Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (Nmnat) mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
A technology of mononucleotide adenosine and transferase, which is applied in the fields of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenosine transferase mutants and their coding genes and applications, and can solve the problem of high production cost of NAD and the high production cost of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenosine Eliminate the problems of low purification efficiency and catalytic activity of glycosyltransferase, and achieve high-efficiency purification, improve market competitiveness, and high catalytic activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Amplification and cloning of the gene encoding nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase:
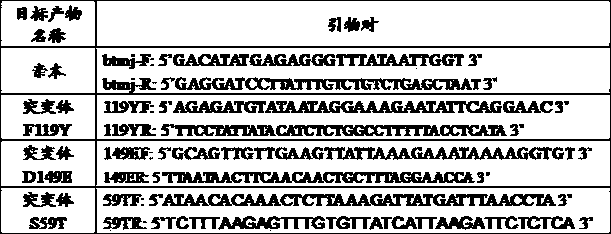
[0033] Primers btmj-F and btmj-R were designed according to the gene sequence of the gene bank (GenBank NP_247520) (as shown in Table 1). The gene encoding nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase was amplified from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii DSM 2661 using the primer pair btmj-F and btmj-R.
[0034]The amplification conditions are: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 10 mM KCl, 10 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 2 mM MgSO 4 , 0.1% Triton X-100, 50 mM dATP, 50 mM dTTP, 50 mM dCTP, 50 mM dGTP, 400 nM primer btmj-F, 400 nM primer btmj-R, 1.0 U Pfu DNA polymerase (Promega, USA), Pick up a little Methanocaldococcus jannaschii DSM 2661 cells with an inoculation loop, and adjust the reaction volume to 50 ml with sterile water.
[0035] The PCR amplification reaction program was: 95°C for 3 minutes, 35 cycles: 95°C for 50 seconds, 50°C for 30 seconds and 72°C for 1 minute, and finally 72°...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Site-directed mutagenesis at position 119 of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase:
[0040] In order to mutate the Phe (F) at the 119th position in the parental amino acid sequence to Tyr (Y) to obtain the mutant F119Y, the plasmid pRSET-btmj in Example 1 was used as a template to design primer pairs 119YF and 119YR (as shown in Table 1 Show).
[0041] The primer pair btmj-F and 119YR was used to amplify the F-YR fragment, and the primer pair 119YF and btmj-R was used to amplify the YF-R fragment.
[0042] The amplification reaction conditions are: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 10 mM KCl, 10 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 2 mM MgSO 4 , 0.1% Triton X-100, 50 mM dATP, 50 mM dTTP, 50 mM dCTP, 50 mM dGTP, 1.5 U Pfu DNA polymerase (Promega, USA), 20 ng pRSET-btmj, and 400 nM primers btmj-F and 400 nM primer 119YR (or, 400 nM primer 119YF and 400 nM primer btmj-R), adjust the reaction volume to 50 μl with sterile water.
[0043] The PCR amplification reaction program was: 95...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Site-directed mutagenesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenosyltransferase mutants at position 149:
[0050] In order to mutate the Asp(D) at the 149th position in the parental amino acid sequence to Glu(E) to obtain the mutant D149E, the plasmid pRSET-btmj (see Example 1) was used as a template to design primer pairs 149EF and 149ER (as shown in Table 1 shown).
[0051] The primer pair btmj-F and 149ER was used to amplify the F-ER fragment, and the primer pair 149EF and btmj-R was used to amplify the EF-R fragment. The specific sequences of primers btmj-F and btmj-R are shown in Table 1.
[0052] The above amplification reaction conditions are: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 10 mM KCl, 10 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 2 mM MgSO 4 , 0.1% Triton X-100, 50 mM dATP, 50 mM dTTP, 50 mM dCTP, 50 mM dGTP, 400 nM primer btmj-F and 400 nM primer 149ER, or 400 nM primer 149EF and 400 nM primer btmj-R, 1.5 U Pfu DNA polymerase (Promega, USA), 20 ng pRSET-btmj, and adjust the reaction volu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com