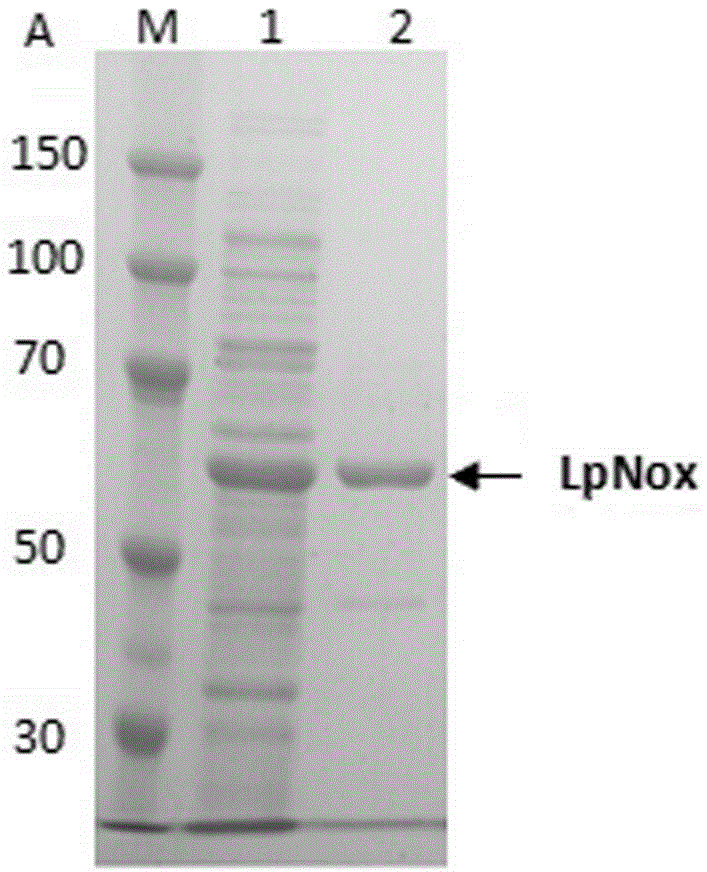
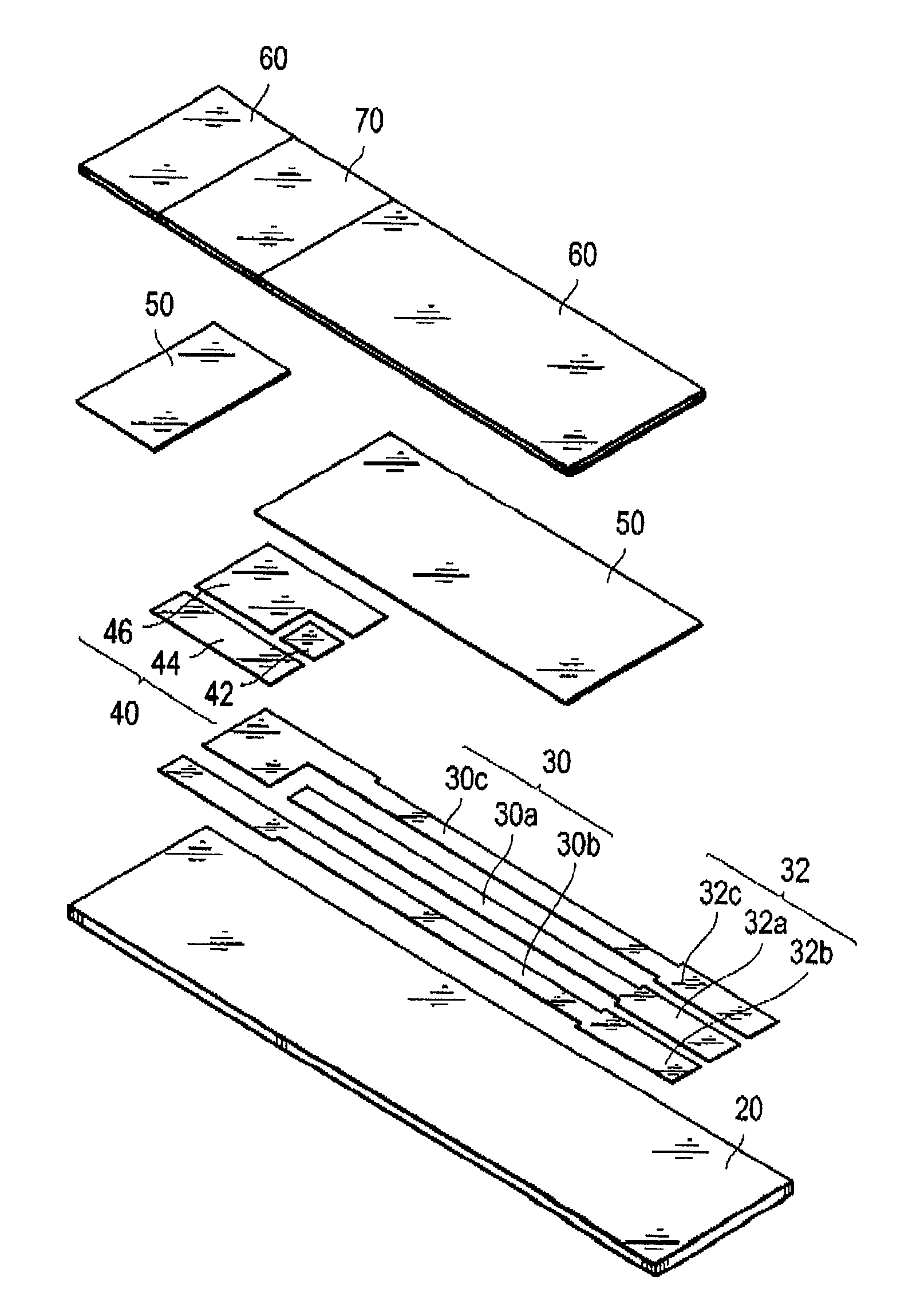
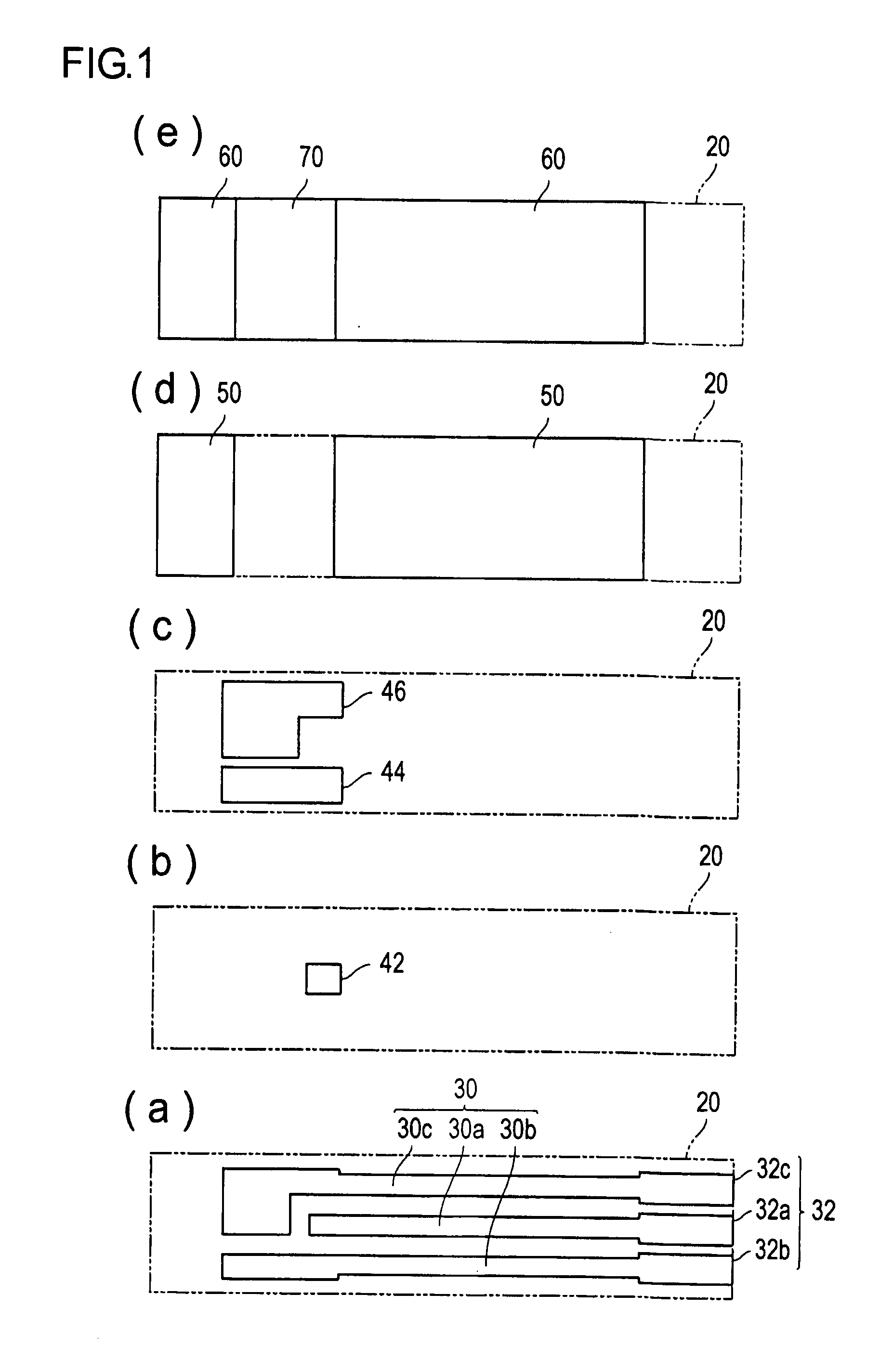
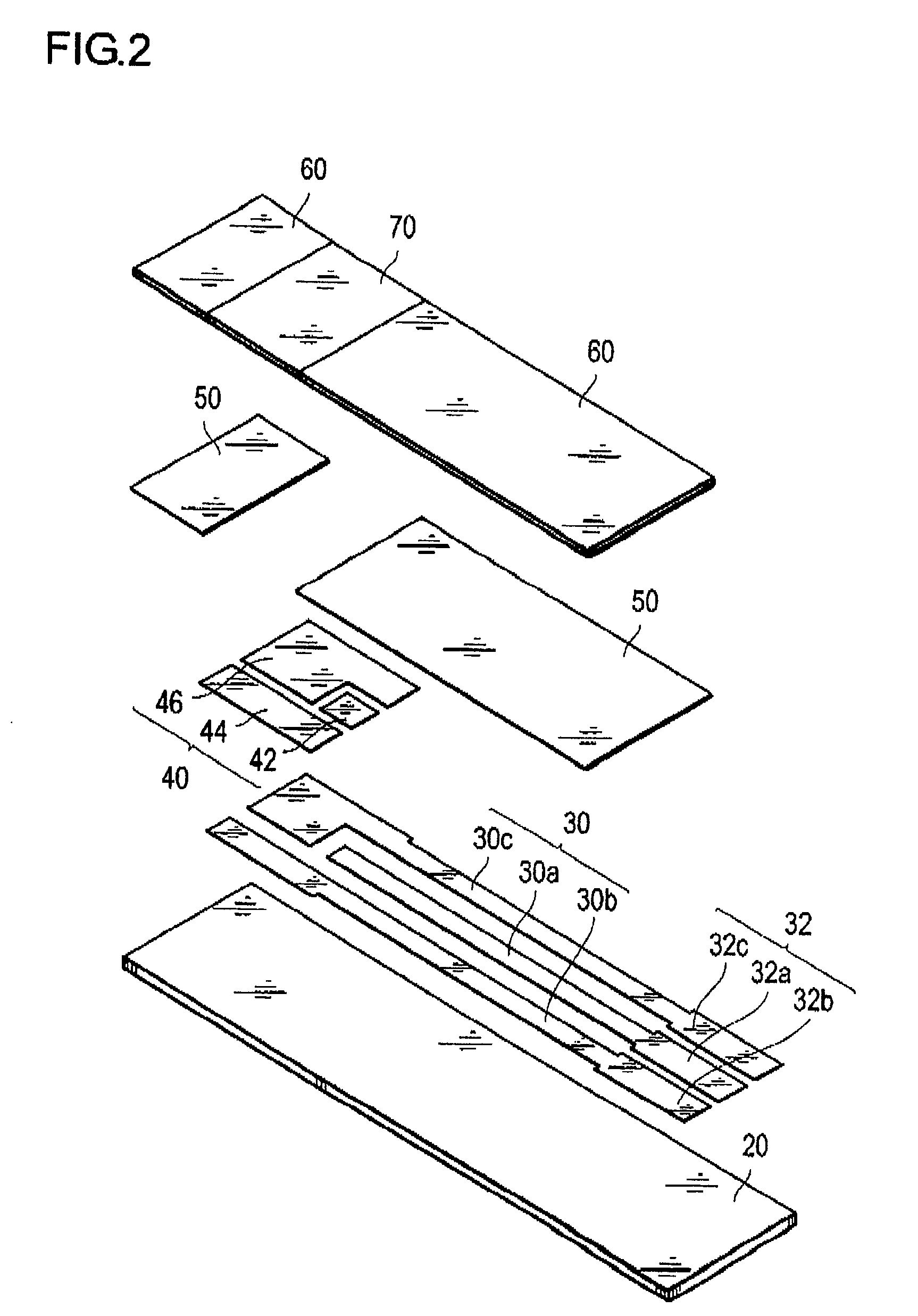
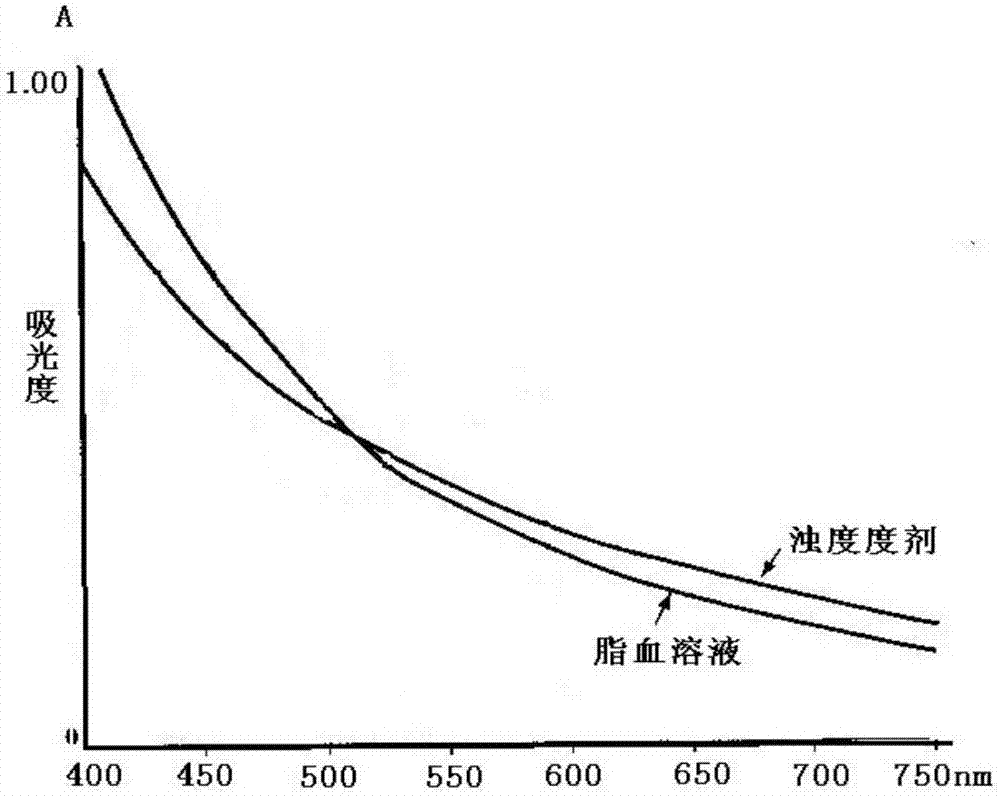
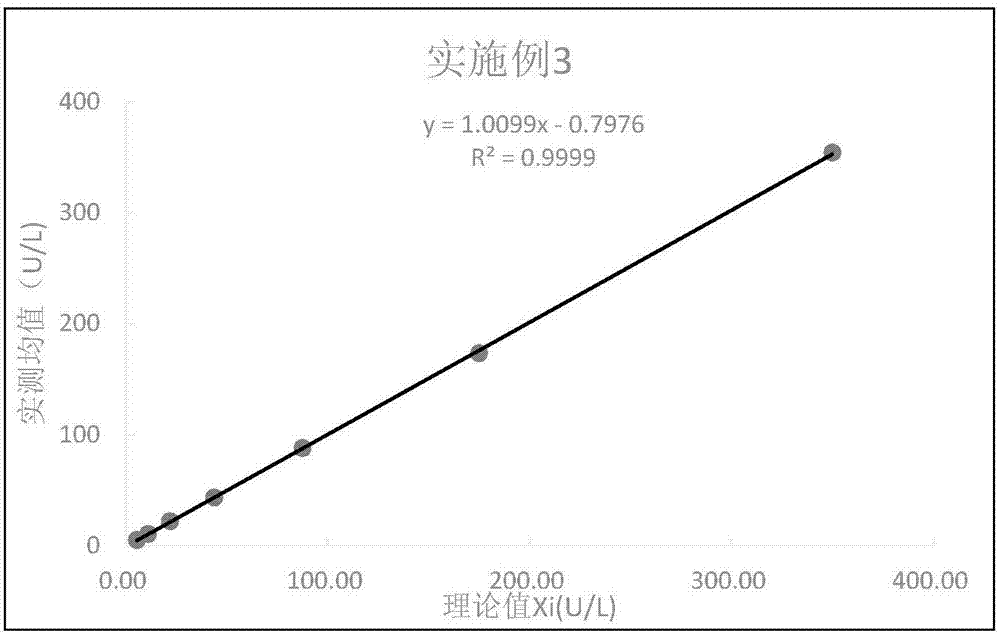
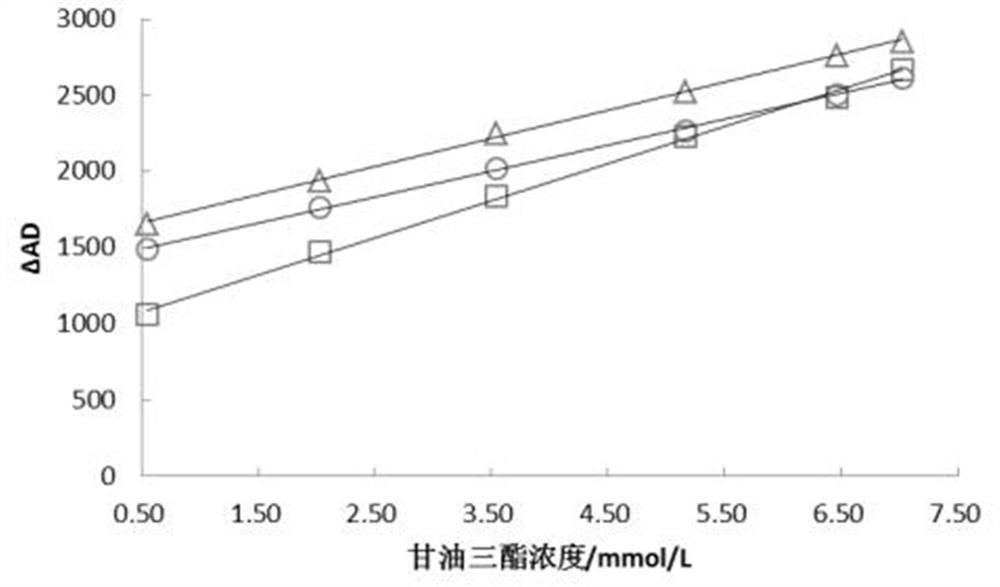
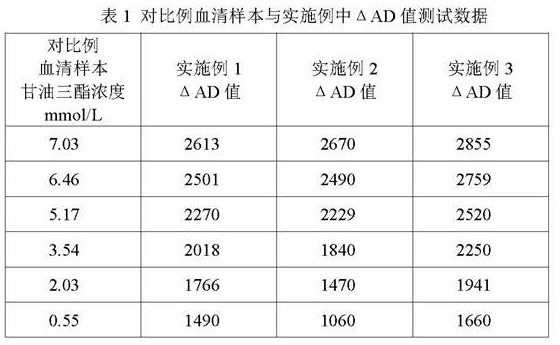
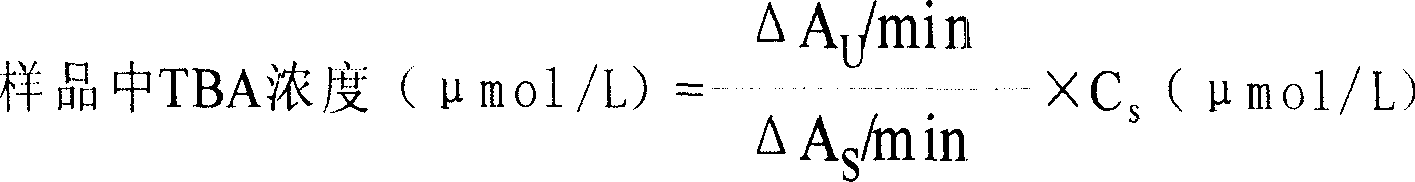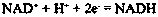Patents
Literature
52 results about "Glycerol dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
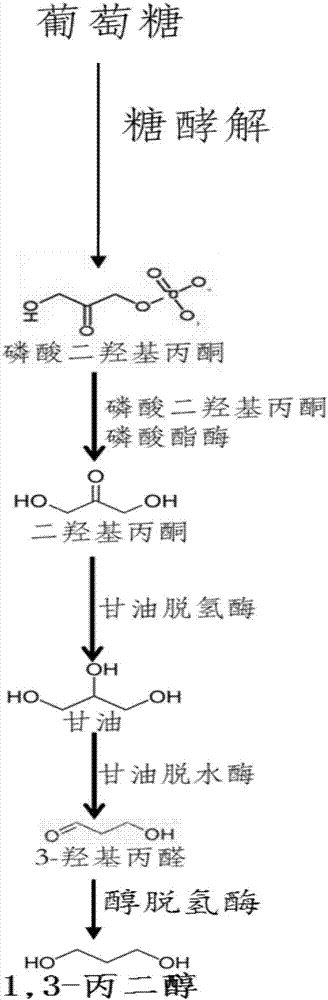
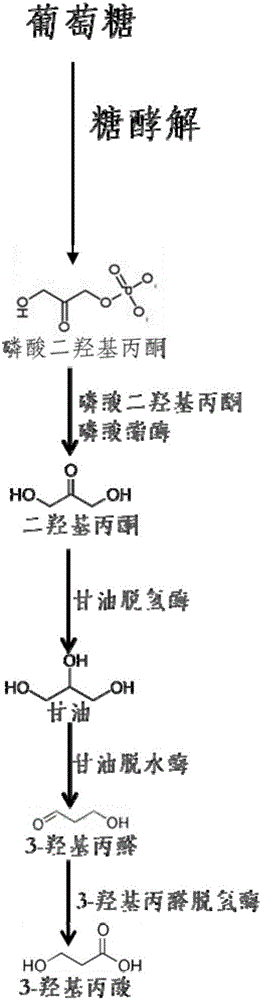
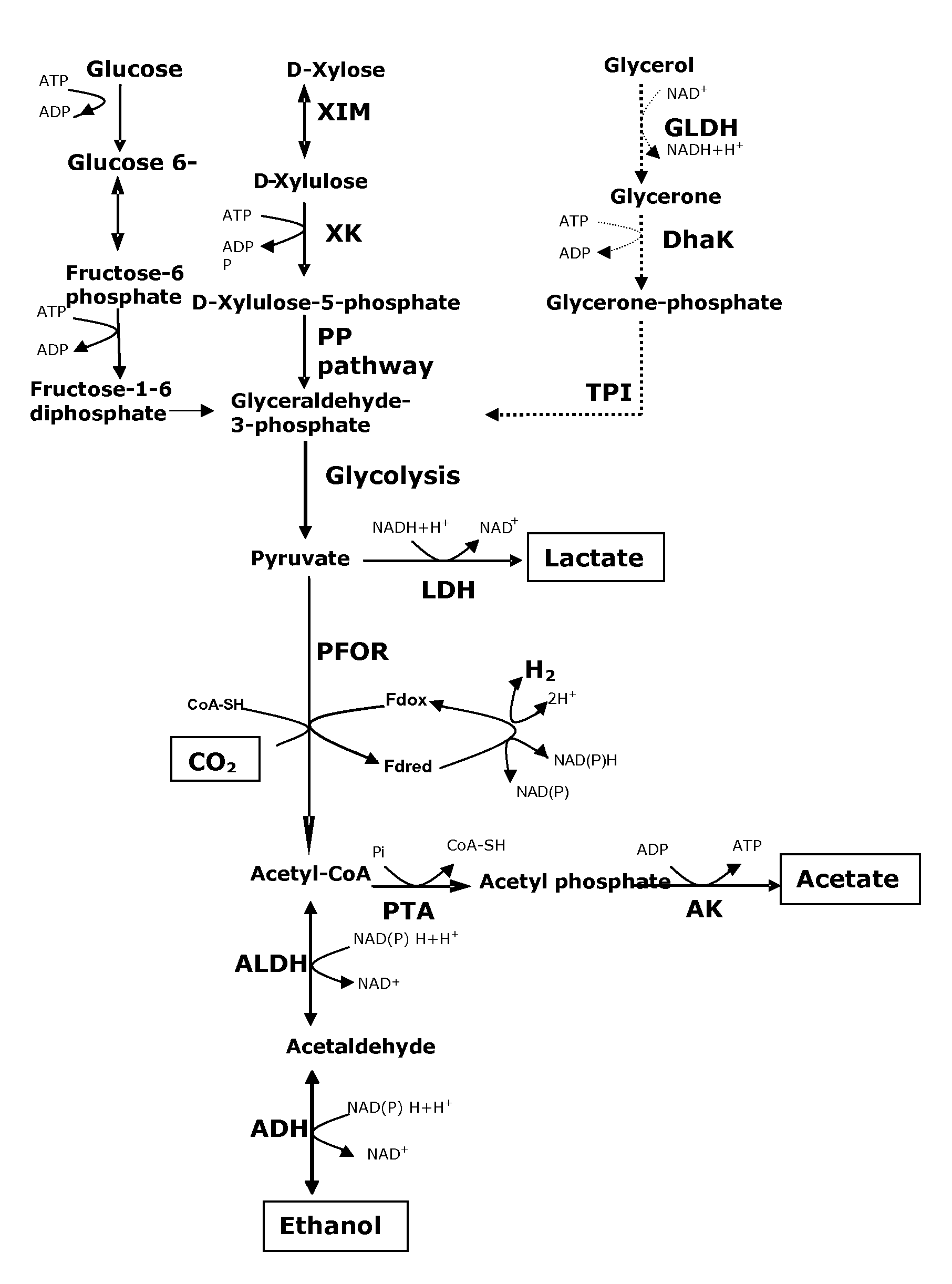
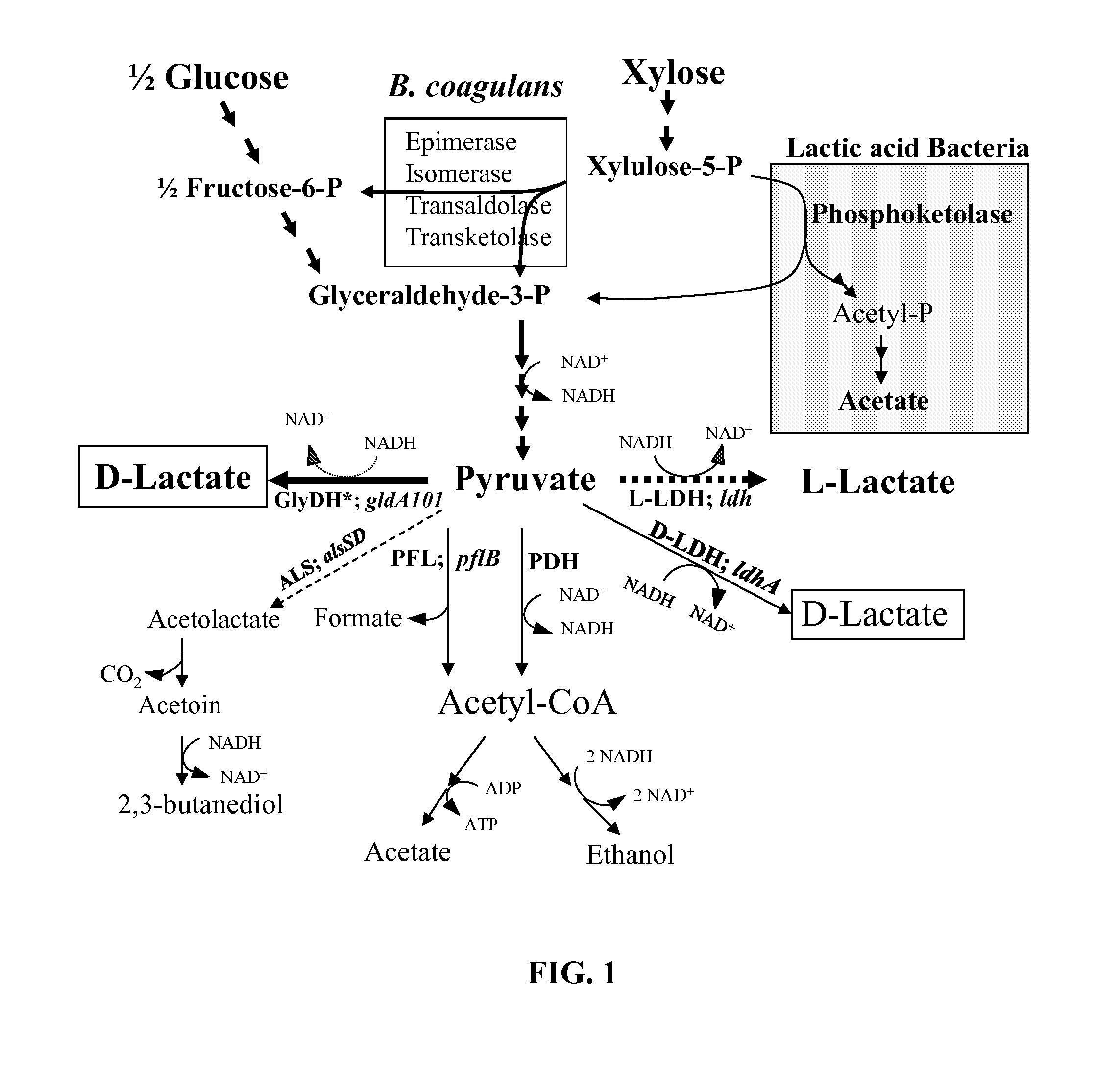
Glycerol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.6, also known as NAD⁺-linked glycerol dehydrogenase, glycerol: NAD⁺ 2-oxidoreductase, GDH, GlDH, GlyDH) is an enzyme in the oxidoreductase family that utilizes the NAD⁺ to catalyze the oxidation of glycerol to form glycerone (dihydroxyacetone).
Biosensor
InactiveUS20090236222A1Reduced measurement accuracyImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerA lipoprotein
It is an object of the present invention to provide a sensor, which is capable of measuring, quickly and in high accuracy, concentration of neutral fat from a sample such as a biological sample or the like, without executing pretreatment of the sample. This object is attained by a biosensor for measuring concentration of neutral fat, based on value of current flowing in the electrode system, having: an insulating substrate; an electrode system having a working electrode and a counter electrode, formed onto the insulating substrate; and a reaction layer having a lipoprotein lipase, a glycerol dehydrogenase and an electron mediator, formed at the upper part or the vicinity of the electrode system.
Owner:CCI HLDG INC +1
Kit for diagnosing diseases in system of liver and gall
InactiveCN101003831AExtended storage timeUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDisease causePolymer
This invention relates to a test kit for diagnosing hepatic and biliary diseases. The test kit has such advantages as high stability, high accuracy and high sensitivity. The test kit comprises two reagents. Reagent 1 comprises oxidized thio coenzyme, buffer solution, preservative, and anti-interference agent. Reagent 2 comprises 3alpha-HSD, reduced coenzyme, buffer solution, preservative, complexing agent, polymer accelerator, stabilizer, and one of formate dehydrogenase-formic acid-NAD, glutamate dehydrogenase-glutamic acid-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-glucose-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, glucose dehydrogenase-xylose-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, lactate dehydrogenase-alpha-ketoglutarate-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, and glycerol dehydrogenase-ethylene glycol-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme.
Owner:王贤理
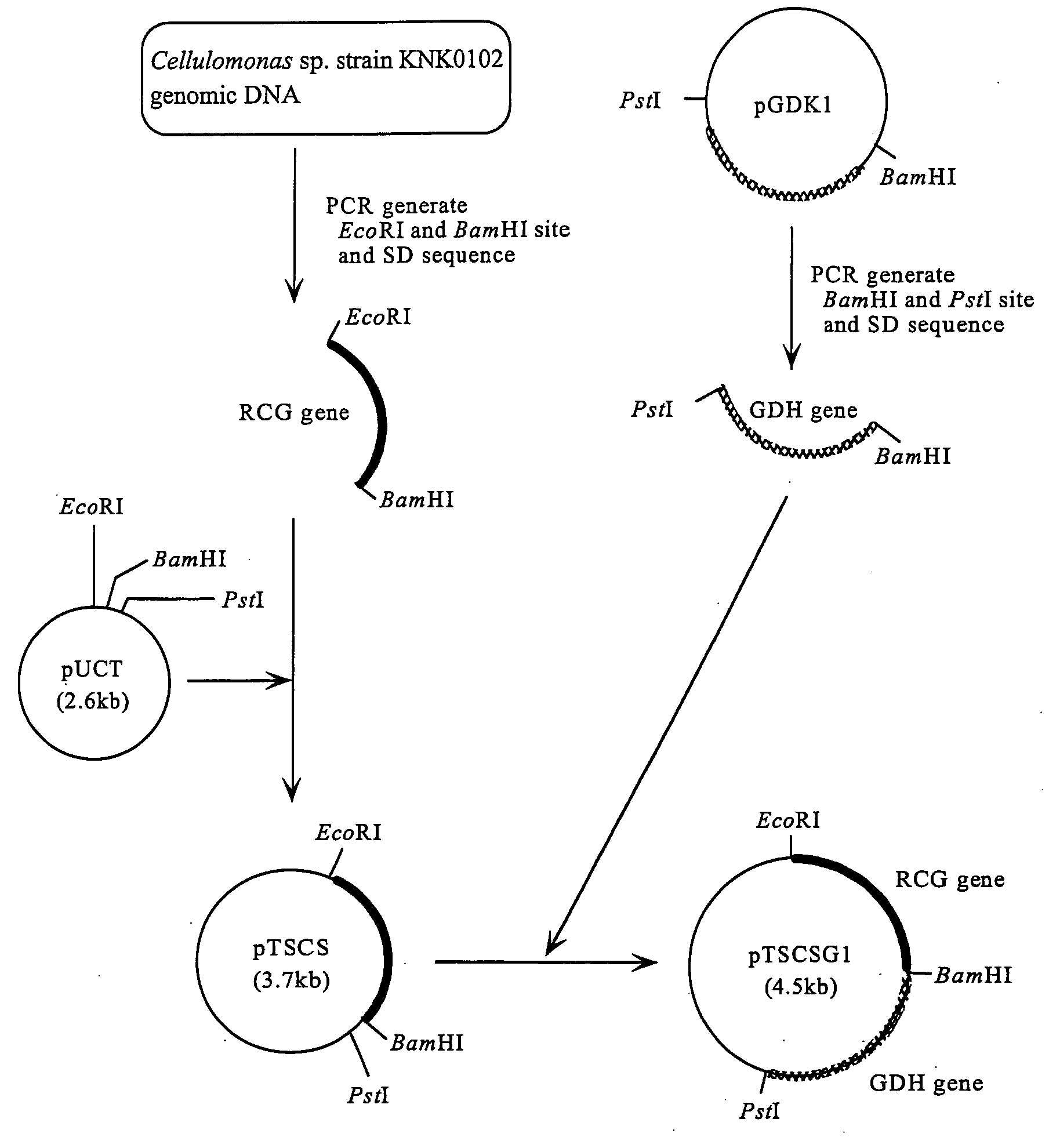
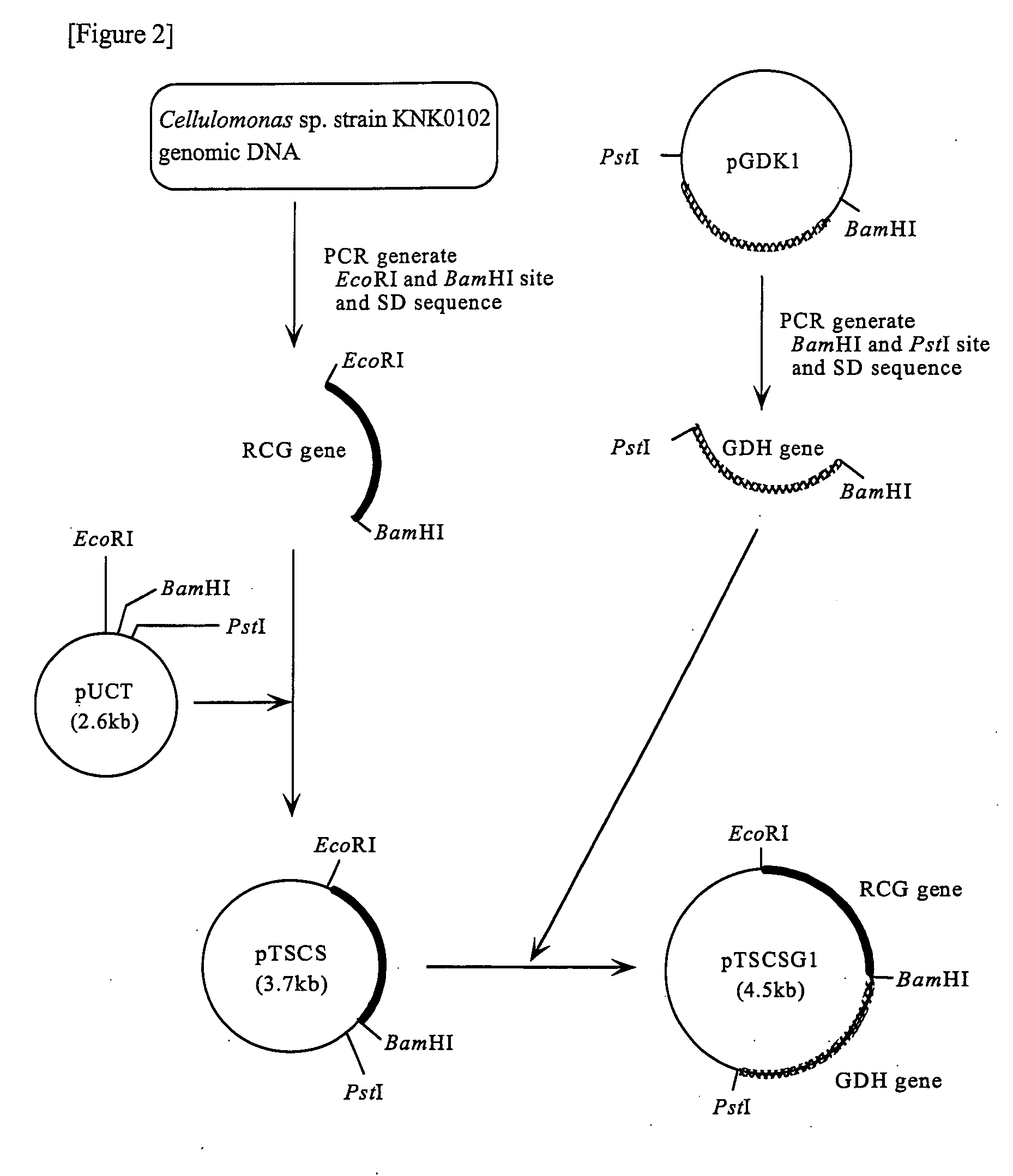
Method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol through fermentation via recombinant microbes
PendingCN106906248AAddressing Biosecurity IssuesLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphoric acidBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol through fermentation via recombinant microbes. According to the invention, an endogenous dihydroxypropanone phosphatein phosphatase gene hdpA is over-expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum to reinforce removal of phosphoric acid from dihydroxypropanone phosphatein so as to produce dihydroxypropanone; exogenous glycerol dehydrogenase is introduced to convert dihydroxypropanone into glycerin; and glycerin finally produces 1,3-propylene glycol under the action of exogenous glycerol dehydratase and an activator thereof and alcohol dehydrogenase. Corynebacterium glutamicum can use different cheap raw materials for fermentation, and cheap corn steep liquor can be used as a nutritional component to replace expensive yeast powder, so cost for raw materials is further reduced, and the problems in biosecurity and tolerance of the bacterial strain to a substrate and a product are overcome; and thalli obtained in the process of fermentation can be used as a product for a feed additive. The method provided by the invention produces few by-products and can further simplify the separating process of 1,3-propylene glycol.
Owner:GUANGDONG TSINGDA SMART BIOTECH CO LTD
Water type NADH oxidase of reproducible coenzyme NAD+ and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105331589AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationDihydroxyacetoneGlycerol dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to NADH oxidase in the field of biotechnology and particularly provides water type NADH oxidase of reproducible coenzyme NAD+ and an encoding gene and application thereof. The oxidase is represented by an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. By the adoption of the water type NADH oxidase, 1,3-dihydroxyacetone can be produced through in-vitro serial connection and glycerin conversion of the oxidase and glycerol dehydrogenase. Compared with a chemical method for preparing the 1,3-dihydroxyacetone, the method has the advantages of being moderate in reaction condition, friendly to environment, simple in operation, easy to amplify and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring glucose oxidase without interference of blood lipid
InactiveCN107884401AImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsQuinone
The invention discloses a method for measuring glucose oxidase without the interference of blood lipid. The method utilizes visible light to test a material according to the color change of reactions.According to the method, a reagent I comprises lipoprotein lipase, glycerol dehydrogenase, NAD+, Triton X-100, and mutarotase; and a reagent II comprises following effective components: glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and 4-amino antipyrine, and 2,4-dichlorophenol. The method comprises the following steps: placing serum and the reagent I in a water bath with a temperature of 37 DEG C for 3 to 5 minutes so as to convert triglyceride into dihydroxyl acetone under the action of lipoprotein lipase and glycerol dehydrogenase; and then adding the reagent II. Under the action of glucose oxidase and peroxidase, glucose, 4-amino antipyrine, and 2,4-dichlorophenol carry out condensation reactions to generate red quinone-imine. The first step is taken as blank by an instrument, and the glucose contentis calculated on the basis of quinone-imine generated in the step two.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
Multi-titer live vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101659958AApparently multivalent immune protectionGood application prospectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptideSignal peptide
The invention provides a recombinant plasmid, a multi-titer live vaccine as well as preparation methods and the application thereof. The provided recombinant plasmid contains a fusion gene sequence ofsignal peptides of vibrio anguillarum metalloprotease and aeromonas hydrophila 3-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase; the preparation method of the recombinant plasmid comprises the following steps: (A) establishing signal peptide-3-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase fusion gene; (B) enzyme-cutting the fusion gene and a carrier; and (C) connecting the enzyme-cutting fusion gene and the enzyme-cutting carrier. The multi-titer live vaccine is prepared by converting the recombinant plasmid into vibrio anguillarum attenuated strains; and the preparation method of the multi-titer live vaccine comprises thefollowing steps: (A) establishing the recombinant plasmid containing signal peptides of vibrio anguillarum metalloprotease and aeromonas hydrophila 3-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase; and (B) converting the recombinant plasmid obtained in the step (A) into vibrio anguillarum attenuated strains. The multi-titer live vaccine is applied to prevent and treat fish diseases caused by vibrio anguillarum and aeromonas hydrophila. The attenuated vaccine provided by the invention has remarkable multi-titer immune protective efficiency, can be used as the live vaccine of vibrio anguillarum and aeromonas hydrophila and has favorable application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105950529ASolving Tolerance IssuesAddress biosecurityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidGlycerol
The invention relates to a 3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, and a construction method and application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain comprises the following steps: in a Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, overexpressing an endogenous dihydroxyacetone phosphate phosphatase gene hdpA, and overexpressing a glyceroldehydrogenase gene gldA, a glycerol anhydrase and activating factor gene pduCDEGH and a 3-hydroxypropylaldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH. When the recombinant strain is used for producing 3-hydracrylic acid by fermentation, the Corynebacterium glutamicum strain can perform fermentation by using different cheap raw materials, thereby further lowering the raw material cost. The 3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain solves the problems of biosafety and acid tolerance. The strain in the fermentation process can be used in a feed additive as a product. The method can generate fewer byproducts, so that the separation process of the end product 3-hydracrylic acid is simplified.
Owner:GUANGDONG TSINGDA SMART BIOTECH CO LTD
Construction and application of 1,3-dihydroxy acetone recombinant genetic engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104845999AIncrease productionEasy to buildBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlycerol
The invention discloses construction and an application of 1,3-dihydroxy acetone recombinant genetic engineering bacteria; with aerobacter aerogenes genome DNA as a template, PCR amplification is applied to obtain a gene (gldA) encoding glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH), the gene (gldA) is cloned onto an escherichia coli expression vector pBluescript SK<->, and a cloned vector pSK-gldA is constructed and is expressed successfully in E.Coli JM109. A method for expressing 1,3-dihydroxy acetone comprises that the engineering bacteria for expressing 1,3-dihydroxy acetone are fermented by using a glycerol-containing culture medium, and the product 1,3-dihydroxy acetone is obtained through filtering a fermented liquid, extracting with an organic solvent, recrystallizing a combined solvent and the like. The construction of the 1,3-dihydroxy acetone high-yielding recombinant genetic engineering bacteria has the advantages of being simple in method, high in yield and low in cost. Based on the above advantages, the engineering bacteria play an important role in biological preparation of the 1,3-dihydroxy acetone and have wide application prospects.
Owner:XUZHOU AOGEMAN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
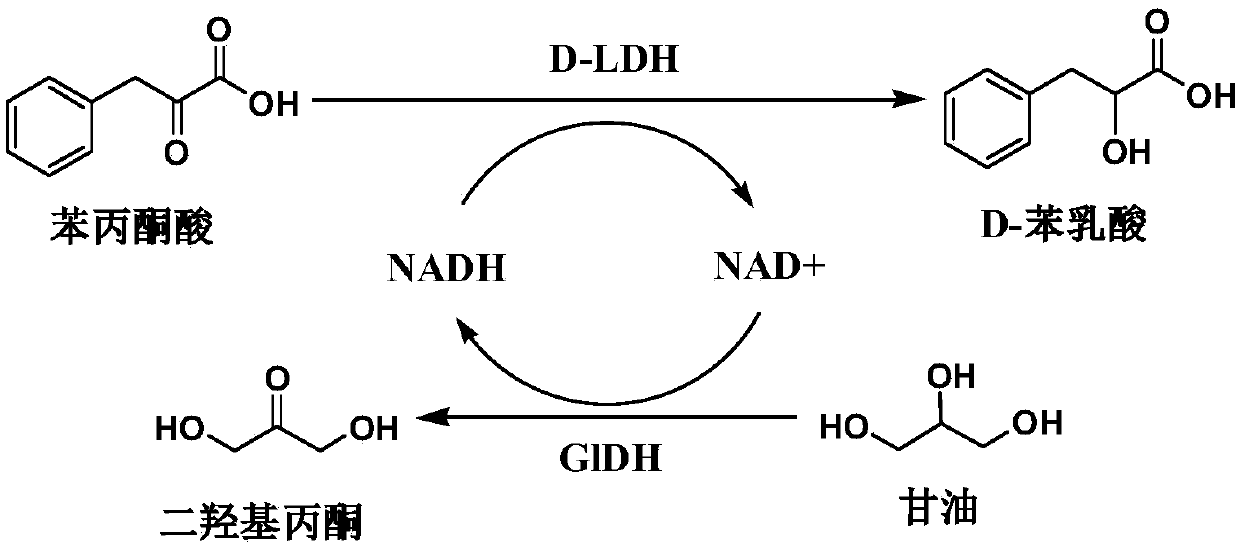
Difunctional fusion protein and method for producing D-phenyllactic acid from same
InactiveCN109628419AEasy to synthesizeReduce usageBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLactate dehydrogenaseChemical synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, particularly relates to D-lactic dehydrogenase and glycerol dehydrogenase fusion protein, and relates to a method for generatingD-phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of engineering bacteria containing the fusion protein. A gene fusion strategy is utilized, D-lactic dehydrogenase (D-LDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (GlDH) are subjected to fusion expression and introduced into a D-phenyllactic acid anabolism means for the first time, and in the reaction of asymmetric synthesis of the D-phenyllactic acid (D-PLA) with phenylpyruvic acid as a substrate, regeneration of coenzyme factors and production of the high-yield D-phenyllactic acid are achieved. The cost is low, the safety is high, glycerol is converted into dihydroxy acetone, and the fusion protein can serve as an important medicine and chemical synthesis intermediate, is widely applied to fine chemical industry, food industry and cosmetic industry andis high in additional value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
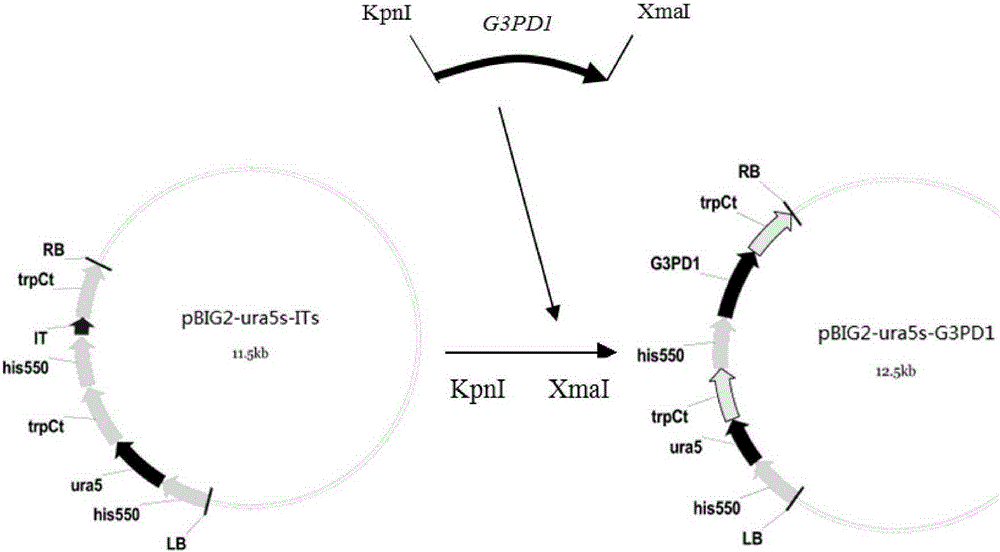
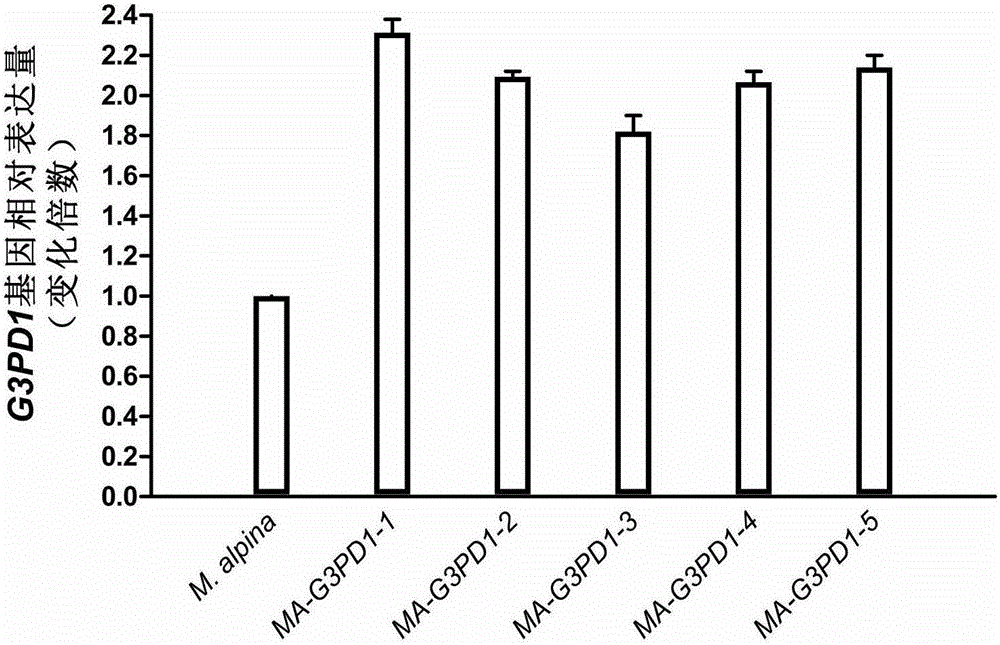
Mortierella alpine strain overexpressing 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase gene(G3PD1), and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant Mortierella alpine strain GPD-1 overexpressing G3PD1 and a construction method. According to the invention, uracil-auxotrophic Mortierella alpine MAU1 is used as a material, Agrobacterium tumefaciens is used for mediation, and a G3PD1-overexpressing recombinant strain with obviously increased lipid content is obtained. Compared with wild Mortierella alpine, the total lipid content of the strain provided in the invention is increased by about 50%, and the transcription amount of G3PD1 is increased by about 2 times; so theoretical and application foundations are laid for subsequent industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for testing triglyceride in serum by using glycerol dehydrogenase
InactiveCN103602718AWill not increase the burdenLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycerolColor changes
The invention discloses a method for testing triglyceride in serum by using glycerol dehydrogenase, belonging to a method for testing a material through color change caused by a test reaction result by utilizing visible light. The technical scheme is as follows: a reagent I simultaneously contains glycerol dehydrogenase and NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)+, and a reagent II contains the effective component of lipoprotein lipase. The method comprises the steps of firstly, subjecting the serum and the reagent I to warm bath at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 3-5min; subjecting free glycerol in the serum and the reagent I to reaction to generate NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrogen); adding the reagent II, and then, carrying out warm bath at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 4-7min; hydrolyzing the triglyceride to generate glycerol, and subjecting the glycerol to reaction to generate NADH; detecting on the position with the wavelength of 340nm by using an instrument; with the NADH generated by the reaction of the reagent I as a blank, calculating the content of the triglyceride according to the NADH generated by the reaction of the reagent II. When used for detecting, the method is not affected by endogenous glycerol; the method for testing the triglyceride is same as other enzyme methods in use and range, few in tool enzyme, little in hybrid enzyme interference, low in reagent cost, economic, convenient, feasible and higher in accuracy.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
Immobilization and application of 1,3-dihydroxy acetone producing recombinant genetic engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104845961AHigh product expressionHigh reusabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationGenetic engineeringAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses immobilization and an application of 1,3-dihydroxy acetone producing recombinant genetic engineering bacteria; a supramolecular template is used for immobilization of the engineering bacteria of an escherichia coli expressed glycerol dehydrogenase gene (gldA). Construction of the engineering bacteria comprises that with a klebsiella pneumoniae genome DNA as a template, PCR amplification is applied to obtain the gene (gldA) encoding glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH), the gene (gldA) is cloned onto an escherichia coli expression vector PET 28a, and a cloned vector PET-gldA is constructed and is expressed successfully in E.coli JM109. A method for expressing 1,3-dihydroxy acetone comprises that the recombinant genetic engineering bacteria immobilized by the supramolecular template are fermented in a glycerol-containing culture medium to obtain the 1,3-dihydroxy acetone. With the immobilized stain, the product expression quantity is high and is up to a maximum of 120 g / L, the repeated use is good, and the product expression quantity still can reach 107 g / L after repeated use for 15 times, an active role is provided in microbial fermentation preparation of the 1,3-dihydroxy acetone, and application prospects are wide.
Owner:XUZHOU AOGEMAN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Kit for detecting lipase
ActiveCN107356544AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPreservativeSolvent
The invention discloses a kit for detecting lipase. The kit is composed of a single reagent, the single reagent is prepared from a 80 mmol / L-160 mmol / L buffer system of which the PH is 8.8, 100 mmol / L-300 mmol / L glyceryl trilaurate, 0.2 mmol / L-0.4 mmol / L beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide trihydrate, 0.5 KU / L-3 KU / L glycerol dehydrogenase, a 0.6 g / L-1 g / L preservative NaN3, a 5 g / L-10 g / L enzyme protective agent and a 0.4%-1.6% developing agent, and deionized water serves as a solvent. The kit for detecting the lipase has the advantages that samples do not need to be pretreated, a full-automatic biochemical analyzer can be directly utilized to conduct large-batch sample detection, and the kit is simple to operate, high in accuracy, good in repeatability, wide in linear range and suitable for clinical application popularization.
Owner:王贤俊
Triglyceride detection reagent, detection test paper and test paper preparation method
InactiveCN111735811AStable detectionReduce the impact of interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTetrazoleA lipoprotein
The invention relates to a triglyceride detection reagent, detection test paper and a test paper preparation method. The detection reagent is prepared from 0.5 to 1.5 KU / ml of lipoprotein lipase, 0.3to 0.5 KU / ml of diaphorase, 0.32 to 0.94 KU / ml of glycerol dehydrogenase, 5 to 15mmol / L of coenzyme I and 2 to 6mmol / L of a chromogenic substance, and further comprises a TritonX-100 solution with themass fraction being 0.2%-1.0% and a buffer solution with the concentration being 0.01 mol / L to 0.1 mol / L; wherein the chromogenic substance is one of nitro tetrazole blue chloride, dimethyl thiazolediphenyl tetrazole bromine blue, sodium dichlorophenol indophenolate, TNBT and iodonitrotrtrazolium chloride, the detection test paper comprises a reaction bottom layer, a reaction layer, a blood filtering layer, a capillary sample introduction layer and a hydrophilic layer, and the detection reagent is located on the upper surface of the reaction layer. The interference influence of other substances on the test result is small, and the reagent detection is more stable.
Owner:民康医疗科技(天津)有限公司
Novel Glycerol Dehydrogenase, Gene Therefor, and Method of Utilizing the Same
InactiveUS20080305534A1Efficient productionEfficient preparationSugar derivativesBacteriaGlycerolGel electrophoresis
The present invention provides a polypeptide having physicochemical characteristics of (1) to (5) described below:(1) action: to generate (S)-3-chloro-1,2-propanediol by stereoselectively reducing 1-chloro-3-hydroxyacetone using NADH as a coenzyme;(2) molecular weight: about 340,000 by gel-filtration and about 43,000 by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis;(3) optimum temperature: from 60 to 70° C.;(4) optimum pH for reduction: 6.0; and(5) optimum pH for oxidation: 9.0.Furthermore, the present invention provides a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing, a DNA encoding the polypeptide, and a transformant producing the polypeptide in large quantities. Still furthermore, the present invention provides a manufacturing method by using the above polypeptide or the above transformant of (S)-3-chloro-1,2-propanediol that is a useful material for pharmaceuticals, etc.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
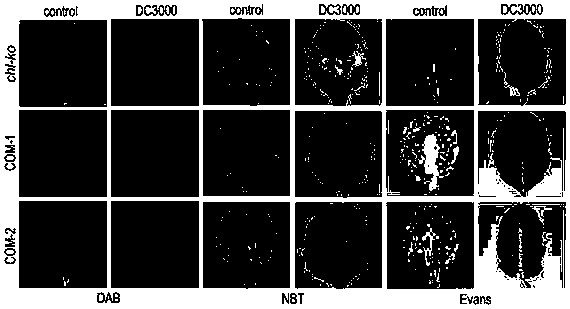
Corn 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ZmGPDH4 and application of coding gene of corn 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ZMGPDH4 in regulating plant stress tolerance
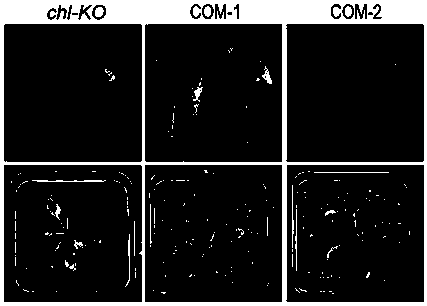
The invention discloses corn 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ZmGPDH4 and application of a coding gene of the corn 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ZmGPDH4 in regulating plant stress tolerance. For the corn 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ZmGPDH4 and the application disclosed by the invention, by taking a corn GPDH gene family member ZmGPDH4 as a research object, and the corn GPDH gene family member ZmGPDH4 is transferred to an arabidopsis mutant to obtain T3 generation homozygous transformants; two transformants of COM-1 and COM-2 in the T3 generation homozygous transformants are selected to perform disease-resistant function identification; and by taking the arabidopsis mutant as a control, changes in contents of 3-glycerophosphate and glycerinum and physiological phenotype of the ZmGPDH4 transgenic arabidopsis under the germ stress are studied. A result shows that under the germ Pst DC3000 stress treatment condition, the contents of 3-glycerophosphate and glycerinum in the ZmGPDH4 transgenic arabidopsis are significantly higher than those in the arabidopsis mutant, and the disease infection condition of the the ZmGPDH4 transgenic arabidopsis is significantly better than that of the control. The result shows that the ZmGPDH4 can significantly improve the disease resistance of transgenic plants and can be applied to cultivation of a corn anti-reverse variety as an inverse gene.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Increased ethanol production in recombinant bacteria
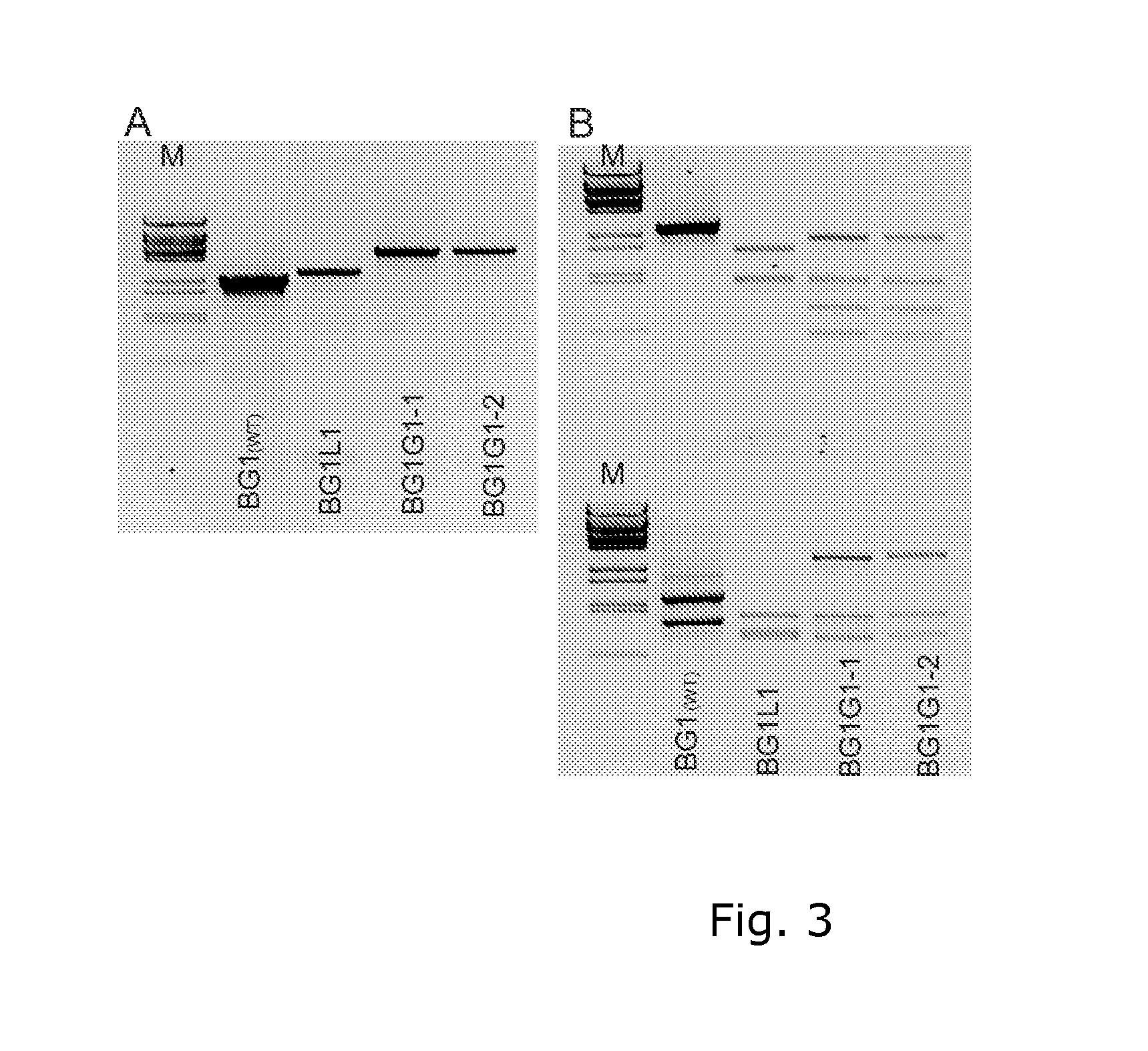
The invention pertains to a recombinant bacterium with enhanced ethanol production characteristics when cultivated in a growth medium comprising glycerol. The recombinant bacterium comprises an inserted heterologous gene encoding glycerol dehydrogenase, and / or an up-regulated native gene encoding glycerol dehydrogenase. Particularly there is provided the recombinant bacterium BG1G1 of the Thermoanaerobacter mathranii species with an inserted heterologous gene encoding the E.C. 1.1.1.6 type, a NAD dependent glycerol dehydrogenase obtained from Thermotoga maritima.
Owner:BIO GASOL IPR APS
High-sensitivity lipase kit
InactiveCN109490227AImprove stabilityHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsPunchingPreservative
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity lipase kit, which is prepared from the following components: a punching system at a concentration of 70 to 180 mmol / L and having a pH of 8.0 to 9.0, glyceroltrilaurate at a concentration of 90 to 350 mmol / L, oxidized coenzyme I at a concentration of 0.1 to 0.5 mmol / L, glycerol dehydrogenase at a concentration of 0.3 to 4 KU / L, an enzyme protective agentat a concentration of 4 to 12 g / L, a stabilizer at a concentration of 0.5 to 1.5 g / L, and a developing agent at a concentration of 0 .2 to 2.0 g / 100mL. The lipase kit disclosed by the invention does not contain a preservative, and the stability of the kit is obviously improved by controlling the mass ratio of the stabilizer to the enzyme protective agent, thereby avoiding interference caused by the presence of the preservative and improving the detection sensitivity; and the test accuracy is also significantly improved. The specific developing agent is added into the kit to enhance the surfacetension of a water-oil interface, thereby increasing the measurable linear range of a reagent; and furthermore, the detection result of the kit is accurate and high in repetitiveness.
Owner:闫玮钰
Increased ethanol production in recombinant bacteria
ActiveUS20110287501A1Enhanced ethanol production characteristicBacteriaBiofuelsBacteroidesHeterologous
The invention pertains to a recombinant bacterium with enhanced ethanol production characteristics when cultivated in a growth medium comprising glycerol. The recombinant bacterium comprises an inserted heterologous gene encoding glycerol dehydrogenase, and / or an up-regulated native gene encoding glycerol dehydrogenase. Particularly there is provided the recombinant bacterium BG1G1 of the Thermoanaerobacter mathranii species with an inserted heterologous gene encoding the E.C. 1.1.1.6 type, a NAD dependent glycerol dehydrogenase obtained from Thermotoga maritima.
Owner:BIO GASOL IPR APS
Method for preparing chiral amine from multi-enzyme coupled systems
ActiveCN105112468AAchieve recyclingImprove efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationCoupling systemAmine dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for preparing chiral amine from multi-enzyme coupled systems and belongs to the technical field of biological catalysis asymmetric conversion. An amine dehydrogenase and glycerol dehydrogenase coupled system, an amine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase coupled system as well as an amine dehydrogenase, glycerol dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase coupled system are constructed, and asymmetric preparation of the chiral amine and regeneration of coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide are realized. The multi-enzyme coupled systems and the method for preparing the chiral amine from the multi-enzyme coupled systems have advantages that the product conversion rate is high, the reaction condition is mild, operation is simple, the coenzyme can be regenerated and the like, the cost is low, the enzyme utilization rate is high, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
High-yield propionic acid propionibacterium jensenii engineering bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN104004700AIncrease productionImprove fermentation production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidPropionibacterium jensenii
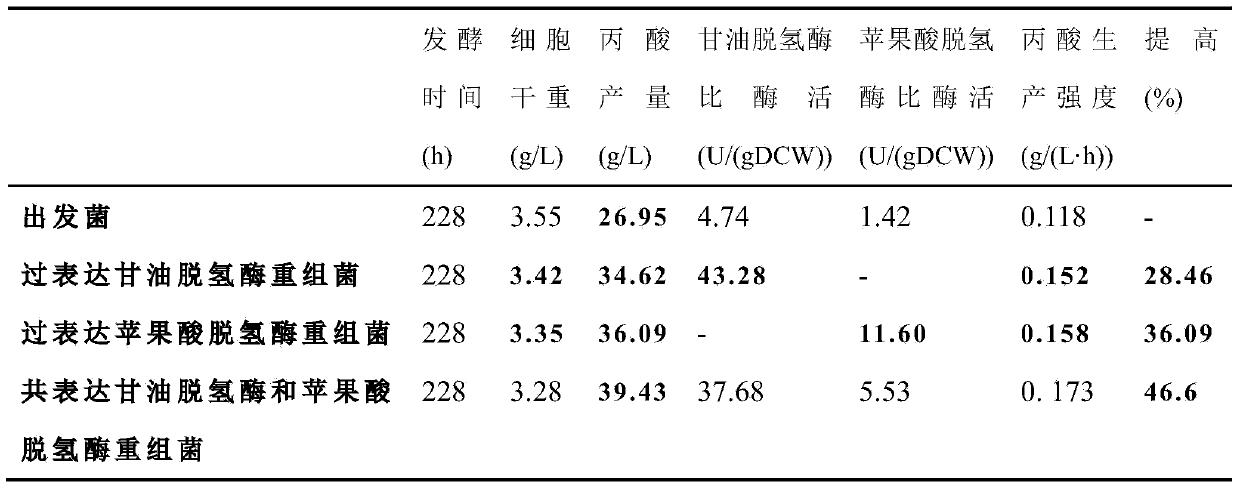
The invention discloses a high-yield propionic acid propionibacterium jensenii engineering bacterium and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A molecular method is adopted. The propionibacterium jensenii engineering bacterium serves as a host, and overexpression is carried out on malate dehydrogenase (mdh) from Klebsiella pneumoniae, or overexpression is simultaneously carried out on glycerol dehydrogenase (gldA) from the Klebsiella pneumoniae. Compared with an original strain, the propionic acid yield of recombination and mixing coexpression glycerol dehydrogenase of overexpression malate dehydrogenase and the propionic acid yield of a recombinant strain of the malate dehydrogenase are 36.09 g / L and 39.43 g / L respectively, and are improved by 33.91 % and 46.3 % respectively than that of the original strain. The method provides new ideas for modifying the propionibacterium jensenii and improving productivity of propionic acid fermentation in the industrial biotechnology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for fermenting to produce acetoin by utilizing bacillus licheniformis engineered strain
ActiveCN109486871AReduce outputIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for fermenting to produce acetoin by utilizing a bacillus licheniformis engineered strain. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out glycerol dehydrogenase genes gdh and 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase genes budC by taking bacillus licheniformis 10-1-A as an original strain, replacing lactic dehydrogenase genes ldh with NADH oxidase genes nox in Thermococcus profundus DT5432, and constructing a bacillus licheniformis engineered strain capable of being used for producing acetoin; taking glucose as a substrate, biologically fermenting the strain, and preparing the acetoin from fermentation liquor. Experiments prove that the engineered strain disclosed by the invention is capable of producing 82.14g / L of acetoin, and the production efficiency reaches2.28g / L per hour. Moreover, the cost in the production process is low, the yield is high, and the method has excellent application value and considerable economic benefits.
Owner:山东大学深圳研究院 +1
Preparation method of lipase detection kit
InactiveCN107449746AStrong specificityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingPreservativeGlycerol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a lipase detection kit. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a buffer solution with the concentration of 80 to 160mmol / L, adjusting a PH value to be 8.8, and taking the buffer solution as a reaction solvent; adding a developing agent composition, stirring while adding, controlling the rotating speed at 120r / pm and continuously stirring for 15 minutes; then adding a certain amount of enzyme protectant, and respectively adding 100 to 300 mmol / L of laurostearin as a substrate, 0.2 to 0.4 mmol / L of oxidized coenzyme I and 0.5 to 3KU / L of glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH) after the enzyme protectant is completely dissolved, wherein the enzyme protectant is added before the oxidized coenzyme I is added; finally, adding 0.6 to 1g / L of NaN3 as a preservative, and sealing and storing the NaN3 at the temperature of 2 to 8 DEG C after the NaN3 and the solution are uniformly mixed. The method can be used for preparing the lipase detection kit.
Owner:王贤俊
Genetic engineering bacteria producing glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH) and GDH preparation method
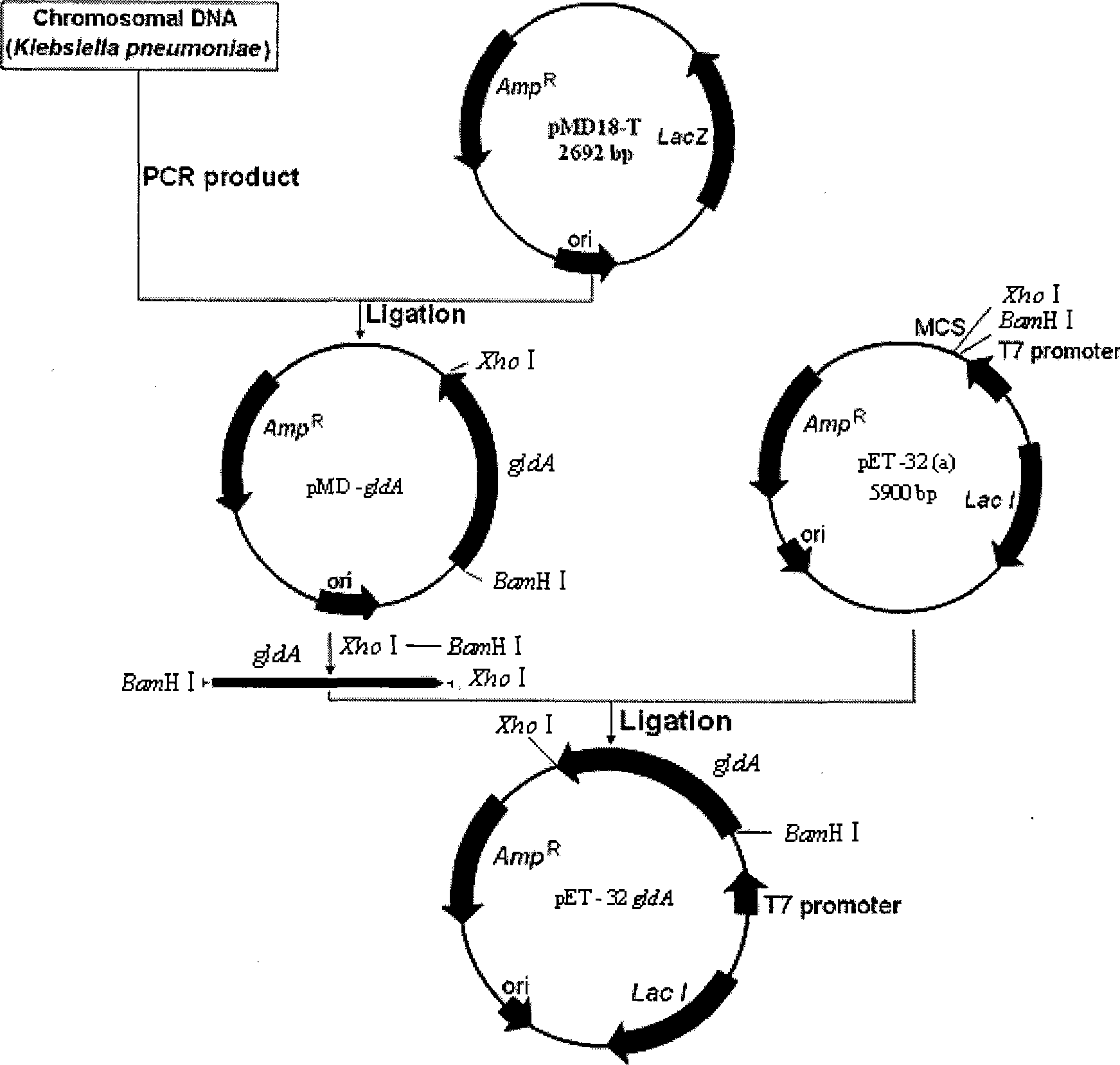
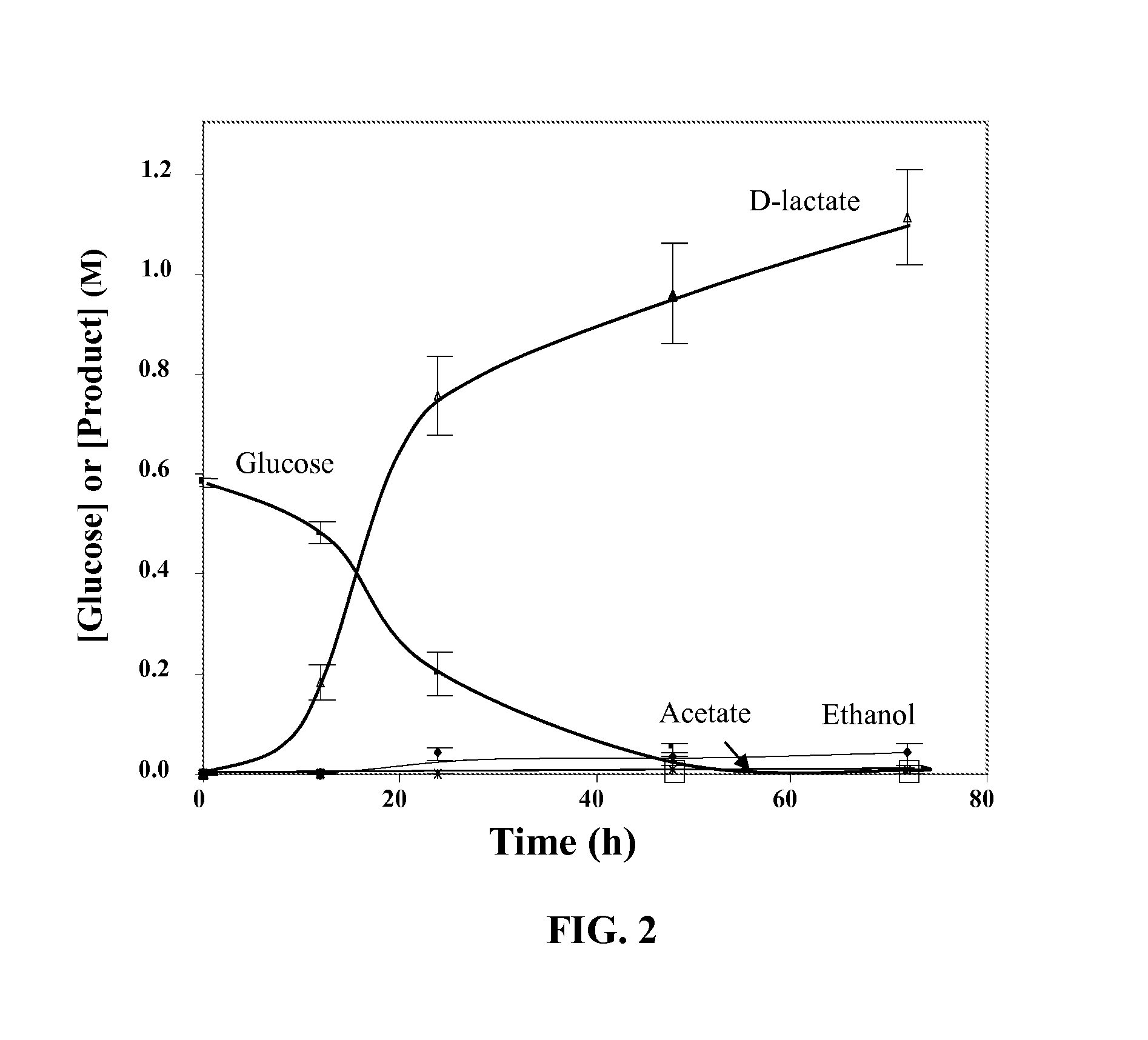
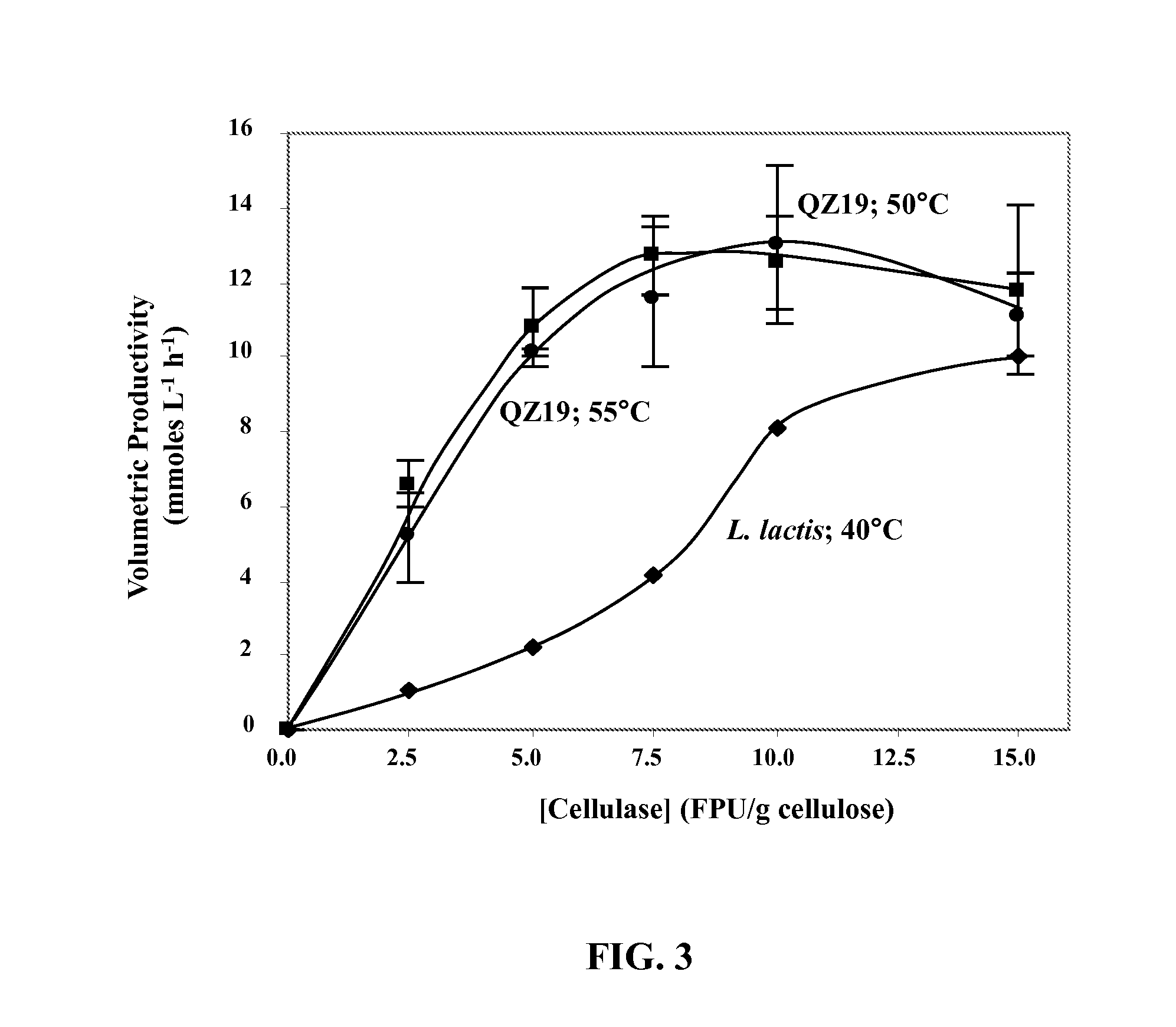
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, which comprises the following steps: adopting a PCR technology to clone a gldA gene from klebsiella pneumoniae DSM 1115, constructing an Escherichia coli expression vector pET-32gldA containing the gldA gene and transforming the Escherichia coli expression vector to Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) so as to obtain a recombinant genetic engineering strain E.coli-pET-gldA which can express glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH); and culturing recombinant bacteria to OD 0.4-1.2, and obtaining recombinant glycerol dehydrogenase through lactose-induced expression. The invention can be applied to producing dihydroxyacetone which is widely used in medicine, pesticides, cosmetics and food additives through an enzymatic process.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Transgenic yeast and method for producing ethanol using the same
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Variants of glycerol dehydrogenase having d-lactate dehydrogenase activity and uses thereof
The present invention provides methods of designing and generating glycerol dehydrogenase (GlyDH) variants that have altered function as compared to a parent polypeptide. The present invention further provides nucleic acids encoding GlyDH polypeptide variants having altered function as compared to the parent polypeptide. Host cells comprising polynucleotides encoding GlyDH variants and methods of producing lactic acids are also provided in various aspects of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Transgenic yeast and method for producing ethanol using the same
ActiveUS20200109373A1Increased ethanol yieldImprove abilitiesFungiBiofuelsMitochondrial transportMicrobiology
The present disclosure is intended to reduce the amount of glycerin produced as a byproduct in ethanol fermentation to a significant extent using a transgenic yeast comprising a gene having the pentose assimilating ability and encoding glycerin dehydrogenase having a mitochondrial transport signal introduced thereinto.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for preparing saxagliptin chiral intermediate by enzyme-catalyzed asymmetric transamination reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing a saxagliptin chiral intermediate through an enzyme-catalyzed asymmetric transamination reaction. The present invention couples phenylalanine dehydrogenase (phenylalanine dehydrogenase, PDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (Glycerol dehydrogenase, GDH) in an aqueous solution containing amino groups, using saxagliptin intermediate and glycerol as substrates, and at the same time Generate 1,3-dihydroxyacetone (DHA) and saxagliptin chiral intermediates, and realize the cyclic regeneration of coenzyme NAD+, realizing the efficient synthesis of saxagliptin chiral intermediates.
Owner:福州基石医药科技有限公司
Ammonia ion diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and ammonia ion concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464342AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoric acidPyrophosphate
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring ammonia (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, glutamic acid, adenyl pyrophosphate, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphoric acid, magnesium chloride, glutamoyl synthetase, glycerokinase, glycerol dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A genetically engineered bacterium producing β-carotene and its construction method
ActiveCN109609579BIncrease storage capacityIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneHexokinase
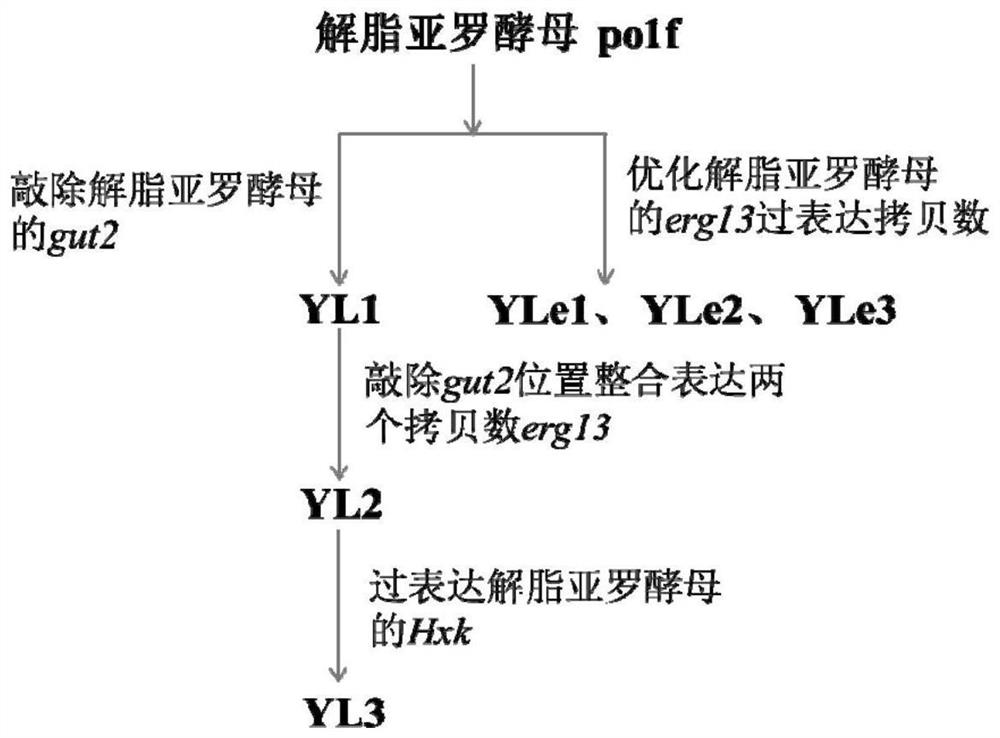
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium producing β-carotene and a construction method thereof. Firstly, in Yarrowia lipolytica, 3-phosphate glycerol dehydrogenase in the glycolytic pathway of the β-carotene synthesis pathway is knocked out gut2 gene, and then free expression of two copies of the endogenous β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaric acid synthase erg13 gene of Yarrowia lipolytica, integrated expression of Yarrowia lipolytica endogenous at the position where the gut2 gene was knocked out two copies of the erg13 gene; and then freely express the endogenous hexokinase Hxk gene of Yarrowia lipolytica, screen positive transformants, and obtain the engineering strain of Yarrowia lipolytica producing β-carotene, which is fermented and cultivated , and extracting, separating, and purifying β-carotene, the content of β-carotene can reach 26.6mg / g cell dry weight.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com