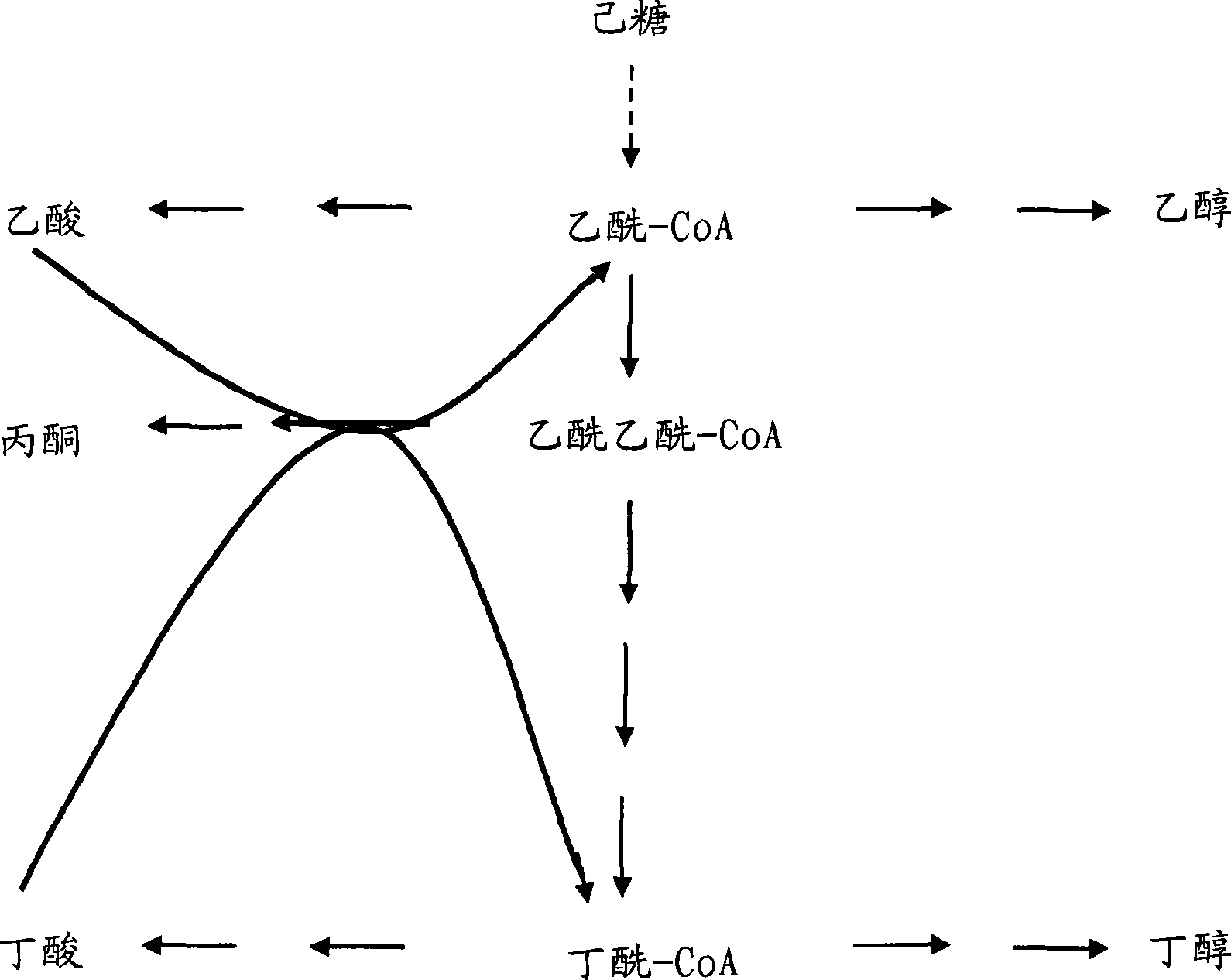
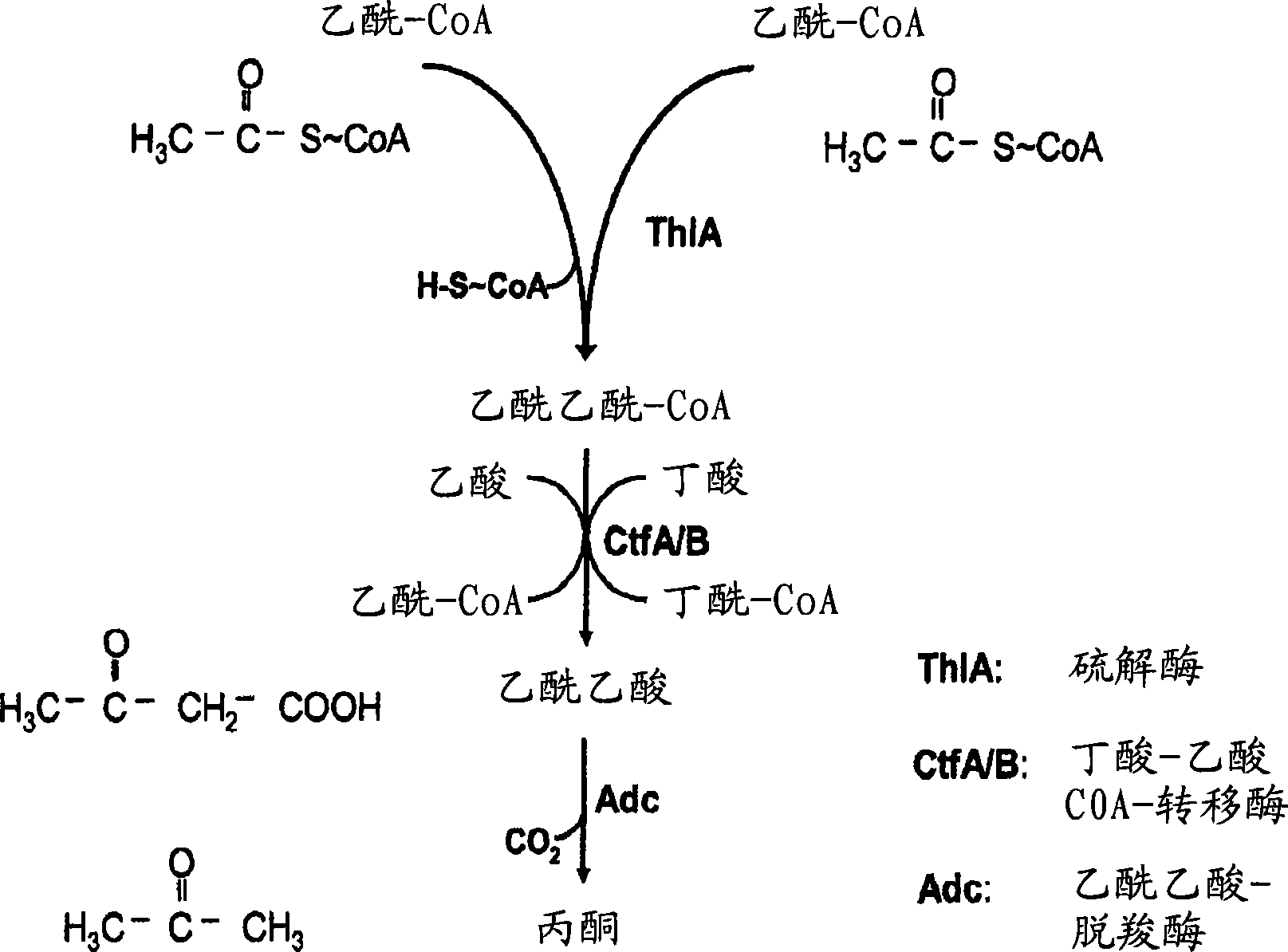
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
A technology of acetone and coenzyme, applied in the field of enzymes and nucleic acids, to achieve the effects of increasing space-time yield, simplifying fermentation process, and simplifying separation and processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The method for preparing acetone of the present invention and the use of the polypeptides and nucleic acids in implementing the method of the present invention are described by the following exemplary methods, and the present invention is not limited to the following exemplary embodiments. It is intended that the documents cited in the description of the present invention incorporate all the contents disclosed therein in the present invention. Polypeptide refers to any chain length. Thus, it also includes any protein, enzyme, in particular acetoacetate-CoA hydrolase, acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase. "Spontaneous conversion" refers to a chemical reaction that produces energy. "Under stringent conditions" hybridization refers to experimental conditions, such as the application of a washing solution at 50-70° C., preferably 60-65° C. in Northern blotting techniques, such as the application of 0.1x SSC buffer containing 0.1% SDS (2Ox SSC ...
Embodiment 1
[0109] Example 1: Thioesterase II (TEII) from Bacillus subtilis srf )
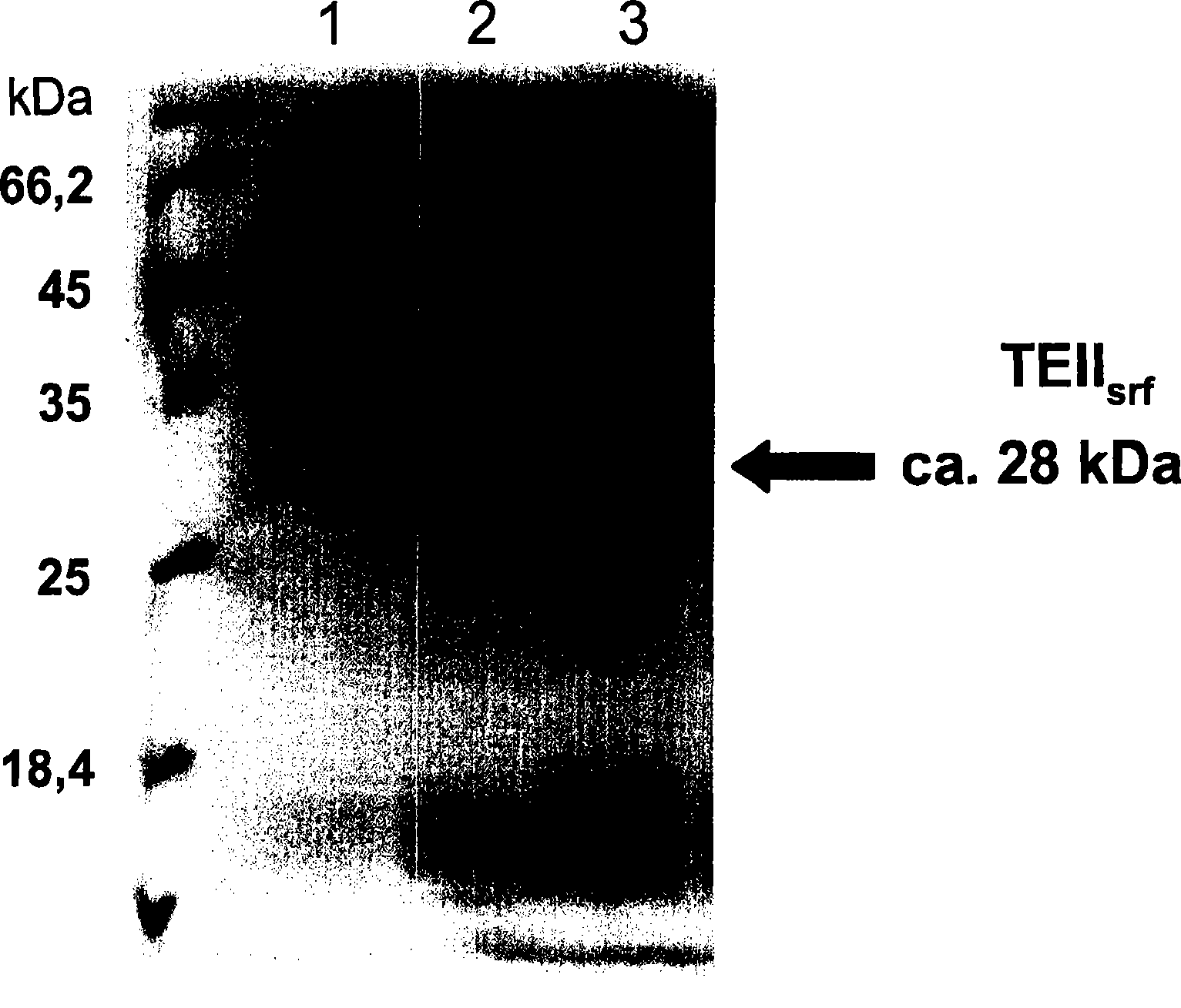
[0110] This enzyme is related to the non-ribosomal peptide synthase used in the formation of surfactant peptides (peptide antibiotics) in Bacillus subtilis ATCC 21332. Schwarzer et al. were able to clone the corresponding gene into the plasmid pQE60 that mediates the fusion of the target protein with the C-terminal His tag (pTEIIsrf) and purify the protein (28kDa) (Schwarzer D., H.D.Mootz, U.Linne, M.A.Marahiel .2002.Regeneration of misprimed nonribosomal peptidesythetases by type II thioesterases.PNAS 99:14083-14088). In the following study, the hydrolytic activity of the protein with acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA as substrates was demonstrated.
[0111] Plasmid pTEIIsrf with SEQ ID NO.13 was prepared as described by Schwarzer D, Mootz HD, Linne U, Marahiel MA (Regeneration of misprimed nonribosomal peptide sythetases by type II thioesterases. Proc Natl AcadSci US A. 2002 Oct 29; 99 (22 ): 14083-8).
...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2: Acetoacetyl-CoA Synthetase (AACS) from S. meliloti
[0119] With the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3 and the corresponding cDNA sequence shown in SEQ ID No.4, the acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase (AACS) from Sinorhizobium meliloti catalyzes the consumption of ATP by acetoacetate and coenzyme A is converted to acetoacetyl-CoA and AMP. Within the framework of the present invention, however, the reverse reaction is of interest.
[0120] Such as Aneja, P., R.Dziak, G.-Q.Cai, T.C.Charles.2002. Identification of an Acetoacetyl Coenzyme A synthetase-Dependent Pathway for Utilization of L-(+)-3-hydroxybutyrate in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J.Bacteriol. The corresponding gene acsA2 was cloned into the expression vector pET30Xa / LIC as described in 184:1571-1577. The plasmid "pRD112" obtained in this way mediates the fusion of the N-terminus of the target protein with the His tag, thereby facilitating the 2+ -Purification by affinity chromatography on NTA agarose.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com