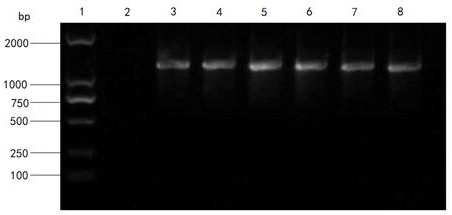
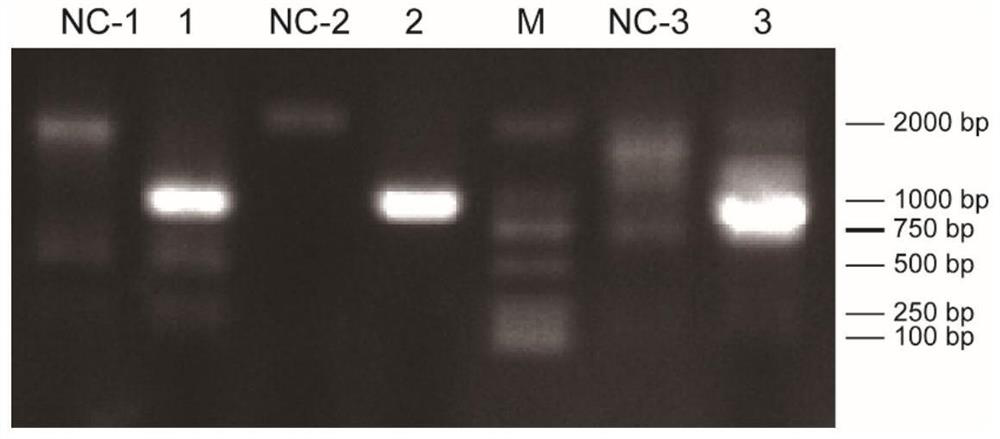
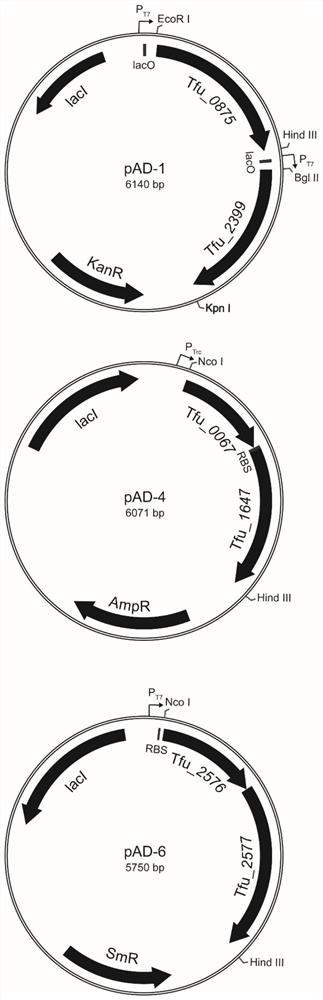
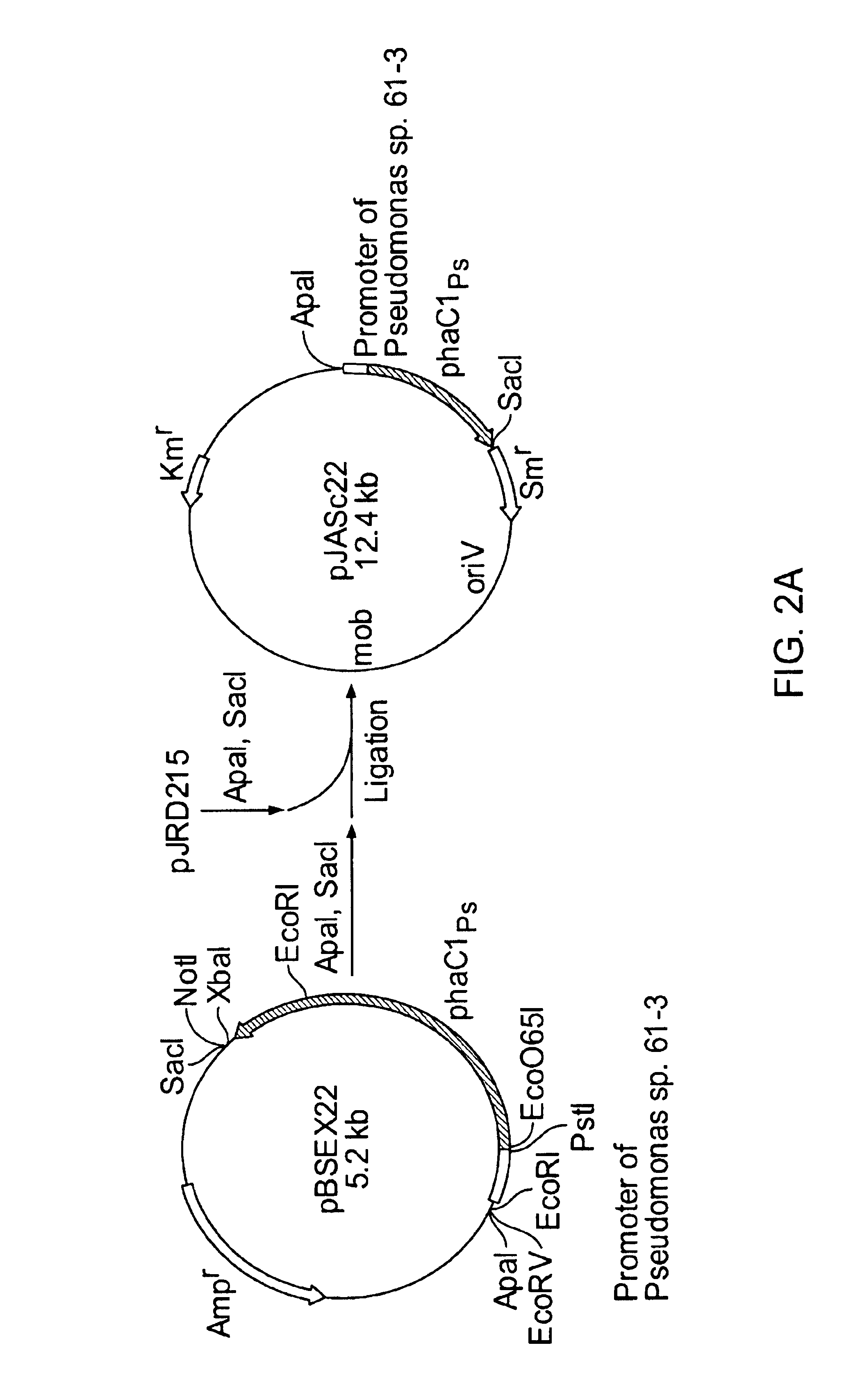
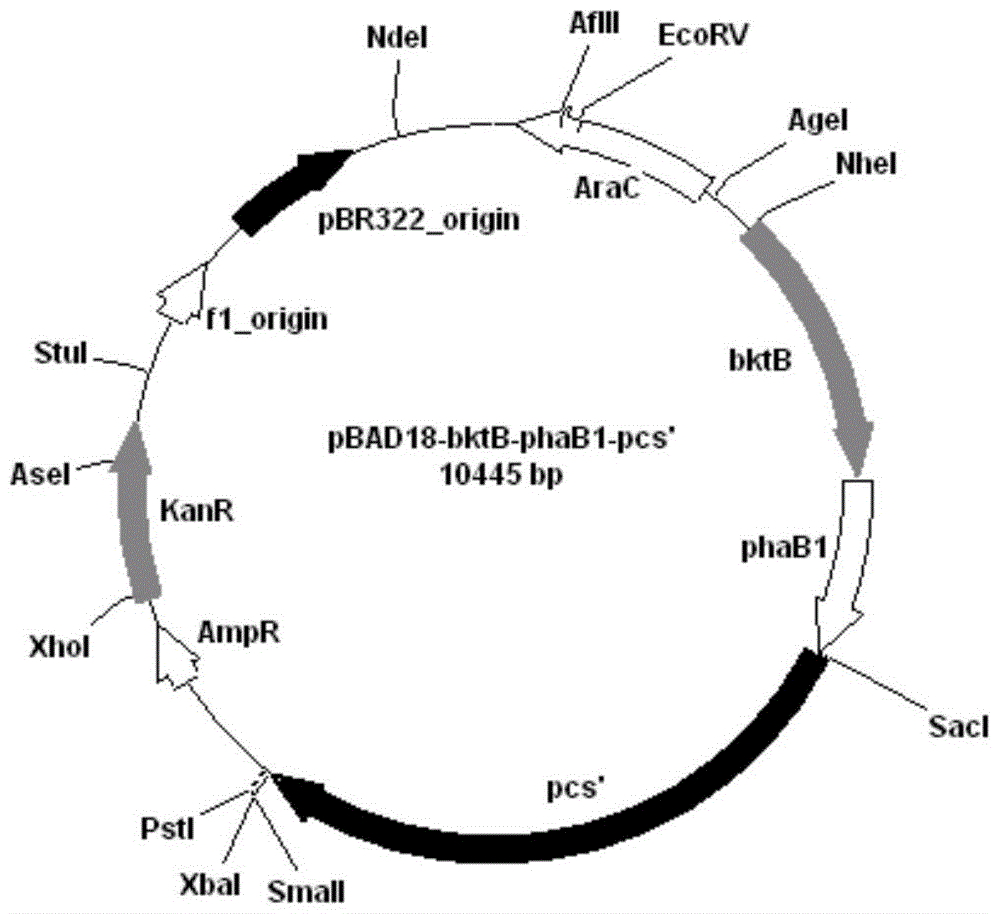
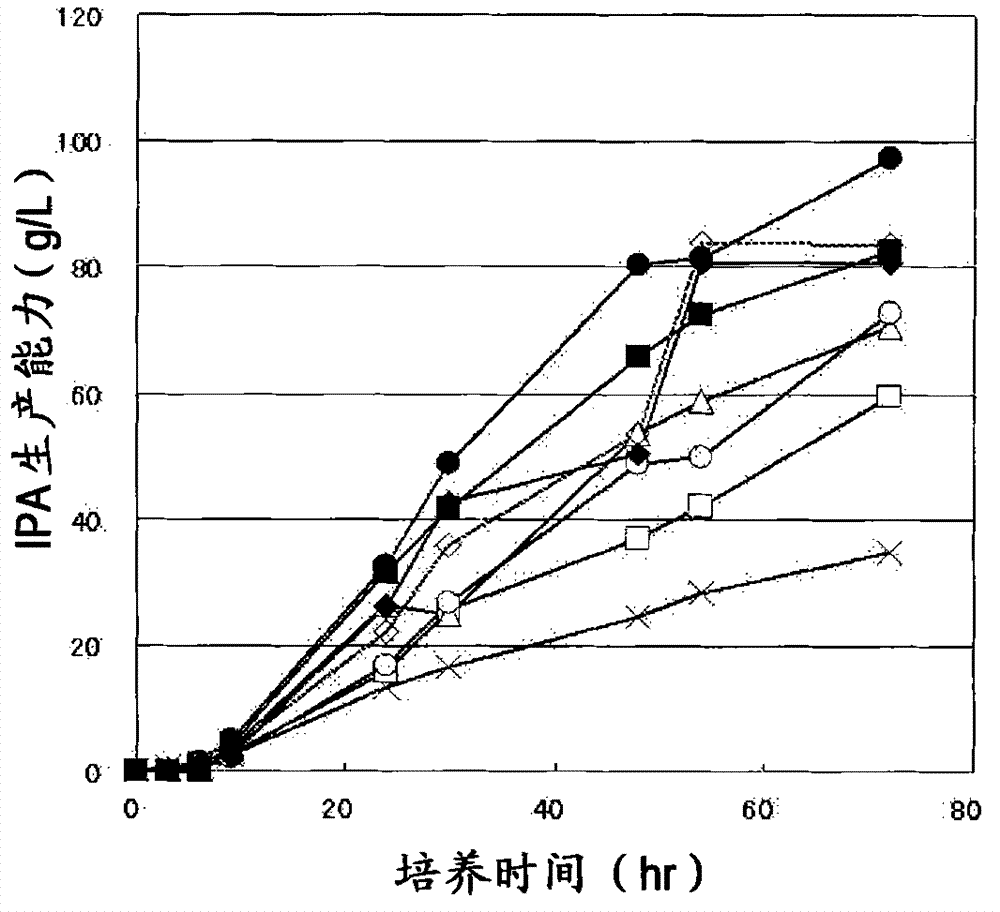
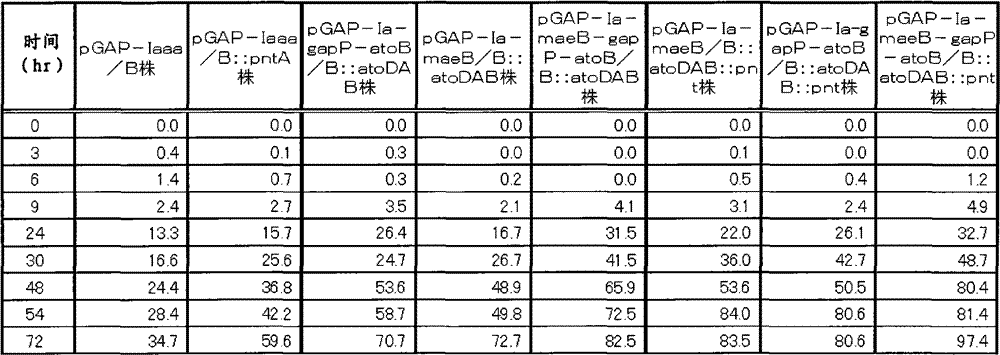
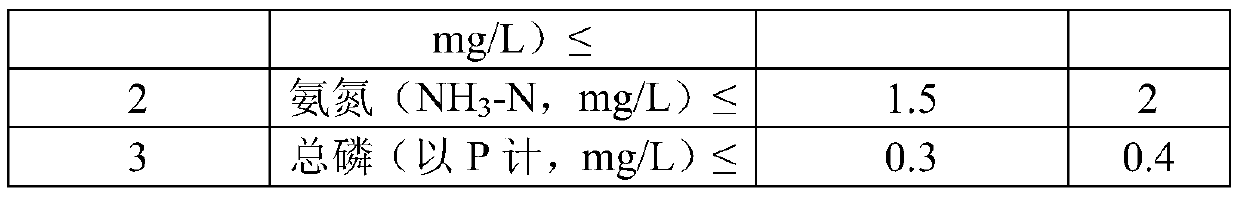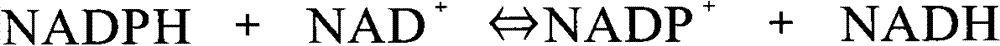Patents
Literature
69 results about "Thiolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
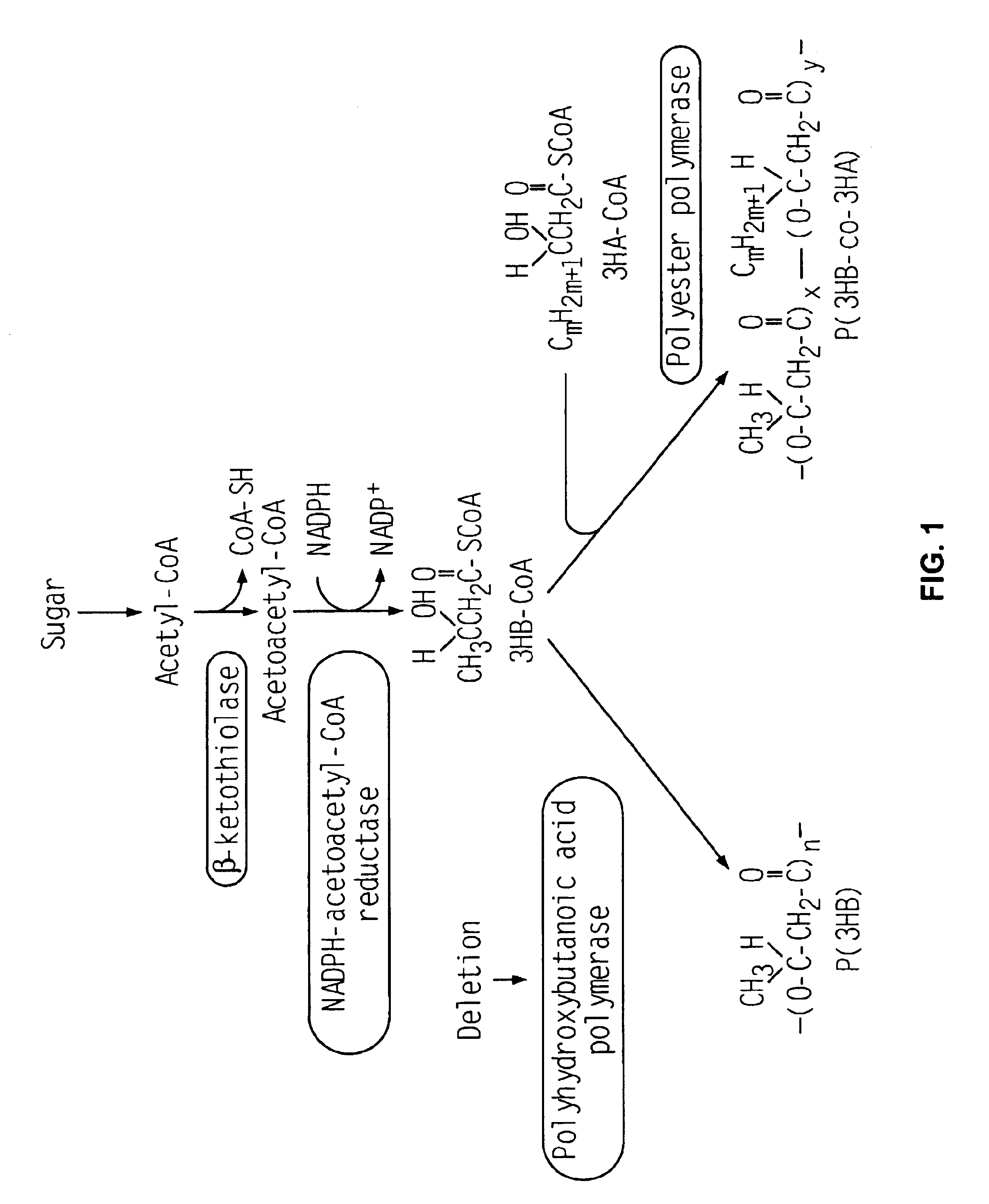
Thiolases, also known as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferases (ACAT), are enzymes which convert two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway. Thiolases are ubiquitous enzymes that have key roles in many vital biochemical pathways, including the beta oxidation pathway of fatty acid degradation and various biosynthetic pathways. Members of the thiolase family can be divided into two broad categories: degradative thiolases (EC 2.3.1.16) and biosynthetic thiolases (EC 2.3.1.9). These two different types of thiolase are found both in eukaryotes and in prokaryotes: acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (EC:2.3.1.9) and 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (EC:2.3.1.16). 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (also called thiolase I) has a broad chain-length specificity for its substrates and is involved in degradative pathways such as fatty acid beta-oxidation. Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (also called thiolase II) is specific for the thiolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA and involved in biosynthetic pathways such as beta-hydroxybutyric acid synthesis or steroid biogenesis.
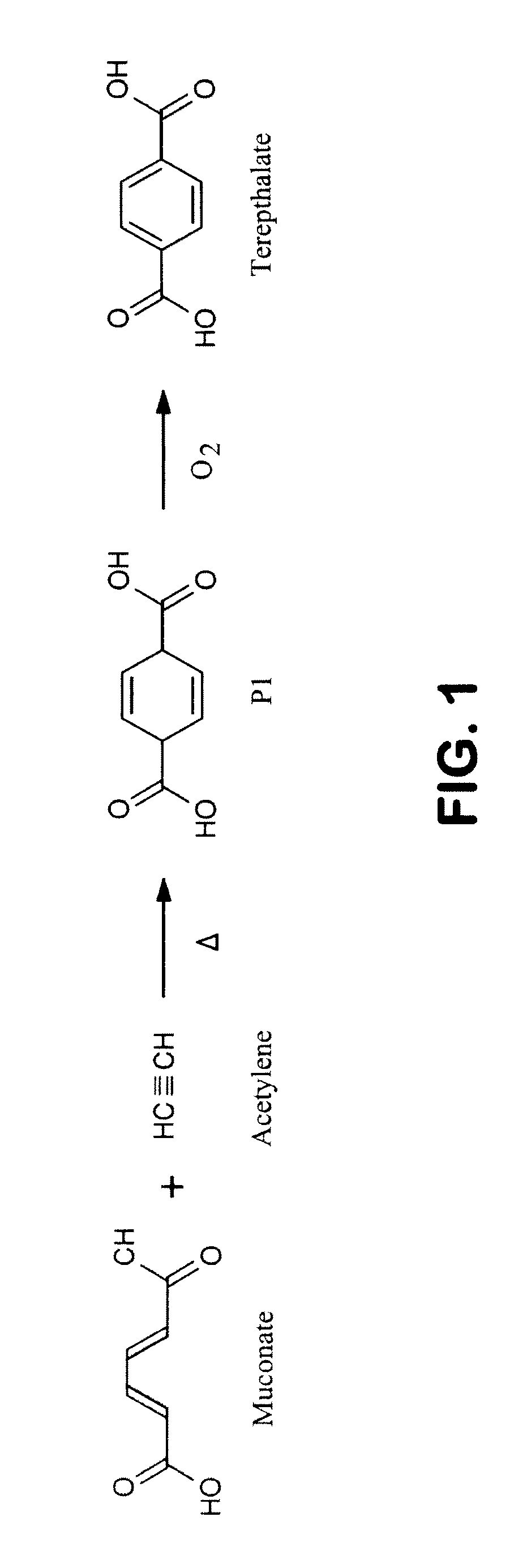
Semi-synthetic terephthalic acid via microorganisms that produce muconic acid
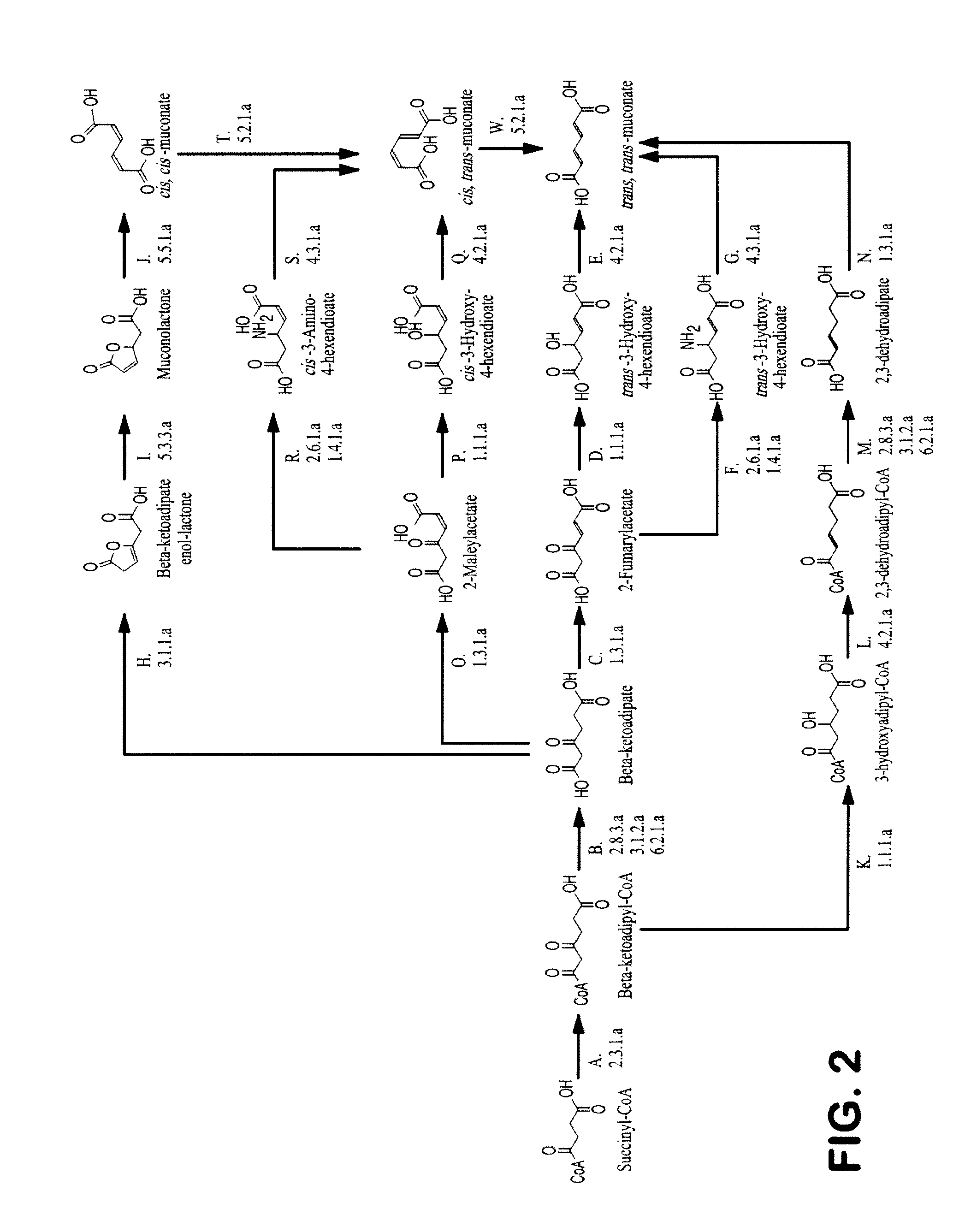
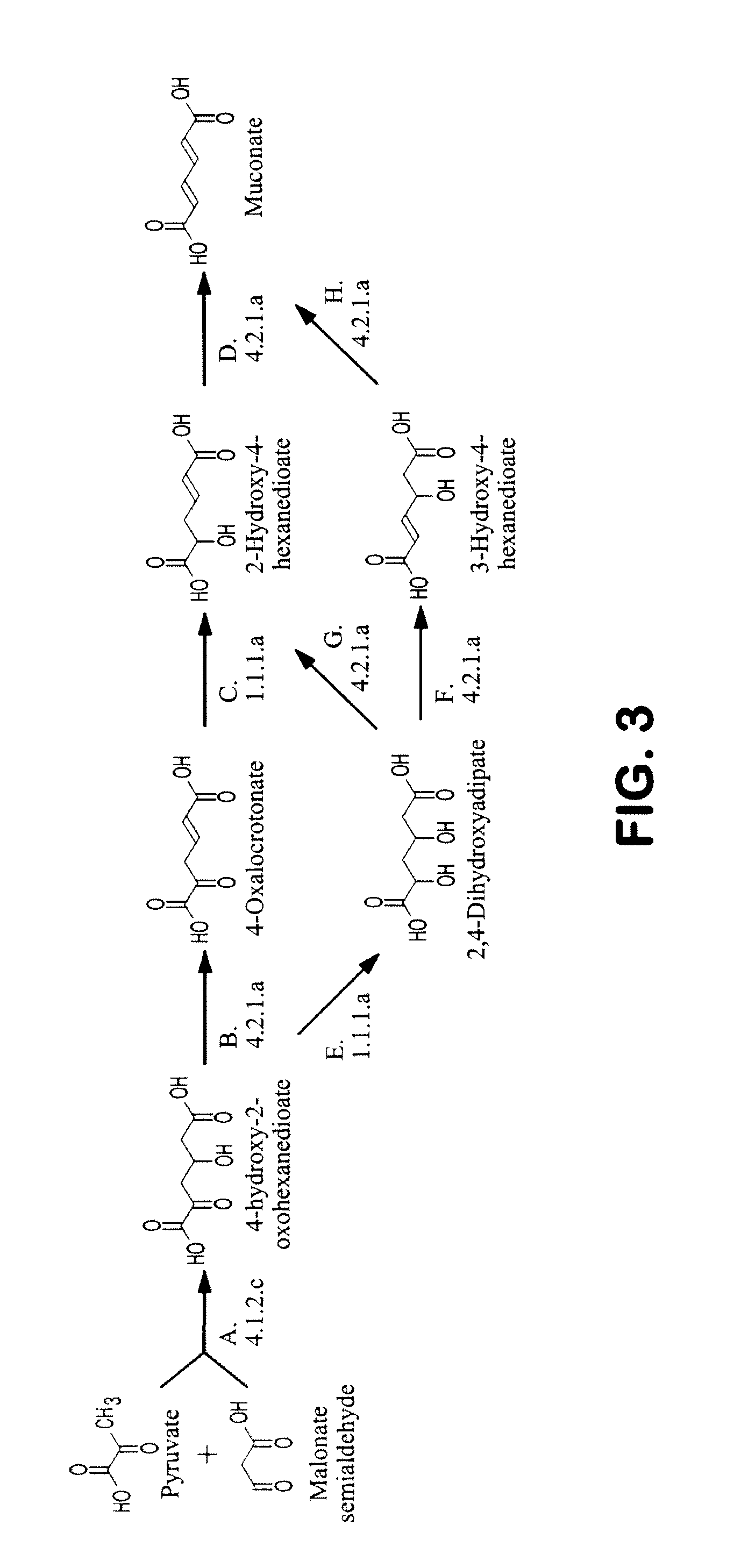
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a muconate pathway having at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a muconate pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce muconate. The muconate pathway including an enzyme selected from the group consisting of a beta-ketothiolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA transferase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA ligase, a 2-fumarylacetate reductase, a 2-fumarylacetate dehydrogenase, a trans-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminotransferase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a trans-3-amino-4-hexenoate deaminase, a beta-ketoadipate enol-lactone hydrolase, a muconolactone isomerase, a muconate cycloisomerase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a 3-hydroxyadipyl-CoA dehydratase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA transferase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA ligase, a muconate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate dehydrogenase, a cis-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-maleylacetate aminoatransferase, a 2-maleylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a cis-3-amino-4-hexendioate deaminase, and a muconate cis / trans isomerase. Other muconate pathway enzymes also are provided. Additionally provided are methods of producing muconate.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
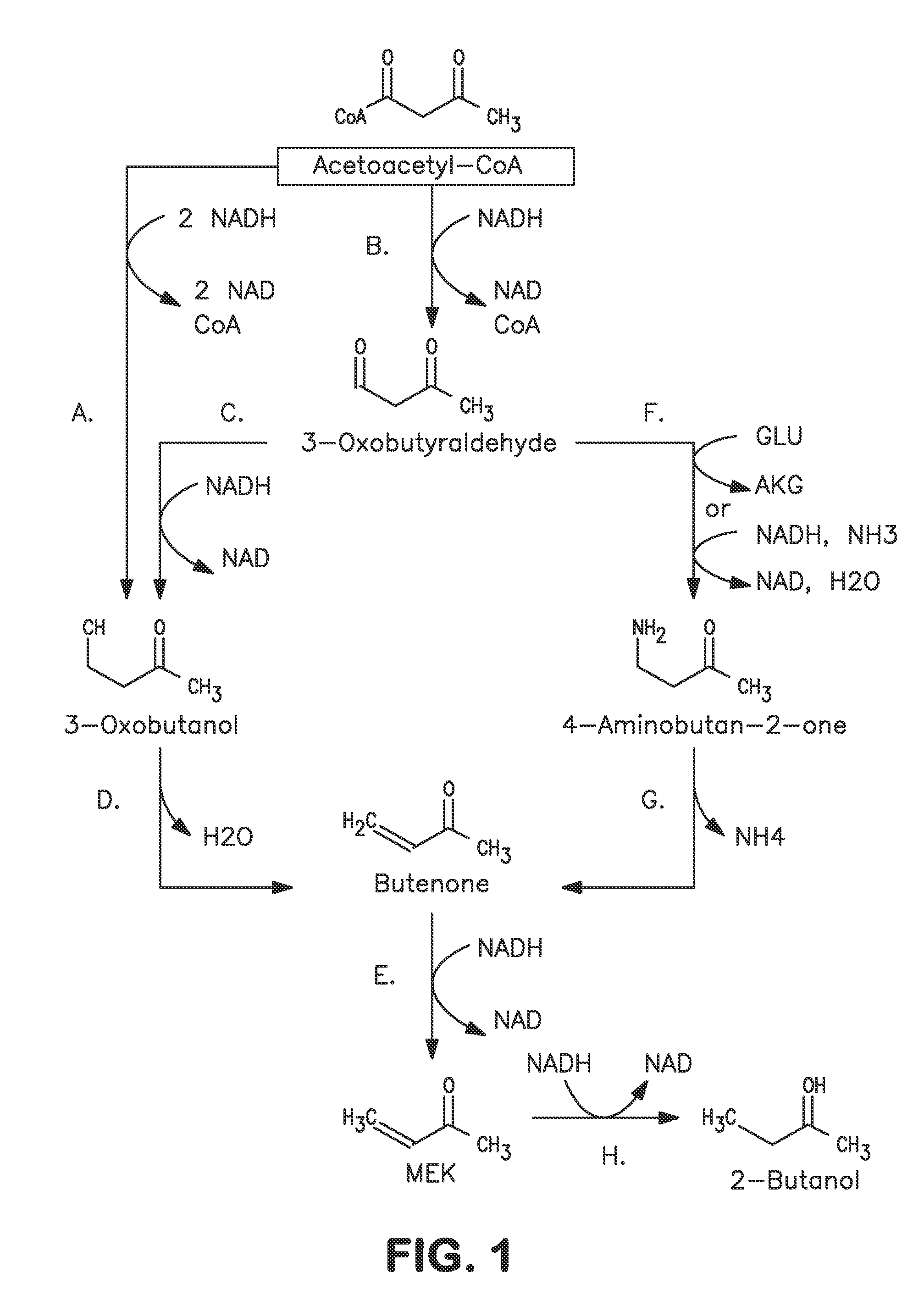
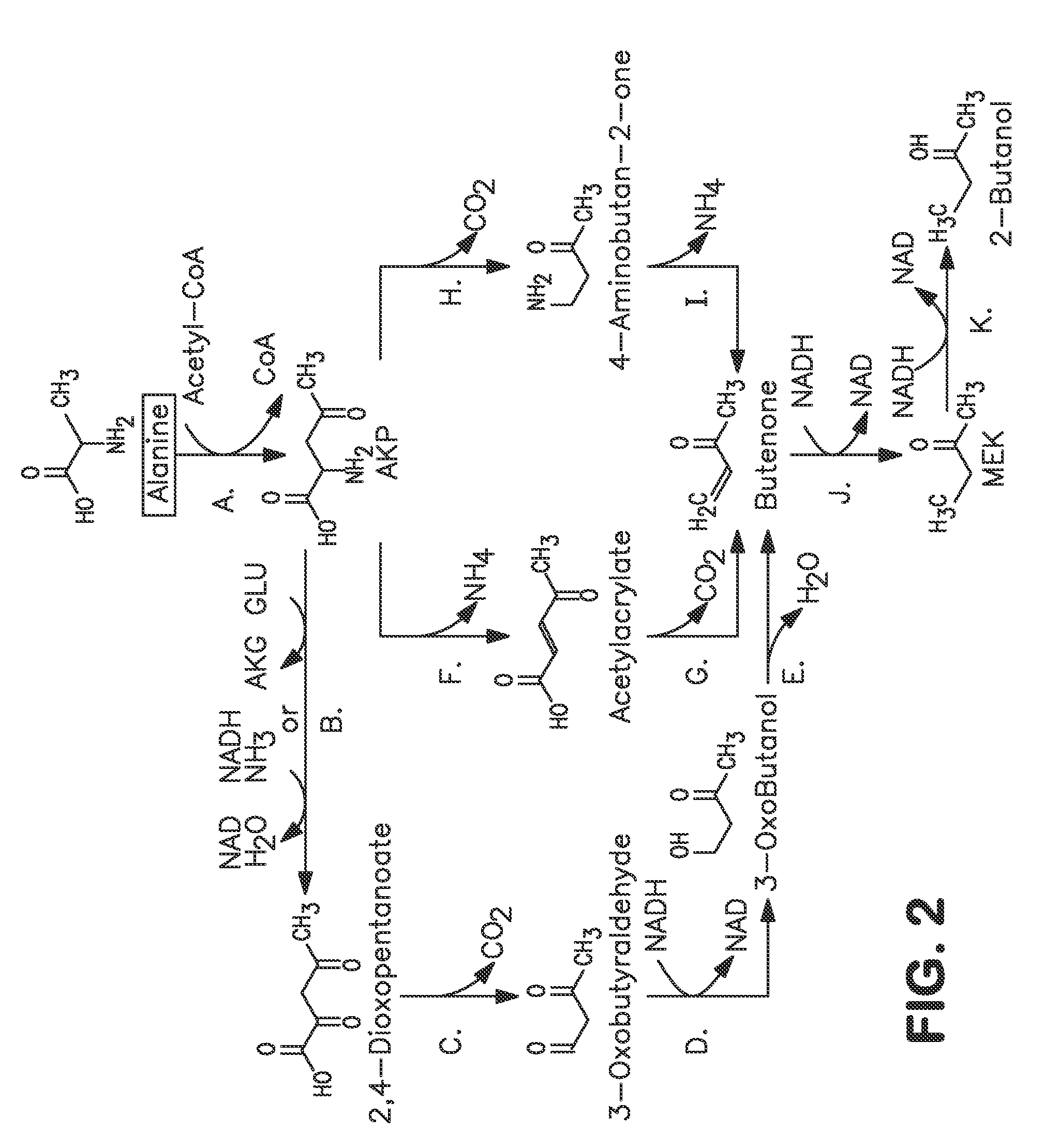
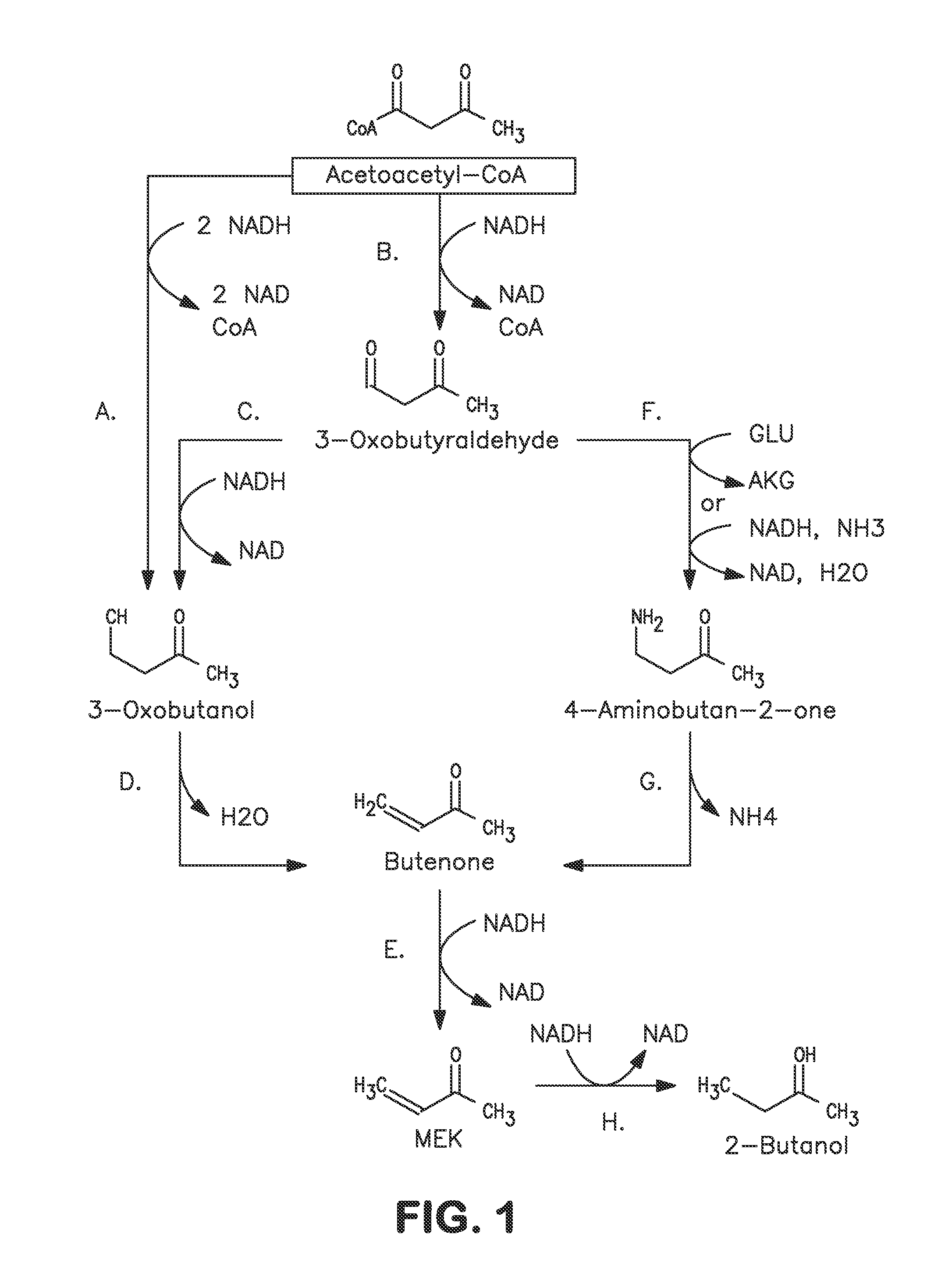
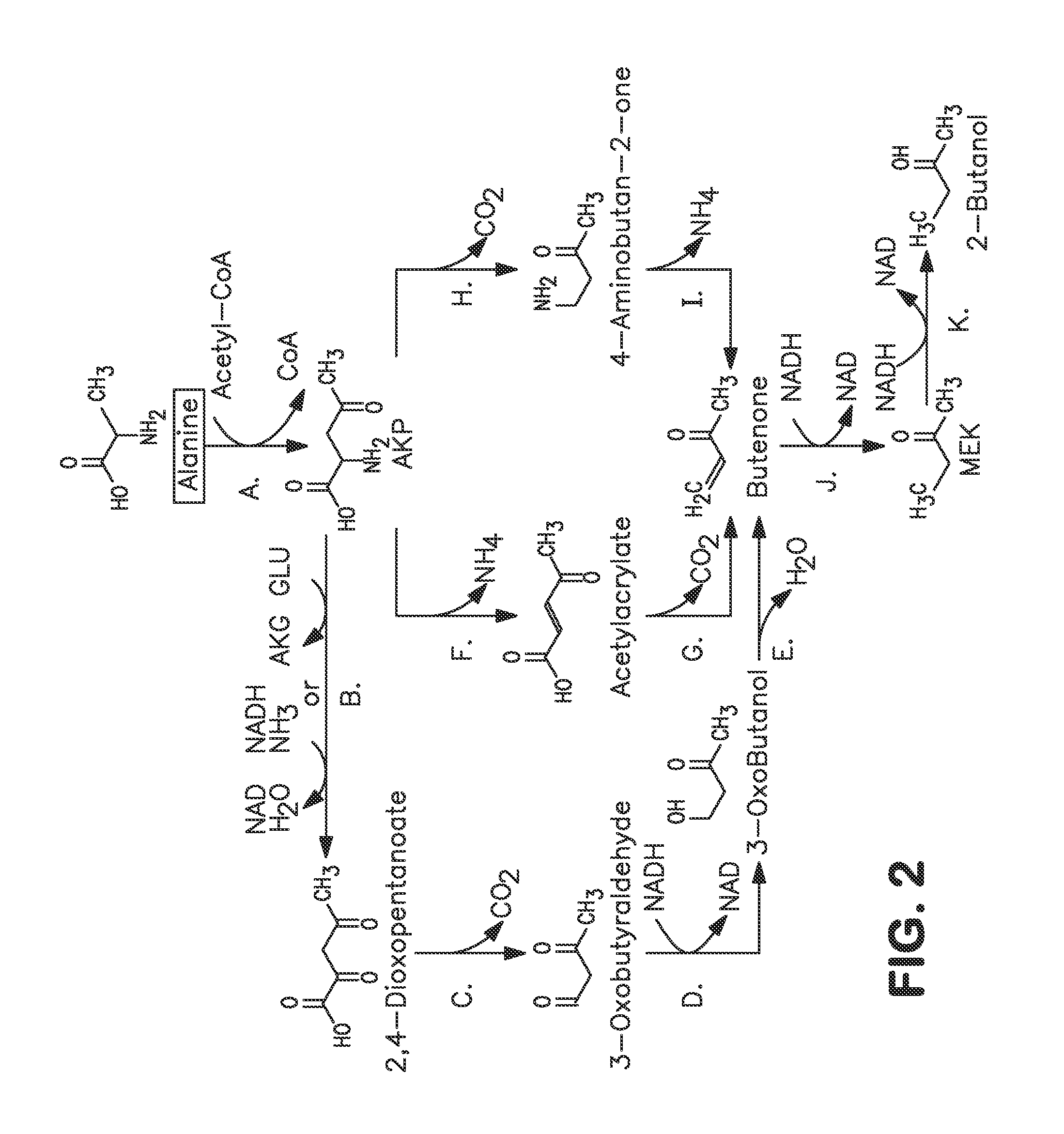
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of mek and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Isopropyl alcohol- producing bacterium and method of producing isopropyl alcohol using the same
ActiveUS20100311135A1Decrease productivityProduce significantBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAcetoacetate decarboxylase activityBiochemistry
The invention provides: an isopropyl alcohol-producing bacterium which has an acetoacetate decarboxylase activity, an isopropyl alcohol dehydrogenase activity, a CoA transferase activity and a thiolase activity having been imparted thereto and is capable of producing isopropyl alcohol from a plant-derived material; a method of producing isopropyl alcohol whereby isopropyl alcohol is produced from a plant-derived material by using this isopropyl alcohol-producing bacterium; and an apparatus therefor.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
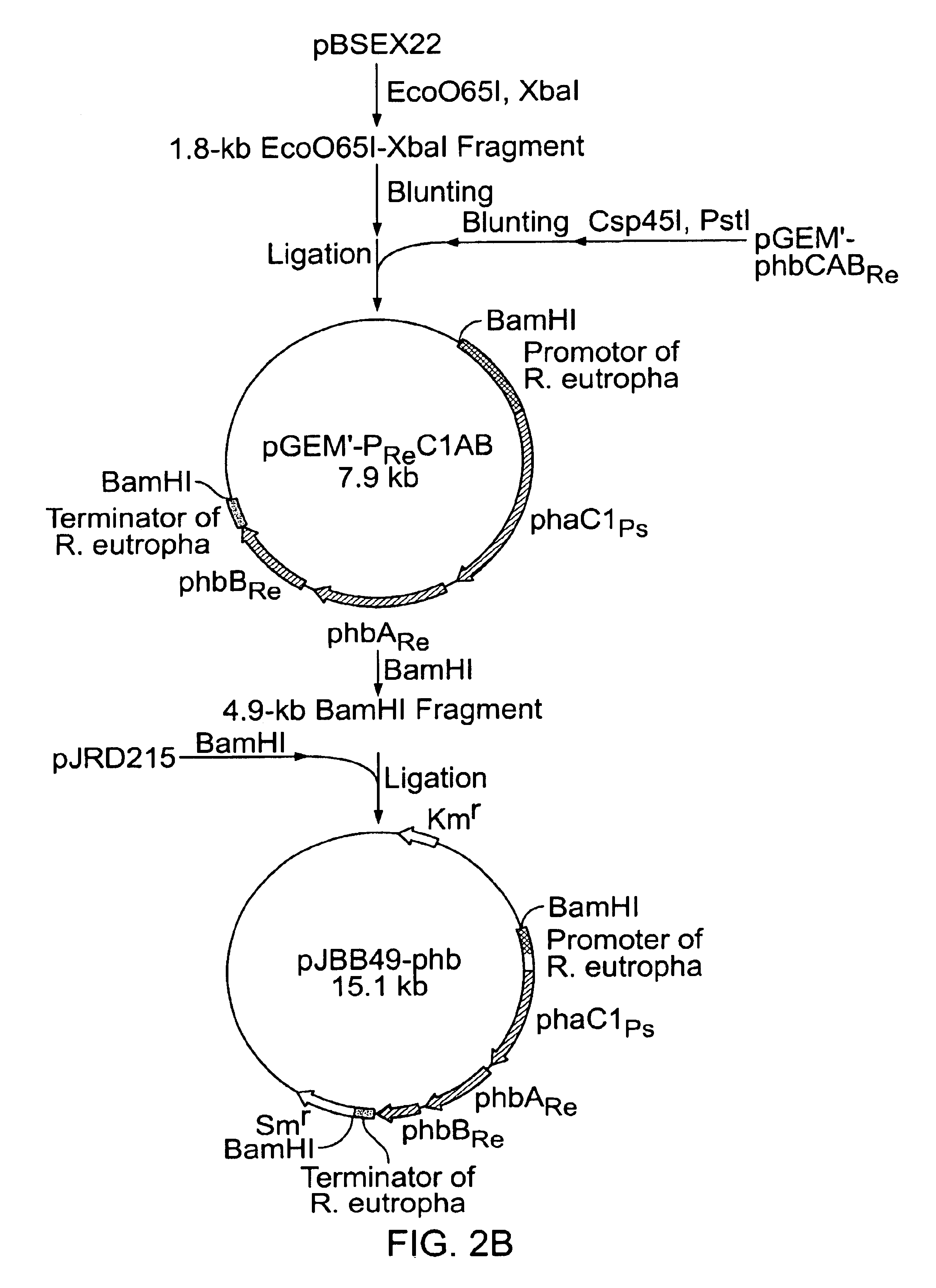
Method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof
ActiveCN101845414AHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof. Recombinant pseudomonas putida is prepared by the method comprising the following steps of: depriving coding functions of 3-hydroxyfatty acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase coding gene and 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase coding gene in pseudomonas putida to obtain recombinant pseudomonas putida, and recording the recombinant pseudomonas putida as recombinant pseudomonas putida I. Experiments prove that the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer, particularly medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer (C4-C14), can be obtained by using the recombinant bacteria organism to synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate. The obtained hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer has high purity and high yield. The method of the invention can synthesize the medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer with random length, and overcomes the defect that only one 3-hydroxybutyrate (HB) homopolymer can be obtained by biosynthesis in the prior art. Therefore, the method of the invention has broad application prospect in the biosynthesis field of the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant saccharomycetes for high yield of sandalwood oil as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111434773AOvercoming extraction deficienciesMeet the level of industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySandalwood oil
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomycetes for high yield of sandalwood oil as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant saccharomycetes. The method comprises the following steps: 1) integrating genes such as acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase gene and the like which are derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae and are driven by a strong promoter and CYP450 reductase gene whichis driven by a weak promoter into a saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 genome of an original strain in a homologous recombination manner; 2) replacing a promoter of a squalene synthase gene in the recombinant bacteria; knocking out genes such as galactose modulin 80 genes; and (3) inserting a sandalene synthase gene driven by a strong promoter and a CYP450 monooxygenase gene into the multi-copy freeplasmid to obtain an expression plasmid, and introducing the expression plasmid into the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae obtained in the step (2) to obtain the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for high yield of sandalwood oil. According to the method, the defect that sandalwood oil is extracted from sandalwood is overcome, and the yield of each liter of sandalwood oil of the recombinant yeast strain reaches 1g. Industrial production requirements can be met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
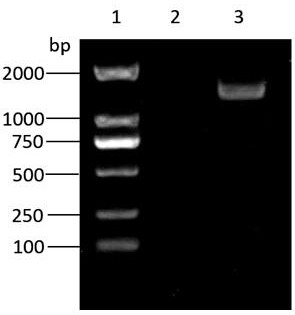
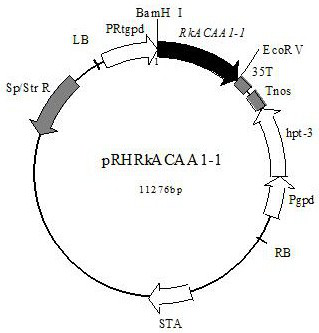
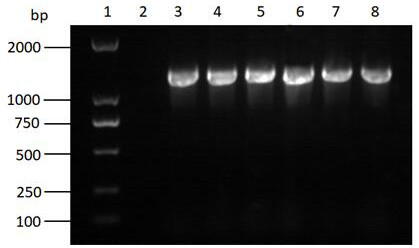
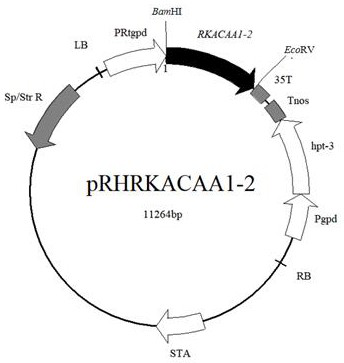
3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene RkACAA1-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN113621630AIncrease contentIncreased transcript levelsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene RkACAA1-1. A nucleotide sequence of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene RkACAA1-1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and an amino acid sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The gene is separated from rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235, the gene is transformed into the rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235, and an experimental result shows that the overexpression of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene RkACAA1-1 can cause the increase of total carotenoids in a rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 strain. According to the 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene RkACAA1-1 and the application thereof, the rhodosporidium kratochvilovae is modified by a genetic engineering means to increase the content of the carotenoids, so that good application prospects and economic benefits are provided for industrial production of the carotenoids, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of the carotenoids.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Depilating composition for less thiolase process and the water bath depilation method therewith
InactiveCN1526289AReduce pollutionSave pollution control costsSlaughtering accessoriesFiberWater baths
The present invention is depilating composition for less thiolase process and the water bath depilation method therewith. The water bath depilation method features the depilation process including placing leather blank after soaking, eliminating meat and fat into rotating drum; adding water, surfactant and sodium bicarbonate and rotating for 30 min; adding ammonium chloride and rotating for 30 min; adding proteinase and rotating for 60-120 min; adding sodium sulfide and rotating for 60 min; adding hydrogen peroxide and rotating for 30 min; rotating 5 times for 5-10 min each in each hour; and stopping for one night to complete the water bath depilation process, with the total period being 15-24 hr. The said method has good depilation effect, can disperse fiber further and make leather soft and light colored. In addition, the said process has less sulfide pollution and its effluent has low COD and low BOD5.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
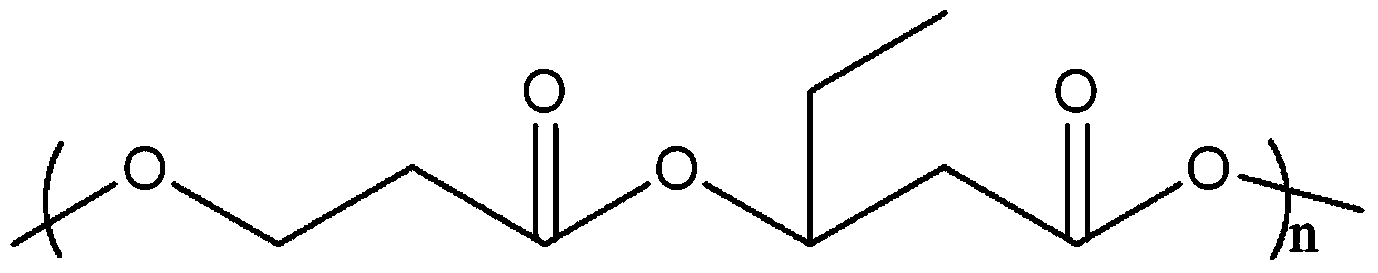
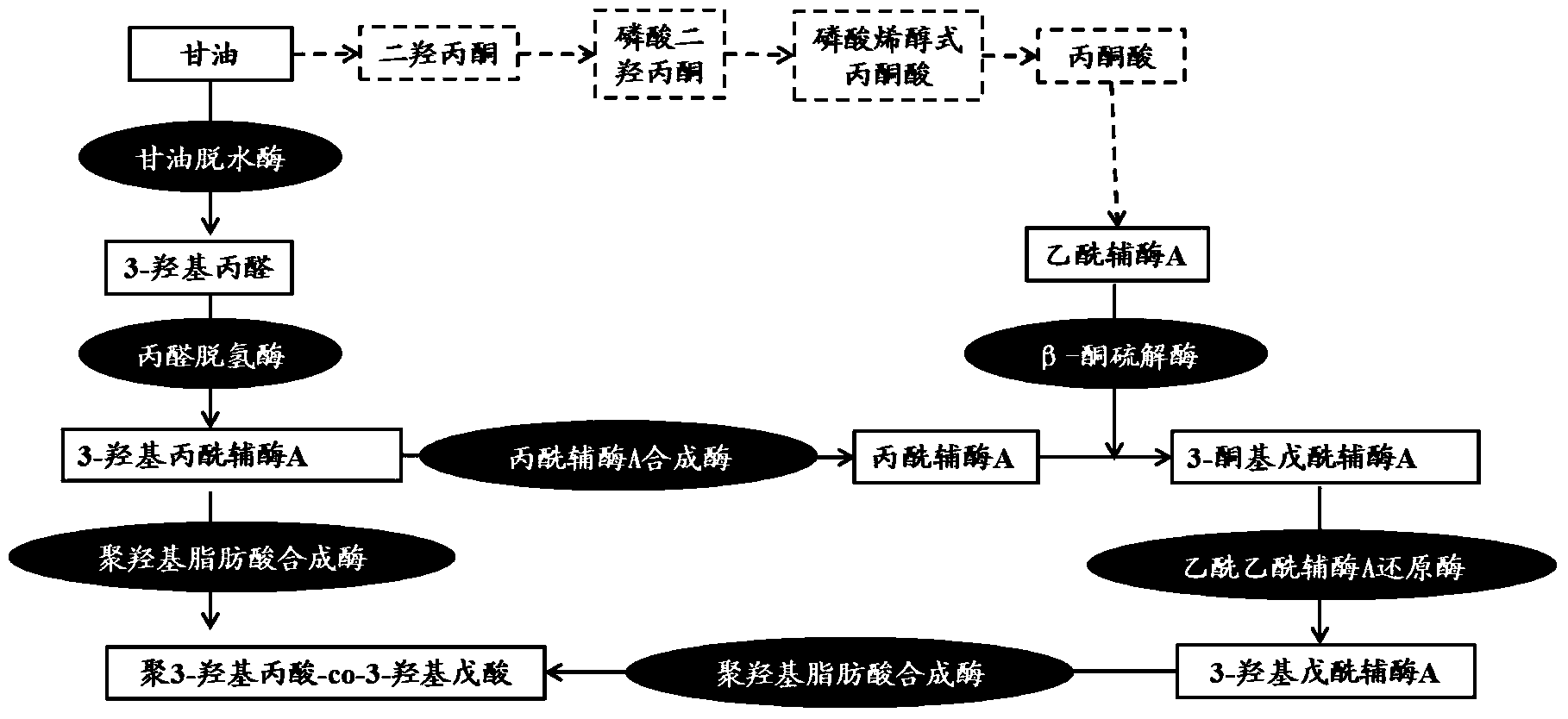
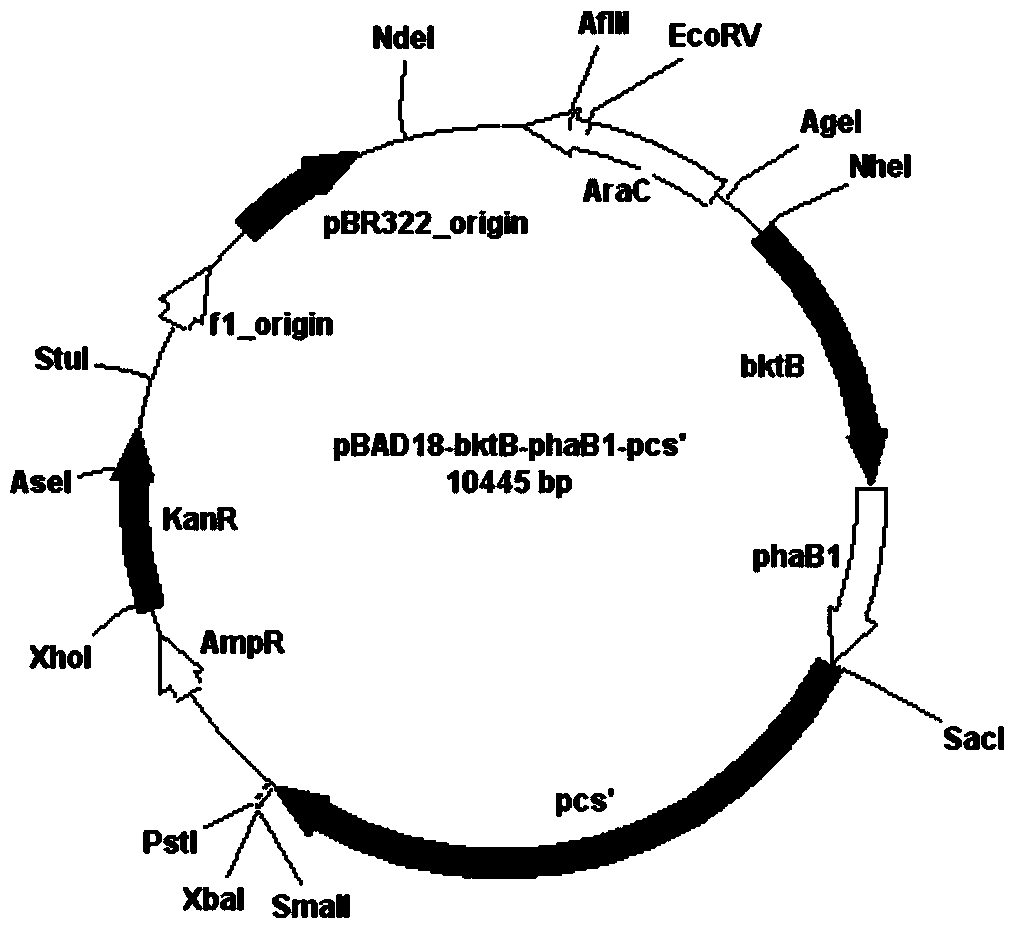
Poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and production method thereof
ActiveCN104046659AHigh melting pointReduce crystallinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, a glycerol dehydratase gene and a glycerol dehydratase re-activating enzyme gene are integrated with a host strain genome by a gene integration technology, a polyhydroxy fatty acid synthase gene, a propionaldehyde dehydrogenase gene, a beta-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene, an acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductase gene and a propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene are introduced, and a recombinant gene engineering strain has the ability of biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, the poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid is obtained in a biosynthesis manner for the first time; compared with poly-3-hydracrylic acid, the obtained poly 3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid has a higher melting point and lower crystallinity, has good degradability and can serve as a packaging material, a medical implant material, a drug sustained-release material and an electrochemical material.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene RKACAA1-2 and application thereof
ActiveCN113652440AIncrease contentEasy to synthesizeFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene RKACAA1-2, the nucleotide sequence of the 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene RKACAA1-2 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the amino acid sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2; the gene is separated from rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235, the gene is transferred into the rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 through transformation, and the experimental result shows that the overexpression of the RKACAA1-2 gene can cause the improvement of the carotenoid synthesis level of the YM25235 strain; according to the gene, the microorganisms are modified by means of genetic engineering, so that the yield of carotenoid in the microorganisms is increased, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
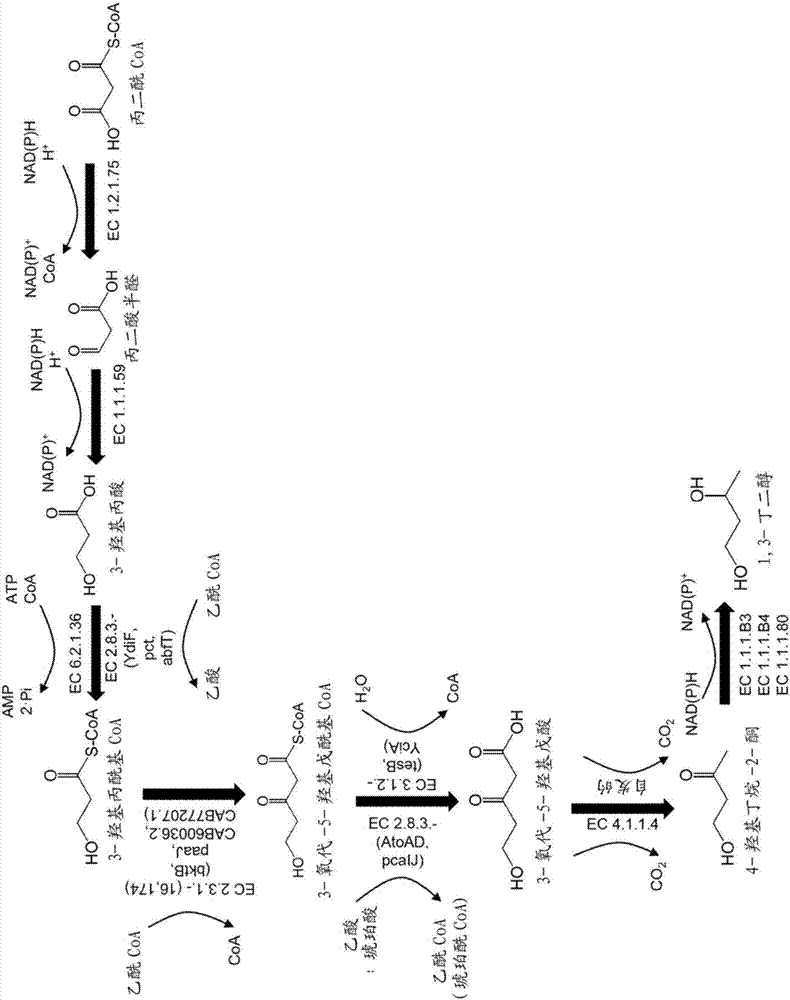
Biosynthesis of 1,3-butanediol
This document describes biochemical pathways for producing 1,3-butanediol using a polypetide having Beta-ketothiolase activity to form a 3-oxo-5-hydroxypentanoyl-CoA intermediate that can be enzymatically converted to 1,3-butanediol, as well as recombinant hosts producing 1,3-butanediol.
Owner:INVISTA TEXTILES (U K) LTD
A kind of β-ketothiolase related to the 3-hv monomer synthesis of phbv, its coding gene and application
The invention provides a research and an application of beta-ketothiolase in extreme halophilic archaeon, wherein beta-ketothiolase is related to 3-HV monomer synthesis of a biodegradable material PHBV. The protein provided by the invention is a protein showed by the following description (1) or (2): (1) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence represented by a sequence 1 in the sequence table; (2) a protein formed after the amino acid sequence represented by the sequence 1 is processed after substitutions and / or deletions and / or additions of one or more amino acid residues, wherein the obtained protein is derived from the protein represented by (1), and is PHBV and / or 3-HV related. As a result of experiments, when the coding gene of the poly(3-hydrobutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and / or 3-hydroxyalkanoate synthesis related protein is introduced into host bacteria, the molar ratio of generated 3-HV monomer for synthesizing PHBV is greater than 3-HV generated from the host bacteria.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
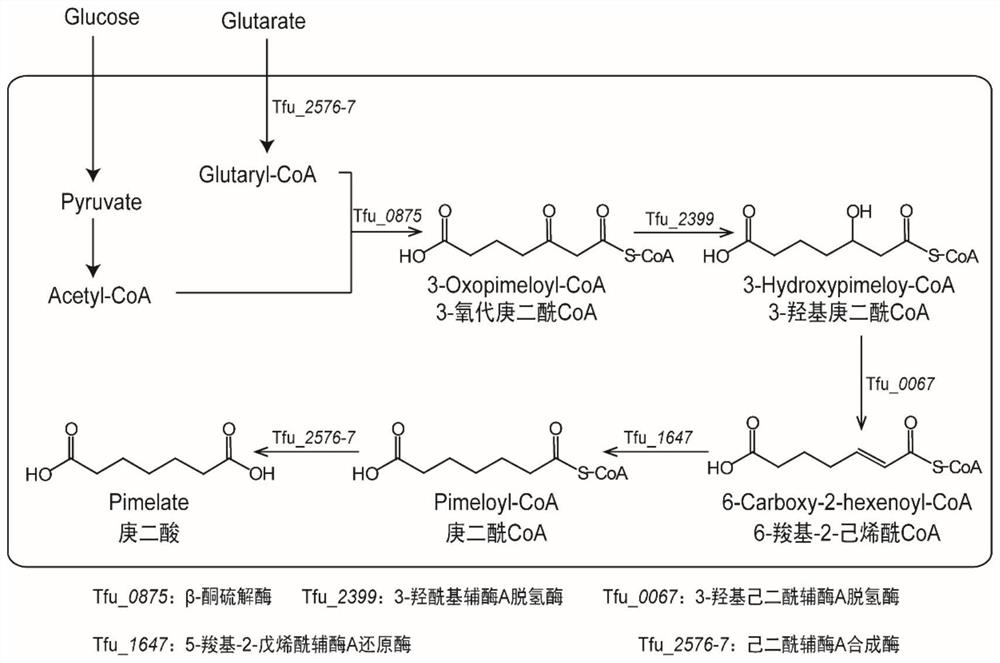
Full-biosynthesis method of pimelic acid
ActiveCN113817782ASimple processIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCarboxyl radical
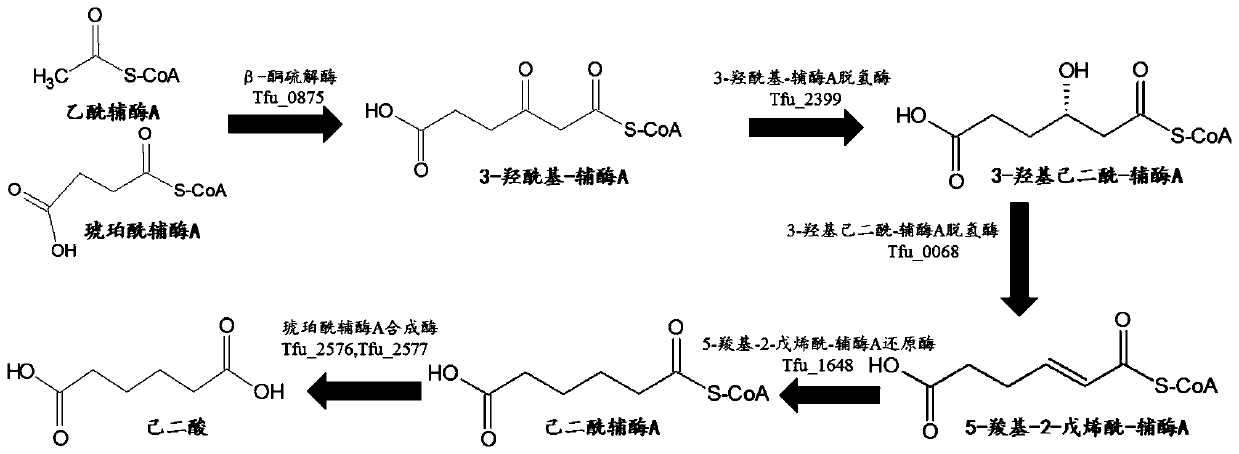
The invention discloses a full-biosynthesis method of pimelic acid, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) with a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), an acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase gene (atoB) and a succinyl-CoA synthetase alpha subunit gene (sucD) knocked out is used as a host, genes of beta-ketothiolase, 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, 3-hydroxyadipyl dehydrogenase, 5-carboxyl-2-pentenoyl coenzyme A reductase and adipyl coenzyme A synthetase from thermopsis fusca are overexpressed in modules, and the yield of pimelic acid can reach 252.60mg.L < -1 > through fermentation optimization of added inorganic salt in a culture medium. A new route is provided for synthesis of pimelic acid in the Escherichia coli host, and a new idea is provided for industrial fermentation production of pimelic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of producing copolymer polyester
A transformant, whose polyhydroxybutanoic acid polymerase gene is disrupted, having a recombinant vector containing a polyester polymerase gene, a beta-ketothiolase gene, and a NADPH-acetoacetyl CoA reductase gene.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
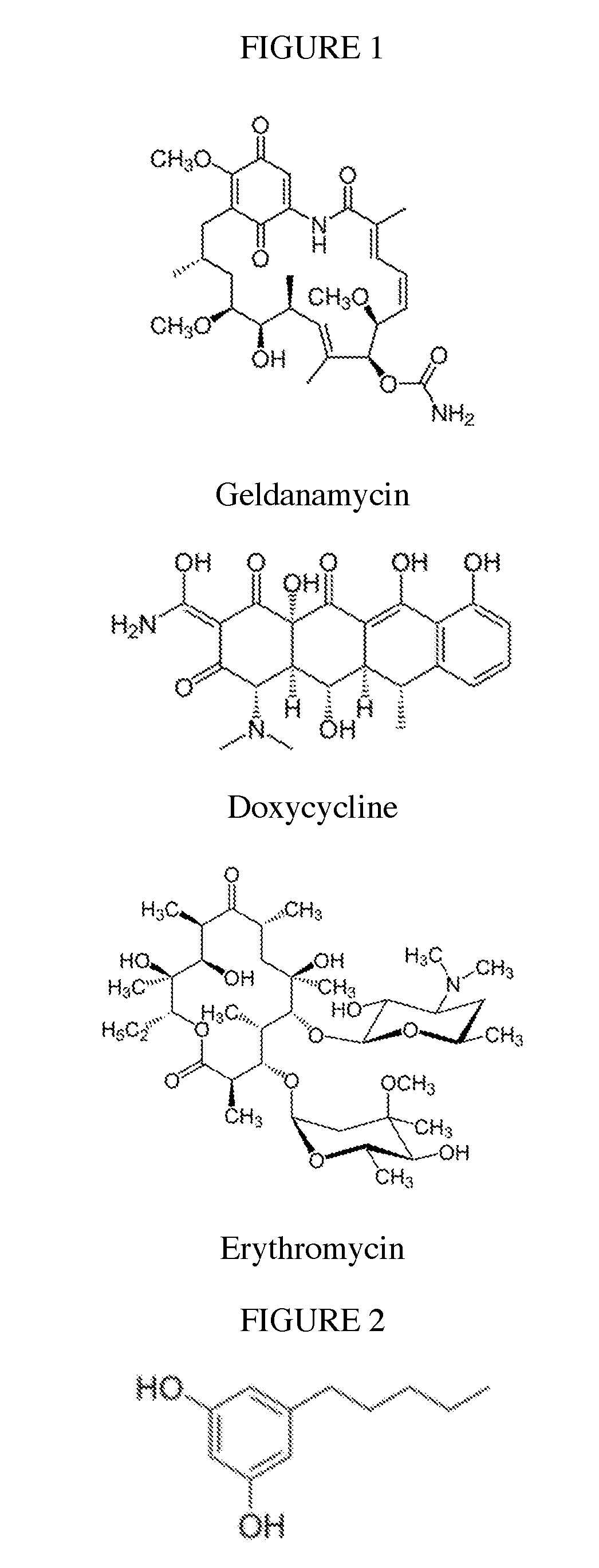
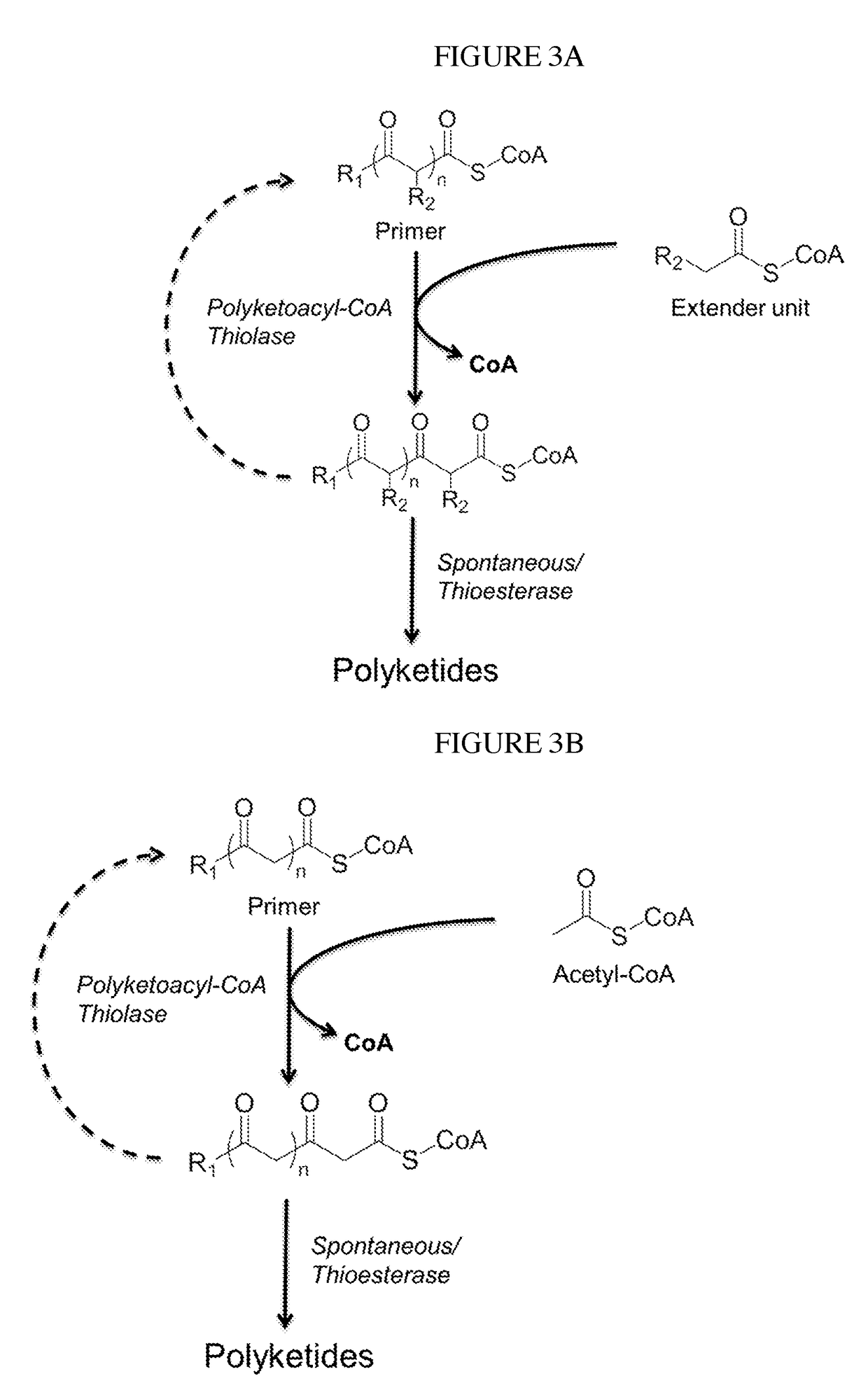
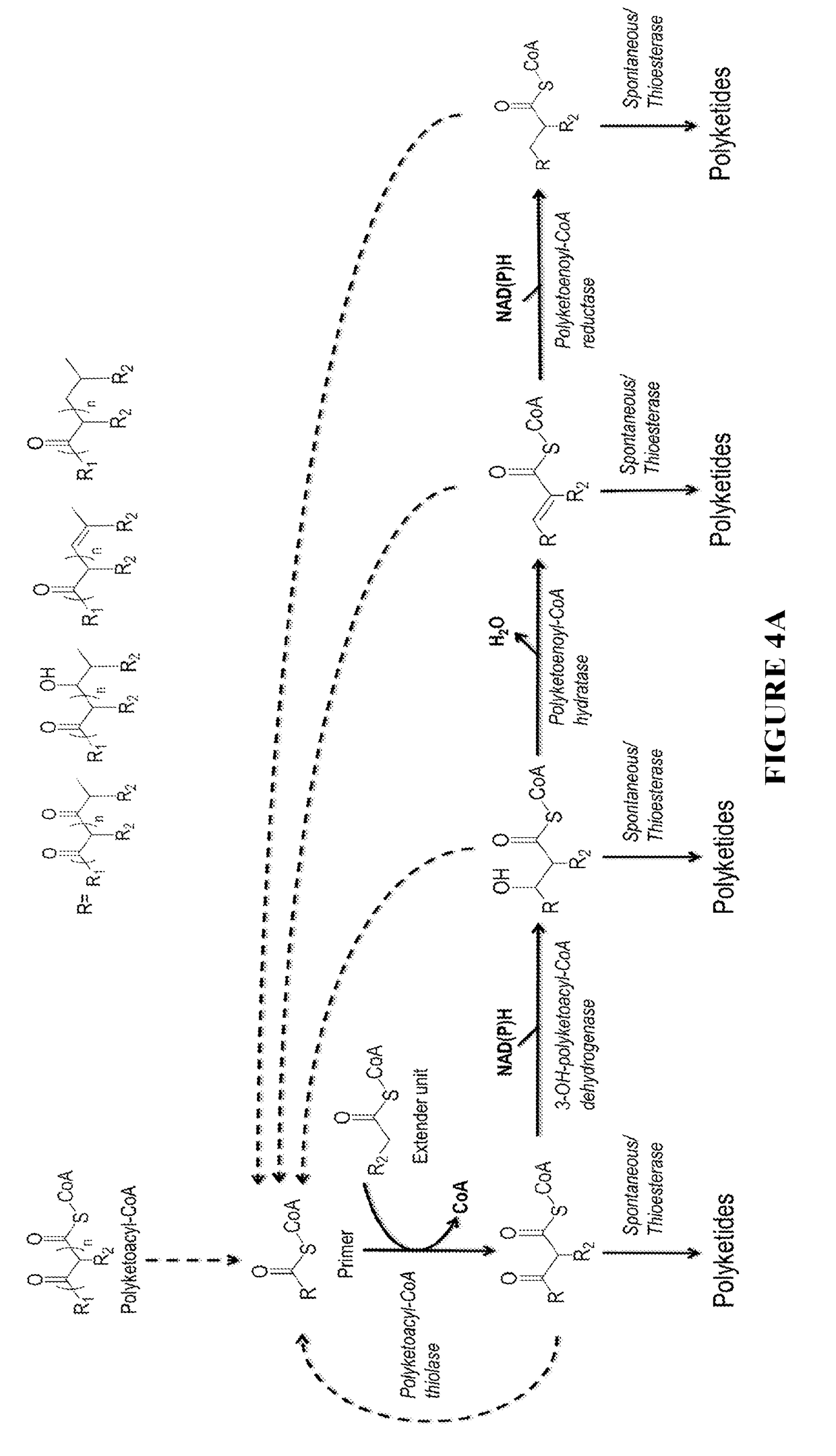
Biosynthesis of polyketides
InactiveUS20190002848A1Increase diversityWide-ranging product diversityAcyltransferasesFermentationClaisen condensationPolyketide biosynthesis
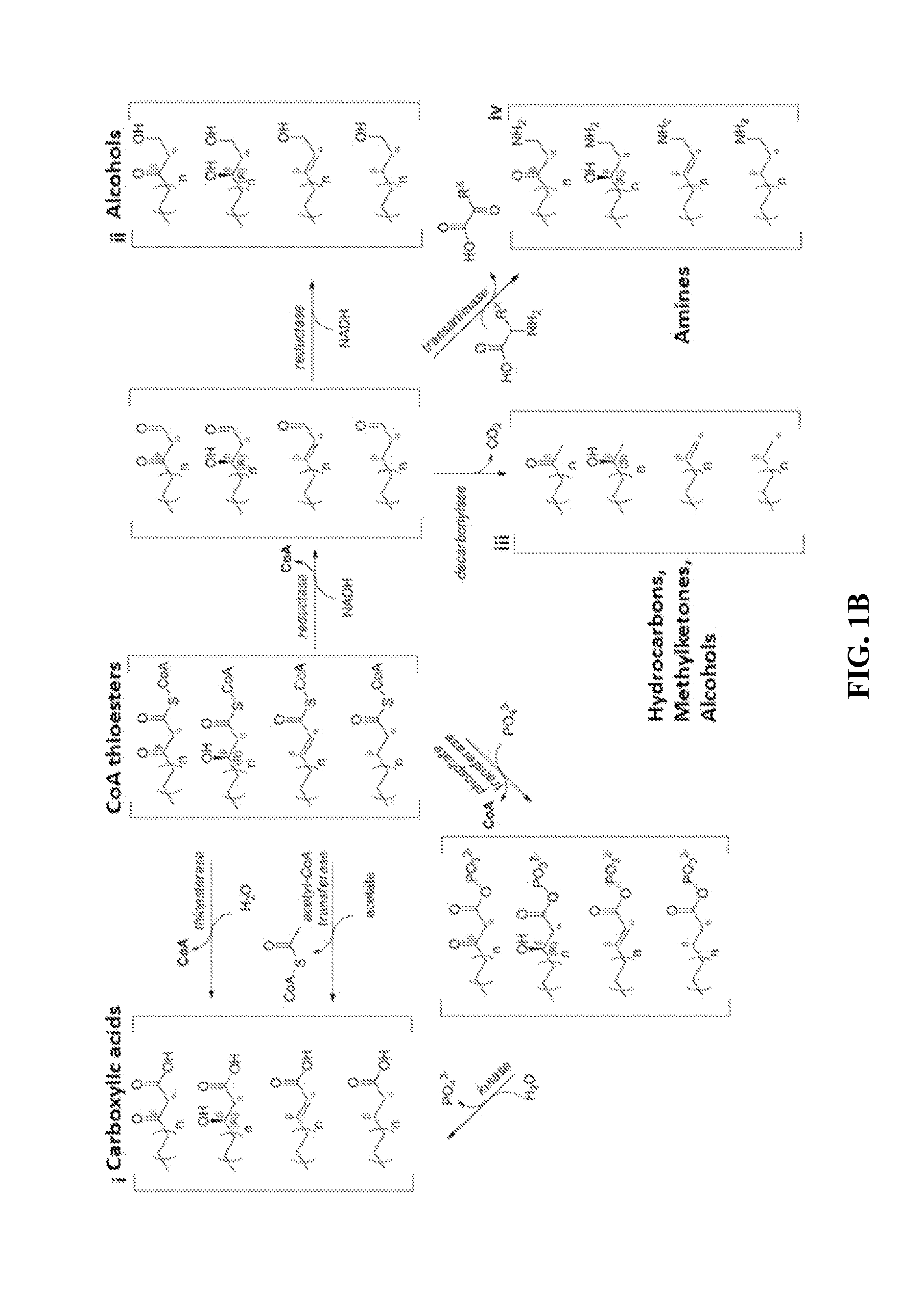
This disclosure generally relates to the use of microorganisms to make various functionalized polyketides through polyketoacyl-CoA thiolase-catalyzed non-decarboxylative condensation reactions instead of decarboxylative reactions catalyzed by polyketide synthases. Native or engineered polyketoacyl-CoA thiolases catalyze the non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation in an iterative manner (i.e. multiple rounds) between two either unsubstituted or functionalized ketoacyl-CoAs (and polyketoacyl-CoAs) serving as the primers and acyl-CoAs serving as the extender unit to generate (and elongate) polyketoacyl-CoAs. Before the next round of polyketoacyl-CoA thiolase reaction, the β-keto group of the polyketide chain of polyketoacyl-CoA can be reduced and modified step-wise by 3-OH-polyketoacyl-CoA dehydrogenase or polyketoenoyl-CoA hydratase or polyketoenoyl-CoA reductase. Dehydrogenase converts the β-keto group to β-hydroxy group. Hydratase converts the β-hydroxy group to α-β-double-bond. Reductase converts the α-β-double-bond to single bond. Spontaneous or thioesterase catalyzed termination reaction terminates the elongation of polyketide chain of polyketoacyl-CoA at any point through CoA removal and spontaneous reactions rearrange the structure, generating the final functional polyketide products.
Owner:GONZALEZ RAMON
Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme a thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof
ActiveUS20180087082A1Increase productionSimple chemical reactionMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesADAMTS ProteinsAcyl coenzyme A
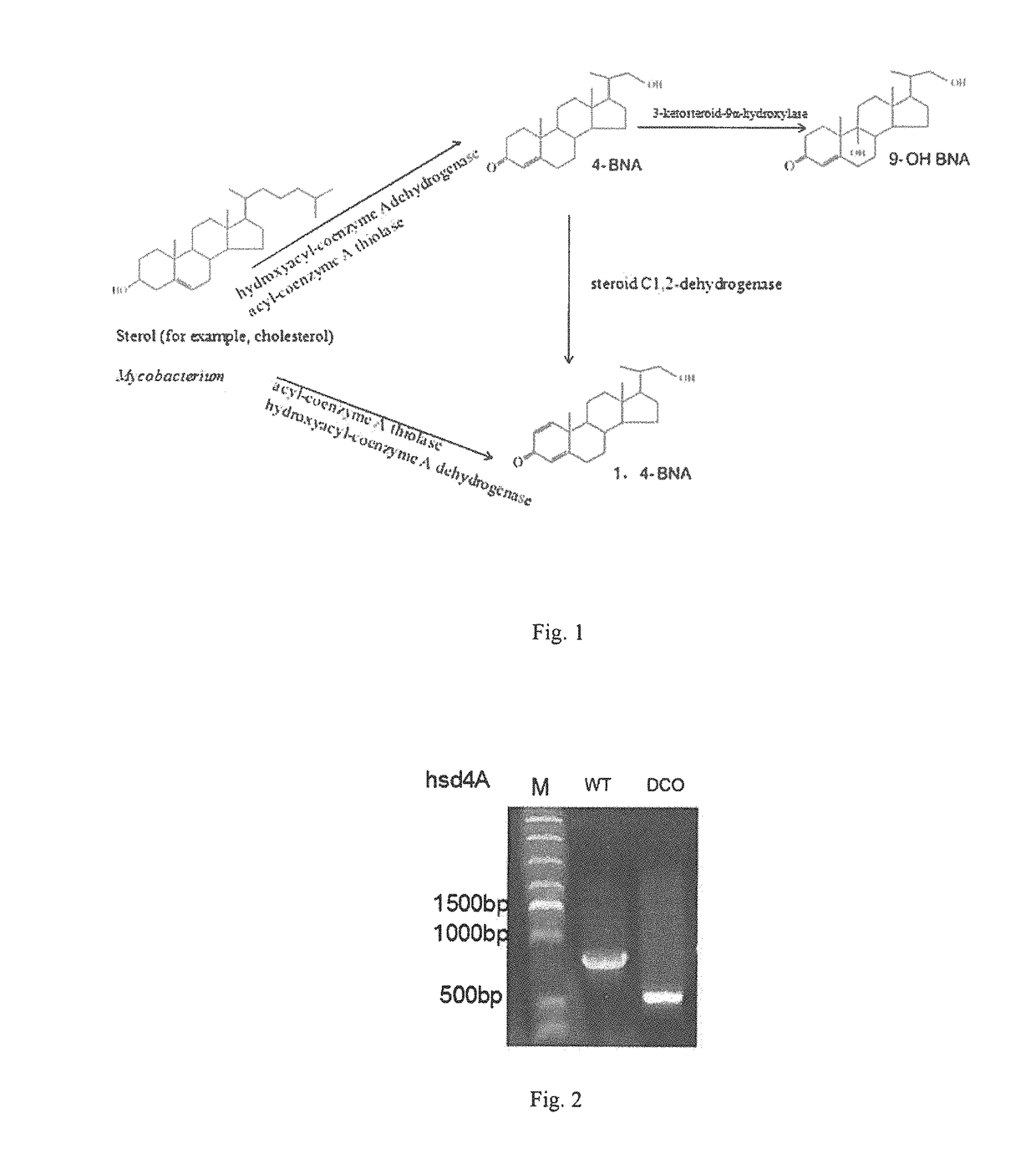
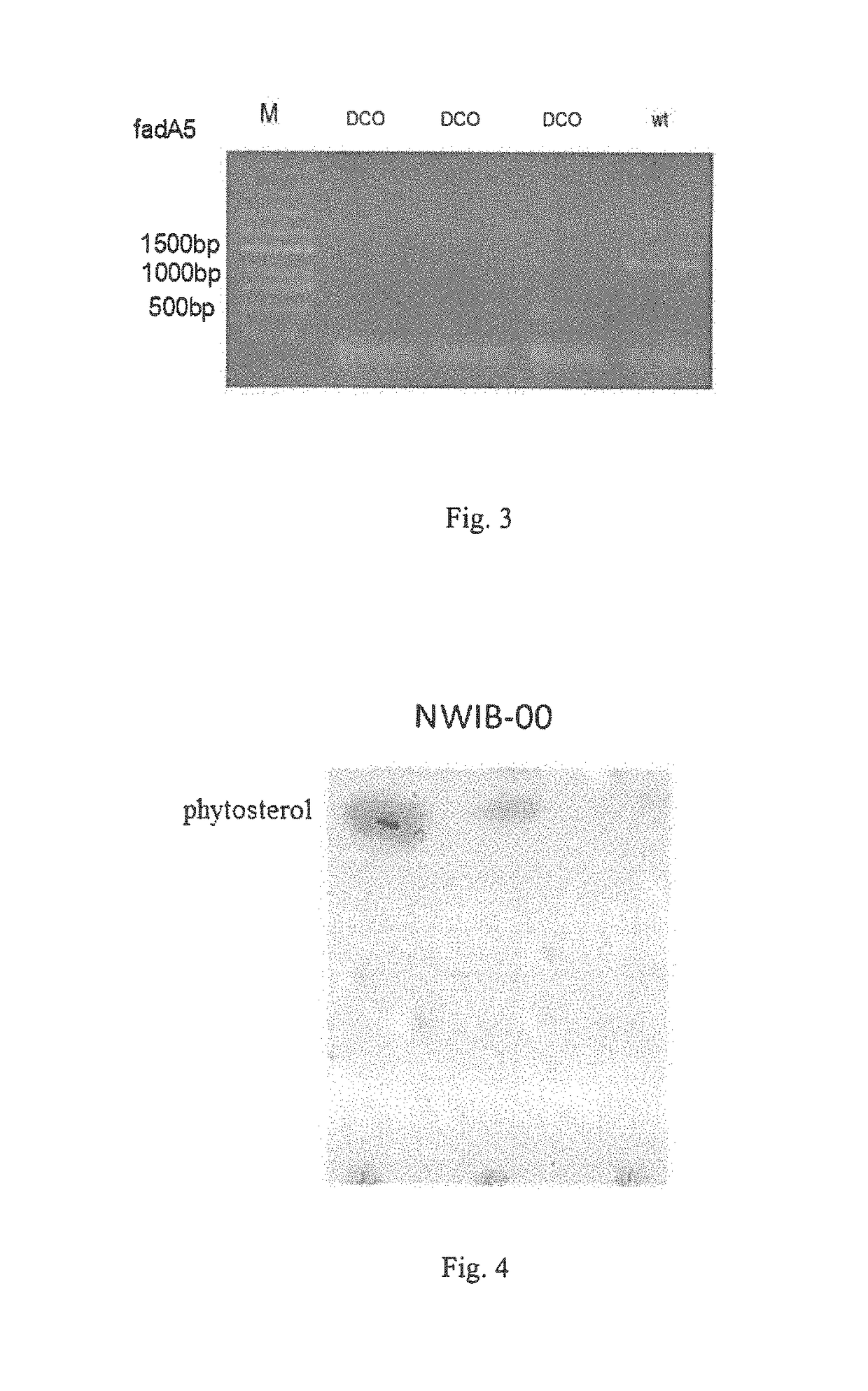
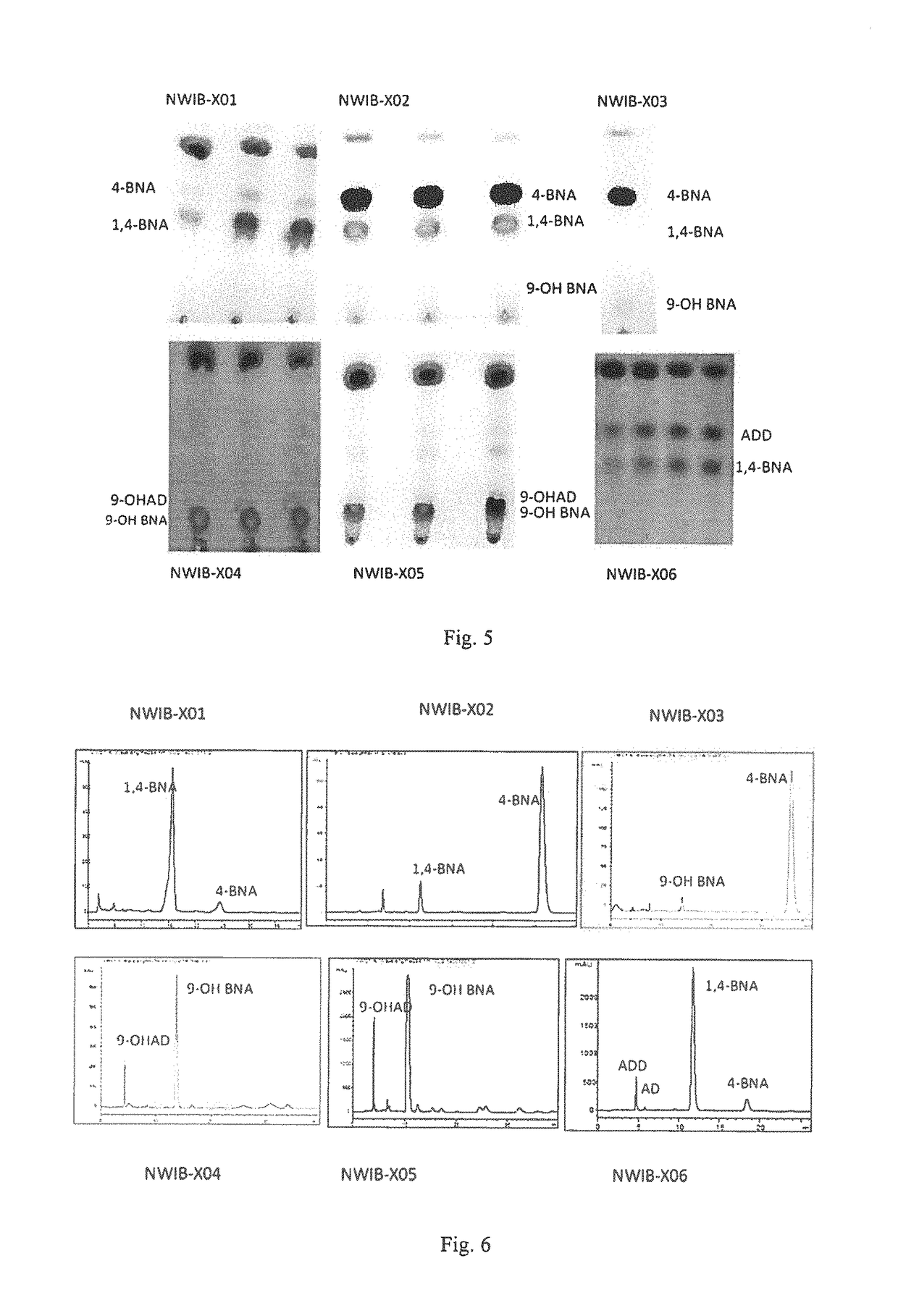
The present invention provides a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof. The hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene encodes a protein (i) or (ii) as follows: (i) having an amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO 2; (ii) derived by substituting, deleting or inserting one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence defined by (i) and having the same function as that of the protein of (i). The present invention constructs genetically engineered Mycobacterium strains lacking of a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene or an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, which are used in the preparation of steroidal compounds, such as 1,4-BNA, 4-BNA, 9-OH-BNA, etc . . . Further, the invention improves the production efficiency and product quality of steroidal drug, improves the utilization of drug precursors, reduces the production costs, and provides the advantages of mild reaction conditions, environmentally friendly, and high economic and social benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof
ActiveCN101845414BHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaEthylene Homopolymers
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
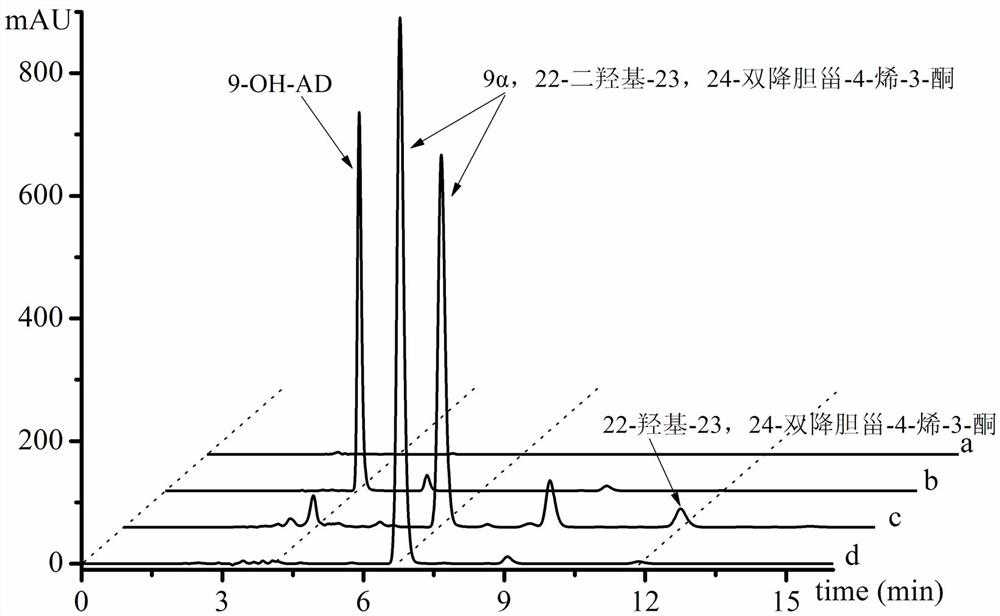
Genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof to preparation of 9alpha,22-dihydroxy-23,24-bisnorcholest-4-ene-3-ketone
ActiveCN112094797AReduce pollutionEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKetoneEngineered genetic
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to a mycobacterium genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof to preparation of 9alpha,22-dihydroxy-23,24-bisnorcholest-4-ene-3-ketone. The genetically engineered bacterium is constructed by inactivating three genes kstd 1, kstd 2 and kstd 3 of 3-sterone-delta1-dehydrogenase in mycobacteria and overexpressing genes encoding acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase / thiolase and DNA binding protein, and can selectively generate 9alpha,22-dihydroxy-23,24-bisnorcholest-4-ene-3-ketone, thereby reducing byproduct 9-OH-AD. The production efficiency and the product quality are greatly improved, the product is easy to separate and purify, the production cost is reduced, and meanwhile, the pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
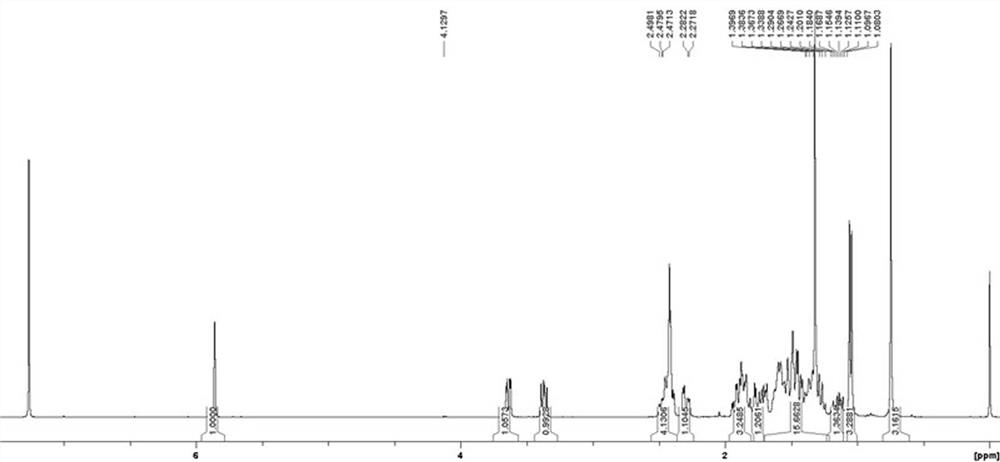
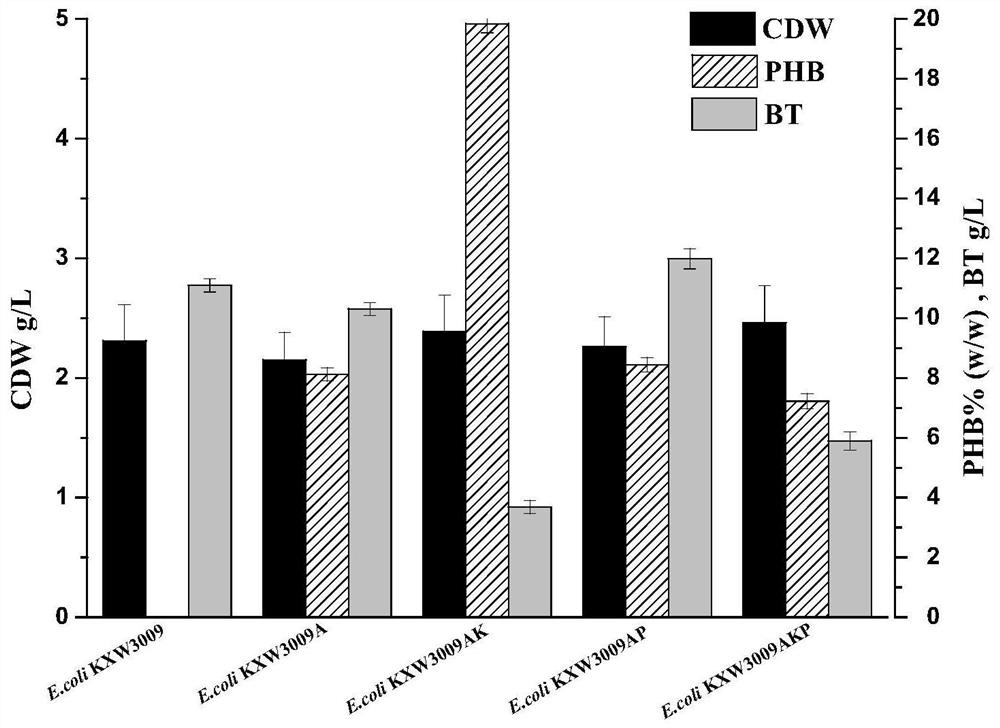
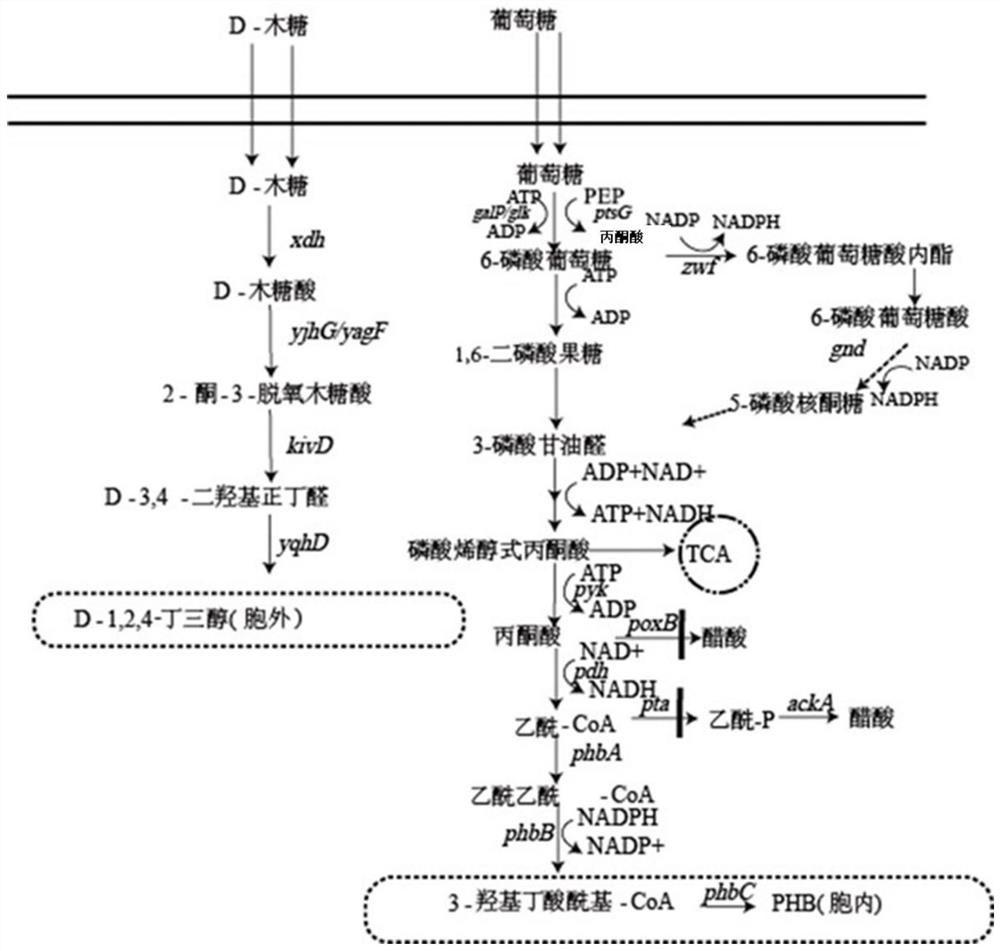
Method for co-production of D-1,2,4-butanetriol and PHB by metabolic modification of escherichia coli, and application
PendingCN112094793AReduce fermentation costsEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPHA synthase
The invention discloses a method for co-production of D-1,2,4-butanetriol and PHB by metabolic modification of escherichia coli, and application, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the invention, a genetic engineering method is applied; and plasmids with over-expression of beta-keto thiolase PhbA, acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductase PhbB and PHA synthase PhbC from alcaligeneseutrophus are transferred into engineering bacteria E.coli KXM3009 to construct a synthetic route of PHB. Furthermore, the gene glk related to glycolysis is over-expressed, so that co-production of 1,2,4-butantriol and PHB is realized; and a foundation is laid for co-production of multiple added-value products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
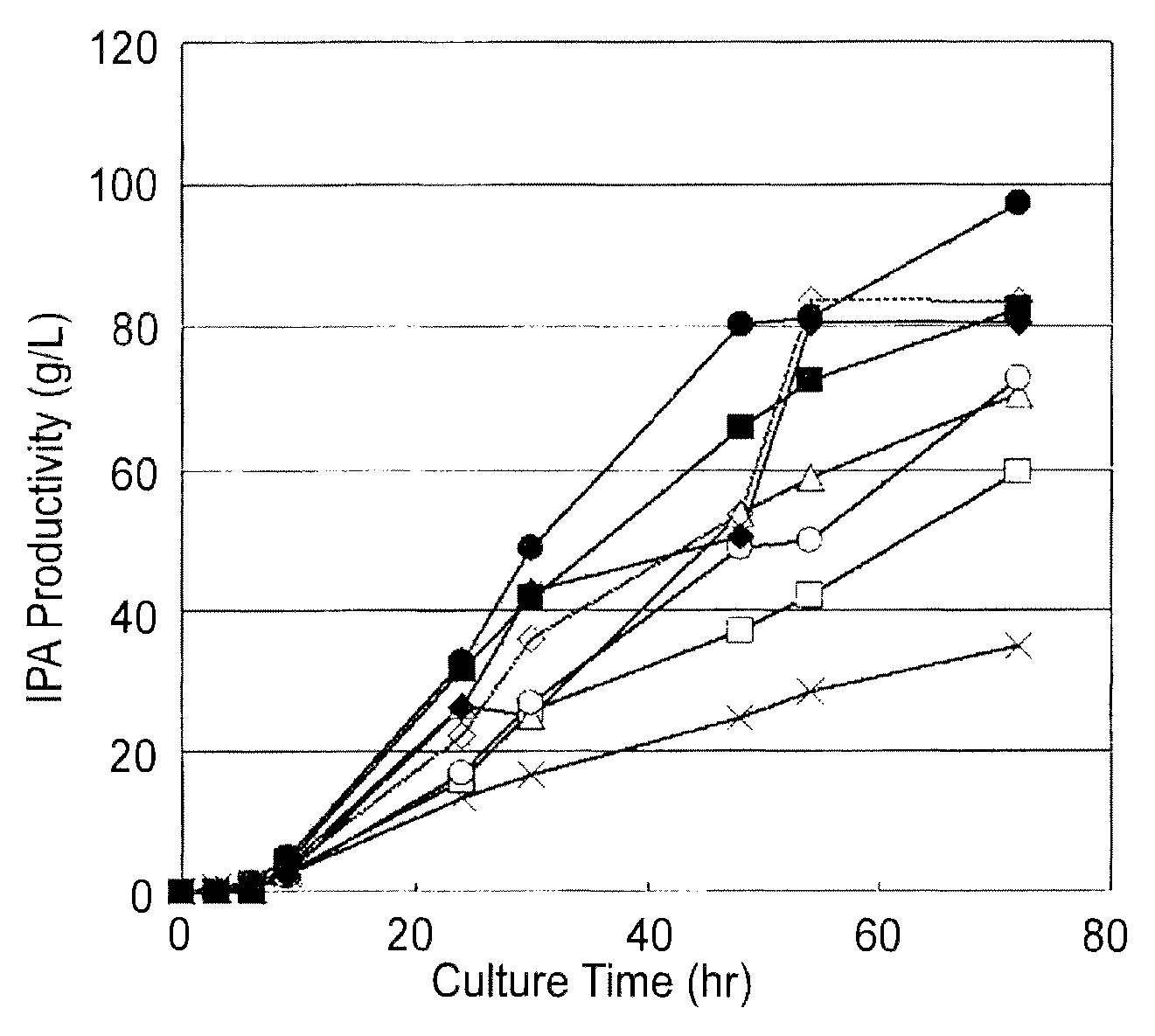
Highly productive isopropyl alcohol-producing bacterium
ActiveUS8932845B2Increase chanceHigh yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliIsopropyl alcohol
An isopropyl alcohol-producing Escherichia coli equipped with an isopropyl alcohol production system, having at least one enhanced enzyme activity selected from the group consisting of an enhanced malate dehydrogenase activity, an enhanced NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase (AB-specific) activity, and an enhanced thiolase activity, and an isopropyl alcohol producing method including producing isopropyl alcohol from a plant-derived raw material using the isopropyl alcohol-producing Escherichia coli.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Method for producing adipic acid by utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN111484942ADe novo synthesisStrong stress resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesCarboxyl radicalAcyl group
The invention discloses a method for producing adipic acid by utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 wild type strain or a saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 strain with LSC1 gene knocked out is used as a host; the beta-ketothiolase gene, the 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, the 3-hydroxyadipoyl dehydrogenase gene, the 5-carboxyl-2-pentenyl coenzyme A reductase gene and the adipoyl coenzyme A in a T.fusca adipic acid reverse degradation pathway are overexpressed by modules, wherein the yield of adipic acid can reach 0.033-0.113 g / L. Due to the excellent stress resistance, acid resistance, hereditary stability and food safety of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, the invention providesa basis for industrial fermentation production of adipic acid by saccharomyces cerevisiae hosts.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel microorganism of the genus bacillus
InactiveUS20140273122A1Efficient productionBacteriaAcyltransferasesAcetoacetate decarboxylase activityMicrobiology
The invention provides a microorganism of the genus Bacillus, including one or more gene(s) selected from a group consisting of a gene conferring thiolase activity, a gene conferring CoA transferase activity and a gene conferring acetoacetate decarboxylase activity, wherein the microorganism produces acetone.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Recombinant microorganisms and uses therefor
The invention provides recombinant microorganisms and methods for the production of acetone from gaseous substrates. For example, the recombinant microorganism may be modified to express an exogenous thiolase, an exogenous CoA transferase, and an exogenous decarboxylase.
Owner:LANZATECH NEW ZEALAND LTD
Engineering bacteria expressing coenzyme A transferase and beta-keto thiolase and use thereof
InactiveCN101475956AIncrease productionImprove conversion efficiencyMicroorganismsFermentationEscherichia coliAcetic acid
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Compound native microorganism domestication enzyme for efficiently improving urban black and odorous water body, and method for treating urban black and odorous water body
ActiveCN111073869ATo promote metabolismEasy to removeMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a compound native microorganism domestication enzyme for efficiently improving an urban black and odorous water body, and a method for treating the urban and odorous water body. The compound native microorganism domestication enzyme comprises acetyl CoA acyltransferase, 1-phosphofructokinase, pyruvate phosphate dikinase, beta-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme dehydrogenase, 3-phosphoglycerate kinase, NAD-dependent beta-hydroxybutyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase, and thiolase. The method for treating the urban black and odorous water body comprises the following steps: preparation andactivation of the compound native microorganism domestication enzyme; putting of the activated compound native microorganism domestication enzyme into the black and odorous water body for a period oftime; and then aquatic plant construction. The compound native microorganism domestication enzyme of the invention has the advantages of efficiently improving the quality of the black and odorous sewage water body. In addition, the treatment method of the invention has the advantages of efficiently purifying the water body, and continuously adjusting and optimizing the water body environment.
Owner:北京京阳环保工程有限公司
A kind of poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid copolymer and production method thereof
ActiveCN104046659BReduce crystallinityHigh melting pointBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, a glycerol dehydratase gene and a glycerol dehydratase re-activating enzyme gene are integrated with a host strain genome by a gene integration technology, a polyhydroxy fatty acid synthase gene, a propionaldehyde dehydrogenase gene, a beta-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene, an acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductase gene and a propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene are introduced, and a recombinant gene engineering strain has the ability of biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, the poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid is obtained in a biosynthesis manner for the first time; compared with poly-3-hydracrylic acid, the obtained poly 3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid has a higher melting point and lower crystallinity, has good degradability and can serve as a packaging material, a medical implant material, a drug sustained-release material and an electrochemical material.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Highly productive isopropyl alcohol-producing bacterium
The invention provides an Escherichia coli which comprises an isopropyl alcohol production system. The isopropyl alcohol-producing Escherichia coli has at least one enhanced enzymatic activity that is selected from the group consisting of enhanced malate dehydrogenase activity, enhanced NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase (AB-specific) activity and enhanced thiolase activity. Also disclosed is a method for producing isopropyl alcohol, which comprises a process wherein isopropyl alcohol is produced from a plant-derived starting material using the above-described isopropyl alcohol-producing Escherichia coli.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Type ii fatty acid synthesis enzymes in reverse ß-oxidation
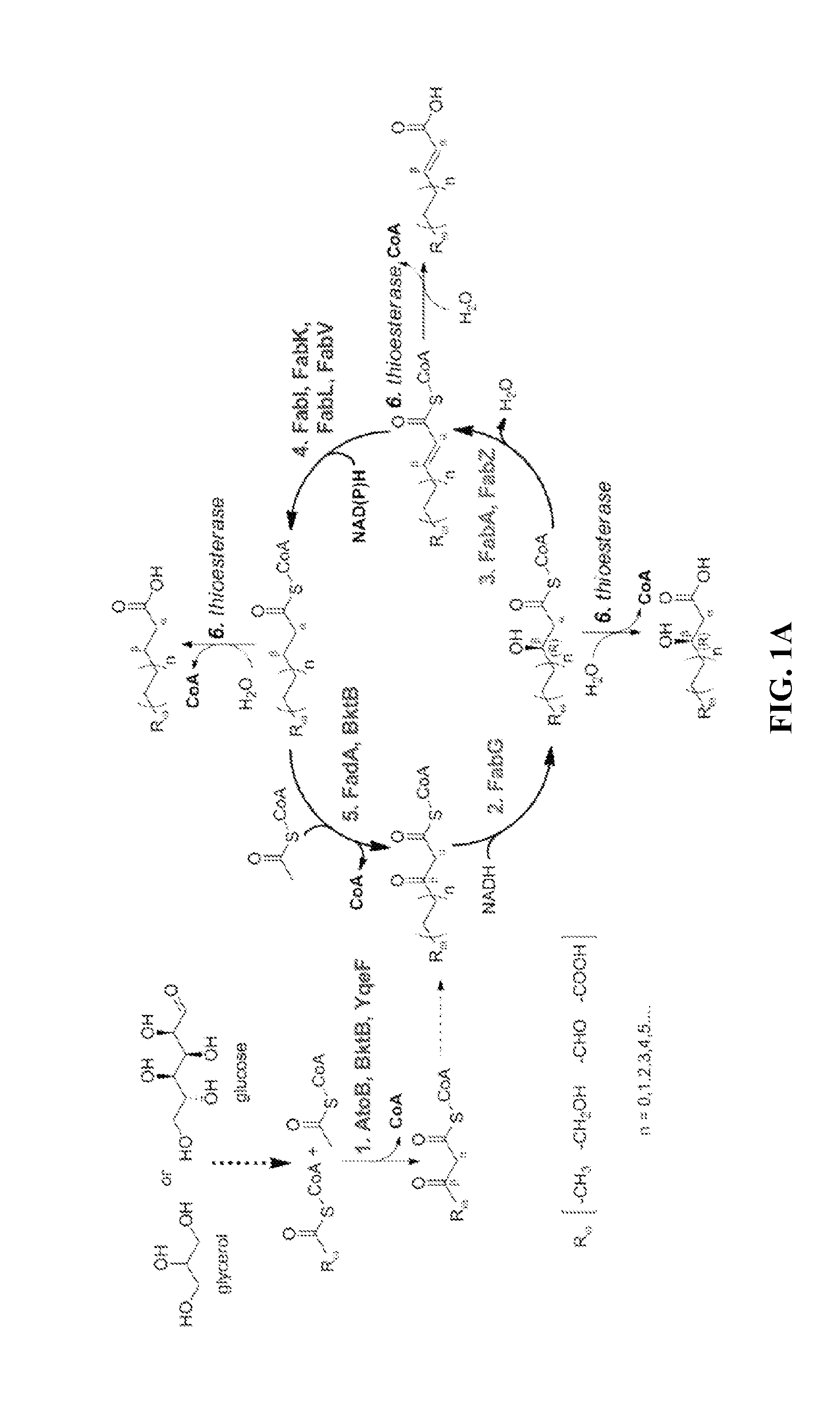
This disclosure describes enzymes from the type II (a discrete set of enzymes) fatty acid synthesis (“FAS”) pathway that can be used in combination with thiolases to operate a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. A combination of thiolases with one or more of 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabG, others), 3-hydroxyacyl-[acp] dehydratase (FabA, FabZ, others), and enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabI, FabK, FabL, FabV, others) yields a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. If only one or two enzymes are used, the remaining enzymes will be traditional beta oxidation enzymes. Once this cycle is coupled with the appropriate priming and termination pathways, the production of carboxylic acids, alcohols, hydrocarbons, amines and their α-, β-, and ω-functionalized derivatives from renewable carbon sources can be achieved.
Owner:RICE UNIV
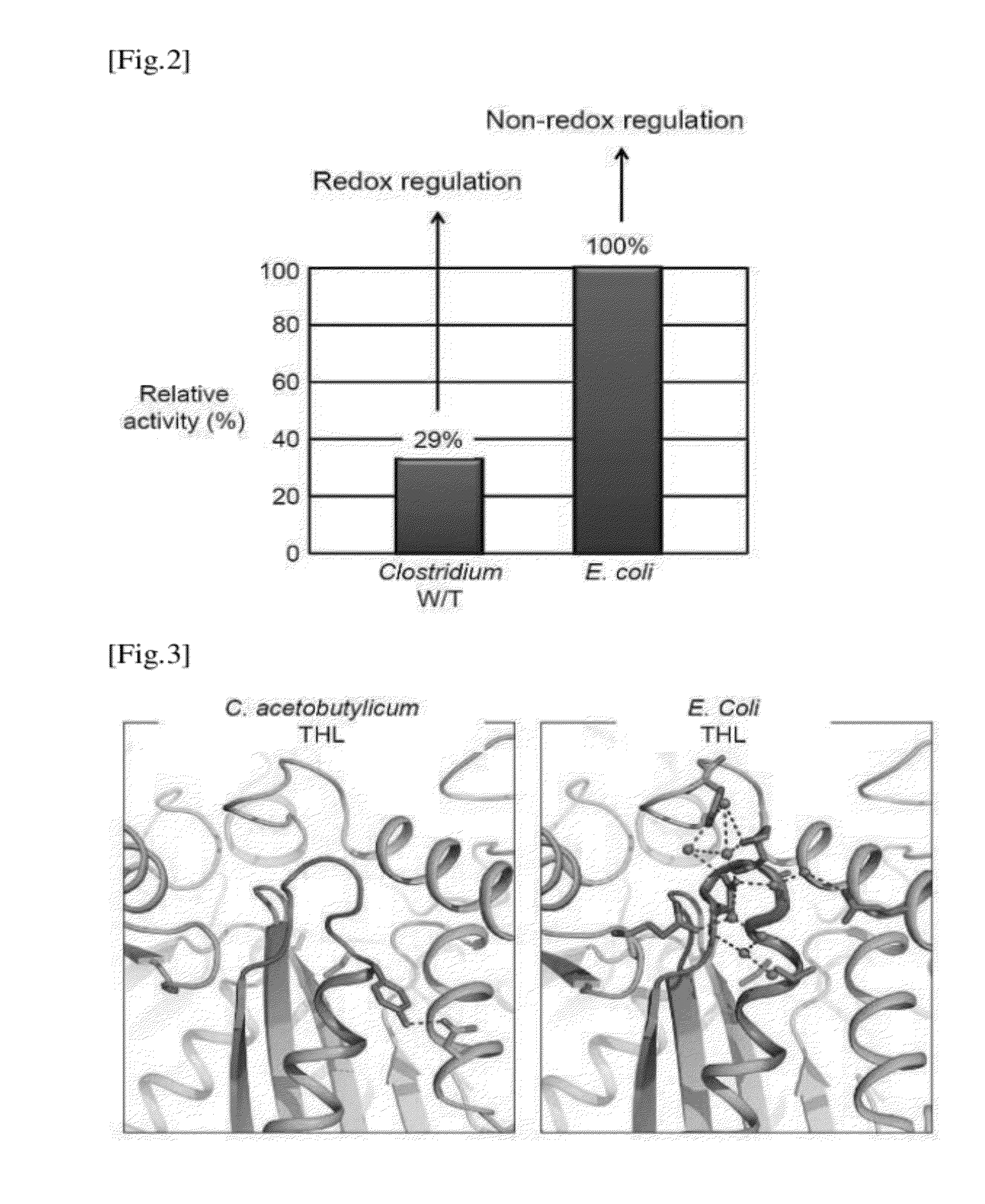
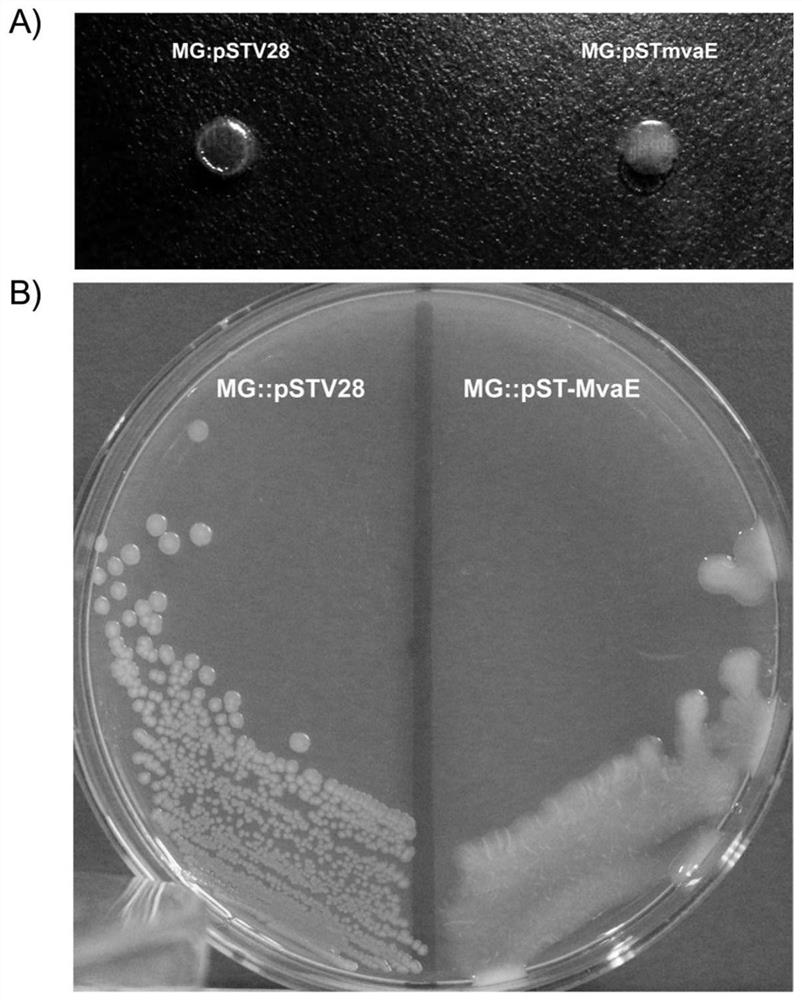
Thiolase with Improved Activity and Method of Producing Biobutanol Using the Same
The present invention relates to a modified thiolase protein with an improved activity, a polynucleotide encoding the modified protein, an expression vector including the polynucleotide, and a transformant, to a composition for producing a biobutanol including the thiolase with an improved activity or a cell expressing the thiolase, and to a method of producing the biobutanol.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Difunctional thiolase gene MvaE, expression vector, recombinant strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a difunctional thiolase gene MvaE. The invention further discloses difunctional thiolase, an expression cassette, a recombinant vector, recombinant bacteria or cells and application thereof. The invention further discloses a method for producing fatty acid. The difunctional thiolase gene MvaE disclosed by the invention can utilize rich culture media containing glucose, glycerol or other carbon sources as raw materials under facultative anaerobic conditions, so that the fatty acid content of C<14:0>, C<16:0> and C<18:0> in host bacteria can be remarkably increased, and the increasing amplitude of the difunctional thiolase gene MvaE is different from 27% to 213% according to different host strains.
Owner:扬州麦塔瑞思生物科技有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com