Recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum for efficiently converting straw biomass carbon source as well as construction method and application of recombinant clostridium acetobutylicum
A biomass carbon source, the technology of Clostridium acetobutylicum, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low butanol yield and production intensity, low xylose conversion efficiency, long fermentation cycle, etc., to improve butanol yield and production Intensity, promotion of butanol synthesis and metabolism, and improvement of fermentation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1: the construction of recombinant plasmid and Clostridium acetobutylicum
[0050] 1. Gene fragment synthesis and recombinant plasmid construction
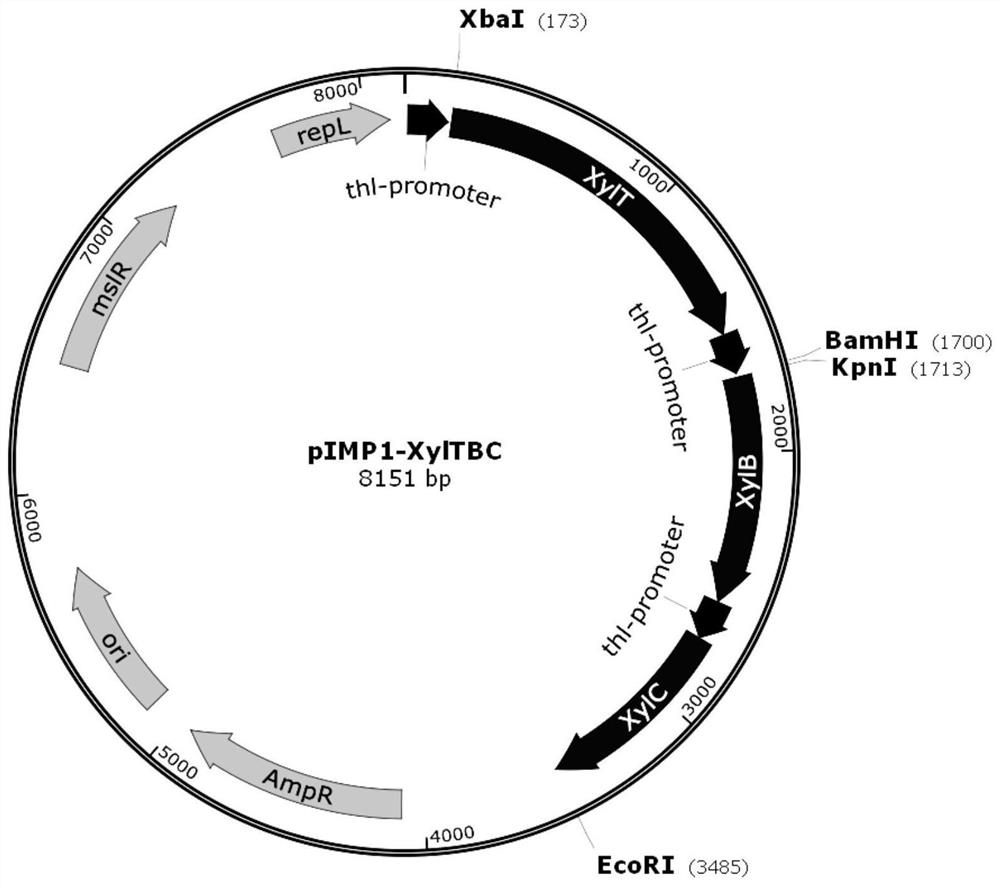
[0051] According to the information retrieved by NCBI (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / gene), the involved promoter thl, Clostridium acetobutylicum xylose transporter gene xylT, Caulobacter crescentus xylose dehydrogenase and The sequence information of the xylolactonase-encoding genes xylB and xylC is shown below. The gene fragments xylT-thl and xylB-thl-xylC were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., where xylB-thl-xylC selects the enzyme cleavage site Point KpnI / EcoRI into the vector plasmid pIMP1 [Mermelstein L.D., Welker N.E., Bennett G.N., Papoutsakis E.T. Expression of cloned homologous fermentative genes in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824.Nature Biotechnology, 1992,10(2):190-5.], xylT-thl Select restriction site XbaI / BamHI to connect into vector plasmid pIMP1. It was verified by enz...
Embodiment 2
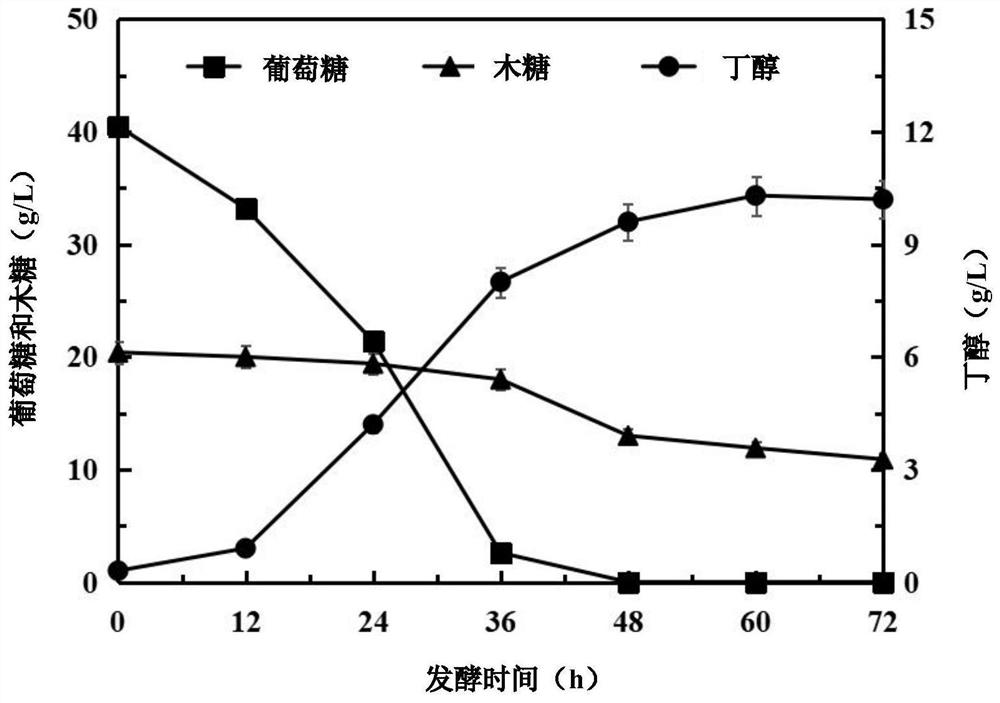
[0063]Example 2: Comparison of glucose and xylose fermentation between the control strain Clostridium acetobutylicum and the recombinant strain Clostridium acetobutylicum TXYL under uncontrolled pH conditions
[0064] Specifically, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0065] 1. Activation culture: Inoculate the recombinant strain Clostridium acetobutylicum TXYL constructed in Example 1 and the control strain Clostridium acetobutylicum into the liquid activation medium (the experimental group contains erythromycin resistance) respectively, and place them in an anaerobic environment for static cultivation , the culture temperature is 37°C, and the static activation culture is used for seed culture for 24 hours;
[0066] 2. Seed culture: the activated bacterial classification in step 1 is inoculated in the liquid seed culture medium (the experimental group contains erythromycin resistance) by 10% (v / v) inoculum, and placed in an anaerobic environment for shaking flask ...
Embodiment 3
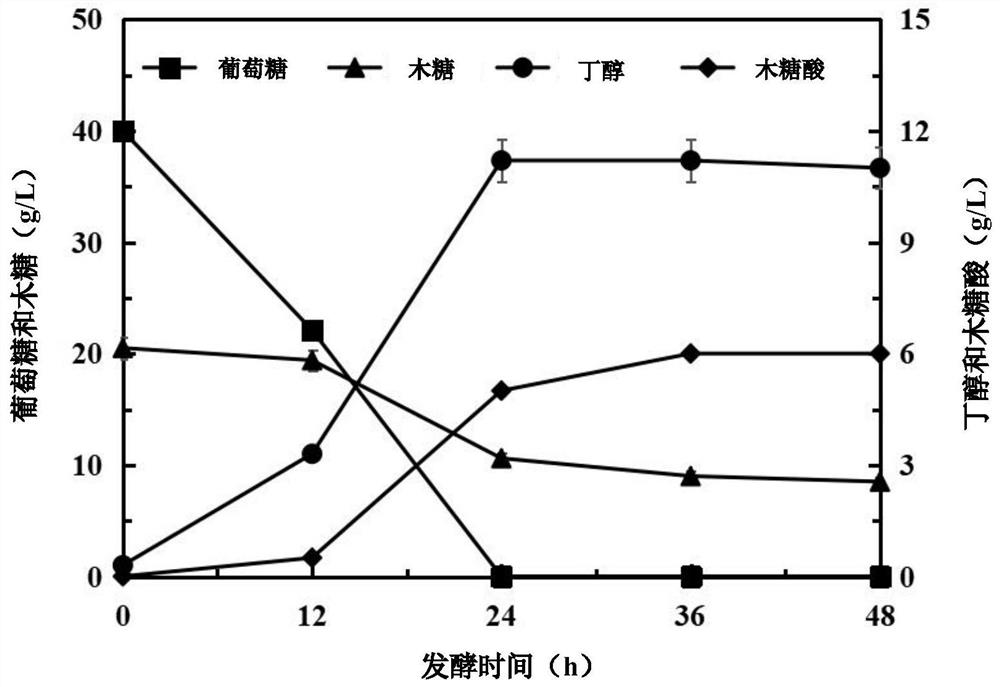
[0069] Example 3: Under the condition of adding 10g / L calcium carbonate, comparison of glucose and xylose fermentation by control strain Clostridium acetobutylicum and recombinant strain Clostridium acetobutylicum TXYL
[0070] Specifically, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0071] 1. Activation culture: the same as the activation culture step in Example 2.
[0072] 2, seed cultivation: with the seed cultivation step of embodiment 2.
[0073] 3. Fermentation culture: Biotec-3BG-4 fermenter (Shanghai Baoxing Biological Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd.) was used for anaerobic fermentation. Controlled at 37°C, the stirring speed was 150rpm, and the fermenter was fed with N before inoculation. 2 to remove dissolved oxygen from the fermentation medium. After inoculation, 10g / L calcium carbonate was added to control the pH range of 5-6 throughout the fermentation process, and the fermentation was carried out for 72 hours.
[0074] Figure 4 The control strain Clost...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com