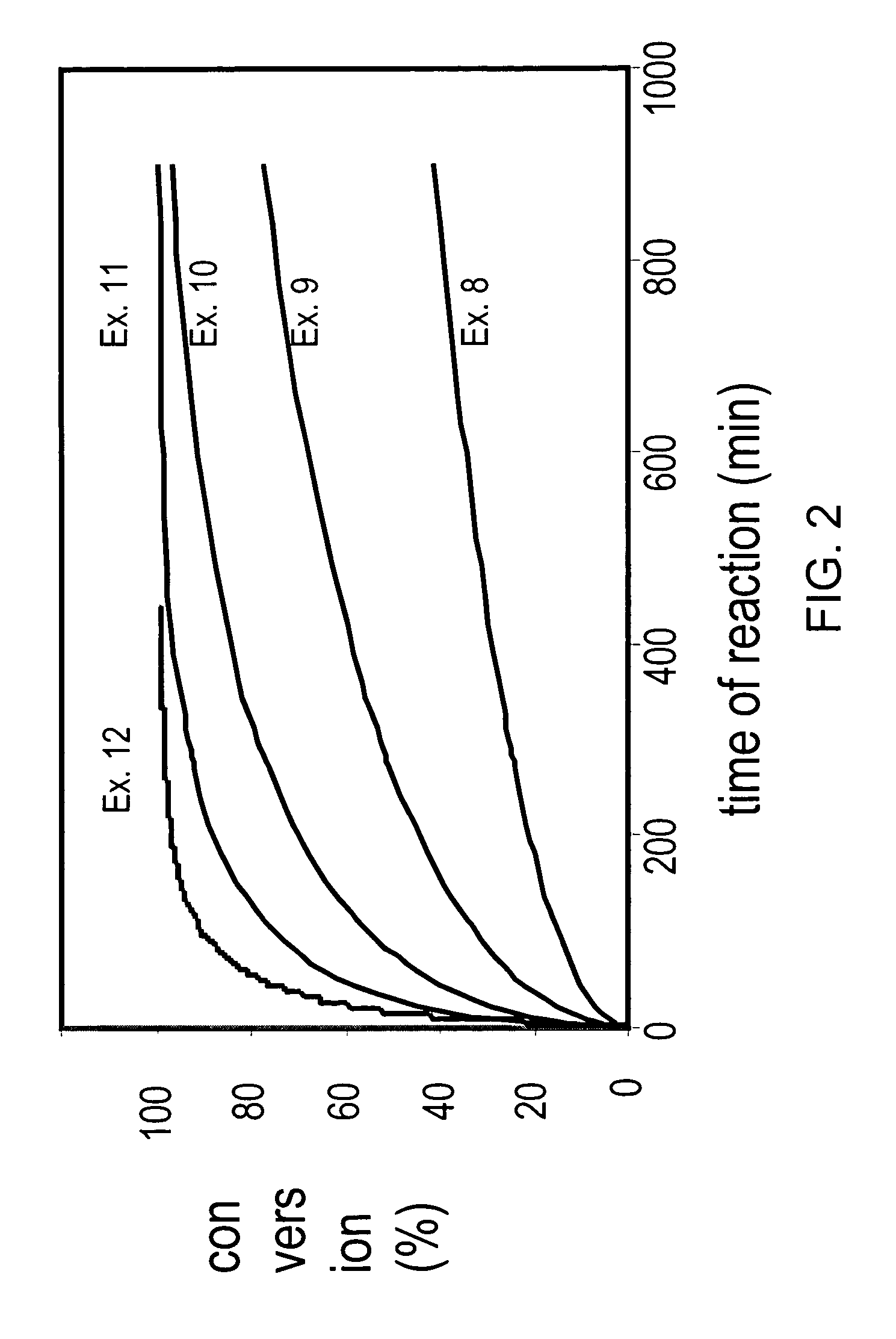
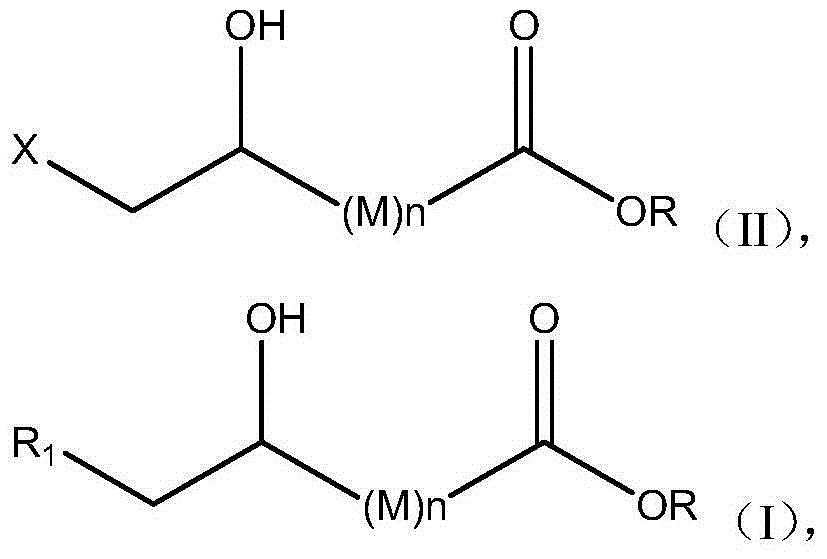
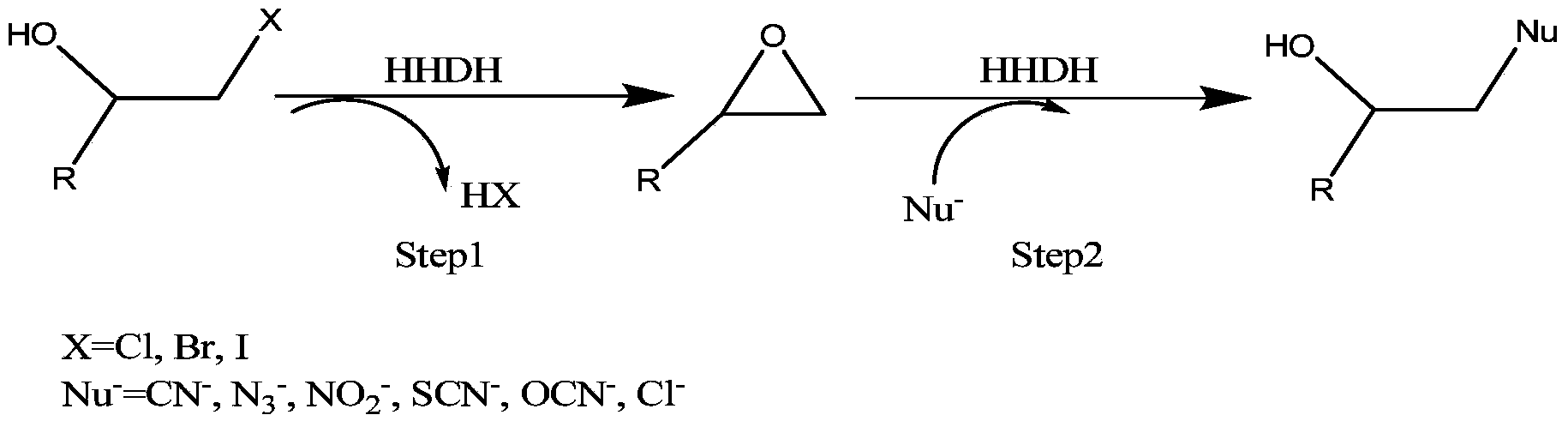
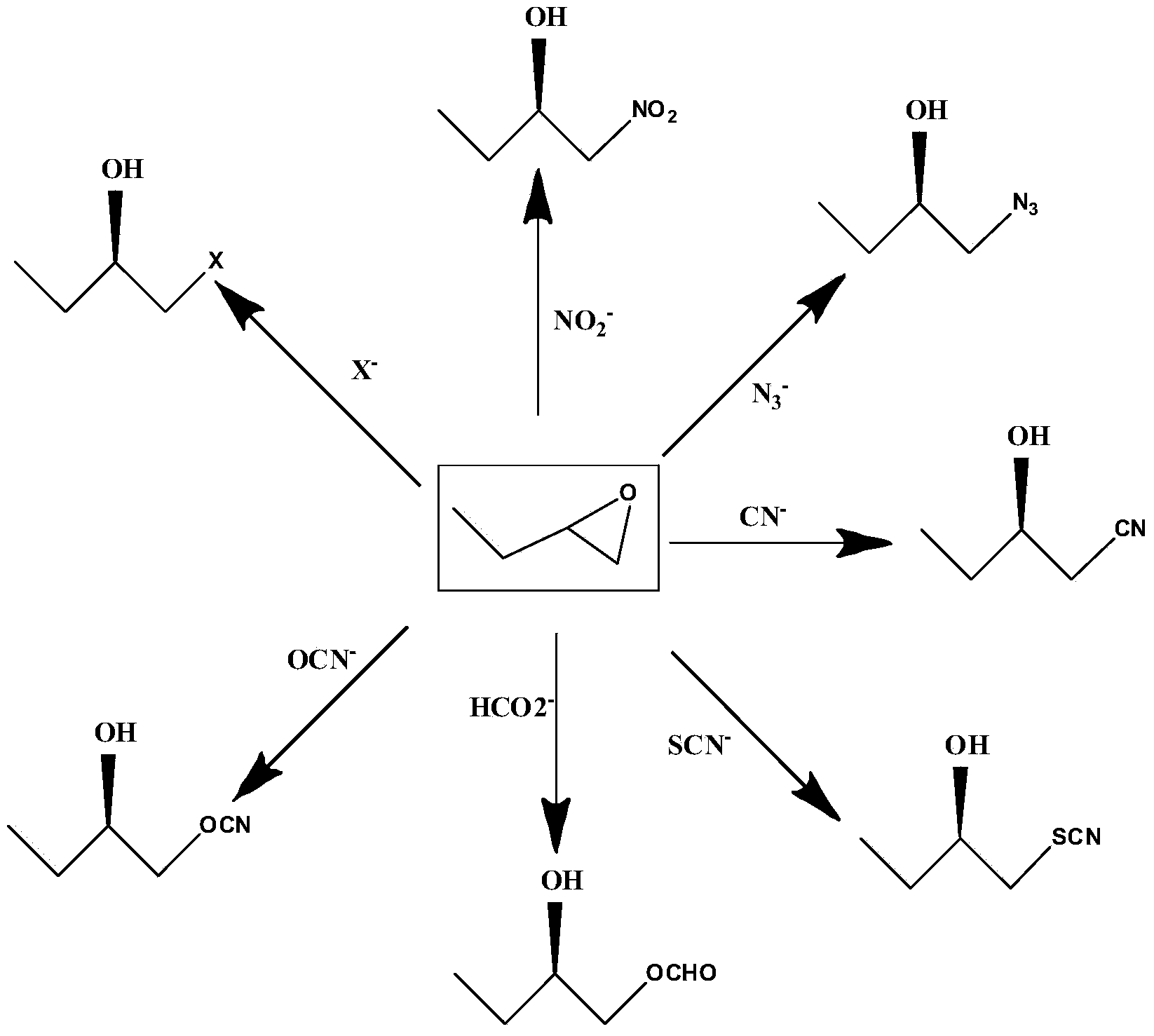
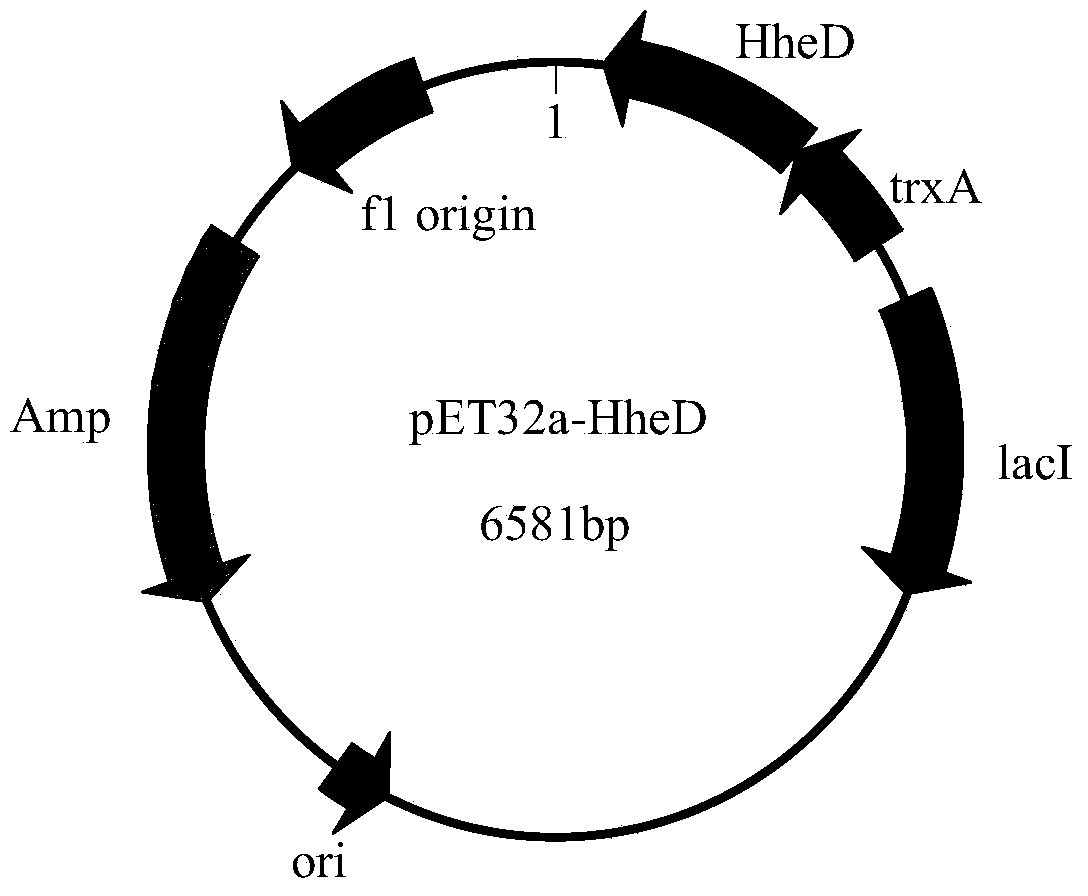
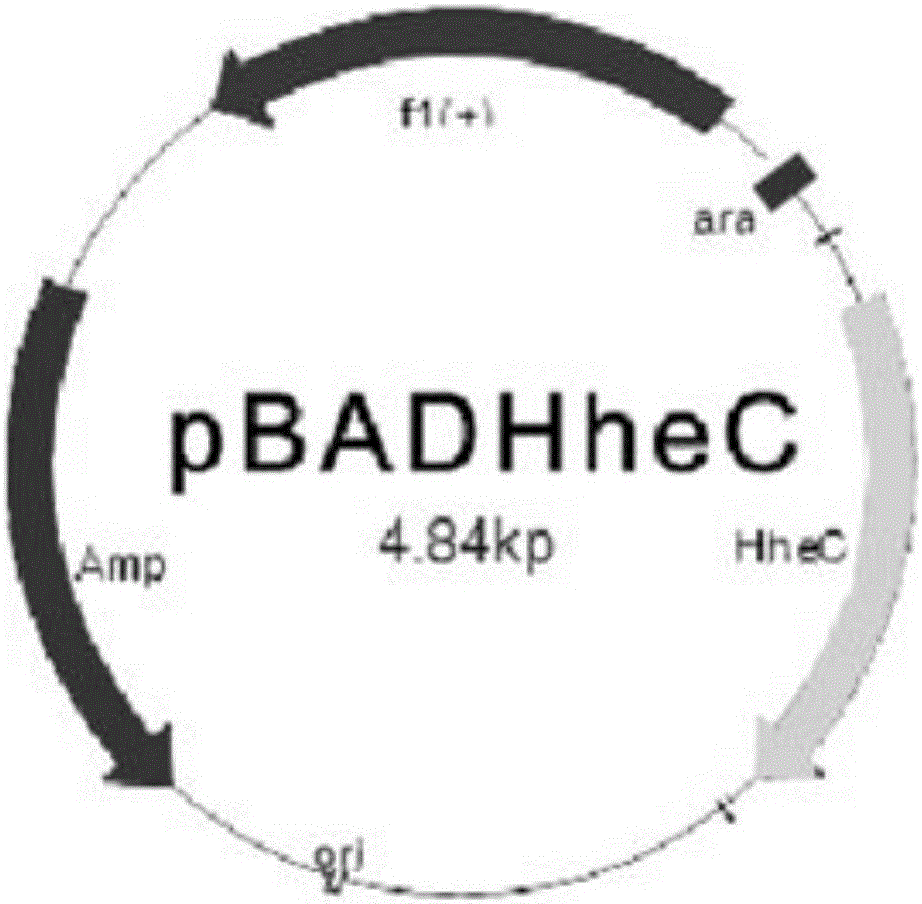
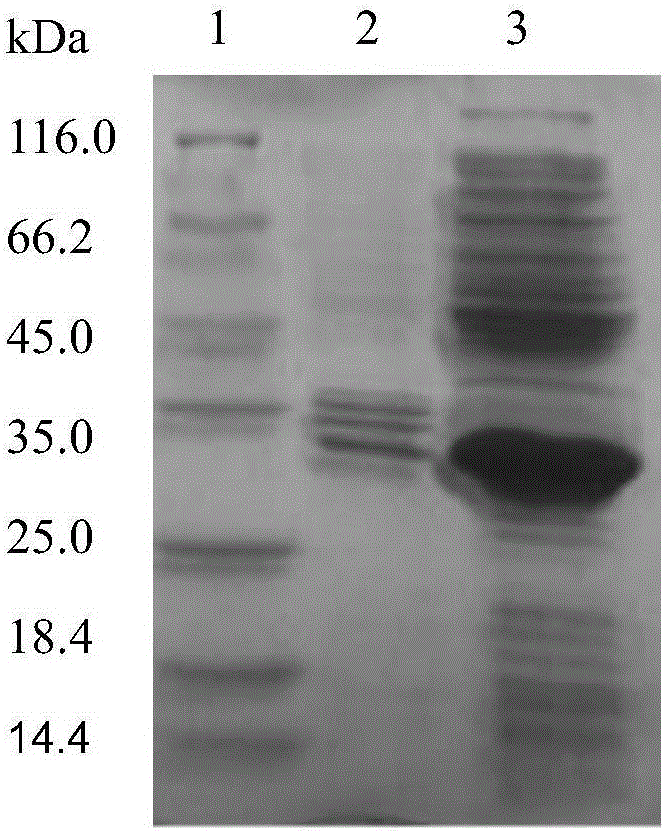
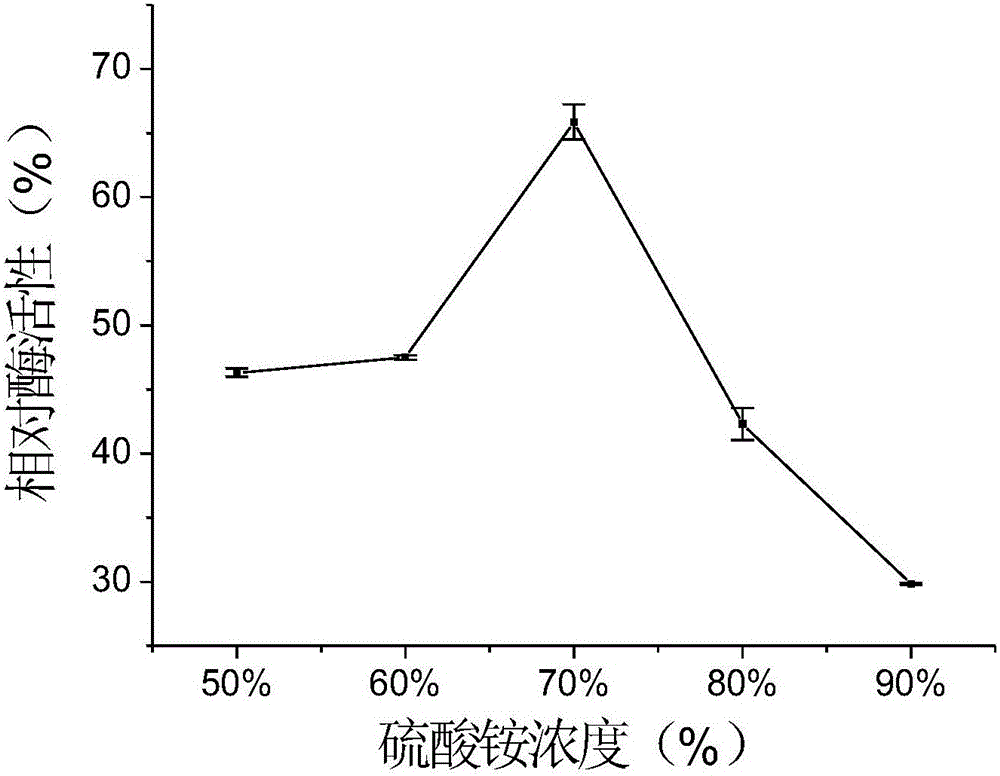
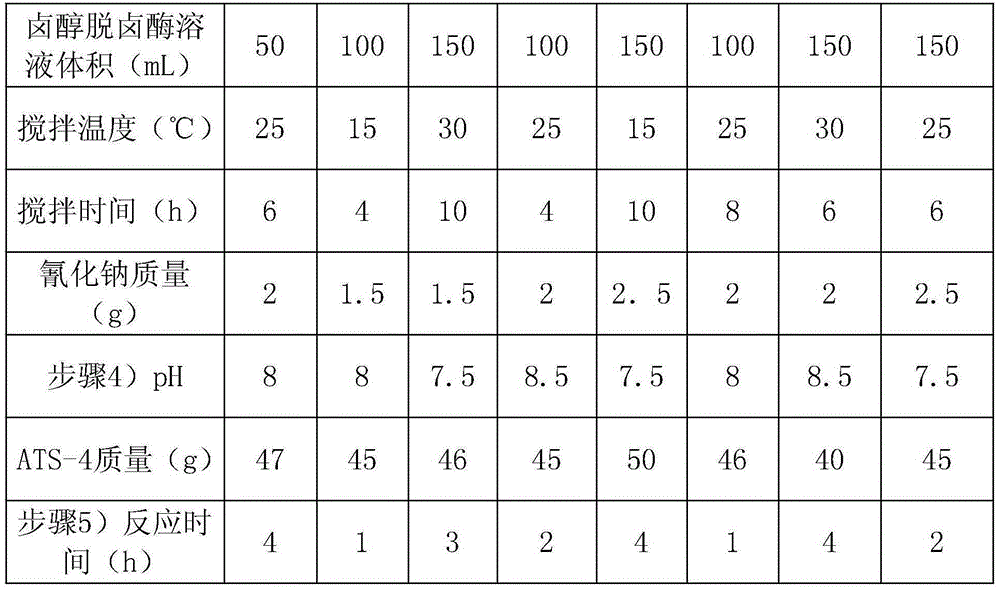
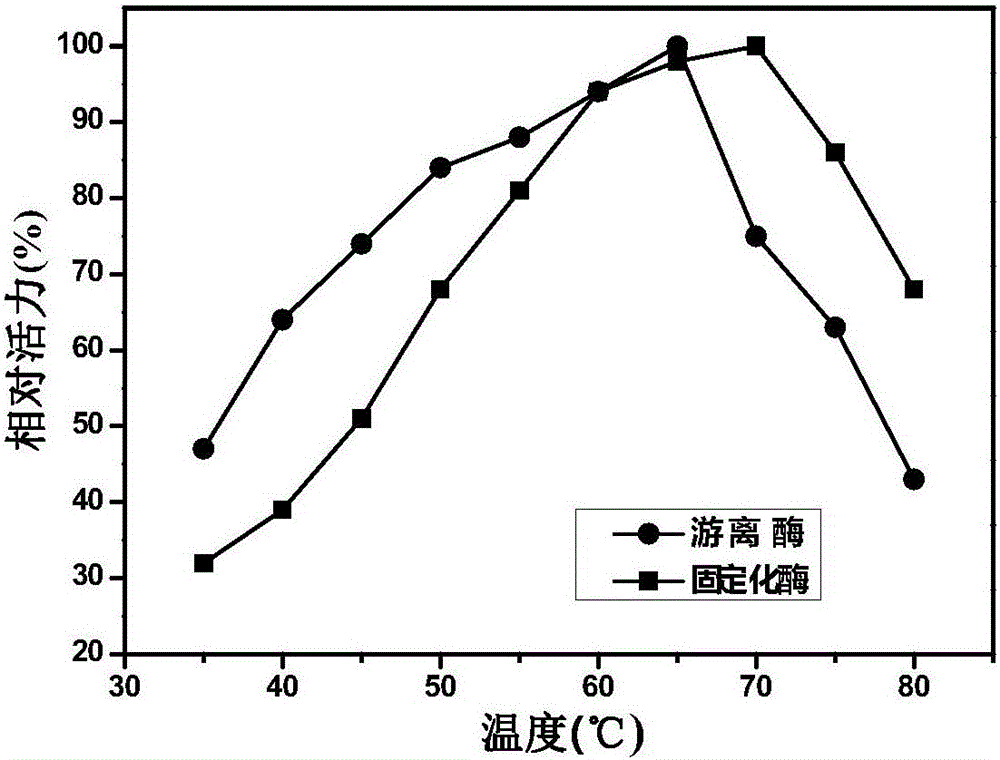
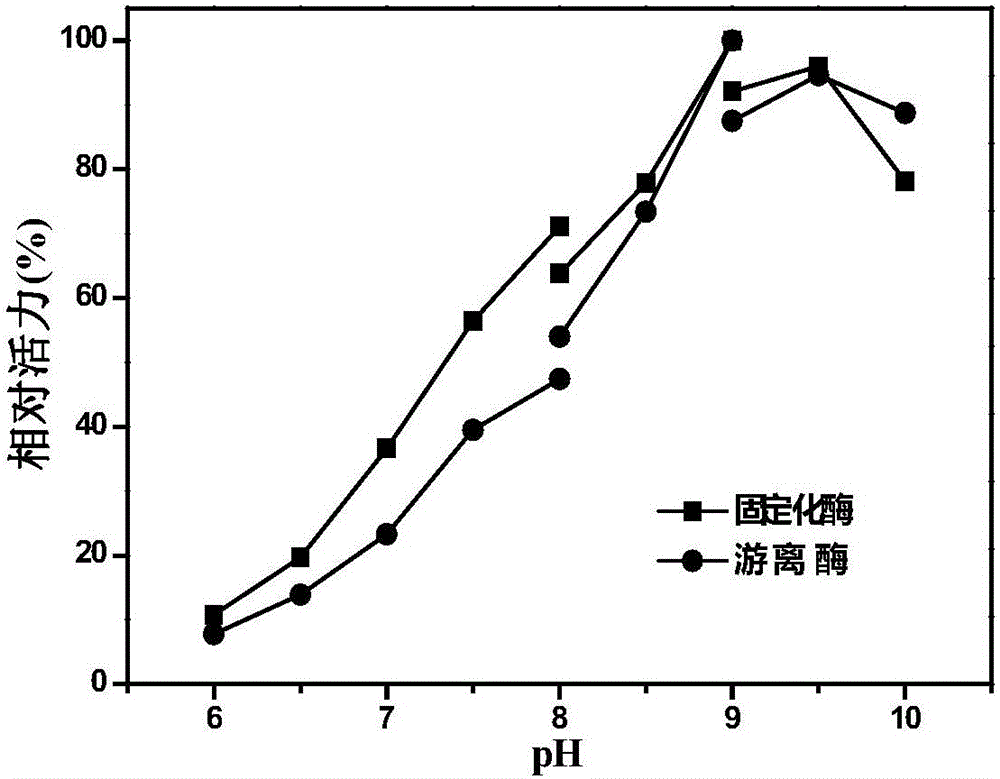
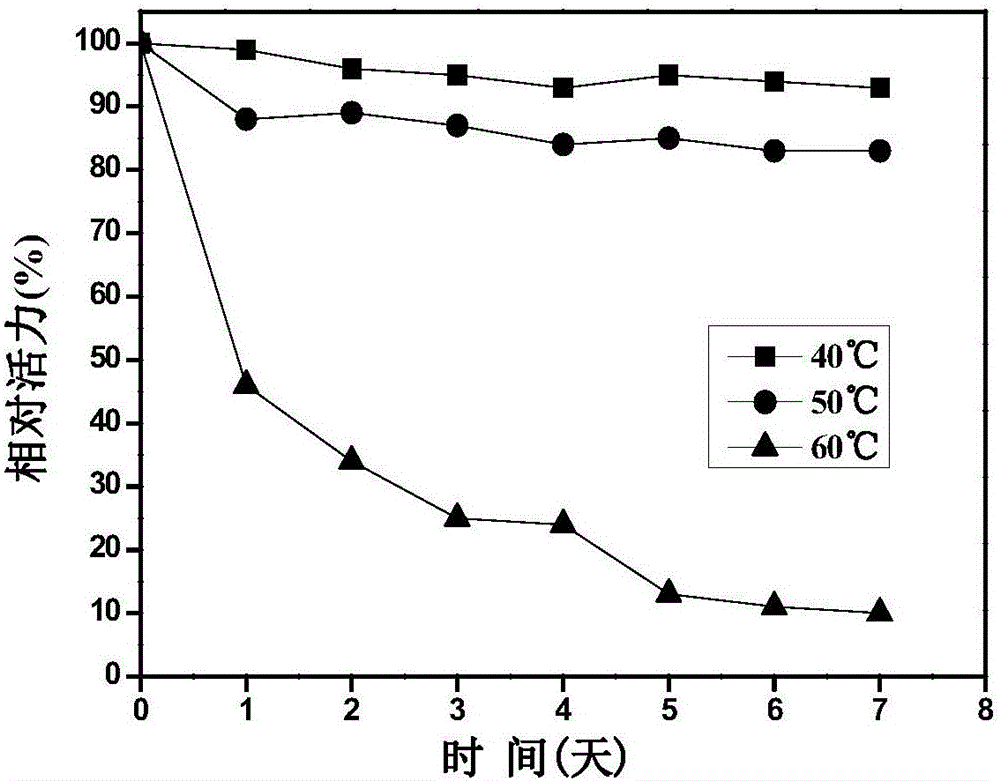
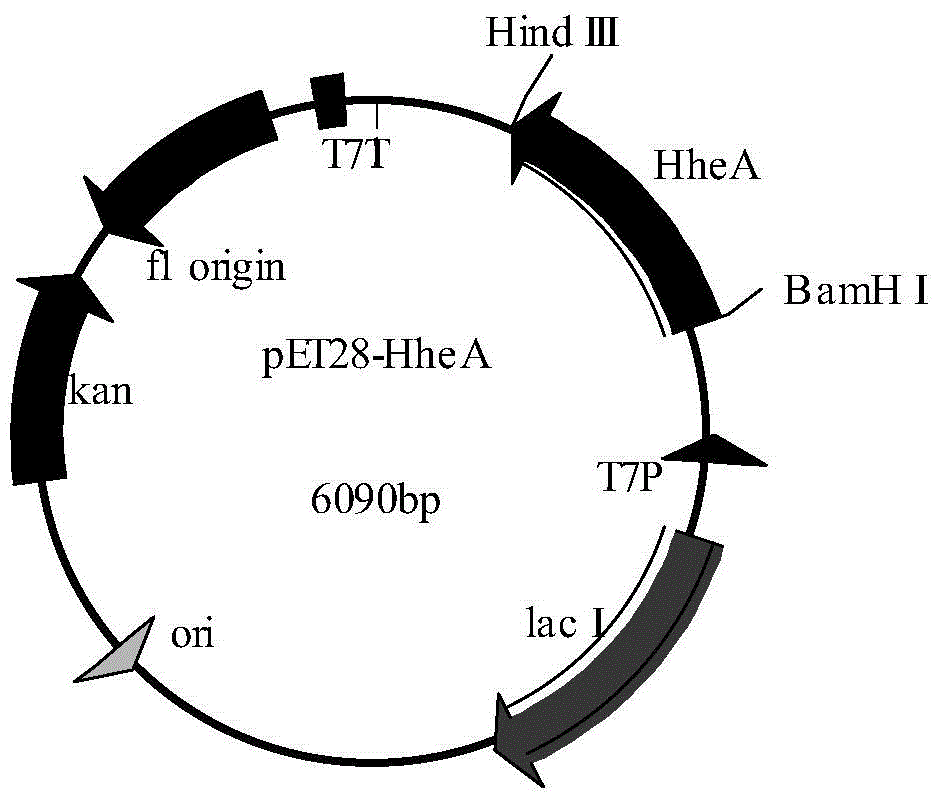
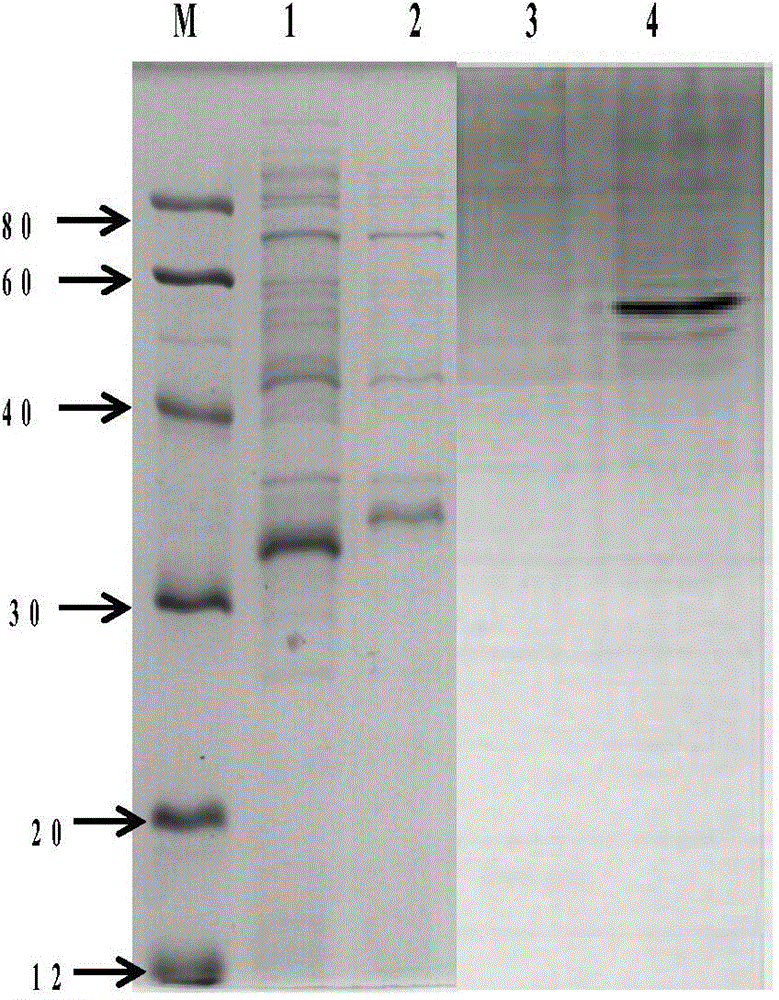
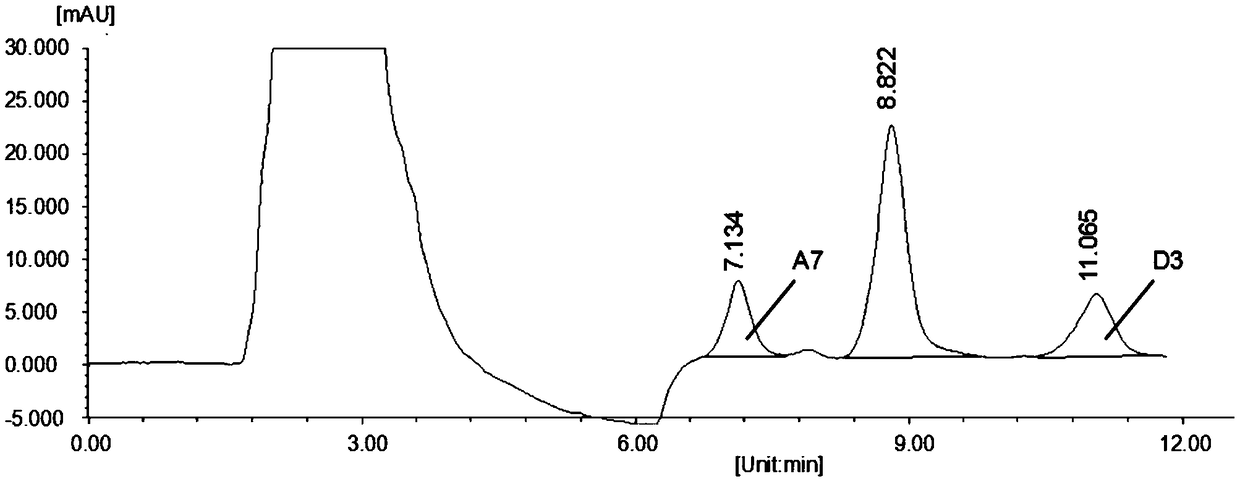
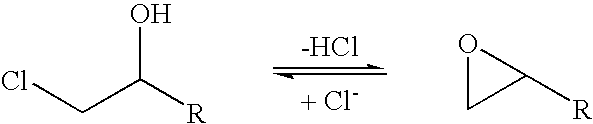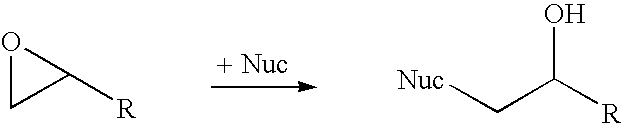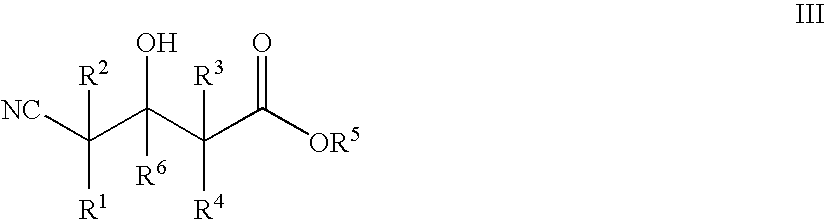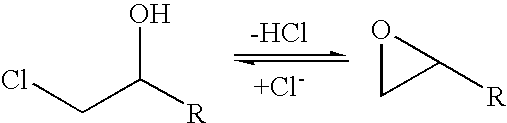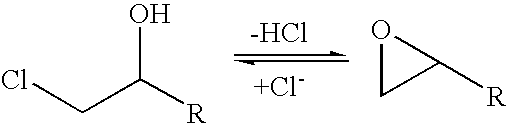Patents
Literature
59 results about "Halohydrin dehalogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
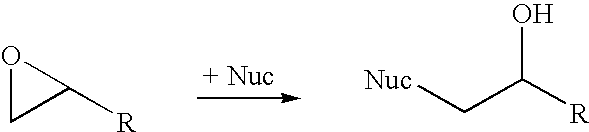
A halohydrin dehalogenase is an enzyme involved in the bacterial degradation of vicinal halohydrins. In several species of bacteria, it catalyses the dehalogenation of halohydrins to produce the corresponding epoxides. Different isoforms of the enzyme fall into one of three groups, A, B or C. Halogenases of the same class are genetically similar, but differ greatly from halogenases from a different group. Currently the most well-studied isoform is HheC which is purified from the bacterial species Agrobacterium radiobacter. The ability to dehalogenate organic compounds as well as form enantiomeric selective epoxides have generated interest in the potential of this enzyme in the biochemical field.
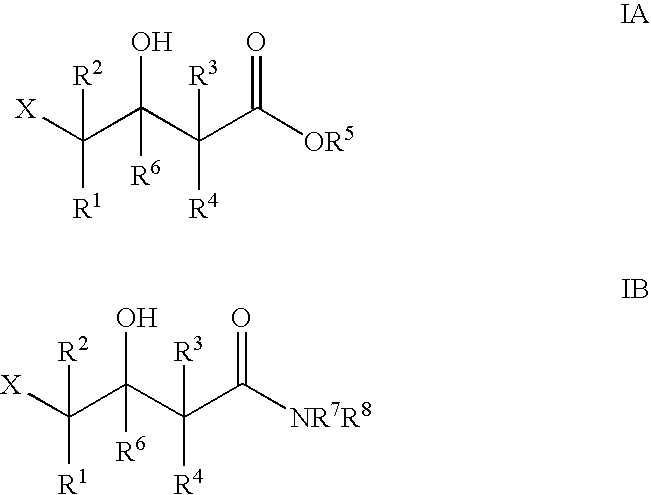
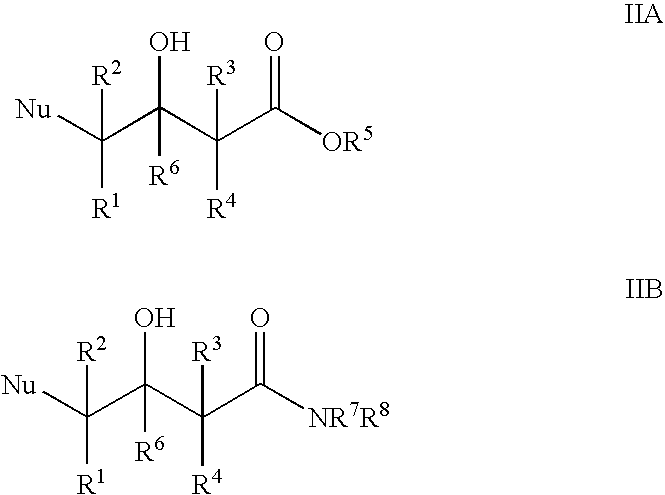
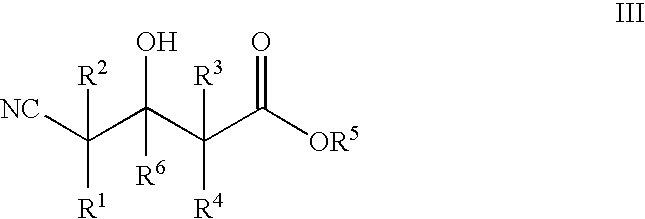
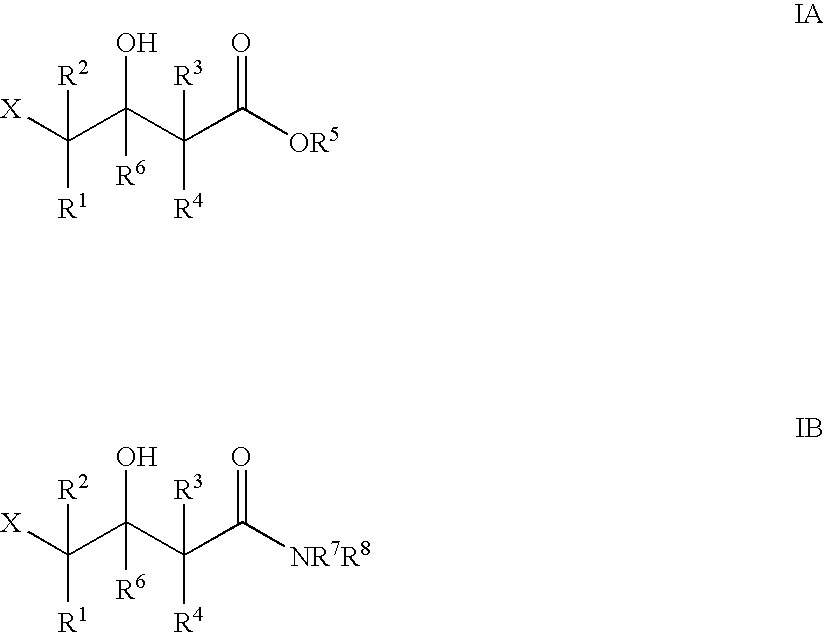
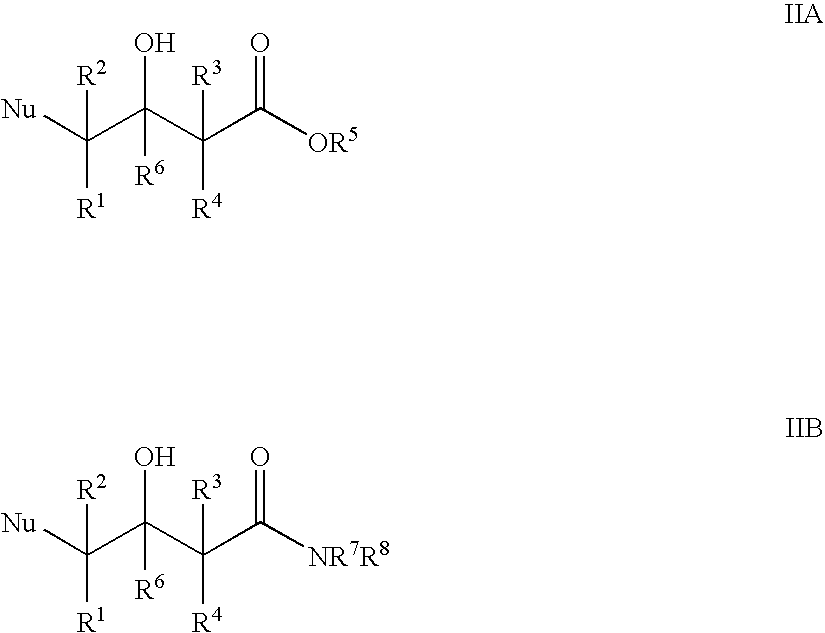
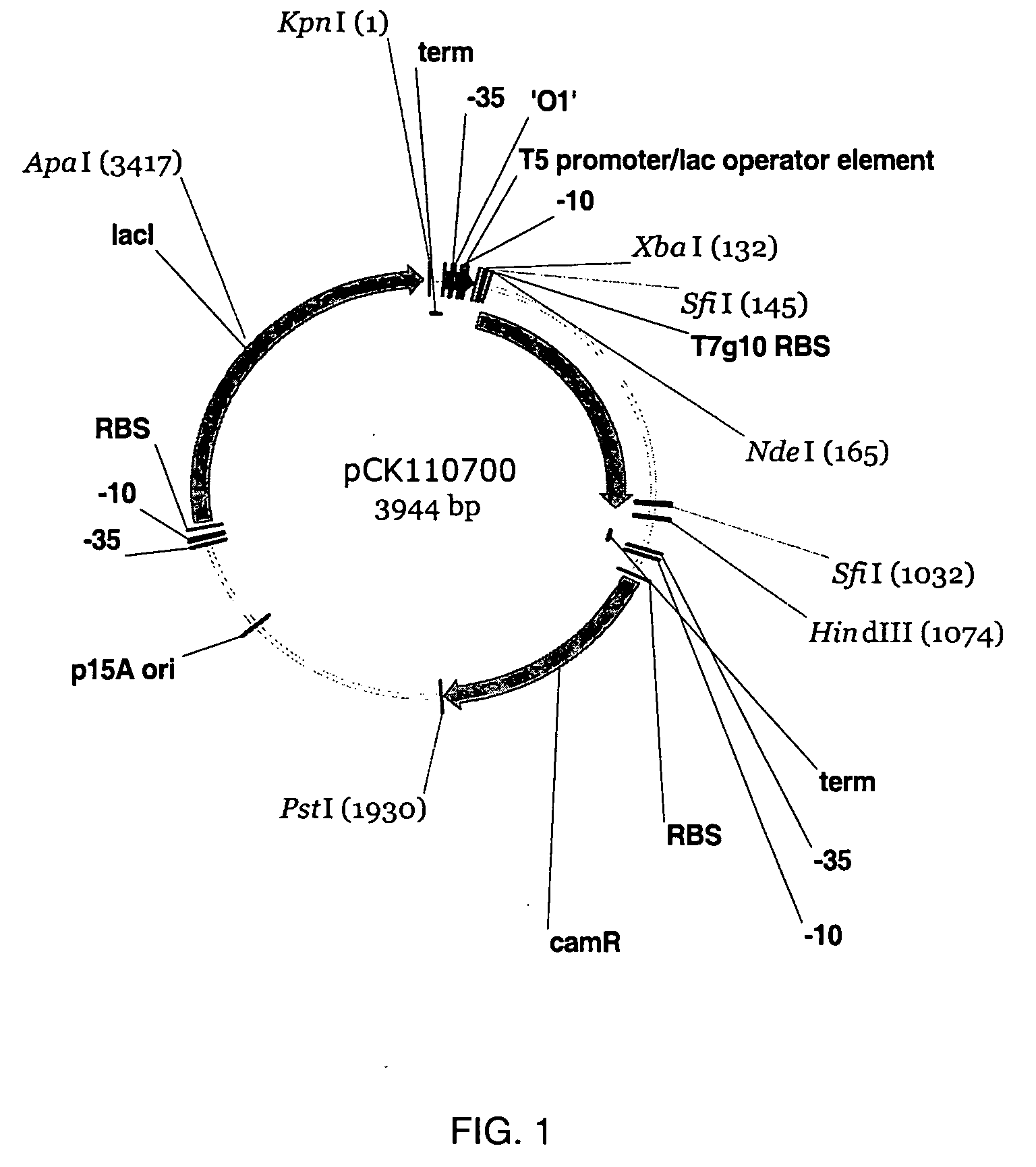
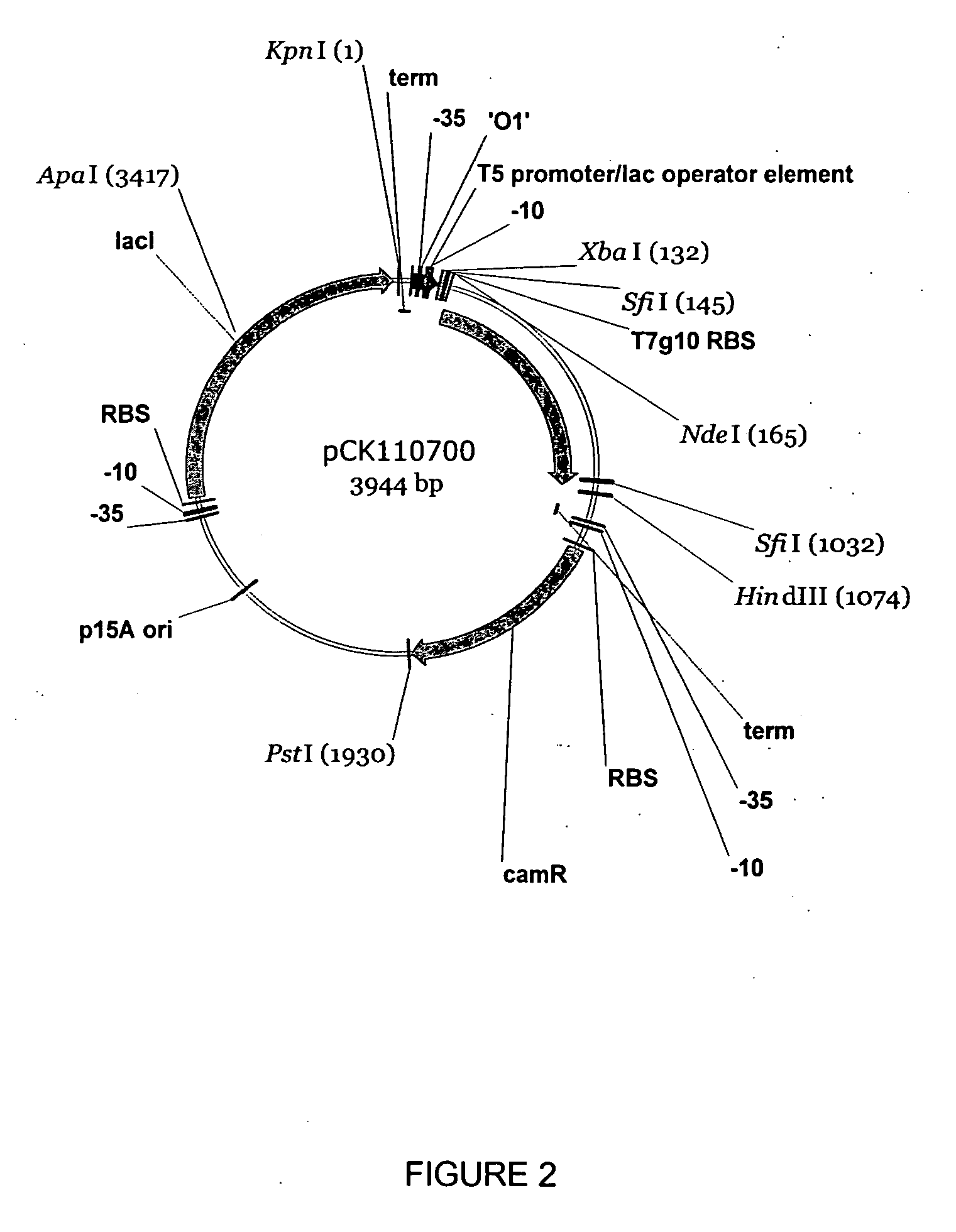
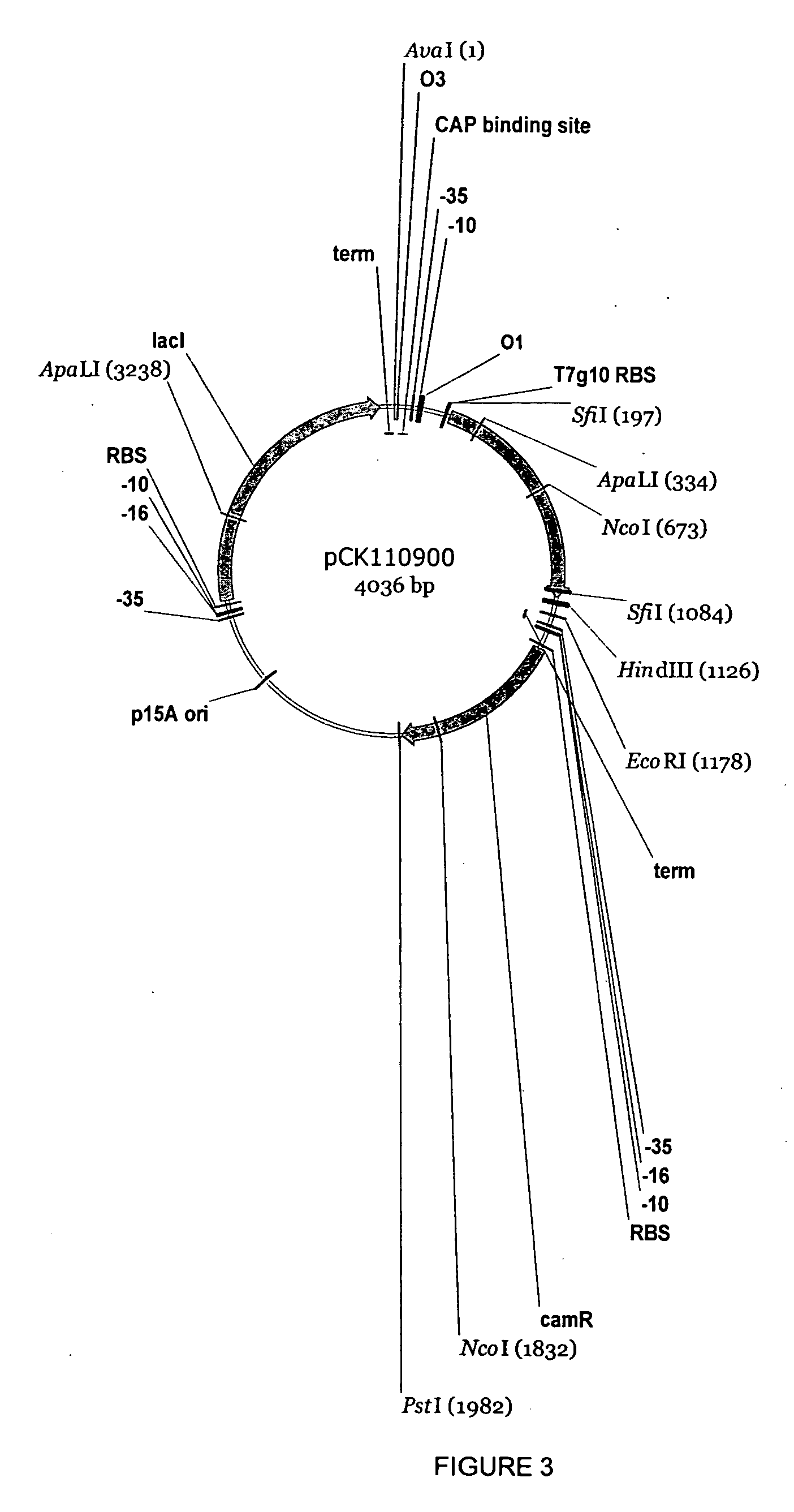
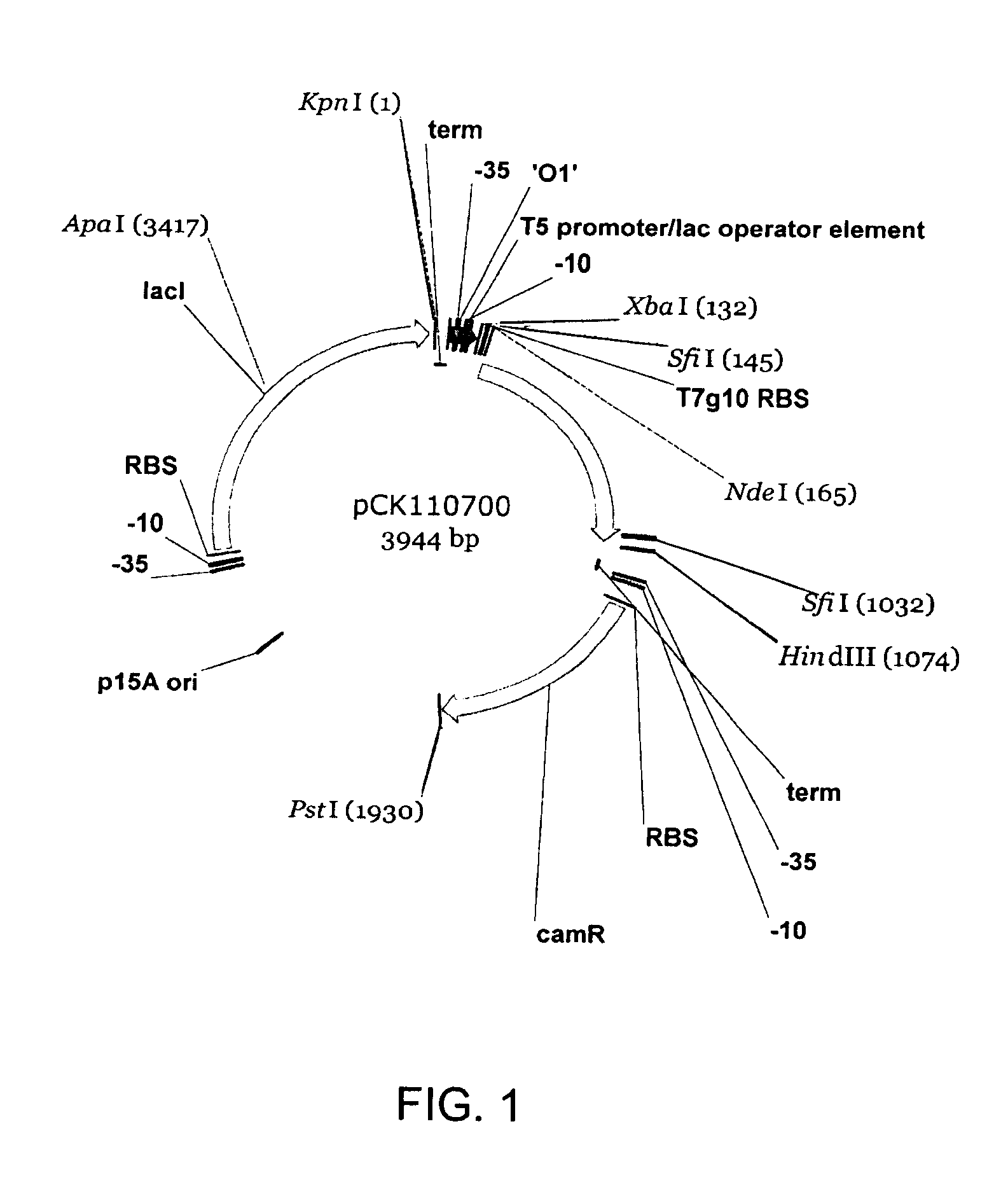
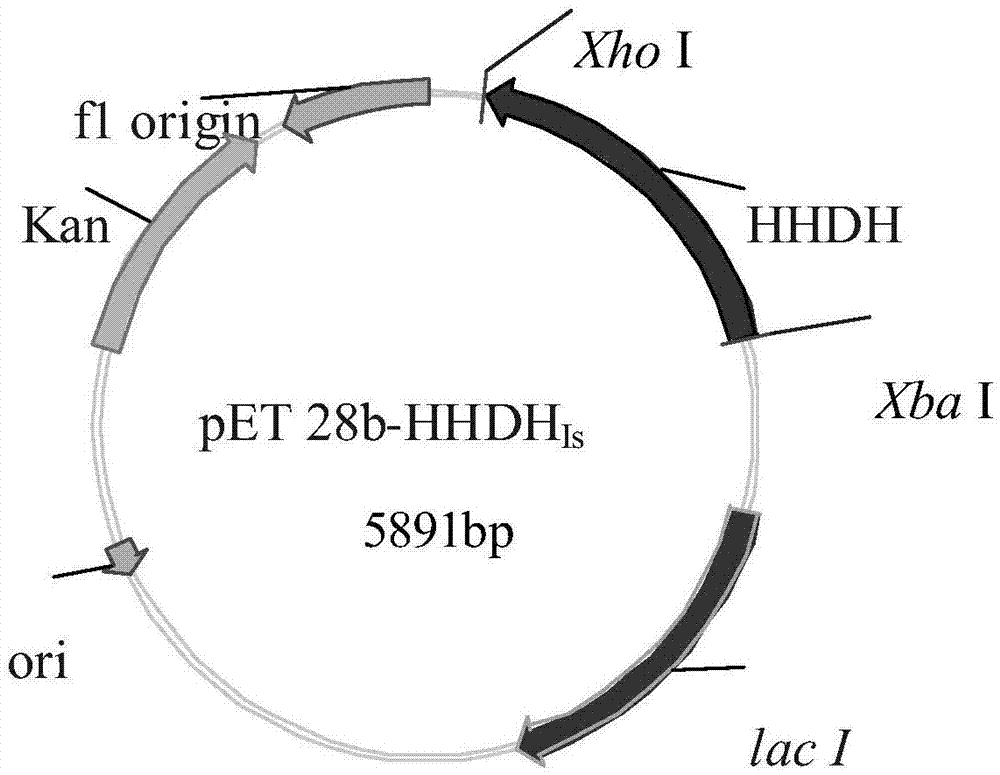
Halohydrin dehalogenases and related polynucleotides
The present invention relates to novel halohydrin dehalogenase polypeptides and the polynucleotides that encode them. These polypeptides are useful in the production of 4-substituted-3-butyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters. The invention also provides related vectors, host cells and methods.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxy substituted carboxylic acid esters
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives The present invention also provides methods and compositions for preparing vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Halohydrin dehalogenases and related polynucleotides
The present invention relates to novel halohydrin dehalogenase polypeptides and the polynucleotides that encode them. These polypeptides are useful in the production of 4-substituted-3-butyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters. The invention also provides related vectors, host cells and methods.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Halohydrin dehalogenases and related polynucleotides
The present invention relates to novel halohydrin dehalogenase polypeptides and the polynucleotides that encode them. These polypeptides are useful in the production of 4-substituted-3-butyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters. The invention also provides related vectors, host cells and methods.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives The present invention also provides methods and compositions for preparing vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
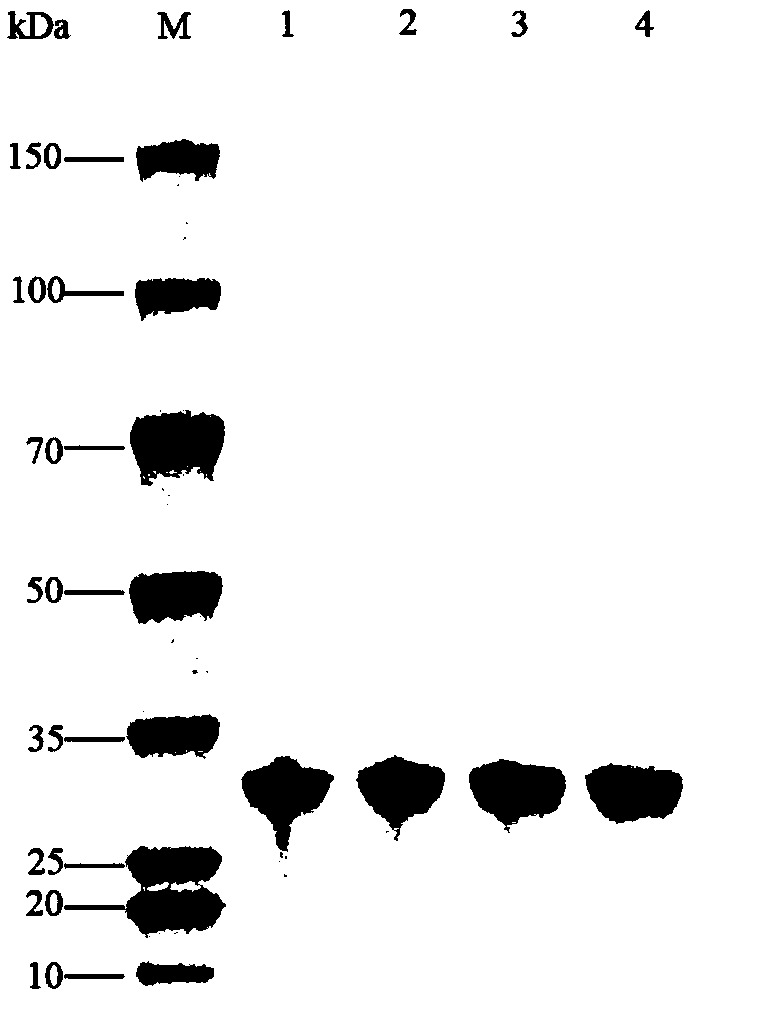
Recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase, and mutant and engineering strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN104745556AEnhanced asymmetric dehalogenation synthesisHigh enantioselectivityBacteriaHydrolasesEpoxyAlcohol
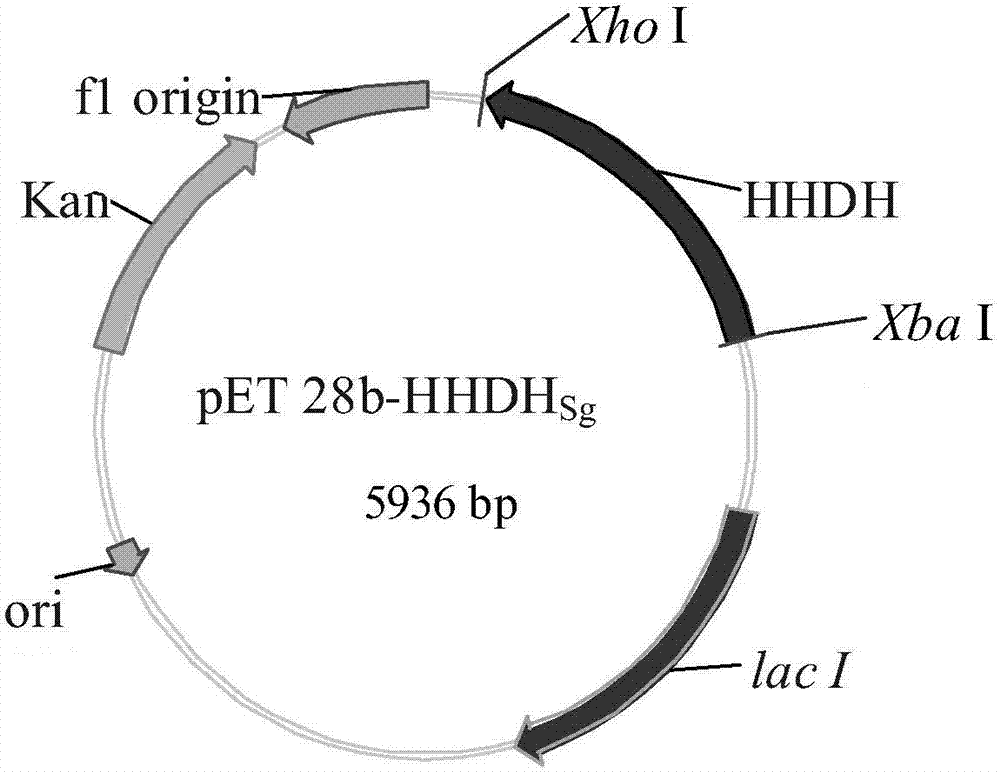
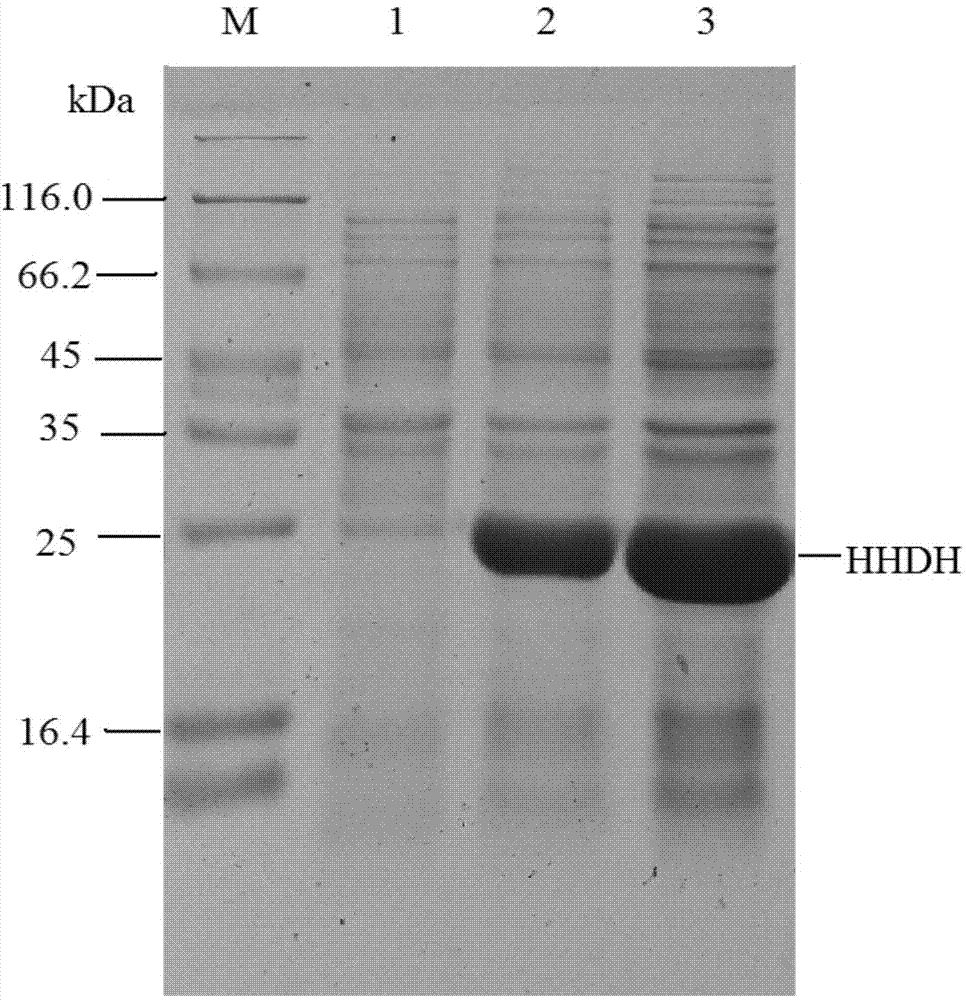
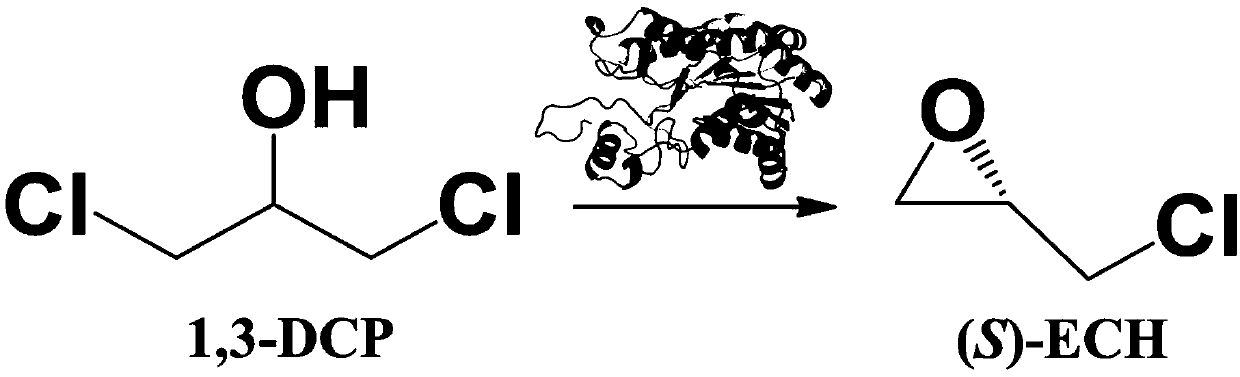
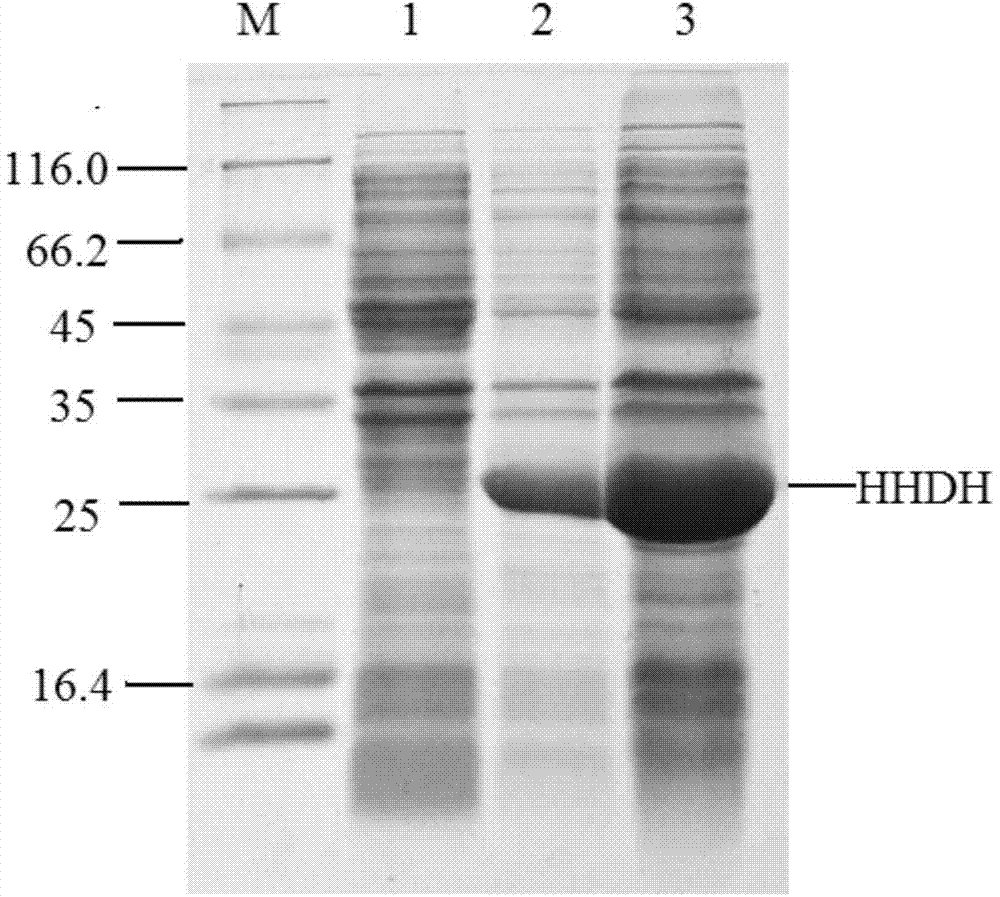
The invention discloses a recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase and a mutant, an engineering strain and applications thereof. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase is shown in SEQ ID No: 2. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase and the mutant of recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase in catalyzing asymmetric dehalogenation of 1,3-dichloropropanol so as to synthesize (S)-epoxy chloropropane and in preparing other chiral epoxides and beta-substituted alcohol. Compared with other halohydrin dehalogenases, the halohydrin dehalogenase obtained according to the invention and the mutant thereof have higher enantioselectivity and have an extremely good industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Halohydrin dehalogenases and related polynucleotides
The present invention relates to novel halohydrin dehalogenase polypeptides and the polynucleotides that encode them. These polypeptides are useful in the production of 4-substituted-3-butyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters. The invention also provides related vectors, host cells and methods.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Halohydrin dehalogenase and its use in synthesis of statin drug intermediate
The invention discloses a halohydrin dehalogenase with high catalytic activity, a high reaction yield and good environmental friendliness and an enzyme chemical synthesis method for replacement synthesis of a 6-substituted-3, 5-dihydroxyhexanoate derivative through the halohydrin dehalogenase and further synthesis of a statin drug intermediate. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence for coding the halohydrin dehalogenase, a recombinant expression vector containing the nucleic acid sequence, a recombinant expression transformant, a preparation method of the halohydrin dehalogenase and a use of the halohydrin dehalogenase in a catalytic replacement reaction.
Owner:ABIOCHEM BIOTECH CO LTD
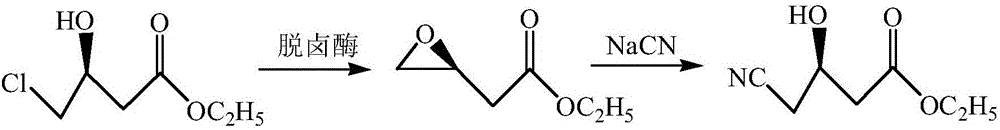
Parvibaculum lavamentivorans ZJB 14001, halohydrin dehalogenase enzyme gene, enzyme, engineered bacterium and application
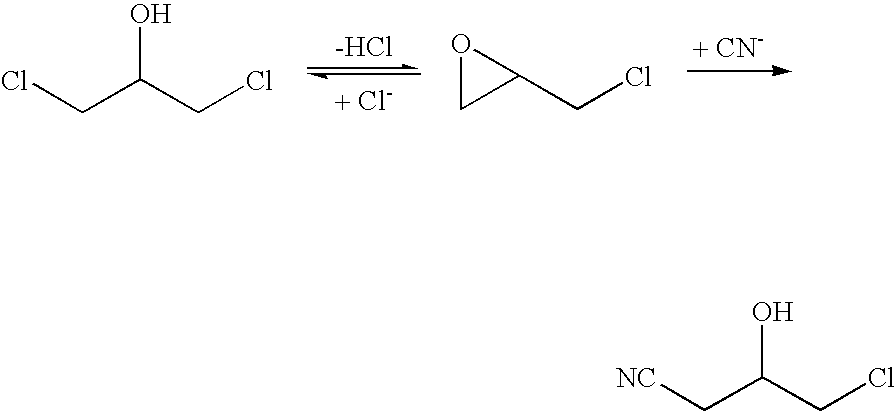
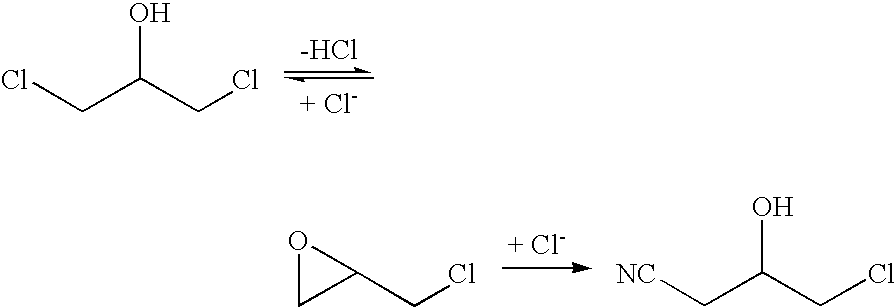
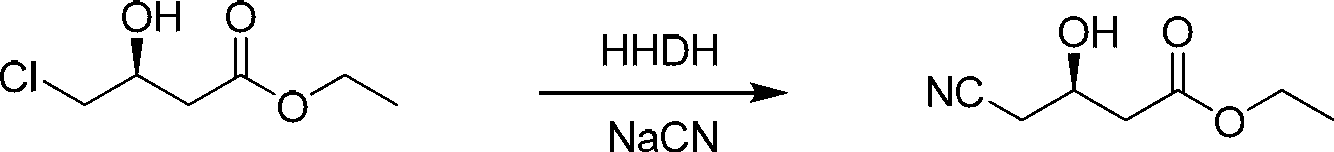
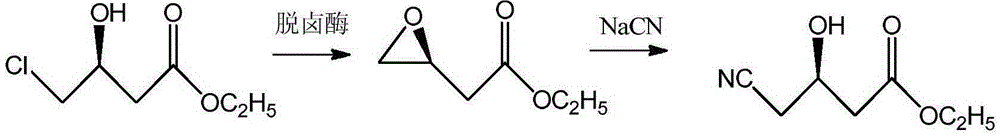
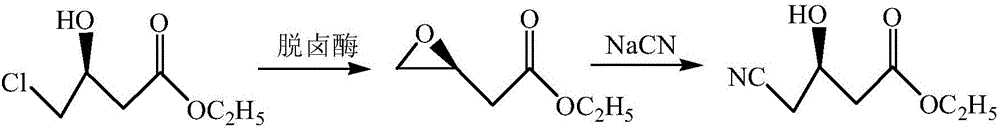
The invention provides a halohydrin dehalogenase encoded gene, a recombinant vector containing the gene, and a recombinant genetically engineered bacterium, and provides a novel bacterial strain, namely parvibaculum lavamentivorans ZJB 14001, of the gene. The recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase is regarded as an invertase to synthesize epoxy chloropropane by taking catalysis of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol as an example, to prepare (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyronitrile by taking catalysis of CN-mediated (S)-epoxy chloropropane with a ring-opening reaction as an example, and to respectively prepare (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyronitrile and ethyl-(R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate by taking catalysis of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol and (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyronitrile as an example with CN-mediated ring opening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate
InactiveCN106047848AHigh mechanical strengthImprove thermal stabilityCarbon-halide lyasesOn/in organic carrierHeat resistanceBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a preparation method of a crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate, and belongs to the field of biological chemical engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a bovine serum albumin preparation serving as a protecting agent into coarse halohydrin dehalogenase liquid, and preparing the crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate from an ammonium sulfate solution serving as a precipitant and glutaraldehyde serving as a crosslinking agent, wherein the coarse halohydrin dehalogenase liquid is prepared by building recombinant bacteria for prokaryote external induction expression. The preparation method is simple in experimental operation and low in cost; the prepared crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate is higher in mechanical strength and heat resistance and can be repeatedly used; an experiment shows that the immobilized enzyme amount can be over 80 percent of the total enzyme amount under the optimal preparation condition; the activity of the crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate is 470.2 U / g; compared with the enzyme activity of free coarse enzyme, the relative enzyme activity is up to 91.36 percent, so that the crosslinking halohydrin dehalogenase aggregate can be widely applied to degrading of environment pollutants such as organic halide and catalysis in a synthesis process of chiral drugs.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant derived from ADI (Agrobacterium radiobacter) and application of halohydrin dehalogenase mutant to preparation of (S)-epichlorohydrin
ActiveCN109593749AHigh stereoselectivitySimple reaction systemCarbon-halide lyasesGenetic engineeringAgrobacterium radiobacterPhosphate
The invention relates to a halohydrin dehalogenase mutant derived from ADI (Agrobacterium radiobacter) and an application of the halohydrin dehalogenase mutant to preparation of (S)-epichlorohydrin. The mutation site is one of the following: (1) 81st site, (2) 86th site and (3) 94th site. A plurality of mutant strains are obtained by modification of halohydrin dehalogenase, (S)-ECH prepared from 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol by conversion has extremely high stereoselectivity. In a phosphate buffer system, (S)-ECH with optical purity (e.e. value) larger than 99% can be prepared by catalysis. The technology has outstanding advantages of excellent enzyme stereoselectivity, simple reaction system, easy-to-control operation process, low production cost and the like, and has good industrial application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of ethyl (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate
InactiveCN105132488AHigh recovery rateImprove operational stabilityFermentationCyanideEthyl Chloride
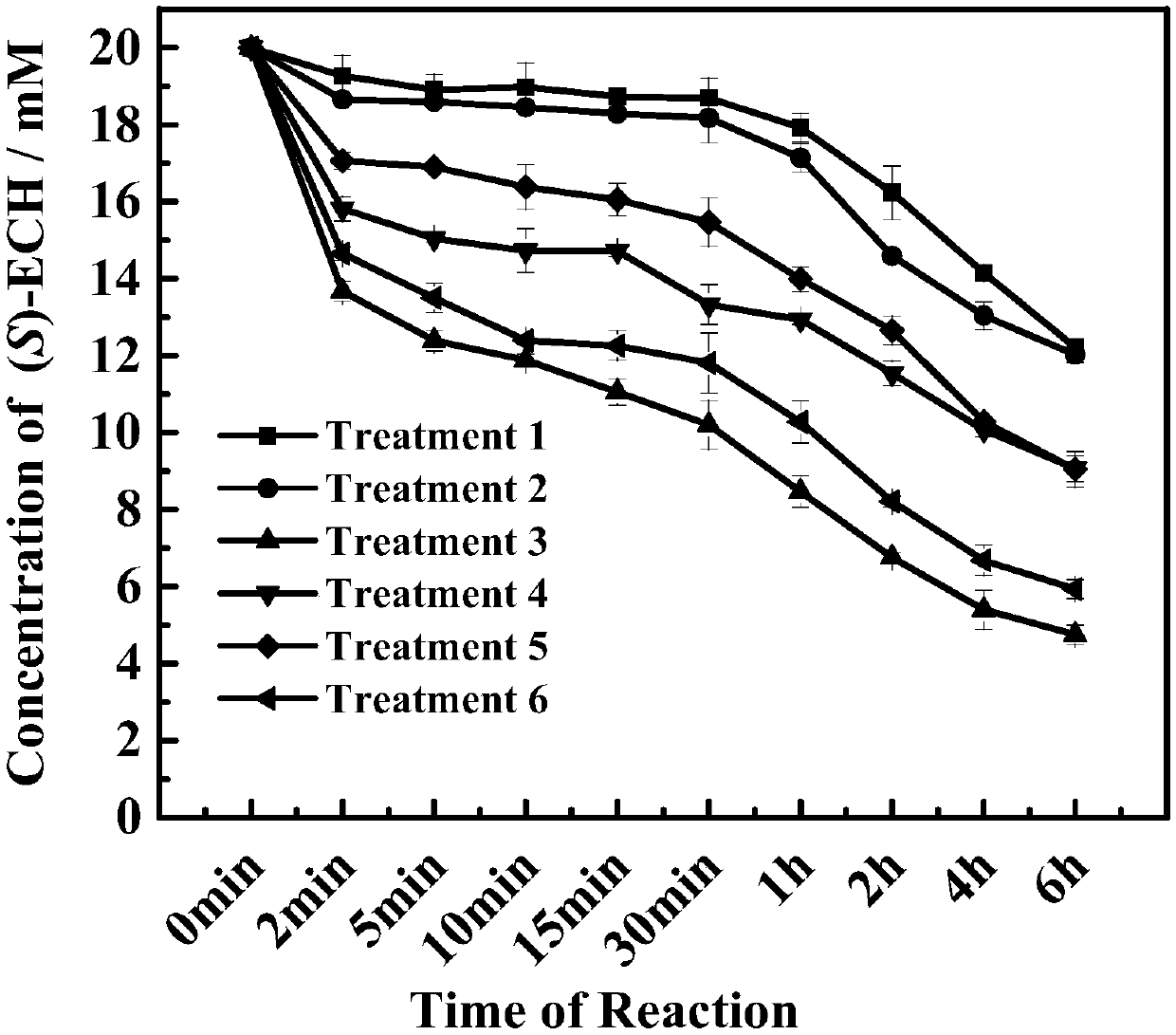
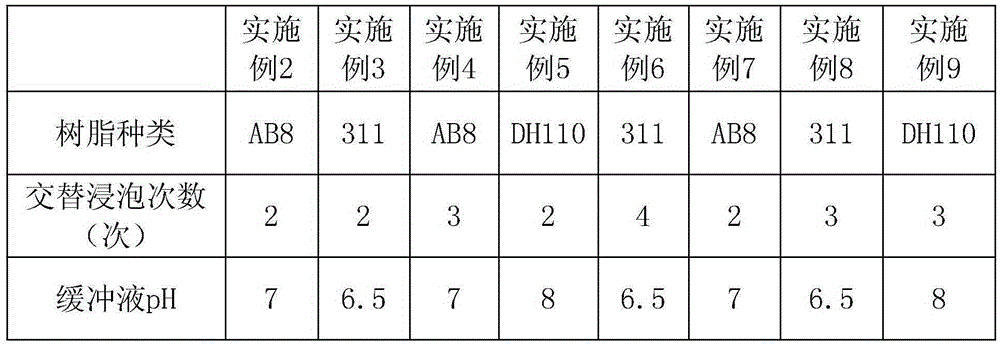
The invention discloses a preparation method of ethyl (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate. According to the preparation method, ethyl (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate is taken as a substrate, immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase is taken as a catalyst, the substrate and the catalyst react with cyanide salt under the condition of pH value in a range from 6.5 to 8.0, and ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate is obtained; a preparation method of immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase comprises steps as follows: adsorbent resin is added to a halohydrin dehalogenase solution, the halohydrin dehalogenase is adsorbed on the adsorbent resin and crosslinked by a difunctional crosslinking agent, finally, the adsorbent resin is separated from the halohydrin dehalogenase solution and washed, and the immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase is obtained. The enzyme recovery rate of the immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase is high, the operation stability is high, reduction of production cost is facilitated, when the immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase is used for preparing ethyl (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate, the process is simple, the resolution effect is excellent, e.e. value can be up to 99%, particularly, the postprocessing is simpler, and the yield can be higher than 91%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Biological preparation method of (R)-4-cyano-hydroxybutanoate
ActiveCN103014082AIncrease concentrationHigh purityFermentationSodium cyanideSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to a biological preparation method of (R)-4-cyano-hydroxybutanoate. According to the biological preparation method, (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxybutanoate is used as a substrate; under the action of a biocatalyst, the substrate reacts with sodium cyanide to generate a target product (R)-4-cyano-hydroxybutanoate; the biocatalyst is recombination halohydrin dehalogenase; and the reaction is carried out in a water phase with the pH of 6 to 8. According to the invention, by adopting the recombination halohydrin dehalogenase, the concentration of the substrate is improved and the enzyme dosage is reduced, so that production cost is reduced. Moreover, by optimizing the process, both purity and yield of the product are improved.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Process of using resin-immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase to catalytically synthesize (R)-4-cyan-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate
The invention relates to a process of using resin-immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase to catalytically synthesize (R)-4-cyan-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate. The process includes that (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy ethyl butyrate (ATS-4) is used as a substrate to enzymatically synthesize ATS-5; aiming at the defect that an enzymatic method is low in reaction rate and conversion rate, resin is selected as a carrier, and adsorption method HDHH is adopted. By the process, enzyme can be repeatedly utilized, and substrate conversion rate and product yield are increased, so that production cost is lowered. Experiments show that fixation rate of HHDH is above 45%, ATS-5 product generation rate of the first time is above 75% and even reaches up to 94.13%, and second-time conversion rate of immobilized enzyme after being recycled is above 35% and reaches 50% at most. The process is mild in reaction condition, free of enzyme residue, supportive of enzyme recycling, high in reaction speed, low in cost, high in product yield, free of adverse reaction and suitable for industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:NANTONG WANNIANCHANG PHARMA +1
Immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase and application thereof
InactiveCN105838700AWide variety of sourcesReduce fermentation costsCarbon-halide lyasesOn/in organic carrierEpoxyAlcohol
The invention discloses immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase and an application thereof. The immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase has high conversion efficiency on a halohydrin substrate, is strong in substrate tolerance, and has excellent catalysis selectivity on the substrate and structural analogues thereof. In the invention, recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase is successfully fixed on the surface of an epoxy resin carrier through multipoint covalence, and through low-salt adsorption and addition of glycerol as a protection agent of an enzyme activity center, enzyme activity loss during immobilization is effectively reduced. The immobilization method is simple in operation, is low in raw materials cost, and is suitable for large-scale operation. The immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase has homogeneous property, high stability and good repeatability. With the immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase,epoxy chloropropane, (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxylethyl butyrate, (S)-2,3-dichloro-1-propyl alcohol and the like can be synthesized. The immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase can be continuously used for more than 50 batches before significant reduction of activity of the immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase and also has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant for improving enantioselectivity and application thereof
ActiveCN110423740AHigh enantioselectivityImprove efficiencyBacteriaCarbon-halide lyasesArginineWild type
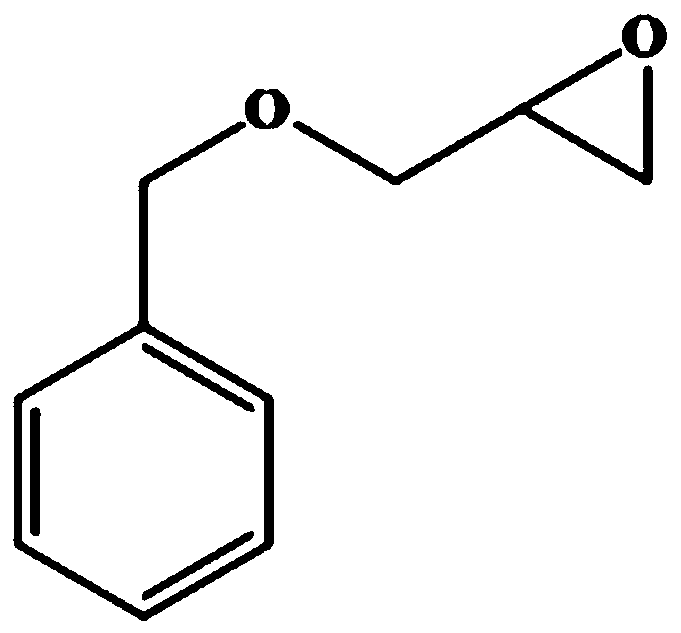
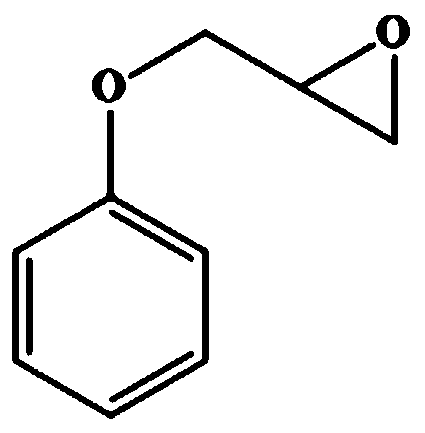
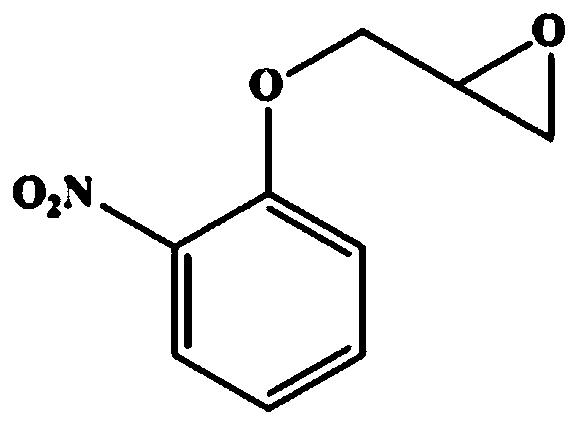
The invention relates to a halohydrin dehalogenase mutant for improving enantioselectivity and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and biocatalysis. The halohydrin dehalogenase mutant is obtained by carrying out single-point mutation or combined mutation on 89th arginine, 137th valine, 178th proline, 179th asparagine and 187th phenylalanine in a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Compared with wild type halohydrin dehalogenase, the mutant obtained by the invention obviously improves enantioselectivity (E value) during the preparation of (S)-o-nitrophenyl glycidyl ether, (R)-benzyl glycidyl ether and (R)-phenyl glycidyl ether, the maximum improvement is 44.6, 2.9 and 9.4 times of the original enzyme respectively, and has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Engineering bacterium and application thereof in preparation of atorvastatin drug intermediate
ActiveCN104651290AImprove conversion rateHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyTert butyl
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium and an application thereof in preparation of an atorvastatin drug intermediate. The engineering bacterium comprises a host cell and a target gene transferred into the host cell, wherein the target gene is a halohydrin dehalogenase gene of which a base sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The engineering bacterium constructed by introducing the halohydrin dehalogenase gene shown in SEQ ID NO.3 into the host cell is capable of expressing halohydrin dehalogenase HheA; and catalysis of tert-butyl (S)-6-chloro-5-hydroxy-3-carbonyl hexanoate into tert-butyl (R)-6-cyano-5-hydroxy-3-carbonyl hexanoate and catalysis of tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dyhydroxy hexanoate into tert-butyl (3R,5R)-6-cyano-3,5-dyhydroxy hexanoate can be realized through the catalysis action of enzyme. The reaction conditions are mild; the operation is simple and convenient; and the conversion rate and the purity of a product are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and applications thereof
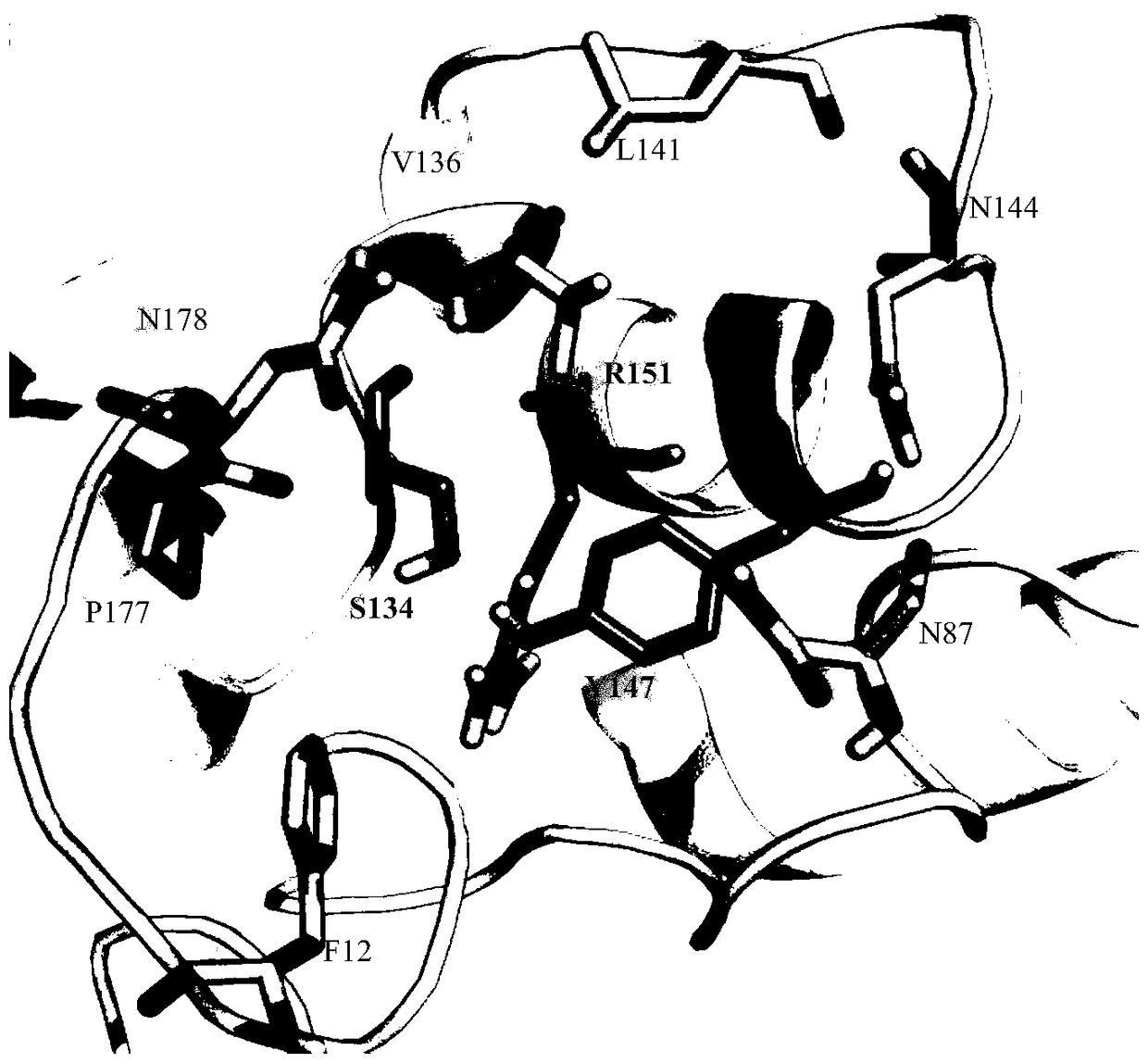
The invention discloses a halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and applications thereof, wherein the mutant is subjected to one or a plurality of the following mutations that the arginine at the site 84 isreplaced by alanine, serine, histidine or asparagine, the arginine at the site 88 is replaced by leucine, valine, threonine, cysteine, phenylalanine or isoleucine, the valine at the site 136 is replaced by threonine or serine, and the asparagine at the site 144 is replaced by cysteine, histidine or threonine. According to the present invention, the halohydrin dehalogenase HheAAM is modified by respectively using the directed evolution and the semi-rational design, wherein the results show that the sites 84, 88, 136 and 144 can affect the enzyme activity; and the four key sites are subjected tocombined mutation by using the iterative saturation mutation strategy, and are subjected to random combined mutation by using the combined active site saturation experiment strategy, such that the specific enzyme activity of the screened mutant is 801.59 U.g<-1>, and is 12 times the specific enzyme activity of the original enzyme.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compound immobilized enzyme used for preparing statins and preparation method of compound immobilized enzyme
ActiveCN105925558AImprove utilization efficiencyEasy to separateCarbon-halide lyasesOxidoreductasesHydroxybutyric acidActive enzyme
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical industry, and mainly relates to a compound immobilized enzyme used for preparing statins, as well as a preparation method and applications of the compound immobilized enzyme. The compound immobilized enzyme provided by the invention is prepared through the manner of fixing active enzyme in an immobilized enzyme carrier through the fixing manner of adsorption, covalent binding, embedding, microencapsulation or crosslinking, wherein the active enzyme is composed of ketoreductase and / or halohydrin dehalogenase, and the mass percent of the ketoreductase in the active enzyme is 0%-100%. The immobilized enzyme product is applied to the process for producing the midbody, namely, ethyl(S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate and / or ethyl(R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyate of the products including atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, pitavastatin and the like. Compared with the liquid enzyme, the compound immobilized enzyme provided by the invention has the advantages that the production cost is reduced, the labor intensity is alleviated, the utilization efficiency of enzyme is improved, the discharge of waste water, waste gas and industrial residue is reduced, and the environment is protected.
Owner:河北周酶生物科技有限公司
Method for utilizing halohydrin dehalogenase engineering fungi to prepare R-phenyl glycidyl ether
ActiveCN107881182AHigh enantioselectivityHigh catalytic activityBacteriaCarbon-halide lyasesGeneChemistry
The invention discloses a method for utilizing halohydrin dehalogenase engineering fungi to prepare R-phenyl glycidyl ether, and relates to the field of preparing chiral drug midbody R-phenyl glycidylether. By means of the method for utilizing the halohydrin dehalogenase engineering fungi to prepare R-phenyl glycidyl ether, an engineering fungus thalli containing a halohydrin dehalogenas gene isused as a catalyst, a phenyl glycidyl ether substrate is catalyzed and converted to obtain R-phenyl glycidyl ether, and the method has high enantiomer selectivity and a very high catalysis activity and is environmentally friendly in the producing process.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Rapid screening method for halohydrin dehalogenase
ActiveCN104342483AImprove efficiencyHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPrimary screening
The invention relates to an enzyme screening method, particularly to a screening method for a halohydrin dehalogenase. Halohydrin dehalogenase with high enzyme activity is screened by pH color development and a primary screening-secondary screening two-step method. By employing a deep-hole plate for microminiaturized culture, the invention realizes high throughput culture and high throughput preparation of a crude enzyme liquid. PH change is utilized as a breakthrough to screen halohydrin dehalogenase with high enzyme activity, the efficiency is high, the cost is low, and the speed is fast. Fewer media and reagents are consumed. The method provided by the invention makes mechanized automatic operation come true, and with the help of an automated high-throughput screening instrument, the amount of labor can be greatly reduced further, the screening flux can be improved.
Owner:NANJING NUOYUN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase, encoding gene, vector, engineering bacteria, and applications of recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase
ActiveCN104774828AHigh catalytic activityAchieve conversionBacteriaCarbon-halide lyasesHigh concentrationEthyl 3-hydroxybutyrate
The present invention discloses a recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase, an encoding gene, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a recombinant bacterial containing the gene, and applications of the recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase in catalysis synthesis of (R)-4-cyano-ethyl 3-hydroxybutyrate through dehalogenation of (S)-4-chloro-ethyl 3-hydroxybutyrate. Compared with other halohydrin dehalogenases, the halohydrin dehalogenase obtained through the method has characteristics of high catalytic activity, high concentration substrate and product tolerance, and industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Pseudomoas umsongensis YC1612 for producing halohydrin dehalogenases and application and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a pseudomoas umsongensis YC1612 for producing halohydrin dehalogenases and an application and preparing method thereof and belongs to the field of microorganisms. The preservation number of the pseudomoas umsongensis YC1612 is CCTCC NO:M 2017173. The pseudomoas umsongensis YC1612 can produce the halohydrin dehalogenases, and can catalyze epoxide to be subjected to ring opening and prepare chirality epoxide and beta- to replace alcohol in the presence of nucleophilic reagents. When N3- is used as the nucleophilic reagents and o-methyl phenyl glycidyl ether is catalyzed to conduct ring opening reaction, the ee value of (S)-o-methyl phenyl glycidyl ether can reach 98%, and the ee value of generated (R)-1-nitrine-3-(2- methylphenoxy)-2- propyl alcohol reaches 96.8%. The pseudomoas umsongensis YC1612 can be applied to the situation that the epoxide is catalyzed to be subjected to selective ring opening and the chirality epoxide and the beta- are prepared to replace the alcohol, and has a significant application prospect.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and application thereof
PendingCN110699345AHigh stereoselectivityHigh selectivityBacteriaCarbon-halide lyasesEnzyme GeneGlycidyl ethers
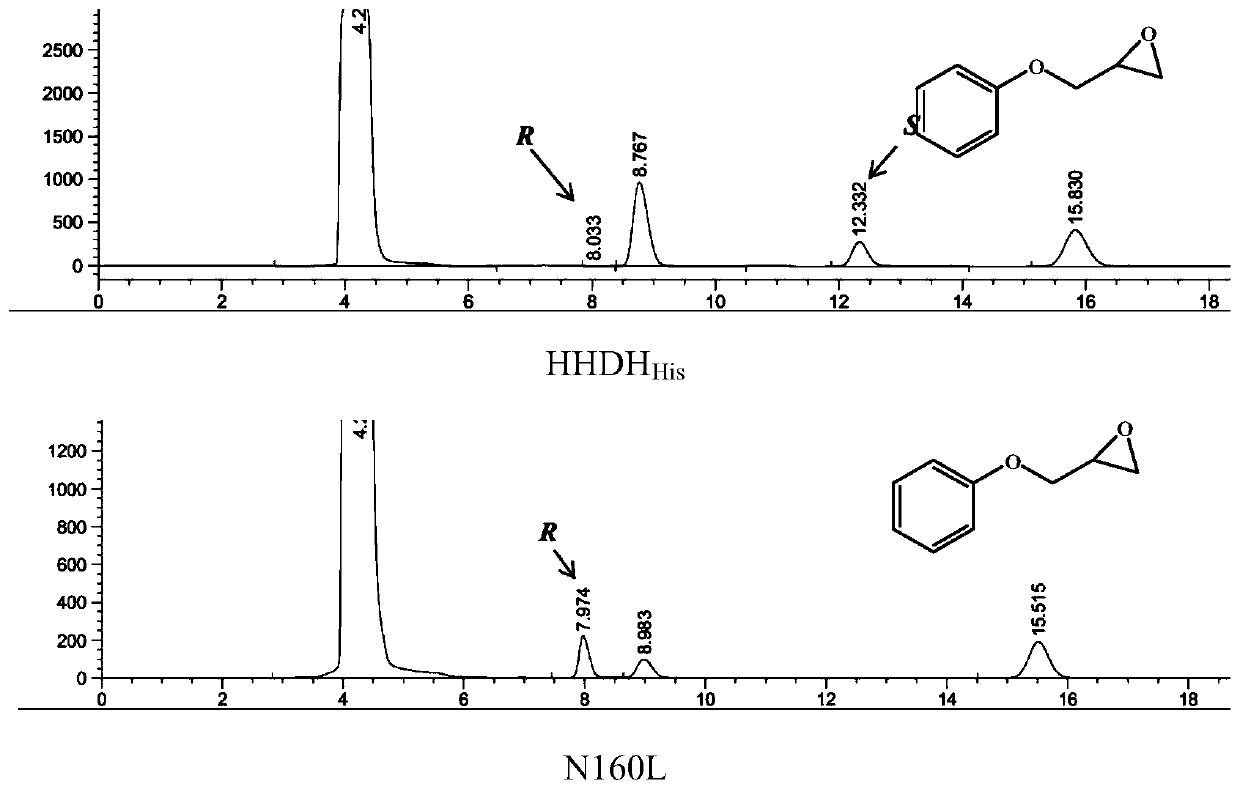
The invention first discloses a halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and application thereof. According to the invention, a database mining technology is used to mine potential halohydrin dehalogenase genes, and the halohydrin dehalogenase genes are induced to express in engineering bacteria to obtain a new halohydrin dehalogenase. Semi-rational design and modification of the enzyme is performed, and (R, S)-PGE is used as a model substrate to obtain two mutants with improved stereoselectivity, which are Q159L and N160Lrespectively. The enantioselectivity of the two mutants is increased approximatelyfrom 9.85 to 21.80 and 21.10respectively. The selectivity of the mutant N160L is opposite to selectivity of the original enzyme. The selectivity to various substrates of the two mutants is improved to a certain extent. In particular, the E value of the mutant N160L for the substrate P-methylphenyl glycidyl ether is increased to 25.77, which is 13.93 times greater than E value of the original HHDHHis.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Preparation method for catalytic synthesis of (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutanoate by halohydrin dehalogenases
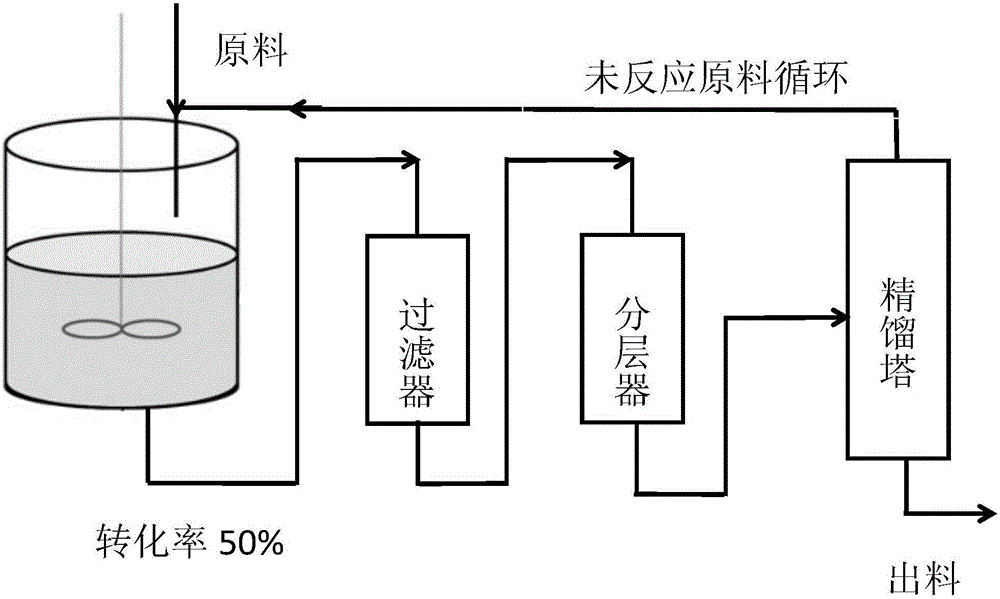
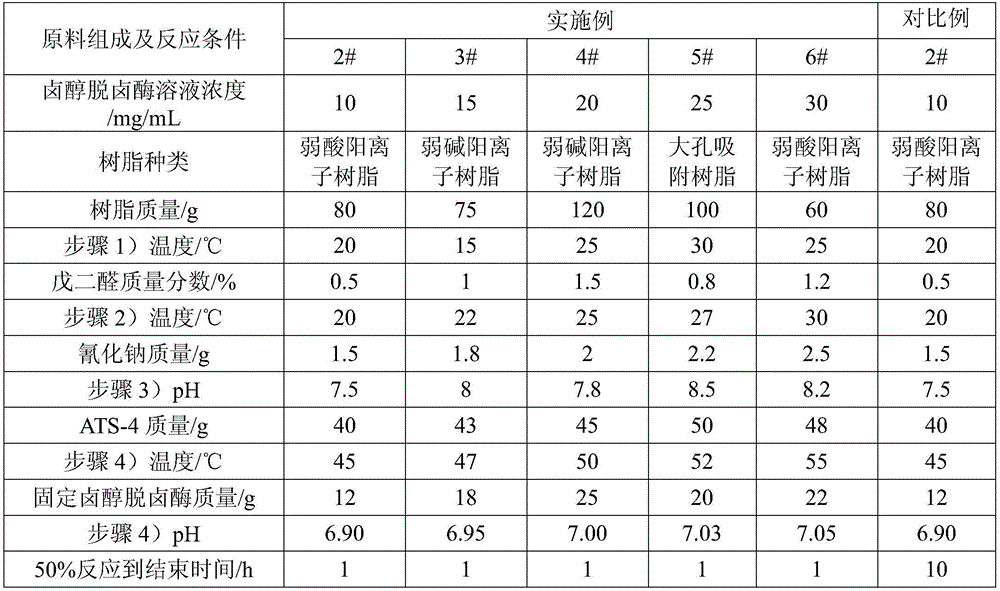
The invention relates to a preparation method for catalytic synthesis of (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutanoate by halohydrin dehalogenases. According to the invention, (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate (ATS-4) is taken as a substrate, and (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutanoate (ATS-5) is enzymatically synthesized, by aiming at the defects of the enzymatic method of slow reaction rate and low conversion rate, resin is selected as a carrier, halohydrin dehalogenases are adsorbed, and a reaction system of which the conversion rate is 50% is introduced into a distillation device, so that the residence time of enzymes in the reaction system is shortened, the enzyme inactivation is reduced, the enzymes can be recycled, and the utilization rate of the enzymes is increased. The preparation method for the catalytic synthesis of (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutanoate by halohydrin dehalogenases disclosed by the invention is mild in reaction conditions, quick in reaction speed, low in cost, good in operation stability, high in conversion rate which is up to 98.8%-99.4% and free of side effects, and the prepared products are high in optical purity and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
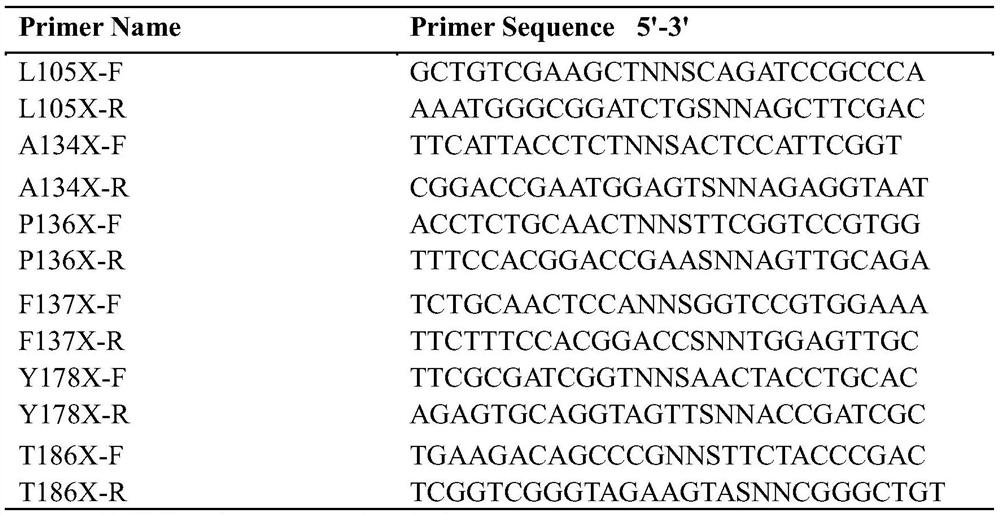
Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and application thereof in synthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin
ActiveCN111647588AIncrease enzyme activityChange structureBacteriaCarbon-halide lyasesSodium phosphatesSingle mutation
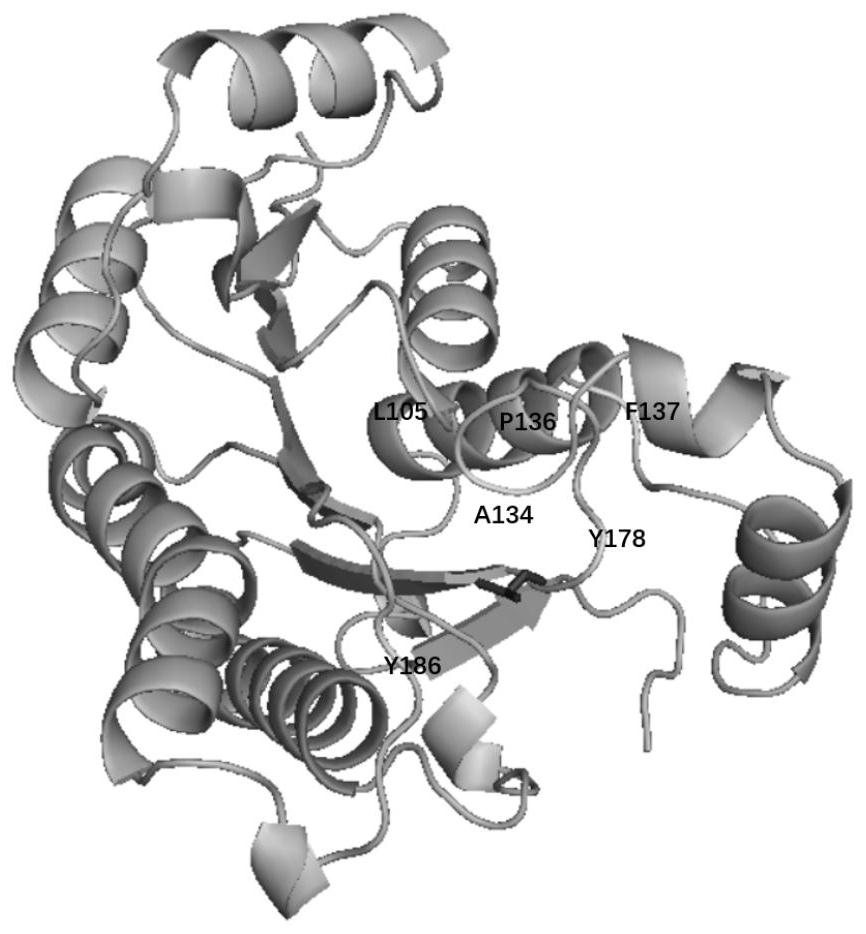
The invention discloses a halohydrin dehalogenase mutant and application of the halohydrin dehalogenase mutant in synthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin. The mutant is characterized in that the mutant isobtained by carrying out single mutation or multiple mutation on the 105th site, the 134th site, the 136th site, the 137th site, the 178th site or the 186th site of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The e.e. Value of the product (S)-epichlorohydrin of the halohydrin dehalogenase mutant exceeds 99% by utilizing a water-organic double-phase buffer solution system (the ratio of ethyl acetate to a sodium phosphate buffer solution is 6: 4), and the enzyme activity of wet cells is respectively improved to 100-600U / mL from 23.56 U / mL; the yield reaches 15.9 percent to 80.2 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
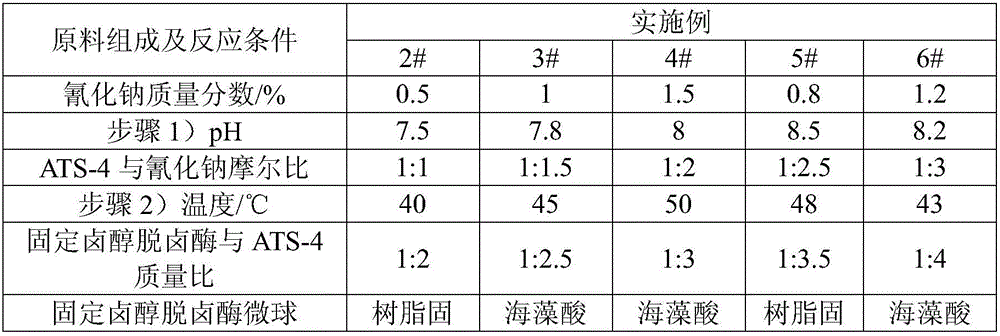
Preparation method for continuous cyclic synthesis of ethyl(R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate
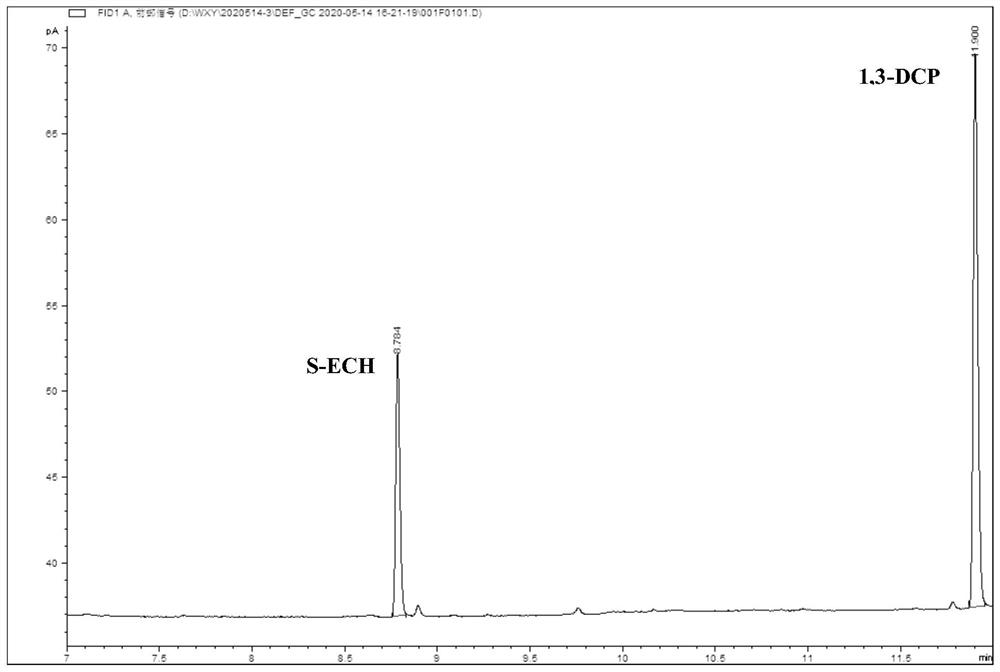
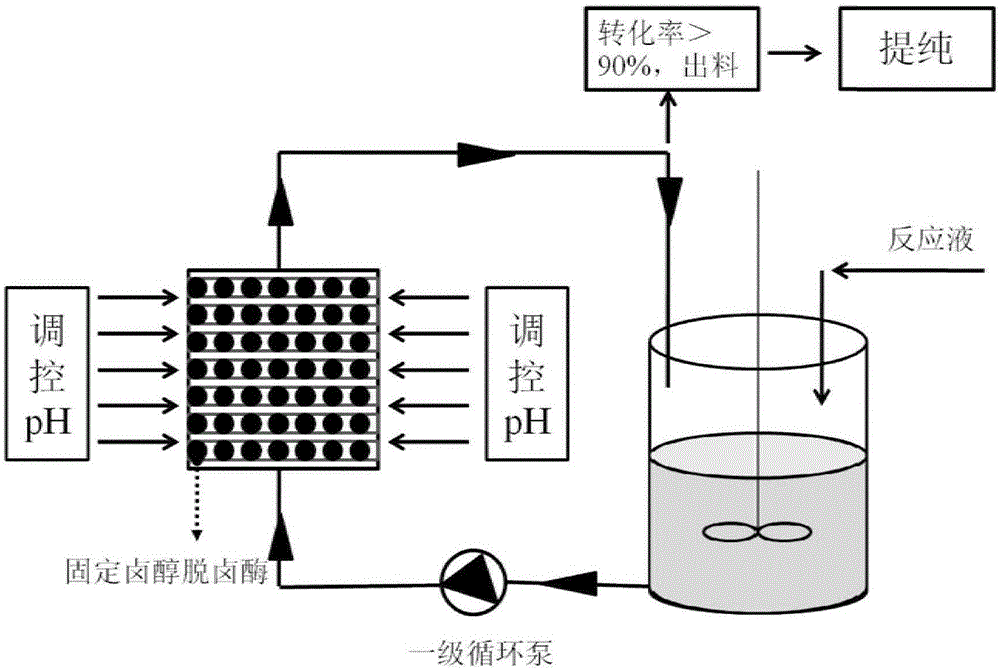
The invention relates to a preparation method for continuous cyclic synthesis of ethyl(R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate. The preparation method comprises the following step: ethyl(S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate(ATS-4) is used as a substrate; ethyl(R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate (ATS-5) is synthesized by adopting an enzymatic method; aiming at the defects that in the enzymatic method reaction process, immobilized enzymes are likely to smash by a stirring paddle to cause the service cycles of the immobilized enzymes to be reduced; a primary circulating pump is utilized to input a reaction liquid from the bottom of a device filled with immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase microspheres capable of regulating and controlling pH and to output the reaction liquid from the upper part of the device, so that a circulation catalytic reaction is realized; the reaction process is detected in real time by utilization of gas chromatography. The immobilized enzyme microspheres cannot be smashed, the service cycle of the immobilized enzyme can be greatly prolonged, the enzyme utilization ratio is high, and the catalytic effect is good; the preparation method is mild in reaction condition, high in reaction speed, low in cost, simple to operate, good in stability, and suitable for industrial continuous production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
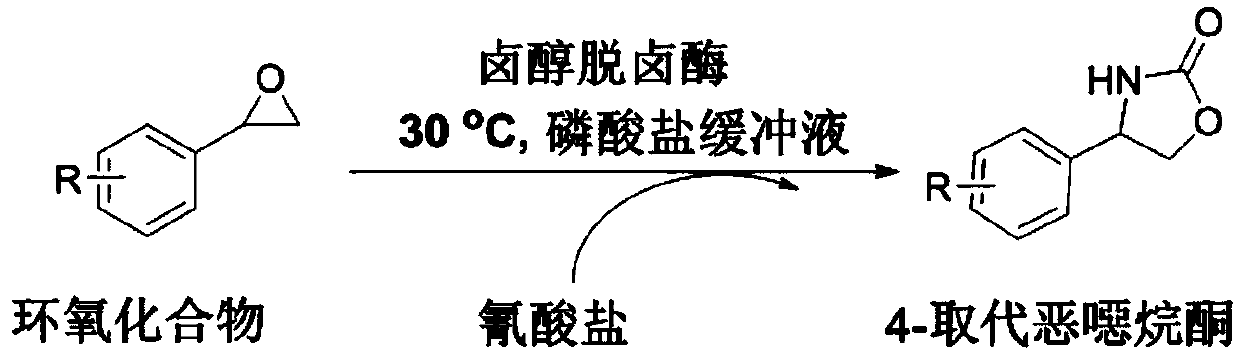
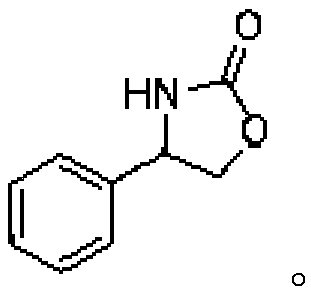
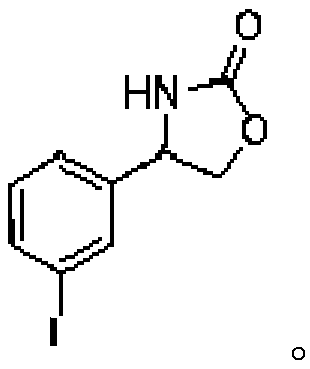
Method of biocatalytically synthesizing 4-substituted oxazolidinone compound
The invention discloses a biocatalytic technology of synthesizing a 4-substituted oxazolidinone compound by carrying out a reaction on a halohydrin dehalogenase catalyzed epoxy compound and cyanate. The reaction takes the epoxy compound as a primer, cyanate as a nucleophilic ring opening reagent and halohydrin dehalogenase which is originated from an Ilumatobacter coccineus strain and has high alpha-offensive ring opening area selectivity as a biocatalyst. The reaction is carried out in a water phase and is mild in reaction condition. The invention is the biocatalytic method of catalyzing theepoxy compound to synthesize the 4-substituted oxazolidinone compound by using the halohydrin dehalogenase for the first time. The method has a wide application prospect in design of an oxazolidinonedrug and green manufacturing aspect thereof.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Continuous preparation method of statin pharmaceutical intermediate namely (R)-3-hydroxyethyl glutarate
ActiveCN104372040ASolve efficiency problemsSolve the costMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidGlutaric acid
The invention discloses a continuous preparation method of a statin pharmaceutical intermediate namely (R)-3-hydroxyethyl glutarate. The preparation method comprises the following technological steps: step one, converting (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyethyl butyrate ((S)-CHBE) into (R)-4-cyan-3-hydroxyethyl butyrate in the presence of a catalyst namely recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase (HHDH); step two, converting the (R)-4-cyan-3-hydroxyethyl butyrate into (R)-3-hydroxyethyl glutarate in the presence of a catalyst namely recombinant nitrilase (NIT); wherein the two catalytic reactions are both carried out in a water solution in a reaction tank. In the provided method, two steps of coupled bio-catalytic reactions are performed and specific recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase (HHDH) and recombinant nitrilase (NIT) are adopted to carry out continuous reactions so as to prepare a key intermediate of statin. The two green catalytic reactions are serially connected and carried out continuously, and the next reaction can be carried out without extracting the intermediate. The provided method has the advantages of continuous operation, high equipment utilization rate, low cost, and simple and convenient operation.
Owner:NANJING NUOYUN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com