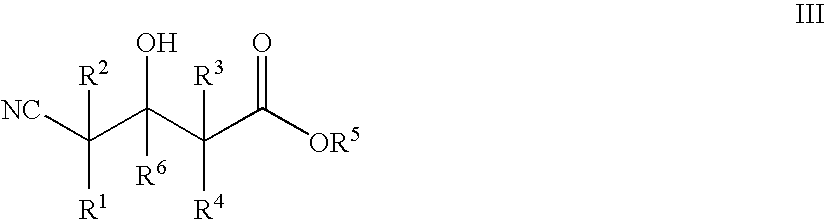Patents
Literature
224 results about "Enzymatic process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The enzymatic process is known to be a clean and environment friendly technique for biodiesel production. It can simultaneously convert both FFA and triglyceride into biodiesel. Through the years, it has been stereotyped into having long reaction times and high operating costs, due to the expensive lipase.
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives
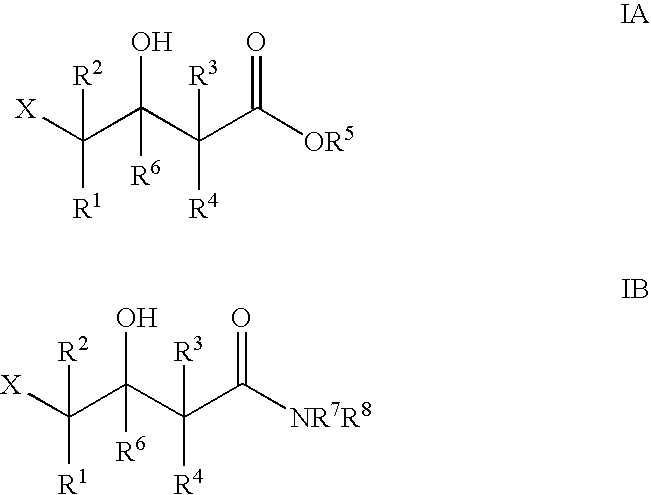
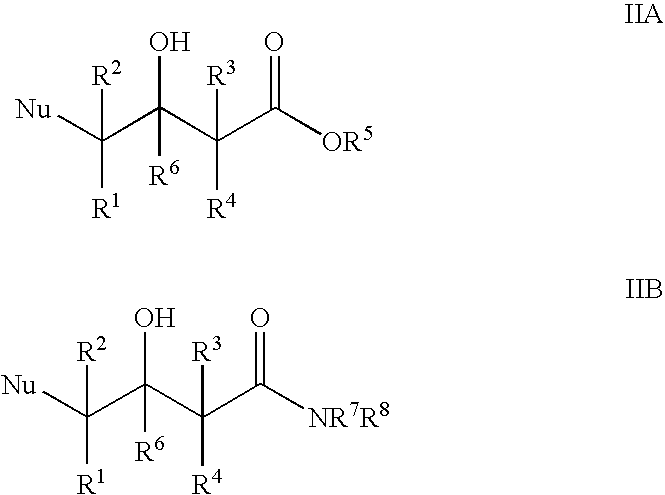
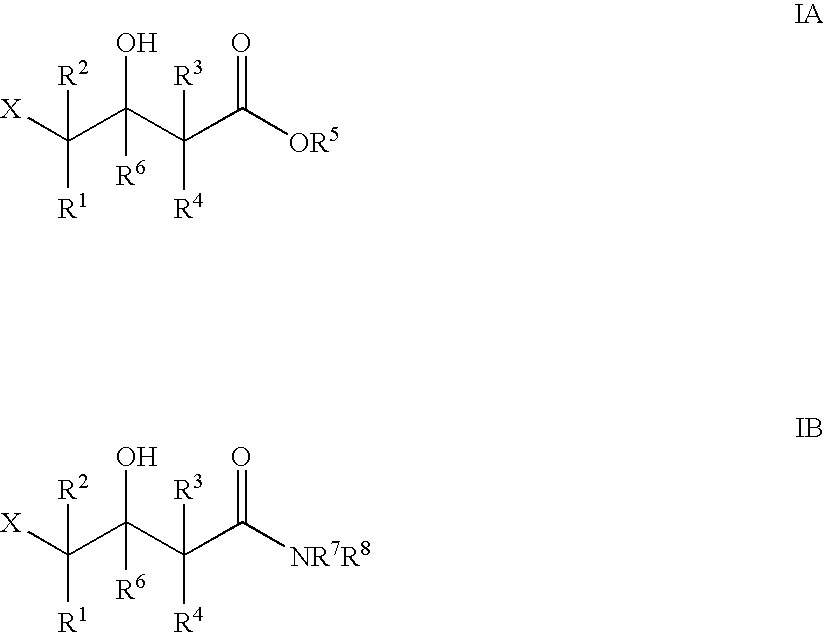
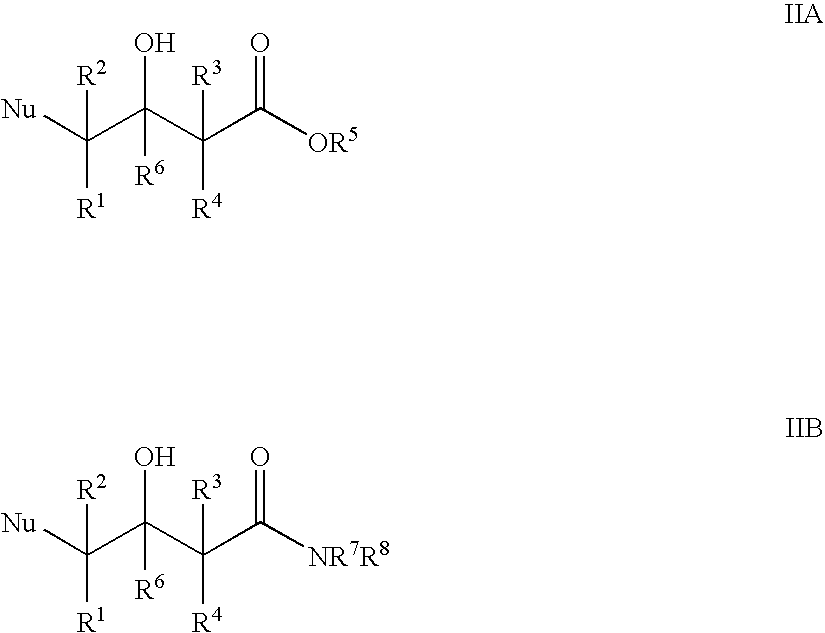
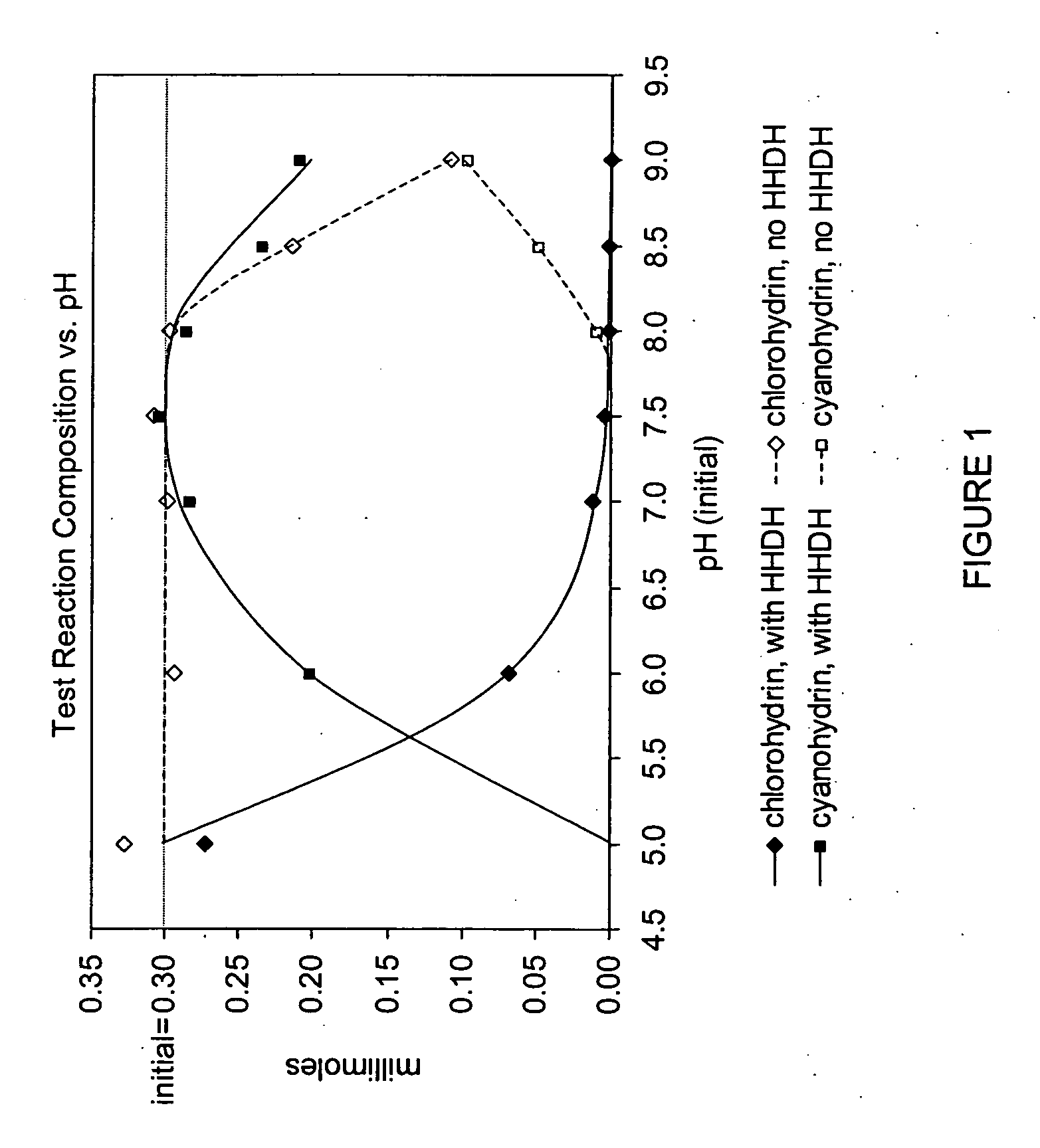
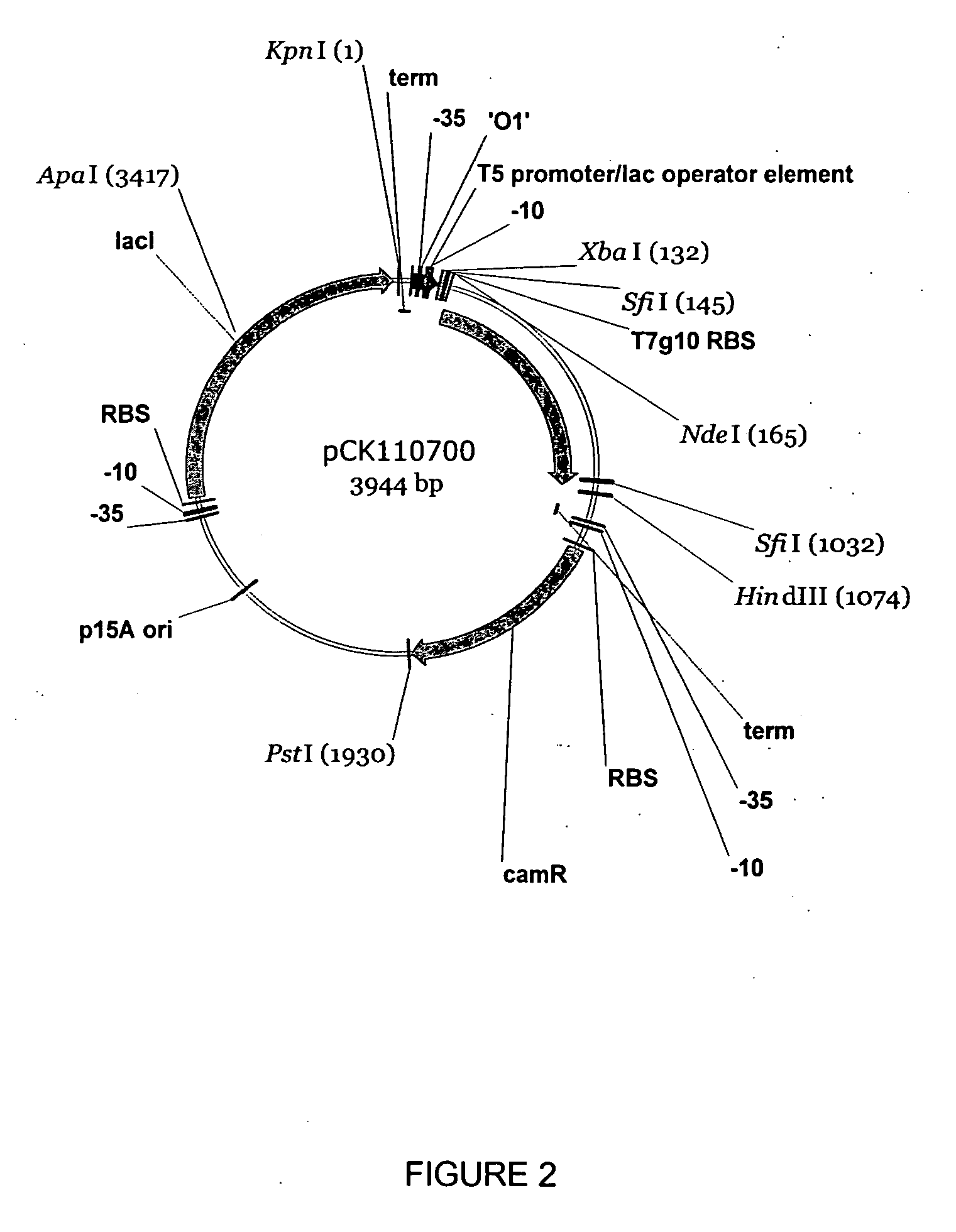
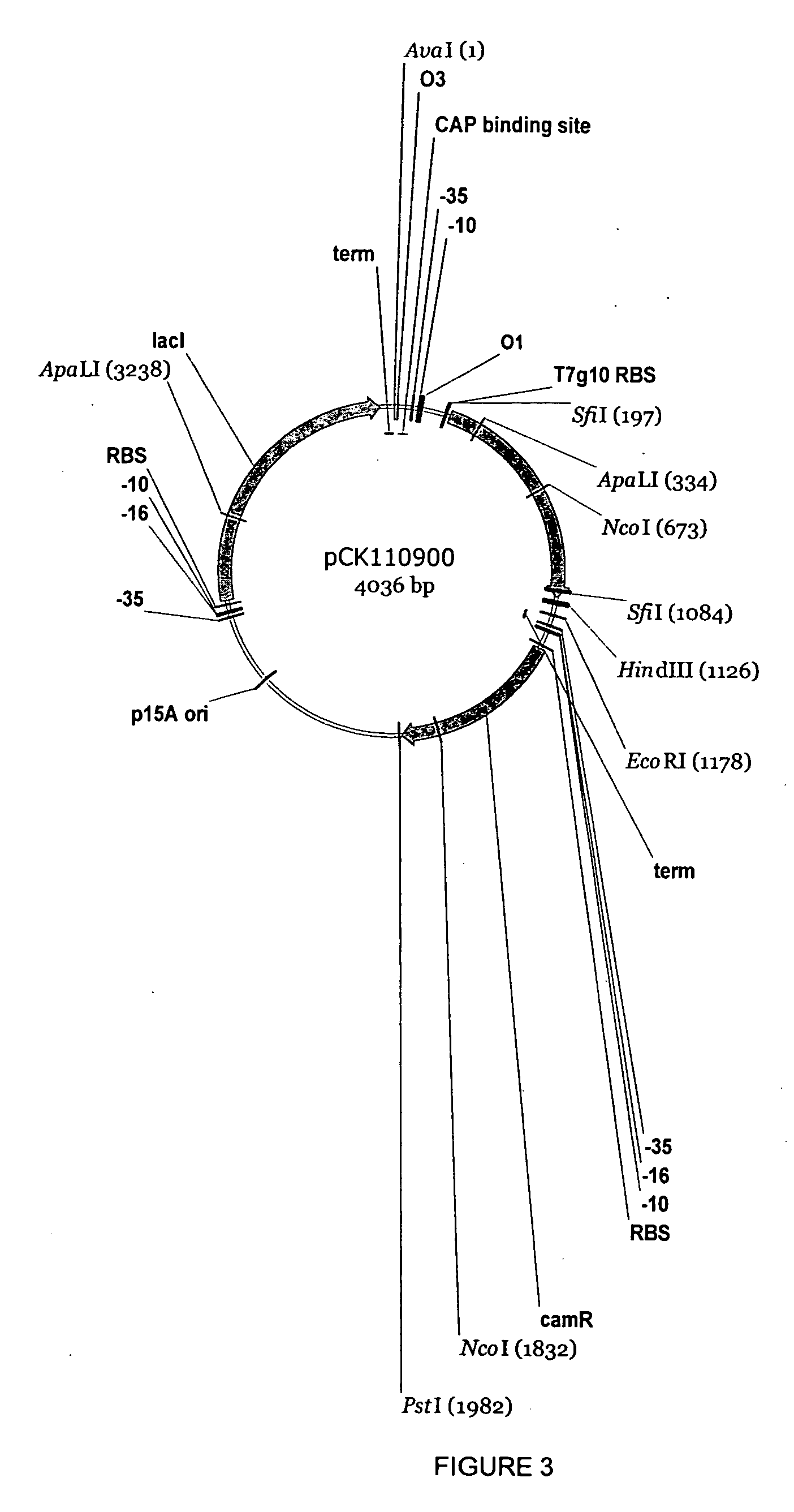
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
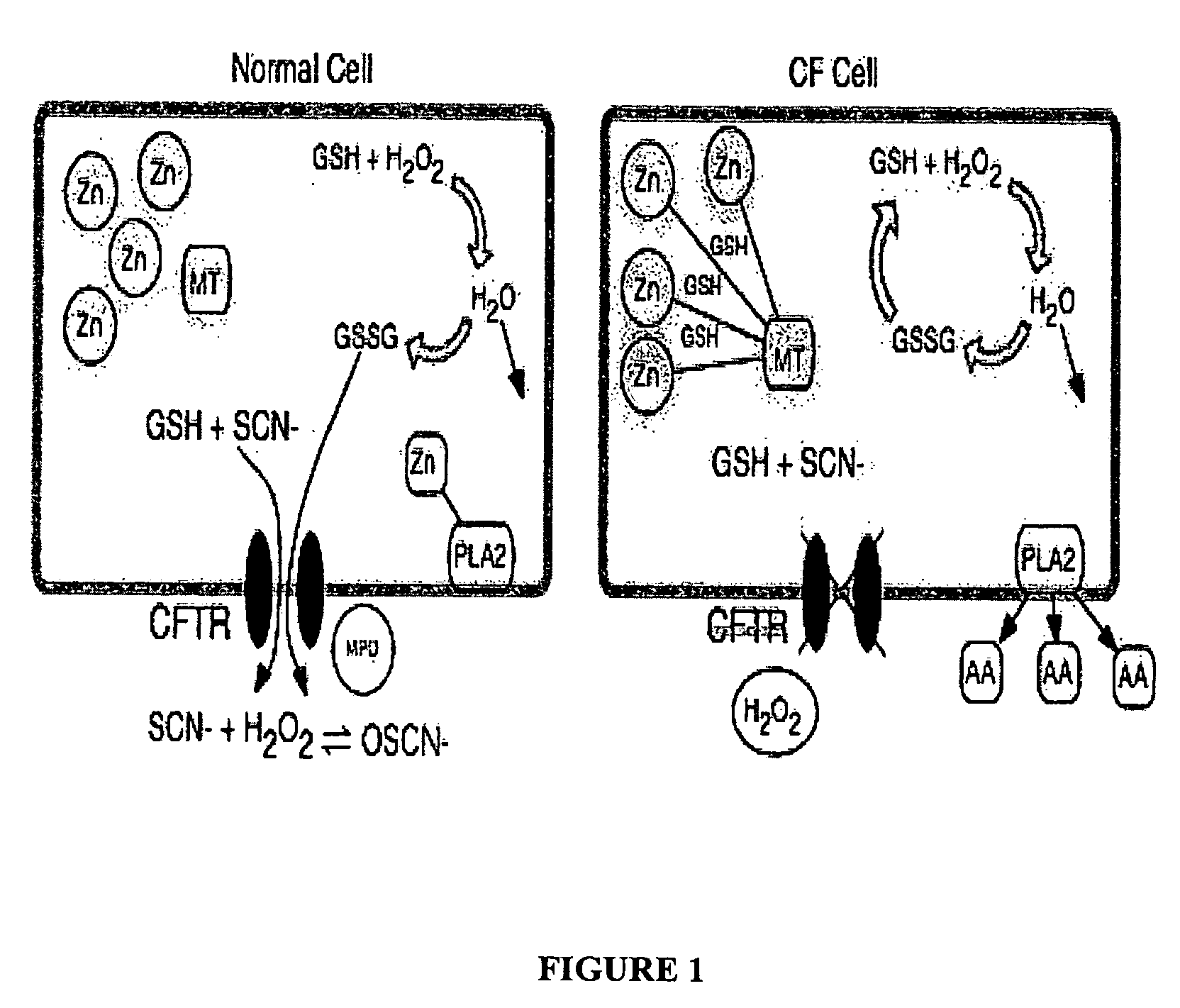
Methods and composition for the treatment of cystic fibrosis and related illnesses
InactiveUS20060258599A1Effective treatmentCorrect cellular GSH imbalancesBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseGlutathione binding
The present invention relates to methods and compositions to treat subjects having cystic fibrosis. These compositions comprise the class of isothiocyanates. Isothiocyanates, absorbed by a cell are conjugated with glutathione GSH by glutathione-s-tranferase (GST). The conjugates are substrates of the multi-drug resistance associated (MRP) / multi-drug resistance (MDR) proteins. These proteins are functionally redundant to the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), allowing for the substrate conjugates to be exported from the cell. The export of GSH conjugates restores intracellular and extracellular levels of GSH to normal levels. Normalizing both extracellular and intracellular GSH via the increased conjugation of isothiocyanates with GSH, and subsequent export, can significantly rectify numerous enzymatic processes and correct the pathologies that are typical of patients suffering from cystic fibrosis.
Owner:CHILDERS MELANIE
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxy substituted carboxylic acid esters
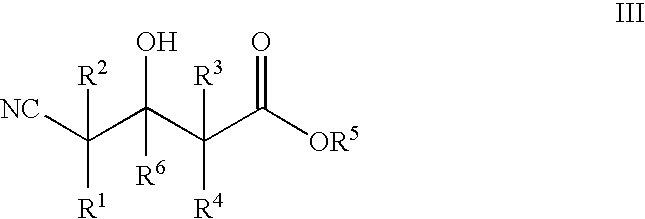
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives The present invention also provides methods and compositions for preparing vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
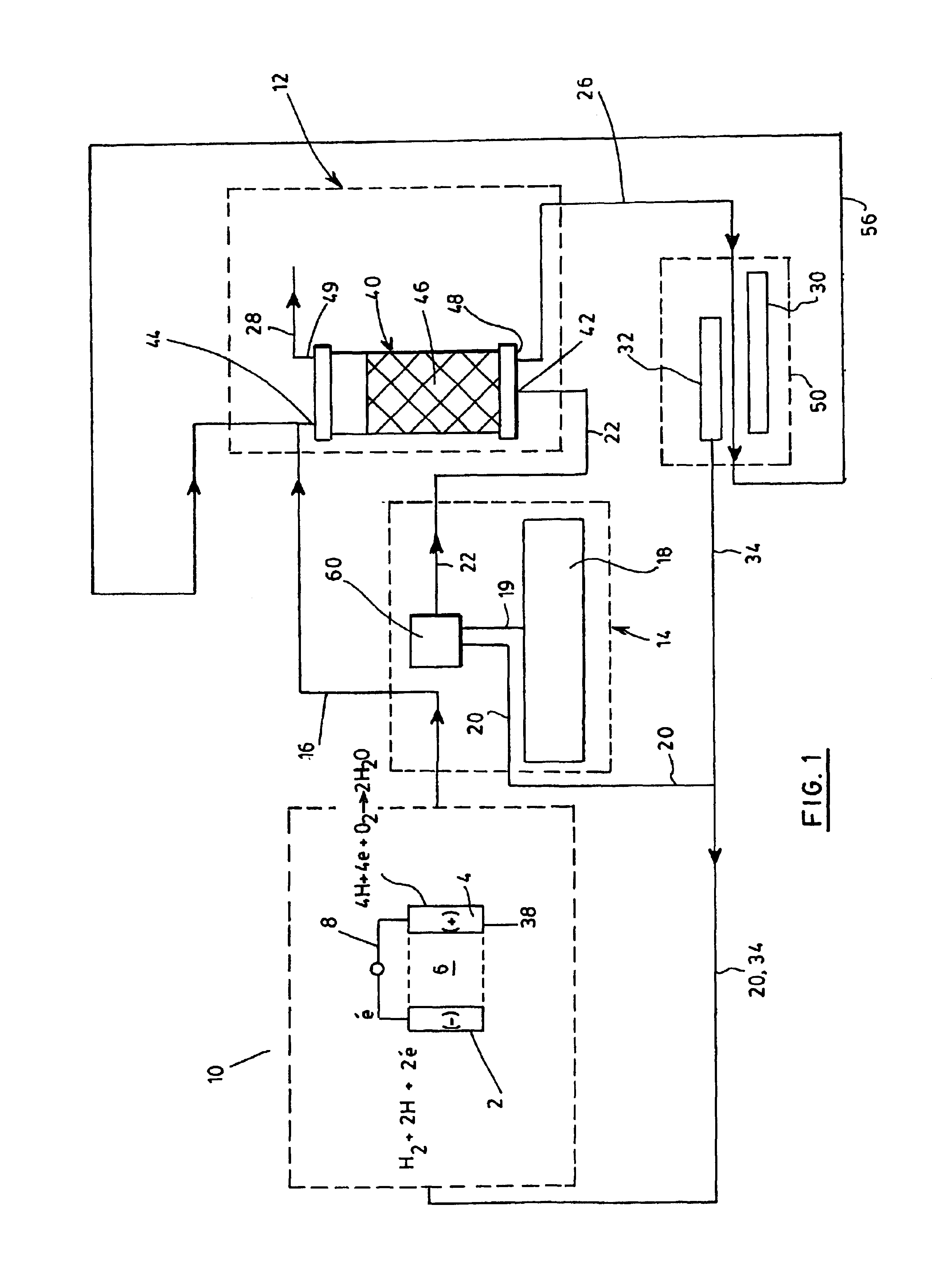
Process for generating electricity with a hydrogen fuel cell
InactiveUS6846584B2Improve hydrogen efficiencySimple and non-pollutingFinal product manufactureRegenerative fuel cellsElectricityCoupling
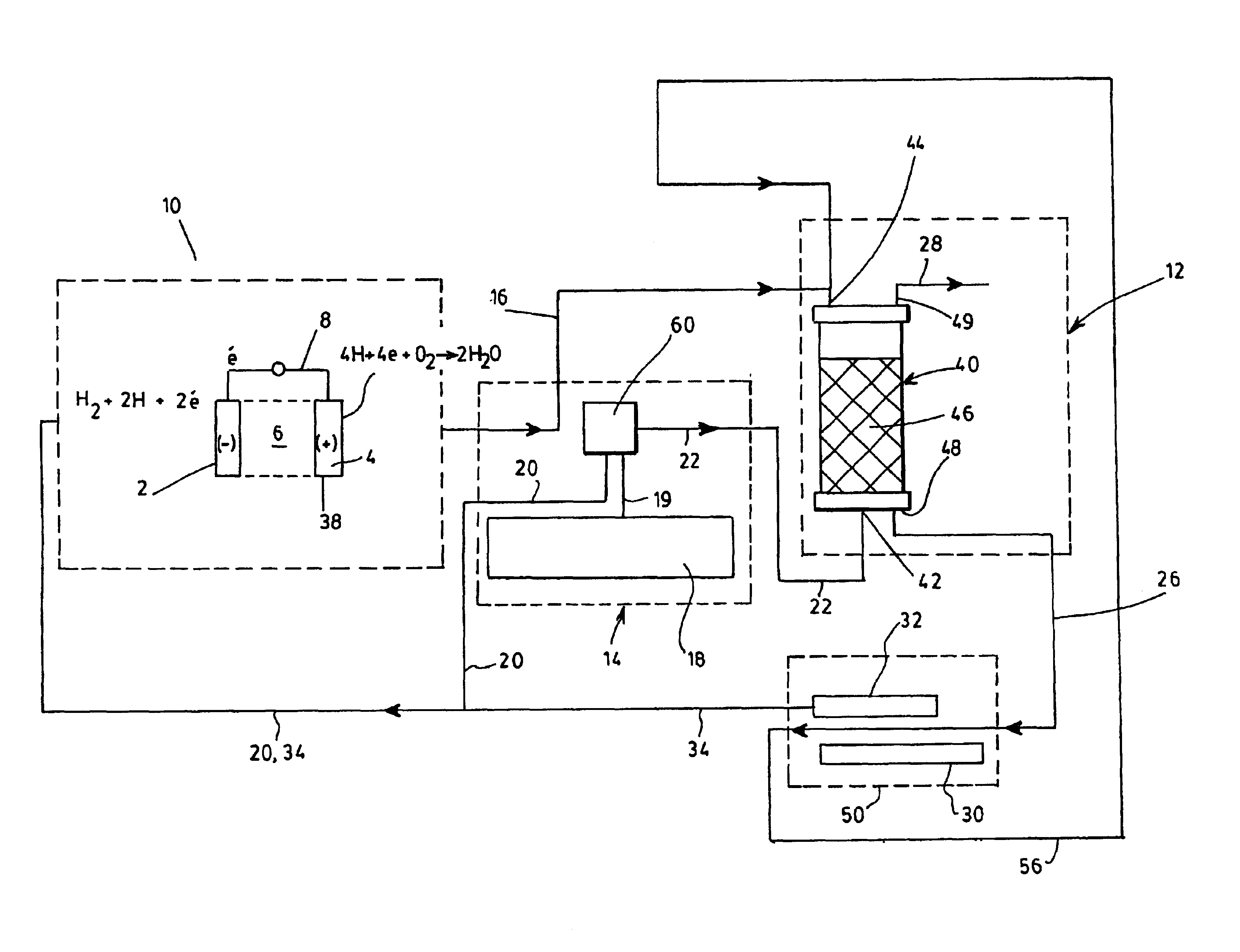
The object of the invention is the coupling of a hydrogen fuel cell to an enzymatic process for the production of electricity and the transformation and sequestration of CO2. Gaseous CO2 emissions from processes such as hydrocarbon reforming are transformed into carbonate or bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions by the enzymatic system in order to prevent their contribution to the greenhouse effect. The hydrogen ions resulting from the enzymatic process are recovered and combined in order to supply the hydrogen fuel cell. Finally, water, a by-product of the oxidizing reaction of the hydrogen fuel cell, is recovered and recycled back into the aqueous enzymatic system.
Owner:CO2 SOLUTION
Process and apparatus for performing a gas-sparged reaction
InactiveUS7201884B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSolubilitySufficient time
An improved process, such as a microbiological or enzymatic process, and apparatus, such as an apparatus for producing a cellular product, comprising introducing a gaseous feed stream of at least one gas of low solubility into an aqueous medium containing a microorganism capable of converting said gaseous feed stream to a cellular product, entraining the gas in the aqueous medium, stirring the gas-entrained aqueous medium so that the gas is retained within the reactor for a time sufficient for the microorganism to convert the majority of the gas to product.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Keratin Hydrolysates, Process for Their Production and Cosmetic Composition Containing the Same
InactiveUS20100196302A1Reduce molecular weightEncourages recyclingCosmetic preparationsHair removalFiberMicroorganism
This present invention provides a process for keratin hydrolysis by means of microbiological and / or enzymatic processes. In particular, the keratin is derived from feathers of animals, such as chicken and are submitted to hydrolysis by a strain of Bacillus sp. The hydrolysates have molecular weight lower than 500 Da, which makes them ideal for cosmetic applications, particularly for applications in compositions for treatment of hair fiber re-building.
Owner:UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DO RIO DE JANEIRO UFRJ
Extraction method for bioactive collagen
ActiveCN103966294AOvercome the shortcomings of incomplete hydrolysisReduce the risk of animal originConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsEnd-groupFiltration
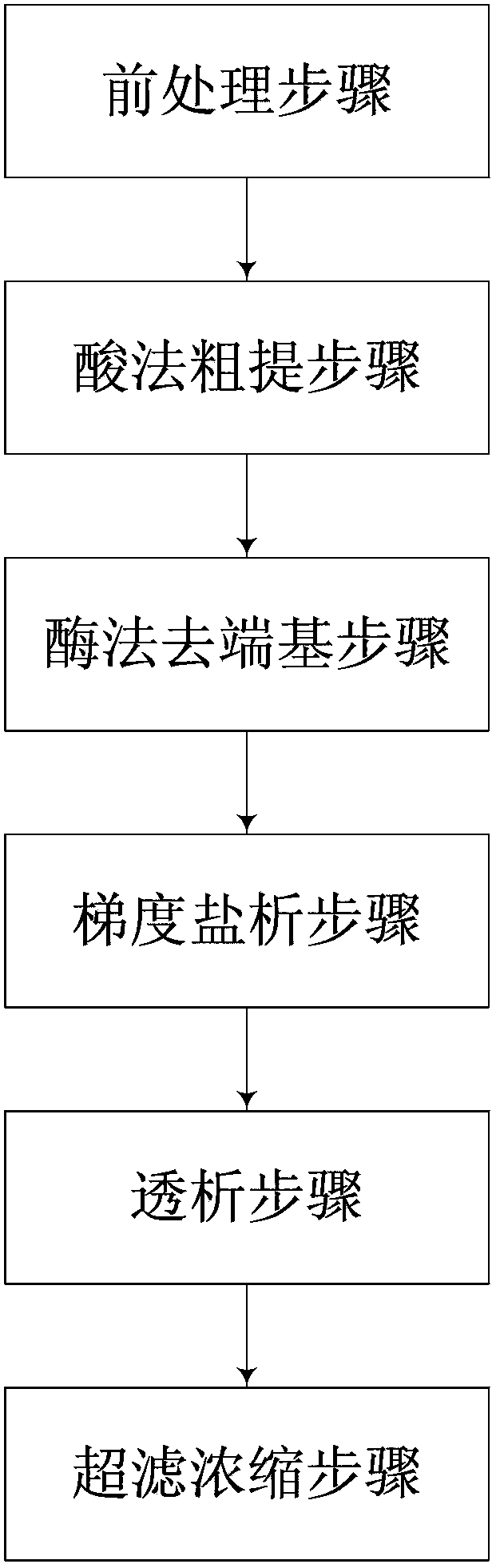
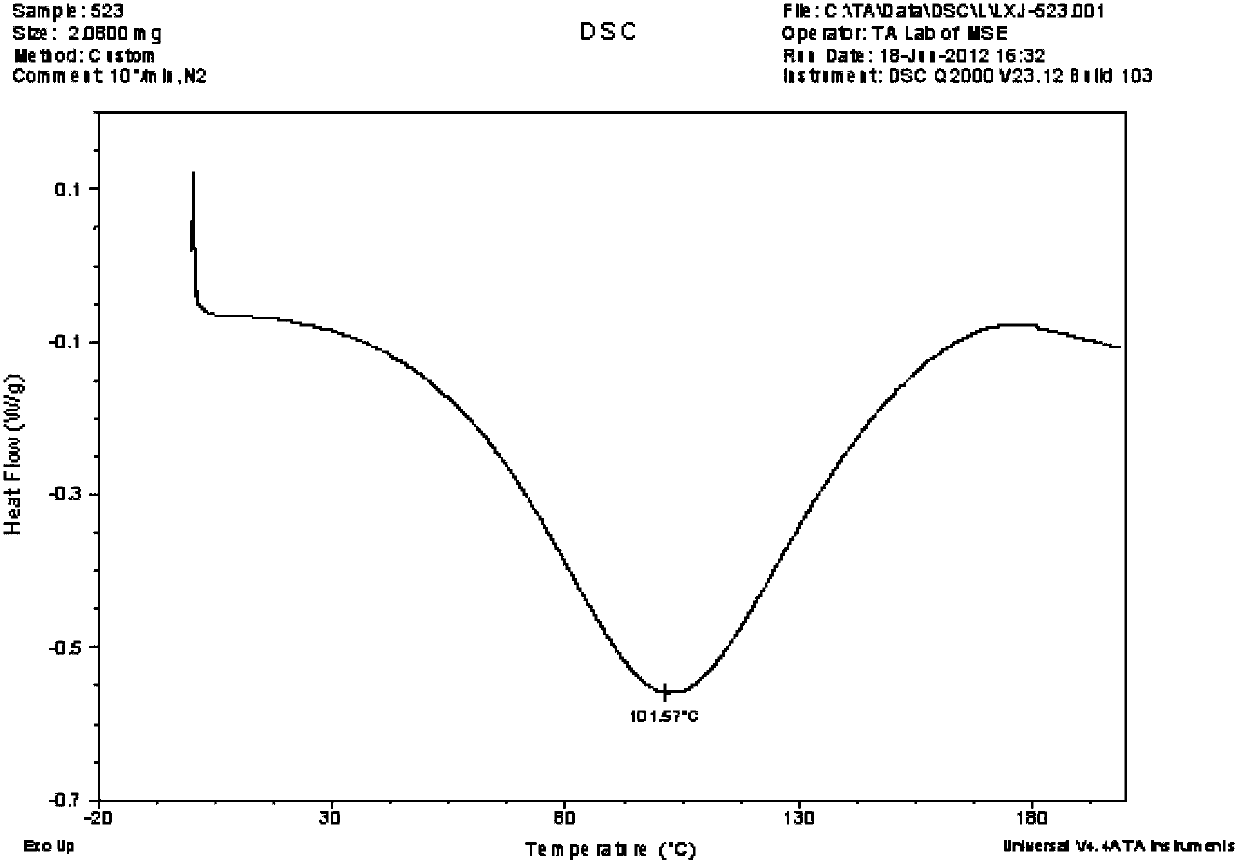
The invention relates to an extraction method for bioactive collagen. The method comprises: a pretreatment step, i.e. pretreating fresh bovine tendon into fragments for standby use; an acid process crude extraction step, i.e. taking 1 part by weight of fragment, adding 4-8 parts by weight of an acetic acid or citric acid solution and conducting stirring, then carrying out coarse filtration, performing high speed centrifugation on a coarse filtrate, then taking the supernatant for standby use; a step of end group removal by an enzymatic process, i.e. adjusting the pH of the supernatant to 9.0, then adding 0.1-0.3% part by weight of Ficus proteinase to conduct enzymolysis digestion; a gradient salting-out step, i.e. using a precipitating agent to conduct multi-gradient salting-out treatment on the solution subjected to enzymolysis to obtain a collagen dissolved solution; and a dialysis step, i.e. loading the collagen dissolved solution into a dialysis bag, using an acetic acid solution and pure water as outer dialysate in order to conduct dialysis, thus obtaining a collagen stock solution with bioactivity. The method provided by the invention combines two existing collagen extraction processes, i.e. the acid process and the enzymatic process, overcomes the low yield defect of the acid process and the incomplete hydrolysis defect of the enzymatic process, and adopts non-animal derived protease, thus reducing the risk of animal origin.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Enzymatic-process method for improving emulsifying property and gelation property of pea protein
InactiveCN101703147AFunctional characteristics are not idealIncrease useVegetable proteins working-upFood industryPea protein
The invention provides an enzymatic-process method for improving emulsifying property and gelation property of pea protein, which belongs to the technical fields of agricultural-product deep processing and food industry. The invention relates to the modification of transglutaminase (also named glutamine transamine enzyme) to pea protein. The method takes pea protein as raw material and utilizes transglutaminase to modify the pea protein in different degrees so as to improve the emulsifying property and gelation property of the pea protein. A process of modifying the pea protein comprises the steps of mixing pulp, regulate pH, adding the transglutaminase, performing enzyme modification, concentrating, drying and obtaining modified pea protein. The method can obviously improve the emulsifying property and gelation property of the pea protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for extraction of tea seed oil by ultrasound-assisted enzymatic process
InactiveCN103254989AImprove oil yieldNo harmFatty-oils/fats productionEdible oils/fatsAlkaline proteaseCellulose
The invention relates to a method for extraction of tea seed oil by an ultrasound-assisted enzymatic process. The method includes: subjecting tea seeds to hulling, drying and crushing, then mixing the crushed tea seeds with water, conducting a heat treatment to perform enzyme deactivation, then carrying out an ultrasonic treatment, adjusting the pH, then adding alkaline protease and composite cellulose to undergo enzymolysis, conducting centrifugation and taking the upper oil, and performing vacuum drying. Compared with the existing tea oil extraction technologies, the method provided in the invention has the advantages of high oil yield, simple operation, no harm to human body, as well as cheap and easily available equipment, thus being suitable for large scale promotion and application.
Owner:HEYUAN LVKANG ECOLOGICAL AGRI TECH CO LTD
Aroma camellia oil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103725417AAvoid the effects of oil qualityAvoid influenceFatty-oils/fats refiningMaillard reactionCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses an aroma camellia oil which is prepared by adopting the following steps: (1), preparing foots slurry; (2), performing enzymolysis and Maillard reaction; (3), obtaining fragrant digestion grease; and (4), dewatering. According to the fragrant camellia oil, camellia oil foots is adopted as a raw material for preparation, and aroma substances are mainly from a protein denaturation aroma and a aroma formed by reducing sugar in camellia seeds and amino acid in a low-temperature enzymatic process through the Maillard reaction. According to the fragrant camellia oil, the problems of influence of high temperature on quality of the camellia oil in a conventional cooking aroma enhancing procedure, inactivation of active substances in nutritional ingredients in the camellia oil due to the high-temperature long-term Maillard aroma enhancement reaction of and aroma reduction of the camellia seed oil are avoided, and thus the camellia oil which is not damaged in nutrient substances and is thick in aroma is obtained. The camellia oil has the advantages of recycling waste materials, and being simple in process, low in operation cost and stable in product quality. The aroma camellia oil prepared by using the preparation method disclosed by the invention is capable of generating higher economic benefit.
Owner:ANHUI ZHONGSHENG EDIBLE OIL TECH
Mutants of formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii, new gene sequences encoding these and use of the new formate dehydrogenases
InactiveUS6242234B1Longer working lifetimeFungiMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliWild type
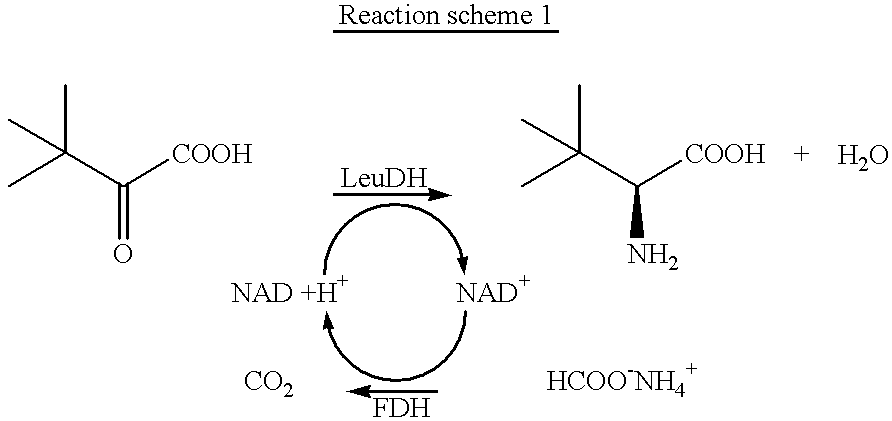
The invention relates to new mutants of formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii, new gene sequences encoding these and use of the new formate dehydrogenases.The wild type FDH used hitherto in the industrial process for preparing amino acids becomes inactive after a certain time. New mutants of this wild type have been produced by targeted mutagenesis of a recombinant FDH from E. coli. The new mutants are preferably used in an enzymatic process for preparing chiral compounds.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Dewatering process
InactiveUS6872314B2Ion-exchange process apparatusOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationSimple Organic CompoundsSimulated moving bed
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Enzyme-catalyzed polycarbonate and polycarbonate ester synthesis
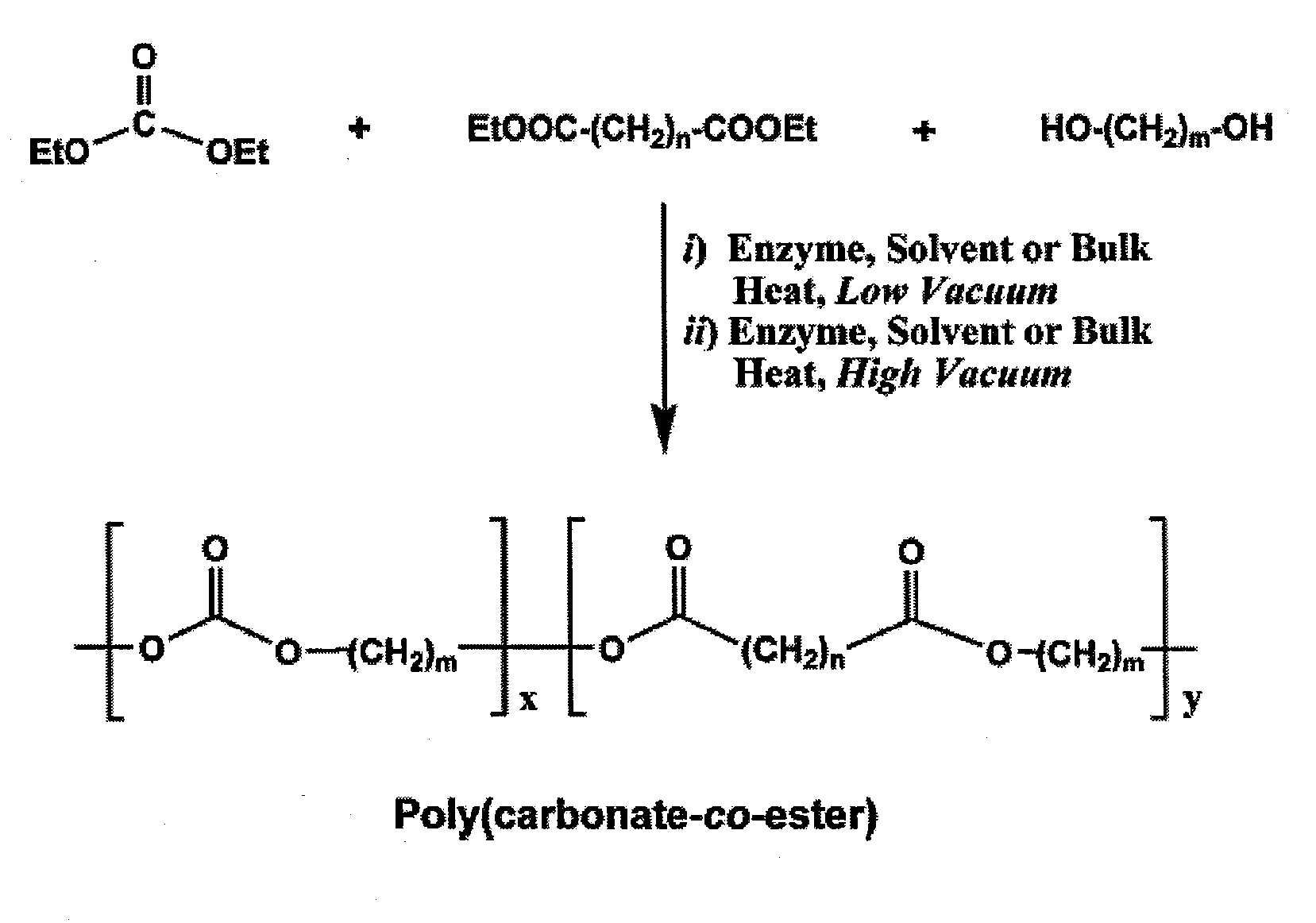
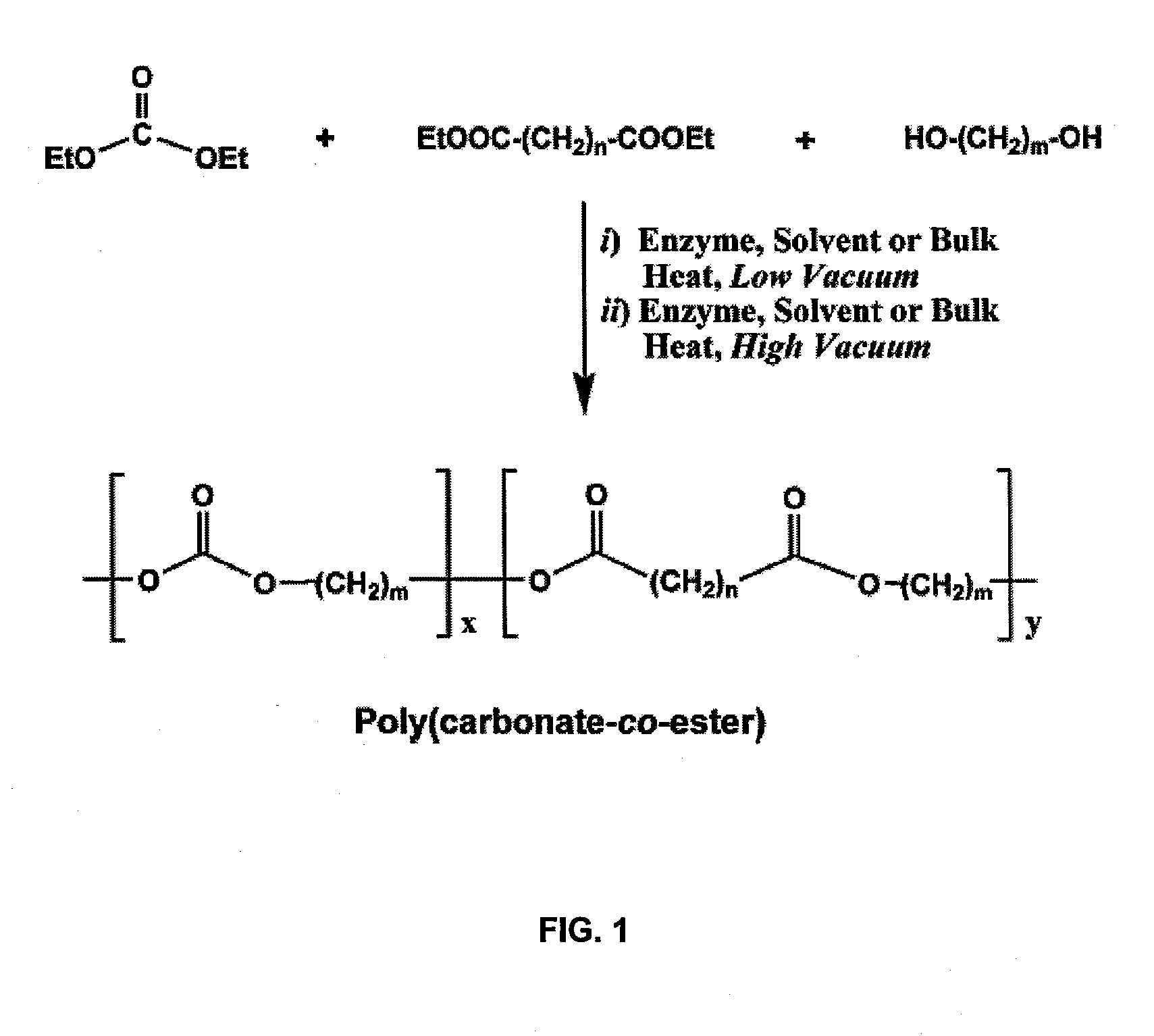
InactiveUS20100041856A1Strong specificityEasy to controlFermentationTransesterificationPolycarbonate
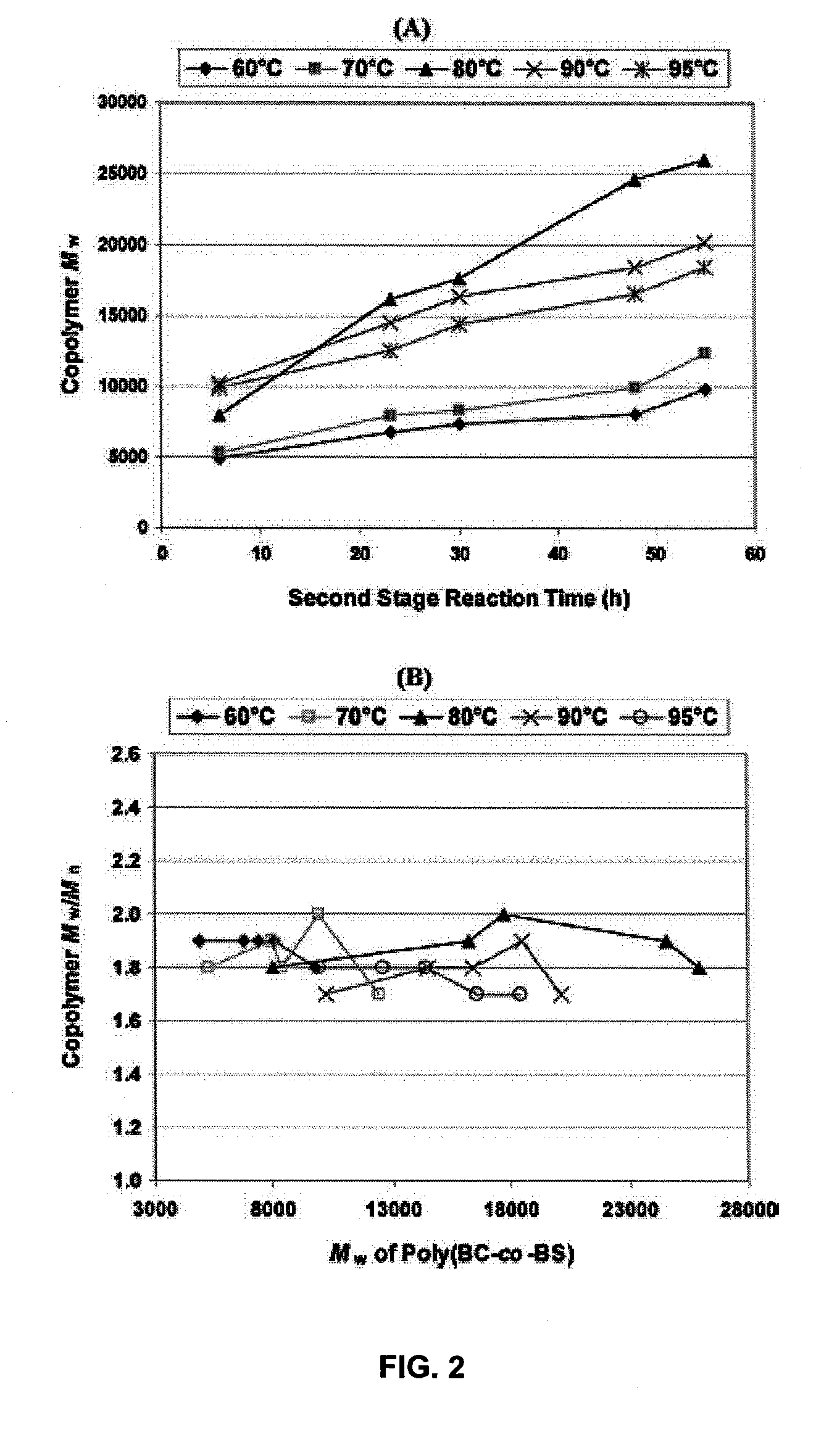
An enzymatic process for preparing aliphatic polycarbonates via terpolymerization or transesterification using a dialkyl carbonate, an aliphatic diester, and an aliphatic diol or triol reactant. A catalyst having an enzyme capable of catalyzing an ester hydrolysis reaction in an aqueous environment is subsequently added to the reaction mixture. Next, polymerization of the reaction proceeds for an allotted time at a temperature≦100° C. Finally, the copolymer is isolated from an the catalyst via filtration.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives The present invention also provides methods and compositions for preparing vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Methods for generating rna copies
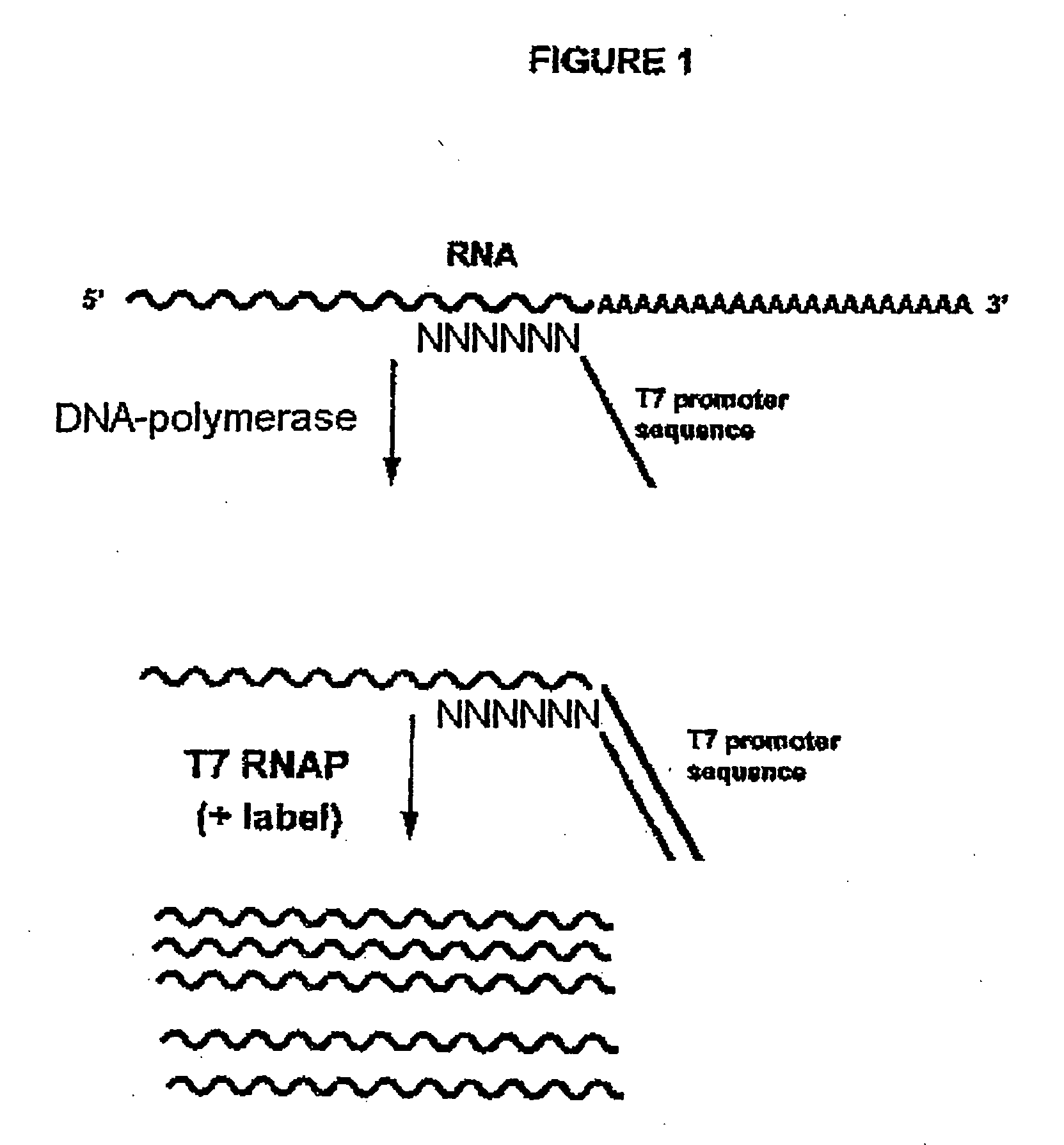
InactiveUS20070128598A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationDna polymerasenOligonucleotide
The present invention is directed to a novel method of efficiently synthesizing, in a non-specific manner, multiple copies of a target RNA. The present invention also relates to kits relating to the same and the use of these copies for determining gene expression pattern. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for generating multiple RNA copies comprising the steps of (a) providing a sample comprising target RNA; wherein said sample is simultaneously contacted with an oligonucleotide comprising at its 5′ side a promoter sequence recognized by an RNA polymerase, wherein each oligonucleotide further comprises a target hybridising sequence, which is a random sequence or a predetermined sequence and possibly a modification at its 3′ terminal end in such a way that extension therefrom is prohibited; and, an enzyme having DNA polymerase activity; an enzyme having RNase H activity; an enzyme having RNA polymerase activity; and, sufficient amounts of dNTPs and rNTPs; and, (b) maintaining the resulting reaction mixture under the appropriate conditions for a sufficient amount of time for the enzymatic process to take place.
Owner:PAMGENE
Method for extracting plant flavone compounds by enzymatic process
InactiveCN101967137AGood curative effectIncrease added valueOrganic chemistryGinkgophyta medical ingredientsBiotechnologyAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for extracting plant flavone compounds by an enzymatic process, which comprises the following steps: (1) lixiviating, wherein enzymolysis water extraction is carried out once, and alcohol extraction is carried out twice; (2) purifying on the columns; (3) and processing the analytic solution to obtain the plant flavone compound product. Under the guidance of biotechnology theory, natural product chemical theory and technology and international drug test standard, the invention formulates an experimental scheme for production, and determines proper enzymatic process extraction technique and flavone glycoside biotransformation technique, thereby obtaining the product with high biological value. The invention determines to compound multiple enzyme preparations, optimizes the optimal transformation conditions and enhances the flavone biotransformation efficiency. The invention formulates a technical scheme of adsorption with macroporous absorbent resin to be used in industrial production, thereby increasing the content of aglycon flavones in the product.
Owner:天津市食品加工工程中心
Process for the production of phospholipids
ActiveUS7034168B2High yieldHigh purityMicroorganism based processesPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsPhospholipaseCarboxylic acid
A new enzymatic process for preparing 1,2-diacylated phospholipids using an enzyme preparation possessing phospholipase activity towards acylation at the sn-1 and sn-2 sites in a microaqueous reaction system. More particularly, the 1,2-diacyl-phospholipids produced according to the esterification / transesterification process are obtainable in high yield and purity and carry identical desired carboxylic acid, preferably fatty acid, acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. The process involves esterification / transesterification (acylation) of a glycerophospholipid, preferably glycerophosphoryl choline (GPC) with a desired carboxylic acid, preferably fatty acid, or their derivatives in the presence of the above mentioned appropriate enzyme preparation. The process of the invention further relates to a process for the production of 1-acyl-2-lyso-glycerophospholipid, preferably 2-lyso-PC by reacting glycerophospholipid, preferably glycerophosphoryl choline (GPC) with a desired carboxylic acid, preferably fatty acid, or their derivatives in the presence of a sn-1 specific phospholipase (PLA1 or PLA1,2) and a solvent, in a microaqueous medium.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Enzymatically synthesized marine phospholipids
InactiveUS20060177486A1Increase ratingsReduce inhibitionFatty acid esterificationClimate change adaptationEnzymatic synthesisRed blood cell
This invention discloses an improved enzymatic process, under organic solvent free conditions, for the incorporation of fatty acids such as omega-3 fatty acids into phospholipids. The rate of transesterification is increased 4 times by adding a base to the reaction mixture, typically an amine. The invention also discloses novel phospholipid compositions as well as novel use of the phospholipid compositions as a food supplement, a fish feed, animal feed and human food. In addition to methods for enriching prey organisms used in aquaculture, methods of reducing arachidonic acid levels in mammalian plasma / red blood cells and methods for increasing DHA levels in the mammalian brain.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ASA
Multifunctional supramolecular hydrogels as biomaterials
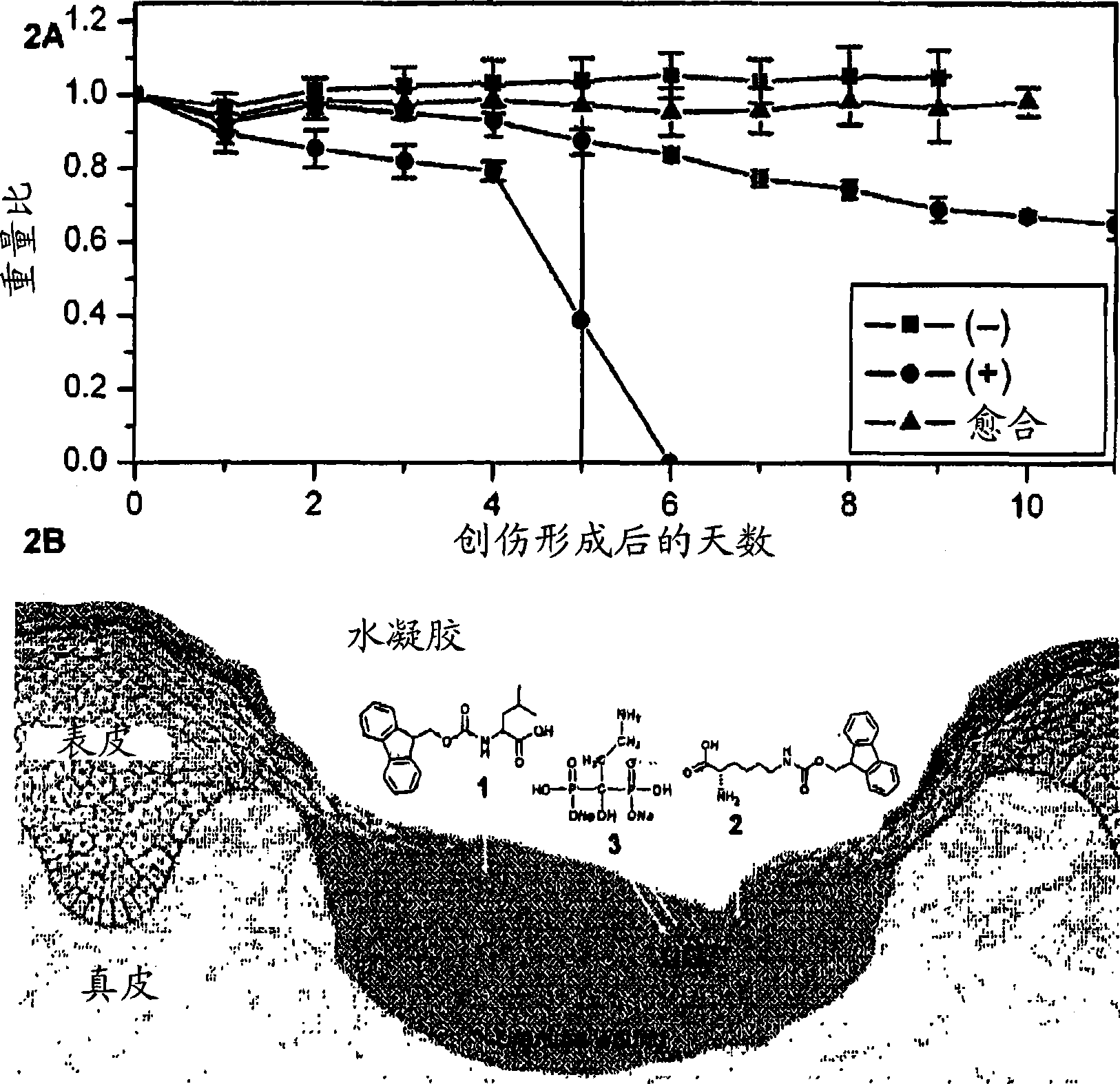
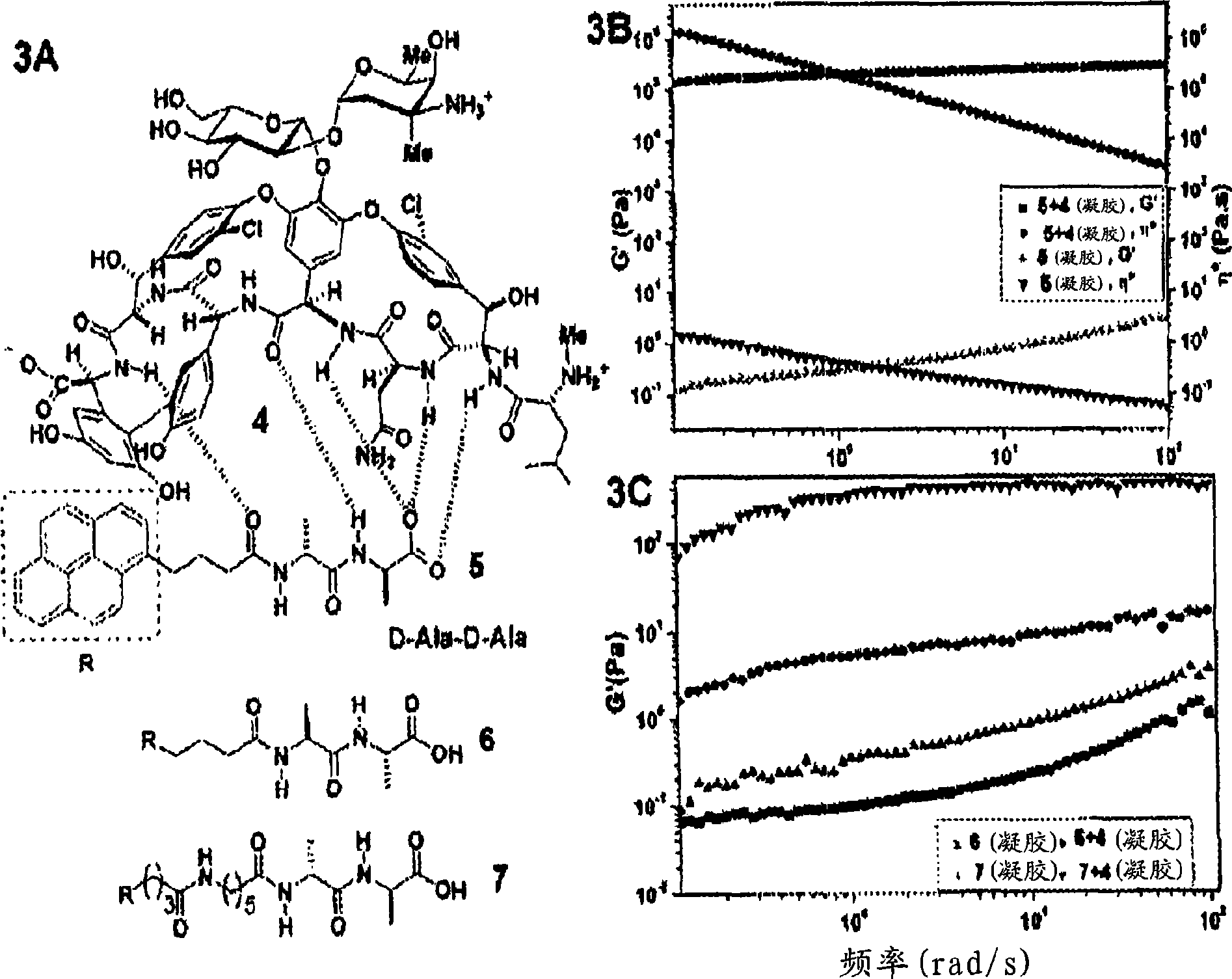
The present invention pertains to the design and application of a supramolecular hydrogel having a three-dimensional, selfassembling, elastic, network structure comprising non-polymeric, functional molecules and a liquid medium, whereby the functional molecules are noncovalently crosslinked. The functional molecules may be, for instance, anti-inflammatory molecules, antibiotics, metal chelators, anticancer agents, small peptides, surface-modified nanoparticles, or a combination thereof. The design of the hydrogel includes: 1) modifying functional molecules to convert them into hydrogelators while enhancing or maintaining their therapeutic properties and 2) triggering -the hydrogelation process by physical, chemical, or enzymatic processes, thereby resulting in the creation of a supramolecular hydrogel via formation of non-covalent crosslinks by the functional molecules. Applications of the present invention include use of the supramolecular hydrogel, for instance, as a biomaterial for wound healing, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and drug / inhibitor screening.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enzymatic process for the preparation of an acetylated phospholipid
InactiveUS6403344B1Simple enzymaticEconomically inexpensiveHydrolasesFermentationPhospholipidEnzymatic process
The present invention provides an enzymatic process for the preparation of an acetylated phospholipid from a lecithin by acetylating the lecithin in the presence of vinyl acetate and a catalyst comprising lipase from Mucor miehei having 1,3-position specificity, separating the desired acetylated phospholipid.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for cell-free production of chemicals
An enzymatic process is described for the production of chemicals from carbon sources. In particular, according to one aspect, a process for the production of a target organic compound from a carbon source by a cell-free enzyme system is disclosed.
Owner:CASCAT GMBH
Preparation method of soya-bean milk
The present invention discloses a preparation method of soya-bean milk and belongs to the technical field of food processing. The preparation method is as follows: weighing the dried beans, adding water, beating, and then adding cellulase or a compound enzyme of cellulase and other enzymes for enzymolysis; after enzymolysis, separating soybean milk and soybean residue to obtain clarified soybean milk; and homogenizing and sterilizing the clarified soybean milk. The preparation method uses in the enzymatic process, so that the soybean milk has taste and flavor better than the ordinary milk added with alkali; the yield of milk is improved; the produced soybean milk has the nutrition and health effects, in order to meet the demand for soybean products of consumers.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting sesame oil
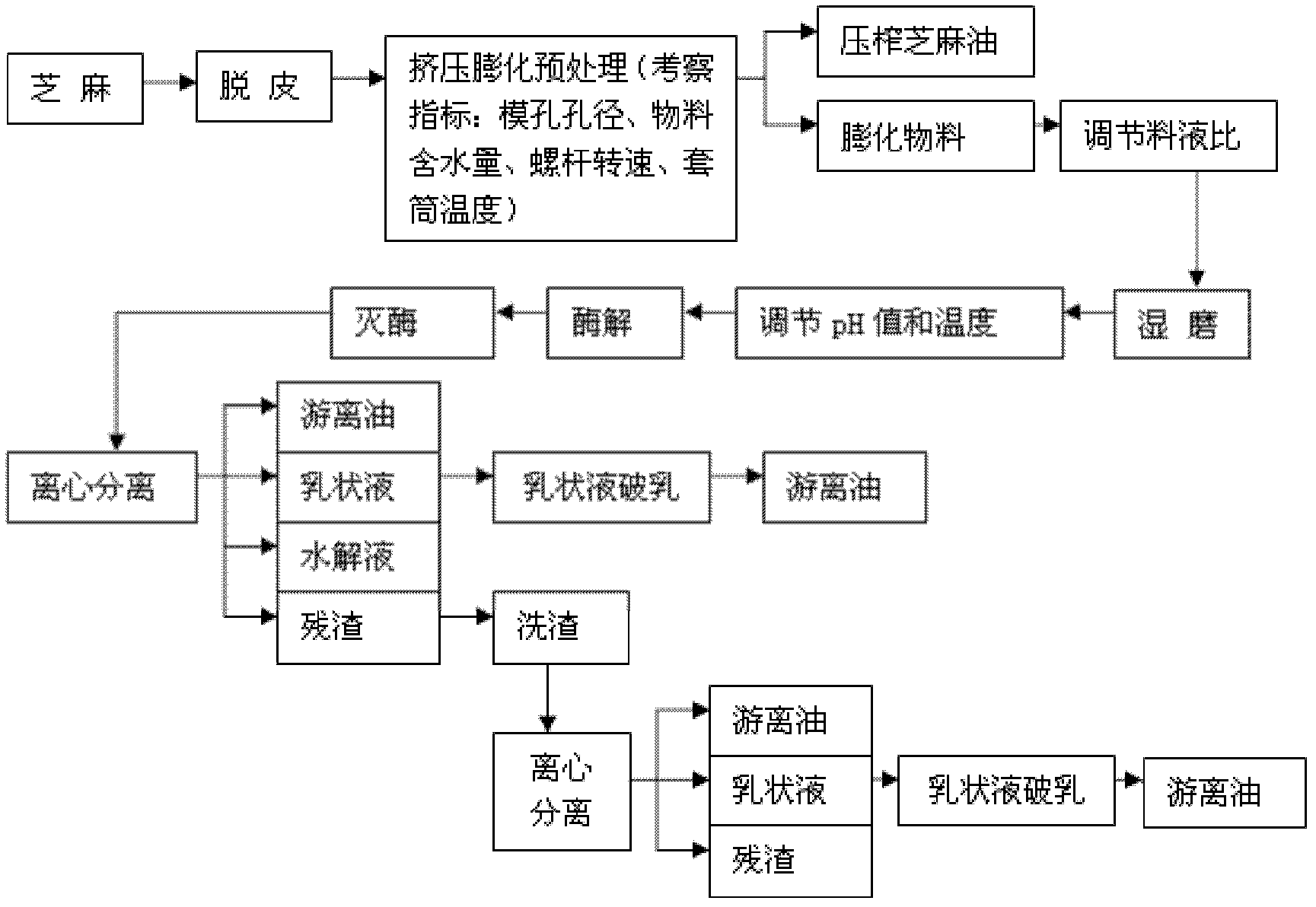
InactiveCN102559367AQuality improvementImprove qualityFatty-oils/fats productionEnzymatic processProtease
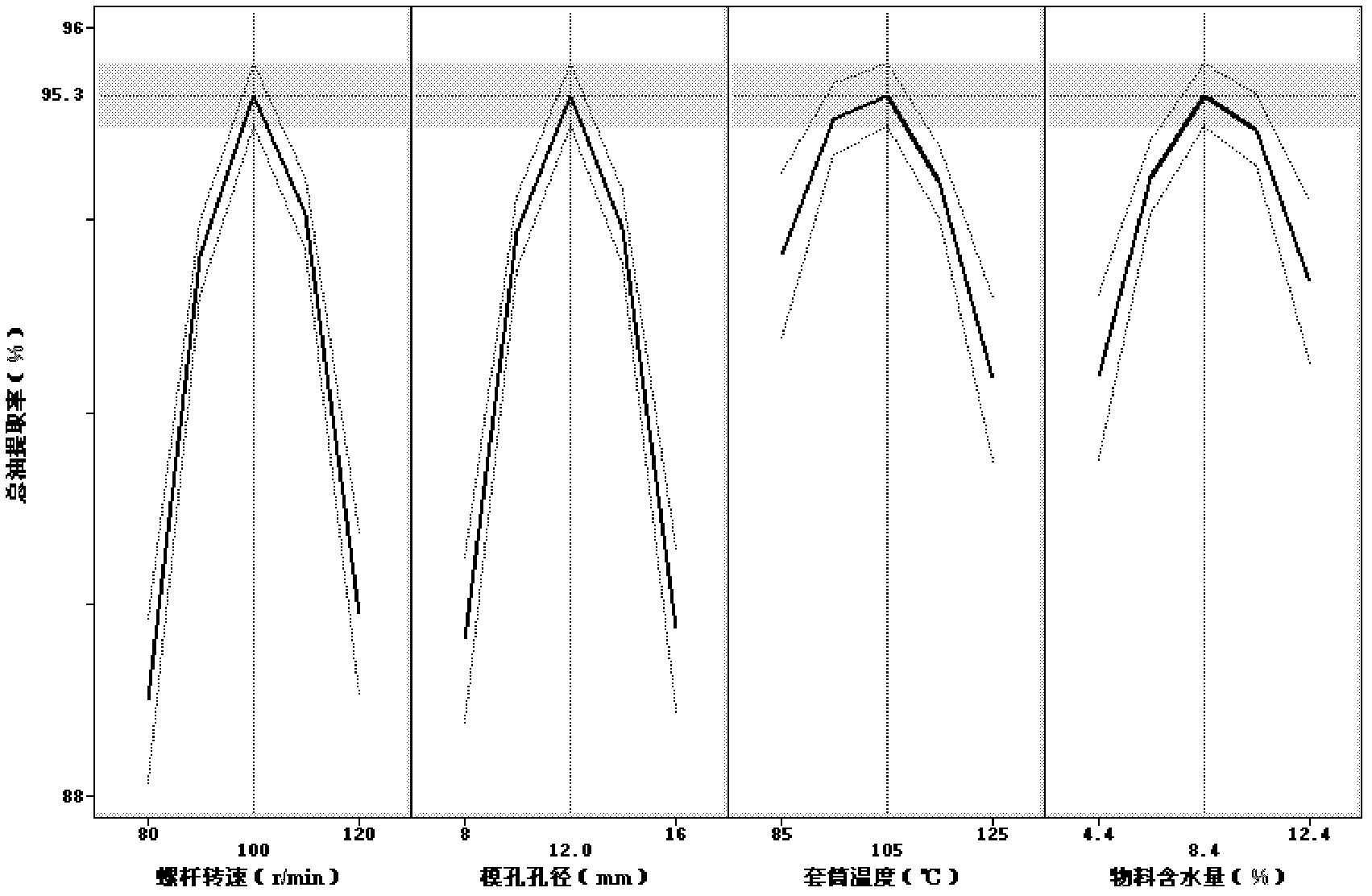
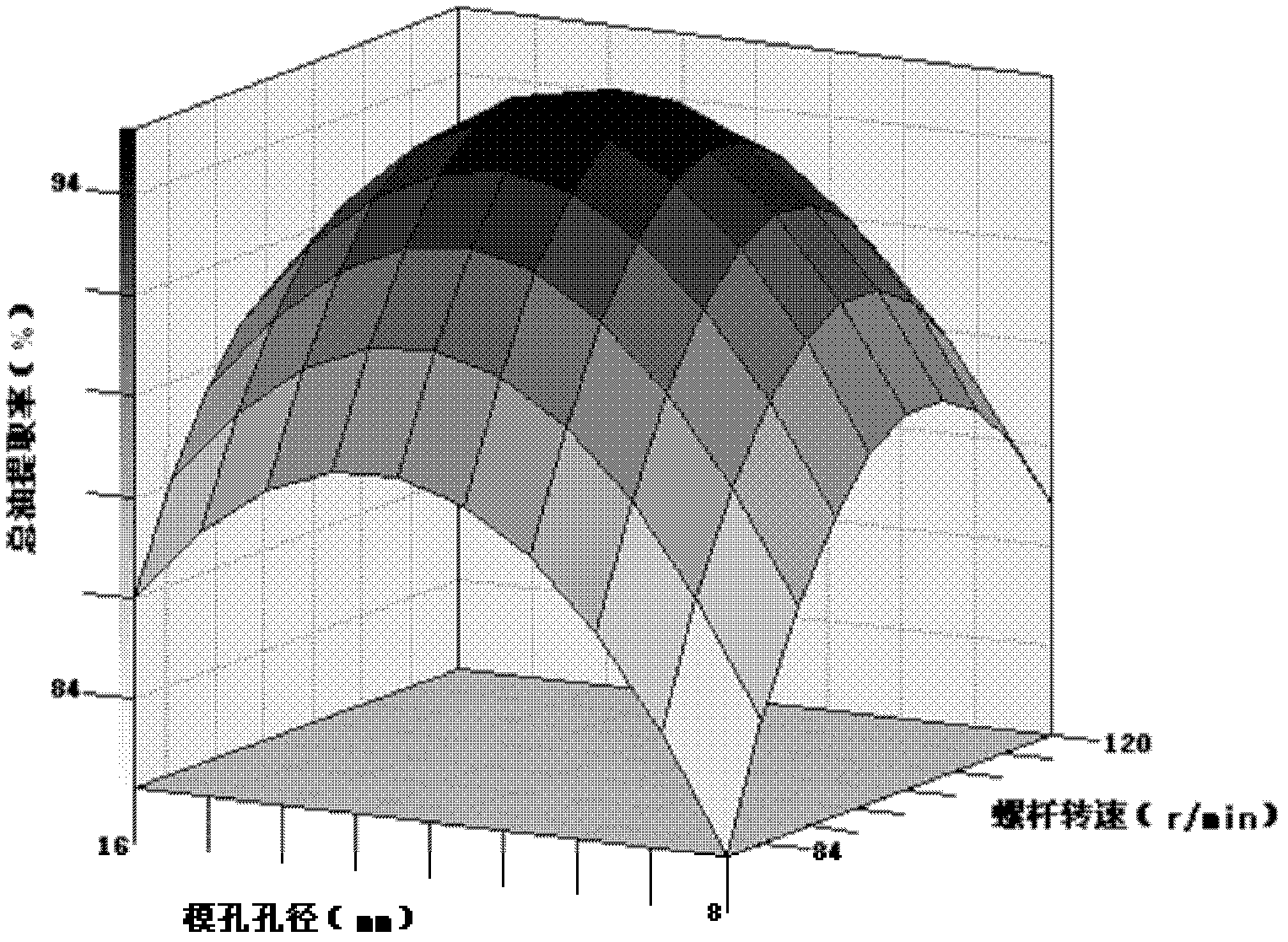
The invention relates to a method for extracting sesame oil and fat, which comprises the following steps: extruding and puffing sesames in a single-screw extruder, recovering oil and fat by using a pressing cage and obtaining squeezed sesame oil; mixing the extruded and puffed sesames with water, grinding the mixture on a wet grinder to obtain mixed solution, adding protease into the mixed solution for enzymolysis to obtain enzymatic solution; and deactivating enzyme in the enzymatic solution, performing centrifugal separation, and obtaining free sesame oil and fat. According to the invention, the sesame oil and fat are separated by an aqueous enzymatic process which combines extruding and puffing pretreatment and biological enzyme, the equipment is simple and safe for operation and can produce high-quality sesame oil with high nutrition value and low-denaturation high-quality sesame proteins and peptides. According to the results of test and comparison tests, the method can achieve a total oil extraction rate of about 93.18 percent under an enzymatic process condition, and can achieve a higher total oil extraction rate of about 97.98 percent.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enzymatic process for the production of mannosylerythritol lipids from lignocellulosic materials
The present invention relates to processes for the production of microbial glycolipids, mannosylerythritol lipids (MEL), from lignocellulosic carbon source. These processes are characterized in that the use of lignocellulosic materials for the production of a microbial glycolipids, MEL, comprising a fermentation preferably using fungi of the genus Pseudozyma or other microorganisms such as genetically modified fungi or bacteria. The processes for production of microbial glycolipids, MEL comprise three steps: pretreatment of lignocellulosic material; enzymatic hydrolysis; and fermentation. The enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation may take place sequentially or simultaneously with addition of exogenous enzymes or simultaneously with enzymes produced by the microorganism itself. The produced microbial glycolipids have applications as: biosurfactants; antimicrobials; anticancer agents; wound healing factors; stabilizer agents on storage and purification of proteins or vaccines; drugs and gene deliver agents; antifreeze agents.
Owner:INST SUPERIOR TECH +1
Method for extracting rapeseed oil through near-infrared preprocessing auxiliary aqueous enzymatic process
ActiveCN107057830AHigh extraction rateLow acid valueFatty-oils/fats refiningFatty-oils/fats productionFlavorOil and grease
The invention discloses a method for extracting rapeseed oil through a near-infrared preprocessing auxiliary aqueous enzymatic process and belongs to the field of food deep processing. In order to solve the problems of low boiled oil extraction rate and insufficient grease flavor of the single aqueous enzymatic method for extracting rapeseed oil, high-quality cabbage type double-low peeling rapeseeds are taken as raw materials, a near-infrared heating technique is adopted for preprocessing the rapeseed oil, and an aqueous enzymatic process oil extraction technique is adopted for preparing high-quality rapeseed oil.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzymatic process combined with hot caustic extraction for the removal of hemicelluloses from paper-grade pulp
ActiveUS20170350072A1Reduction in yieldHigh yieldPulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesHemicelluloseEnzymatic process
The present invention relates to the removal of hemicelluloses from paper-grade alkaline pulp thereby upgrading the pulp e.g. into dissolving-grade pulp using a combination of enzyme treatment, hot caustic extraction and optionally one or more bleaching steps.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
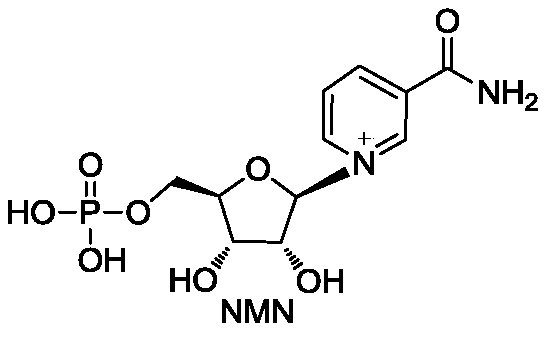
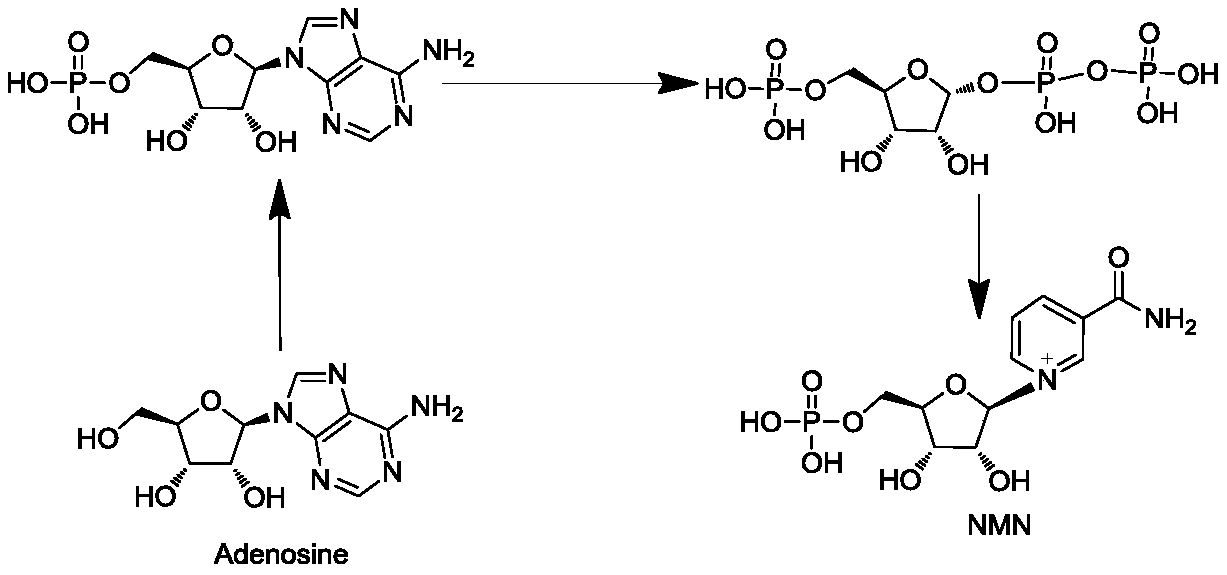
Enzyme composition for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide and method for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide by enzymatic process
The invention relates to the technical fields of biopharmacy and biochemical industry, and in particular relates to an enzyme composition for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide and a method for preparing the nicotinamide mononucleotide by an enzymatic process. The enzyme composition is composed of adenosine kinase, adenine phosphoribosyl transferase and nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase.The three enzymes provided by the invention can be reasonably combined for efficient catalytic preparation of the nicotinamide mononucleotide. The enzyme composition provided by the invention can be recycled, has low costs, saves energy and protects the environment; the method for preparing the nicotinamide mononucleotide by the enzymatic process provided by the invention uses adenosine as a substrate, the enzyme composition is added, so that the nicotinamide mononucleotide can be prepared at low cost, safely and reliably, the cost of a current route can be reduced, and the method can be suitable for large-scale production and provides guarantee for the use of the nicotinamide mononucleotide in the fields of biocatalysis and drugs.
Owner:杭州唯泰生物药业有限公司 +1
Preparation method of shrimp powder compound seasoning
InactiveCN102823834AMild reaction conditionsEasy to makeFood preparationNeutral proteaseFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of shrimp powder compound seasoning, which comprises the following steps of: 1) taking fresh shrimp leftovers, adding distilled water, cooking, pulping and filtering; adding flavor enzyme and neutral protease into shrimp head pulp, adding Alcalase alkaline protease, adjusting the pH, controlling the temperature, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis, cooling and freeze-drying; 2) adding reducing sugar into an enzymatic hydrolysate, heating and reacting, and cooling and freeze-drying; 3) adding other seasonings into a product cooled and freeze-dried in the step 2) and uniformly mixing; and 4) drying to prepare the shrimp powder compound seasoning. The preparation method of the shrimp powder compound seasoning has the beneficial effects that hydrolyzed animal protein obtained by utilizing an enzymatic hydrolysis technology contains rich free amino acid, facilitates the digestion and the absorption of human bodies and can be used for fragrance enhancement of the seasoning; and by adopting an enzymatic process, the reaction conditions are mild, the preparation is simple, and the original flavor is furthest kept. The compound seasoning prepared by various auxiliary materials is strong in fragrance and delicious in shrimp flavor and is senior seasoning integrating the effects of seasoning nutrition and health care.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG TAOYUAN FOOD
Concentration of fatty acid alkyl esters by enzymatic reactions with glycerol
InactiveUS20060286266A1Food safetyFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningOrganic solventGlycerol
An enzymatic process for the kinetic separation of alkyl esters under organic solvent free conditions is disclosed. Alkyl esters obtained from e.g. fish oil are reacted with glycerol, in the presence of water, at different rates in an evacuated chamber. The reaction is terminated prior to reaching equilibrium and the enriched alkyl ester fraction is isolated from the reaction mixture by short path distillation.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
Chemo-enzymatic process for proteome-wide mapping of post-translational modification
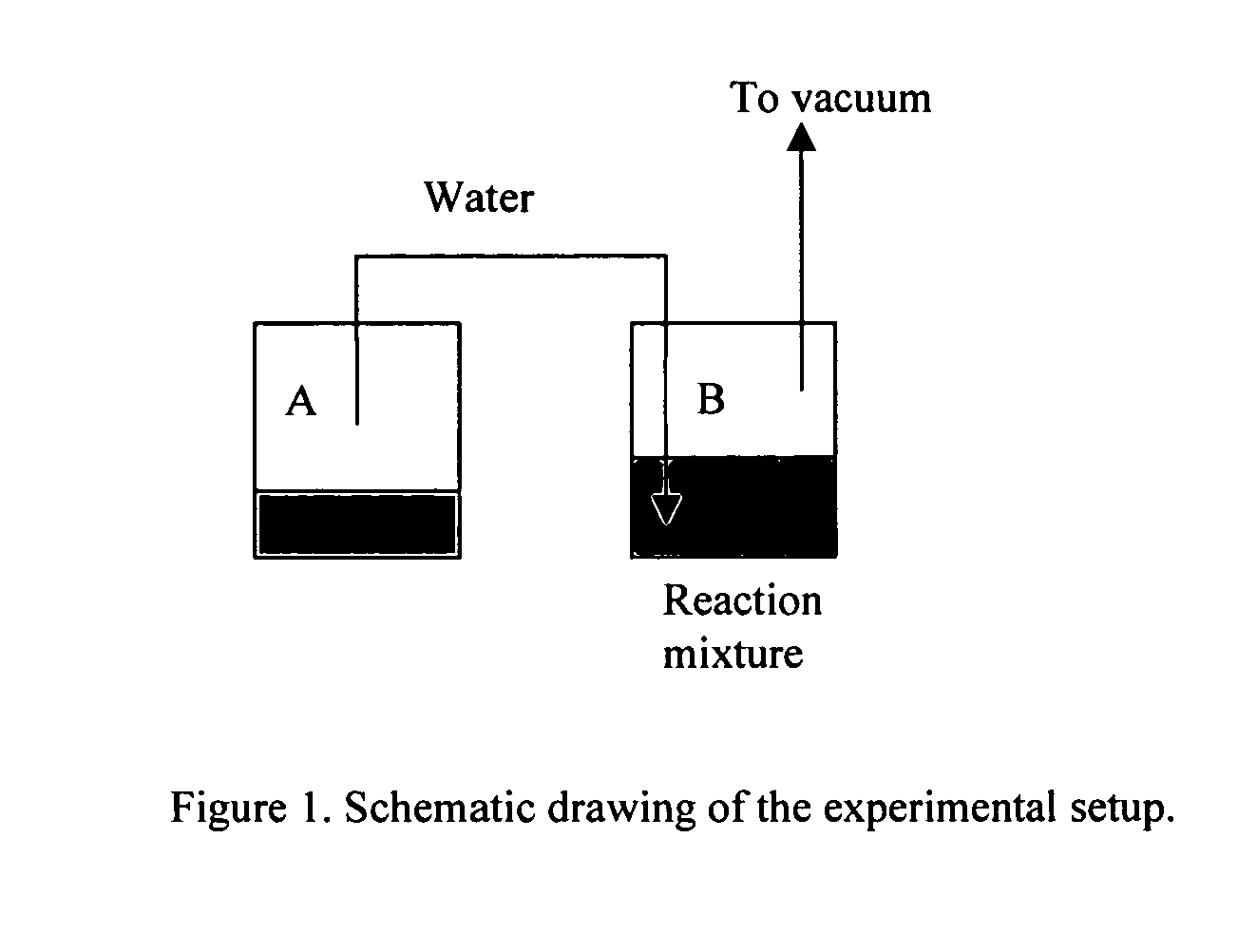
InactiveUS20060246531A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsPost translationalChemo enzymatic
The invention provides a method for mapping the location of the post-translational modifications of a post-translationally modified peptide. Also provided is a solid-phase support that includes a reagent for modifying a post-translationally modified amino acid residues of a post-translationally modified, converting it into a substrate for a peptidase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com