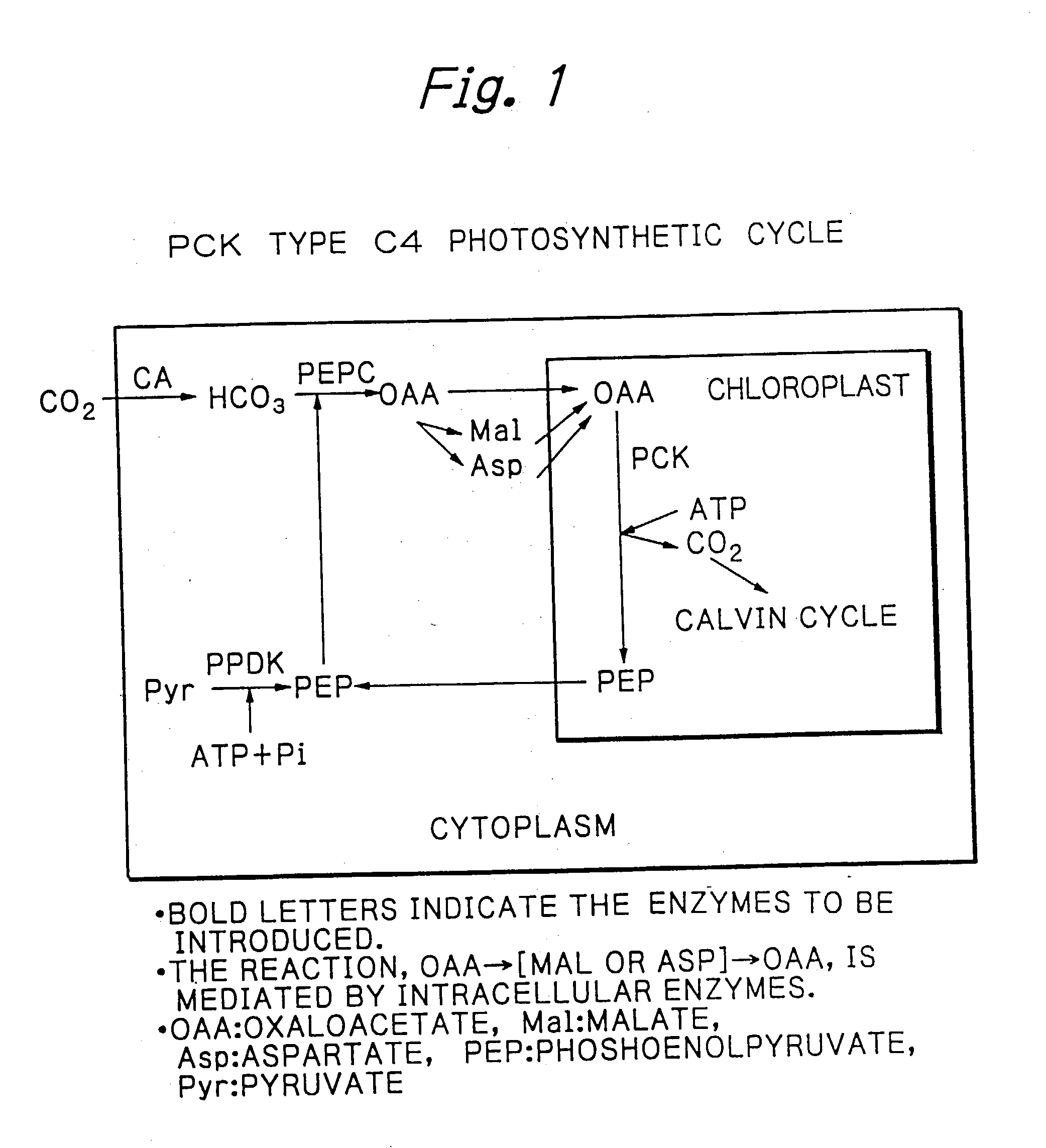
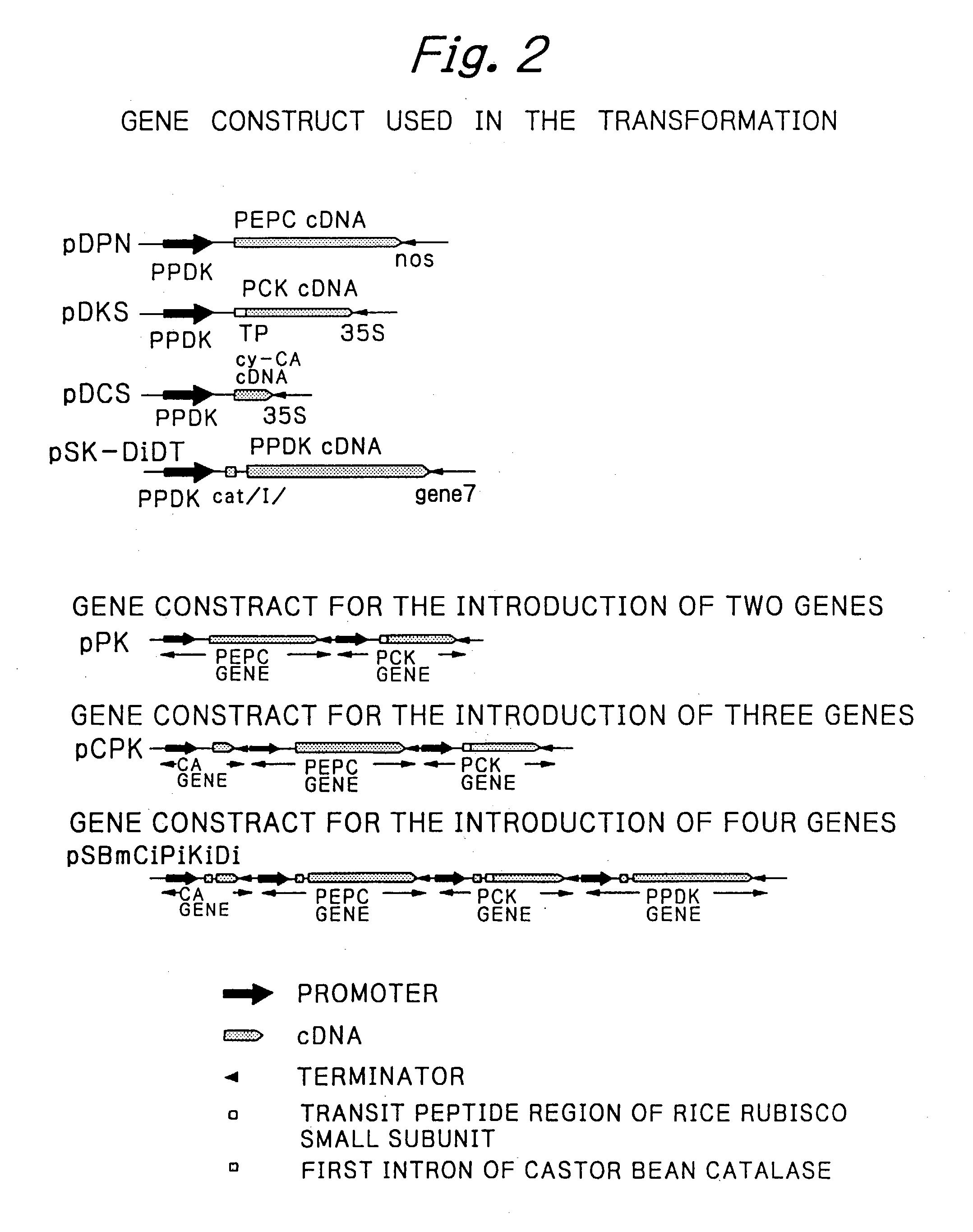
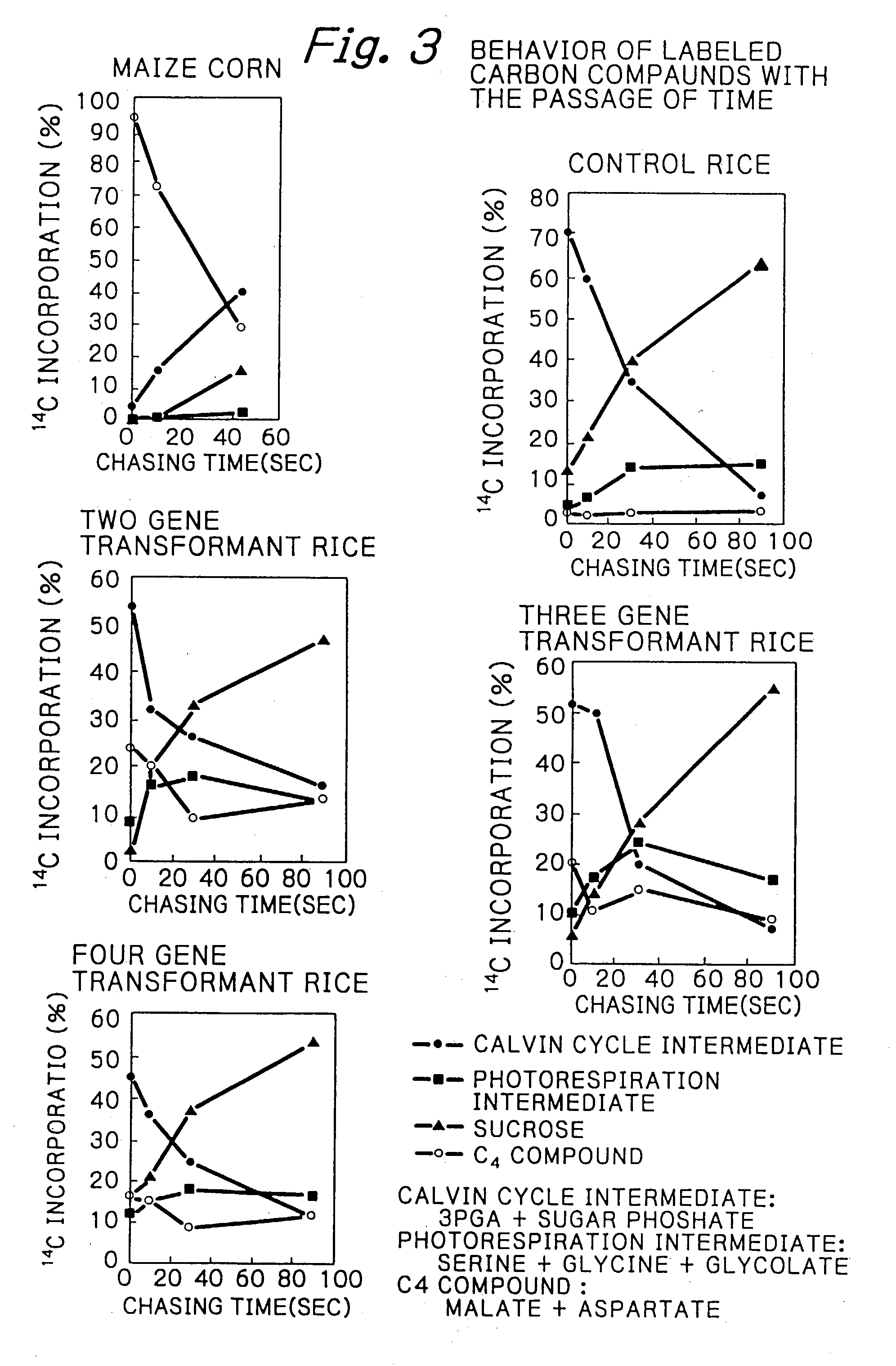
PCK-type C4 cycle
a c4 cycle, c4 technology, applied in the field of c4 cycle, can solve the problems of difficult cross-over between c3 and c4, and the failure of the attempt to introduce the properties of a c4 plant,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Transgenes
[0047] (1) Promoter sequence
[0048] The DNA fragment of the corn C4 type PPDK promoter region was obtained by the PCR method (Mcpherson, M. J., Quirke, P. and Taylor, GR. ed.: PCR. A practical approach, Oxford Express Press, Oxford NY (1991)) with the use of the following two synthetic primers prepared on the basis of a known nucleotide sequence (Glackin, C. A. and Grula, J. W. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:3004-3008):
1 5'-CTAAAGACATGGAGGTGGAAG-3' (5' side) (SEQ ID NO:6) 5'-GTAGCTCGATGGGTGCACG-3'. (3' side) (SEQ ID NO:7)
[0049] The amplification was carried out by using maize genomic DNA as the template, which had been obtained by extracting total nucleic acids from a maize inbred B73 green leaf by the SDS-phenol method followed by purification by cesium chloride-ethidium bromide ultracentrifugation. The DNA fragment thus obtained was inserted into the cloning site of a plasmid vector pCR1000 (manufactured by Invitrogen, USA). The plasmid thus obtained...
example 2
Construction of Transformants
[0082] A Japonica rice (cultivar "Tsukinohikari") was used throughout the transformation study of rice.
[0083] Rice transformants having pDPN, pDKS and pDCS introduced thereinto were constructed by the electroporation method previously described (Japanese Patent Public Disclosure Hei 8-80197).
[0084] Rice transformants having pSB4PK, pSB4CPK and pSB4CiPiDiKi introduced thereinto were constructed by the Agrobacterium method reported described (Hiei, Y. et al. (1994) Plant J. 6:271-282).
[0085] These transformants were grown in an air-conditioned green house (daylight period: 16 hours, daytime: 28.degree. C., nighttime: 23.degree. C.).
example 3
Detection of Enzyme Proteins and Measurement of Enzymatic Activities
[0086] About 0.1 g of the green leaves of the transformants or control rice ("Tsukinohikari") was homogenized in 1 ml of an ice-cold extraction buffer (50 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.0, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 2 mM manganese chloride, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 1 mM phosphoric acid, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% 2-mercaptoethanol, 20% glycerol, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mM benzamidine, 1 mM 6-amino-n-caproic acid, 0.2% (w / w) isoascorbic acid, and 2% (w / v) polyclar AT). The homogenate was centrifuged at 15,000.times.g for 20 minutes at 4.degree. C. Then the obtained supernatant was desalted by passing through an NAP5.TM. column (manufactured by Pharmacia, Sweden) which had been equilibrated at room temperature with a column buffer (50 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.0, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 2 mM manganese chloride, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% 2-mercaptoethanol, and 20% glycerol) to thereby give a crude extract. The chlorophyll content in the homogenate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com