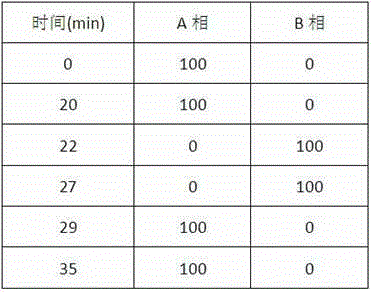
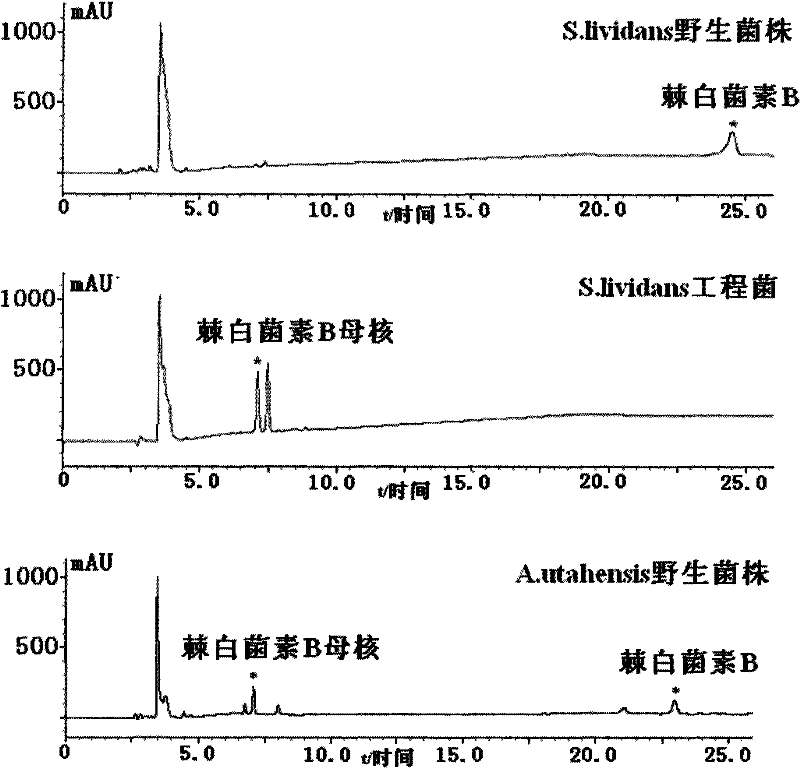
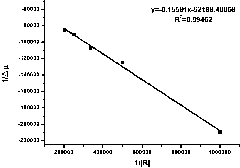
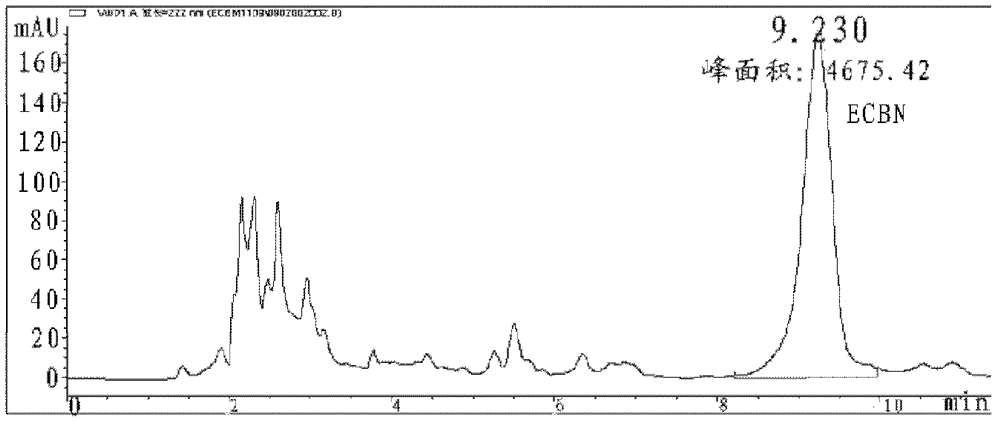
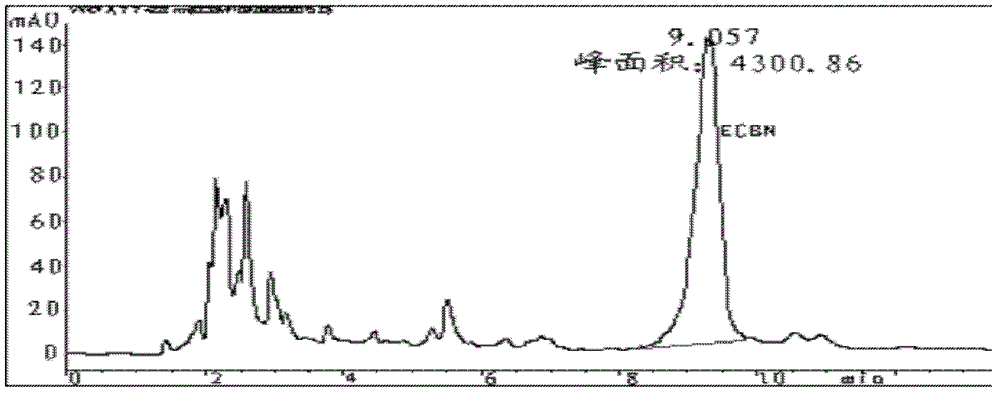
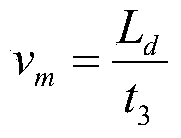Patents
Literature
60 results about "Echinocandin B" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
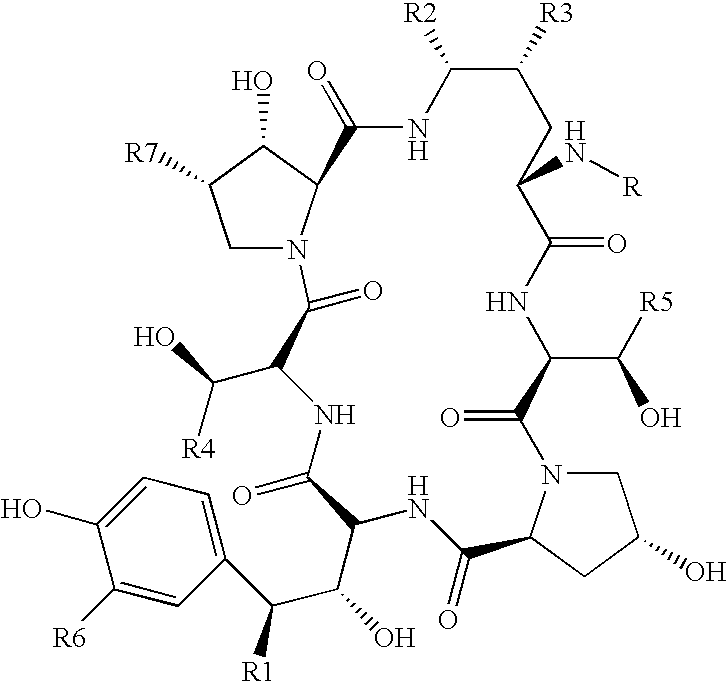
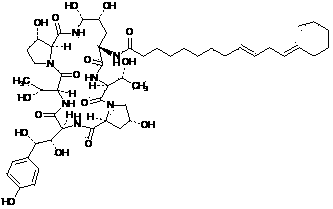
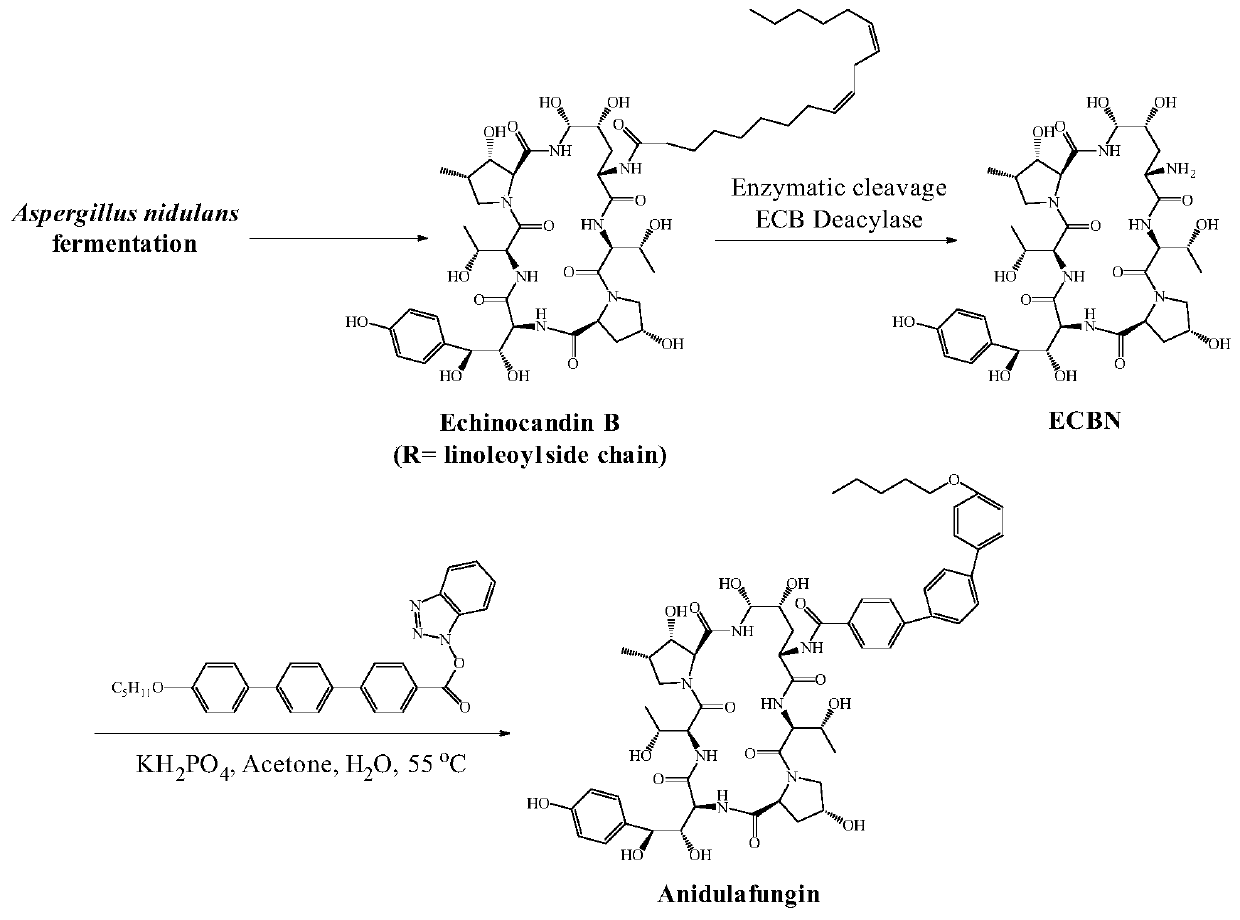
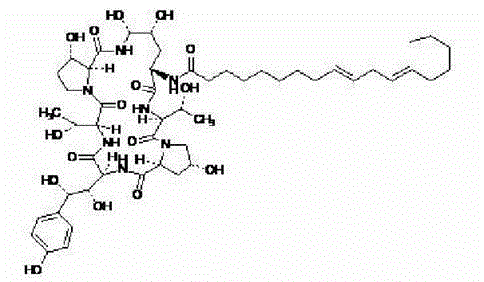
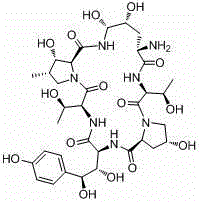
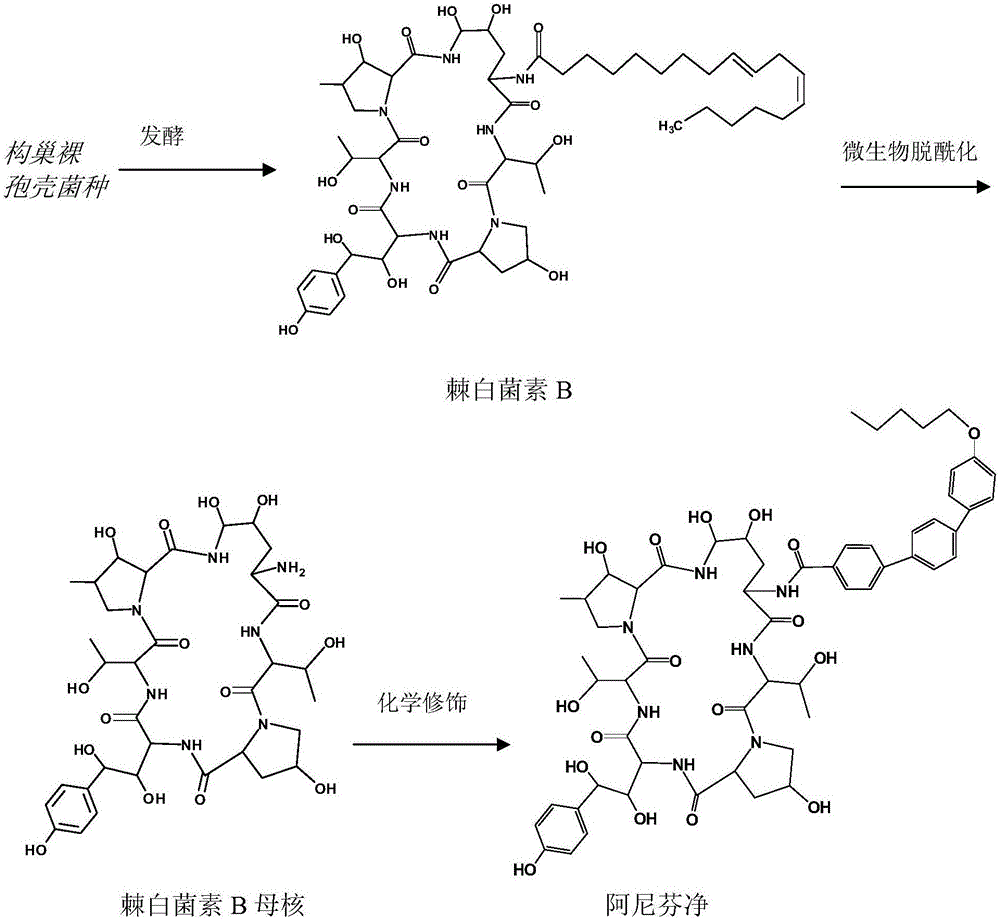
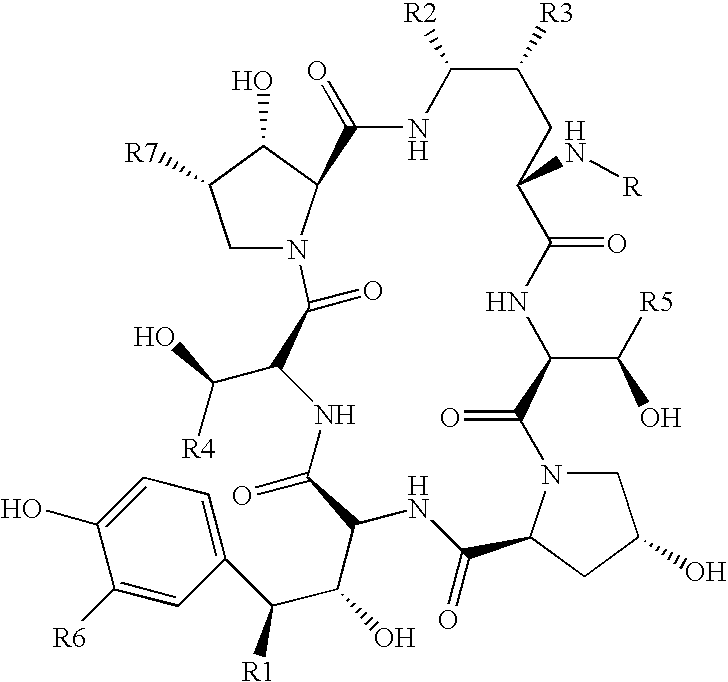
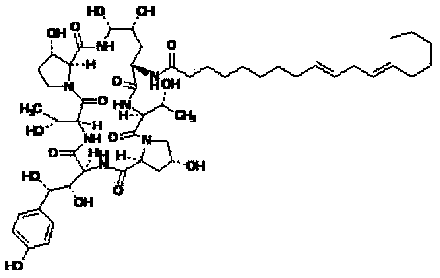
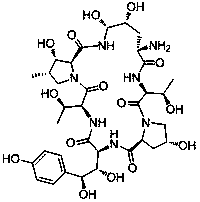
Echinocandin B, a lipopeptide, is a naturally occurring cyclic hexapeptide with a linoleoyl side chain. It belongs to a class of antifungal agents called echinocandins, which inhibits the synthesis of glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall, via noncompetitive inhibition of a crucial enzyme, β-(1→3)-D-glucan synthase. Echinocandin B is a fermentation product of Aspergillus nidulans and the closely related species, A. rugulosus; discovered in 1974 in A. nidulans var. echinulatus strain A 32204 in Germany, it was the first of the echinocandin class of antifungals.
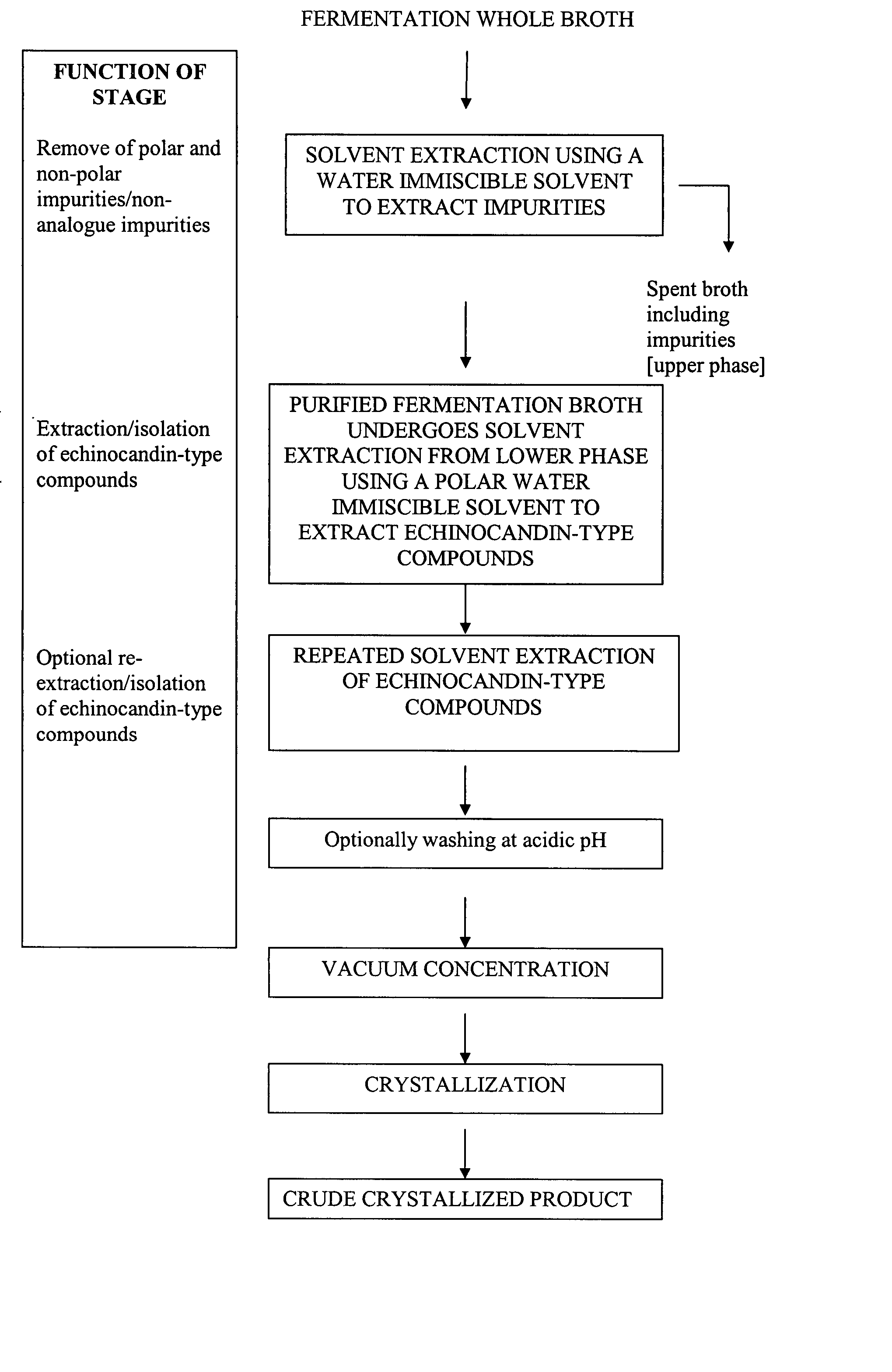
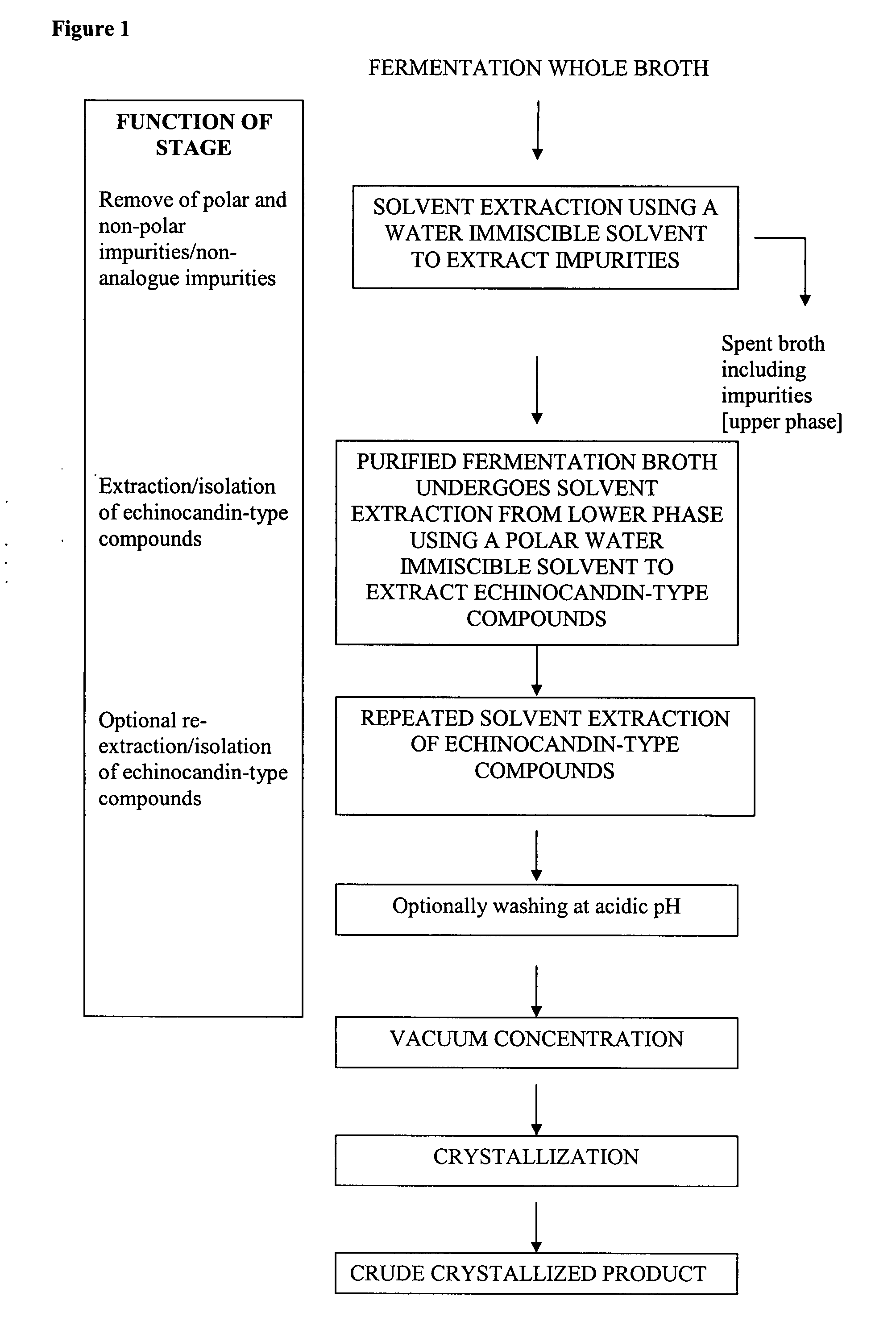
Purification processes for echinocandin-type compounds
InactiveUS20080108806A1Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPurification methodsEchinocandin B
The present invention provides a method of preparing and purifying echinocandin-type compounds, such as pneumocandin Bo, WF 11899A, and echinocandin B. These compounds are fermentation products that are used to prepare semi-synthetic products such as the antifungal products Caspofungin, Mycafungin, and Anidulafungin.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Echinocandin B high-producing strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103289901APromote stable and high yieldStable genetic traitsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEchinocandin B
The invention discloses an Echinocandin B high-producing strain which is a mutant strain of Aspergillus rugulovalvus ATCC 58398. The strain is collected in the General Microorganism Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms and has the collection number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 5413. The invention also discloses application of the Echinocandin B high-producing strain. By using the obtained Echinocandin B high-producing strain, the yield of the prepared Echinocandin B reaches about 800 mg / l.
Owner:NOVOCODEX BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
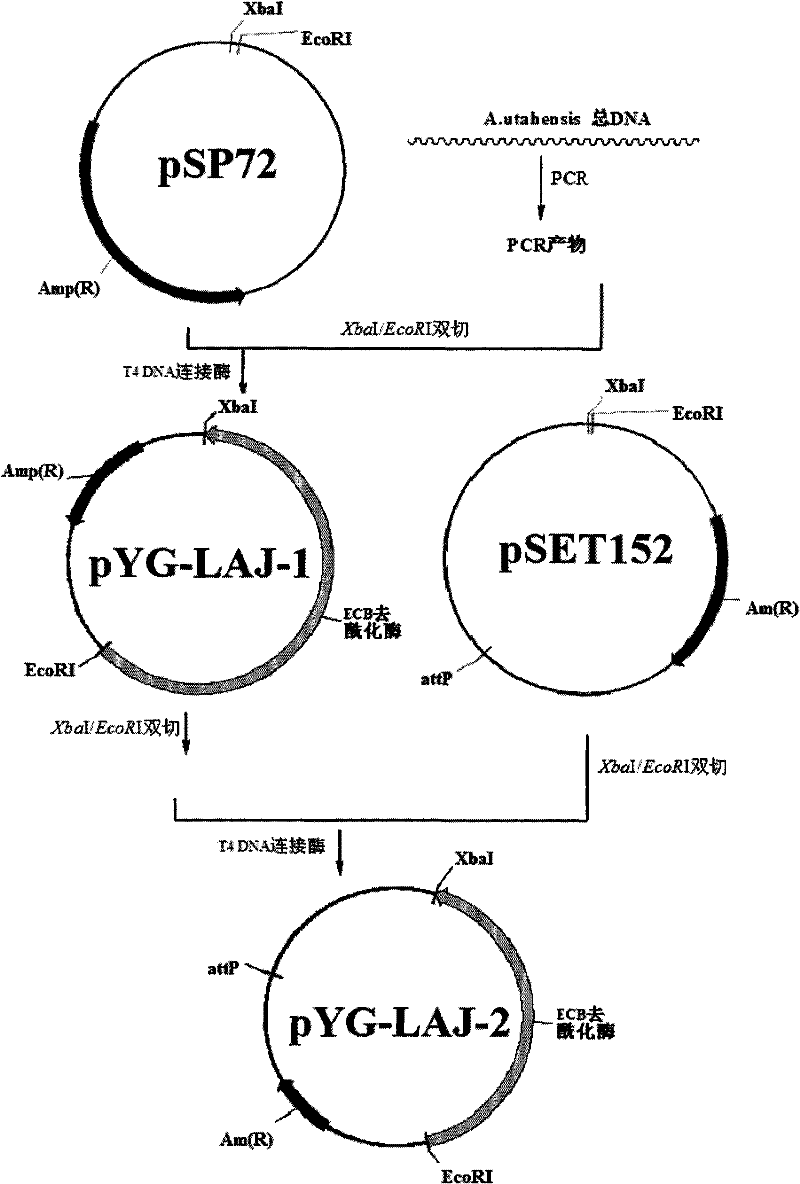
Gene engineering bacterium for high efficiency conversion of echinocandin B and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102443560AIncrease productionImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEchinocandin BMicrobiology
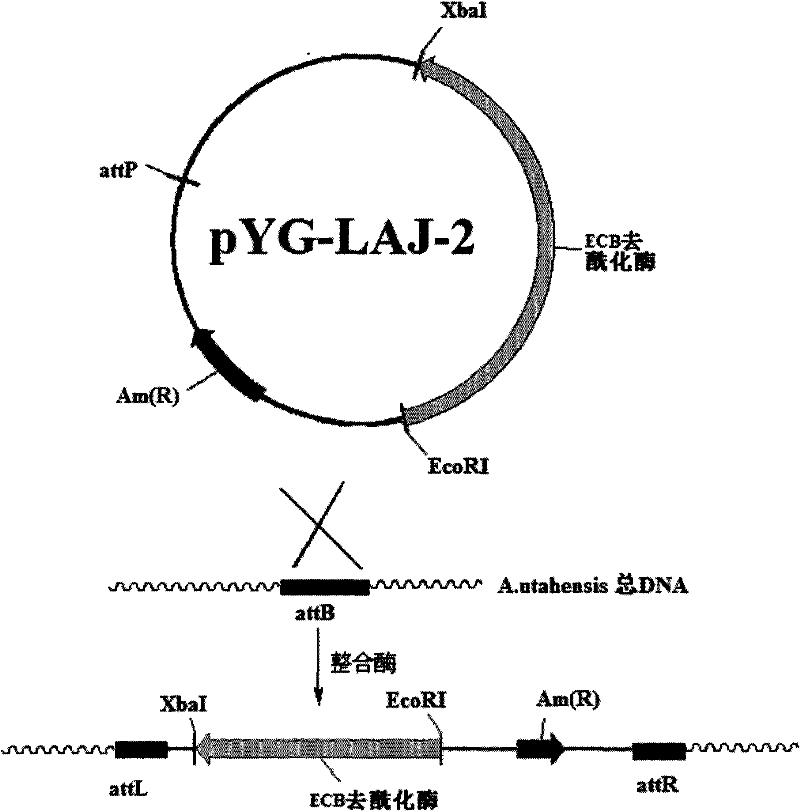
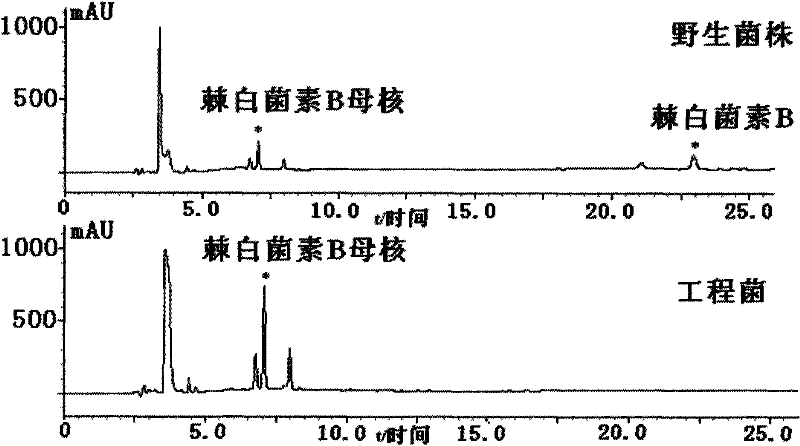
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterium for the high efficiency conversion of echinocandin B and a preparation method thereof. The echinocandin B is an engineering bacterium of an expression cassette integrated with echinocandin B deacetylase gene in a genome of Actinoplanes utahensis wild strain. The conversion of echinocandin B verifies that the conversion efficiency of the gene engineering bacterium is 1.8 times the conversion efficiency of the wide stain.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD
Method for converting echinocandin B into echinocandin B parent nucleus through microbial fermentation
ActiveCN103374593AHigh molar conversionEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a method for converting echinocandin B into an echinocandin B parent nucleus through microbial fermentation. The method is characterized by comprising the following step of: adding an echinocandin B substrate in a fermentation process to carry out conversion, wherein the echinocandin B substrate is added in batches or added in a flowing manner.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENYUAN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Separation purification method and use of echinocandin B
ActiveCN103724403AReduce usageAvoid excessive demandsAntimycoticsPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyCyclic peptide
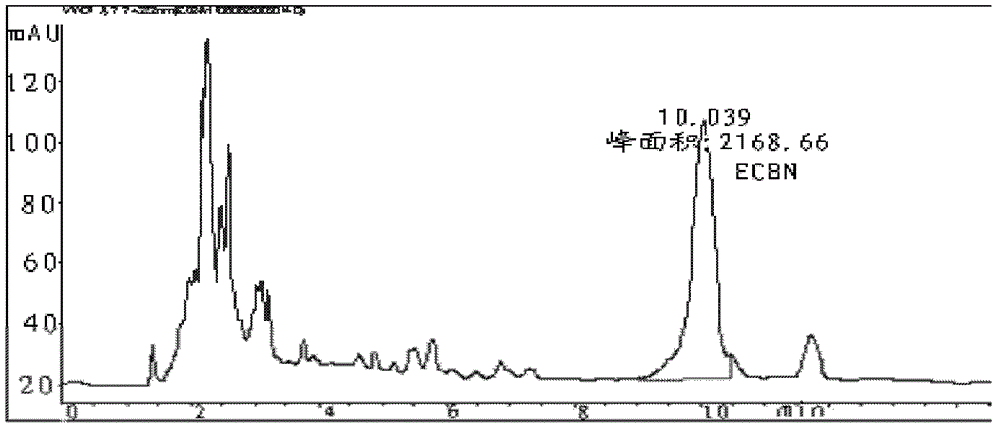
The invention provides a method for separating echinocandin B from fermentation broth and a use of echinocandin B. The method comprises the following steps that through fermentation broth acidification, extraction and concentration, concentrated liquid is obtained; and the concentrated liquid is fed into a reverse phase silica gel column and then is subjected to separation and concentration so that echinocandin B is obtained. The echinocandin B separated by the method has high purity and is a good raw material for preparation of echinocandin cyclopeptide parent nucleus and antifungal drugs. The method has a high finished product yield, utilizes safe and cheap solvent and instruments, has a low production cost and simple processes and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHONGQING QIANTAI BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE +1
Method for converting echinocandin B by using microbial enzyme
ActiveCN103074403AEasy to separate and purifyHigh molar conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventPhosphate
The invention provides a method for converting echinocandin B (ECB) by using microbial enzyme. The method comprises the steps that: (1) microbes are fermented, such that echinocandin B deacylase is obtained; (2) when fermentation is finished, phosphate is added into the fermentation broth; ultrasonic processing is carried out; and supernatant is obtained by centrifugation, and the supernatant is echinocandin B deacylase crude enzyme solution; (3) the crude enzyme solution is purified, such that echinocandin B deacylase enzyme solution is obtained; (4) echinocandin B is dissolved in ethanol, and is mixed with the deacylase enzyme solution; mixing and stirring are carried out, such that the material is converted into echinocandins B nucleus; when conversion is finished, filtering is carried out; and the filtrate is obtained; and (5) the filtrate is processed by using macroporous adsorption resin; echinocandins B nucleus is absorbed on resin; and echinocandins B nucleus is eluted by using an organic solvent. According to the invention, a molar conversion rate is high, a conversion time is short, an obtained product is easy to separate and to purify, and ECB deacylase can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Method for preparing echinocandin B parent nucleus
ActiveCN103387606AEasy to operateSuitable for large-scale industrial productionPeptidesFiltrationEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for preparing echinocandin B parent nucleus. The method comprises the steps that: (1) when echinocandin B conversion is finished, pump filtration is carried out; a filtrate is obtained, and the filtrate is processed by using an acidic alumina column; (2) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (1) is regulated to 4-5; rotary evaporation concentration is carried out; the material is processed by using macroporous non-polar resin; salt is removed by water washing; and a methanol aqueous solution is used for gradient elution; (3) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (3) is regulated to 6-7; the material is processed by using reversed-phase filler chromatographic column; and a methanol aqueous solution is used for elution; and (4) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (3) is regulated to 4-5; rotary evaporation concentration is carried out; and lyophilization is carried out, such that echinocandin B parent nucleus is obtained. With the method, a final purity of echinocandin B parent nucleus can be improved to higher than 95%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENYUAN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Recombinant ECB (echinocandin B) deacylase mutant and application
ActiveCN109897843AImprove catalytic performanceHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesAgricultural scienceDouble mutation
The invention discloses a recombinant ECB (echinocandin B) deacylase mutant and an application in synthesis of ECB parent nucleus from the ECB by biocatalysis. The deacylase mutant is obtained throughsingle mutation or double mutation of the 287th and 527th sites of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. AuEBDA primary structure and enzyme conformation are changed through mutation of an auebda gene sequence, and the catalytic performance of AuEBDA is improved. Influences of G287Q and R527V substitution on activity of ECB deacylase are systemically analyzed. The enzyme activity of constructed double mutant AuEBDA-G287Q / R527V is improved by 2.5 times than that of parent wild AuEBDA, and the catalytic efficiency kcat / Km is increased by 2.9 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for increasing yield of anidulafungin precursor compound Echinocandin B
ActiveCN103509840ARaise the level of fermentationIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-threonineOrnithine synthesis
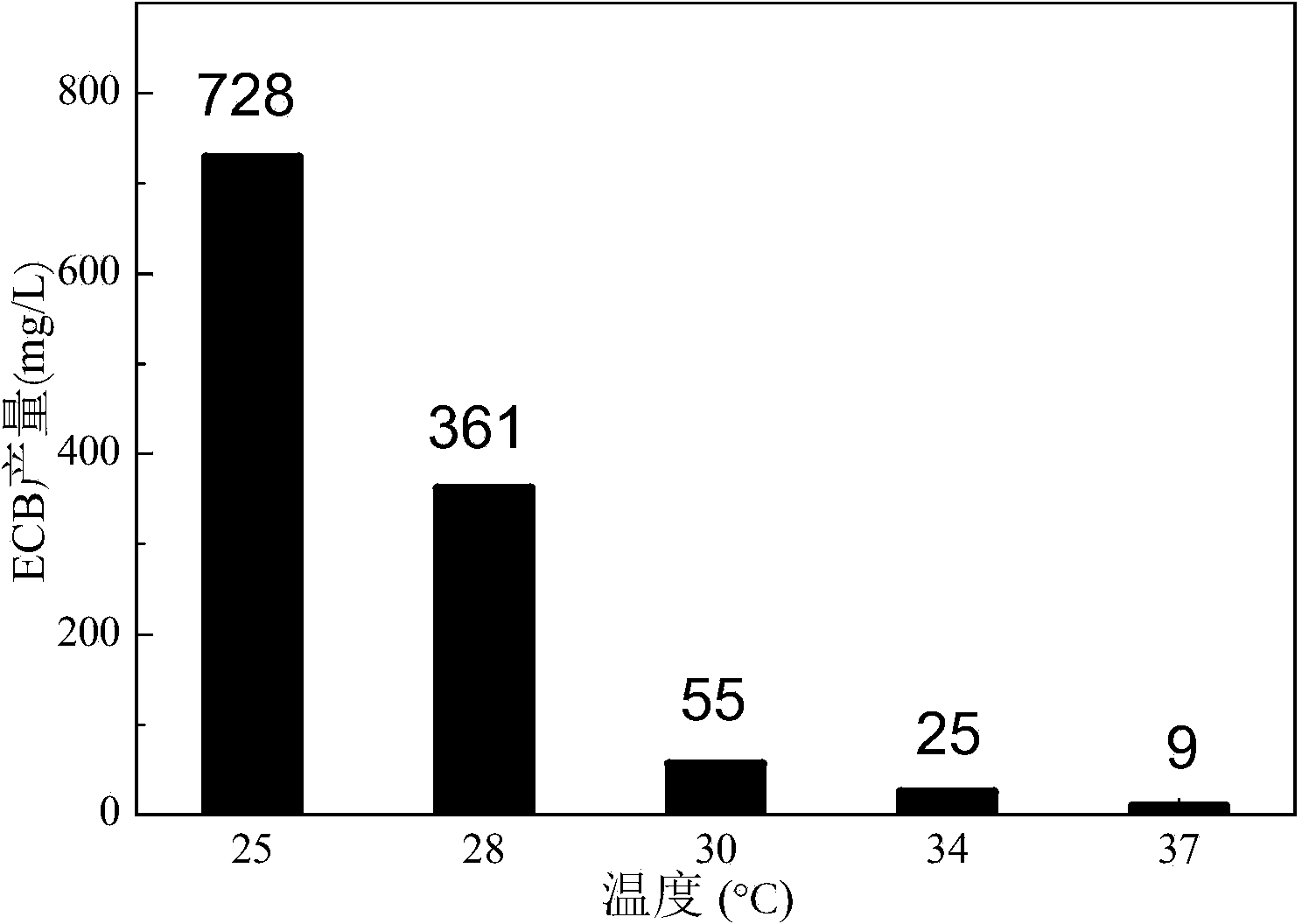
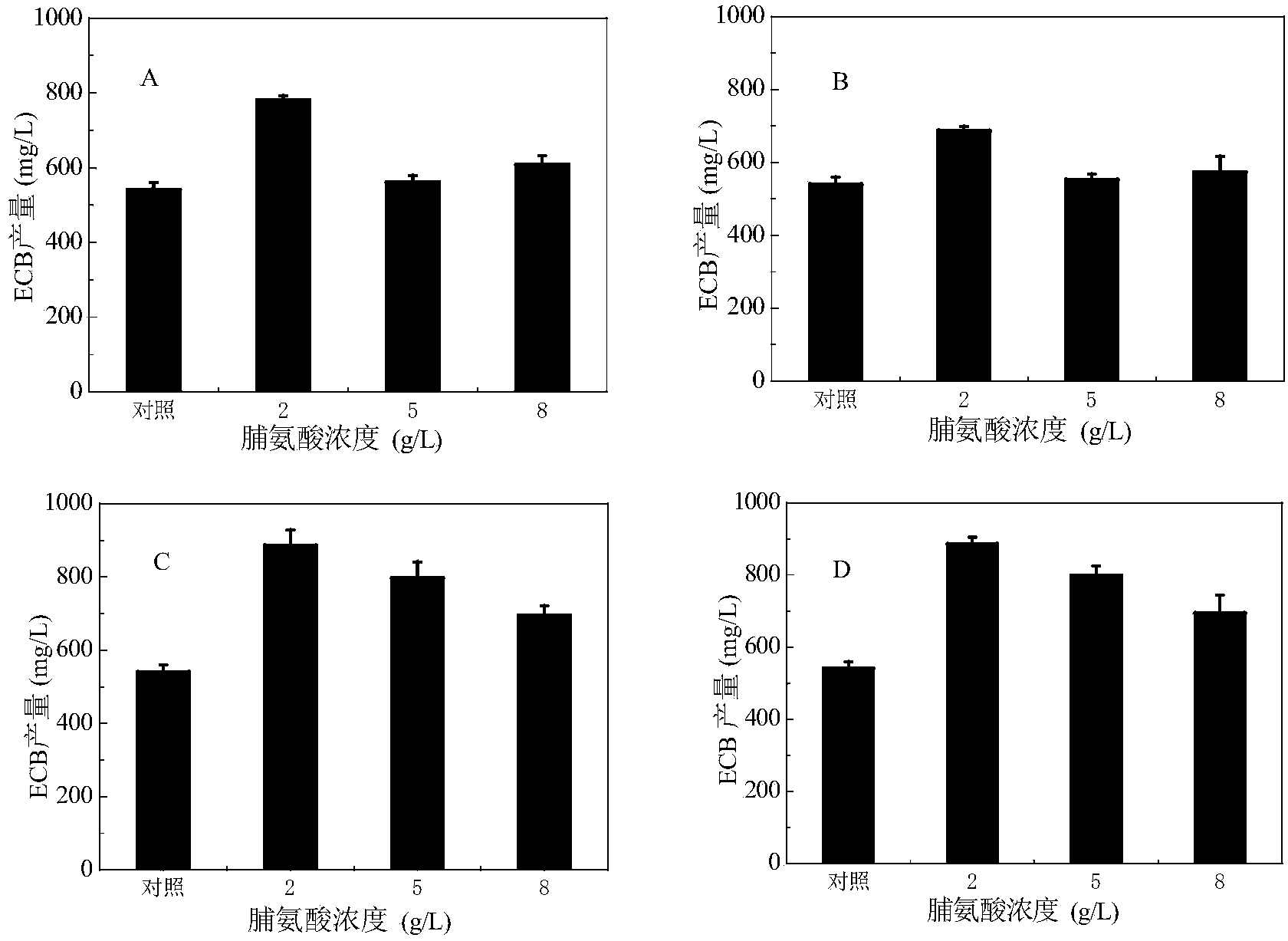
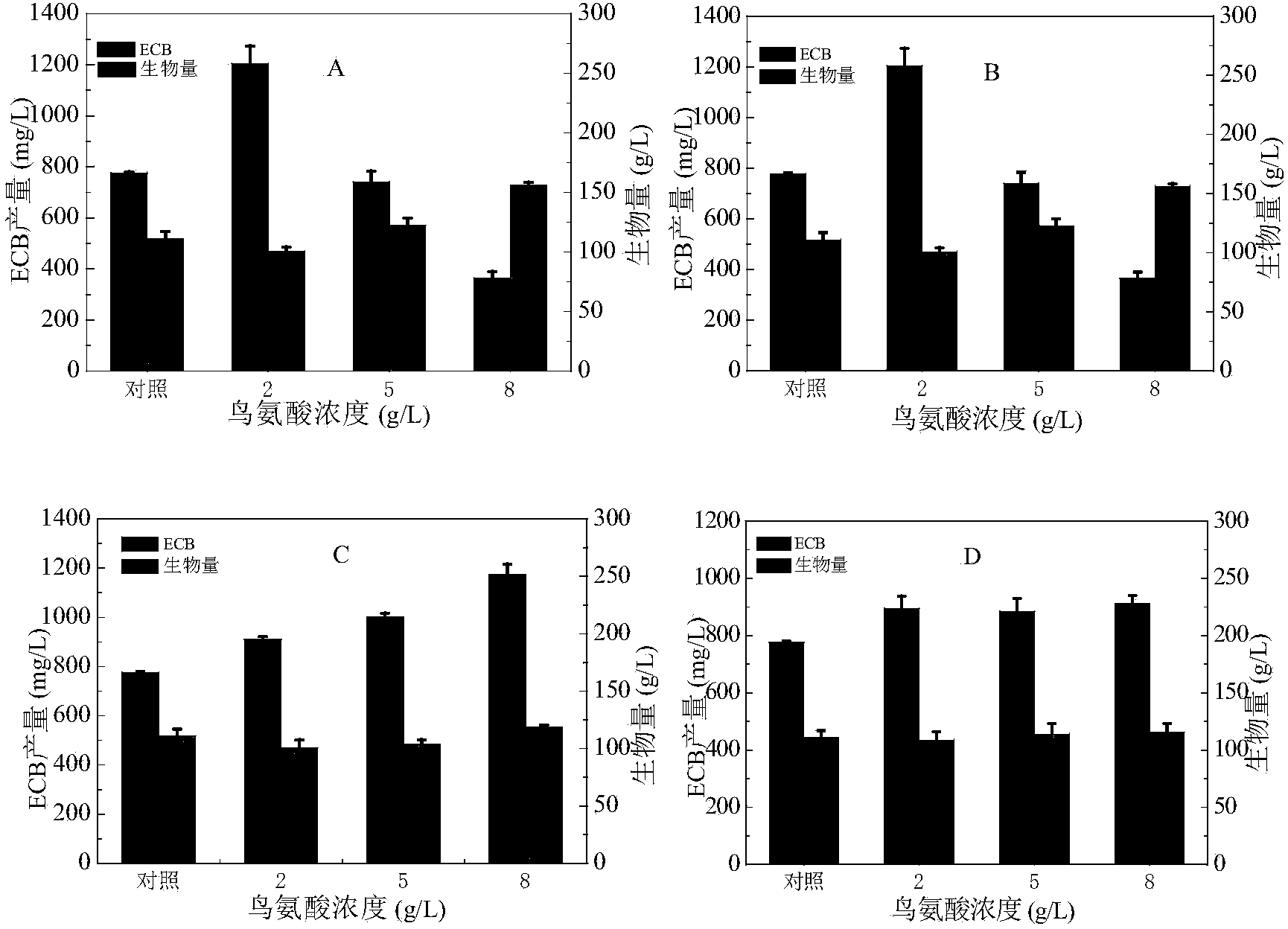
The invention provides a method for increasing the yield of an anidulafungin precursor compound Echinocandin B (ECB). The method comprises the following steps: preparing a fermentation culture medium for culturing Aspergillus nidulans for synthesizing ECB, inoculating aspergillus nidulans, culturing for 3 days at 28-37 DEG C, and continuously culturing at 25 DEG C till the fermentation is accomplished. Compared with constant temperature culture, the method adopts the strategy that the ECB is cultured at 37 DEG C at the early three days and is cultured at 25 DEG C at the later 9 days, so that the yield of the ECB is increased to be 1,237mg / L from 728mg / L; in addition, the yield of the ECB is increased to be 850mg / L from 540mg / L by adding 2g / L proline on the sixth day; and the yield of the ECB can be respectively increased by 21.9% and 55.2% by adding 2g / L threonine and 2g / L ornithine into the culture medium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Screening method of high-producing strain of producing strain of echinocandins B
ActiveCN107779402ASimple and fast operationSimple stepsFungiMutant preparationInhibition zoneOrganic solvent
The invention establishes a screening method of a high-producing strain of a producing strain of echinocandins B, and a strain obtained by screened is preserved. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly, according to the characteristic of feedback inhibition of a product of the producing strain of the echinocandins B, adding an appropriate amount of echinocandins B into a screening plate for primary screening, so as to screen out strains with the characteristic of feedback inhibition of the product removed; next, soaking mycelia, inducing the strains into an organic solvent,extracting the echinocandins B in the mycelia, and rescreening the high-producing strain of the echinocandins B from the primarily screened strains according to the size of an inhibition zone by adopting the inhibition of the echinocandins B on candida albicans, so as to achieve the purpose of rescreening; finally, investigating the production capacity of the screened out high-producing strain with a fermentation shake flask. The screening method is simple, convenient and efficient, so that the screening period is greatly shortened, and the screening efficient of the strain is improved.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
A microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B
ActiveCN105648000AImprove solubilityEasy to extractMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingBiotechnologyEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B, and particularly relates to a method of converting the echinocandin B into an echinocandin B nucleus. The method includes performing microbial fermentation to produce echinocandin B deacylase, extracting to obtain crude enzyme, and converting through adding the crude enzyme and the echinocandin B in a batch manner. The method is high in mole conversion ratio, high in product concentration, and beneficial to separation and purification. An echinocandin B substrate can be recovered and reutilized, thus reducing a production cost.
Owner:CHONGQING QIANTAI BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE +1
Method for fermenting high-yield echinocandins B through aspergillus nidulans
ActiveCN108342437AControl the shape of bacteriaImprove and stabilize fermentation yieldMicroorganism based processesPeptidesMyceliumEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a method for fermenting high-yield echinocandins B through aspergillus nidulans. The method includes the steps that a fermentation culture medium is inoculated with the aspergillus nidulans, culture is carried out at the temperature of 25 DEG C, fermentation liquor containing echinocandins B is obtained, the fermentation liquor is separated and purified, and echinocandins Bare obtained; by optimizing the varieties of carbon sources, adding particles and the like, the forms of mycelia in the fermentation process of the aspergillus nidulans are controlled, the mycelia are coccoid, and the problems that as the mycelia are too long during fermentation, the viscosity is high, dissolved oxygen is low, and mass transfer is insufficient are solved; by analyzing key metabolism components in the ECB synthesis process and optimizing a precursor adding strategy in the fermentation process, the yield of fermentation products is further increased by one time or above, and broad application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Emericella nidulans for producing echinocandin B and application of emericella nidulans
ActiveCN106497794AStable genetic traitsGood reproducibilityFungiMicroorganism based processesEchinocandin BFermentation
The invention discloses emericella nidulans for producing echinocandin B and application of the emericella nidulans. The preservation number of the emericella nidulans is CGMCC No.10988. When the emericella nidulans for producing echinocandin B is adopted for tank fermentation, the yield of echinocandin B can be up to 4016mg / L. The emericella nidulans for producing echinocandin B, which is disclosed by the invention, is high in emericella nidulans fermentation valence, and has a very good application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Preparation method of deoxy analog of Echinocandin B
InactiveCN101993477AReduced purification stepsLower conversion costsPeptide preparation methodsEchinocandin BEthyl acetate
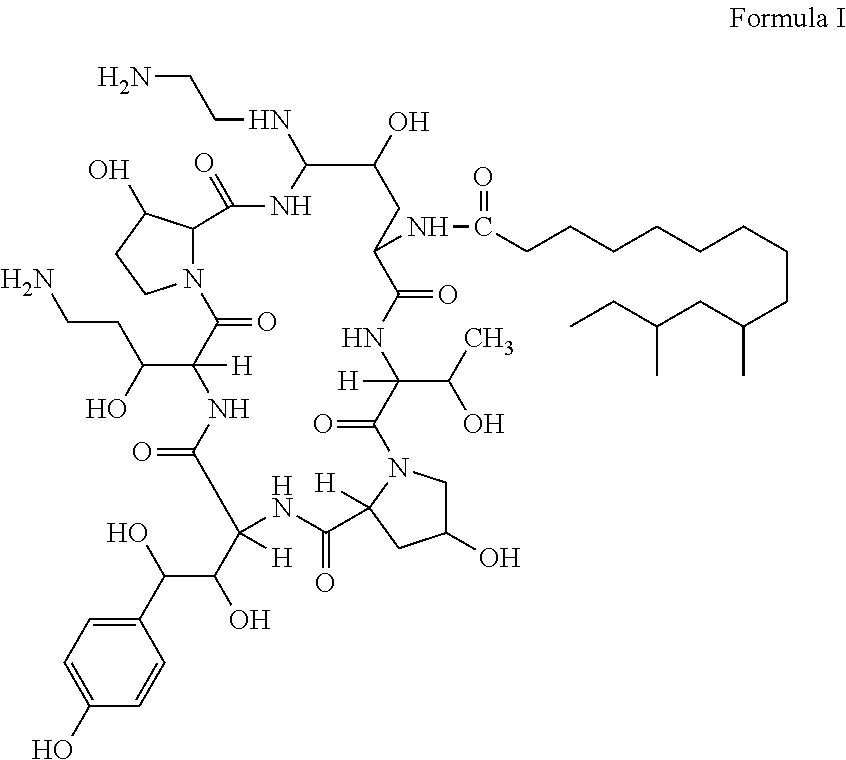
The invention discloses a preparation method of a deoxy analog of Echinocandin B. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing a fermenting mixture of Echinocandin B with an organic solvent to obtain a solution 1; (2) mixing the solution 1 with an acid water solution to obtain a solution 2; and (3) standing the solution 2 at the temperature of 30-50 DEG C for 12-60h to obtain the deoxy analog of a compound shown as formula I, in the formula, R is linolenic acyl, R1=OH, R2=OH, and R3=OH; the organic solvent is selected from methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, acetone or chloroform; acid in the acid water solution is selected from hydrochloric acid, acetic acid or citric acid, wherein the concentration of the acid is 1-3mol / L; and pH of the solution 2 is 1-6.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Gene engineering bacterium for efficiently converting Echinocandin B and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102443561AAvoid the disadvantages of poor genetic stability and prone to reverse mutationsStable conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEchinocandin BTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterium for efficiently converting Echinocandin B and a preparation method thereof. The gene engineering bacterium is the engineering bacterium with an expression cassette of Echinocandin B acylase removal genes integrated in a genome of a wild strain of Streptomyces lividans. Through the conversion verification of the Echinocandin B, compared with that of the wild strain of Actinoplanes utahensis, the conversion speed of the gene engineering bacterium is improved by 1.5 times.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Hydrate of echinocandin B mother nucleus or salt thereof, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105669839AImprove stabilitySuitable for large-scale productionPeptidesFermentationEchinocandin BMedicinal chemistry
The invention provides a hydrate of echinocandin B mother nucleus or salt thereof. When mass percentage of water in the hydrate is 7.0-31.0%, the hydrate has excellent stability. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method and an application of the hydrate of echinocandin B mother nucleus or the salt thereof.
Owner:JIANGSU SENRAN CHEM +1
Method for preparing echinocandin B parent nucleus
ActiveCN103387606BEasy to operateSuitable for large-scale industrial productionPeptidesFiltrationEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for preparing echinocandin B parent nucleus. The method comprises the steps that: (1) when echinocandin B conversion is finished, pump filtration is carried out; a filtrate is obtained, and the filtrate is processed by using an acidic alumina column; (2) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (1) is regulated to 4-5; rotary evaporation concentration is carried out; the material is processed by using macroporous non-polar resin; salt is removed by water washing; and a methanol aqueous solution is used for gradient elution; (3) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (3) is regulated to 6-7; the material is processed by using reversed-phase filler chromatographic column; and a methanol aqueous solution is used for elution; and (4) the pH of the liquid collected in the step (3) is regulated to 4-5; rotary evaporation concentration is carried out; and lyophilization is carried out, such that echinocandin B parent nucleus is obtained. With the method, a final purity of echinocandin B parent nucleus can be improved to higher than 95%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENYUAN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for purifying echinocandin B parent nucleus
The invention discloses a method for purifying echinocandin B parent nucleus. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing solid-liquid separation on a conversion solution; 2) concentrating, and removing the moisture from the liquid obtained in the step 1); 3) crystallizing; and 4) separating crystals. The crystallizing method used in the method disclosed by the invention is simple andconvenient to operate, time-saving, low in cost and suitable for continuous production on various scales; the product obtained by crystallization is high in purity; and the adopted non-polar solvent is easily recycled, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing echinocandin B as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109593661AIncrease productionAvoid single exchangeFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEchinocandin B
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria for producing echinocandin B as well as a construction method and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacteria are characterized inthat a polyketide synthase gene associated with the synthesis of sterigmatomycin in a genome of the genetically engineered bacteria is inactivated or is genetically modified so as not to express the sterigmatomycin. The genetically engineered bacteria for producing echinocandin B as well as the construction method and the application thereof disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that the mononuclear treatment is not required to be performed on a strain in the construction process of the genetically engineered bacteria, so that the problems such as single exchange occurring through homologous recombination, poor genetic stability and easy reversion mutation are solved; the genetically engineered bacteria does not produce the sterigmatomycin, and the yield of the echinocandin B can be improved by 44 percent compared with that of a wild strain; through multiple passages, the fermentation property still remains stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Method for determining binding constants of echinocandins medicine and protein
InactiveCN103995037AReduces electrolyte dissociationAccurate determination of effective electrophoretic mobilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAntifungalPressure.drive
The invention discloses a method for determining binding constants of an echinocandins medicine and protein. Aiming at a hotspot echinocandins medicine developed from an existing antifungal medicine, the pressure-driven affinity capillary electrophoresis method is used for rapidly and accurately determining the binding constants of a receptor and a ligand; the binding of ECB (Echinocandins B) and BSA (Bull Serum Albumin) is determined, effective electrophoresis mobility of ECB in protein buffering solutions with different concentration can be accurately determined, and then the binding constants are calculated. The method is used for determining the binding of ECB and BSA so as to determine that ECB belongs to a strong binding type medicine; the method provides data support on knowing medicine effect expression of the echinocandins medicine and provides optimization evidences to subsequent data screening.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for converting echinocandin B by using microbial enzyme
ActiveCN103074403BEasy to separate and purifyHigh molar conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismOrganic solvent
The invention provides a method for converting echinocandin B (ECB) by using microbial enzyme. The method comprises the steps that: (1) microbes are fermented, such that echinocandin B deacylase is obtained; (2) when fermentation is finished, phosphate is added into the fermentation broth; ultrasonic processing is carried out; and supernatant is obtained by centrifugation, and the supernatant is echinocandin B deacylase crude enzyme solution; (3) the crude enzyme solution is purified, such that echinocandin B deacylase enzyme solution is obtained; (4) echinocandin B is dissolved in ethanol, and is mixed with the deacylase enzyme solution; mixing and stirring are carried out, such that the material is converted into echinocandins B nucleus; when conversion is finished, filtering is carried out; and the filtrate is obtained; and (5) the filtrate is processed by using macroporous adsorption resin; echinocandins B nucleus is absorbed on resin; and echinocandins B nucleus is eluted by using an organic solvent. According to the invention, a molar conversion rate is high, a conversion time is short, an obtained product is easy to separate and to purify, and ECB deacylase can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Purification processes for echinocandin-type compounds
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Method for cultivating roses through interspecific hybridization
ActiveCN113475384AStable traitsOvercoming barriers to interspecies hybridizationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyAnthesis
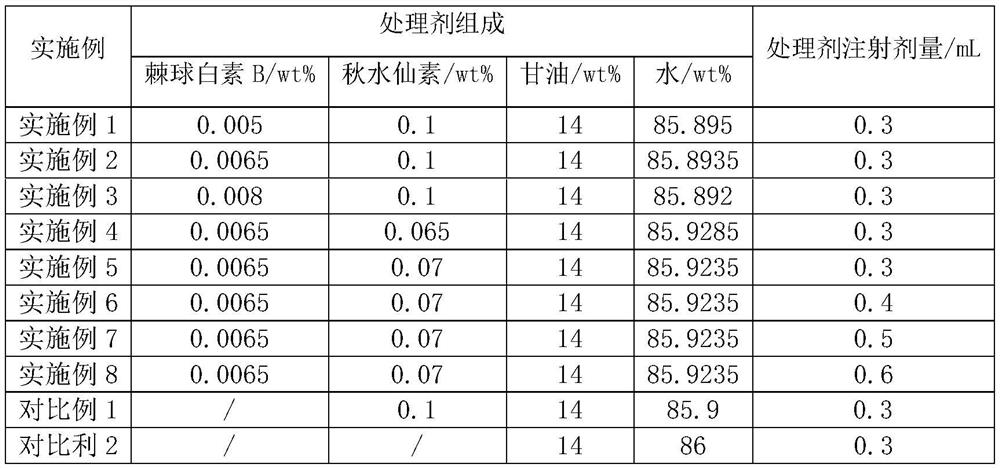
The invention discloses a method for cultivating roses through interspecific hybridization. The method comprises the following steps: S1, taking a female parent A line as Rosa Salvia and a male parent B line as Rosa rugosa 'Suyu', collecting pollen of the male parent B line, pollinating the pollen on stigmas of the female parent A line for hybridization, and cultivating and screening out the progeny F1 with continuous flowering characters of the female parent A line rosa and comprehensive characters of the male parent B line roses, wherein a treating agent is injected into the concave part of the receptacle before pollination of the female parent A line, and the treating agent is prepared from echinocandin B with the concentration of 0.005 wt% to 0.008 wt% and colchicine with the concentration of 0.01 wt% to 0.07 wt%; S2, performing selfing purification on the F1 to generate a plant F2 (pw) of which the flower color takes white as a main color and pink as an edging and a plant F2 (P) of which the flower color is pink; S3, performing selfing purification on the F2 to obtain pink edged white roses with stable target characters. The rose variety with high resistance and long flowering period is obtained.
Owner:柒久园艺科技(北京)有限公司 +1
Preparation method of anidulafungin precursor
The invention discloses a novel method of converting echinocandin B into echinocandin B parent nucleus. A crosslinked enzyme aggregation technique is applied to the process of conversion of echinocandin B into echinocandin B parent nucleus. The method comprises: preparing deacylase crosslinked enzyme aggregate with deacylase; allowing the crosslinked enzyme aggregate to convert echinocandin B intoechinocandin B parent nucleus. The preparation method enables the molar conversion rate to reach 85% to 90%; the production process is simplified; the cost is lowered.
Owner:BRIGHTGENE BIO MEDICAL TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD +1
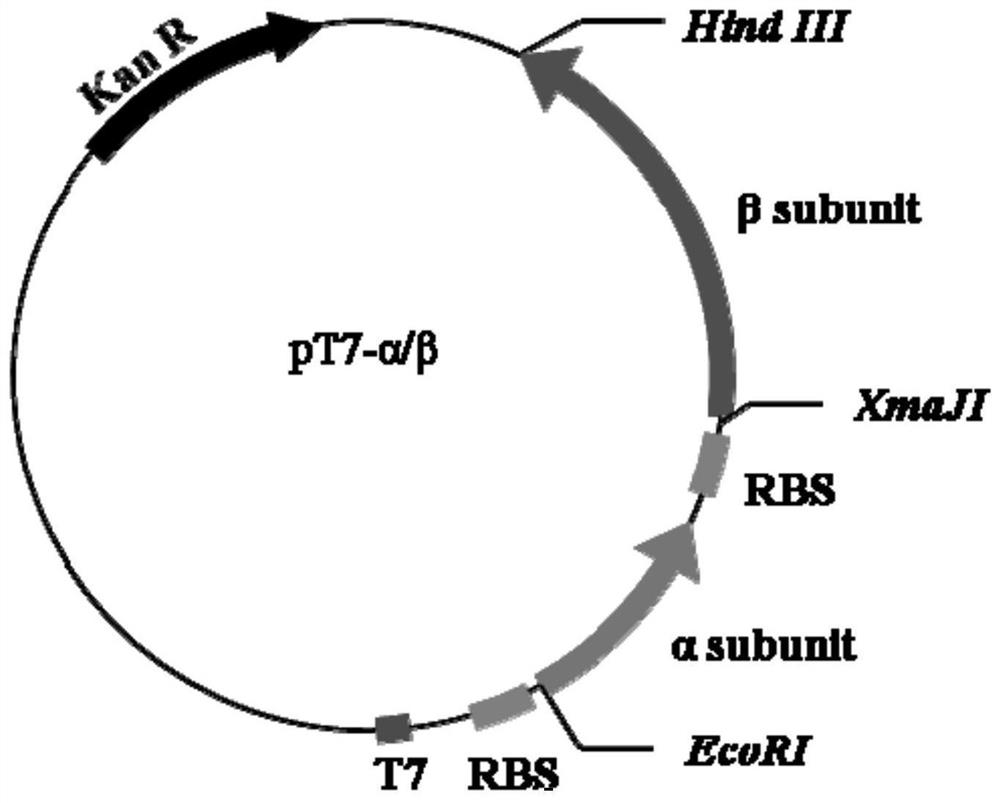
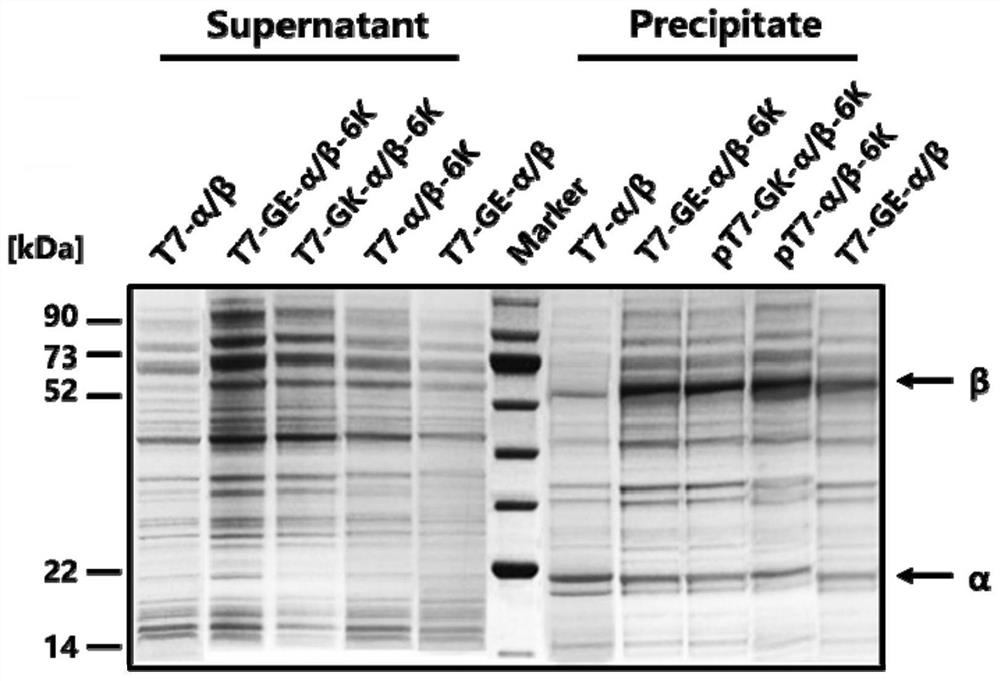
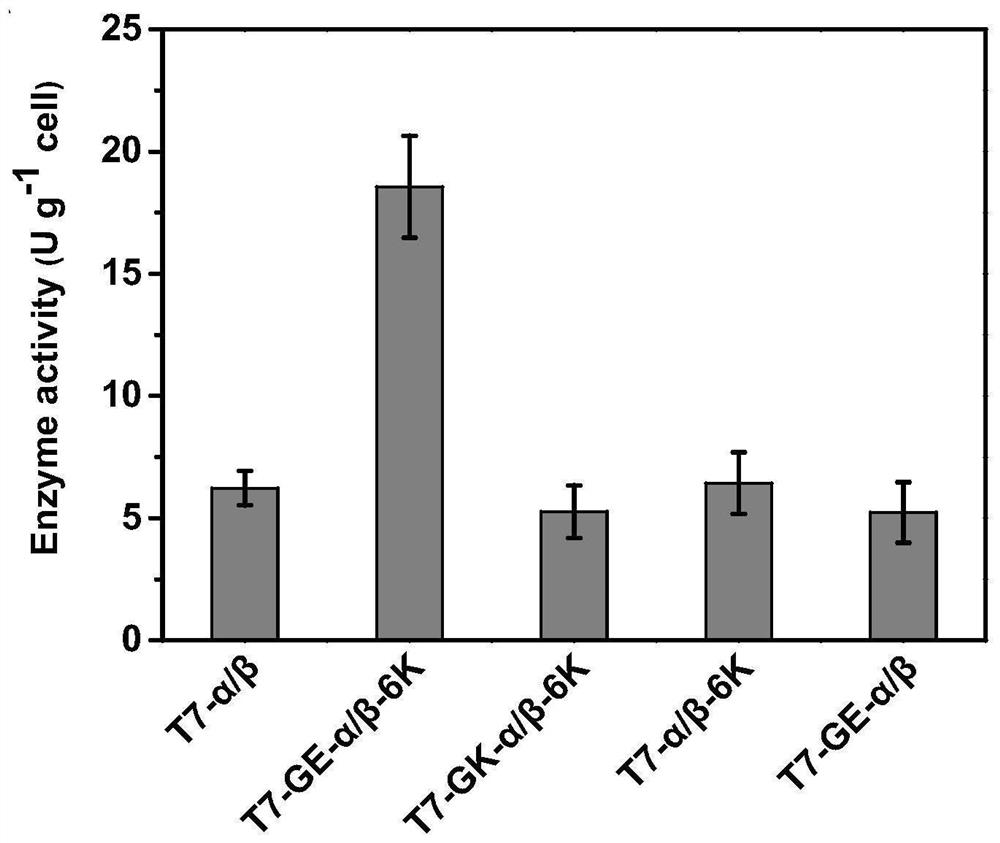
Expression cassette for recombinant expression of echinocandin B deacylase and application thereof
ActiveCN113174398AExpress effectively and efficientlyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaEchinocandin BPromoter
The invention discloses an expression cassette for recombinant expression of echinocandin B deacylase and an application thereof. The expression cassette comprises a promoter nucleic acid sequence, an RBS nucleic acid sequence, a nucleic acid sequence for coding an OmpA signal peptide, a nucleic acid sequence for coding a first lyotropic peptide, a nucleic acid sequence for coding an echinocandin B deacylase alpha subunit, a first termination codon, an RBS nucleic acid sequence, a nucleic acid sequence for coding an OmpA signal peptide , a nucleic acid sequence for encoding echinocandin B deacylase beta subunit, a nucleic acid sequence for encoding second solubilizing peptide, and second stop codon which are connected in sequence, wherein the amino acid sequence of the first solubilizing peptide is GEGEG, and and the amino acid sequence of the second solubilizing peptide is KKKKKK. The expression cassette can be used for expression to obtain the echinocandins B deacylase, the echinocandins B deacylase can be effectively and efficiently expressed by adding the two specific sequence dissolution promoting peptides, and the enzyme activity of thalli obtained through fermentation culture can reach 57.88 U / g after the thalli are broken.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for converting echinocandin B through actinoplanes utahensis
PendingCN107779487AImprove stabilityImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierOrganic solventEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a method for converting echinocandin B through actinoplanes utahensis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing actinoplanes utahensis so as to obtain a bacterial liquid, centrifuging to collect bacteria, suspending the bacteria in a buffer saline solution, adding a sodium alginate solution, uniformly mixing, stably injecting into a CaCl2 solution, performingimmobilization, and putting the immobilized beads into a column for later use; (2) dissolving echinocandin B into an organic solvent, putting into the buffer saline solution till the concentration ofthe echinocandin B is 0.1-5g / L, further putting the echinocandin B into the column obtained in the step 1), and performing conversion. The method has the remarkable advantages of being simple in process and low in cost, and the prepared immobilized cells have the advantages of good stability, high conversion rates and multiple times of repeated use.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
A kind of echinocandin b microbial enzyme conversion method
ActiveCN105648000BEasy to extractLow costMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingMicroorganismEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B, and particularly relates to a method of converting the echinocandin B into an echinocandin B nucleus. The method includes performing microbial fermentation to produce echinocandin B deacylase, extracting to obtain crude enzyme, and converting through adding the crude enzyme and the echinocandin B in a batch manner. The method is high in mole conversion ratio, high in product concentration, and beneficial to separation and purification. An echinocandin B substrate can be recovered and reutilized, thus reducing a production cost.
Owner:CHONGQING QIANTAI BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE +1
Method for converting echinomycin B by immobilized microbial enzyme
InactiveCN109593809AEasy to storeEasy to separate and extractPeptidesFermentationEchinocandin BPre cooling
The invention discloses a method for converting echinomycin B by an immobilized microbial enzyme, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1), fermentingactinoplanesutahensis, collecting mycelia, disrupting cells through ultrasonic disruption by using a cell disrupting device, centrifuging, taking a supernatant to obtain a crude enzyme solution of echinomycin B deacylase; (2), slowly adding an ammonium sulfate solution into the crude enzyme solution in the step (1) to obtain a precipitate; (3), dissolving the precipitate in the step (2) in a buffered salt solution; (4), adding odium alginate into the solution in the step (3), stirring uniformly, then dropwise adding a pre-cooled aqueous calcium chloride solution, placing in a refrigerator overnight, and filtering to obtain the immobilized microbial enzyme; and (5), dissolving echinomycin B in ethanol, and adding the immobilized microbial enzyme in the step (4), converting, and collecting afiltrate to obtain an echinocandin B mother nucleus solution. By the method, the conversion rate is high, the conversion time is short, a product is easy to separate, a conversion solution contains less pigments, and the immobilized enzyme is easy to store and can be reused.
Owner:CHENGDU YATU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for preparing antifungal cyclic lipopeptide echinocandin B
ActiveCN107778358AAvoid the problem of clogging and contaminating macroporous resin columnsThe process steps are simplePeptide preparation methodsAlcoholEchinocandin B
The invention provides a method for preparing antifungal cyclic lipopeptide echinocandin B. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing solid-liquid separation on an ECB (Echinocandin) fermentation broth; 2) enriching with a macroporous adsorption resin ADS-17 or X-5; 3) eluting the macroporous adsorption resin with hot absolute methyl alcohol, and combining eluants; 4) concentrating the eluants, adding a sodium chloride solution, stirring, cooling for crystal separation, and drying crude ECB filter cakes; 5) filtering the crude ECB filter cakes with methanol, and treating filtratewith a reverse phase resin column XT30; 6) concentrating the reverse phase resin column XT30 eluant, adding the sodium chloride solution, stirring, cooling for crystal separation, and drying ECB filter cakes; 7) collecting a dried ECB product. By adopting the method, the problems that byproducts are hard to elute and solvents are wasted are simply and effectively solved. Solid-liquid separation of water-containing ECB can be effectively completed, and product degradation is remarkably reduced. The method is simple and feasible and is applicable to industrial production, and the final purity of the echinocandin B is improved to 99% or greater.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
A kind of preparation method of high-purity echinocandin b mother nucleus
ActiveCN103910783BQuality improvementHigh clarityPeptide preparation methodsOrganic solventFreeze-drying
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com