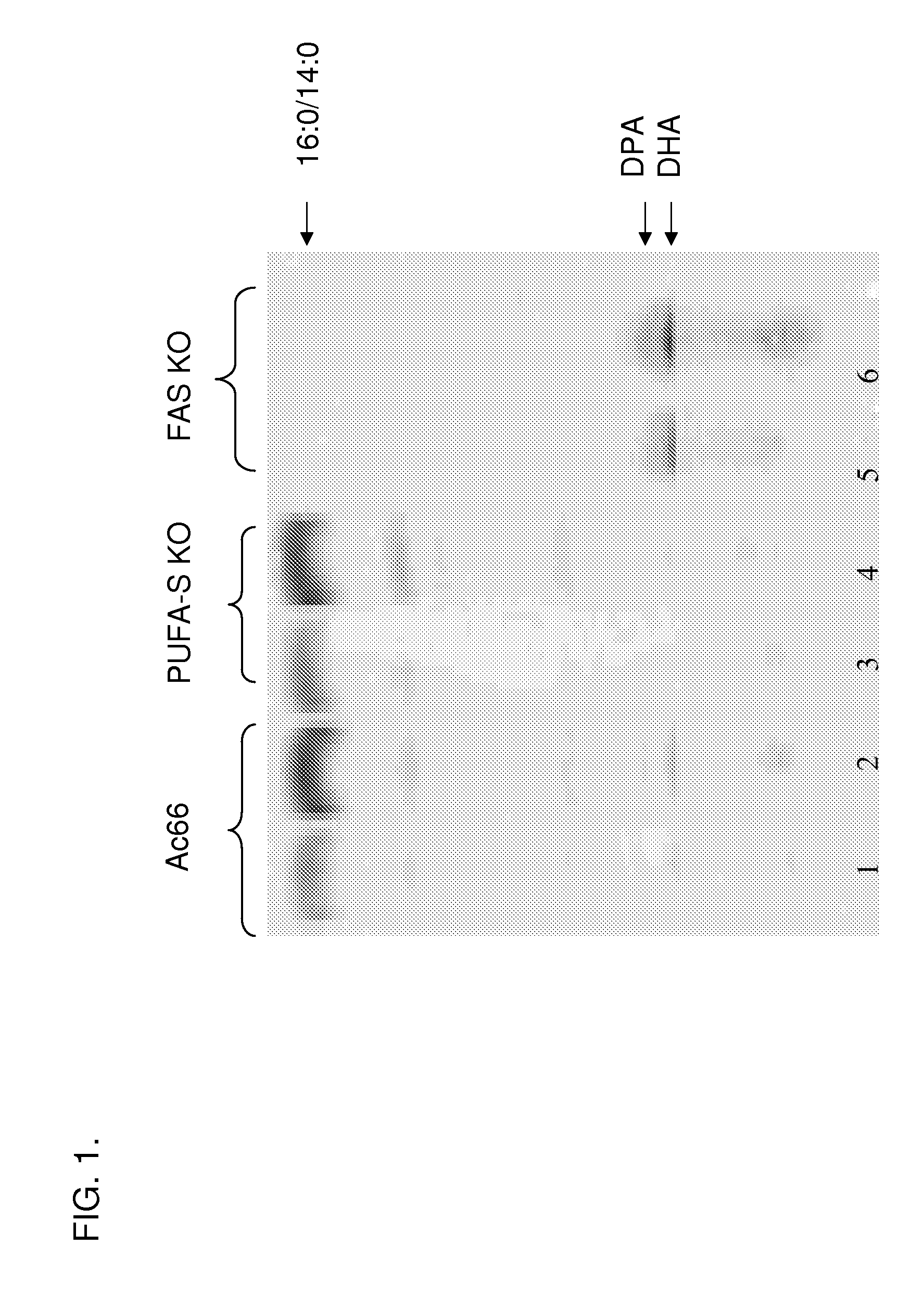
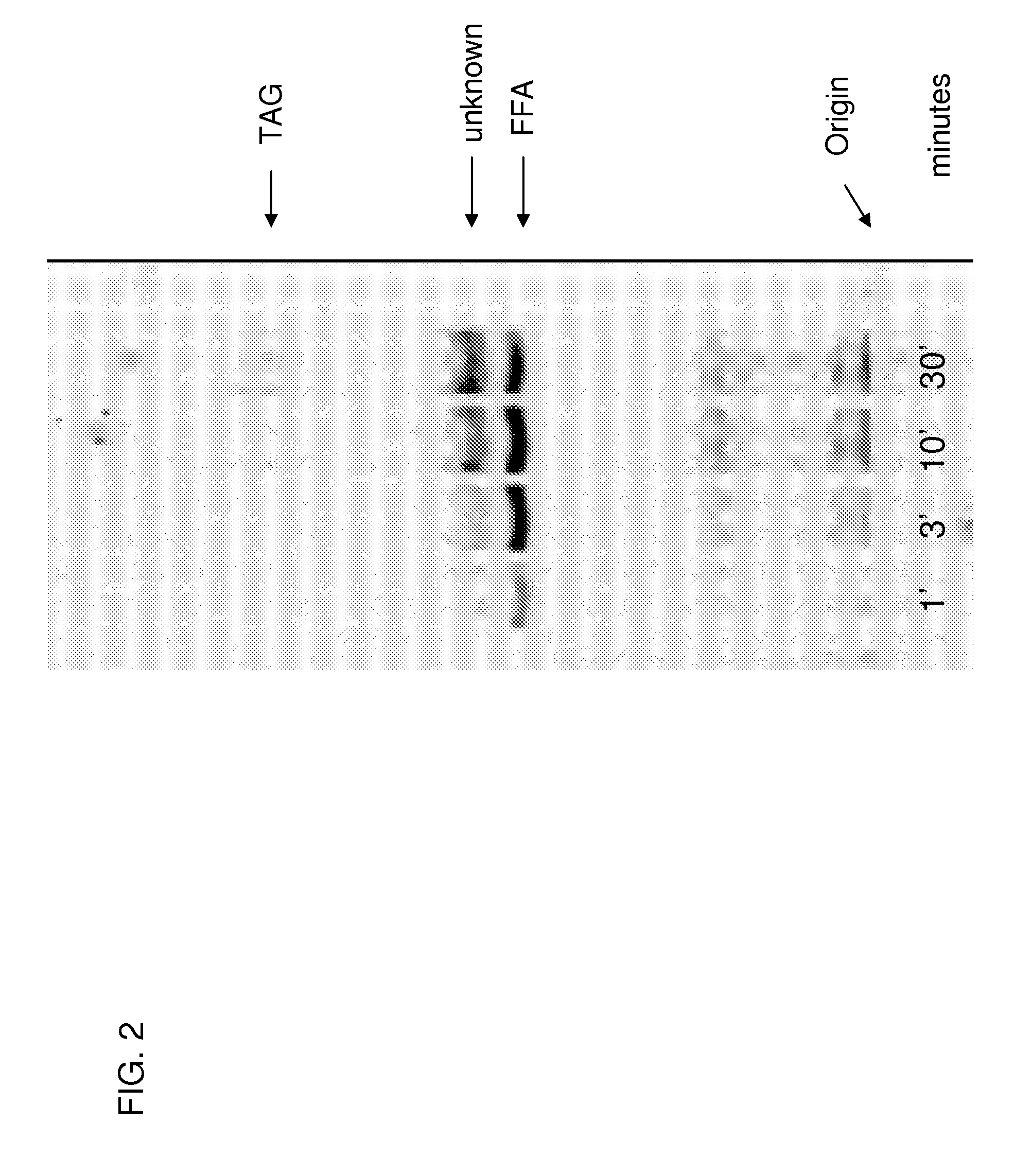
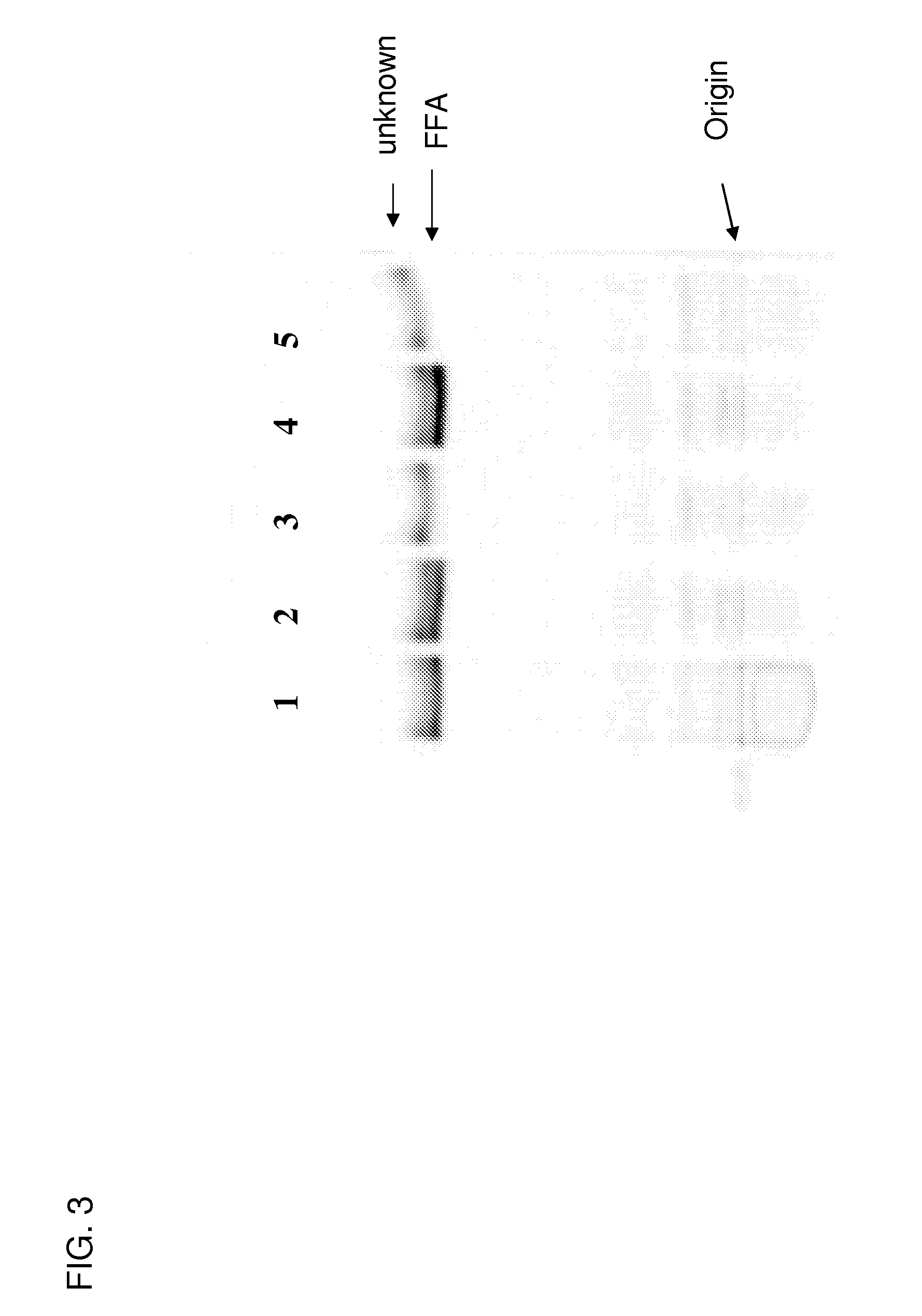
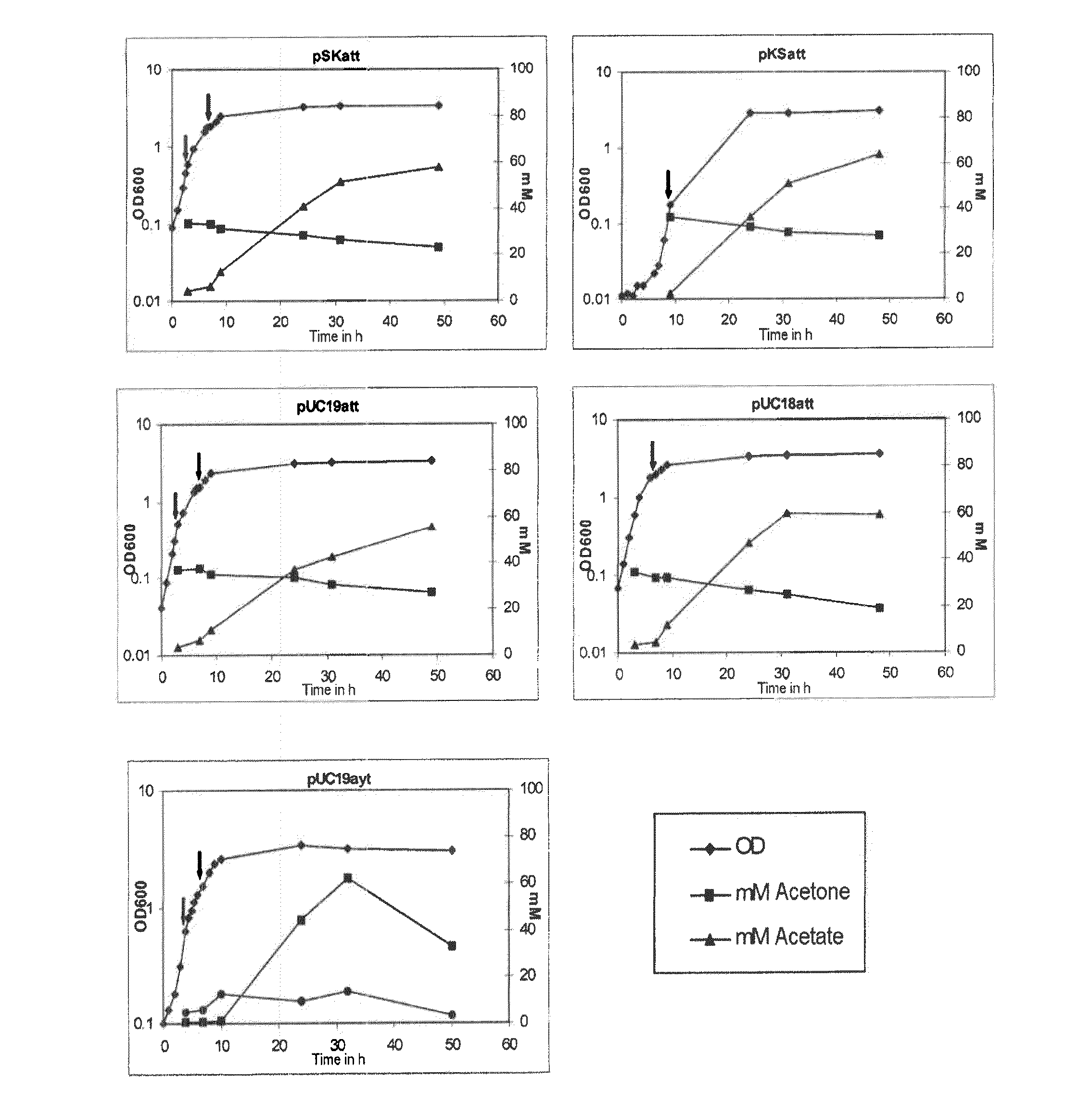
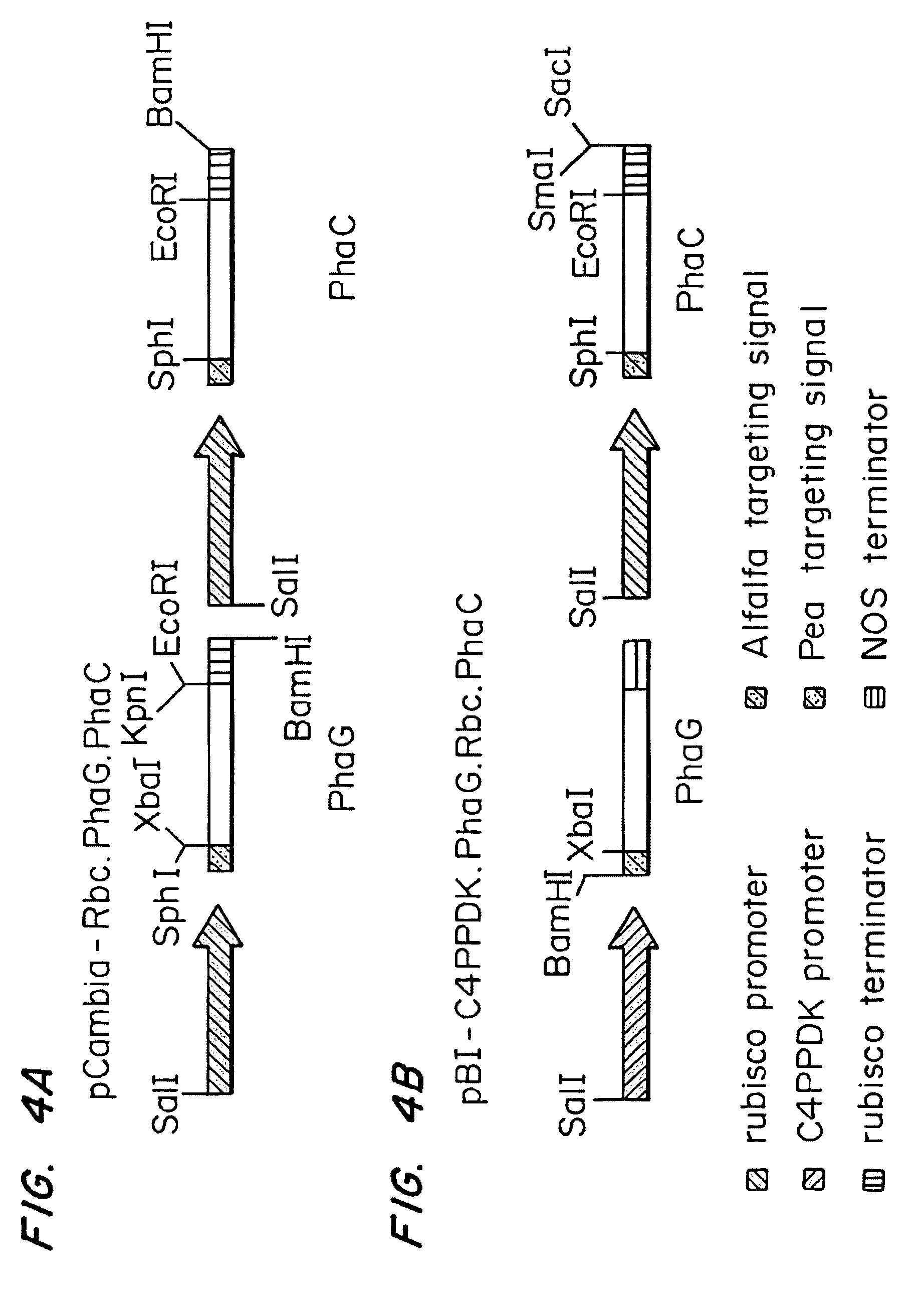
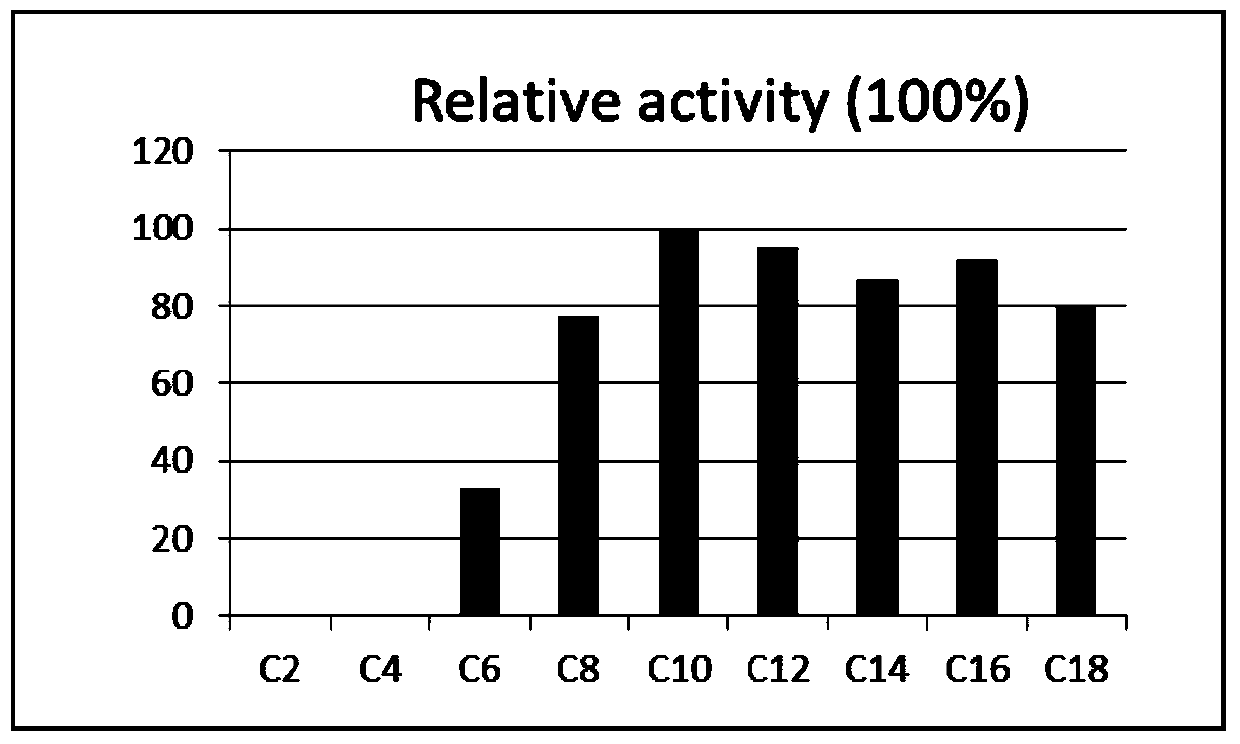
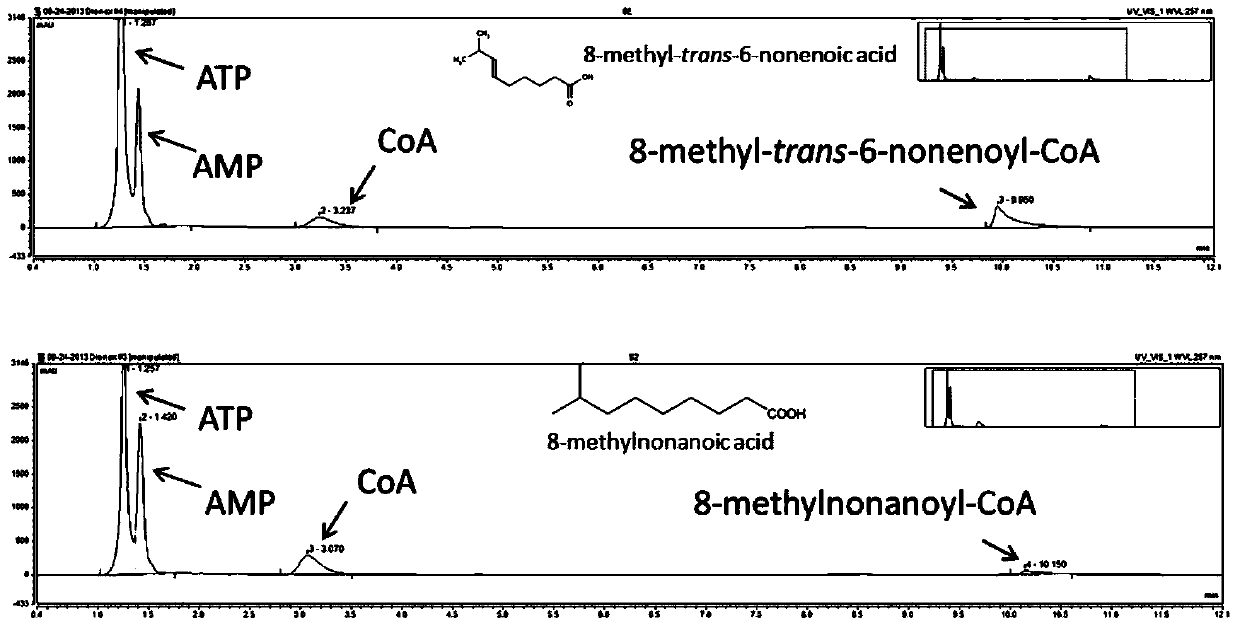
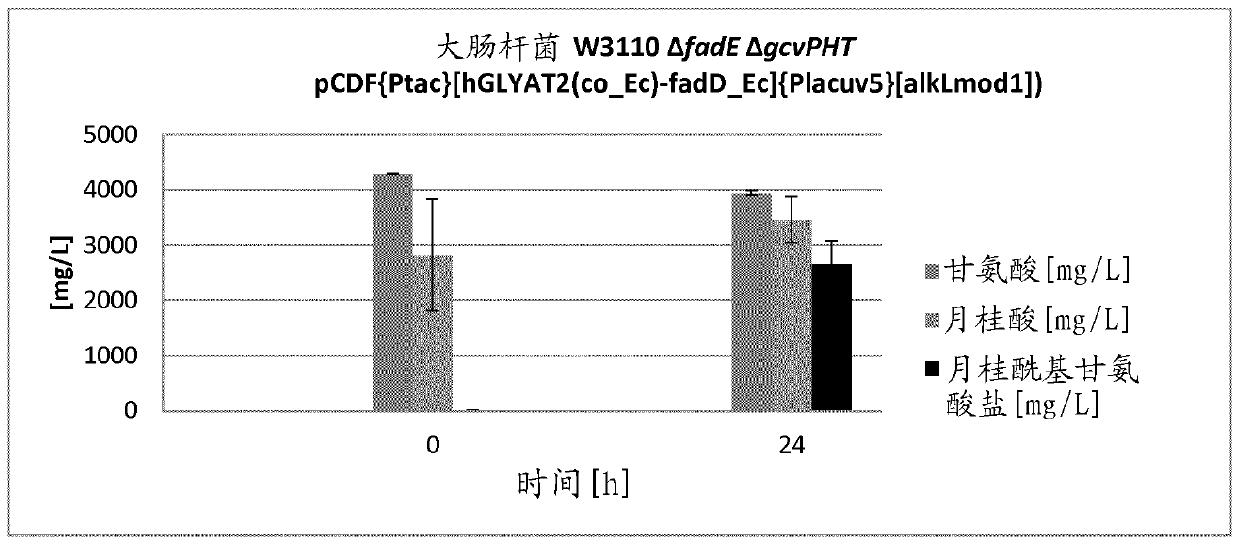
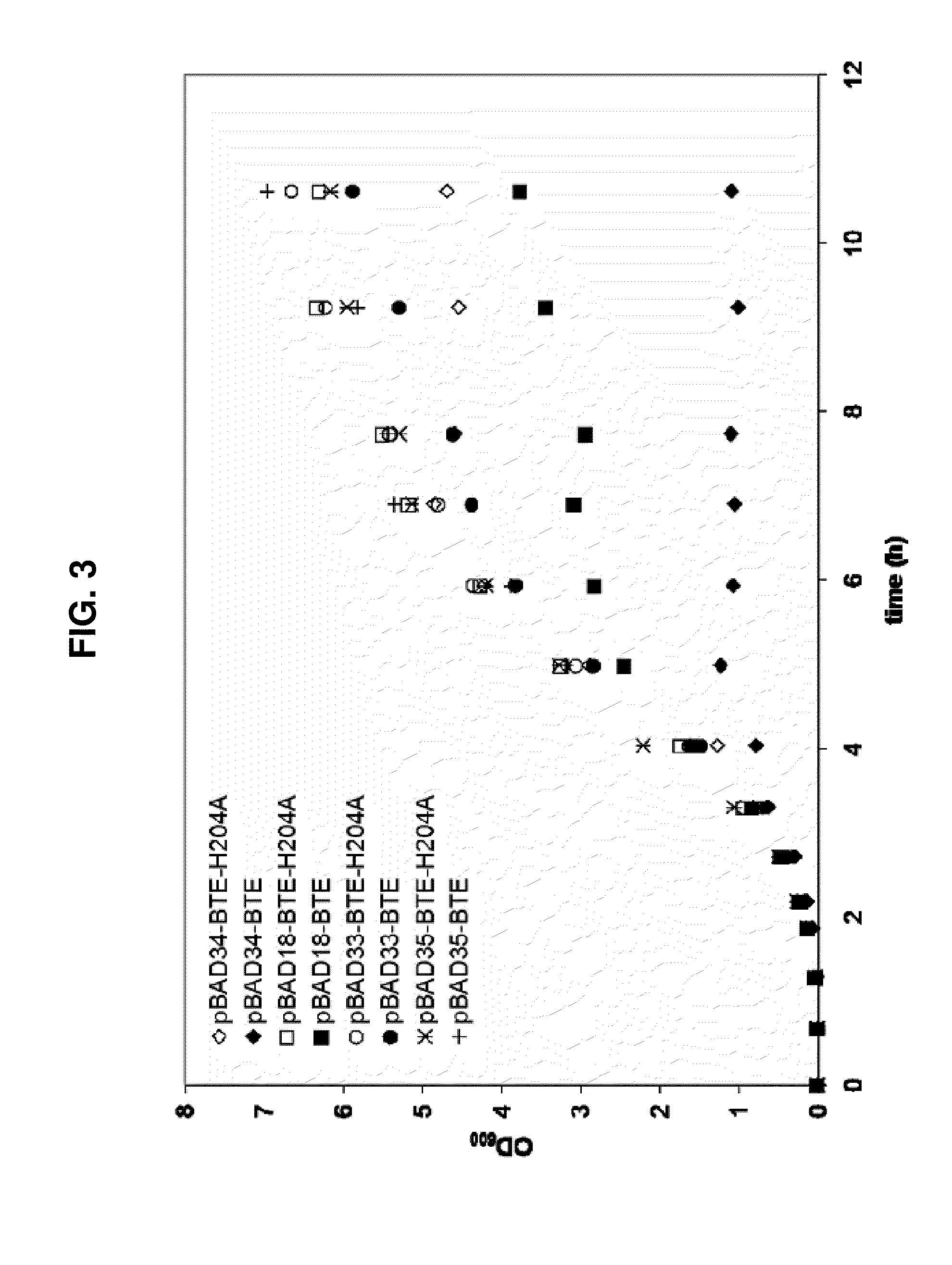
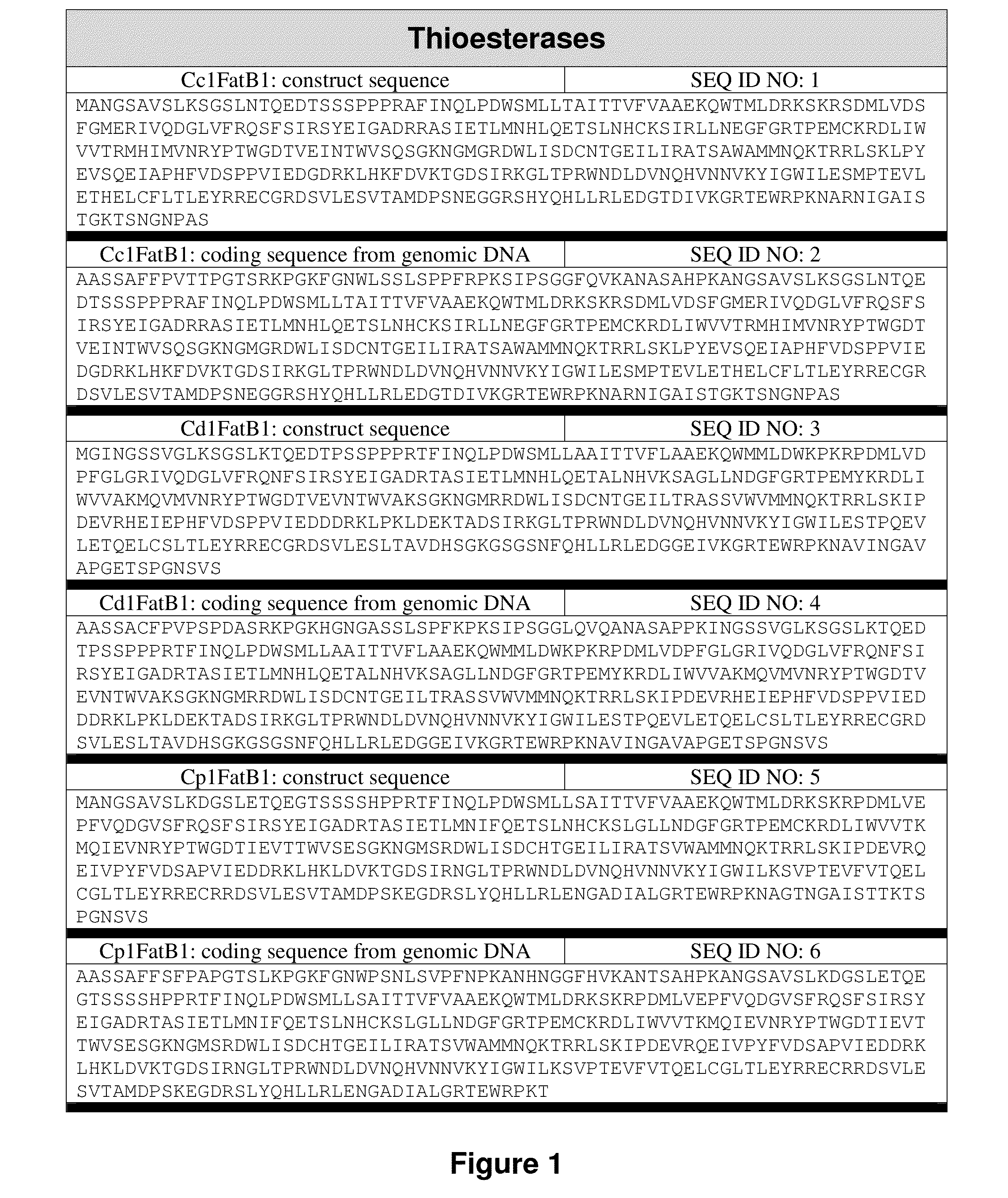
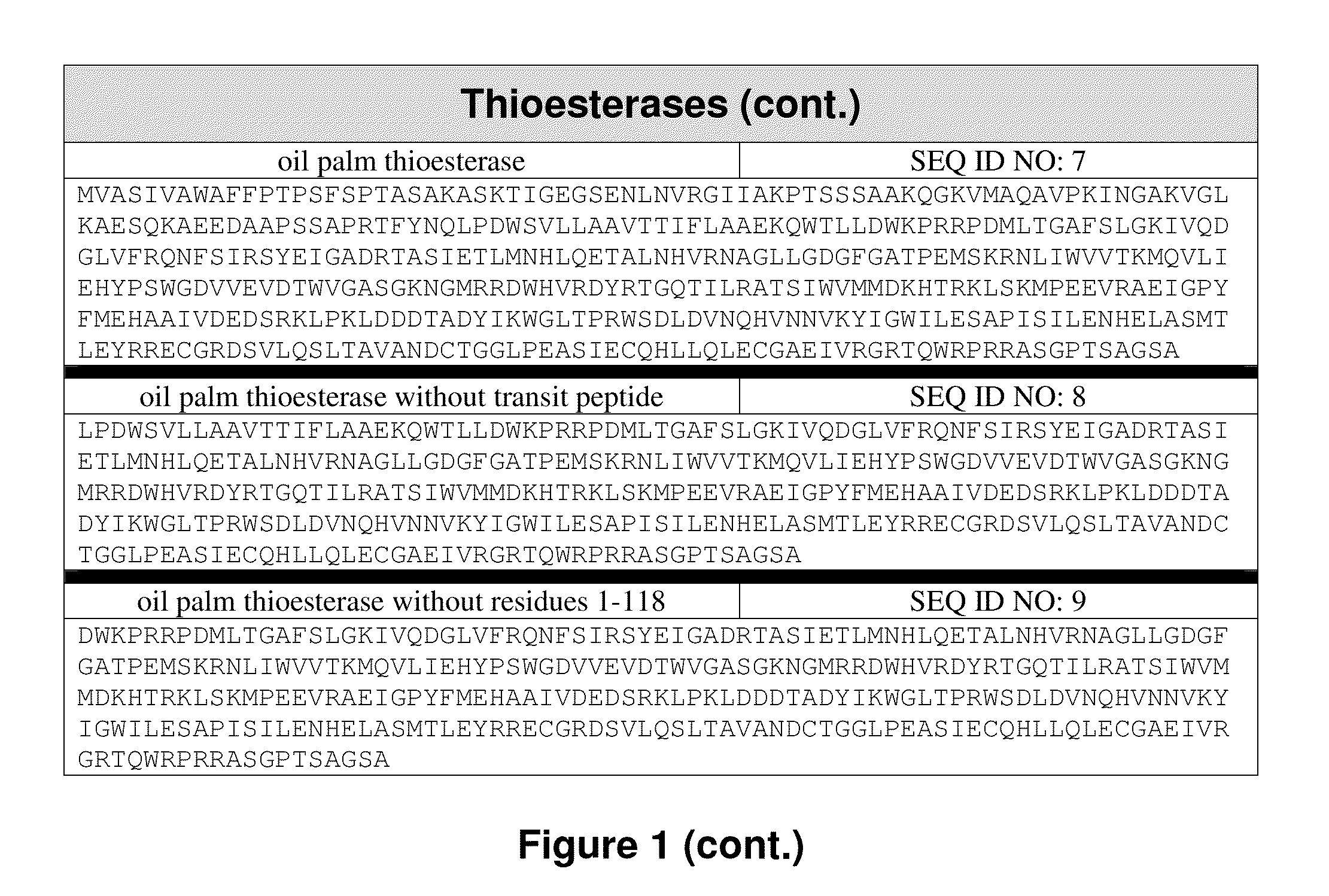
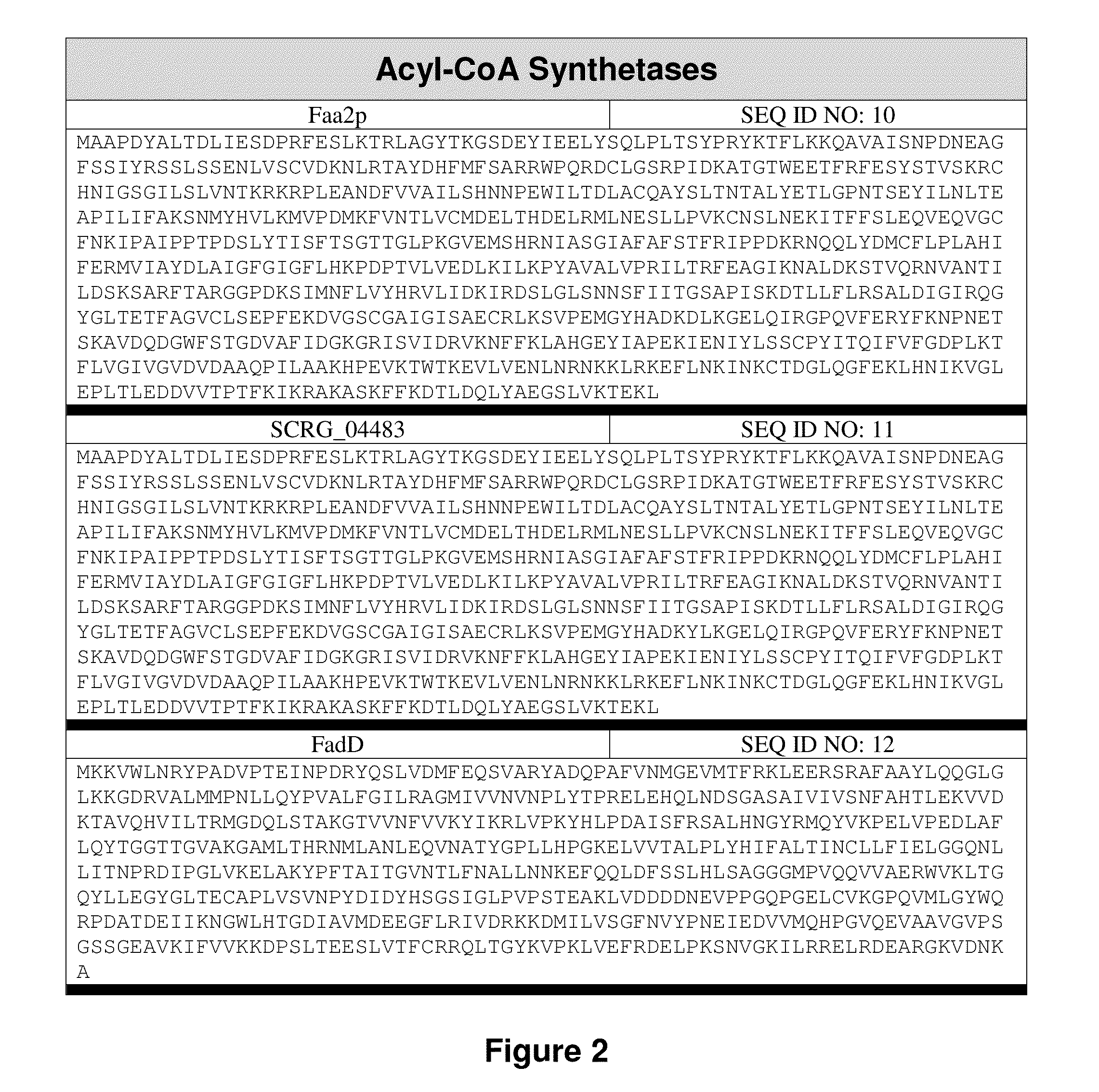
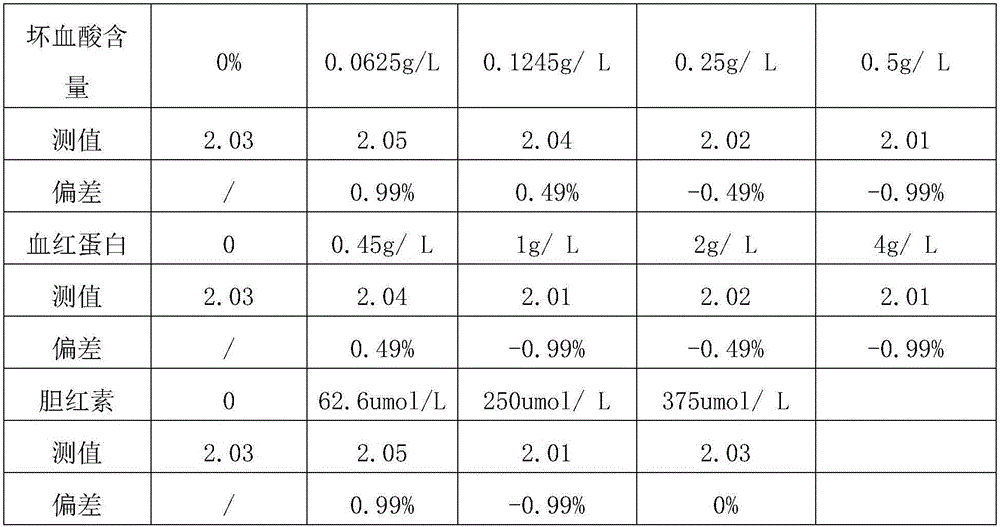
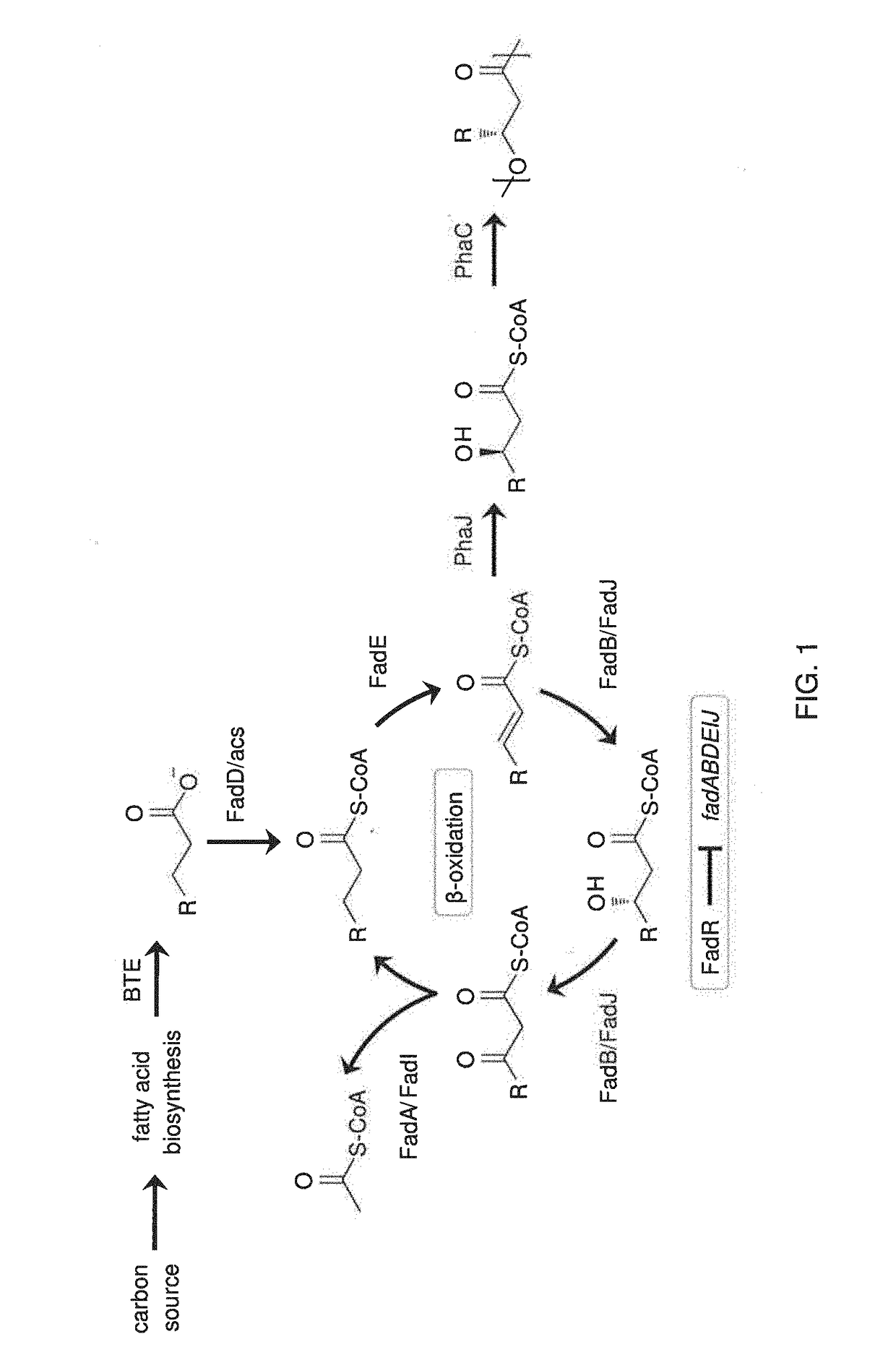
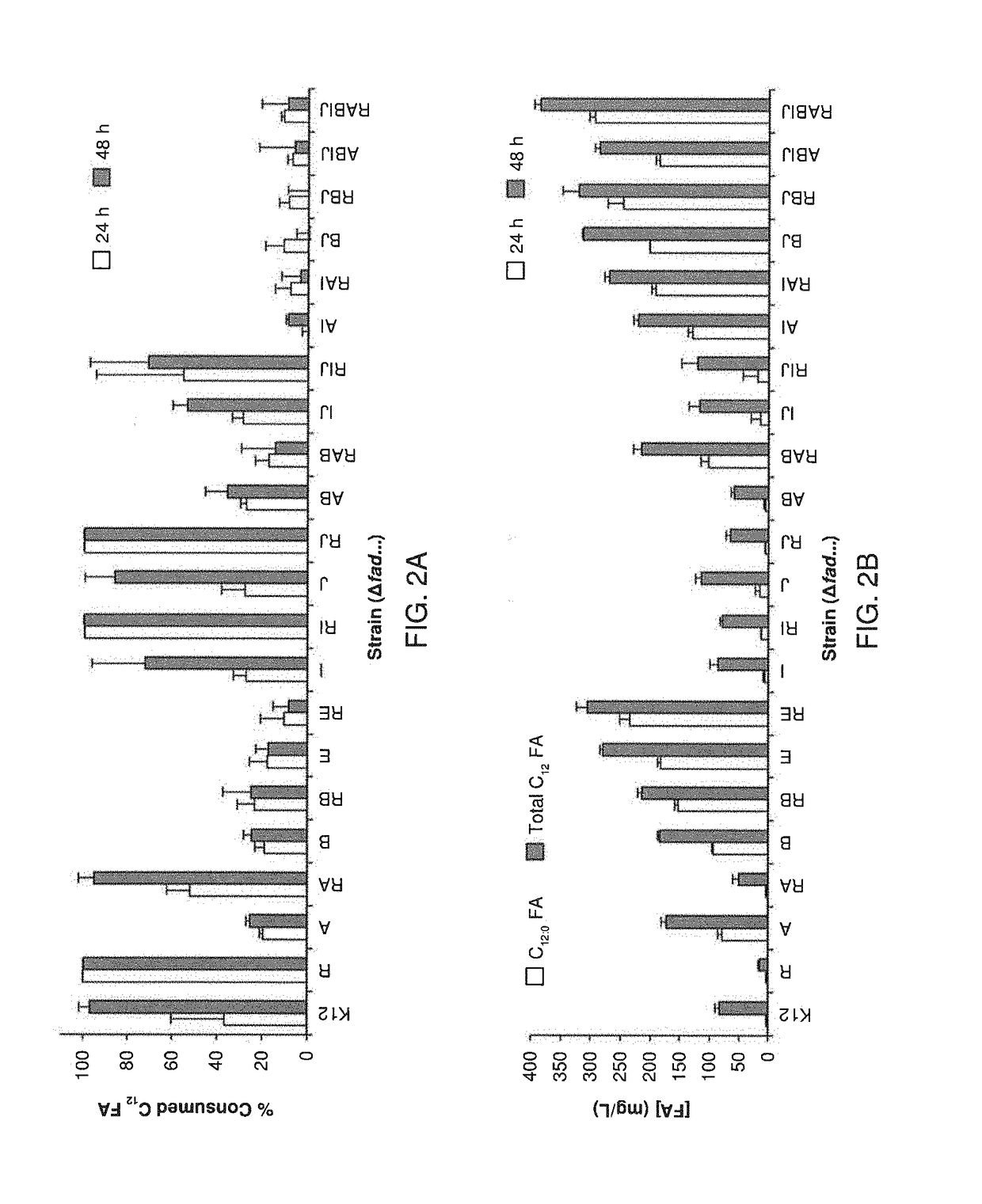
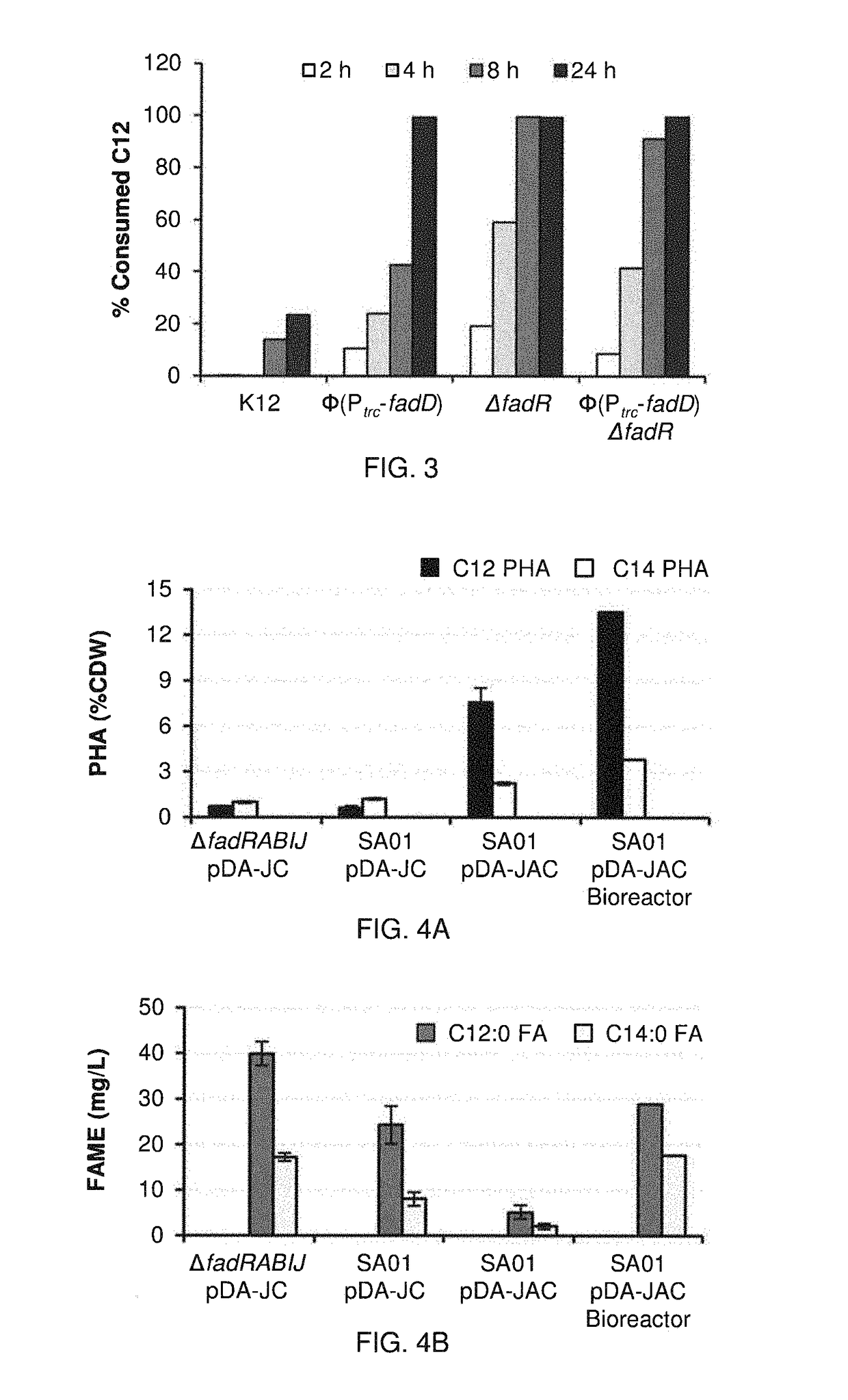
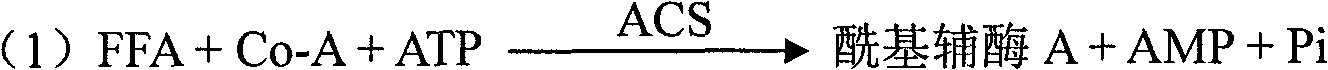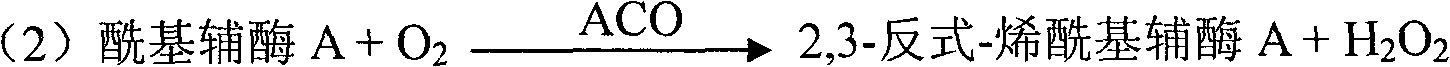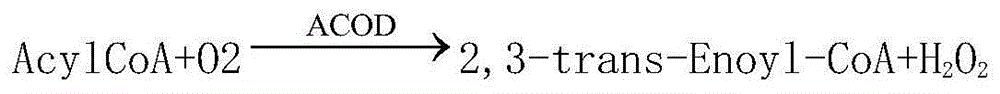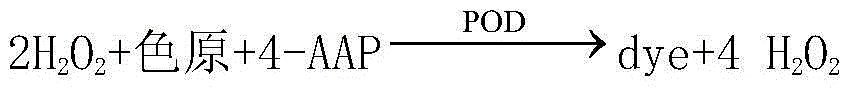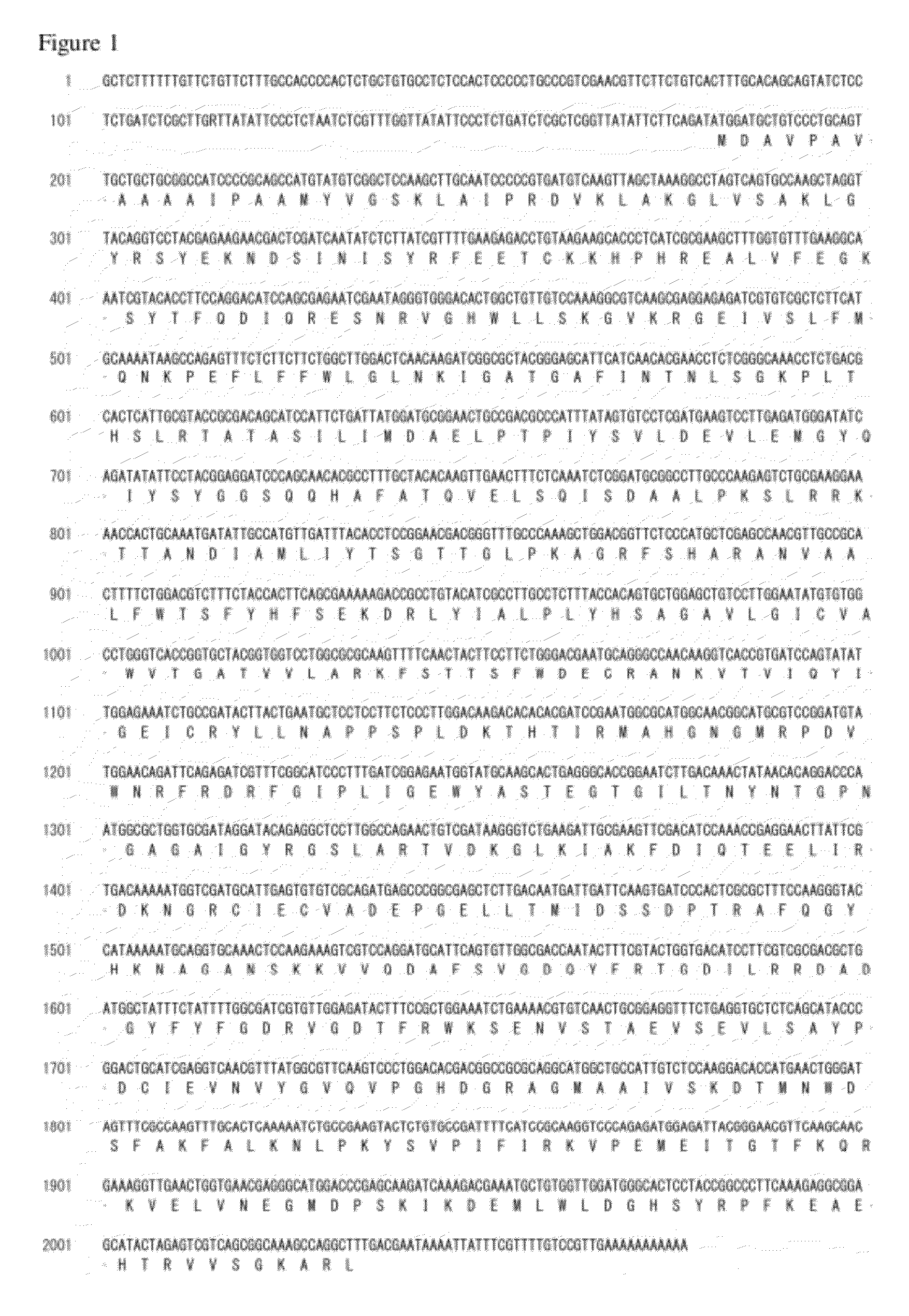Patents
Literature
43 results about "Acyl Coenzyme A Synthetases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using PUFA polyketide synthase systems
InactiveUS20070245431A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
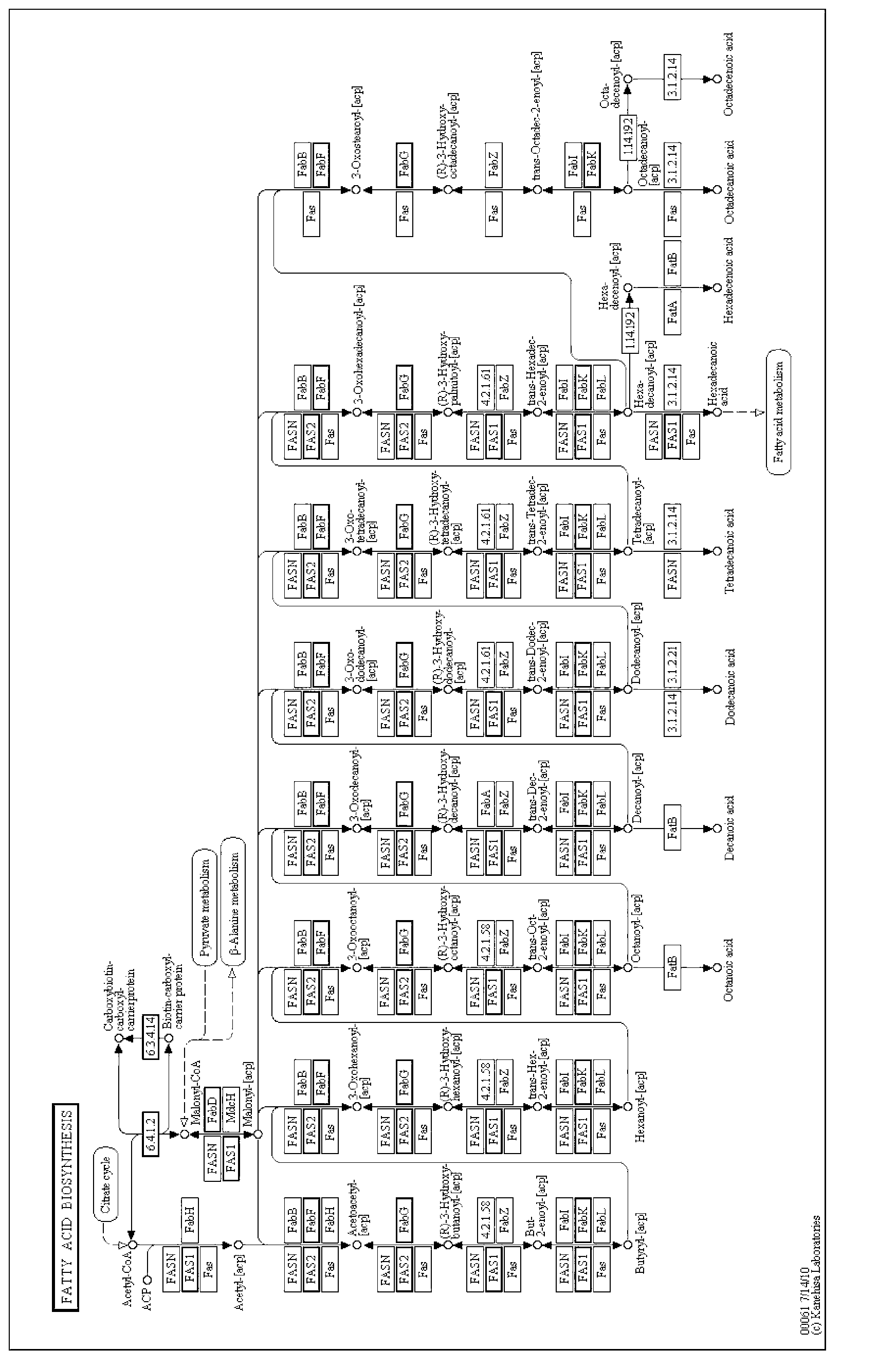
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the plant or plant cell, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
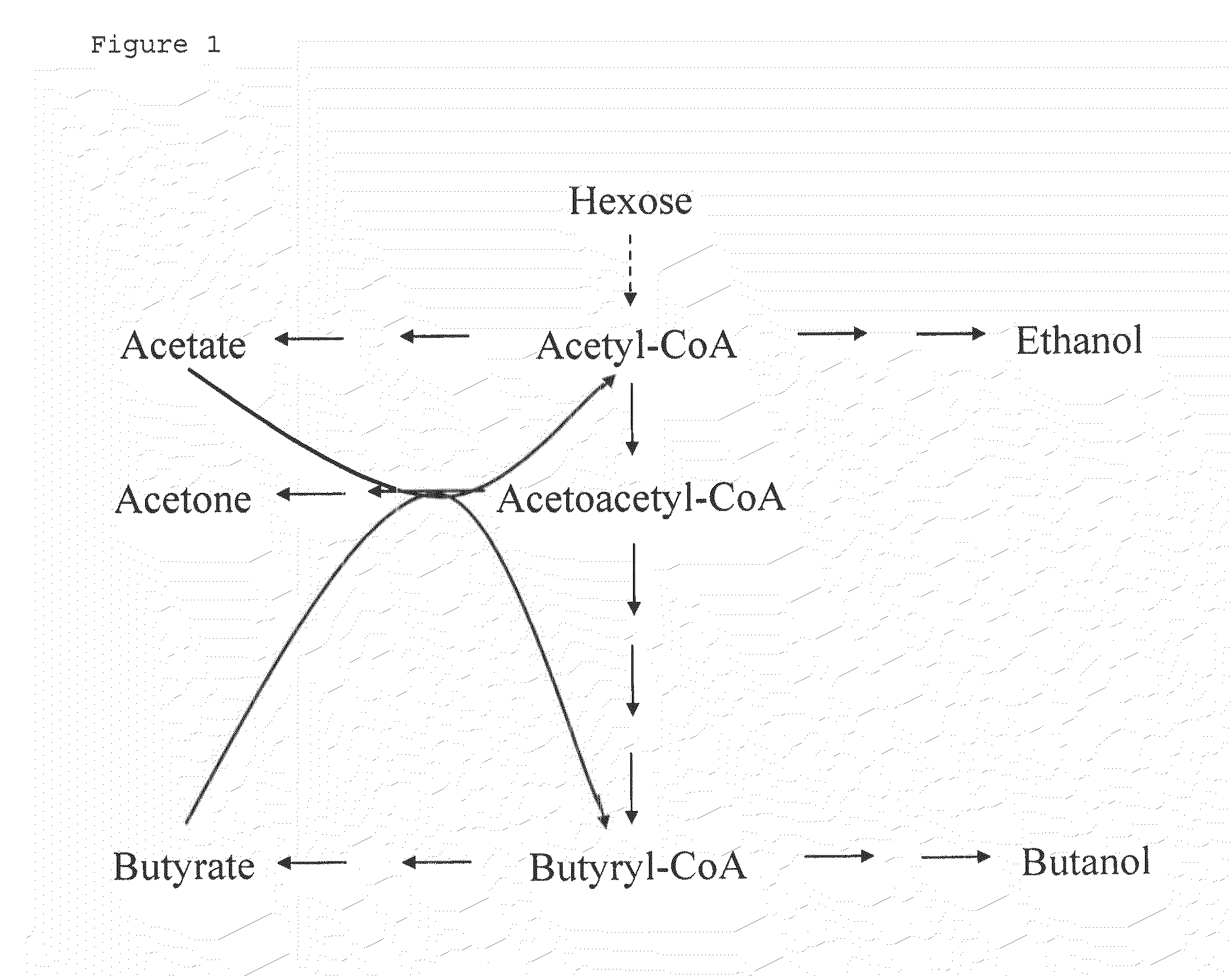
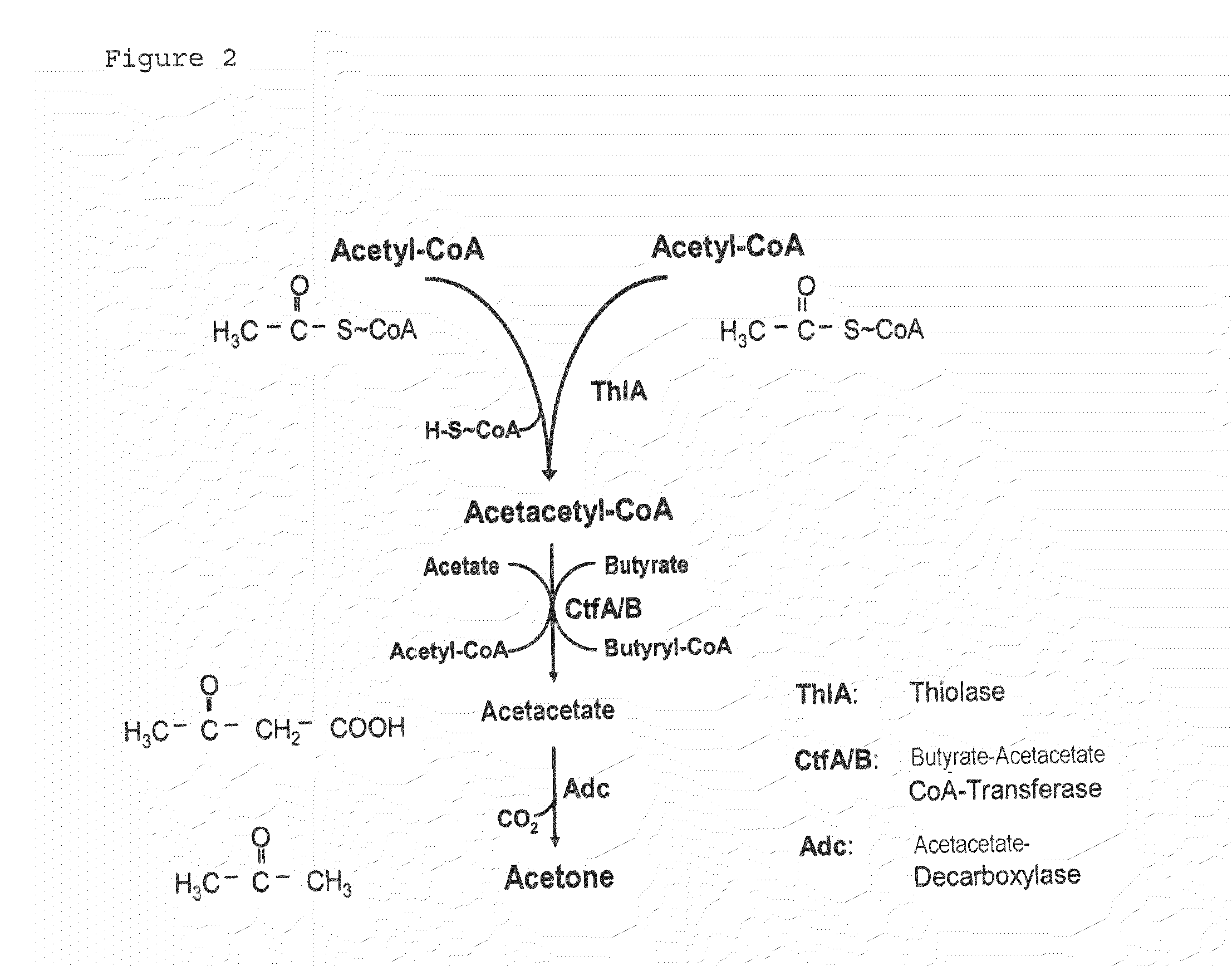
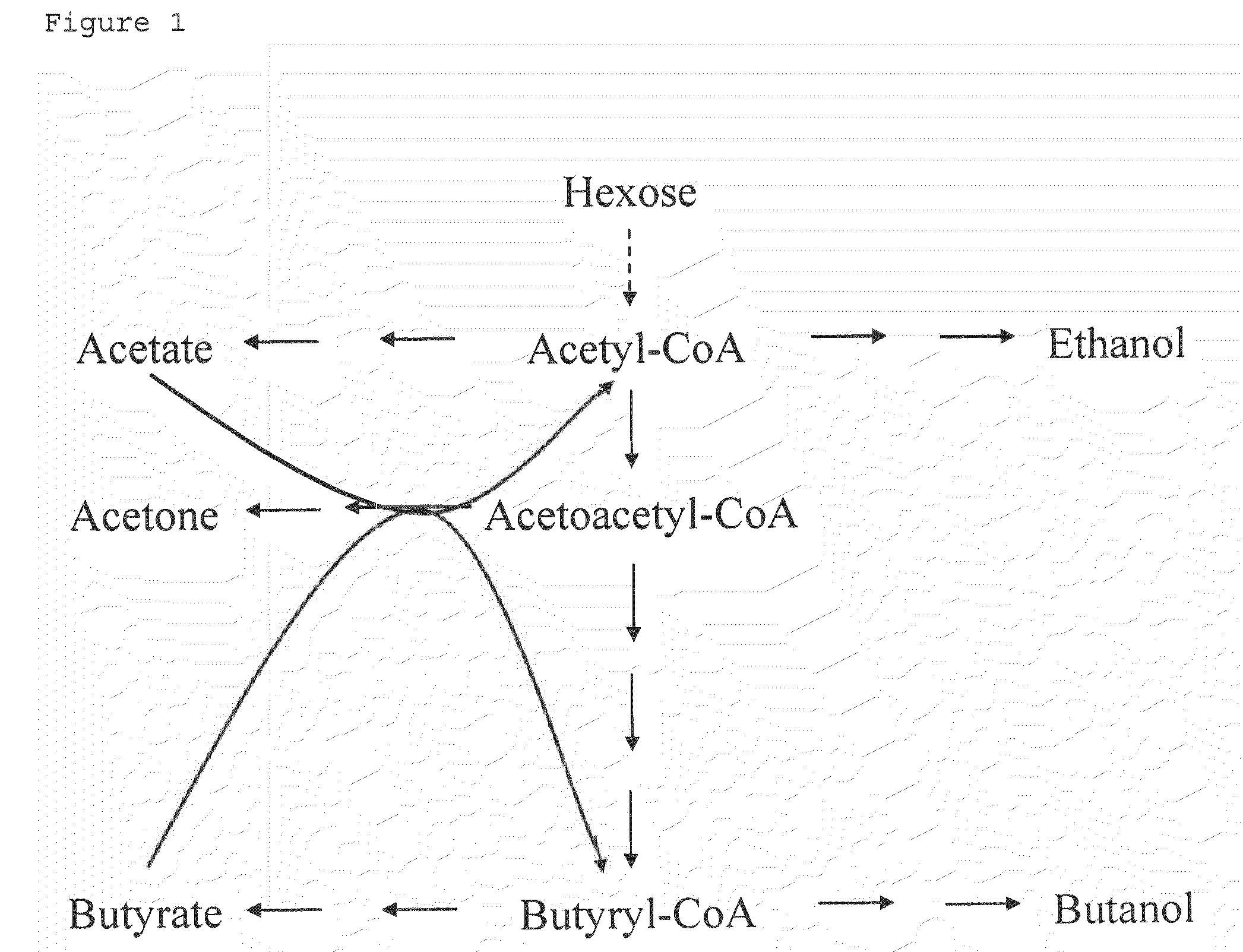
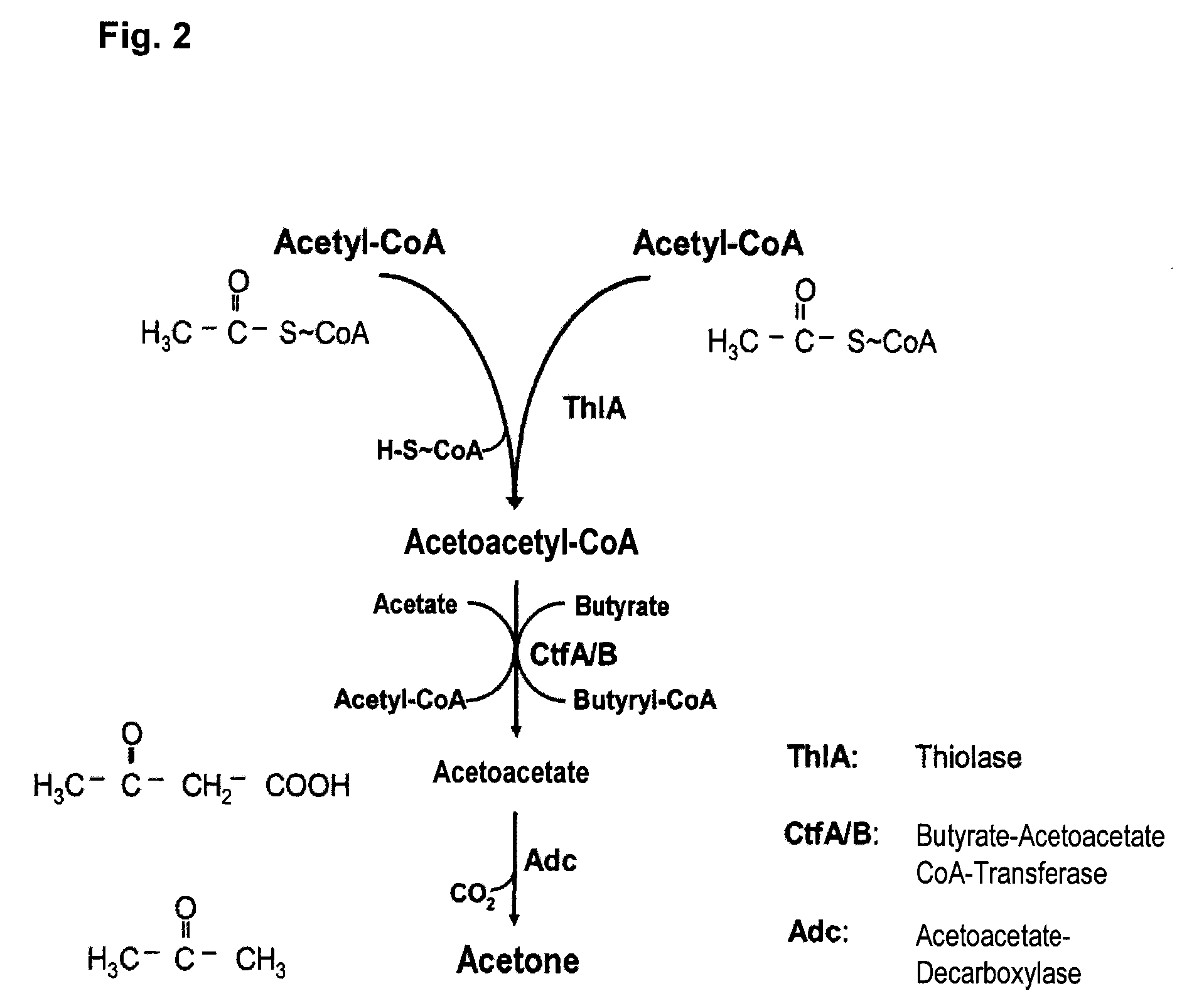
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
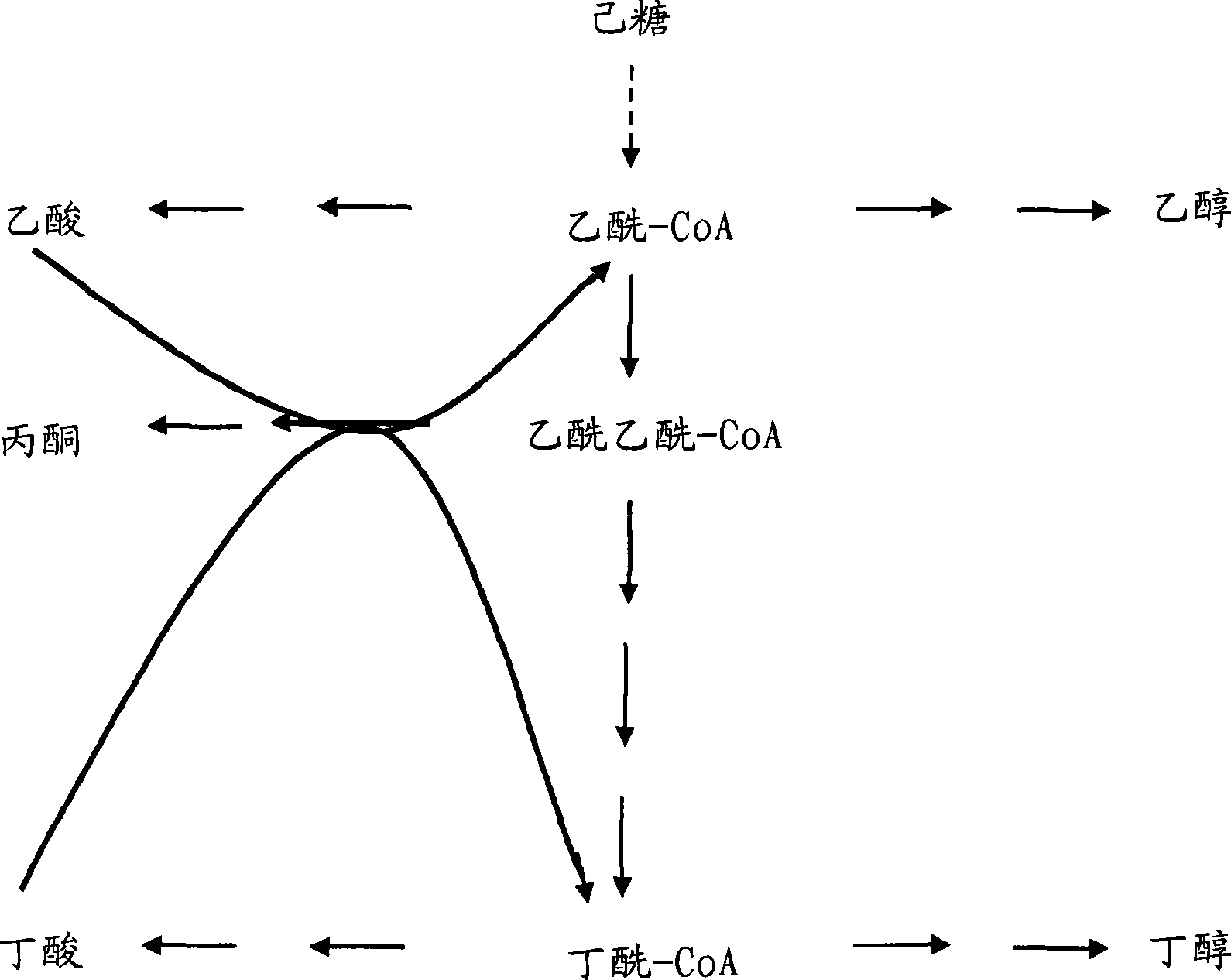
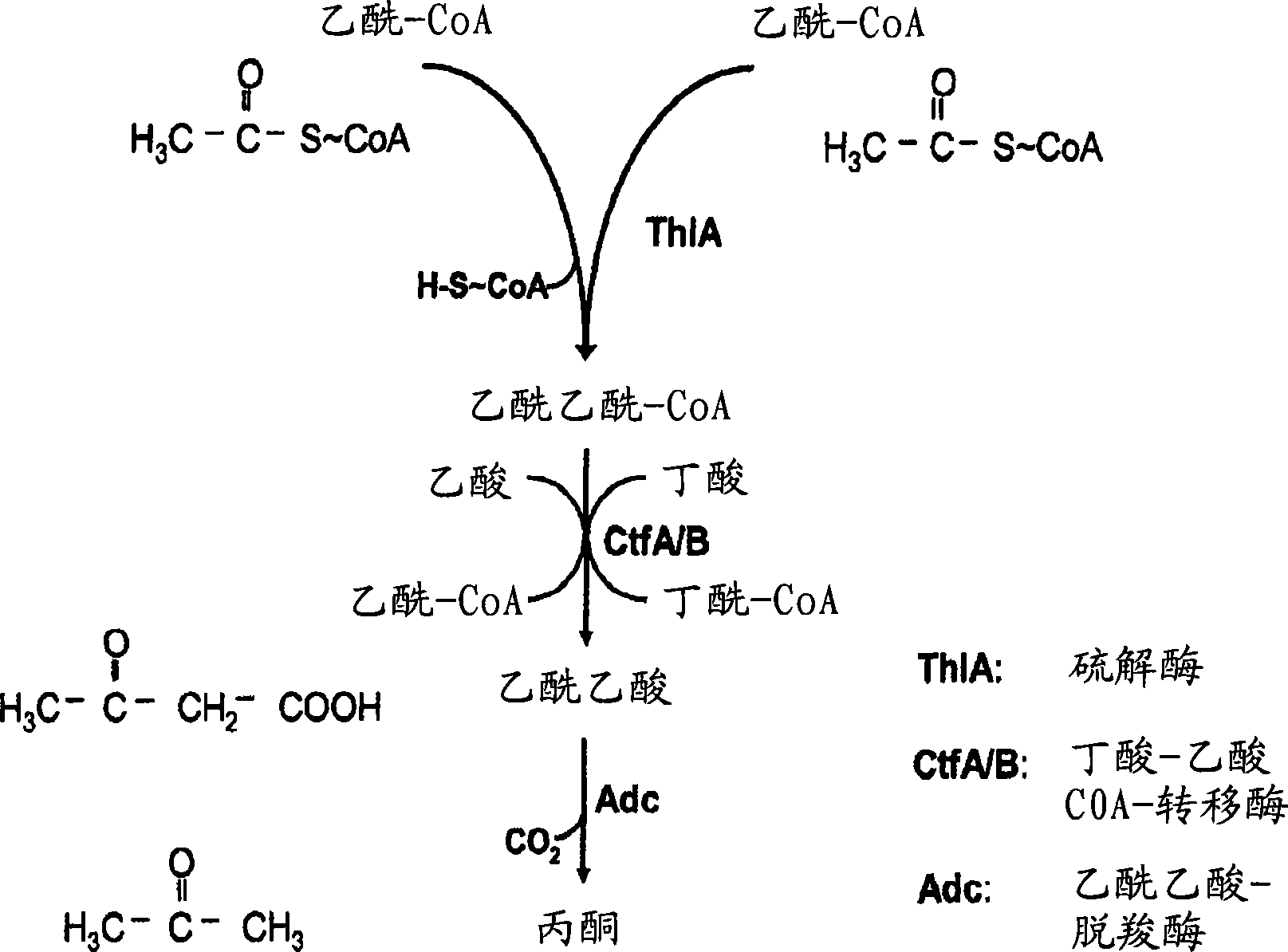
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
InactiveCN101573451AImprove the level ofReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or toincrease the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils o btained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
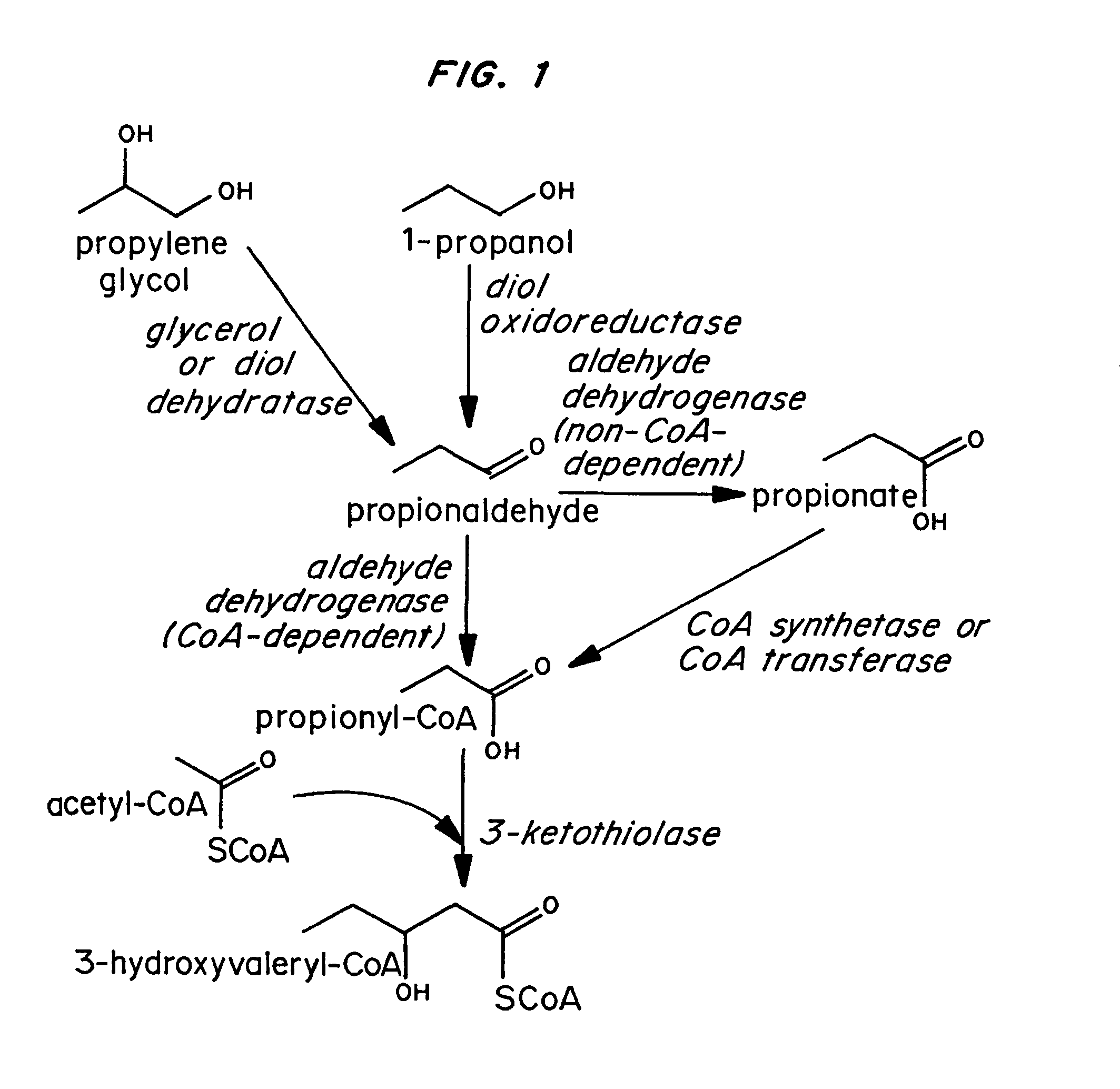
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
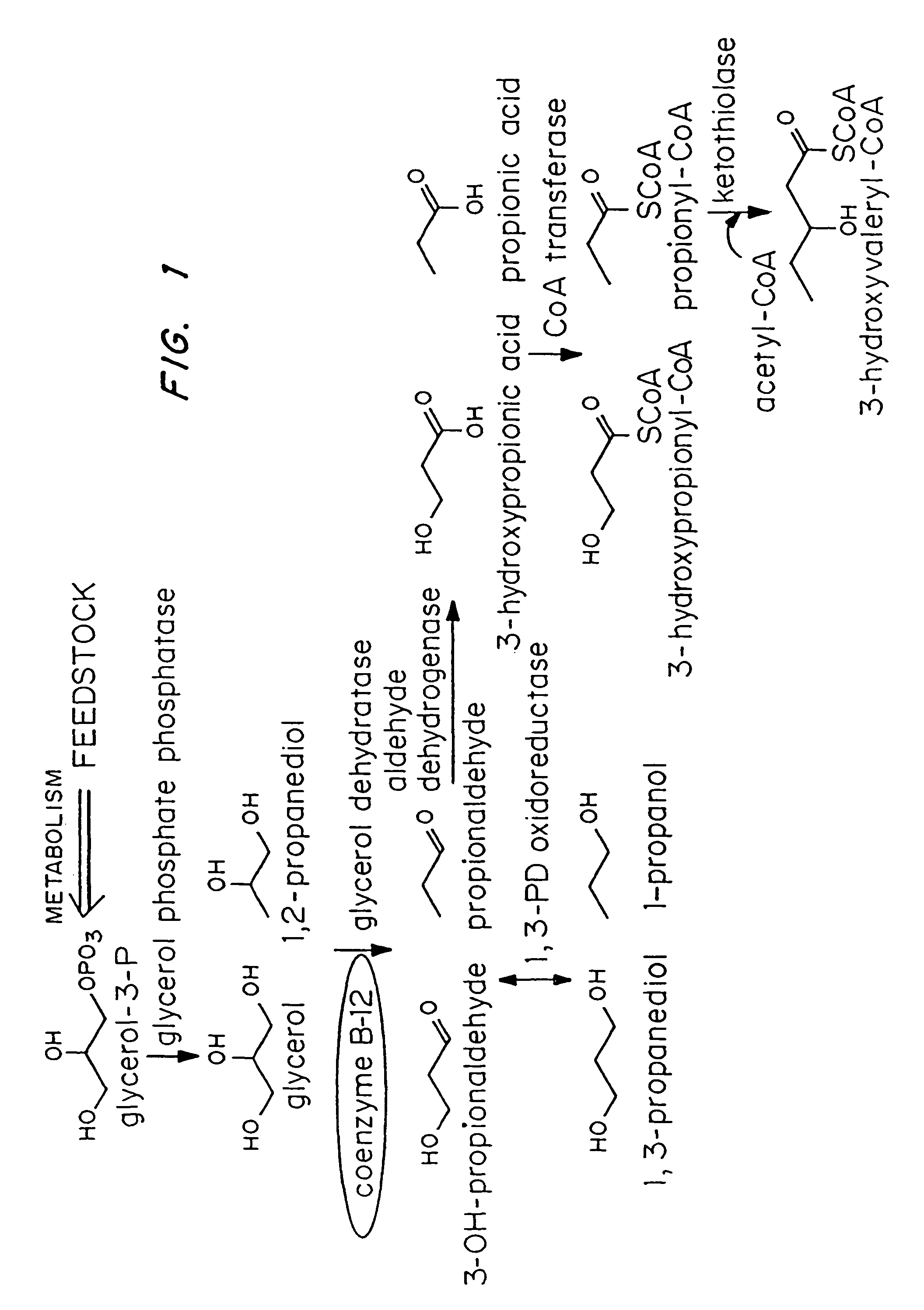
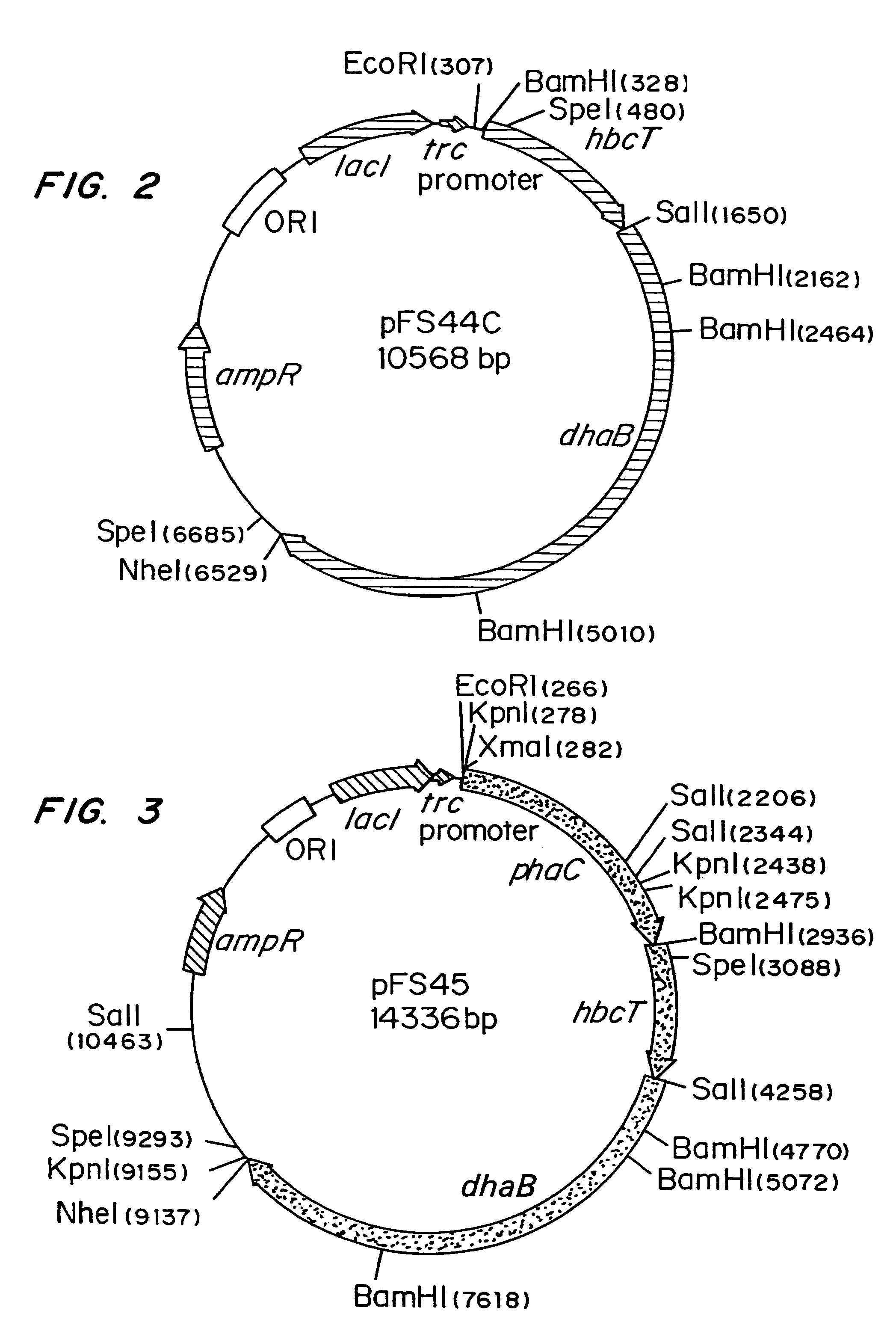
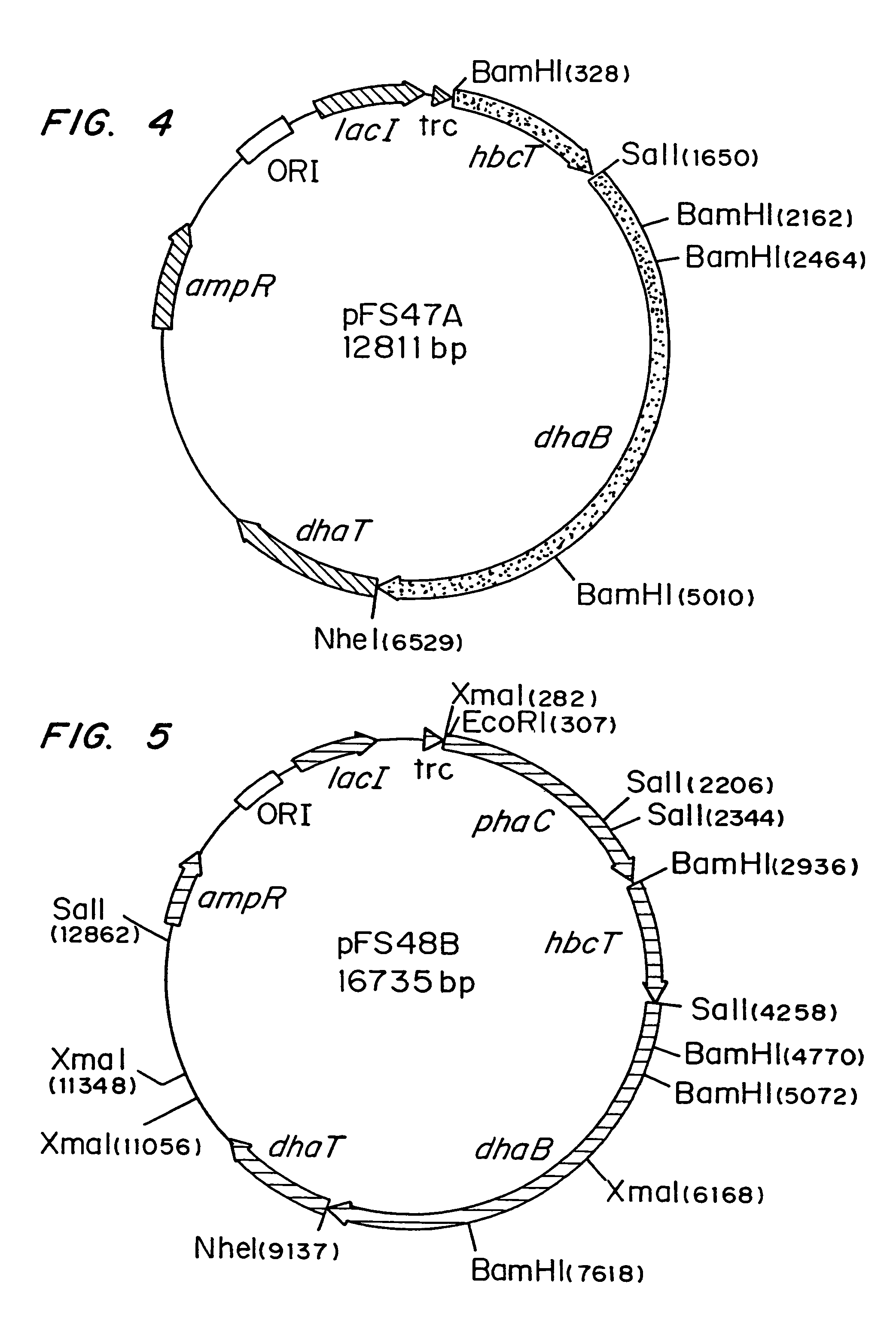
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalerate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Kit and method for clinically detecting serum or plasma free fatty acid
ActiveCN102634565ADetection speedImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-coenzyme A oxidase
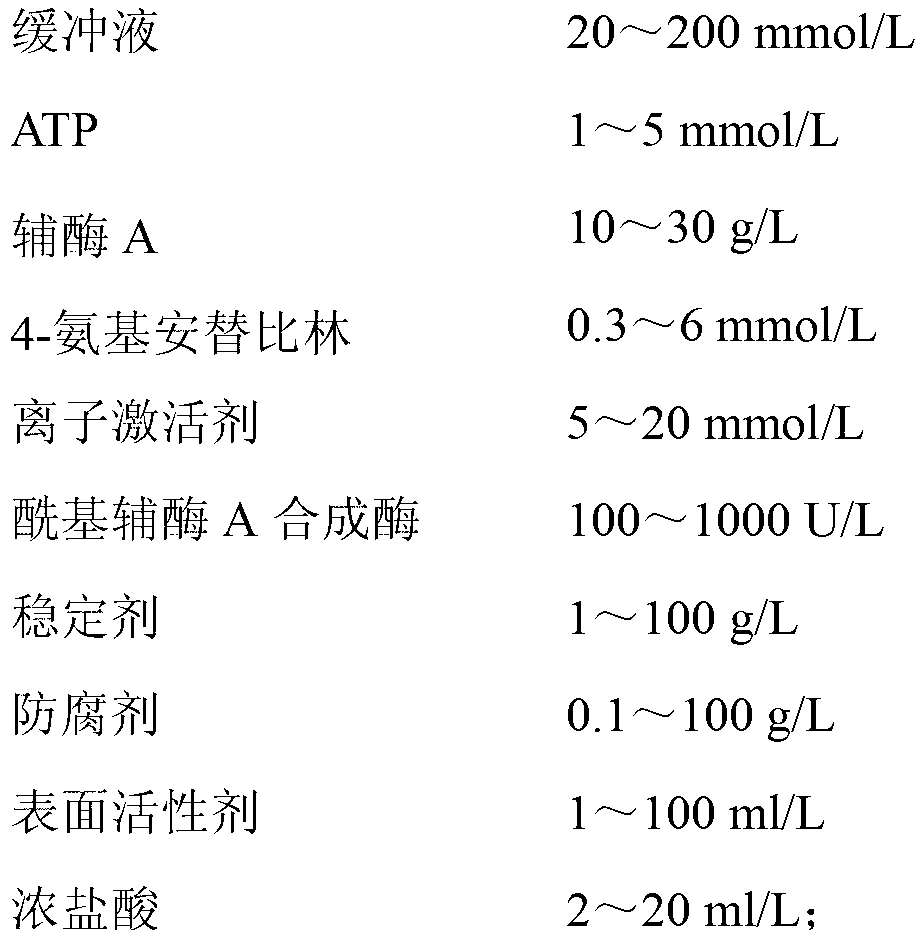
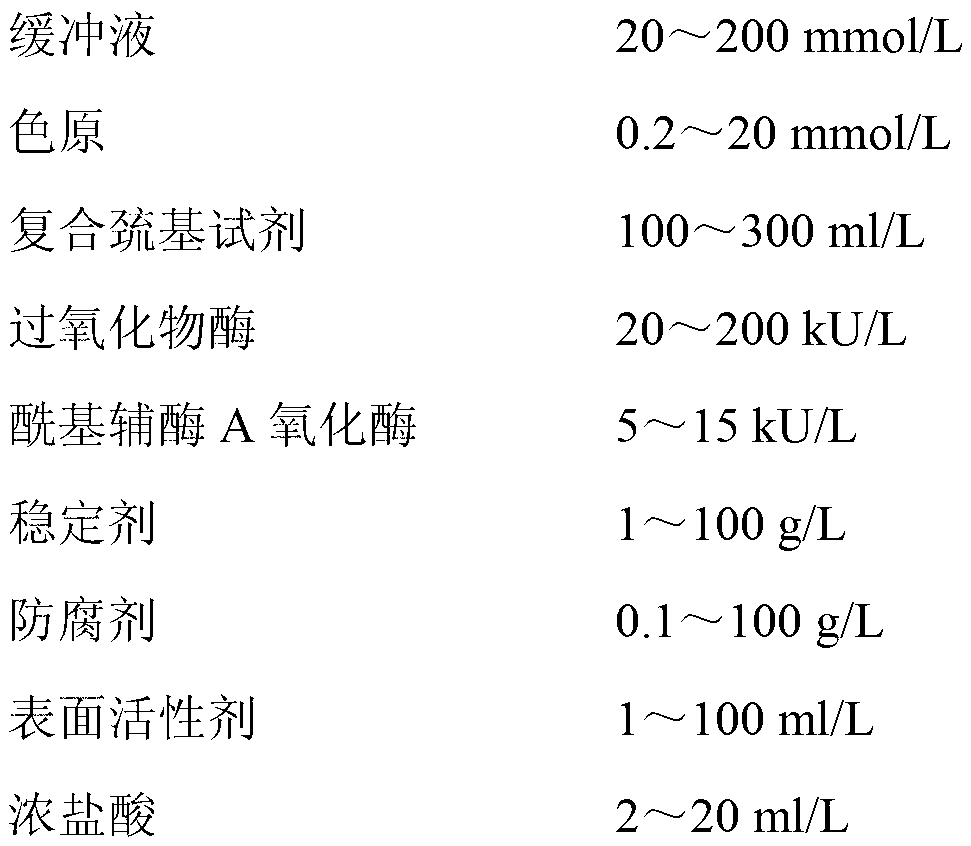
The invention discloses a kit and method for clinically detecting serum or plasma free fatty acid. The kit is composed of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises a buffer, ATP, a coenzyme A, 4-amino antipyrine, an ion activator, an acyl coenzyme A synthetase, stabilizer, a preservative, a surfactant, and concentrated hydrochloric acid, and the reagent 2 comprises a buffer, a chromogen, a composite sulfhydryl reagent, a peroxidase, an acyl coenzyme A oxidase, a stabilizer, a preservative, a surfactant and concentrated hydrochloric acid. The kit has the advantages of good stability, high specificity of the free fatty acid, and wide linear range. The serum or plasma free fatty acid is detected by the enzyme method, and the method has the advantages of high precision, andsmall measuring error.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Production of medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates from fatty acid biosynthetic pathways
InactiveUS7786355B2Improve the level ofBacteriaHydrolasesPeroxisomal enzymeAcyl Coenzyme A Synthetases
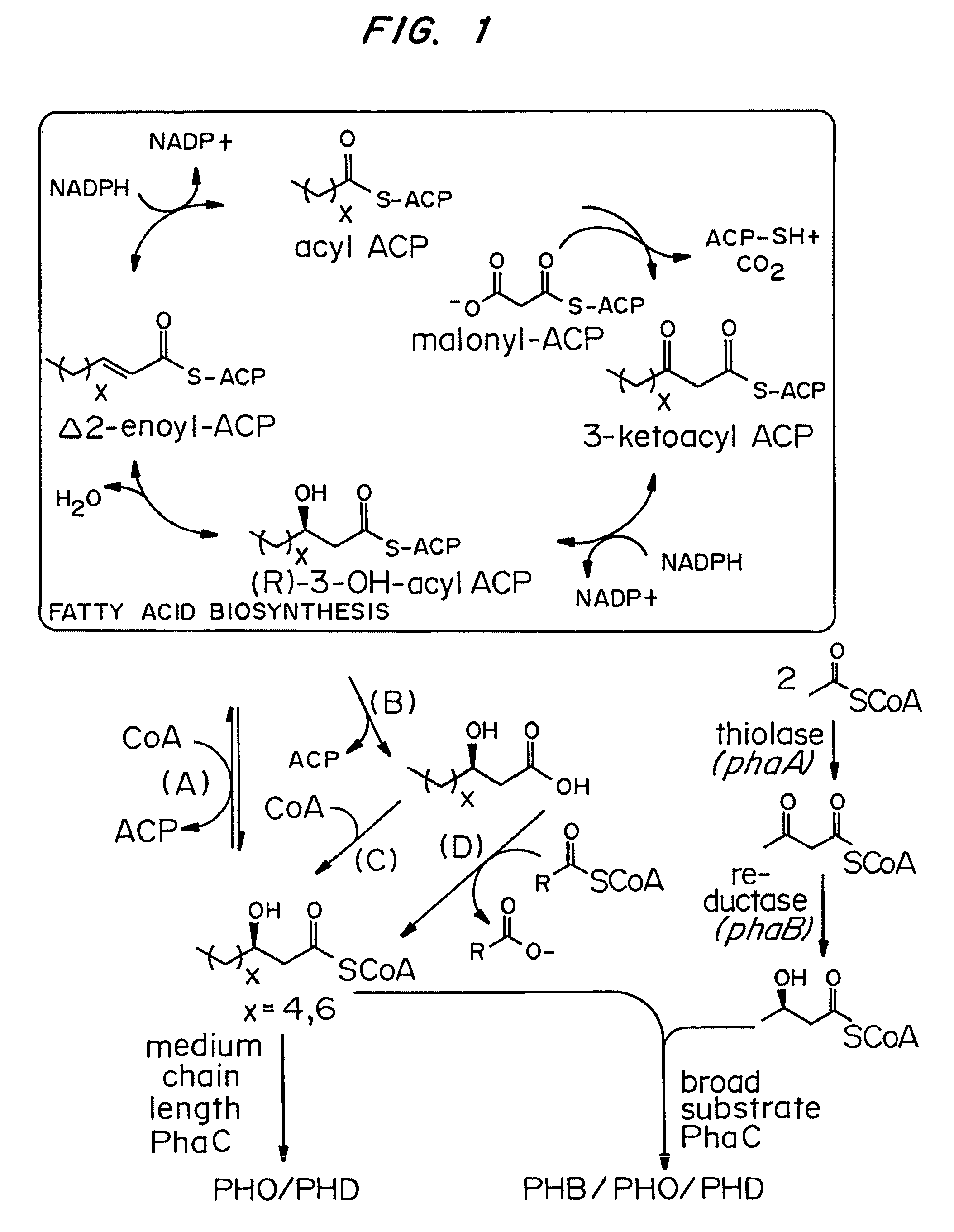
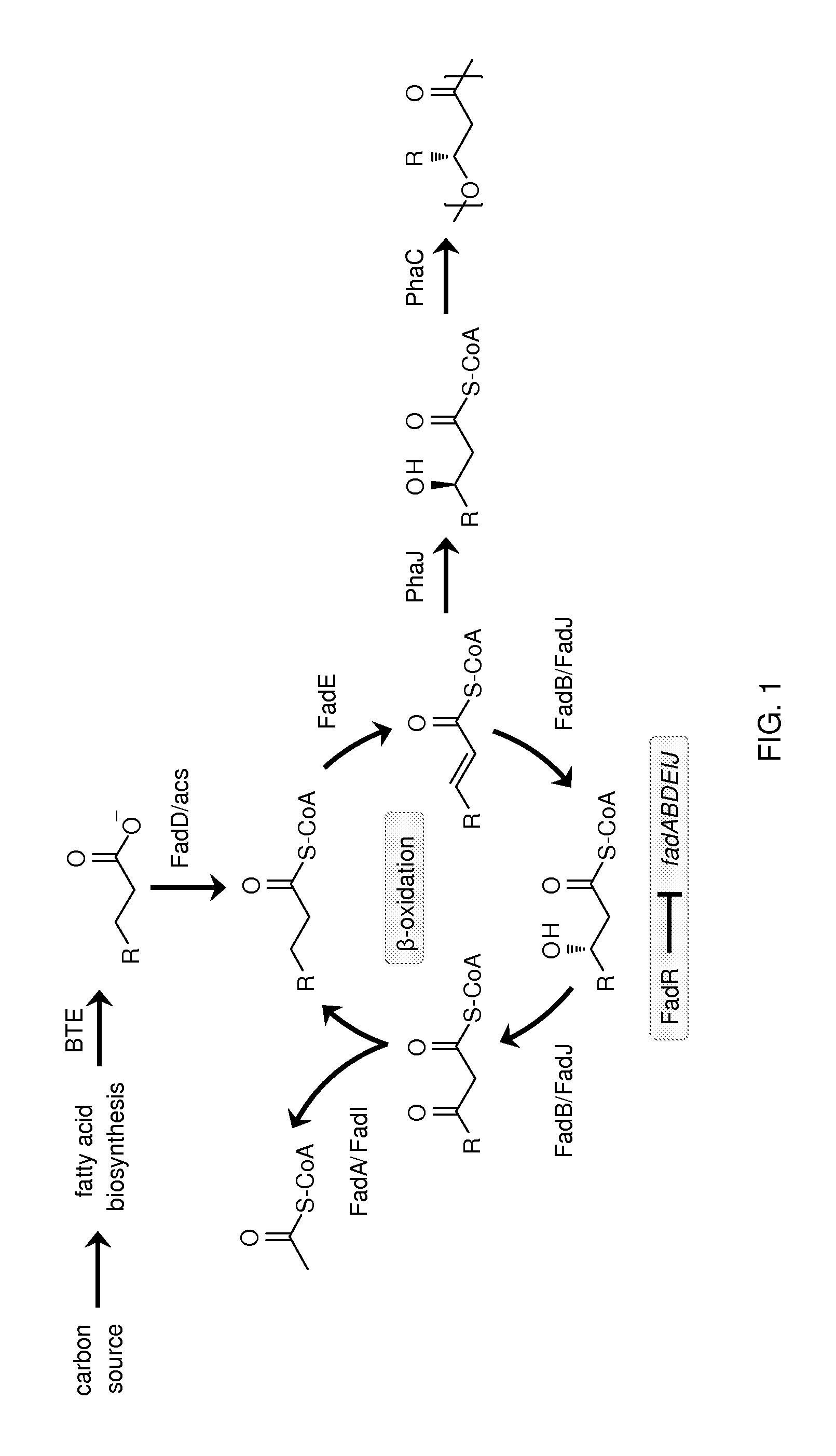
Methods for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from fatty acid biosynthetic pathways using a 3-hydroxy acyl ACP thioesterase, a PHA synthase, and an acyl CoA synthetase, have been developed. Methodology for enabling PHA production from fatty acid biosynthetic pathways in non-native bacterial PHA producers and plants using an enzyme having the catalytic activity of 3-hydroxy acyl ACP thioesterase, an acyl CoA synthetase with substrate specificity for medium chain length 3-hydroxy fatty acids, and a medium chain length PHA synthase, has been developed. Acyl CoA synthetase activity can be supplied either by the endogenous acyl CoA synthetase of the host organism, when sufficiently expressed, or the host organism's activity can be supplemented by the expression of a recombinant acyl CoA synthetase gene. New strategies are described for plant based PHA production in the chloroplasts, cytosol, and peroxisomes of biomass crops as well as the plastids, cytosol, and peroxisomes of oil seed crops.
Owner:METABOLIX
Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase and application thereof
Owner:WUXI NEWWAY FERMENTATION TECH RES INST
Enzyme for synthesizing cetyl-coenzyme A through cordyceps sinensis, gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103087998AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesNucleotide
The invention relates to long-chain-acyl-coenzyme A synthetase for synthesizing metabolic cetyl-coenzyme A with the start that Bailing producing strain cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis is participated in palmatic acid, a gene for coding the enzyme and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the long-chain-acyl-coenzyme A synthetase and the sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 1 or SEQ ID No. 3 have more than 90% of homology. According to the invention, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing cetyl-coenzyme A through palmatic acid is researched in principle in a detailed manner as follows: clone DNA of a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria through transduction, conversion and combined transfer methods; gene expression is biologically synthesized by adjusting the cetyl-coenzyme A; high expressivity of host long-chain-acyl-coenzyme A synthetase is given; an effective way for enlarging the yield of the cetyl-coenzyme A is provided; and the cetyl-coenzyme A has a significant application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method, reagent and kit for quantitatively detecting free fatty acid
InactiveCN104678107AAccurate detectionSimple and fast operationBiological testingAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesPeroxidase
The invention relates to a reagent for quantitatively detecting the content of free fatty acid in human serum. The reagent comprises a reagent I and a reagent II which are respectively placed, wherein the reagent I comprises sodium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, magnesium chloride, fatty acyl-coenzyme A synthetase, ascorbic acid oxidase, coenzyme A, ATP and 4-aminoantipyrine, and the reagent II contains sodium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, phenoxy ethanol, fatty acyl-coenzyme A oxidase, peroxidase, chromogen and a surfactant. The kit and the detection method only need dozens of microlitres of serum without centrifugal or electrophoresis and other separation treatments, are simple and convenient to operate, can be used for meeting the requirement of full-automatic analysis, and are suitable for timely accurate detection of large-scale samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG KAICHENG BIOTECH
Biosynthetic production of acyl amino acids
InactiveCN107075463ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polynucleotide encoding acyl-coa synthetase homolog and use thereof
ActiveUS20120322992A1Improve production efficiencyEfficient preparationCosmetic preparationsFungiAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
The present invention relates to an acyl-CoA synthetase homolog protein from microorganisms of the genus Mortierella, a polynucleotide encoding the protein, and so on. The invention provides polynucleotides comprising an acyl-CoA synthetase homolog protein gene from, e.g., Mortierella alpina, expression vectors comprising these polynucleotides and transformants thereof, a method for producing lipids or fatty acids using the transformants, food products containing the lipids or fatty acids produced by the method, etc.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for synthesizing biodiesel with microorganisms in vivo
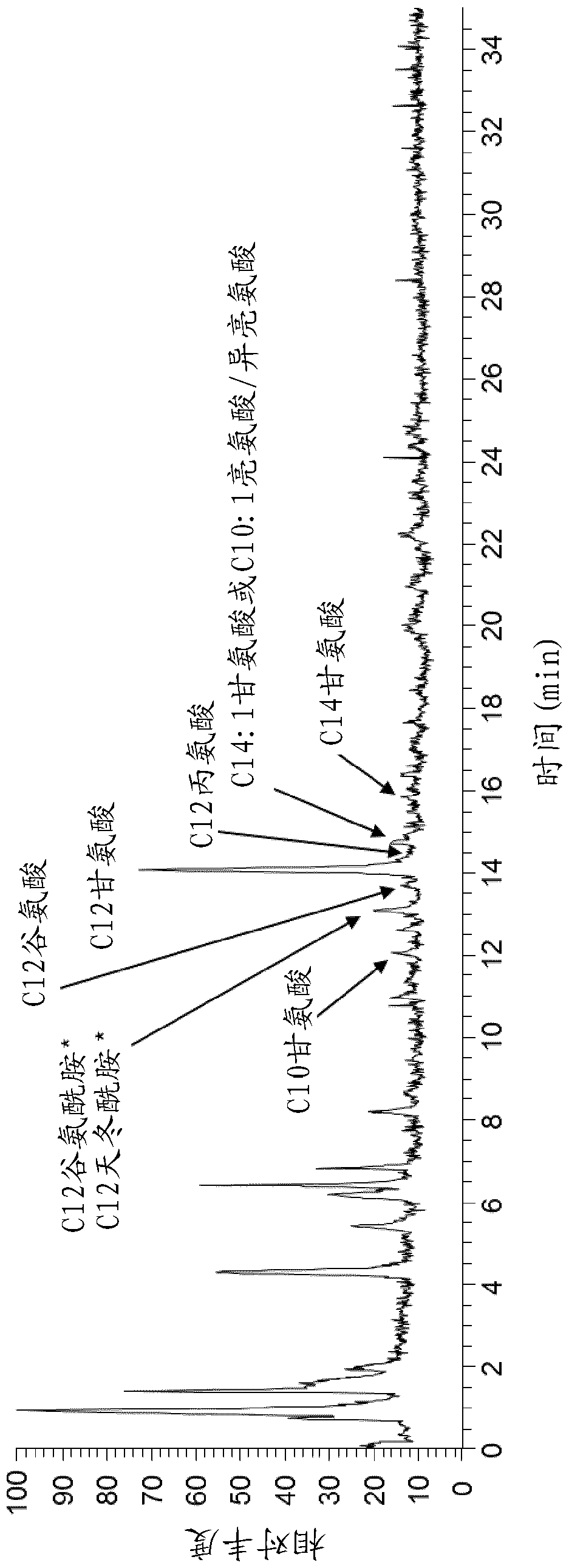
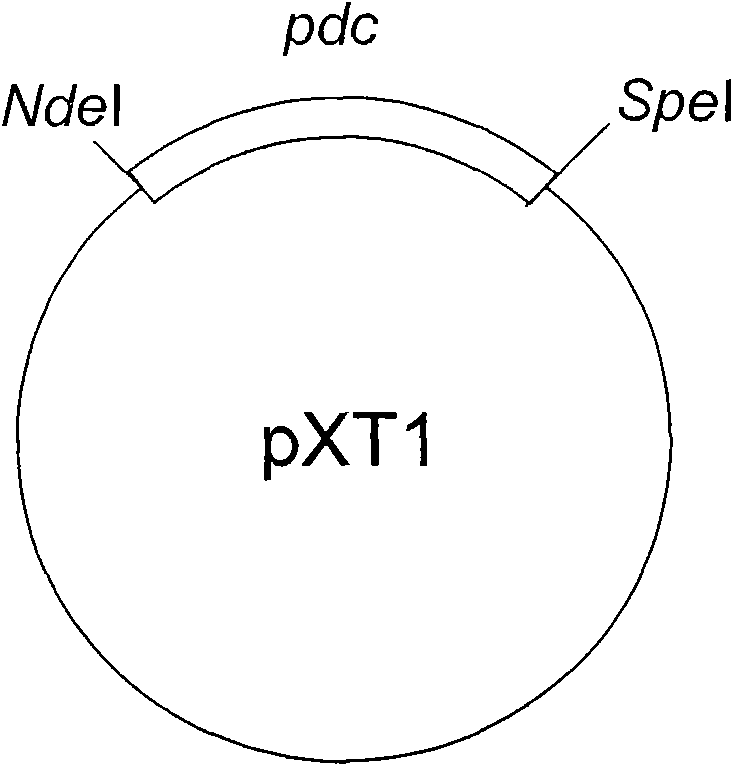
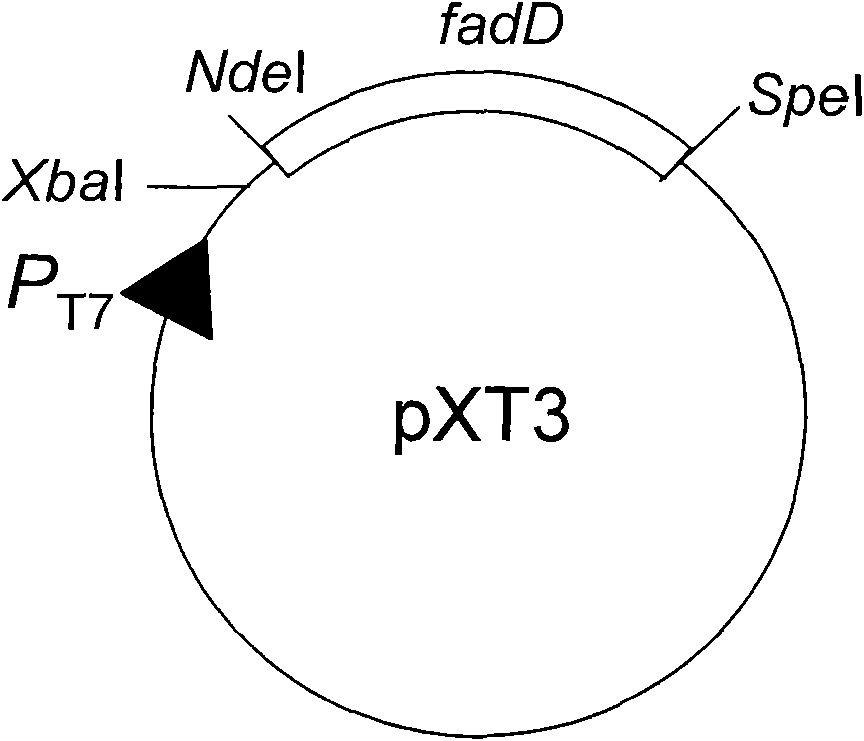
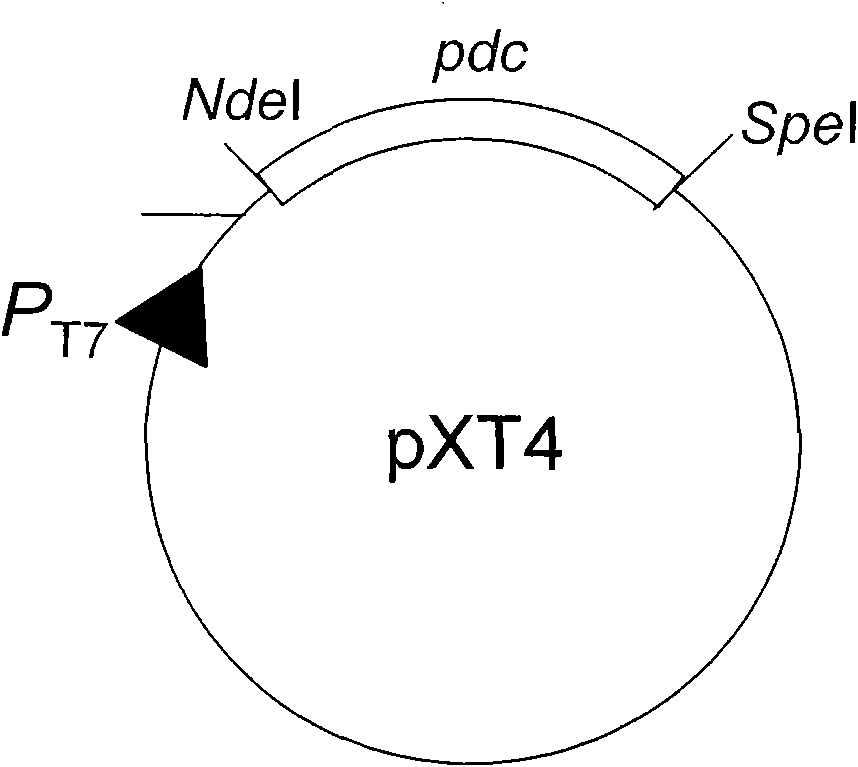
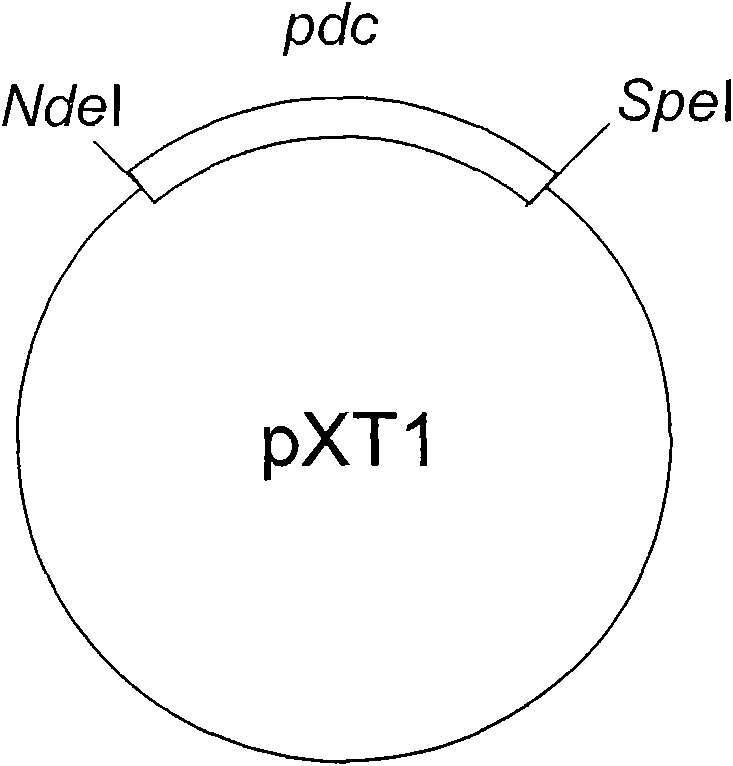
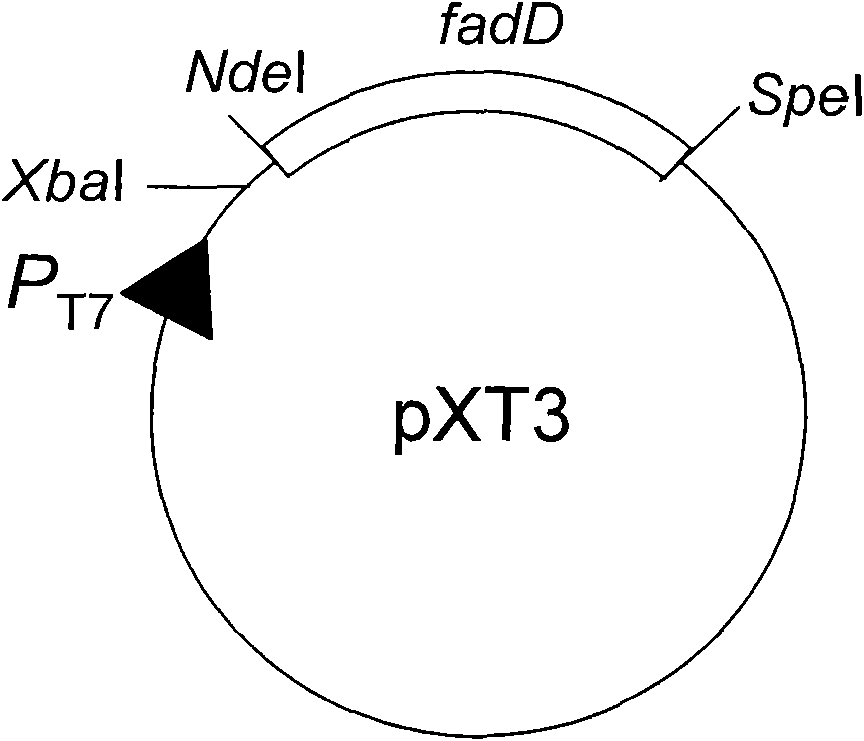
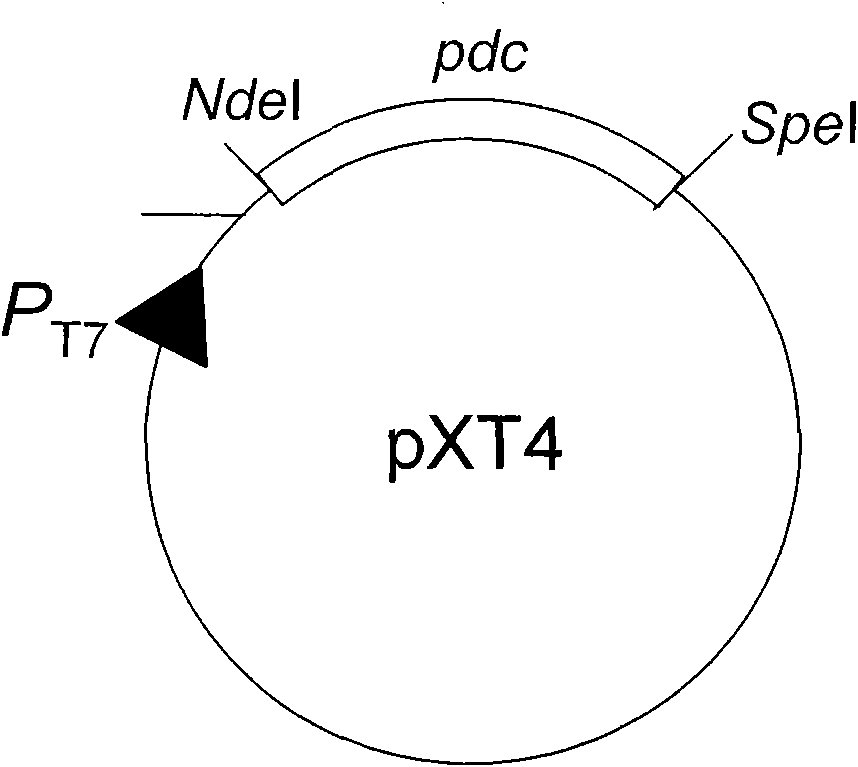
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing biodiesel with microorganisms in vivo, which is realized in escherichia coli. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively cloning an acinetobacter wax fat synthetase gene atfA, an escherichia coli acyl coenzyme A synthetase gene fadD, a zymomonas mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase gene pdc and an alcohol dehydrogenase gene adhB gene on a pET expression vector in series to obtain a plasmid pXT11; transferring the plasmid pXT11 into escherichia coli containing a plasmid pMSD8 and a plasmid pMSD15 to obtain an escherichia coli stain XT31; and generating biodiesel by the escherichia coli stain XT31. The method realizes the microbial transformation from sugar to the biodiesel, lays the foundation for biologically preparing the biodiesel from lignocelluloses, and radically solves the problem of insufficient raw material supply in biodiesel preparation. A step of esterifying methanol is not needed in the technology, thereby the cost is greatly reduced and the problems that glycerol as a side product is formed, and the like are avoided.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
Byosynthetic Production of Acyl Amino Acids
InactiveUS20170130248A1PurityYield andLigasesAcyltransferasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
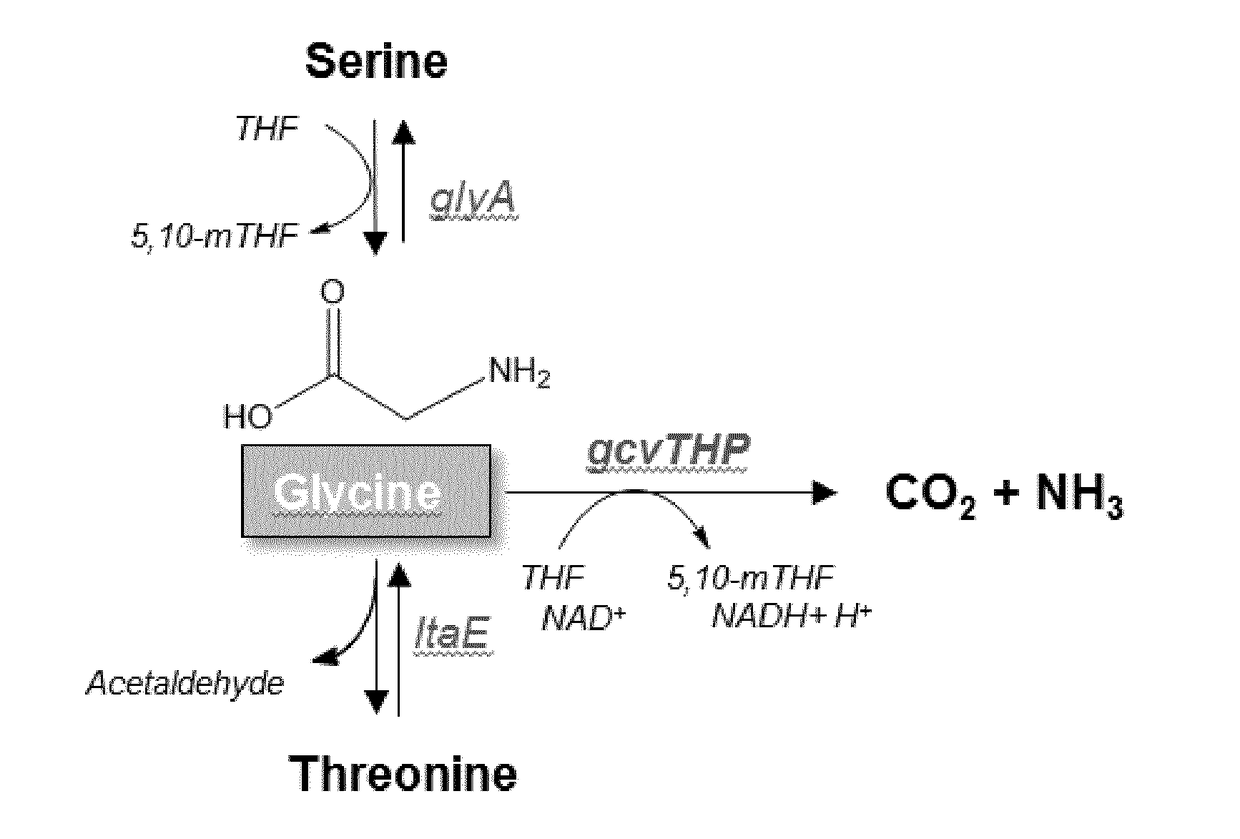
The present invention relates to a cell for producing acyl glycinates wherein the cell is genetically modified to compriseat least a first genetic mutation that increases the expression relative to the wild type cell of an amino acid-N-acyl-transferase,at least a second genetic mutation that increases the expression relative to the wild type cell of an acyl-CoA synthetase, andat least a third genetic mutation that decreases the expression relative to the wild type cell of at least one enzyme selected from the group consisting of an enzyme of the glycine cleavage system, glycine hydroxymethyltransferase (GlyA) and threonine aldolase (LtaE).
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with a defined composition from an unrelated carbon source
Cells and methods for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates. The cells comprise one or more recombinant genes selected from an R-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a PHA polymerase gene, a thioesterase gene, and an acyl-CoA-synthetase gene. The cells further have one or more genes functionally deleted. The functionally deleted genes include such genes as an enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene. The recombinant cells are capable of using producing polyhydroxyalkanoates with a high proportion of monomers having the same carbon length from non-lipid substrates, such as carbohydrates.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
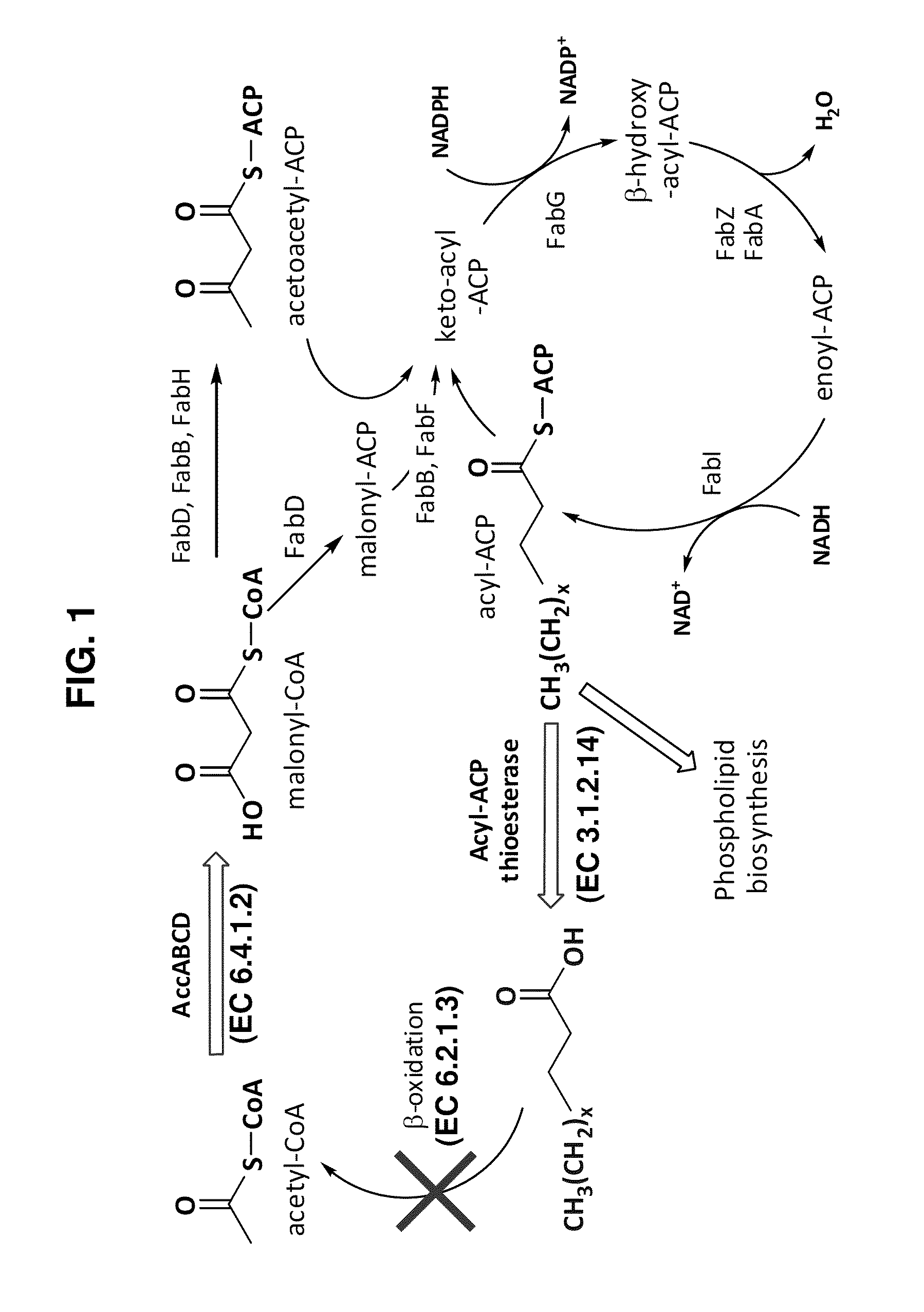
Fatty acid-producing hosts
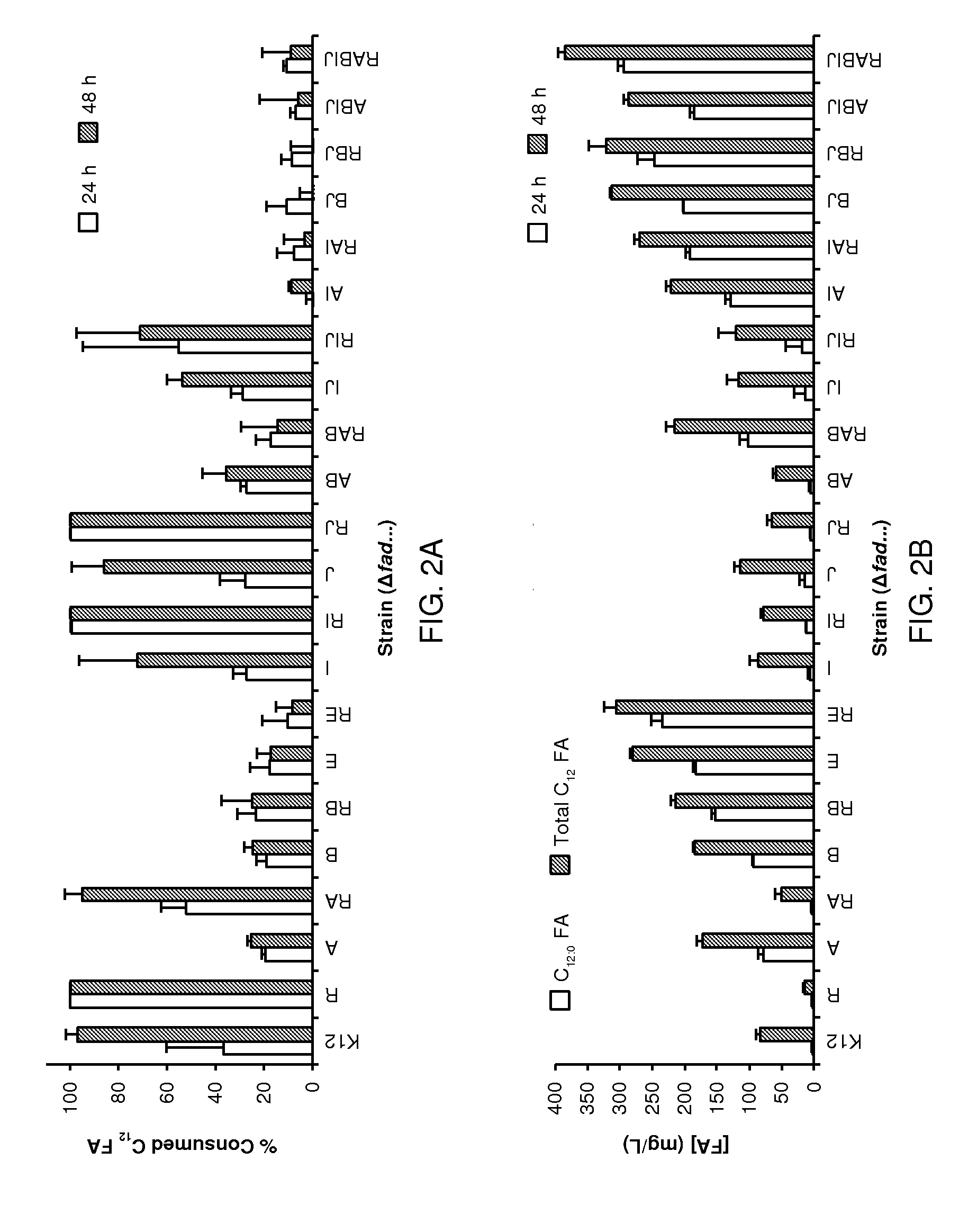
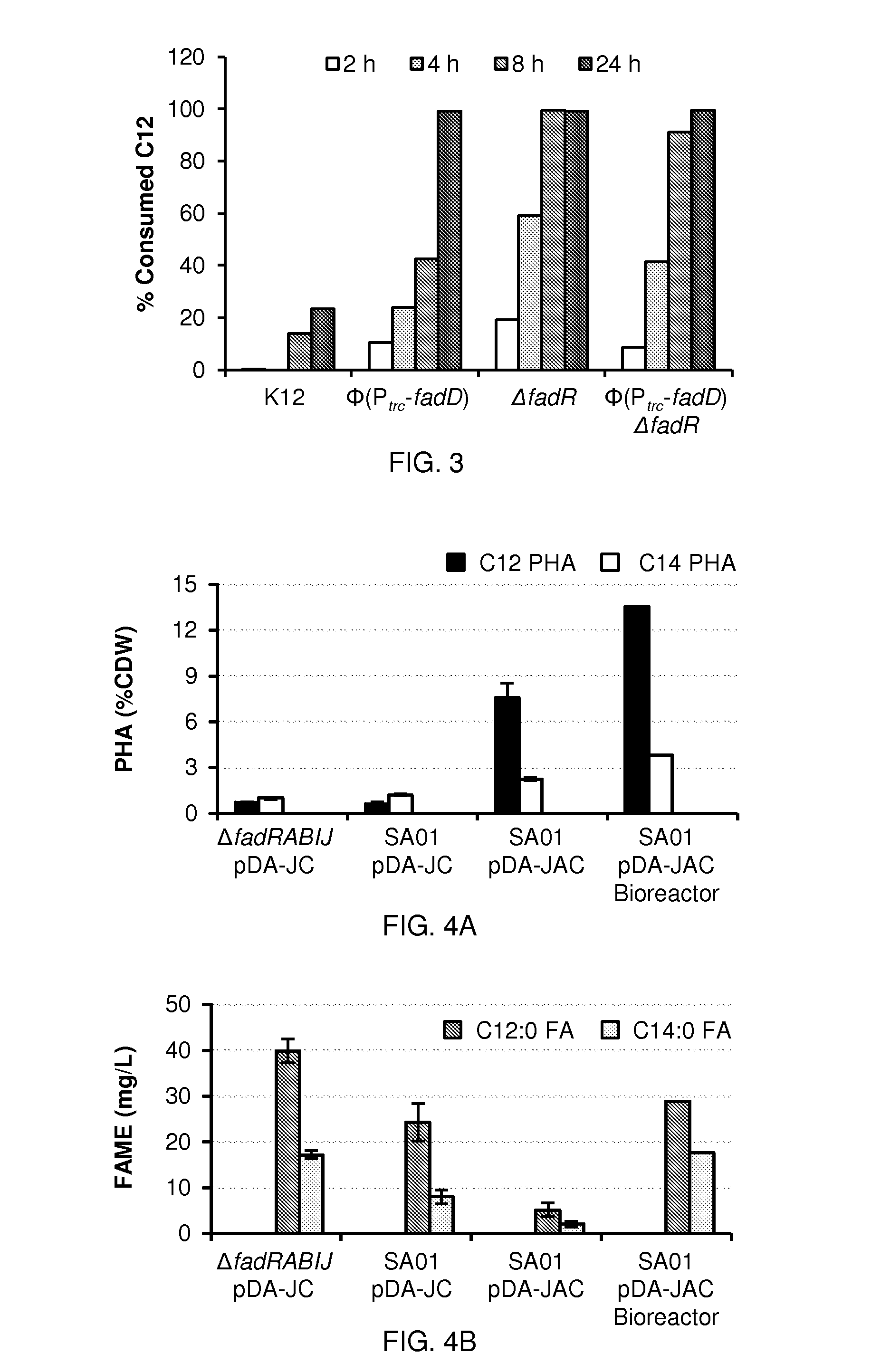
Described are hosts for overproducing a fatty acid product such as a fatty acid. The hosts include an exogenous nucleic acid encoding a thioesterase and, optionally, an exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, wherein an acyl-CoA synthetase in the hosts are functionally deleted. The hosts preferably include the nucleic acid encoding the thioesterase at an intermediate copy number. The hosts are preferably recombinantly stable and growth-competent at 37° C. Methods of producing a fatty acid product comprising culturing such hosts at 37° C. are also described.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Four-gene pathway for wax ester synthesis
ActiveUS8962299B2Reduce the amount of solutionEfficient and cost-effectiveSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesPhylum Cyanobacteria
The invention relates to methods for producing a wax ester in recombinant host cells engineered to express a thioesterase, an acyl-CoA synthetase, an alcohol-forming fatty acyl reductase, and a wax ester synthase. The methods of the invention may take place in photosynthetic microorganisms, and particularly in cyanobacteria. Isolated nucleotide molecules and vectors expressing the thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase, alcohol-forming fatty acyl reductase, and wax ester synthase, recombinant host cells expressing the thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase, alcohol-forming fatty acyl reductase, and wax ester synthase, and systems for producing a wax ester via a pathway using these four enzymes, are also provided.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for increasing fermentation yield of polyketone compounds
ActiveCN104513840AImprove fermentation yieldEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAcyl Coenzyme A Synthetases
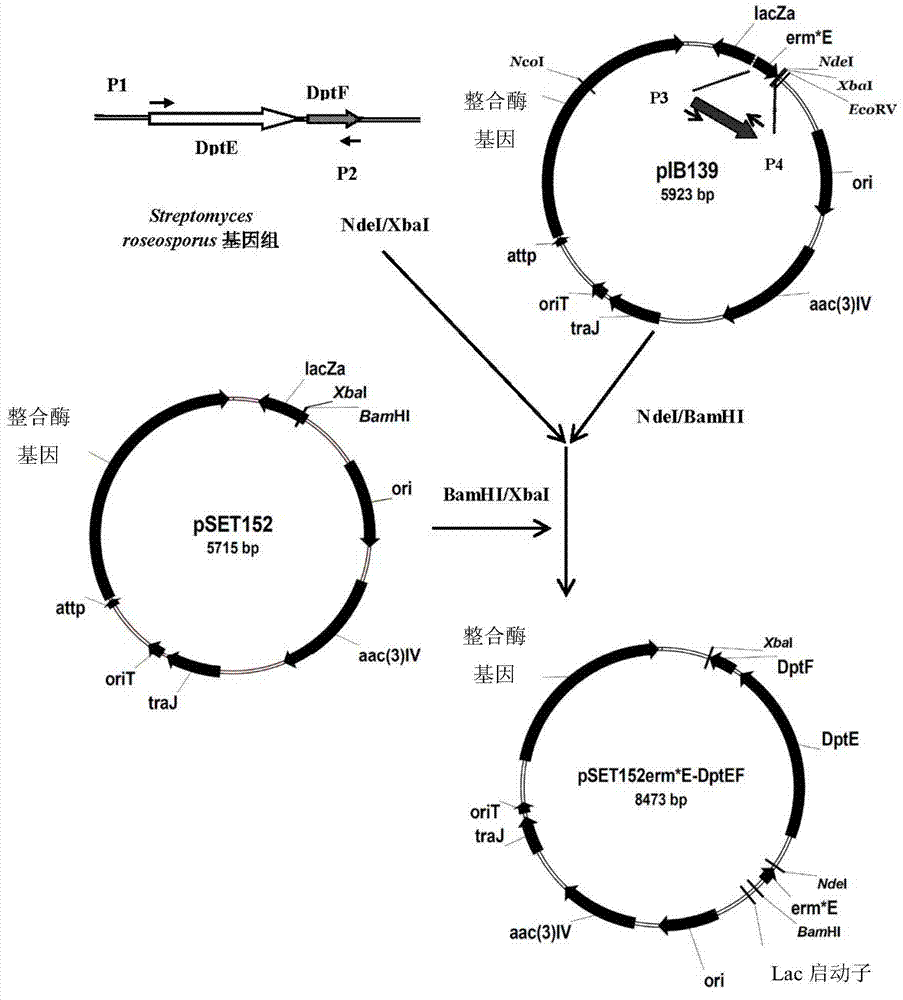
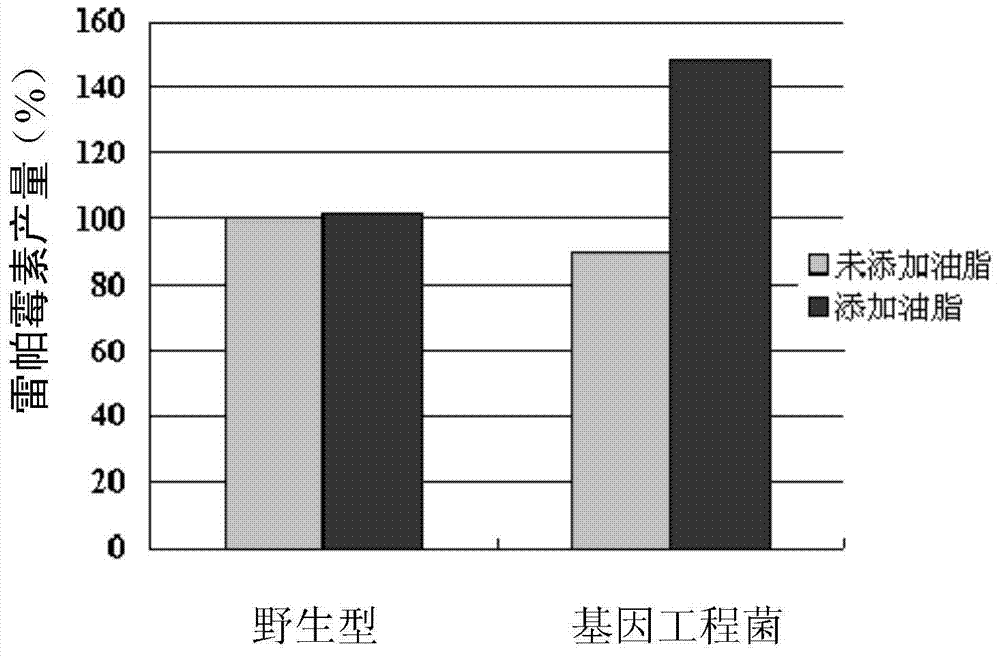
The invention discloses a method for increasing fermentation yield of polyketone compounds. The method includes steps of: (1) culturing genetically engineered bacteria of an overexpressed acyl-coenzyme A synthesizing enzyme and an acyl carrier protein in a culture medium added with natural grease; and (2) extracting the polyketone compounds from a fermented product. The genetically engineered bacteria are a recombination expression transformant of the overexpressed acyl-coenzyme A synthesizing enzyme and the acyl carrier protein, which is prepared through conjugational transfer by an actinomycete onto recombinant escherichia coli containing a recombinant expression vector expressing the overexpressed acyl-coenzyme A synthesizing enzyme and the acyl carrier protein. In the method, an exogenetic acyl-coenzyme A synthesizing enzyme and an exogenetic acyl carrier protein are overexpressed in the bacteria generating the polyketone compounds through gene engineering technologies, so that by means of cheap natural grease as a raw material, the fermentation yield of the polyketone compounds is increased, wherein the method is never reported in references. The method is simple in operations, can provide precursors for synthesizing the polyketone compounds through the cheap natural grease, is low in cost and is convenient to popularize.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveCN101423850AIncrease productionFavorable direction offsetHydrolasesLigasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for the preparation of acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising the process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA to give acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA, and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to give acetone and CO2, which process is characterized in that, in process step B, the coenzyme A is not transferred to an acceptor molecule. Moreover, surprisingly, process step B is catalyzed by enzymes from the classes acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase. This is an entirely novel metabolic pathway since the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without the simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never been described before for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Polynucleotide encoding acyl-CoA synthetase homolog and use thereof
ActiveUS9289007B2Improve production efficiencyEfficient preparationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
The present invention relates to an acyl-CoA synthetase homolog protein from microorganisms of the genus Mortierella, a polynucleotide encoding the protein, and so on. The invention provides polynucleotides comprising an acyl-CoA synthetase homolog protein gene from, e.g., Mortierella alpina, expression vectors comprising these polynucleotides and transformants thereof, a method for producing lipids or fatty acids using the transformants, food products containing the lipids or fatty acids produced by the method, etc.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
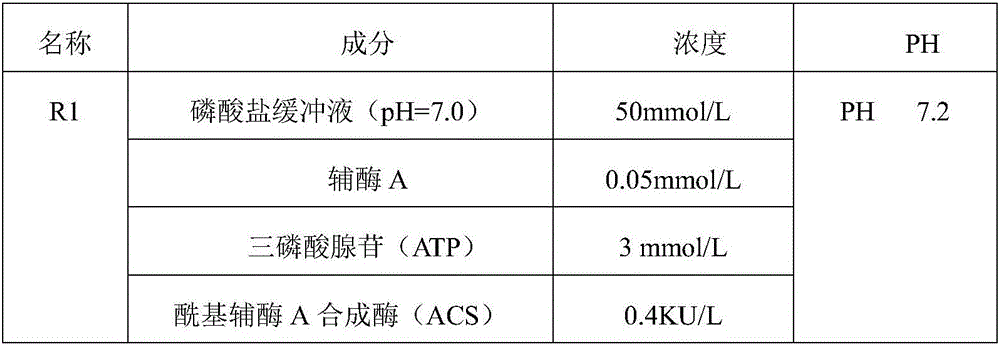
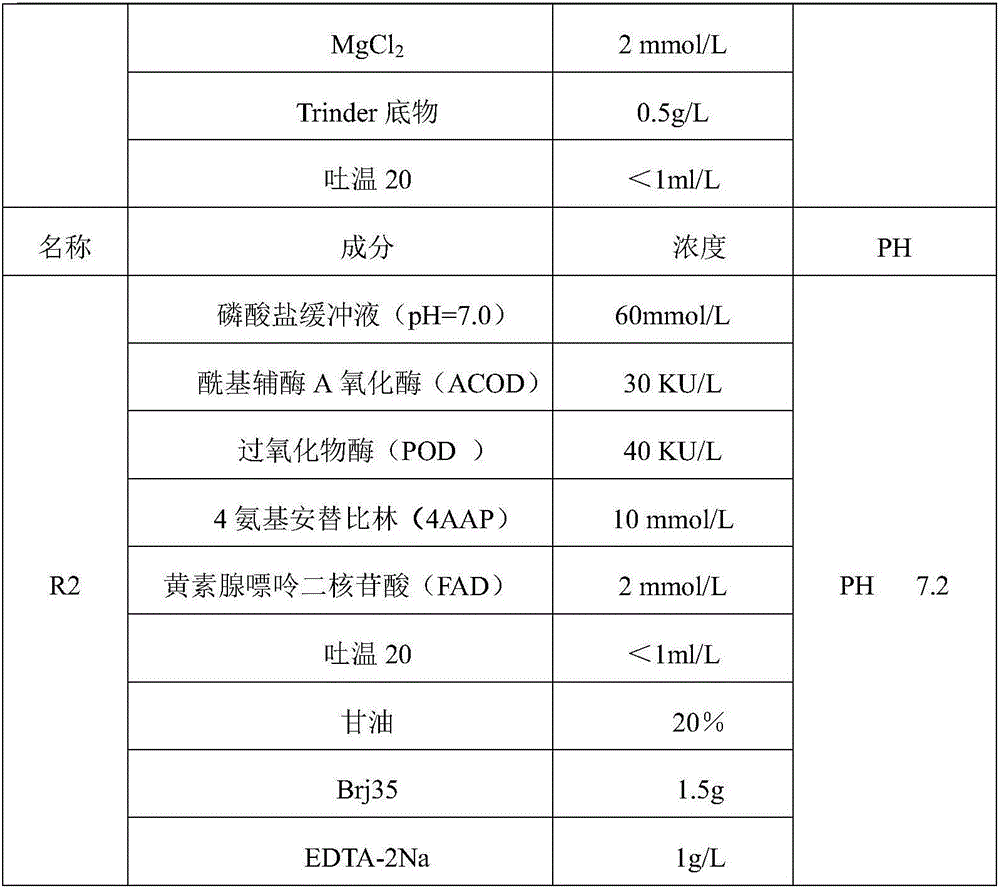
Free fatty acid determining kit and preparation method thereof
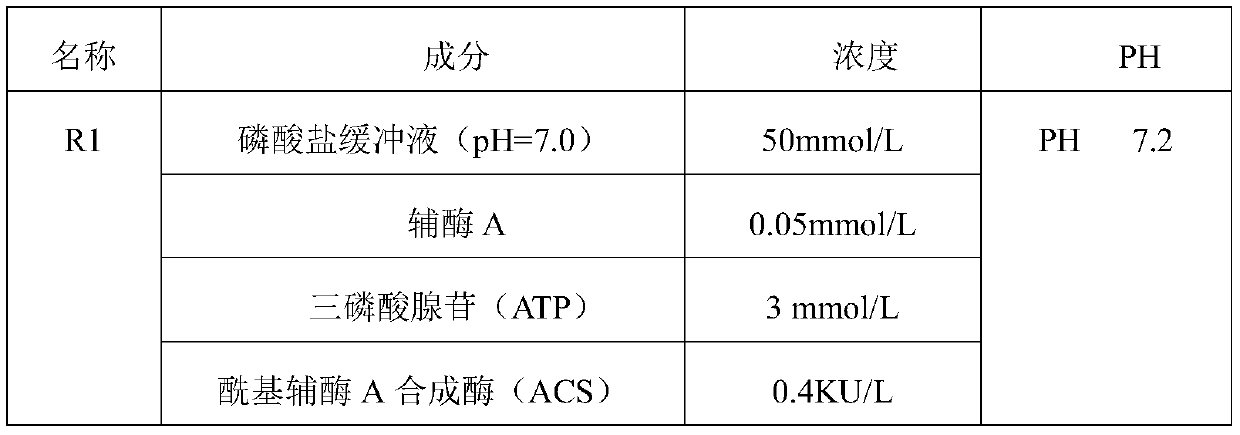
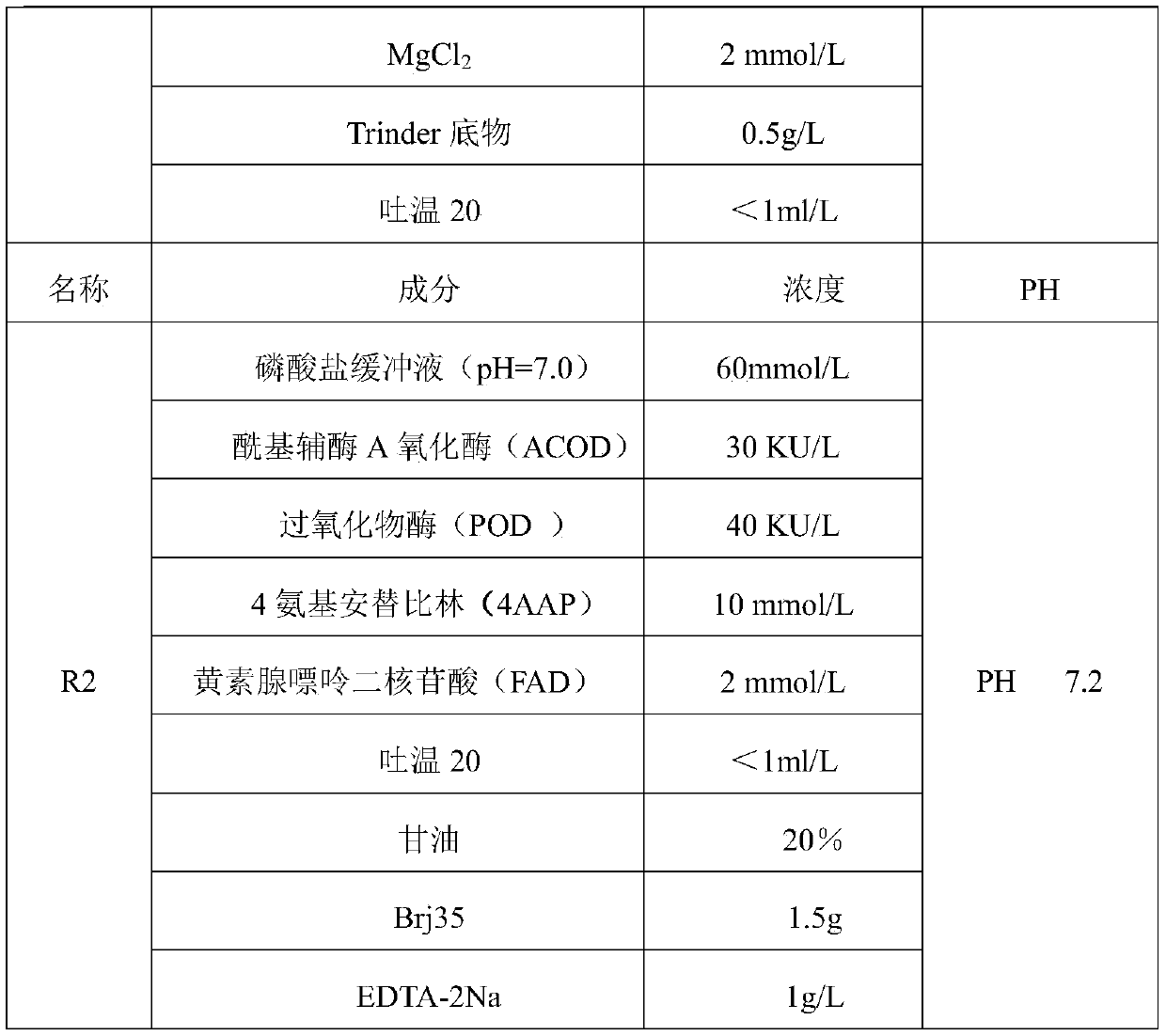
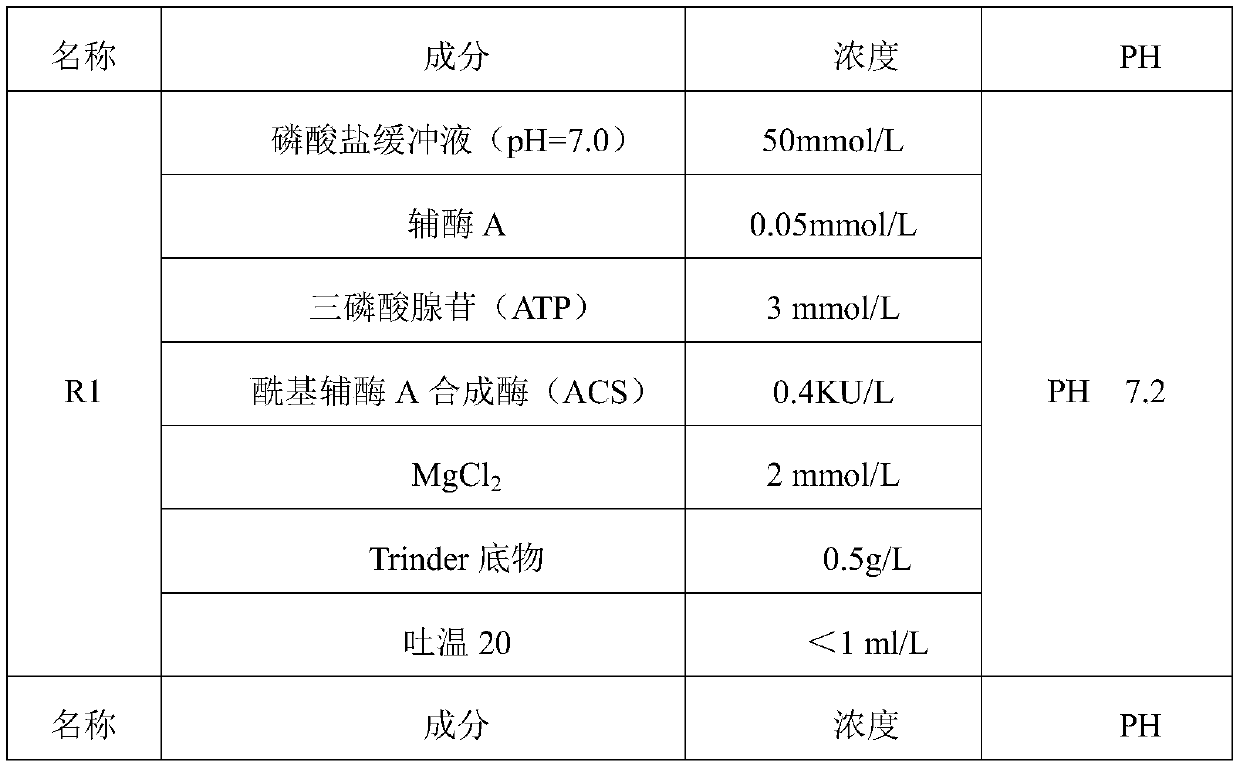
ActiveCN106191213AHigh viscosityLow viscosityMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl-coenzyme A oxidaseFlavin adenine dinucleotide
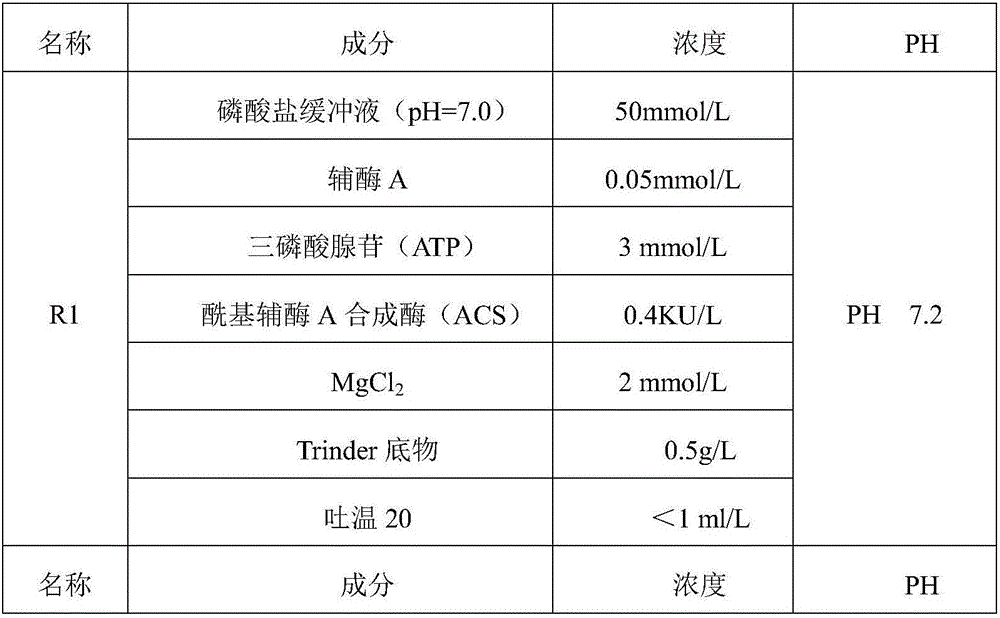
The invention relates to the technical field of free fatty acid determining, in particular to a free fatty acid determining kit. The kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the R1 is prepared from coenzyme A, triphosadenine, acyl coenzyme A synthetase, MgCl2, a Trinder substrate and Tween-20, and has the pH of 7.2; the R2 is prepared from flavin adenine dinucleotide, 4 amino-antipyrine, peroxidase, acyl coenzyme A oxidase, Tween-20, glycerinum, 1 to 1.5g / L of brij35-1 and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt and has the pH of 7.2. By adding different combinations of protein protecting agents, the enzyme activity stability is prolonged; the 37-DEG C stability of the enzyme is prolonged from 7 days to 10 days; the enzyme denaturation is slowed down; the reagent R2 cannot easily generate precipitate.
Owner:中拓生物有限公司
Free fatty acid detection kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108103142AHigh activityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAcyl-coenzyme A oxidaseFlavin adenine dinucleotide
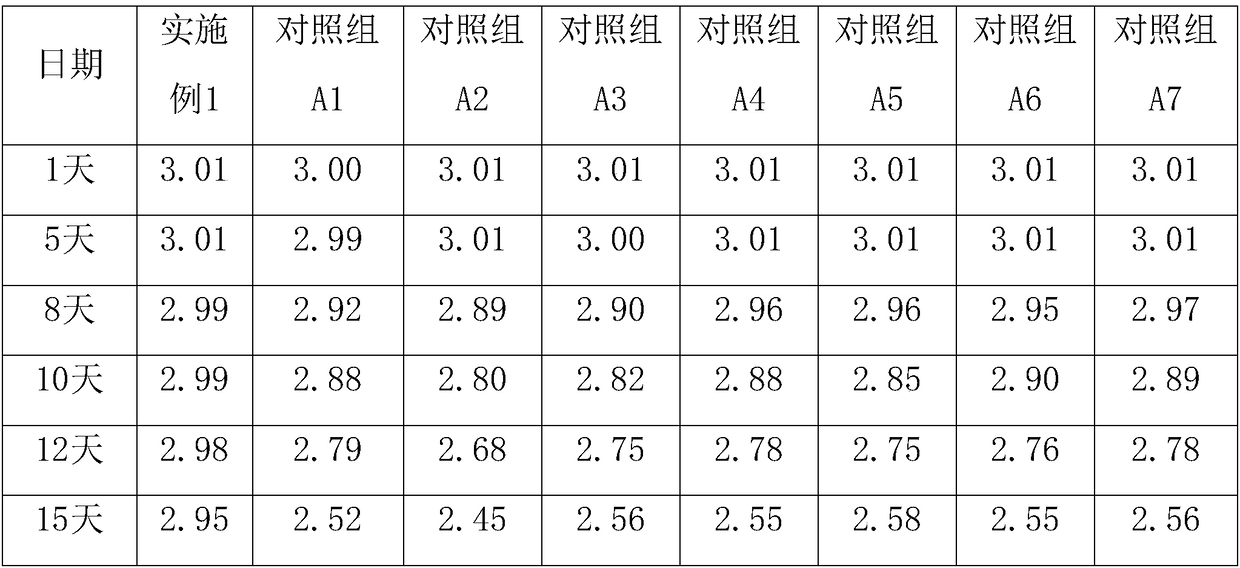
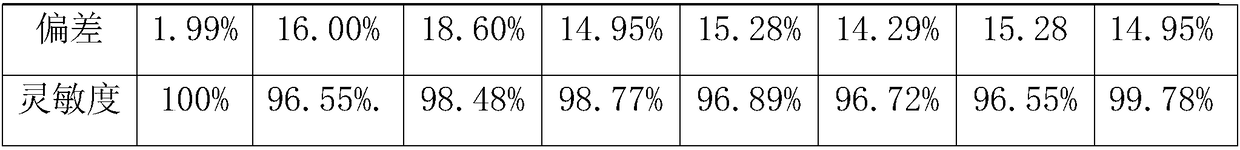
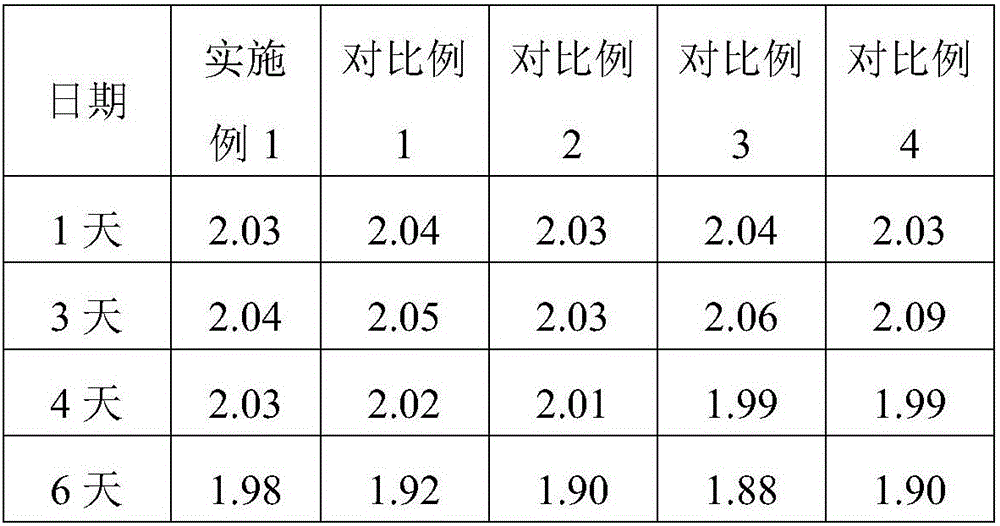
The invention discloses a free fatty acid detection kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises reagents A and B, wherein the reagent A is prepared from the following components: sodium dihydrogen phosphate, a coenzyme A, triphosadenine, acyl coenzyme A synthetase, MgCl2, Trinder substrate and a proper amount of magnetized water, and the pH value is regulated to 7.2. The reagent B is prepared from the following components: sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 4-aminoantipyrine, acyl coenzyme A oxidase, peroxidase, flavin adenine dinucleotide, EDTA-2Na, N-sodium cocoanutylglutamate, sodiumlauryl ether sulphate, sodium N-acyl-L-serine, mannitol, sodium citrate and a proper amount of magnetized water, and the pH value is regulated to 7.2. The kit has the advantages of high and stable enzymatic activity and long preservation life; after the kit is preserved for about 15 days at 35-37 DEG C, the deviation of the detection result is only 1.99%; and the sensitivity is improved by 3.45%.
Owner:李宏奎
Detection kit of non-esterified fatty acids and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106191206AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce risk costMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl-coenzyme A oxidaseFlavin adenine dinucleotide
The invention relates to the field of medical detection technology, and especially relates to a detection kit of non-esterified fatty acids. The kit comprises a reagent 1 and a reagent; the reagent 1 comprises sodium dihydrogen phosphate, coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, acyl coenzyme A synthetase, MgCl2, and a Trinder substrate, wherein the pH value is adjusted to 7.2; the reagent 2 comprises sodium dihydrogen phosphate, flavin adenine dinucleotide, 4-aminoantipyrine, acyl coenzyme A synthetase, peroxidase, alkyl glucoside APG0810, mannitol, EDTA-2Na, and polyoxyethylene dodecyl ether, where the pH value is adjusted to 7.2. Surfactants in the reagents are selected, so that activity of various enzymes is stable and are not easy to precipitate, shelf-life is prolonged, enterprise risk cost is reduced, and enterprise benefits are improved.
Owner:HONGKUI BIOLOGICAL CHINA CO LTD
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with a defined composition from an unrelated carbon source
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
A kind of free fatty acid determination kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106191213BHigh viscosityLow viscosityMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-coenzyme A oxidase
The invention relates to the technical field of free fatty acid determining, in particular to a free fatty acid determining kit. The kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the R1 is prepared from coenzyme A, triphosadenine, acyl coenzyme A synthetase, MgCl2, a Trinder substrate and Tween-20, and has the pH of 7.2; the R2 is prepared from flavin adenine dinucleotide, 4 amino-antipyrine, peroxidase, acyl coenzyme A oxidase, Tween-20, glycerinum, 1 to 1.5g / L of brij35-1 and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt and has the pH of 7.2. By adding different combinations of protein protecting agents, the enzyme activity stability is prolonged; the 37-DEG C stability of the enzyme is prolonged from 7 days to 10 days; the enzyme denaturation is slowed down; the reagent R2 cannot easily generate precipitate.
Owner:中拓生物有限公司
Plant acyl-CoA synthetases
InactiveUS7105722B2Inhibit expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The present invention relates to genes encoding plant acyl-CoA synthetases and methods of their use. In particular, the present invention is related to plant acyl-coenzyme A synthetases. The present invention encompasses both native and recombinant wild-type forms of the enzymes, as well as mutant and variant forms, some of which possess altered characteristics relative to the wild-type enzyme. The present invention also relates to methods of using acyl-CoA synthetases, including altered expression in transgenic plants and expression in prokaryotes and cell culture systems.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production by coenzyme A-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase pathways
Organisms are provided containing genes encoding one or more enzymes, Coenzyme-A-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase, β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase and / or PHA synthase. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are heterologous genes provided by genetic engineering. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers comprising 3-hydroxalkanoate monomers other than 3-hydroxybutryrate wherein these 3-hydroxyalkanoate units are derived from the enzyme-catalyzed conversion of alcohols to 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA monomers, where at least one step in the conversion pathway involves a Co-enzyme A-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers for articles such as films, latexes, coatings, adhesives, fibers, binders, resins, and medical devices.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS8986961B2YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalyzed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Compositions and methods for treating proliferative diseases
InactiveUS20120178782A1Treating and preventing psoriasisBiocidePill deliveryAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
Synergistic pharmaceutical compositions and the methods for preventing and treating proliferative diseases such as cancer and psoriasis. The compositions comprise synergistic combinations of: (i) an acyl-CoA-synthetase enzyme inhibitor (AcsI4), (ii) a compound having an inhibiting effect on enzymes with cyclooxygenase activity (COX); and (iii) a compound selected from a 5-lypoxygenase enzyme (LOX-5) inhibitor and a leukotriene receptor antagonist.
Owner:PODESTA ERNESTO JORGE
Method for synthesizing biodiesel with microorganisms in vivo
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing biodiesel with microorganisms in vivo, which is realized in escherichia coli. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively cloning an acinetobacter wax fat synthetase gene atfA, an escherichia coli acyl coenzyme A synthetase gene fadD, a zymomonas mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase gene pdc and an alcohol dehydrogenase gene adhB gene on a pET expression vector in series to obtain a plasmid pXT11; transferring the plasmid pXT11 into escherichia coli containing a plasmid pMSD8 and a plasmid pMSD15 to obtain an escherichia coli stain XT31; and generating biodiesel by the escherichia coli stain XT31. The method realizes the microbial transformation from sugar to the biodiesel, lays the foundation for biologically preparing the biodiesel from lignocelluloses, and radically solves the problem of insufficient raw material supply in biodiesel preparation. A step of esterifying methanol is not needed in the technology, thereby the cost is greatly reduced and the problems that glycerol as a side product is formed, and the like are avoided.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
Kit and method for clinically detecting serum or plasma free fatty acid
ActiveCN102634565BDetection speedImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-coenzyme A oxidase
The invention discloses a kit and method for clinically detecting serum or plasma free fatty acid. The kit is composed of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises a buffer, ATP, a coenzyme A, 4-amino antipyrine, an ion activator, an acyl coenzyme A synthetase, stabilizer, a preservative, a surfactant, and concentrated hydrochloric acid, and the reagent 2 comprises a buffer, a chromogen, a composite sulfhydryl reagent, a peroxidase, an acyl coenzyme A oxidase, a stabilizer, a preservative, a surfactant and concentrated hydrochloric acid. The kit has the advantages of good stability, high specificity of the free fatty acid, and wide linear range. The serum or plasma free fatty acid is detected by the enzyme method, and the method has the advantages of high precision, andsmall measuring error.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com