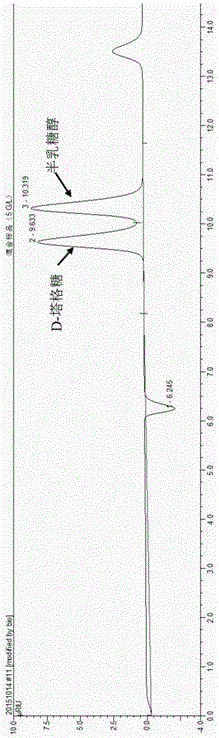
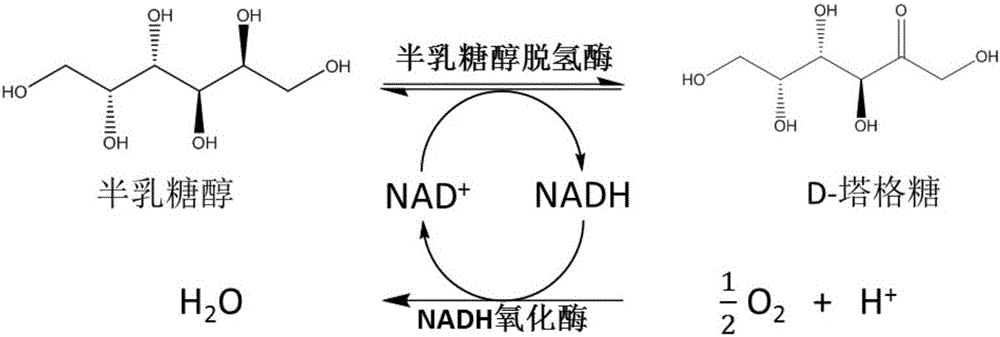
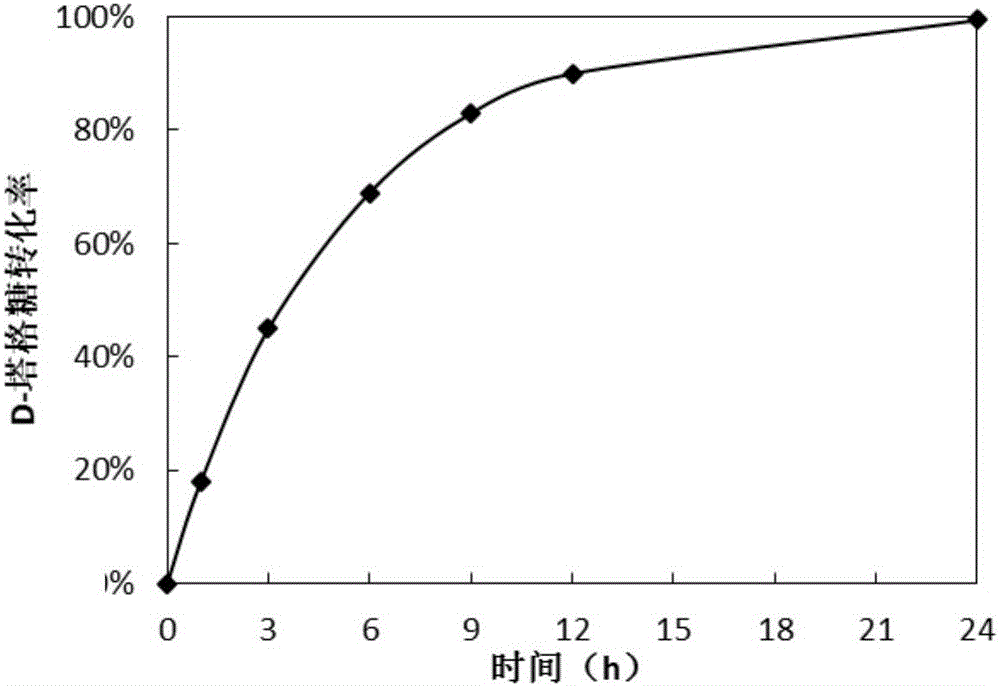
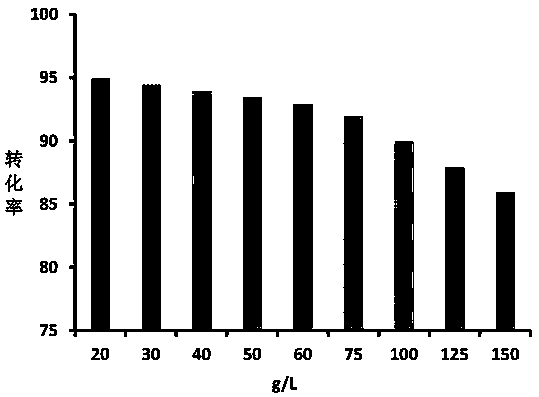
ActiveCN105734092AReduced downstream operationsReduce manufacturing costNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesHydrogenArabinose isomerase
The invention discloses a method for preparing D-tagatose by an enzyme process. The method comprises the following steps: 1) separately establishing engineering bacteria containing galactitol dehydrogenase gene and engineering bacteria containing NADH oxidase gene or establishing coexpression engineering bacteria containing galactitol dehydrogenase gene and NADH oxidase gene; 2) fermenting the established engineering bacteria to obtain a whole cell containing galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase; and 3) with the whole cell containing galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase or the free enzyme of galactitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase as a catalyst, catalyzing the galactitol by taking NAD+ as a hydrogen acceptor in a weakly alkaline condition to obtain D-tagatose. Compared with traditional production method depending on L-arabinose isomerase, in the invention, the substrate conversion rate is high (>99.0%) and the product is easy to separate; and moreover, the co-product of a coenzyme circulation system adopted in the method is water which does not influence the separation and purification of the principal product.
Owner:江苏中酶生物科技有限公司
A method for biosynthesizing d-tagatose with immobilized enzyme catalyst
ActiveCN107937454BHigh activityImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyTagatose
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and specifically relates to a method for biosynthesis of D-tagatose by an immobilized enzyme catalyst. The method for biosynthesis of theD-tagatose by the immobilized enzyme catalyst is as follows: first, recombinant Bacillus subtilis is prepared, and an L-arabinose isomerase immobilized enzyme catalyst is constructed; and recombinantBacillus subtilis spores are added to a D-galactose reaction solution for transformation by oscillation under certain conditions to obtain the D-tagatose. The novel food-safe immobilized enzyme catalyst is constructed, the biotransformation process for biosynthesis of the D-tagatose by the immobilized enzyme catalyst is optimized, the transformation rate is improved, the specific activity of theimmobilized enzyme catalyst is as high as 2.10* 10<-9> U / spore, and the transformation rate of the D-tagatose reaches 95%. A new green, safe, high-efficiency and economical D-tagatose synthesis technology and method are developed, the high-efficiency production of the food-grade D-tagatose is realized, and the method has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:镇江百泰生物科技有限公司
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TALl (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Novel bacillus arabinose isomerase gene cloning and expression method and use
The invention relates to an L-arabinose isomerase gene L-AI separated from Bacillus sp. SYBC hb4 and its cloning and expression method and use, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises separating L-AI from Bacillus sp. SYBC hb4, constructing an expression vector pCold II-ai, and transferring the expression vector pCold II-ai into an escherichia coli expression strain BL21(DE3) so that high-efficiency expression is realized. The recombinase arabinose isomerase can utilize lactose produced by industrial production under the action of lactase to refine waste water and produce D-tagatose. The D-tagatose is a novel low-energy sweetener and can reduce obesity. The D-tagatose has effects of reducing blood sugar, is suitable for diabetic patients, can improve intestinal tract flora and can inhibit intestinal tract pathogenic bacteria. D-tagatose has a great application prospect in fields of medicines and industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway and production method of xylitol using the same
ActiveUS8343736B2Easy to useImprove productivityMicroorganismsRecombinant DNA-technology[Candida] apicolaArabitol
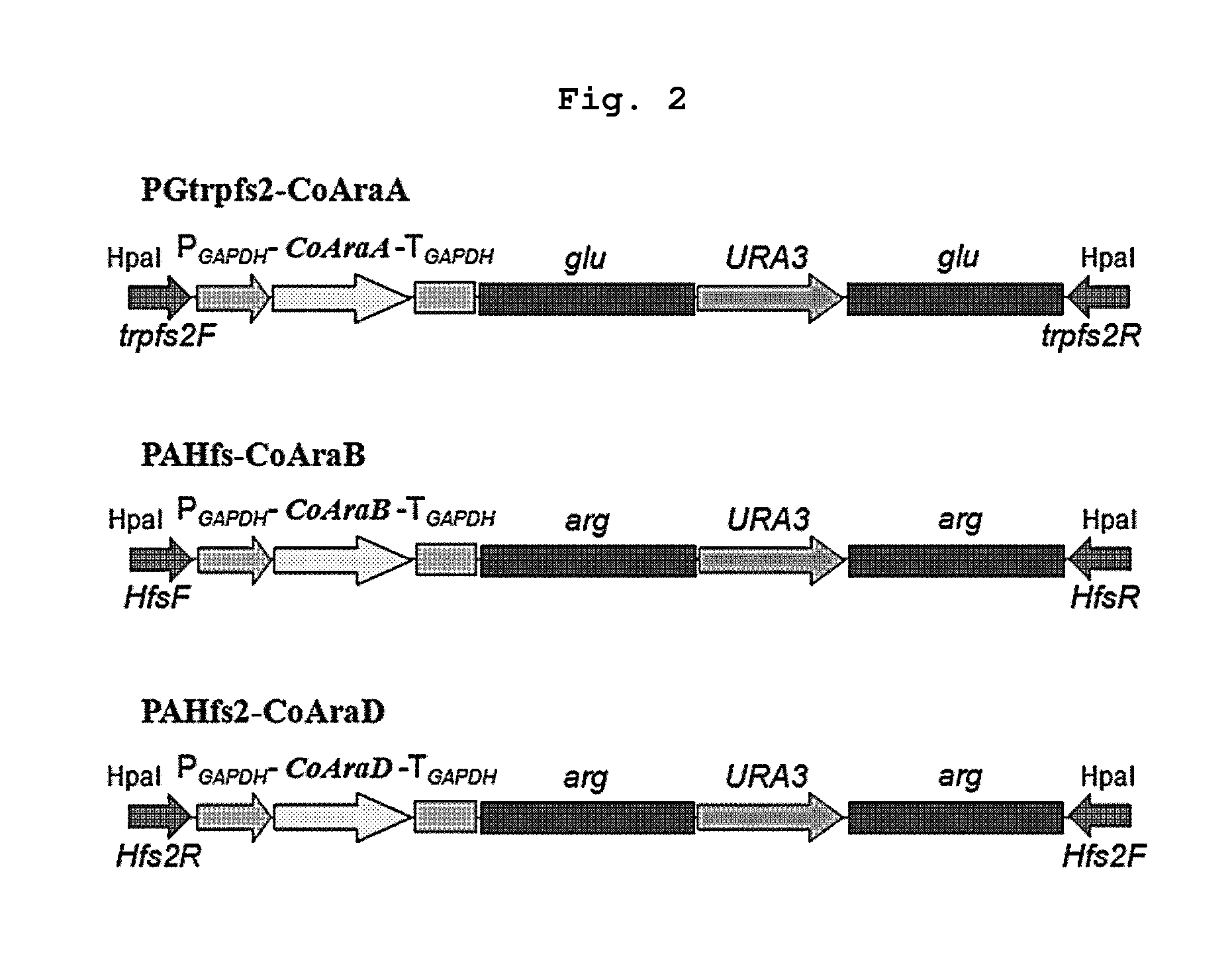
The present invention relates to an efficient production method of xylitol by using the xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway to inhibit the production of arabitol, the byproduct, and instead to use arabinose only for cell metabolism in xylose / arabinose mixed medium. More precisely, to express efficiently L-arabinose isomerase (araA), L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Candida tropicalis, codon optimization was performed. Then, each gene was inserted in the gene expression cassette containing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and the selection marker URA3, which was introduced into Candida sp. microorganism. As a result, arabitol, the byproduct interrupting the purification and crystallization of xylitol could be inhibited, making the production method of xylitol of the present invention more efficient. The xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway of the present invention can be effectively used for the production of xylitol with high productivity by inhibiting the generation of arabitol.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
L-arabinose isomerase variants with improved conversion activity and method for production of D-tagatose using them
The present invention relates to the development of an L-arabinose isomerase variant from Thermotoga neapolitana DSM 5068, which is a kind of thermophile, on the basis of protein molecular modeling. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method of producing D-tagatose from D-galactose by using the enzyme or a microorganism of the genus Corynebacterium expressing the enzyme.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for biosynthesis of D-tagatose by immobilized enzyme catalyst
ActiveCN107937454AHigh specific vitalityHigh activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesDrug biotransformationBacillus subtilis
Owner:镇江百泰生物科技有限公司
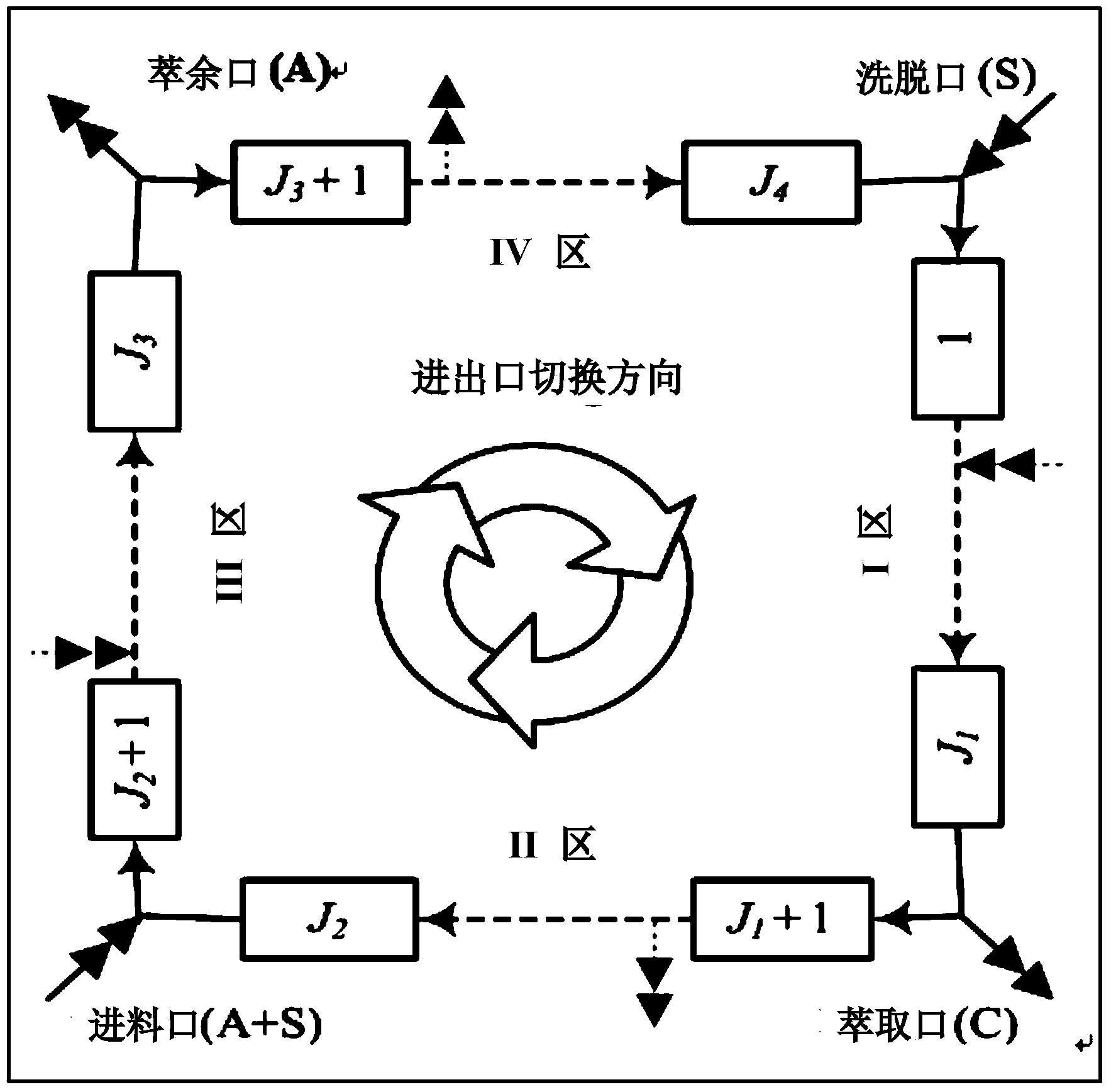
D-tagatose production method based on enzymatic isomerization reaction and continuous chromatographic separation in-situ coupling
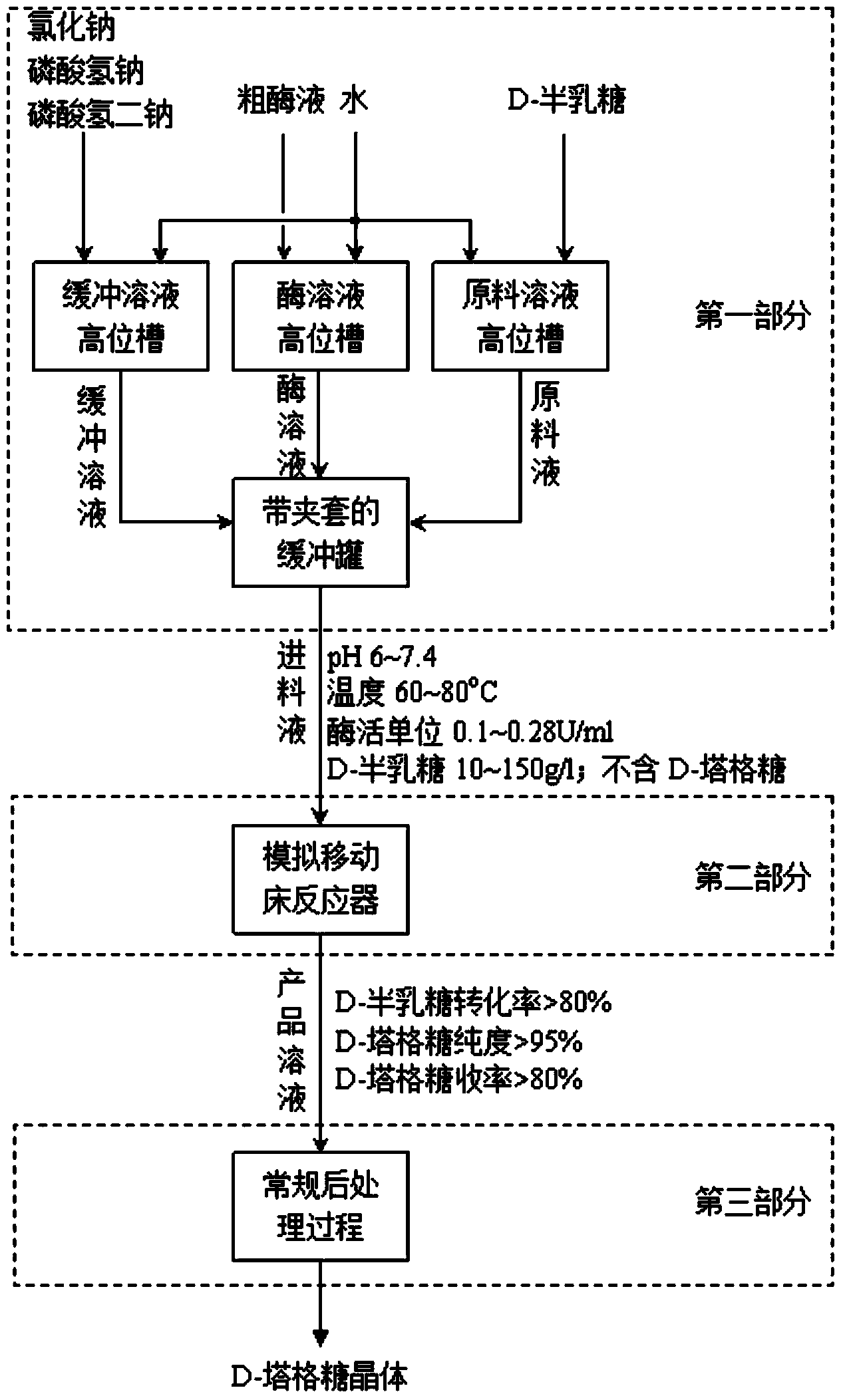
ActiveCN103923959AOvercoming Feedback InhibitionOvercoming Reversible Reaction Chemical Equilibrium LimitationsSugar derivativesFermentationChemical industryChromatographic separation
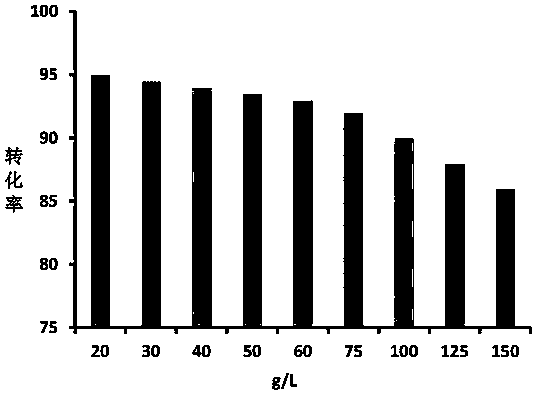
The invention belongs to the field of biology and chemical industry, and particularly discloses a method for continuously producing D-tagatose by adopting D-galactose as a raw material on the basis of enzymatic isomerization reaction and a continuous chromatographic separation in-situ coupling technology. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a buffering solution; adequately dissolving the thermophilic L-arabinose isomerase in the water to obtain an enzyme solution; adequately dissolving D-galactose in the water to obtain a raw material solution; mixing and preheating the raw material solution, the buffering solution and the enzyme solution to obtain a feeding solution of a simulated moving bed reactor (SMBR); and placing the feeding solution into the SMBR to obtain a D-tagatose product solution through the in-situ reaction and separation. By determining the appropriate operating condition of the SMBR, the conversion rate of the D-galactose reaches more than 80 percent, the purity of the D-tagatose reaches more than 95 percent, and the yield is more than 80 percent. The method is low in cost, less in pollution and high in conversion rate; moreover, continuity in production can be realized, the consistency of the product quality can be guaranteed, and the commercialized application prospect is good.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
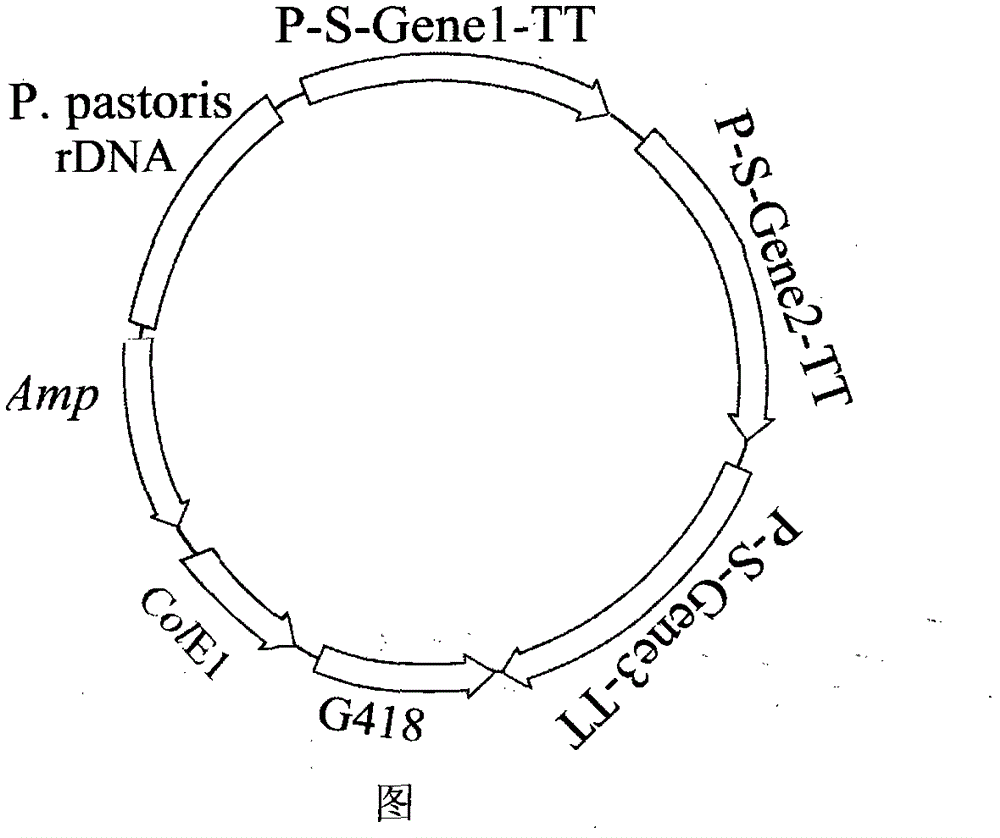
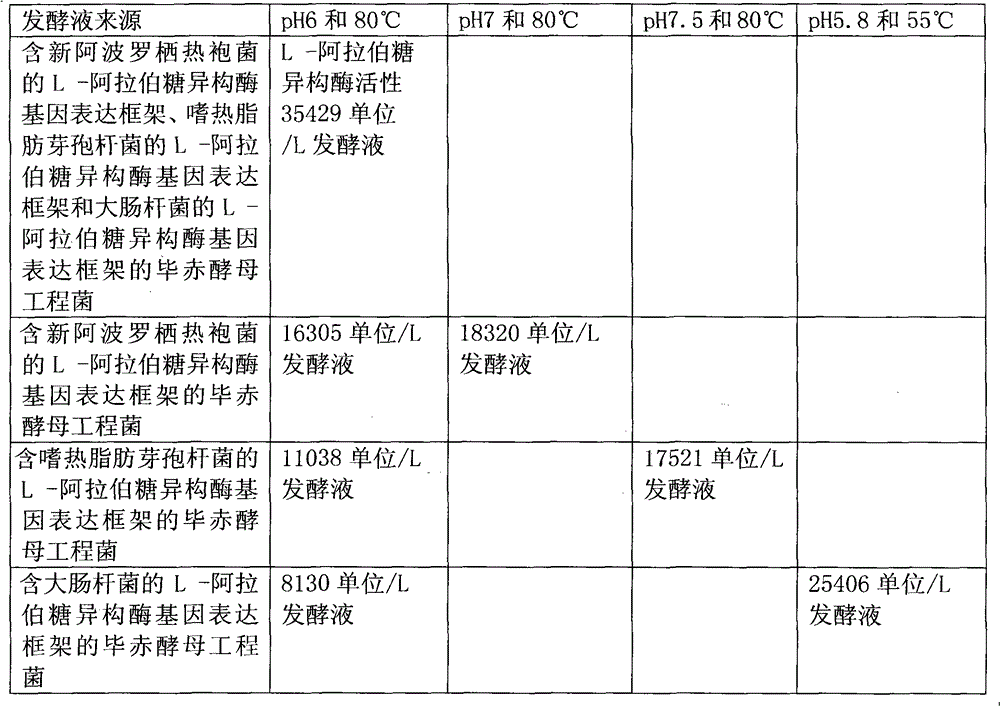
Method for producing recombinant mixed L-arabinose isomerase
The invention discloses a method for producing recombinant mixed L-arabinose isomerase and belongs to the field of biological technology. The method comprises the steps of: first, cloning L-arabinose isomerase genes of bacillus stearothermophilus, thermotoga neapolitana and escherichia coli; constructing a pichia pastoris expression vector containing expression frameworks of the three L-arabinose isomerase genes and converting the vector into pichia pastoris to obtain engineering bacteria; and fermenting the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria to produce the recombinant mixed L-arabinose isomerase. The recombinant mixed enzyme has much higher enzymatic activity than a single enzyme with pichia pastoris as an expression vector, and has high enzymatic activity for isomerizing D-galactose into D-tagatose at a pH of 6.0 and at a temperature of 80 DEG C, which meet the production condition of isomerizing D-galactose into D-tagatose. The method provided by the invention is conducive to the solution of the problem that development of the industry of producing D-tagatose by an enzymic method is constrained as there is no L-arabinose isomerase that meets the requirements of an optimum pH of 5.0-6.0 and an optimum temperature of above 45 DEG C to produce bacterial strains, and thus helps promote the industry of producing D-tagatose by an enzymic method.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for efficiently introducing L-arabinose isomerase
InactiveCN102888389AQuick foldIncrease active expressionMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesActive enzymeProtein target
The invention discloses a method for efficiently introducing L-arabinose isomerase. According to the method, in the inducible expression process that an L-arabinose isomerase recombinant bacterium constructed by lactose operon plasmid pET-22b(+) expresses a targeted protein, enzyme substrate D-galactose is added, so that the effective folding of the L-arabinose isomerase is promoted, the activity expression of the L-arabinose isomerase is efficiently introduced, and the expression of active enzyme is effectively improved. By the method, the expression and the fermentation enzyme activity of the active L-arabinose isomerase by the L-arabinose isomerase recombinant bacterium constructed by the lactose operon plasmid pET-22b(+) are improved, so that the fermentation production cost of the g L-arabinose isomerase can be greatly reduced; and the obtained product L-arabinose isomerase is novel carbohydrase which can catalyze the D-galactose to be synthesized into high value-added functional rare sugar-D-tagatose, and has wide market prospect.
Owner:J JIANGSU LIANGFENG FOODSTUFF GROUP
Recombinant L-arabinose isomerase LPAI and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN113151235AEfficient expressionPromote accumulationMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesTagatoseIsomerase
The invention provides a recombinant L-arabinose isomerase LPAI and a construction method and application thereof. The recombinant L-arabinose isomerase LPAI is constructed by utilizing a genetic engineering means; and the recombinant L-arabinose isomerase LPAI can be applied to preparation of D-tagatose by taking D-galactose as a substrate, and the problems of low conversion efficiency, high cost and the like in a D-tagatose production process are effectively solved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing functional seasoning syrup through biological fermentation method
InactiveCN108077882APreserve freshnessPrevent moistureFood ingredient as taste affecting agentTagatoseCannabis
The invention belongs to the technical field of sugar making, and particularly relates to a method for preparing functional seasoning syrup through a biological fermentation method. The syrup is prepared from sugarcane juice, brown granulated sugar, brown sugar, galactose, yellow corn steep liquor, fructus cannabis pulp, sucrose mutase, fructosyl transferase, trehalose synthase, arabinose isomerase, flavor yeast and lysozyme; the materials are subjected to grading fermentation, filtration, lysozyme sterilization, concentration and other processes to prepare the seasoning syrup. The functionalseasoning syrup has multiple effects, and the problems that a seasoning sugar product in the market is monotonous in effect and has many side defects are effectively solved. The functional syrup is prepared through biological fermentation method, three prebiotic factors including isomaltitol, fructo-oligosaccharide and tagatose are generated through fermentation, and the product is endowed with the prebiotic functional factors. The biological preservative is used, and is safe and free of health risks; the product also overcomes the defects that after common syrup is used for cooking, dishes are hardened, viscous, likely to change colors and the like.
Owner:NANNING ZONGLIAN TECH
L-arabinose isomerase and application thereof in production of L-ribulose
ActiveCN105483108AIncrease enzyme activityBroad application prospectsBacteriaIsomerasesThermal stabilityGenetically engineered
The invention discloses L-arabinose isomerase and application thereof in production of L-ribulose. The invention further discloses a gene sequence SEQ ID NO:1 for coding the L-arabinose isomerase, a genetically engineered bacterium containing the L-arabinose isomerase and a construction method thereof and application of the L-arabinose isomerase and the genetically engineered bacterium thereof in production of the L-ribulose. The L-arabinose isomerase has higher catalytic efficiency on L-arabinose on the condition that the temperature ranges from 20 DEG C to 70 DEG C and the pH ranges from 5.0 to 10.0, and the activity and the thermal stability of the L-arabinose isomerase can be greatly promoted in the presence of low-concentration irons such as Mn<2+> and Co<2+>. Under the optimal catalytic conditions, by means of the L-arabinose isomerase, the conversion rate of the L-arabinose can reach 95 percent or above, and the L-arabinose isomerase has very important significance and economic value to biological production of the L-ribulose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for regulating and expressing L-arabinose isomerase by using Pichia methanolica pGAP
InactiveCN101831418AReduce manufacturing costEase of mass productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Agarase-3,6-anhydro-l-galactosidase-arabinose isomerase enzyme complex and method for production of tagatose from agar using the same
ActiveUS20210009982A1High production costMaximize production efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPolypeptide with affinity tagTagatoseIsomerase
The present disclosure relates to an enzyme complex of arabinose isomerase, agarase and 3,6-anhydro galactosidase and a method for producing tagatose by degrading agar using the same. By using the enzyme complex according to the present disclosure, agar obtained from marine biomass can be degraded effectively and useful physiologically active substances such as tagatose can be obtained effectively therefrom.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Food grade thermophilic arabinose isomerase expressed from gras, and tagatose manufacturing method by using it
The present invention relates to a thermophilic arabinose isomerase and a method of manufacturing tagatose using the same, and more precisely, a gene encoding arabinose isomerase originating from the thermophile Geobacillus stearothermophilus DSM22, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a method of preparing a food grade thermophilic arabinose isomerase from the recombinant GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) strain transformed with the said expression vector, and a method of preparing tagatose from galactose using the said enzyme.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Galactose to tagatose isomerization at moderate temperatures with high conversion and productivity
PendingUS20210269839A1Improve balance conversionLoss of activityOxidoreductasesIsomerasesTagatoseMicroorganism
Disclosed are components and methods for preparing tagatose from galactose via isomerization reactions using engineered components. The engineered components include microbial cells and methods for preparing microbial cells that have been engineered to catalyze isomerization of galactose to tagatose, in which the microbial cells express cytoplasmically an exogenous L-arabinose isomerase enzyme. The disclosed microbial cells may further be modified for use in methods for preparing tagatose from galactose via isomerization reactions where the microbial cells are treated with reagents that permeabilize the cells. The disclosed methods enable isomerization reactions of galactose to tagatose at relatively high rates, high conversions, and elevated temperatures.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
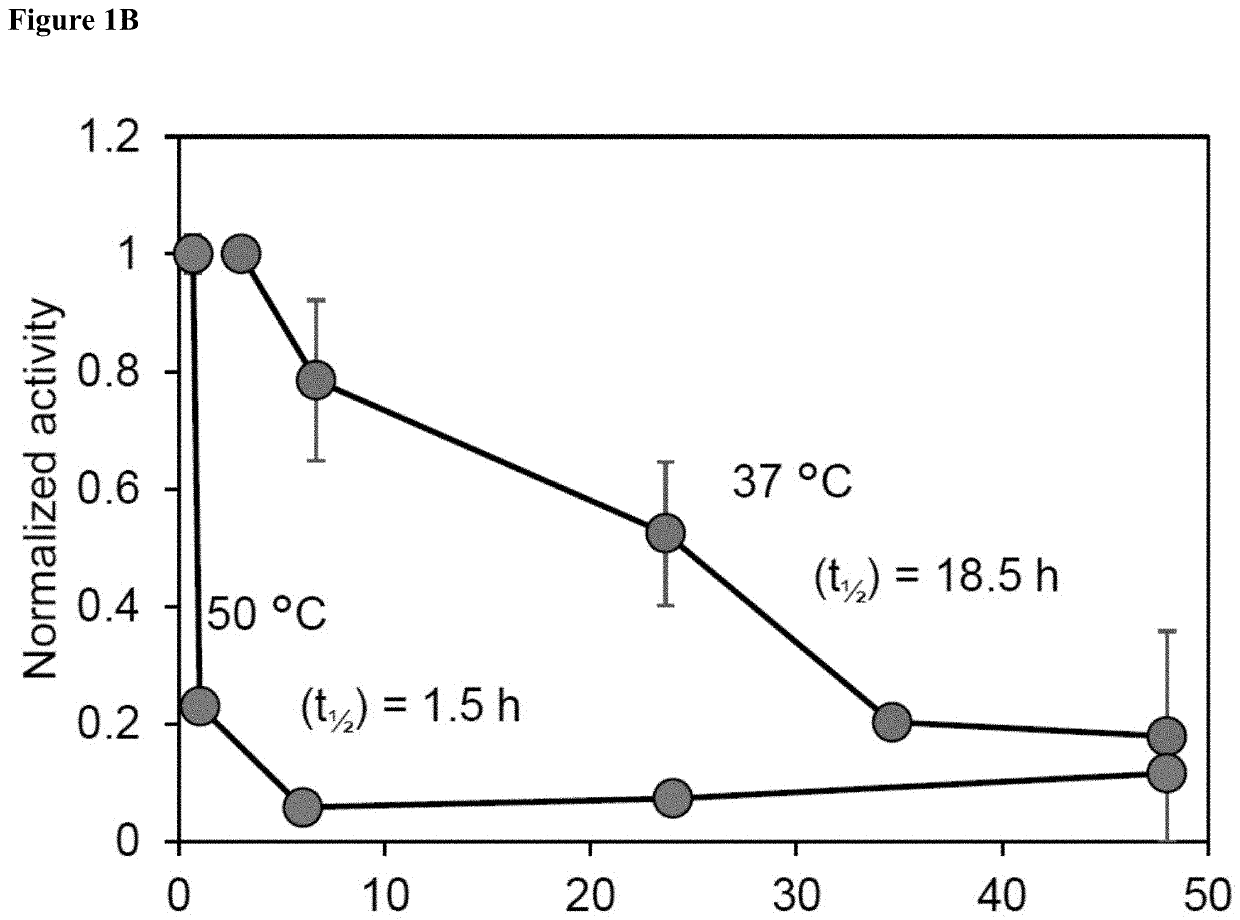
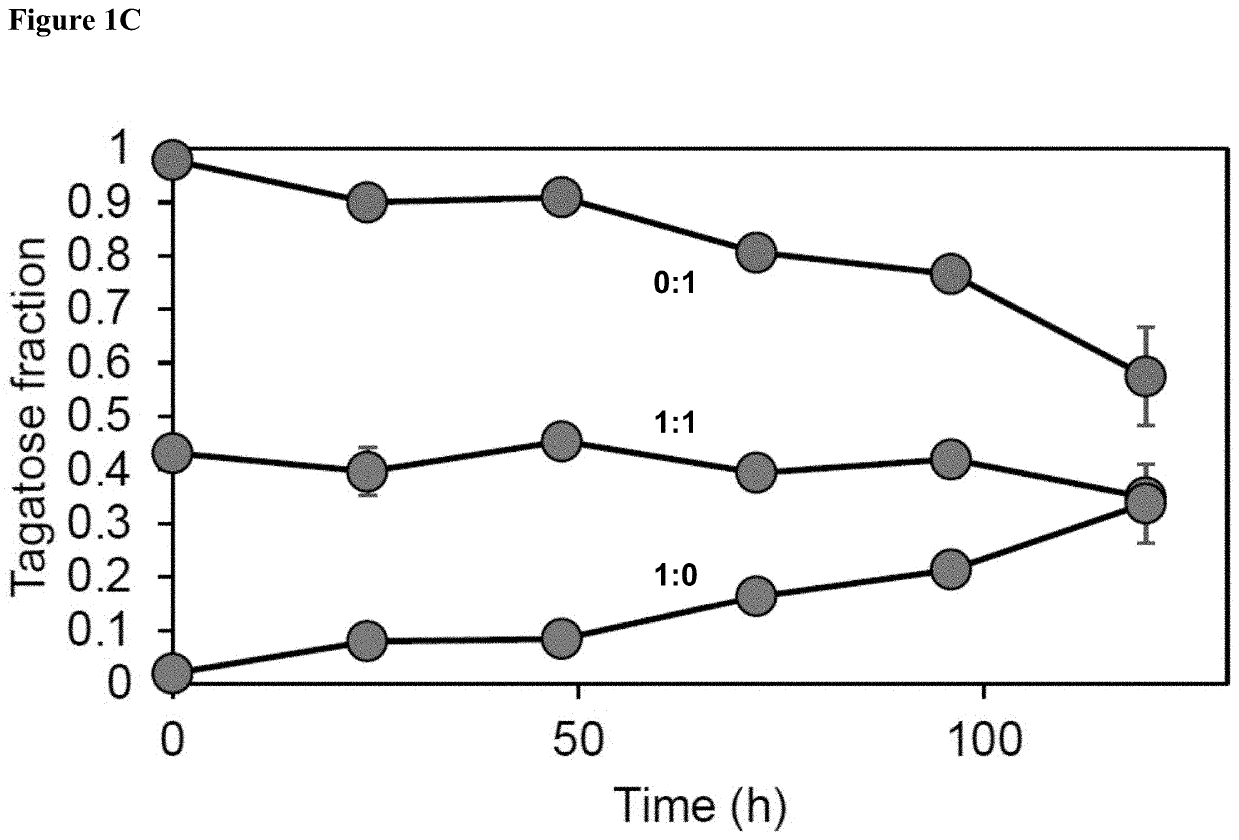
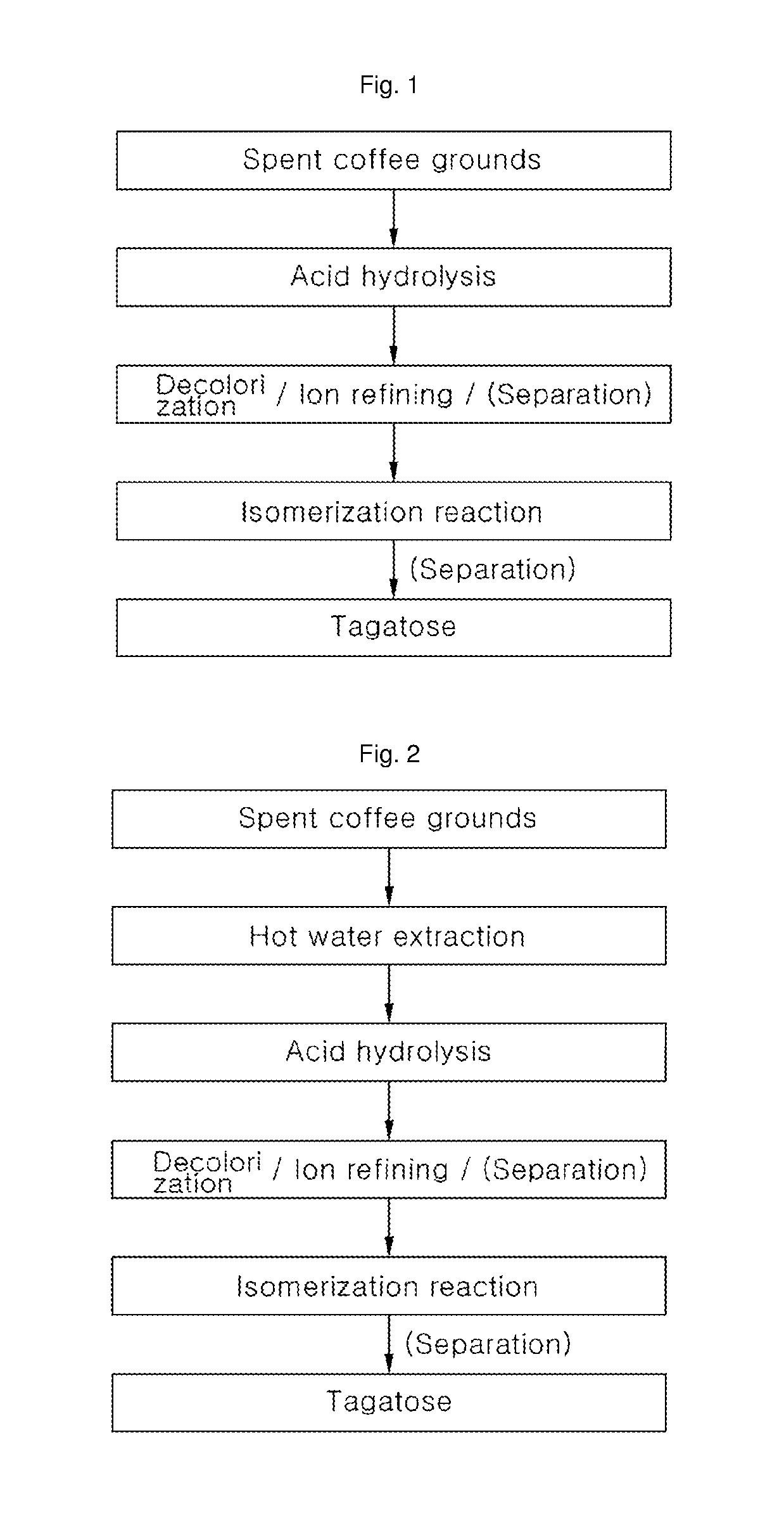
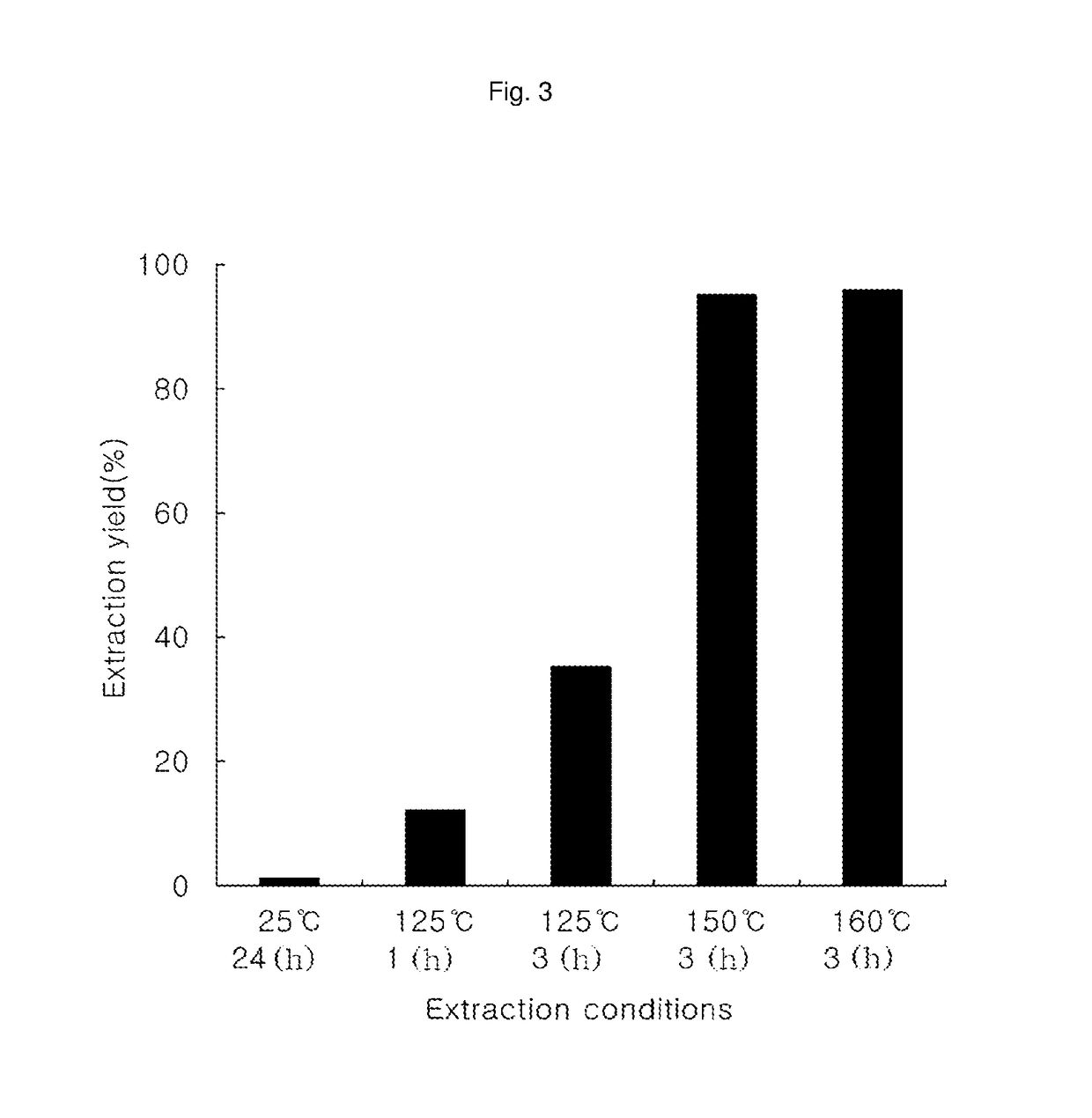
Method for preparing tagatose from residue after extracting coffee
ActiveUS9879296B2Low costAvoid wasting resourcesOxidoreductasesIsomerasesHydrolysateArabinose isomerase
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com