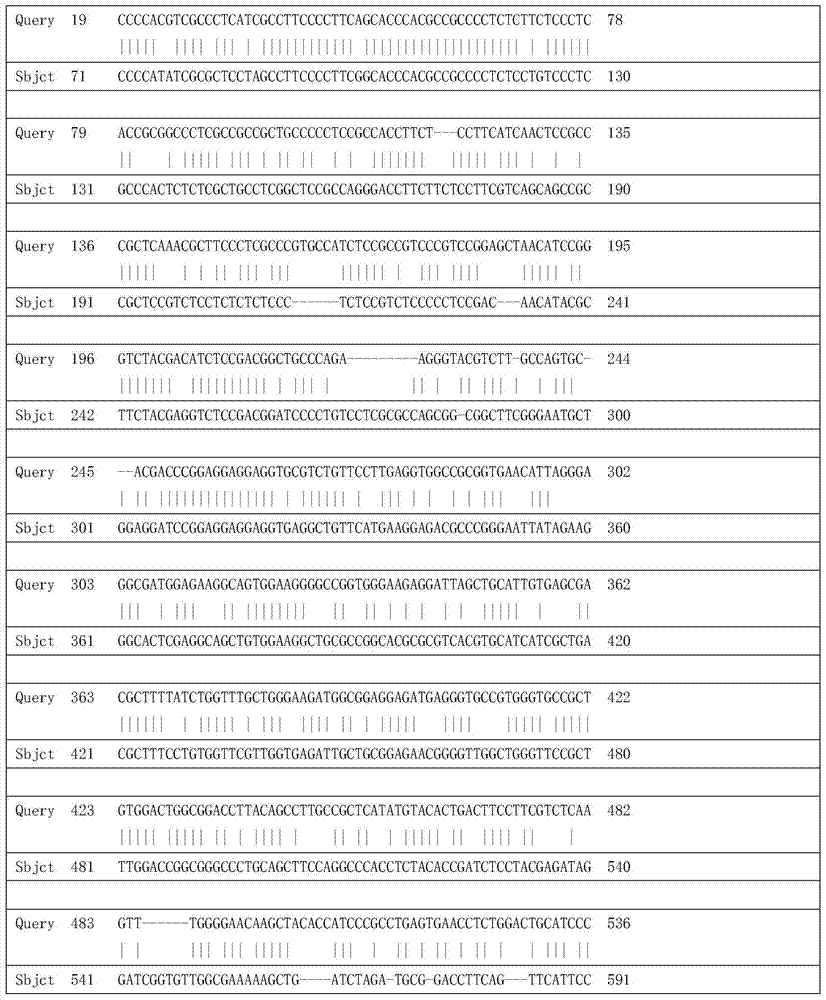
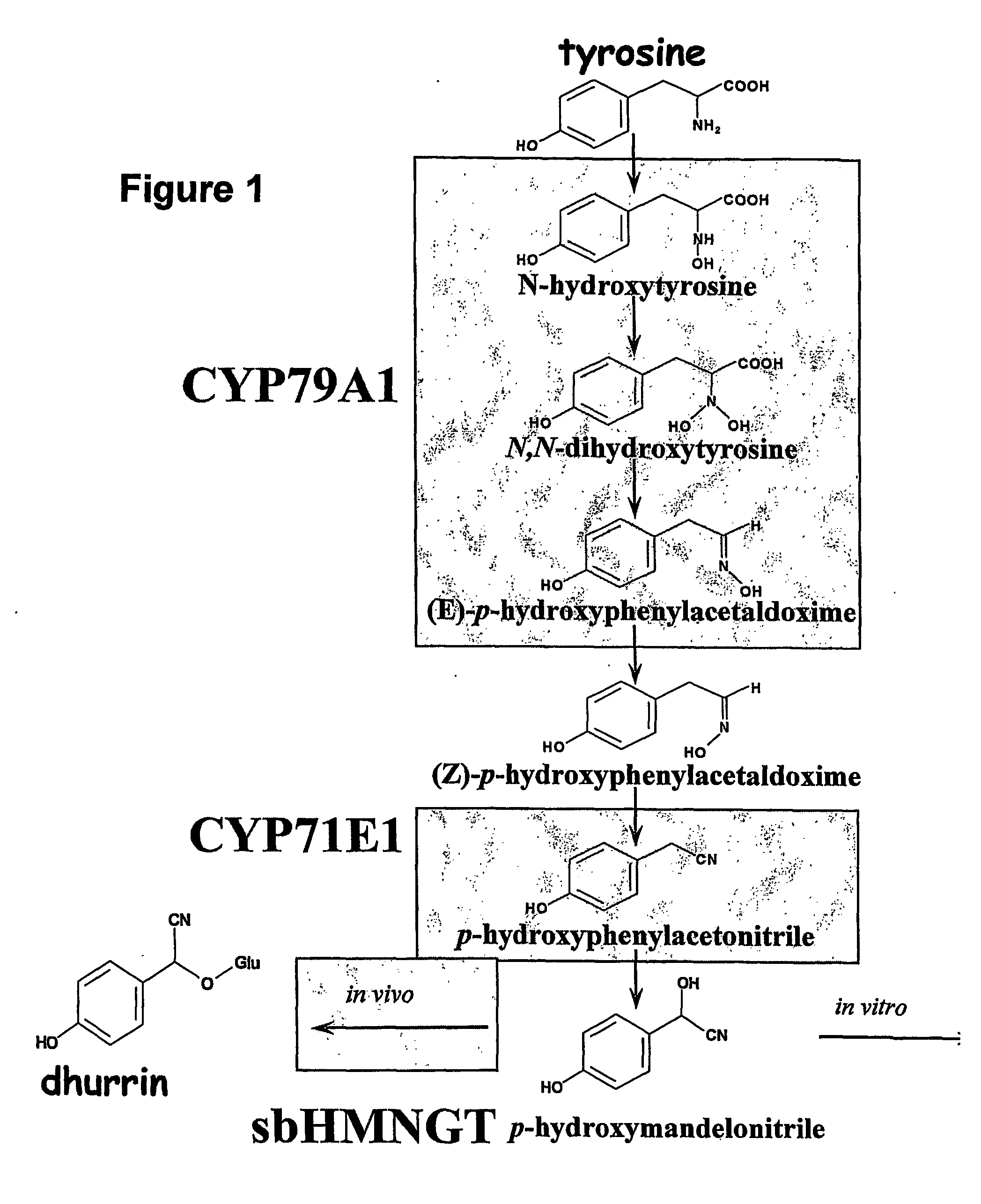
Patents
Literature
289 results about "Glycosyltransferase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
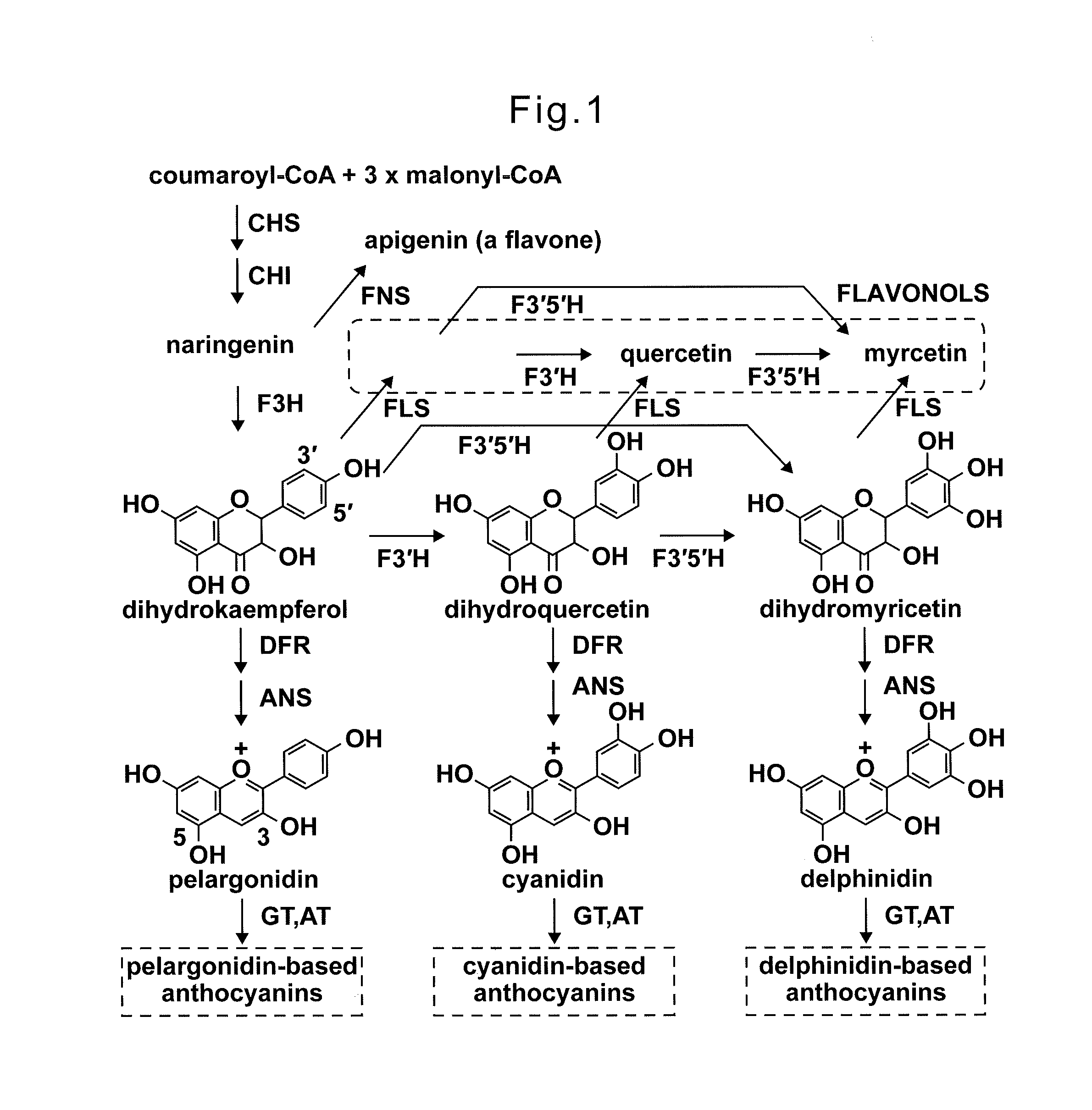
Genes that encode the class of enzymes that catalyze the transfer of glycosyl groups to an acceptor; often another carbohydrate molecule, a protein, or inorganic phosphate. Some enzymes in this class catalyze hydrolysis - the transfer of a glycosyl group to water. Subclasses include Hexosyltransferases, Pentosyltransferases, and Sialyltransferases. (NCI)
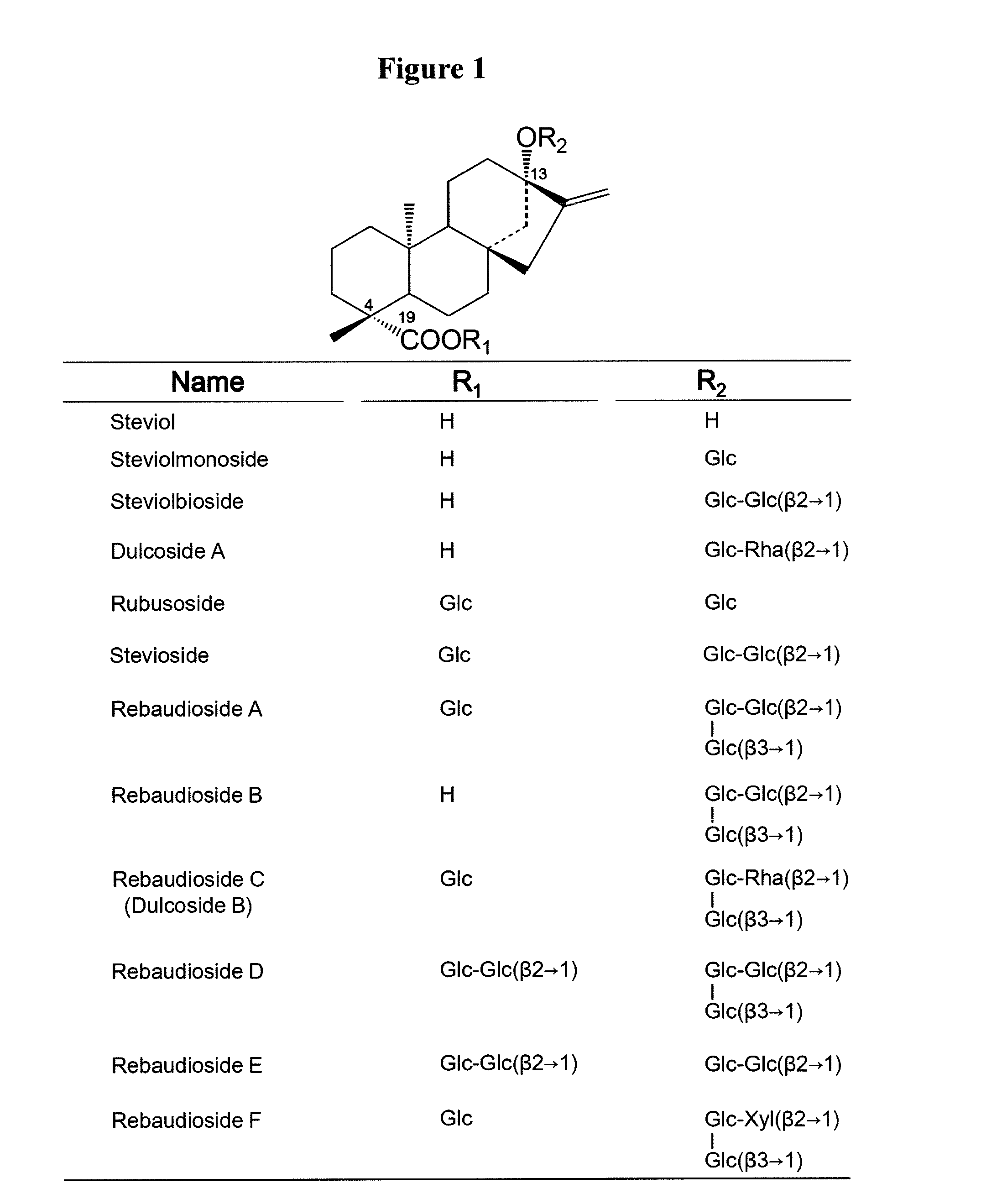
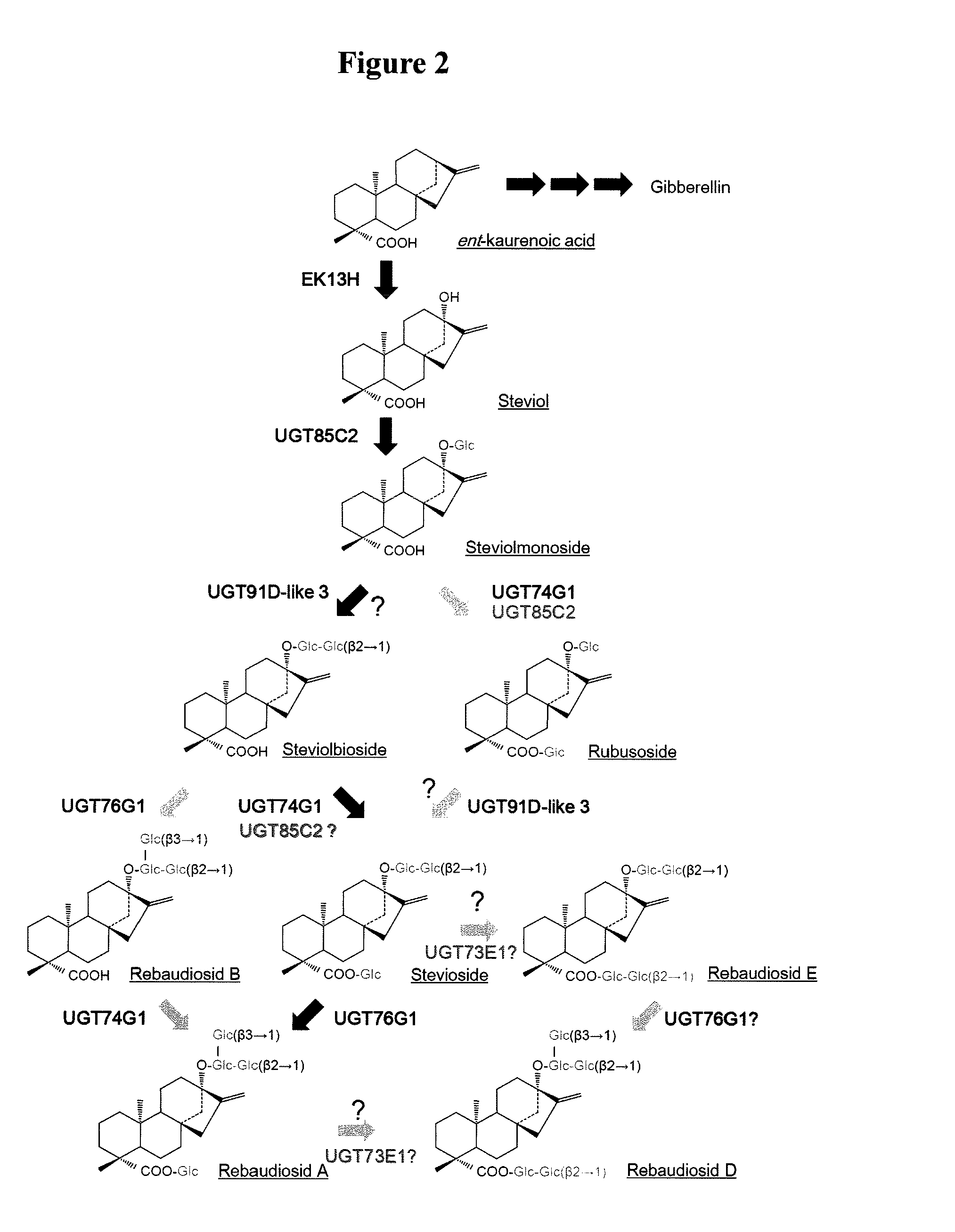
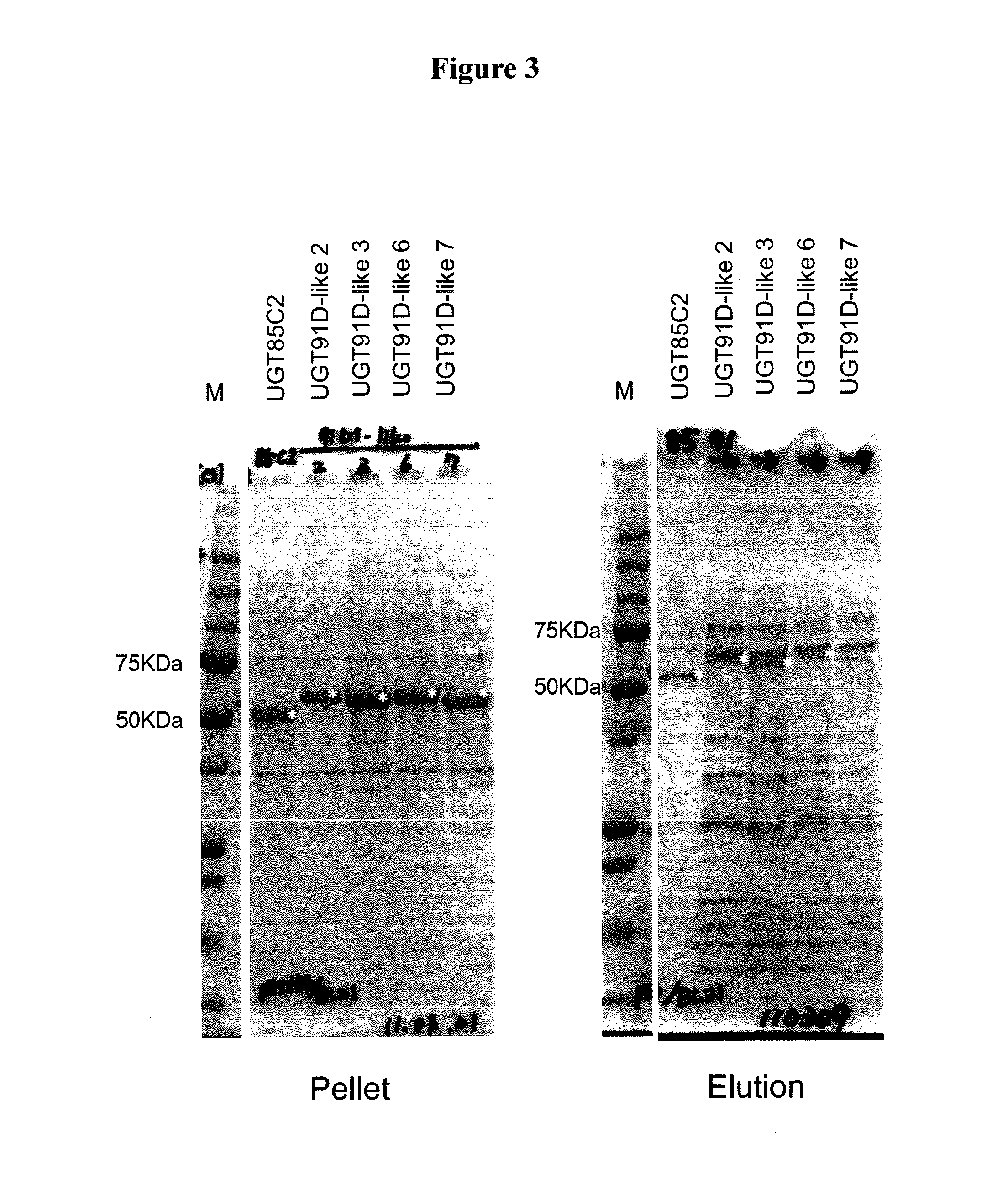
Steviol glucosyltransferases and genes encoding the same
ActiveUS20150159188A1Efficient extractionImprove efficiencyBiocideCosmetic preparationsGeneSteviol glycoside
Steviol glucosyltransferases and methods for producing steviol glycosides using the enzymes are provided.The present invention provides steviol glucosyltransferases and methods for producing steviol glycosides using the enzymes. The invention also provides transformants into which steviol glucosyltransferase genes are introduced and methods for preparing the transformants.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase gene clone and expression
InactiveCN101294149ACyclization activityImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
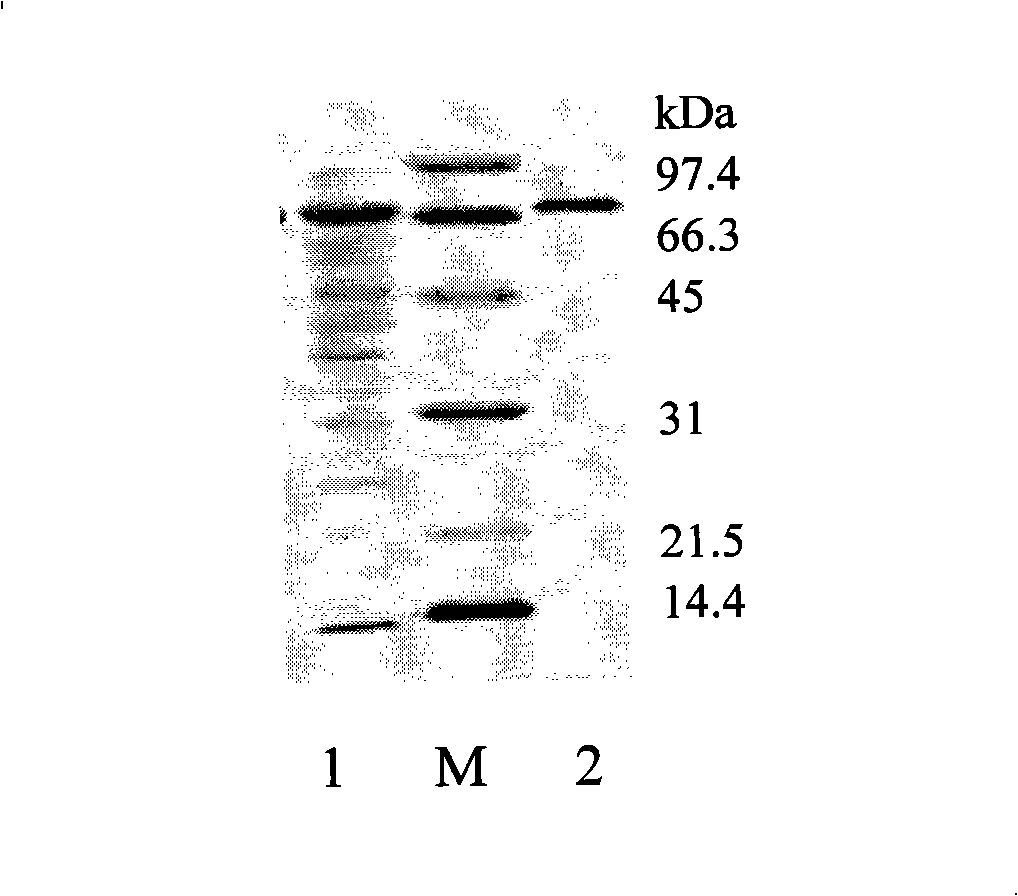
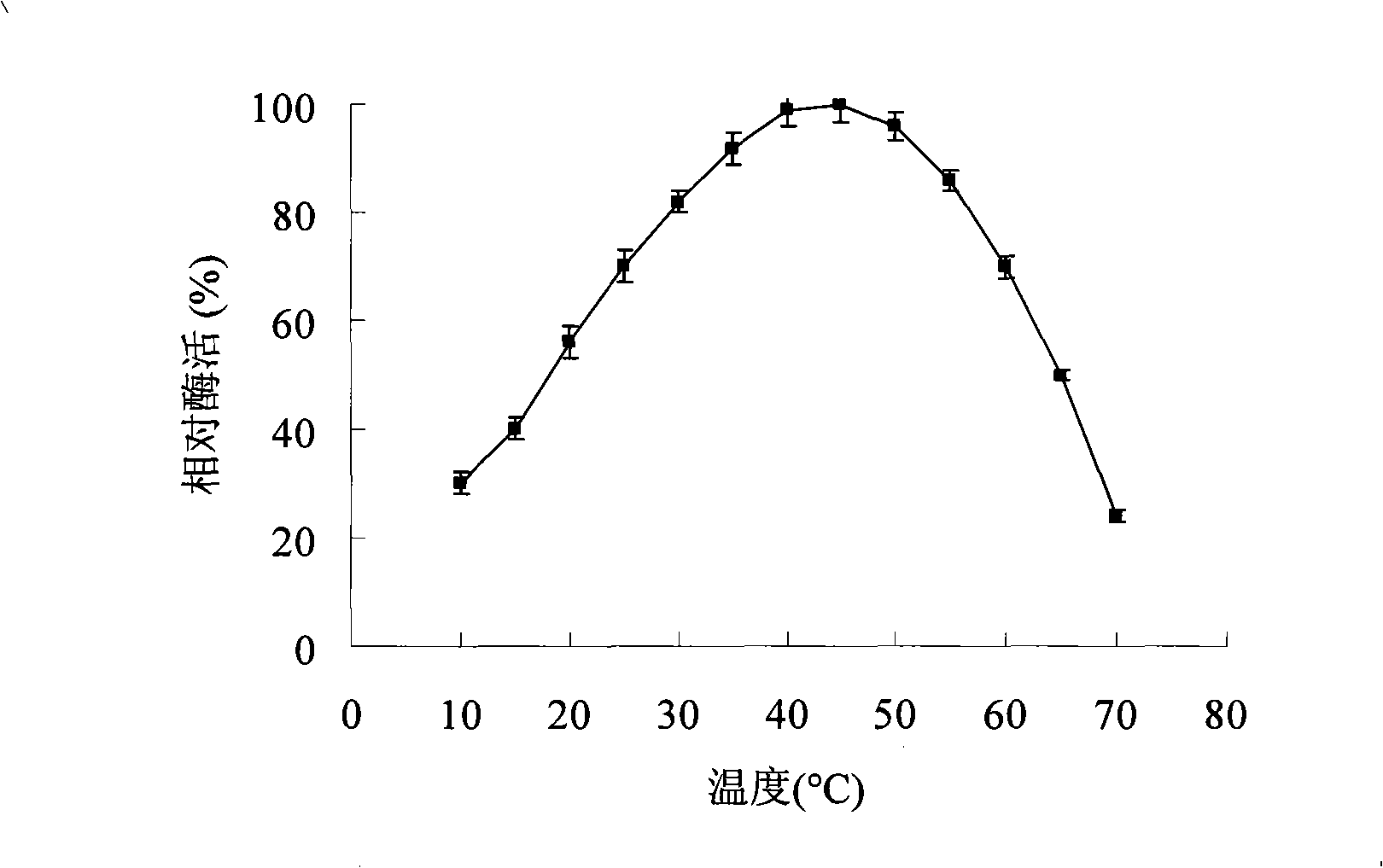
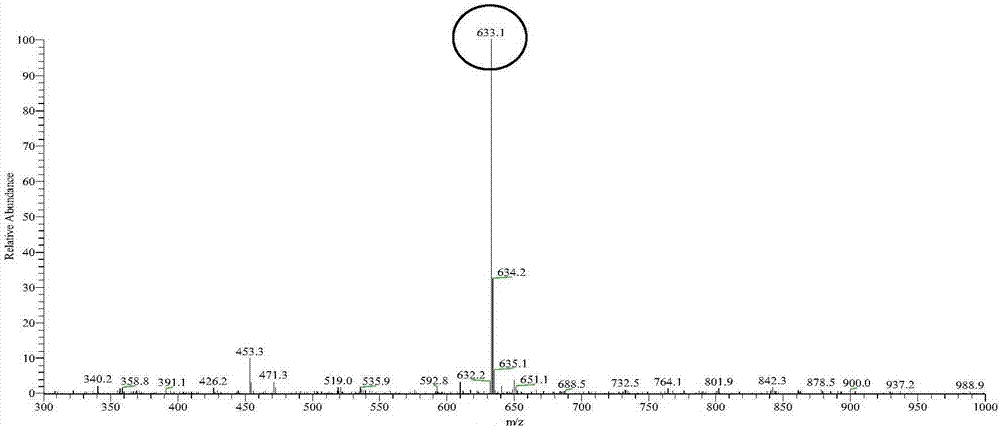
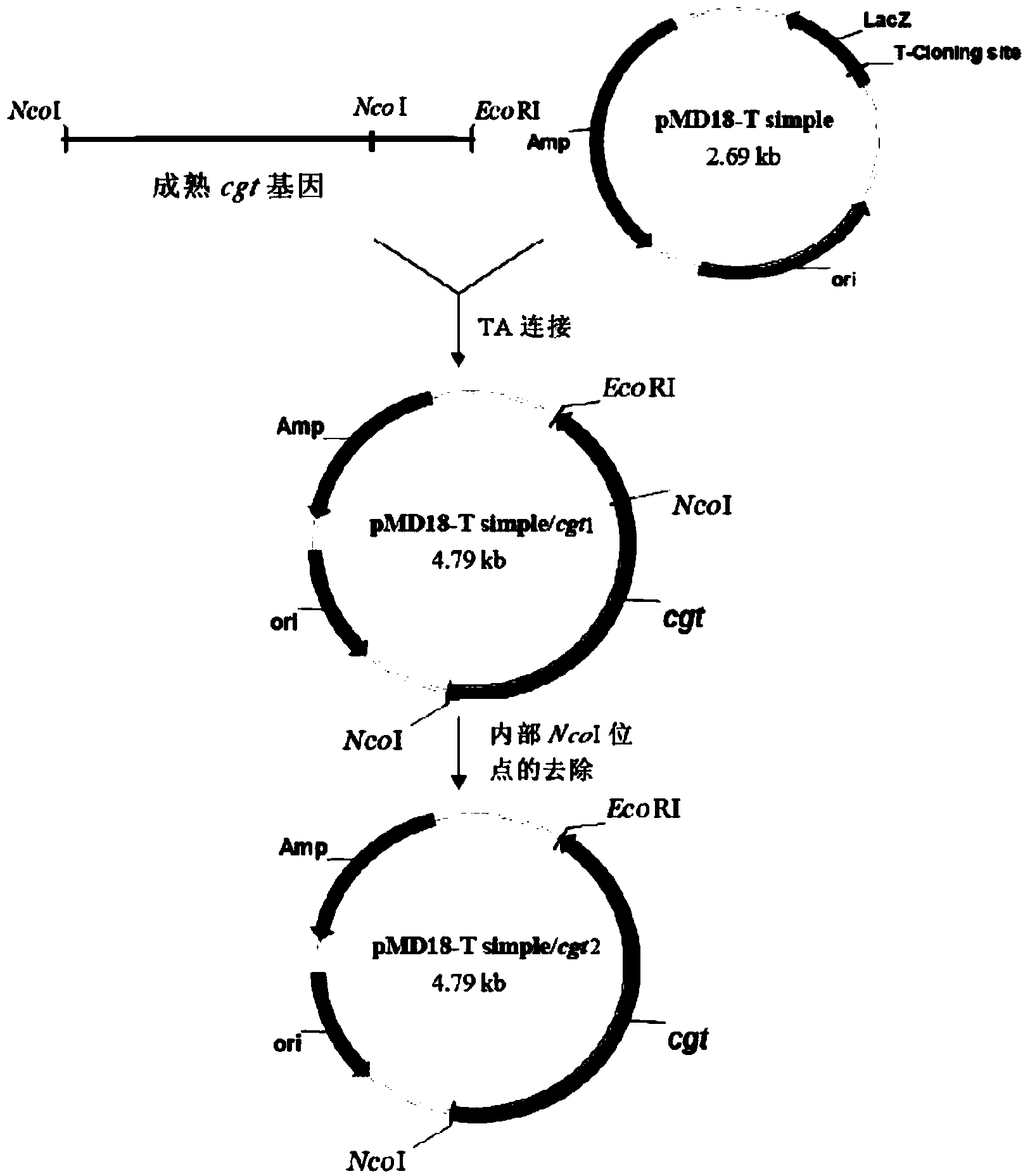
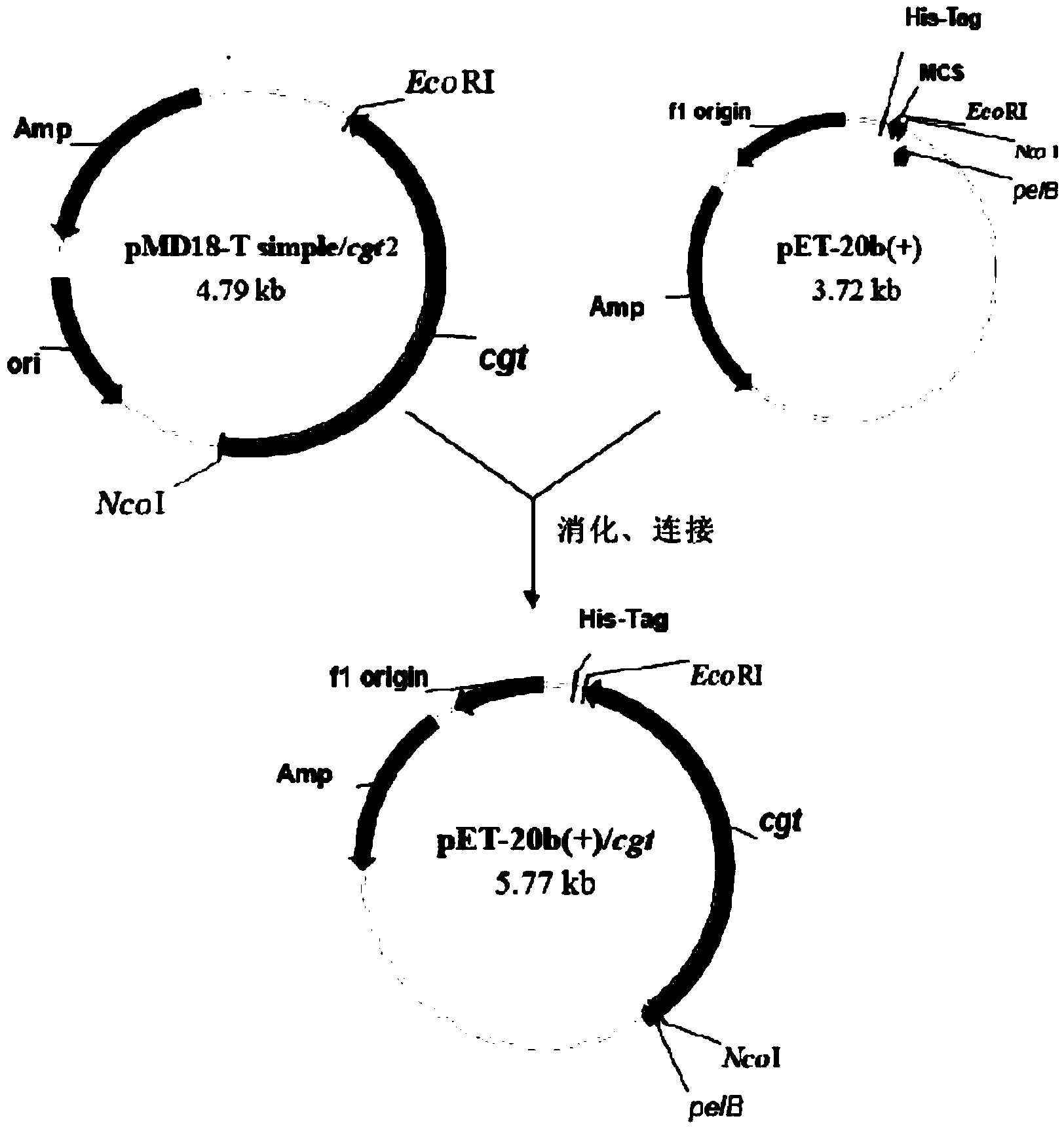
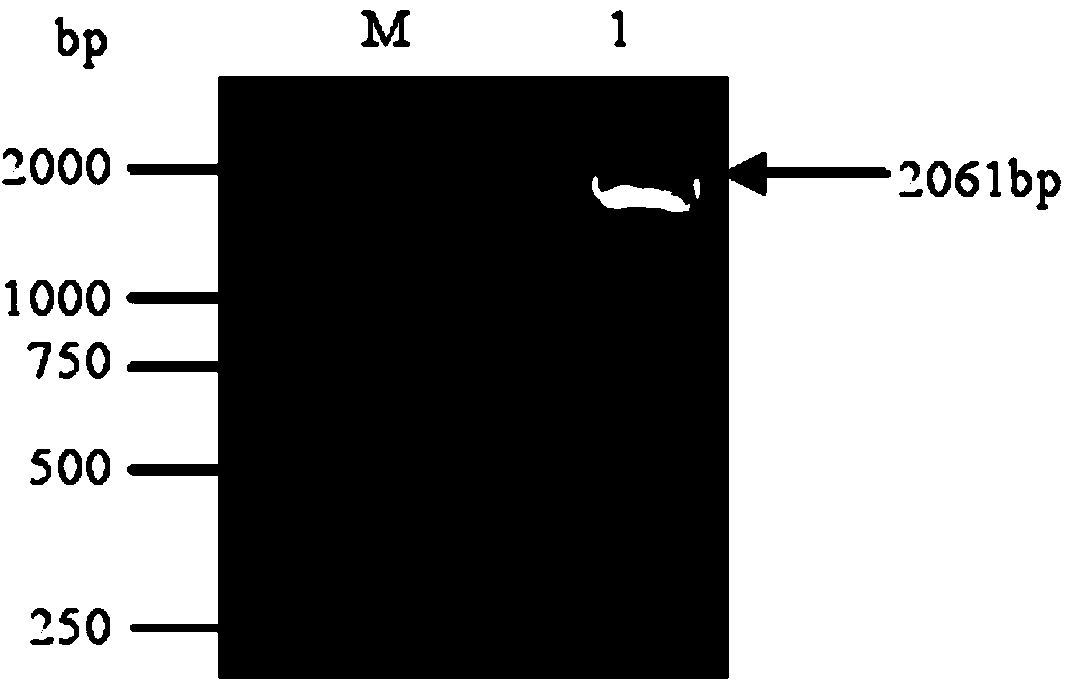
The invention relates to the clone and the expression of alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (alpha-CGTase), which belong to the field of enzyme gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The cgt gene expression method comprises the following steps: obtaining cgt gene SEQ ID NO:1 from total DNA of Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01; selecting plasmid pET20b(+) as the expression vector of cgt gene; and selecting E.coli BL21(DE3) as the expression host to achieve high-efficiency extracellular expression of the cgt gene, wherein the cgt gene has 2,061 nucleotides and 687 coded amino acids; prokaryotic expression plasmid is constructed; and alpha-CGTase is expressed by transformed E.coli. Recombinase has cyclization activity and can transform starch and relevant matrix into cyclodextrin. The recombined alpha-CGTase has an optimal temperature of 40 to 45 DEG C and an optimal pH value of 5.5, and has higher thermal stability below 40 DEG C and poor thermal stability above 50 DEG C. The alpha-CGTase meets the requirement for industrial application such as food and medicines, and can be used for industrial production of alpha-cyclodextrin and beta-cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glycosyltransferase gene
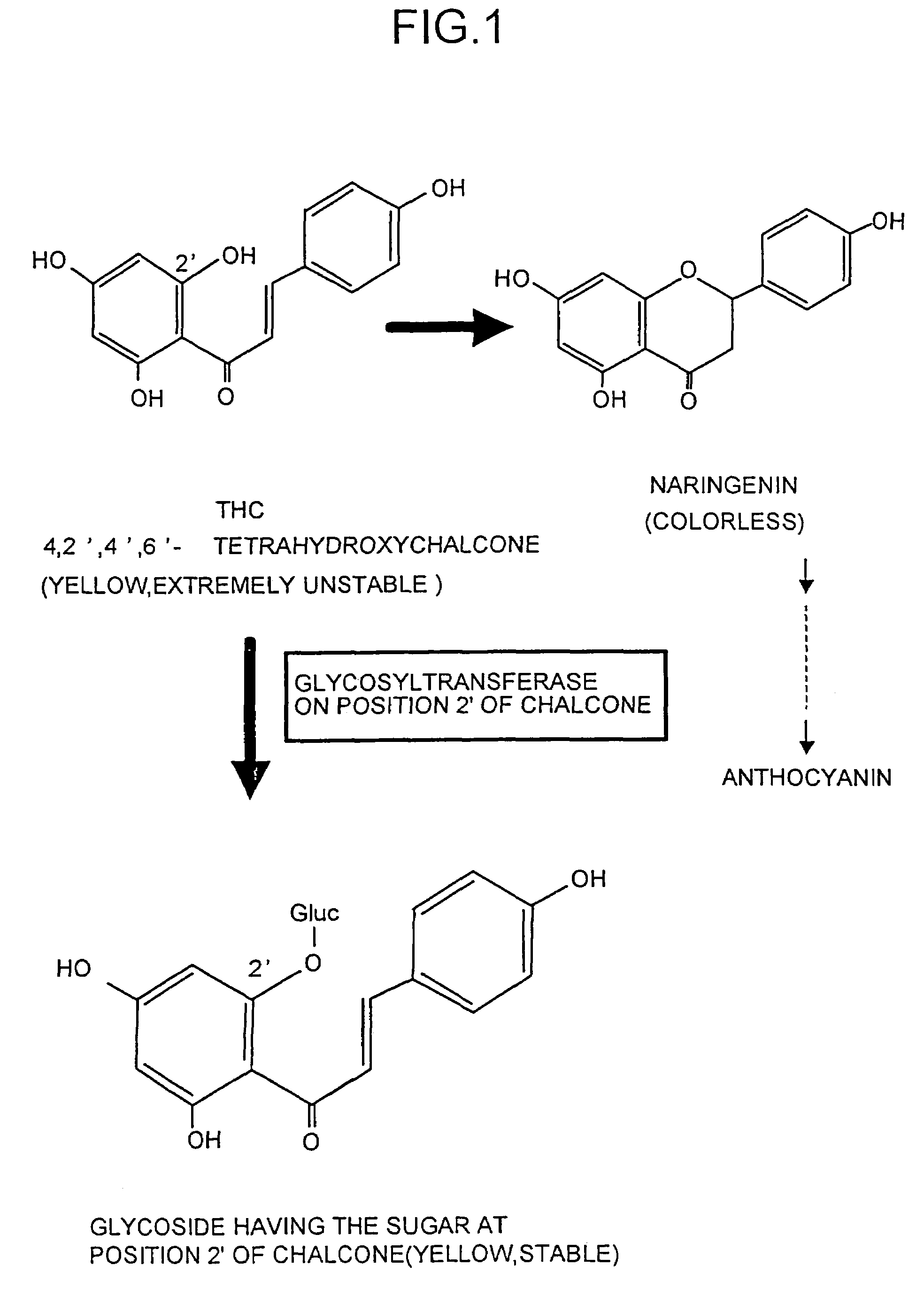
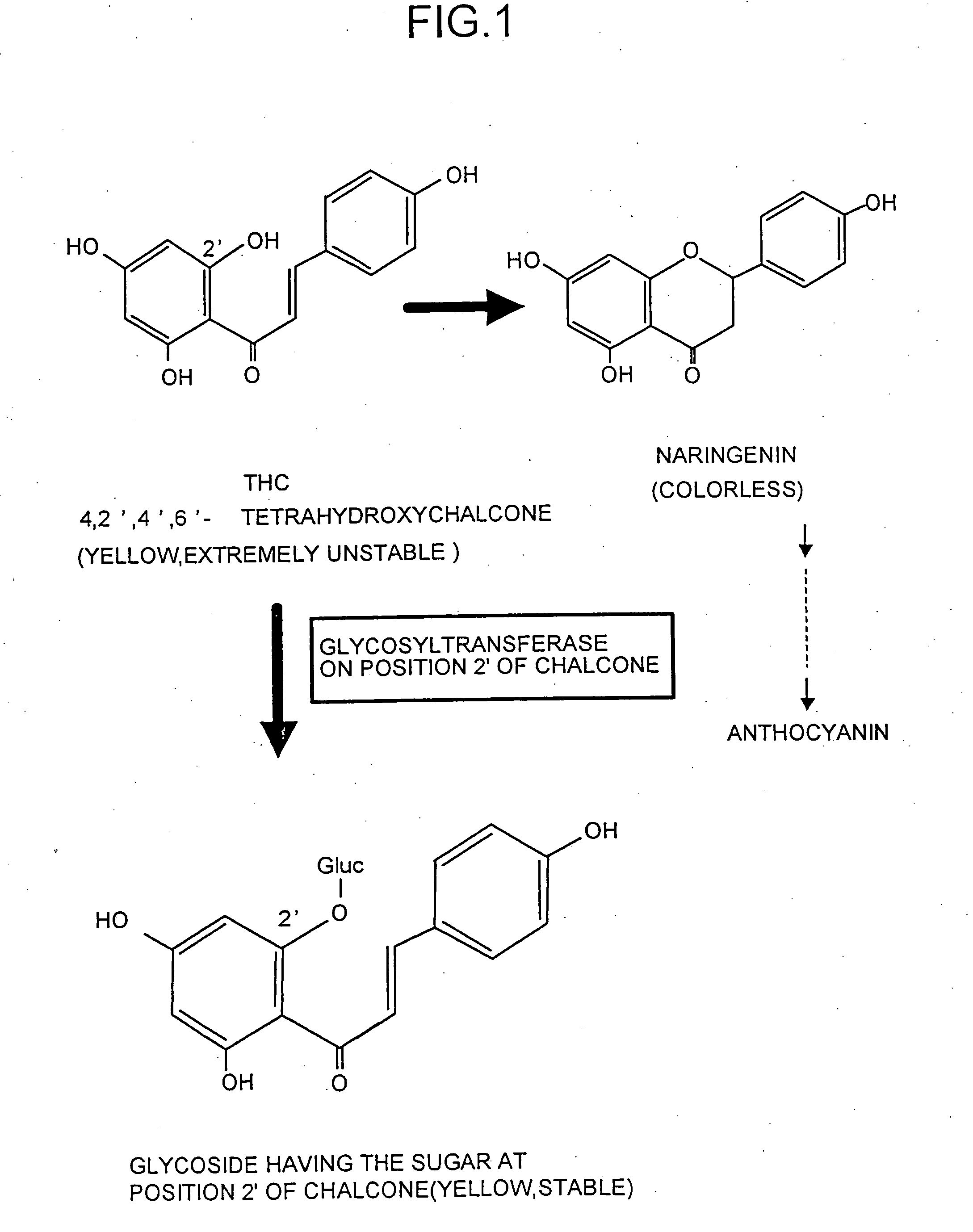
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
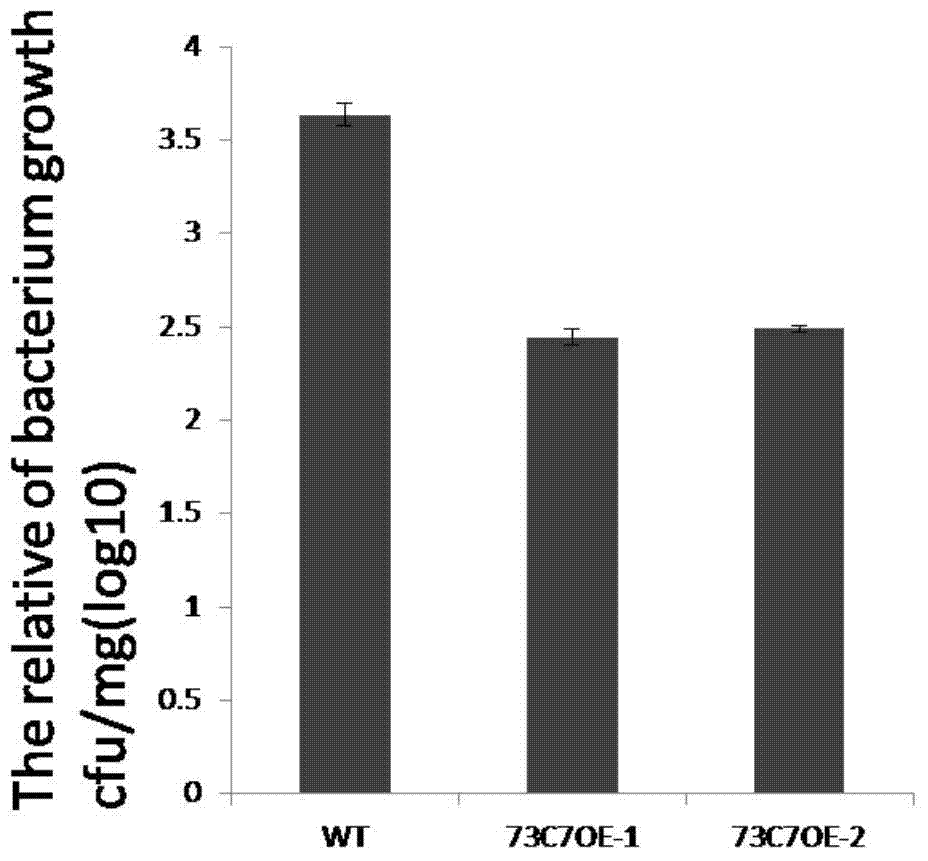
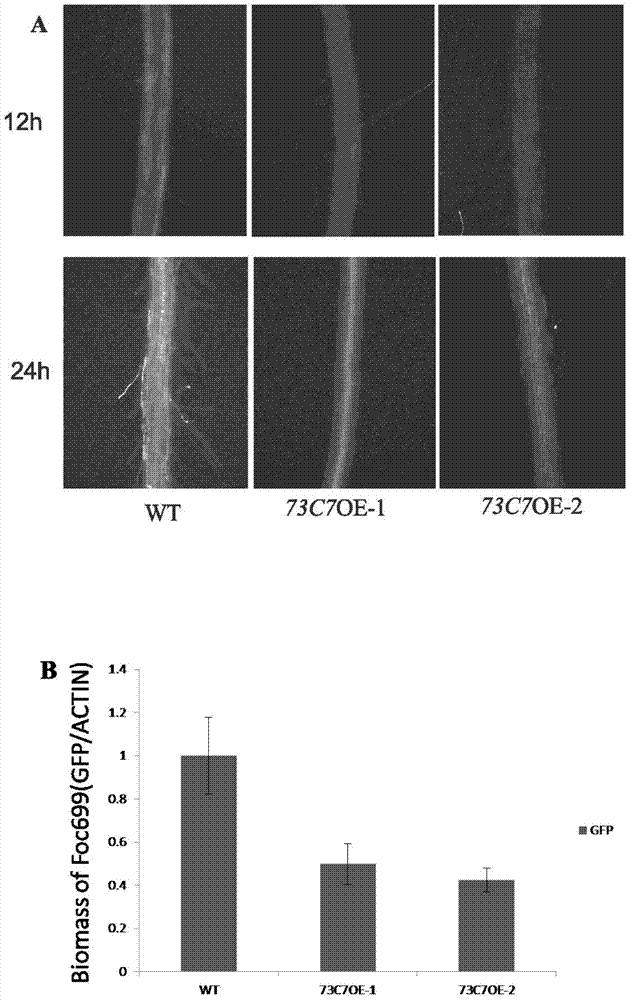
Application of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 in improving plant disease resistance
InactiveCN104845990AImprove disease resistanceIncrease varietyGenetic engineeringFermentationNucleotideArabidopsis
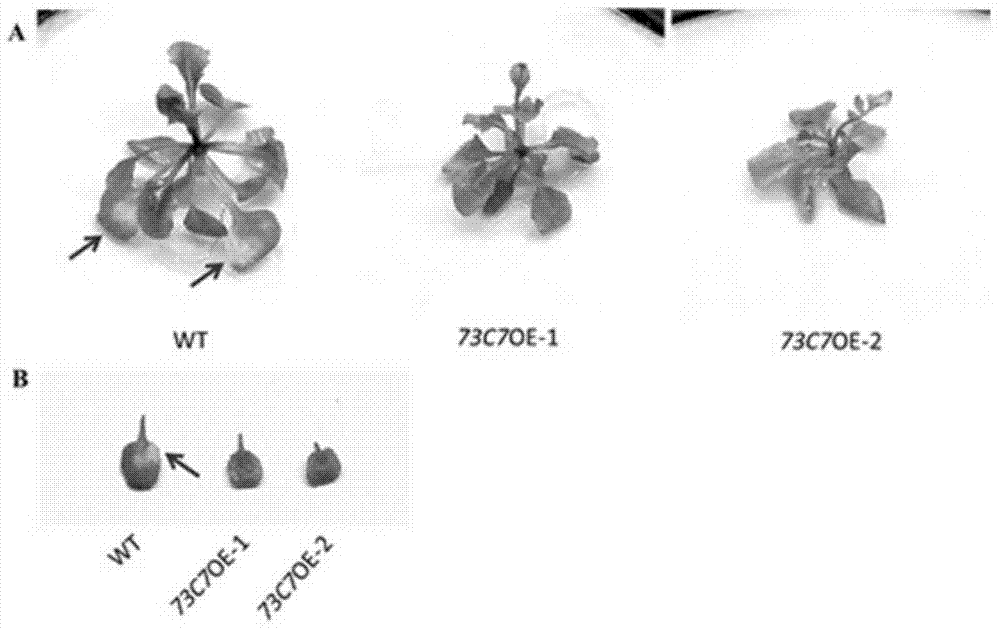
The invention discloses an application of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 in improving plant disease resistance, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 is shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and is cloned by RT-PCR from Arabidopsis thaliana. The ene UGT73C7 is used to construct a plant overexpressing vector for plant transgene operation, so as to obtain the transgenic plants. The detection results show that the disease resistance of the transgenic plants is significantly improved, suggesting that new disease-resistant plants can be created after the implementation of the application disclosed by the invention, and the application can be used for the subsequent crop variety improvement and has great significance for China's agricultural production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
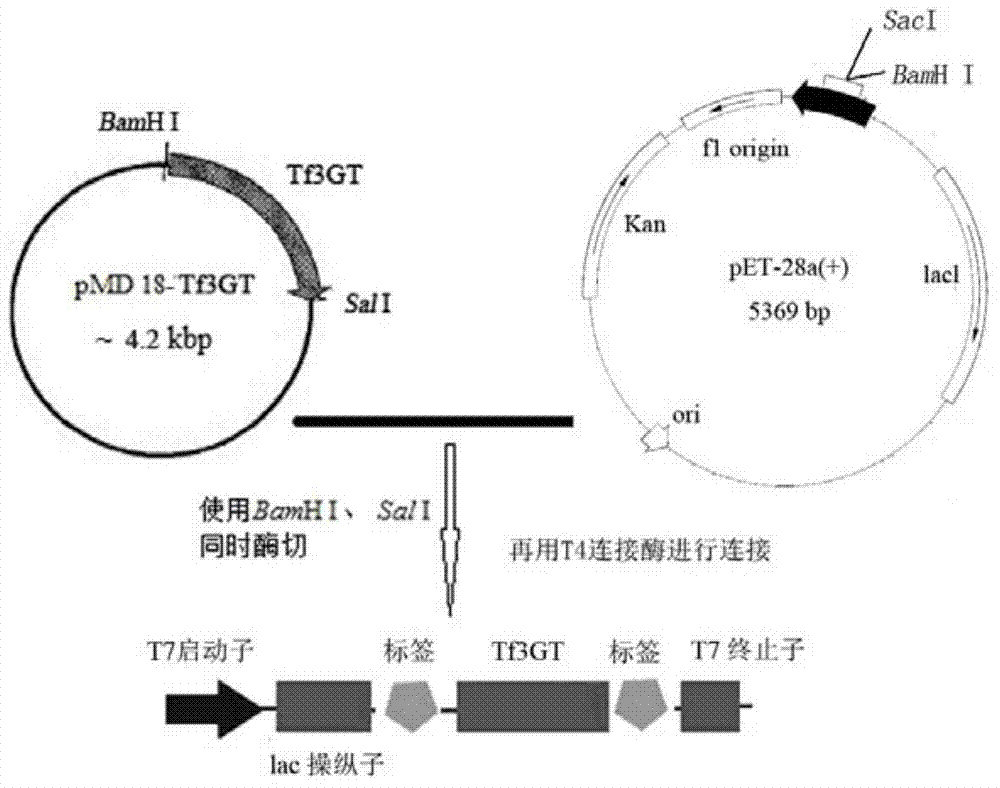
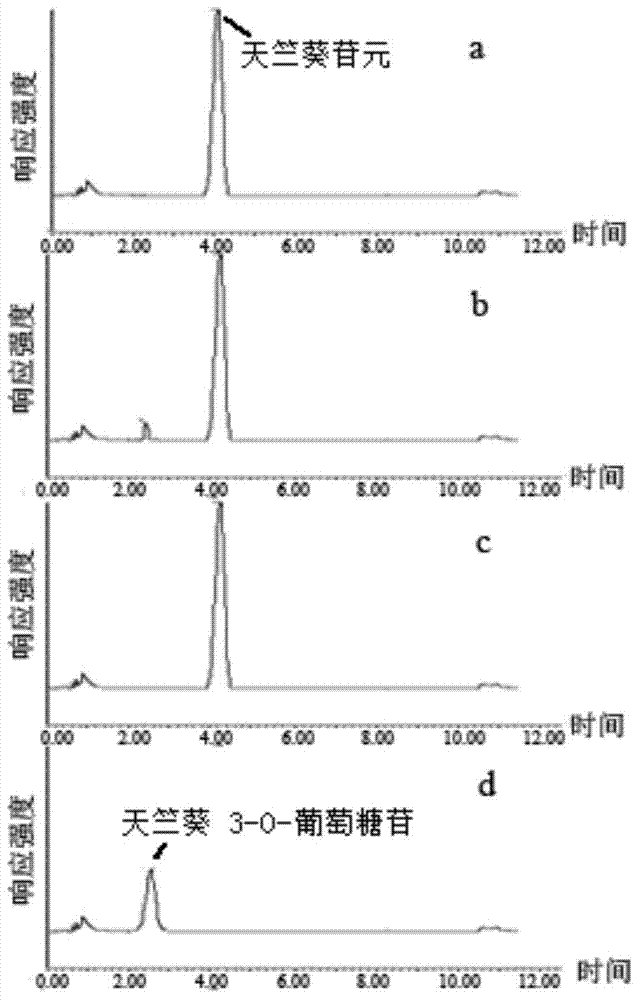
Tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and coding gene thereof
InactiveCN103695382AImprove viewing valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityTransgene
The invention discloses a tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein is a protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2, or a protein with tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase activity obtained by substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids on the basis of the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 for coding the protein. When the tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT gene is expressed in Escherichia coli cells, the recombinant flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase protein can promote anthocyanin and UDP-glucose to react and generate the anthocyanin. The Tf3GT coding sequence has application value in modification of varieties by a transgenic technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1
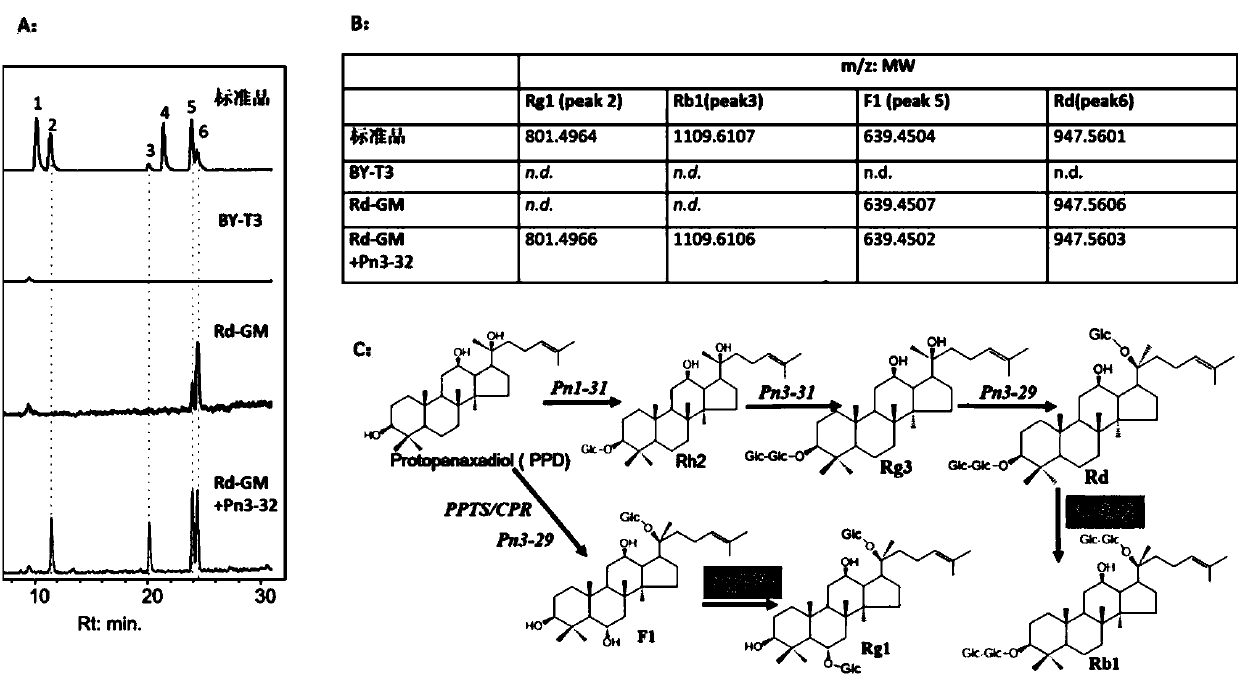
The invention discloses applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in the construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1. A glycosyltransferase genePn3-32 which can catalyze ginsenoside Rd to generate ginsenoside Rb1 can be successfully identified through a synthetic biological method; and the gene can simultaneously catalyze ginsenoside F1 to generate ginsenoside Rg1 and construct recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Through experiments, the constructed recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1 can simultaneously generate the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Pn1-31, Pn-3-29, Pn3-31 and Pn3-32 glycosyltransferase genes in medicinal plant radix notoginseng are firstly utilized to continuously catalyze protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol to synthetize the ginsenoside Rb1, the ginsenoside Rg1 and corresponding intermediates, so that novel cases can be provided formicrobial strains to produce natural products.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of producing a low molecular weight organic compound in a cell
ActiveUS20060275877A1Reduce the amount of solutionFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
Owner:EVOLVA SA
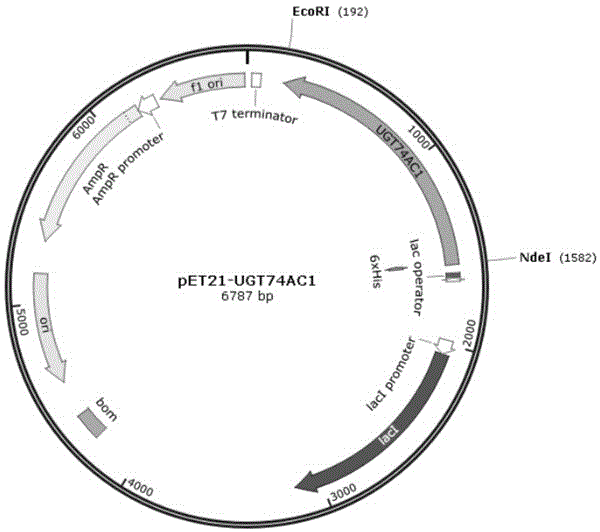
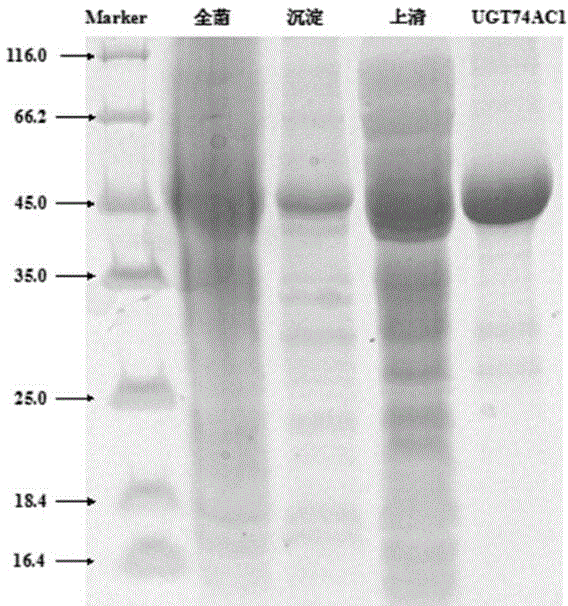
Mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene UGT74AC1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) and application of glycosyltransferase with a gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) code in synthetic mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) has a nucleotide coding sequence shown in SEQIDNO.1 and a peptide sequence shown in SEQIDNO.2. By utilization of an expression of the mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) in escherichia coli, the recombinant glycosyltransferase (i)UGT74AC1( / i) can catalyze mogrol and UDP-glucose to react, thereby generating the mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) disclosed by the invention can be applied to the artificial synthesis of the mogrosideIE. Meanwhile, the gene has an important application value in the aspect of improving momordica grosvenori by the utilization of a transgenic technology to improve the content of the mogroside.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
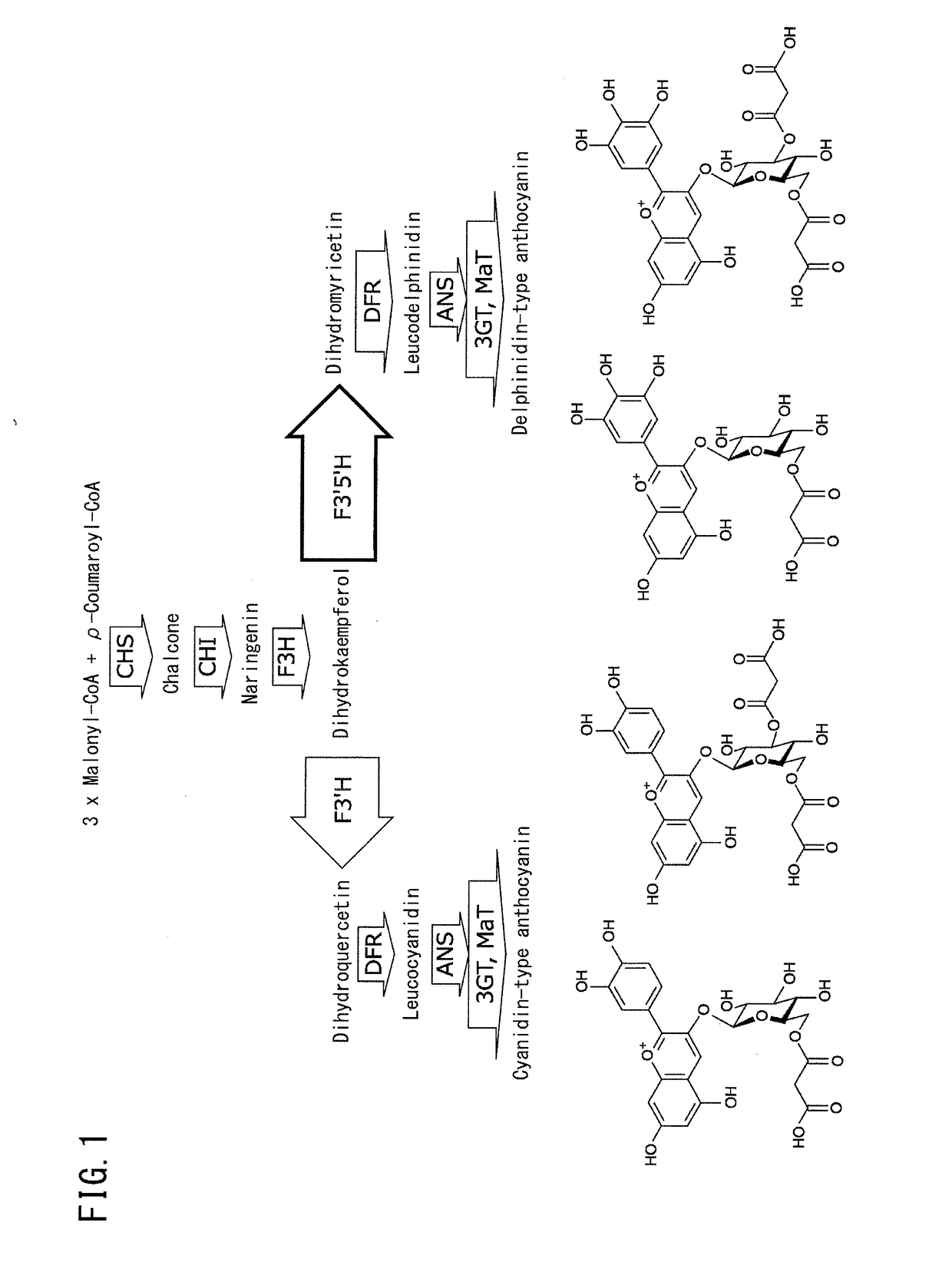
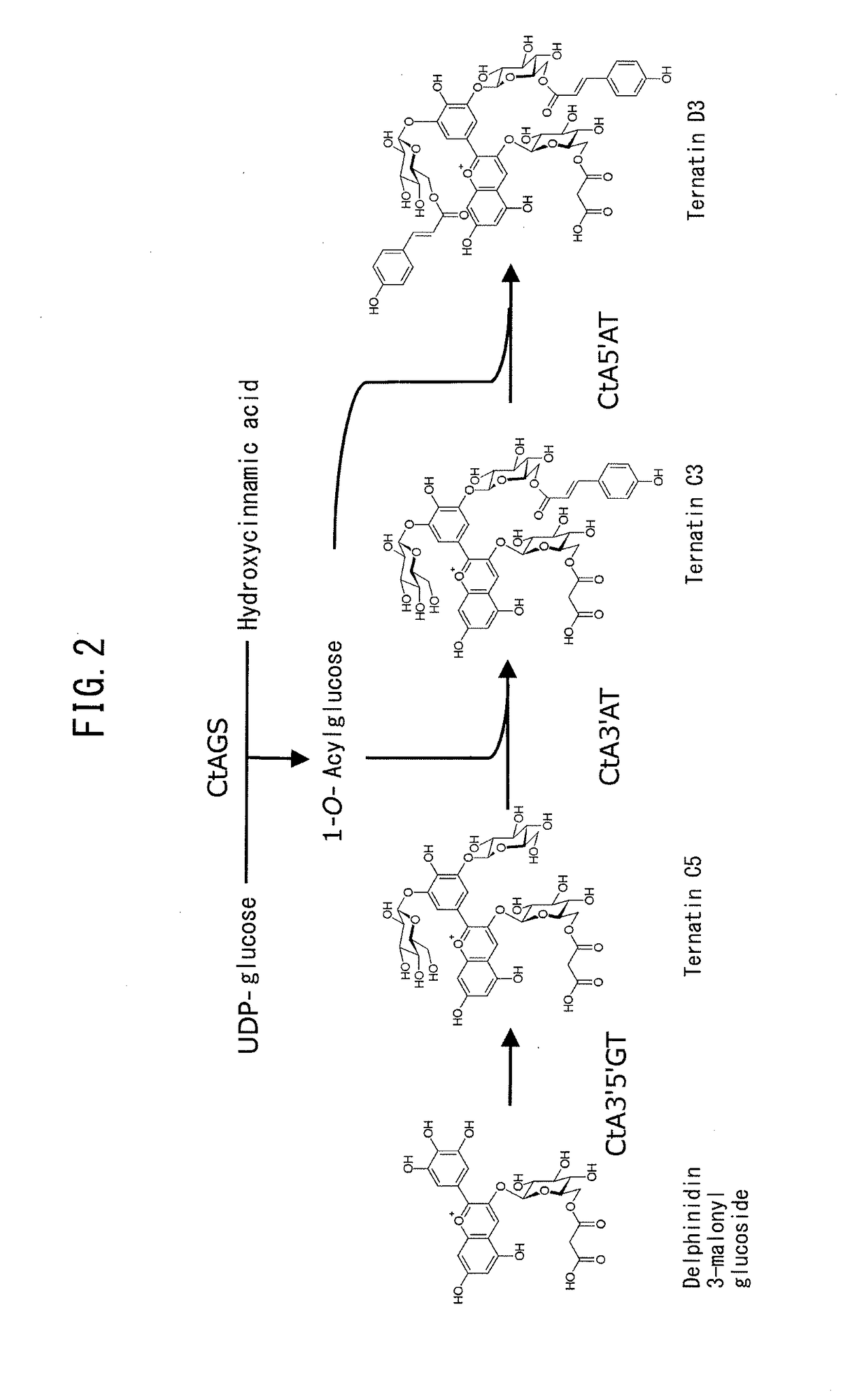
Creation of chrysanthemum with blue flower color
Provided are transformed chrysanthemum plants having blue flower color, their self-fertilized progenies or cross-fertilized progenies thereof, a vegetative propagated plants thereof, and a part, a tissue or a cell of the plant body. Anthocyanin 3′,5′-O-glucosyltransferase gene (CtA3′5′GT) derived from Clitoria ternatea and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene derived from Campanula (CamF3′5′H) are coexpressed in chrysanthemum petals.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
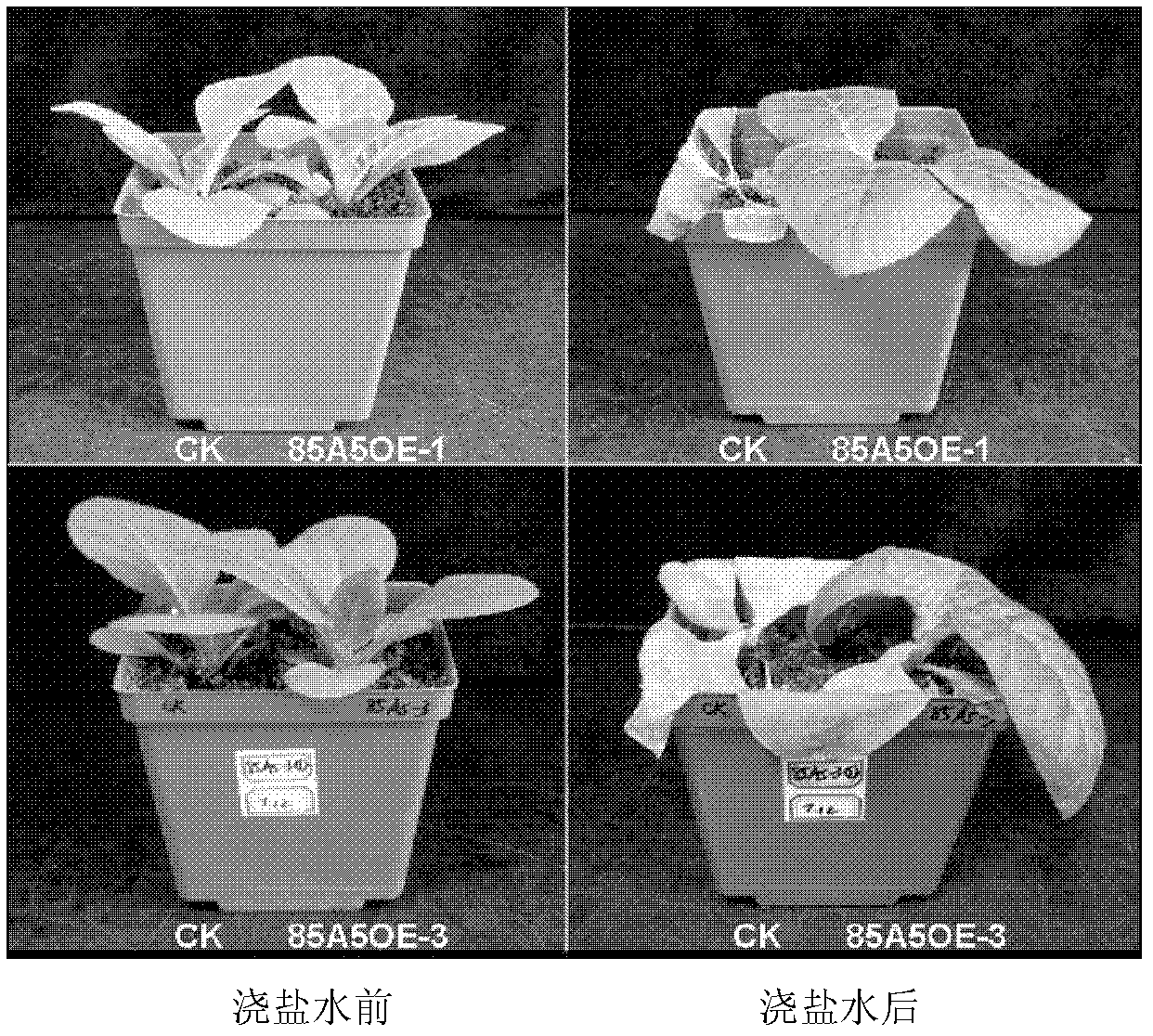
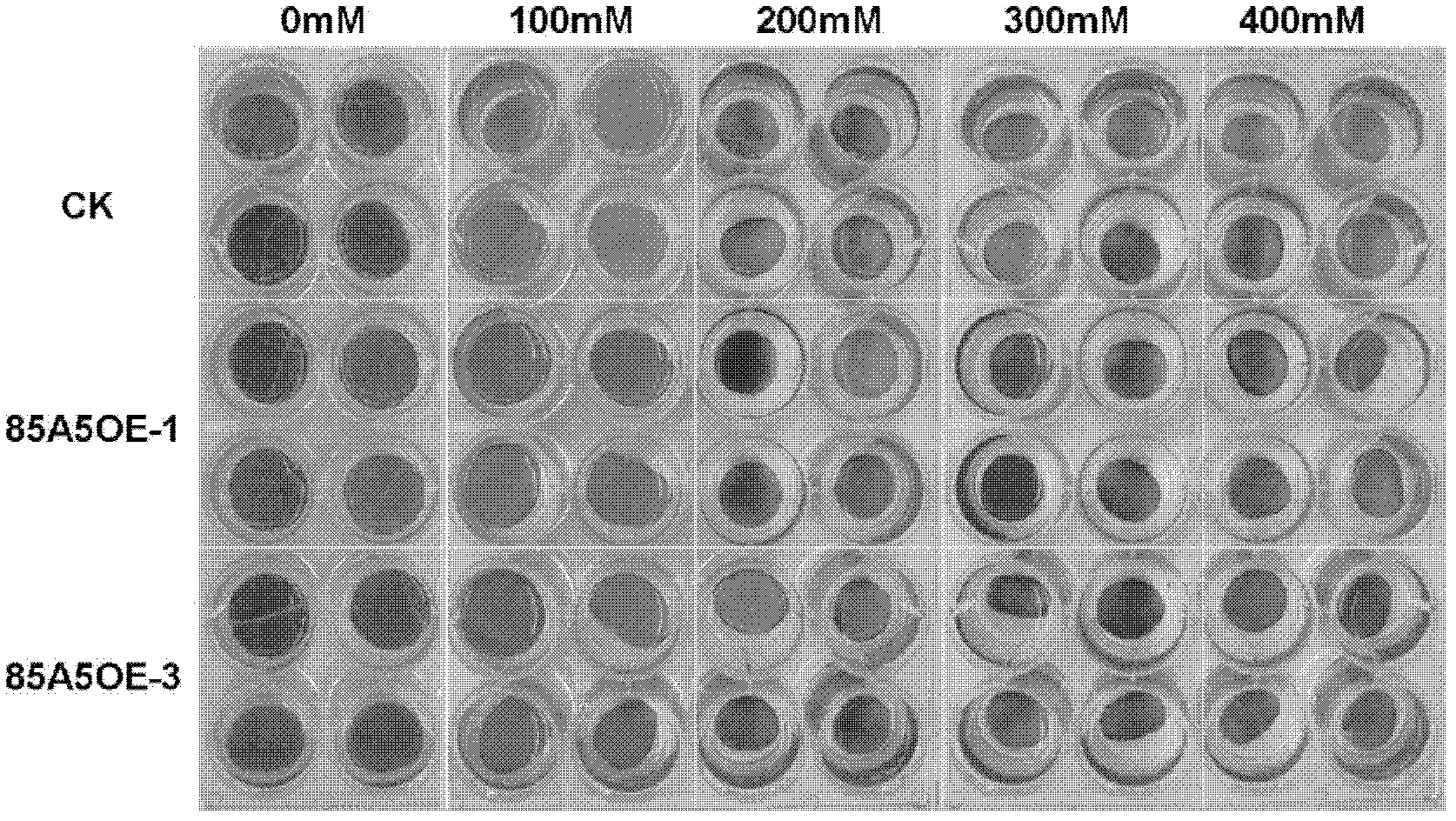
Application of glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 of Arabidopsis thaliana to improvement of salt tolerance of plants
InactiveCN102586293AImprove salt toleranceIncrease varietyFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 of Arabidopsis thaliana to the improvement of salt tolerance of plants. A nucleotide sequence of the glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 is shown as SEQ ID No.1; and the glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A5 is cloned from the Arabidopsis thaliana by a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology. The gene UGT85A5 is utilized to construct a plant overexpression vector and perform transgenic operation of the plants to obtain transgenic plants. The detection shows that the salt tolerance of the transgenic plants is remarkably improved, so that a novel salt-tolerant plant can be created after the invention is implemented; and the gene can be used for subsequent crop variety improvement, and has a great significance for the agricultural production in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene and application
The invention discloses a rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene is shown as SEQID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence asshown in SEQID NO:2 is coded. A glucosyltransferase gene sequence is screened out according to a CDS sequence provided by a rhizoma gastrodiae transcriptome, a nest type PCR primer is designed, and through amplification and splicing, an overall length sequence of the glucosyltransferase gene is obtained; a prokaryotic expression vector pGEX4T-UGT is constructed, proteins are obtained through expression and purification, a eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, subcellular localization is performed on expression of a UGT gene, glucosyltransferase is transferred into monokaryon honey mushroom mycelia by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infection method for the constructed eukaryotic expression vector pH2GW7.0 35S-UGT, transgene honey mushrooms are obtained, biosynthetic gastrodin is used,the rhizoma gastrodiae is artificially cultured by the transgene honey mushrooms, the content of gastrodin in the rhizoma gastrodiae is increased, and besides, the gastrodin can also be produced through culturing genetic engineering honey mushrooms.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
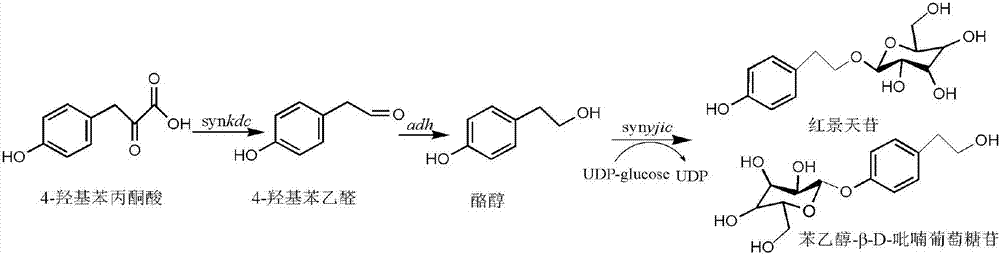
Recombinant bacteria for producing salidroside and analogue thereof, and construction method and use
InactiveCN107460203AResolve source issuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalidrosideMicrobiology
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for producing salidroside and analogue thereof, and a construction method and use. The construction method comprises the steps of synthesizing keto-decarboxylase gene synkdc and glycosyl transferase gene synyjic, and connecting to a vector pRSFDuet-1 to construct a recombinant vector pSynkdc1-yjic; enabling T7RNA polymerase gene to be free or integrated to SyBE-002447 base bacterial strain, and introducing pSynkdc1-yjic to obtain SyBE-218011 and SyBE-218013 bacterial stains; and directly integrating synkdc and synyjic to SyBE-002447 chromosome, and removing feaB and ushA in a knockout manner to obtain a SyBE-218015 bacterial strain. The bacterial strain disclosed in the invention can be used for producing salidroside and analogue thereof through fermentation, so that the problem existing in source of the salidroside and analogue thereof can be solved, and cost can be lowered.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Application of guided glycosyltransferase gene
InactiveCN109735556ASafeImprove screening efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCompetent cellFood borne
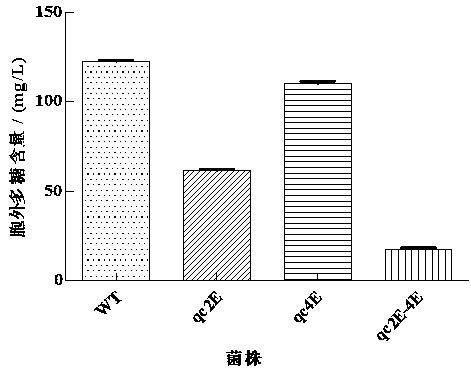
The invention discloses application of a guided glycosyltransferase gene, namely application of the guided glycosyltransferase gene cps2E and cps4E in improving lactobacillus plantarum extracellular polysaccharide synthesis; the cps2E and cps4E genes and a temperature-sensitive plasmid pFED760 are recombined to construct a knockout vector, the knockout vector is guided into food-borne lactobacillus plantarum competent cells, and then by means of homologous recombination, cps2E and cps4E genes are constructed to knock out strains YM 4-3-deltacps2E, YM 4-3-deltacps4E and YM 4-3-deltacps2E-4E; the capacity of the strains producing extracellular polysaccharide is determined through a phenol-sulfuric acid method, it is found that the capacity of knocking out extracellular polysaccharide produced by the strains is lower than that of wild type strains, and the double knockout strain extracellular polysaccharide yield is very low, so that the cps2E and cps4E genes play a key role in the extracellular polysaccharide synthesis, and the application has great potential in extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis research and application fields.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
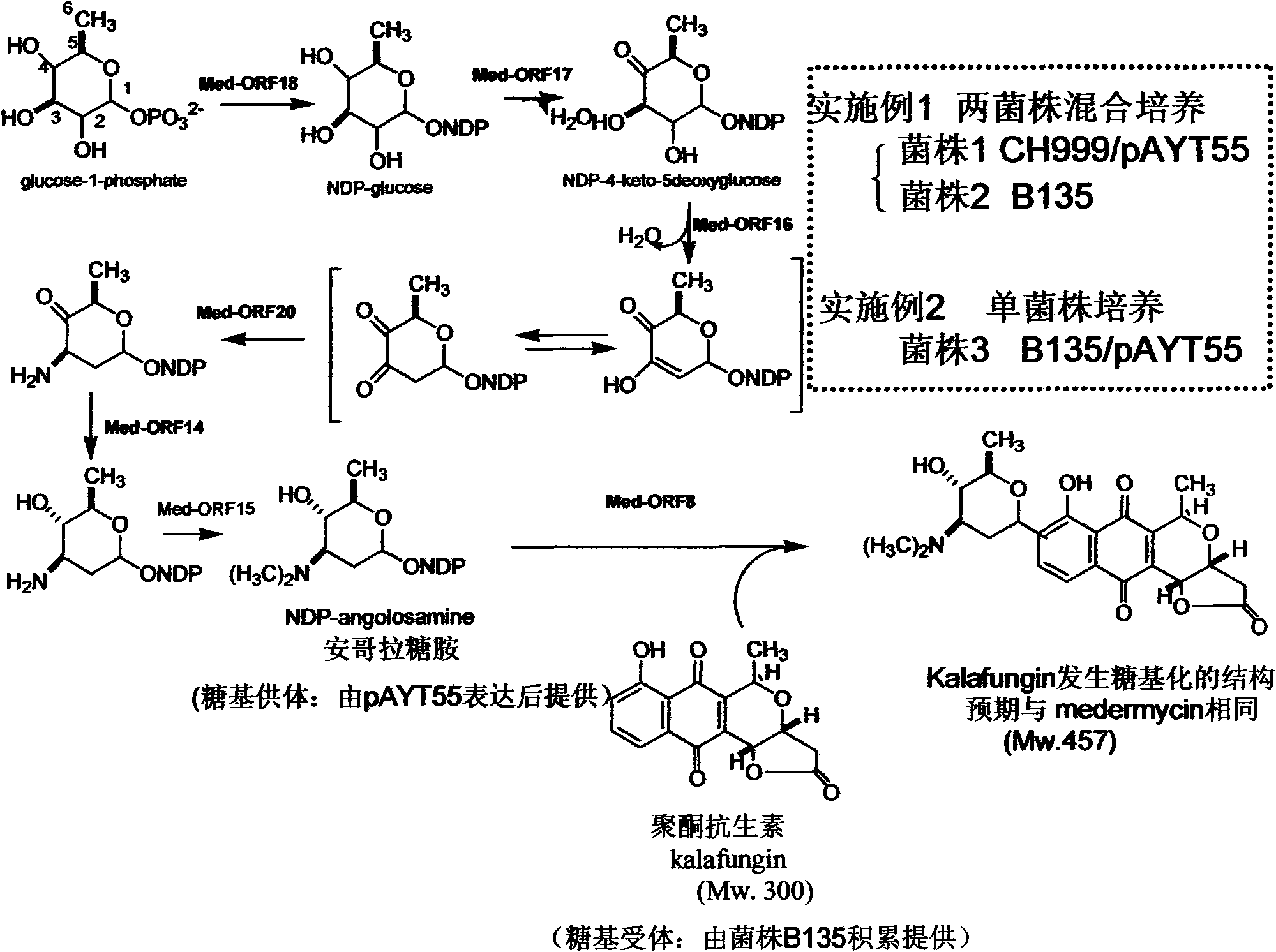
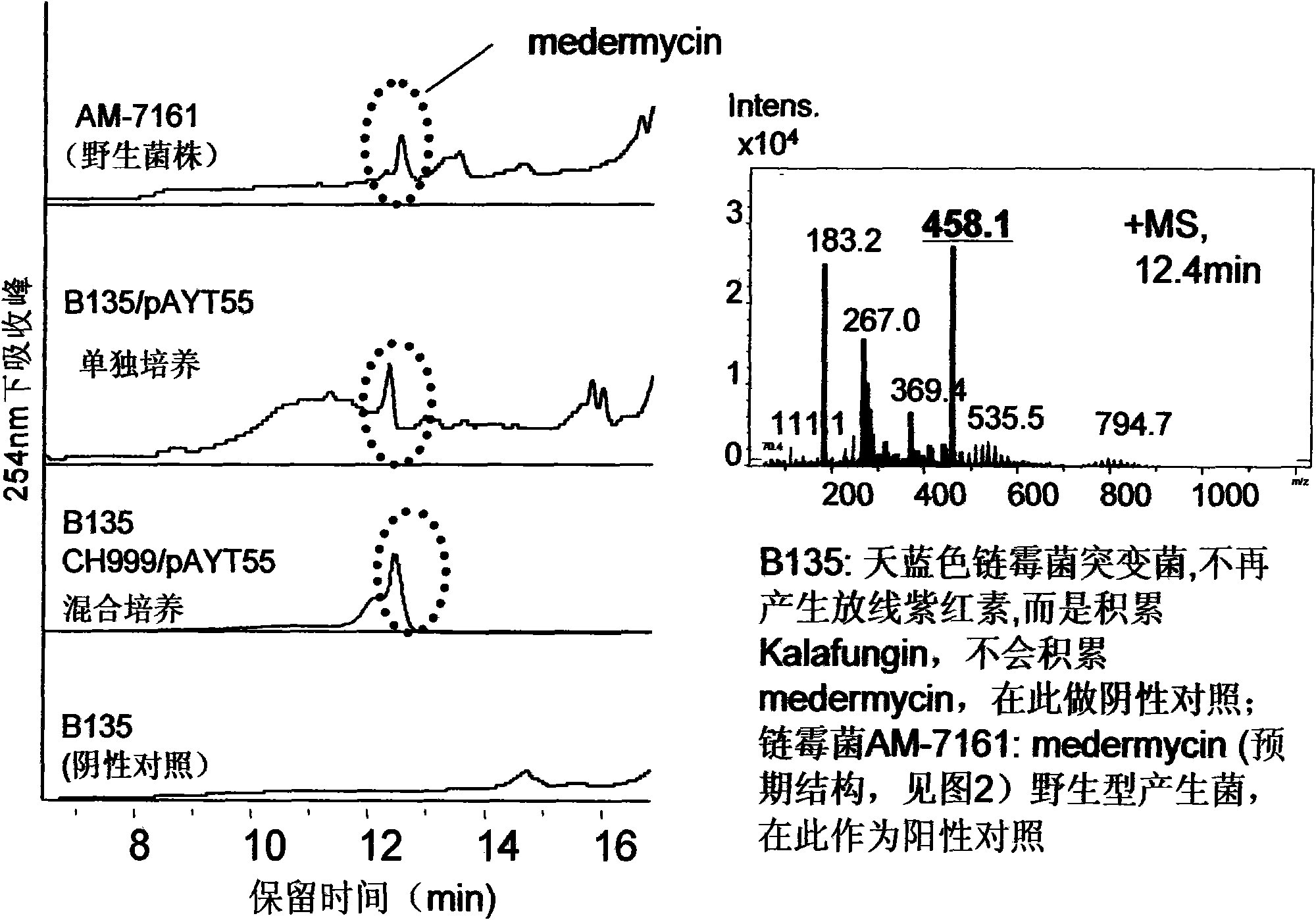
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
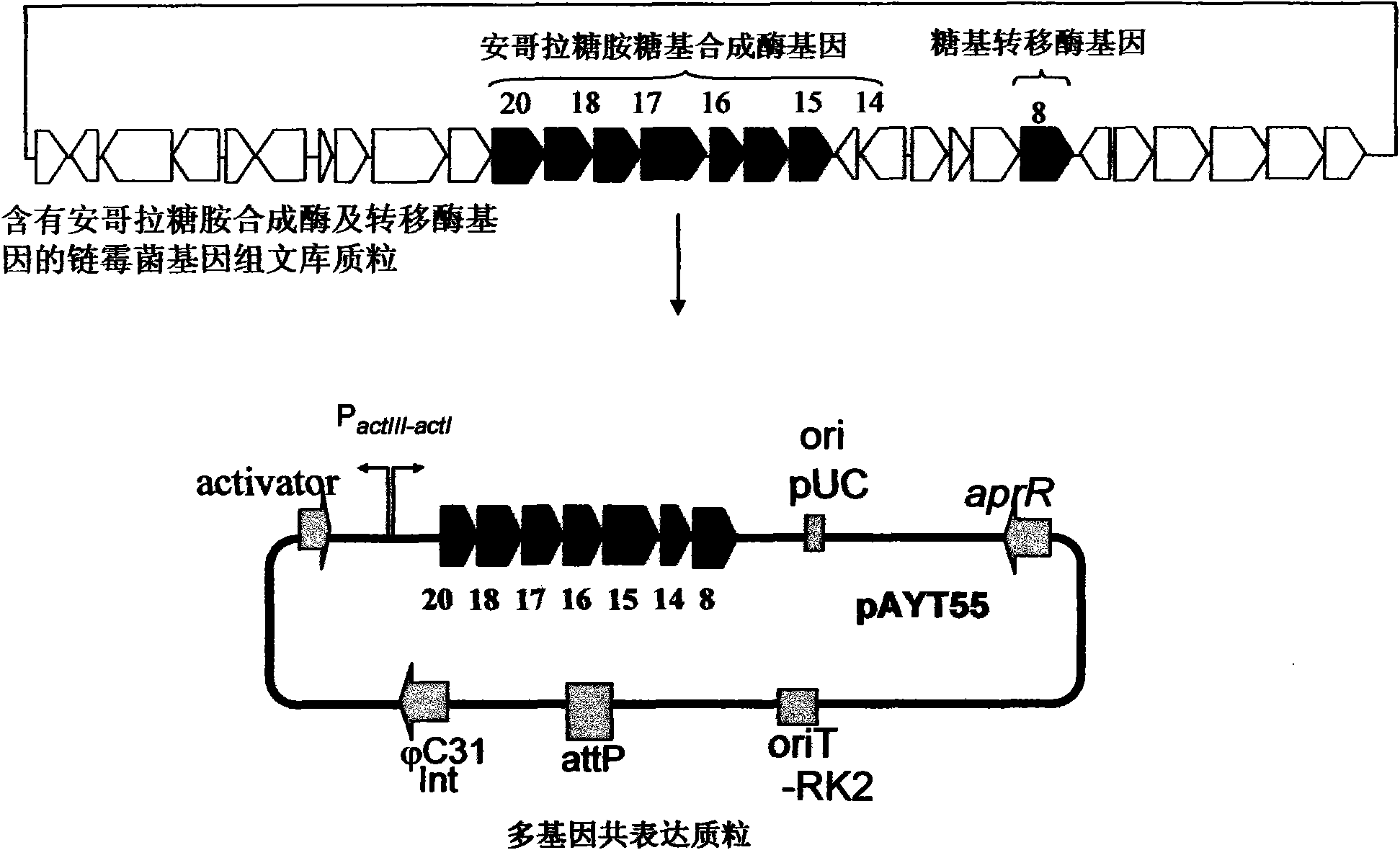
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
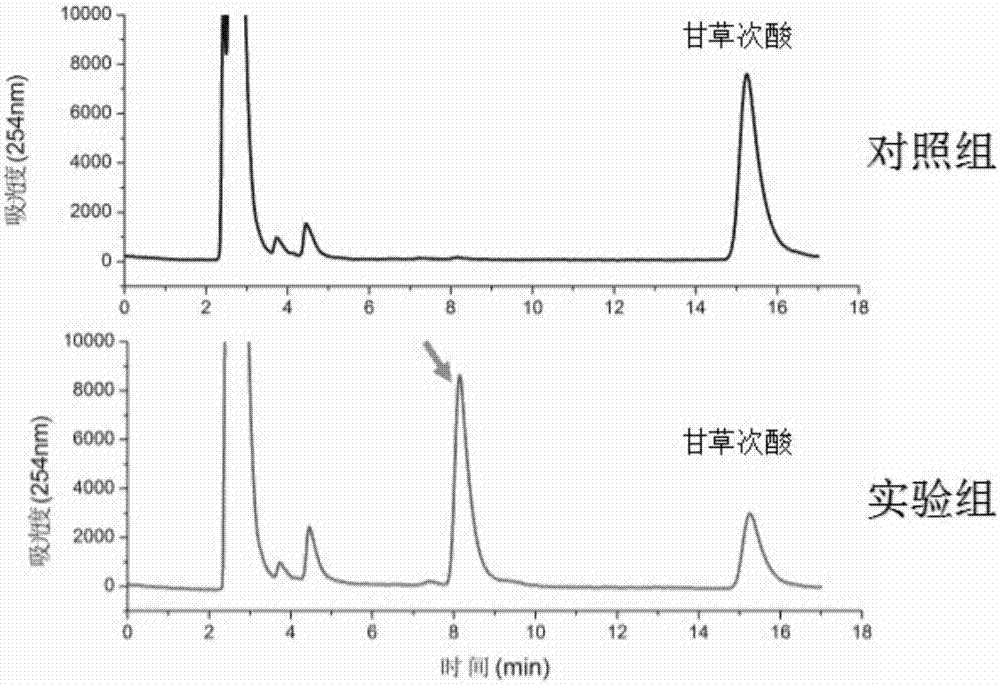
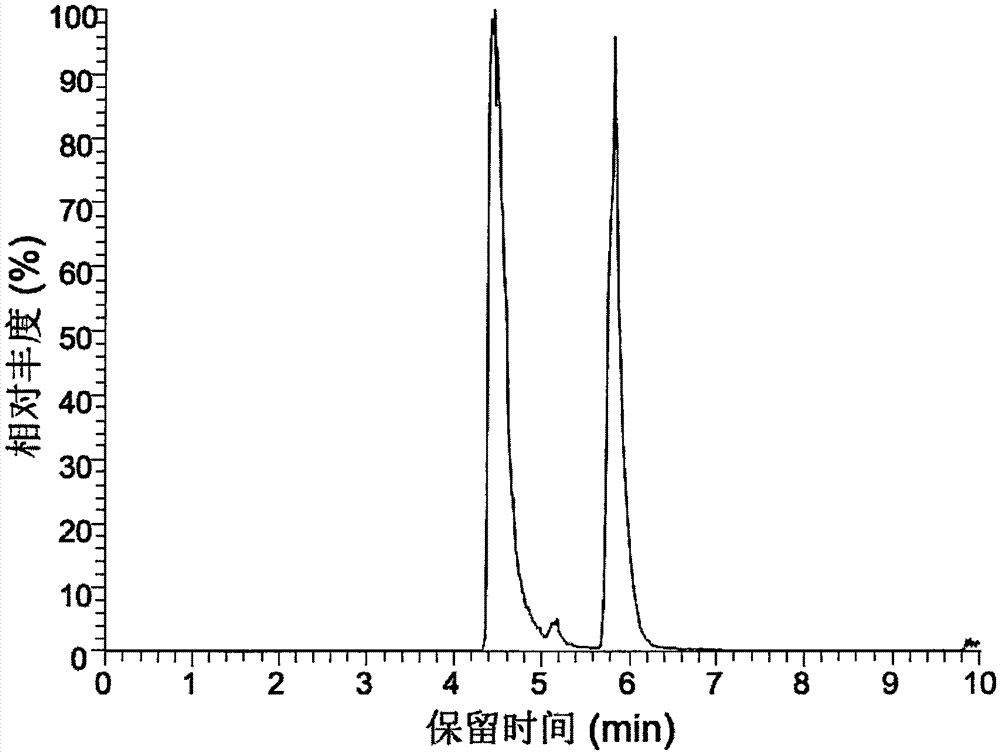
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with enzymic method
ActiveCN107502599AHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsTransferasesGenetic engineeringChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with an enzymic method and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Glycosyltransferase gene Unigene14953, Unigene20323UGT73C11, UGT73C5 and UGT73C6 from plant licorice, barbarea vulgaris or Arabidopsis are cloned or chemically synthesized, escherichia coli is preferably selected as host bacteria, and genetically engineered bacteria containing glycosyl transferase is established; recombinant glycosyl transferase serves as glycyrrhetinic acid substrate and uridine diphosphate glucose, and 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid can be synthesized efficiently in pH value of 5.0-11.0 and at the temperature of 25-55DEG C conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
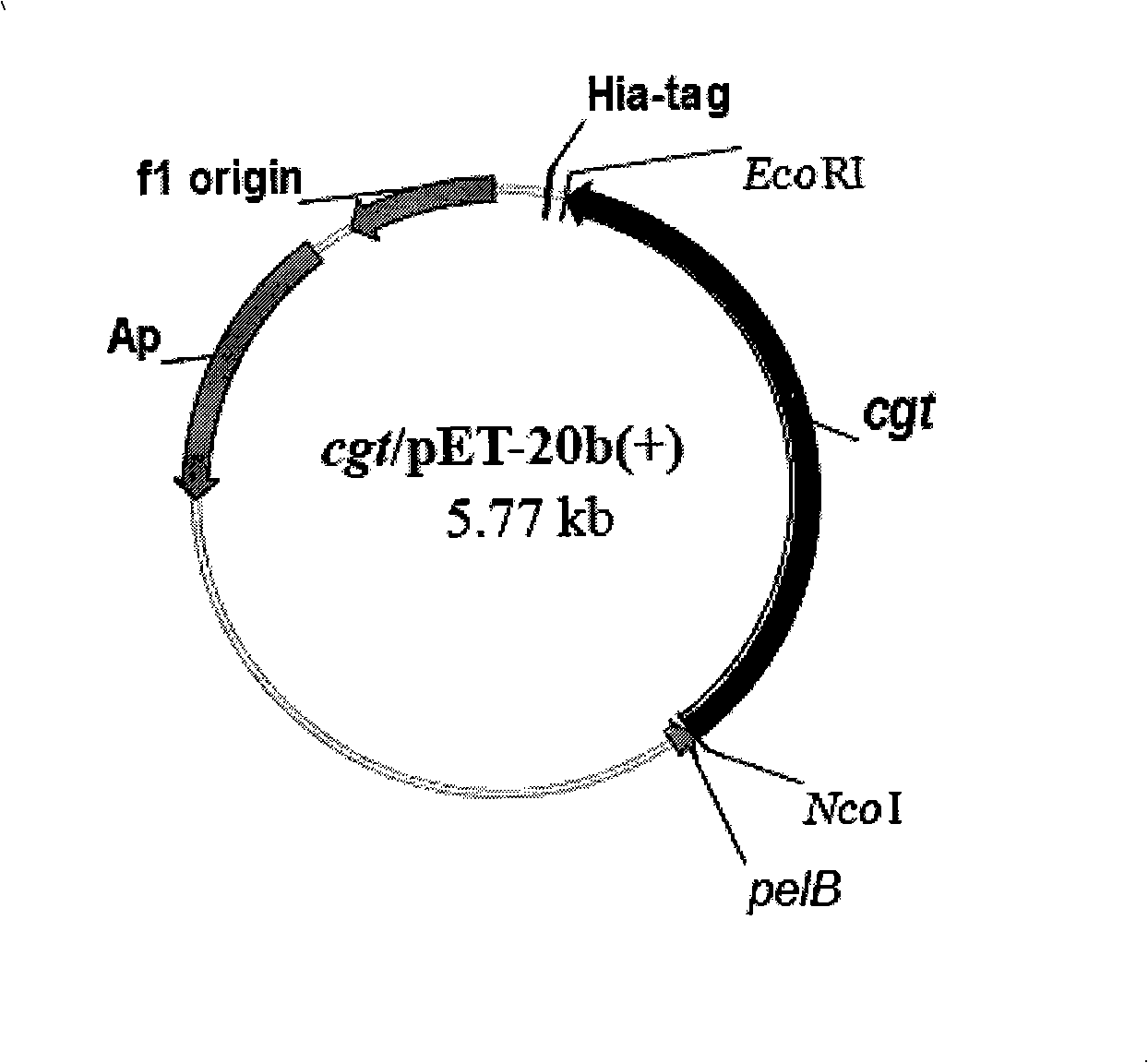
Alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and the application thereof and relates to an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene, an encoding enzyme, a carrier and an engineering bacterium which are extracted from paenibacillus macerans and the application thereof. The alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene can be connected with an expression vector to construct an expression recombinant plasmid (pET-20b(+) / cgt) containing the gene, the expression recombinant plasmid is then transferred into escherichia coli E.coil BL21, then recombinant escherichia coli is obtained, and the recombinant escherichia coli can secrete expression recombinant starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, so that cyclodextrin is prepared through biotransformation reaction with glucose polymer such as starch, glycogen and oligosaccharide as substrate.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Nucleotide specific against 0-antigen of colibacillus 0107
A nucleotide specific to the O-antigen of Escherichia coli O107 is a complete nucleotide sequence of the genom for controlling the synthesis of O-antigen in Escherichia coli O107 such as the separated nucleotide shown by SEQ ID No.1. It has 13188 bases, or has one or more inserted, deletional or substituted base but keeps the function of said separated nucleotide. It also includes the oligonucleotide of glycosyltransferase gene and oligose unit treating gene in O-antigen genom. A method for using said oligonucleotide to detect Escherichia coli O107 is also disclosed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Application of glycosyltransferase gene
InactiveCN112280795ASafeImprove screening efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideBacilli
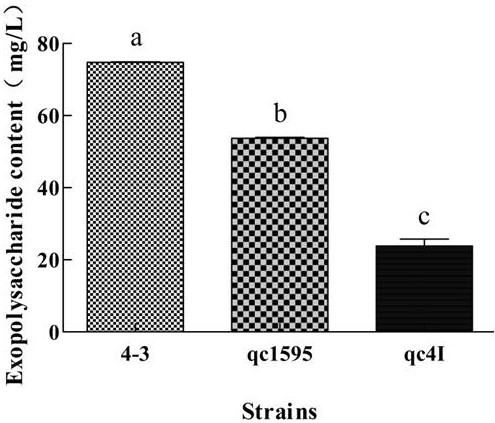
The invention discloses an application of a glycosyltransferase gene, namely an application of the glycosyltransferase gene in improving the synthesis of lactobacillus plantarum exopolysaccharides; wherein the glycosyltransferase gene is a gene orf1595 or a gene cps4I, the nucleotide sequence of the gene orf1595 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene cps4I is as shownin SEQ ID NO: 2; an orf1595 or cps4I gene and a temperature-sensitive plasmid are recombined to construct a knockout vector, the knockout vector is introduced into a food-borne lactobacillus plantarum competent cell, and then a gene knockout strain is constructed through homologous recombination; a phenol sulfuric acid method is adopted to determine the exopolysaccharide production capacity of the strain, it is found that the exopolysaccharide production capacity of the knocked-out strain is lower than that of a wild strain, orf1595 or cps4I genes play a key role in exopolysaccharide synthesis, and the method has huge potential in the fields of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis research and application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel glycosyltransferase gene
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for preparing rice humidity and temperature sensitive type male sterile material and related gene
The invention discloses a method for preparing a rice humidity and temperature sensitive type male sterile material and a related gene. The method for preparing the rice humidity and temperature sensitive type male sterile material comprises the following steps: reducing activity of a protein in a target plant, reducing the content of the protein in the target plant, inhibiting expression of an encoding gene of the protein in the target plant, or knocking off the encoding gene of the protein in the target plant, thereby obtaining a rice humidity and temperature sensitive type male sterile plant, wherein the protein is one of which an amino acid sequence A1) or A2): A1) is sequence 2 in a sequence table; and the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 in the sequence table is substituted and / or deleted and / or added by one or more amino acid residues and has proteins of same functions. By controlling a glycosyl transferase OsUGT gene and an encoding protein of the gene of rice, the rice humidity and temperature sensitive type male sterile material is obtained, and conversion of rice fertility under different humidity and temperature conditions is achieved.
Owner:ZHONGKENONGFU (BEIJING) BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Nucleotide specific against o-antigen of colibacillus 0150
A nucleotide specific to the O-antigen of Escherichia coli O150 is a complete nucleotide sequence of the genom for controlling the synthesis of O-antigen in Escherichia coli O150, such as the separated nucleotide shown by SEQ ID No:1. It has 13552 bases, or has one or more inserted, deletional, or substituted bases, but keeps the function of said separated nucleotide. It also includes the oligonucleotide of glycosyltransferase gene and oligose unit treating gene in O-antigen genom. Said oligonucleotide can be used to detect Escherichia coli O150.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Novel glycosyltransferase gene and use thereof
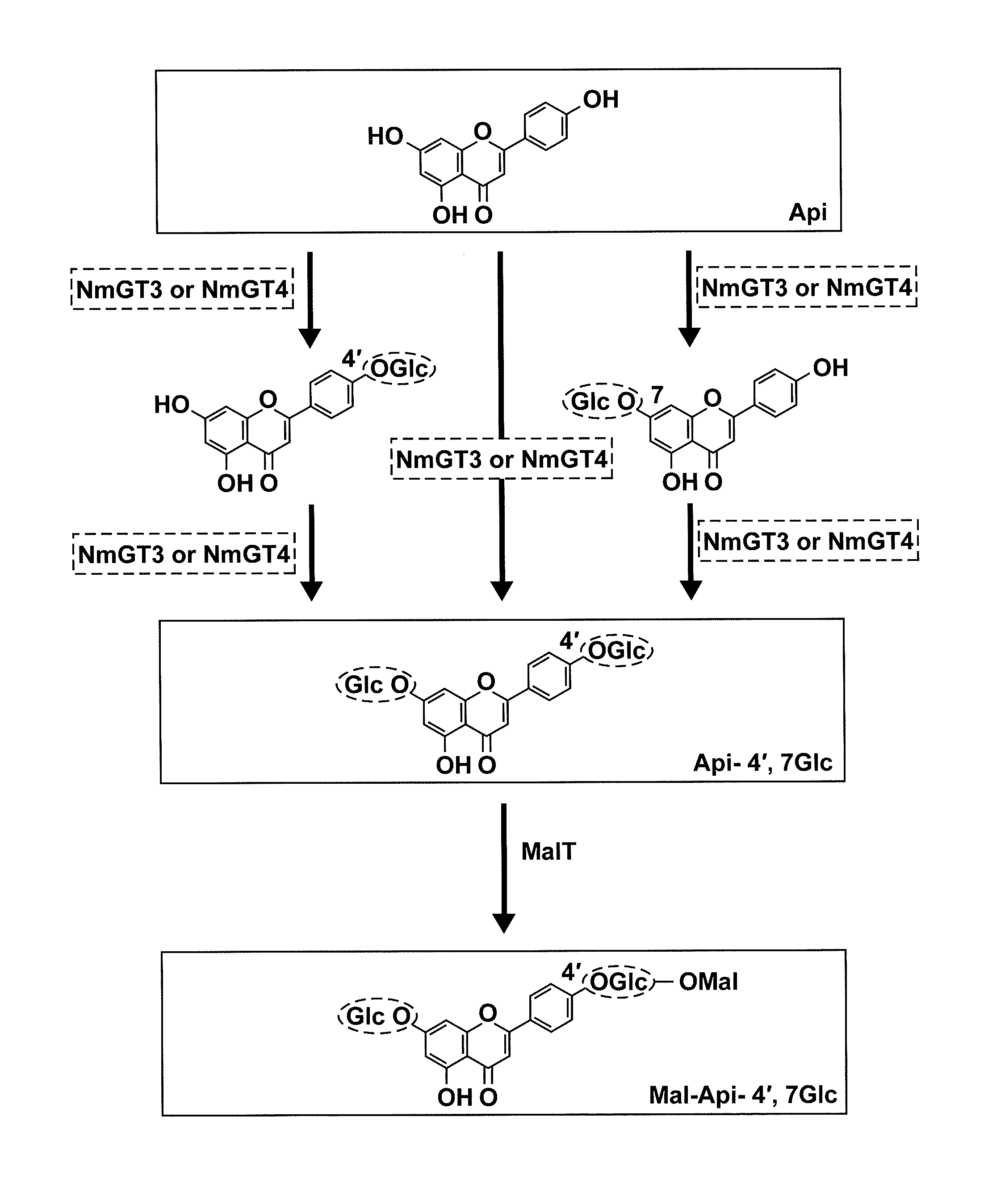
Provided is a polynucleotide encoding a protein having an activity to transfer a sugar to the hydroxy groups at the 4′- and 7-positions of a flavone. The polynucleotide is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a polynucleotide which comprises a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, or 12; (b) a polynucleotide which hybridizes to a polynucleotide comprising a base sequence complementary to a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, or 12 under high stringency conditions, and encodes a protein having an activity to transfer a sugar to the hydroxy groups at the 4′- and 7-positions of a flavone; (c) a polynucleotide which encodes a protein comprising an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, or 13; (d) a polynucleotide which encodes a protein comprising an amino acid sequence in which one or more amino acids have been deleted, substituted, inserted, and / or added in an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, or 13 and having an activity to transfer a sugar to the hydroxy groups at the 4′- and 7-positions of a flavone; etc.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Glycosyltransferase gene gtfC from Amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfC of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfC gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfC protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfC gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Glycosyltransferase gene GFTD from amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfD of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfD gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfD protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfD gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
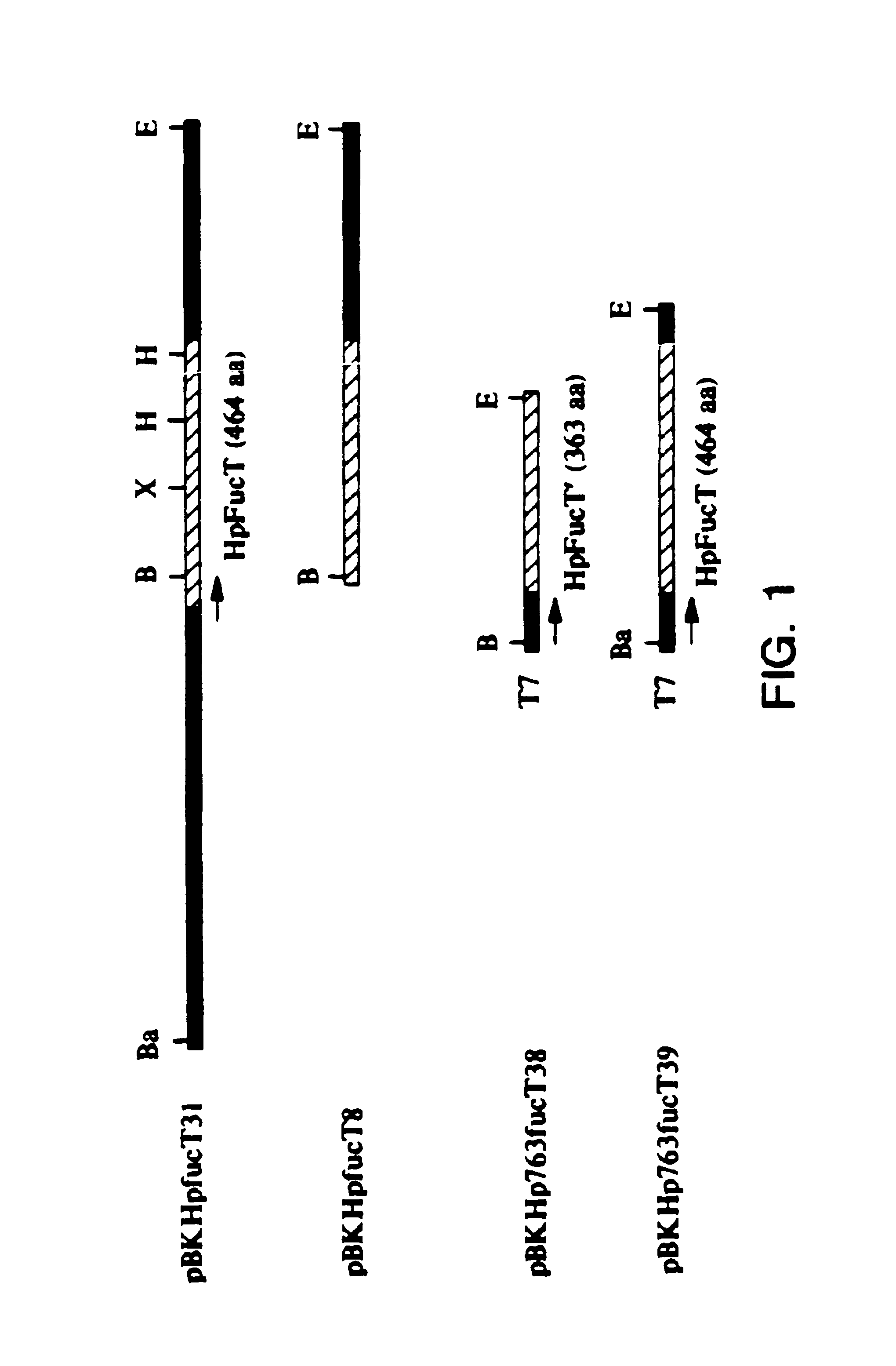
Α-1,3 fucosyltransferases and expression systems for making and expressing them
A bacterial α1,3-fucosyltransferase gene and deduced amino acid sequence is provided. The gene is useful for preparing α1,3-fucosyltransferase polypeptide, and active fragment thereof, which can be used in the production of oligosaccharides such as Lewis X, Lewis Y, and siayl Lewis X, which are structurally similar to certain tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens found in mammals. These product glycoconjugates also have research and diagnostic utility in the development of assays to detect mammalian tumors. In addition the polypeptide of the invention can be used to develop diagnostic and research assays to determine the presence of H. pylori in human specimens.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Gene chip for serotype detection of shigella and its detection process and reagent kit
InactiveCN1986830AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme GeneSerotype
The present invention relates to gene chip for serotype detection of Shigalla and its detection process and kit. The gene chip includes solid phase carrier and supported oligonucleotide probe, which includes the DNA segment selected from Shigalla 16S rRNA sequence and the DNA segment selected from oligose unit treating enzyme gene, glycosyl transferase gene or rfpB gene of one or several different serotype Shigalla O-antigen gene cluster. Through amplifying and marking the detected genome DNA with the designed primer and hybridization with the said gene chip, different serotype of Shigalla may be detected based on the hybridization signal. The present invention has simple operation, high accuracy, high repeatability and capacity of directing medicine administration.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
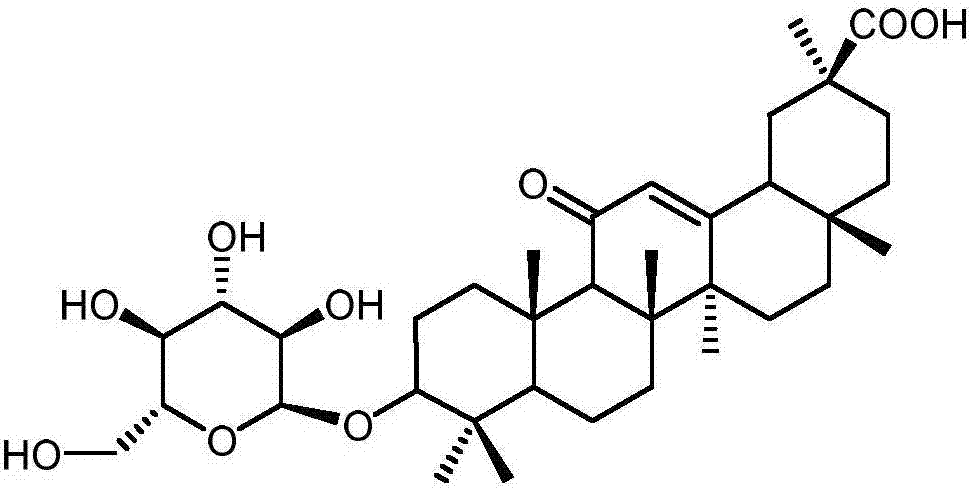
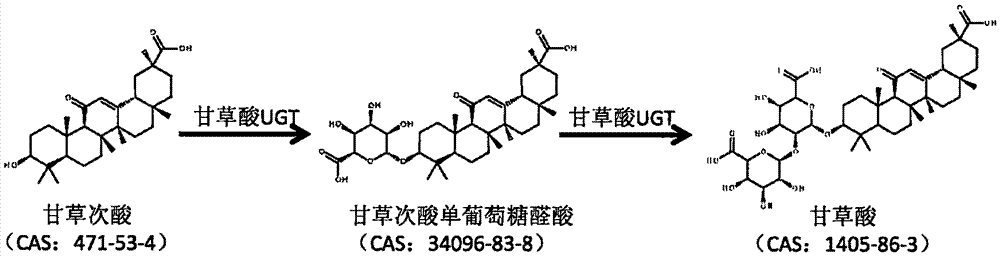
Glycosyl transferase gene participating in glycyrrhizic acid biosynthesis, and encoding product and application thereof
The invention discloses a glycosyl transferase (UGT) gene participating in glycyrrhizic acid biosynthesis, and an encoding product and application thereof, which belong to the field of medicinal plant gene engineering. The gene is obtained from radix glycyrrhizae through cloning for the first time, is a key enzyme gene for a glycyrrhizic acid anabolic route, and can directly catalyze to produce glycyrrhizic acid. A nucleotide sequence provided by the invention is represented by SEQ ID No.1, and an encoded protein sequence thereof is represented by SEQ ID No.2. The gene provided by the invention is closely related to biosynthesis of the glycyrrhizic acid, and is of great significance on adjusting the glycyrrhizic acid content in plants and artificial production of the glycyrrhizic acid.
Owner:刘春生
Glycosyltransferase gene gtfB from Amycolatopsis orientalis
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds encoding the glycosyltransferase protein GtfB of Amycolatopsis orientalis. Also provided are vectors carrying the gtfB gene, transformed heterologous host cells for expressing the GtfB protein, and methods for producing glycopeptide compounds using the cloned gtfB gene.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method for utilizing monoterpene glycosyltransferase
InactiveUS9518282B2Efficient productionEfficient extractionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycosideGlycosylation
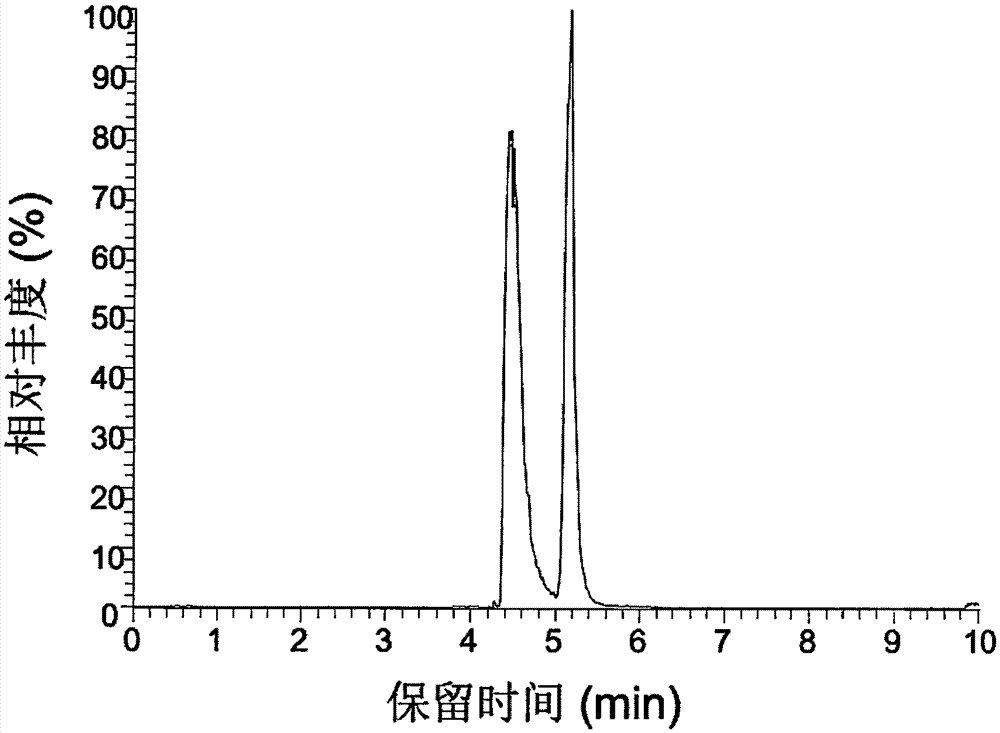
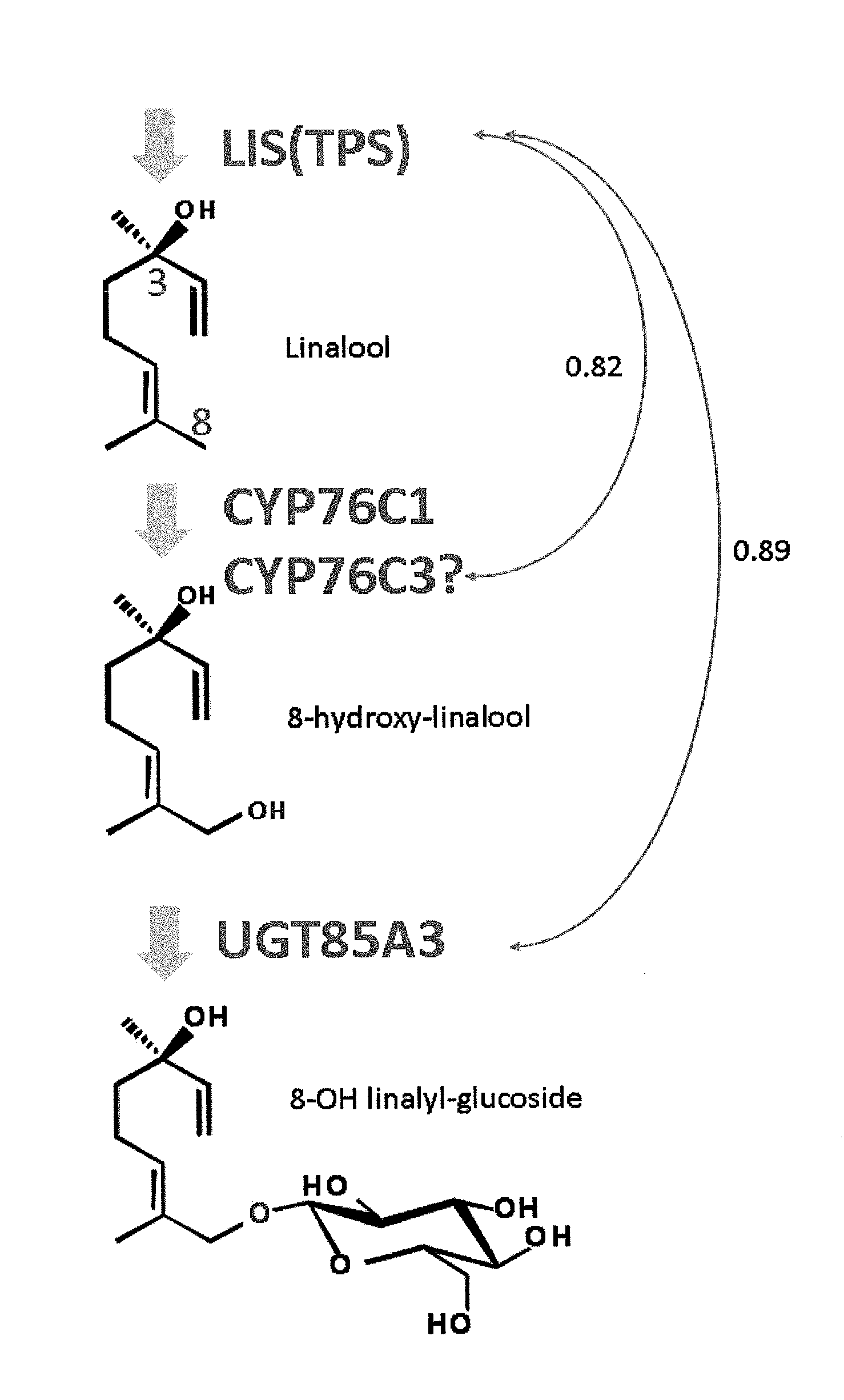
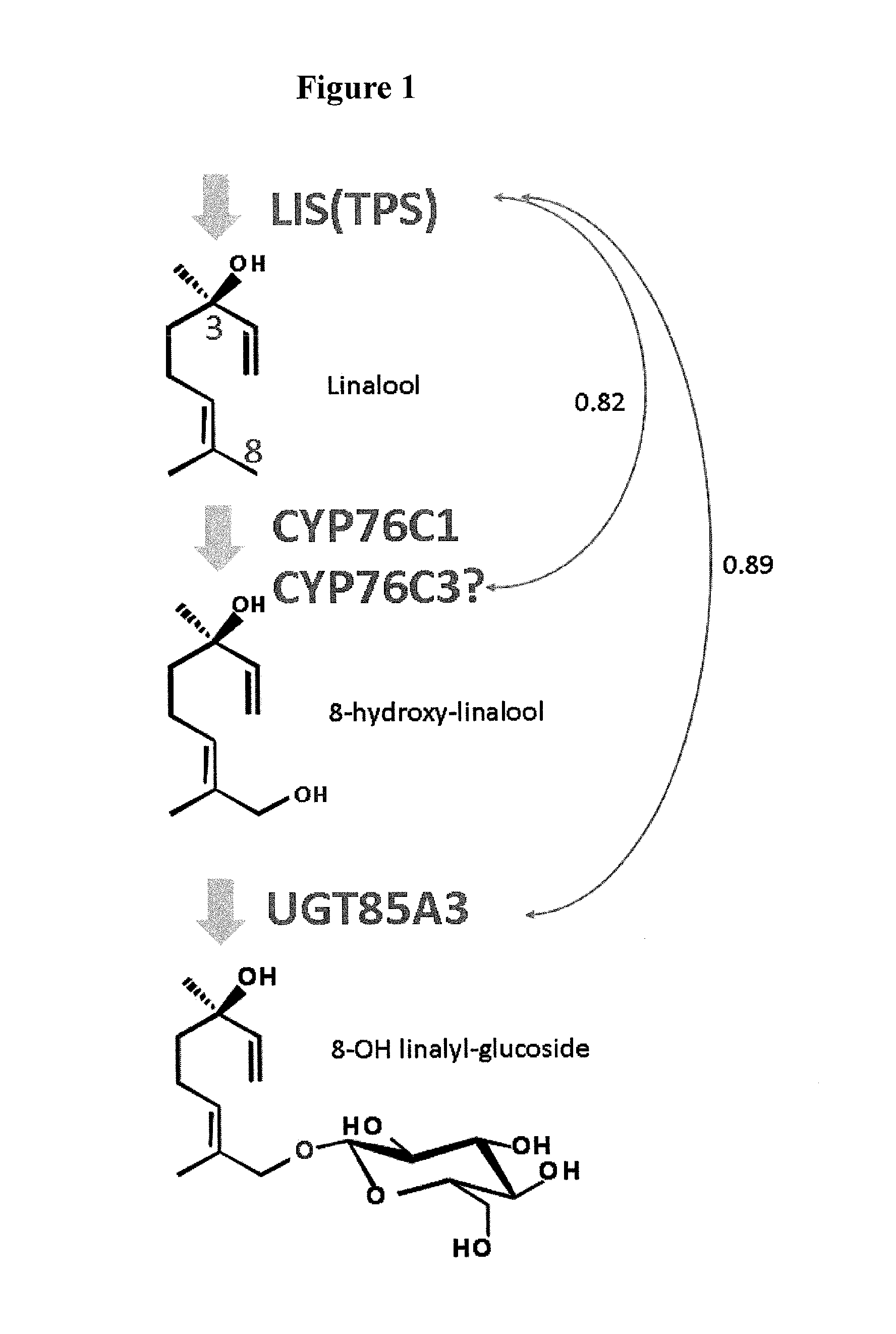
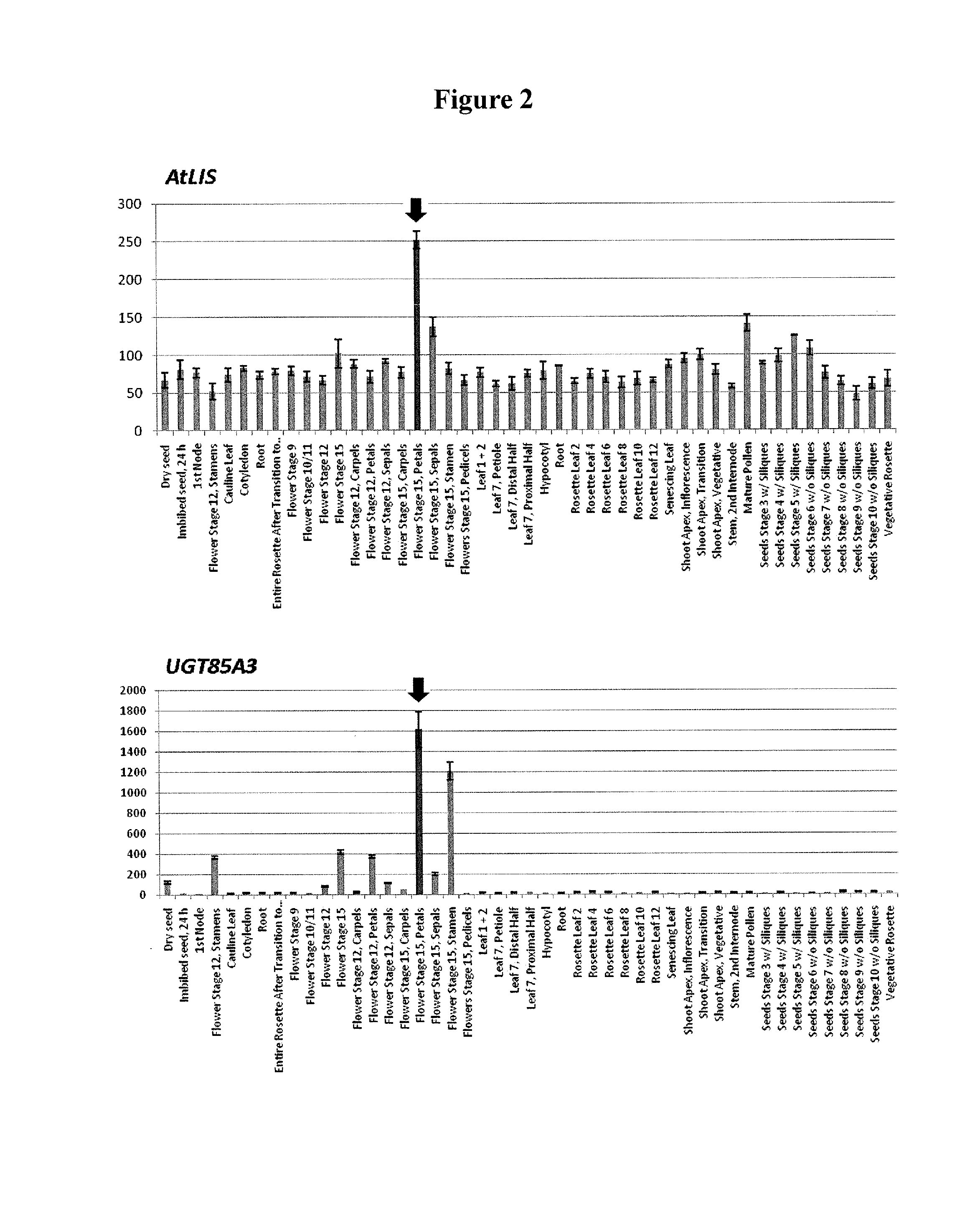
The object of the present invention is to provide a novel method for producing a terpene 8-glycoside.The present invention provides a method for producing a terpene 8-glycoside by means of glycosyltransferase acting on the 8-position of terpenes. The present invention provides a transformant transformed with a gene for the glycosyltransferase acting on the 8-position of terpenes and a method for producing such a transformant. The present invention provides a plant modified to suppress the expression of a protein having glycosylation activity on the 8-position of a monoterpene compound.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for preparing thermal reversible starch based gelatin with controllable gelatin strength by enzyme method
InactiveCN110656139AImprove temperature stabilityImprove conversion rateFermentationFood scienceEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for preparing thermal reversible starch based gelatin with controllable gelatin strength by an enzyme method, and belongs to the technical field of starch modification. The method comprises the steps of cloning 4-alpha-Glyt (Tu alpha GT) in Thermoproteus uzoniensis (Thermoproteus uzoniensis), performing escherichia coli heterologous expression, performing enzymology nature characterization, and determining that the 4-alpha-Glyt (Tu alpha GT) is 4 alpha GT, the enzyme has good temperature stability and substrate tolerance, high-concentration starch can be catalyzed at high temperature for modification, and the side chain of branched chain starch can be prolonged. According to the method for preparing thermal reversible starch based gelatin with controllablegelatin strength by an enzyme method, the starch is used as the raw material, an appropriate amount of the 4-alpha-Glyt is added, an appropriate additive quantity and appropriate action time are selected, and the high strength anabiotic resisting starch based gelatin can be prepared.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com