Halohydrin dehalogenase mutant derived from ADI (Agrobacterium radiobacter) and application of halohydrin dehalogenase mutant to preparation of (S)-epichlorohydrin
A halohydrin dehalogenase, epichlorohydrin technology, applied in the application, halocarbon lyase, enzyme and other directions, can solve the stereoselectivity and reaction system obstacles of halohydrin dehalogenase, cannot achieve optical purity, cannot satisfy Industrial application and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy control of the operation process, good industrial application value, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Construction of Halohydrin Dehalogenase Site-Directed Saturation Mutation Library
[0032] Primers were designed according to the GenBank AAK92099 gene sequence (see Table 1). Use primers I81X-F and I81X-R, F86X-F and F86X-R, V94X-F and V94X-R, respectively, to carry out site-directed saturation mutation on the parental HheC gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1) experiment. 50 μL PCR reaction system: 25 μL 2×Phanta Max Buffer, 1 μL dNTP, 1 μL P1 (50 μM) and P2 (50 μM), 2 μL (100-200ng) parental plasmid template, 1 μL Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNApolymerase, 19 μL deionized water.
[0033] PCR program: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3min, 30 cycles: 95°C for 15s, holding at a suitable annealing temperature for 15s, 72°C for 3min30s, and finally extending at 72°C for 10min.
[0034] After the PCR products were verified by agarose nucleic acid electrophoresis, the products were purified using PCR cleanup Kit. After PCR was positive by 0.9% agarose gel...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Screening of Halohydrin Dehalogenase Single-point Saturation Mutation Library
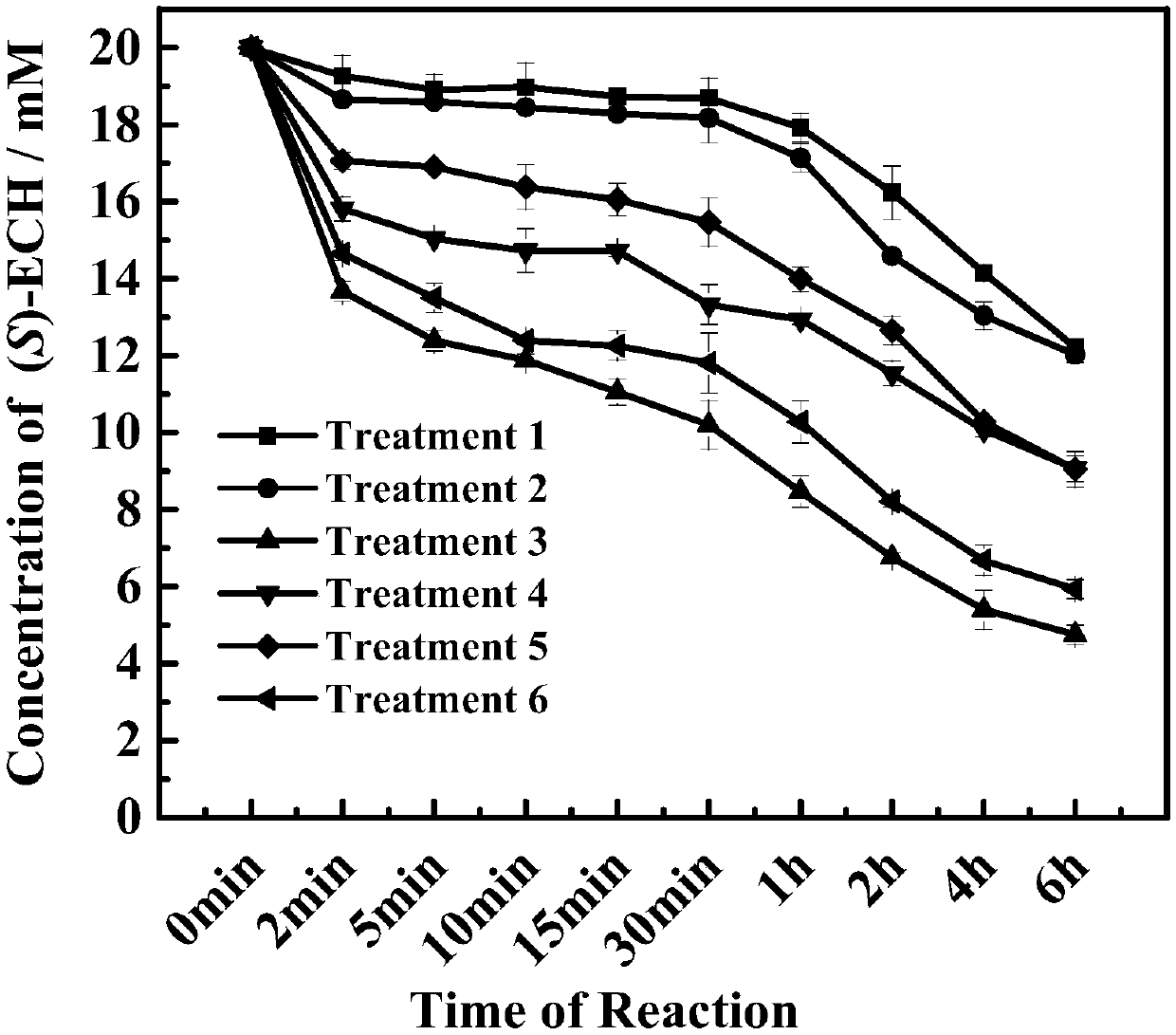
[0036] Pick a single colony clone (the mutant library constructed in Example 1) and culture it in a 2 mL deep 96-well plate containing 1 mL LB and 50 μg / mL kana resistance. At the same time, three parents were selected as controls. A 2 mL deep 96-well plate was cultured at 37°C for 5 hours, then 100 μL of the bacterial solution was transferred to another sterile 2 mL 96-well plate, and 100 μL of 30% (wt / vol) sterile glycerol was added to it. Add 100 μL of LB medium containing 50 μg / mL kana-resistance and 1 mM IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside) to the remaining 900 μL bacterial liquid, and place at 28°C for induction for 12-14 hours. The induced strain was centrifuged at 3,000×g and 4°C for 30 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the bacterial cells were collected. 500 μL of reaction system (200 mM phosphate buffer, 1.3-dichloro-2-propanol) was added to each well, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Construction of Halohydrin Dehalogenase Iterative Saturation Mutation Library
[0039] Primers were designed according to the GenBank AAK92099 gene sequence (see Table 1). Use primers F86X-F and F86X-R, V94X-F and V94X-R, respectively, and use the 81st position preferred mutant plasmid as a template to carry out iterative saturation mutations at positions 86 and 94. 50 μL PCR reaction system: 25 μL 2 ×Phanta Max Buffer, 1 μL dNTP, 1 μL P1 (50 μM) and P2 (50 μM), 2 μL (100-200ng) parental plasmid template, 1 μL Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNA polymerase, 19 μL deionized water. PCR program: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3min, 30 cycles: 95°C for 15s, holding at a suitable annealing temperature for 15s, 72°C for 3min30s, and finally extending at 72°C for 10min. After the PCR products were verified by agarose nucleic acid electrophoresis, the products were purified using PCR cleanupKit. After the PCR was positive by 0.9% agarose gel electrophoresis analysis, take ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com