Rapid screening system for Lactococcus lactis with knocked-in exogenous genes as well as construction method and application of rapid screening system
A technology of Lactococcus lactis and exogenous genes, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of heavy workload, time-consuming and laborious, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
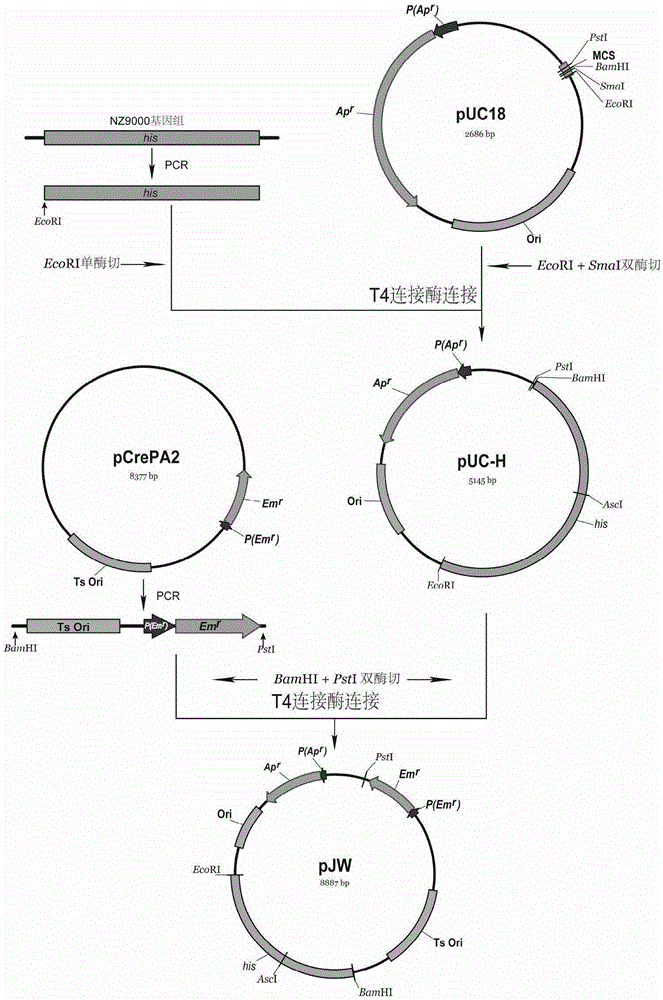
[0065]Example 1: Construction of thermosensitive plasmid pJW.
[0066] 1) Primer design: according to the NZ9000 genome his gene sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2), Ts-Em r Fragment sequence (SEQIDNO: 5) design PCR primer, base sequence is as follows:
[0067] Primer name
Primer sequence (underlined is the introduced restriction site)
Restriction sites
HisF
AAA GAATTC TAAAGTAATTTTCATCAATTTTTTCTAAGC
His R
GTTTGGGAGTCGCCTTTGGCTC
-
Tf
AAA GGATCC TGATCGTTAAATTTATACTGCAAT
TT
AAA CTGCAG TACCTAATAATTTATCTACATTCCC
PstI
[0068] 2) PCR amplification of his gene: using NZ9000 genomic DNA as a template, PCR was performed with primers HisF (SEQ ID NO: 18) and HisR (SEQ ID NO: 19) to amplify his gene, the method is as follows:
[0069] The reaction system of PCR is:
2×PrimerS TAR Max Premix
25 μL
NZ9000 genome
1μL
Primer HisF (20μM)
1μL
Pri...
Embodiment 2
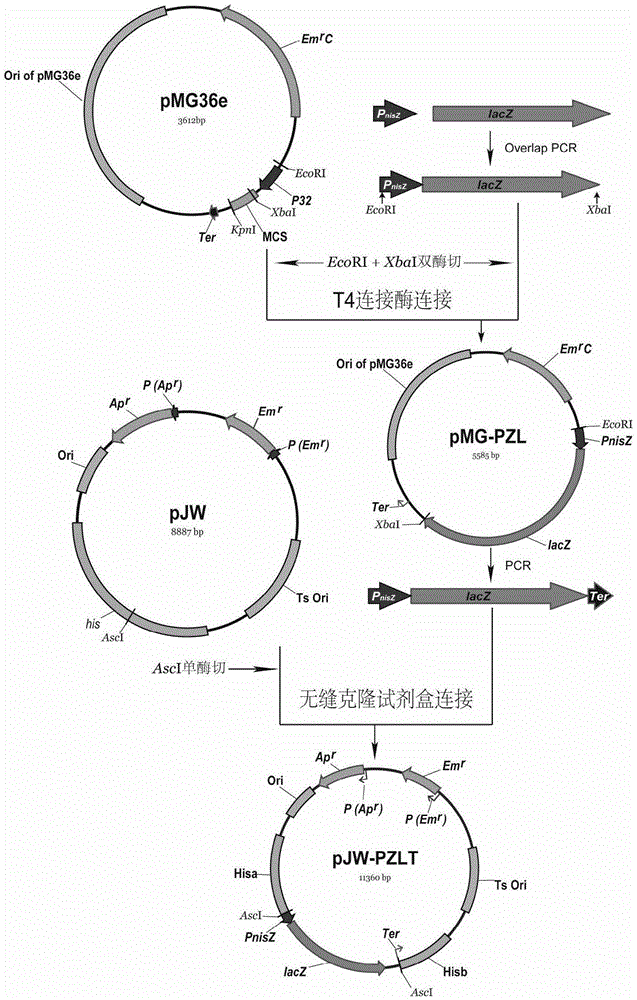
[0079] Example 2 Construction of the knock-in vector pJW-PZLT of the lacZ gene expression sequence (PZLT fragment).
[0080] 1).P nisZ Fragment Synthesis: According to P nisZ Promoter sequence (SEQ ID NO: 6), synthesized by Huada Gene promoter P nisZ and cloned into the pEASY plasmid to construct the plasmid pEASY-P nisZ .
[0081] 2). OverlapPCR to obtain the PZL fragment:
[0082] (1). Primer design: according to P nisZ Sequence, Lactobacillus acidophilus β-galactosidase lacZ gene sequence (SEQ ID NO: 7) designed OverlapPCR primers, the base sequence is as follows:
[0083]
[0084] Among them, PZR and LF have a 30bp complementary sequence.
[0085] (2). With pEASY-P nisZ The plasmid was used as a template, and PCR was carried out with primers PZF (SEQ ID NO: 22) and PZR (SEQ ID NO: 23) to amplify P nisZ Fragment, the method is as follows:
[0086] The reaction system of PCR is:
2×PrimerSTAR Max Premix
25 μL
pEASY-P nisZ plas...
Embodiment 3
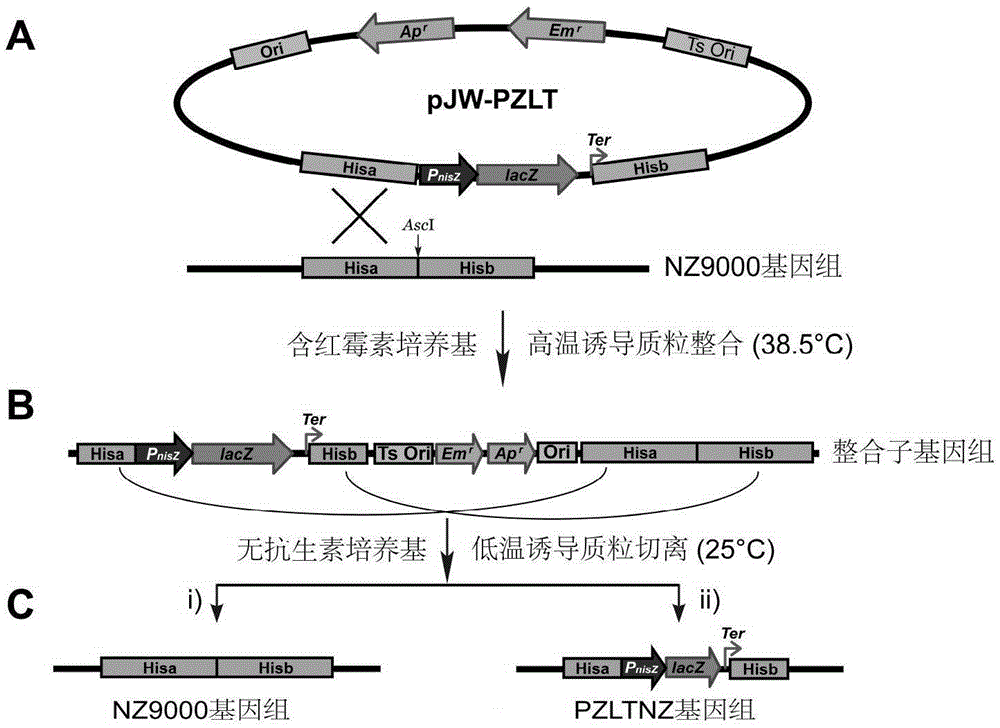
[0105] Example 3 Construction, screening and identification of Lactococcus lactis NZ9000 strain PZLT fragment knock-in strain
[0106] 1). Preparation of Lactococcus lactis electroporation competent cells:
[0107] The recipient bacterium Lactococcus lactis (NZ9000) was inoculated in M17GS medium, and after static culture at 30°C overnight, inoculated with SGM17 medium at a ratio of 1:100, and cultured statically at 30°C until the bacterial solution OD 600 = 0.2 to 0.3 (about 4 hr). The bacterial solution was quickly cooled on ice for 30 minutes, refrigerated and centrifuged at 3200g for 30 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant was discarded. Place the bacteria on ice, gently resuspend with about 200mL pre-cooled GS solution, centrifuge at 3200g, 4°C for 20min, discard the supernatant; repeat the above step twice (the GS solution is reduced to 100mL and 50mL respectively). Add 1 mL of GS solution to the bottom of the bacteria to resuspend, and use immediately after aliquoting ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com