Engineering strain for directly producing gernebcin and use thereof
A technology of tobramycin and engineering bacteria, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, bacteria, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing production costs, facilitating quality control, and simplifying production processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The present invention mainly comprises following major steps:
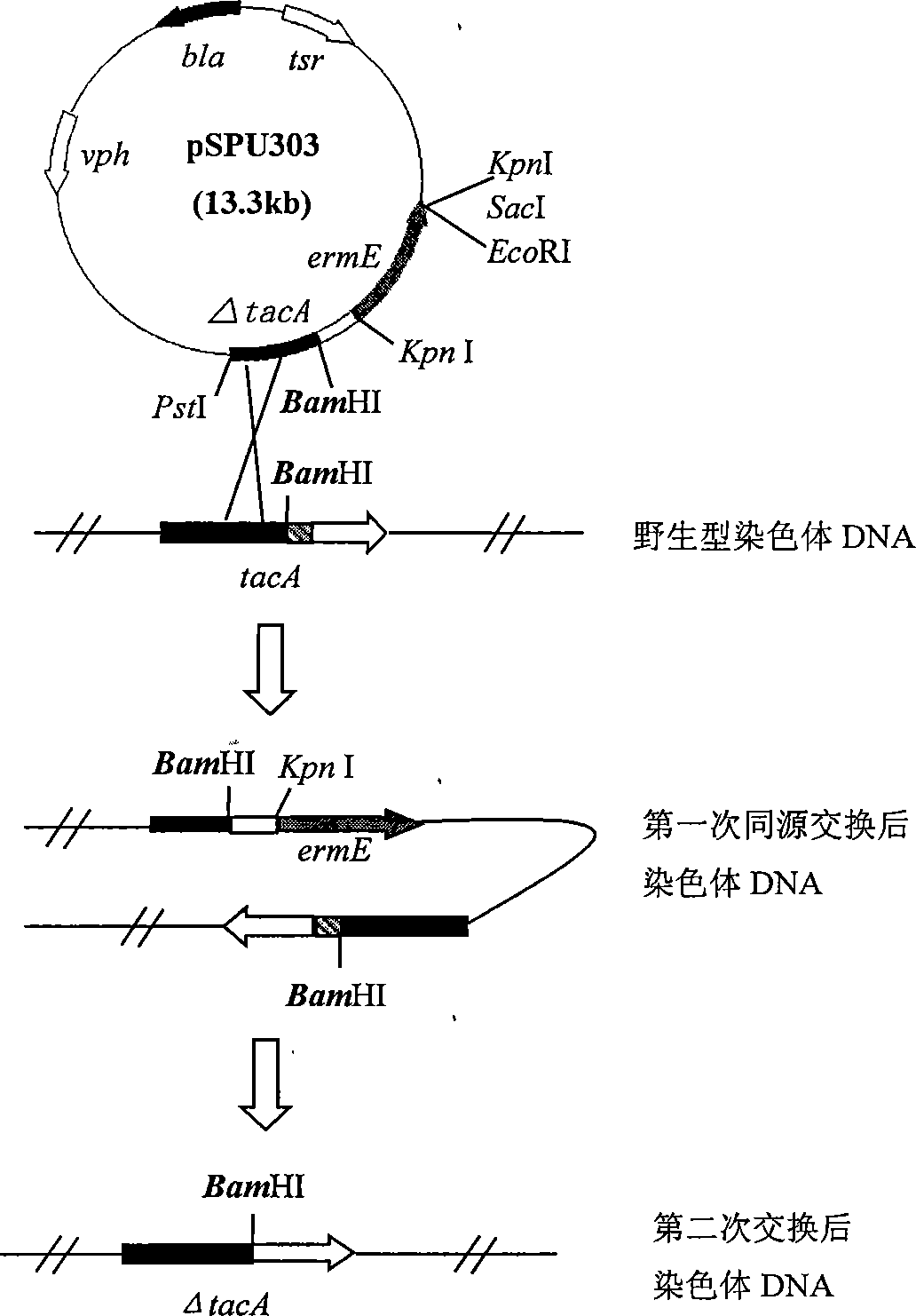
[0029] 1. Construction of tacA gene blocking plasmid
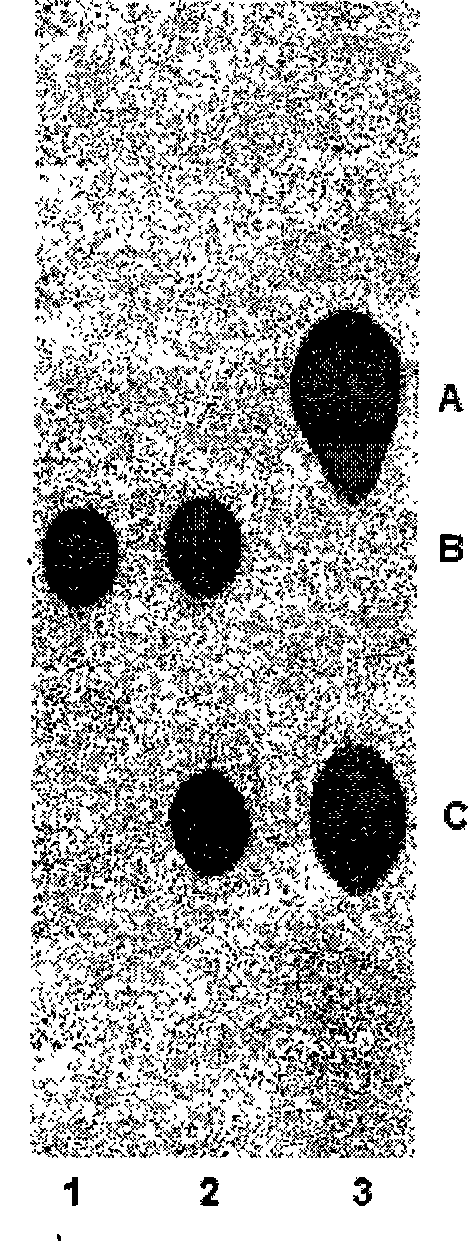
[0030] According to the sequence of the tobramycin biosynthetic gene cluster (GenBank Accession Number AJ579650) published by Madan Kumar Kharel et al., two pairs of primers were designed on the upstream and downstream of the tacA gene, and two fragments were obtained by PCR amplification using the total DNA of Streptomyces fugus as a template PCR1-2 and PCR3-4. The two-fragment ligation product was named ΔtacA, which deleted 111 bases at the 5' end, 260 bases inside and 88 bases at the 3' end of the tacA gene. ΔtacA was ligated into vector pIJ2925 to obtain pSPU301. The erythromycin resistance gene ermE was then connected to the KpnI site in pSPU301 (pXZ1 was digested with KpnI to recover a fragment of about 1.6 Kb in size) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pSPU302, and finally the ΔtacB+ermE was connected to BamHI in the vector pHZ132 by digesting w...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: utilize tobramycin genetically engineered bacteria to produce tobramycin
[0047] The tobramycin genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention can be directly used in production, and the tobramycin is extracted after the strain is fermented as an antibacterial drug.
[0048] 1. Shake flask fermentation of tobramycin genetically engineered bacteria
[0049] Seed medium: raw soybean powder 10g, glucose 10g, peptone 3g, yeast powder 1g, corn flour 5g, CaCO 3 (Light weight) 1g, add tap water to 1L.
[0050] Fermentation medium: soluble starch 20, raw soybean powder 20g, glucose 10g, NH 4 Cl5g, CaCO 3 (light) 5g, MgSO 4 4 g, FeSO 4 0.05g, ZnSO 4 0.03g, MnCl 2 0.3g, soybean oil 0.6mL / 40mL, add tap water to 1L.
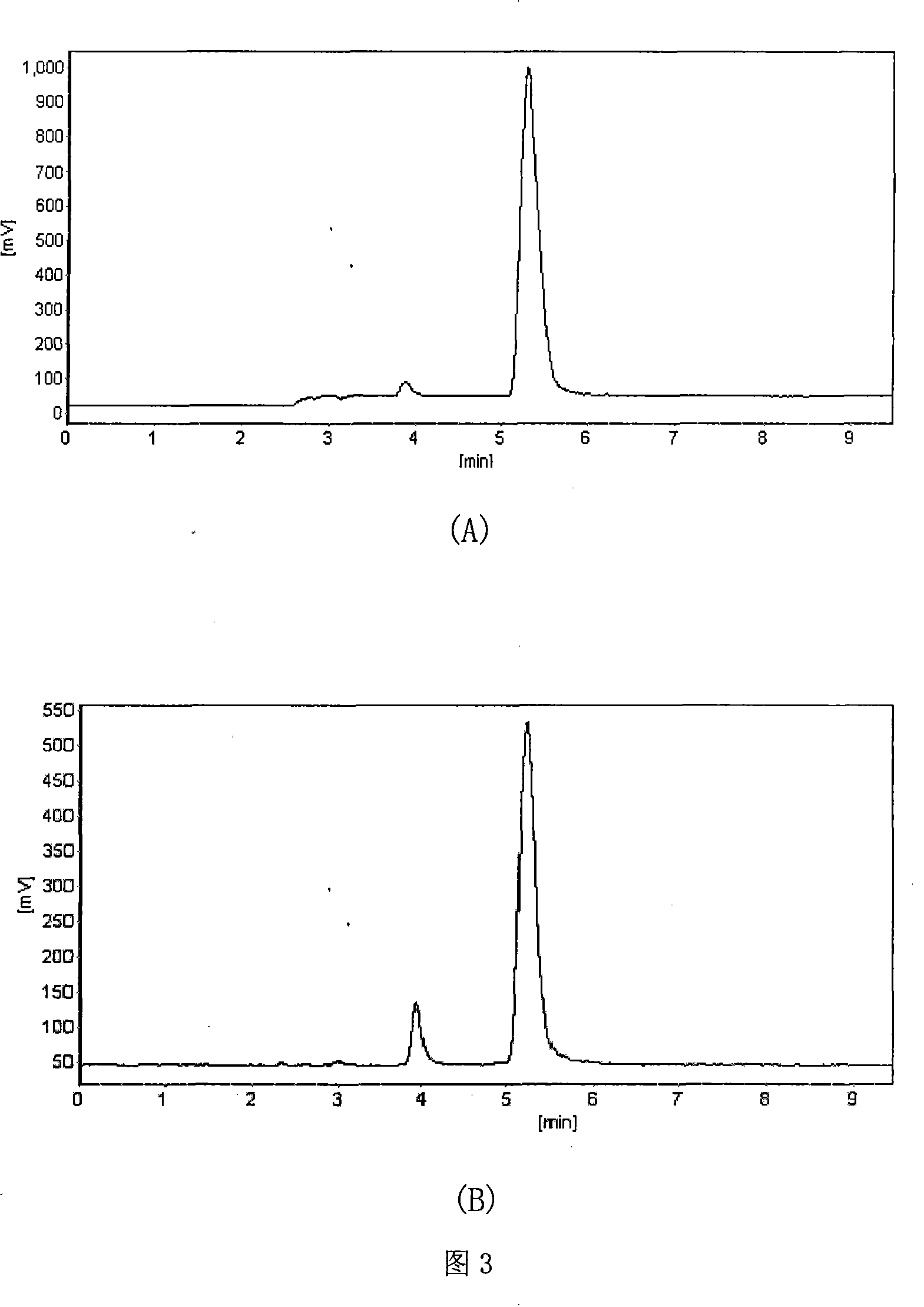
[0051] The genetically engineered bacterium Streptomyces fugus H6 (pSPU303-3) obtained in step 3 of Example 1 was subjected to shake-flask fermentation. Before the fermentation, the single colony with rich sporulation was isolat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com