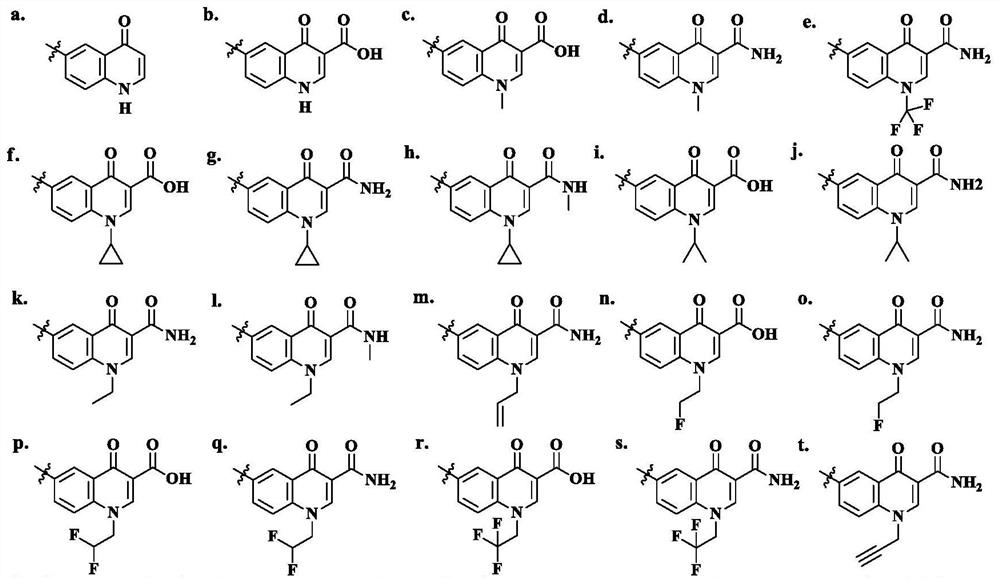
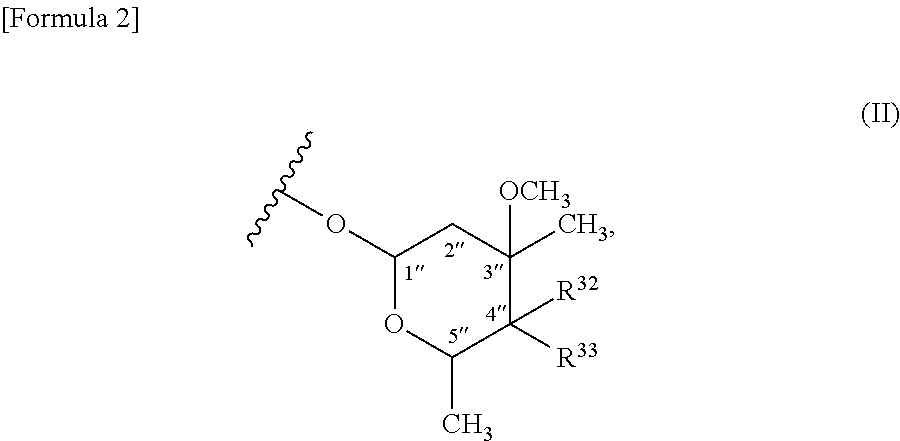
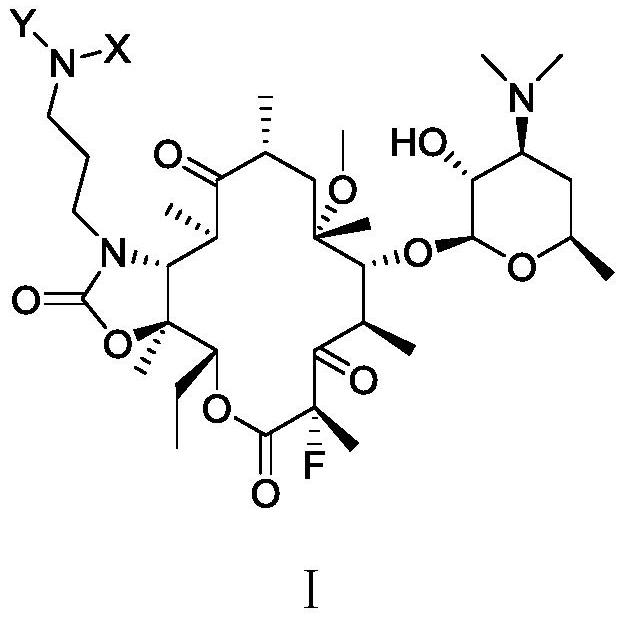
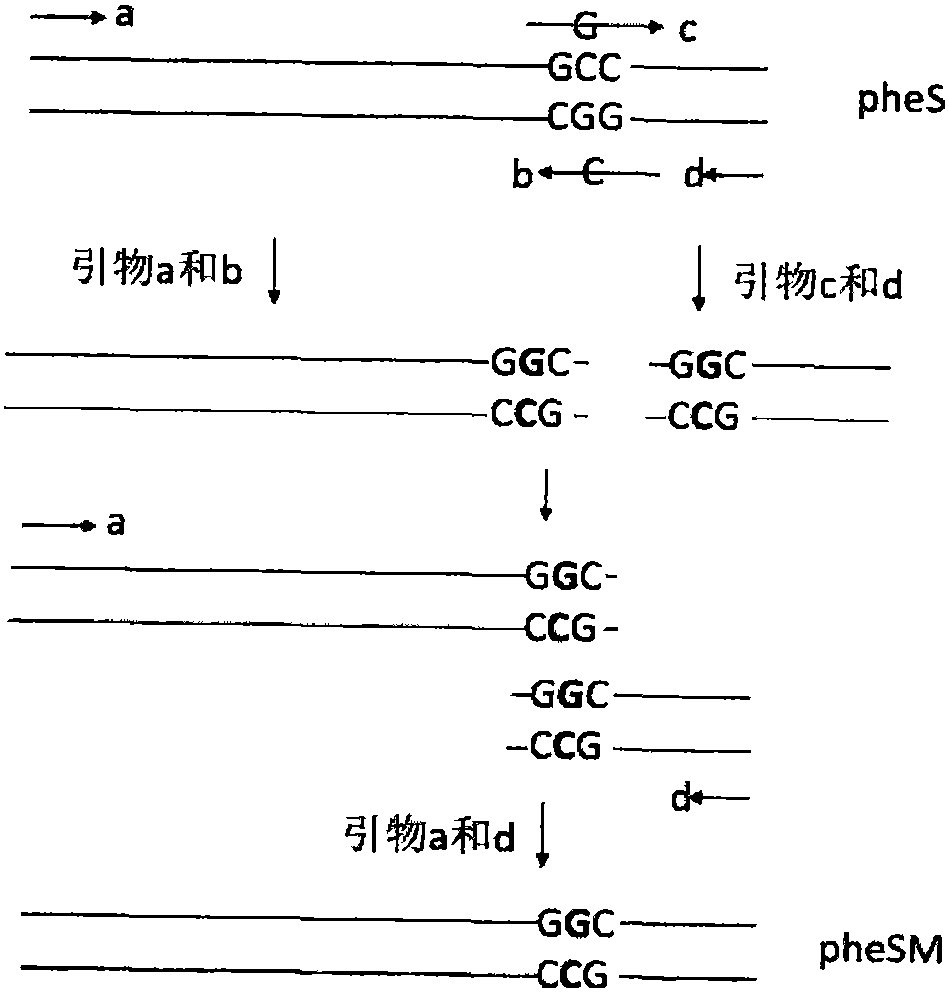Patents
Literature
31 results about "Erythromycin resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Erythromycin resistance among streptococci can be due to target-site modification by an rRNA-methylating enzyme or by an efflux system. Sensitivity testing and antibiotic policy are dependent on the mechanisms of macrolide resistance in streptococci.
Gene series technology for increasing main component content of gene engineering isovaleryl selectomycin
ActiveCN101649325ARaise the ratioSimple extraction processMicroorganism based processesFermentationGene engineeringBiology
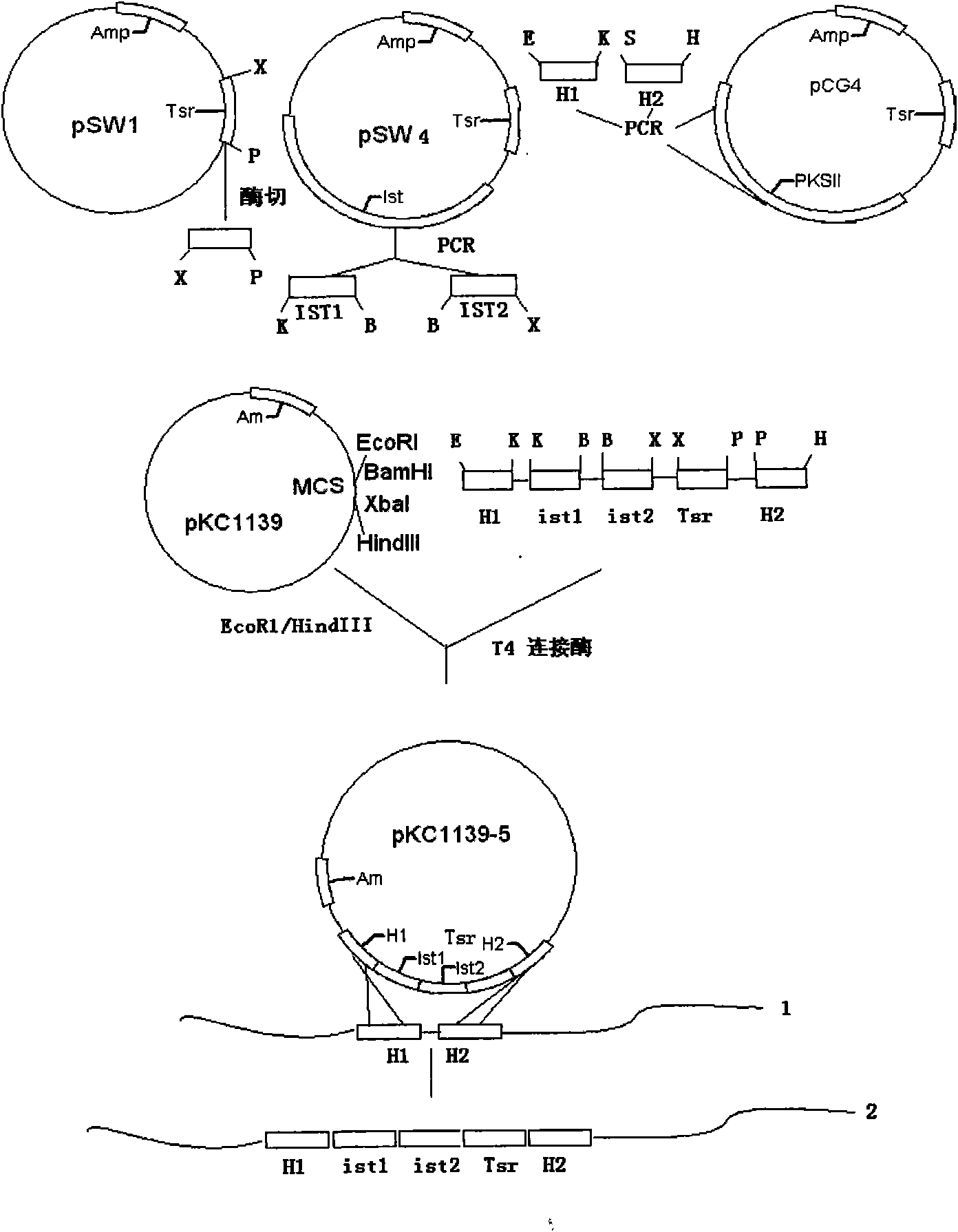
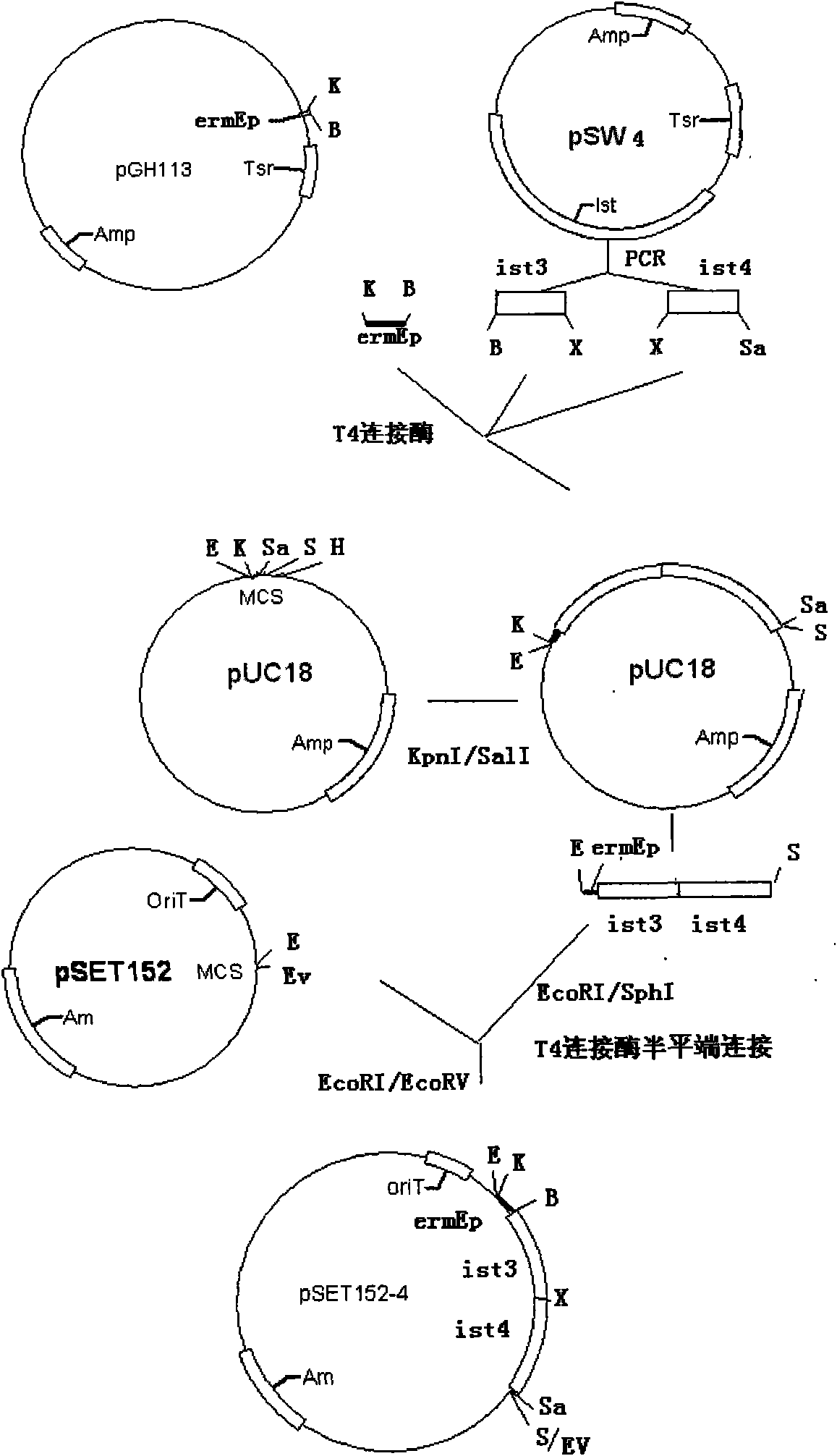
The invention relates to the application of a gene engineering technology in increasing an antibiotic component, in particular to a gene series technology for increasing the main component content ofgene engineering isovaleryl selectomycin. The gene series technology comprises the following steps: connecting ist genes which are closely related to selectomycin isovaleryl acylation in Beta selectomycin gene engineering bacteria in series; increasing the bacterial isovaleryl acylation generating capability by increasing gene dosage; using a promoter erythrocin resistance gene erm promoter sequence with strong promotion activity to replace the original ist gene promoter sequence so as to increase the expression of the series ist genes, and improve the proportion of isovaleryl selectomycin main components of the gene engineering bacteria from a headstream.
Owner:SHENYANG TONGLIAN GRP CO LTD
Detection chip for drug resistance gene of bacteria, and application thereof
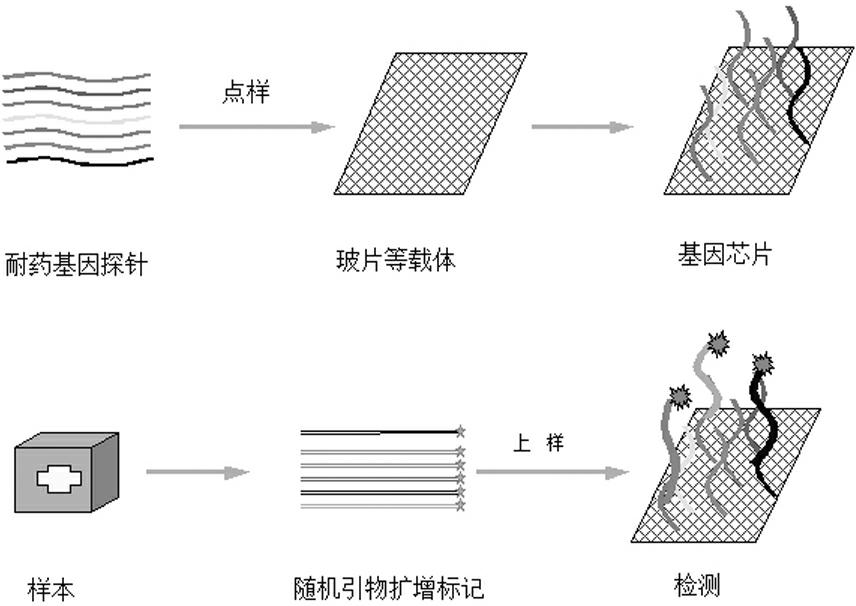
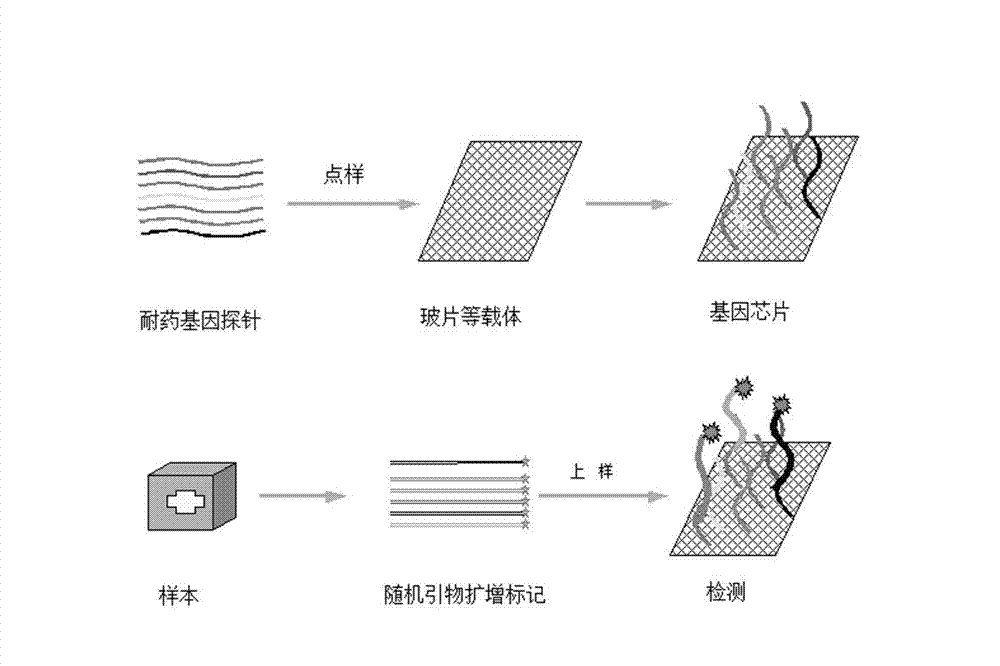
InactiveCN102321763AStrong specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOligonucleotideThroughput
The present invention relates to a high-throughput detection chip for drug resistance gene of bacteria, and an application thereof. The detection chip comprises 117 gene probes, the drug resistance gene probes are selected from 17 categories of drug resistance genes, which comprise extended spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, tetracycline resistance gene, aminoglycoside resistance gene, disinfectant resistance gene, erythromycin resistance gene, macrolide efflux gene, vancomycin resistance gene, multidrug resistance efflux pump gene, mupirocin resistance gene, sulfanilamide resistance gene, tylosin resistance gene, fluoroquinolone resistance gene, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and commonly-used genetic engineering vector resistance gene. The chip is adopted for detecting the resistance gene of the pathogenic bacteria. The chip is characterized in that: the chip comprises (1) 117-oligonucleotide probe composition and quality control probes of 17 categories of the drug resistance genes; (2) probe arrays, wherein the oligonucleotide probes are solidified on the vector material through arm molecules to form the probe arrays.
Owner:李越希
Engineering strain for directly producing gernebcin and use thereof
InactiveCN101392229ASimple production processReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsShuttle vectorQuality control
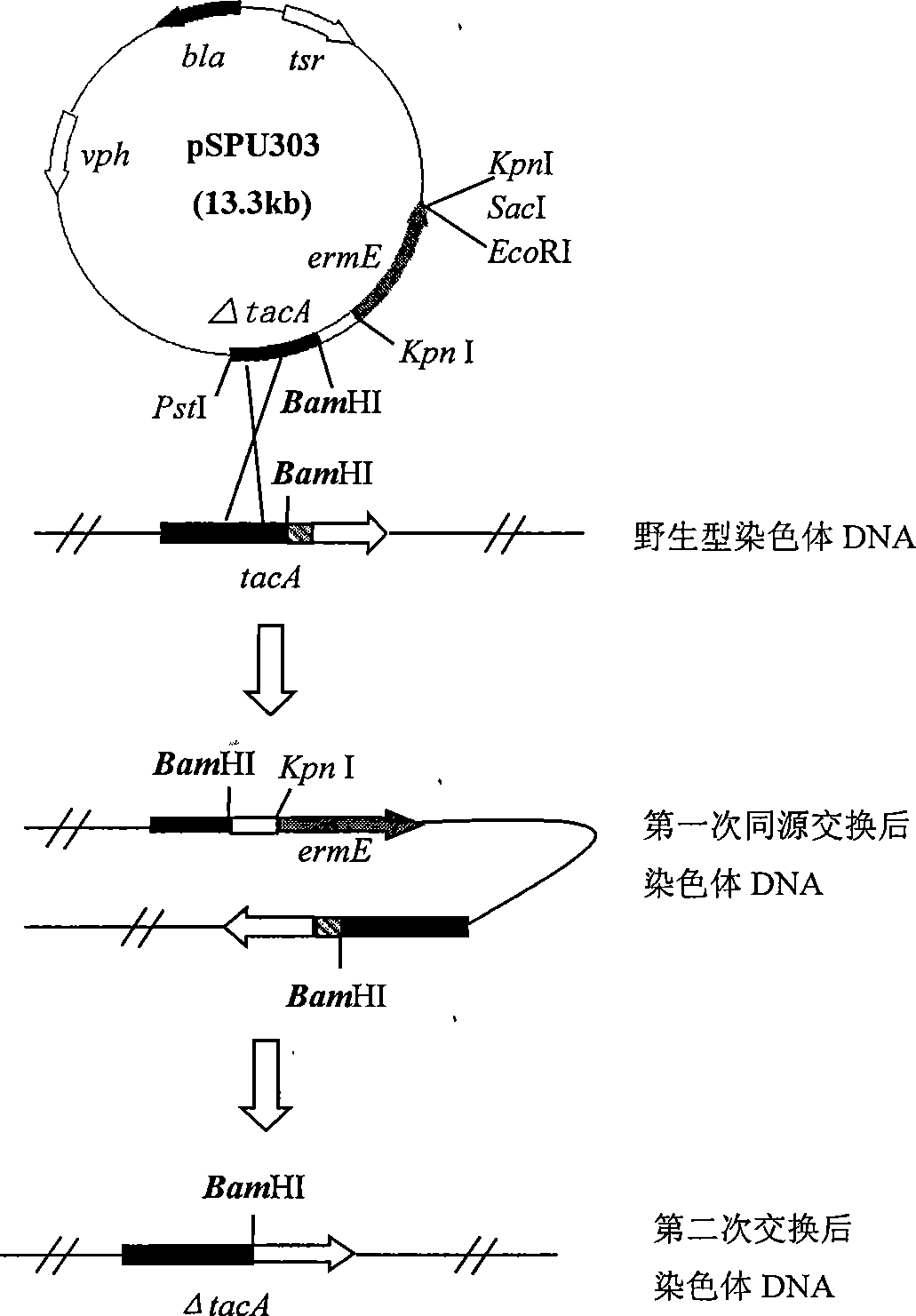
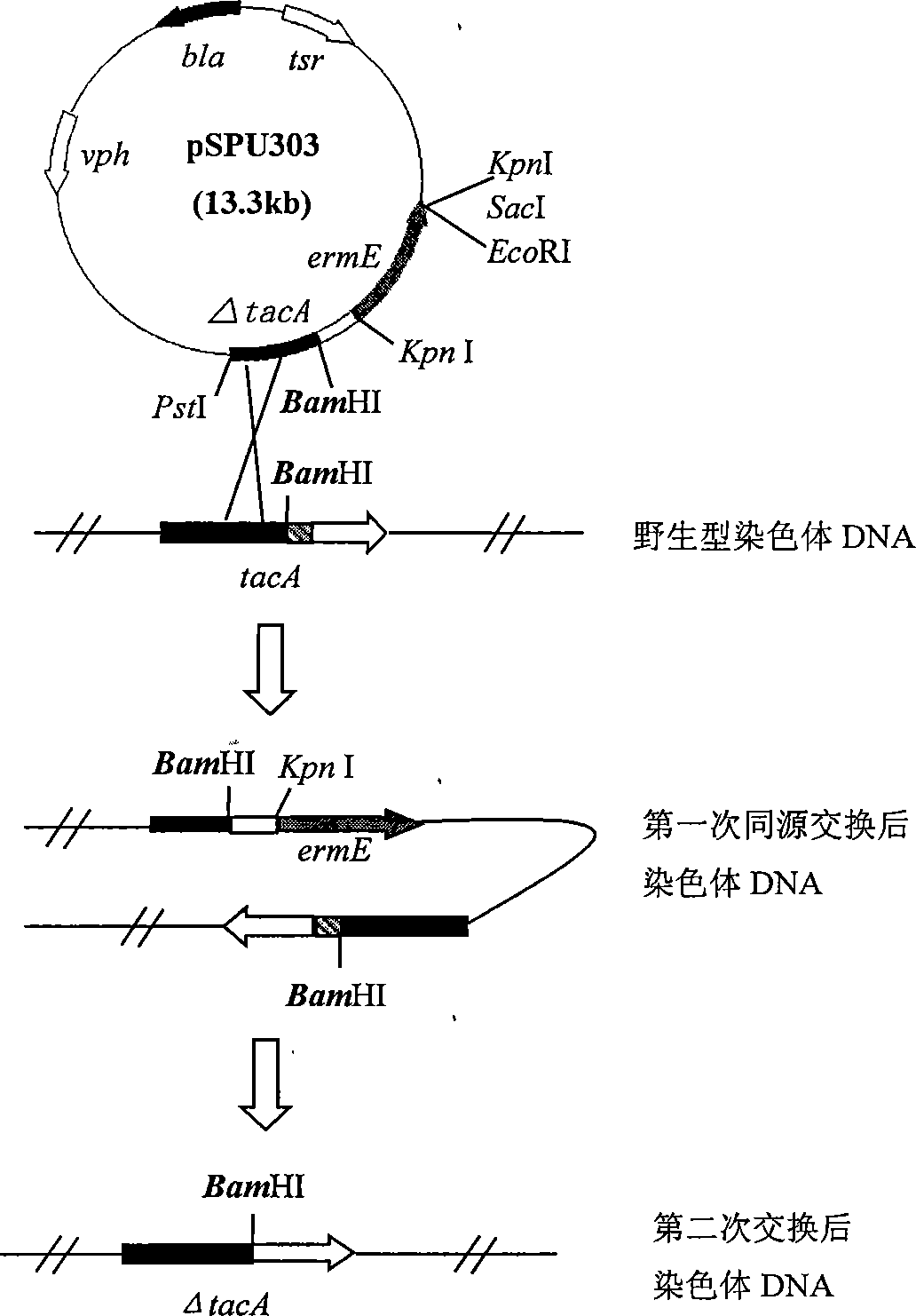
The invention pertains to the field of medical technology and relates to engineering bacteria directly producing tobramycin and the application thereof, which mainly damages carboxamide transferase gene in bacteria produced by the tobramycin, therefore the strain does not produce carboxamide tobramycin any more but tobramycin. The invention, by the method of deleting inactivation within the frame, breaks tacA gene in Streptomyces tenebrarius, comprising the composition of the tacA gene breaking plasmid, the breaking of the transformation of plasmid pSPU303 into Streptomyces tenebrarius H6, the screening of double exchange strains, the detection of fermentation products and the identification of new compositions. The method of deleting inactivation within the frame respectively provides two segments with the upper reach molecular weight and the lower reach molecular weight of the tacA gene not less than 500bp for the PCR, both segments are connected to pIJ2925 simultaneously, one end of the segment is connected to resistance gene of antibiotics that is expressible in the Streptomyces tenebrarius such as erythromycin resistance gene ermE, and three gene segments are connected to shuttle vector pHZ132 by using Bg1II Enzyme cutting. The engineering bacteria directly producing tobramycin and the application thereof can simplify the production technology and reduce the production cost, thus facilitating the quality control of the products.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Lactobacillus food grade expression vector pMG36N and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101654681AAvoid the dangers of diversionReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionFood gradeResistant genes
The invention discloses a lactobacillus food grade expression vector pMG36N which does not contain erythrocin resistance gene, introduces a natural food preservative streptococcus lactis peptide Nisinresistance gene nisI as a selection mark. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the lactobacillus food grade expression vector pMG36N. The lactobacillus food grade expression vector pMG36N does not take the resistance gene, i.e. erythrocin and the like, as a screening mark, enhances the safety of lactobacillus and can be used for food production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Rapid screening system for Lactococcus lactis with knocked-in exogenous genes as well as construction method and application of rapid screening system
InactiveCN105349565AReduce workloadShorten the timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus lactisBiology
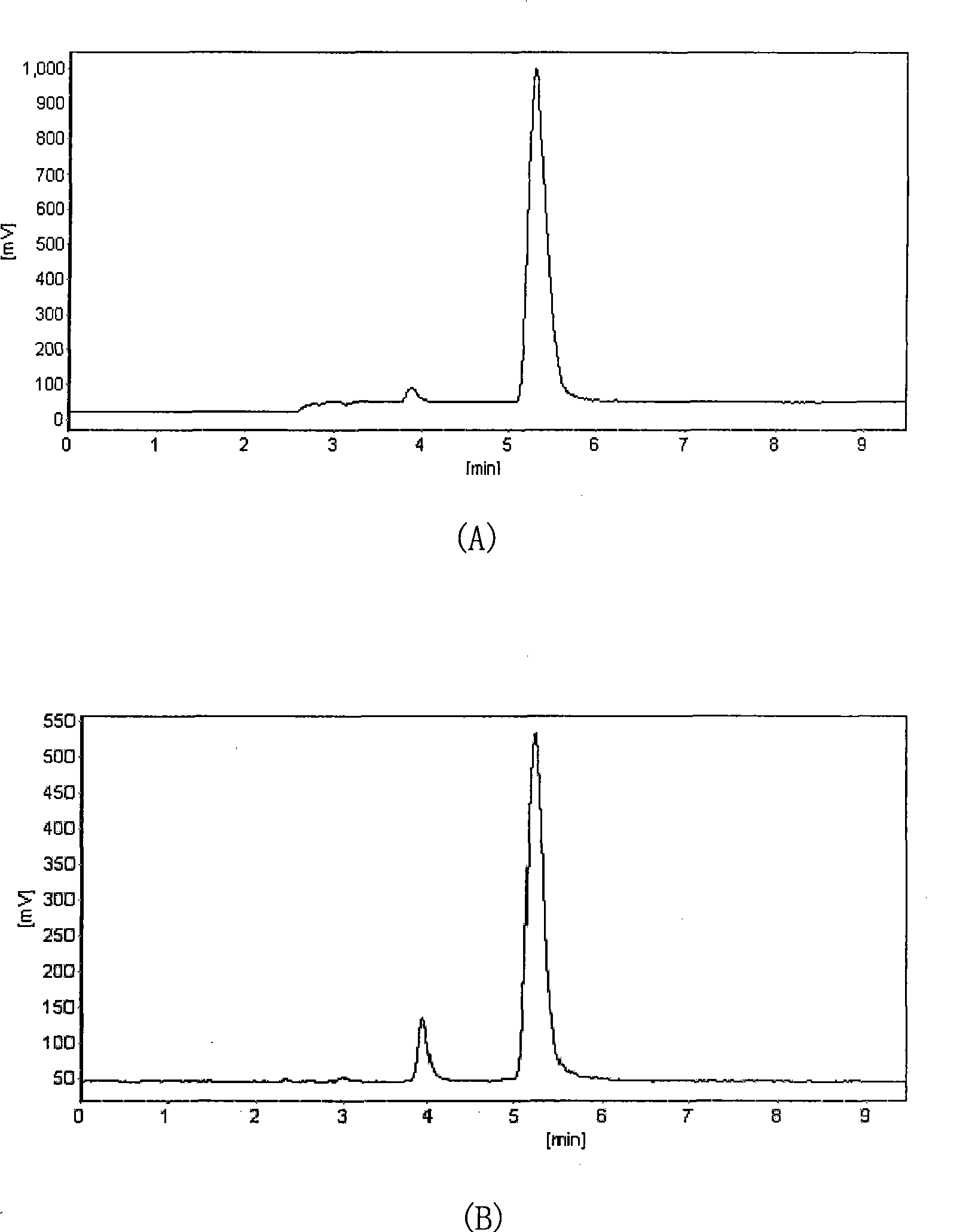
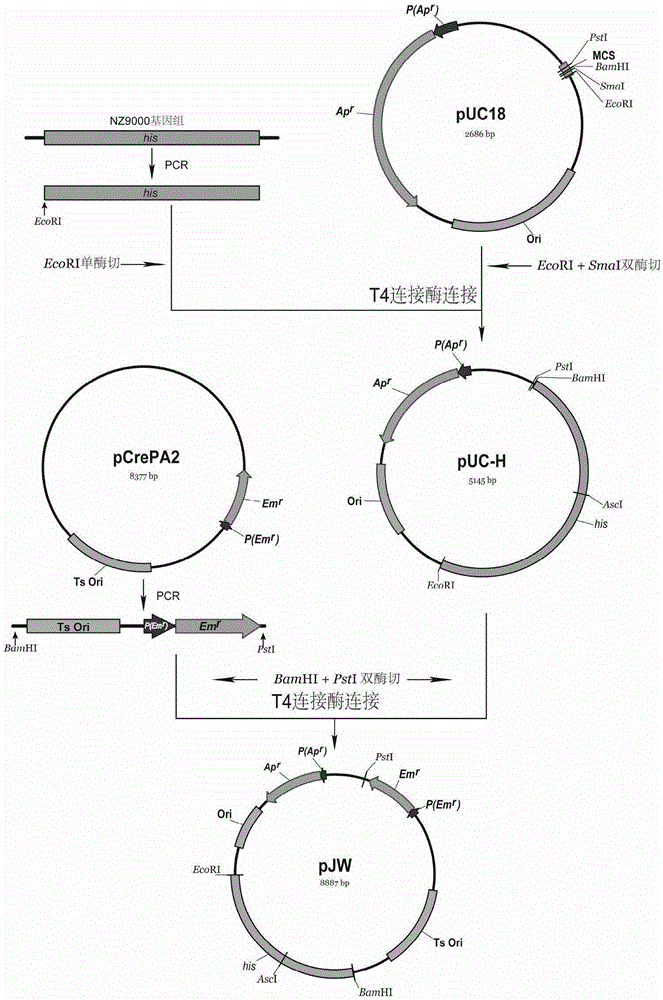
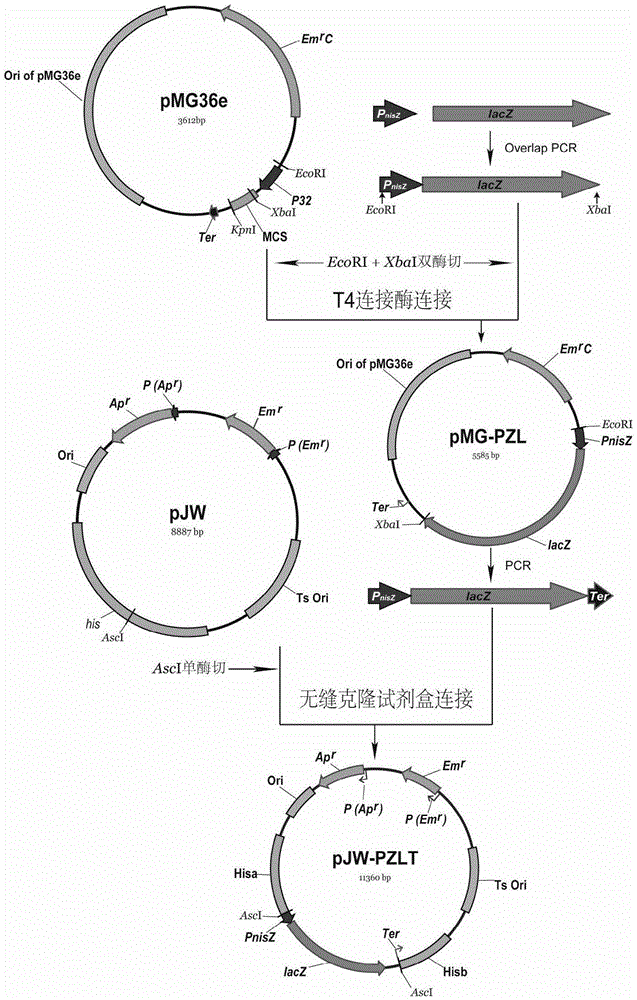
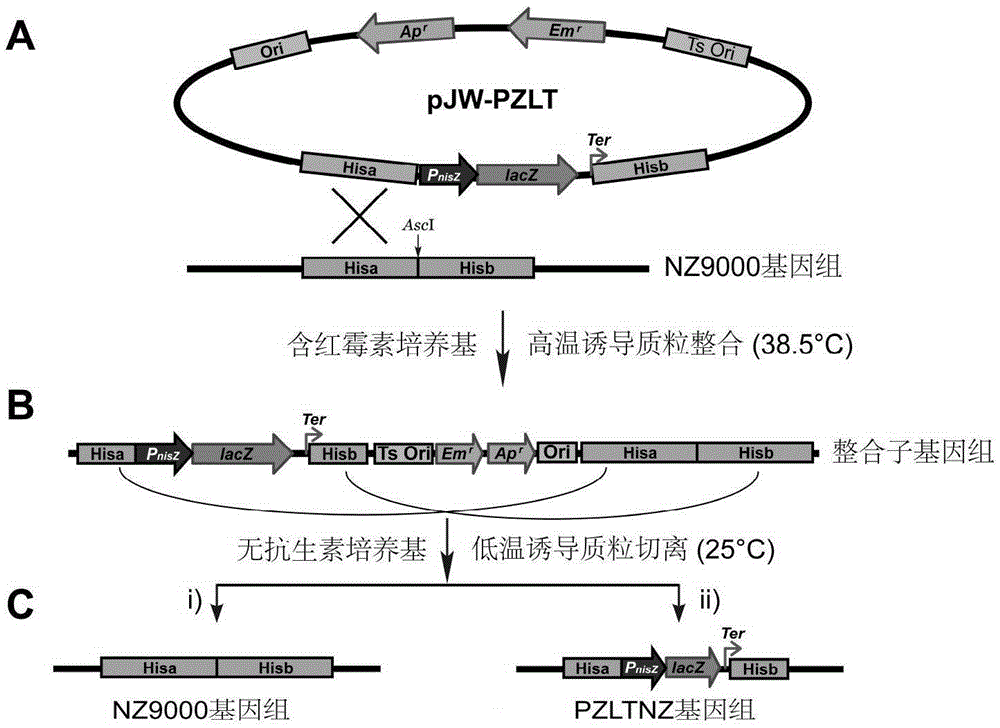
The invention provides a rapid screening system for Lactococcus lactis with knocked-in exogenous genes. The screening system comprises temperature-sensitive plasmids and the Lactococcus lactis, wherein the temperature-sensitive plasmids contain his gene segments and temperature-sensitive replicon-erythromycin resistance gene (Ts-Emr) segments; chromosomes of the Lactococcus lactis contain lacZ gene expression segments. lacZ genes of the Lactococcus lactis cannot be expressed when the exogenous genes are knocked in successfully, so that white colonies are shown on a solid medium containing X-Gal, otherwise, blue colonies are shown, the change from the blue colonies to the white colonies can be directly observed on the solid medium, the screening workload can be greatly reduced, and screening time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for constructing lactobacillus expression plasmid with Nisin as natural resistance selection marker
InactiveCN102586314AImprove securityNot easy to loseVector-based foreign material introductionSequence signalOperability
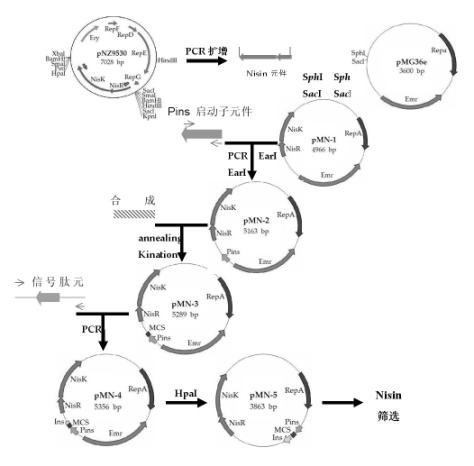
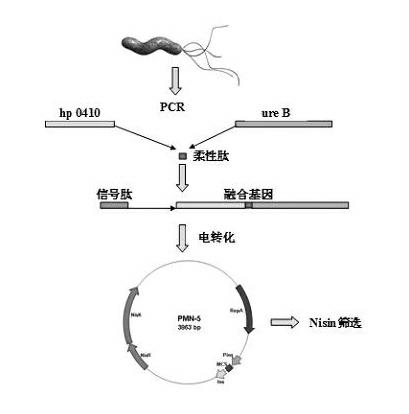
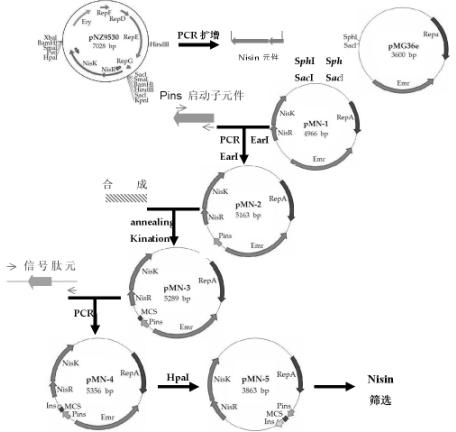
The invention relates to a method for constructing a lactobacillus expression plasmid with Nisin as a natural resistance selection marker, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method is characterized by using a Nisin element from a lactobacillus vector pNZ9530 instead of erythromycin resistance genes of a lactobacillus plasmid pMG36e as the selection marker and realizing construction of a Nisin food-grade expression / secretion vector through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, gene cloning, synthesis of multiple cloning sites, addition of lactobacillus acidophilus signal peptide and elimination of resistance genes. The method has the following beneficial effects: the antibiotic resistance marker vector is replaced by the food-grade selection marker and the constructed food-grade expression / secretion vector is a food-grade live vector, has high safety factors to human body and environment and can be widely applied to application research of vaccines, food and medicines; and the construction method can achieve long-term stable expression of the exogenous antigen genes and obtain the target antigen proteins stably expressed for a long term, is simple and is strong in operability.
Owner:白杨 +2
Building method and application of lactobacillus reuteri resistance-marker-free gene integration system
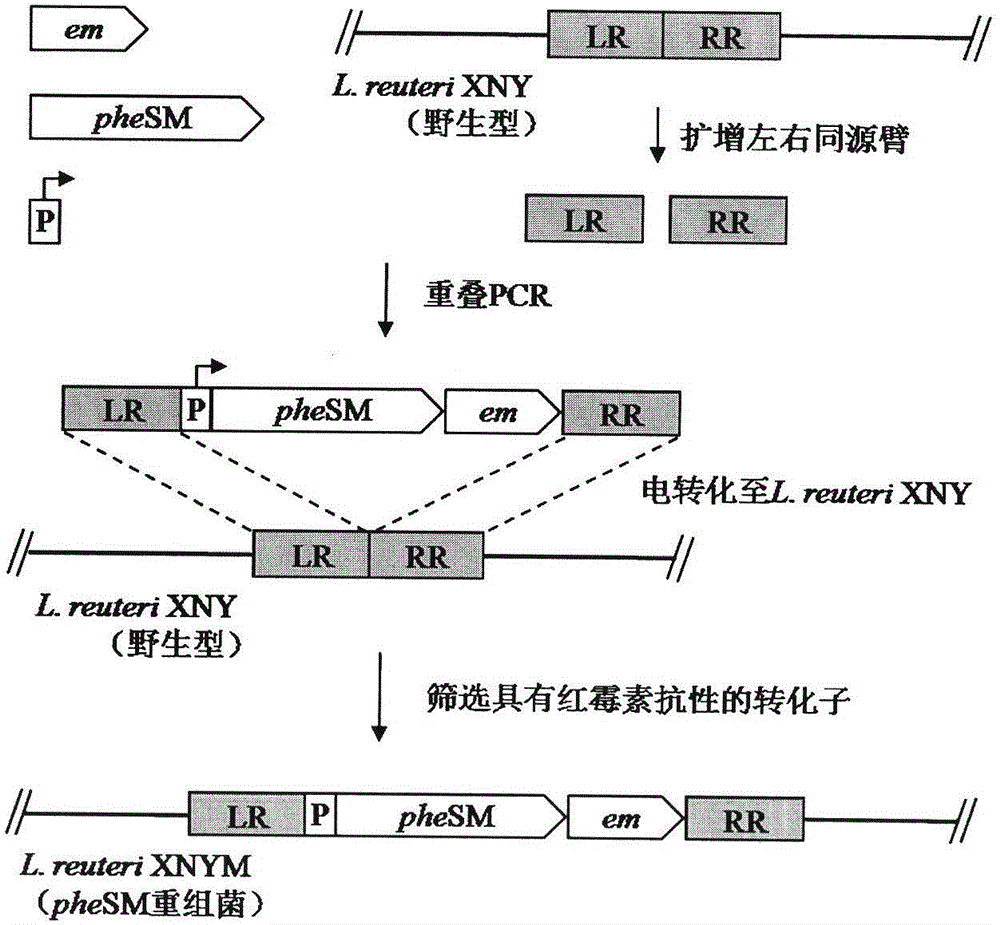
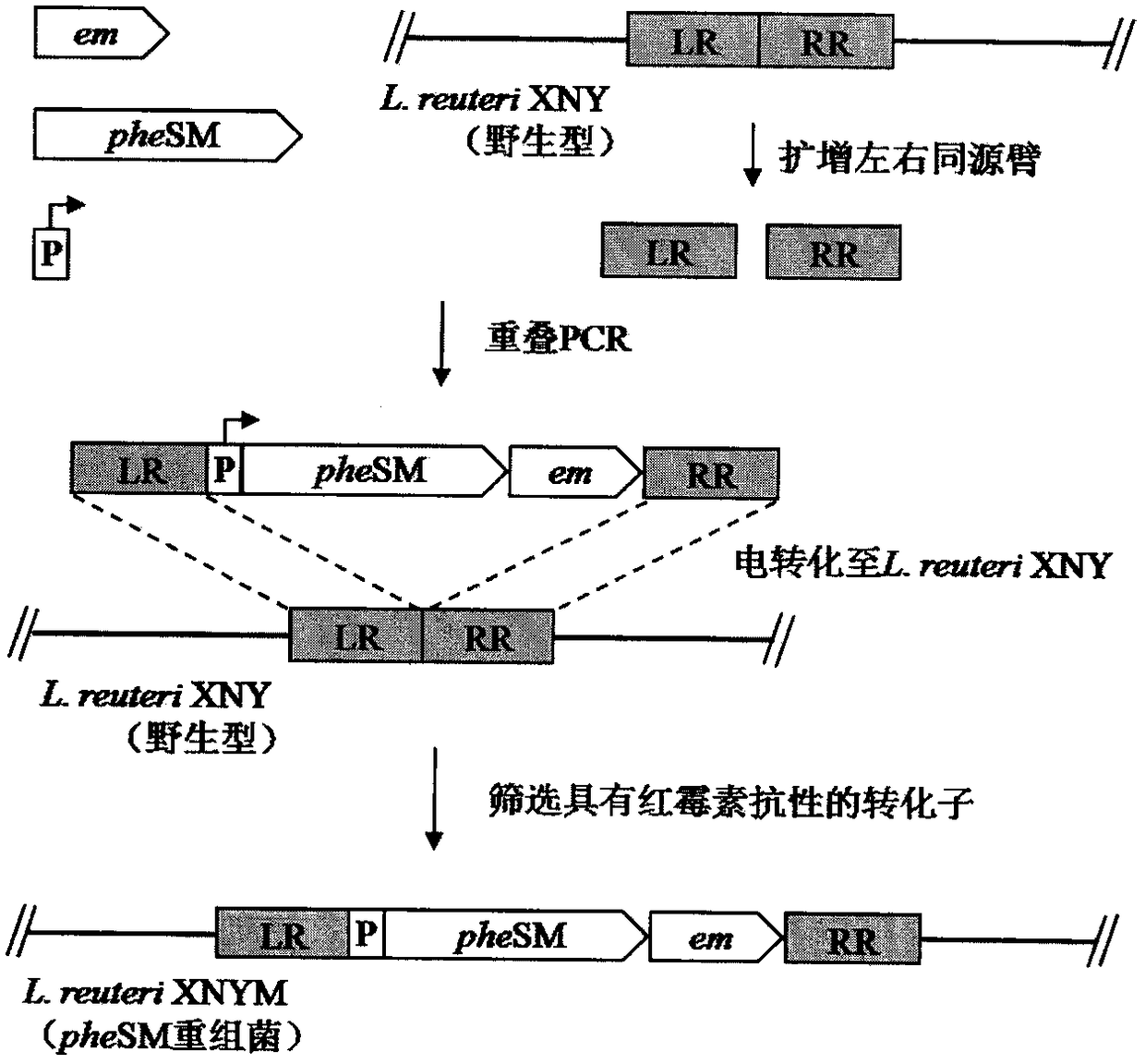
The invention discloses a building method and application of a lactobacillus reuteri resistance-marker-free gene integration system. By means of the point mutation technology, a point mutation gene pheSM of a lactobacillus reuteri pheS gene is obtained, the point mutation gene pheSM and a erythromycin resistance gene are used for building an integrated framework LR-pheSM-em-RR, the integrated framework LR-pheSM-em-RR is electrically converted into L.renteri XNY competent cells, and pheSM genetic recombination lactobacillus L.renteri XNYM is obtained through erythromycin screening; then, the gene integration framework is constructed and inserted, then the gene integration framework is electrically converted into pheSM gene recombination lactobacillus reuteri competent cells, and the lactobacillus reuteri without resistance markers can be obtained through para-chlorophenylalanine acid resistance screening. According to the method, resistance genes are not introduced into host bacteria genomes, so that biological safety hidden hazards of the resistance genes and the polarity effect of the resistance genes on upstream genes and downstream genes are avoided. By means of the system, gene targeted integration can be carried out on the host bacteria for multiple times.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Overexpressed UGPase (UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase) gene and method for constructing recombinant lactobacillus acidophilus thereof
ActiveCN106520794AImprove freeze-drying survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphorylationLactobacillus acidophilus
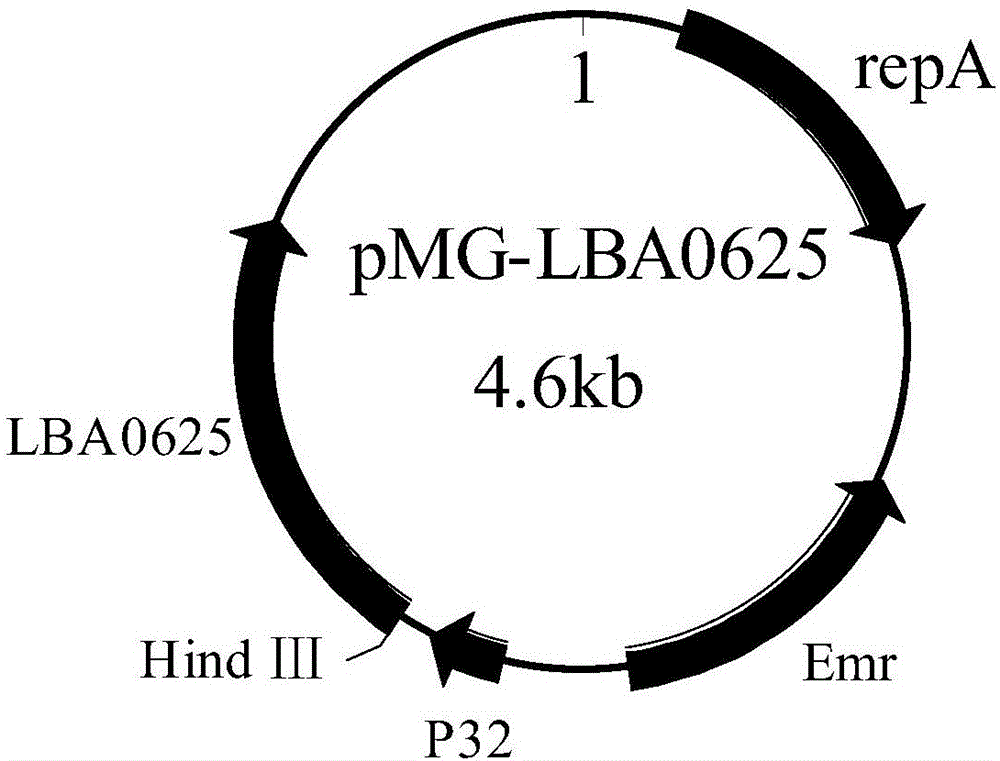
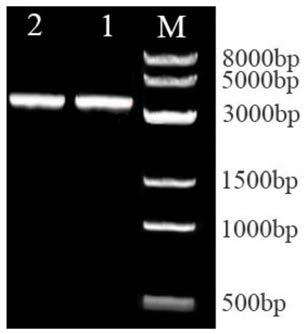
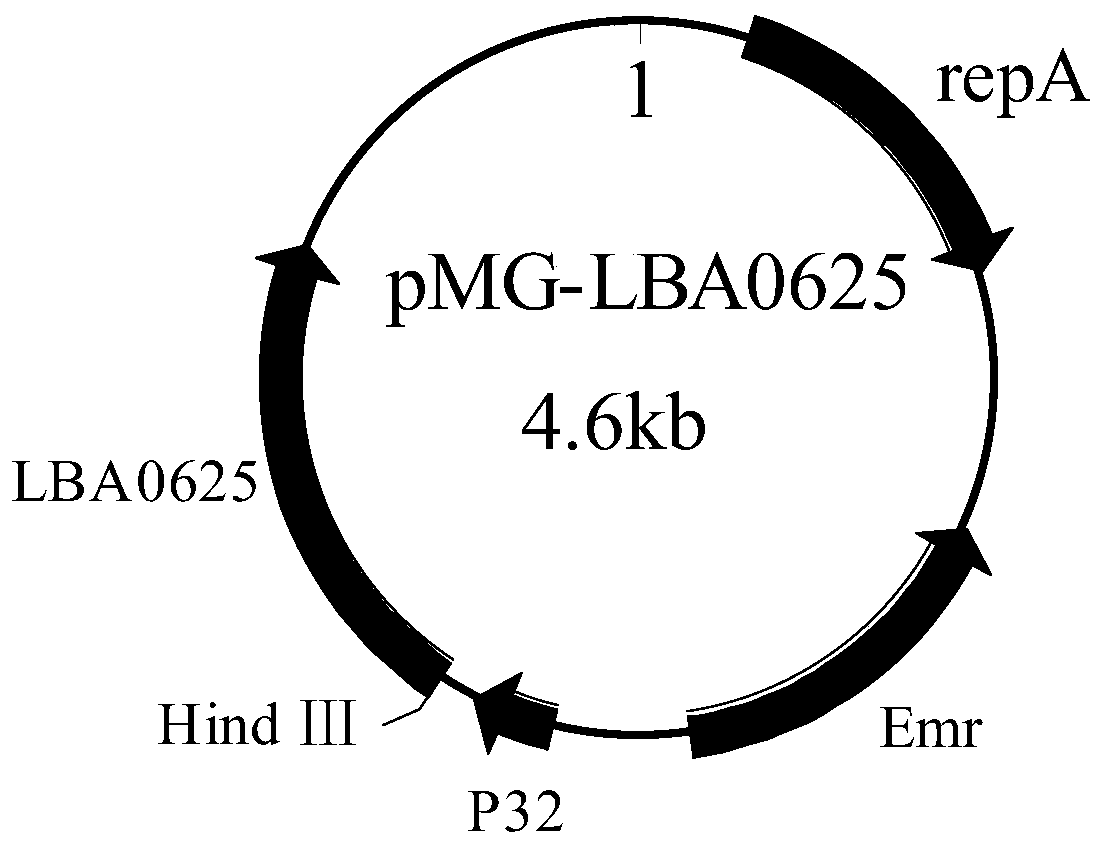
The invention discloses an overexpressed UGPase (UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase) gene and a method for constructing recombinant lactobacillus acidophilus thereof. The method is characterized by comprising the specific steps as follows: (1) a UGPase gene LBA0625 is amplified with lactobacillus acidophilus genome DNA as a template; an expression vector pMG36e is subjected to single restriction digest with restriction enzyme Hind III, and after dephosphorylation and gel recovery are performed, a recombinant expression vector is constructed by inserting a PCR amplification product into the expression vector pMG36e; (2) an overexpression plasmid subjected to extraction and concentration is imported into lactobacillus acidophilus through electrotransformation, the lactobacillus acidophilus is resuscitated at 37 DEG C for 2 h, applied to an erythrocin resistant plate and cultured at 37 DEG C for 36 h for screening transformants; the transformants are subjected to PCR verification, and the recombinant lactobacillus acidophilus PLY127-1 of the overexpressed UGPase gene is obtained. The freeze-drying survival rate of the lactobacillus acidophilus can be increased substantially.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
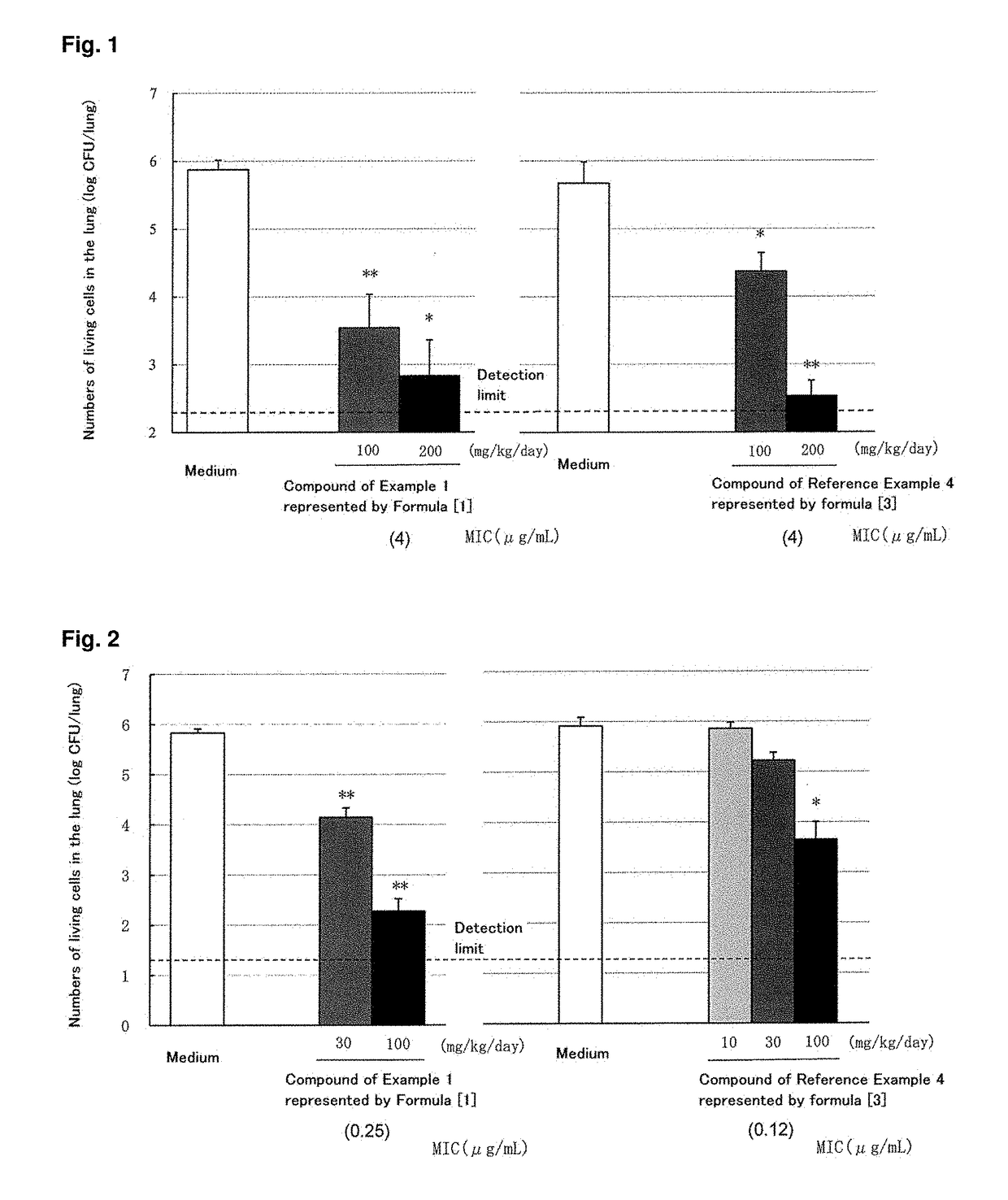
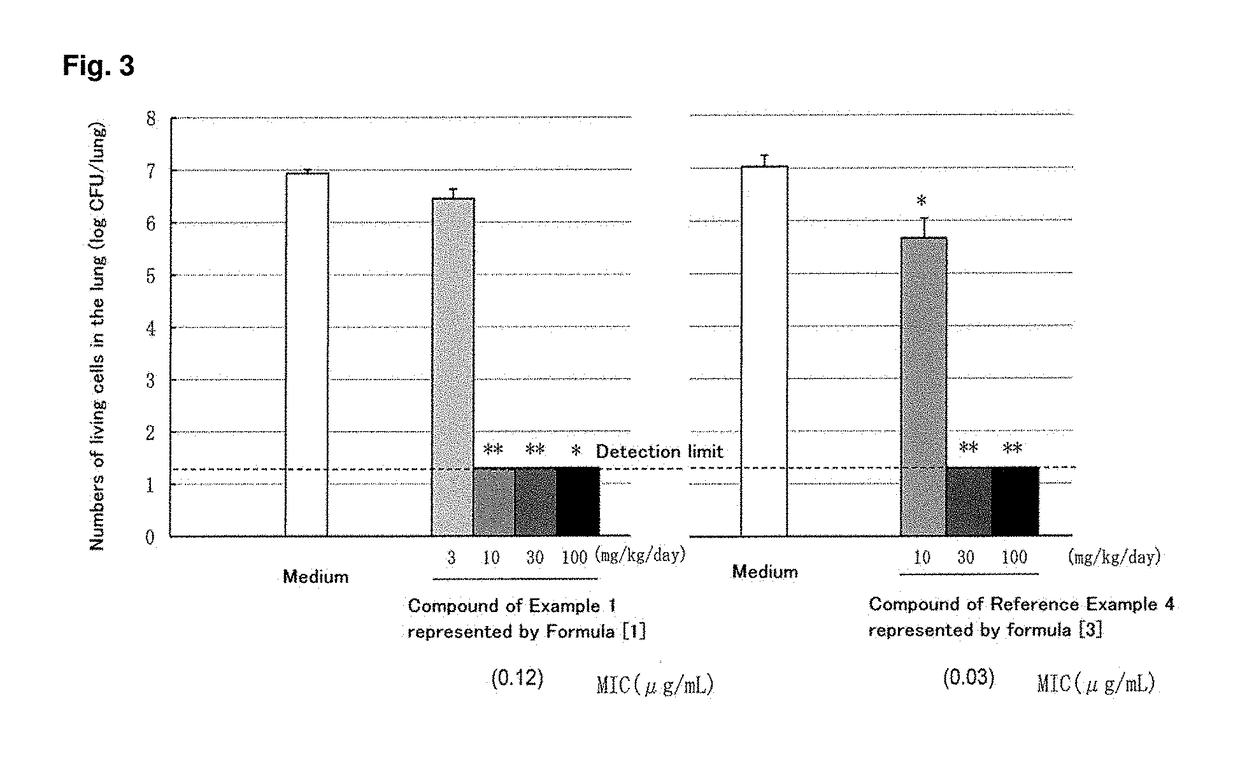
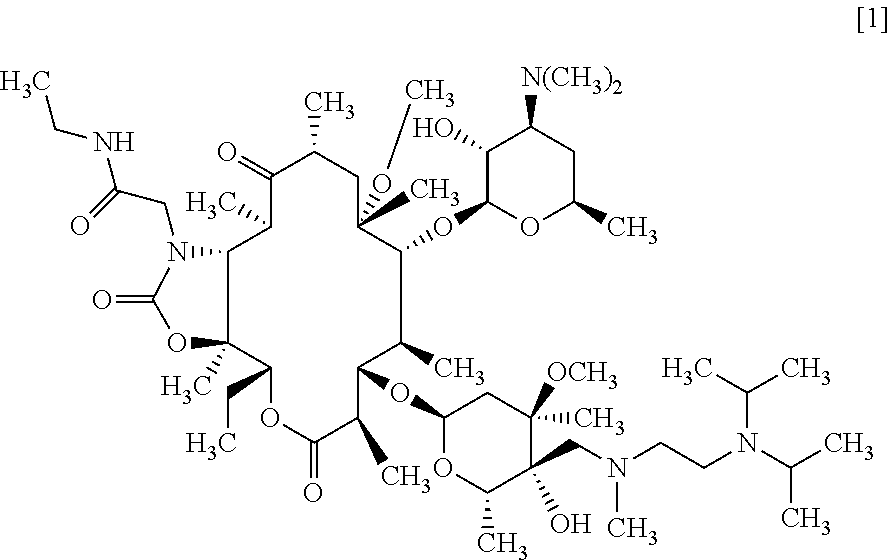
C-4''-substituted macrolide compound
InactiveCN106573953ABroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaCompound a
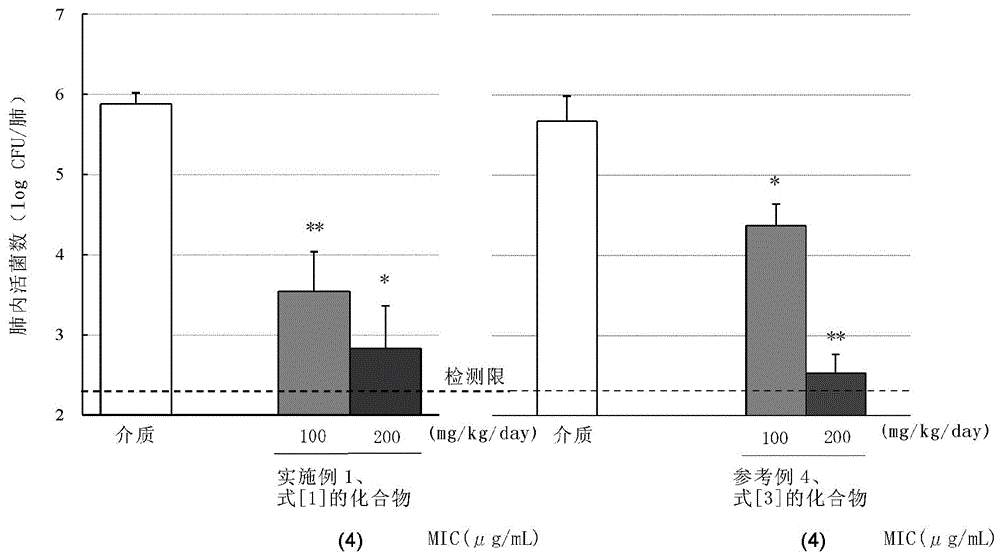
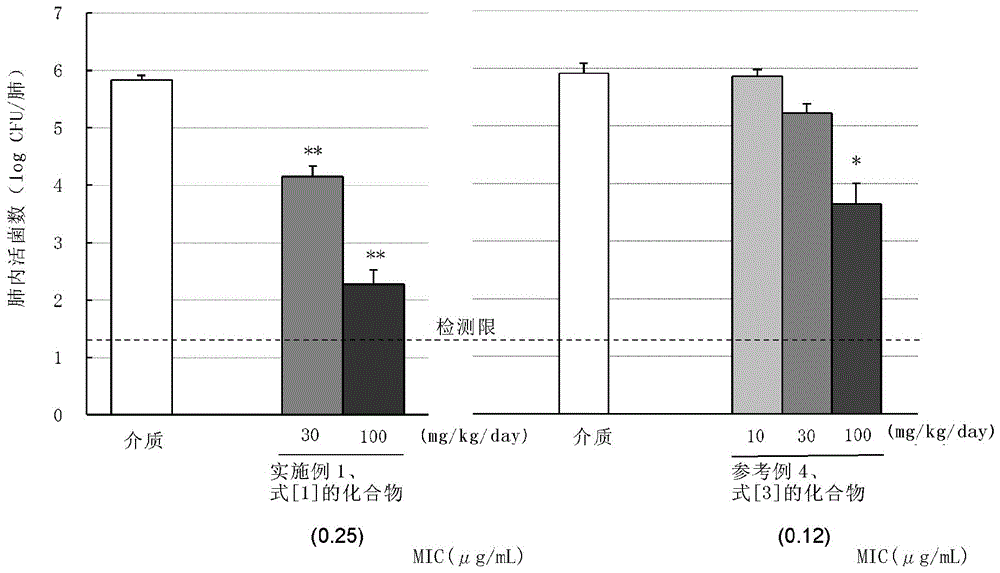
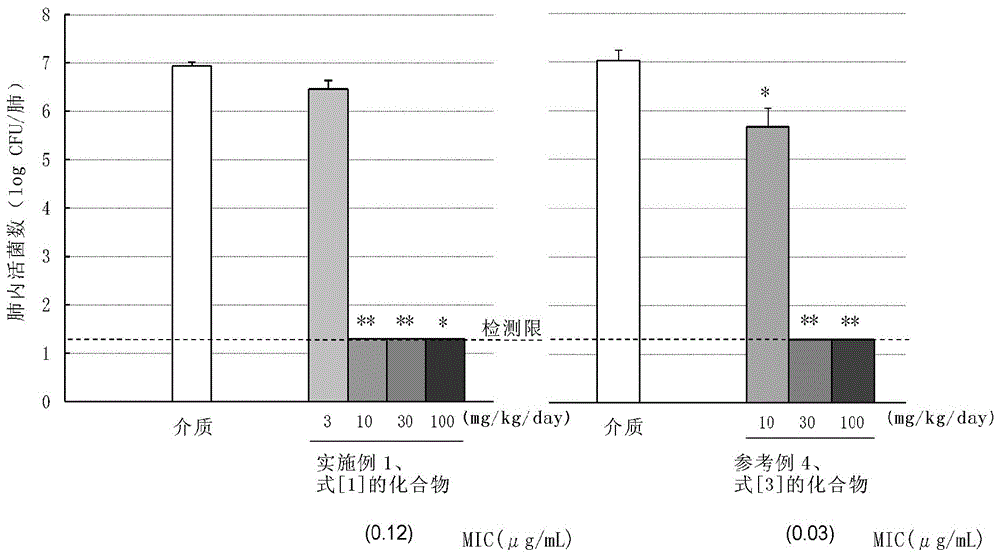
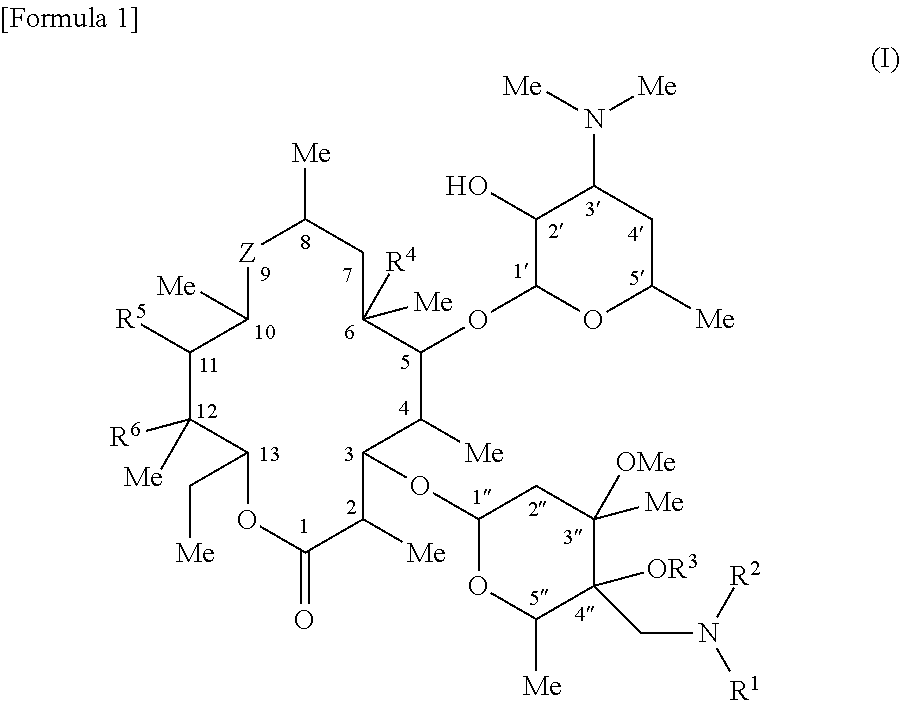
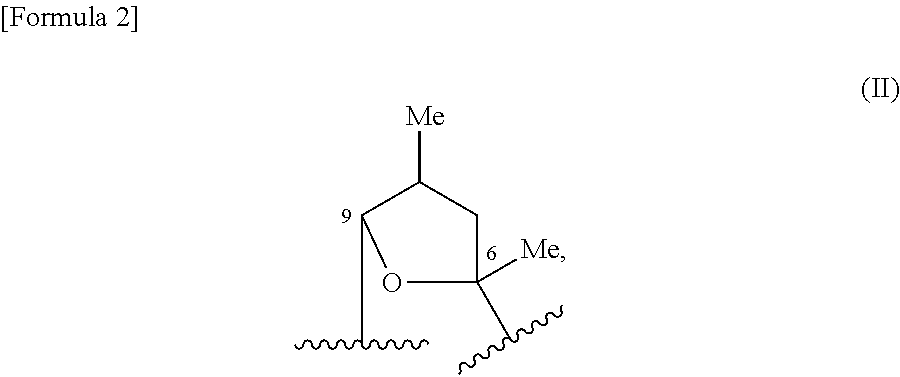
A compound of the following formula [1], which possesses good antimicrobial activity against erythromycin-resistant bacteria, such as resistant pneumococci, streptococci and mycoplasma, against which conventional macrolide antibiotics do not possess sufficient antimicrobial activity. Also provided is a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a hydrate or solvate thereof.
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
C-4″ position substituted macrolide derivative
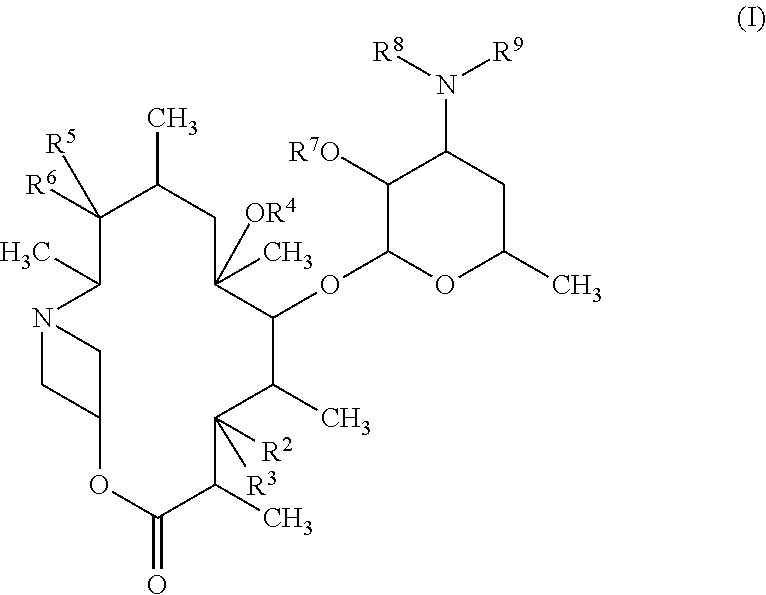
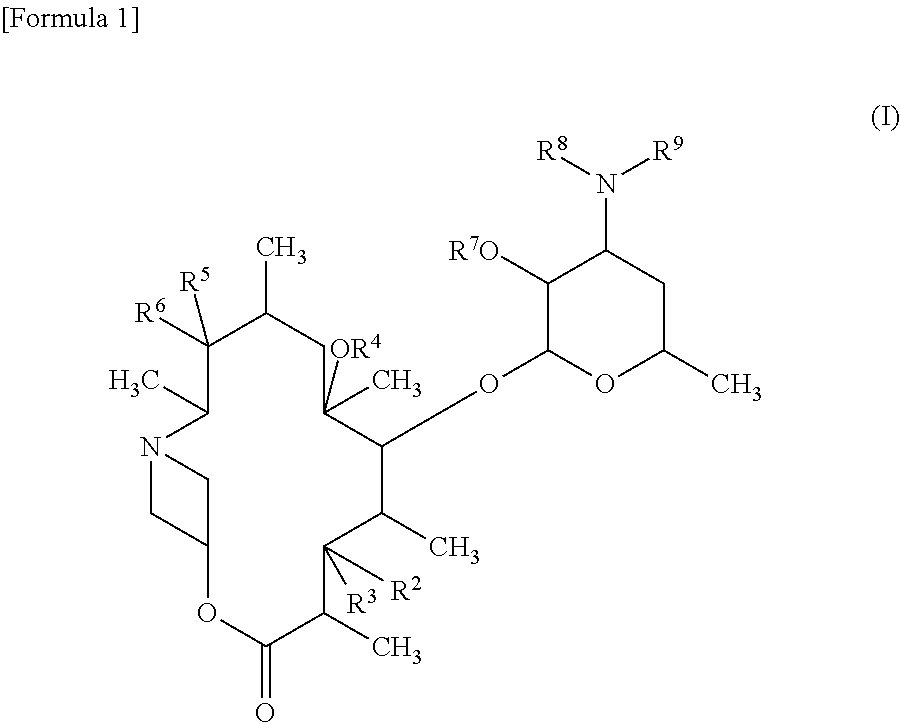
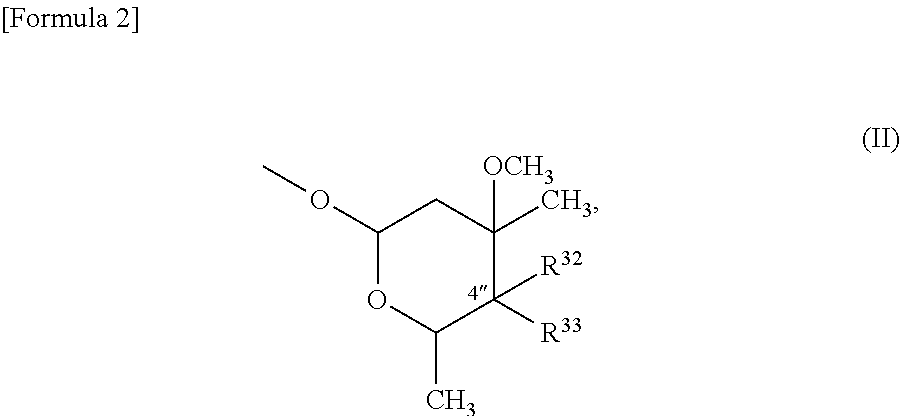
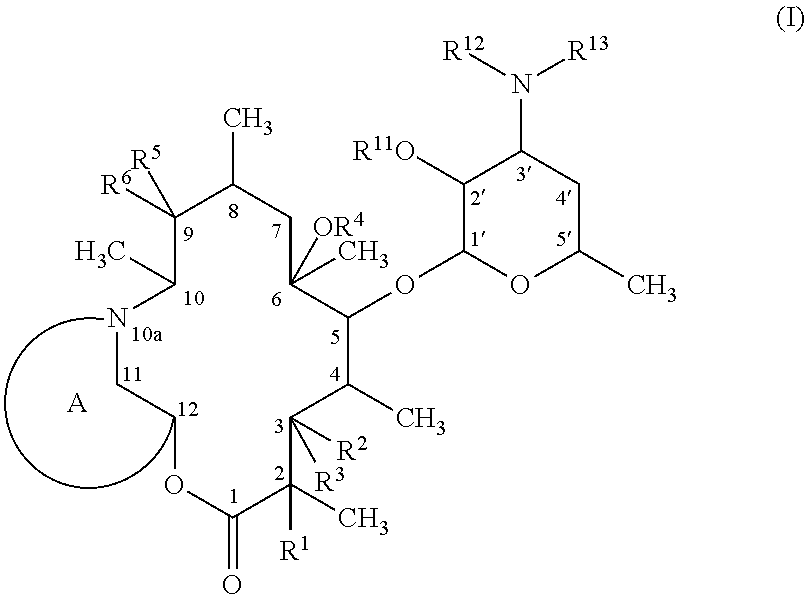
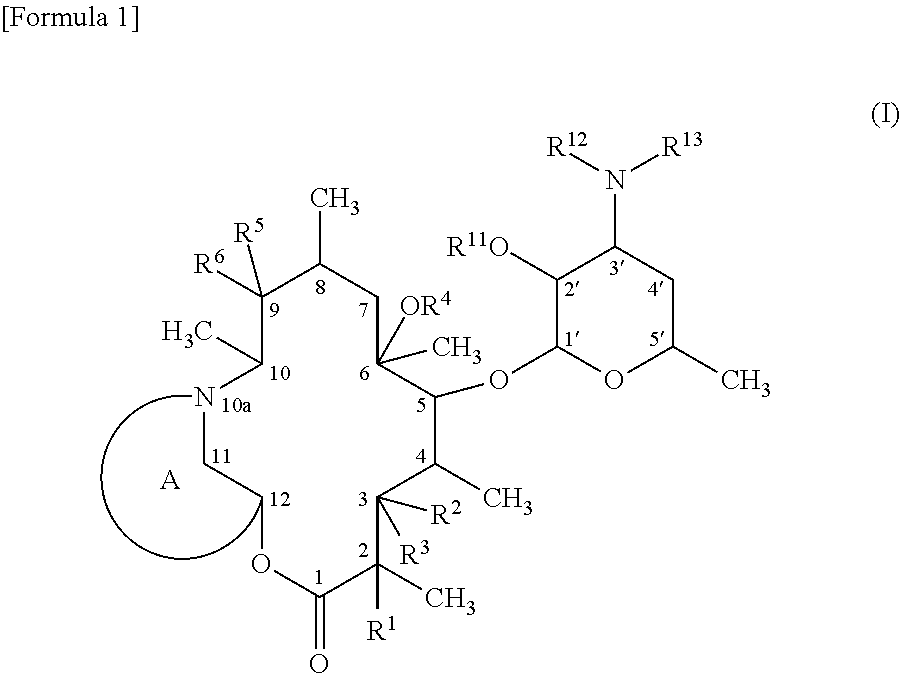
InactiveUS9139609B2High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesResistant bacteriaMacrolide resistance
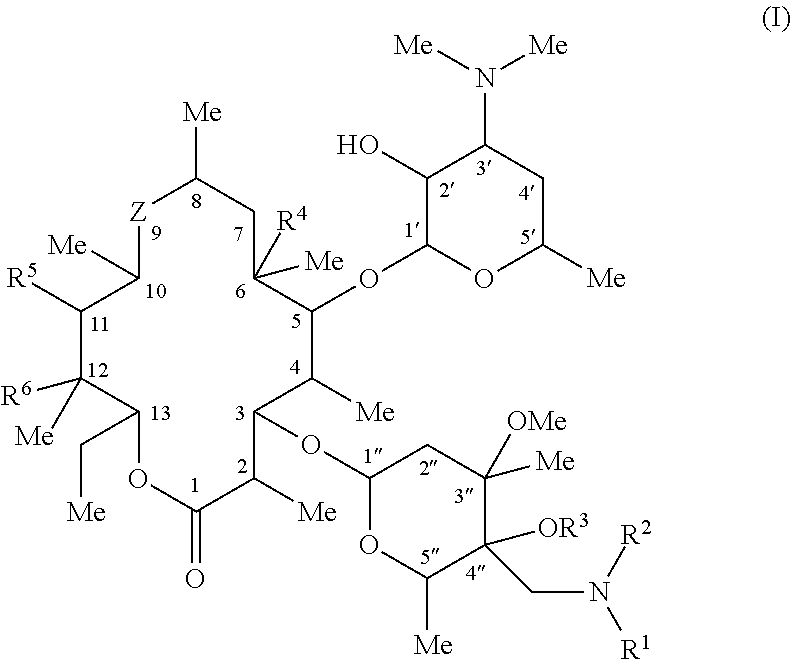
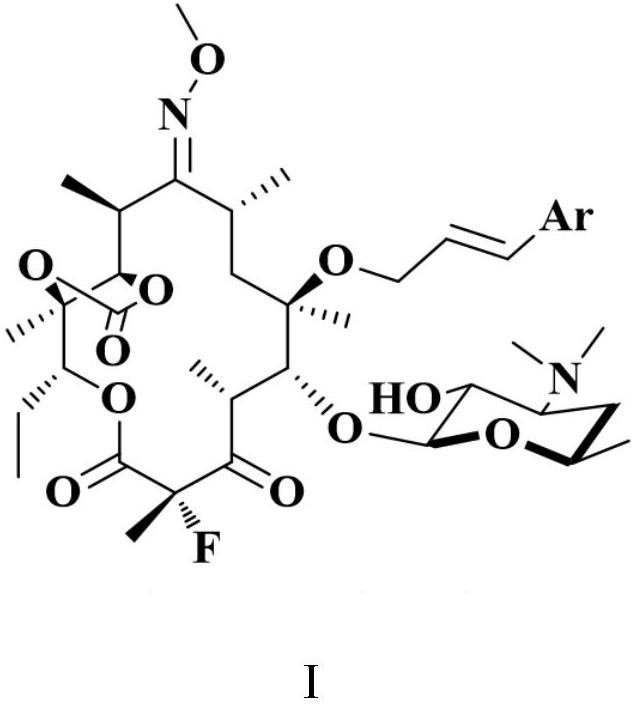
A macrolide compound represented by the formula (I) effective against erythromycin resistant bacteria (for example, resistant pneumococci, streptococci and mycoplasmas).
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
Primer for rapidly detecting drug tolerance of pertussis bordelella erythrocin from specimen and detection method
InactiveCN103667512AWide range of availableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDrug toleranceGene
The invention relates to a primer for rapidly detecting the drug tolerance of pertussis bordelella erythrocin from a specimen and a detection method. The primer includes variable areas on both sides of a locus 2047 specific to a pertussis bordelella 23S rRNA (ribosomal Robonucleic Acid) gene. According to the primer, the technical problems of incapability of carrying out antibiotic susceptibility test, high time consumption of the antibiotic susceptibility test and the like due to incapability of successfully culturing the pertussis bordelella existing in the prior art are solved.
Owner:西安市疾病预防控制中心
C-4" position substituted macrolide derivative
InactiveUS20170267708A1High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesMacrolide resistanceAntibacterial activity
A useful novel compound that shows superior antibacterial activity also against erythromycin resistant bacteria, for example, resistant pneumococci, streptococci, mycoplasmas, and the like, against which sufficient antibacterial activity cannot be obtained with conventional macrolide antibiotics, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a hydrate or a solvate thereof.
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
A method for establishing a Lactobacillus reuteri non-resistance marker gene integration system and its application
InactiveCN105112350BAvoid mutationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesP chlorophenylalaninePhenylalanine
The invention discloses a building method and application of a lactobacillus reuteri resistance-marker-free gene integration system. By means of the point mutation technology, a point mutation gene pheSM of a lactobacillus reuteri pheS gene is obtained, the point mutation gene pheSM and a erythromycin resistance gene are used for building an integrated framework LR-pheSM-em-RR, the integrated framework LR-pheSM-em-RR is electrically converted into L.renteri XNY competent cells, and pheSM genetic recombination lactobacillus L.renteri XNYM is obtained through erythromycin screening; then, the gene integration framework is constructed and inserted, then the gene integration framework is electrically converted into pheSM gene recombination lactobacillus reuteri competent cells, and the lactobacillus reuteri without resistance markers can be obtained through para-chlorophenylalanine acid resistance screening. According to the method, resistance genes are not introduced into host bacteria genomes, so that biological safety hidden hazards of the resistance genes and the polarity effect of the resistance genes on upstream genes and downstream genes are avoided. By means of the system, gene targeted integration can be carried out on the host bacteria for multiple times.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Detection chip for drug resistance gene of bacteria, and application thereof
InactiveCN102321763BStrong specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMacrolide resistanceGenetic engineering
Owner:李越希
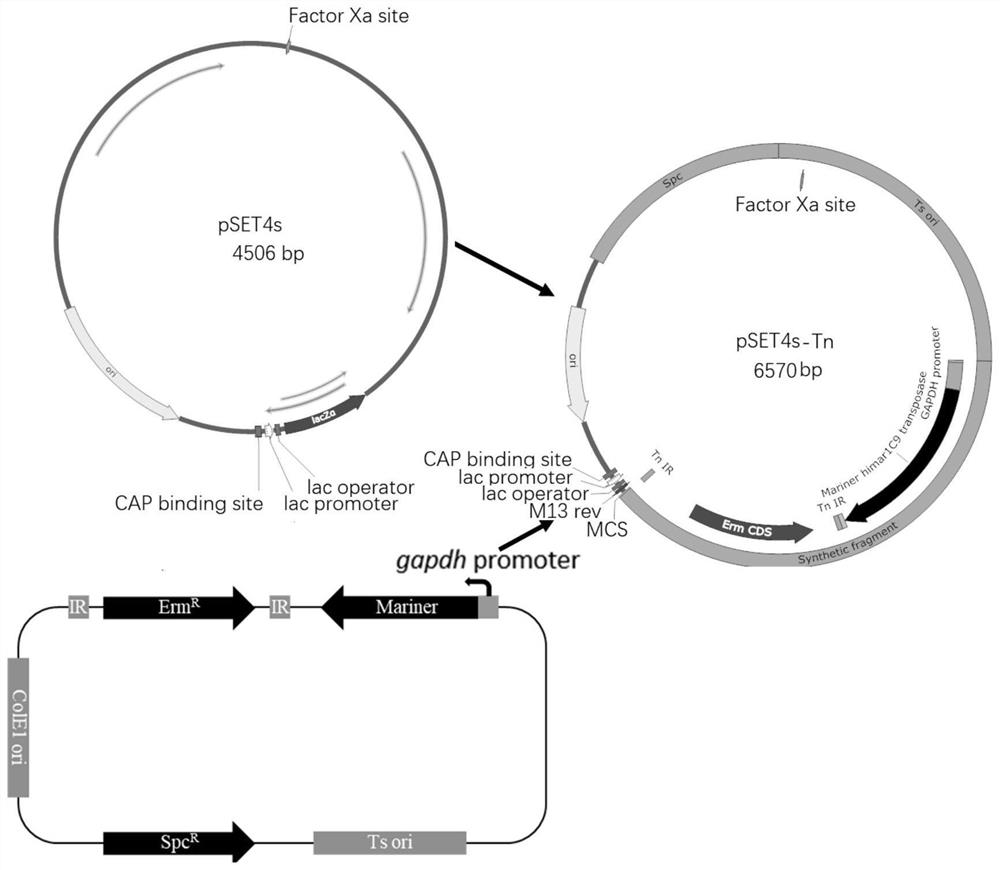
Streptococcus suis efficient transposition mutation system and application thereof
The invention discloses a streptococcus suis efficient transposon mutation system, namely a pSET4s-Tn plasmid, which comprises: (1) a streptococcus suis temperature-sensitive replication element Ts ori; (2) an escherichia coli replication element ColE1ori; (3) a Mariner transposase expression box; (4) a spectinomycin resistance expression cassette (SpcR); and (5) an erythromycin resistance expression cassette (ErmR) containing a transposase recognition sequence (IR) at each of the upstream and the downstream. By utilizing the transposon mutation system, efficient transposon mutation in streptococcus suis can be realized, more than 98% of streptococcus suis can be used as transposon mutants in a single experiment, the transposon is inserted into a TA base site in a streptococcus suis genome, and the transposon insertion site has no obvious preference.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A rapid screening system for exogenous gene knock-in Lactococcus lactis and its construction method and application
InactiveCN105349565BReduce workloadShorten the timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLactococcus lactisBiology
The invention provides a rapid screening system for Lactococcus lactis with knocked-in exogenous genes. The screening system comprises temperature-sensitive plasmids and the Lactococcus lactis, wherein the temperature-sensitive plasmids contain his gene segments and temperature-sensitive replicon-erythromycin resistance gene (Ts-Emr) segments; chromosomes of the Lactococcus lactis contain lacZ gene expression segments. lacZ genes of the Lactococcus lactis cannot be expressed when the exogenous genes are knocked in successfully, so that white colonies are shown on a solid medium containing X-Gal, otherwise, blue colonies are shown, the change from the blue colonies to the white colonies can be directly observed on the solid medium, the screening workload can be greatly reduced, and screening time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
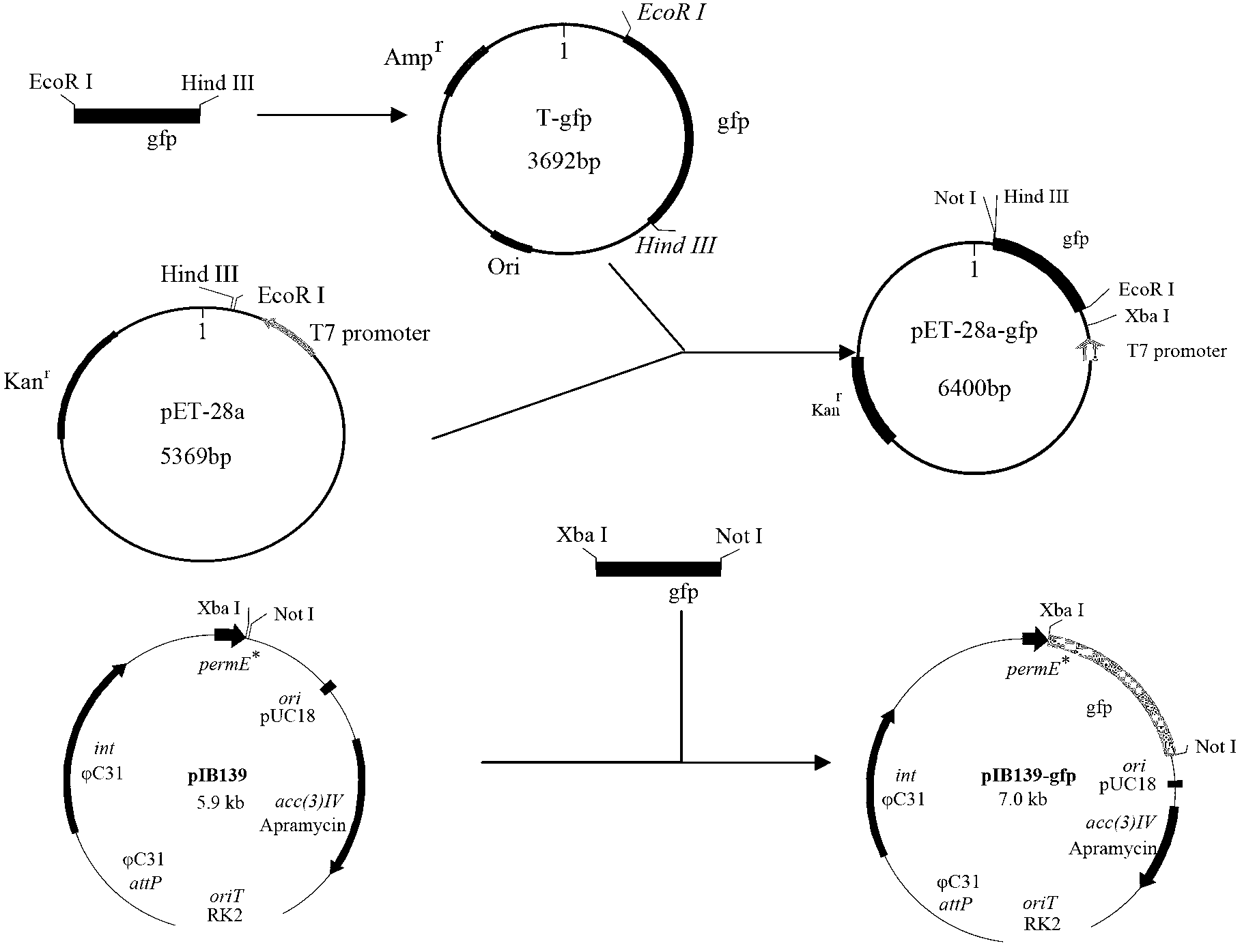
Establishment method of streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system
InactiveCN103289946AImproved ability to synthesize toyocamycinImprove abilitiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesToyocamycinPromoter
The invention discloses an establishment method of a streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system. The establishment method comprises the following steps of: screening a necessary or efficient ingredient of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system by virtue of a green fluorescent protein gene gfp at first, and then constructing the expression system of a target gene, wherein the necessary or efficient ingredient is erythromycin resistance genome constructive promoter permE*; the target gene promotes production of toyocamycin; and the target gene is a haemoglobin gene vgb. The construction processes are as follows: 1) constructing a carrier pIB139-gfp; and 2) integrating the expression carrier into a streptomyces diastatochromogenes chromosome by virtue of a conjugational transfer method, so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium. The invention provides an efficient screening method and application of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system. Compared with the original strain, the recombinant bacterium has the advantages that the toyocamycin yield of the recombinant bacterium is increased by at least 21.2%, and the concentration of the recombinant bacterium is increased by 11.6%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
10a-azalide compound having 4-membered ring structure
InactiveUS8299035B2High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideResistant bacteriaHaemophilus influenzae
A 10a-azalide compound having a 4-membered ring structure crosslinked at the 10a- and 12-positions, which is represented by the formula (I), and is effective on even Haemophilus influenzae, or erythromycin resistant bacteria (e.g., resistant pneunococci and streptococci).
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD +1
A kind of erythromycin derivative and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109942653BEffective treatmentAdapt to industrial productionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic acid formationInfluenza a
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Gene series technology for increasing main component content of gene engineering isovaleryl selectomycin
ActiveCN101649325BRaise the ratioSimple extraction processMicroorganism based processesFermentationGene engineeringBiology
The invention relates to the application of a gene engineering technology in increasing an antibiotic component, in particular to a gene series technology for increasing the main component content of gene engineering isovaleryl selectomycin. The gene series technology comprises the following steps: connecting ist genes which are closely related to selectomycin isovaleryl acylation in Beta selectomycin gene engineering bacteria in series; increasing the bacterial isovaleryl acylation generating capability by increasing gene dosage; using a promoter erythrocin resistance gene erm promoter sequence with strong promotion activity to replace the original ist gene promoter sequence so as to increase the expression of the series ist genes, and improve the proportion of isovaleryl selectomycin main components of the gene engineering bacteria from a headstream.
Owner:SHENYANG TONGLIAN GRP CO LTD
Engineering strain for directly producing gernebcin and use thereof
InactiveCN101392229BSimple production processReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsShuttle vectorAntibiotic resistance genes
The invention pertains to the field of medical technology and relates to engineering bacteria directly producing tobramycin and the application thereof, which mainly damages carboxamide transferase gene in bacteria produced by the tobramycin, therefore the strain does not produce carboxamide tobramycin any more but tobramycin. The invention, by the method of deleting inactivation within the frame, breaks tacA gene in Streptomyces tenebrarius, comprising the composition of the tacA gene breaking plasmid, the breaking of the transformation of plasmid pSPU303 into Streptomyces tenebrarius H6, the screening of double exchange strains, the detection of fermentation products and the identification of new compositions. The method of deleting inactivation within the frame respectively provides two segments with the upper reach molecular weight and the lower reach molecular weight of the tacA gene not less than 500bp for the PCR, both segments are connected to pIJ2925 simultaneously, one end of the segment is connected to resistance gene of antibiotics that is expressible in the Streptomyces tenebrarius such as erythromycin resistance gene ermE, and three gene segments are connected to shuttle vector pHZ132 by using Bg1II Enzyme cutting. The engineering bacteria directly producing tobramycin and the application thereof can simplify the production technology and reduce the production cost, thus facilitating the quality control of the products.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
A kind of hybrid compound of macrolide and quinolone and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109942654BHigh activityAdapt to working productionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStreptococcus pyogenesMacrocyclic lactone
The present invention provides a macrocyclic lactone and quinolone hybrid, characterized in that the macrocyclic lactone and quinolone hybrid include compounds with general formula I and general formula II, or, the macrocyclic lactone and quinolone hybrids include pharmaceutically acceptable salts formed by compounds of the general formula I and II and inorganic acids or organic acids, and the macrolide and quinolone hybrids can be better adapted to industrial production , and has good anti-susceptible and anti-drug resistance against common clinical erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Mora catarrhalis and Haemophilus influenzae Bacterial activity, can effectively treat clinical bacterial pneumonia or pneumonia caused by other microorganisms (such as mycoplasma, Legionella, etc.), and other tissue infections;
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Overexpressed UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene, and construction method and application of recombinant engineering bacterium of overexpressed UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene
PendingCN111019958APromote growthIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaTransferasesStaphylococcus lactisEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses an overexpression UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene, and a construction method and an application of a recombinant engineering bacterium of the overexpression UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene. The gene is a Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 gene from a gene for encoding the UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase, and the nucleotide sequence of the overexpression UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene is represented by SEQ ID No:1 in a sequence table. The construction method comprises the following steps: the UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene segment of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC4356 is cloned and is connected to a pMG36e expression vector, the obtained substance is introduced to Staphylococcus carnosus or Lactococcus lactis by using an electric conversion method, and erythromycin resistance screening and identification are performed to obtain the recombinant engineering strain with the target gene, that is the engineering bacterium of the overexpressed UTP-glucose-1-phosphate-uridine transferase gene. The construction method has the advantages of significantly improving bacterial growth, enzyme activity and the freeze-drying survival rate.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
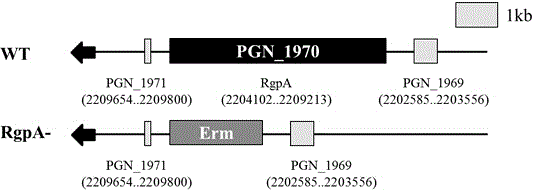
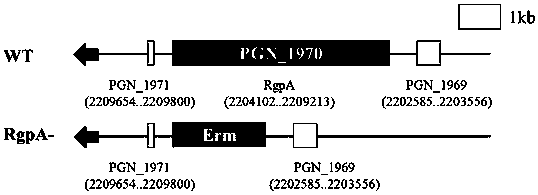
Preparation method of porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain
InactiveCN104962575ANo specific requirementsEasy and flexible operationVector-based foreign material introductionPorphyromonas gingivalisEnzyme
The invention provides a preparation method of a porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain, and relates to the field of oral medicine. The method includes the steps that upstream and downstream homologous arms of porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA genes are amplified; erythrocin resistance gene segments are amplified; homologous recombination fragments with the upstream and downstream homologous arms of the RgpA genes at the two ends and the erythrocin resistance gene segments in the middle positions are constructed; the homologous recombination fragments are converted into porphyromonas gingivalis, homologous recombination is performed, an erythrocin resistance plate is adopted for screening, and then the porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain is obtained. According to the preparation method of the porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain, operation is easy, convenient and flexible, no complex enzyme-cut and link-up or screening is needed, no specificity requirement exists in selection of mutation sites, and recombination efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL
Preparation method of porphyromonas gingivalis rgpa gene knockout mutant strain
InactiveCN104962575BNo specific requirementsEasy and flexible operationVector-based foreign material introductionPorphyromonas gingivalisEnzyme
The invention provides a preparation method of a porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain, and relates to the field of oral medicine. The method includes the steps that upstream and downstream homologous arms of porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA genes are amplified; erythrocin resistance gene segments are amplified; homologous recombination fragments with the upstream and downstream homologous arms of the RgpA genes at the two ends and the erythrocin resistance gene segments in the middle positions are constructed; the homologous recombination fragments are converted into porphyromonas gingivalis, homologous recombination is performed, an erythrocin resistance plate is adopted for screening, and then the porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain is obtained. According to the preparation method of the porphyromonas gingivalis RgpA gene knock-out mutant strain, operation is easy, convenient and flexible, no complex enzyme-cut and link-up or screening is needed, no specificity requirement exists in selection of mutation sites, and recombination efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL
Composition for detecting methicillin-resistant and/or erythromycin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN104195251ADetection time is shortEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDrugStaphylococcus caprae
The invention provides a composition for detecting methicillin-resistant and / or erythromycin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. The composition comprises a primer pair SEQ ID NO.1 / 2, a primer pair SEQ ID NO.3 / 4, a primer pair SEQ ID NO.5 / 6 and a primer pair SEQ ID NO.7 / 8. When the staphylococcus aureus is subjected to bacterial genus identification by using the composition disclosed by the invention as well as a corresponding detection method, MRSA and erythromycin drug-resistant genes can be simultaneously detected. The composition has the advantages of rapidness, high throughput and the like, and the requirement for rapidly and accurately detecting microbes in food is met. By utilizing an mPCR-DHPLC / electrophoresis method established by the invention, the staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and erythromycin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in samples can be simultaneously identified through one time of detection. Moreover, by using the composition, the detection consumes less time, is easy and rapid to operate and suitable for rapid detection requirement and can save lots of labor force and financial resources.
Owner:郑秋月 +4
Overexpression of uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene and its recombinant Lactobacillus acidophilus construction method
ActiveCN106520794BImprove freeze-drying survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylasePhosphorylation
The invention discloses an overexpressed UGPase (UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase) gene and a method for constructing recombinant lactobacillus acidophilus thereof. The method is characterized by comprising the specific steps as follows: (1) a UGPase gene LBA0625 is amplified with lactobacillus acidophilus genome DNA as a template; an expression vector pMG36e is subjected to single restriction digest with restriction enzyme Hind III, and after dephosphorylation and gel recovery are performed, a recombinant expression vector is constructed by inserting a PCR amplification product into the expression vector pMG36e; (2) an overexpression plasmid subjected to extraction and concentration is imported into lactobacillus acidophilus through electrotransformation, the lactobacillus acidophilus is resuscitated at 37 DEG C for 2 h, applied to an erythrocin resistant plate and cultured at 37 DEG C for 36 h for screening transformants; the transformants are subjected to PCR verification, and the recombinant lactobacillus acidophilus PLY127-1 of the overexpressed UGPase gene is obtained. The freeze-drying survival rate of the lactobacillus acidophilus can be increased substantially.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
10a-azalide compound crosslinked at 10a- and 12-positions
InactiveUS20110237784A1High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAzalideResistant bacteria
A novel 10a-azalide compound crosslinked at the 10a- and 12-positions, which is represented by the following formula, and is effective on even Hemophilus influenzae, or erythromycin resistant bacteria (e.g., resistant pneumococci and streptococci).
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD +1
Erythromycin A ketolide antibiotic derivative, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111072740BShort synthetic routeEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainQuinoline
The invention discloses a series of erythromycin A ketolide antibiotics containing an aminoquinoline ring as shown in formula I, a preparation method and application thereof, side chain intermediates of each compound and a synthesis method. The key points of the present invention are: the compound shown in formula I has broad-spectrum antibiotic efficacy, and has outstanding antibacterial activity to sensitive and drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria and negative bacteria, especially to vancomycin The antimicrobial activities of antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Shigella flexneri were significantly better than those of the control drug Telithromycin white. The compound proposed by the invention can be used as a broad-spectrum antibiotic, and has the antibacterial and antiviral activities of inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
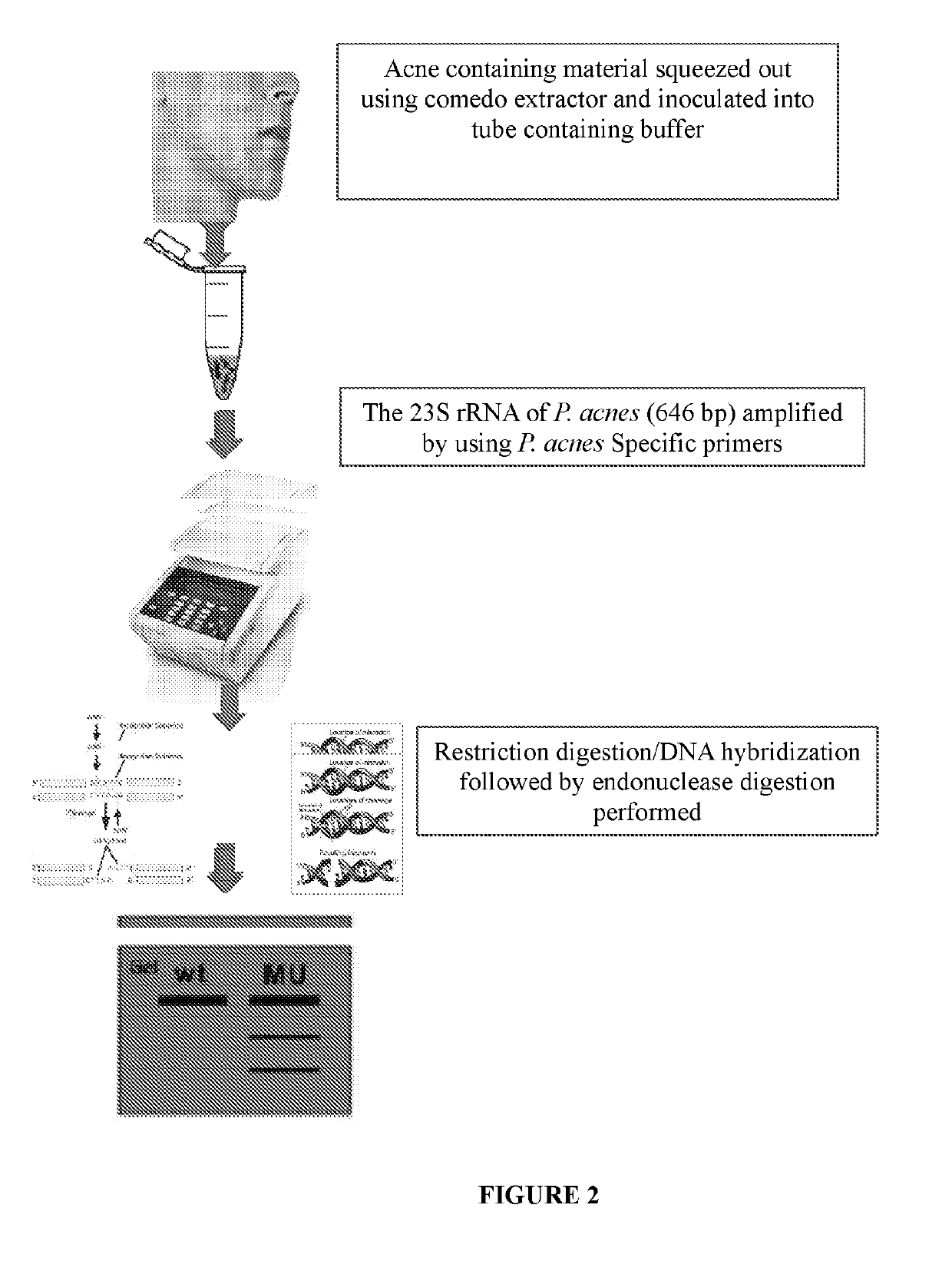
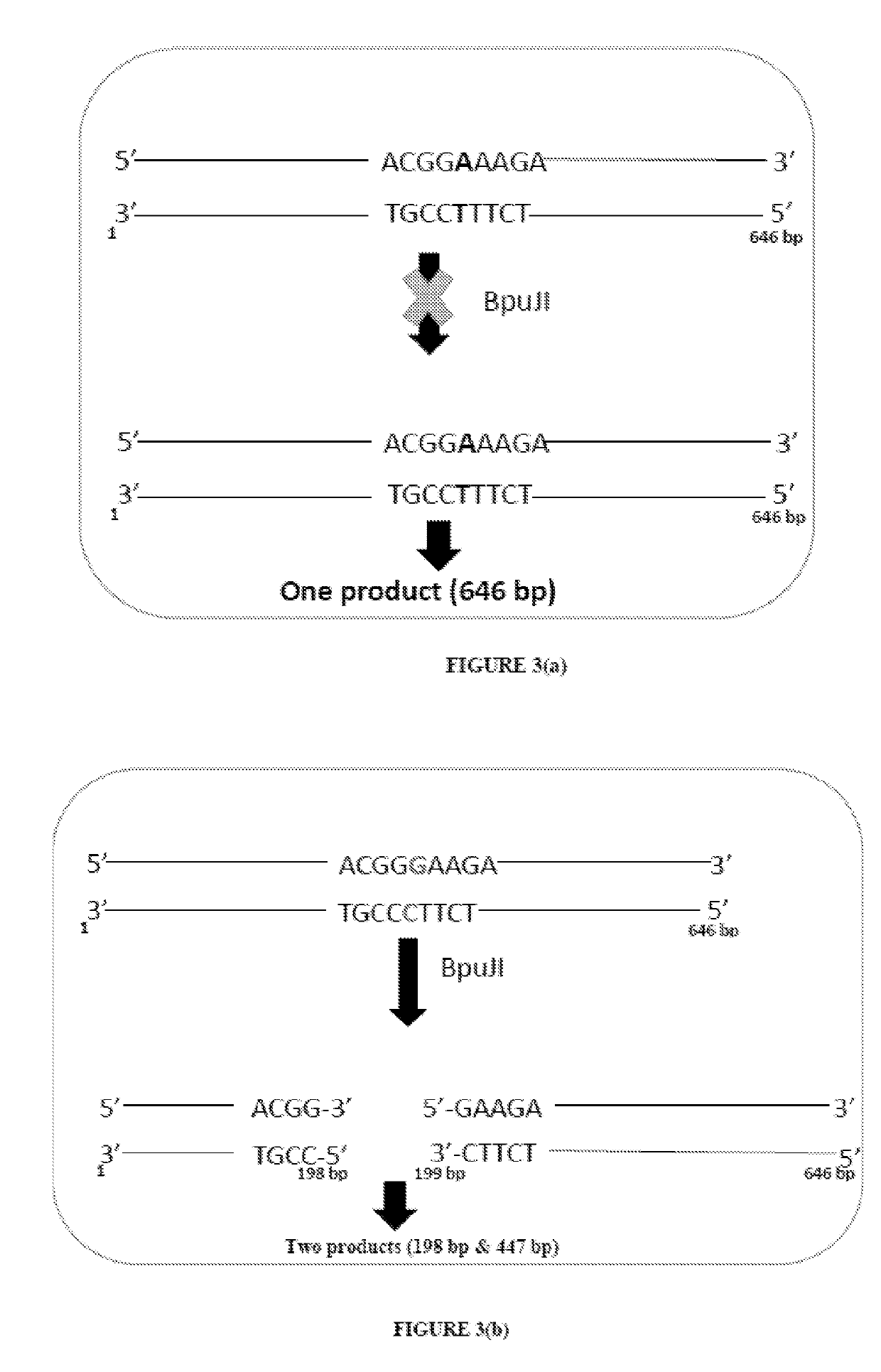
Method of detecting and treating p. acnes and kit thereof
InactiveUS20190119729A1Reduce bacteria countTetracycline active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBacillus acnesAntibiotic Y
The present disclosure relates to method for detecting P. acnes as well as a method for detecting mutation in genomic sequence of 23S rRNA sequence of P. acnes, particularly mutation A2058G. The method comprises amplifying a region of 23S rRNA specific for P. acnes using primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1 and 2 followed by detecting the mutation through selective action of an endonuclease- at a mismatch at the site of said mutation or post-hybridization with specific P. acnes 23S regions followed by mismatch specific endonuclease action. The presence of A2058G mutation confers antibiotic resistance, particularly clindamycin and erythromycin resistance, and thus the present disclosure also relates to methods of treating acne caused by clindamycin resistant P. acnes by using fluoroquinolone based antibiotics.
Owner:VYOME THERAPEUTICS LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com