Patents
Literature
262 results about "Microbial enzymes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial enzymes are identified to play a central role as metabolic catalysts, leading to their usage in various productions and applications , the end usage market for industrial enzymes is tremendously wide-spread with frequent industrial profitable applications (Adrio, et al., 2005).
Antimicrobial compositions and methods
InactiveUS20050053593A1Easy to handleReduce Microbial ContaminationAntibacterial agentsBiocideLipid formationAlcohol sugars
The present invention is generally related to a product and process to reduce the microbial contamination on organic matter, such as processed meat, fruits and vegetables, plant parts, inanimate surfaces such as textiles and stainless steel, and in the mouth or on dental products. In particular, the invention is related to a product and process to disinfect surfaces using an antimicrobial composition containing an antimicrobial lipid, an enhancer selected from the group consisting of bacteriocins, antimicrobial enzymes, sugars, sugar alcohols, iron-binding proteins and derivatives thereof, siderophores, and combinations thereof, and optionally a surfactant.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Producing optically active amino compounds
InactiveUS7169592B2Efficient and inexpensiveSuitable for useSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismNucleotide
Owner:KANEKA CORP
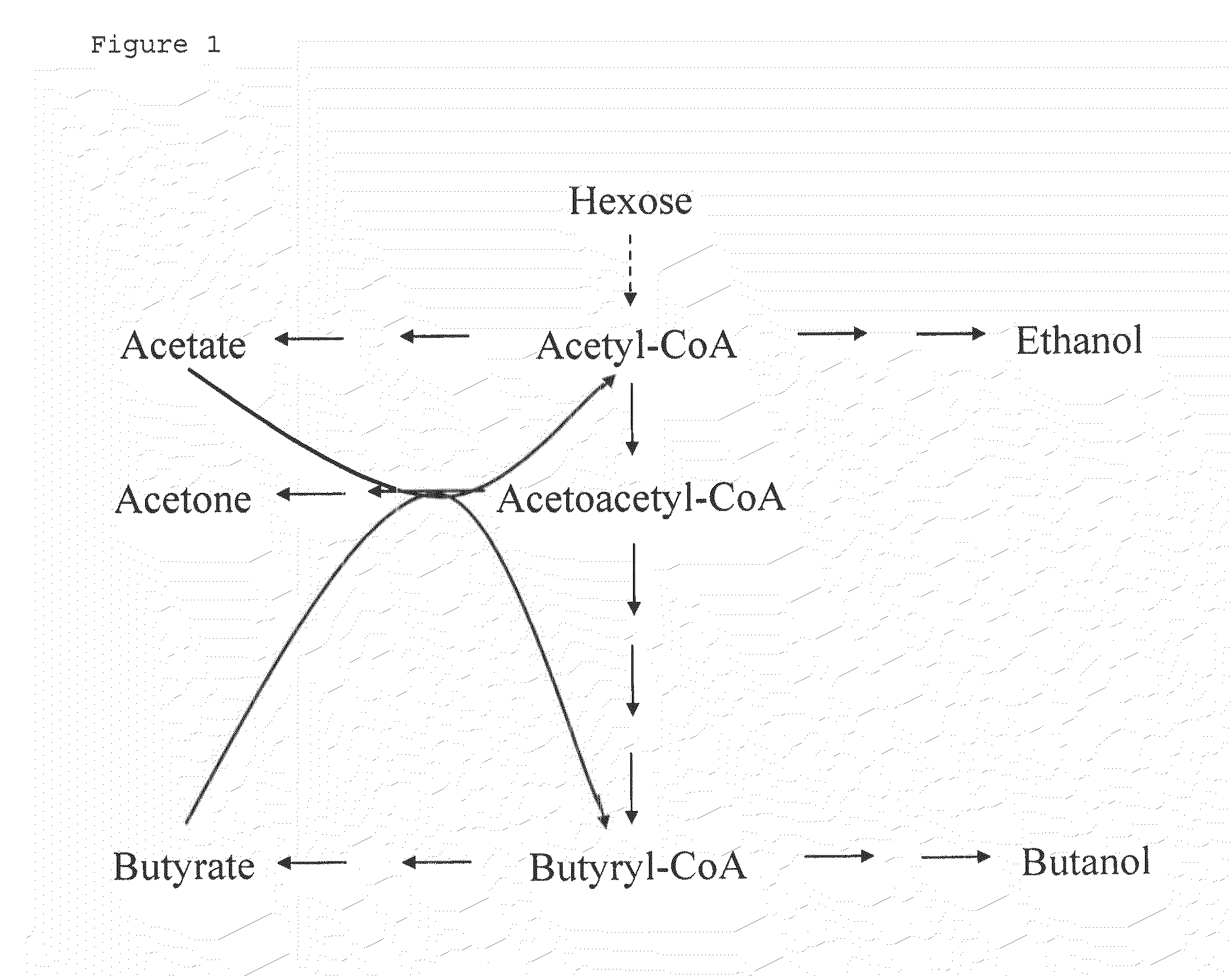
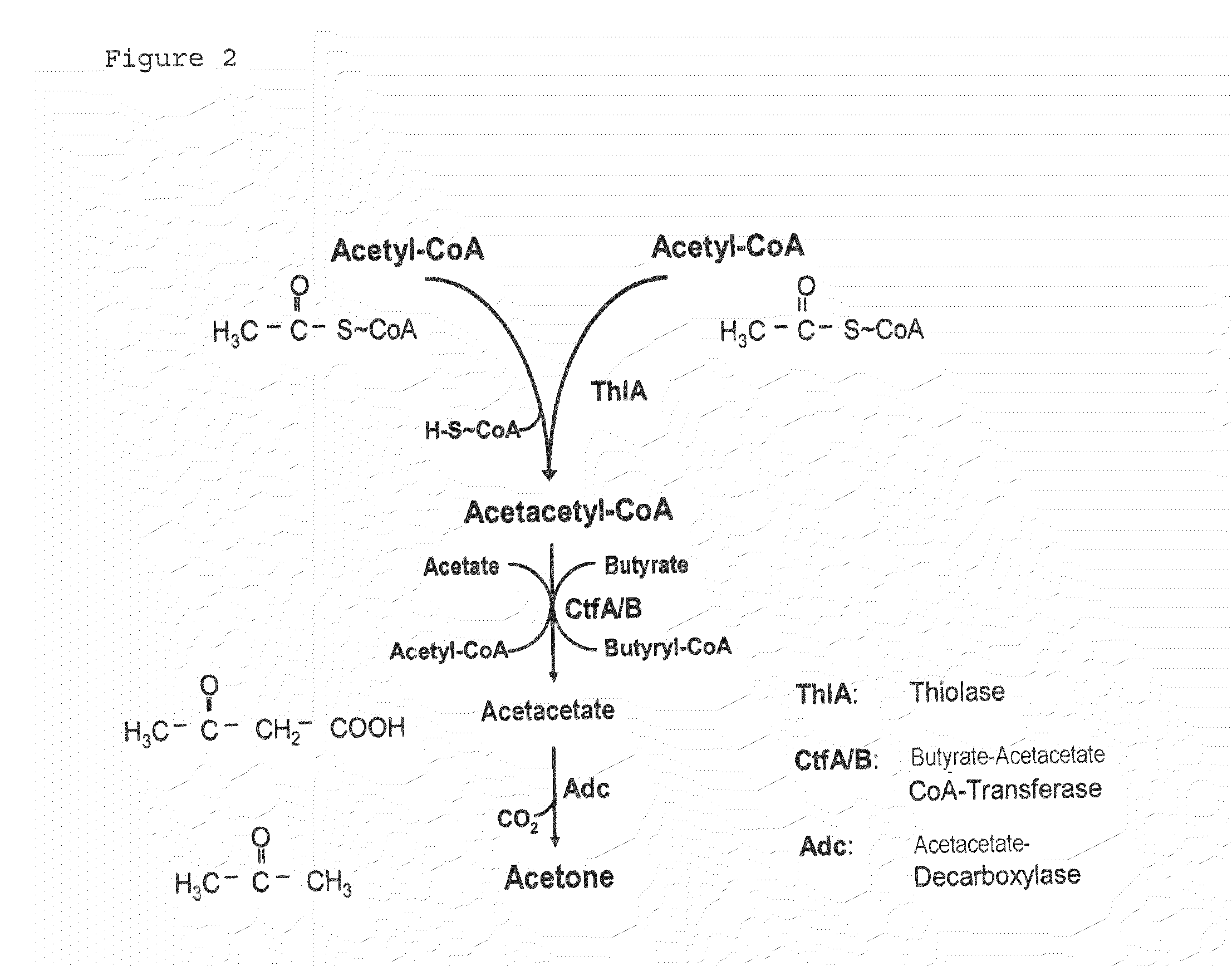
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for producing multi-vitamins and multi-enzymes high protein microorganic agent by multi-bacteria solid fermentation
InactiveCN1552233AImprove disease resistanceQuality improvementFungiFood processingBacterial strainOrganism
A process for preparing the multi-vitamine multi-enzyme high-protein microbial preparation by the solid fermentation of multiple bacterial strains includes such steps as preparing seed culture media, respectively inoculating reticularia, torula yeast, glutamic corynebacteria, Bacillus subtitis, Aspergillus niger, etc into said seed culture media, culturing at 30-35 deg.C for 15-18 hr, inoculating them into the solid culture medium, fermenting at 33+ / -0.5 deg.C for 70-80 hr, and fast drying. Its can be used as the feed containing living microbes, microbial enzymes, vitamines, etc.
Owner:哈尔滨中冠生物工程有限公司
Method for improving quality of the tobacco leaf expanded cut stem by microorganism enzyme
InactiveCN101288505AIncreased total cellulose contentDecreased total cellulose contentFungiTobacco treatmentSucroseSaccharum
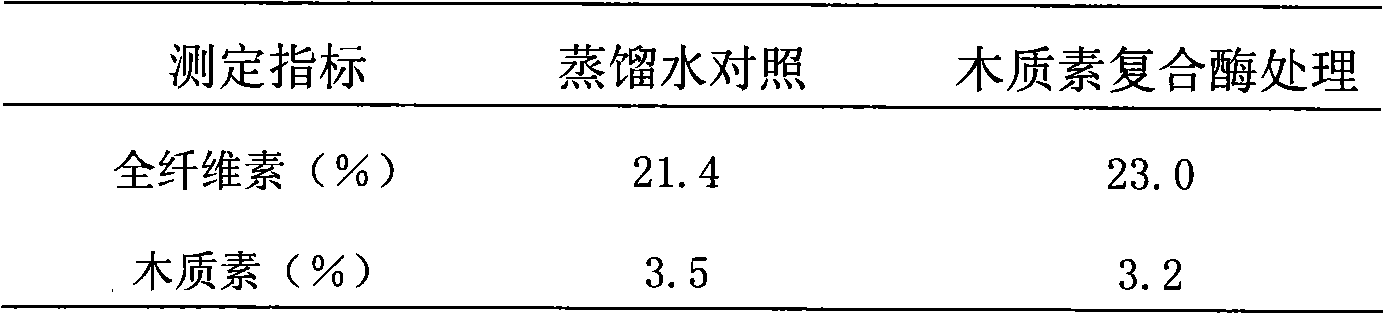
The invention provides a method for improving the quality of expanded cut rolled stem of tobacco by microbial enzyme. The procedures are as follows:1) Preparation of bio-enzyme: (1) Aspergillus niger is activated and cultured by potato cane sugar culture medium and is then transferred into sterilized seed culture medium, and shake cultivation is carried out at the temperature of 28 DEG C for 24 hours with 250r / min<-1>; seed liquid with 10% of inoculation amount is transferred into a sterilized 500ml shake flask (containing 100ml culture liquid for enzyme), and the seed liquid carries out incubation for culturing at the temperature of 25 DEG C for 96 hours and then zymotic liquid is obtained. (2) Extraction of lignin degradation complex enzyme: After being filtered by filter paper, the zymotic liquid is centrifugally separated at the low speed of 1500rpm. The supernatant carries out fractional salting out by (NH4)2SO4 till the saturation is 0.7 to obtain crude enzyme liquid, after the crude enzyme liquid carries out ultrafiltration dialysis, the lignin degradation complex enzyme is obtained. Activities of enzyme components: 350U / L of Lip, 11U / L of MnP and 5.6U / L of Lac; 2) Improvement of the quality of expanded cut rolled stem of tobacco: The expanded cut rolled stem for cigarette is weighed and sprayed evenly by lignin degradation complex enzyme liquid containing 0.2-0.4% of expanded cut rolled stem after being diluted by distilled water at the temperature of 27 DEG C-29 DEG C. The expanded cut rolled stem of tobacco is placed in a sealed container for enzymolysis for 95-97 hours and dried naturally till the moisture content is 12.5%-15%. The result by subjective analysis suggests that the complex enzyme preparation can effectively decrease the lignin content of the expanded cut rolled stem, promote the transformation of aroma matter and improve aroma quality and taste.
Owner:云南万芳生物技术有限公司
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
ActiveCN101302484AImprove volume stabilityIncreased durabilityBacteriaBuilding repairsCulture fluidNutrient solution
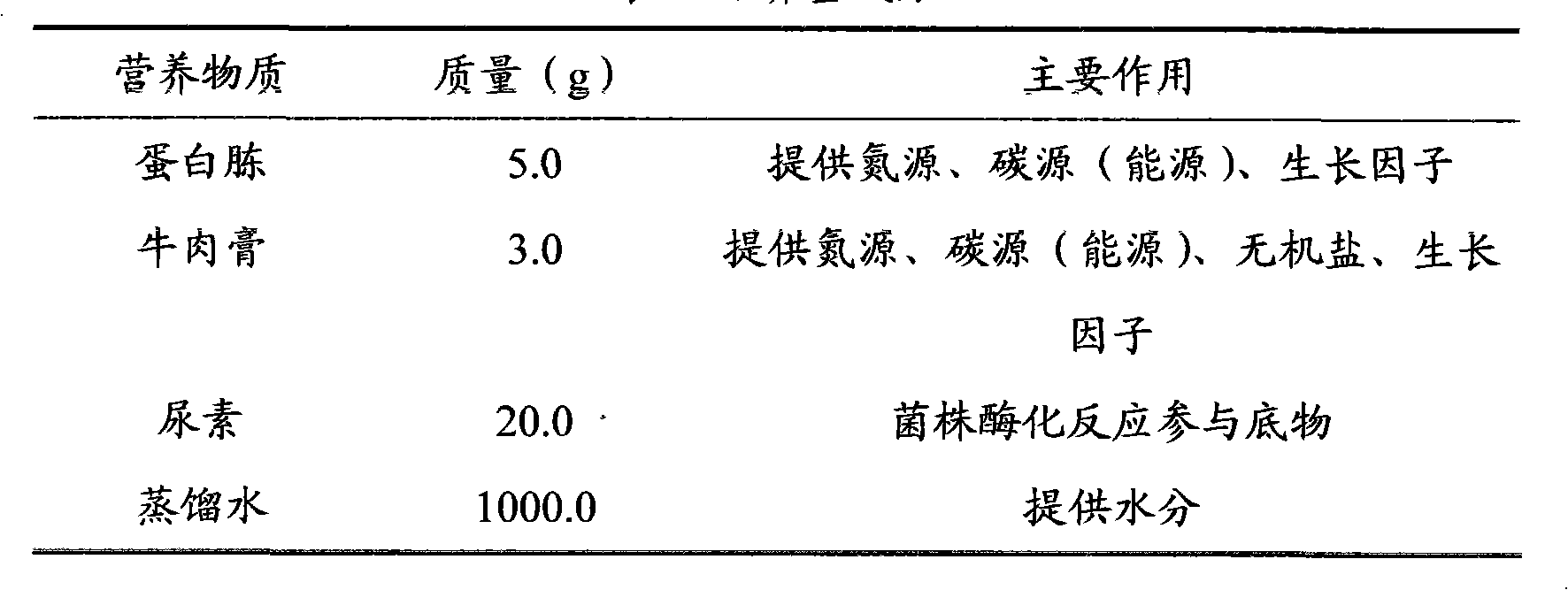
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solution obtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenance is carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources in nature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate and good in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Microorganism of producing D-pantothenic acid enternal ester hydrolase and process for preparing D-pantothenic acid thereof
The invention relates to a method used microorganism enzyme resolution DL-pantoic acid lactone to produce D-pantoic acid. It uses the D-pantoic acid lactone hydrolase strain of the fusarium, gibberella, aspergillus, penicillium, rhizopus, gliocladium, aureobasidium to ferment and culture, uses wet thallus as coarse enzyme, DL-pantoic acid lactone as substrate to produce D-pantoic acid. L- pantoic acid lactone can be reclaimed. The DL-pantoic acid lactone gained by racemization reaction can newly be used to do resolution.
Owner:重庆鑫富化工有限公司 +1
Producing optically active amino compounds
InactiveUS20020192786A1Efficient and inexpensiveSuitable for useBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismNucleotide
To provide a method for preparing optically active compounds, which mainly contain (R)-amino compounds, by microbial enzymes efficiently and inexpensively; a polypeptide having stereoselective transaminase activity which can be suitably used for the above preparation method; and a DNA encoding the polypeptide. A method for preparing an optically active amino compound, characterized in stereoselectively transaminating by acting a transaminase on an amino group acceptor, a ketone compound in the presence of an amino group donor, a primary amine; a DNA comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having stereoselective transaminase activity; and a polypeptide having stereoselective transaminase activity obtainable from a culture of a microorganism belonging to the genus Arthrobacter.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Microbe-enzyme composite preparation used for restoring water in urban and rural polluted river, and its preparation method
ActiveCN102815792AImprove metabolic activityHigh degradation activityWater resource protectionBacteriaBacillus licheniformisAmylase
The invention provides a microbe-enzyme composite preparation used for restoring water in an urban and rural polluted river, and its preparation method. The urban and rural polluted river restoration microbe-enzyme composite preparation is characterized in that the microbe mainly comprises 30-60% of Bacillus licheniformis, 25-35% of a nitrobacterium, and 15-35% of pseudomonas putida; and the composite enzyme mainly comprises 40-60% of a protease, 15-25% of an amylase and 25-35% of a cellulase. The optimized microbe is compounded with the composite enzyme to prepare the microbe-enzyme composite preparation against water of different pollution degrees, the addition amount of the microbe is 1-5g / m<3>, and the addition amount of the composite enzyme is 0.01-0.05g / m<3>. The microbe-enzyme composite preparation is added to the urban and rural polluted river to carry out microbial reinforced restoration with aeration as an auxiliary measure, can effectively improve defects of low microbe metabolism activity, low environmental tolerance, short retention time in the polluted water and the like existing in the prior art, and has a substantial water purifying effect.
Owner:浙江绿凯环保科技股份有限公司
Mixed enzyme production process by solid fermentation of fruits and vegetables and microorganisms
InactiveCN104839638ARetain enzyme activityRetain non-enzyme active ingredientsFood preparationEnvironmental resistanceMicroorganism
The present invention discloses a mixed enzyme production process by solid fermentation of fruits and vegetables and microorganisms and the production process includes the following steps: step one, washing and cleaning fresh fruits and vegetables; step two, juicing the cleaned fruits and vegetables using a juice extractor and obtaining the fruit and vegetable juice and the fruit and vegetable residue; step three, adding water content adjusting raw materials according to different water content of the obtained fruit and vegetable residue to adjust the water content of the fruit and vegetable residue, and mixing the above materials evenly to obtain a base material; step four, putting the step three obtained base material into a fermentation bottle to conduct sterilization; step five, cooling the sterilized fruit and vegetable base material to room temperature, and inoculating microorganism liquid strains to conduct solid fermentation; and step six, after the end of solid fermentation, blending the obtained fruit and vegetable juice into the solid fermented materials, conducting low temperature drying, and thereby obtaining the fruit and vegetable and microorganism mixed enzymes containing both fruit and vegetable enzymes and microbial enzymes. The mixed enzymes can not only fully preserve the enzyme activity of fruits and vegetables, but also obtain the enzyme ingredients of microorganisms, and in addition, the production process can also achieve the full advantage of the entire fruits and vegetables, does not produce any waste, and is ecological and environmental protective.
Owner:杭州德润全健康产业发展有限公司
Method of improving cabo quality
ActiveCN101228967AIncrease irritationReduce woody smellTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentFlavorCellulose
The invention discloses a method for improving the quality of cabo, comprising the following steps: dissolving microbial enzymes in a citric acid solution, uniformly spraying the completely dissolved enzyme solution on the cabo, treating the cabo sprayed with enzyme solution under constant temperature and humidity, and drying, etc. The invention uses the microbial enzyme technique to strengthen the fermentation treatment of the cabo, which reduces the wood flavor of the cabo, improves the irritation caused by undesirable substances such as cellulose. The improved cabo facilitates the process of the subsequent procedures and is added into the group prescription of the tobacco leaves, which increases the comfort of the oral cavity, decreases miscellaneous gases, softens the smoking gas, reduces the content of harmful substances in the cigarette and improves the safety of smoking. The invention has the advantages of simple and easy practice and strong practicality, which is beneficial to reducing the consumption of tobacco leaves and save tobacco leaf resources.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
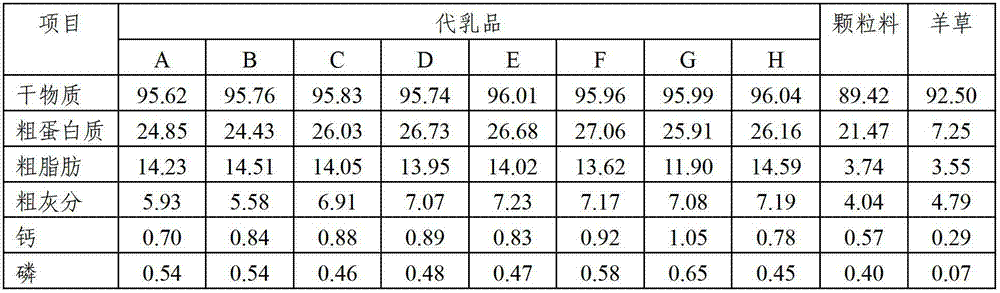
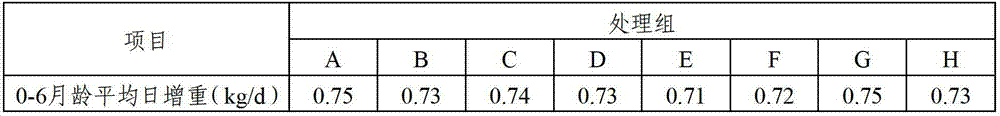
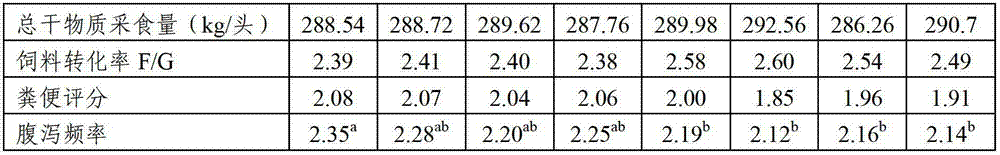
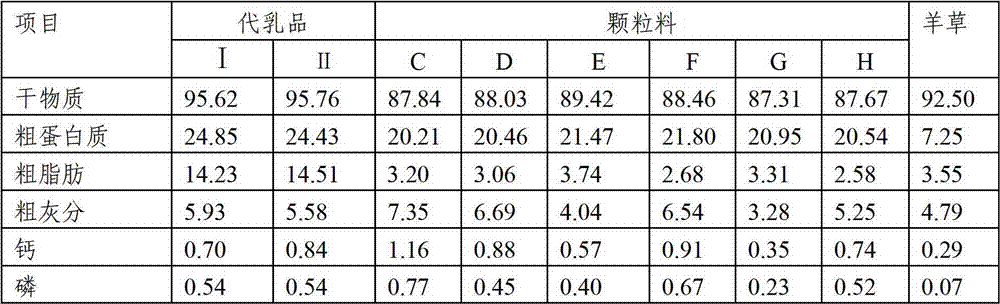
Composite microbial enzymic preparation for calves from 0-6 months of age and milk replacer thereof
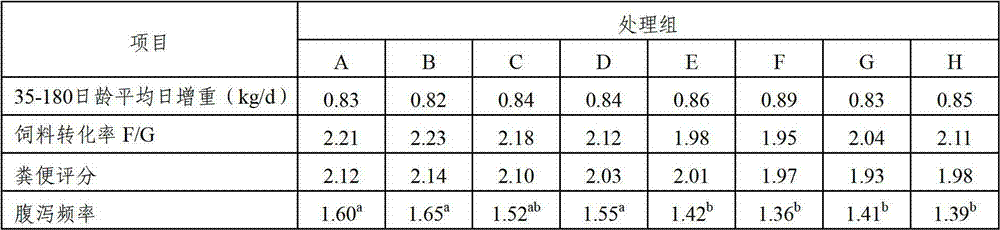
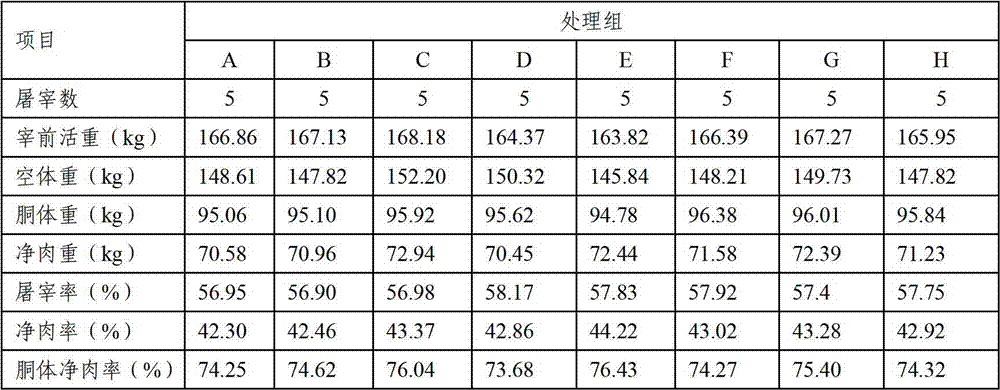
ActiveCN102894220AReduce disease incidenceGood for healthAnimal feeding stuffWhey manufactureMicroorganismDisease
The invention relates to a composite microbial enzymic preparation for calves from 0-6 months of age and a milk replacer thereof. An active ingredient of the composite microbial enzymic preparation comprises, by weight, 25-75 parts of composite microorganism and 15-45 parts of composite enzyme. Tests show that high-quality veal can be prepared after the valves from 0-6 months of age are fed by the milk replacer. Under the premise that meat productivity is not influenced, disease incident of the calves can be reduced, diarrhea is reduced, and health conditions of the calves are improved.
Owner:北京精准动物营养研究中心有限公司
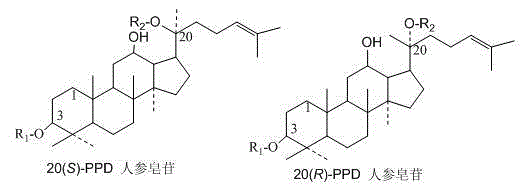
Method for preparing ginseng rare saponin by virtue of microorganism enzymatic conversion of ginsenosid Re
ActiveCN104894204ALow costSimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for preparing ginseng rare saponin by virtue of microorganism enzymatic conversion of ginsenosid Re. According to the method, aspergillus microorganisms are fermented to obtain an enzyme solution, and then the enzyme solution reacts with cheap ginseng with high contents of ginseng saponin Rb3, Rc, Rb2, Rd and the like or western stem and leaf glycol saponin or pseudo-ginseng steam and leaf saponin, so that a high-activity ginseng rare saponin C-Mx, C-Mc, C-Y, C-K mixture and monomers thereof are prepared. The method is low in cost, simple in process and free from pollution; products can be applied to ginseng products, functional foods and cosmetics.
Owner:三蚁科技(广州)有限公司
Method for oriented biosynthesis of GAMG
InactiveCN101603067AImprove reaction efficiencySimple stepsMicroorganism based processesFermentationPenicillium purpurogenumDrug biotransformation
The invention provides a method for oriented biosynthesis of GAMG, and belongs to the technical fields of biosynthesis and biotransformation. The method comprises the following steps: producing corresponding beta-D-glucuronidase by penicillium purpurogenum stoll in a fermentation medium; adding the obtained beta-D-glucuronidase into conversion solution containing glycyrrhizic acid substrate, orientedly hydrolyzing the glycyrrhizic acid under the action of enzyme, and obtaining a coarse product of GAMG; and performing organic solvent extraction, resin adsorption and purification to obtain a GAMG product. The method takes microbialenzyme as a catalyst, and has high reaction efficiency, no pollution, simple steps, and low cost; and the product is single and has high purity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
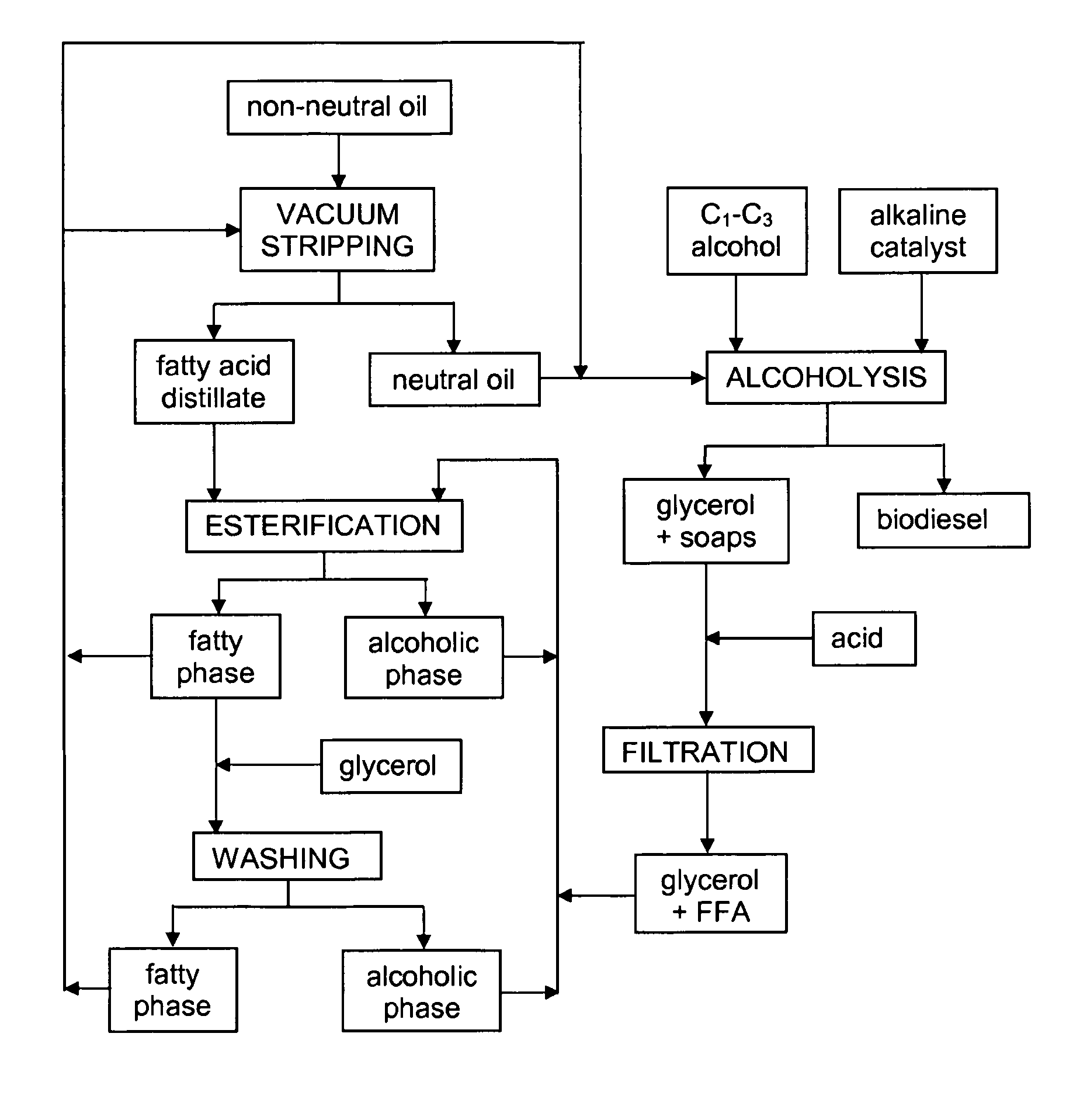
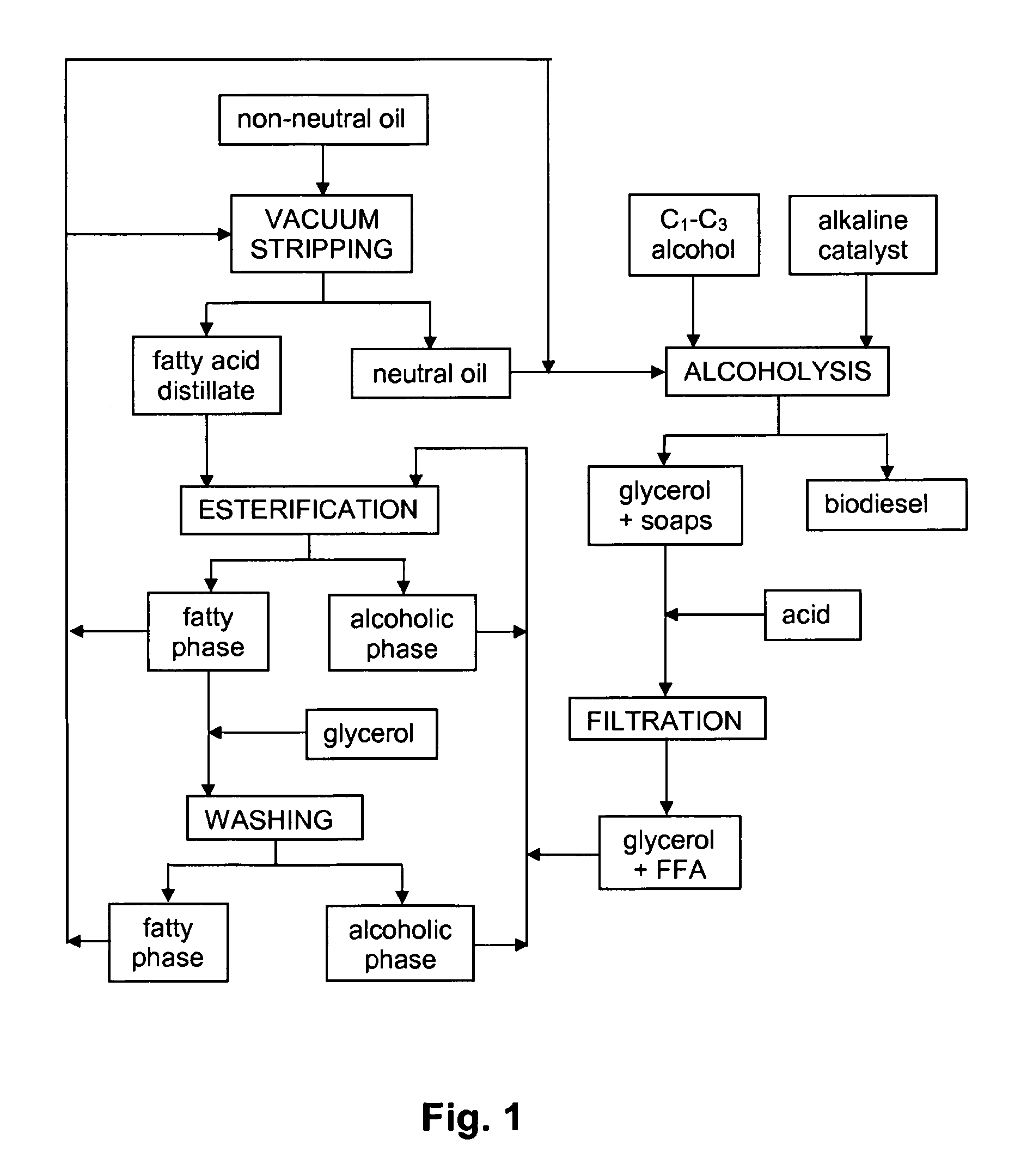
Esterification Process
The invention relates to the utilisation of fatty acid feedstockin the production of biodiesel by the use of microbial enzymes.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Producing esters of fatty acid and C1-C3 alkyl alcohols
InactiveUS8178326B2Maximize productivityYield maximizationBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlcoholBiodiesel
Owner:N V DESMET BALLESTRA GROUP +1
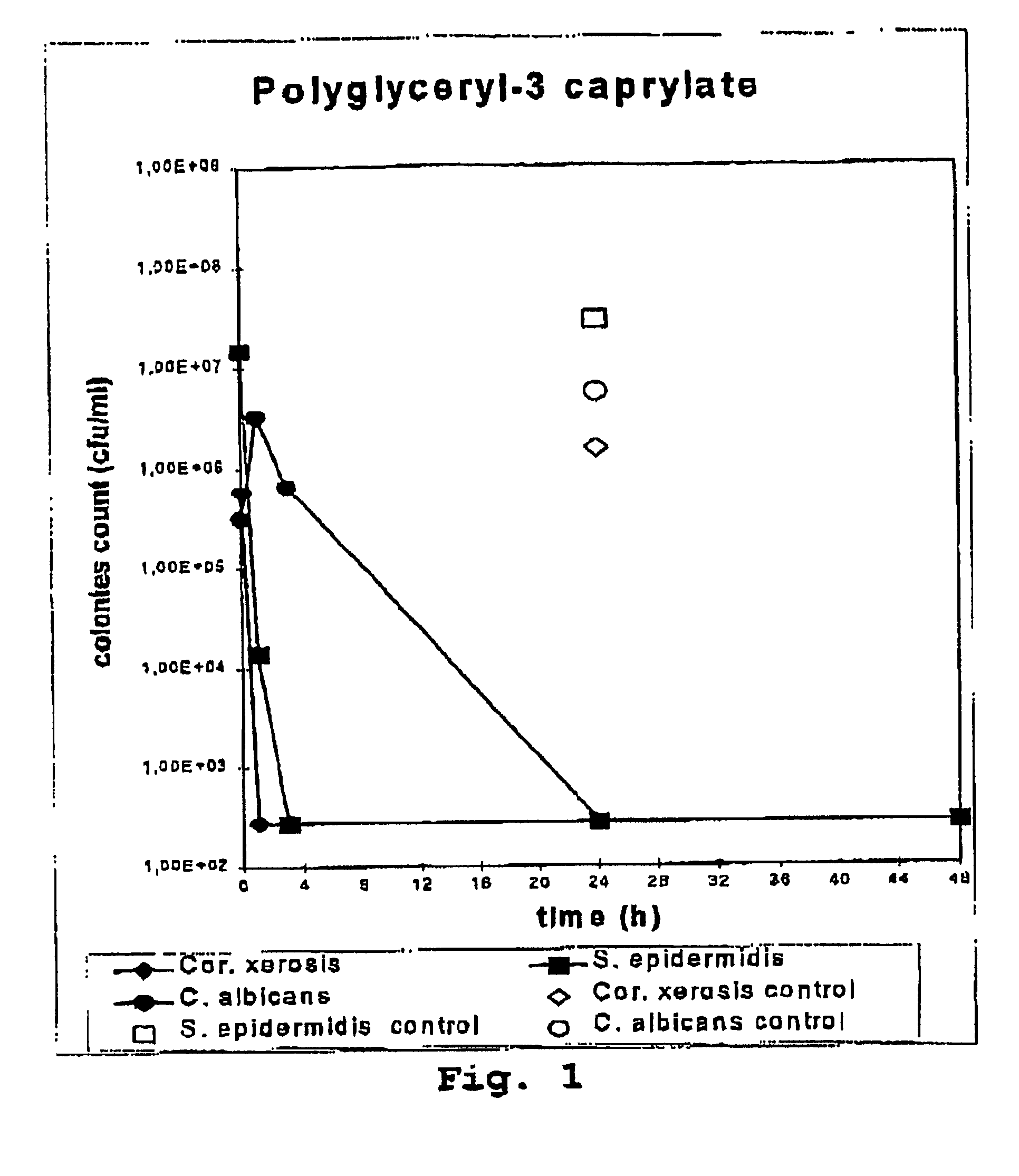
Method and Test-Kit for the Detection and Quantification of Organisms
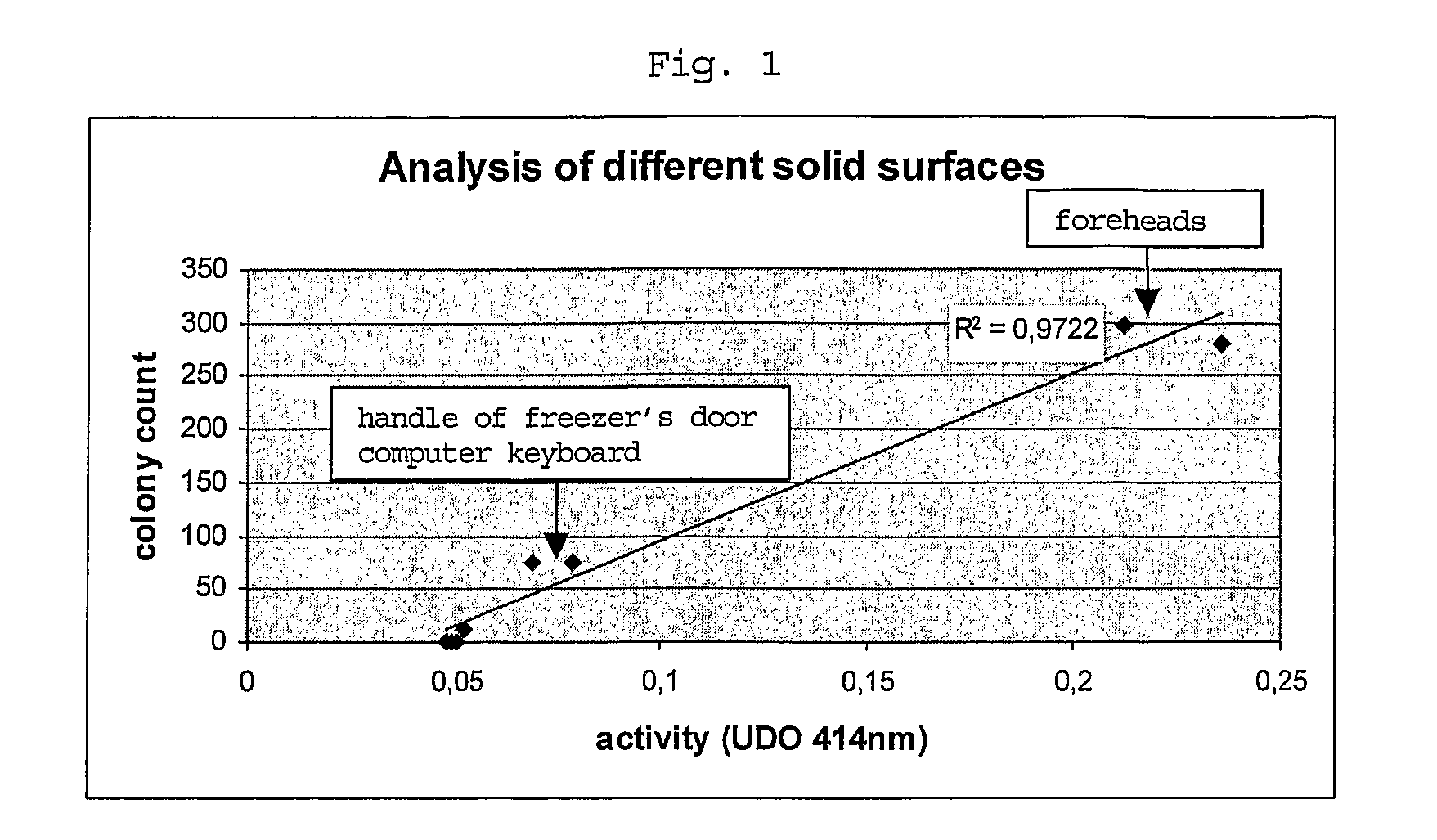
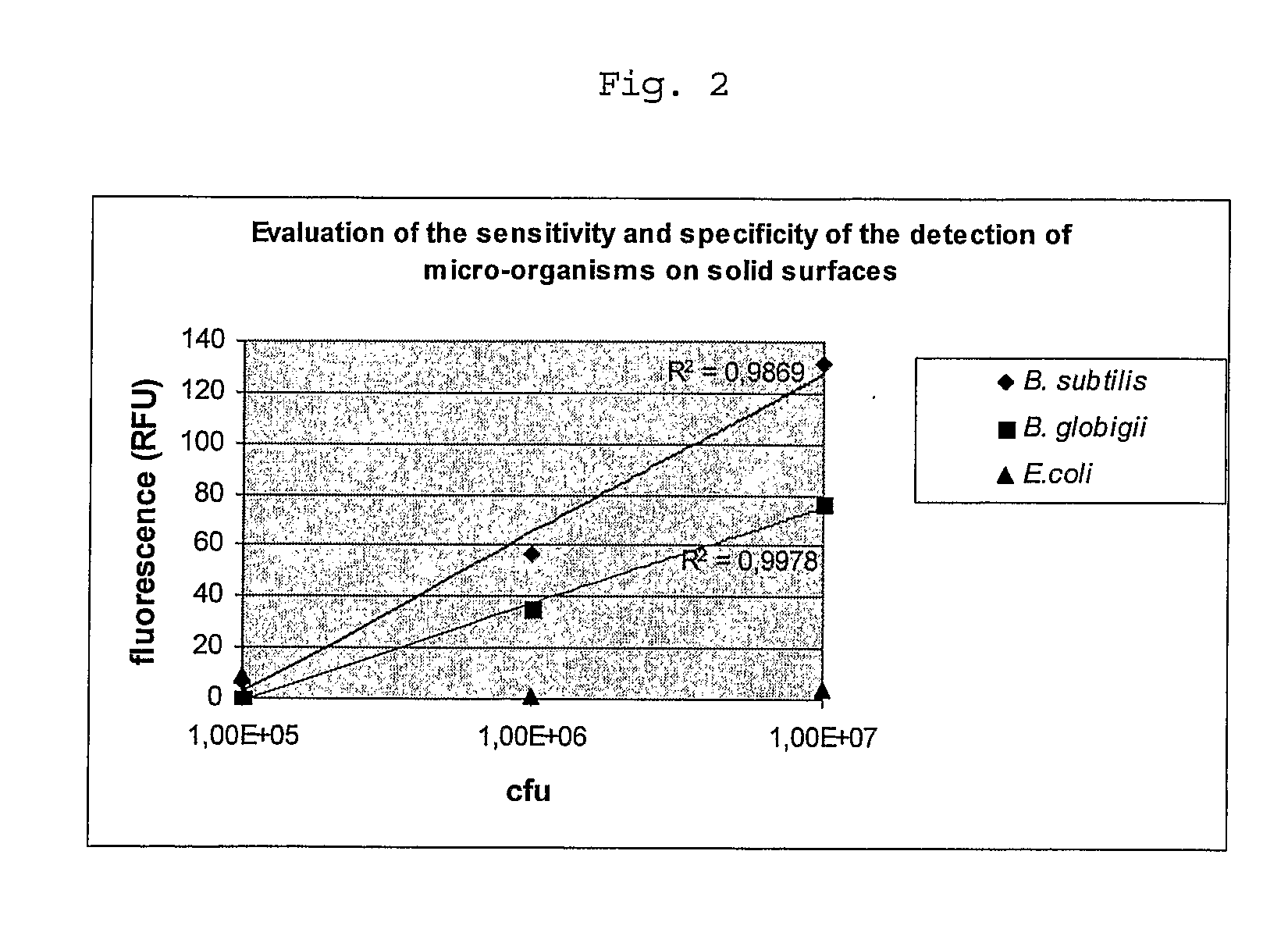
InactiveUS20070264680A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPathogenic microorganismBiological body
The present invention provides methods and test-kits for rapidly detecting and / or quantifying a group of organism, cultivable or not cultivable, sharing the same enzymatic activity. In particular, the methods and kits can be used for example in the field of cosmetics, where the activities of (microbial) enzymes, which are responsible for malodor or dandruff, are detected as an indicator for the presence of particular groups of microorganisms. Furthermore, the effect on substances acting on the causative microbes can be determined rapidly, easily and at low cost.
Owner:PROTEUS
Cleaning cosmetic composition and preparation method thereof
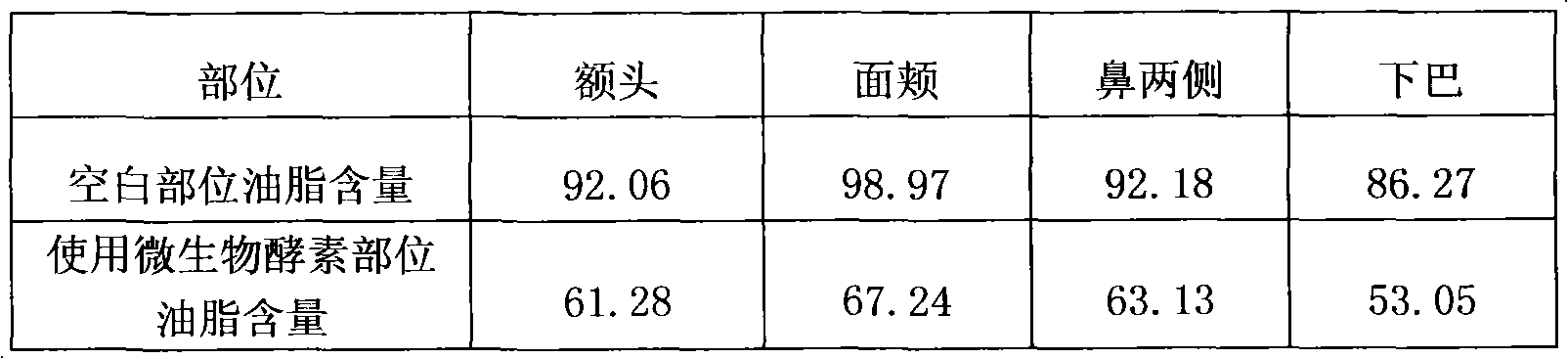
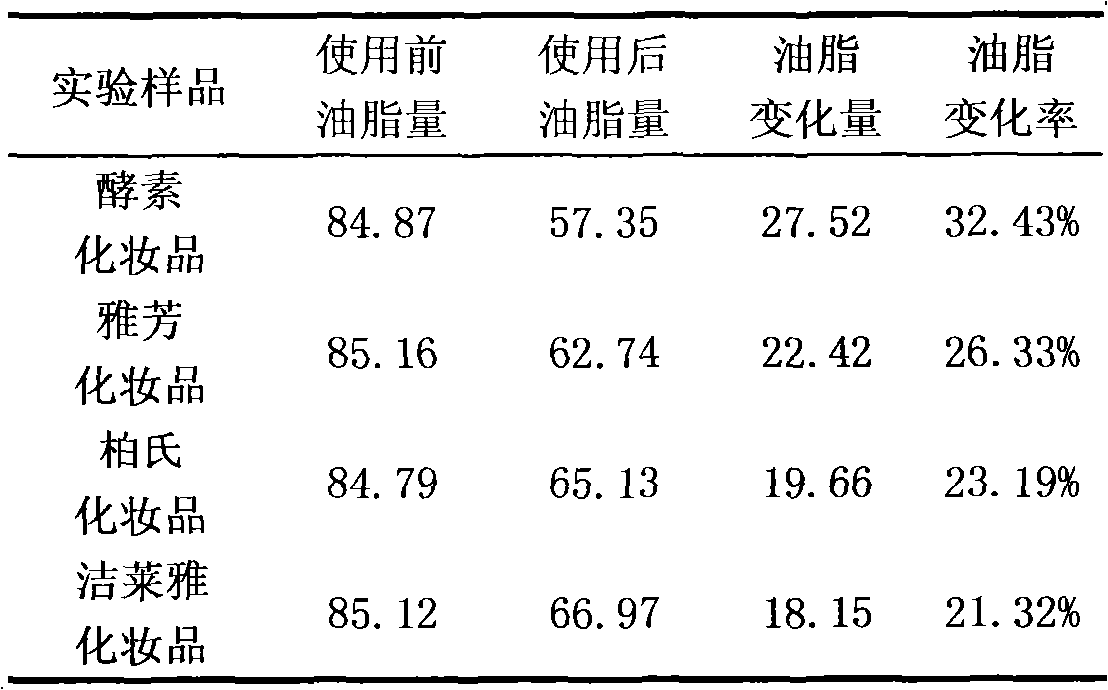
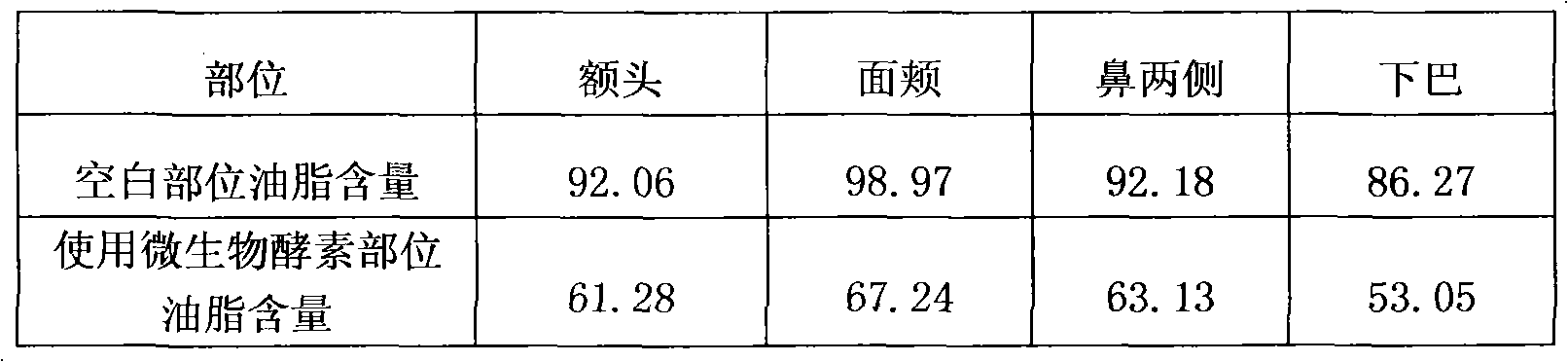
The invention provides a cleaning cosmetic composition which comprises 0.5-5.0% of microbial enzymes by weight and 95.0-99.5% of common cosmetic additives by weight. The cleaning cosmetic composition provided by the invention realizes maximum effective rate of 87.72% and minimum cleaning efficiency of 81.40%, thereby being a good skin care product.
Owner:北京中加保罗生物科技有限公司
Production method of probiotic active milk beverage rich in organic selenium
InactiveCN103329994AStrong selenium-rich abilityImprove the level ofMilk preparationFiltrationBacillus cereus
The invention belongs to the technical field of active milk beverage preparation, and particularly relates to a production method of a probiotic active milk beverage rich in organic selenium. Sodium selenite is added in different stages, so that the best combining condition between yeast and selenium is optimized; the selenium combining quantity is increased; the growth of the growth is facilitated; inorganic selenium is combined into organic selenium; the yeast is separated by a sheet frame press filtration or centrifugal method; selenium-enriched yeast powder is obtained by drying and deactivation, and serves as a raw material for secondary fermentation via probiotics such as bifidobacterium bifidum, lactobacillus bulgaricus, lactobacillus acidophilus, thermophilic streptobacillus and bacillus cereus, and secondary conversion via microbial enzyme; and inorganic selenium left in a yeast cell is converted into selenium protein and seleniferous protein basically completely. Therefore, the probiotic functional food beverage rich in organic selenium is obtained. The product can exert comprehensive health-care effects of the probiotics, the yeast and organic selenium.
Owner:山东硒莱姆生物科技有限公司
Environment-friendly microbial method garbage treatment device and garbage treatment method thereof
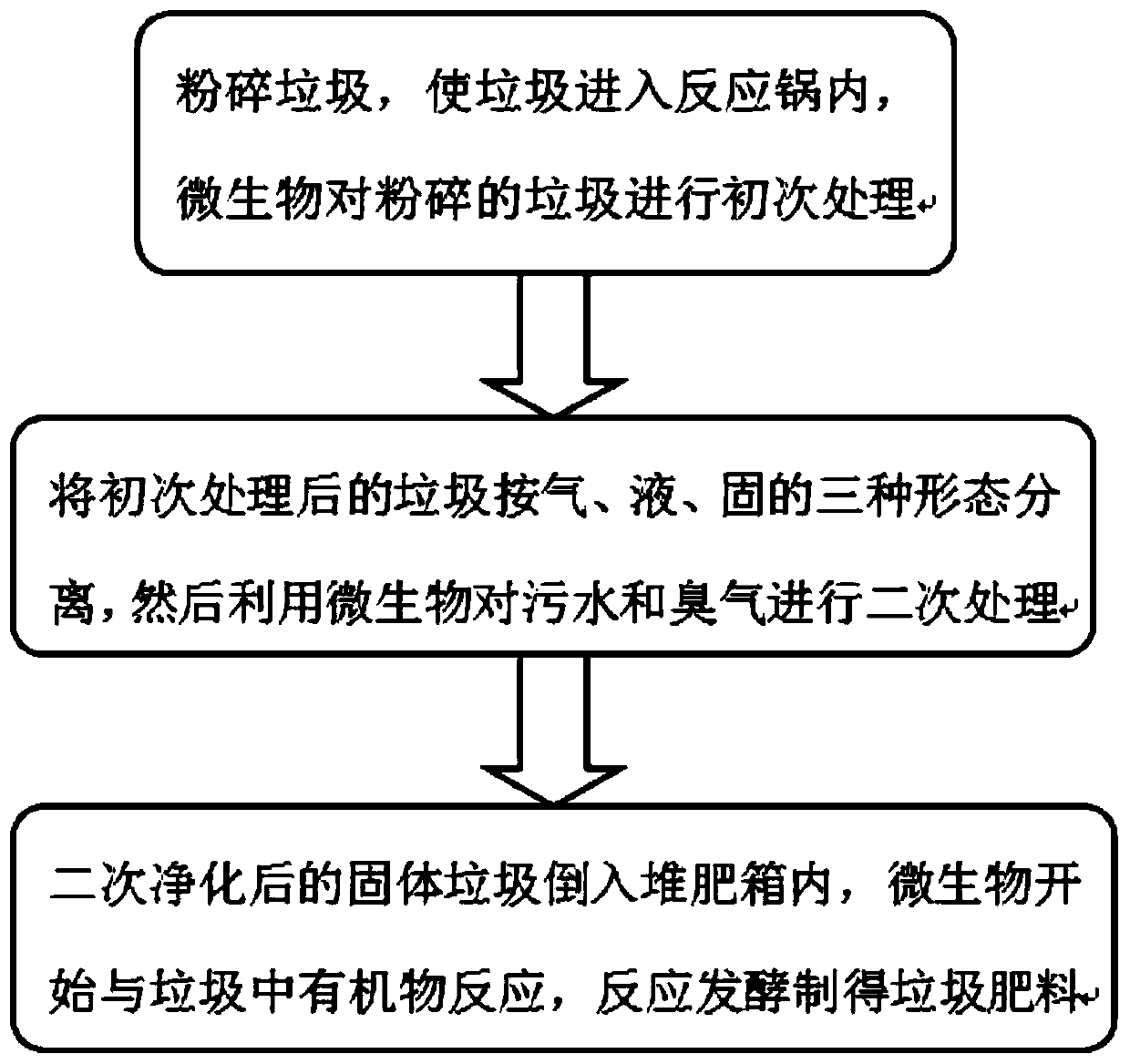
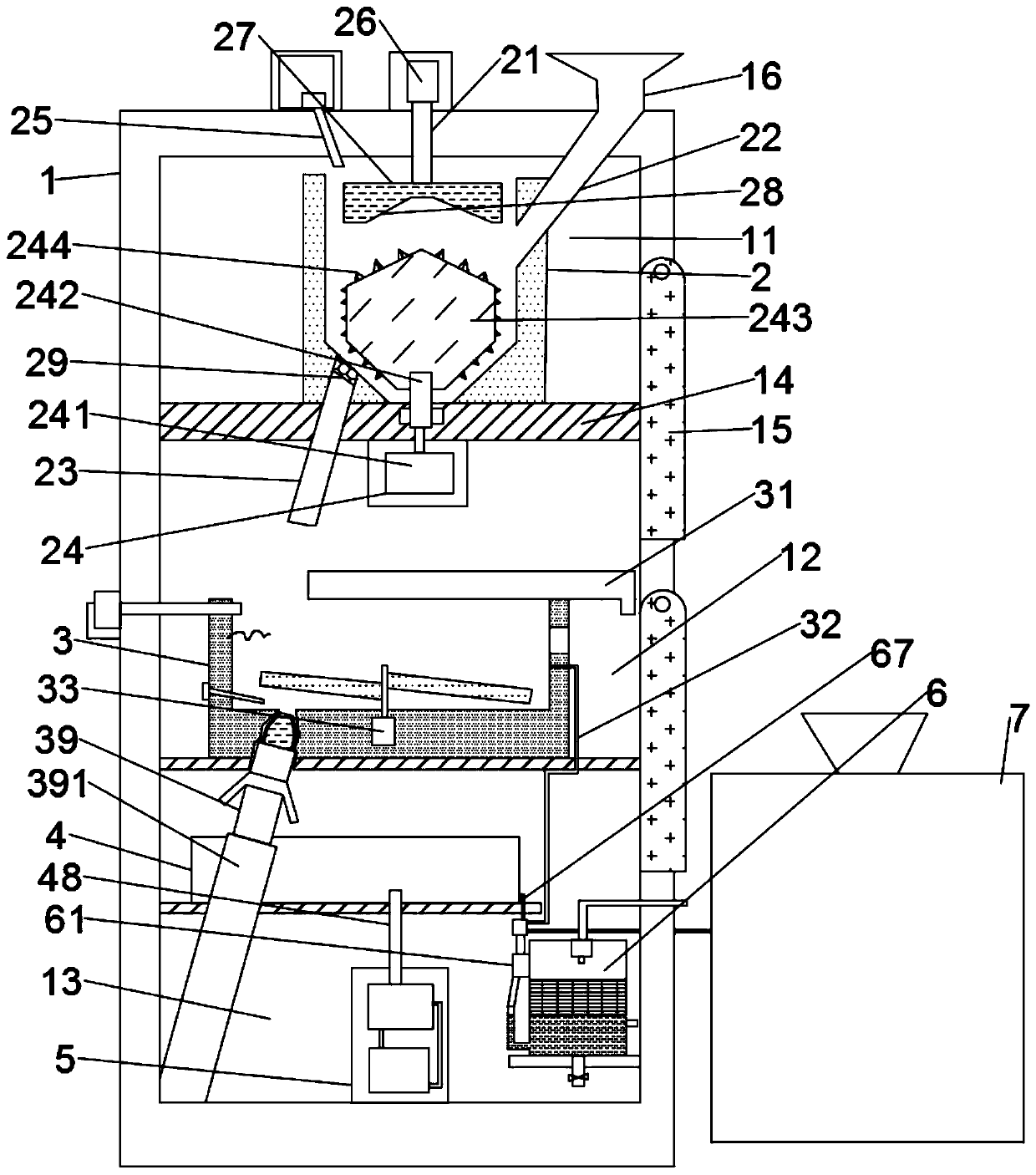
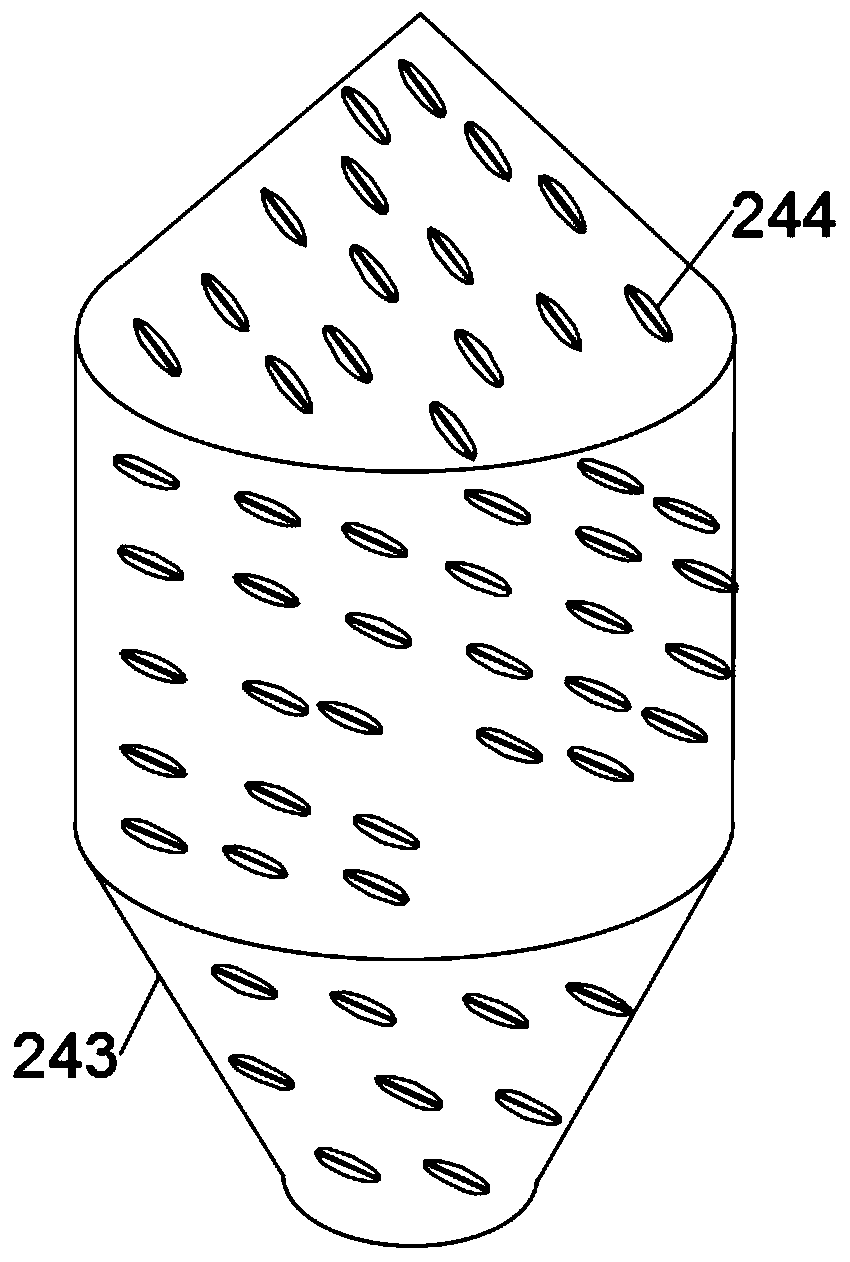
ActiveCN109759417AImprove crushing efficiencyFast crushingBio-organic fraction processingSolid waste disposalOrganic matterToxicity
The invention discloses an environment-friendly microbial method garbage treatment device. The device comprises a treatment box, the upper part and the lower part of the treatment box are sequentiallyinstalled with a crushing cylinder, a reaction pot and a product classification and purification device through a grinding chamber, a microbial reaction chamber and an enzymolysis product treatment chamber; a rotary grinding cutting device is arranged in the crushing cylinder, a uniform rolling stirring device is arranged in the reaction pot, efficient crushing of the rotary grinding device enables the garbage particles to be more finely crushed, the speed of organic matters in the microbial enzymolysis waste is higher, the uniform rolling stirring device can enable the garbage to be fully and uniformly contacted with microorganisms, the area and the toxicity killing efficiency of the primary purification of the garbage are improved; the method comprises the following steps of crushing and grinding the garbage by the rotary grinding cutting device, then the garbage enters the reaction pot, the microorganisms in the reaction pot carry out enzymolysis reaction on the crushed garbage forthe first time, the crushed garbage is uniformly mixed with the microorganisms, the enzymolysis reaction efficiency is high, and the garbage purification treatment is more thorough.
Owner:安徽科柏盛环保设备有限公司
Shark protein antihypertensive peptide and preparation method and application thereof
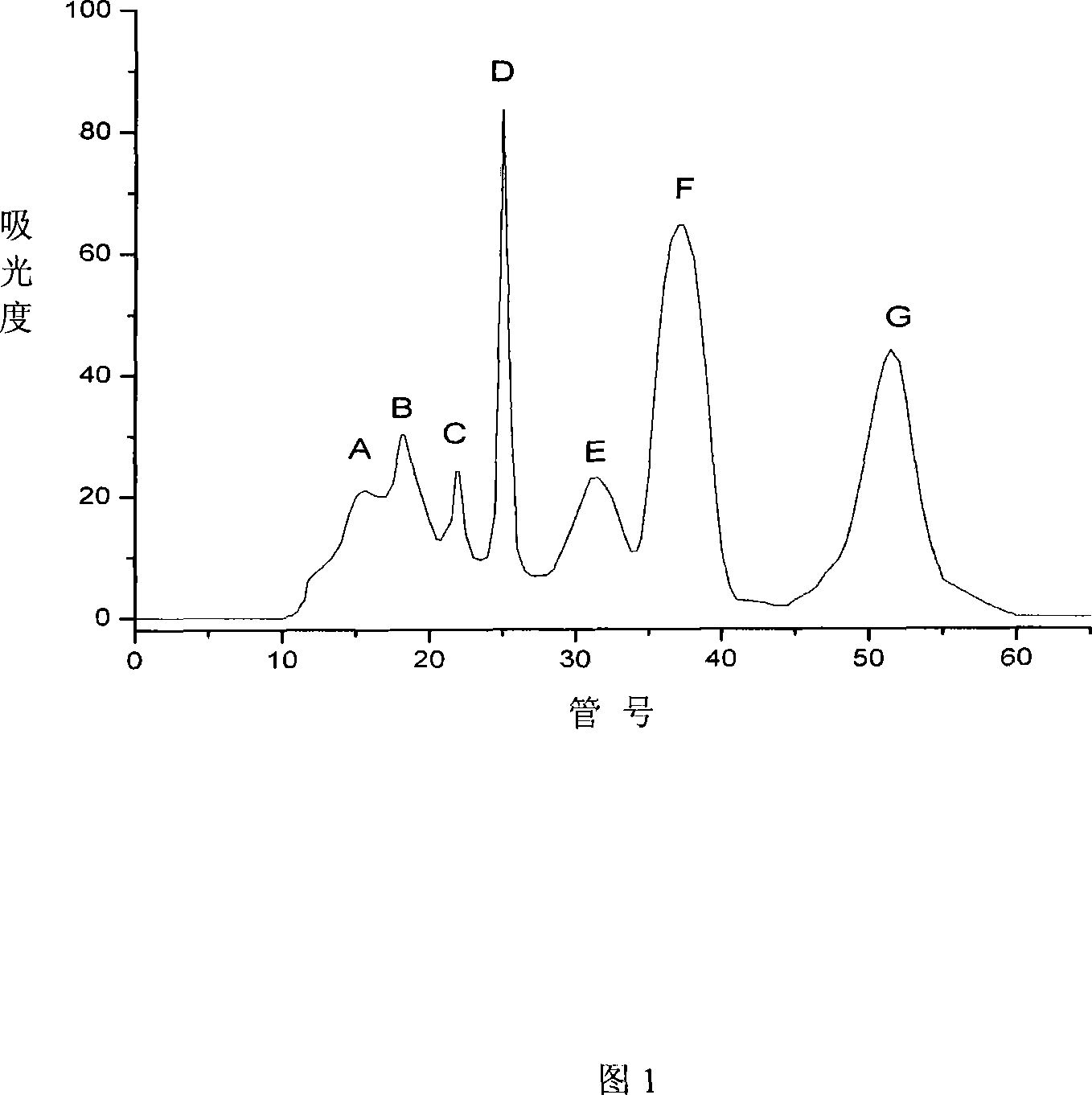
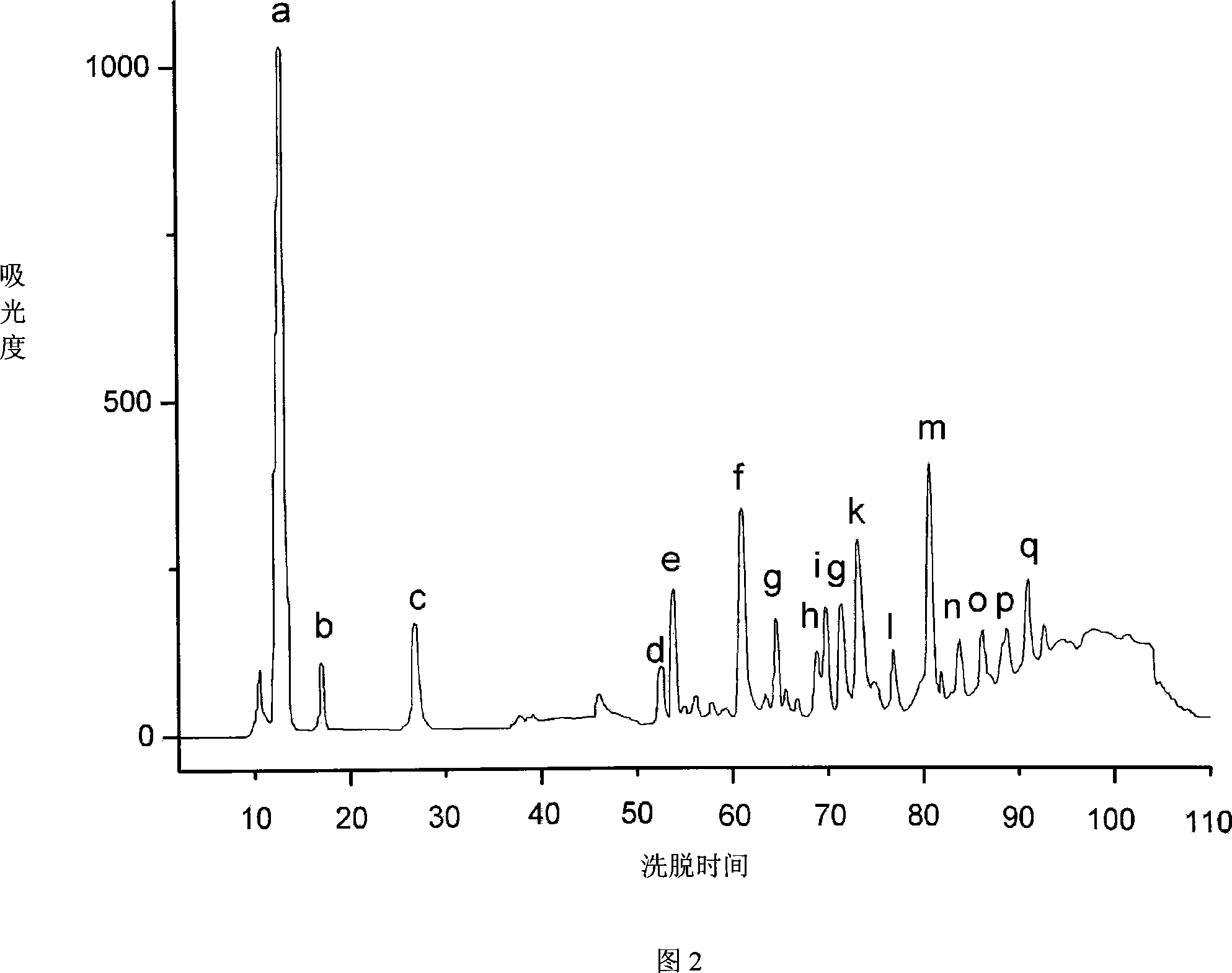
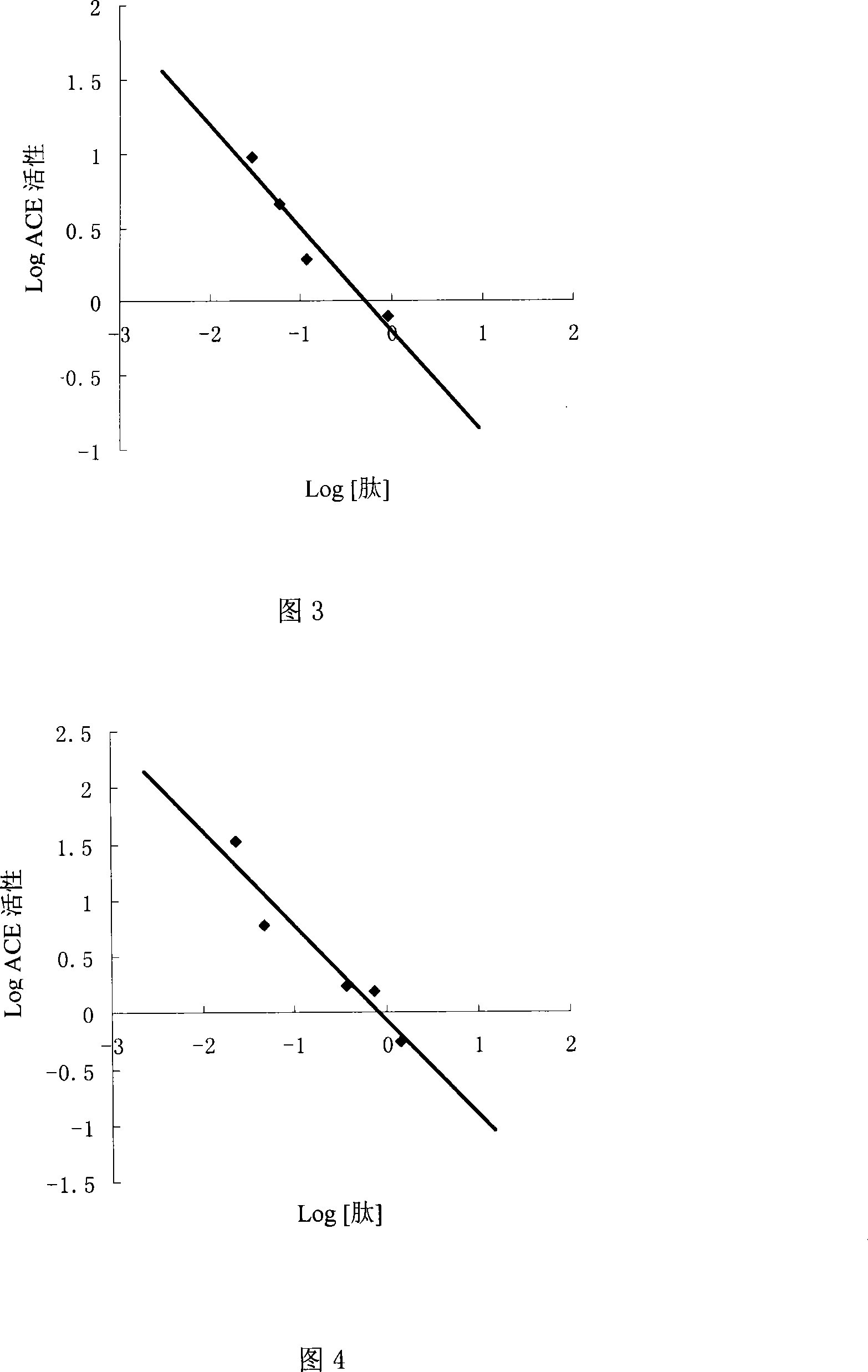
InactiveCN101240016AHigh ACE inhibitory activityGood ACE inhibitory activityPeptide preparation methodsDipeptidesMicrobial enzymesProteolysis
Shark protein antigypertensive peptide, preparation and application thereof, which pertains to marine biology technical field. The novel antigypertensive peptide with two amino acid separated and purified from proteolysis product of shark, has a high inhibiting activity for angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Preparation includes steps of carrying out enzymolysis for shark protein to prepare enzymatic hydrolysate, seperating and purifying peptide from the enzymatic hydrolysate, and sequencing of peptide. The invention is applicable for preparing antihypertensive medicament. The invention apply microbial enzyme technology to deep development of shark, obtain peptide having novel sequence, with high inhibiting activity for ACE.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Composite microorganism enzyme, method for preparing plant nutrient solution by using composite microorganism enzyme, and fertilizer synergist
ActiveUS20170275213A1High activityPresent inventionBio-organic fraction processingEnzymesAmylasePectinase
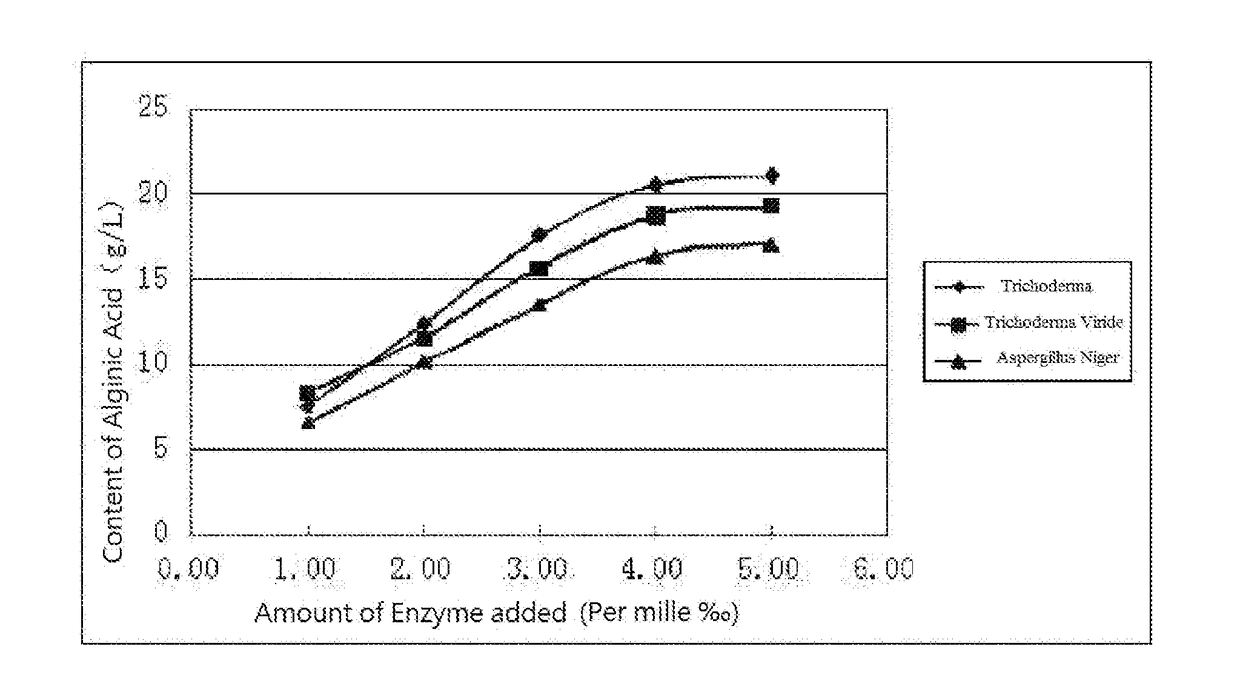
The present invention relates to a composite microorganism enzyme, a method for preparing a plant nutrient solution by using the composite microorganism enzyme, and a fertilizer synergist. The method comprises the following steps: mixing fresh kelp pulp with a composite microorganism enzyme; and performing enzymolysis on the mixture of the fresh kelp pulp and the composite microorganism enzyme in an enzymolysis vessel to obtain the plant nutrient solution; the composite microorganism enzyme comprises more than one kind each of cellulase, pectinase, protease and amylase, the mass percentage of the cellulases and the pectinases being far greater than that of the proteases and the amylases. The present method for preparing a plant nutrient solution involves a simple enzymolysis process, mild reaction conditions, low costs and no other chemical compositions during the reaction processes, and maintains more of the active ingredients of the fresh kelp.
Owner:WEIHAI SHIDAI MARINE BIOTECH
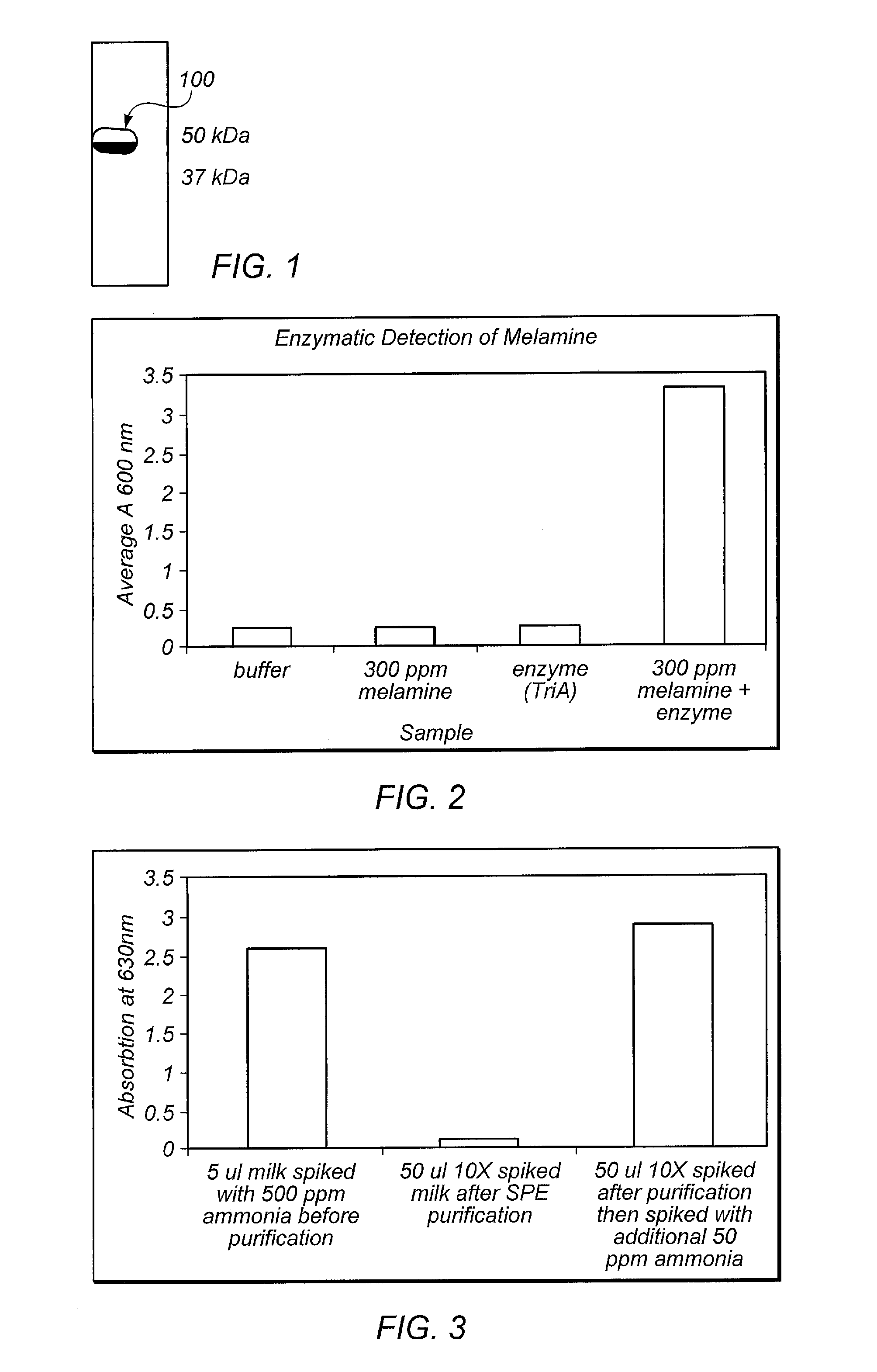
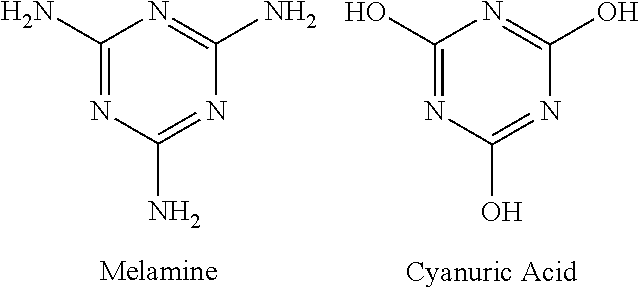
Method and system for enzymatic detection of melamine
ActiveUS20110008809A1Rapid and specific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrobial enzymes
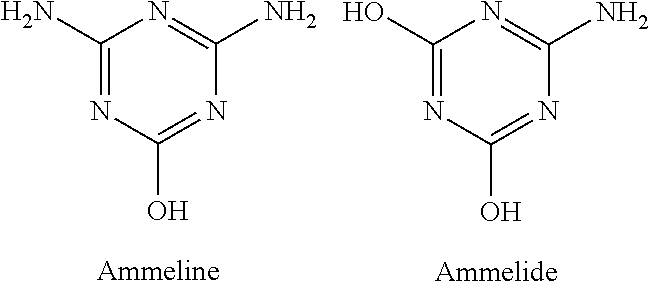
Melamine is a common industrial chemical contaminant which should be absent from food and feed supplies due to melamine's toxicity. Provided is a method to assess the presence of melamine in samples prepared from compositions. The method may include using a microbial enzyme called melamine deaminase which hydrolyzes melamine to ammeline and ammonia. The method may include assessing the presence of any ammonia produced from an enzymatic reaction between the sample and the enzyme.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Microbial enzyme feed additive, its feed formula and preparation method
InactiveCN102488099AImprove conversion ratePromote absorptionAnimal feeding stuffPectinaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a microbial enzyme feed additive, its feed formula and preparation method. The additive is composed of the following components by weight: 30-50 of amylases, 15-35 parts of cellulases, 3-9 parts of xylanases, 10-20 parts of pectinases, 30-50 parts of trypsins, 10-20 parts of adenosine triphosphatases, and 1-2 of a composite bacterial liquid. The microbial enzyme feed additive of the invention comprises a variety of enzymes and microorganisms, and the formula composition is obtained through multiple experiments; various enzymes and microorganisms added to the feed formula can interact on each other and make adjustments so as to greatly improve the protein conversion rate, and meanwhile, the enzymes and beneficial microorganisms can also adjust the digestive system of animals and enhance the absorption of feed nutrition by animals. The microbial enzyme feed additive of the invention can be applied in various common feed. Of course, the feed formula in the invention is a most preferable scheme. The microbial enzyme feed additive in the invention is suitable to chickens, ducks, geese and other poultry, and is also suitable for pigs, cattle and sheep, as well ascan be applied in fish, shrimps and other aquacultures.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DATAINONG FEED
Preparation method of algae extract
InactiveCN108935523APromote absorptionImprove biological activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFiltrationSecondary metabolite
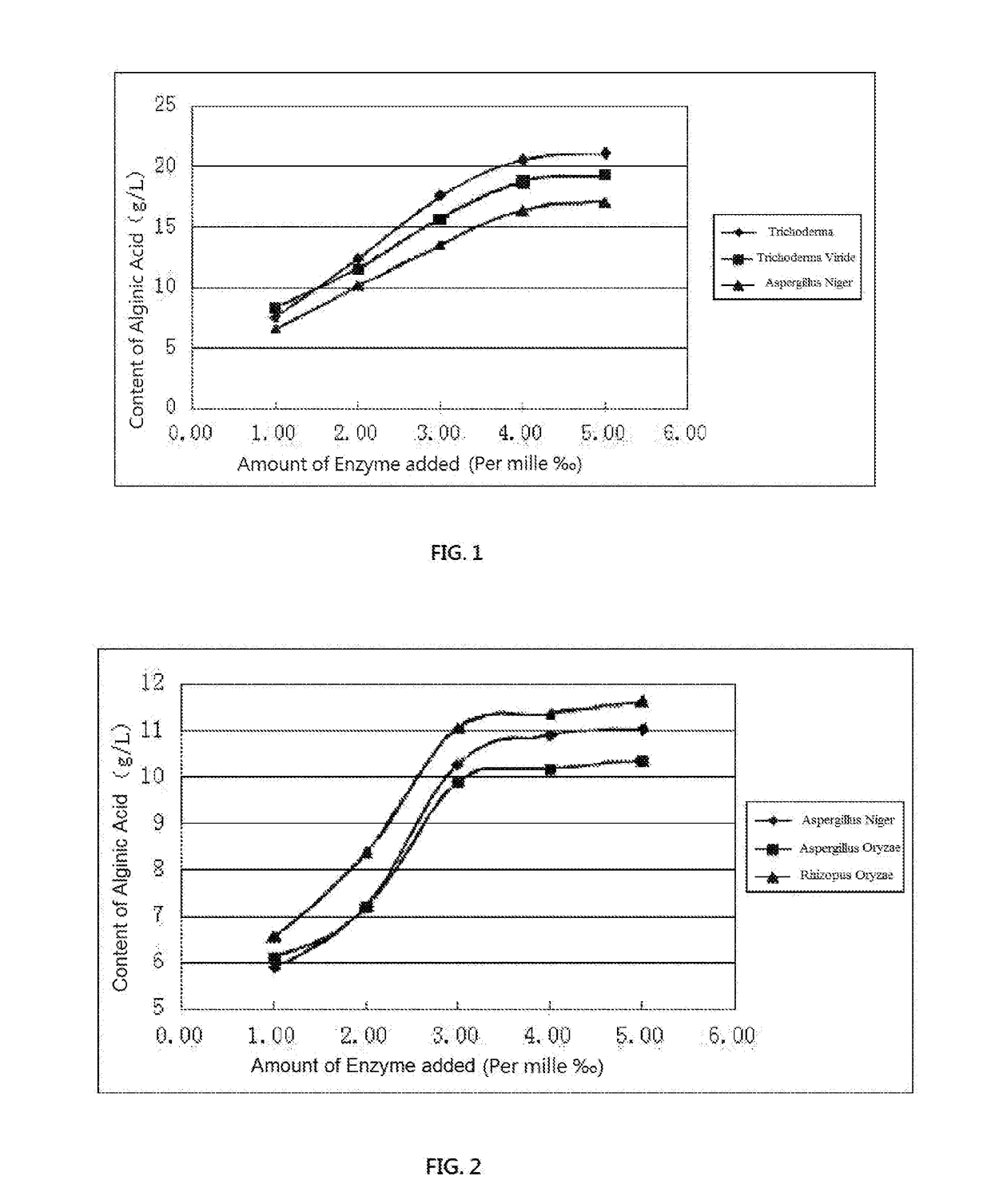
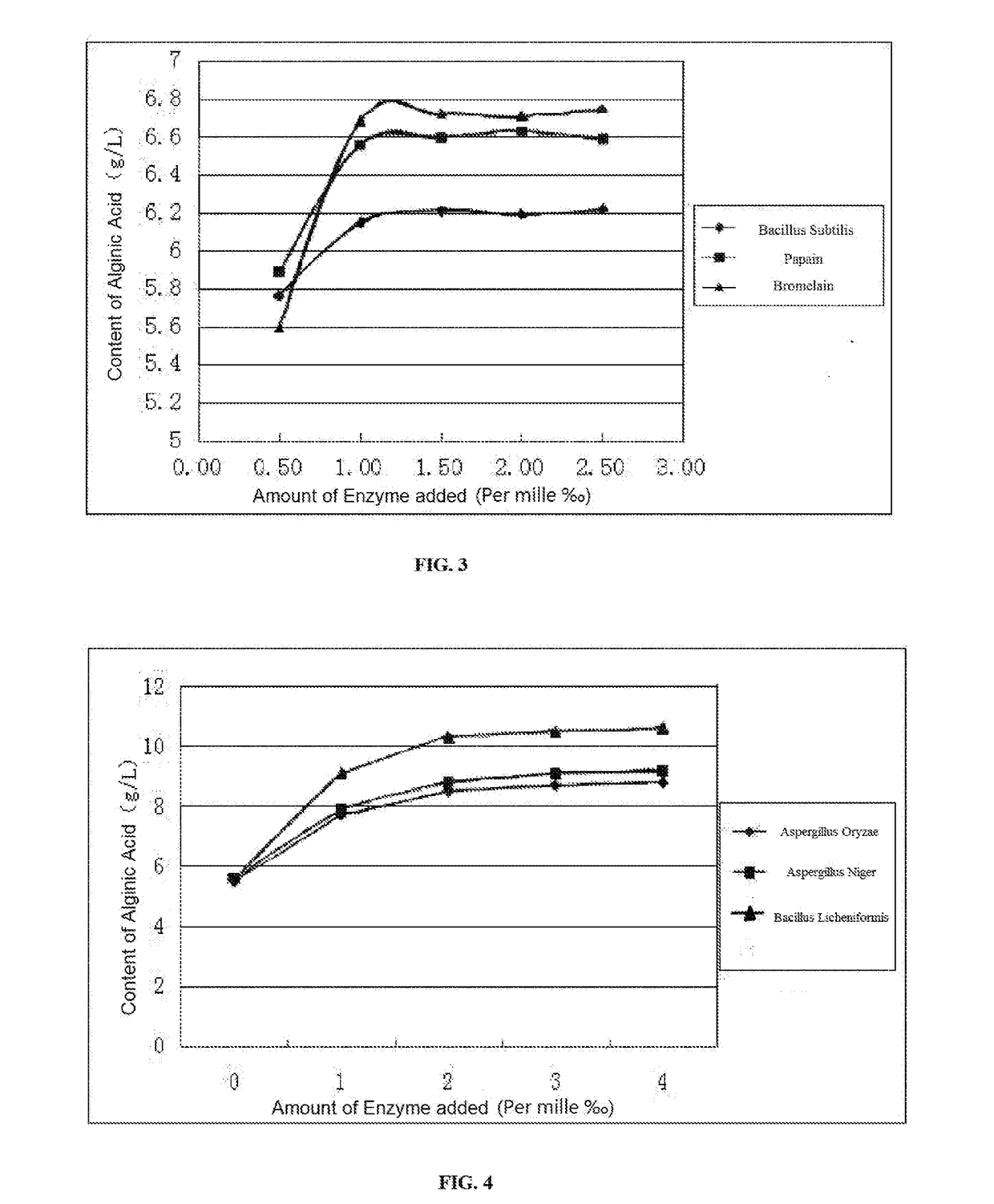
The invention provides a preparation method of algae extract. The preparation method comprises the following steps: impurity removal and cleaning, mincing, homogenization, pH regulation, pressurization and alkaline hydrolysis, fermentation and degradation of compound microbial enzyme and filtration, wherein a filtrate product is algae extracting liquid, and filter residue can be directly compounded into a soil conditioning agent or is dried and prepared into a algae-extract dry-powder product. The active algae extract prepared by the invention has the beneficial effects that the components such as minerals, alginic acid, algae polyphenol, mannitol and beneficial element are retained, protein and polysaccharide components in algae are degraded, and the absorption is easy; beneficial microbes and various enzymes are added, and various microbial secondary metabolites can be generated, so that the biological activity is better.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
Ginseng endogenesis zygorhynchus moelleri mildew as well as method for preparing ginsenoside Rd by utilizing same
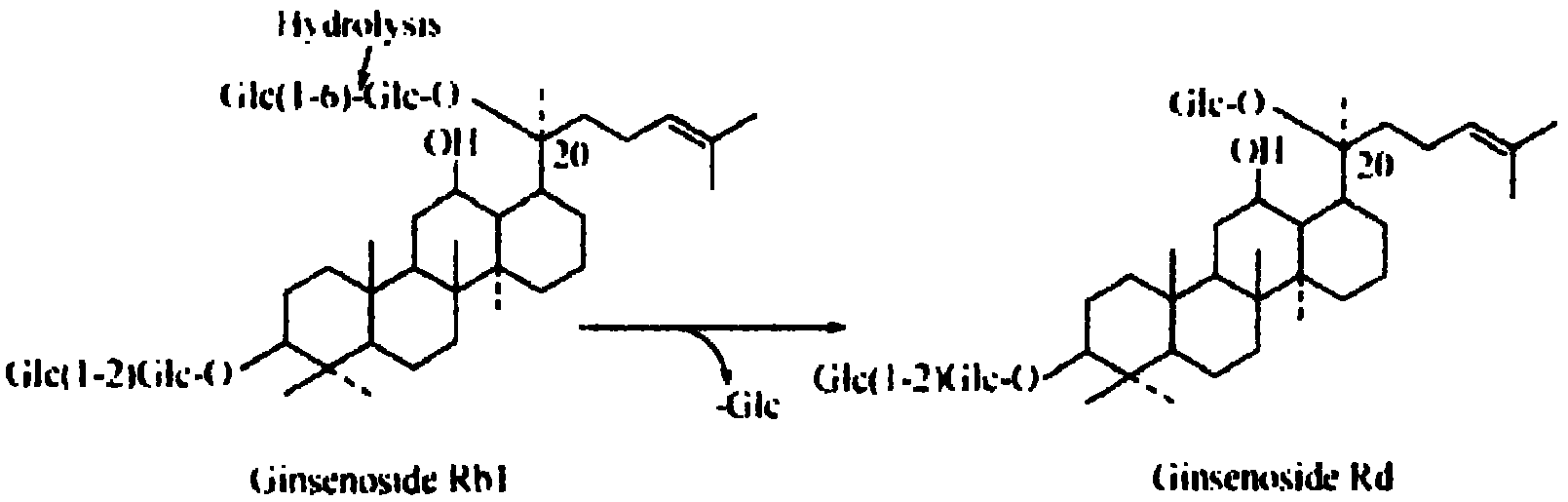
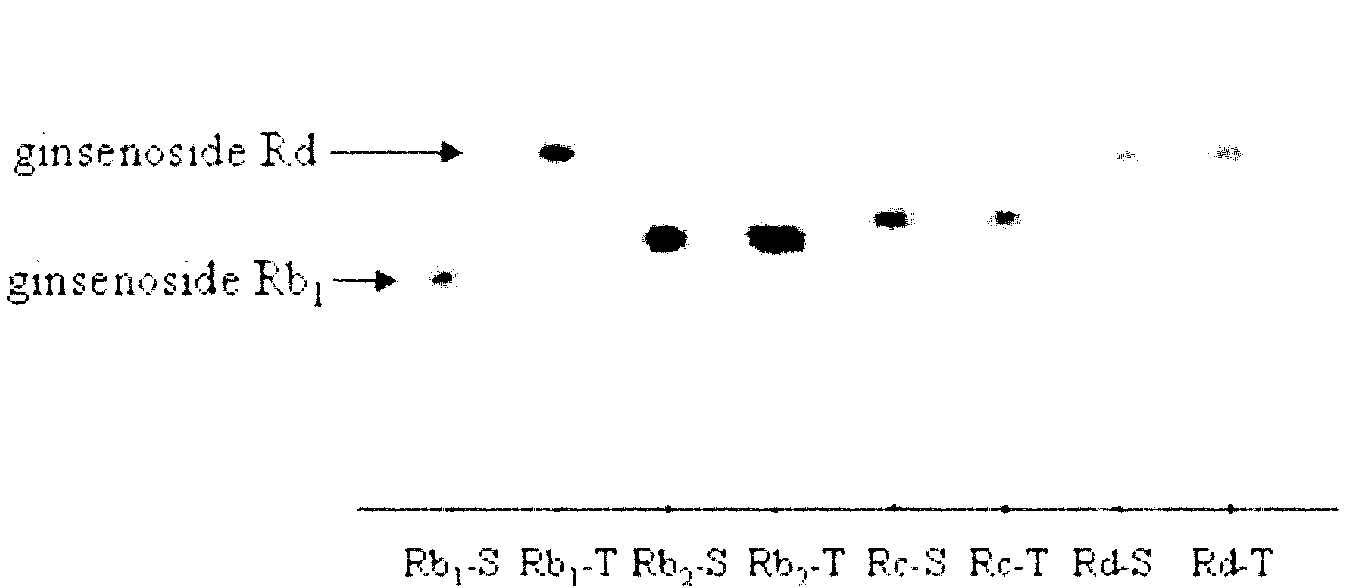
The invention relates to ginseng endogenesis zygorhynchus moelleri mildew (CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection): No.4315). The mildew has the capability for preparing Rd by converting a substrate ginsenoside Rb1 and has higher substrate unicity and product unicity, and the preparation of the ginsenoside Rd by utilizing the mildew can adopt in-site conversion. A method for preparing the ginsenoside Rd comprising the following steps of: dibbling the mildew in a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium containing the ginsenoside Rb1, standing still at 25 DEG C and culturing for 5-7 days or vaccinating the mildew on an enzyme production culture medium by adopting a microorganism enzymic method and culturing at 28 DEG C for 5-7 days, collecting enzyme liquid, mixing with the ginsenoside Rb1 and reacting at 40 DEG C for 24h. The ginsenoside Rd produced by adopting the technical scheme of the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, simplicity, convenience, safety, reliability and low cost without side products, the purity of the fermentation product Rd is higher than 90 percent, and the conversion rate can be higher than 60 percent.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Method for Producing Biodiesel
InactiveUS20100047884A1Maximize productivityYield maximizationBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBiodieselMicrobial enzymes
The invention relates to the utilisation of fatty materials with substantial free fatty acid content in the production of biodiesel by the use of microbial enzymes that are effective in a solvent-free process for the production of esters of fatty acids and C1-C3 alkyl alcohols.
Owner:N V DESMET BALLESTRA GROUP +1
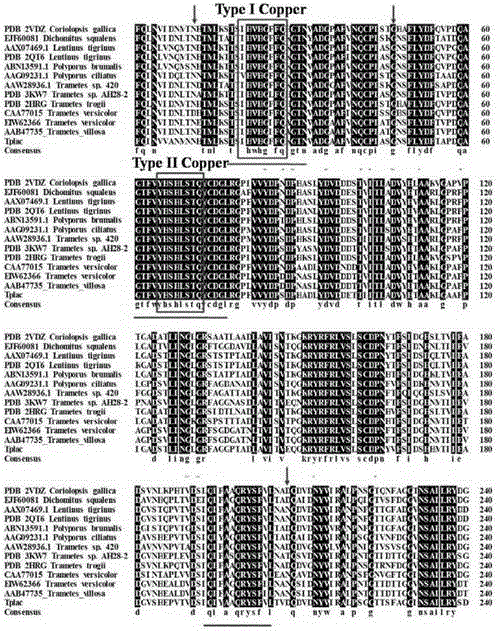
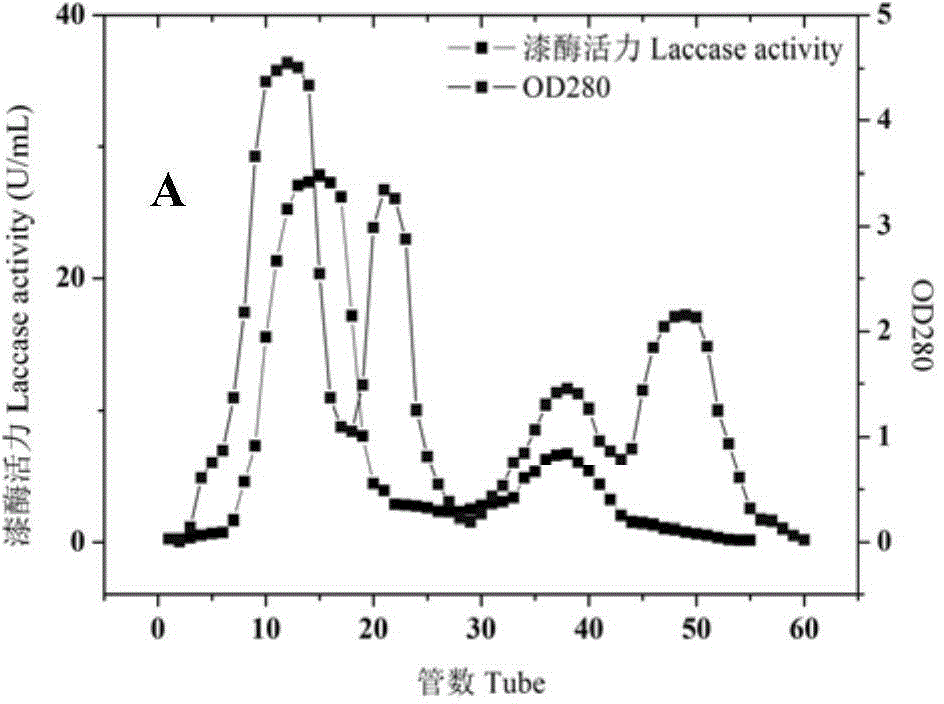
Bacterial strain for producing laccase, method for producing laccase by bacterial strain, produced laccase and application of laccase
InactiveCN104611235ASimple production methodMild culture conditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCongo red
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for converting polydatin to resveratrol by microbial enzyme method
InactiveCN102408999APromote the application of production practiceFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyGlycoside hydrolase
The invention provides a microbial strain aspergillus.aculeatus (CGMCCNo.3876) used for efficiently extracting polydatin and analogues thereof from plant materials such as polygonum cuspidatum, peanut shells, grape skins and the like, and a complex enzyme prepared by fermenting the microbial strain. The complex enzyme of the strain is used for extracting polydatin and analogues thereof by an enzyme method, and the extraction ratio is 2.3%. The extraction ratio of the complex enzyme is improved by 91.7% through treatment compared with the exoenzyme (control) to which the strain aspergillus.aculeatus is not added. The ratio of conversion from polydatin to resveratrol by using the complex enzyme of the strain is above 99.5%. The polygonum cuspidatum glycoside hydrolase purified from the complex enzyme of the strain is used for converting 98% of polydatin to resveratrol, and the conversion ratio is 99.7%. The purity of resveratrol is 98.5%. By the invention, a novel complex enzyme preparation is actually provided for production, the problems of low catalytic activity of enzymes, low conversion ratio, overlong time and high cost in current production upgrading are fundamentally solved, and the production practice application is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Granular material for producing bob veal
The invention relates to a granular material for produing bob veal, and the granular material consists of corn, bran, whey powder, wheat albumen powder, peanut albumen powder, lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan, a compound microbial enzyme preparation, a vitamin complex and a mineral substance compound. Tests show that after calves are fed with the granular material provided by the invention, the granular material and milk powder substitutes can be used together to produce veal with high quality, and on the premise of not influencing the performance of the produced veal, the disease incident of calves can be reduced, and the health status of the calves can be improved.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com