Genetic engineering bacteria producing glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH) and GDH preparation method
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and glycerol dehydrogenase, which is applied in the field of GDH-producing genetically engineered bacteria and its GDH preparation, can solve the problems that the cost and production capacity cannot reach industrial production, and achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
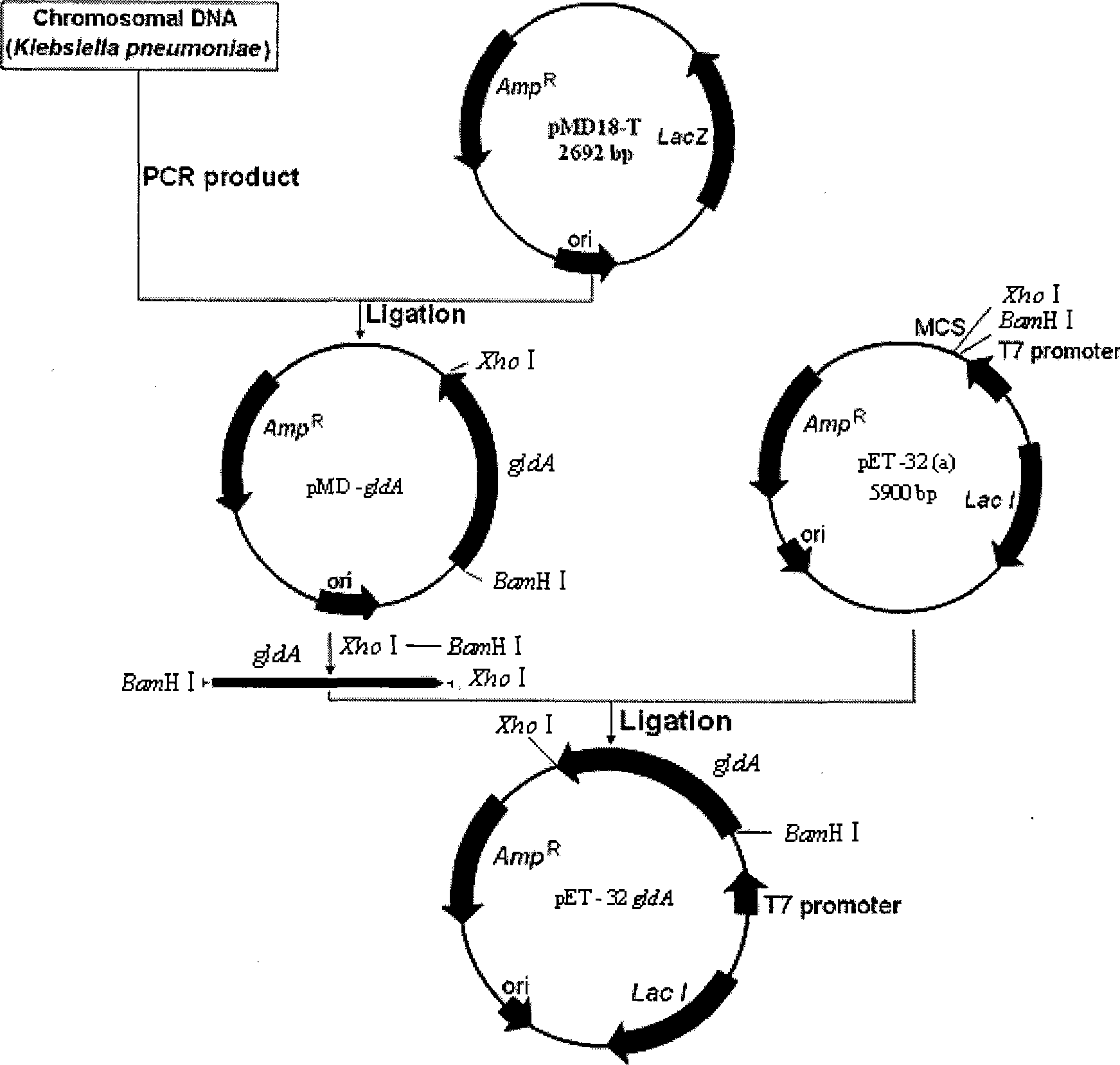
[0012] Construction of recombinant engineering bacteria producing GDH: Total DNA was extracted from Klebsiella pneumoniae DSM 2026 strain by boiling method, with 5′-CGTCGGATCCTACATGCGCACTTATTTGAG-3′ as the front primer and 5′-AATGCTCGAGCGAATTAACGCGCCAGCCAC-3′ as the back primer, and PCR amplification was used to obtain For the target gene gldA, refer to the third edition of the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" written by American Sambrook et al. Insert the target gene into pMD18-T to obtain the recombinant plasmid pMD-gldA. Digested with Xho I, designed a ligation system according to the instructions of T4 DNA Ligation (Biolab), and ligated to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET-32gldA. Specific process such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Cultivation of recombinant engineered bacteria: transfer the recombinant plasmid pET-32gldA into E. coli strain BL21 by thermal transformation method, select the transformants and insert them into 5 mL of LB medium containing 75 μg / mL ampicillin, and culture them in a shaker at 37°C until For several phases, transfer 1-5% of the inoculum to 50 mL of LB medium containing 75 μg / mL ampicillin, shake and culture at 200 rpm, 30-37 °C for 0.5-3 h, and add the inducer lactose until the end. The concentration is 0.5-20mg / mL to induce expression.
Embodiment 3
[0016] Preparation and activity detection of recombinant glycerol dehydrogenase: suspend genetically engineered bacteria in phosphate buffer (containing dithiothreitol), and ultrasonically disrupt cells in an ice bath; remove insoluble cell debris to obtain a cell-free extract, according to Nickel column affinity chromatography is carried out by a conventional method to obtain the recombinant glycerol dehydrogenase.
[0017] GDH dehydrogenates glycerol to dihydroxyacetone, coenzyme I NAD + The hydrogen obtained as an acceptor is reduced to NADH, which has a maximum absorption under ultraviolet light at 340nm. Therefore, according to the increase of absorbance, the activity of GDH was determined by the initial velocity method. Cultured in a 250mL shake flask, the specific activity of GDH obtained after separation and purification is 188U / mg, which is about 2.7 times that of GDH expressed by Keiko in E.coliHB101 / pSE420D, which is 2.7 times higher than that obtained by Chen Hong...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com