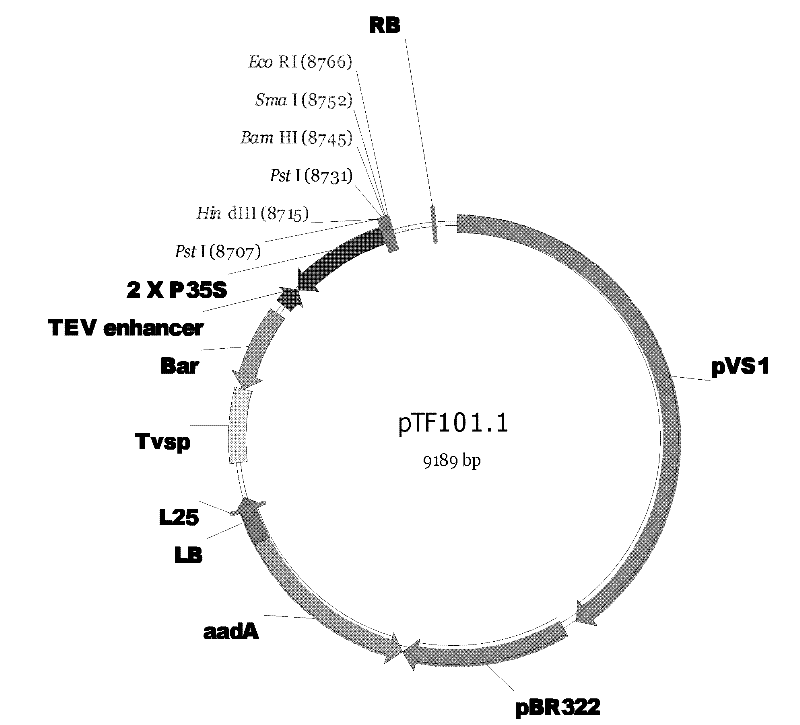
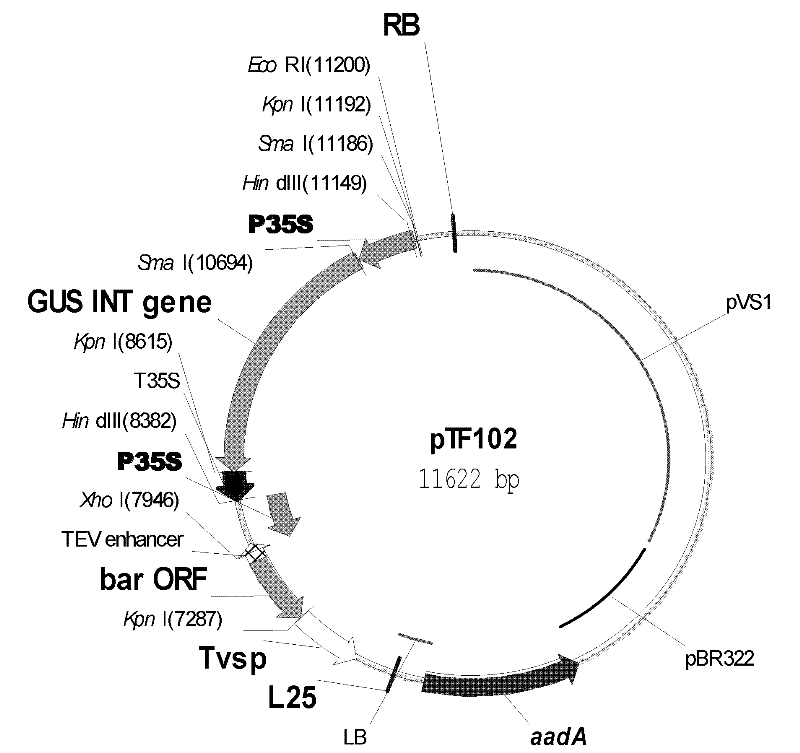
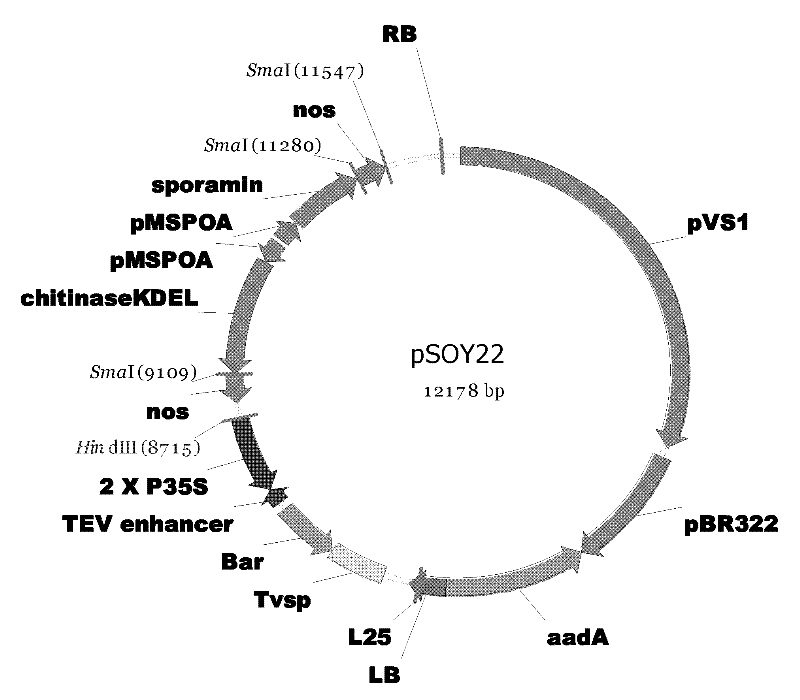
In-vitro tissue culturing method for soybeans under mediation of agrobacterium tumefaciens
A technique of Agrobacterium-mediated tissue culture, applied in the field of soybean in vitro tissue culture, can solve the problems of difficult plant regeneration chimeras, plant growth inhibition, and affect plant metabolism, so as to improve the efficiency of soybean Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, repeat Good sex, increase the effect of bud induction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1. Effect of LA on GUS Transient Expression Rate of Soybean Cotyledon Node Explants
[0048] In this experiment, the soybean variety "Yuechun 04-5" was used to explore the effect of different concentrations (0mg / L; 25mg / L; 50mg / L; 75mg / L; 100mg / L) of LA on the transient expression of GUS mediated by Agrobacterium cotyledons. influences. Soybean cotyledon node explants germinated for 1 day were infected with the pTF102 vector containing the GUS gene and the glufosinate selection marker gene of Agrobacterium EHA101 for 30 minutes, and LA was added at different concentrations in the co-cultivation medium, and after 3 days of co-cultivation, Statistical analysis of Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression rate of GUS in cotyledonary nodes. When the LA concentration was 25mg / L and 50mg / L, the GUS transient expression rate of the explant was higher; and when the LA concentration was increased to 75mg / L and 100mg / L, the GUS transient expression rate decreased signi...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2, LA on soybean cotyledon node explant browning and bud induced regeneration
[0050] The soybean cultivar Yuechun 04-5 was used to explore the effects of different concentrations of LA on bud regeneration of soybean cotyledonary node explants. We found that soybean cotyledon node explants germinated for four days were infected with Agrobacterium LBA4404 without plasmid for 30 minutes, and after adding different concentrations of LA (0mg / L; 25mg / L; 50mg / L; 75mg / L; After 3 days of co-cultivation in the co-culture medium of L), the growth of the explants was obviously different. Such as Figure 4 Different concentrations of LA have a great influence on the growth of cotyledonary node explants. With the increase of LA concentration in the co-culture medium, the browning degree of explants is significantly reduced. When the LA concentration reaches 50mg / L, we found that the explants The hypocotyl curls to the inside, and the higher the concentration, the higher t...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3, Effects of Different Types of Antioxidants on the Transient Expression of Soybean Cotyledon Node Explant Buds
[0052] Soybean cotyledon nodes of soybean variety Yuechun 04-5 germinated for 3 days were used as explants, and the pTF102 vector containing GUS gene and glufosinate selection marker gene of Agrobacterium EHA101 was infected for 30 minutes, and different antibiotics were added to the co-culture. Oxidant such as 25mg / L LA ( Figure 5 -A); 3.3mM cysteine (CYS)+3.3mM dithiothreitol (DTT) ( Figure 5 -B); 3.3mM CYS+3.3mM DTT+30μMAg 2 S 2 o 3 ( Figure 5 -C) and 30 μM Ag 2 S 2 o 3 ( Figure 5 -D) and the control group without any antioxidant ( Figure 5 -E) After 3 days of co-cultivation, the effects of different antioxidants on soybean transformation were determined by measuring the transient expression rate of GUS. Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the transient expression rate of GUS was 75.56% when 25mg / L LA was added to the co-cultu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com