Method for converting echinocandin B by using microbial enzyme
An echinocandin, conversion technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effects of easy separation and purification, improved yield and purity, and high molar conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1), fermentation of echinocandin B deacylase
[0040] Strains: Actinoplanes utahensis NRRL12052, purchased from the American Agricultural Research Culture Collection.
[0041] Medium formula:
[0042] Slant medium: yeast powder 0.3%, malt extract powder 0.3%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1.0%, agar 2.5%, pH 7.0-7.2, cultured at 30°C for 5-7 days
[0043] Seed medium: sucrose 2.5%, oat flour 2%, yeast powder 0.25%, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, KCl 0.05%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.0002%, pH=6.8, cultured at 30°C for 4-5 days
[0044] Fermentation medium: 2.5% sucrose, 1.2% peanut meal powder, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.3%, pH=6.8, cultivated at 30°C for 3-4 days
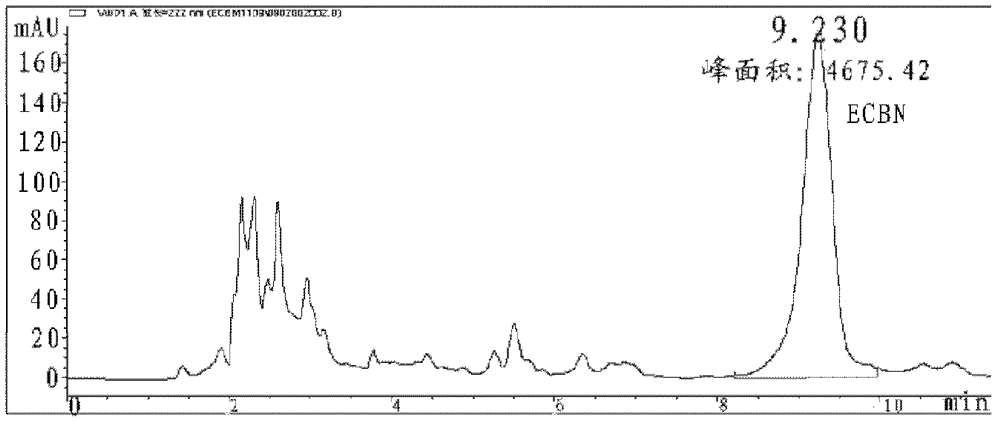
[0045] 2), after the fermentation is completed, add Na to the fermentation broth 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 The O concentrations were 6.10 g / L and 5.8 g / L, respectively, and the pH was adjusted to 6.0 with HCl, sonicated for 1 hour, and the supernatant was collected by centrifugation, wh...
Embodiment 2
[0052] 1), fermentation of echinocandin B deacylase
[0053] Strains: Actinoplanes utahensis NRRL12052, purchased from the American Agricultural Research Culture Collection.
[0054] Medium formula:
[0055] Slant medium: yeast powder 0.3%, malt extract powder 0.3%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1.0%, agar 2.5%, pH 7.0-7.2, cultured at 30°C for 5-7 days
[0056] Seed medium: sucrose 2.5%, oat flour 2%, yeast powder 0.25%, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, KCl 0.05%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.0002%, pH=6.8, cultured at 30°C for 4-5 days
[0057] Fermentation medium: 2.5% sucrose, 1.2% peanut meal powder, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.3%, pH=6.8, cultivated at 30°C for 3-4 days
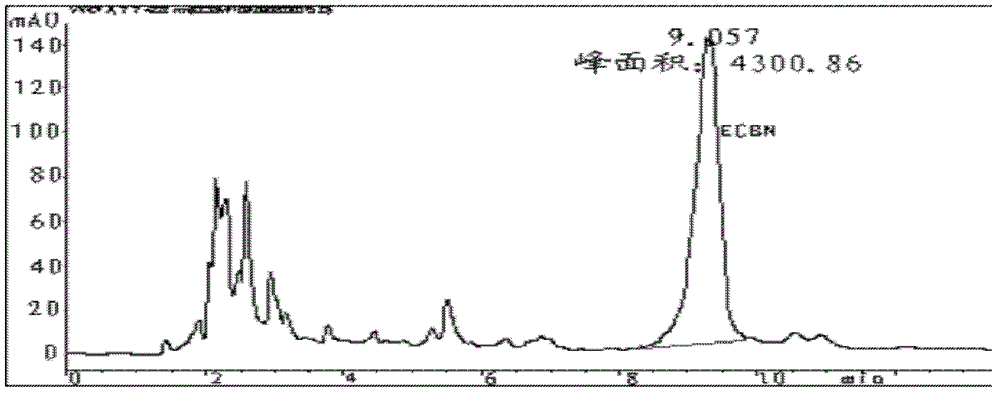
[0058] 2), after the fermentation is completed, add Na to the fermentation broth 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 The O concentrations were 18.20 g / L and 15.15 g / L respectively, the pH was adjusted to 7.0 with NaOH, ultrasonicated for 2 hours, and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation...
Embodiment 3
[0065] 1), fermentation of echinocandin B deacylase
[0066] Strains: Actinoplanes utahensis NRRL12052, purchased from the American Agricultural Research Culture Collection.
[0067] Medium formula:
[0068] Slant medium: yeast powder 0.3%, malt extract powder 0.3%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1.0%, agar 2.5%, pH 7.0-7.2, cultured at 30°C for 5-7 days
[0069] Seed medium: sucrose 2.5%, oat flour 2%, yeast powder 0.25%, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, KCl 0.05%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.0002%, pH=6.8, cultured at 30°C for 4-5 days
[0070] Fermentation medium: 2.5% sucrose, 1.2% peanut meal powder, K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.3%, pH=6.8, cultivated at 30°C for 3-4 days
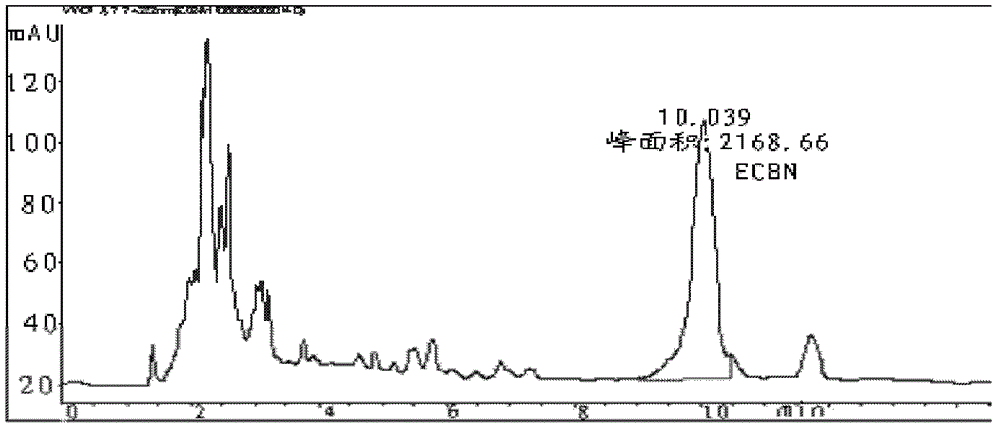
[0071] 2), after the fermentation is completed, add Na to the fermentation broth 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 The O concentrations were 12.20 g / L and 10.15 g / L respectively, the pH was adjusted to 6.8, ultrasonication was performed for 1.5 h, and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com