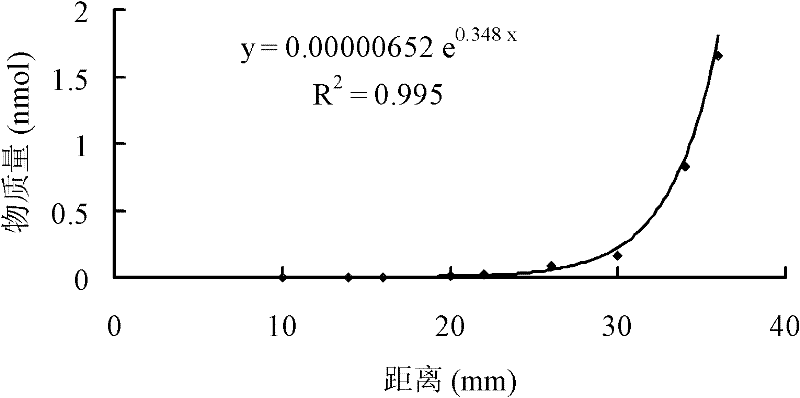
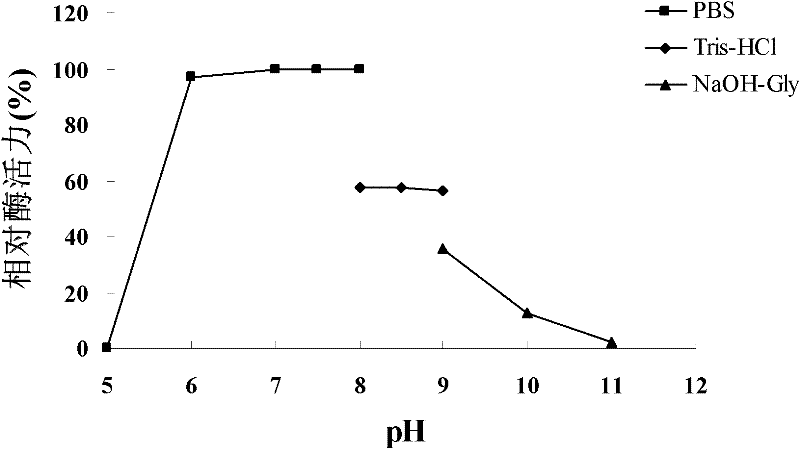
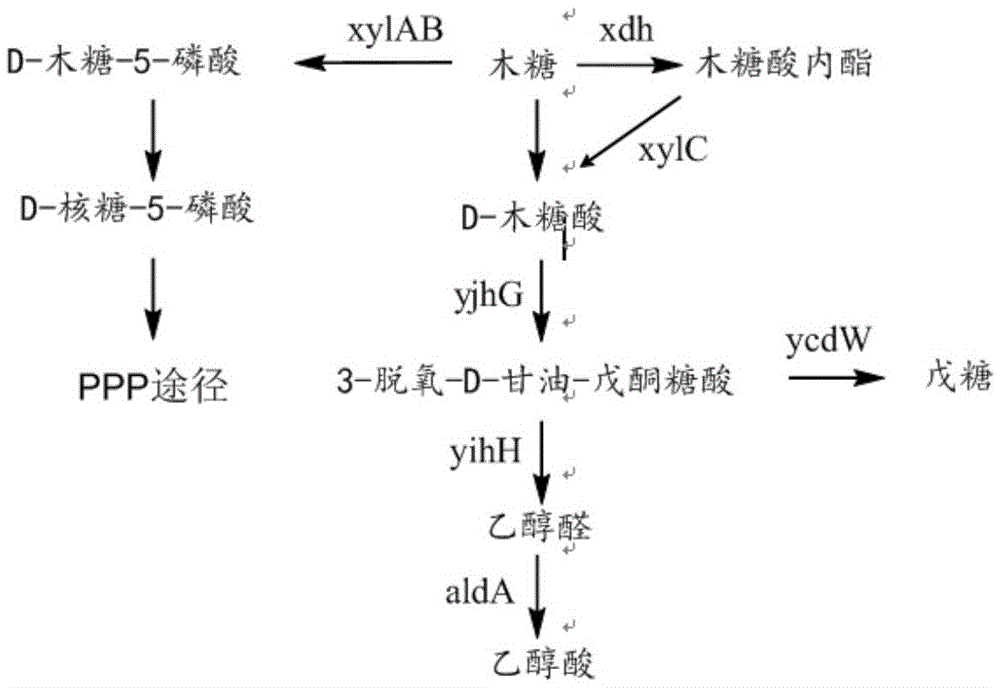
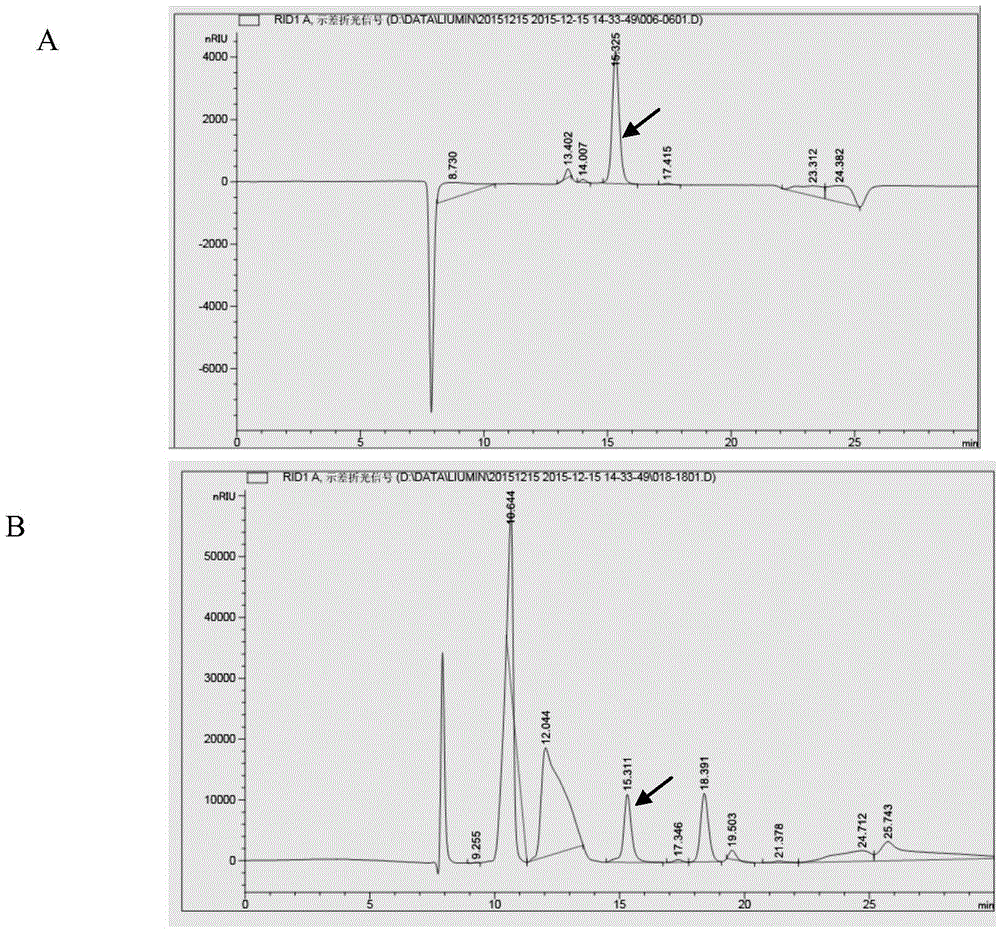
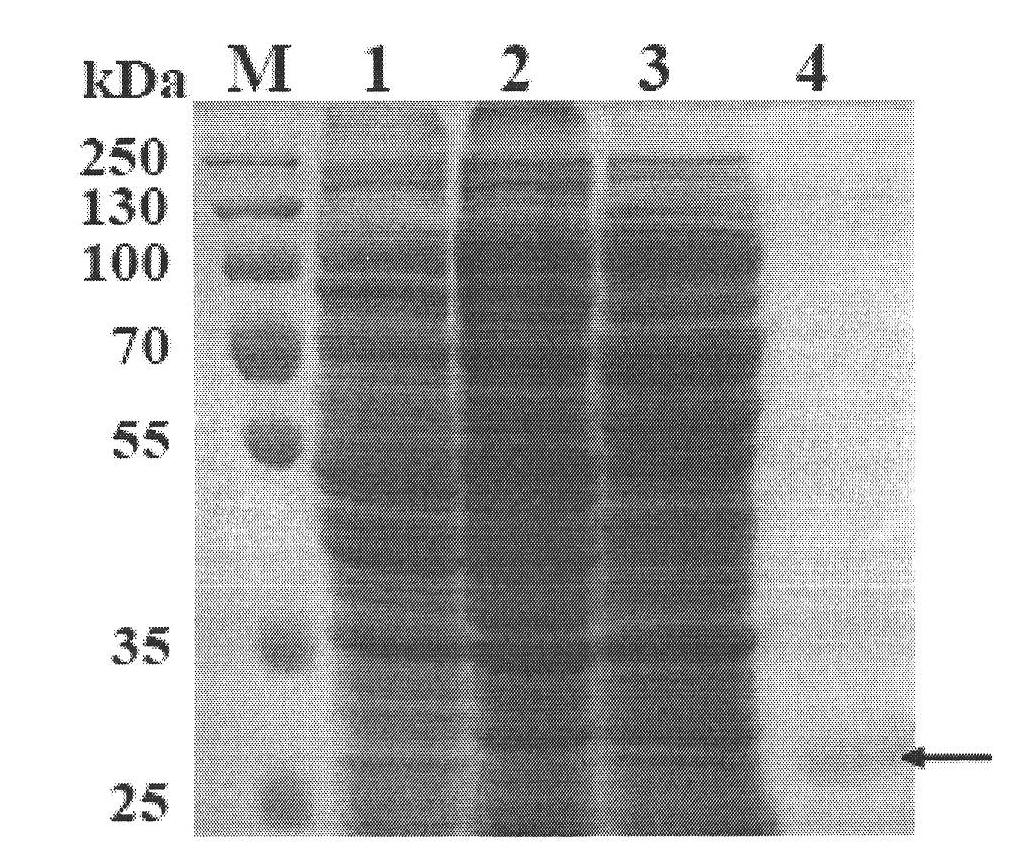
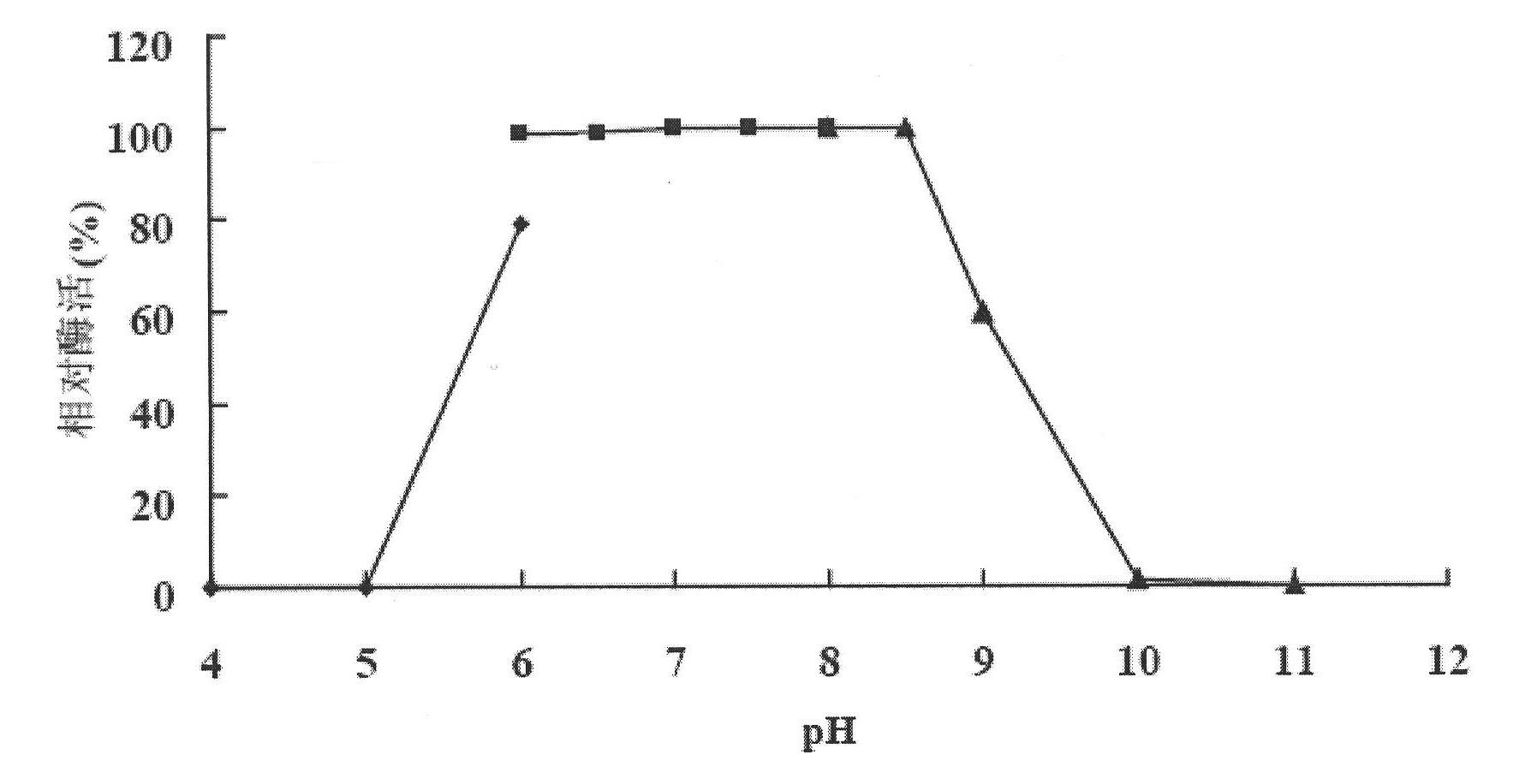
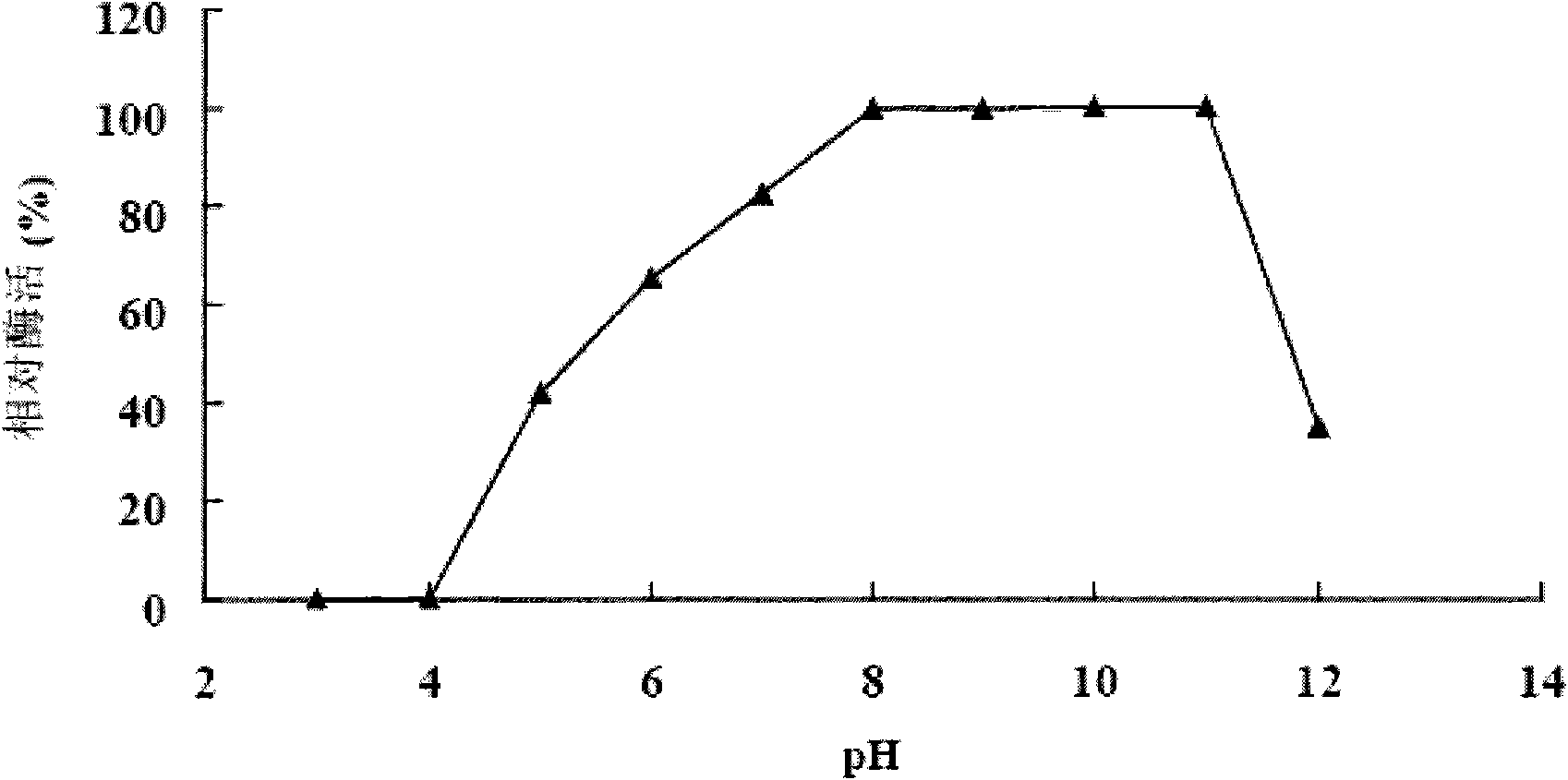
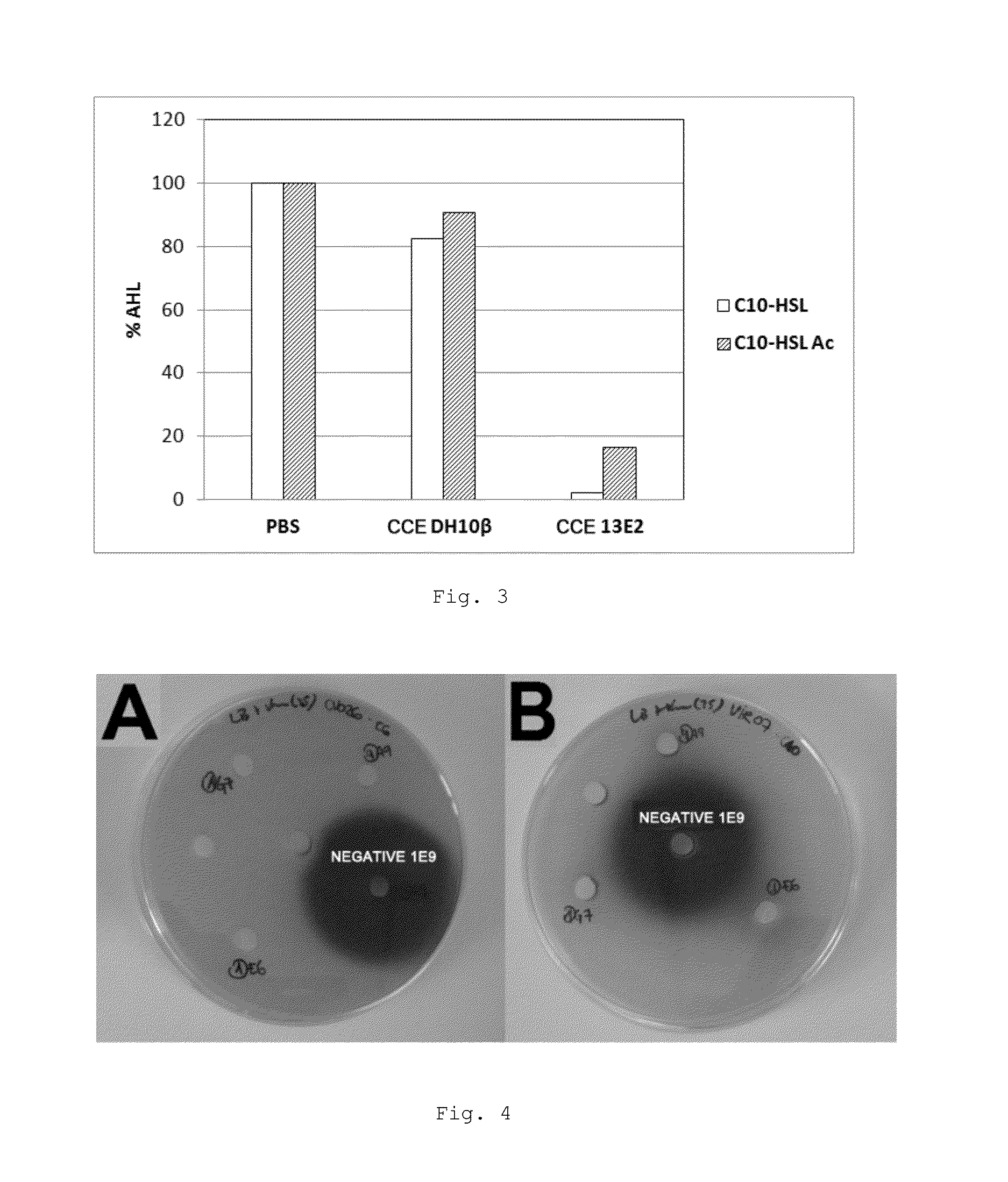
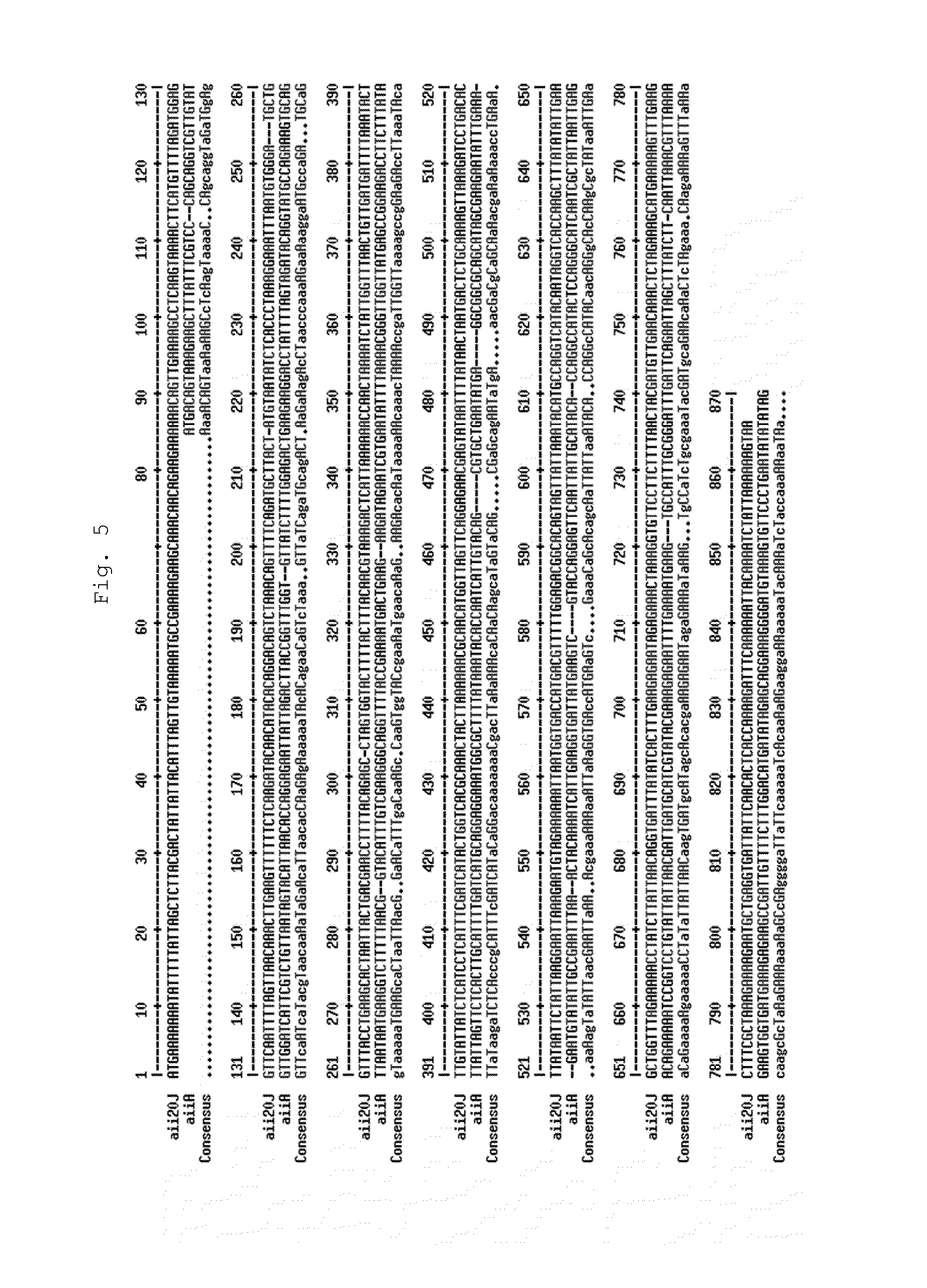
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Lactonase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lactonase (also acyl-homoserine lactonase) is a metalloenzyme, produced by certain species of bacteria, which targets and inactivates acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs). Many species of Proteobacteria from the alpha, beta and gamma classes have been shown to produce acylated homoserine lactones, which are small hormone-like molecules commonly used as communication signals between bacterial cells in a population to regulate certain gene expression and phenotypic behaviours. This type of gene regulation is known as quorum sensing.
N-acylhomoserine lactonas, production method thereof and special recombinant bacterium
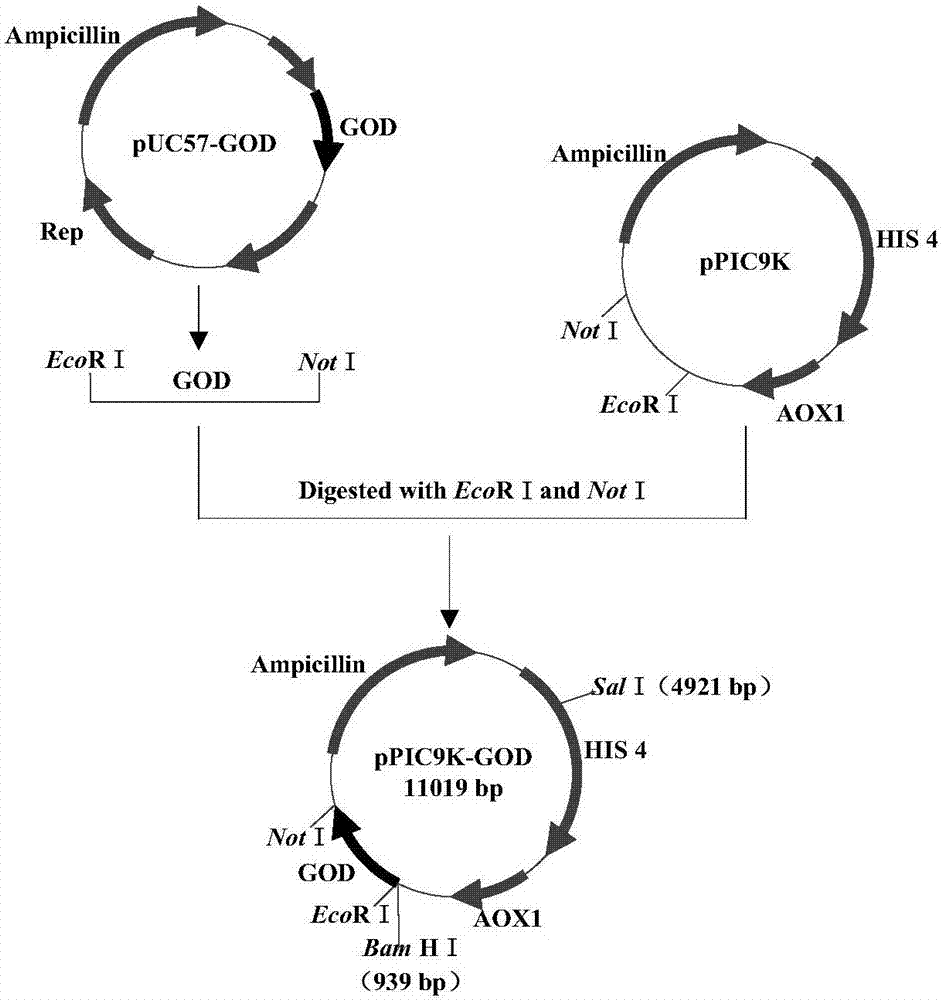
The invention discloses an N-acylhomoserine lactonase, a production method thereof and a special recombinant bacterium. The N-acylhomoserine lactonase is protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses an engineering bacterium which is the recombinant bacterium obtained by introducing the gene for coding the protein into pichia pastoris GS115. The recombinant bacterium has enzyme activity reaching 4034.71U / ml through fermentation.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Manufacture of xylonic acid
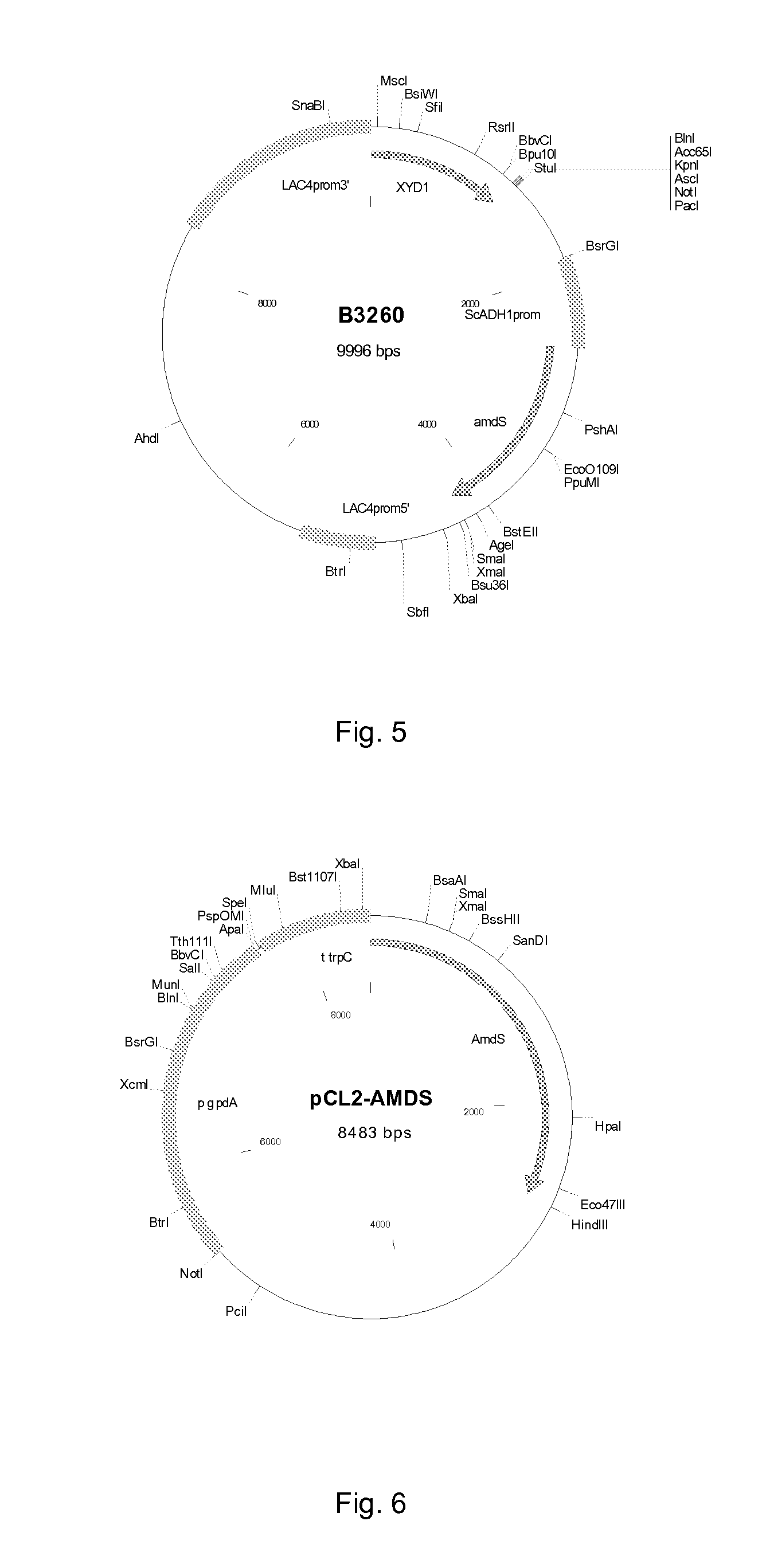
Provided is a method for producing xylonic acid from xylose with a recombinant fungal strain that is genetically modified to express a xylose dehydrogenase gene, which is able to convert xylose to xylonolactone, which is spontaneously or enzymatically hydrolysed to xylonic acid. The xylonic acid is excreted outside the host cell. Xylonate production may be coupled with xylitol production. Alternatively, if xylitol production is not desired, its production is reduced by removing the aldose reductase (or specific xylose reductase) enzyme, which converts xylose to xylitol. Expression of a heterologous lactonase encoding gene may result in higher acid concentrations. The method is suitable for producing xylonic acid from a hemicellulose hydrolysate such as hydrolysed lignocellulosic plant biomass.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT OY
Lactonase and method for degrading alpha-zearalanel through lactonase
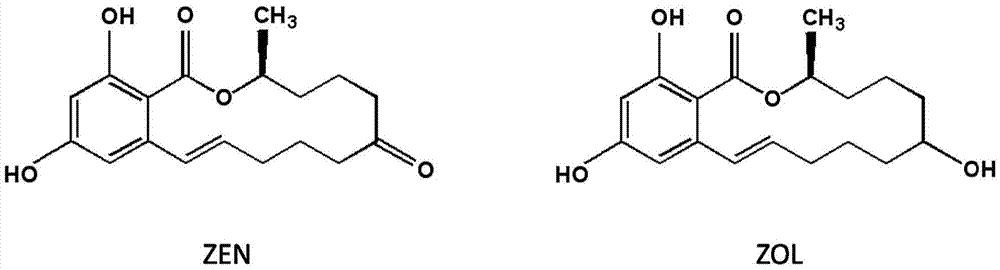
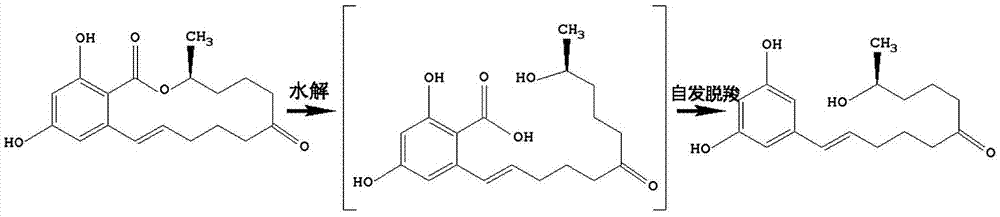
The invention discloses lactonase. An amino acid sequence is the sequence that the 167 amino acid of the serial number 5 is mutated into Histidine from Valine, and the lactonase is used for improving the degrading efficiency of alpha-zearalanel. The invention further discloses a method for degrading the alpha-zearalanel. The alpha-zearalanel is degraded by means of the lactonase, so that the degrading efficiency of the alpha-zearalanel is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Heat-resisting N-acyl homoserine lactonase AiiA-AIO6 with high specific activity as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102212508AHigh enzyme specific activityPromote degradationBiocideBacteriaN-Acyl homoserine lactoneHigh specific activity
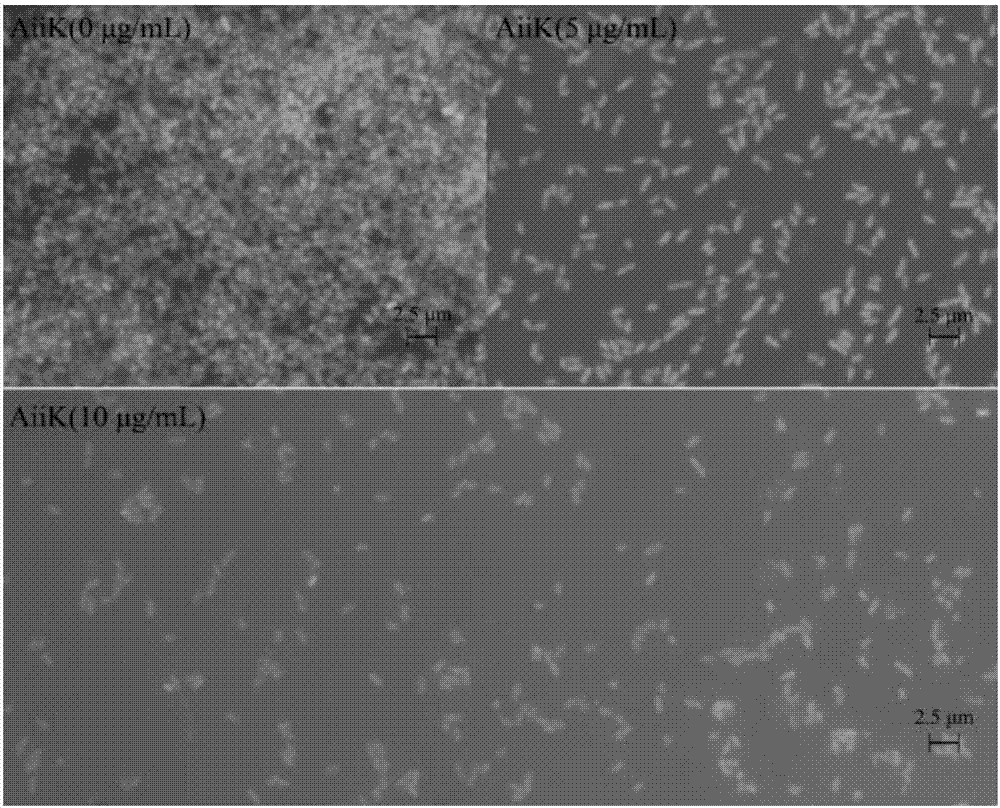
The invention discloses a heat-resisting N-acyl homoserine lactonase AiiA-AIO6 with high specific activity as well as a coding gene and application thereof. A protein provided by the invention is (a) or (b): the protein (a) is composed of amino acid sequences shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table; the protein (b) is obtained through substituting and / or lacking and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of amino acid sequences shown as the sequence 1, has the activity of the N-acyl homoserine lactonase and is derived from the sequence 1. The AiiA-AIO6 protein provided by the invention is a novel N-acyl homoserine lactonase and the N-acyl homoserine lactonase is heat-resisting, has high specific activity, higher protease resistance and better capability of degrading each substrate and can be used as a novel bio-control enzyme preparation.
Owner:北京挑战生物技术有限公司
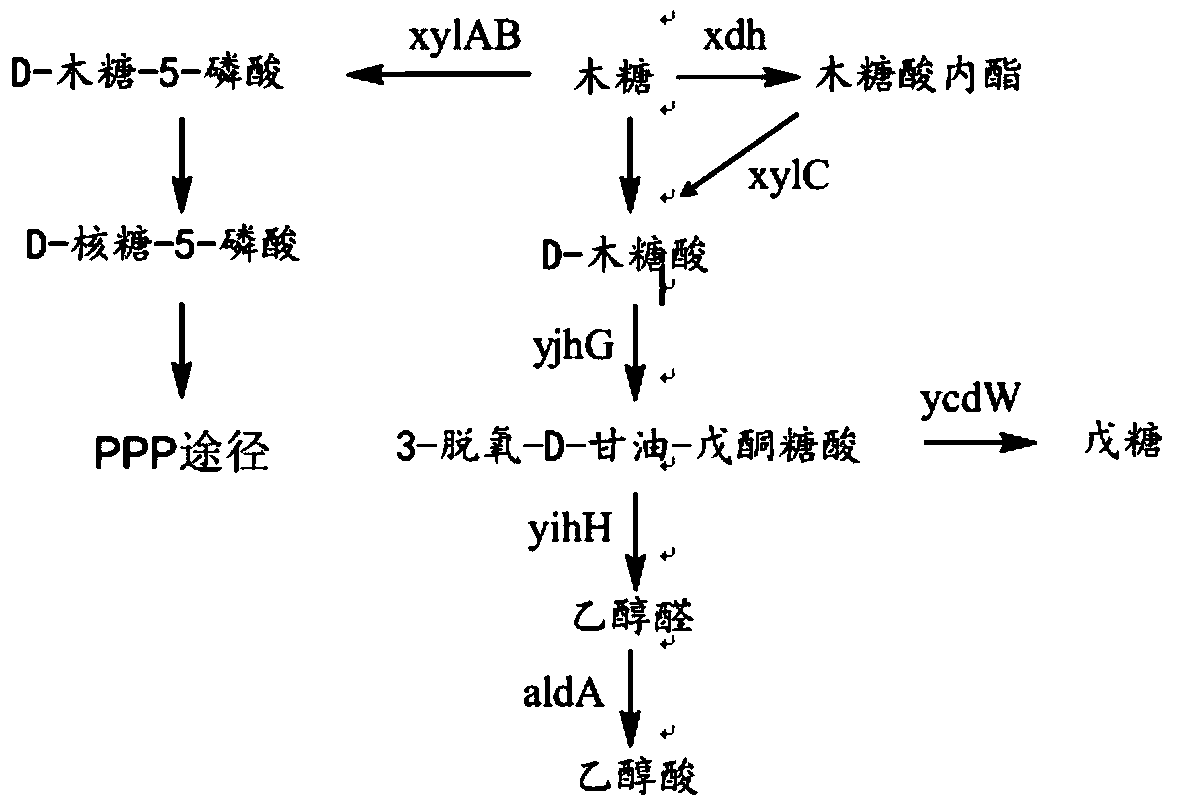
Recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and building method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and a building method and application of the recombinant bacteria and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The xylose dehydrogenase gene, xylonic acid lactonase gene, xylonic acid dehydratase gene, 3-deoxygenation-D-glycerin ketopentose acid aldolase gene and glycolic aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in the recombinant bacteria using the xylose to produce the glycollic acid are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant bacteria and a method using the recombinant bacteria to produce the glycollic acid. By the recombinant bacteria, the biological synthesizing path using D-xylose as the carbon source to form the glycollic acid through glycolic aldehyde conversion is achieved for the first time.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Heat resistant N-acyl-homoserine lactonase AiiA-AI96 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102031236AStrong protease resistancePromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactonaseProtein
The invention discloses a heat resistant N-acyl-homoserine lactonase AiiA-AI96 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The lactonase is the protein as shown in a) or b) below, wherein a) is the protein formed by the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ IN NO:1, and b) is the protein derived from a) through the substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ IN NO:1. The heat resistant lactonase disclosed by the invention has stronger protease resistance and better degradation capacity for various substrates, and can be used as a novel biocontrol enzymic preparation.
Owner:北京挑战生物技术有限公司
DNA for high-level expression of N-acyl homoserine lactonase in yeasts and engineering bacteria constructed thereby
ActiveCN101914556AReduce manufacturing costEfficient expressive abilityFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisYeast
The invention discloses a DNA for high-level expression of N-acyl homoserine lactonase in yeasts and engineering bacteria constructed thereby. The DNA provided by the invention is the DNA expressed by the sequence 2 in a sequence list. On the basis of the traditional homoserine lactonase gene aiiaB546, the DNA sequence thereof is optimized to obtain the optimized gene aiiaB546 M by the method. The expression ability of the optimized gene in Pichia pastoris is obviously higher than that of the gene before optimization. An aiiaB546 M-containing recombinant expression plasmid is constructed; and recombination strains of the high-efficient homoserine lactonase can be obtained by introducing the recombinant expression plasmid into the Pichia pastoris. The expression ability of one of the recombination strains is particularly high. The DNA and the engineering bacteria have great value to the production of the homoserine lactonase.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
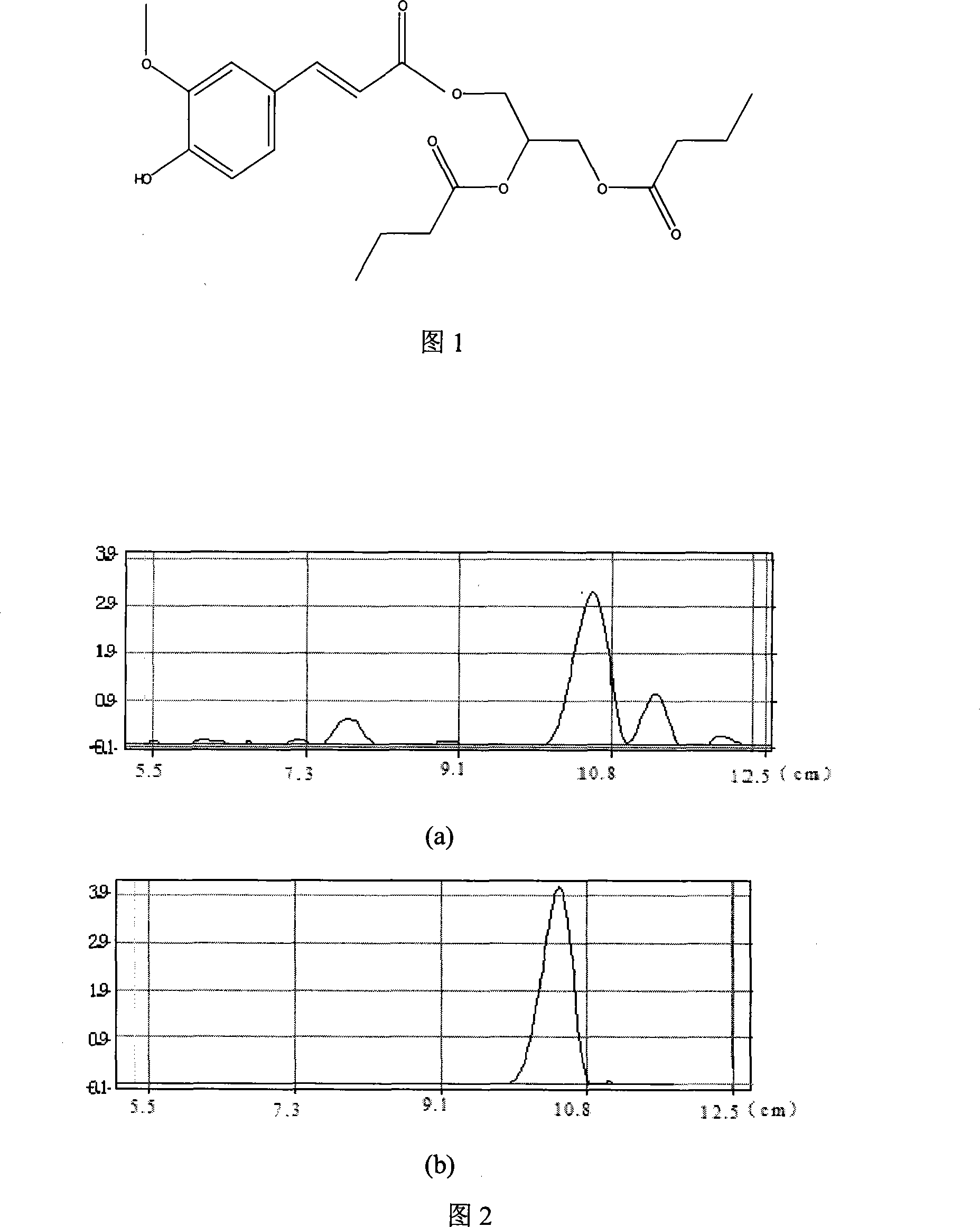
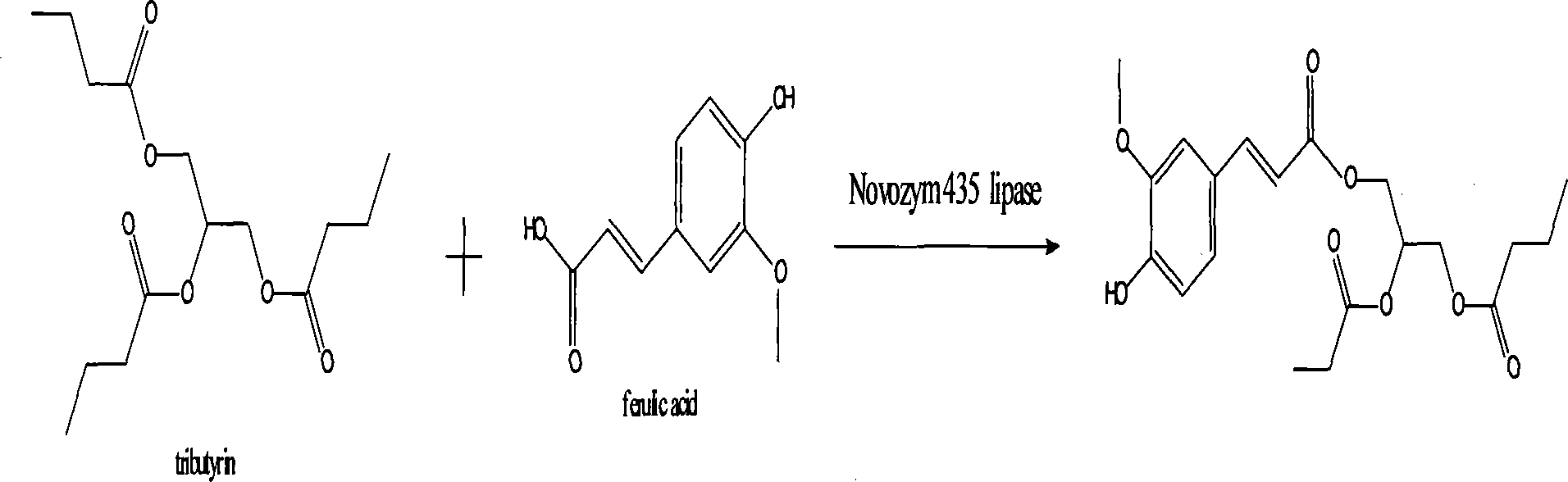
Method for synthesizing functional foodstuff antioxidant feruloylated dibutyrated acylglycerol accelerated by enzyme
InactiveCN101168756AConvenient sourceMild preparation methodFood preservationFermentationSodium bicarbonateEnzymatic synthesis
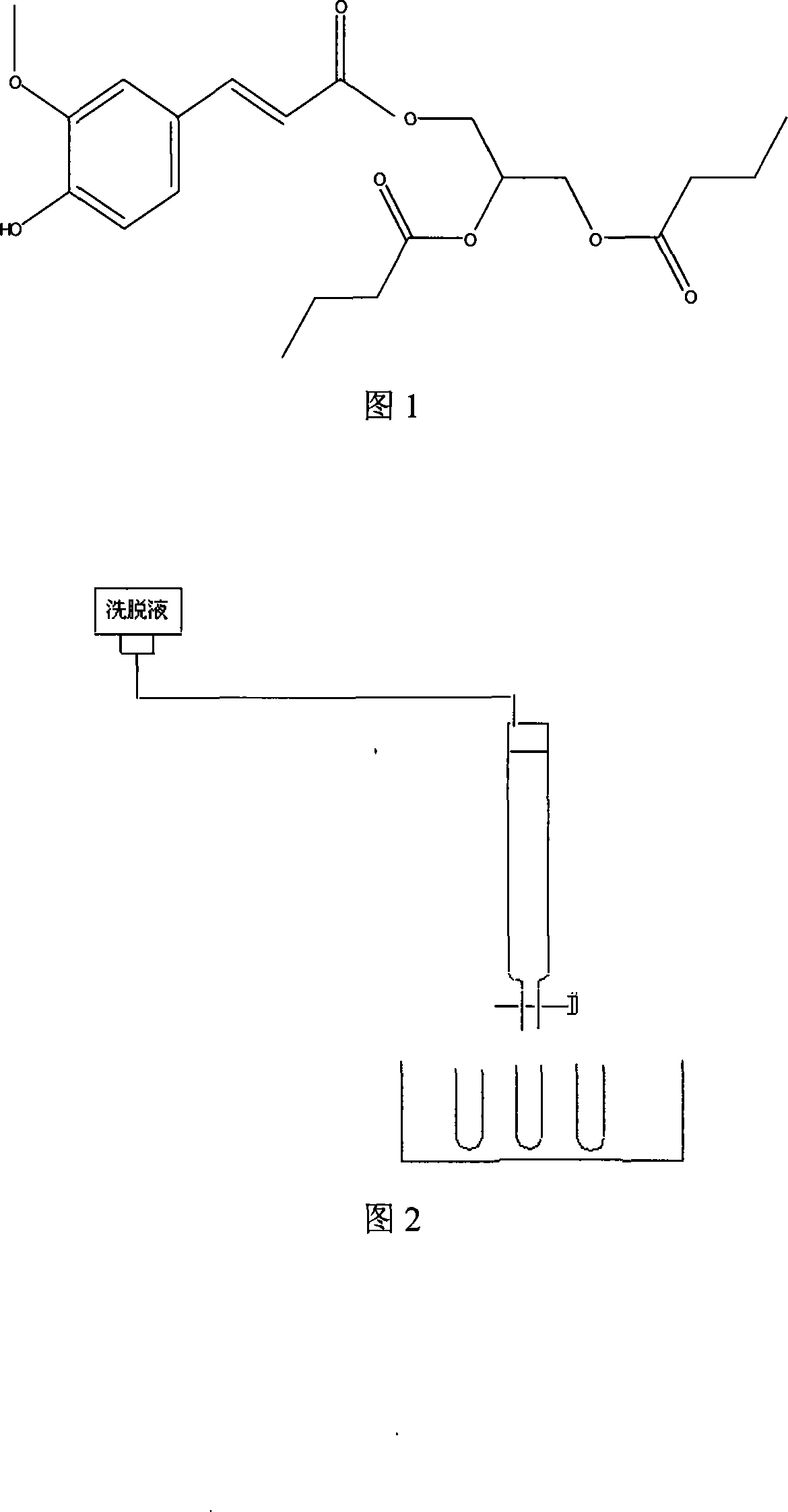
The invention relates to a method for enzymic synthesis of anti oxidant, namely, ferulic acid bis-butanoic acid glyceride of functional food. The invention comprises the following steps: firstly, being catalyzed by thionyl chloride, ferulic acid and absolute ethyl alcohol are heated under reflux and react, are dissolved in ethylether, and are extracted by sodium bicarbonate, the ethylether is removed, and then standstill and seed out are performed to obtain ferulic acid ethyl ester which is then purified; secondly, the obtained ferulic acid ethyl ester, glycerol monobutyralte and tertiary butyl alcohol are reacted in the catalysis of Novozym435 lipase and purified, thereby obtaining the ferulic acid bis-butanoic acid glyceride. The method has mild and safe reaction condition, and prepared oxidant which maintains the property of the ferulic acid and the butanoic acid is released slowly under the function of lactonase in the human body. The method has the functions of being anti-oxidation and anti-fatigue, and removing harmful free radical in the human body, and also has the functions preventing and treating various cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Enzymatic method
InactiveUS20160326555A1Increase conversion rateShorten the timeFermentationAliphatic alcoholCarbon atom
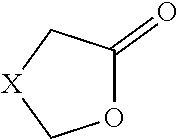
The present invention relates to a method comprising the method steps A) Providing at least one compound of the general formula I) where X=divalent organic radical comprising 1 to 19 carbon atoms B) Contacting the compound of the general formula I) with an enzyme E1 selected from the group esterases, lipases and lactonases, characterized in that method step B) is carried out in the presence of at least one aliphatic alcohol comprising 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
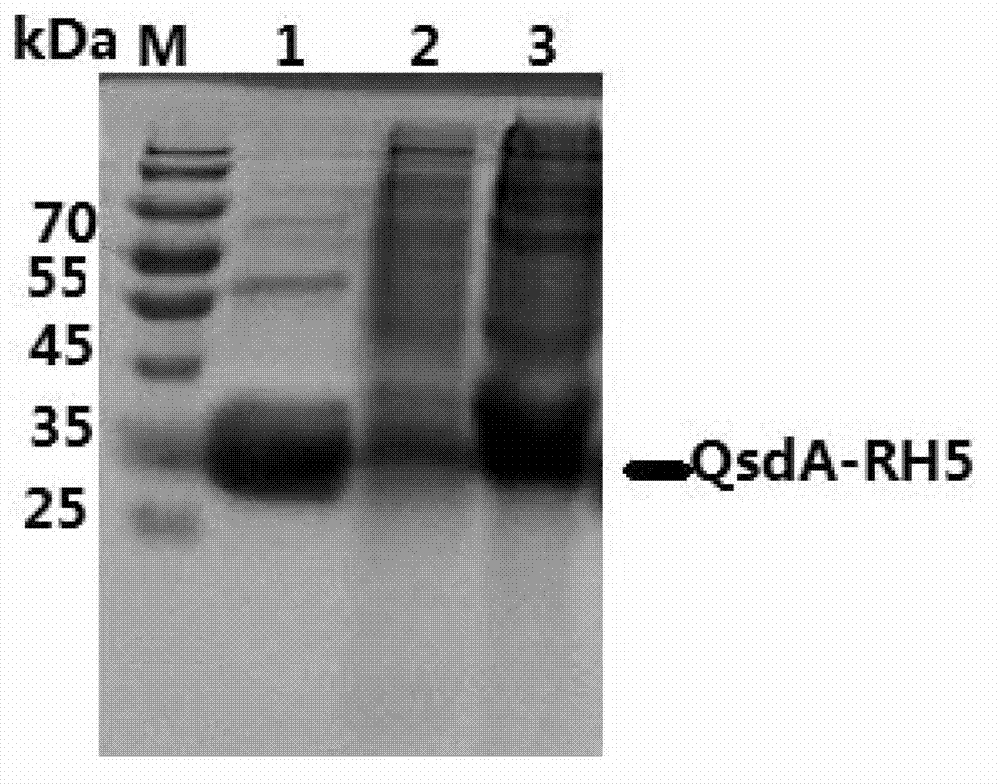
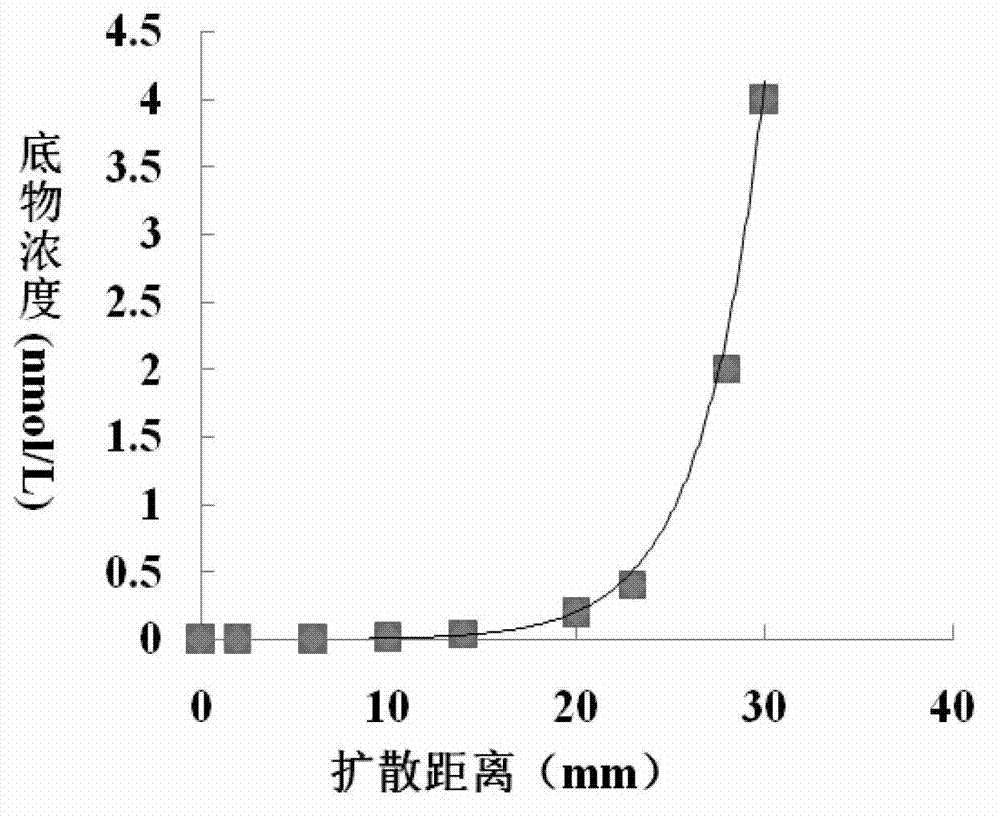
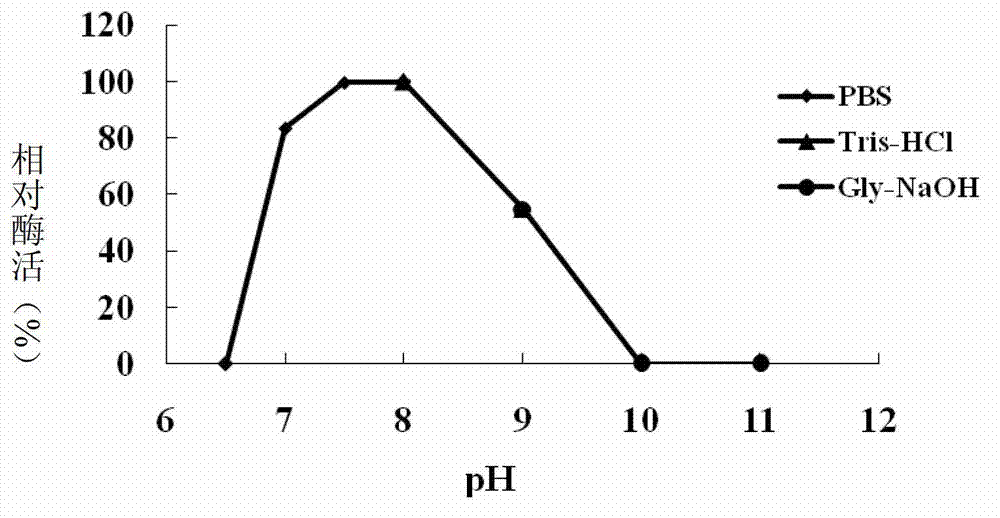
N-acylhomoserine lactonase QsdA-RH5 with substrate specificity and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102965357AHave substrate specificityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesN-Acyl homoserine lactoneThermal stability
The invention discloses N-acylhomoserine lactonase QsdA-RH5 with substrate specificity and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein QsdA-RH5 is (a) protein consisting of the amino acid sequences shown by sequence 1 in a sequence table, or (b) protein obtained by substituting and / or losing and / or adding one or multiple amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 1 in the sequence table, having the function of N-acylhomoserine lactonase and derived from the sequence 1 in the sequence table. Experiments prove that the QsdA-RH5 protein provided by the invention has substrate specificity and can degrade various N-acylhomoserine lactone without substituent groups; the specific activity of the QsdA-RH5 protein serving as N-acylhomoserine lactonase is 292.83U / mg and is stable in a pH range of 4.0-12.0, and more than 90% of enzyme activity can be maintained; and moreover, the thermal stability is better, and relative enzyme activity after keeping temperature at 70 DEG C for 10 minutes is still 100%. The QsdA-RH5 protein provided by the invention can be used for preparing a novel bio-control enzyme preparation.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
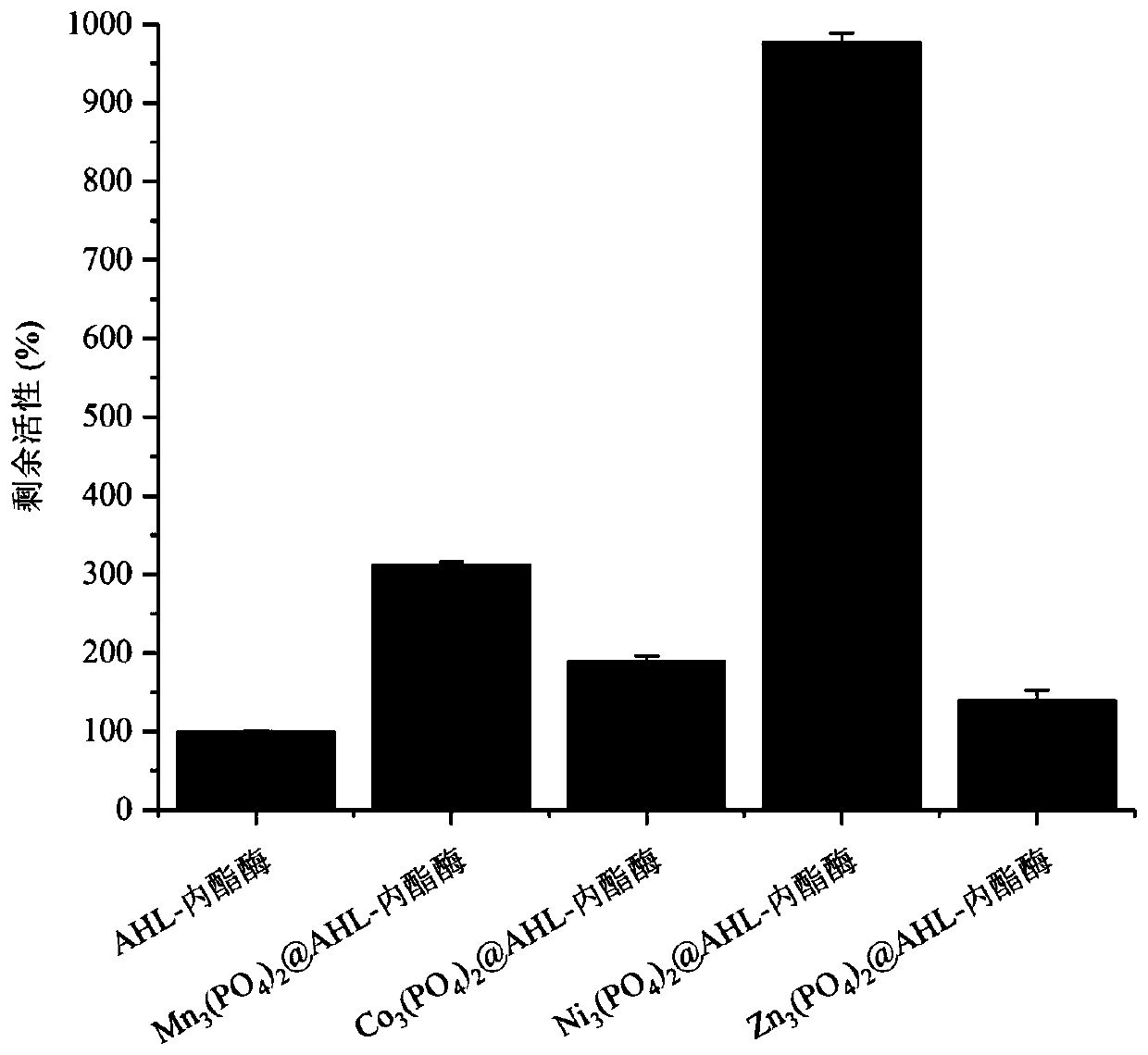
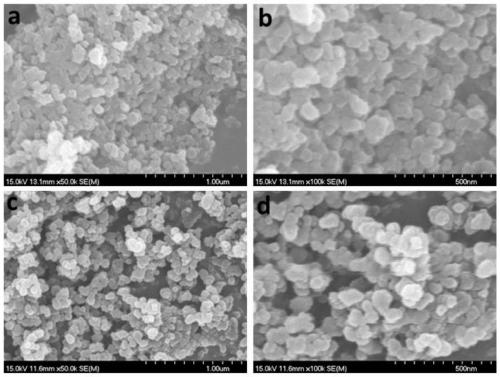
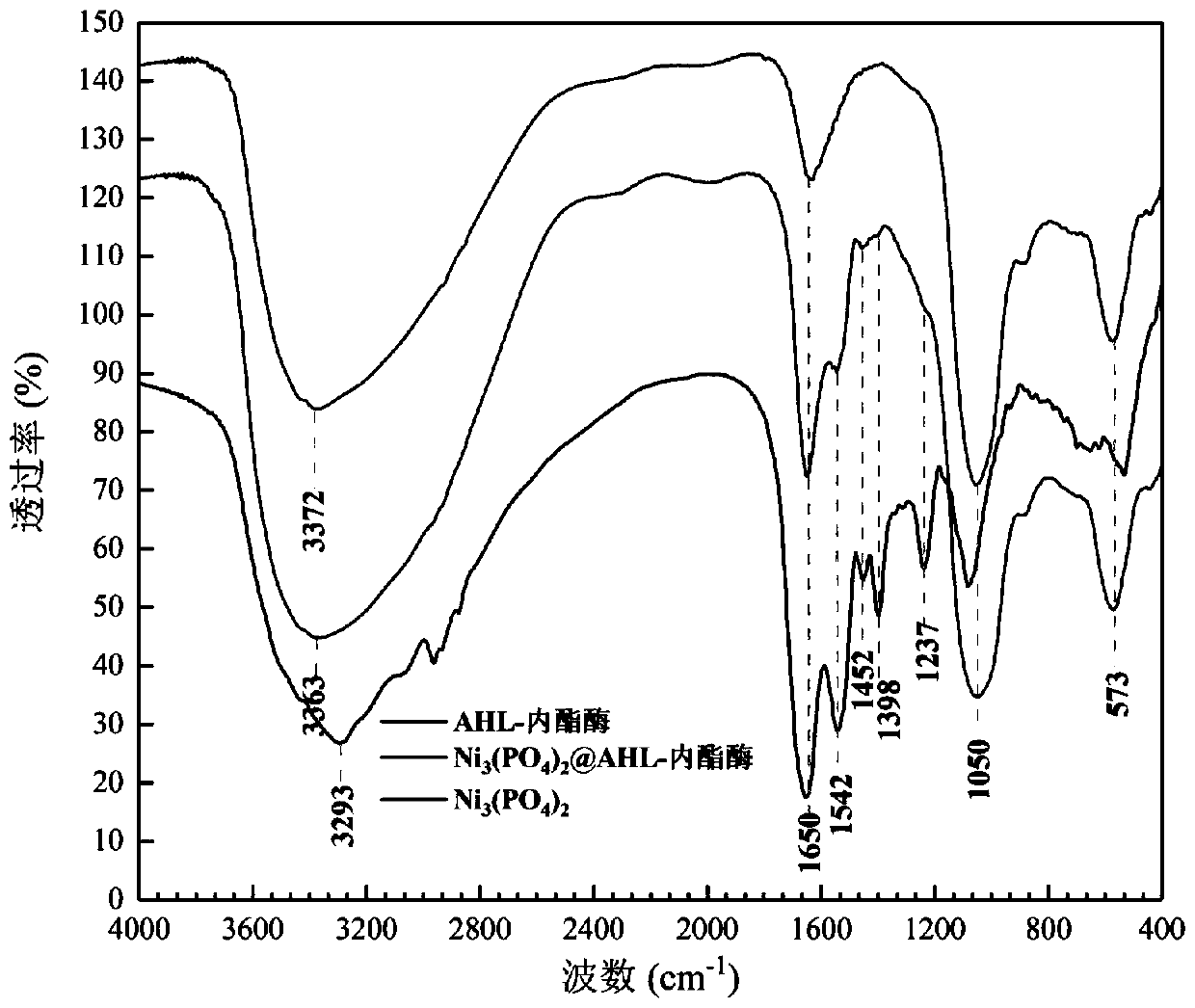
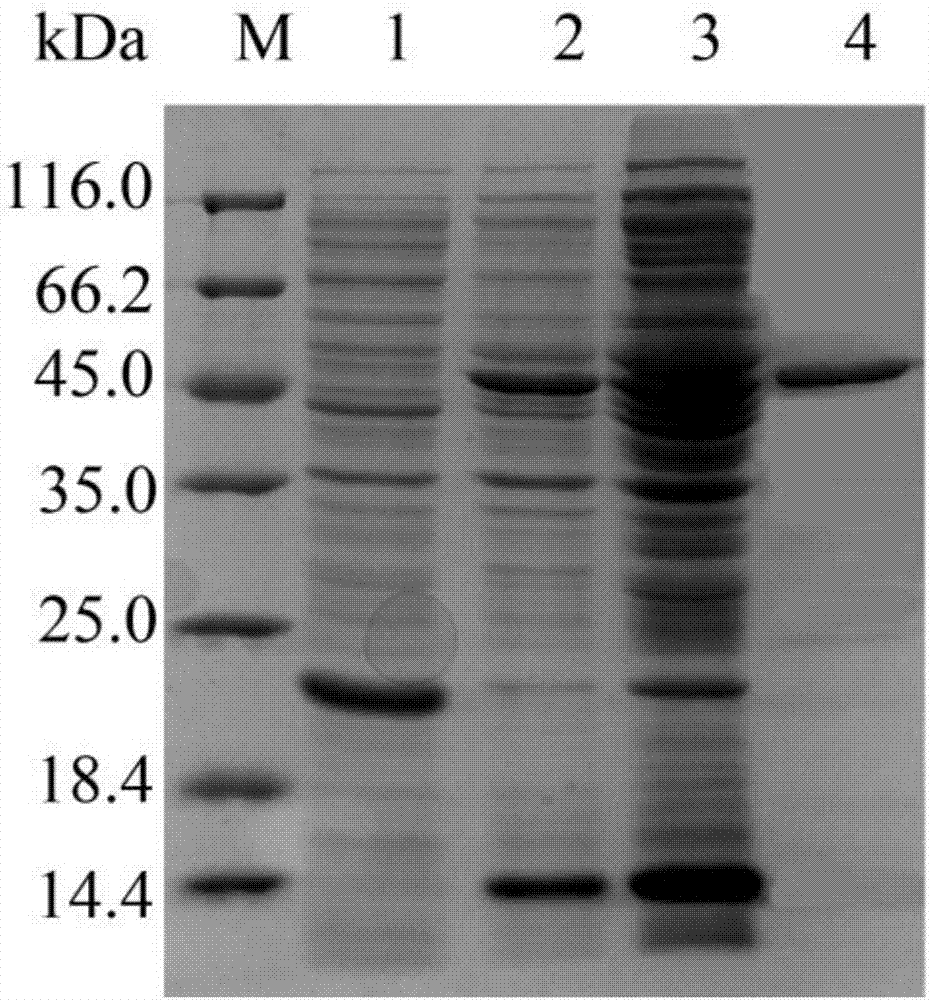
N-acyl homoserine lactonase-inorganic hybrid nano-catalyst and preparation thereof
ActiveCN109988756AEasy to prepareMild preparation conditionsHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationNano catalystHomoserine
The invention discloses an N-acyl homoserine lactonase(AHL-lactonase)-inorganic hybrid nano-catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The nano-catalyst is composed of the organic component and the inorganic component, wherein the organic component is theAHL-lactonase, and the inorganic component is insoluble phosphate, such as zinc, nickel, manganese, cobalt and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the AHL-lactonase and soluble metal salt into a phosphate buffer solution respectively, standing the obtained mixed liquid, removing the supernatant, and carryingout vacuum drying to obtain the AHL-lactonase-inorganic hybrid nano-catalyst with small particle size and stable structure. The preparation method is simple and the activity of the obtained AHL-lactonase-inorganic hybrid nano-catalyst is significantly higher than the activityof free enzymes, and the thermal stability is better; the surface area of small-sized complexes is larger, thereby increasing the contact area with substrate in the reaction. The enzyme substrate has a wide spectrum, can effectively degrade many signal molecules, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
N-acyl homoserine lactonase and medicine thereof
The invention relates to N-acyl homoserine lactonase and a medicine thereof. An amino acid sequence of the N-acyl homoserine lactonase and a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 are at least 90% homologous, and the amino acid sequence of the N-acyl homoserine lactonase has N-acyl homoserine lactonase activity. The invention further provides a nucleotide sequence encoding the lactonase, an expression vector and a heterogenous expression strain. The medicine can treat (pseudomonas aeruginosa) infection. The N-acyl homoserine lactonase catalyzes lactone bonds of N-acyl homoserine lactone to hydrolyze, so that signal molecules between pseudomonas aeruginosa are quenched, and quorum sensing is interfered and inhibited. Compared with other N-acyl homoserine lactonase, the N-acyl homoserine lactonase has wider substrate adaptability and more efficient degradation activity and better effects when serving as the medicine for treating pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for performing secretory expression of glucose oxidase based on optimization of metabolic engineering, recombinant bacterium and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for performing secretory expression of glucose oxidase (GOD) based on the optimization of metabolic engineering, a recombinant bacterium and application thereof. The invention provides a method which can efficiently secretorily express GOD and improve the enzyme activity thereof. The GOD and malic acid dehydrogenase 1 coding gene (mdh1) or 6-phosphogluconolactonase coding gene (sol3) is co-expressed in a yeast strain, so that the efficient expression of the GOD is realized. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a recombinant bacterium for efficiently secreting the GOD built by adopting pichia pastoris as a host.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Peptide with quorum-sensing inhibitory activity, polynucleotide that encodes said peptide, and the uses thereof
The invention relates to the cloning, sequencing and characterization of the gene responsible for Quorum Quenching (QQ) activity against Quorum Sensing (QS) signals of the Tenacibaculum sp. strain 20J (CECT7426). Said gene encodes a peptide having at least lactonase activity with a percentage of identity less than 38% with the lactonases described up until now for other species, as well as the sequences of the homologous genes present in other species of the genus Tenacibaculum. Said peptide shows a broad spectrum of activity degrading optionally substituted N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) of 4-14 carbon atoms in the side chain thereof, is active at pH comprised between 3 and 9, proteinase K- and chymotrypsin-resistant and does not interact with β-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA +1
Erythromycin degrading bacterium RJJ-5 and application thereof
ActiveCN111304098AHigh degradation activityFungiContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention discloses an erythromycin degrading bacterium RJJ-5 and application thereof, a method for degrading erythromycin and an erythromycin degrading bacterium dry powder. The erythromycin degrading bacterium and the application thereof have the advantages that microorganisms capable of degrading erythromycin are obtained through a microbial technology means according to the characteristicsof erythromycin from specific environmental conditions or through transformation, catalytic degradation is conducted on the erythromycin structure through macrocyclic lactonase, transferase, lyase and the like, and a pollution-free metabolite is obtained. Experiments prove that the erythromycin degrading bacterium RJJ-5 can survive in the environment with erythromycin as the only carbon source, the high erythromycin degrading activity is achieved, and the erythromycin degrading rate can reach 50%-75%. The erythromycin degrading bacterium RJJ-5 can be applied to erythromycin degradation in thepolluted environment and has the good application value in the aspects of water treatment and soil remediation.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +2
Inhibitors of P38 Map Kinase
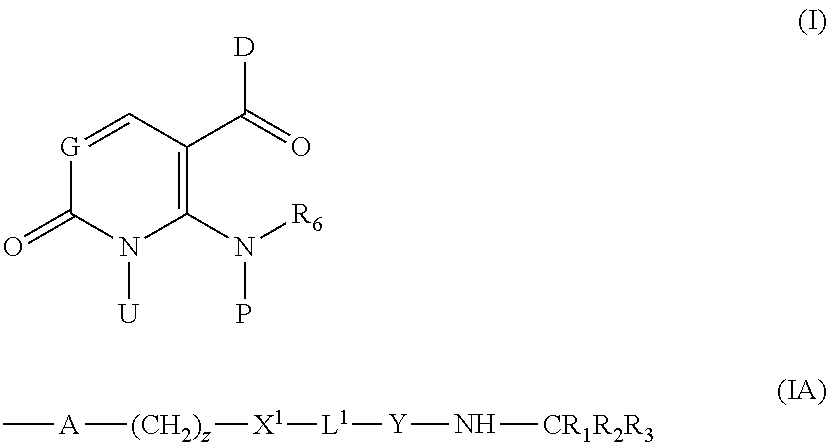
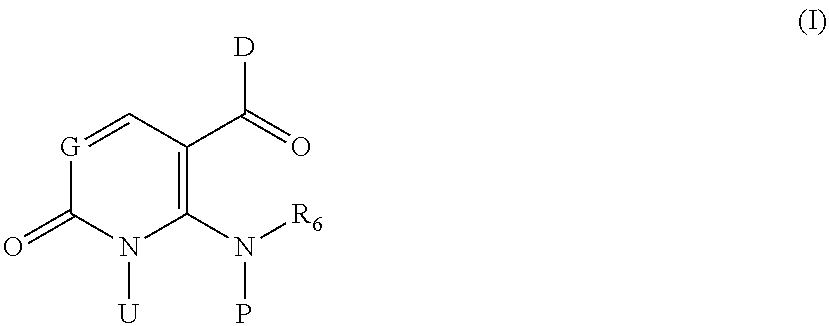
Compounds of formula (I) are p38 MAP kinase inhibitors useful for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: wherein: G is —N═ or —CH═; D is an optionally substituted divalent mono- or bi-cyclic aryl or heteroaryl radical having 5-13 ring members; R6 is hydrogen or optionally substituted CrC3 alkyl; P represents hydrogen and U represents a radical of formula (IA); or U represents hydrogen and P represents a radical of formula (IA); wherein A represents an optionally substituted divalent mono- or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic radical having 5-13 ring members; z is O or 1; —X1-L1-Y— is a linker radical or bond; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular esterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; and R2 and R3 are as defined in the claims.
Owner:MACROPHAGE PHARMA LTD
Bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium with group quenching activity as well as construction method and application of bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN113416682AAvoid harmNo pollution in the processBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacterial disease
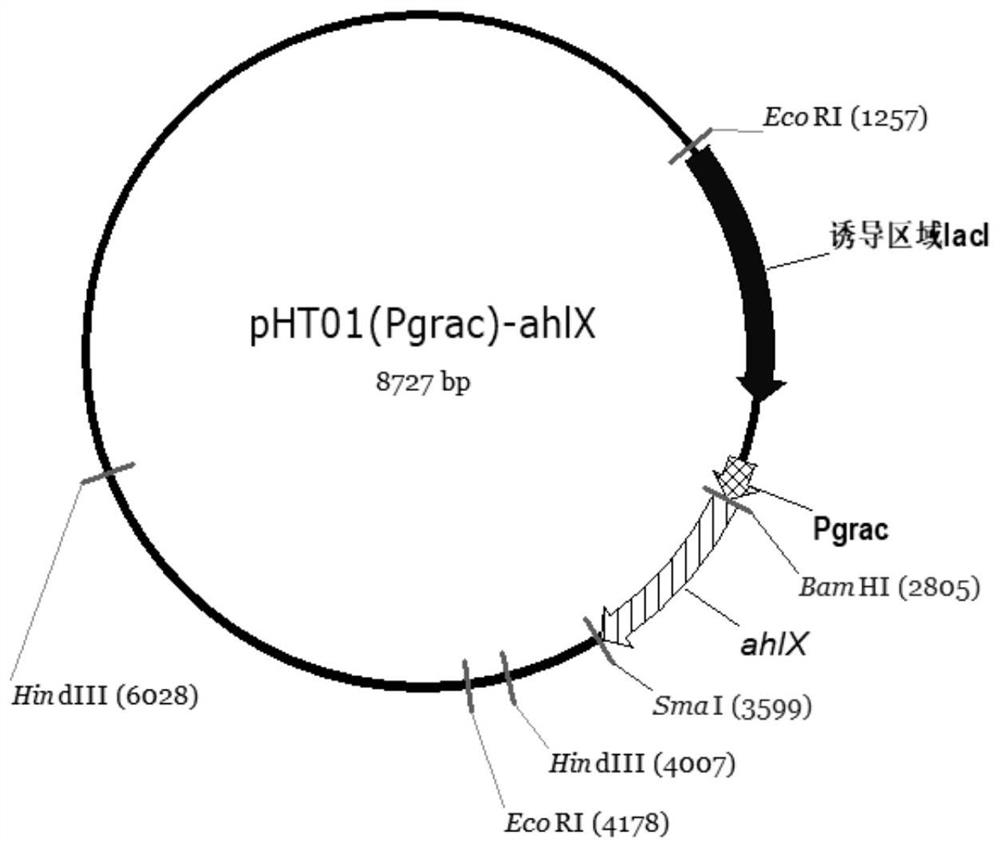
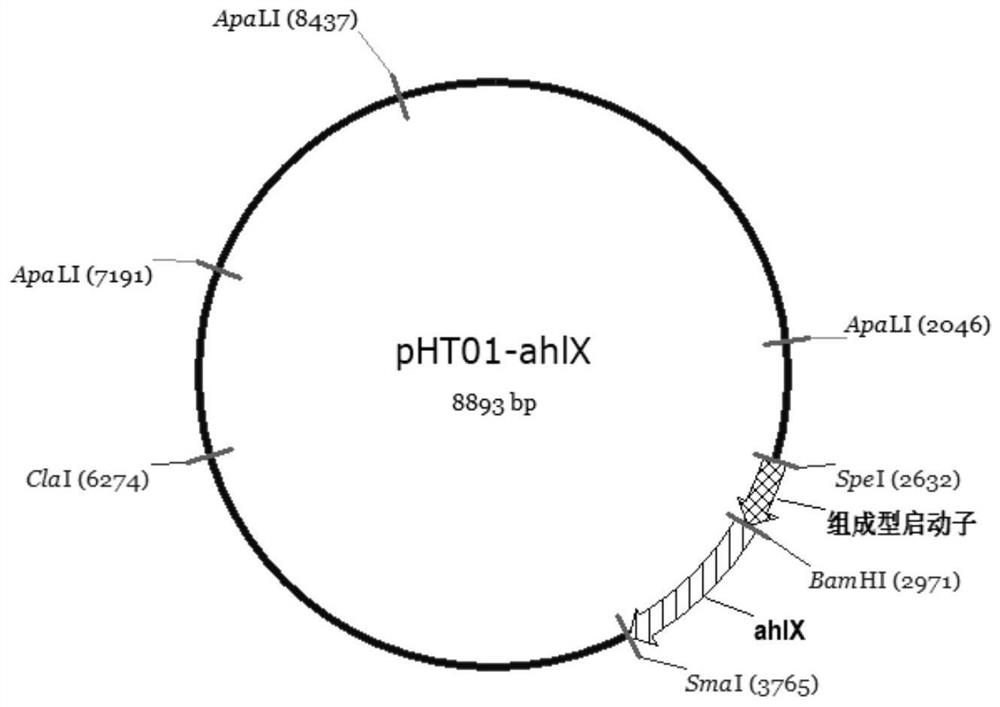
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, in particular to bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium with group quenching activity and application of the bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium. A construction method comprises the steps that acyl homoserine lactonase coding genes are cloned to a bacillus subtilis expression vector, regulatory protein coding genes lacI on the vector are removed, and transferring into bacillus subtilis is carried out to obtain the bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium with group quenching activity. The recombinant bacillus subtilis for expressing AHL lactonase constructed by the invention can continuously express high-activity quorum sensing quenching enzyme AhlX without additionally adding an inducer, the used host is the environment-friendly bacillus subtilis, and the bacillus subtilis has natural advantages in the aspect of preventing and treating plant bacterial diseases, is pollution-free and non-toxic compared with chemical pesticides, has the advantages of no residue and no harm to the environment, is a green prevention and control measure, and has great potential in the aspect of preventing and controlling bacterial diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
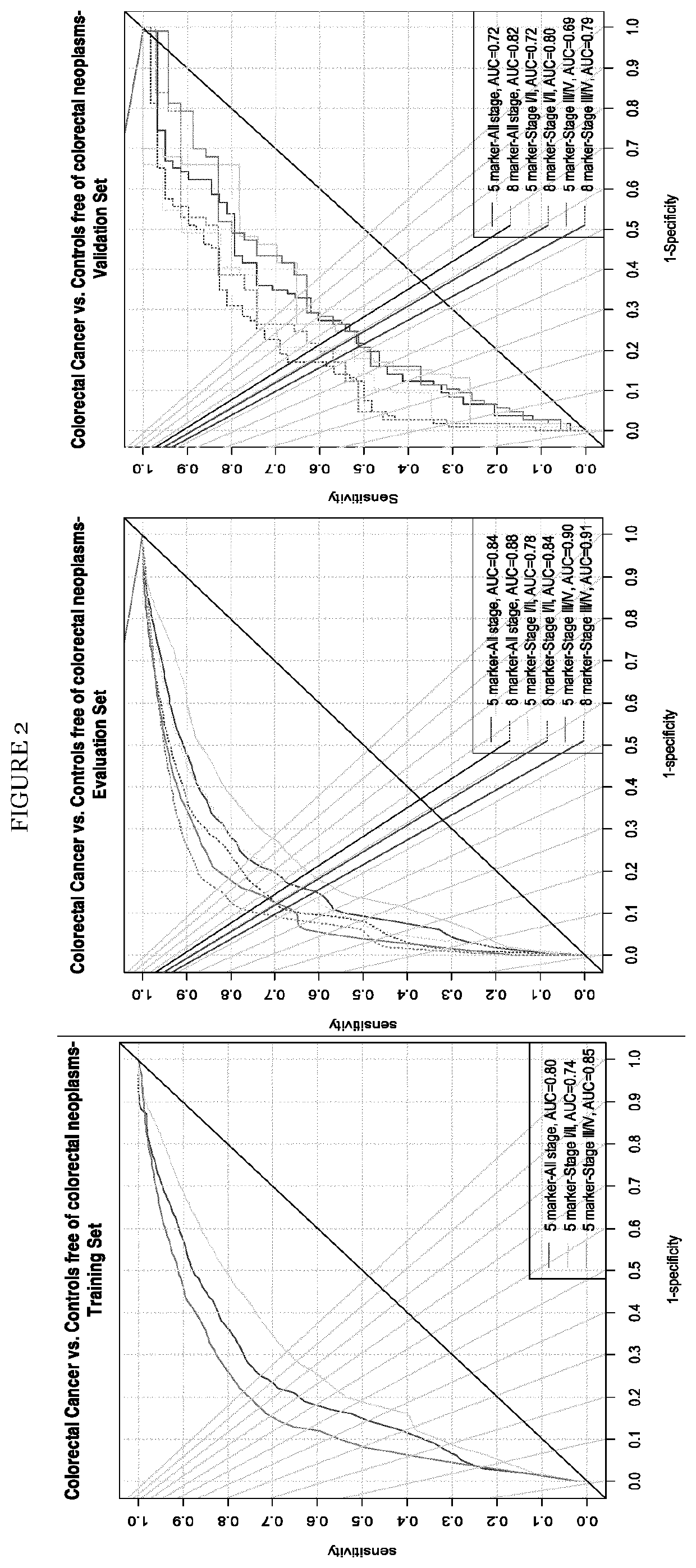
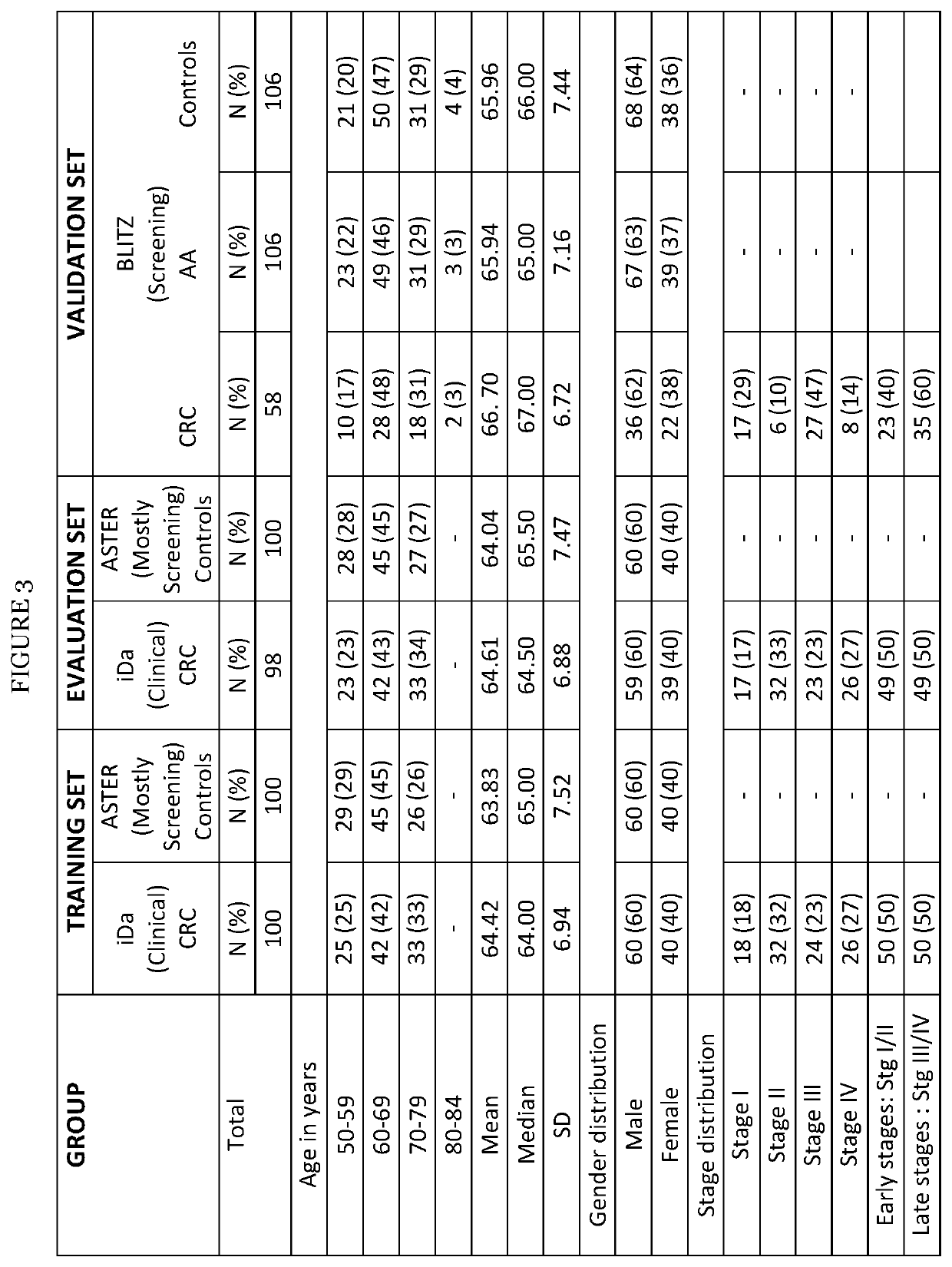
Colorectal cancer screening examination and early detection method
PendingUS20220214345A1Contributes immensely to the global burden of cancersReduce incidenceDisease diagnosisDiseaseBiomarker panel
The present invention pertains to a new method for the diagnosis, prognosis, stratification and / or monitoring of a therapy, of cancer, preferably colorectal cancer (CRC), in a subject. The method is based on the determination of the level of a panel of least one, preferably 3, 4 and most preferably at least 5, protein biomarker selected from the group consisting of the protein biomarkers Amphiregulin (AREG), Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), Insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2), Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 (KRT19), Mannan binding lectin serine protease 1 (MASP1), Osteopontin (OPN), Serum paraoxonase lactonase 3 (PON3) and Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TR), in the biological sample obtained from the subject. The new biomarker panel of the invention allows diagnosing and even stratifying various cancer diseases. Furthermore, provided are diagnostic kits for performing the non-invasive methods of the invention. Since the biomarker panel of the invention provides a statistically robust method independent of the protein detection technology used, and considering that the biomarker panel of the invention is detected in plasma samples of the subjects, the invention provides an early detection screening examination that may be applied to a larger population.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
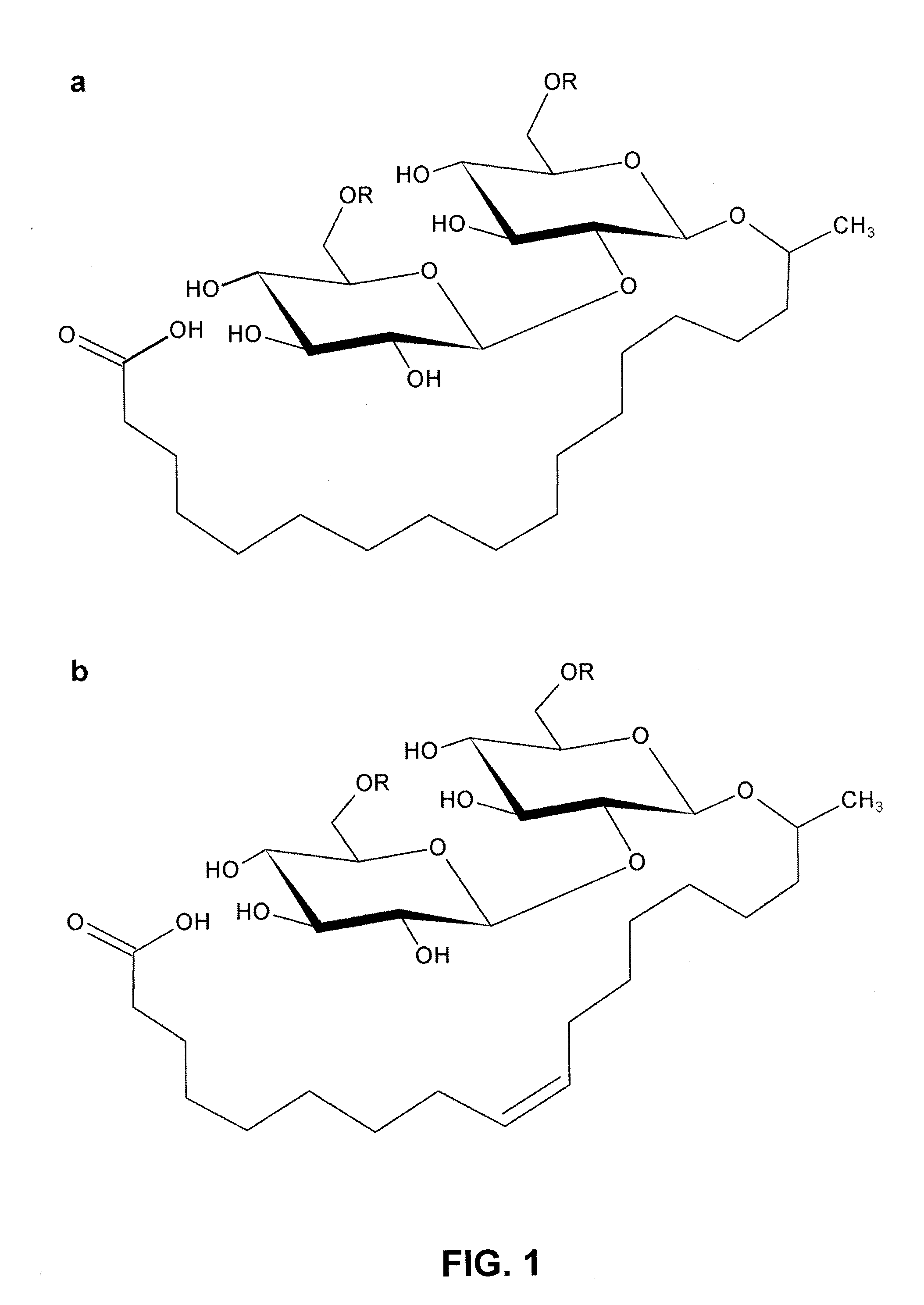
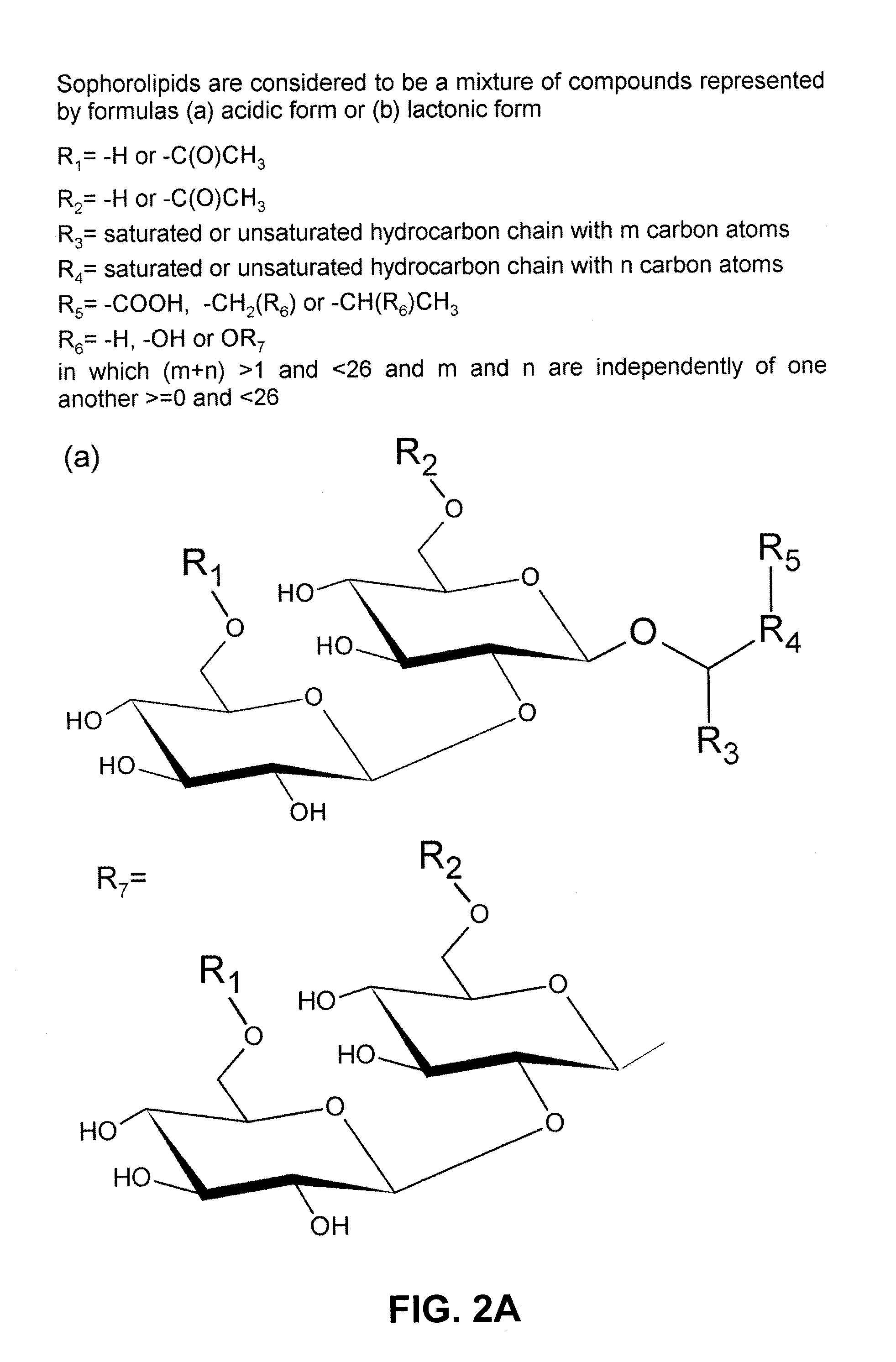
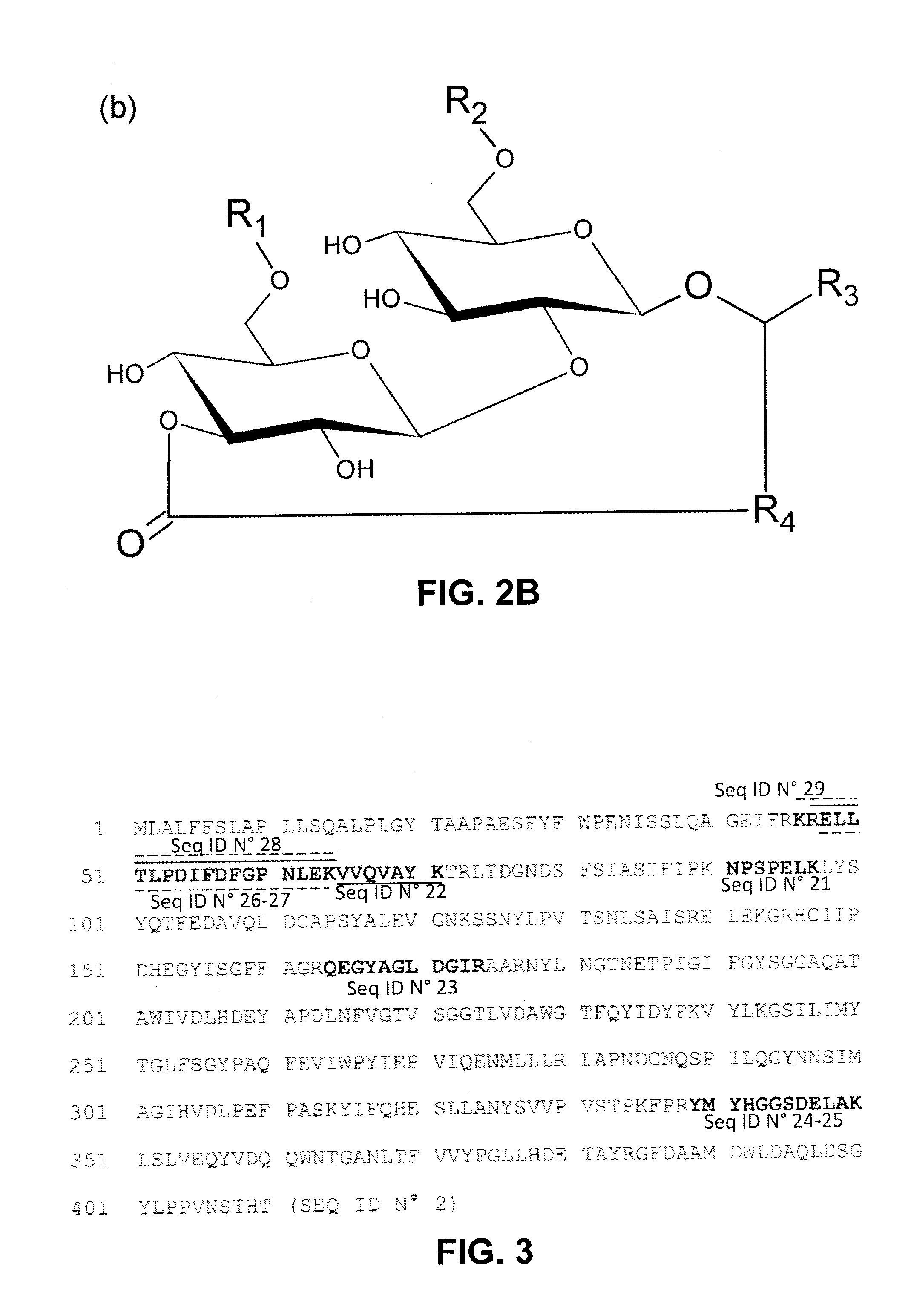
Lactonase derived from candida bombicola and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140335567A1Good foaming effectGood water solubilitySugar derivativesHydrolasesLipid formation[Candida] apicola
The present disclosure relates to an enzyme derived from Candida bombicola that is capable of lactonizing or polymerizing carbohydrate-containing compounds, lipids, fatty acids, hydroxylated fatty acids, alcohols, dicarboxylic acids or mixtures thereof. Hence, host cells comprising the latter enzyme can be used, via the formation of intra- or inter-molecular ester-bounds, to produce, for example, lactonized sophorolipids or polymers of acidic sophorolipids. On the other hand, host cells having lost their capability to produce a functional enzyme disclosed herein can be used to produce 100% acidic sophorolipids.
Owner:UNIV GENT
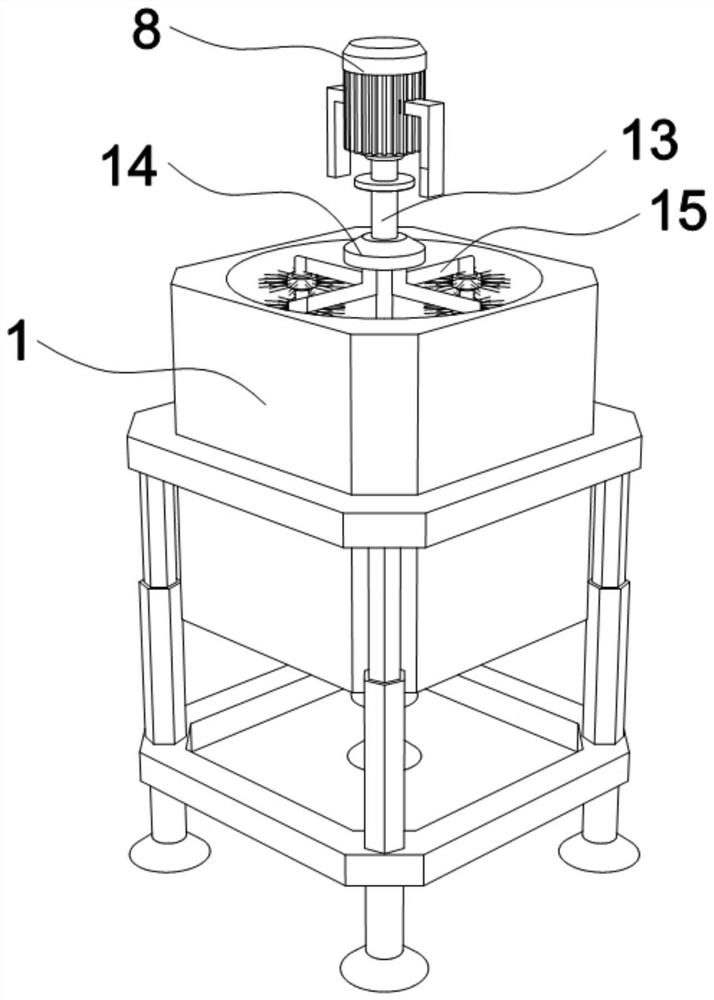
Production device of lactonase
ActiveCN114540160AWell mixedComprehensive cleaningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectric machineStructural engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of lactonase, in particular to a lactonase production device which comprises a bin body, a controller is arranged on one side of the bin body, a top cover is arranged on the upper surface of the bin body, a motor is arranged in the center of the top of the top cover, and one side of the top of the top cover communicates with a feeding pipe; a round pipe penetrating through the top cover is arranged at the bottom of the motor, and a round block is arranged at the end, away from the motor, of the round pipe. Meanwhile, high-frequency irregular up-and-down movement of the main fixing blocks and the auxiliary fixing blocks on the outer surfaces of the supporting rods can be achieved through cooperation of the main fixing blocks and the auxiliary fixing blocks on the outer surfaces of the multiple sets of supporting rods, springs and a bottom-layer circular plate, the cleaning effect on the inner wall of the bin body is improved, then high-frequency impact is conducted on the bottom-layer circular plate, and the service life of the bin body is prolonged. And the bottom of the bin body is vibrated and cleaned in cooperation with a large brush, the cleaning effect is guaranteed, and the cleaning performance is improved.
Owner:JIAOZUO UNIV
Manufacture of xylonic acid
Provided is a method for producing xylonic acid from xylose with a recombinant fungal strain that is genetically modified to express a xylose dehydrogenase gene, which is able to convert xylose to xylonolactone, which is spontaneously or enzymatically hydrolyzed to xylonic acid. The xylonic acid is excreted outside the host cell. Xylonate production may be coupled with xylitol production. Alternatively, if xylitol production is not desired, its production is reduced by removing the aldose reductase (or specific xylose reductase) enzyme, which converts xylose to xylitol. Expression of a heterologous lactonase encoding gene may result in higher acid concentrations. The method is suitable for producing xylonic acid from a hemicellulose hydrolysate such as hydrolyzed lignocellulosic plant biomass.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Construction method of synthetic strain for generating fengycin by transforming xylose through regulating and controlling Dahms pathway
The invention provides a construction method of a synthetic strain for generating fengycin by transforming xylose through regulating and controlling a Dahms pathway. The construction method comprises the following steps of: connecting a promoter gene P43, xylose dehydrogenase xylB, xylC, a xylosic acid lactonase gene yjhG and a 2-ketone-3-deoxyxylosic acid dehydratase gene yjhH in series to prepare a Dahms xylose pathway module into a shuttle vector pHY300PLK; meanwhile, starting from metabolite glycolaldehyde of the Dahms pathway, connecting an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldA, malic acid synthetase aceB, malic acid dehydrogenase mdh and the promoter P43 in series to prepare an glycolaldehyde back-complement TCA regulating and controlling module into a shuttle vector pHP13; co-expressing the two shuttle vectors in a chassis strain to construct a fengycin high-quality strain BSU02 which is synthesized by co-expressing and transforming the xylose through the Dahms module and the glycolaldehyde back-complement TCA regulating and controlling module.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Feed additive for improving intestinal health index of broiler chickens and application of feed additive
ActiveCN114424800AImprove survival rateIncrease production capacityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyFeed additive
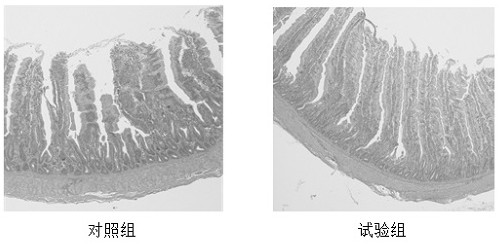
The invention provides a novel feed additive for improving the intestinal health index of broiler chickens and application thereof, the active ingredients of the feed additive are N-acyl homoserine lactonase and lactic acid bacteria, and the N-acyl homoserine lactonase and lactic acid bacteria can synergistically inhibit the reproduction of harmful bacteria. Broiler chicken breeding tests show that N-acyl homoserine lactonase and lactic acid bacteria have a synergistic effect, and the additive can improve the intestinal villus height of broiler chickens, reduce the overall inflammatory response of intestinal tracts, obviously reduce intestinal bleeding points of the broiler chickens and improve the health condition of the intestinal tracts, so that the survival rate and production performance of the broiler chickens are improved.
Owner:北京挑战生物技术有限公司 +1
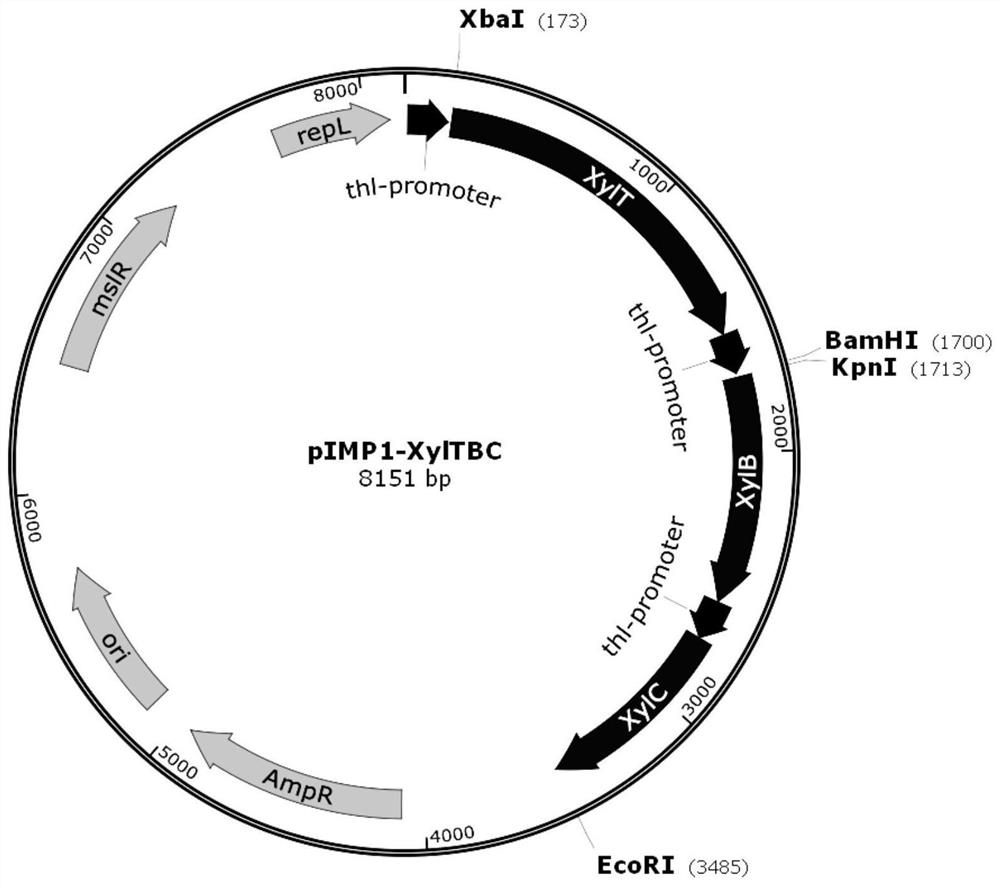
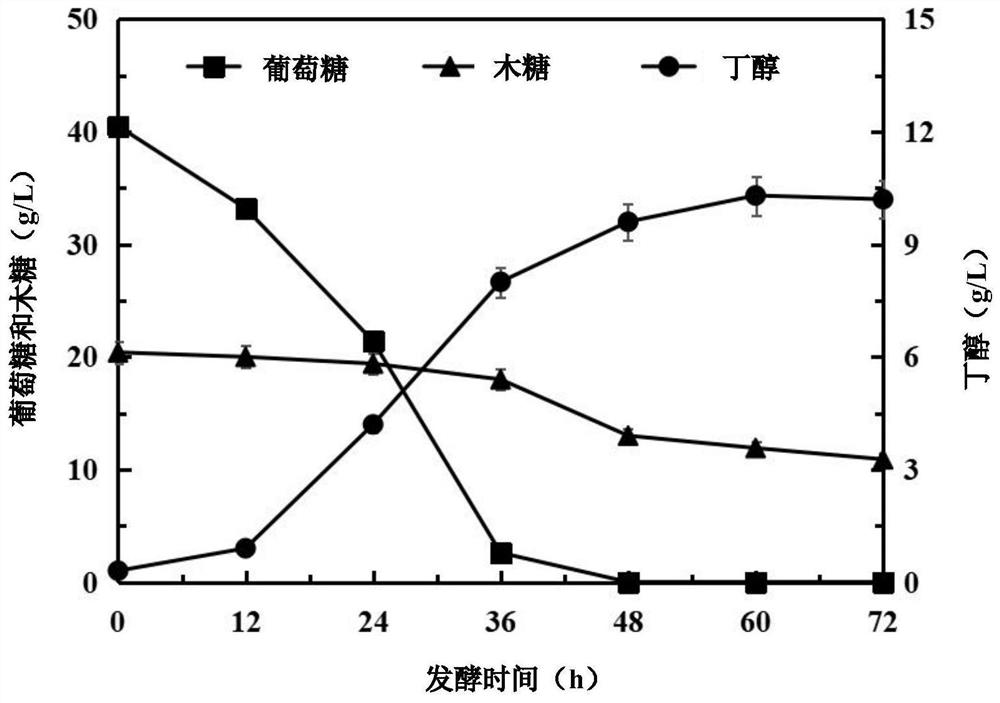
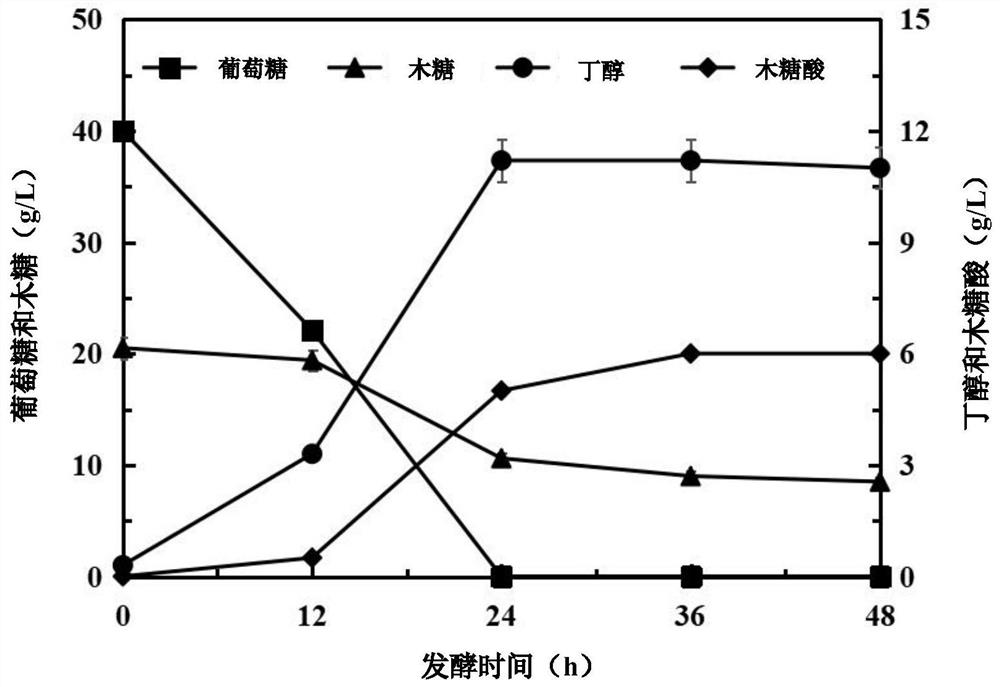
Recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum for efficiently converting straw biomass carbon source as well as construction method and application of recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum
ActiveCN111979167AEfficient conversionImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyBiomass carbon
The invention provides recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum for efficiently converting a straw biomass carbon source as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum. The recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum for efficiently converting the straw biomass carbon source is a clostridium acetobutylicum strain which is over-expressed by clostridium acetobutylicum xylose transporter protein, caulobacter crescentus xylose dehydrogenase and xylose lactonase in a synergistic manner. Specifically, the recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum is clostridiumacetobutylicum TXYL and was preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 8th 2020, and the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M 2020107. The recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum for efficiently converting the straw biomass carbon source is applied to fermentation of straw hydrolysate to produce butanol, the fermentation period is shortened to 24 hours, the consumptionrate of glucose and xylose is increased, the utilization rate of the xylose is increased, efficient conversion of straw glucose and xylose carbon sources is realized, and the yield of the butanol andthe production intensity are remarkably improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Multiple-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for macrolide drug resistance genes of staphylococcus infecting livestock and use method
PendingCN106480219AImprove detection efficiencyQuick evaluationMicrobiological testing/measurementMacrolide resistancePathogenic bacteria
The invention relates to a triple-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for macrolide drug resistance genes of staphylococcus infecting livestock. The kit comprises three pairs of PCR primers for amplifying drug resistance genes of to-be-detected bacteria, a template preparation reagent and a bacterial drug resistance gene multiple-amplification reagent. Compared with a conventional drug sensitive test, the multiple-type method has the advantages that the detection time is shortened from days to one day. Pathogenic bacteria often contain multiple macrocyclic lactonase genes. The technology meets the demands for detecting multiple genes simultaneously, and the detection accuracy and specificity are improved; the technology can be used for detecting three macrolide type drug resistance genes in clinical bacteria isolates.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for synthesizing antioxidant feruloylated dibutyrated acylglycerol accelerated by solvent-free system enzyme
InactiveCN101168755AConvenient sourceMild preparation methodFood preservationFermentationSodium bicarbonateEnzymatic synthesis
The invention relates to a method for solvent system free enzymic synthesis of anti oxidant, namely, ferulic acid bis-butanoic acid glyceride. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, being catalyzed by thionyl chloride, ferulic acid and absolute ethyl alcohol are heated under reflux and reaction, are dissolved in ethylether, and are extracted by sodium bicarbonate, the ethylether is removed, and then standstill and seed out are performed to obtain ferulic acid ethyl ester which is then purified; secondly, by utilizing the characteristic that glycerol monobutyralte is liquid at room temperature, the obtained ferulic acid ethyl ester and the glycerol monobutyralte are directly used as the reaction medium and the substrate, and are reacted in the catalysis of Novozym435 lipase and purified, thereby obtaining the ferulic acid bis-butanoic acid glyceride. The method has mild and safe reaction condition, and prepared oxidant which maintains the property of the ferulic acid and the butanoic acid is released slowly under the function of lactonase in the human body. The method has the functions of being anti-oxidation and anti-fatigue, and removing harmful free radical in the human body, and also has the functions of preventing and treating various cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The method does not use organic solvent, thus simple post treatment is ensured and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
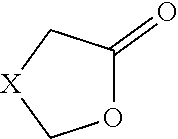
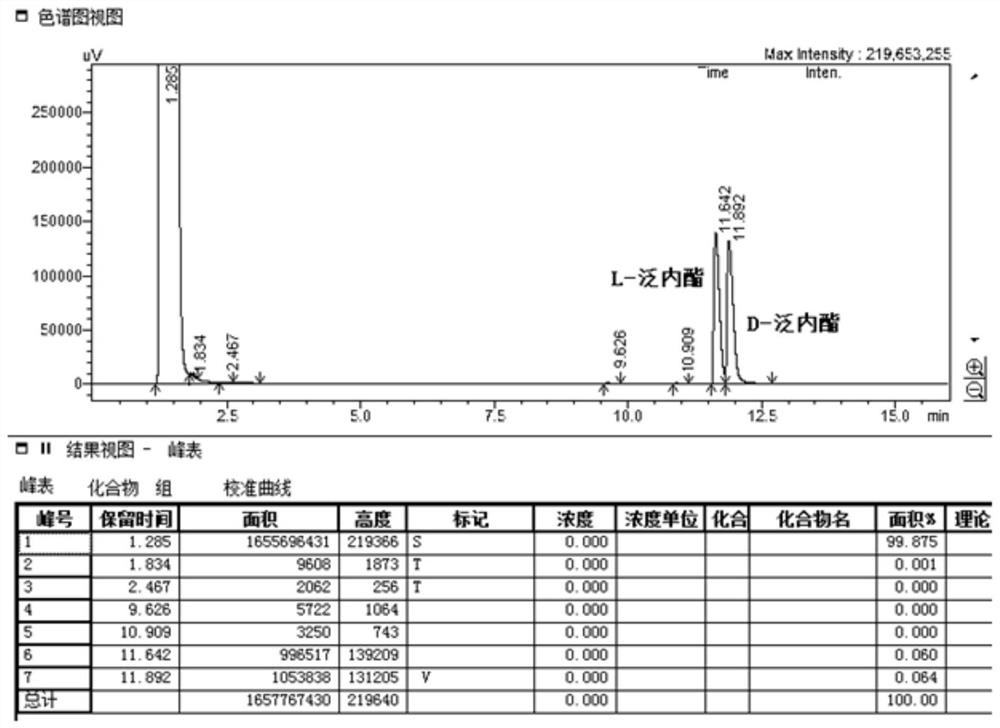
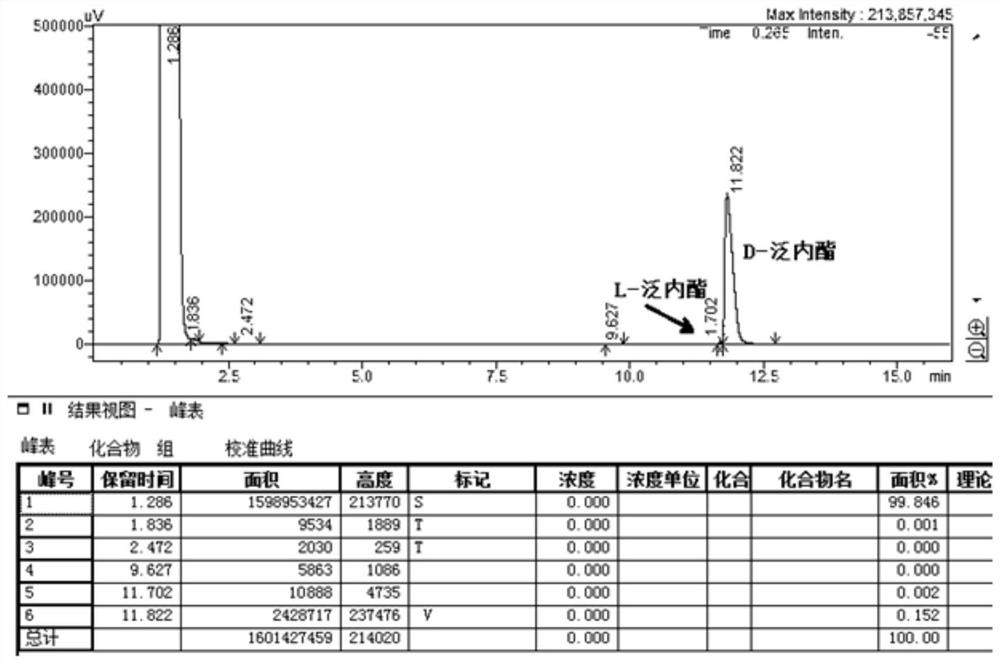
Aspergillus niger strain bfa010-7 with high production of L-lactone hydrolase and its application in the preparation of d-pantolactone
The invention discloses a black mold BFA010-7 with high production of D-pantolactonase obtained through soil screening and low-temperature plasma mutagenesis, the preservation number is CGMCC 14631, and the above-mentioned Aspergillus niger strain BFA010-7 is prepared Application of D‑pantotolactone. In the present invention, the Aspergillus niger mycelium is grown and propagated in the sponge block by embedding, and then the immobilized cell catalyst is prepared by a chemical cross-linking method. The whole process is simple, easy, cheap and practical, and easy to scale up. The prepared immobilized cell catalyst has the advantages of high activity, good operational stability, easy separation and recovery, etc., and has a good application prospect in the industrial production process of calcium D-pantothenate.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIFUAN ENZYME TECH
A recombinant bacterium that utilizes xylose to produce glycolic acid and its construction method and application
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and a building method and application of the recombinant bacteria and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The xylose dehydrogenase gene, xylonic acid lactonase gene, xylonic acid dehydratase gene, 3-deoxygenation-D-glycerin ketopentose acid aldolase gene and glycolic aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in the recombinant bacteria using the xylose to produce the glycollic acid are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant bacteria and a method using the recombinant bacteria to produce the glycollic acid. By the recombinant bacteria, the biological synthesizing path using D-xylose as the carbon source to form the glycollic acid through glycolic aldehyde conversion is achieved for the first time.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase, gene and application thereof
ActiveCN112961847AEfficient degradationInhibition of early proliferationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDisinfectantPseudomonas
The invention discloses a bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase, a gene and application thereof. The invention firstly discloses the bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses the application of the bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase in the treatment of dental chair type equipment. The disclosed bacillus velezensis YtnP-homologous lactonase can be used for remarkably inhibiting early proliferation, biofilm formation and virulence factor release of pseudomonas aeruginosa, is an effective way for reducing opportunistic pathogenic bacterium infection, and can be used as a novel dental hygiene treatment disinfectant.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY +1
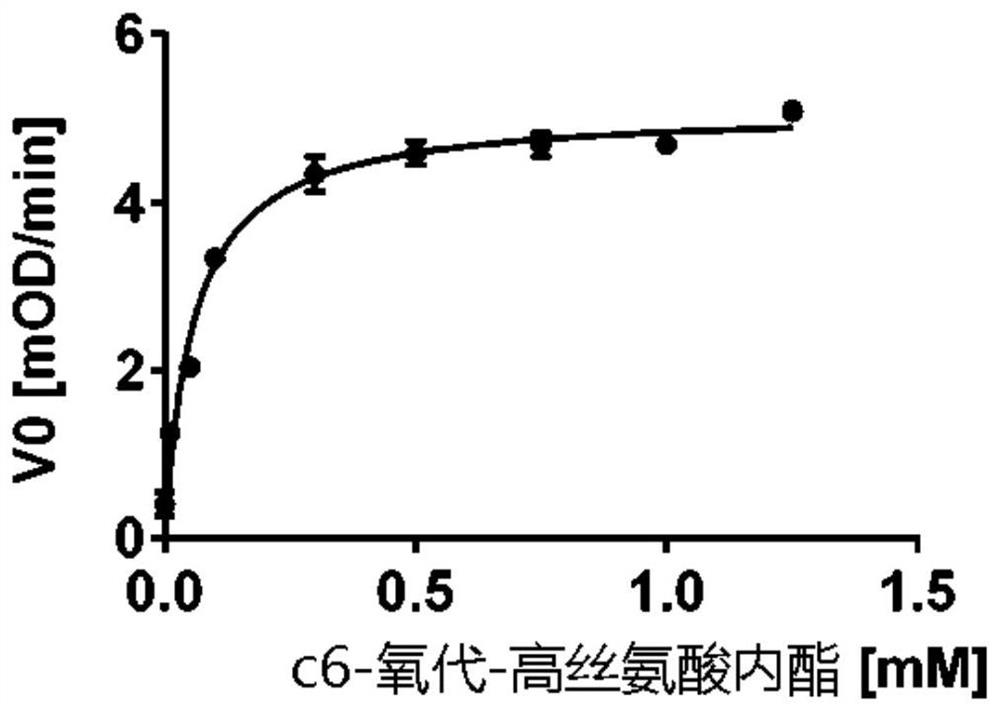
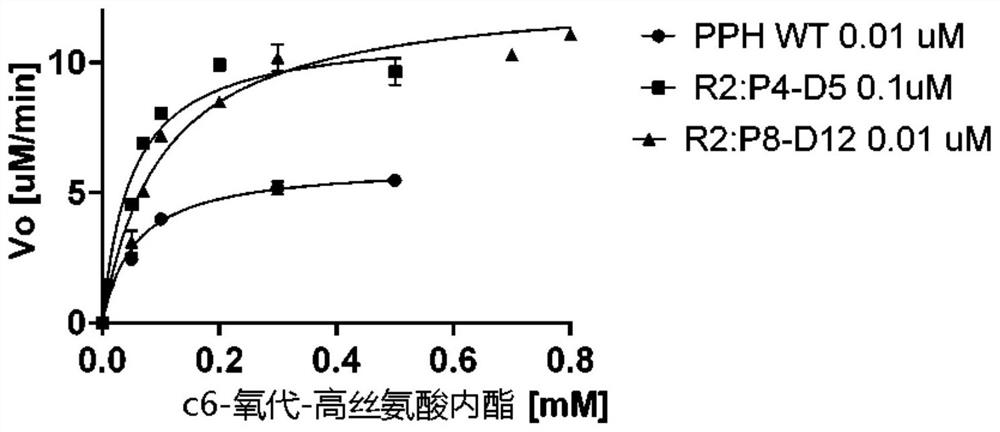
Stable mutants of quorum quenching lactonase and their use in treatment of pathogens
Provided are mutant phosphotriesterase-like lactonases or functional fragments thereof, as well as nucleic acid molecules and vectors encoding the same. Furthermore, in addition to cells expressing the mutant phosphotriesterase-like lactonase and methods of producing them, methods of treating or preventing bacterial infections in a host, such as a plant or a portion thereof, an organ or plant propagation material, are provided, the method comprises administering to it the mutant phosphotriesterase-like lactonase or wild type enzyme.
Owner:米加尔加利里研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com