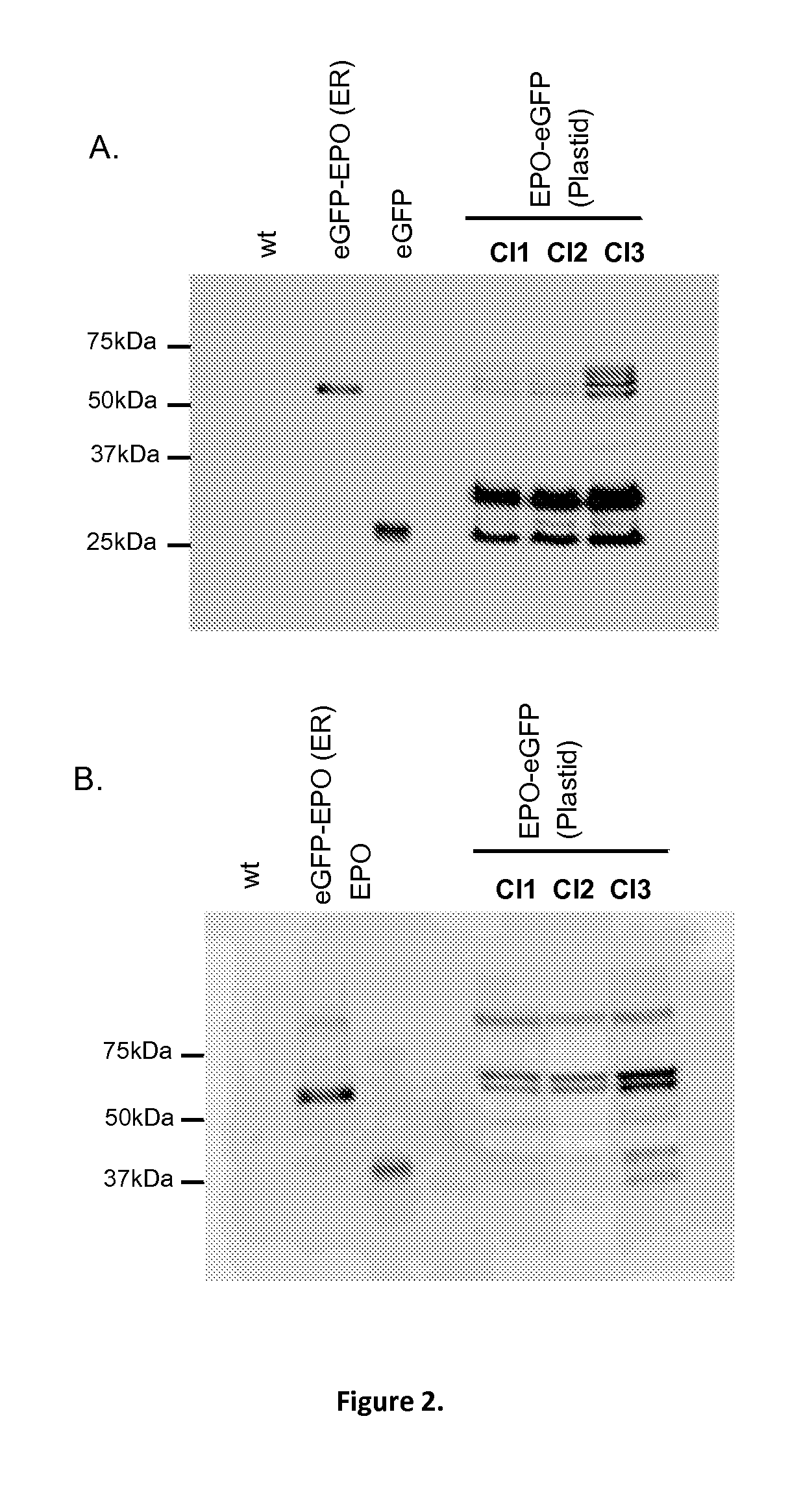
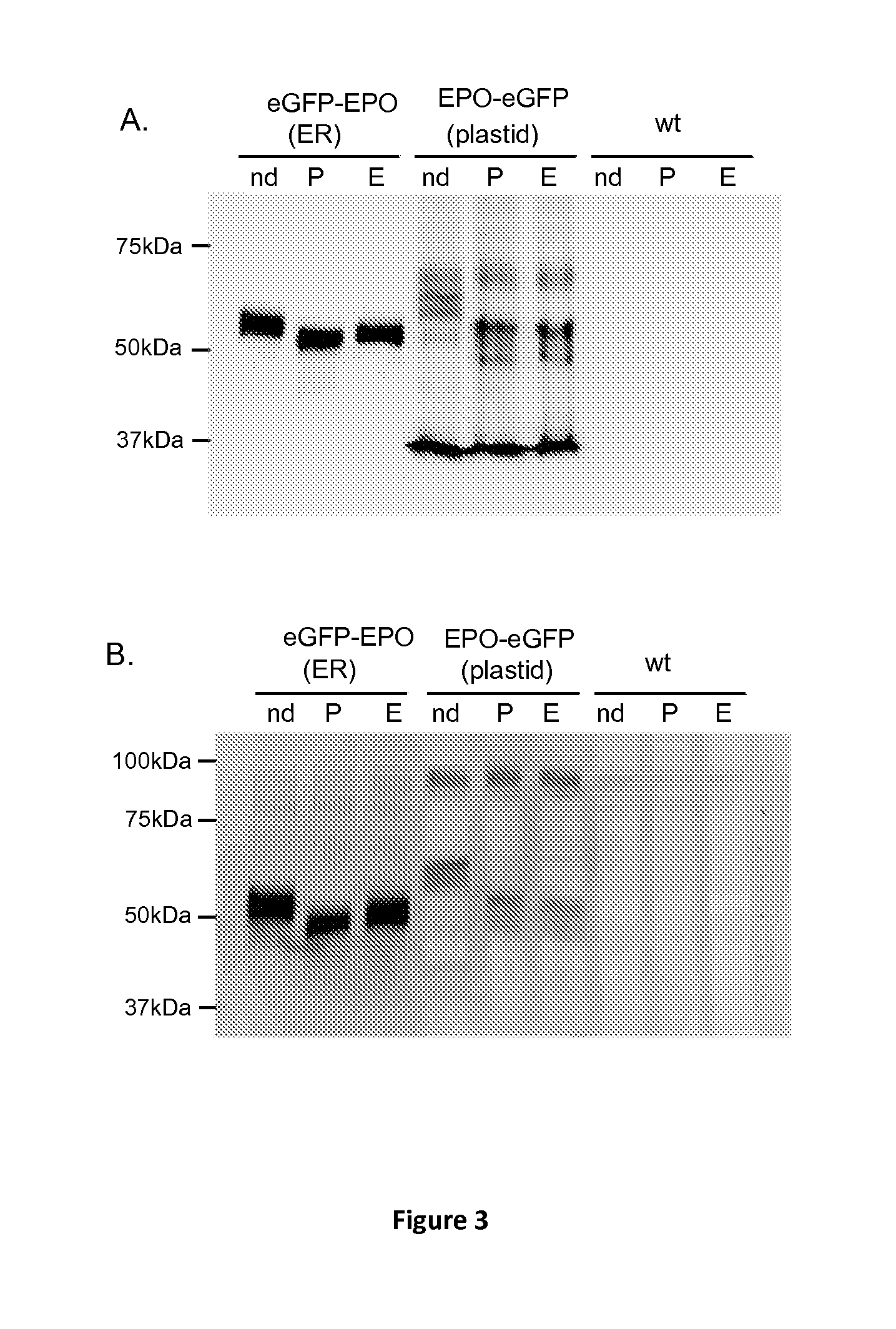
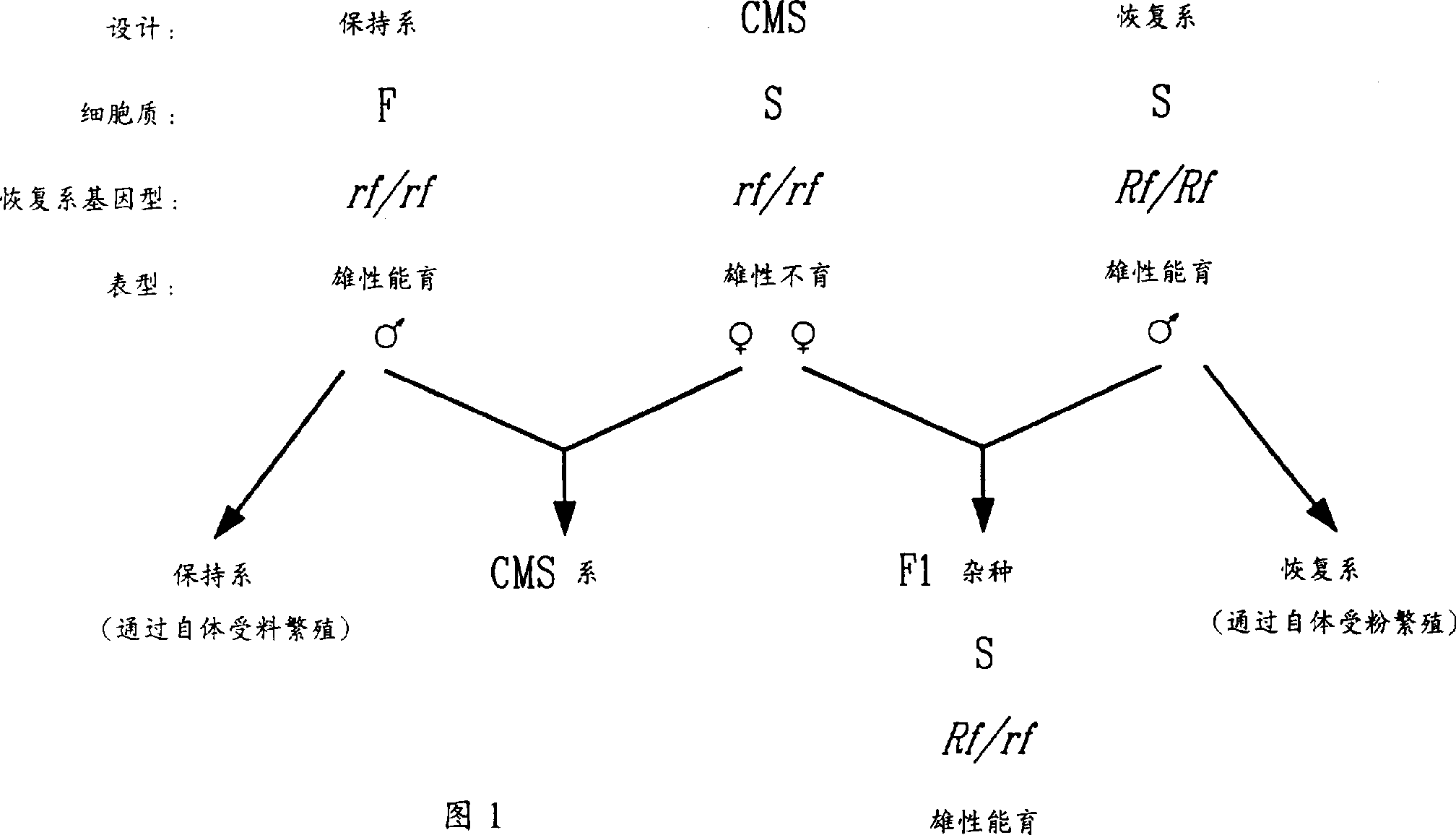
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Transit Peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The N-terminal sequence of a protein that is required to direct the localization of a cytoplasmic protein to a subcellular membrane-bound organelle.
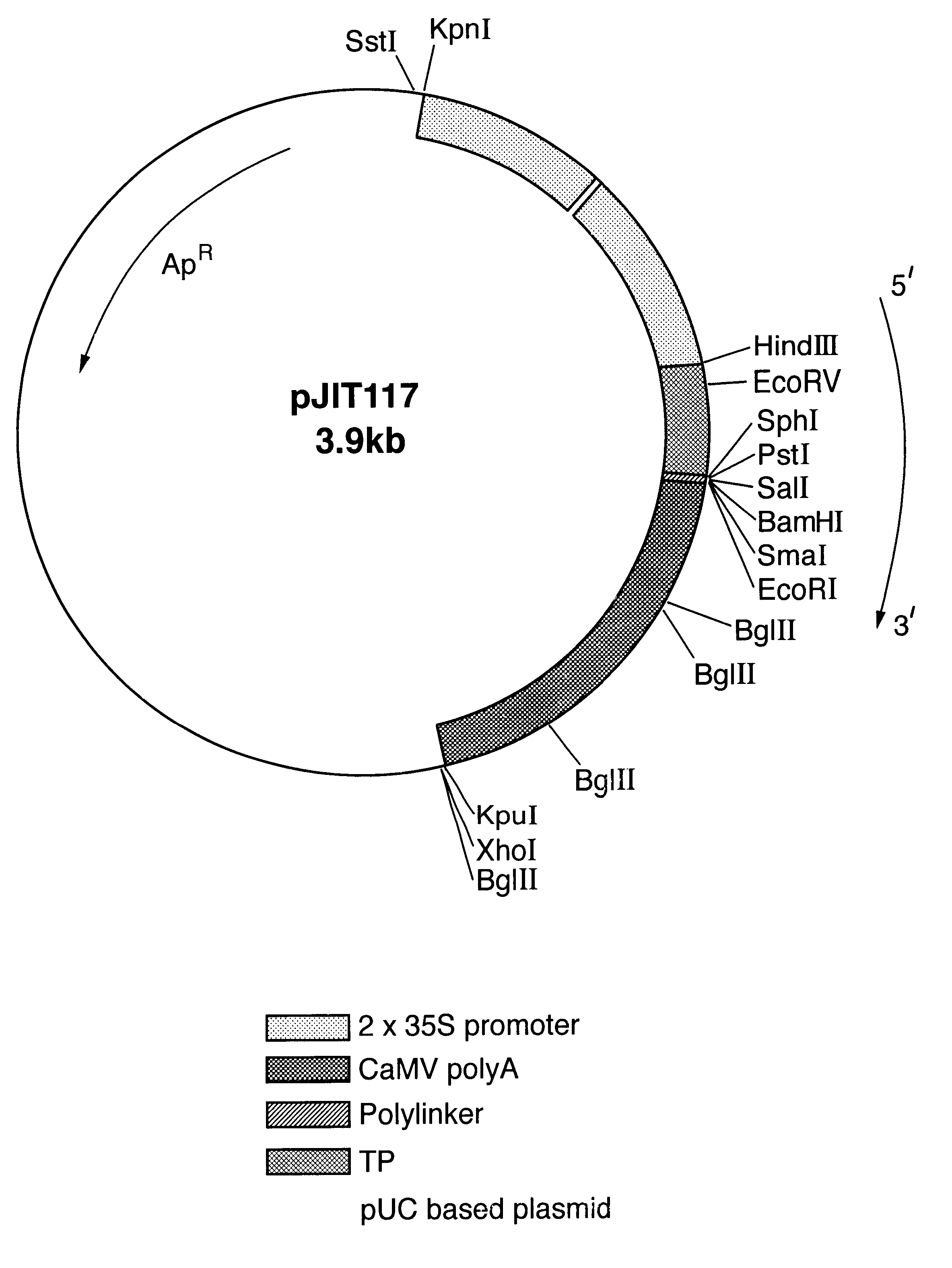
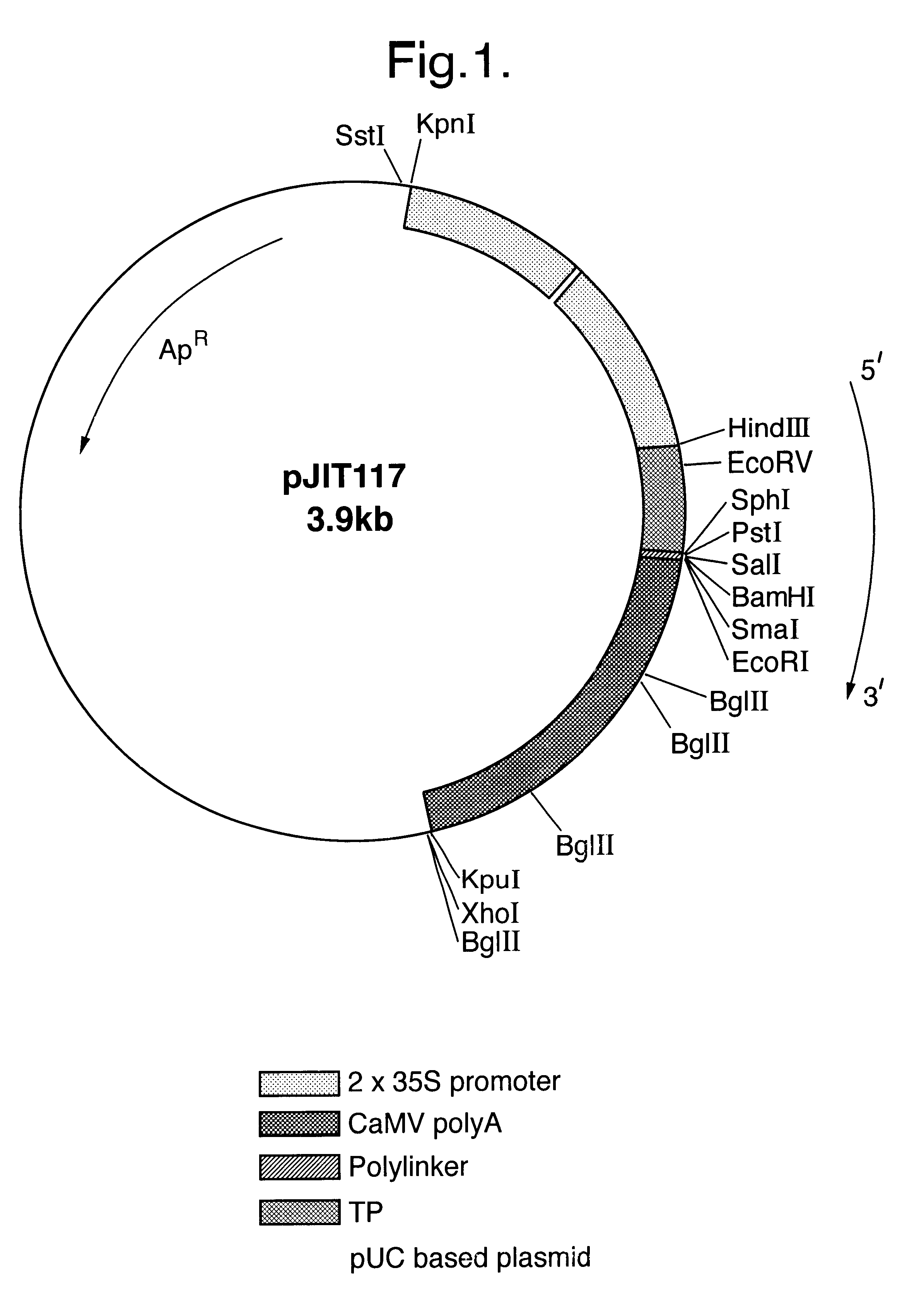
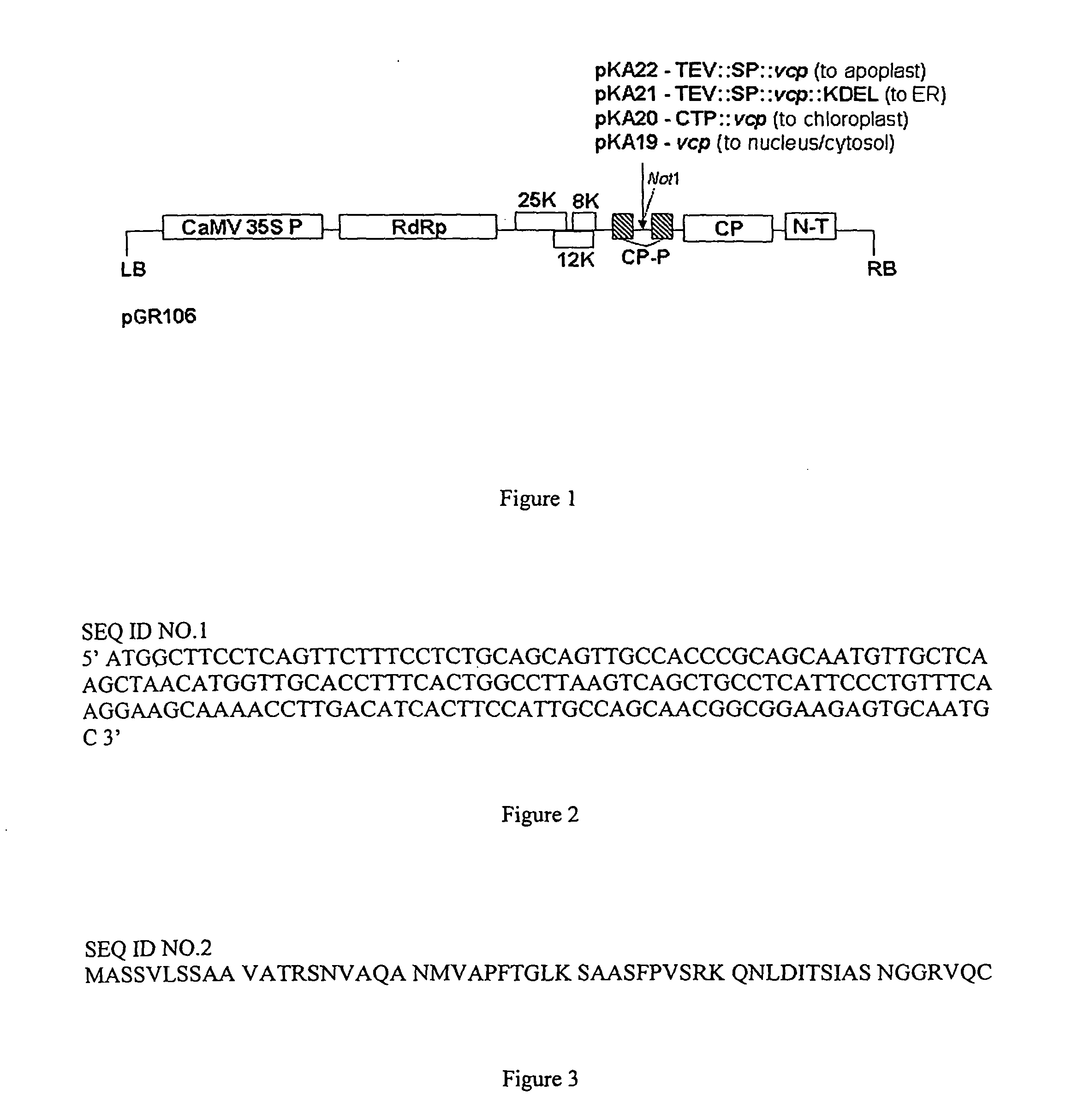
Chimeric gene for the transformation of plants
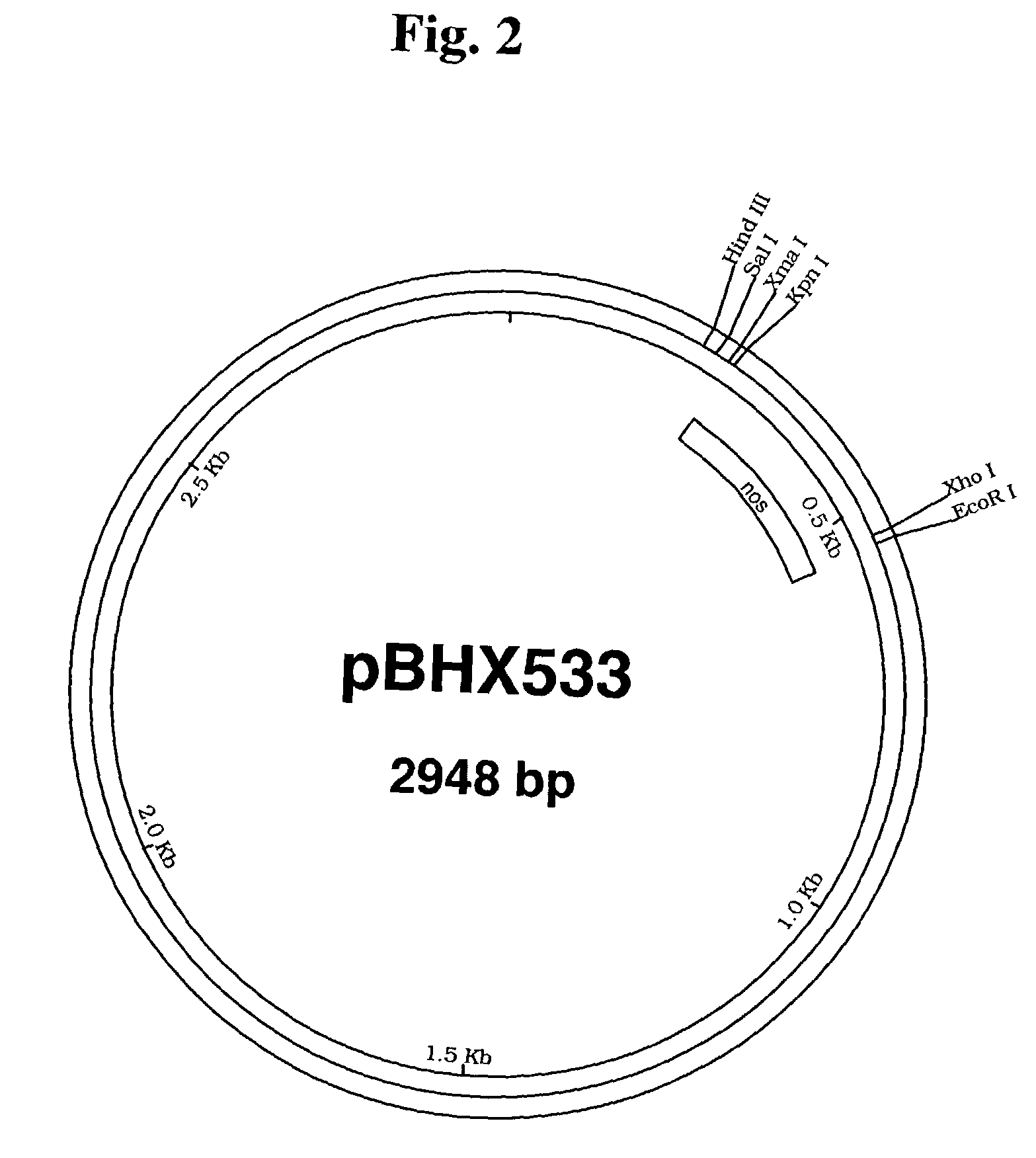
InactiveUSRE37287E1Most efficientPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationIncreased tolerance
Chimeric gene for conferring to plants an increased tolerance to a herbicide having as its target EPSPS comprises, in the direction of transcription, a promoter region, a transit peptide region, a coding sequence for glyphosate tolerance and a polyandenylation signal region, wherein the transit peptide region comprises, in the direction of translation, at least one transit peptide of a plant gene encoding a plastid-localized enzyme and then a second transit peptide of a plant gene encoding, a plastid-localized enzyme. Production of glyphosate-tolerant plants is disclosed.
Owner:BAYER SAS
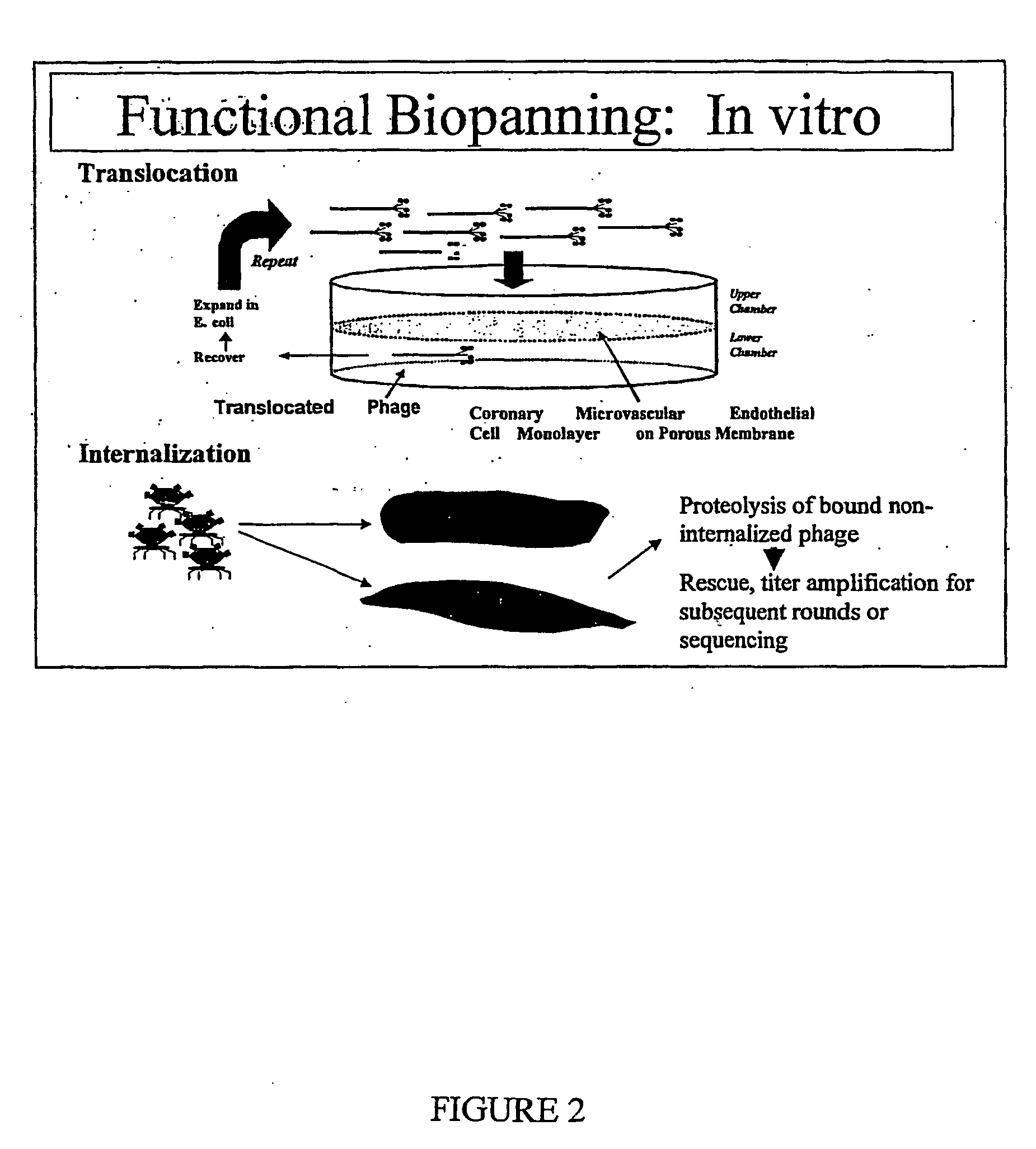
Transport agents for crossing the blood-brain barrier and into brain cancer cells, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080213185A1Facilitate entryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescence/biological staining preparationBrain cancersMethod of images
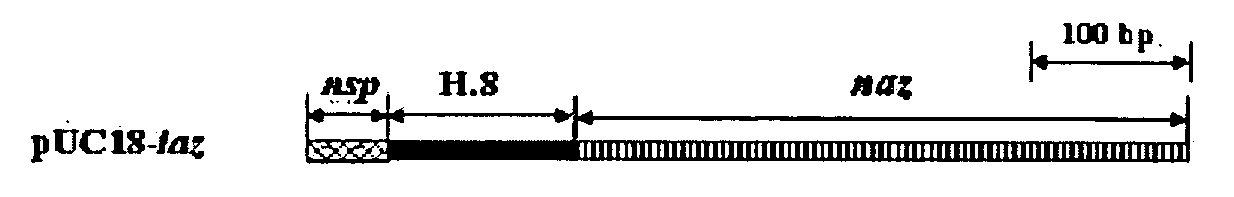
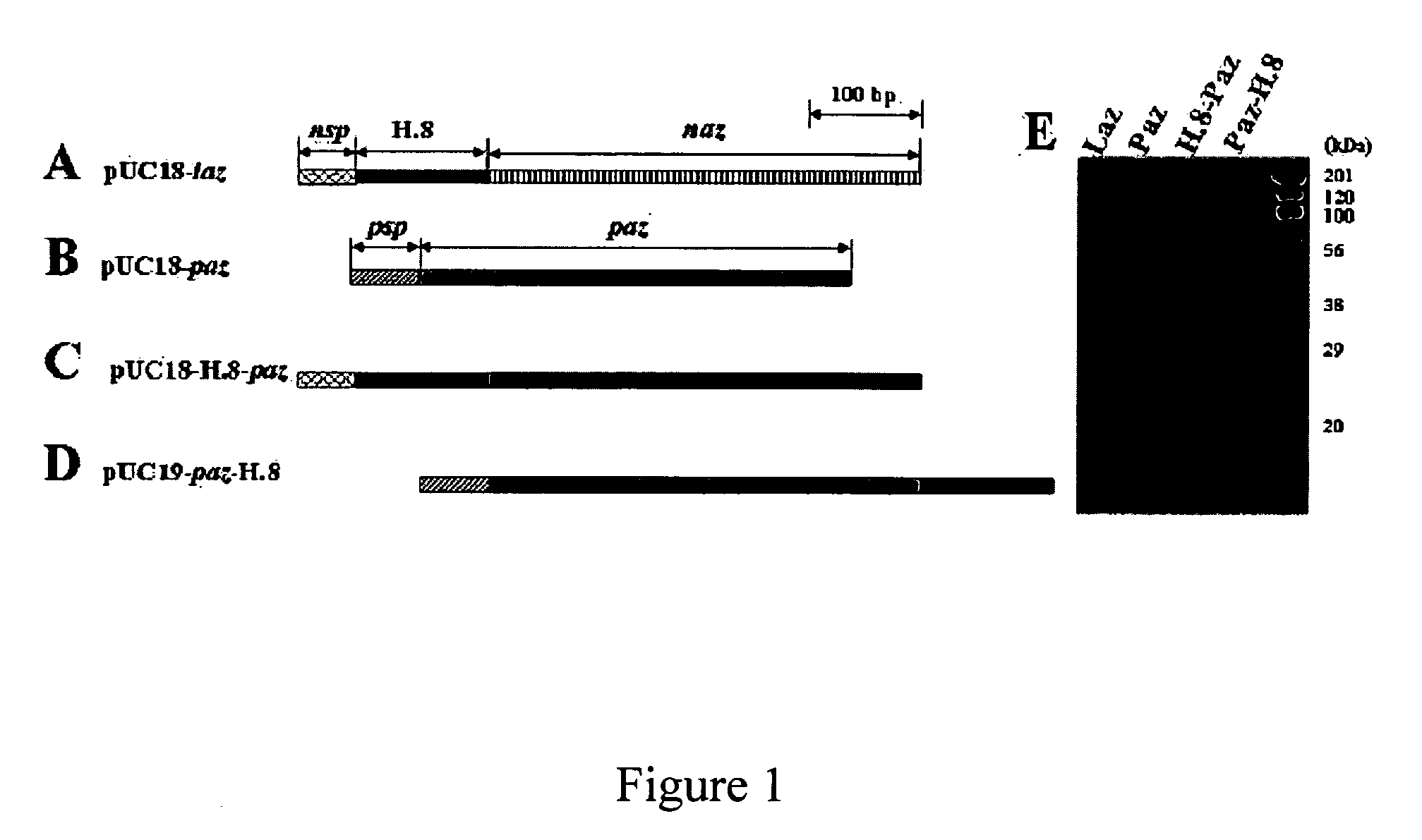
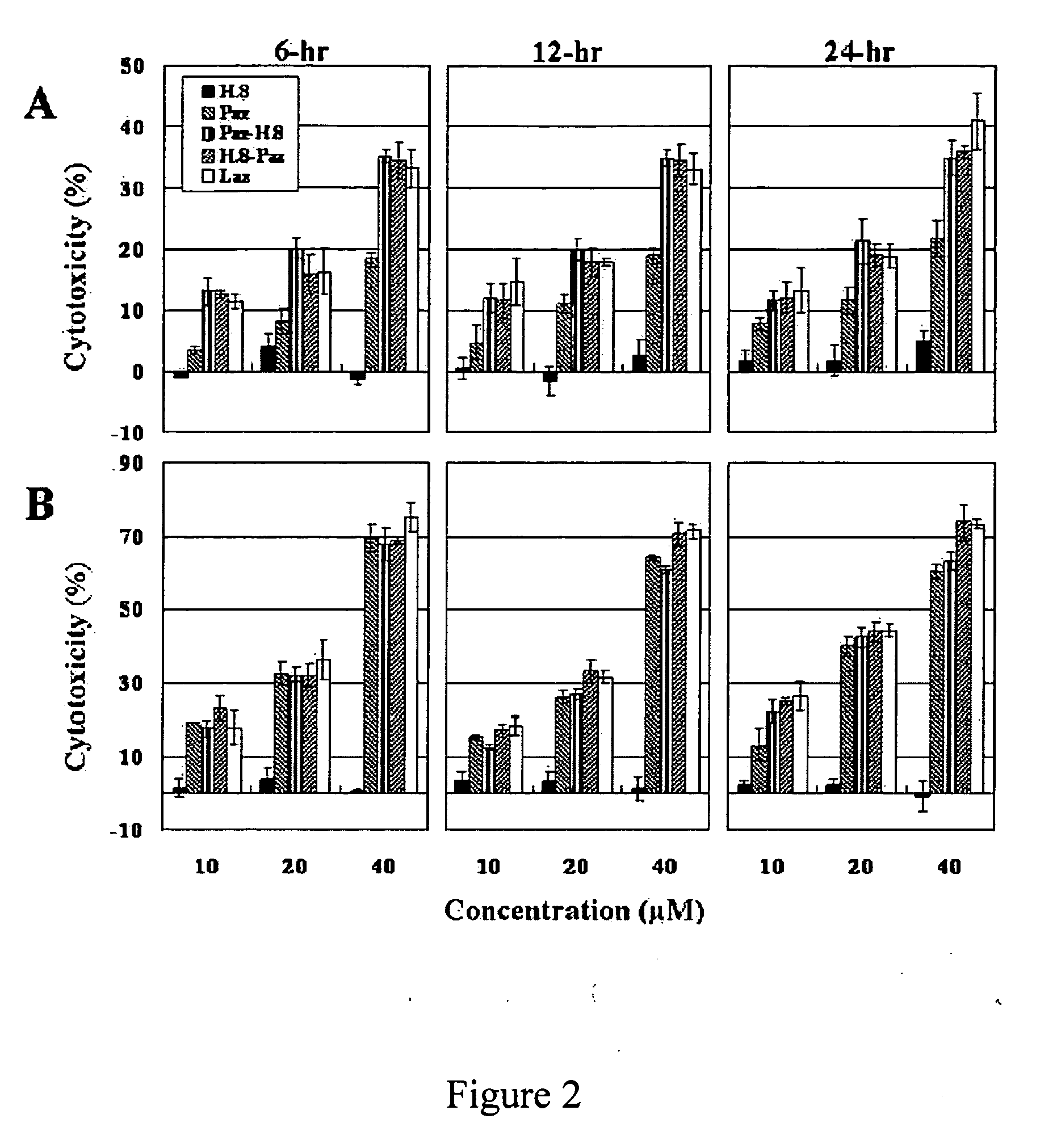
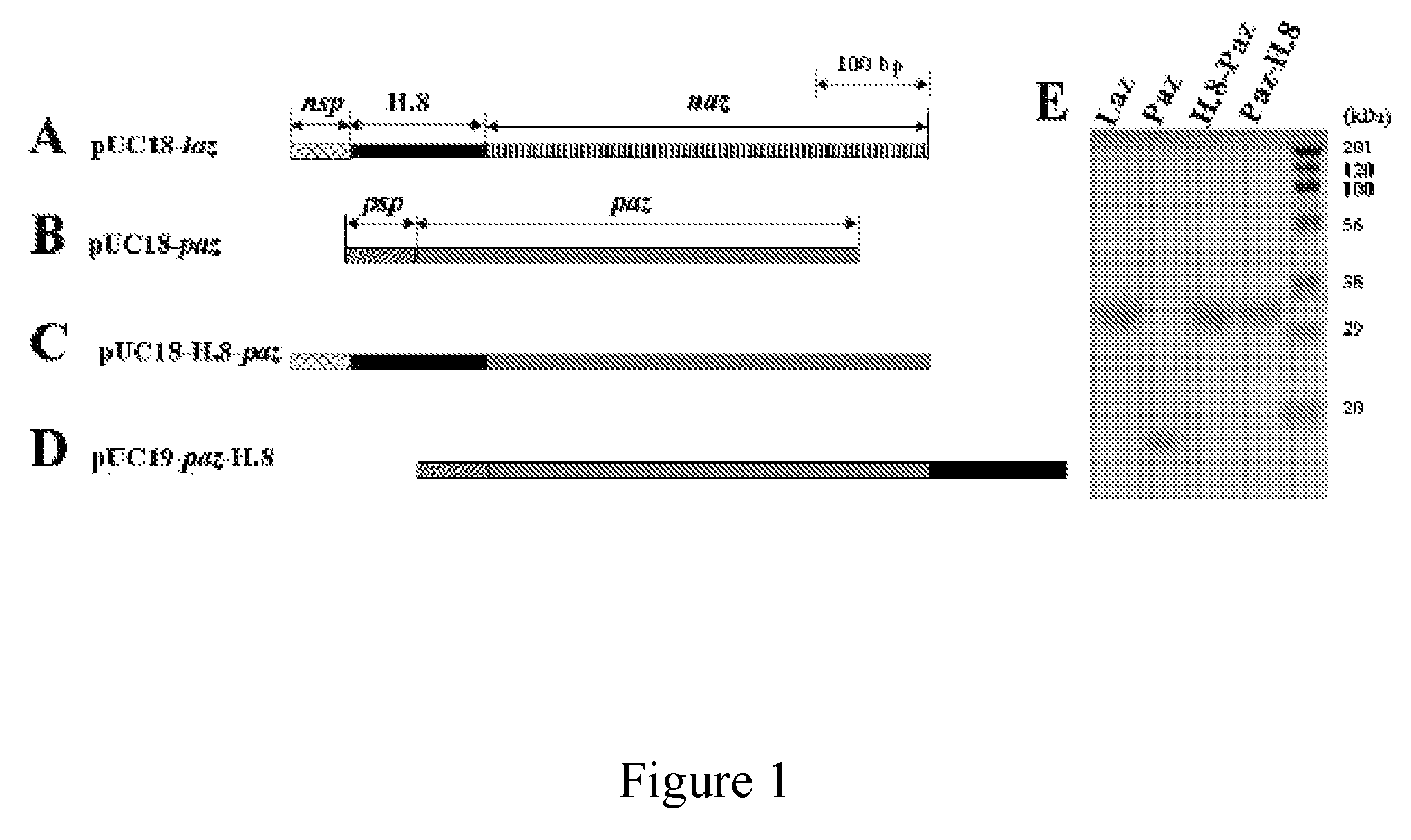
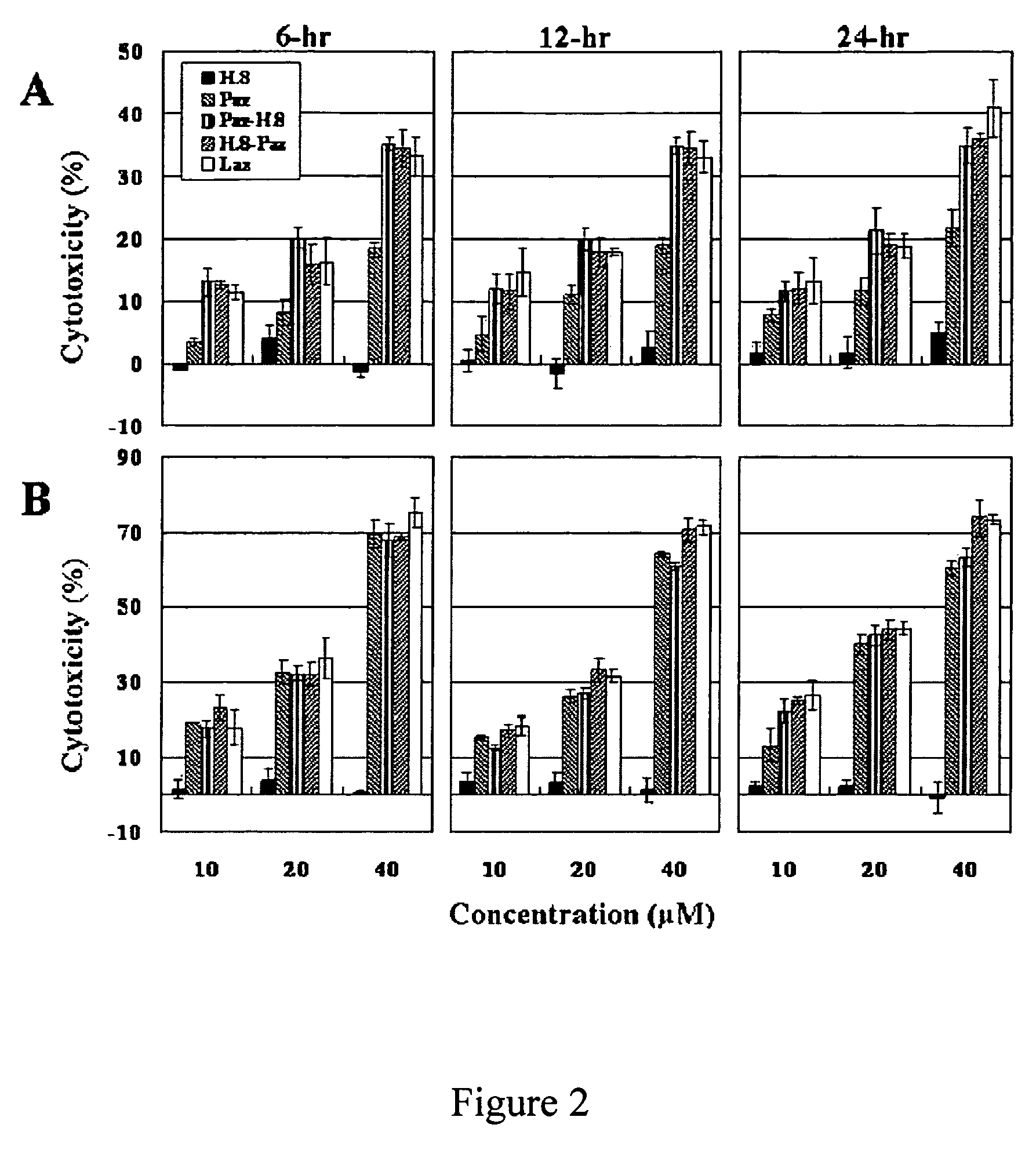
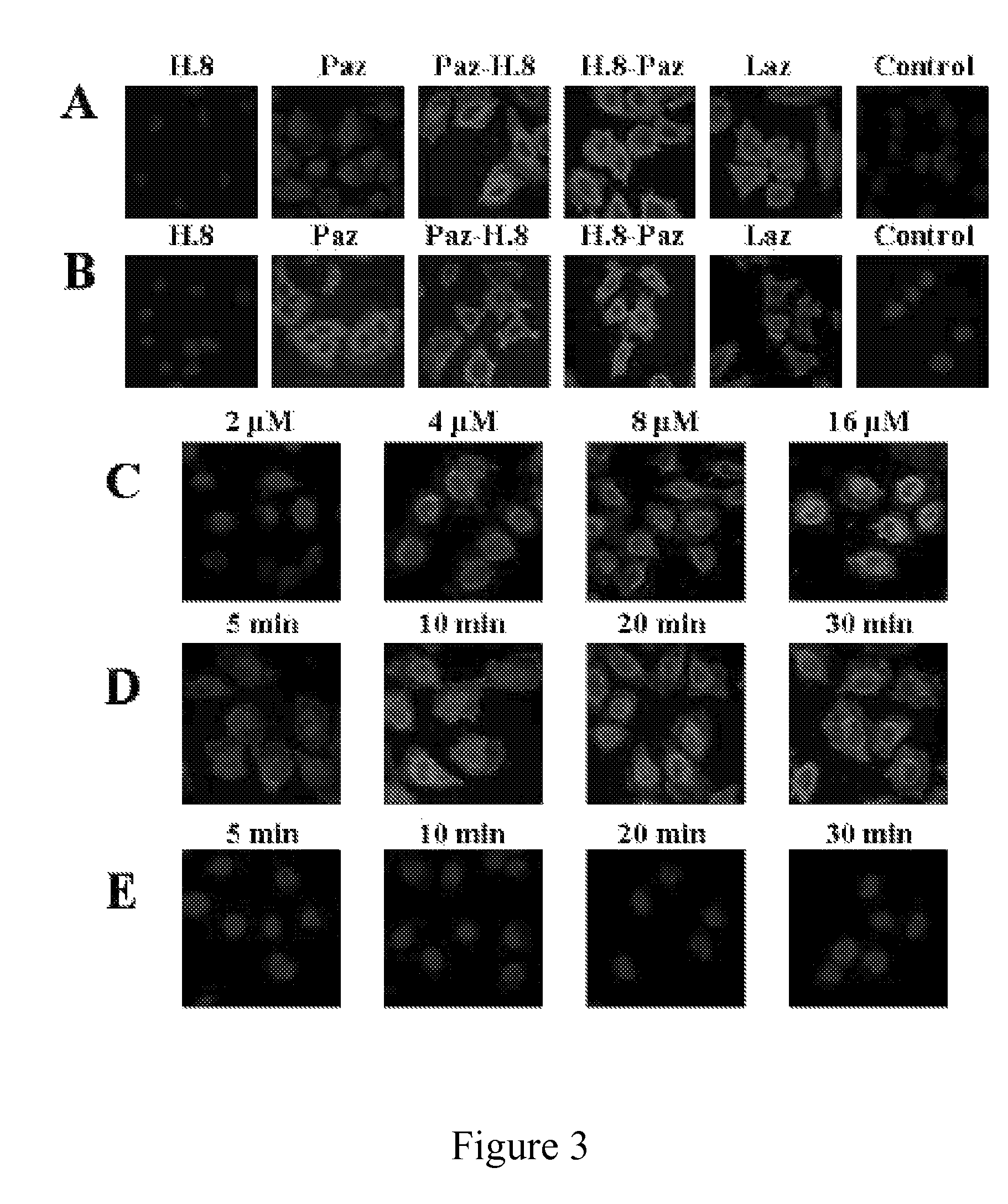
The present invention discloses methods and materials for delivering a cargo compound into a brain cancer cell and / or across the blood-brain barrier. Delivery of the cargo compound is accomplished by the use of protein transport peptides derived from Neisseria outer membrane proteins, such as Laz. The invention also provides synthetic transit peptides comprised of the pentapeptide AAEAP. The invention further discloses methods for treating cancer, and specifically brain cancer, as well as other brain-related conditions. Further, the invention provides methods of imaging and diagnosing cancer, particular brain cancer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Transport agents for crossing the blood-brain barrier and into brain cancer cells, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7807183B2Facilitate entryLuminescence/biological staining preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsBrain cancersMethod of images
The present invention discloses methods and materials for delivering a cargo compound into a brain cancer cell and / or across the blood-brain barrier. Delivery of the cargo compound is accomplished by the use of protein transport peptides derived from Neisseria outer membrane proteins, such as Laz. The invention also provides synthetic transit peptides comprised of the pentapeptide AAEAP (SEQ ID NO: 25). The invention further discloses methods for treating cancer, and specifically brain cancer, as well as other brain-related conditions. Further, the invention provides methods of imaging and diagnosing cancer, particularly brain cancer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
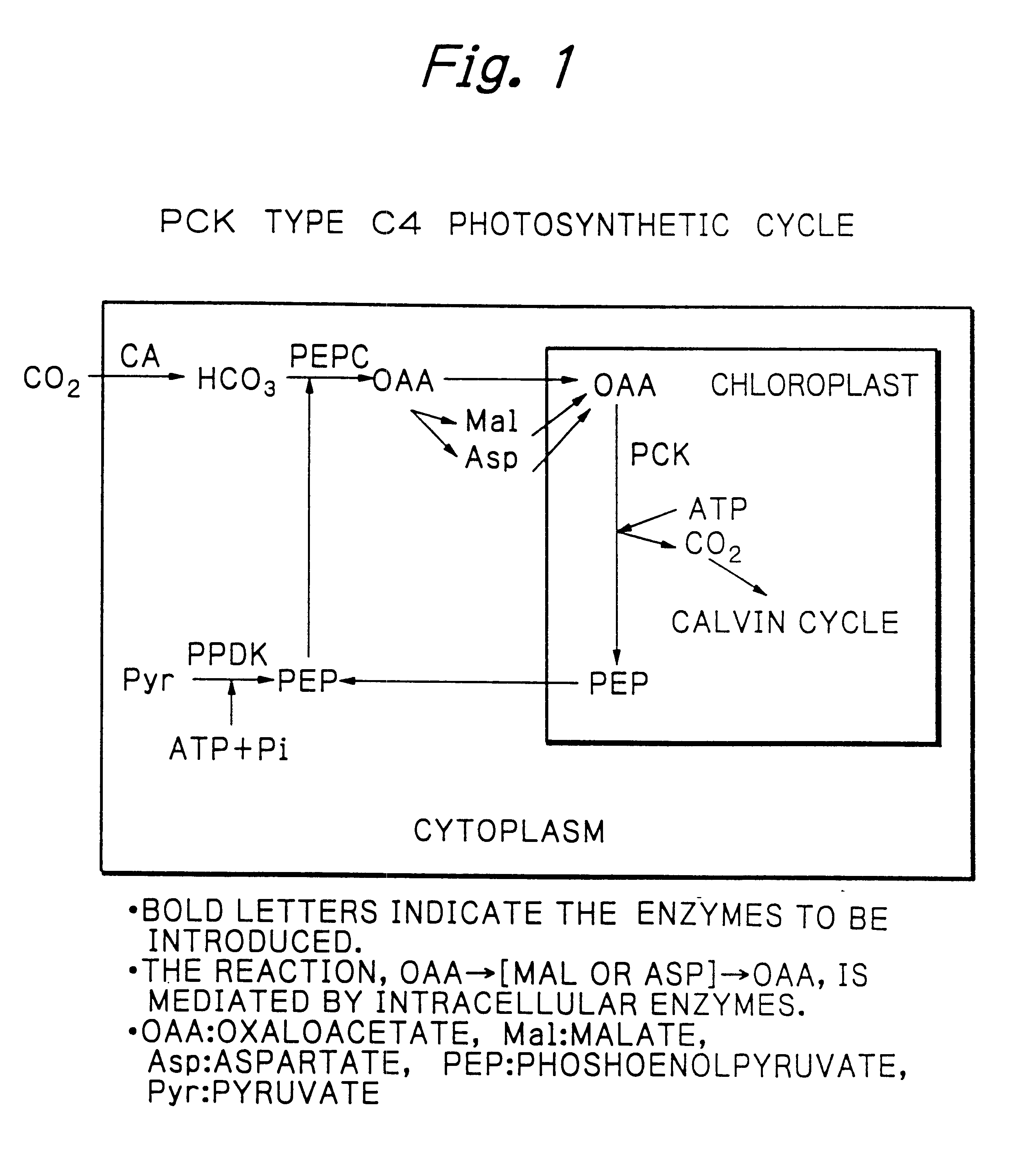
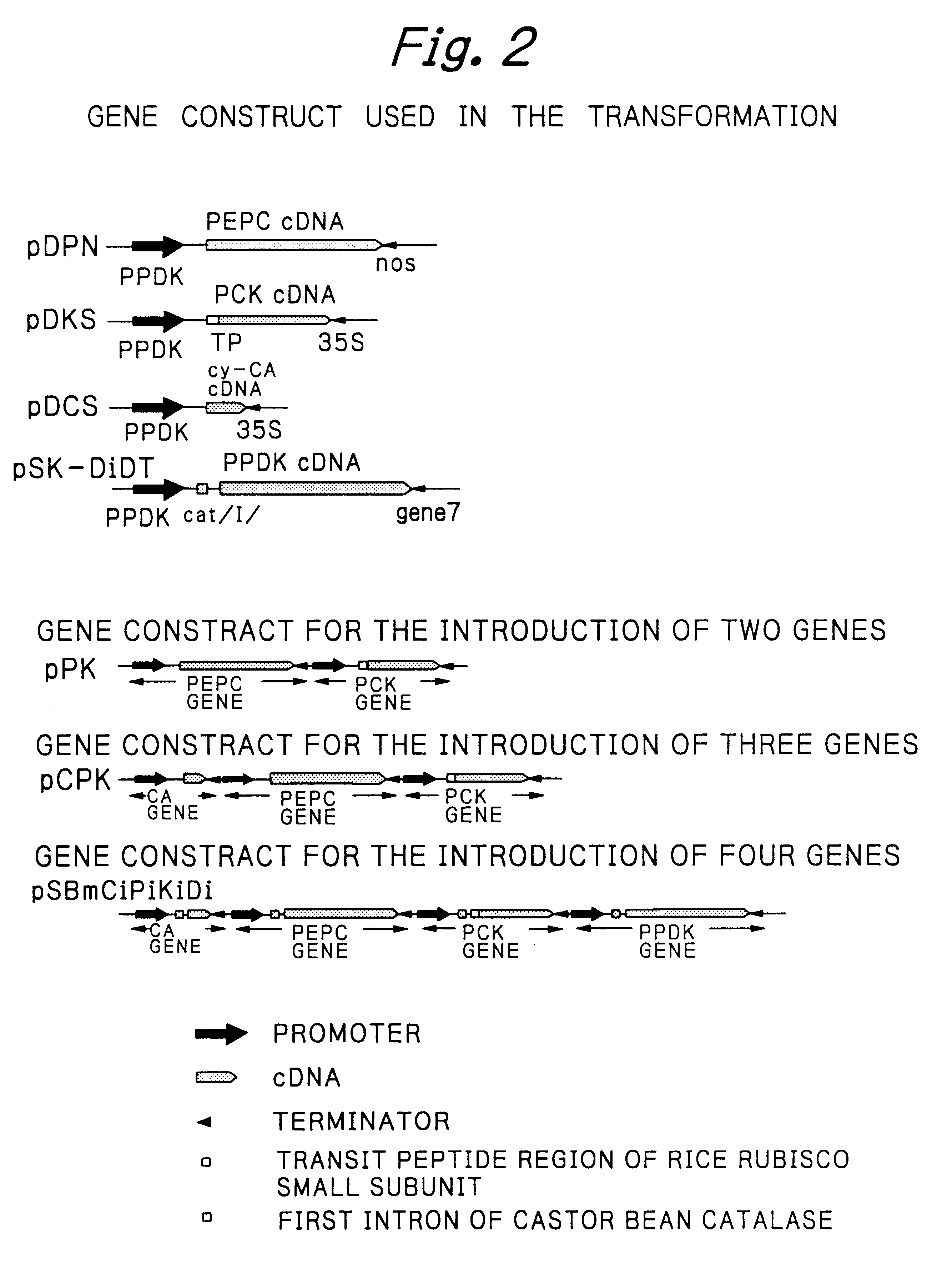
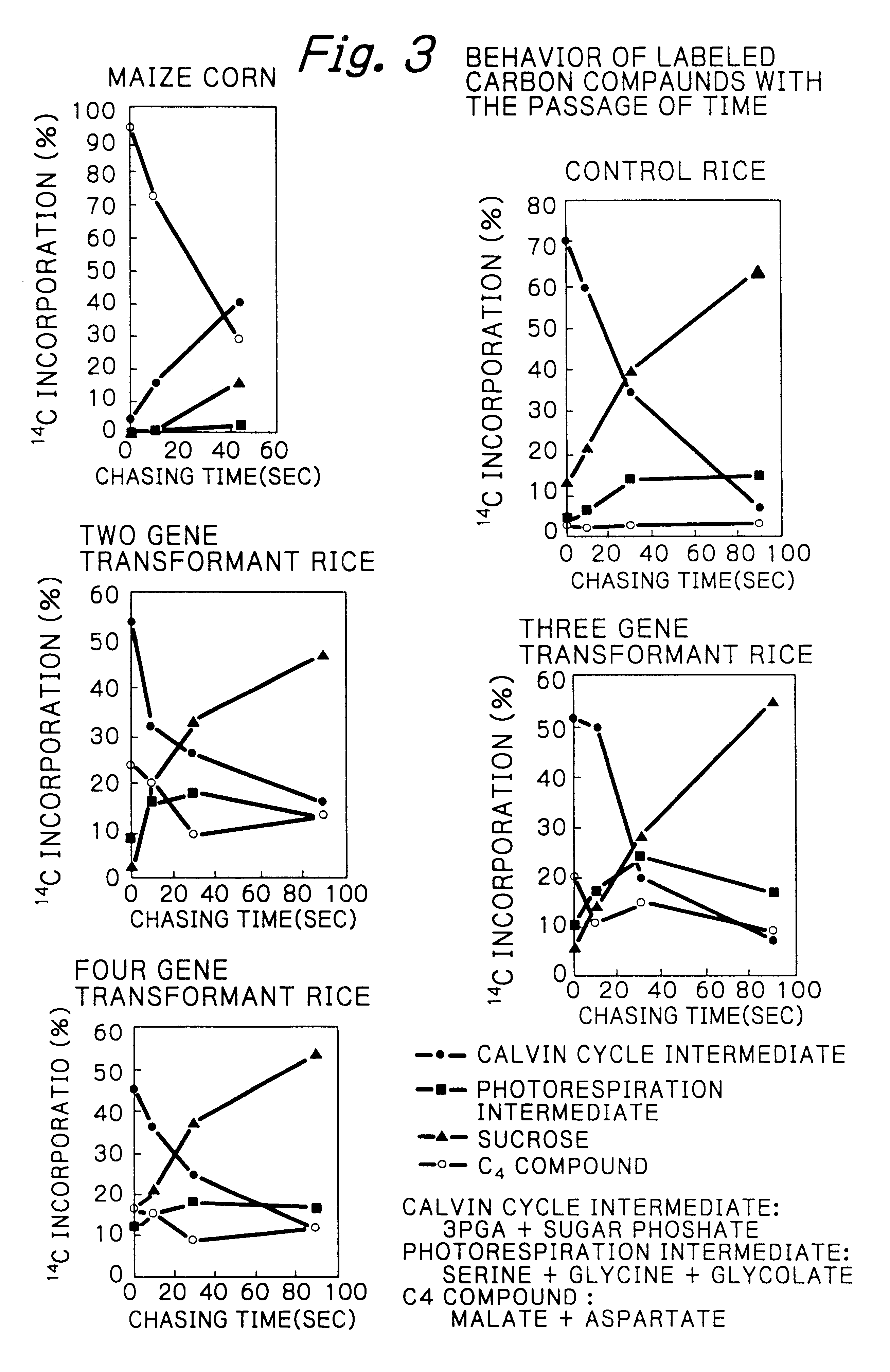
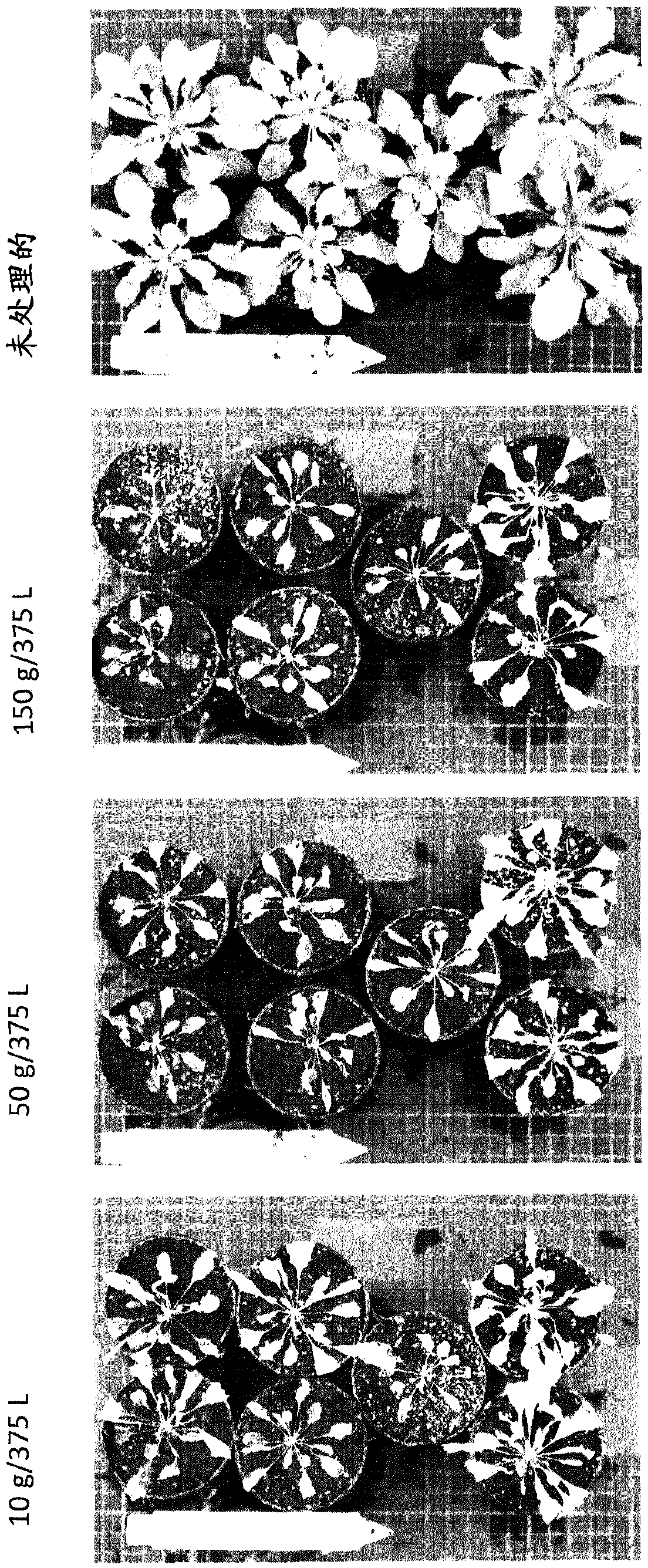
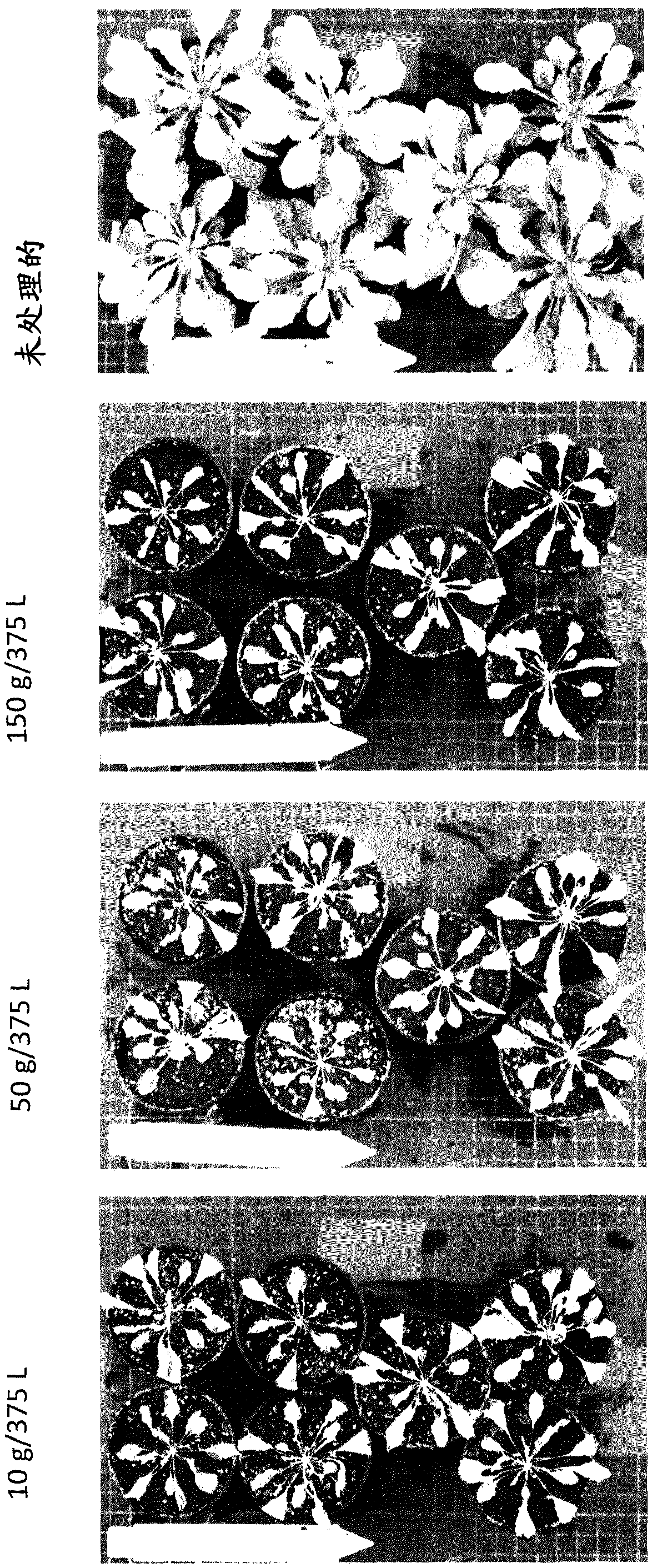
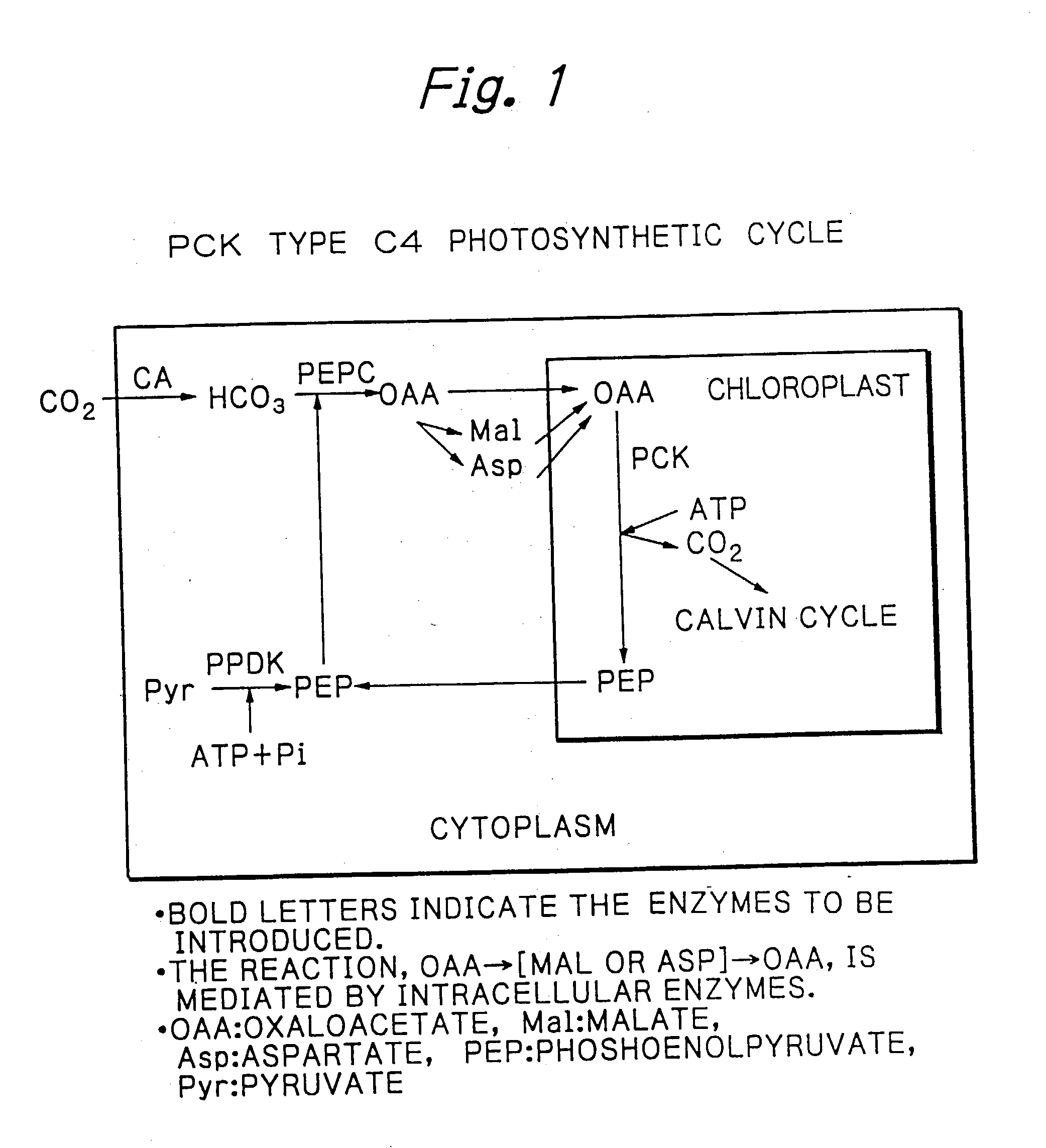
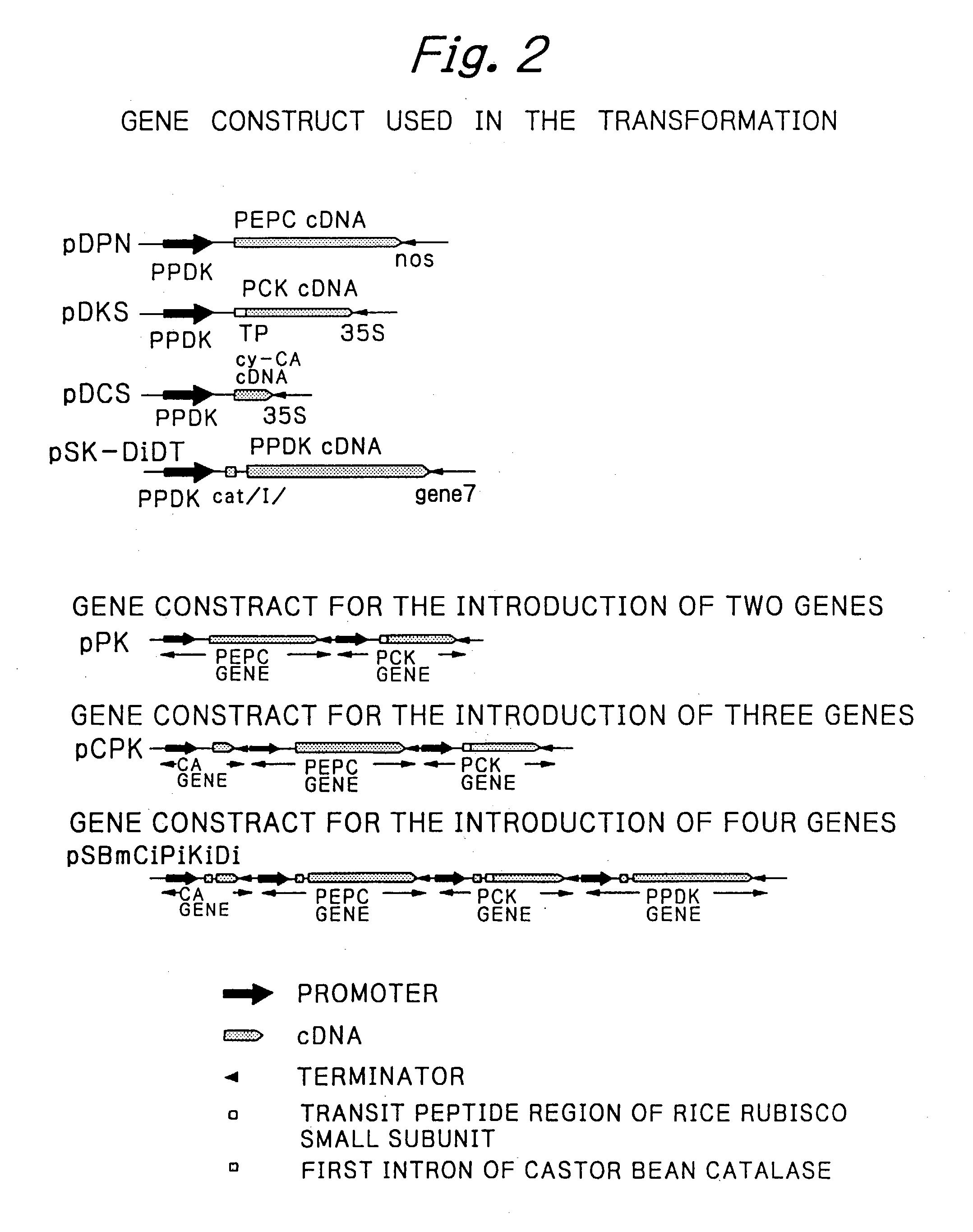
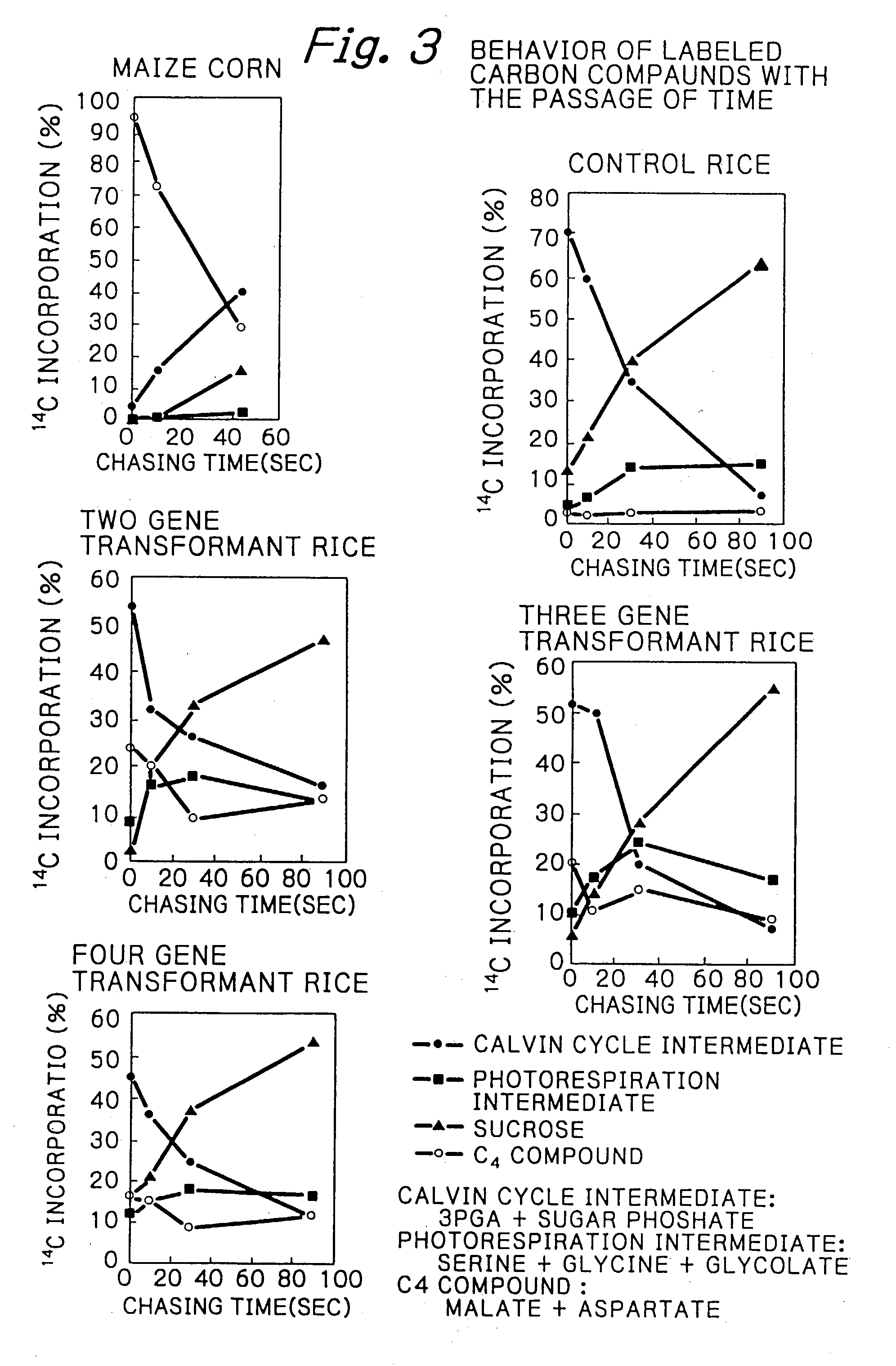
Rice plants transformed to provide a PCK-type C4 cycle and methods of making
The present invention relates a method for transforming a rice plant to provide it with a C4 photosynthetic pathway by way of the introduction of some genes participating in a C4 photosynthetic pathway. To this end, the method of the invention comprises introducing a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) and a gene coding for a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) which has been connected with a DNA fragment coding for a transit peptide into a rice plant.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Transport peptides and uses therefor
The invention describes isolated transport peptides, which cross the cell membrane of a cell and / or home to a target cell. The invention also describes a transport complex in which a transport peptide is linked to a cargo moiety to be delivered into / to a cell. Methods are disclosed describing delivery of a transport complex into and / or to a cell. Vectors and host cells comprising transport peptides and transport complexes are also described, as well as pharmaceutical compositions including transport complexes of the present invention.
Owner:YALE UNIV
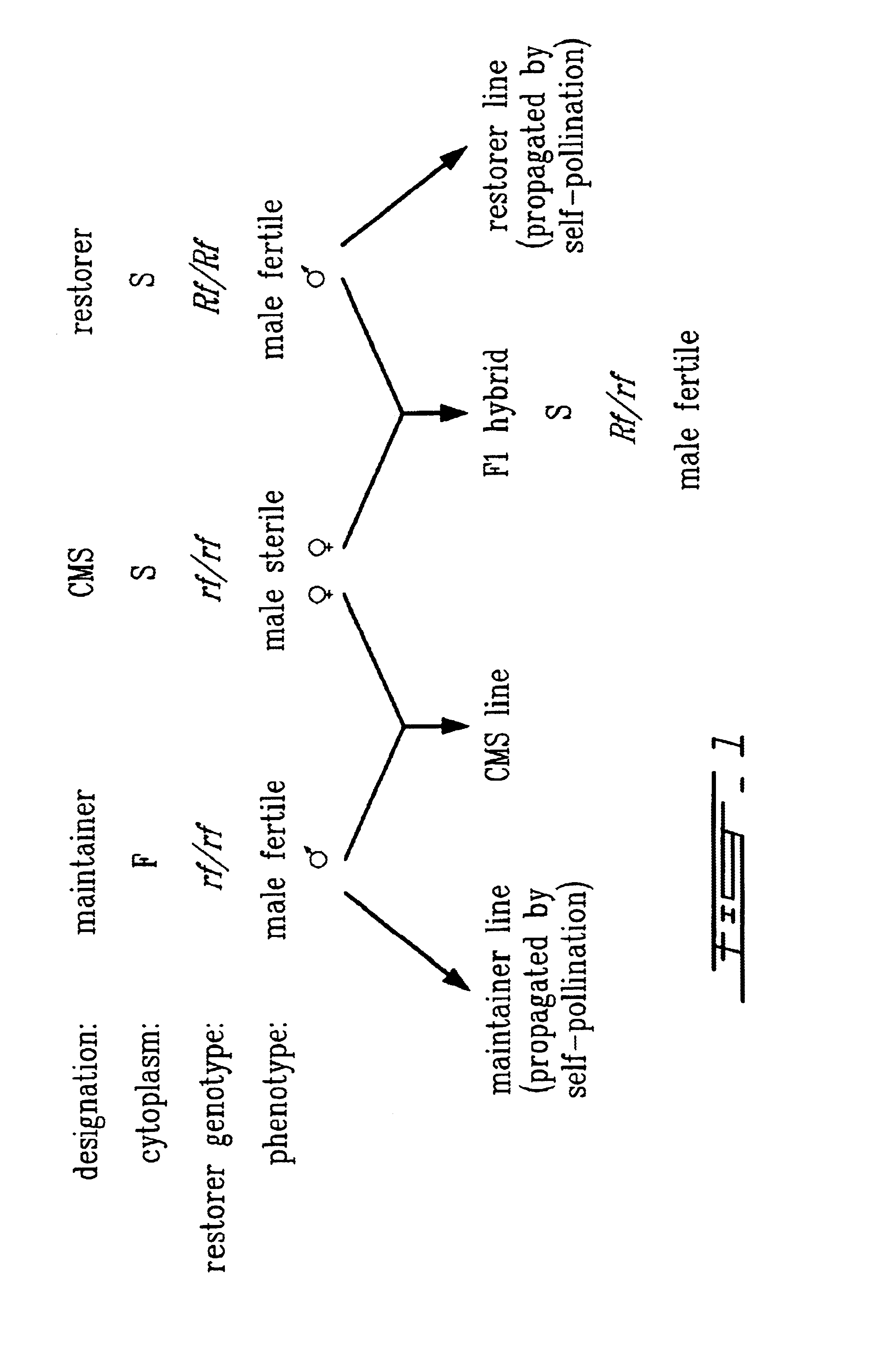
Method for enhancement of naturally occurring cytoplasmic male sterility and for restoration of male sterility and for restoration of male fertility and uses thereof in hybrid crop production
InactiveUS6951970B2Easy maintenanceShorten the timeOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesPlant cellTransit Peptide
The present invention relates to methods for enhancement of naturally occurring cytoplastic male sterility and for restoration of male fertility and uses thereof in hybrid crop production. There is also disclosed a method for restoration of male fertility to cytoplasmic male sterile plants; which comprises the steps of: a) introducing into the nucleus of a plant cell a gene construct essentially consisting of a sequence encoding a mitochondrial transit peptide fused upstream of and in frame with an edited form of a normal mitochondrial gene that is co-transcribed with an usual CMS-associated mitochondrial gene; b) selecting for plant cells that have acquired the gene construct in step a); and c) inducing regeneration of selected plant cells to produce a mature plant.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
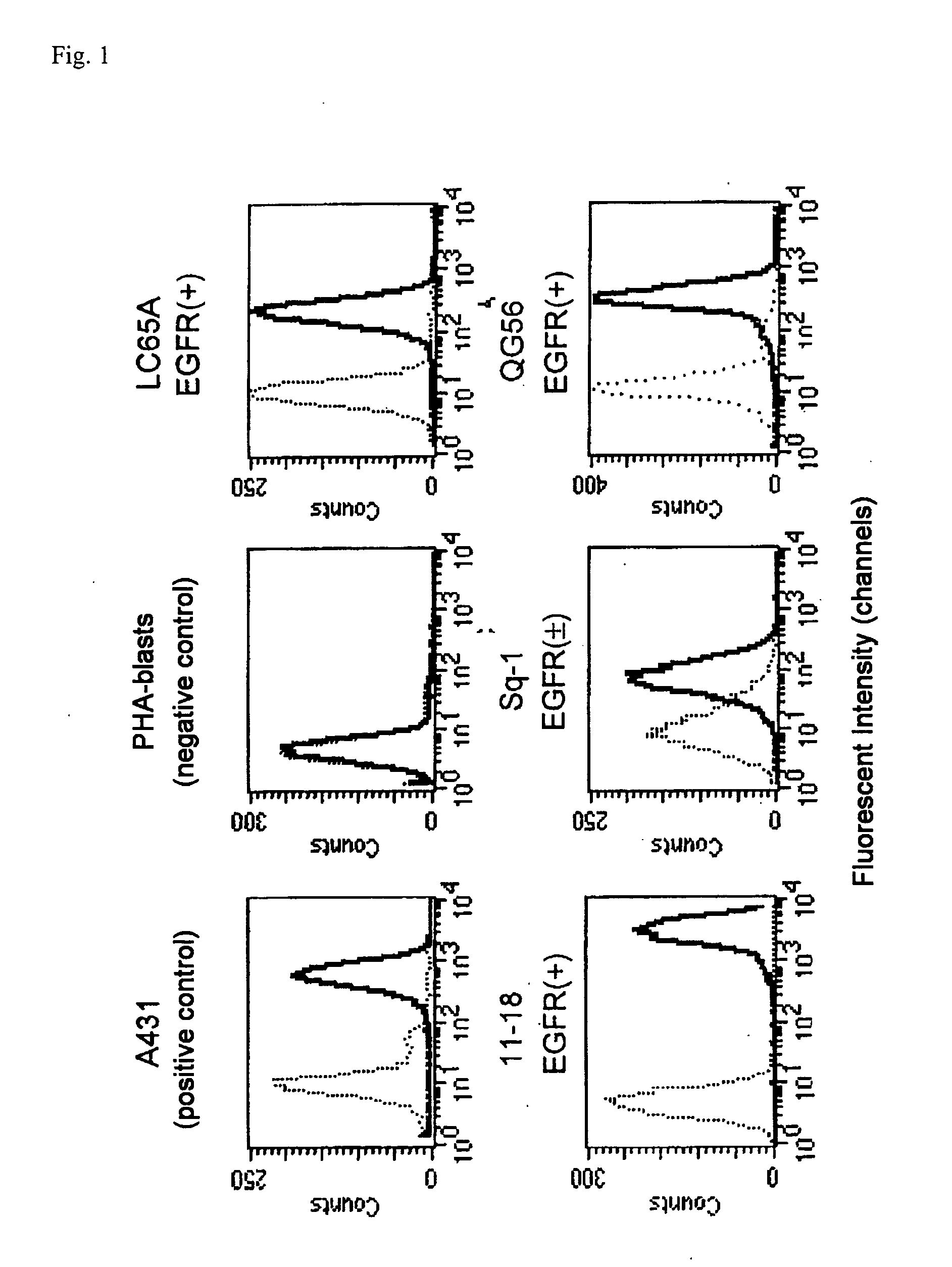
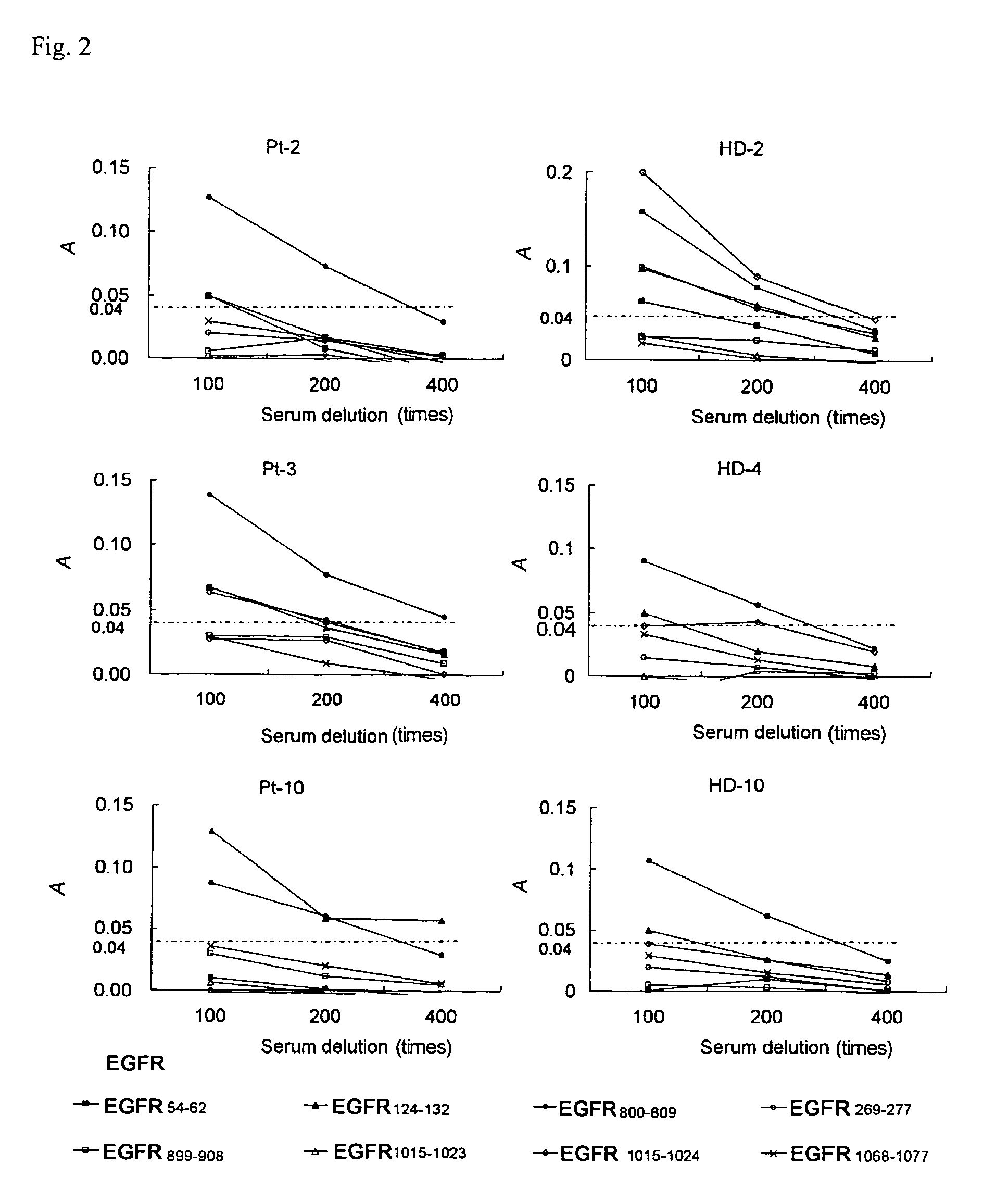
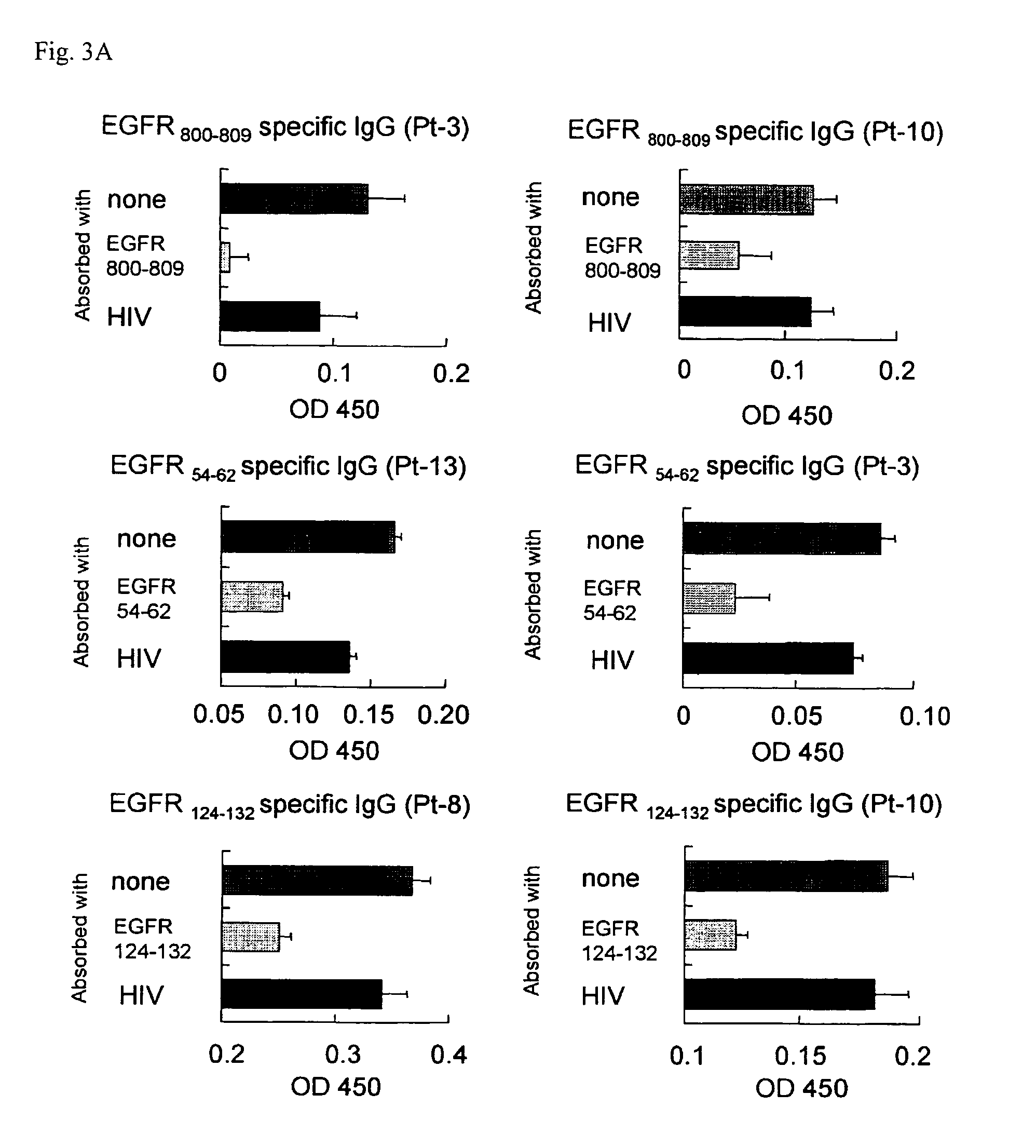
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Derived Peptides
ActiveUS20080119399A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHuman epidermal growth factor receptorTransit Peptide
The object of the invention is to provide an EGFR-derived peptide useful for EGFR-based immunotherapy.The invention provides an EGFR-derived peptide capable of inducing both cellular and humoral immune responses and mutant peptide thereof and a polypeptide comprising said peptide, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the same, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:BRIGHTPATH BIOTHERAPEUTICS CO LTD
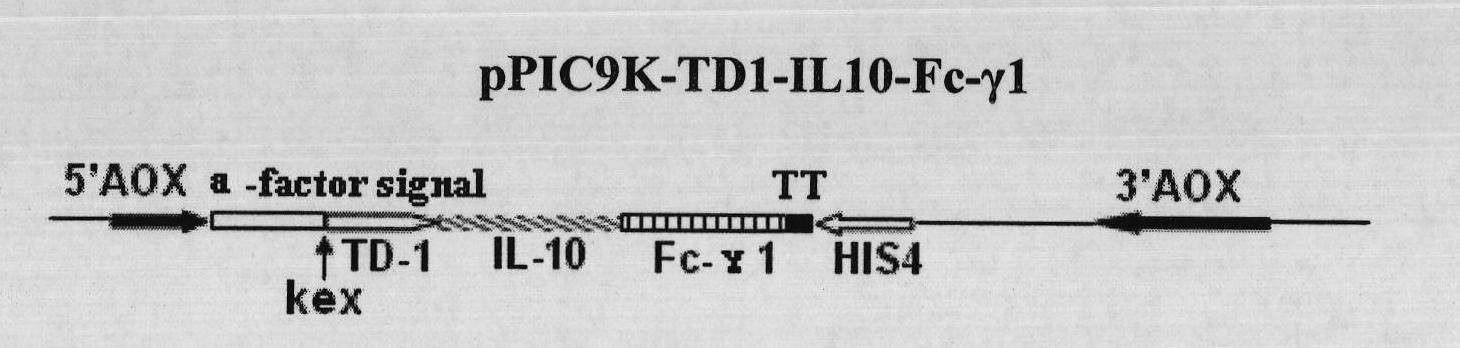
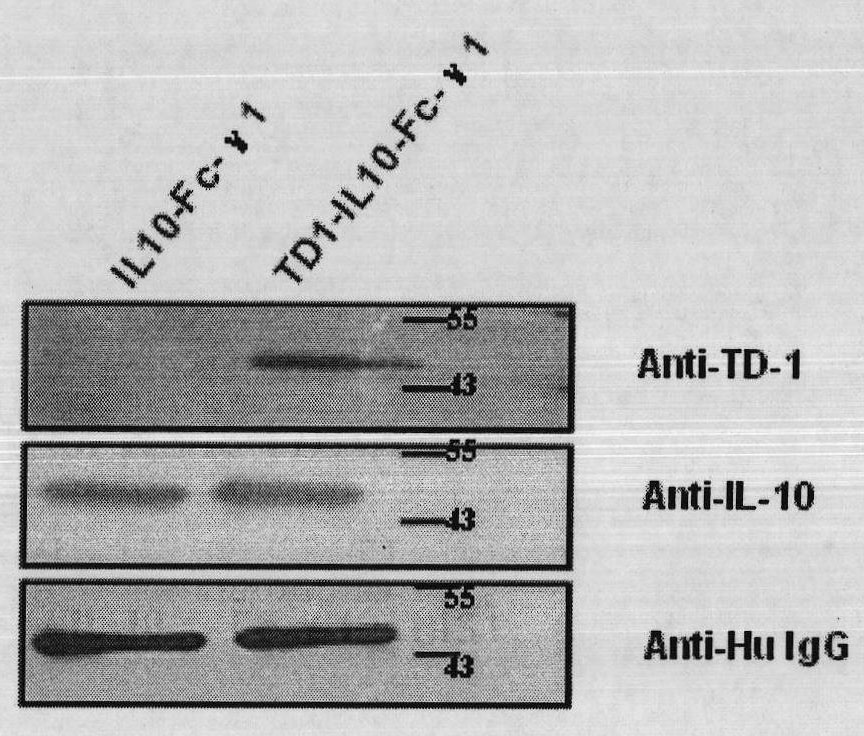
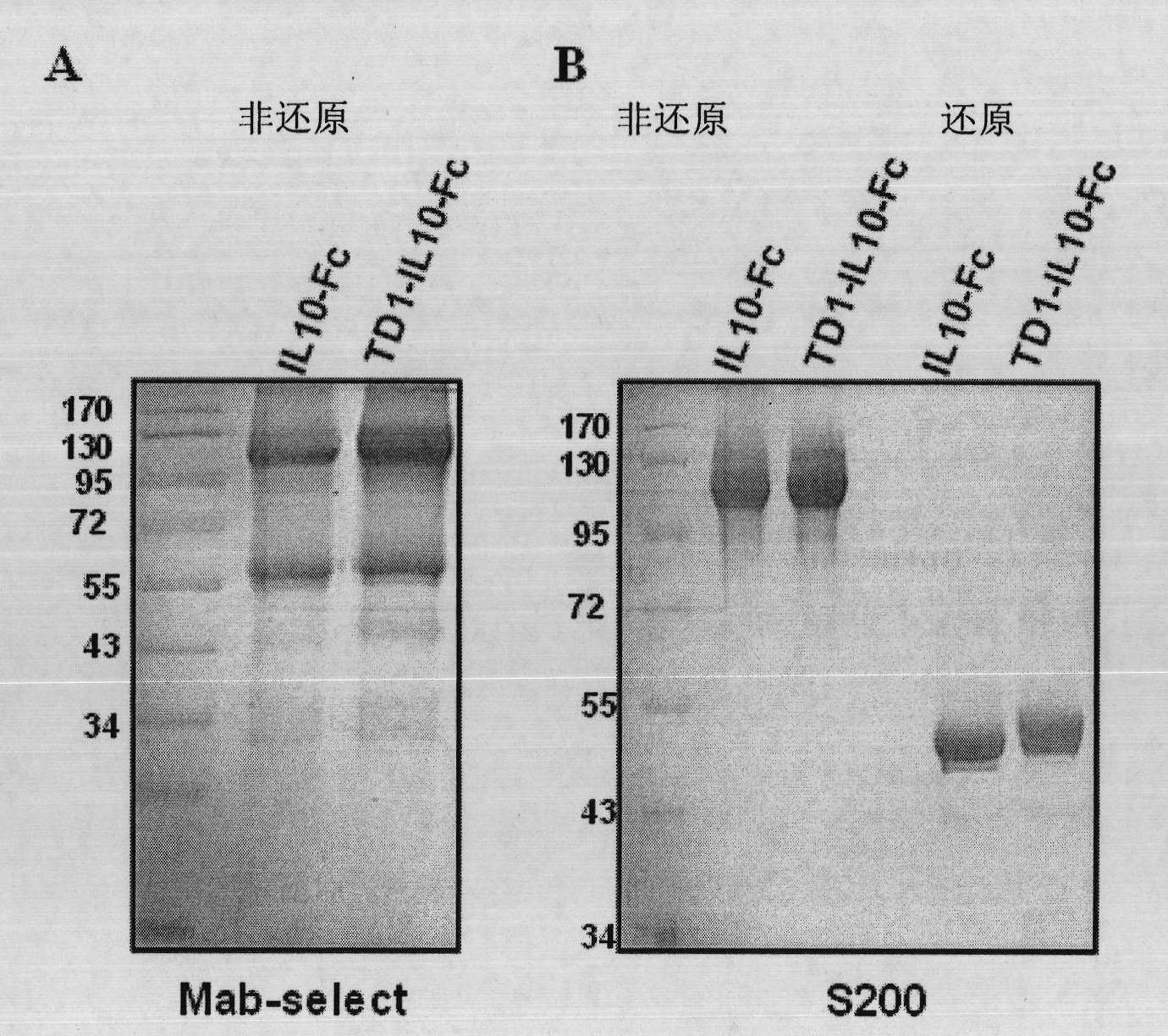
Fusion protein with transdermal capability and interleukin-10 activity as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101962413AEasy to purifyShorten the production cycleFungiBacteriaInterleukin 10White blood cell
The invention discloses a fusion protein with transdermal capability and interleukin 10 activity as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The fusion protein provided by the invention is formed by connecting any one protein of (1) human IgG Fc-gamma1 or the mutain thereof and (2) human IgG Fc-gamma2 or the mutain thereof on the carboxyl terminal of a human interleukin 10 protein, and connecting a transit peptide on an amino terminal; wherein the amino acid sequence of the human interleukin 10 protein is the amino acid sequence from the 12th site to the 171st site on the amino terminal of a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and the amino acid sequence of the transit peptide is the amino acid sequence from the 1st site to the 11th site on the amino terminal of the sequence 2 in the sequence table. Tests prove that the fusion protein provided in the invention has the transdermal capability and the interleukin 10 activity simultaneously, and has greater practical significance and broad application prospect in the field of the preparation of medicaments for treating autoimmunity reaction and especially psoriasis.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
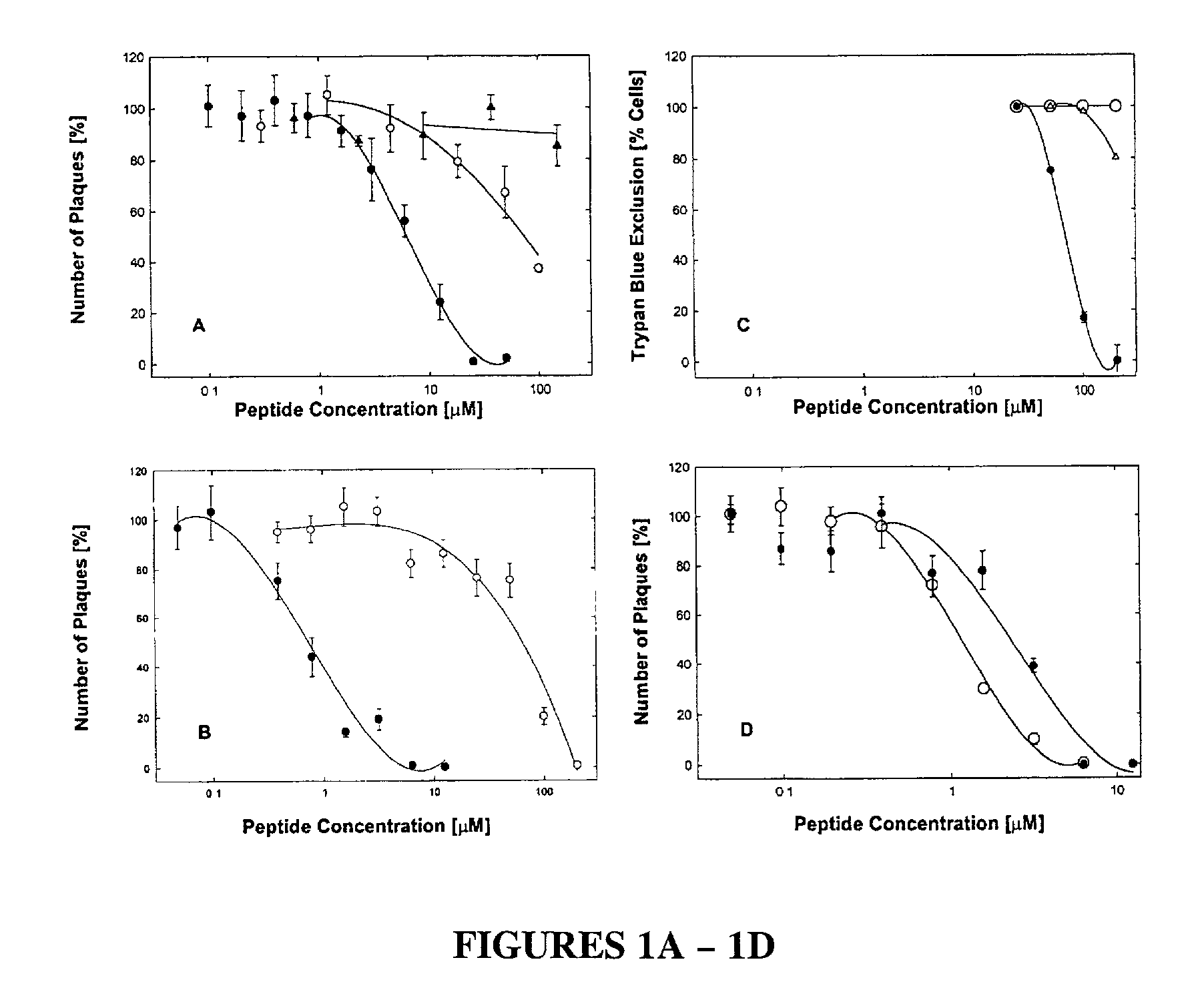
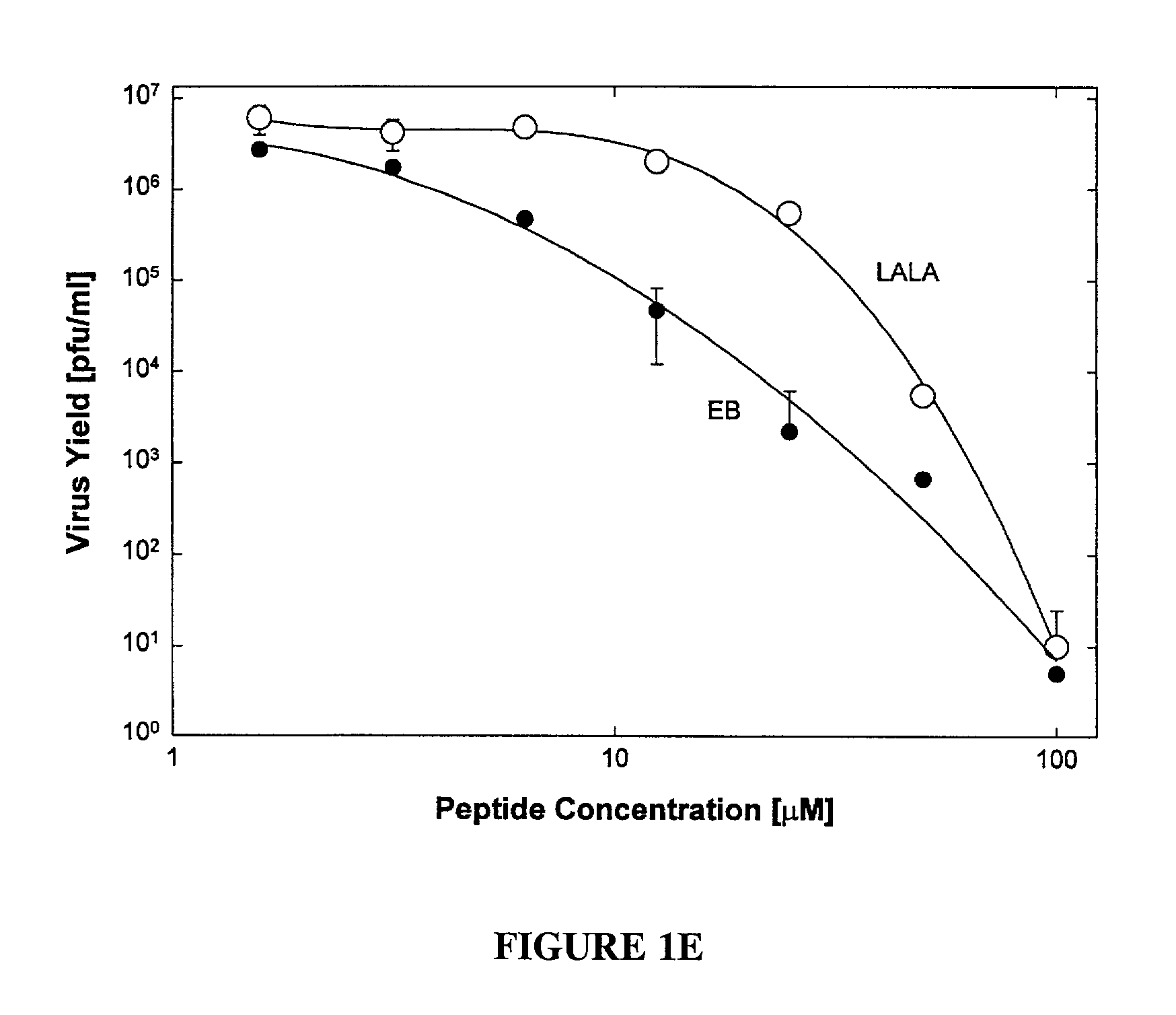
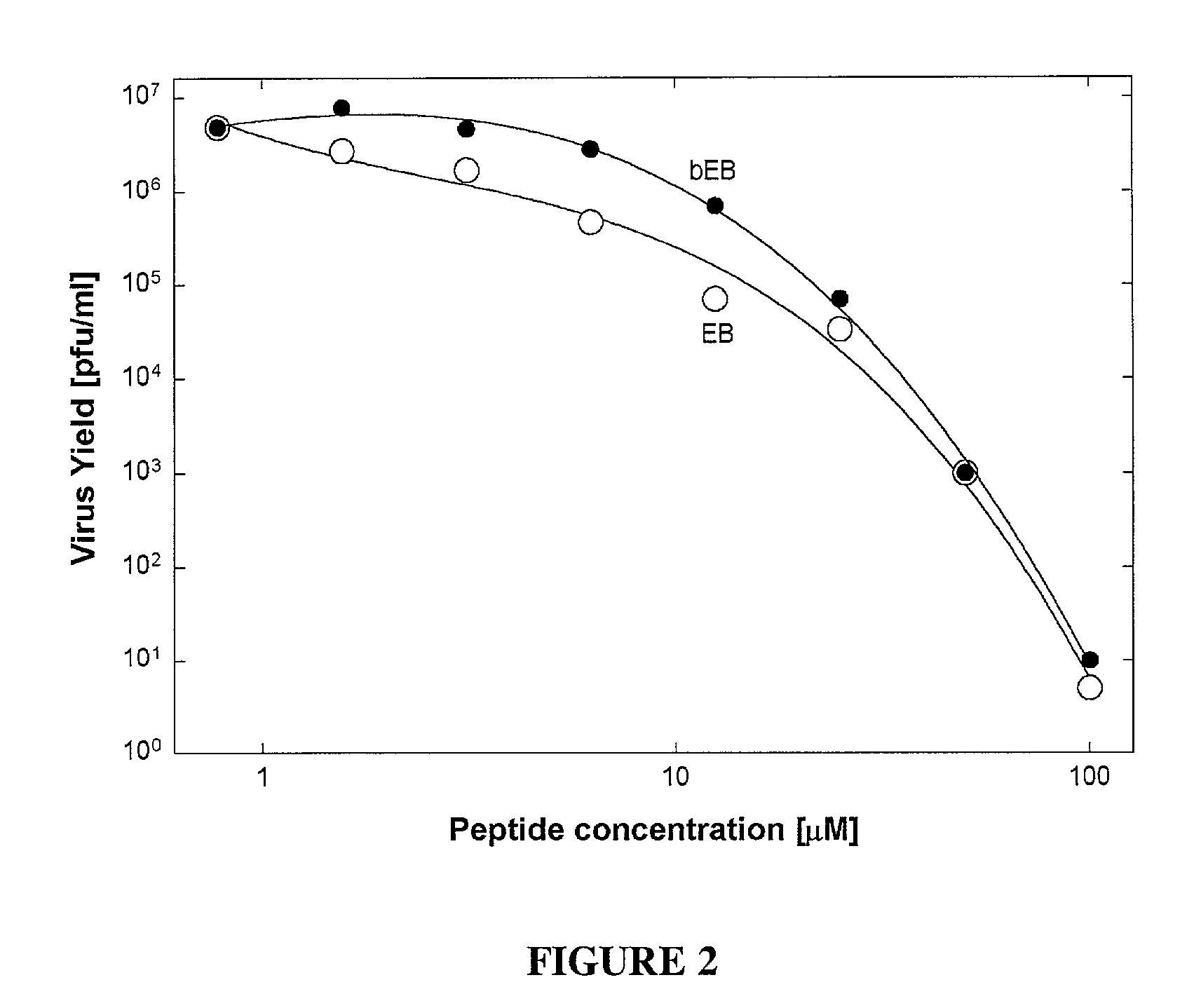
Pharmacologically active antiviral peptides and methods of their use
This invention relates to peptides having antiviral properties. The antiviral peptides comprise membrane transiting peptides, and active fragments and derivatives of such peptides. The antiviral peptides exhibit activity against a broad spectrum of viruses, including enveloped and nonenveloped viruses, and are used in pharmaceutical compositions to prevent and / or treat viral infections.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Epidermal growth factor receptor-derived peptides
ActiveUS7655751B2BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHuman epidermal growth factor receptorTransit Peptide
The object of the invention is to provide an EGFR-derived peptide useful for EGFR-based immunotherapy.The invention provides an EGFR-derived peptide capable of inducing both cellular and humoral immune responses and mutant peptide thereof and a polypeptide comprising said peptide, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the same, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:BRIGHTPATH BIOTHERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Inhibitor of cell proliferation and methods of use thereof
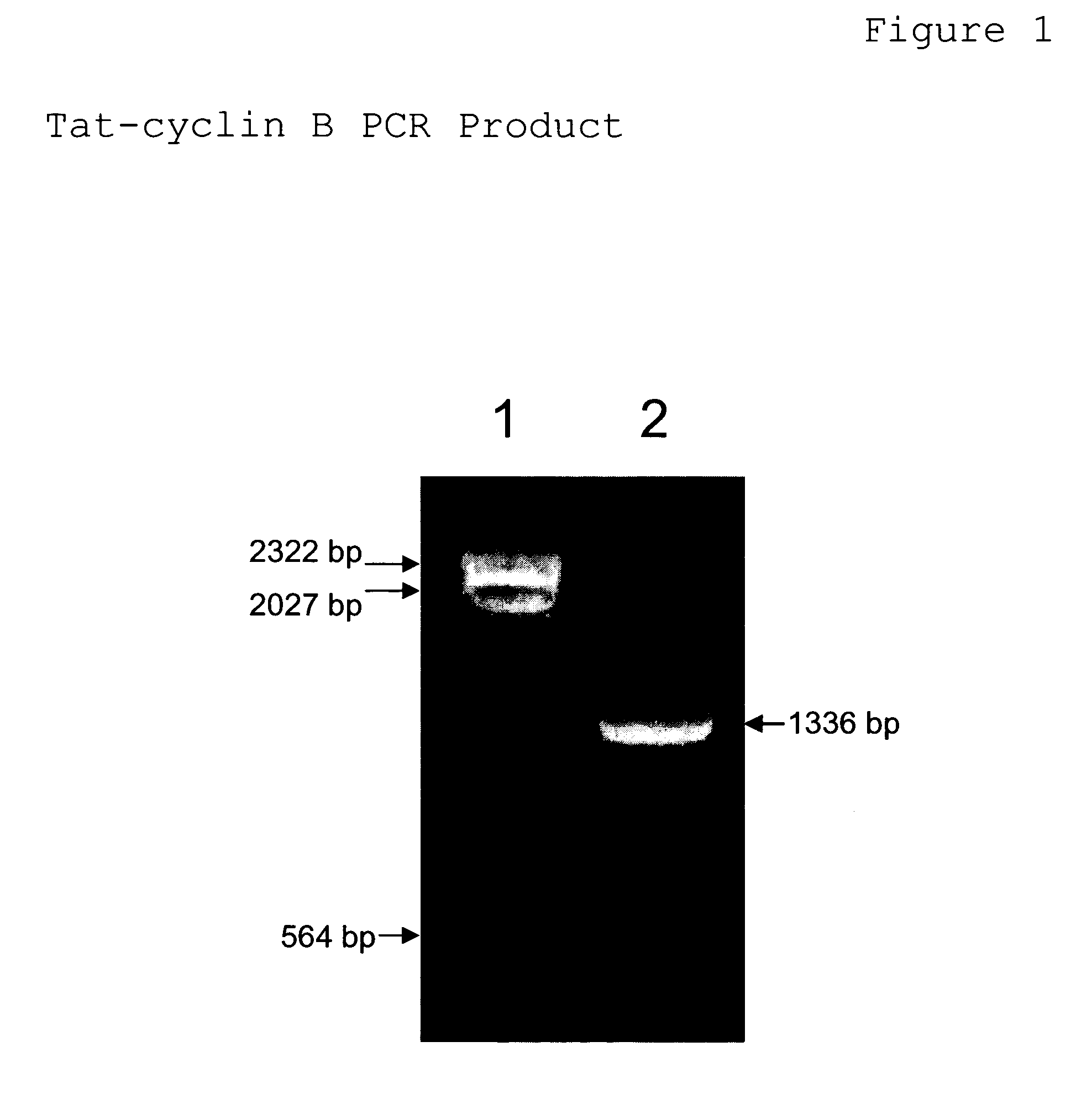
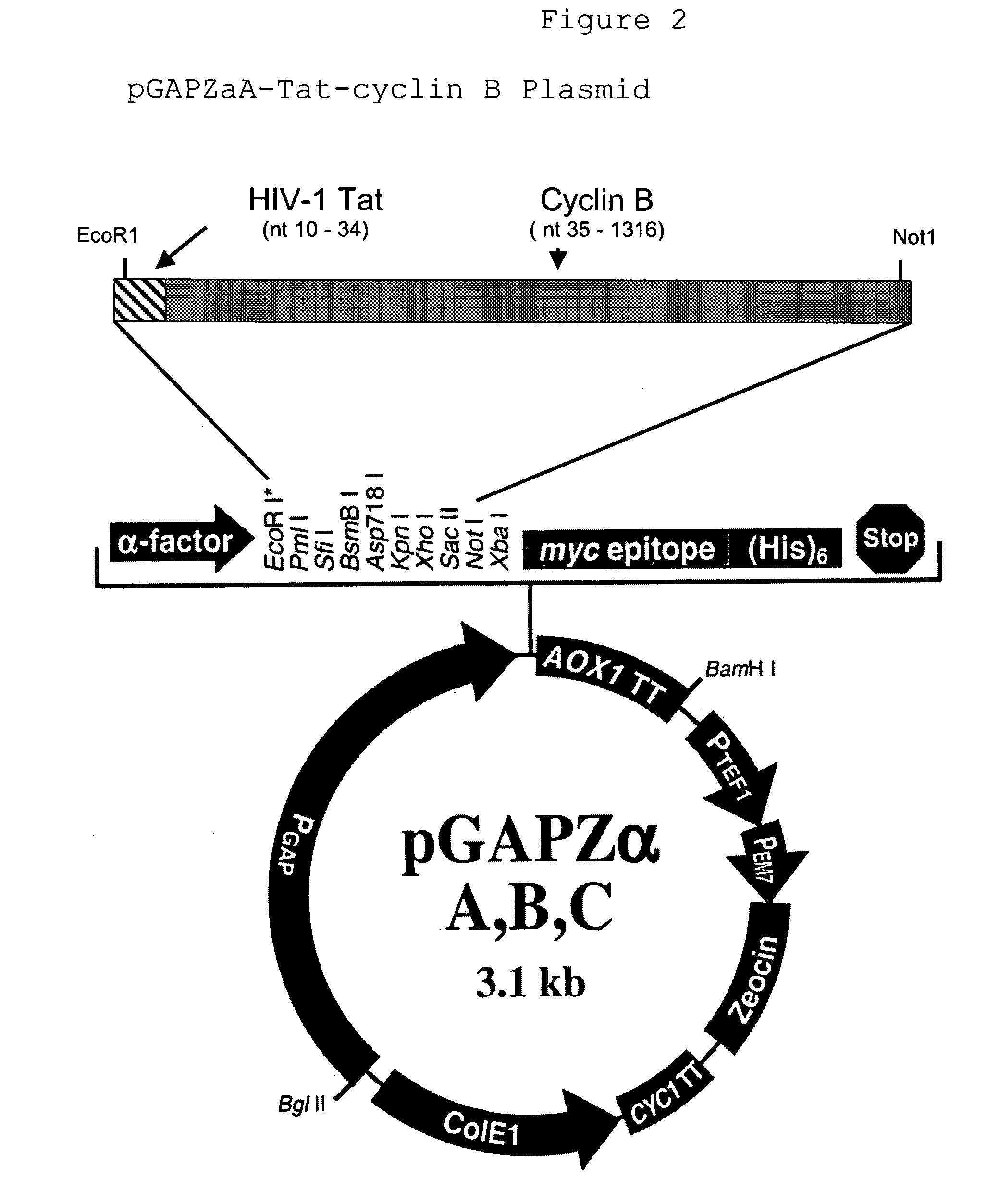
An chimerical polypeptide that arrests proliferating cells in mitosis is provided. In general the polypeptide has an N-terminal transit peptide, such as HIV-1 Tat, and a C-terminal cell-cycle effector, such as a G2 / M cyclin or a cytostatic factor. A polynucleotide under the control of a heterologous promoter that encodes a polypeptide that arrests cells in mitosis is also provided. The polynucleotide may, for example, encode a G2 / M cyclin. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the agent that inhibits transit through mitosis is provided. A method of treating patients suffering from a hyperplasia, such as cancer, psoriasis or benign prostate hyperplasia is provided.
Owner:NUCLEUS REMODELING
Isolated human transporter proteins, nucleic acid molecules encoding human transporter proteins, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050123982A1Sure easyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHuman DNA sequencingAmino acid
The present invention provides amino acid sequences of peptides that are encoded by genes within the human genome, the transporter peptides of the present invention. The present invention specifically provides isolated peptide and nucleic acid molecules, methods of identifying orthologs and paralogs of the transporter peptides, and methods of identifying modulators of the transporter peptides.
Owner:APPLERA
Down-regulation and silencing of allergen genes in transgenic peanut plants
InactiveUS20050114924A1Reduced and undetectable allergen protein contentReduced protein contentOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesTransgeneAmino acid
An allergen-free transgenic peanut seed is produced by recombinant methods. Peanut plants are transformed with multiple copies of each of the allergen genes, or fragments thereof, to suppress gene expression and allergen protein production. Alternatively, peanut plants are transformed with peanut allergen antisense genes introduced into the peanut genome as antisense fragments, sense fragments, or combinations of both antisense and sense fragments. Peanut transgenes are under the control of the 35S promoter, or the promoter of the Ara h2 gene to produce antisense RNAs, sense RNAs, and double-stranded RNAs for suppressing allergen protein production in peanut plants. A full length genomic clone for allergen Ara h2 is isolated and sequenced. The ORF is 622 nucleotides long. The predicted encoded protein is 207 amino acids long and includes a putative transit peptide of 21 residues. One polyadenilation signal is identified at position 951. Six additional stop codons are observed. A promoter region was revealed containing a putative TATA box located at position−72. Homologous regions were identified between Ara h2, h6, and h7, and between Ara h3 and h4, and between Ara h1P41B and Ara h1P17. The homologous regions will be used for the screening of peanut genomic library to isolate all peanut allergen genes and for down-regulation and silencing of multiple peanut allergen genes.
Owner:DODO HORTENSE +3
Starch encapsulation
InactiveUS7141659B2Prevent degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyTransit Peptide
The present invention relates to a recombinant nucleic acid encoding a hybrid polypeptide which comprises a transit peptide for the translocation of the polypeptide into an appropriate organelles such as plastids, a starch-encapsulating region from maize starch synthase and a payload polypeptide, wherein said payload polypeptide can be either N- or C-terminal to the starch encapsulating region. The invention also relates to the expression vectors comprising said nucleic acid, and hosts comprising the said vector. Also, the invention encompasses methods of producing the hybrid polypeptide thereof from starch and particularly from starch granules, and industrial uses of the payload polypeptide recombinantly produced in said hybrid polypeptide wherein said payload polypeptide is a biologically active molecule.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
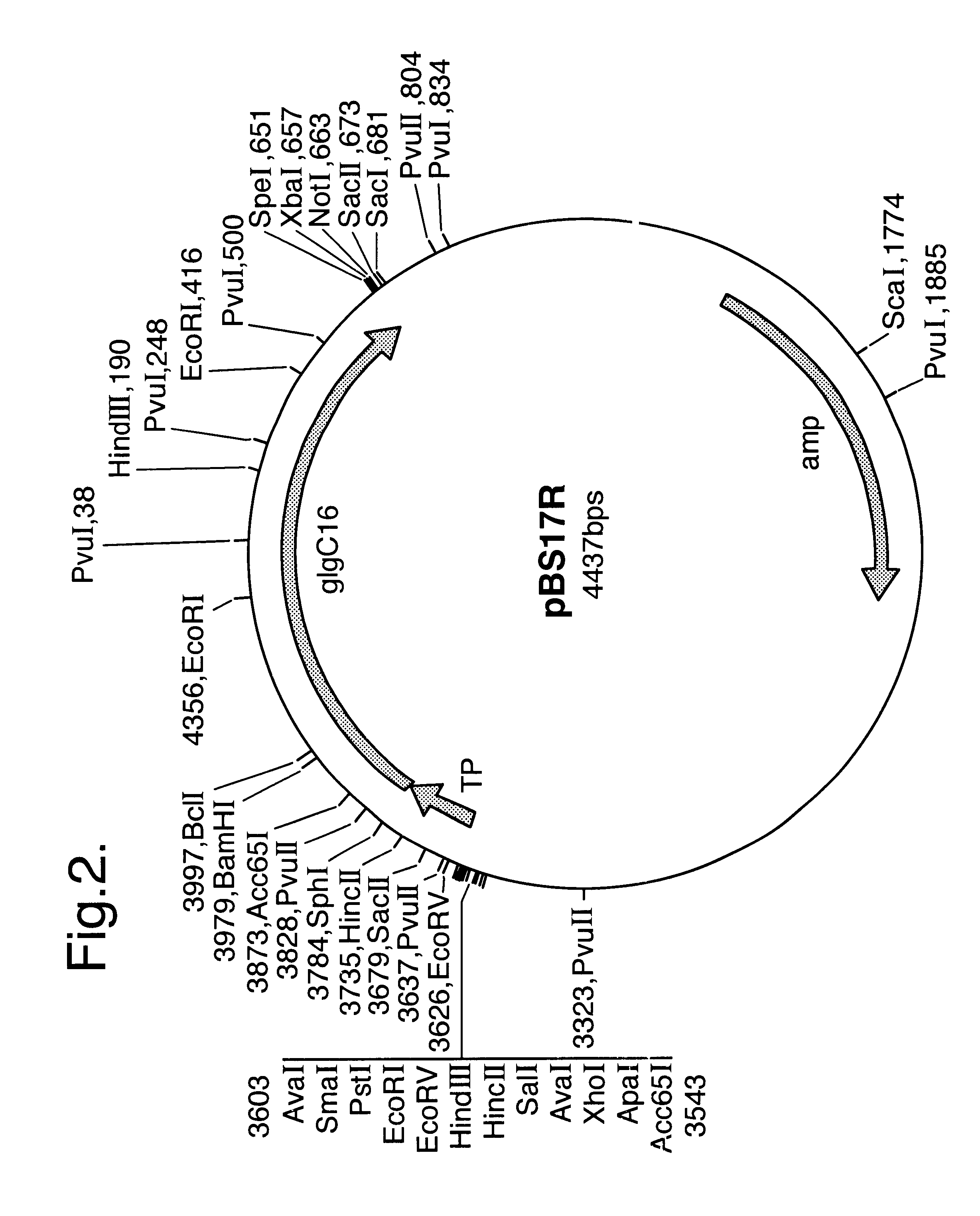
Genetically modified plants with altered starch
Starch of wheat and maize plants is altered by the introduction of a chimeric gene comprising a glycogen synthase coding sequence under the control of a promoter directing expression and a terminator. A transit peptide for translocation of the glycogen synthase to the plant plastid may also be included in the chimeric gene. The starch has altered processing characteristics, in particular an increased chain length.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
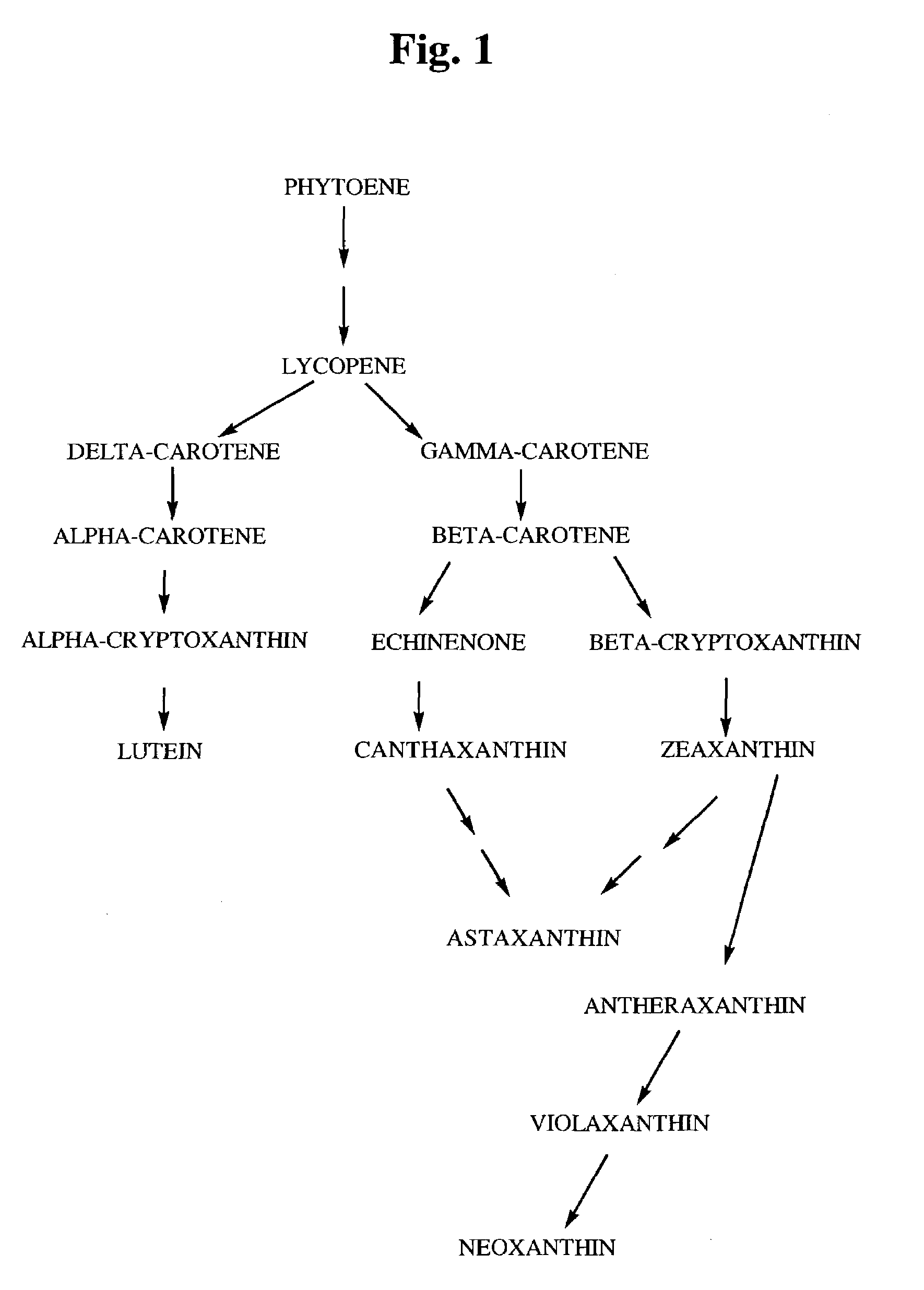
4-ketocarotenoids in flower petals
InactiveUS7223909B2BiocideOther foreign material introduction processesCarotenoid formationZeaxanthin
The formation of a carotenoid compound containing a 4-keto-β-ionene ring such as astaxanthin or canthaxanthin in flowers, and particularly in the corolla and reproductive parts of a flower of a higher plant whose flowers produce a carotenoid compound containing a β-ionene ring such as β-carotene or zeaxanthin, but otherwise do not produce astaxanthin or canthaxanthin is disclosed. One or more genes controlled by a promoter are inserted (transformed) into a higher plant. The inserted gene encodes a chimeric enzyme including (a) a carotenoid-forming enzyme that is at least a ketolase. That gene is operatively linked to (b) a plastid-directed transit peptide. Some higher plants to be transformed produce at least zeaxanthin or β-carotene in their flowers prior to transformation, whereas other plants produce little if any colored carotenoid pigments prior to transformation and are transformed with a cassette of carotenoids-forming genes. Methods of transformation and use of the transformed plants are described.
Owner:BALL HORTICULTURAL
Plant expression vector and application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch
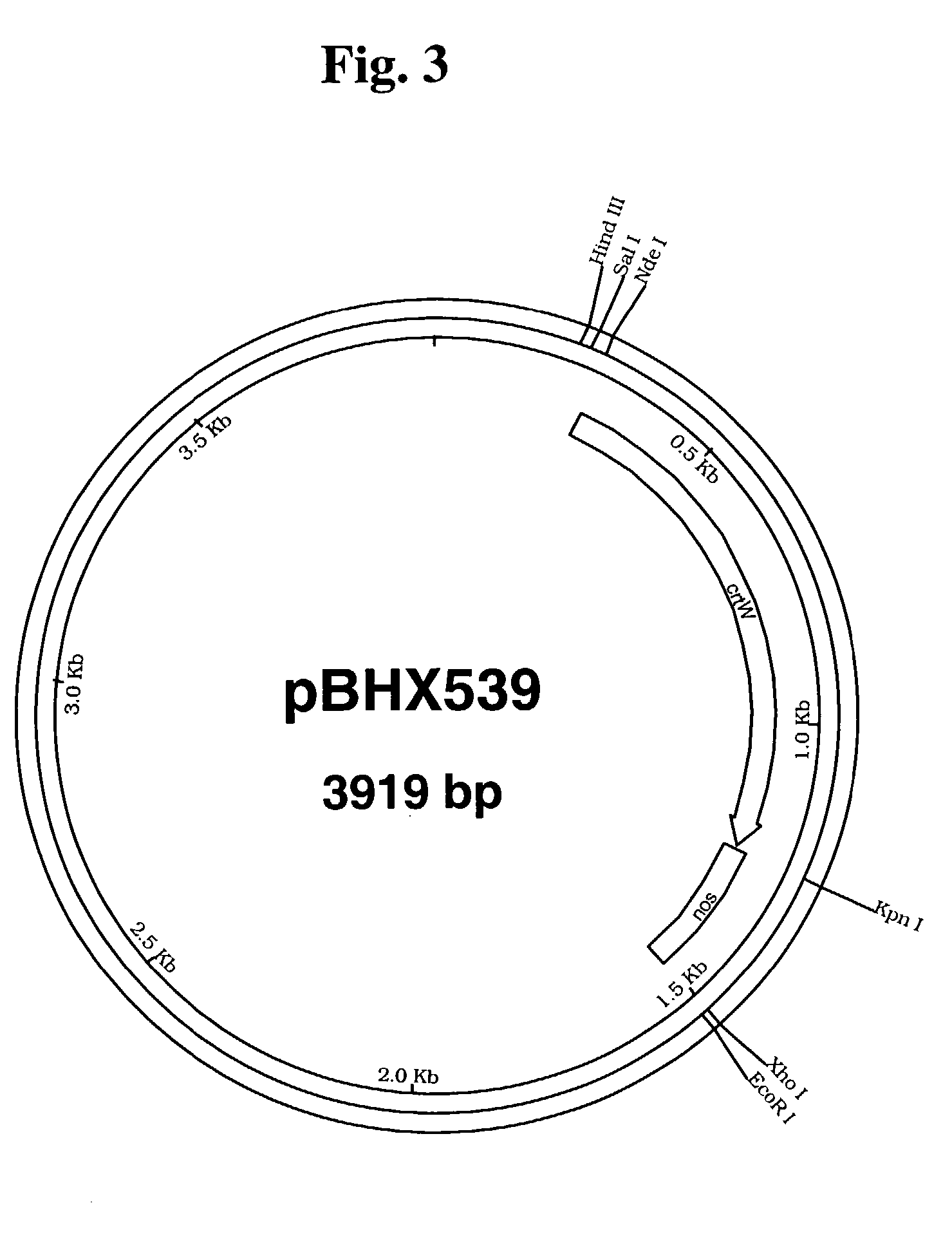
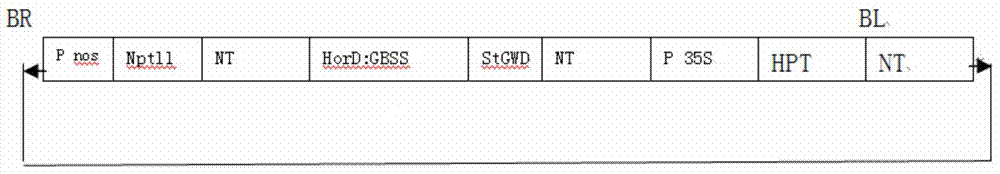
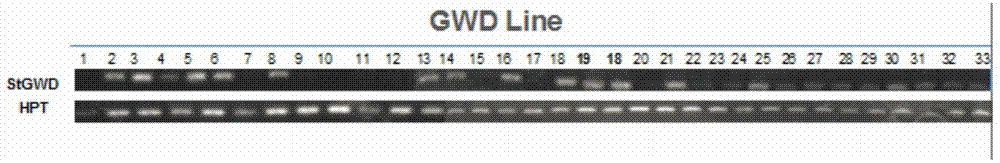
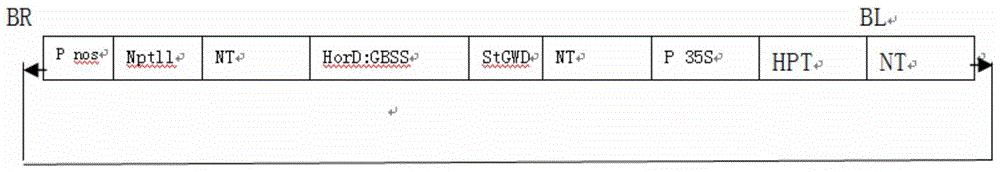
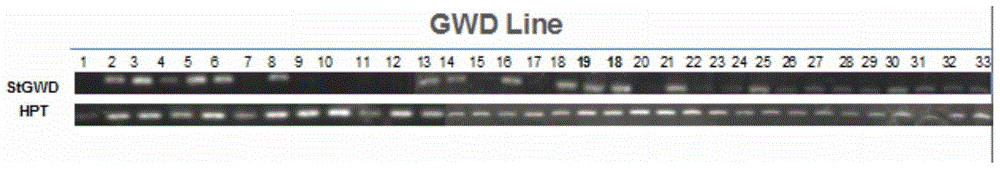
ActiveCN104232681AIncrease contentAchieve modificationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch. The plant expression vector comprises a target gene inserting into an original vector and a promoter, wherein the target gene comprises a transit peptides gene segment of granule-bound starch synthase and a potato glucan-water dikinase gene which are sequentially connected, and the promoter is a barley endosperm specific promoter HorD. For the plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch, the potato glucan-water dikinase gene is transferred into rice, and the starch of the rice can be phosphorylated through the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene, so that the modification of the starch is realized. The potato glucan-water dikinase is led to amyloid through the transit peptides of the granule-bound starch synthase, and phosphorylation modification is performed on the starch. According to the invention, the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene in the rice endosperm can be promoted through the barley endosperm specific promoter HorD, and the phosphorus content in the rice starch is greatly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Production of high mannose glycosylated proteins stored in the plastid of microalgae
The present invention concerns a transformed microalga producing a protein harboring a “high mannose” pattern of glycosylation in the plastid of the transformed microalga, wherein 1) the transformed microalga has a Chloroplast Endoplasmic Reticulum (CER); 2) the microalga has been transformed with a nucleic acid sequence operatively linked to a promoter, the nucleic acid sequence encoding an amino acid sequence including (i) an amino-terminal bipartite topogenic signal (BTS) sequence composed of at least a signal peptide followed by a transit peptide; and (ii) The sequence of the protein, 3) the xylosyltransferases and fucosyltransferases of the microalga have not been inactivated; 4) the N-acetylglycosyltransferase I of the microalga has not been inactivated, preferably the N-acetylglycosyltranferases II, III, IV, V and VI, mannosidase II and glycosyltransferases of the microalga have not been inactivated.
Owner:ALGENICS
Method for enhancement of naturally occurring cytoplasmic male sterility and for restoration of male fertility and uses thereof in hybrid crop prodn.
The present invention relates to methods for enhancement of naturally occurring cytoplasmic male sterility and for restoration of male fertility and uses thereof in hybrid crop production. There is also disclosed a method for restoration of male fertility to cytoplasmic male sterile plants; which comprises the steps of: a) introducing into the nucleus of a plant cell a gene construct essentially consisting of a sequence encoding a mitochondrial transit peptide fused upstream of and in frame with an edited form of a normal mitochondrial gene that is co-transcribed with an unusual CMS-associated mitochondrial gene; b) selecting for plan cells that have acquired the gene construct in step a); and c) inducing regeneration of selected plant cells to produce a mature plant.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Methods and Compositions for Expressing Proteins In Plants
InactiveUS20110138495A1Suppression problemSugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsBiologyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Methods and compositions comprising an expression construct and a suppressor of posttranscriptional gene silencing construct are described. The expression construct and suppressor construct may comprise a viral amplicon. The expression construct may comprise fusing the target gene to the 3′ and / or 5′ end of a gene encoding a transit peptide sequence or a signaling peptide sequences. The transit or signal peptide sequence directs the target gene product to a subcellular location. Methods comprise the production of several heterologous proteins in a single plant. The invention comprises methods for plant production and protein harvest that will yield useful amounts of the desired protein(s) in as little as one to two weeks after the initiation of the production cycle. Methods for the inoculation of recipient plants by spraying with recombinant Agrobacterium suspensions containing the constructs of interest are taught.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Dual transit peptides for targeting polypeptides
PendingCN109154003AVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationHeterologousNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention refers to a recombinant chimeric nucleic acid molecule comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a dual transit peptide operably linked to a heterologous nucleic acid sequenceencoding a polypeptide of interest which, when overexpressed in a plant, confers herbicide tolerance to said plant.
Owner:BASF AGRO BV
PCK-type C4 cycle
InactiveUS20030221219A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseDNA fragmentation
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Down-regulation and silencing of allergen genes in transgenic peanut seeds
InactiveUS20110004959A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
An allergen-free transgenic peanut seed is produced by recombinant methods. Peanut plants are transformed with multiple copies of each of the allergen genes, or fragments thereof, to suppress gene expression and allergen protein production. Alternatively, peanut plants are transformed with peanut allergen antisense genes introduced into the peanut genome as antisense fragments, sense fragments, or combinations of both antisense and sense fragments. Peanut transgenes are under the control of the 35S promoter, or the promoter of the Ara h2 gene to produce antisense RNAs, sense RNAs, and double-stranded RNAs for suppressing allergen protein production in peanut plants. A full length genomic clone for allergen Ara h2 is isolated and sequenced. The ORF is 622 nucleotides long. The predicted encoded protein is 207 amino acids long and includes a putative transit peptide of 21 residues. One polyadenilation signal is identified at position 951. Six additional stop codons are observed. A promoter region was revealed containing a putative TATA box located at position −72. Homologous regions were identified between Ara h2, h6, and h7, and between Ara h3 and h4, and between Ara h1P41B and Ara h1P17. The homologous regions will be used for the screening of peanut genomic library to isolate all peanut allergen genes and for down-regulation and silencing of multiple peanut allergen genes.
Owner:NGATEGEN INC +1
Down-regulation and silencing of allergen genes in transgenic peanut seeds
Owner:NGATEGEN INC +1
Method for high efficiency protein delivery into plastids
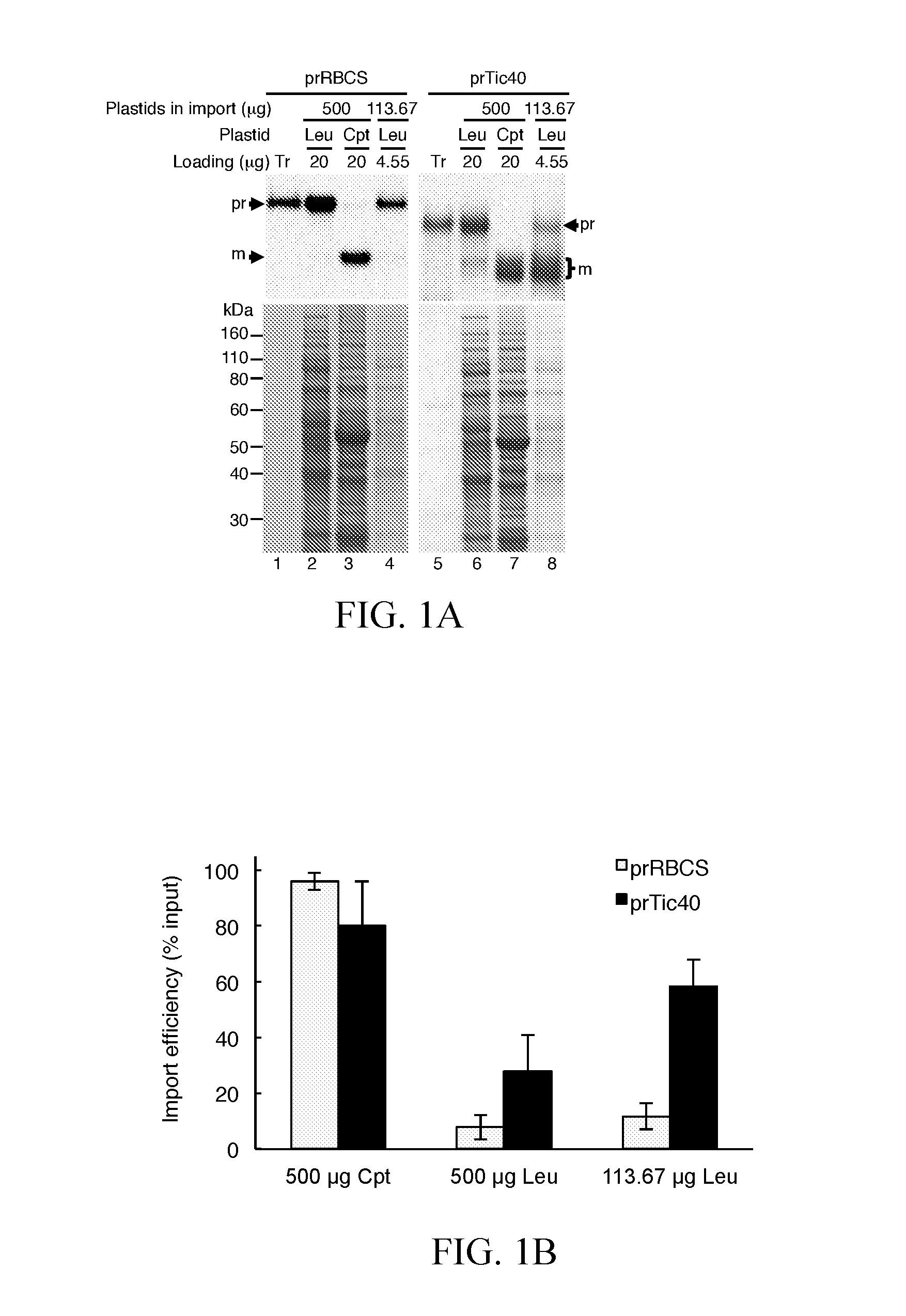
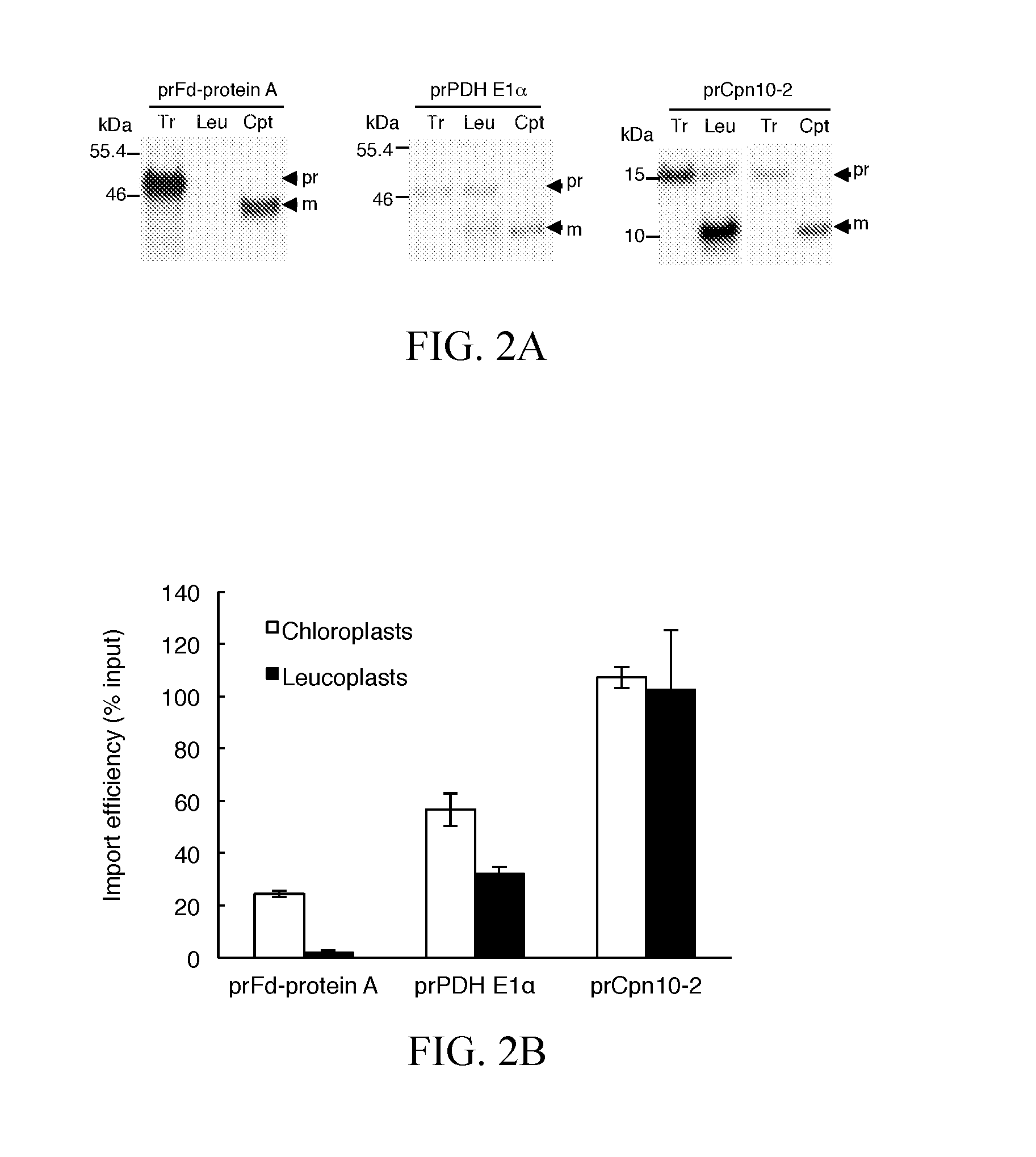
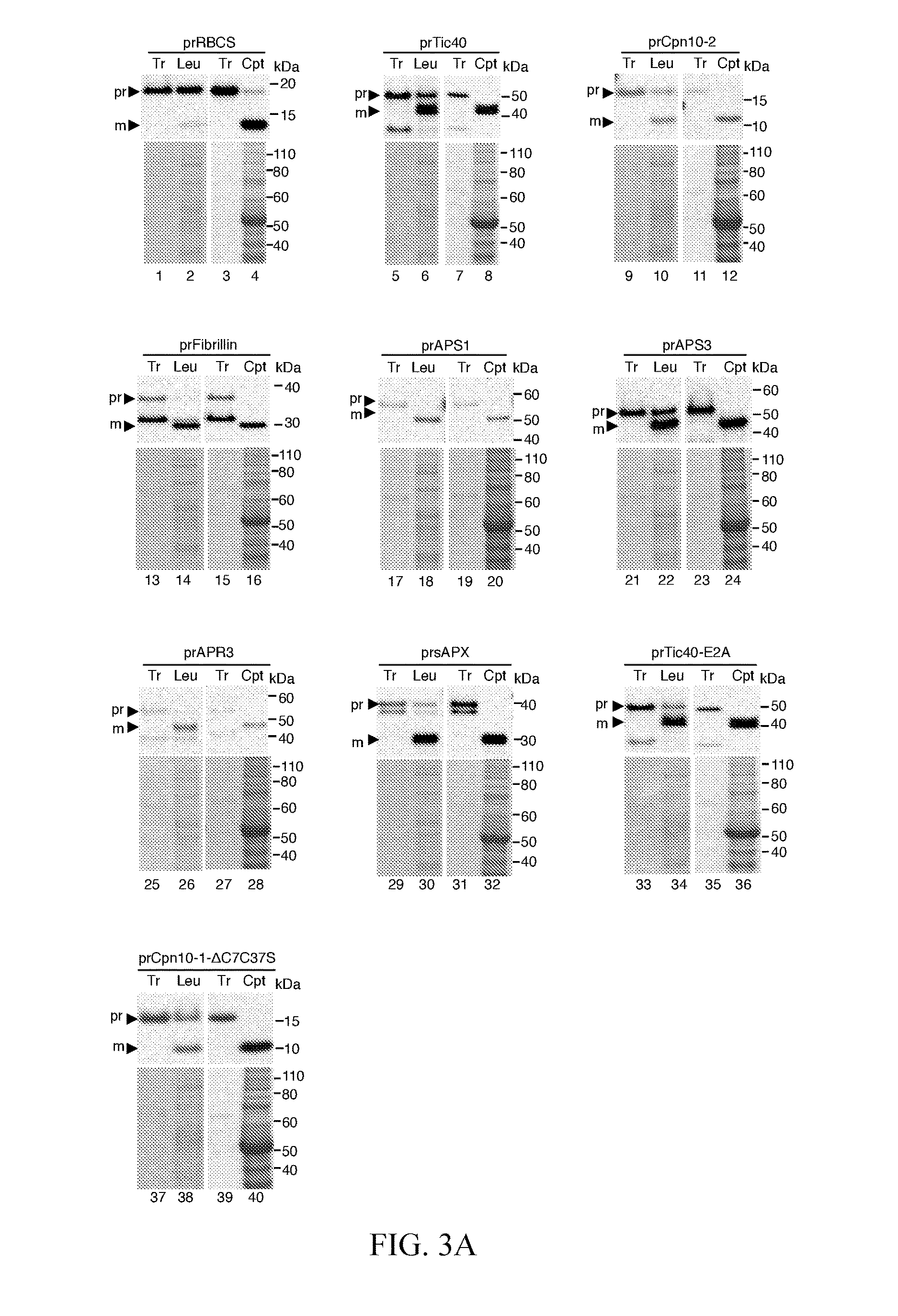
ActiveUS20170016011A1High leucoplast import efficiencyImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionChaperoninRecombinant DNA
The present invention provides a recombinant DNA molecule encoding a fusion protein, comprising a first DNA sequence encoding a high-efficiency transit peptide operably linked to a second DNA sequence encoding a passenger protein, wherein the high-efficiency transit peptide is selected from the group consisting of transit peptides of the precursors of translocon at the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts 40 kD (prTic40), chaperonin 10-2 (prCpn10-2), Fibrillin 1B (prFibrillin), ATP sulfurylase 1 (prAPS1), ATP sulfurylase 3 (prAPS3), 5′-adenylylsulfate reductase 3 (prAPR3), stromal ascorbate peroxidase (prsAPX), prTic40-E2A (a prTic40 variant), prCpn10-1-ΔC7C37S (a chaperonin 10-1 variant), a functional fragment of any of the transit peptides and an equivalent thereof. And the present invention also provides a method of high efficiency delivery of a protein into plastids using the high-efficiency transit peptides.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Fusion proteins and methods for treating HIV infection and aids related symptoms
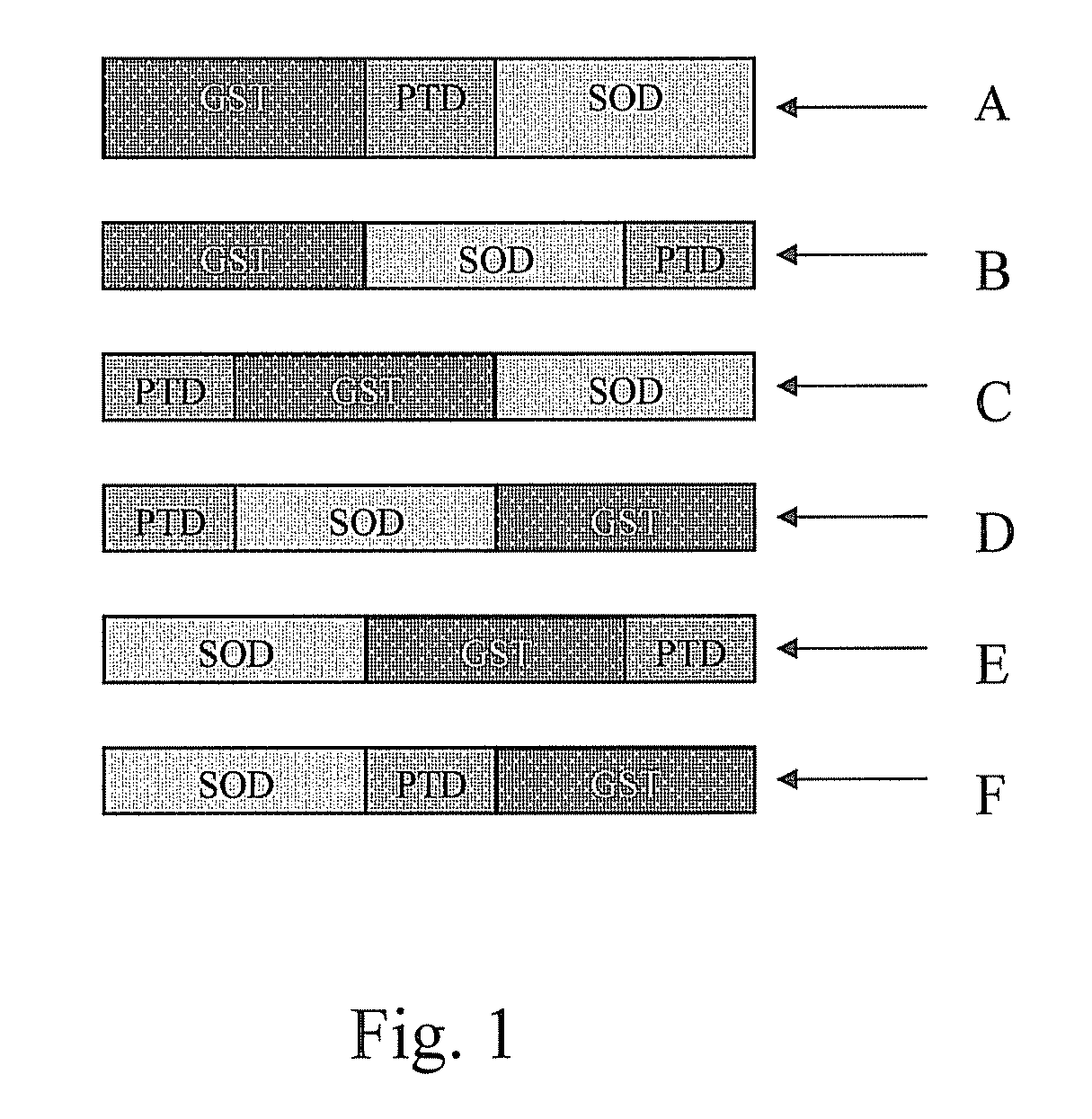
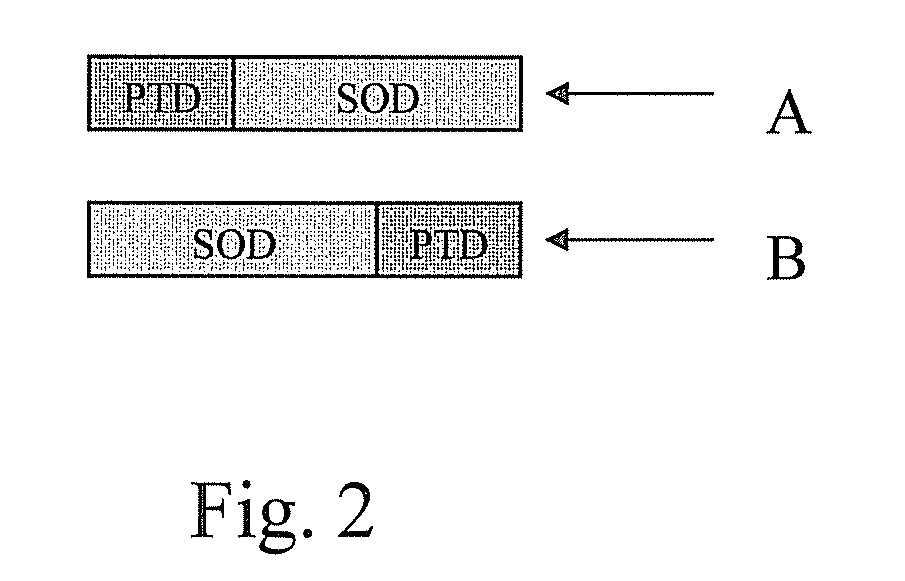
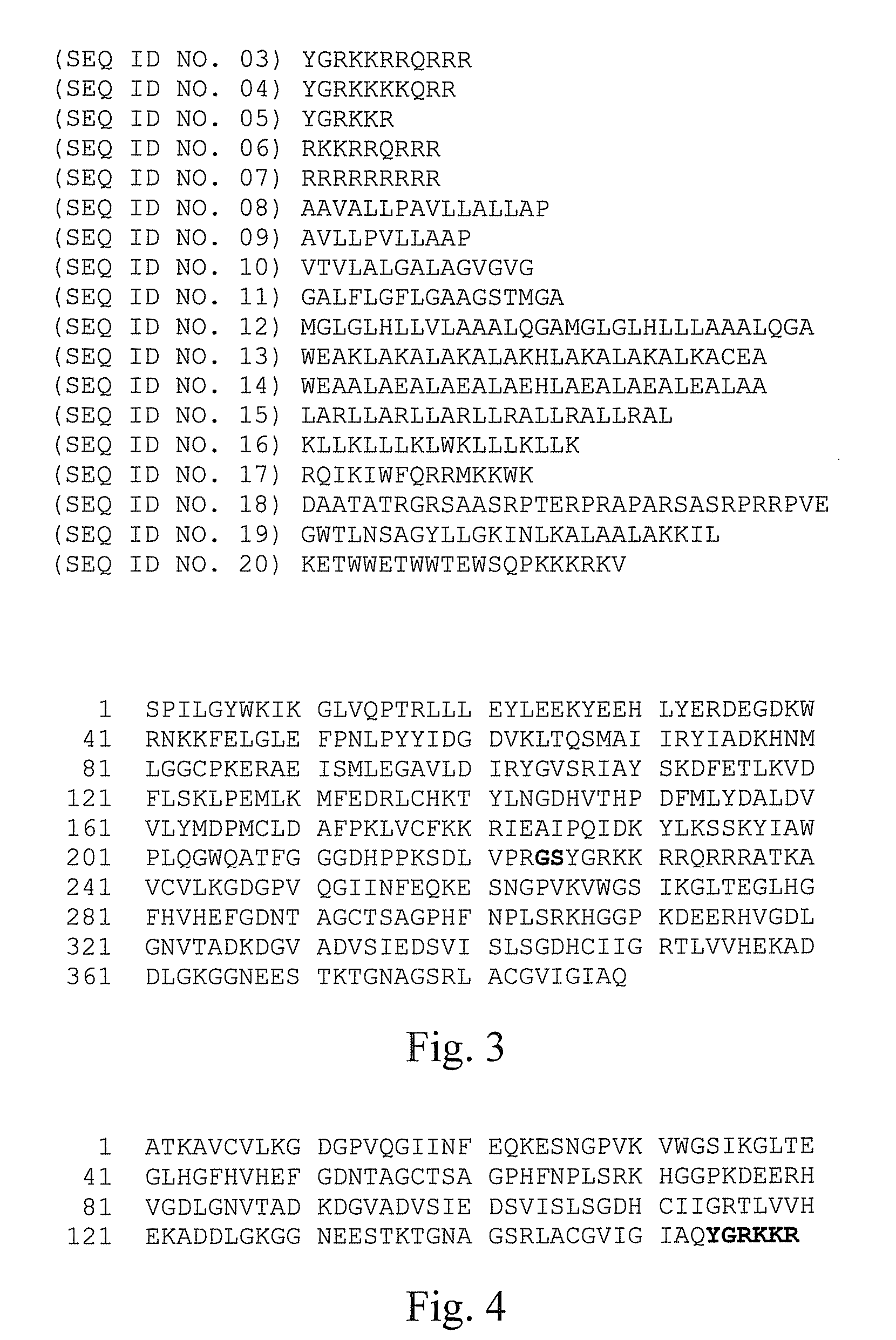
ActiveUS20130336946A1Avoid virus infectionGrowth inhibitionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsTransit PeptideSuperoxide dismutase
The present invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions and methods for using a fusion protein comprising a superoxide dismutase and a transit peptide. The present invention also discloses pharmaceutical compositions and methods for using the fusion protein in combination with other antiretroviral agents for treating patients with AIDS or HTV infection.
Owner:TIANJIN XIJI BIOTECH
Compositions and methods for enhancing plant photosynthetic activity
Methods for improving the efficiency of photosynthesis in plants exposed to suboptimal light conditions. Photosynthesis enhancement is achieved by transformation and expression of one or more exogenous chromophores in the chloroplast of plants or in the cytoplasm under the control of a transit peptide which directs it to the chloroplast or a compartment within the chloroplast. Preferred chromophores have excitation max in the green-yellow light spectrum. Chains of chromophores can be used to capture and emit light from one to the other until the emitted wave length is in the range that can be efficiently utilize by the native light harvest complex.
Owner:FUTURAGENE ISRAEL
A method for positioning and expressing foreign protein in mitochondria
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A plant expression vector and its application in the preparation of phosphorylated modified rice starch
ActiveCN104232681BAchieve modificationHigh polymorphismVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGranule-Bound Starch Synthase
The invention discloses a plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch. The plant expression vector comprises a target gene inserting into an original vector and a promoter, wherein the target gene comprises a transit peptides gene segment of granule-bound starch synthase and a potato glucan-water dikinase gene which are sequentially connected, and the promoter is a barley endosperm specific promoter HorD. For the plant expression vector and the application thereof in preparing phosphorylation modified rice starch, the potato glucan-water dikinase gene is transferred into rice, and the starch of the rice can be phosphorylated through the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene, so that the modification of the starch is realized. The potato glucan-water dikinase is led to amyloid through the transit peptides of the granule-bound starch synthase, and phosphorylation modification is performed on the starch. According to the invention, the expression of the potato glucan-water dikinase gene in the rice endosperm can be promoted through the barley endosperm specific promoter HorD, and the phosphorus content in the rice starch is greatly increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fusion proteins and methods for treating HIV infection and aids related symptoms
ActiveUS20160175405A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsMedicineTransit Peptide
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for using a fusion protein having a superoxide dismutase and a transit peptide are described. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for using the fusion protein in combination with other antiretroviral agents for treating patients with AIDS or HTV infection are also described.
Owner:TIANJIN XIJI BIOTECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com