Patents
Literature
433 results about "Transferase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transferase Genes encode enzymes (Transferases) that transfer a group, such as a methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor). (NCI)
Knockout swine and methods for making the same
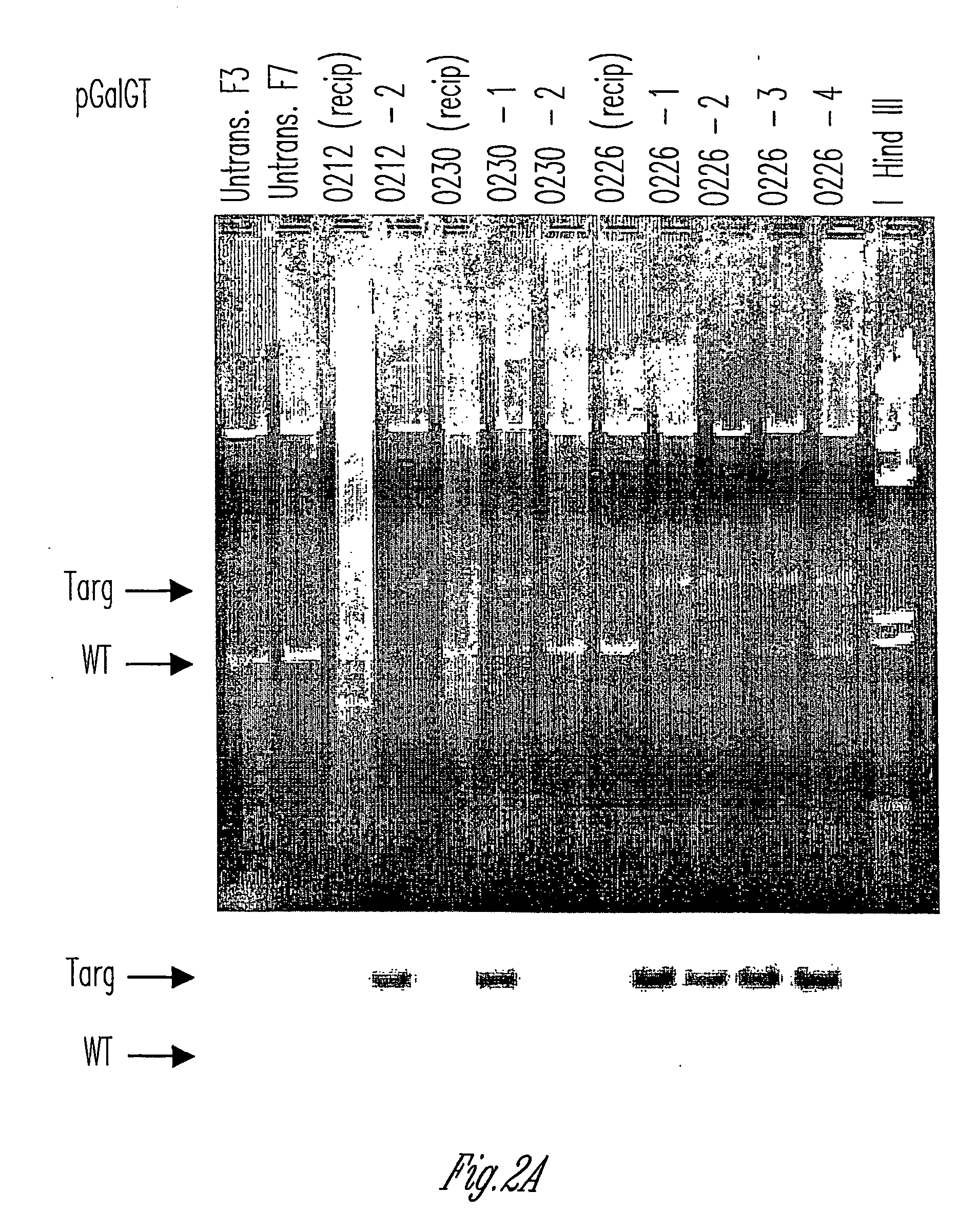
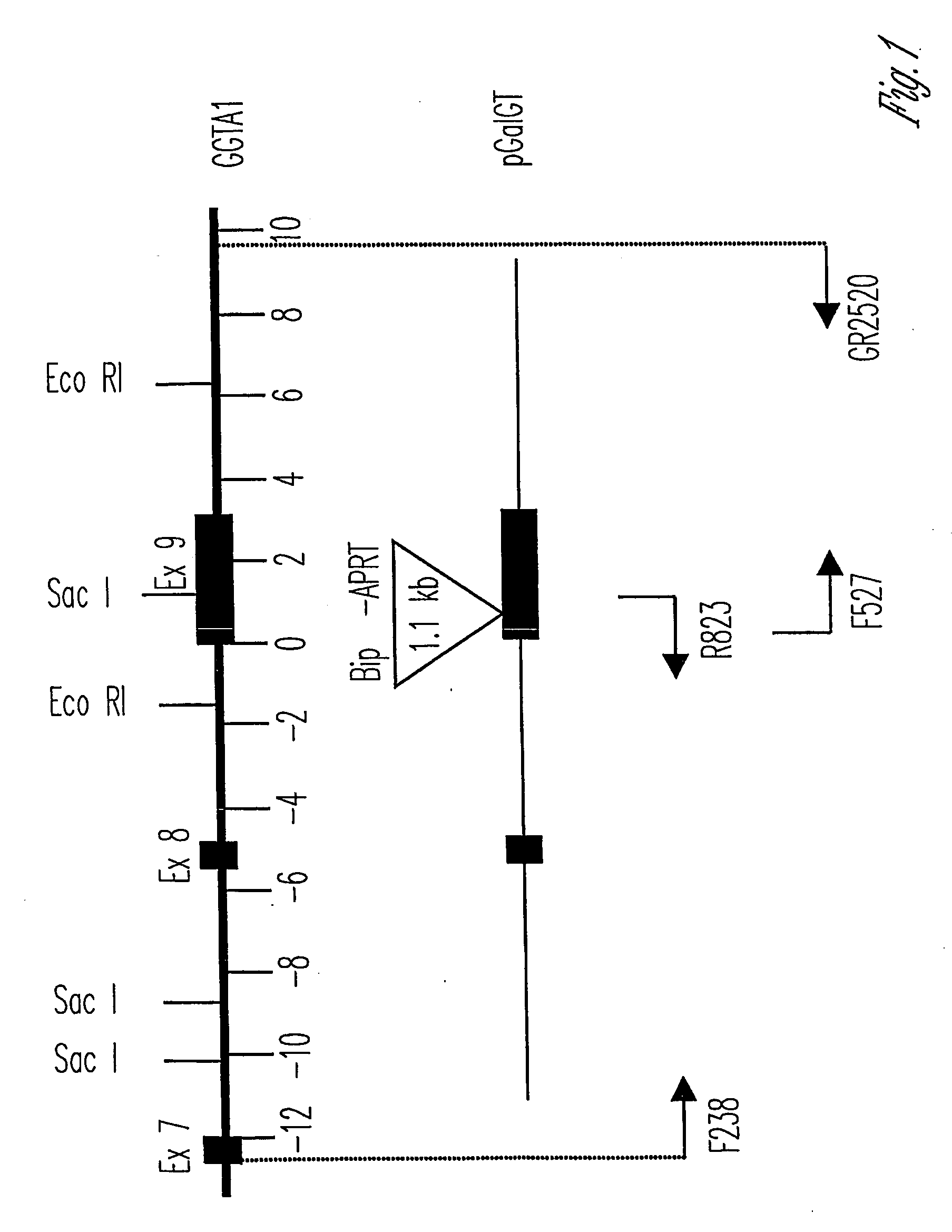
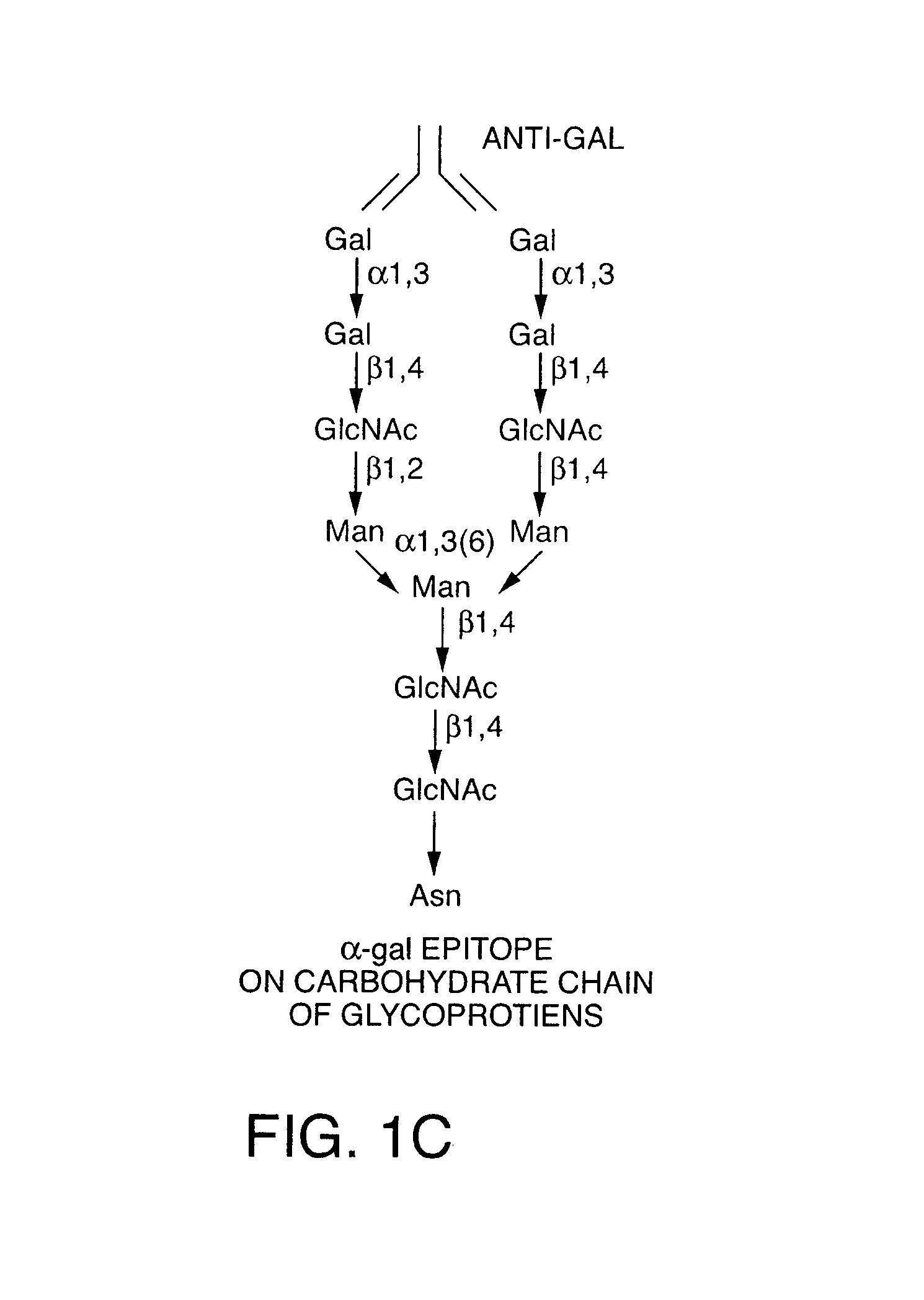
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
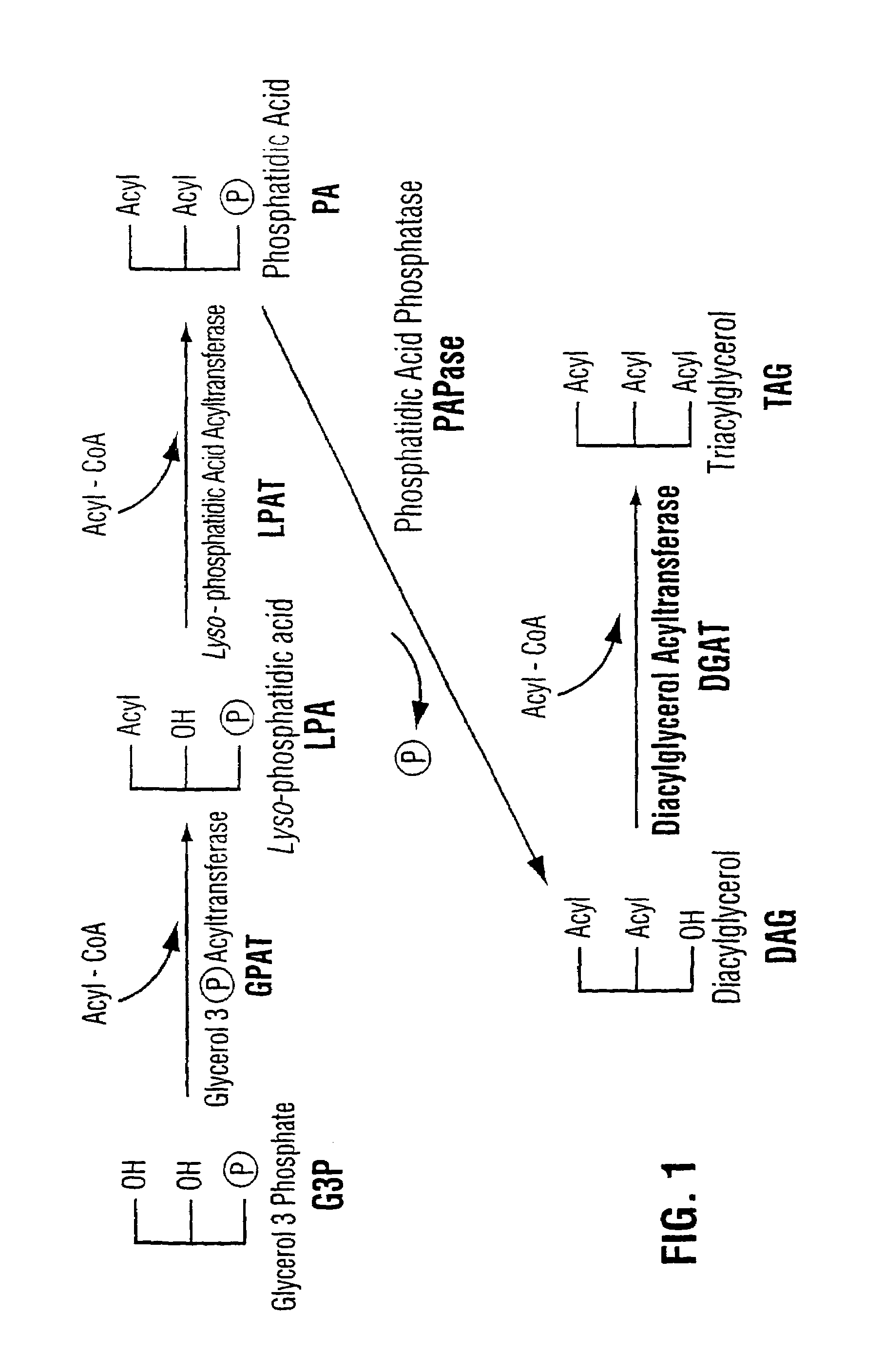
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS7015373B1Reduced DGAT activityReduce rateSugar derivativesTransferasesBrassicaceaePlanting seed
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase gene clone and expression
InactiveCN101294149ACyclization activityImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
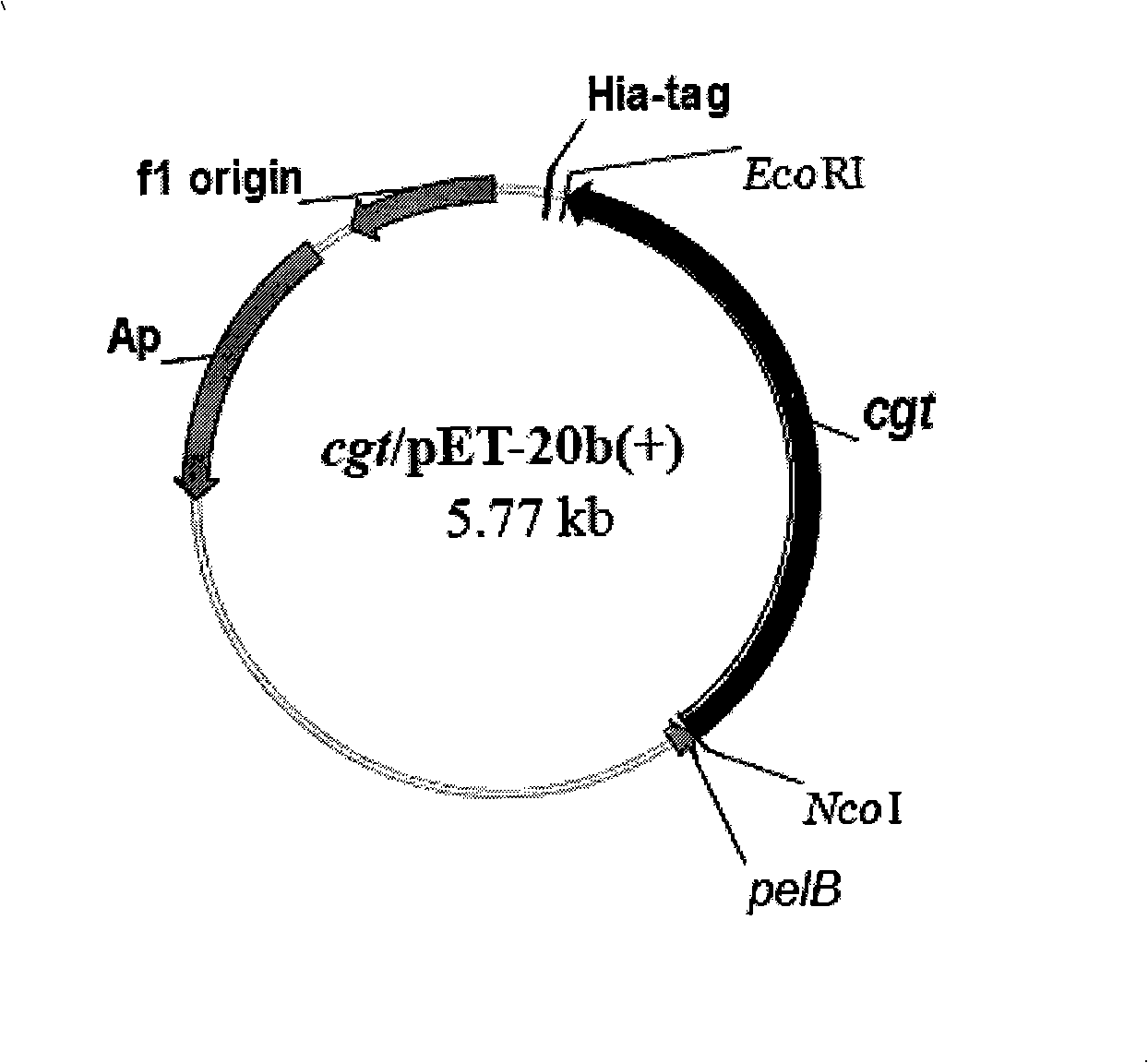
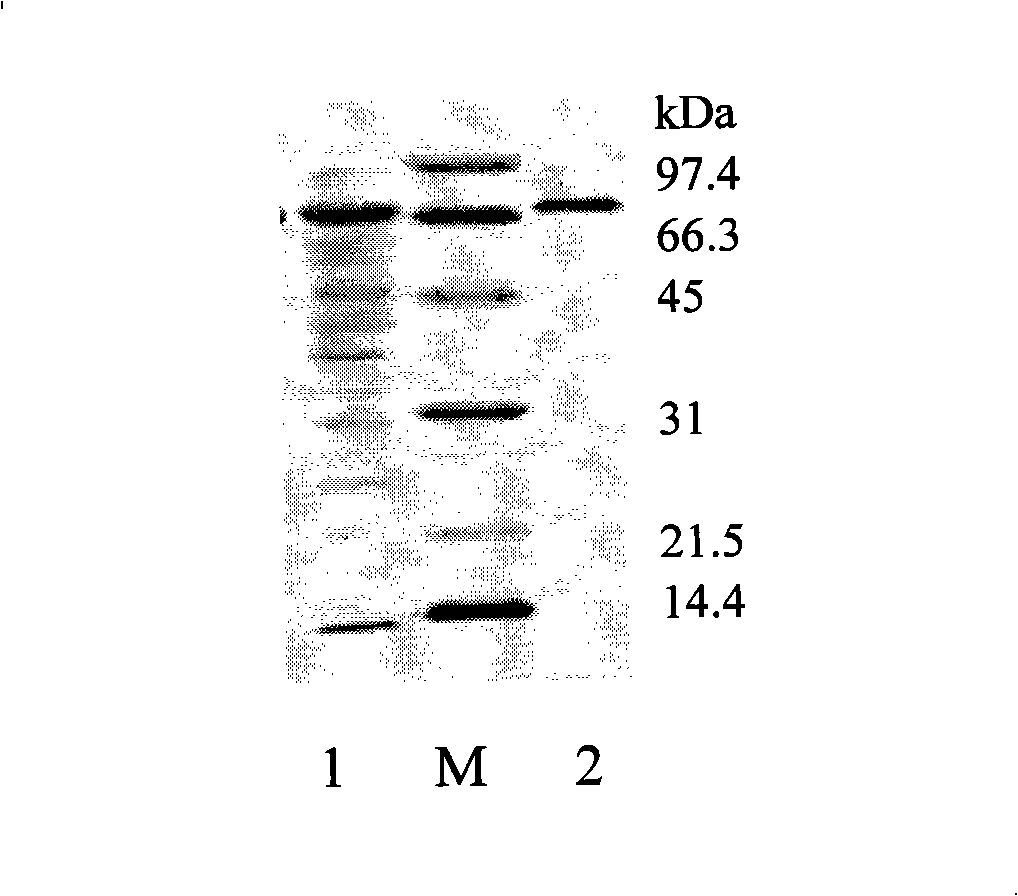
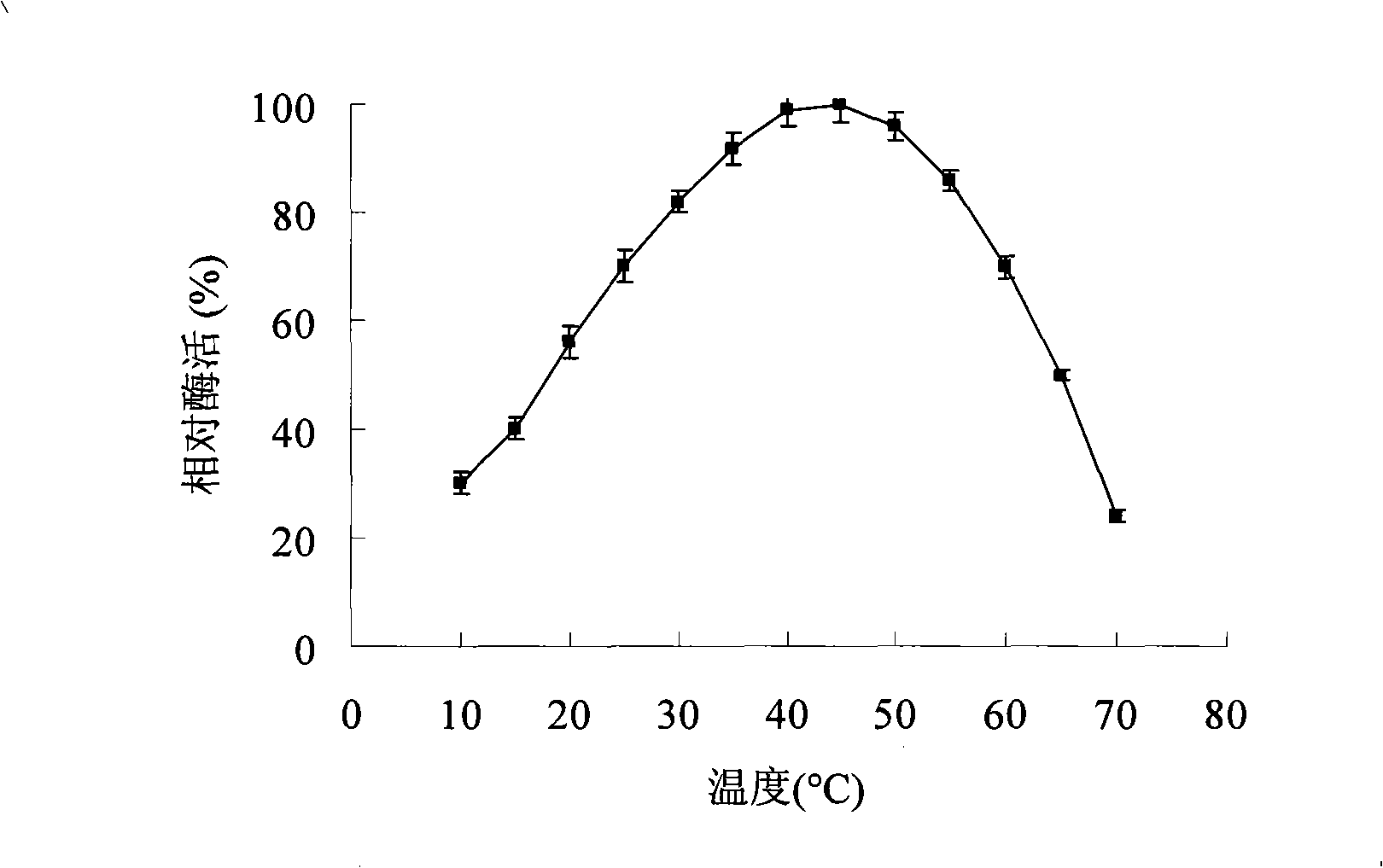
The invention relates to the clone and the expression of alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (alpha-CGTase), which belong to the field of enzyme gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The cgt gene expression method comprises the following steps: obtaining cgt gene SEQ ID NO:1 from total DNA of Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01; selecting plasmid pET20b(+) as the expression vector of cgt gene; and selecting E.coli BL21(DE3) as the expression host to achieve high-efficiency extracellular expression of the cgt gene, wherein the cgt gene has 2,061 nucleotides and 687 coded amino acids; prokaryotic expression plasmid is constructed; and alpha-CGTase is expressed by transformed E.coli. Recombinase has cyclization activity and can transform starch and relevant matrix into cyclodextrin. The recombined alpha-CGTase has an optimal temperature of 40 to 45 DEG C and an optimal pH value of 5.5, and has higher thermal stability below 40 DEG C and poor thermal stability above 50 DEG C. The alpha-CGTase meets the requirement for industrial application such as food and medicines, and can be used for industrial production of alpha-cyclodextrin and beta-cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
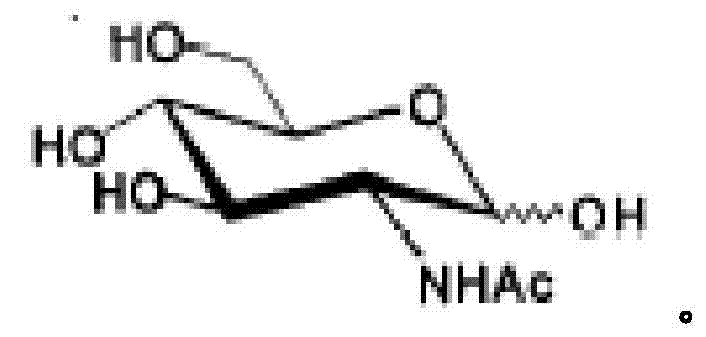
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
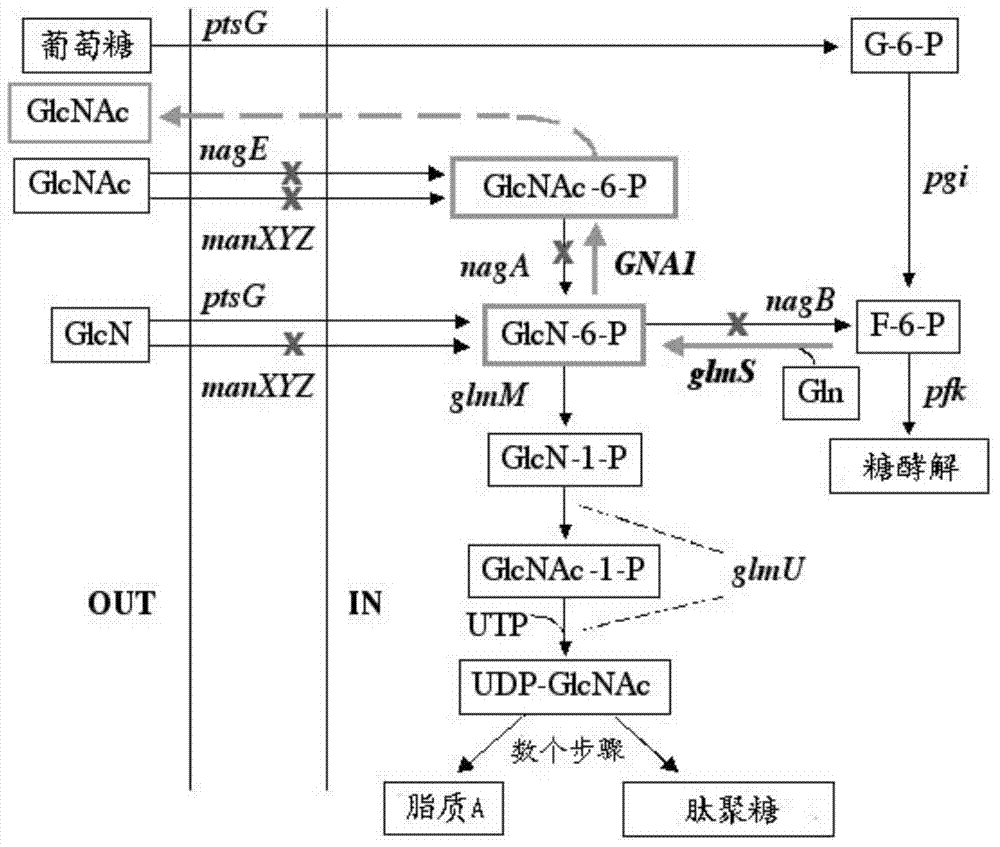
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
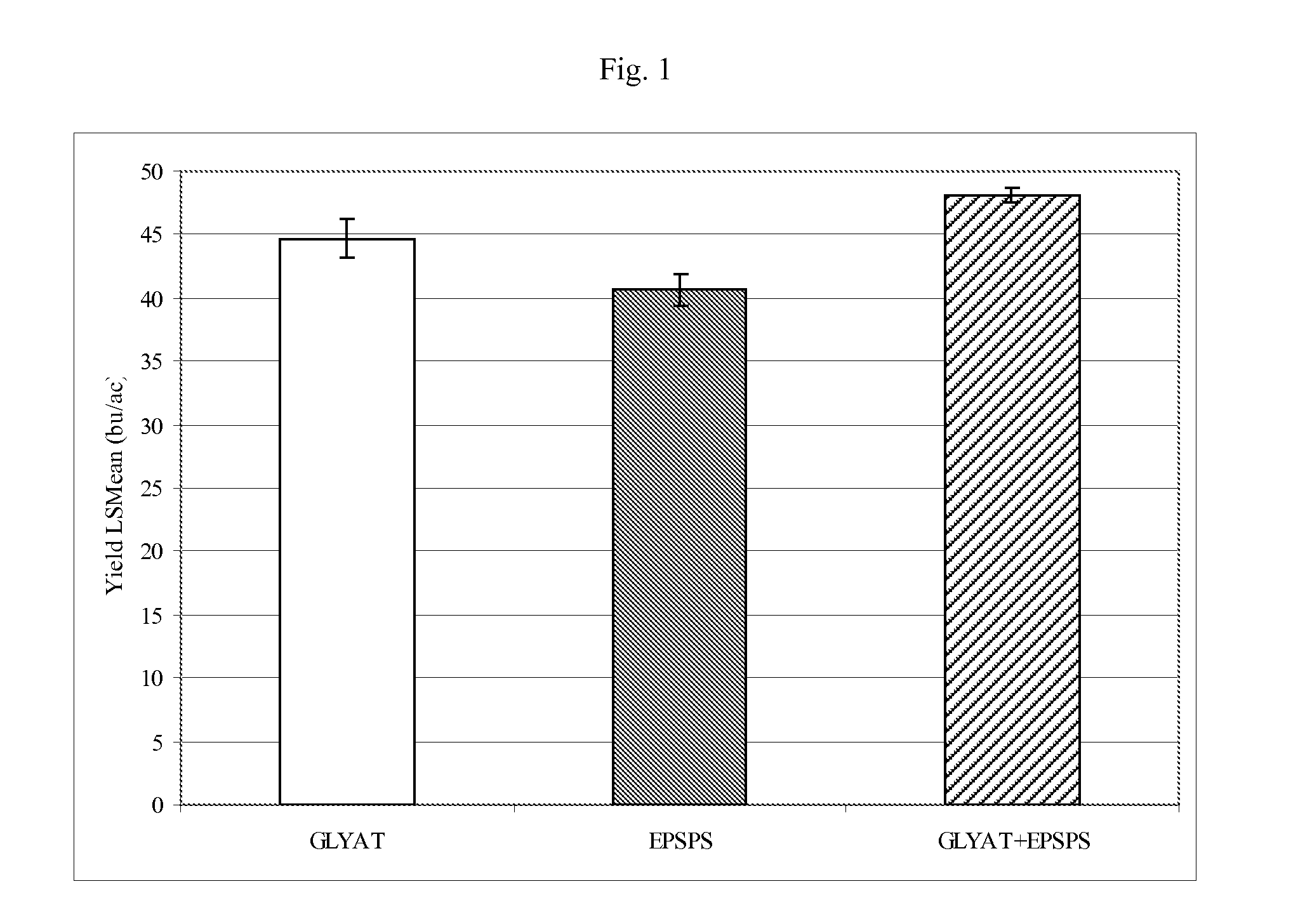
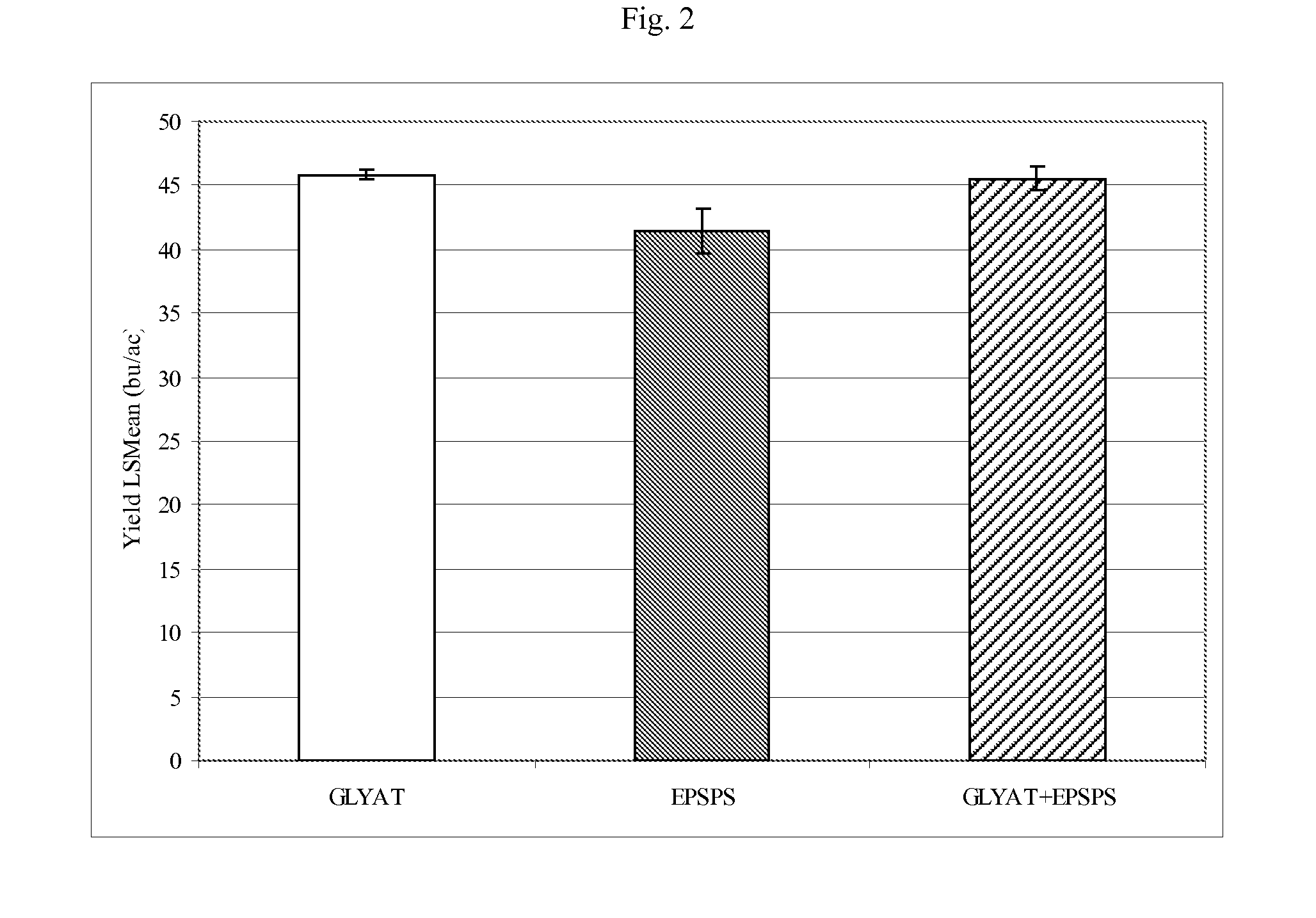
Novel glyphosate-n-acetyltransferase (GAT) genes
Methods and compositions for improving yield in a plant are provided. Methods of improving yield include treating plants with an effective amount of glyphosate, wherein the plant express at least two heterologous polypeptides that impart tolerance to glyphosate via distinct modes of action. In one non-limiting method, the first polypeptide has glyphosate N-acetyl transferase activity and the second polypeptide comprises a glyphosate-tolerant EPSPS polypeptide.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
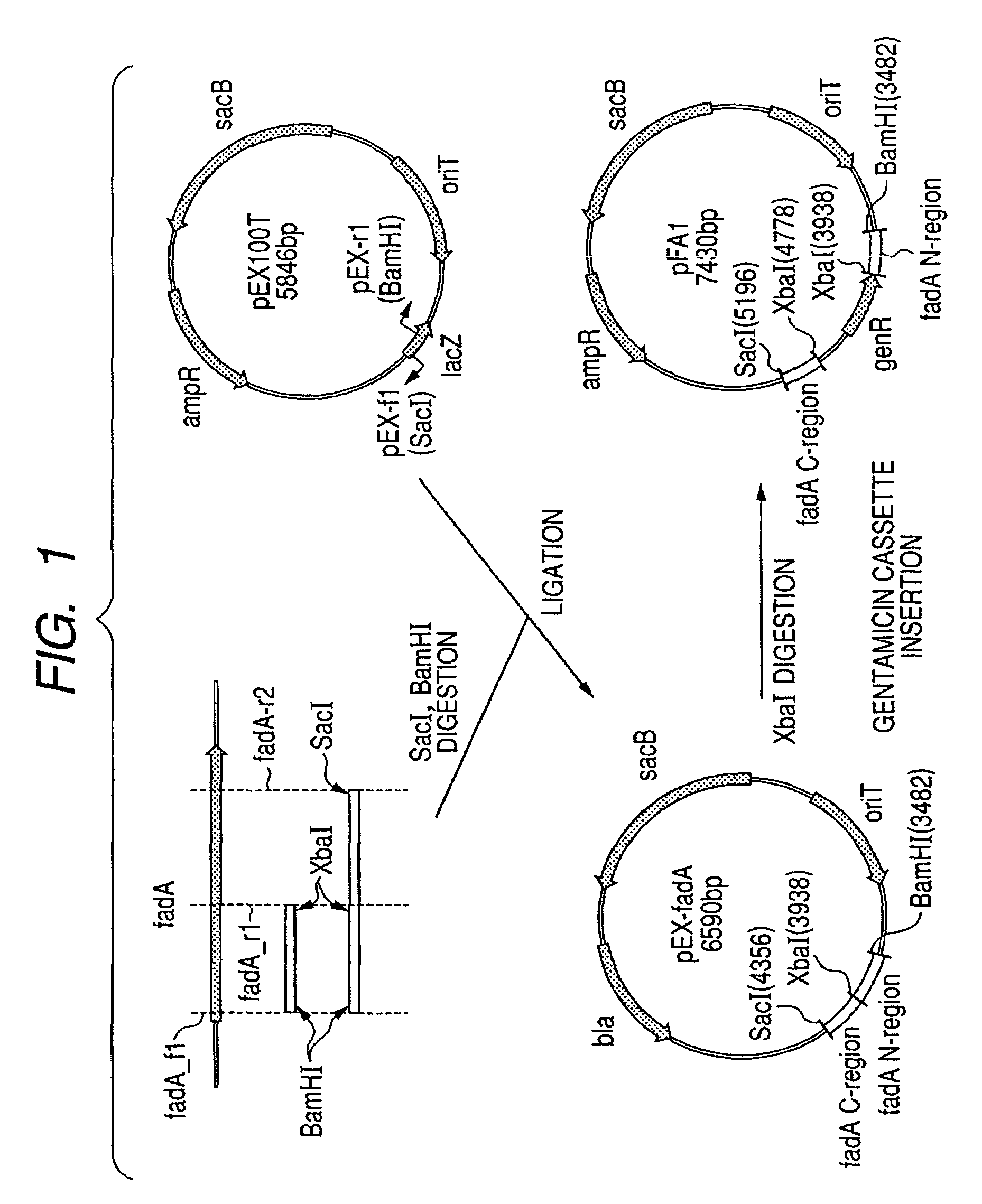
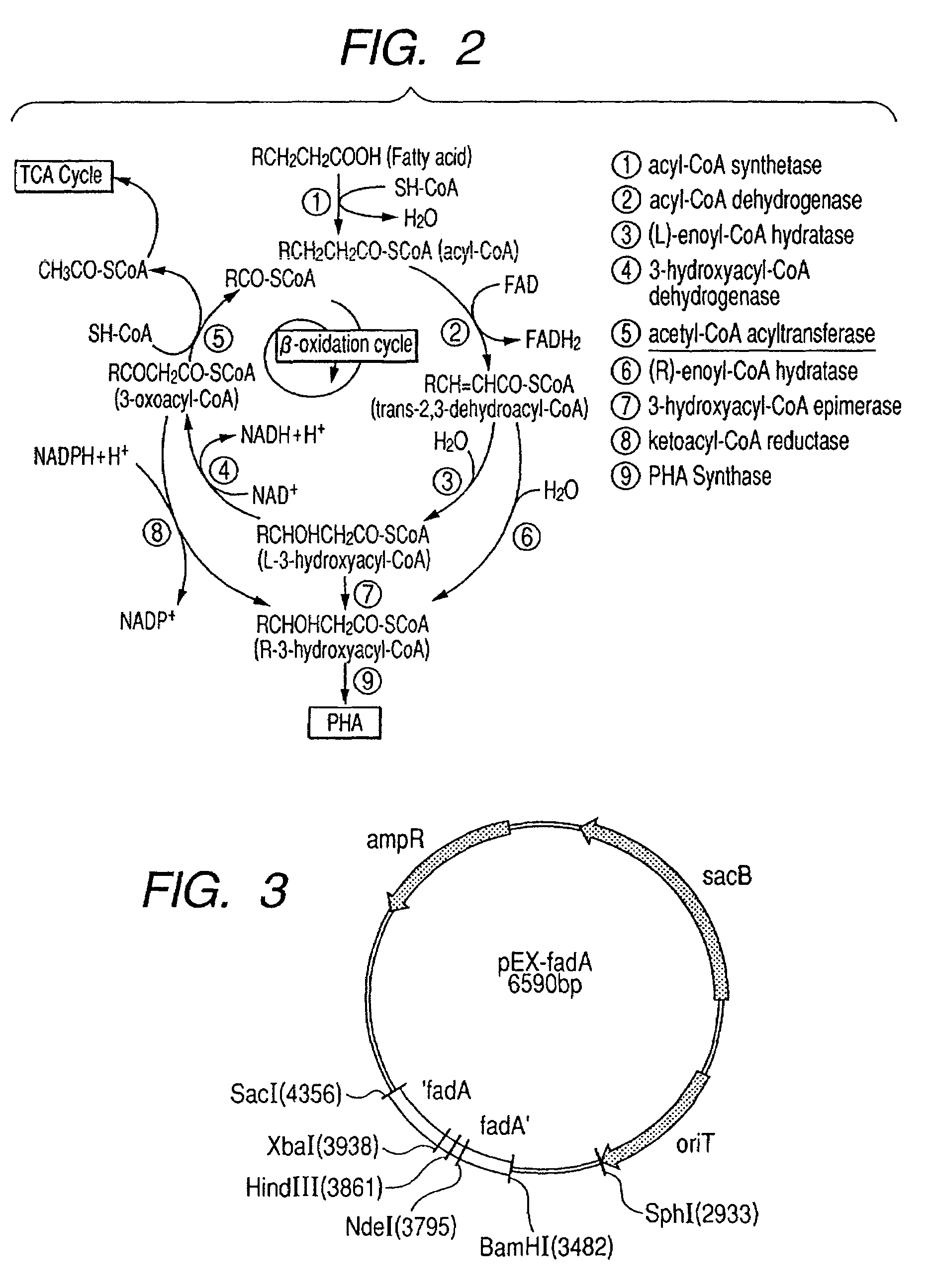
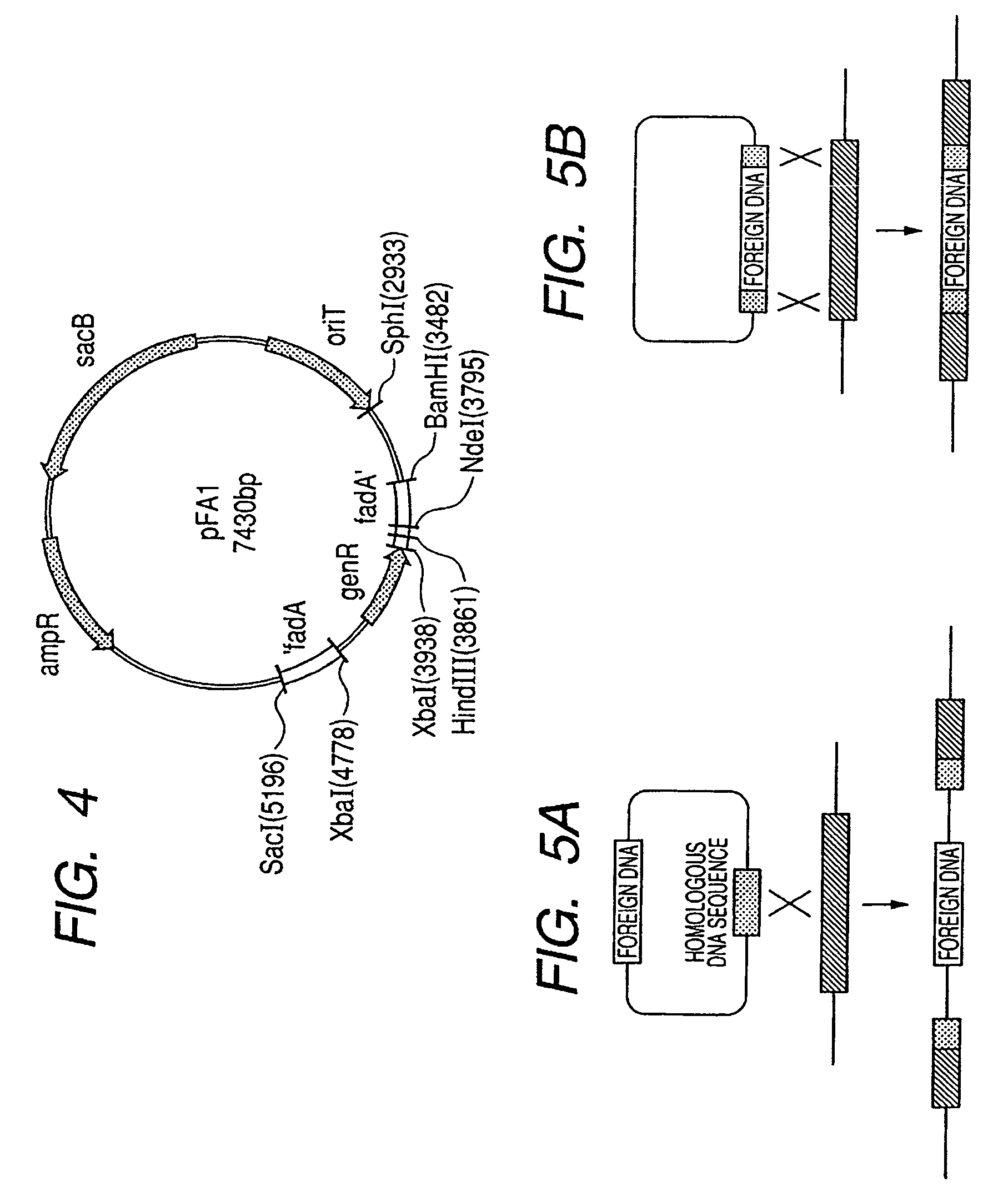
Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene disrupted bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
A method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate with improved productivity and composition is provided. Polyhydroxyalkanoate is produced by a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which a gene encoding acetyl-CoA acyltransferase is disrupted.
Owner:CANON KK
Pichia pastoris strain with deletion of alpha-1,6-mannose transferase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN101195809ALow immunogenicityEasy to getFungiMicroorganism based processesBio engineeringPichia
The invention discloses Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent and the establishing method, which belongs to the biological engineering field. The collection number of the Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent is CGMCC No.1853. The invention has the advantages that the Pichia pastoris strain with alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase absent built by the invention can prevent the generation of excessive manna saccharify, when expressing extrinsic glucoprotein, reduce the immunogenicity of the pressed protein, and therefore, the invention has important application value in the biomedical field, and other fields; simultaneously, the strain can also be applied to the further gene knockout or the metabolic engineering reconstruction. The invention also builds a method for knocking out the alpha-1, 6-mannosyl transferase gene through secondary homologous recombination, mutant strain can be relatively easily obtained through the method, therefore the sieving workload is greatly reduced, and the success ratio is improved.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) sequence for encoding parietchloris incise diacylglycerol acyltransferase and application thereof
The invention relates to a separated deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) sequence. The DNA sequence comprises a nucleotide sequence (a) of SEQIDNO.1 or SEQIDNO.2; or a nucleotide sequence (b) complementary with the nucleotide sequence (a). The invention further provides a recombinant expression vector containing the nucleotide sequence, a genetic engineering host cell and application of the nucleotide sequence, the recombinant expression vector and the host cell for encoding the diacylglycerol acyltransferase or producing triacylglycerol. The DNA sequence has the advantages that a cDNA full-length sequence and a DNA full-length sequence of a parietchloris incise diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene are obtained by screening, encoded protein of the gene has a triacylglycerol synthesis capability by expression of the gene in a TAG synthesis defect strain H1246 of yeast, and conditions are created for utilizing the gene to achieve large-scale synthesis of triacylglycerol by genetic operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and establishment method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN109735479AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneLactose transport
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and an establishment method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis. Recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained in the mode that a lactose transport enzyme gene is subjected to reinforcement expression in a gene group of bacillus subtilis 168, and exogenous fucosyltransferase, fucokinase and gtp-mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase genes are expressed. According to recombinant bacillus subtilis, the lactose transport enzyme gene is subjected to reinforcement expression on the gene group, expression of the lactose transport enzyme is effectively reinforced, the efficiency of transferring exogenous lactose into cytoplasm is improved, the concentration of lactose in cytoplasm is increased, and synthesis of 2'-fucosyllactose is promoted. The establishment method of recombinant bacillus subtilis is simple and convenient to use and has good application prospects.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
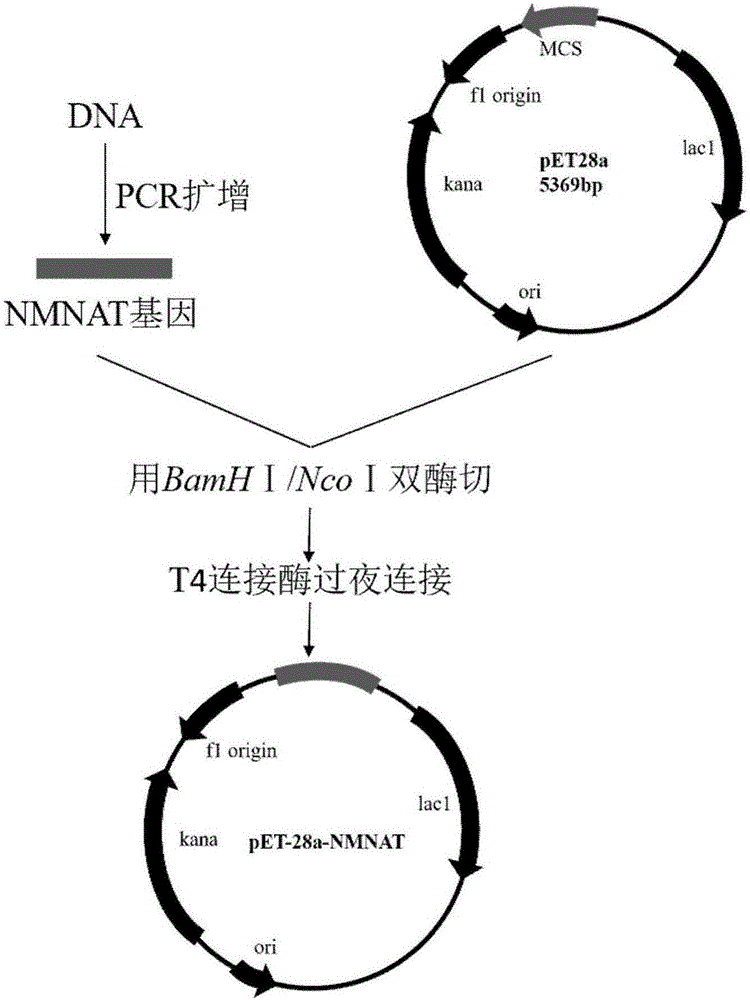
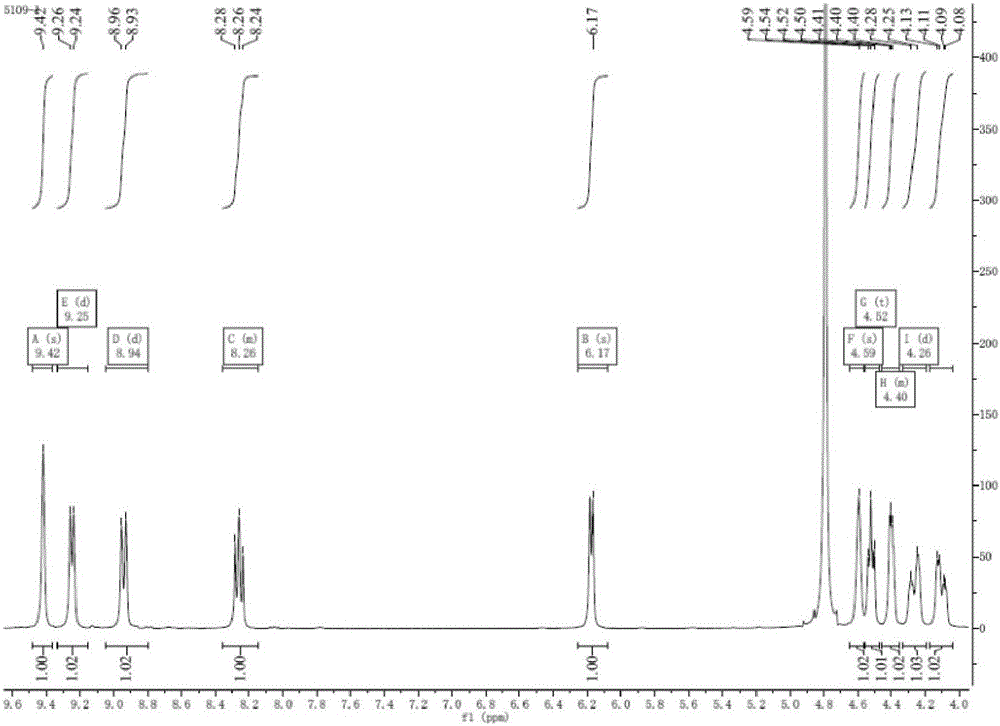
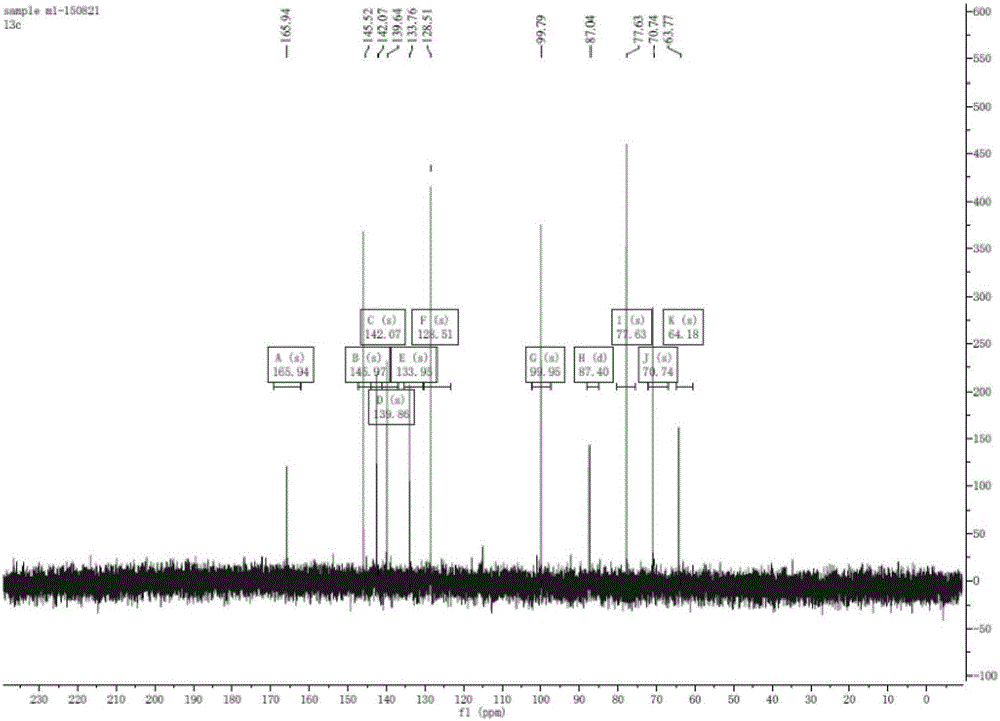
Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (Nmnat) mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103710321AHigh catalytic activityReduce manufacturing costTransferasesGenetic engineeringNicotinamide mononucleotideNicotinamide Mononucleotide Adenylyltransferase
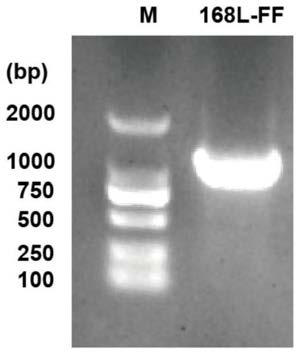
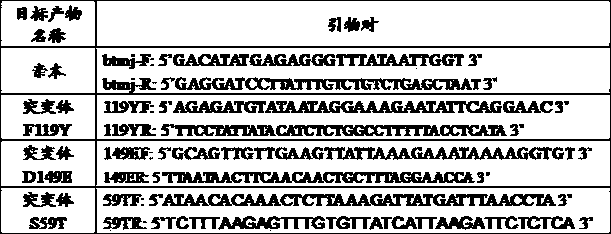
The invention discloses a nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (Nmnat) mutant as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. The Nmnat mutant is obtained through point mutation of a sequence 2 in a sequence table and point mutation is mutation of at least one of the 119 site, the 149 site and the 59 site of the sequence. The Nmnat mutant with high catalytic activity is finally obtained through site-specific mutagenesis of the gene sequence of Nmnat. The mutant can be efficiently purified through a simple purification scheme, thus reducing the production cost of NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and improving the market competitiveness of corresponding products.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
Echinococcus granulosusglutathione transferase gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and provides an Echinococcus granulosusglutathione transferase gene a base sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also provides a protein encoded by the Echinococcus granulosusglutathione transferase gene. The amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the Echinococcus granulosusglutathione transferase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, or is the same as 1st-219th amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. The recombinant protein can be used for immunodiagnosis of cystic echinococcosis patients and can be used for coating a plate; and the serums of the patients having cystic echinococcosis, alveolitoid echinococcosis, cysticercosis and other parasite diseases and healthy people are detected by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the obtained sensitivity and specificity are respectively 72.41% and 92.36%.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
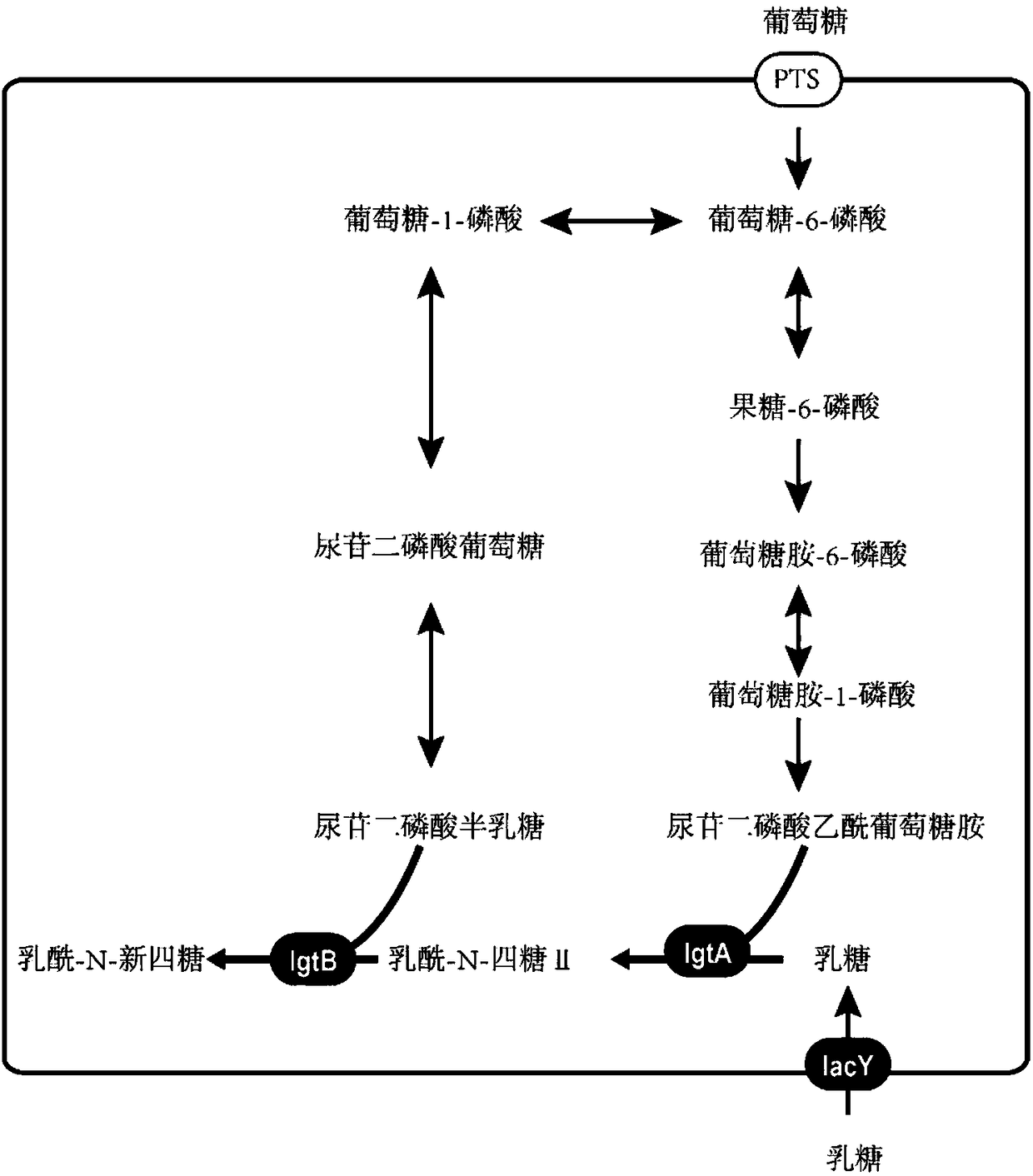
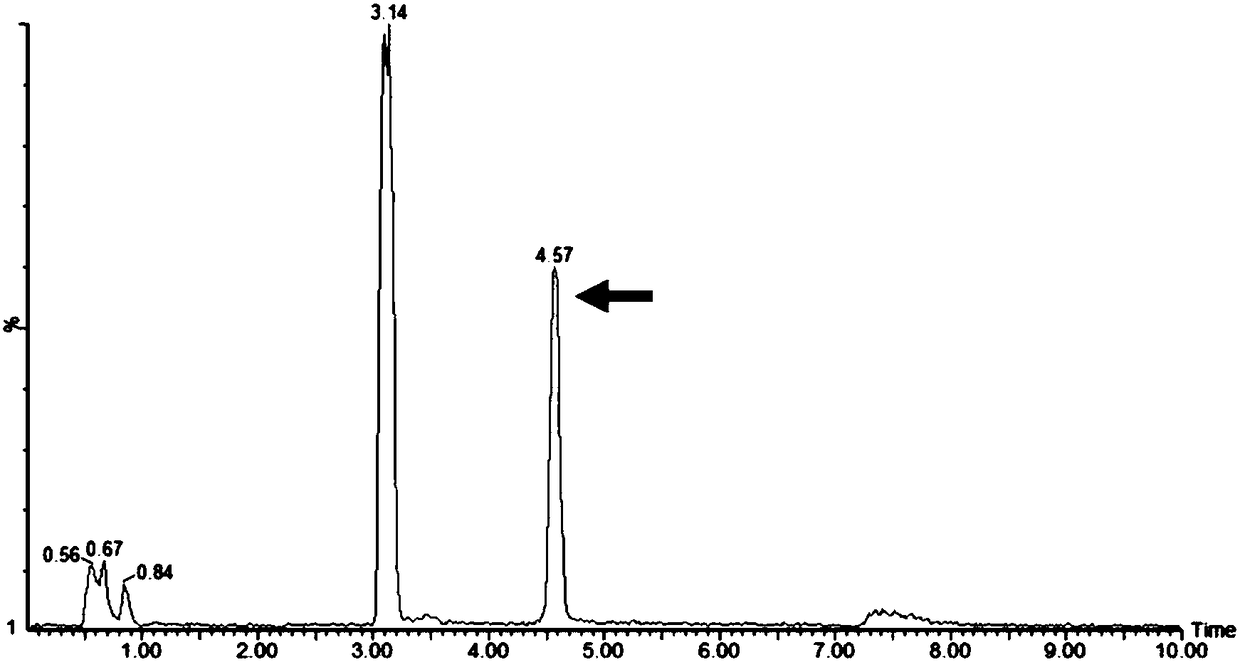
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose and construction method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is integrated with lactose permease genes in a recombinant manner on bacillus subtilis 168 genome and converts plasmids which contain beta-1,3-N-glucoaminotransferase genes and beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase gene in bacillus subtilis 168. Uridine diphosphate galactose and acetylglucosamine uridine diphosphate in a metabolic pathway of the bacillus subtilis are used as precusor substances, lactose only needs to be added exogenously and is transferred into cells under theeffect of lactamase to synthesize the lactyl-N-neotetraose which is secreted to ectoenzyme. The accumulation amount of the lactyl-N-neotetraose synthesized by the recombinant bacillus subtilis reaches 1071 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for production of the lactyl-N-neotetraose through further metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtilis.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
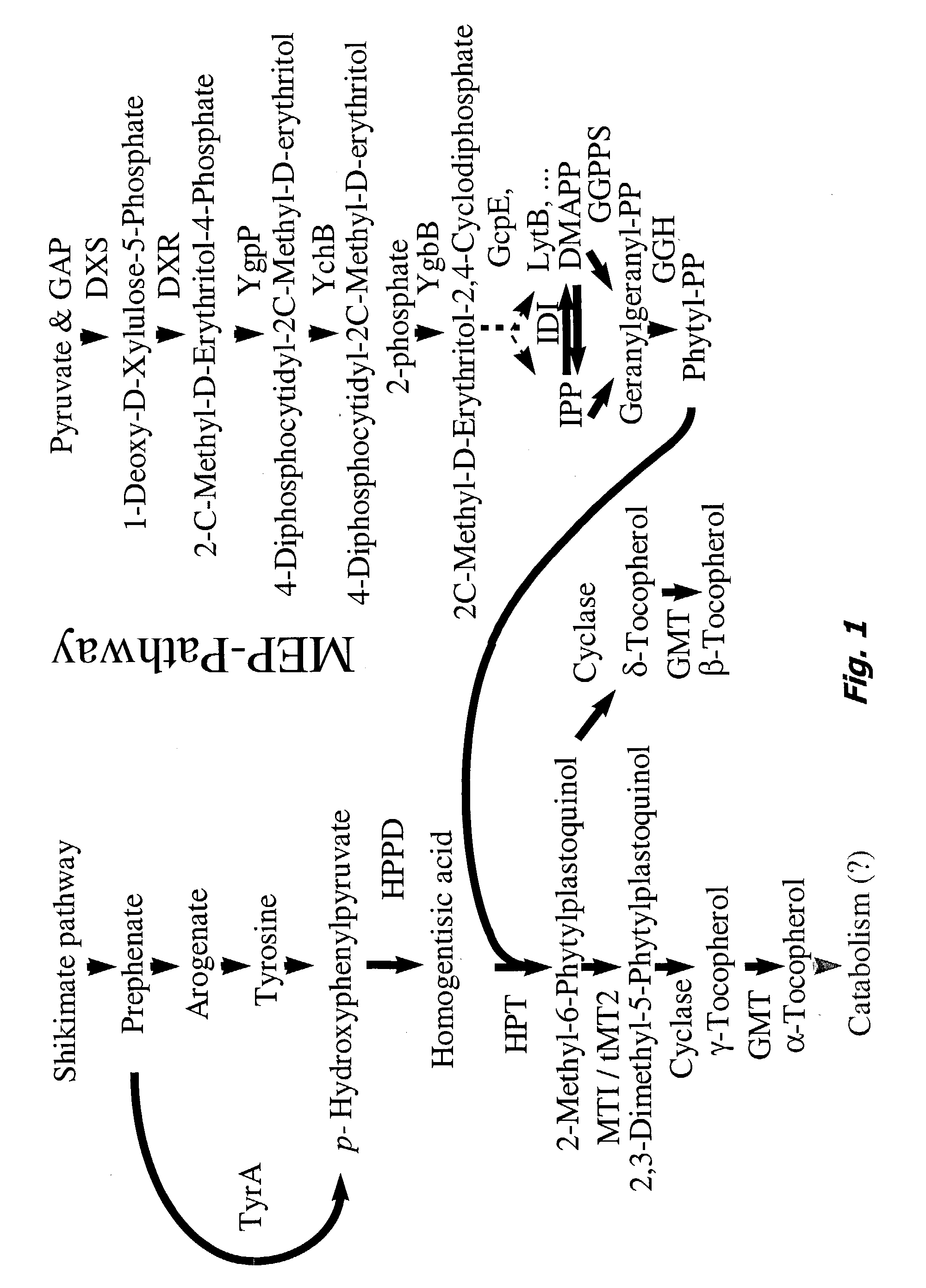
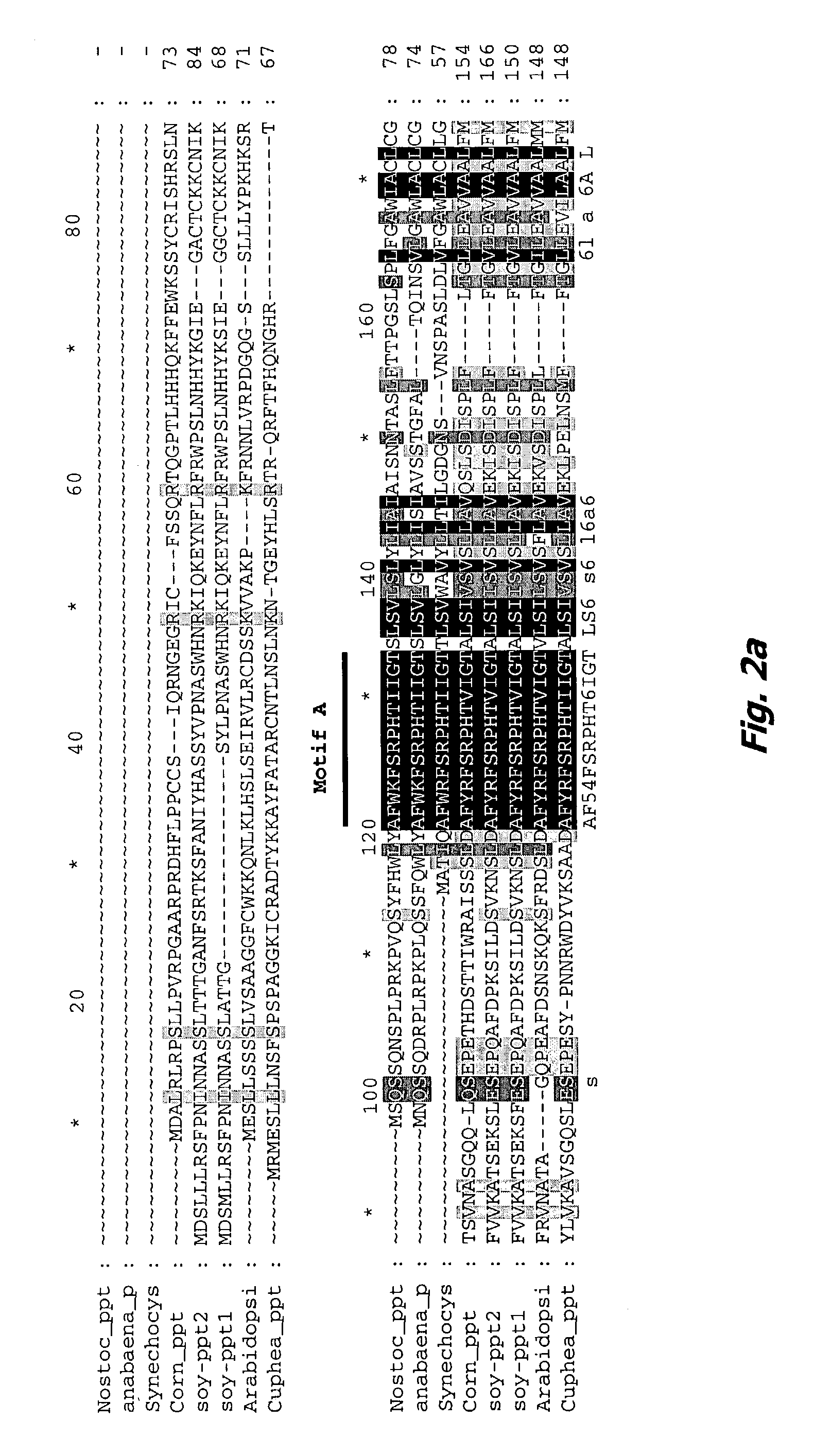
Homogentisate prenyl transferase gene (HPT2) from arabidopsis and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and biochemistry. More specifically, the present invention relates to genes and polypeptides associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway, namely those encoding homogentisate prenyl transferase activity, and uses thereof. In particular, the sequence of the HPT2 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is disclosed for expression in any plant species to increase the levels of tocopherol.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
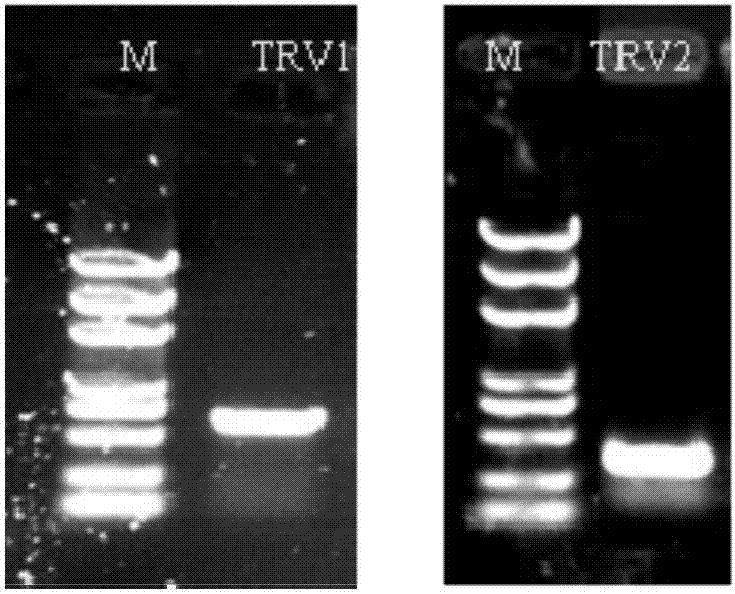
VIGS silence system for identifying peony UDPglucose Flavonoid Glucosyl-Transferase gene
ActiveCN107245497AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a VIGS silence system for identifying a peony UDPglucose Flavonoid Glucosyl-Transferase gene. The VIGS silence system for identifying a peony UDPglucose Flavonoid Glucosyl-Transferase gene comprises a recombinant vector which is obtained by adding desired genes to a VIGS silence vector. The desired genes are nucleotide sequences shown as a first sequence in a sequence table and / and nucleotide sequences shown as a third sequence in the sequence table. The UDPglucose Flavonoid Glucosyl-Transferase gene PsUF3GT and a PsUF5GT conserved segment are cloned by homology-based cloning technologies as target genes to construct TRV2 vector, so that the VIGS silence system is built successfully, and amount of gene expression of the UDPglucose Flavonoid Glucosyl-Transferase gene PsUF3GT and the PsUF5GT conserved segment and total anthocyanin content are reduced. The system has great significance for peony genes function study and lays foundation for analyzing an molecular mechanism formed by peony splash.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
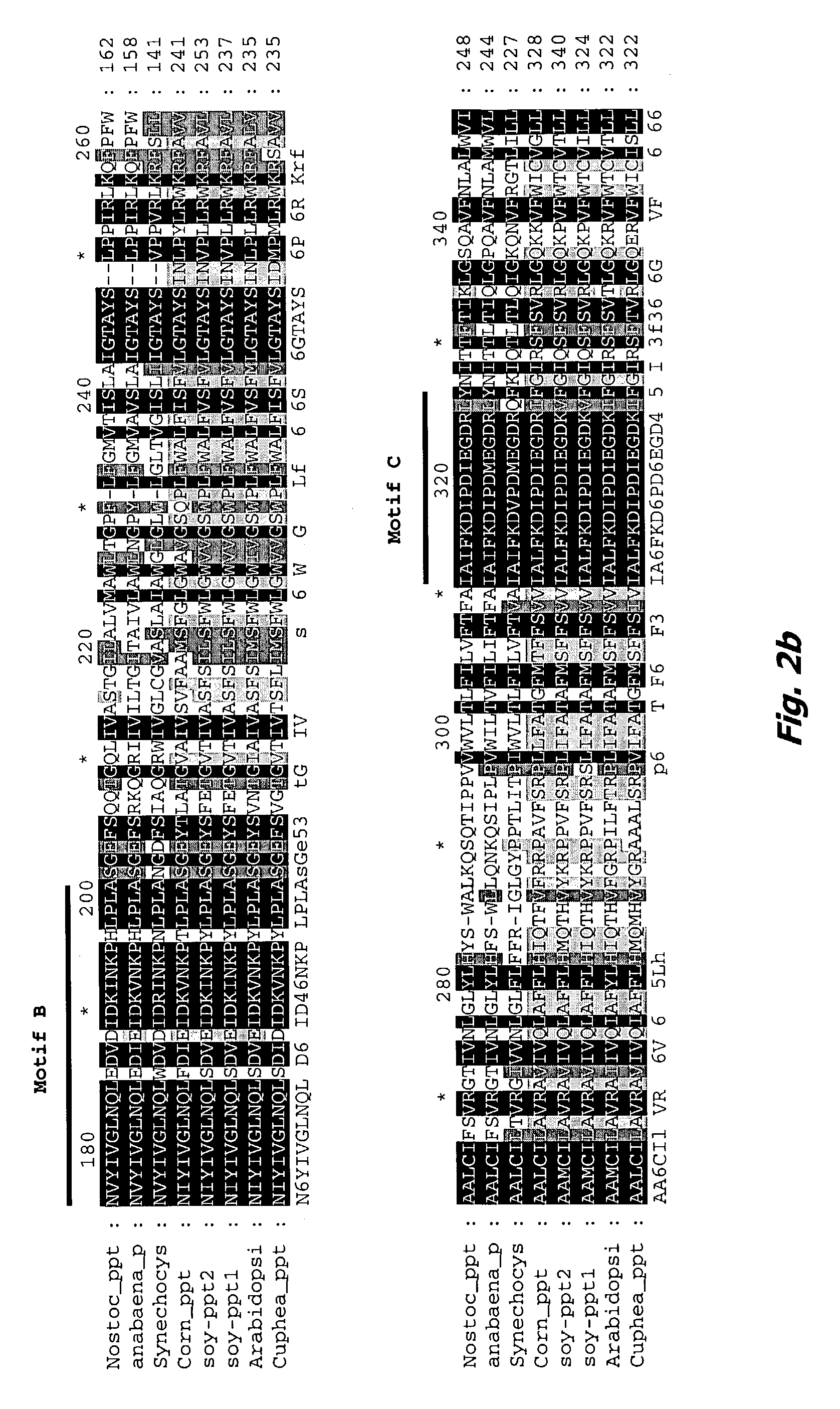
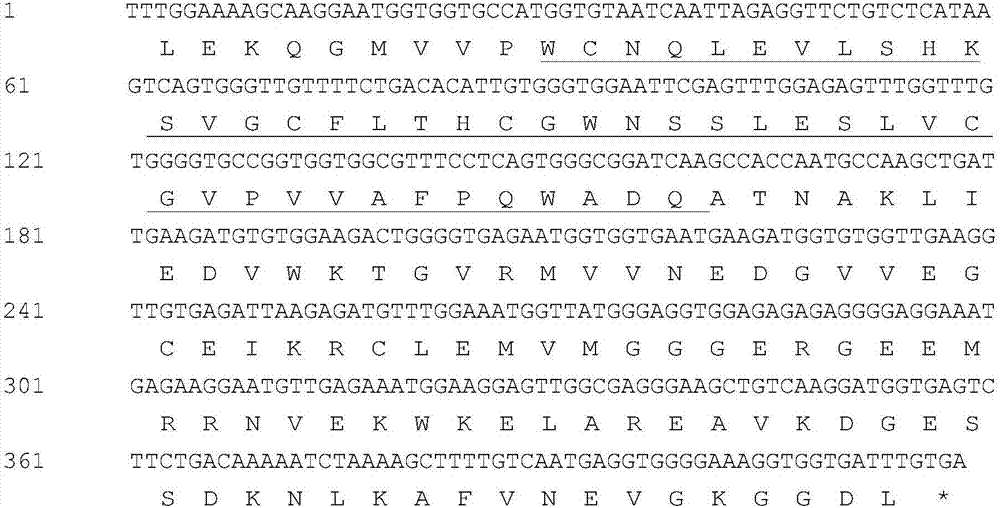
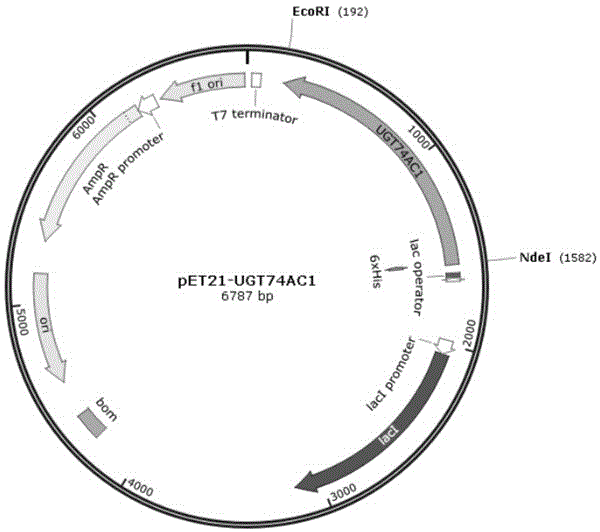
Mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene UGT74AC1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) and application of glycosyltransferase with a gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) code in synthetic mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) has a nucleotide coding sequence shown in SEQIDNO.1 and a peptide sequence shown in SEQIDNO.2. By utilization of an expression of the mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) in escherichia coli, the recombinant glycosyltransferase (i)UGT74AC1( / i) can catalyze mogrol and UDP-glucose to react, thereby generating the mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) disclosed by the invention can be applied to the artificial synthesis of the mogrosideIE. Meanwhile, the gene has an important application value in the aspect of improving momordica grosvenori by the utilization of a transgenic technology to improve the content of the mogroside.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
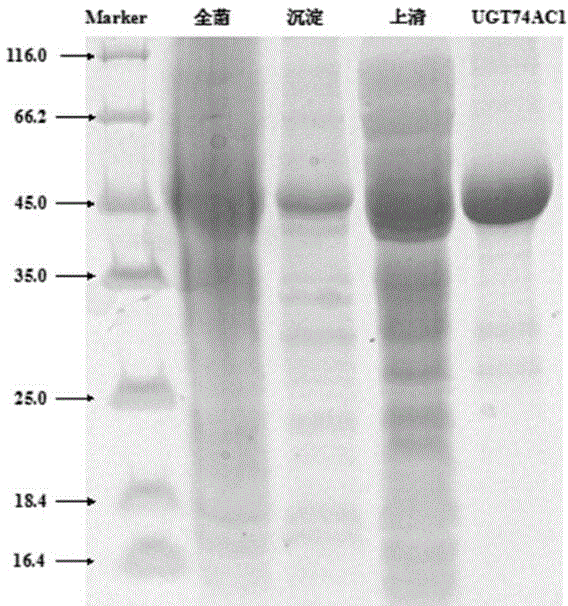
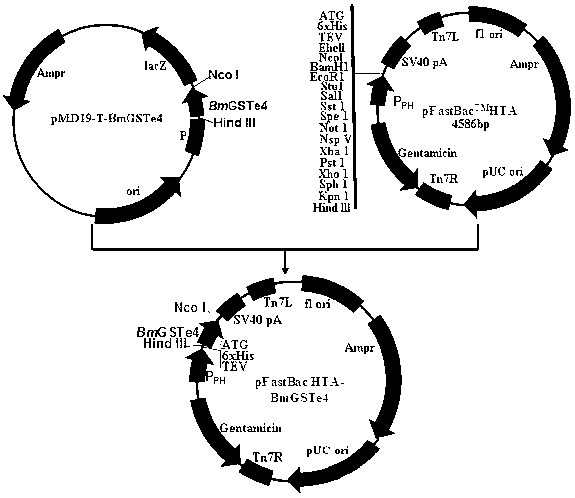
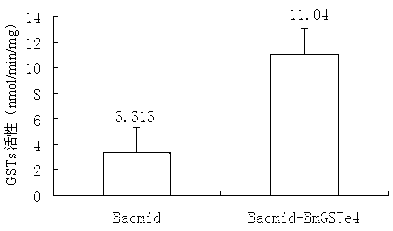
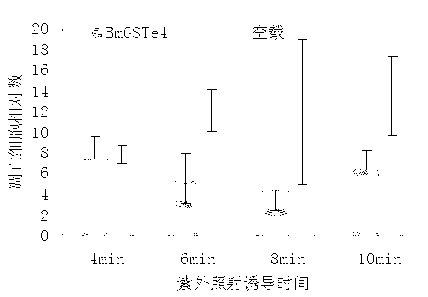
Bombyx mori glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe4 gene
InactiveCN103160524AHas GSTs activityInhibit apoptosisTransferasesMicroorganism based processesOrder LepidopteraNucleotide
The invention discloses a bombyx mori glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe4 gene with a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQIDNo.1, and the expression product thereof has glutathione-S-transferase (GSTs) activity, because GSTs plays an important role in the formation of pesticide resistance and oxidation resistance of insects, and bombyx mori is a lepidopterous insect-model organism, a biological control pesticide which can specifically kill lepidoptera pests and is harmless to other beneficial insects is expected to be designed through taking BmGSTe4 genes as targets. In addition, in the invention, a situation that BmGSTe4 genes have a function of inhibiting cell apoptosis is found, therefore, the BmGSTe4 genes can be used as potential targets of anti-cancer drug screening.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
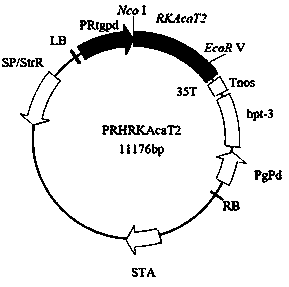
Acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof
ActiveCN109666683AIncreased transcript levelsIncrease contentAcyltransferasesGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase gene RKAcaT2 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the amino acid sequence encoded by thegene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the gene is a key enzyme gene synthesized by carotenoid in Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 and has the functions of the acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase, and the carotenoid produced by the Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 can be controlled; microorganisms are transformed through the genetic engineering means so as to increase the yield of carotenoid inthe microorganisms, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of the carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Immunochemically modified and sterilized xenografts and allografts
InactiveUS20070010897A1Improve integrityEasy to inactivateNew breed animal cellsTissue regenerationHeterograftsAlcohol
The invention provides an article of manufacture comprising a substantially non-immunogenic xenograft for implantation into humans. The xenograft is a body part dissected from a transgenic 1,3-α-galactosyltransferase gene-deficient animal, wherein the cells of the body part are dead. The invention also provides methods for preparing a xenograft by removing a body part from a transgenic animal, which is 1,3-α-galactosyltransferase gene-deficient, to provide a xenograft; optionally washing the xenograft in saline and alcohol; subjecting the xenograft to a cellular disruption treatment; optionally treating the xenograft with crosslinking agents, and optionally treating the xenograft with a proteoglycan-depleting factor. The invention further provides a method for sterilizing xenograft material, having the steps of obtaining substantially non-immunogenic xenograft material; treating the xenograft material with at least one crosslinking agent; and subjecting the crosslinked xenograft material to a radiation treatment.
Owner:APERION BIOLOGICS
Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105755019AGood removal effectEfficient catalytic conversionTransferasesMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The amino acid sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses an expression vector; a method comprises the steps of using the expression vector for transforming the host cell, culturing a transformant, and acquiring nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene from culture, so as to obtain the recombinant nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene. The invention discloses application of the recombinant nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene to in vitro conversion of nicotinamide mononucleoside NMN into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD<+>. The invention also discloses a synthesis method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD<+>. The method uses nicotinamide mononucleoside NMN as raw material to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD<+> under the action of the recombinant nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase gene.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Materials and methods for management of hyperacute rejection in human xenotransplantation
InactiveUS7201899B2Eliminating and reducing hyperacute rejectionReduce and eliminate hyperacute rejection responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPlant Germ CellsMammal
Human pre-formed xenoantibodies play an important role in the hyperacute rejection response in human xenotransplantation. Disclosed are materials and methods for removing or neutralizing such antibodies. Also disclosed are materials and methods for reducing or eliminating the epitopes in the donor organs that are recognized by such antibodies. Such epitopes are formed as the result of activity by the enzyme α-1,3 galactosyltransferase. The porcine gene encoding α-1,3 galactosyltransferase is disclosed, as are materials and methods for inactivating (“knocking out”) the α-1,3 galactosyltransferase gene in mammalian cells and embryos. Included are nucleic acid constructs useful for inactivating the α-1,3 galactosyltransferase gene in a target cell. Also disclosed is a novel leukemia inhibitory factor (T-LIF) that is useful for maintenance of embryonic stem cells and primordial germ cells in culture.
Owner:BRESAGEN +1
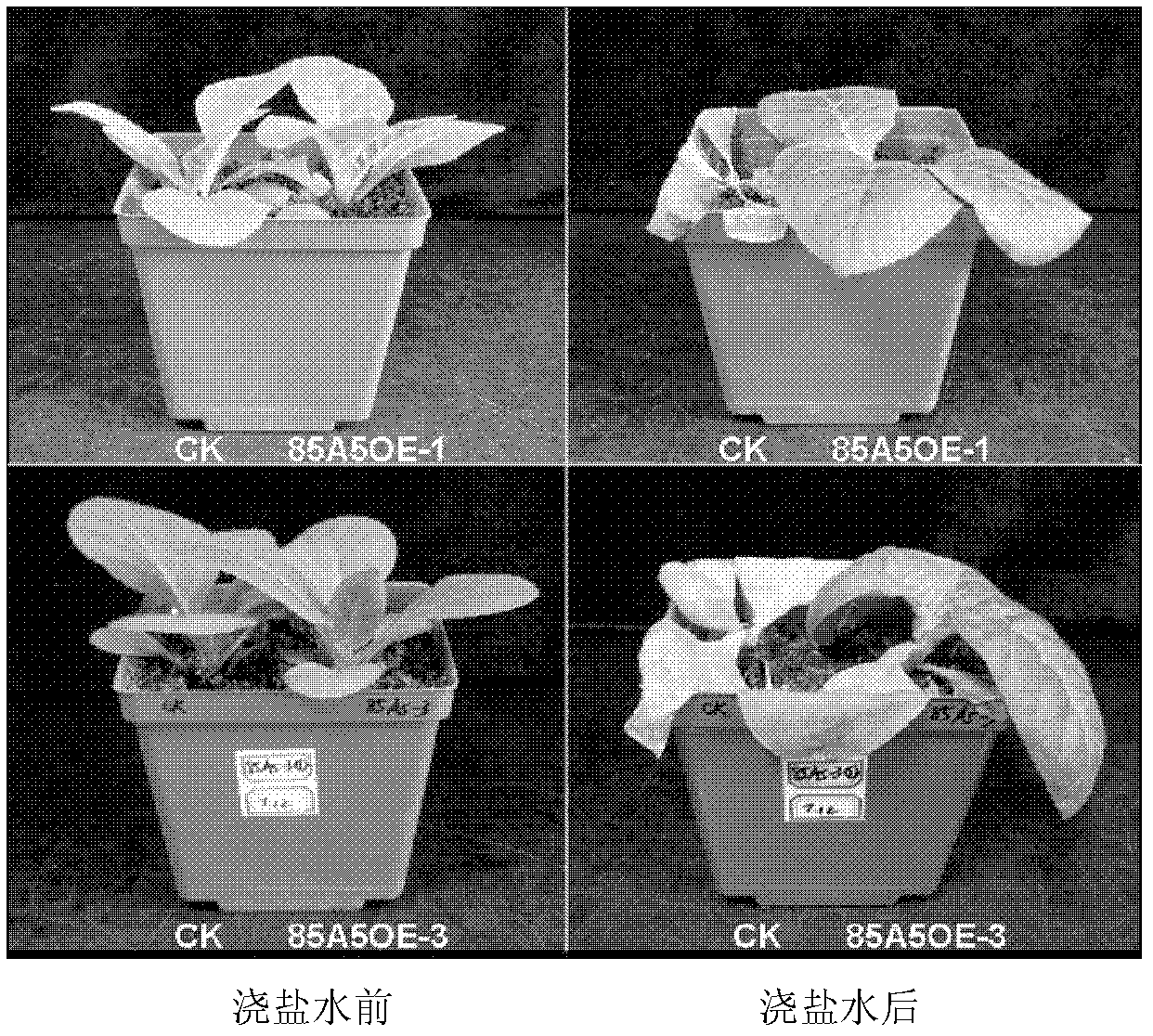
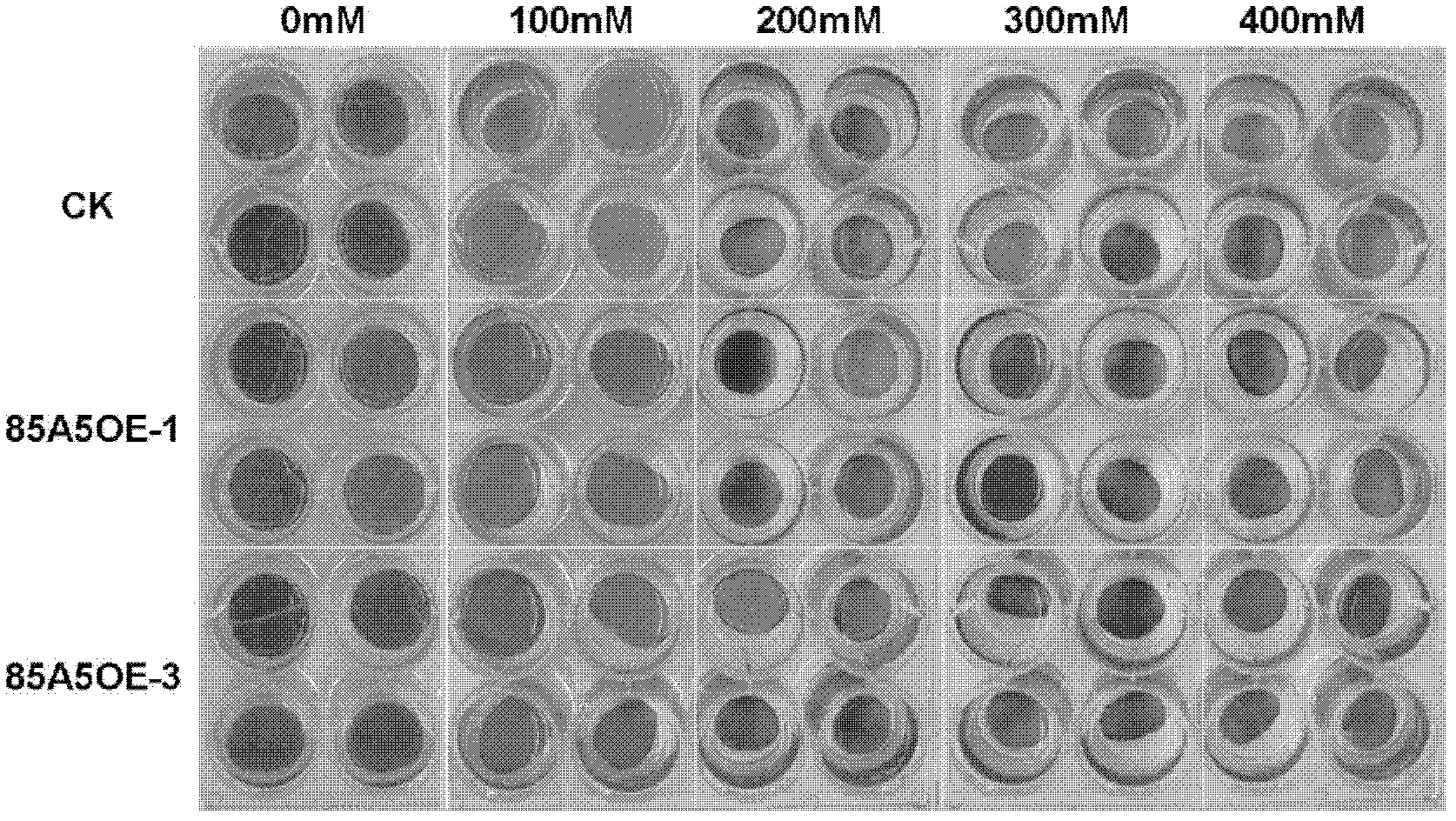
Application of glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 of Arabidopsis thaliana to improvement of salt tolerance of plants
InactiveCN102586293AImprove salt toleranceIncrease varietyFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 of Arabidopsis thaliana to the improvement of salt tolerance of plants. A nucleotide sequence of the glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 is shown as SEQ ID No.1; and the glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 is cloned from the Arabidopsis thaliana by a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology. The gene UGT85A5 is utilized to construct a plant overexpression vector and perform transgenic operation of the plants to obtain transgenic plants. The detection shows that the salt tolerance of the transgenic plants is remarkably improved, so that a novel salt-tolerant plant can be created after the invention is implemented; and the gene can be used for subsequent crop variety improvement, and has a great significance for the agricultural production in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
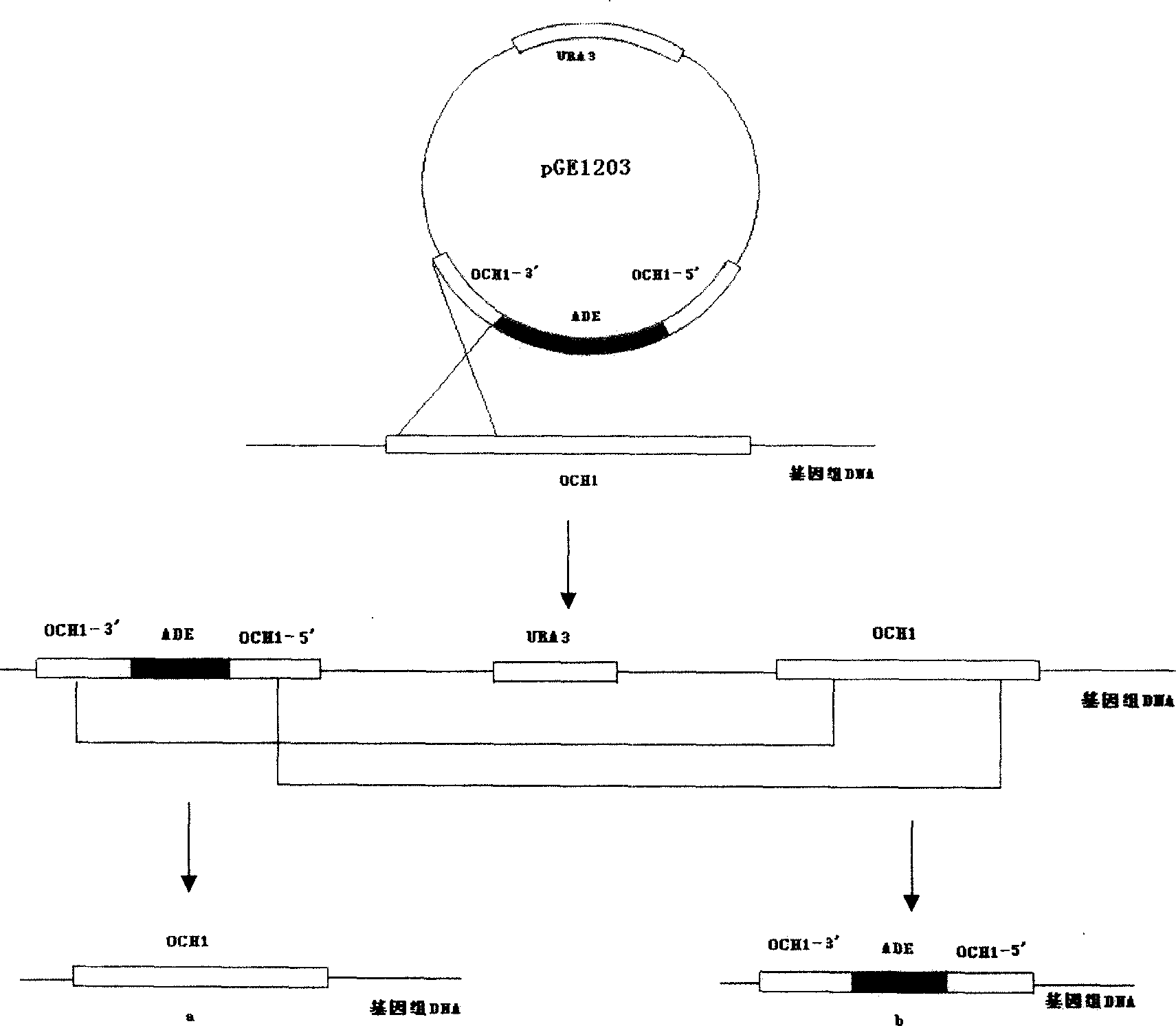
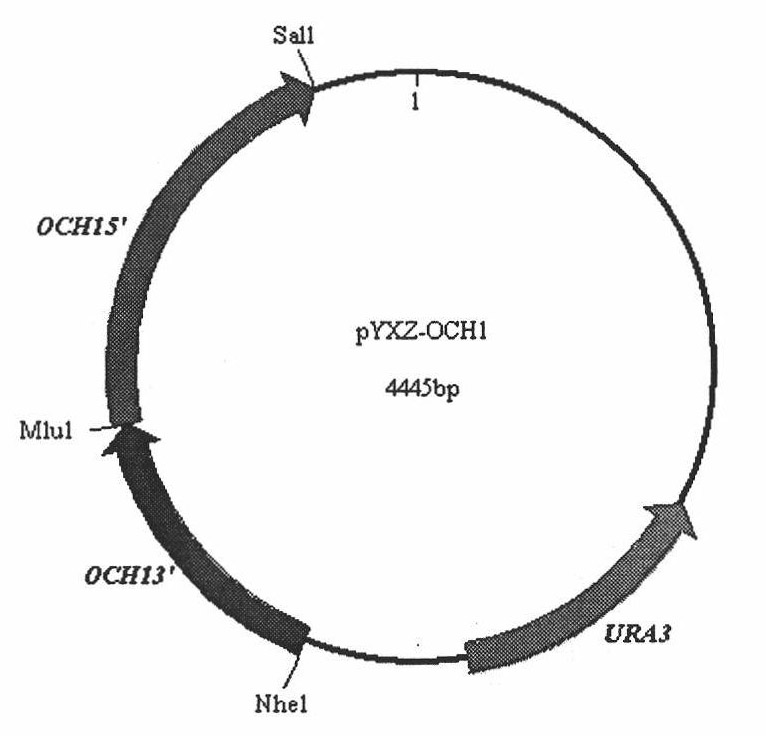
Preparation and application of OCH1 genetic flaw type P. pastoris X-33 bacterial strain
InactiveCN102120967AReduce in quantitySmall molecular weightFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastMicrobiology
The invention discloses preparation and application of an alpha-1,6 mannose transferase gene (och1) flaw type P. pastoris X-33 bacterial strain, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The engineering bacterial strain P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) is characterized in that a target gene knockout method by double-exchange homologous recombination is adopted, and a URA3 gene serves as a selective marker to knock out the alpha-1,6 mannose transferase gene (och1) of the P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) to obtain the P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) bacterial strain with OCH1 gene knockout. The bacterial strain provides a P. pastoris expression system which modifies protein by virtue of low N-glycosylation modification and provides a favourable basis for further glycosylation modification. The bacterial strain has the advantage of great potential application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gama-tocopherol methyl transferase gene, its coding vector and uses
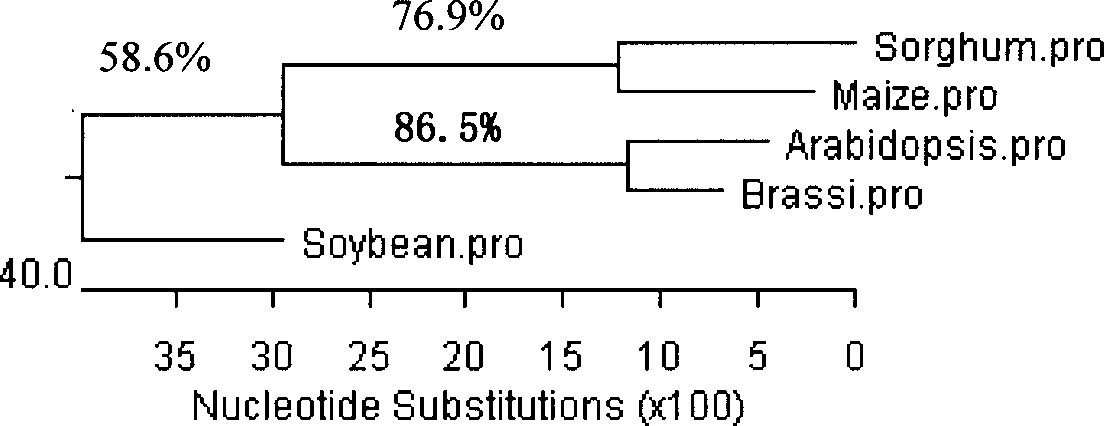
This invention discloses a gamma- tocopherol methyl transfer enzyme that from corn and soybean, their code gene and their use in the plant gene project field. This invention uses RACE and RT-PCR technique, it obtains the span cDNA code sequence of gamma- tocopherol methyl transfer enzyme showed by the SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 3 from the corn of high oil 115 and soybean (9525) which all belongs to the oil plants, and it obtains the gamma- tocopherol methyl transfer enzyme with biological activity through prokaryotes expression, and it also compares with the difference of gamma-TMT enzyme activity form different sources. This invention transforms the pattern plant from the related code sequence, through HPLC analysis, the content of the alpha- tocopherol of the transfer gene plant leafage is improved by 2-5 times comparing to that of the wild leafage. This invention is to cut a new way for culturing the new plant of oil plants with high vitamin E content.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
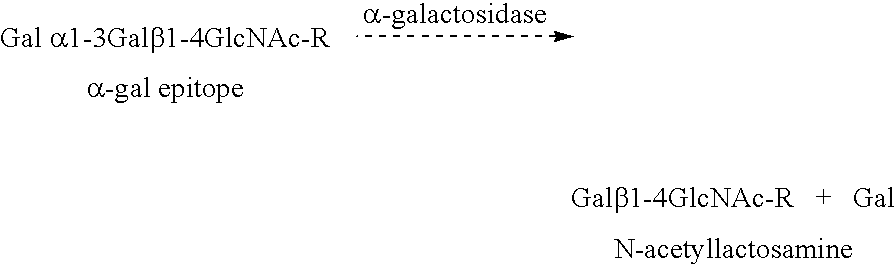
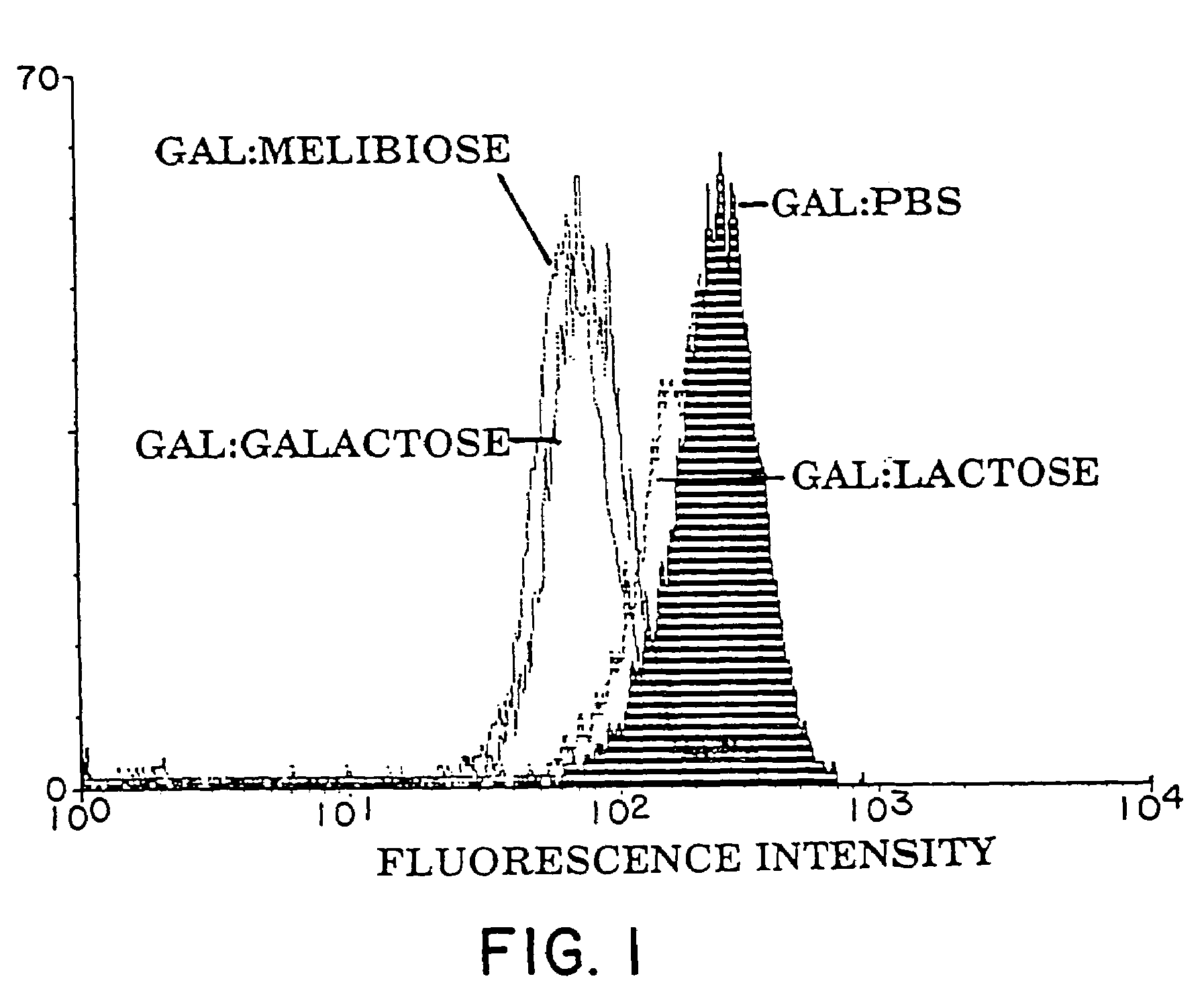
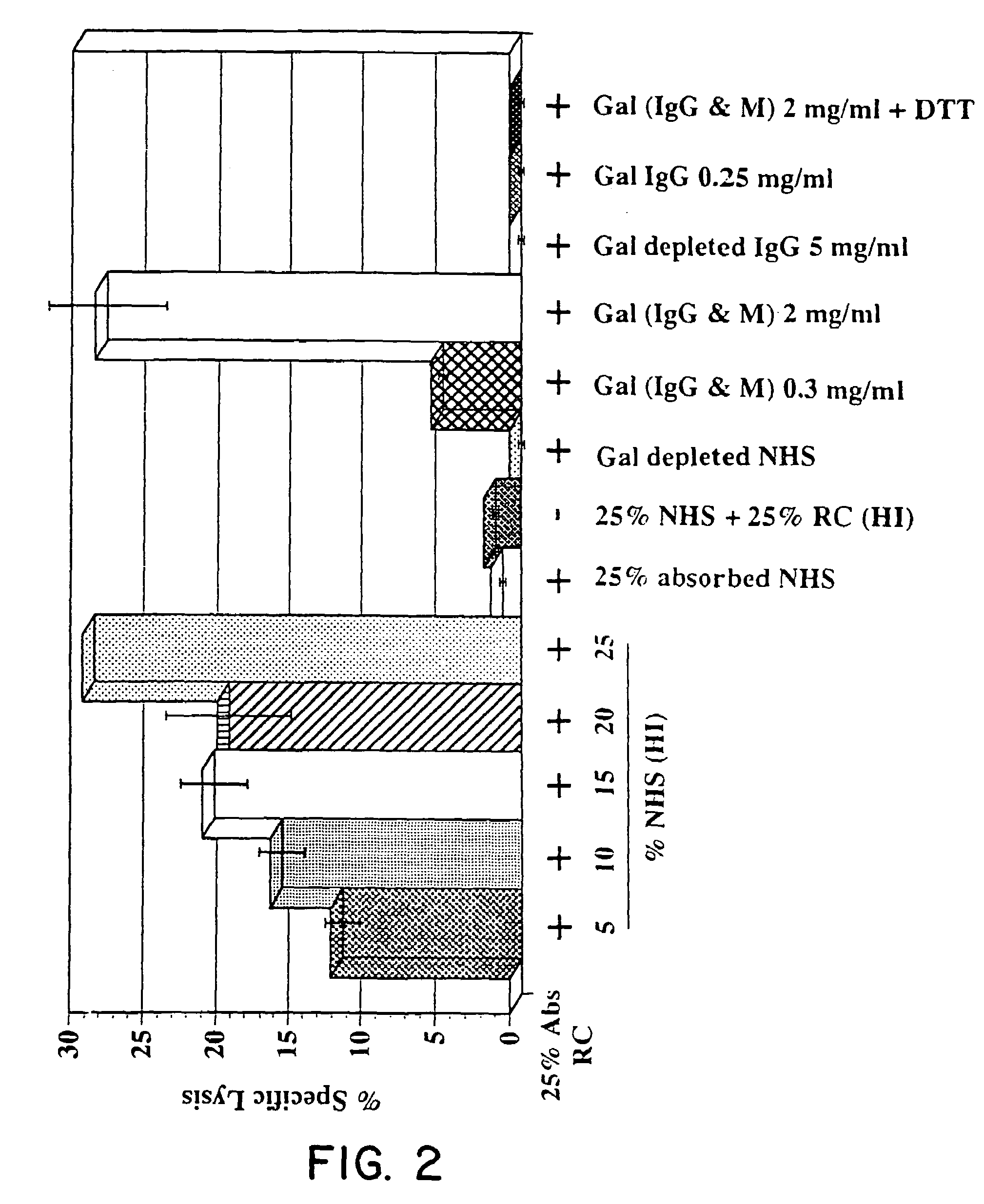
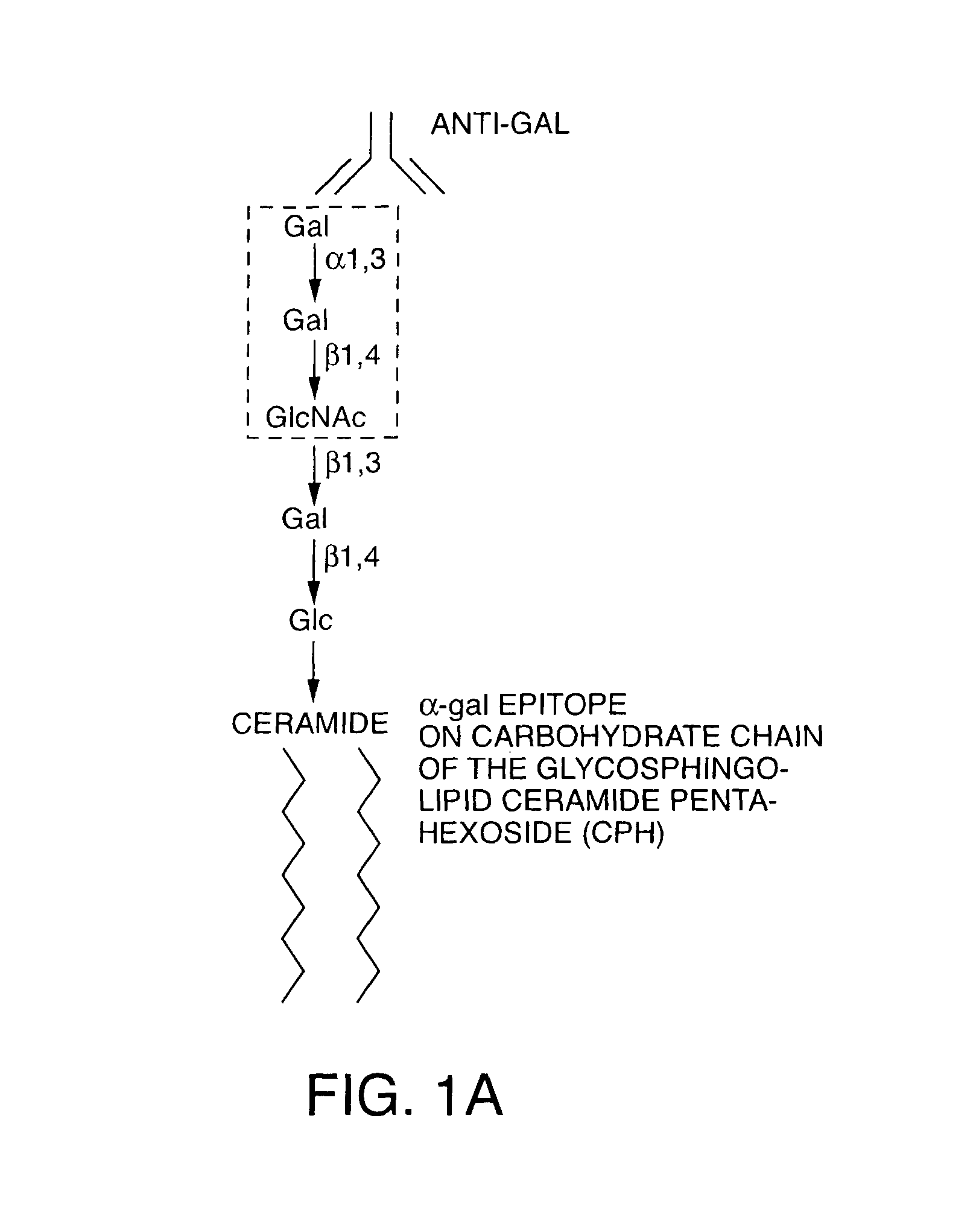
Tumor lesion regression and conversion in situ into autologous tumor vaccines by compositions that result in anti-Gal antibody binding
The present invention discloses that an intratumoral injection of: i) glycolipids with α-gal epitope; ii) gene vectors comprising an α1,3galactosyltransferase gene; or iii) a mixture of α1,3galactosyltransferase, neuraminidase, and uridine diphosphate galactose results in tumor regression and / or destruction. Binding of the natural anti-Gal antibody to de novo expressed tumoral α-gal epitopes induces inflammation resulting in an anti-Gal antibody mediated opsonization of tumor cells and their uptake by antigen presenting cells. These antigen presenting cells migrate to draining lymph nodes and activate tumor specific T cells thereby converting the treated tumor lesions into in situ autologous tumor vaccines. This therapy can be applied to patients with multiple lesions and in neo-adjuvant therapy to patients before tumor resection. In addition to the regression and / or destruction of the treated tumor, such a vaccine will help in the immune mediated destruction of micrometastases that are not detectable during the removal of the treated tumor.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL SCHOOL
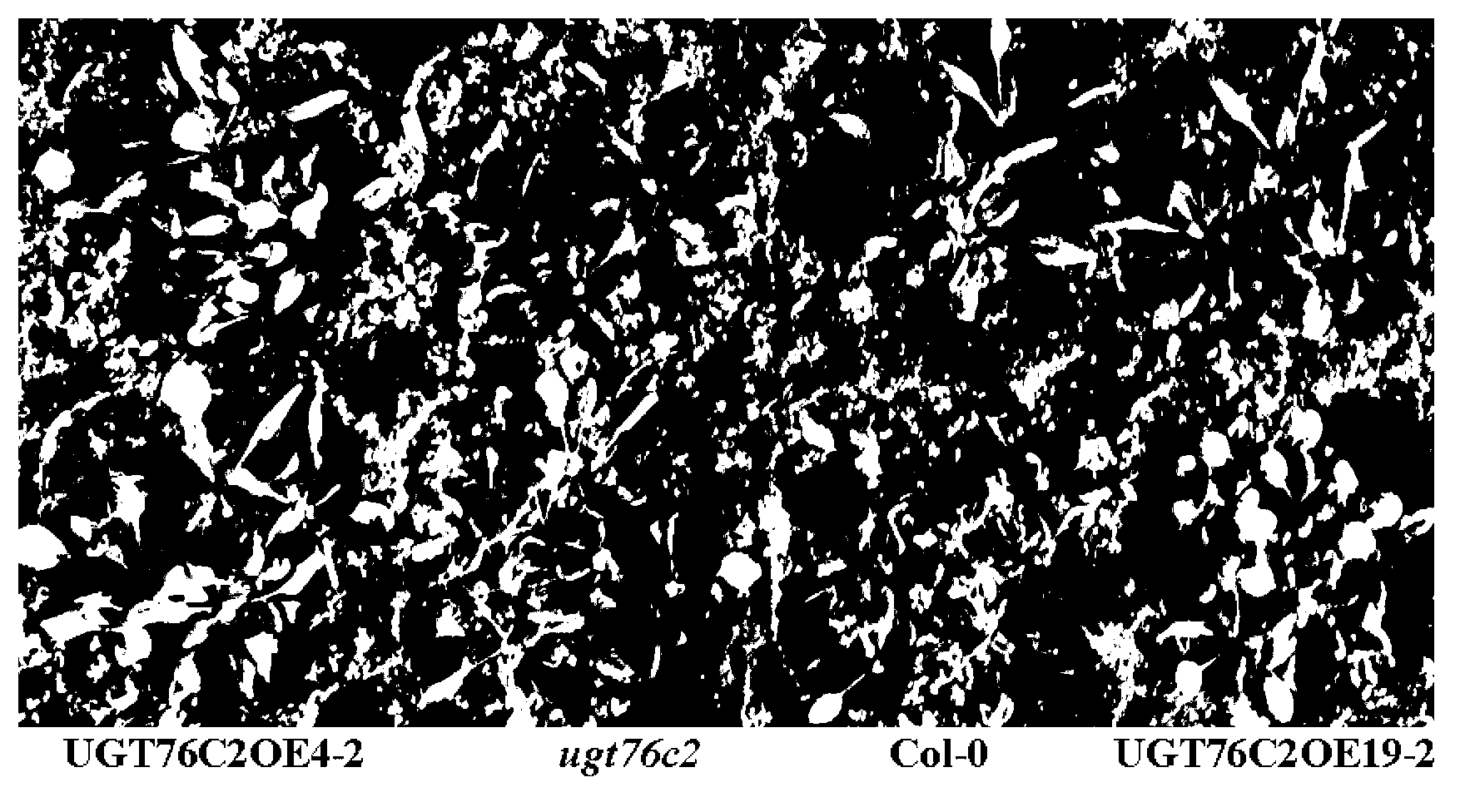
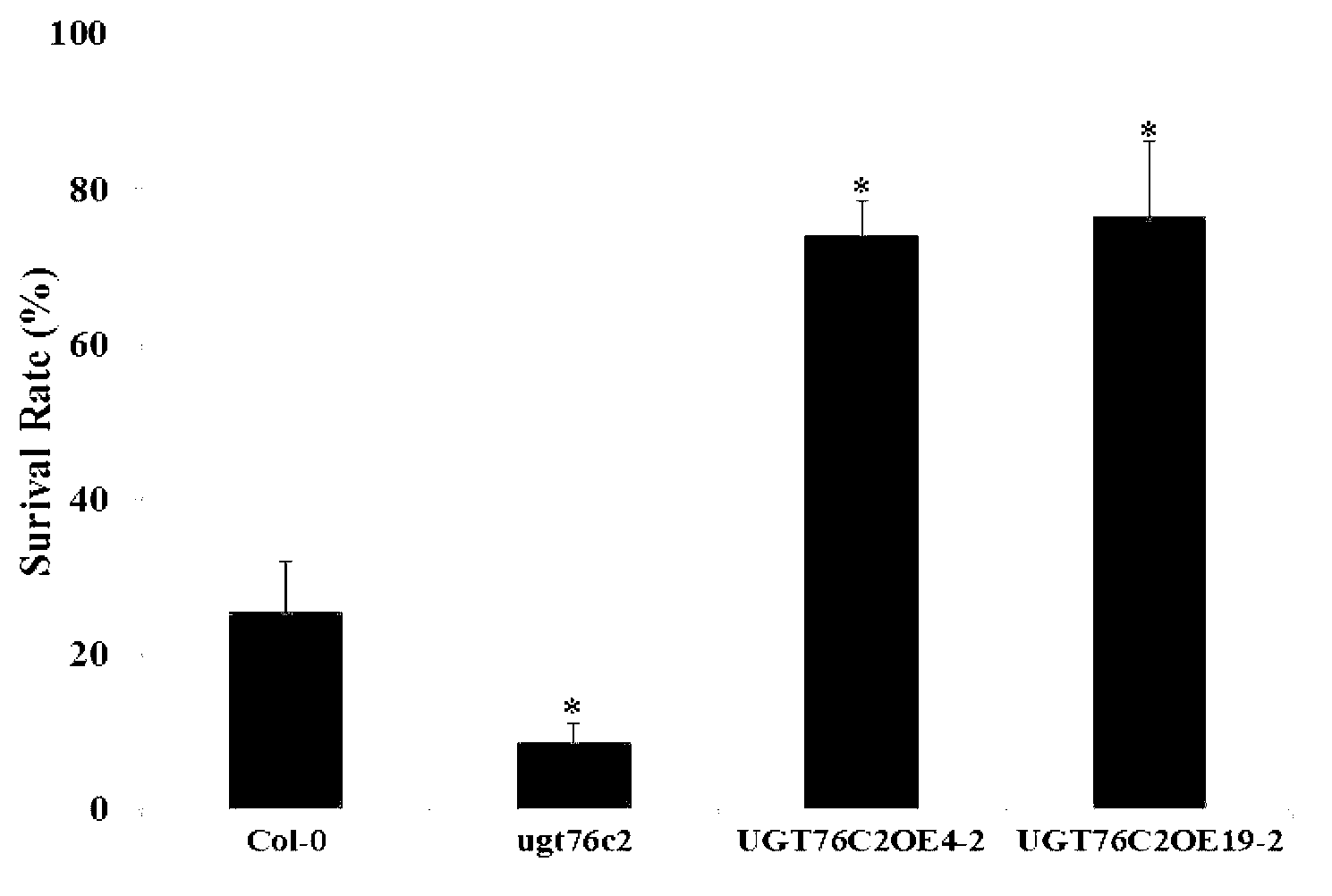
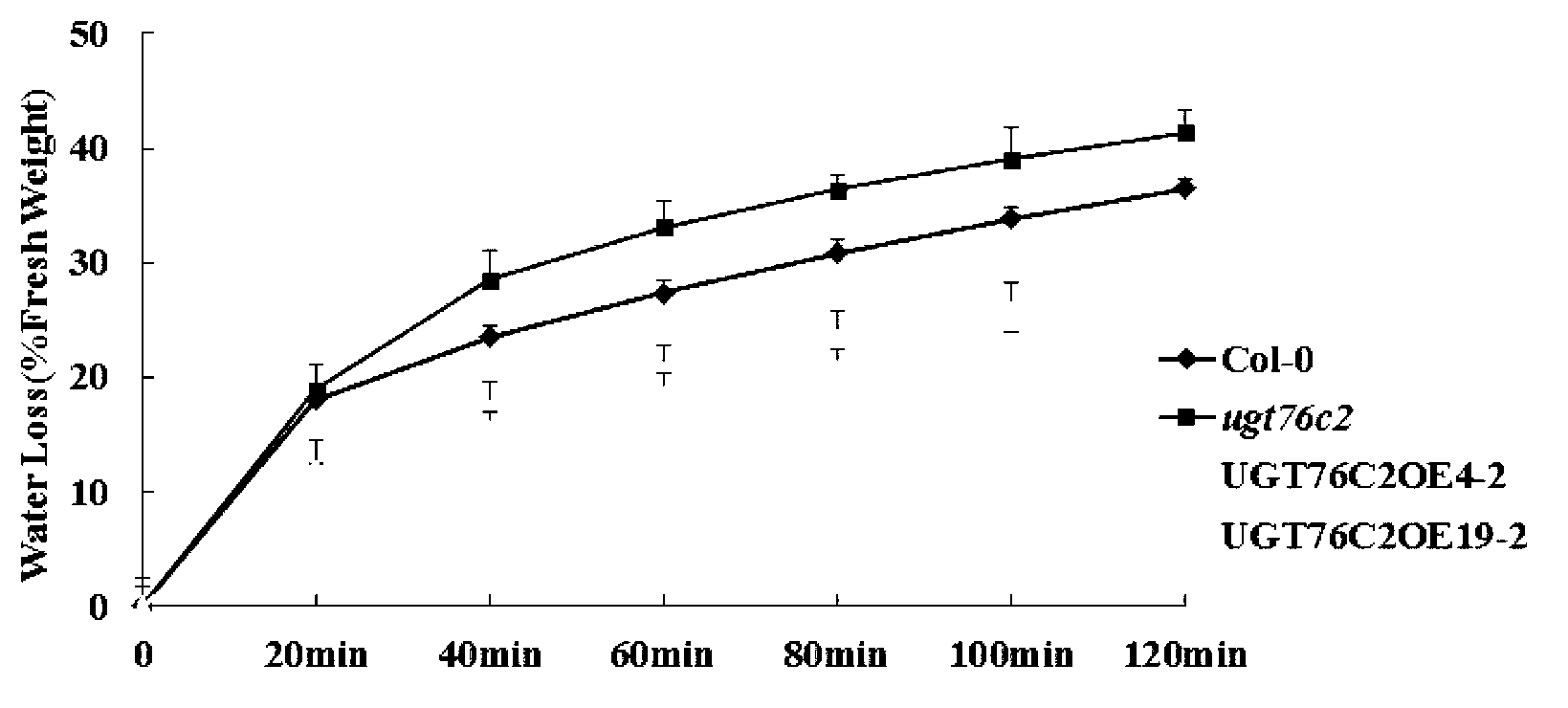
Application of arabidopsis glycosyl transferase gene UGT 76C2 in improving plant drought resistance
InactiveCN102796762AImprove drought toleranceIncrease varietyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideArabidopsis
The invention discloses an application of an arabidopsis glycosyl transferase gene UGT 76C2 in improving plant drought resistance, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the glycosyl transferase gene UGT 76C2 is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and is cloned from arabidopsis through a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology. The application utilizes the gene UGT 76C2 to structure a plant over expression carrier, the plant transgenic operation is carried out, and a transgenic plant is obtained. Tests prove that drought resistance of the transgenic plant is obviously improved, and indicate that a novel drought-resistant plant can be created after the glycosyl transferase gene UGT 76C2 is implemented; and the glycosyl transferase gene UGT 76C2 can be used for subsequent crop variety improvement, and has an important meaning to agricultural production of China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for producing salidroside and analogue thereof, and construction method and use
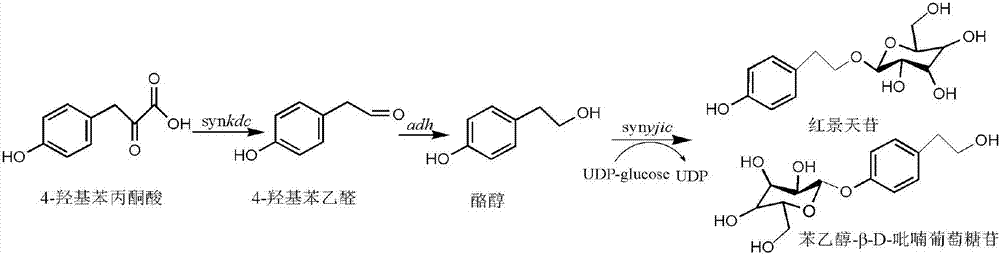
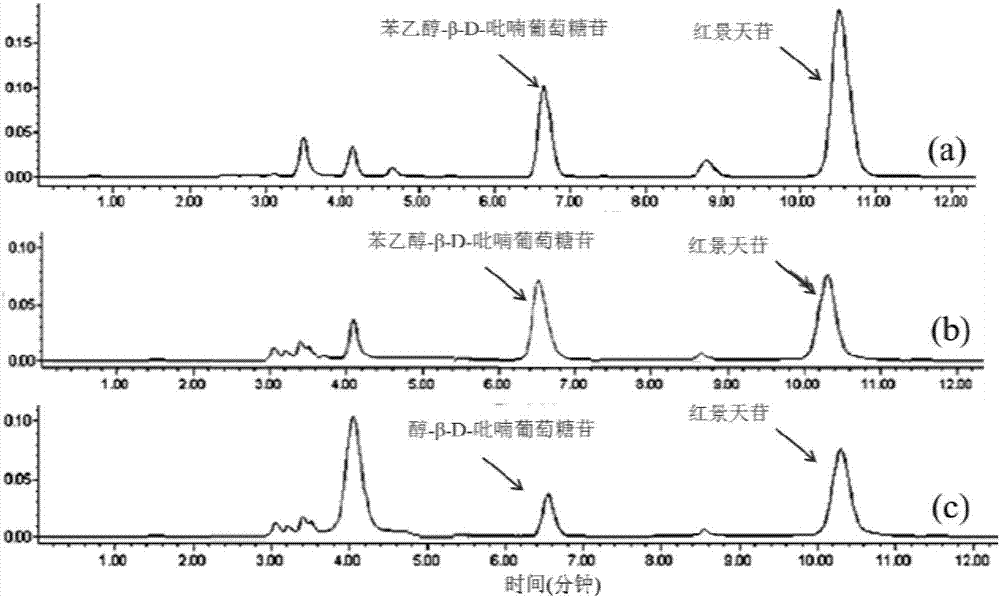
InactiveCN107460203AResolve source issuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalidrosideMicrobiology
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for producing salidroside and analogue thereof, and a construction method and use. The construction method comprises the steps of synthesizing keto-decarboxylase gene synkdc and glycosyl transferase gene synyjic, and connecting to a vector pRSFDuet-1 to construct a recombinant vector pSynkdc1-yjic; enabling T7RNA polymerase gene to be free or integrated to SyBE-002447 base bacterial strain, and introducing pSynkdc1-yjic to obtain SyBE-218011 and SyBE-218013 bacterial stains; and directly integrating synkdc and synyjic to SyBE-002447 chromosome, and removing feaB and ushA in a knockout manner to obtain a SyBE-218015 bacterial strain. The bacterial strain disclosed in the invention can be used for producing salidroside and analogue thereof through fermentation, so that the problem existing in source of the salidroside and analogue thereof can be solved, and cost can be lowered.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
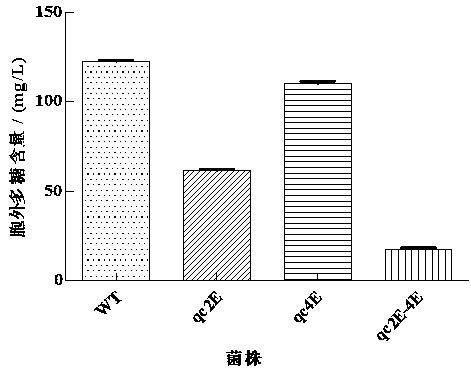
Application of guided glycosyltransferase gene
InactiveCN109735556ASafeImprove screening efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCompetent cellFood borne
The invention discloses application of a guided glycosyltransferase gene, namely application of the guided glycosyltransferase gene cps2E and cps4E in improving lactobacillus plantarum extracellular polysaccharide synthesis; the cps2E and cps4E genes and a temperature-sensitive plasmid pFED760 are recombined to construct a knockout vector, the knockout vector is guided into food-borne lactobacillus plantarum competent cells, and then by means of homologous recombination, cps2E and cps4E genes are constructed to knock out strains YM 4-3-deltacps2E, YM 4-3-deltacps4E and YM 4-3-deltacps2E-4E; the capacity of the strains producing extracellular polysaccharide is determined through a phenol-sulfuric acid method, it is found that the capacity of knocking out extracellular polysaccharide produced by the strains is lower than that of wild type strains, and the double knockout strain extracellular polysaccharide yield is very low, so that the cps2E and cps4E genes play a key role in the extracellular polysaccharide synthesis, and the application has great potential in extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis research and application fields.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for fermentative production of menaquinone-7 using escherichia coli
InactiveCN102168116ASuitable for productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
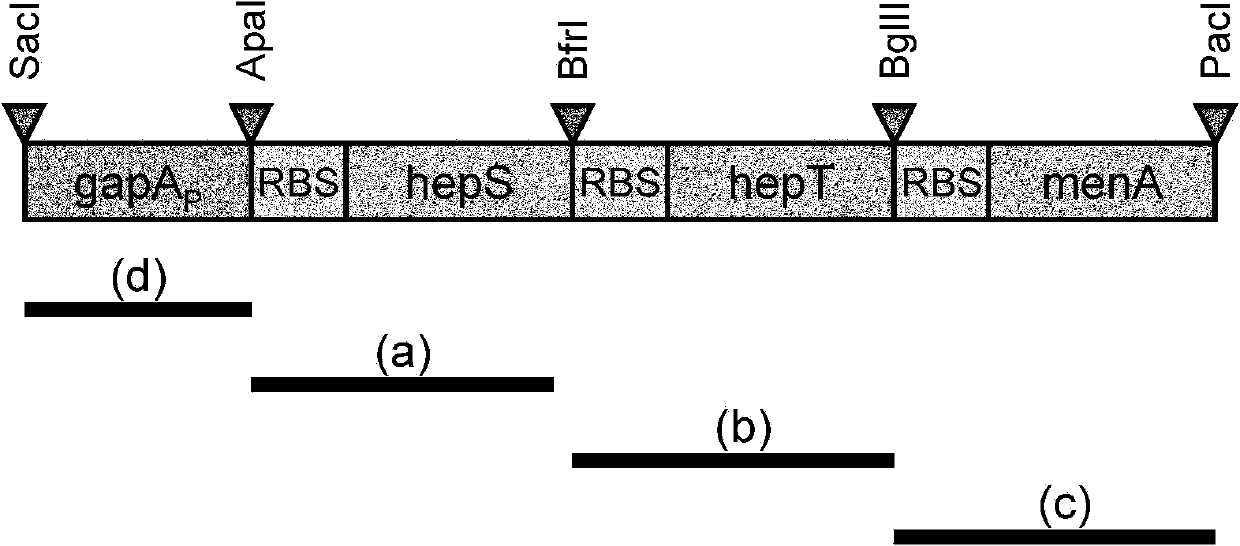
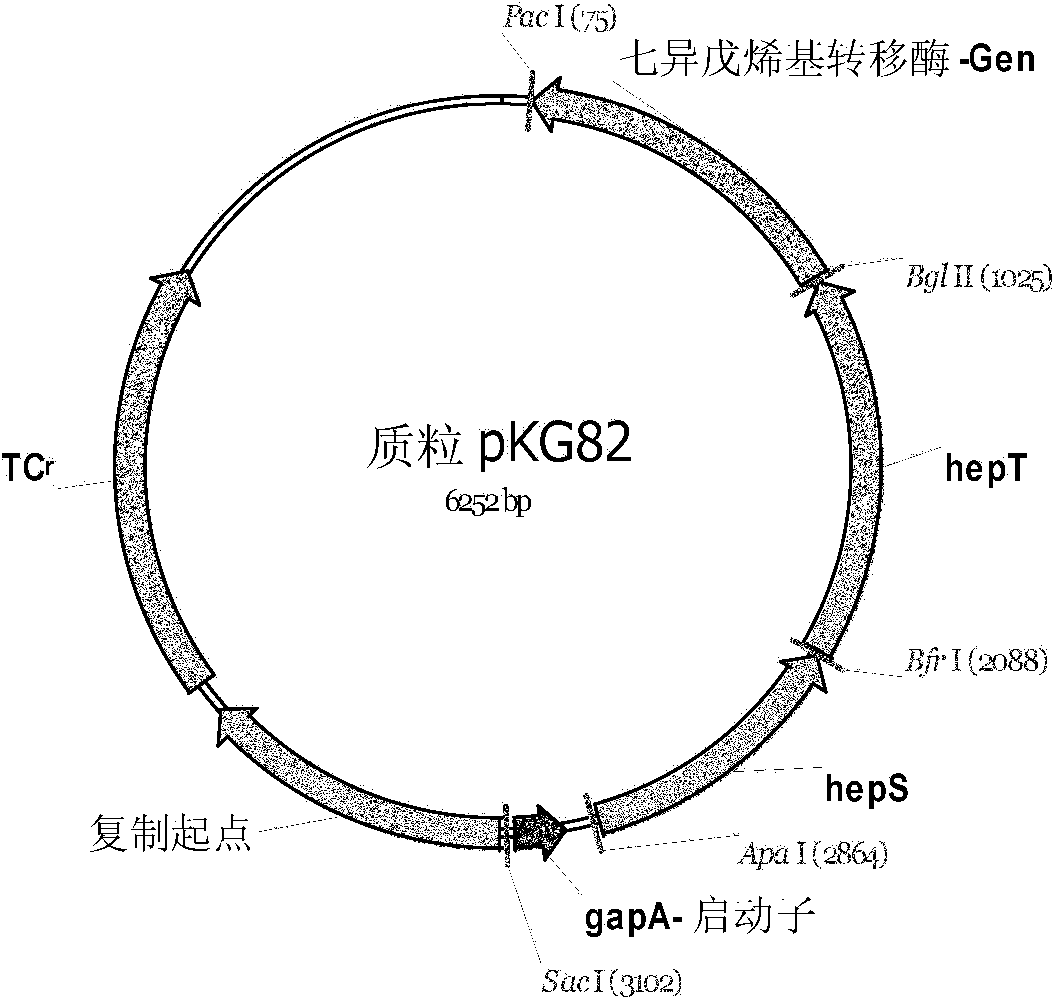
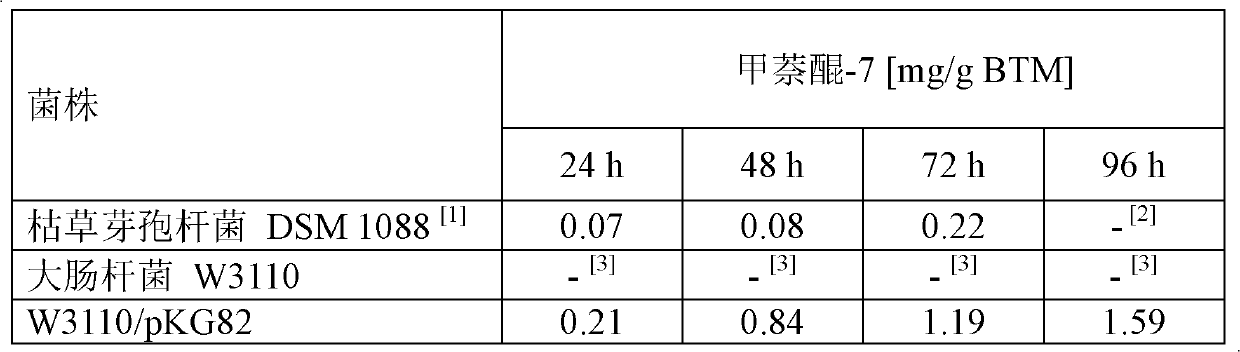
The invention relates to a method of producing menaquinone-7, characterized in that cells of an E. coli strain comprising the B. subtilis DSM 1088 hepS gene, the B. subtilis DSM 1088 hepT gene and the putative B. subtilis DSM 1088 heptaprenyl transferase gene are fermented in a fermentation medium, with menaquinone-7 being accumulated in the cells of the fermented E. coli strain.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
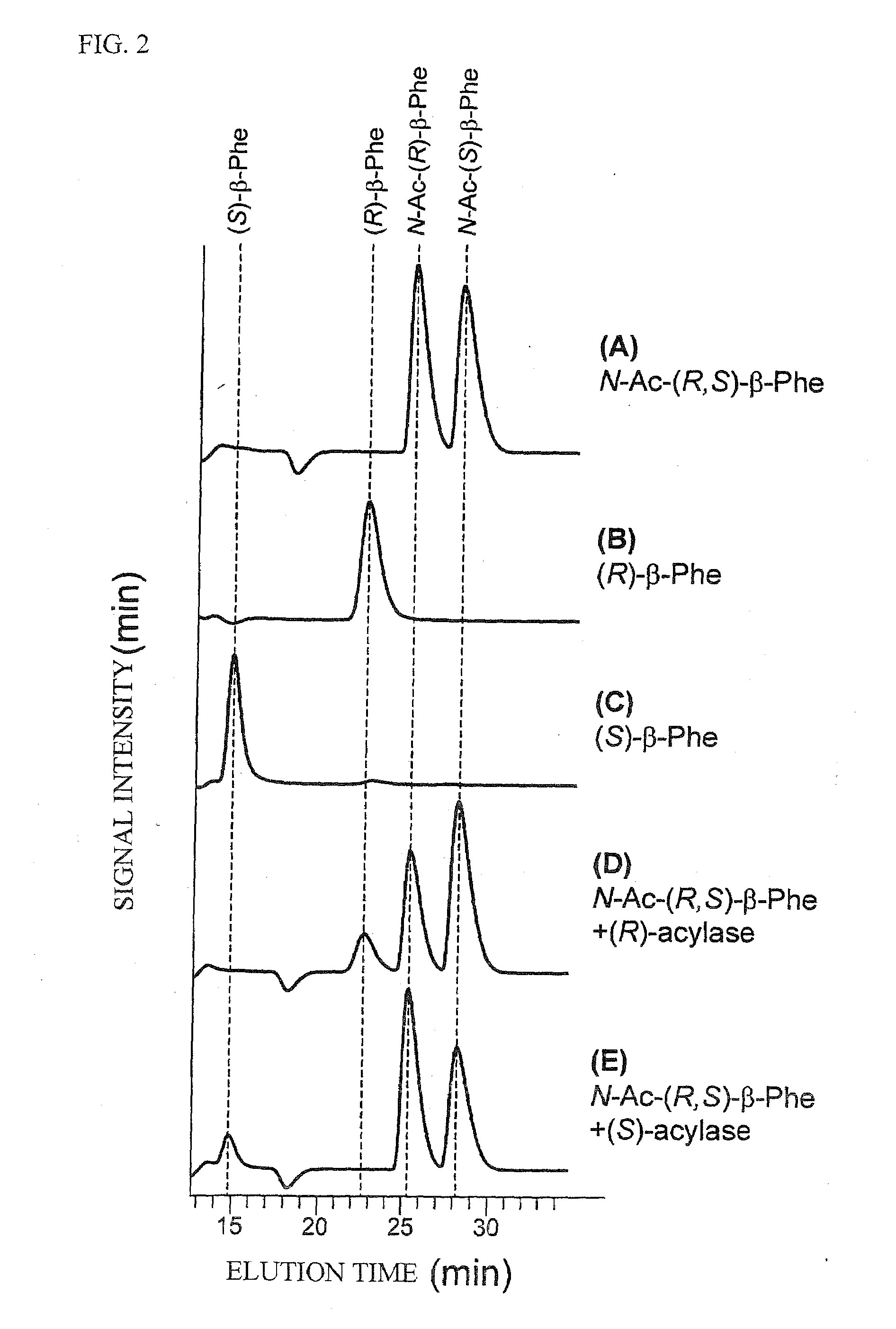
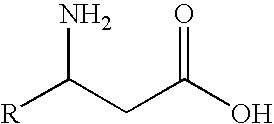
N-Acetyl-(R,S)-beta-Amino Acid Acylase Gene
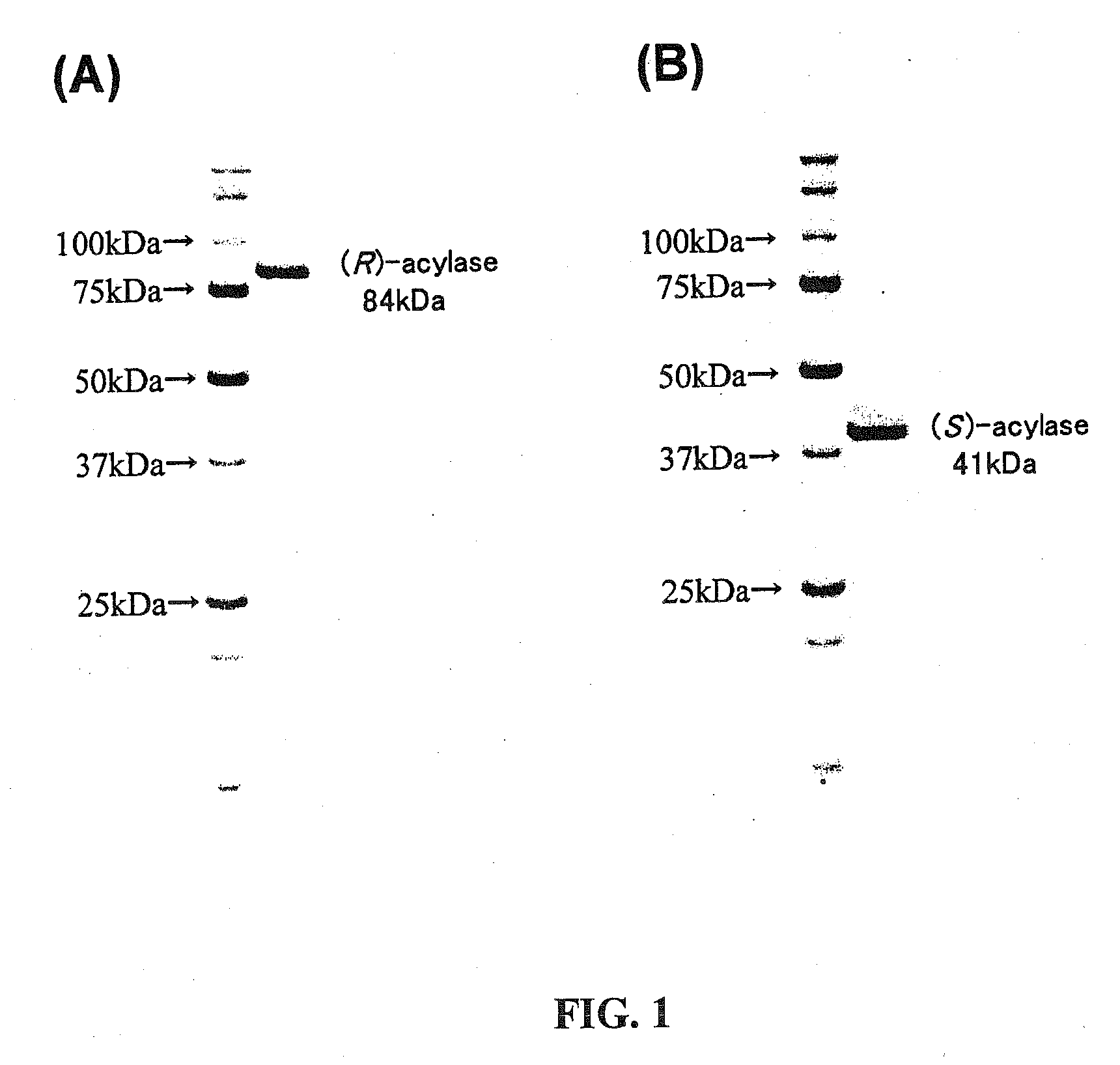
The present invention provides genes that encode the N-acetyl-(R,S)-β-amino acid acylases. The N-acetyl-(R,S)-β-amino acid acylases were isolated and purified from bacterial cells and the nucleotide sequences were determined. A host, such as Escherichia coli, was used to construct a high-expression system for these genes. The N-acetyl-(R)-β-amino acid acylase produced by Burkholderia sp. AJ110349 (FERM BP-10366) includes, for example, the protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 8. The gene encoding this enzyme includes, for example, the DNA having the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 7. The N-acetyl-(S)-β-amino acid acylase produced by Burkholderia sp. AJ110349 (FERM BP-10366) includes, for example, the protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 10. The gene encoding this enzyme includes, for example, the DNA having the nucleotide sequence shown inshown in SEQ. ID. NO. 9. The N-acetyl-(R)-β-amino acid acylase produced by Variovorax sp. AJ110348 (FERM BP-10367) includes, for example, the protein comprised of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 12. The gene encoding this enzyme includes, for example, the DNA having the nucleotide sequence shown inshown in SEQ. ID. NO. 11.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
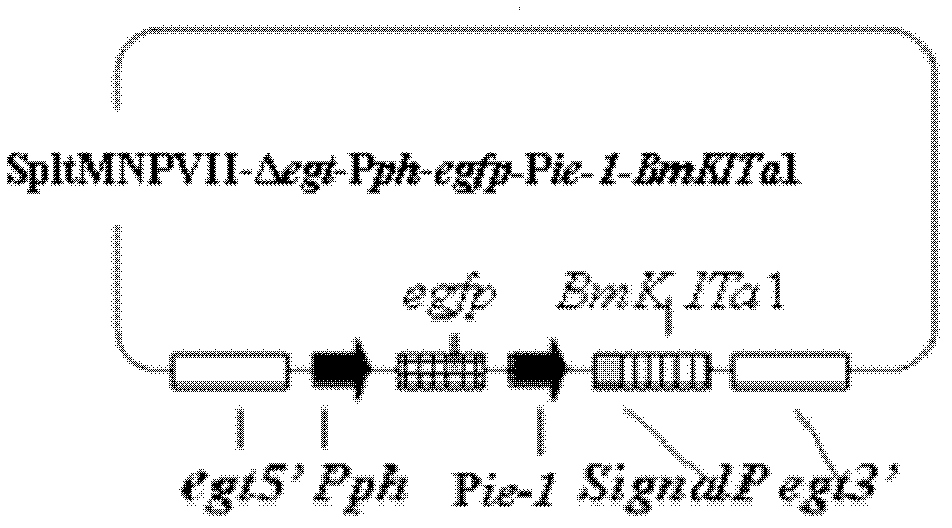
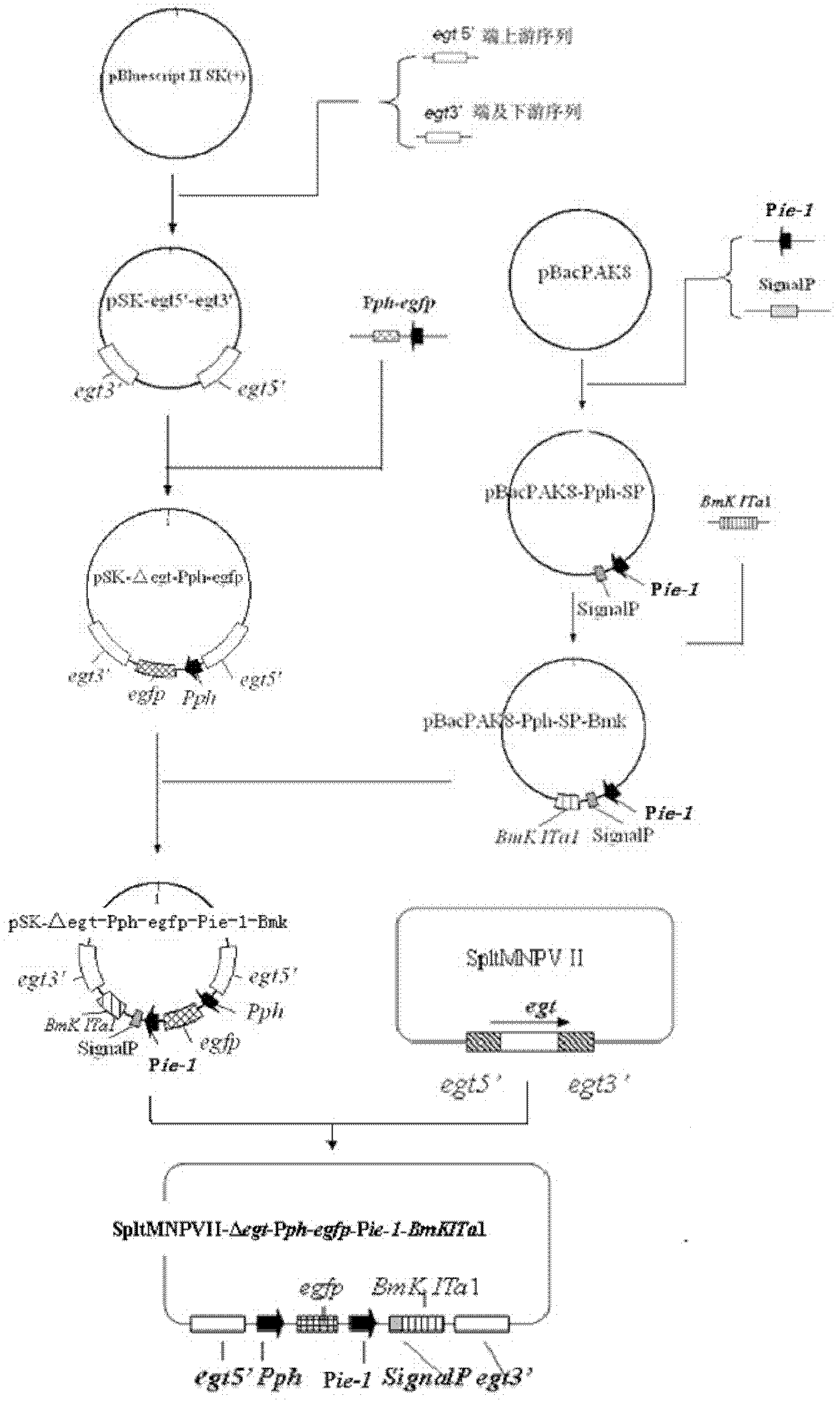
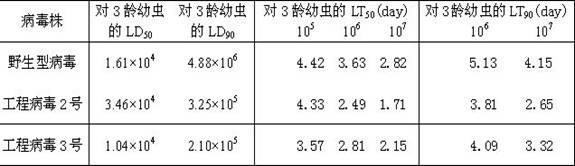
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com