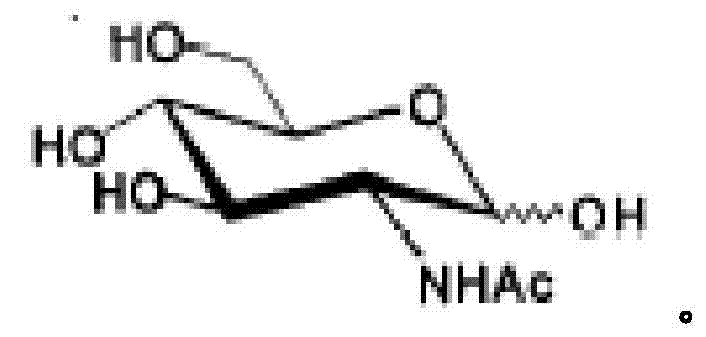
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and acetylamino, which is applied in the field of genetically engineered bacteria for efficient production of N-acetylglucosamine, can solve problems such as unstable enzyme activity of glucosamine 6-phosphate synthase, and achieve broad industrial application prospects and stability. Good, high fermentation yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 , Construction of recombinant plasmid pET28a-glmS
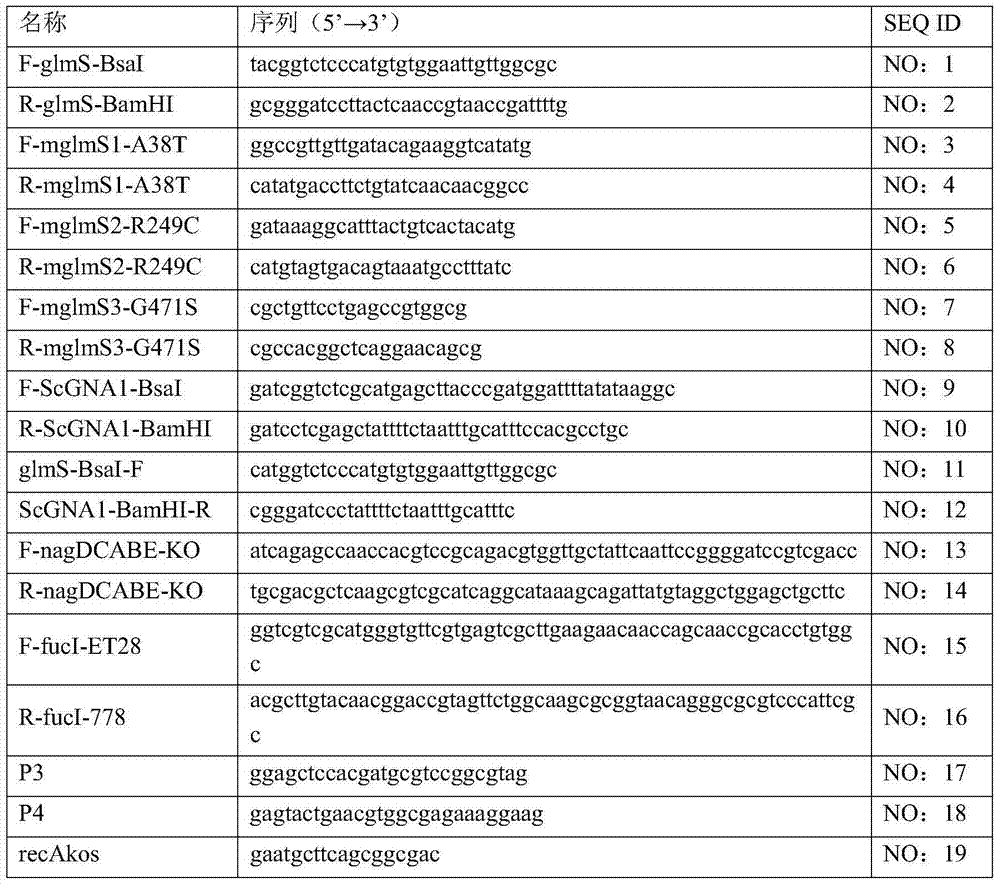
[0045] The wild-type glucosamine 6-phosphate synthase gene glmS is derived from Escherichia coli W3110, NCBI accession number: 89106884, and the size is 1830bp. Using the Escherichia coli W3110 genome as a template, use F-glmS-BsaI and R-glmS-BamHI primers to perform PCR amplification to obtain the glmS gene. After the amplified product is recovered, it is digested with BsaI and BamHI, and pET-28a(+) vector The plasmid was double-digested with NcoI and BamHI, and the above two fragments were ligated, transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells and screened for kanamycin resistance to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET28a-glmS.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 , Construction of recombinant plasmid pET28a-mglmS
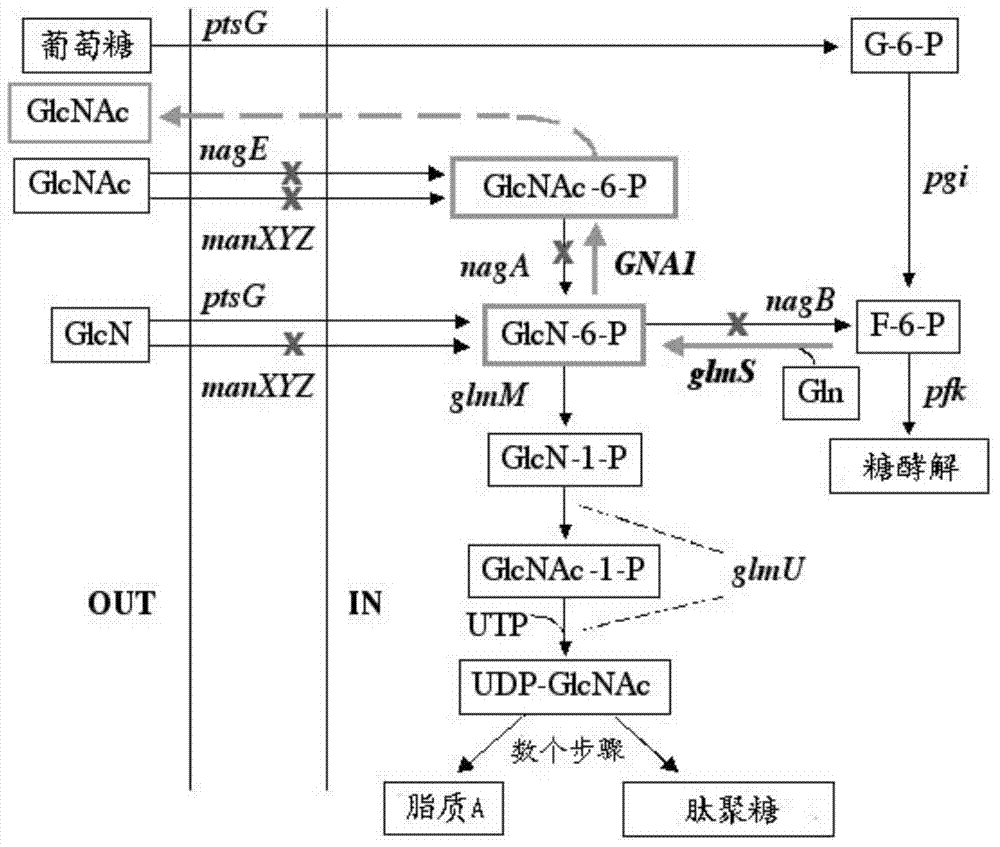
[0047] According to literature reports (Deng MD, Severson DK, Grund AD, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for industrial production of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. Metabolic Engineering, 2005, 7:201-214), wild-type glucosamine 6-phosphate Synthetase activity is subject to feedback inhibition by the metabolite glucosamine-6-phosphate of this synthetic pathway, which is one of the key factors for the limited production of N-acetylglucosamine.
[0048] GlmS (A38T / R249C / G471S) is a mutant that can tolerate glucosamine inhibition and can increase the yield of the final product. Therefore, on the basis of cloning wild-type glmS, glmS was subjected to site-directed mutation to obtain glmS (A38T / R249C / G471S) mutant, named mglmS.
[0049] The experimental operation of site-directed mutagenesis at A38T site is as follows:
[0050]Using the recombinant plasmid pET28a-glmS as a template, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 , Construction of recombinant plasmid pET28a-ScGNA1
[0053] N-acetylglucosamine transferase gene ScGNA1 is derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast), NCBI accession number: 4115732, with a size of 480bp. Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome as a template, use F-ScGNA1-BsaI and R-ScGNA1-BamHI primers to perform PCR amplification to obtain the ScGNA1 gene. After the amplified product is recovered, it is double-digested with BsaI and BamHI and used for pET-28a(+) plasmid NcoI and BamHI double digestion, the above two fragments were ligated, transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells and screened for kanamycin resistance to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET28a-ScGNA1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com