Gene engineering bacterium for efficiently converting Echinocandin B and preparation method thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and echinocandin, which is applied in the field of genetically engineered bacteria that can efficiently transform echinocandin B and its preparation, can solve the problem of low efficiency of transforming echinocandin B and long growth cycle of actinomycetes. and other issues to achieve the effect of stable conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Cloning of erythromycin resistance gene promoter and echinocandin B deacylase gene coding sequence
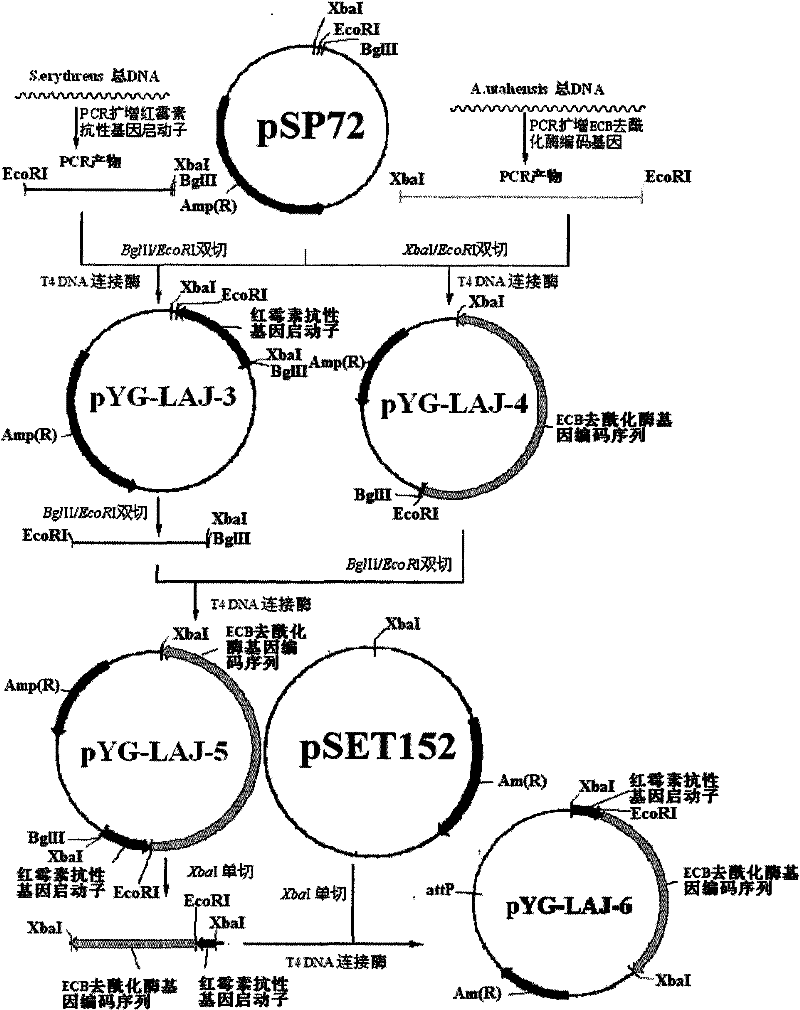
[0033] First, the total genome of the erythromycin-producing strain S.erythraea HL 3168E3 (ie S.erythraea ATCC11635) was used as a template to clone the erythromycin resistance gene promoter, the upstream primer: 5'-AAAAGATCTTCTAGAAGCCCGACCCGAGCA-3'; the downstream primer: 5' -AAAGAATTCTCCGGAGGTCGCACC-3', PCR was performed, and the resulting PCR product was purified and connected to plasmid pSP72 (purchased from Takara Company) to obtain plasmid pYG-LAJ-3, and sequenced, the sequence was compared with the online sequence (Gene ID: 4940594) Origin is 100%. The plasmid pYG-LAJ-3 was directly digested to obtain the erythromycin resistance gene promoter (EcoR I / Bgl II).
[0034] Primers were designed according to the echinocandin B deacylase gene and its sequence (Gene ID: 33036681) in GenBank, upstream: 5'-AAAAGATCTTCTAGAAGCCCGACCCGAGCA-3'; downstream: 5'-AAAGAAT...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Construction of specific site integration plasmid, conjugative transfer
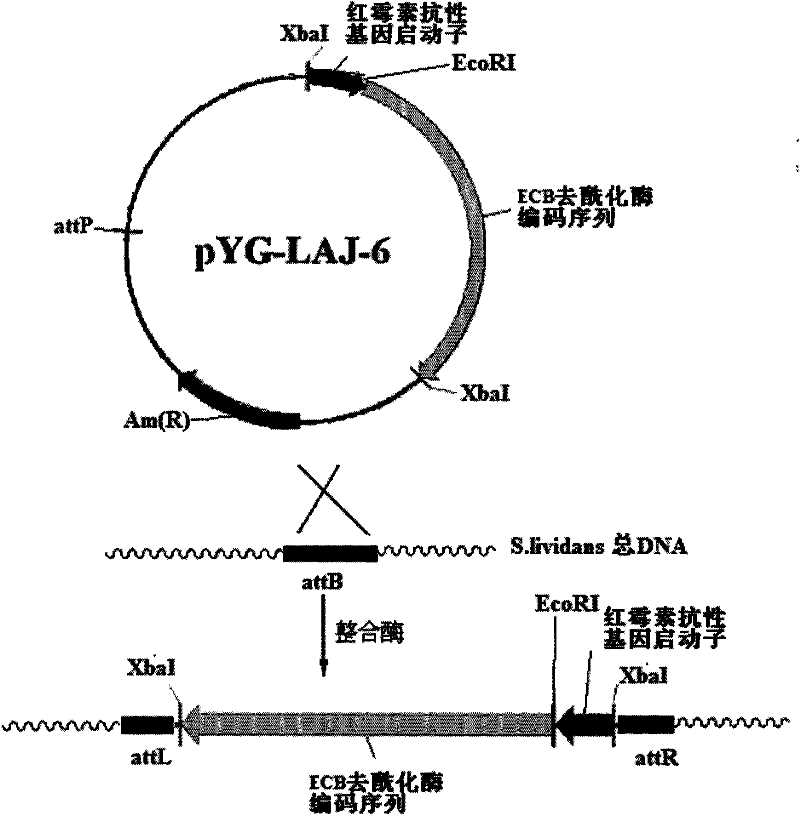
[0037] The erythromycin resistance gene promoter obtained in Example 1 and the fragment (XbaI / XbaI) of the echinocandin B deacylase gene coding sequence were connected into the plasmid pSET152 (XbaI / XbaI, dephosphorylated) purchased from Takara Company ) to obtain plasmid pYG-LAJ-6. This recombinant plasmid is an integrated plasmid containing the erythromycin resistance gene promoter and the echinocandin B deacylase gene coding sequence. This recombinant plasmid is used to transform Escherichia coli DH5α, and the transformants are picked and cultured in LB. The plasmid was digested and verified by PCR, and the site-specific integration plasmid pYG-LAJ-6 was finally constructed. The schematic diagram of the above plasmid construction process is shown in figure 1 .
[0038] Streptomyces lividans TK24 (CPCC 260835, derived from the Medicinal Microorganism Collection Center of China Commi...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Screening of Specific Site Homologous Recombination Engineering Bacteria
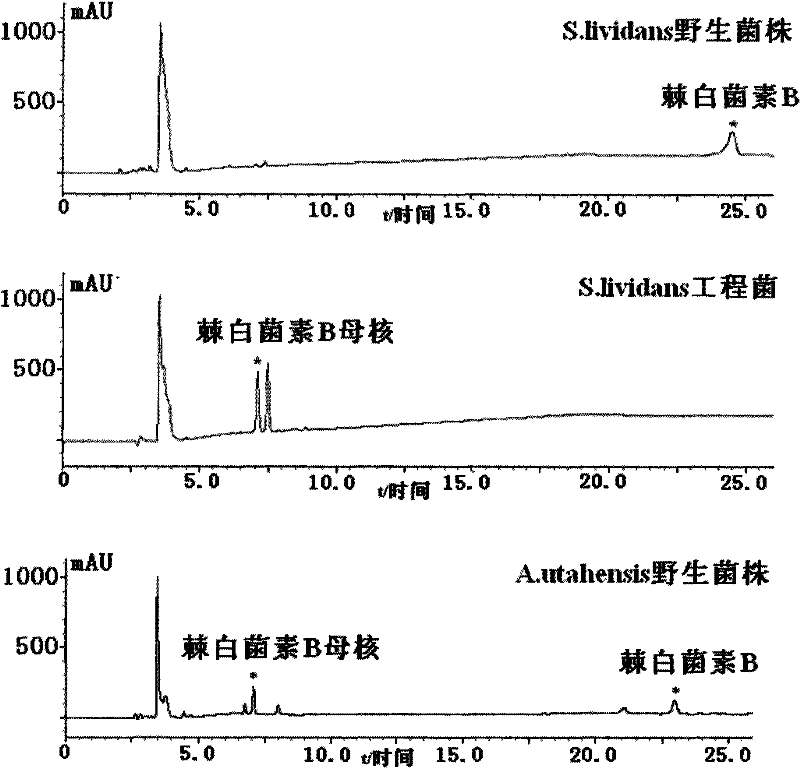
[0040] The zygotes were picked and cultured in TSB containing abramycin (50 μg / ml), and then the bacterial solution was applied to a slant medium containing abramycin (50 μg / ml) (soluble starch 2.0%, NaCl 0.05%) , K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 0.05%, KNO 3 0.1%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.001%, purified agar powder 2.0%, pH 7.4), cultivated at 30°C. Because pSET152 contains phage The integration site (attP), which can be specifically homologously integrated with the attB site in the genome of Streptomyces lividans, integrates the abramycin resistance gene and erythromycin resistance gene carried by the plasmid pYG-LAJ-6 The promoter and echinocandin B deacylase gene were inserted into the attB site in the chromosome of Streptomyces lividans, and amplified synchronously with chromosome replication, and the zygote could stably express the abramycin resistance gene and Echinocan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com