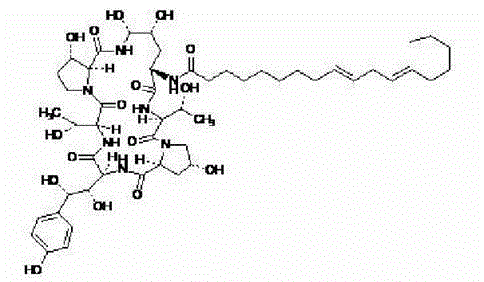
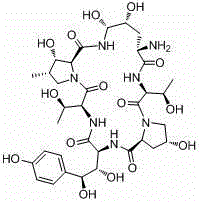
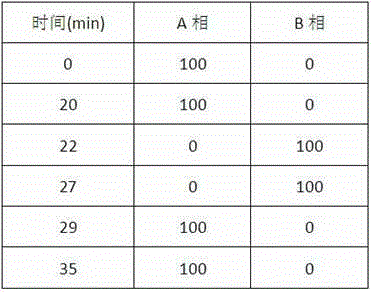
A microbial enzymatic conversion method for echinocandin B
An echinocandin and its conversion technology can be used in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., and can solve problems such as negative effects on deacylase activity, cumbersome crude enzyme extraction process, and unfavorable scale-up production. To achieve the effect of less negative impact on enzyme activity, favorable for separation and purification, and good commercial value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Fermentation and Crude Enzyme Production of Echinocandin B Deacylase Strain
[0040] Strain: Streptomycesalbus (Streptomycesalbus), preservation number: ATCC21725; -80°C cryopreservation;
[0041] Seed medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 0.5%, yeast powder 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1%, pH about 6.8~7.2, culture at 30°C for 1~2 days;
[0042] Fermentation medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 1%, yeast powder 1%, peptone 1%, glucose 3%, sodium chloride 0.5%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1%, pH about 6.8~7.2 , cultured at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0043] Inoculate the genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces albicans into the seed medium, culture at 30°C for 1-2 days, then inoculate 5% of the fermentation volume in the fermentation medium, and culture at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0044] After the fermentation is completed, the fermentation broth is filtered to obtain a supernatant, ammonium sulfate is added according to...
Embodiment 4
[0062] Example 4 Fermentation and Crude Enzyme Production of Echinocandin B Deacylase Strains
[0063] Strain: Streptomycesalbus (Streptomycesalbus), preservation number: ATCC21725; -80°C cryopreservation;
[0064] Seed medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 0.5%, yeast powder 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1%, pH about 6.8~7.2, culture at 30°C for 1~2 days;
[0065] Fermentation medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 1%, yeast powder 1%, peptone 1%, glucose 3%, sodium chloride 0.5%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1%, pH about 6.8~7.2 , cultured at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0066] Inoculate the genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces albicans into the seed medium, culture at 30°C for 1-2 days, then inoculate 5% of the fermentation volume in the fermentation medium, and culture at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0067] After the fermentation is completed, filter the fermentation broth to obtain a supernatant, add sodium chloride according to 40% (w / v...
Embodiment 6
[0078] Example 6 Fermentation and Crude Enzyme Production of Echinocandin B Deacylase Strain
[0079] Strain: Streptomycesalbus (Streptomycesalbus), preservation number: ATCC21725; -80°C cryopreservation;
[0080] Seed medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 0.5%, yeast powder 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1%, pH about 6.8~7.2, culture at 30°C for 1~2 days;
[0081] Fermentation medium: hot fried soybean cake powder 1%, yeast powder 1%, peptone 1%, glucose 3%, sodium chloride 0.5%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1%, pH about 6.8~7.2 , cultured at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0082] Inoculate the genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces albicans into the seed medium, culture at 30°C for 1-2 days, then inoculate 5% of the fermentation volume in the fermentation medium, and culture at 30°C for 2-3 days;
[0083] After the fermentation is completed, filter the fermentation broth to obtain a supernatant, add sodium sulfate according to 80% (w / v) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com