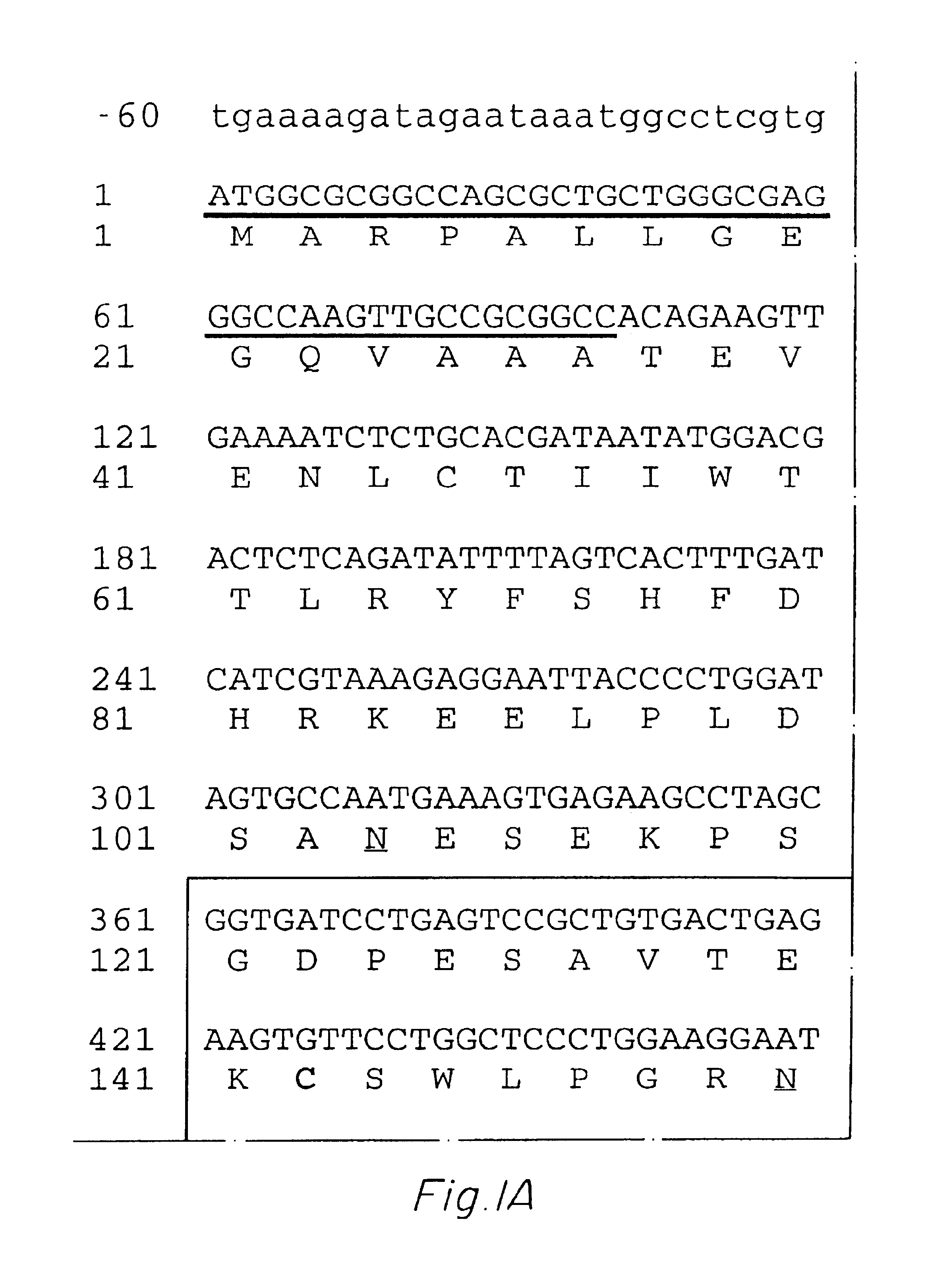
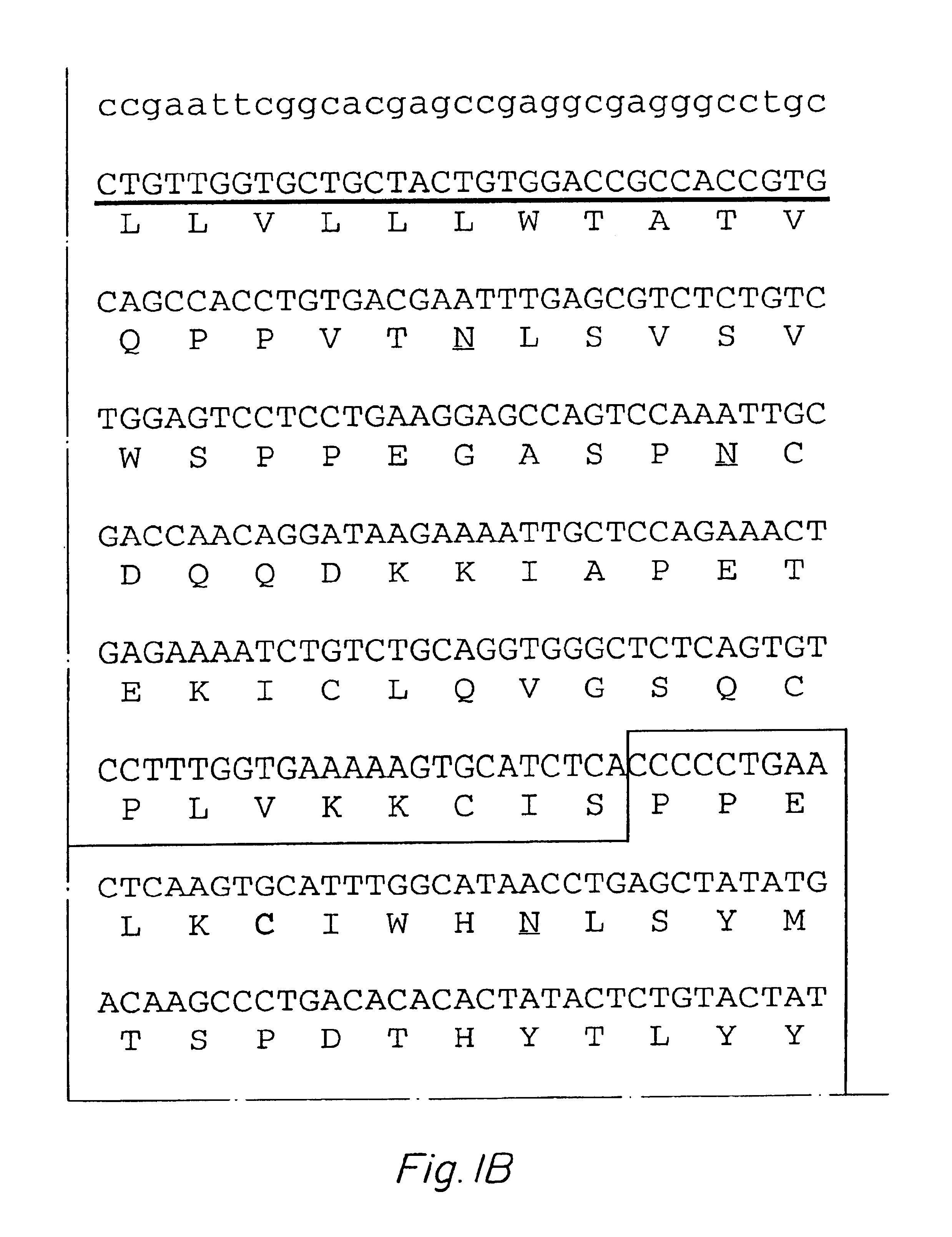
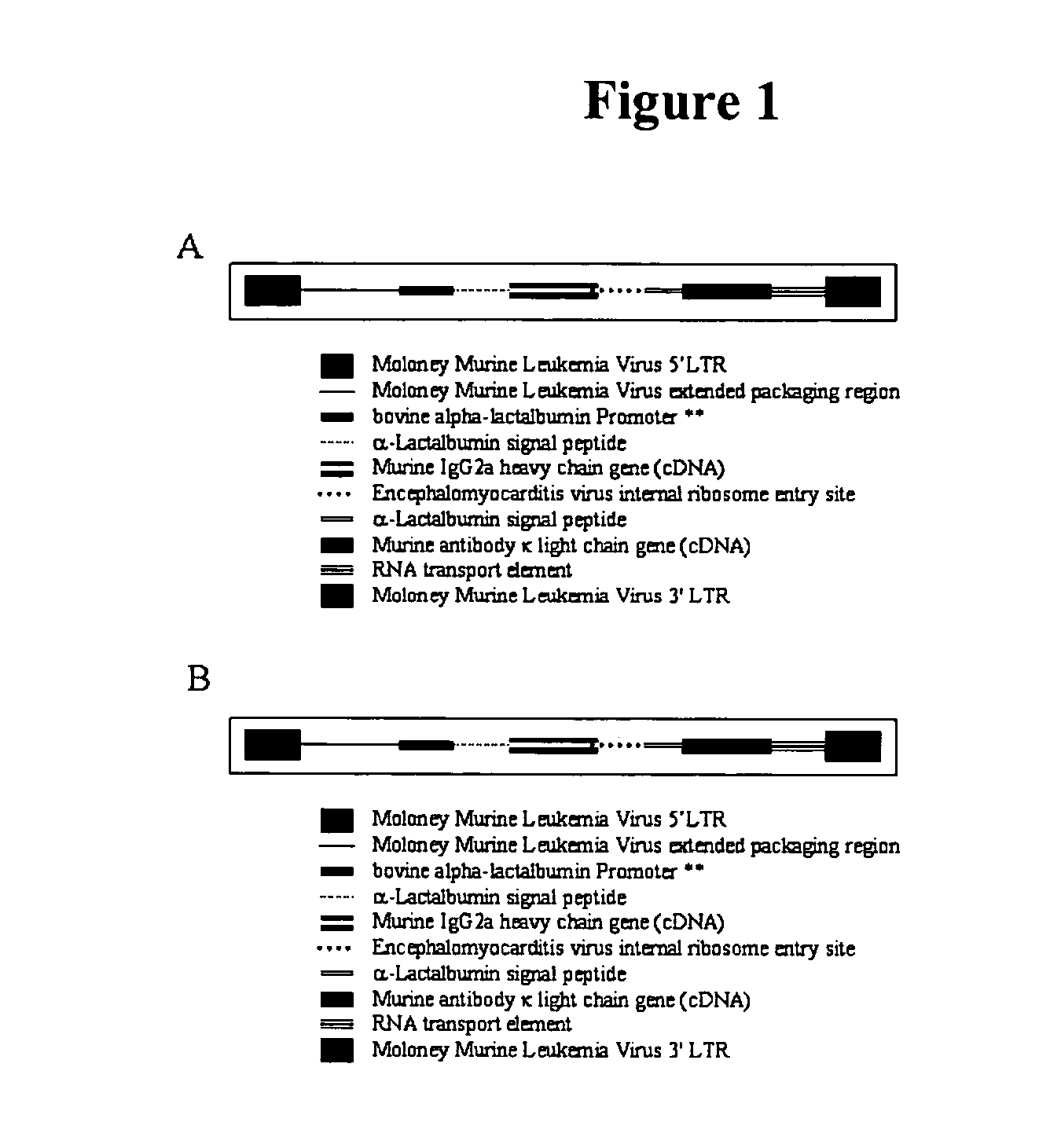
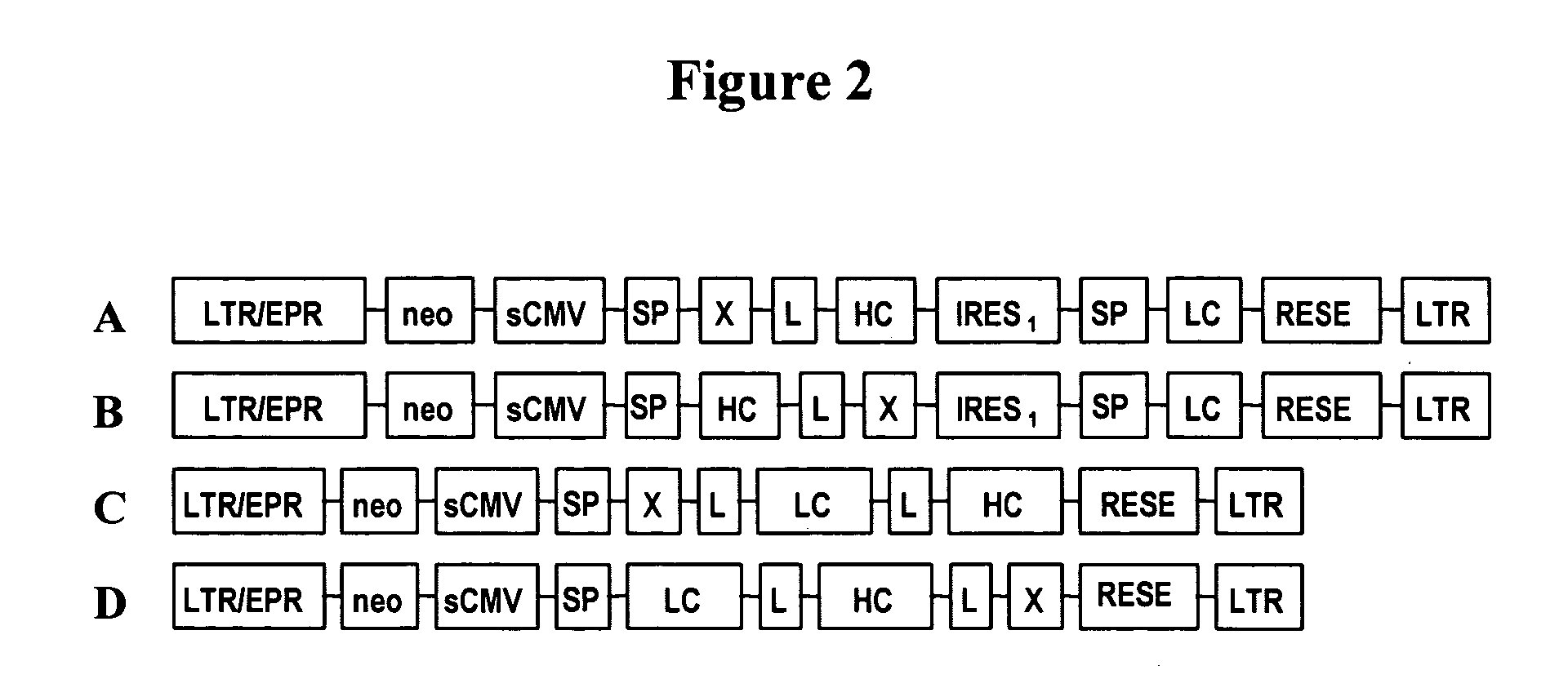
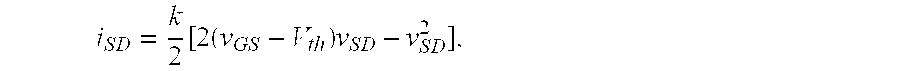Patents
Literature
205 results about "Receptor molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Receptor Definition. A receptor is a protein which binds to a specific molecule. The molecule it binds is known as the ligand. A ligand may be any molecule, from inorganic minerals to organism -created proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters. The ligand binds to the ligand-binding site on the receptor protein.
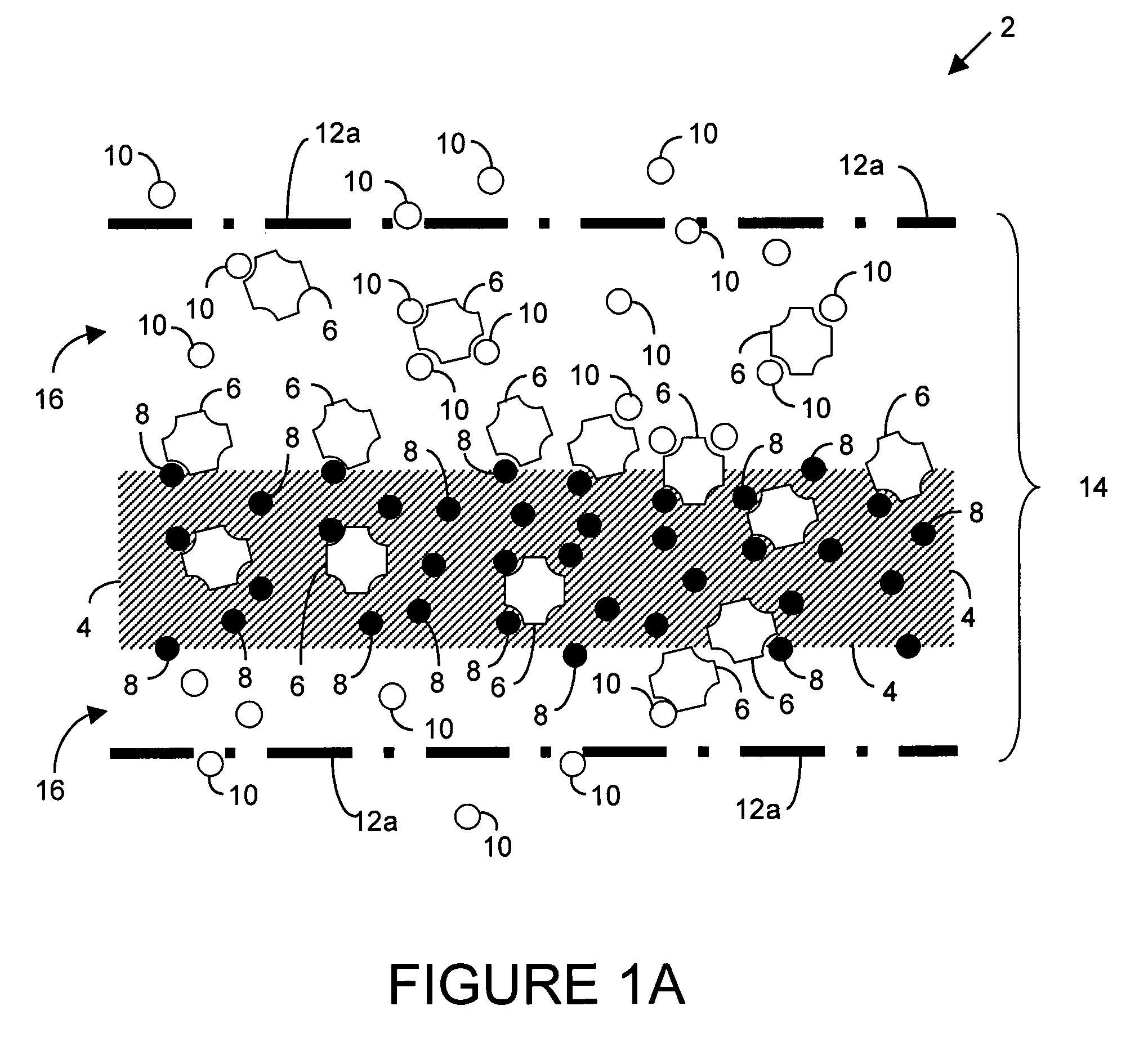
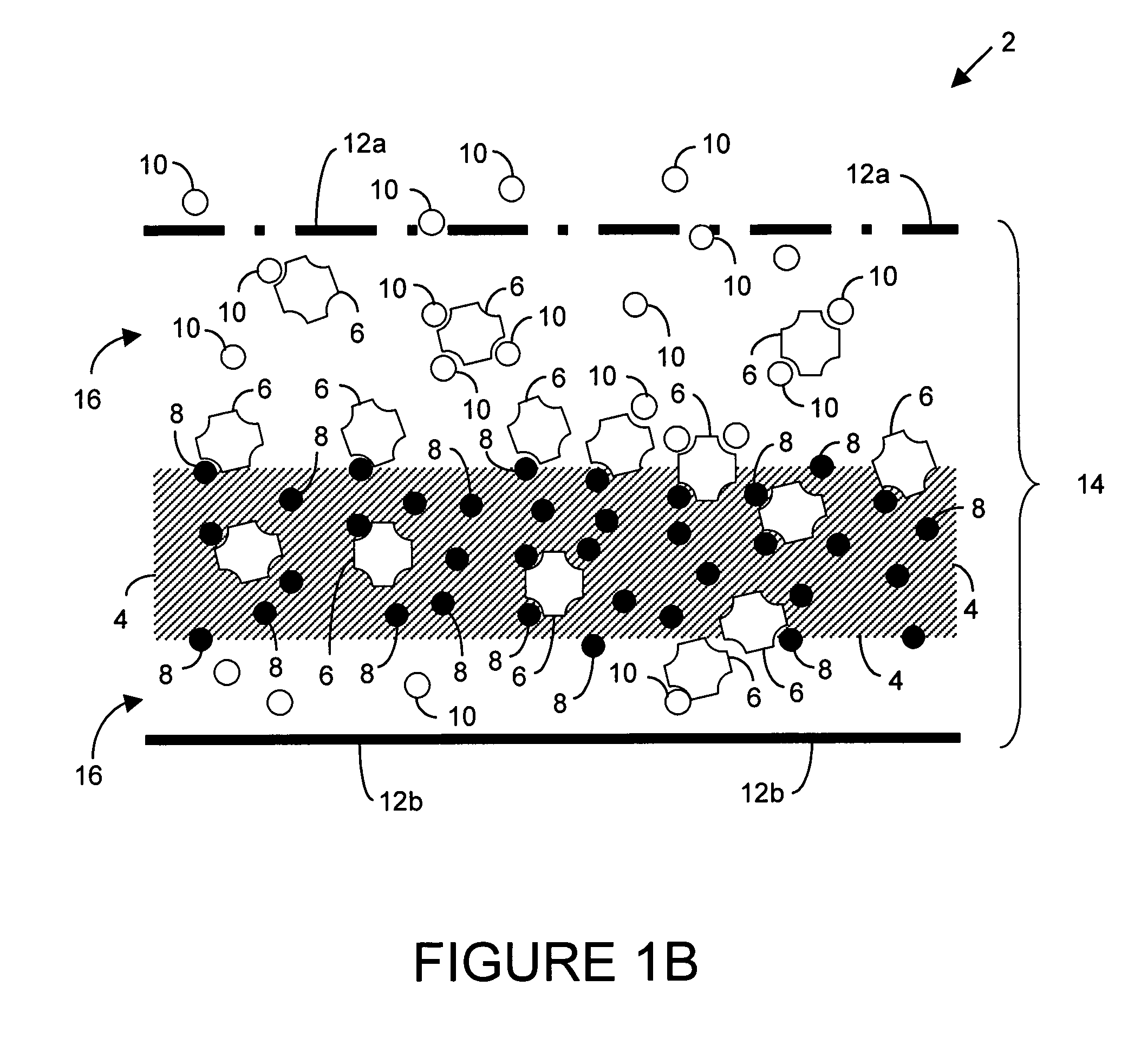
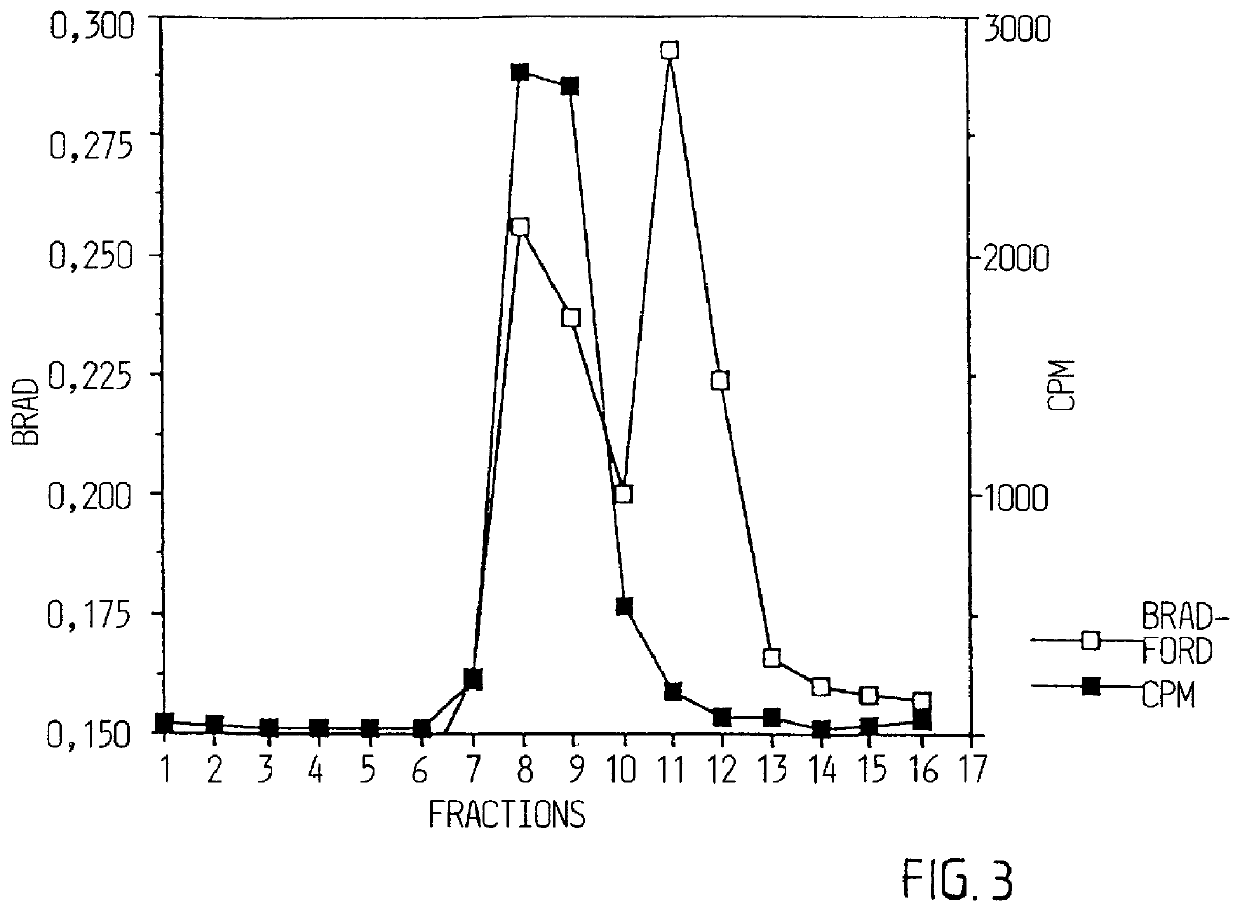
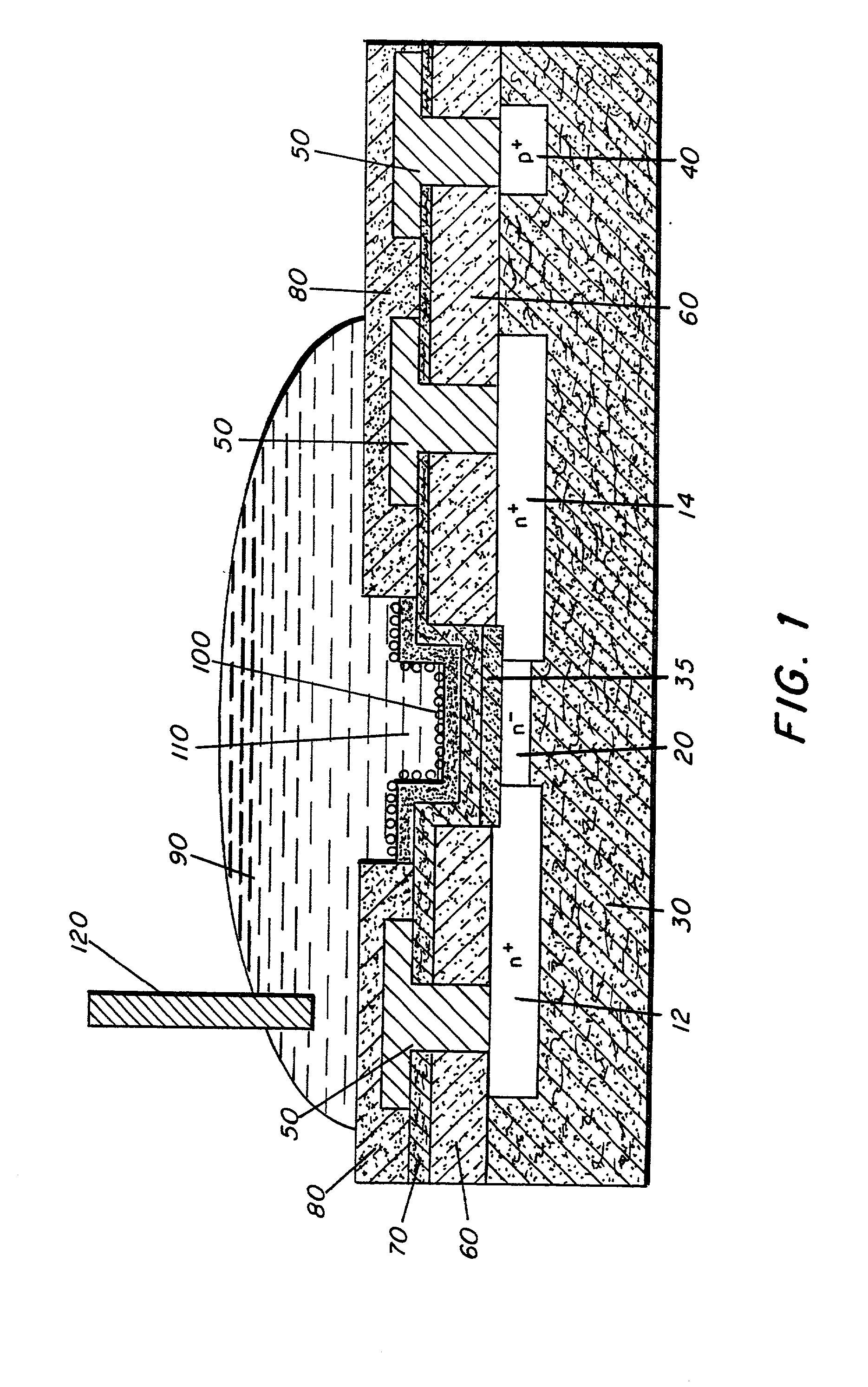
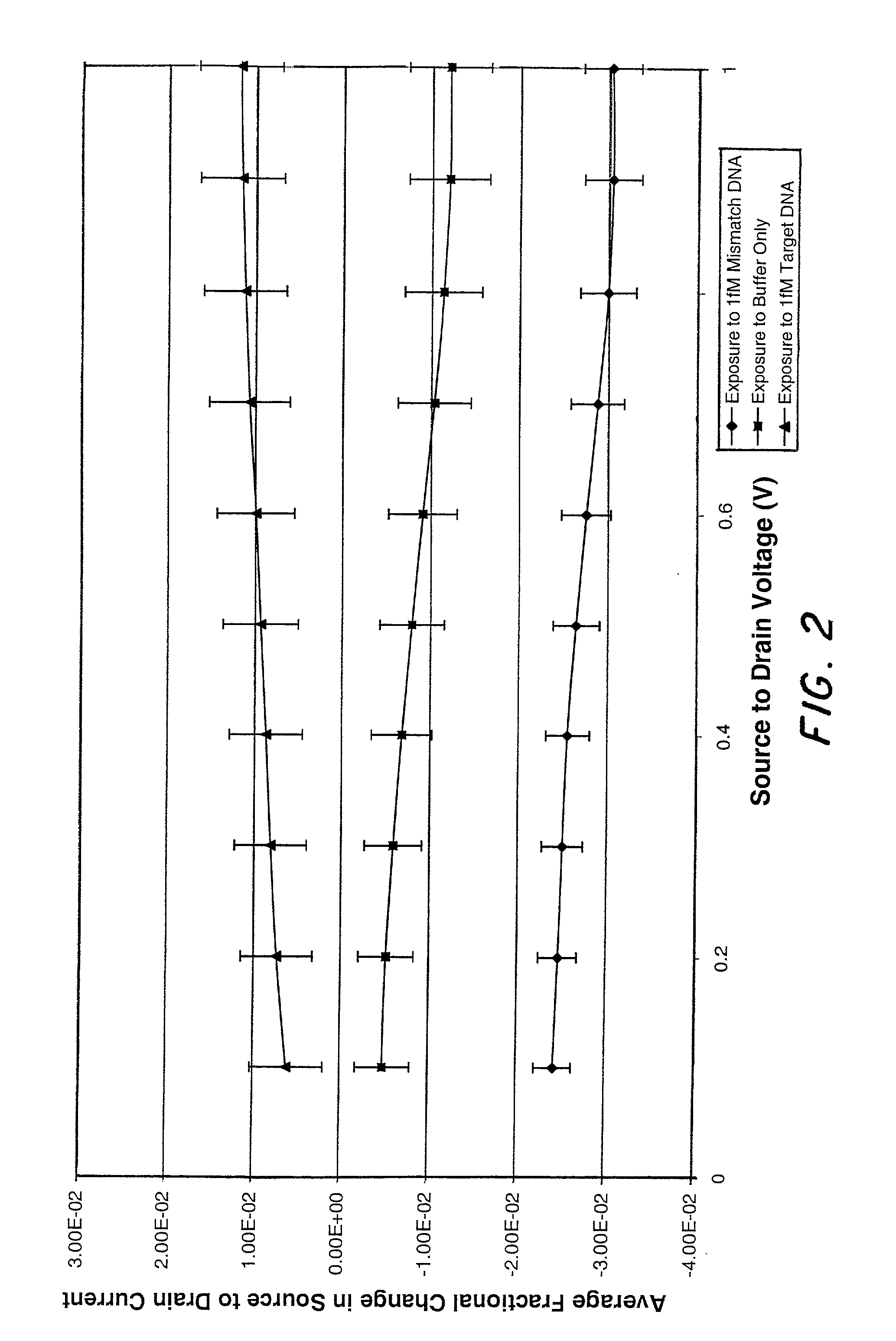
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
InactiveUS6482639B2Sensitive and accurate detectionWide scope of practical and worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
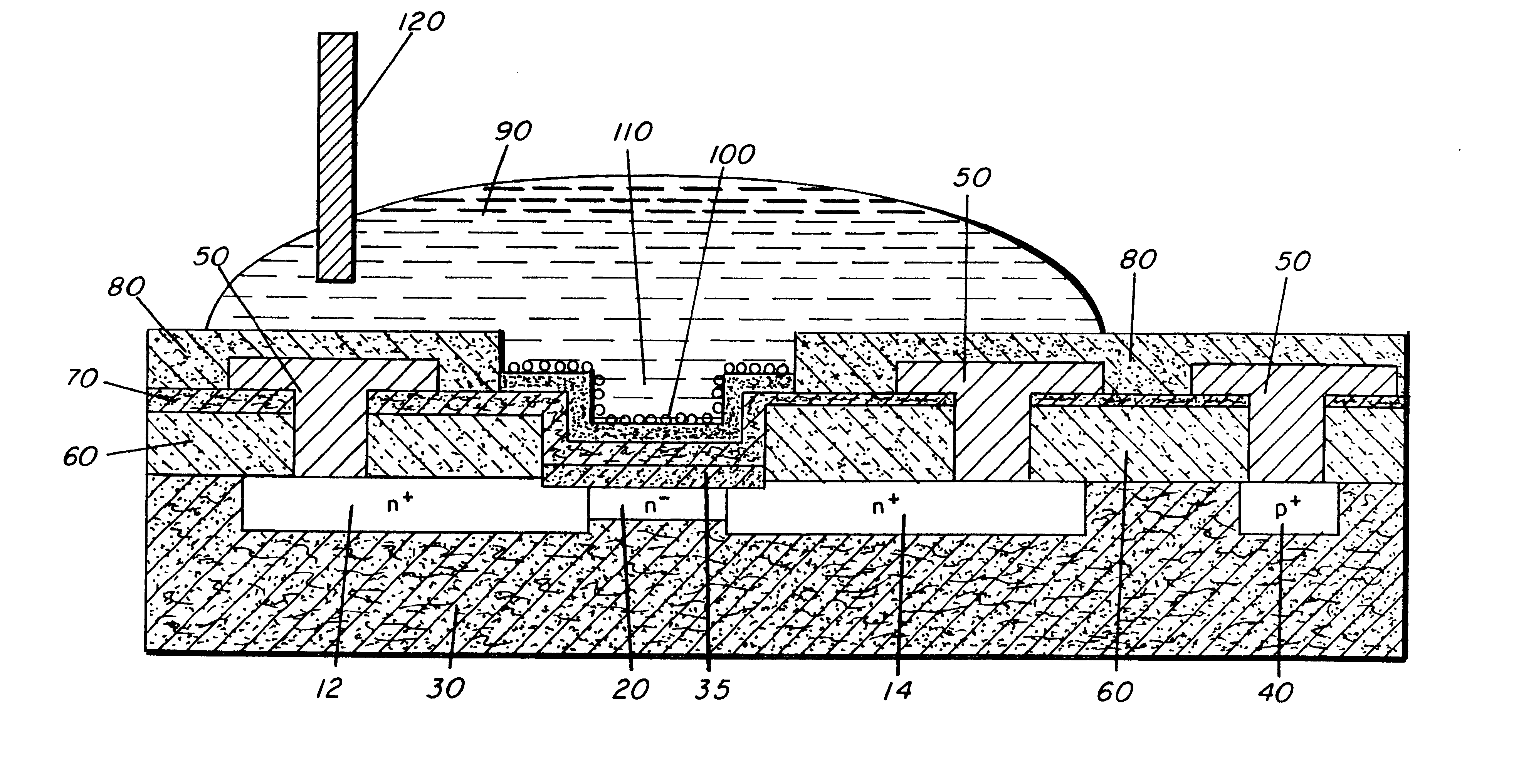
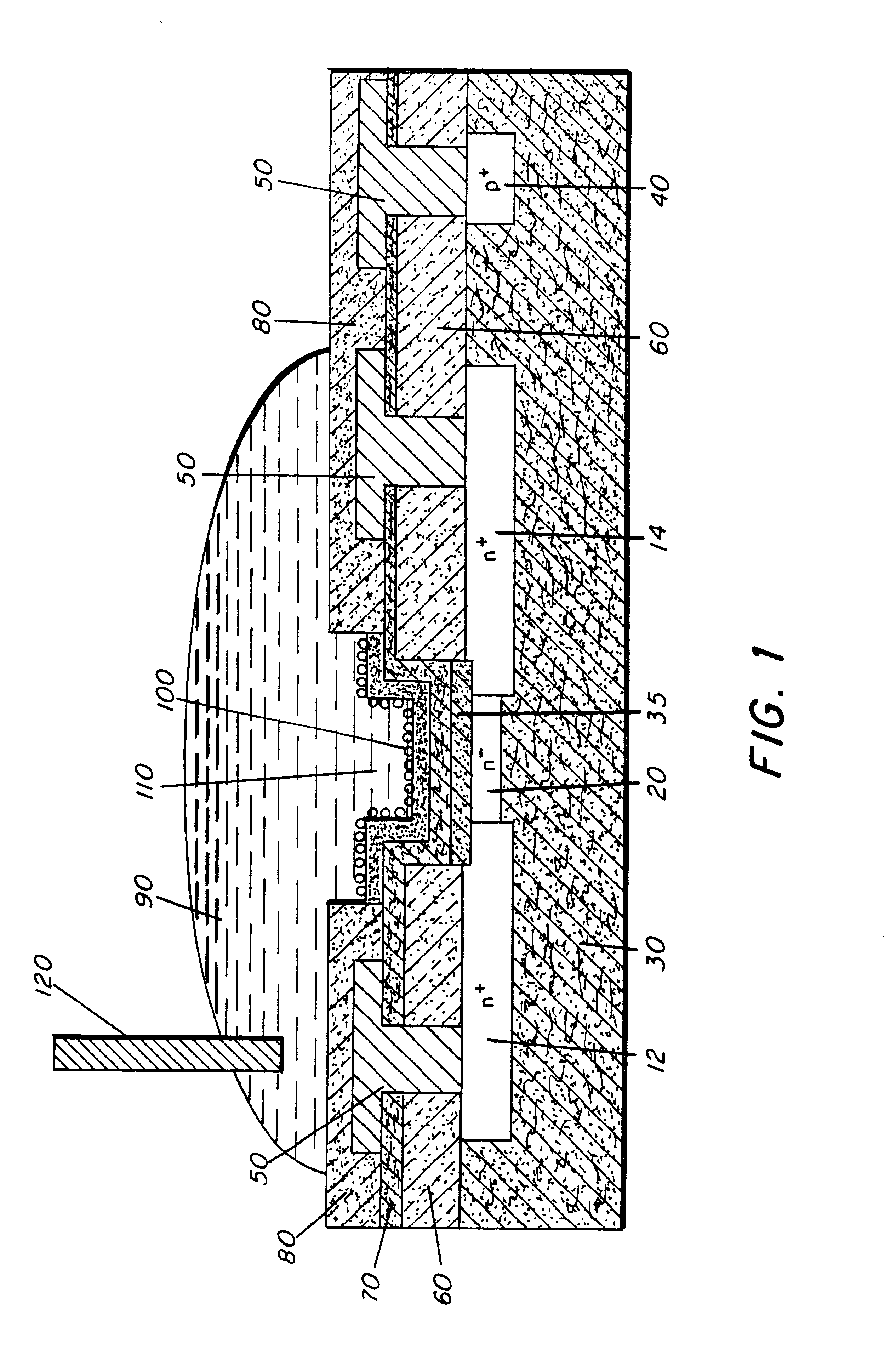
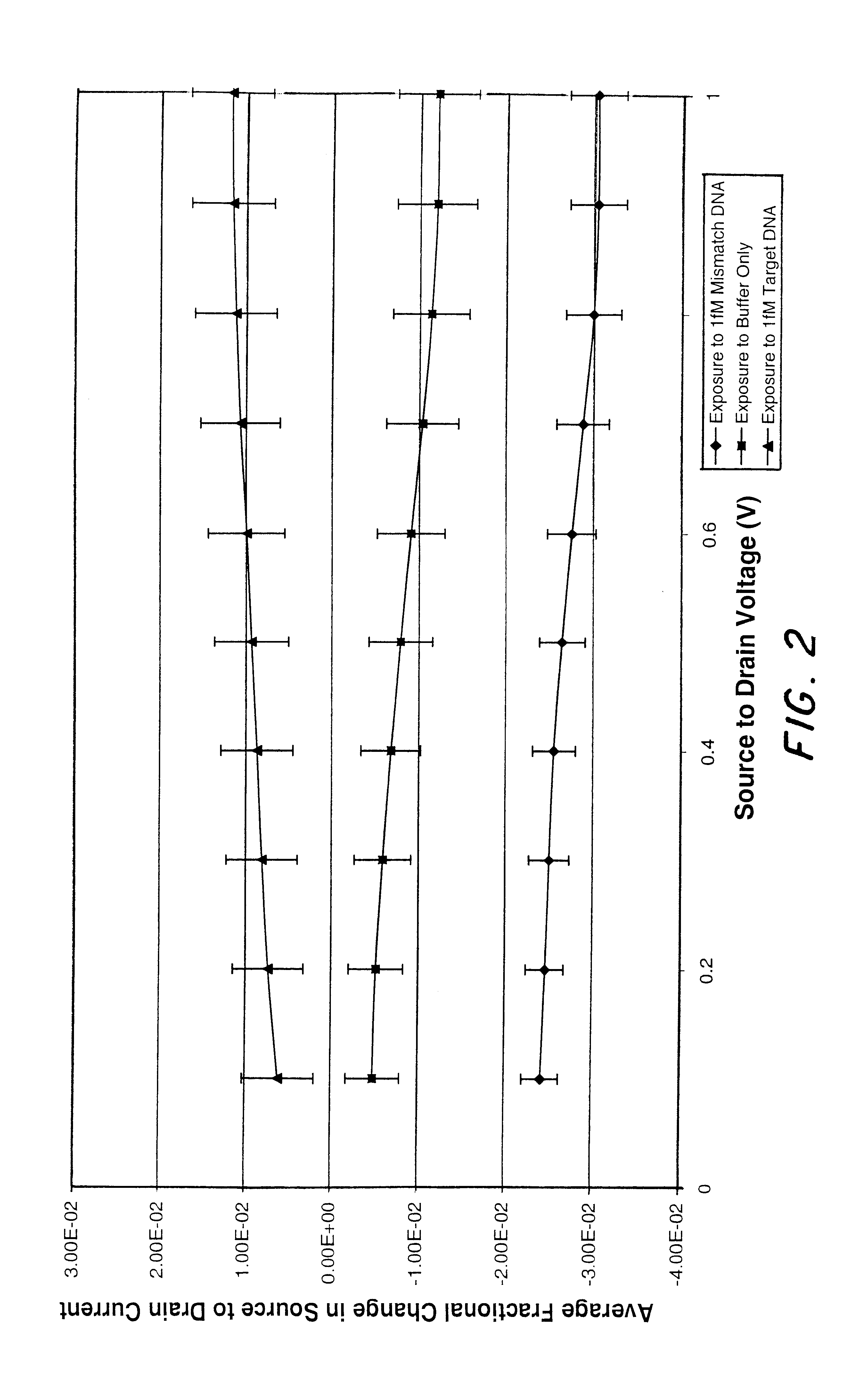
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System, device and method for determining the concentration of an analyte
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is a system, a device and a method for sensing the concentration of an analyte in a fluid (for example, a fluid sample) or matrix. The analyte may be glucose or other chemical of interest. The fluid or matrix may be, for example, the fluid or matrix in the body of an animal (for example, human), or any other suitable fluid or matrix in which it is desired to know the concentration of an analyte. In one embodiment, the invention is a system and / or device that includes one or more layers having a plurality of analyte-equivalents and mobile or fixed receptor molecules with specific binding sites for the analyte-equivalents and analytes under analysis (for example, glucose). The receptor molecules, when exposed to or in the presence of analyte (that resides, for example, in a fluid in an animal), bind with the analyte (or vice versa). As such, some or all (or substantially all) of the receptor molecules within a given layer may bind with the analyte, which results in a change in the optical properties of one or more of the layers. These layer(s) may be examined or interrogated, via optical techniques, whereby the optical response of the layers and / or, in particular, the substance within the layer(s), may be measured, evaluated and / or analyzed.
Owner:BIO TEX LTD INC
Iscom or iscom-matrix comprising hydrophobic receptor molecules for antigenic substances
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 00287 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 17, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 17, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 20, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 30726 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 28, 1997Lipid-containing particles such as iscoms, iscom-matrix or vesicles such as micelles or liposomes that comprise one or more hydrophobic receptor molecules for targeting and antigenic substances, which receptor molecules have been integrated in the particle and are chosen from lipid-containing receptors or receptors that are hydrophobic, which receptor molecules bind to the antigenic substances.
Owner:MOREIN BROR +2
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
InactiveUS20020012937A1Wide scope of practicalWide scope of worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
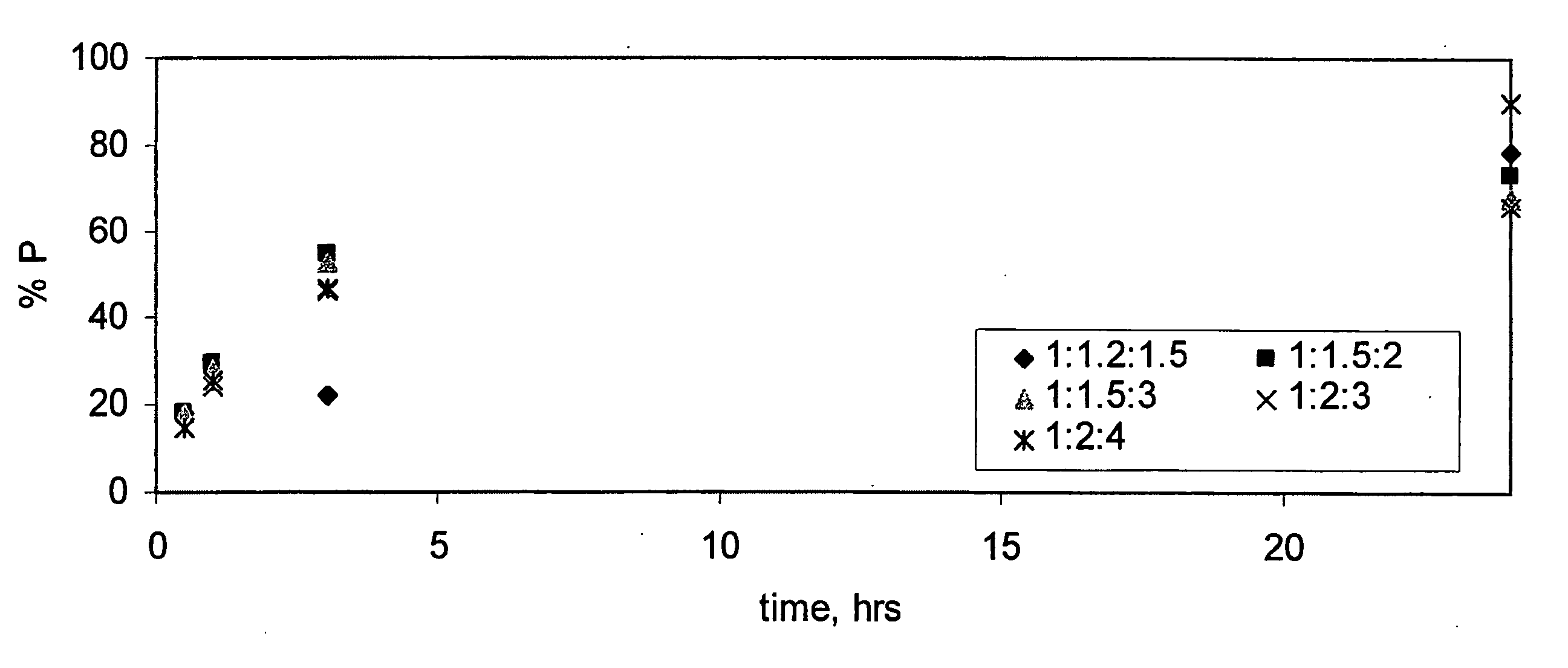
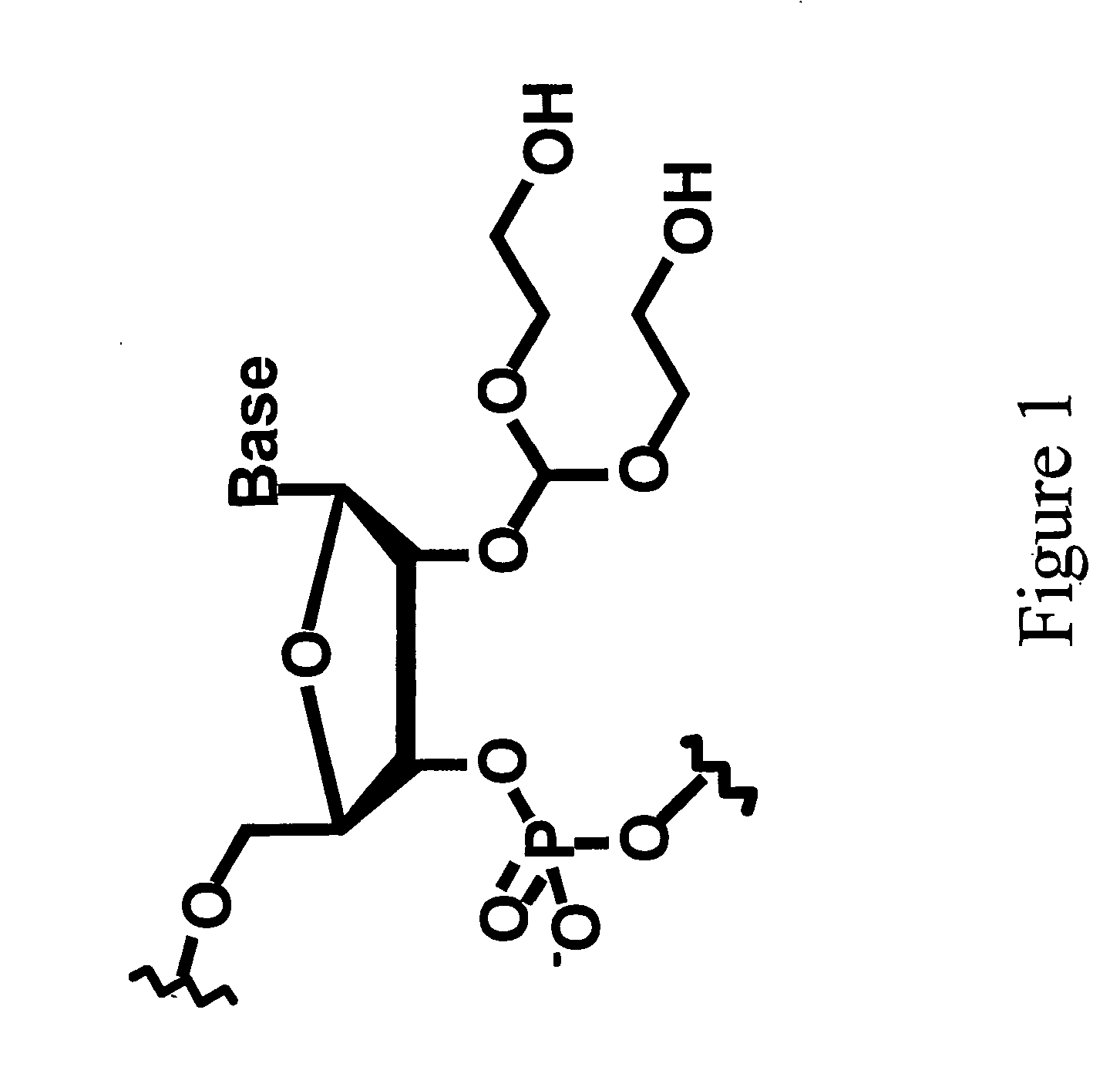
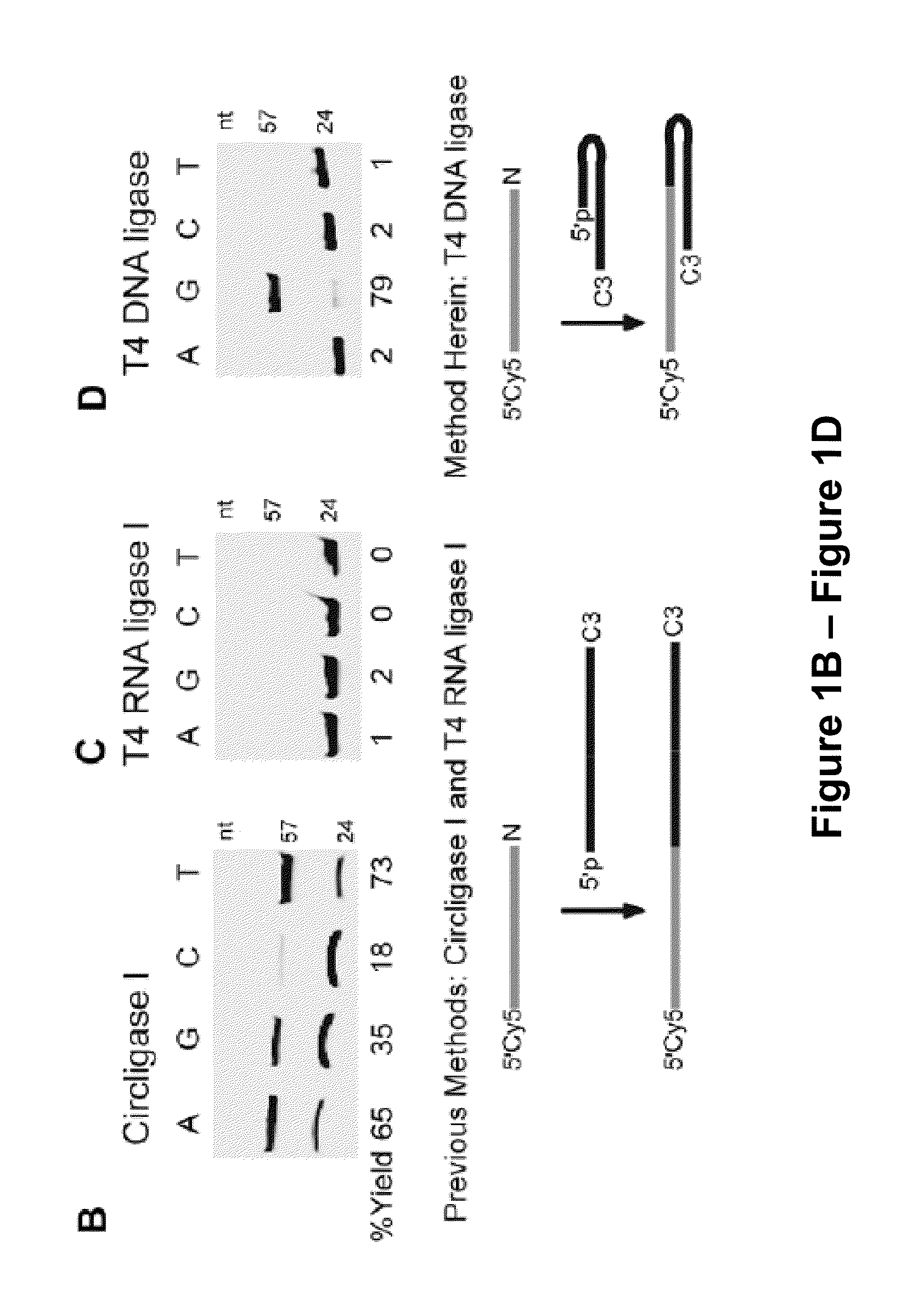
Splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribounucleotides
InactiveUS20050130201A1Ligate RNA moleculesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolyribonucleotides
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribonucleotides using an RNA polymerizing enzyme. The invention provides ligating ribonucleotides comprising ligating a donor RNA molecule to an acceptor RNA molecule in the presence of RNA ligase and a splint, wherein the donor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety, the acceptor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety and the splint is comprised of a polyribonucleotide. The invention also provides splints for use in splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis using an RNA polymerizing enzyme.
Owner:DHARMACON INC
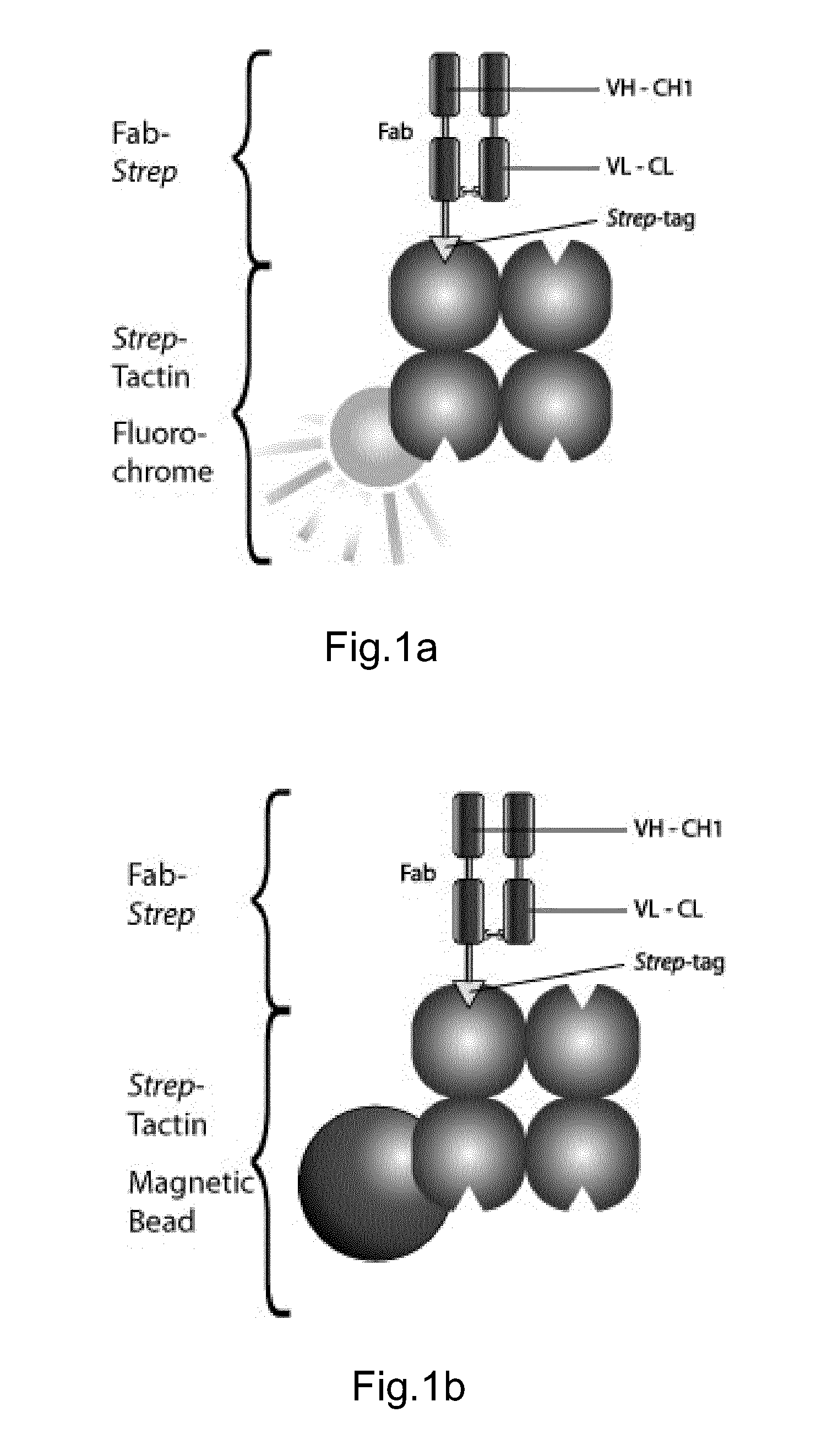
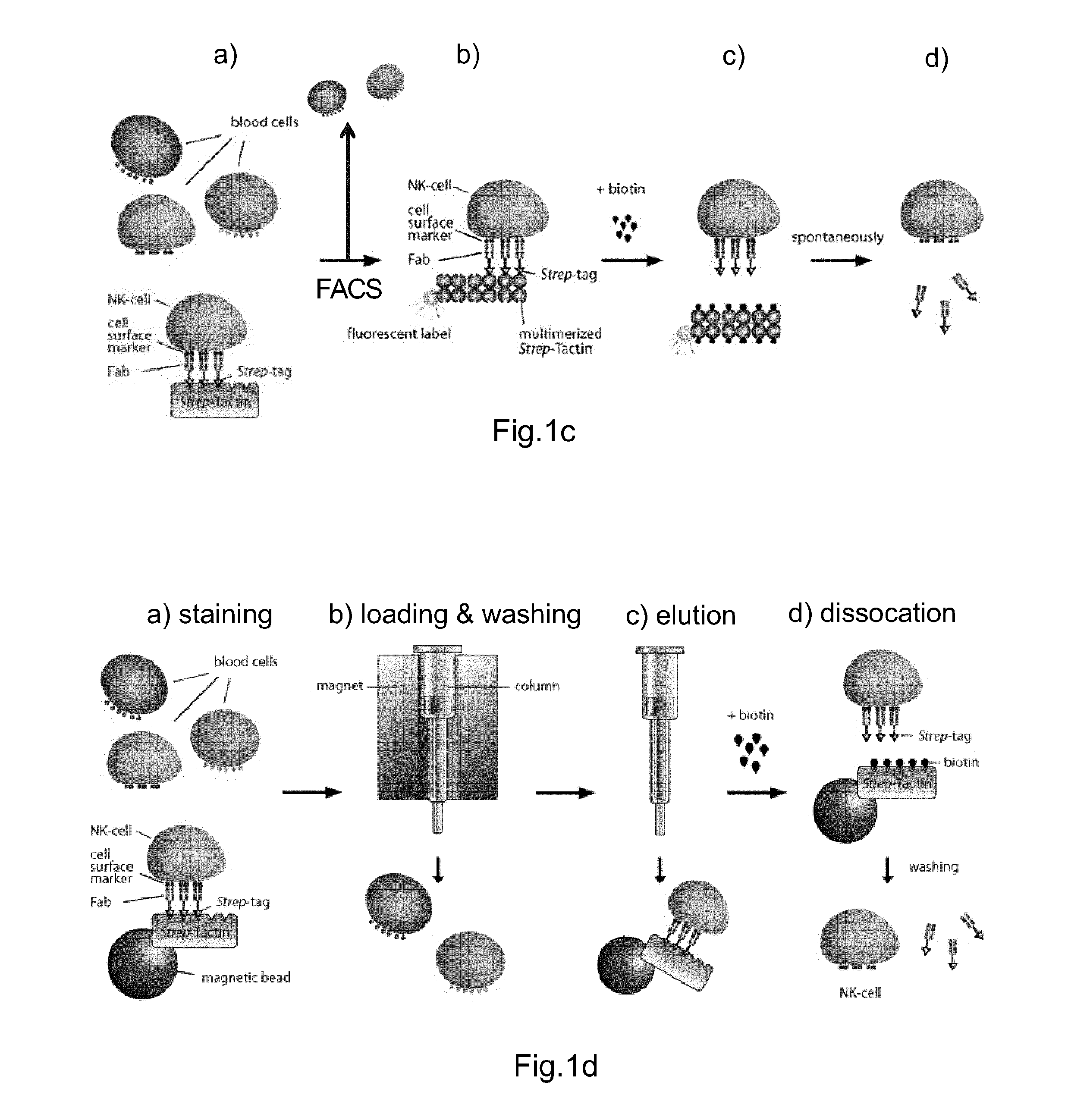
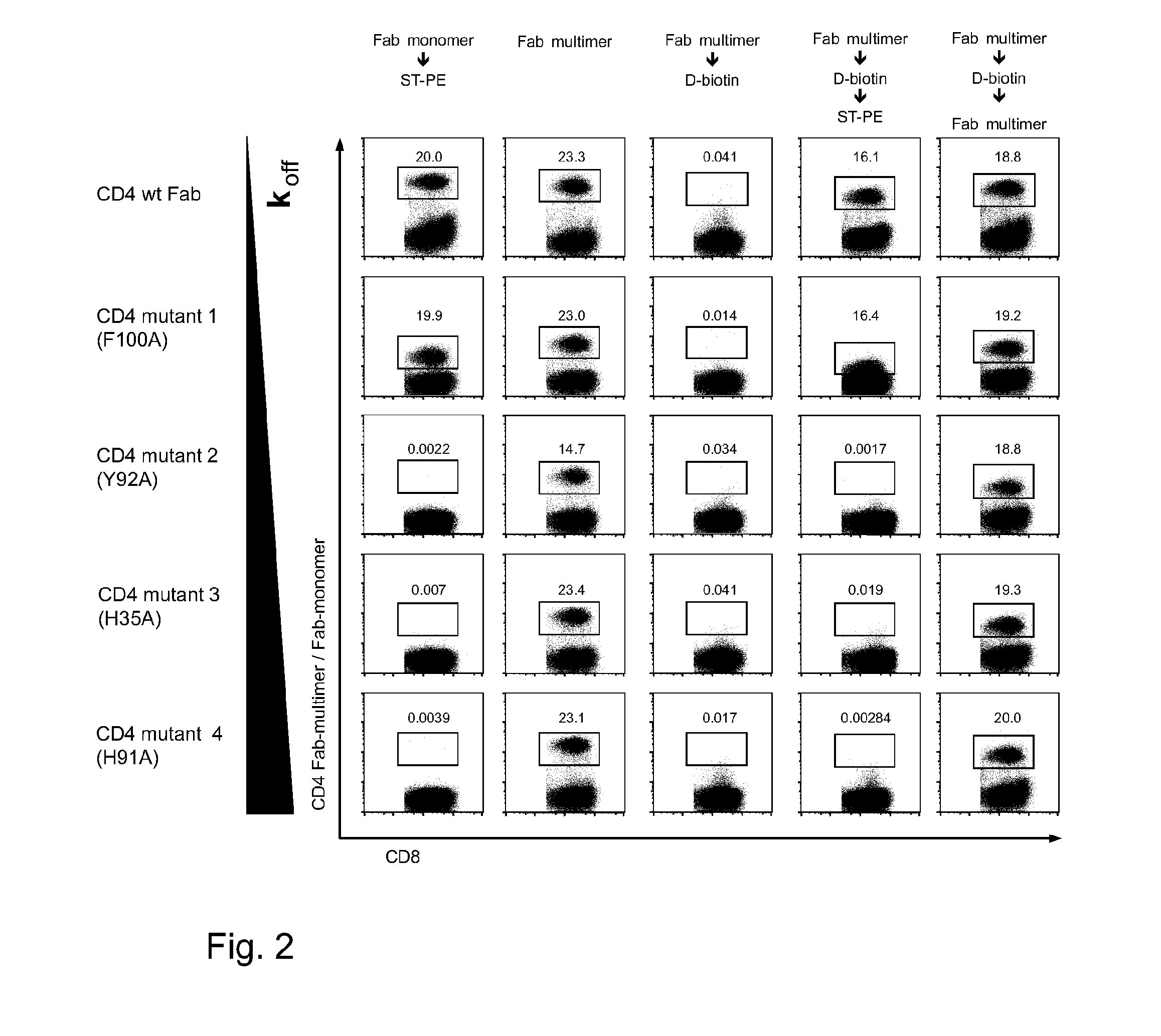
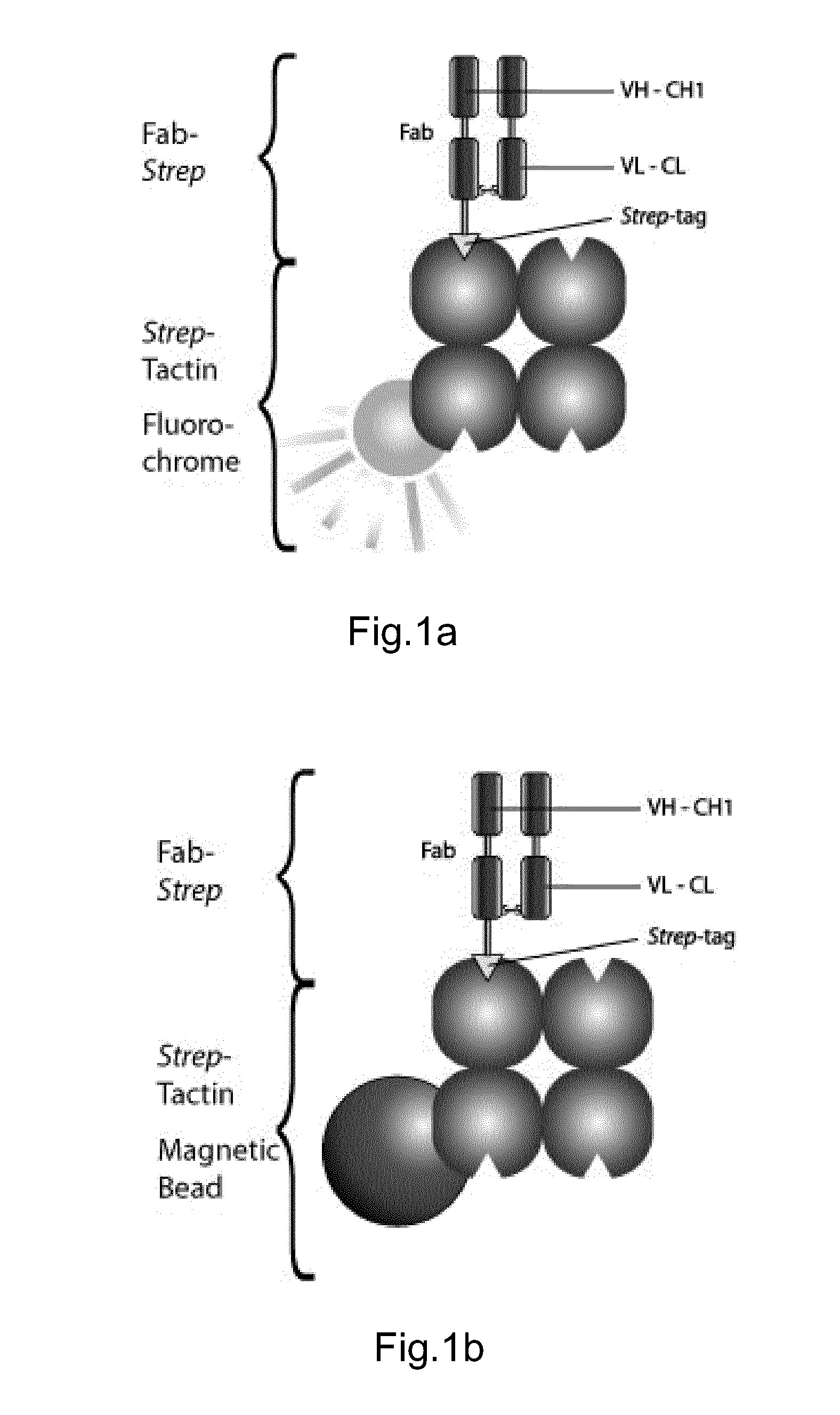
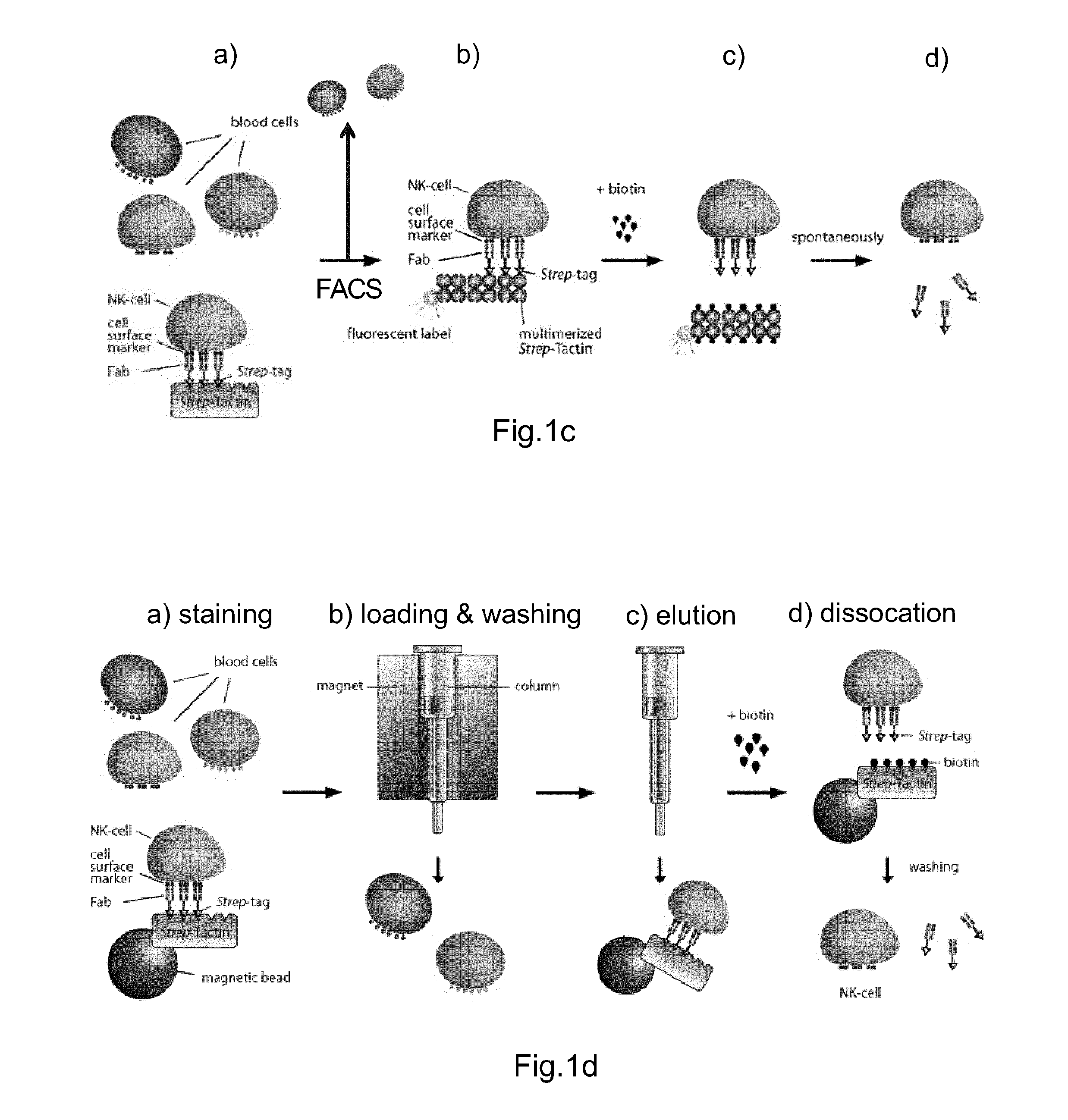
Method of reversibly staining a target cell
The present invention relates to methods of reversibly staining a target cell. The invention also relates to methods of isolating a target cell or a target cell population that is defined by the presence of at least one common specific receptor molecule. The invention also provides kits that can be used to carry out the methods of the invention.
Owner:IBA LIFESCIENCES GMBH
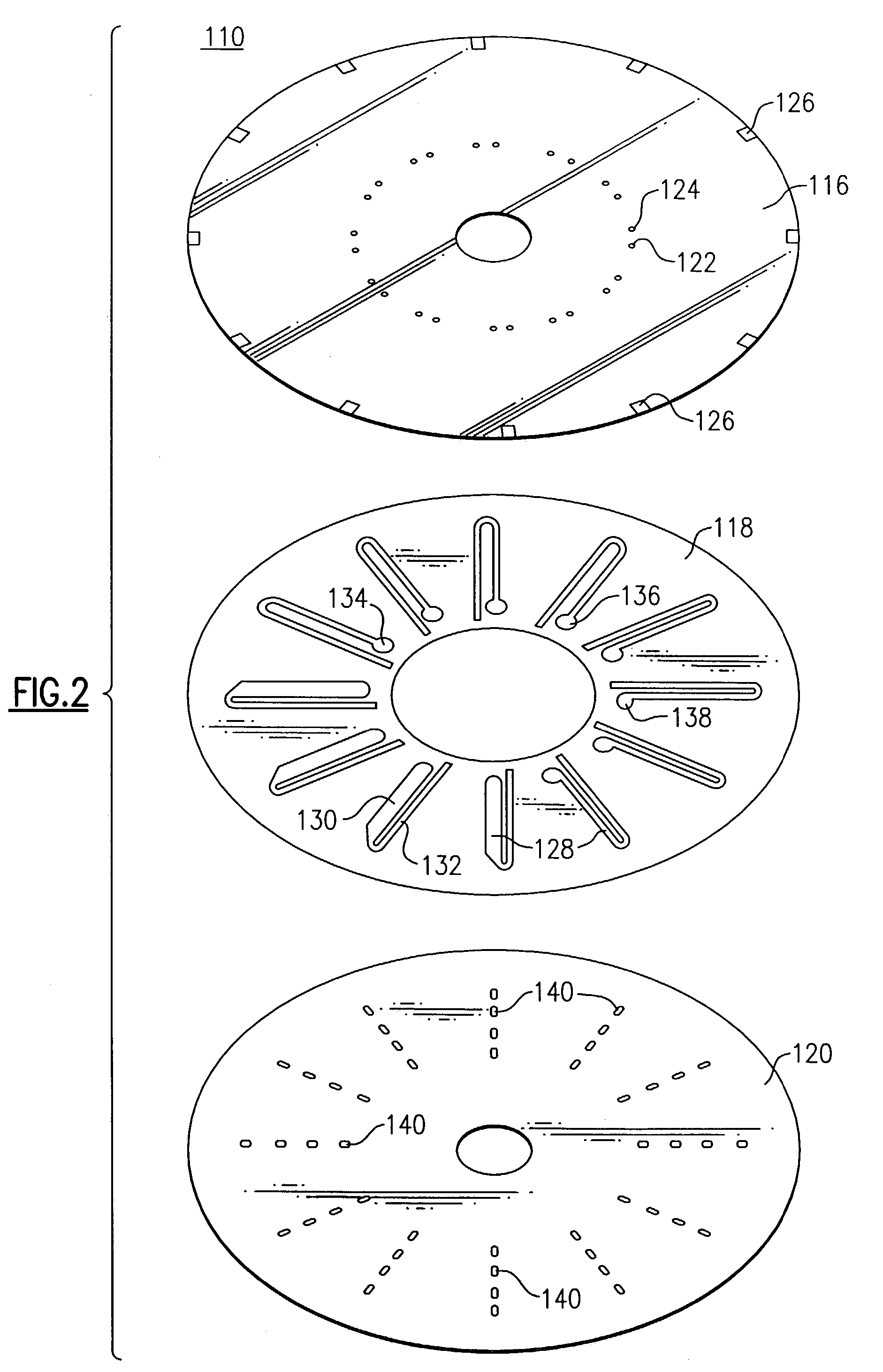
Multi-purpose optical analysis disc for conducting assays and related methods for attaching capture agents
InactiveUS20050003459A1Material nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by optical meansReceptor moleculeAnalytical chemistry
The present invention relates to optical bio-disc systems and related test methods and to immobilizing receptor molecules on optical bio-discs. When a sample is injected into a fluidic circuit, the target agent binds to a capture agent or probe bound in a capture zone. A signal is generated from tags attached to a reporter probe that has specific affinity to the target agent. The assays and methods of the present invention are implemented on a bio-disc. The bio-disc includes a flow channel having capture zones in fluid communication with a mixing chamber and a peripheral waste reservoir. The bio-disc is implemented on an optical disc that has information encoding format such as a CD. A bio-disc drive assembly is employed to rotate the disc, read and process any encoded information, and analyze the samples in the flow channel of the bio-disc.
Owner:VINDUR TECH
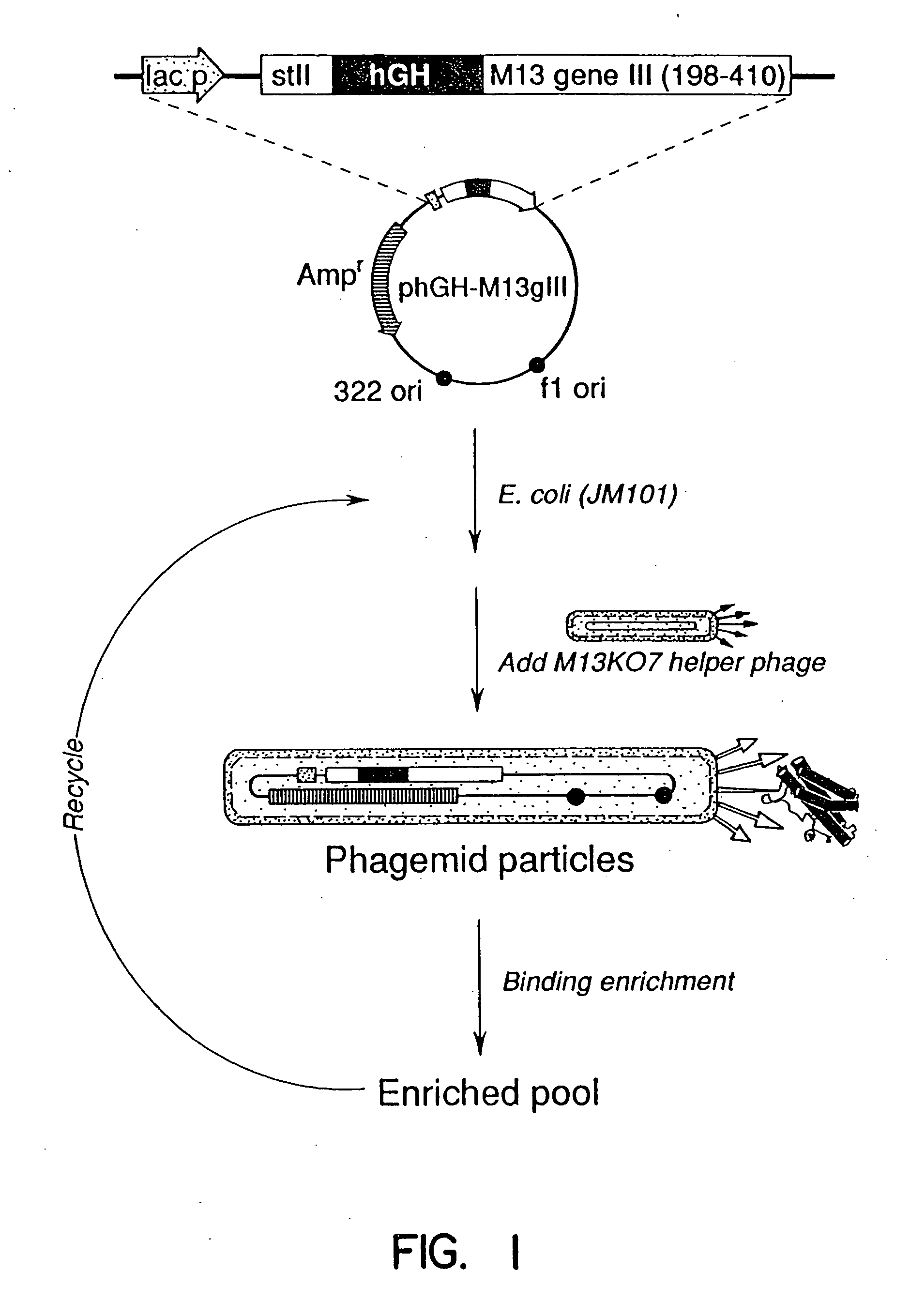
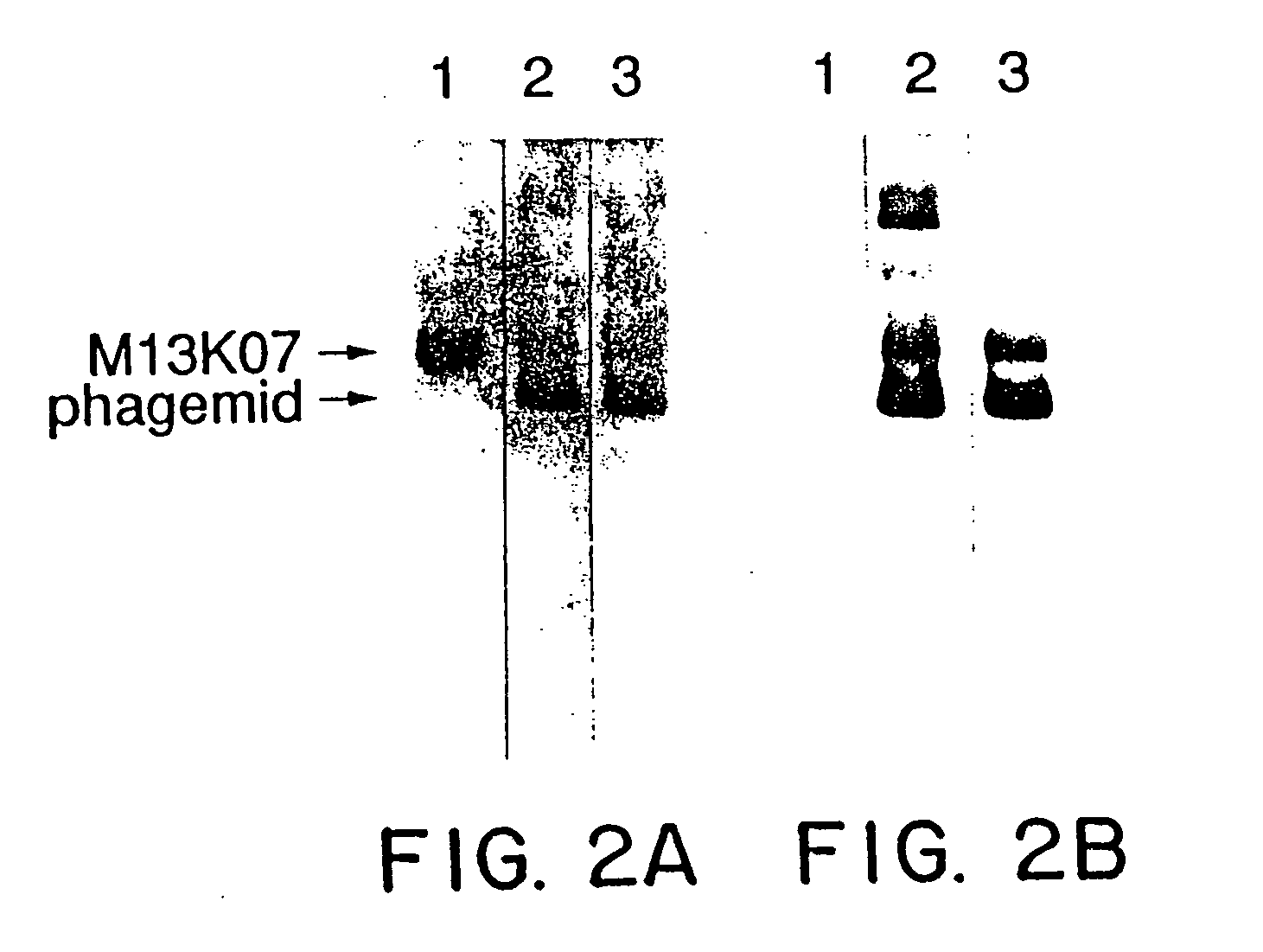
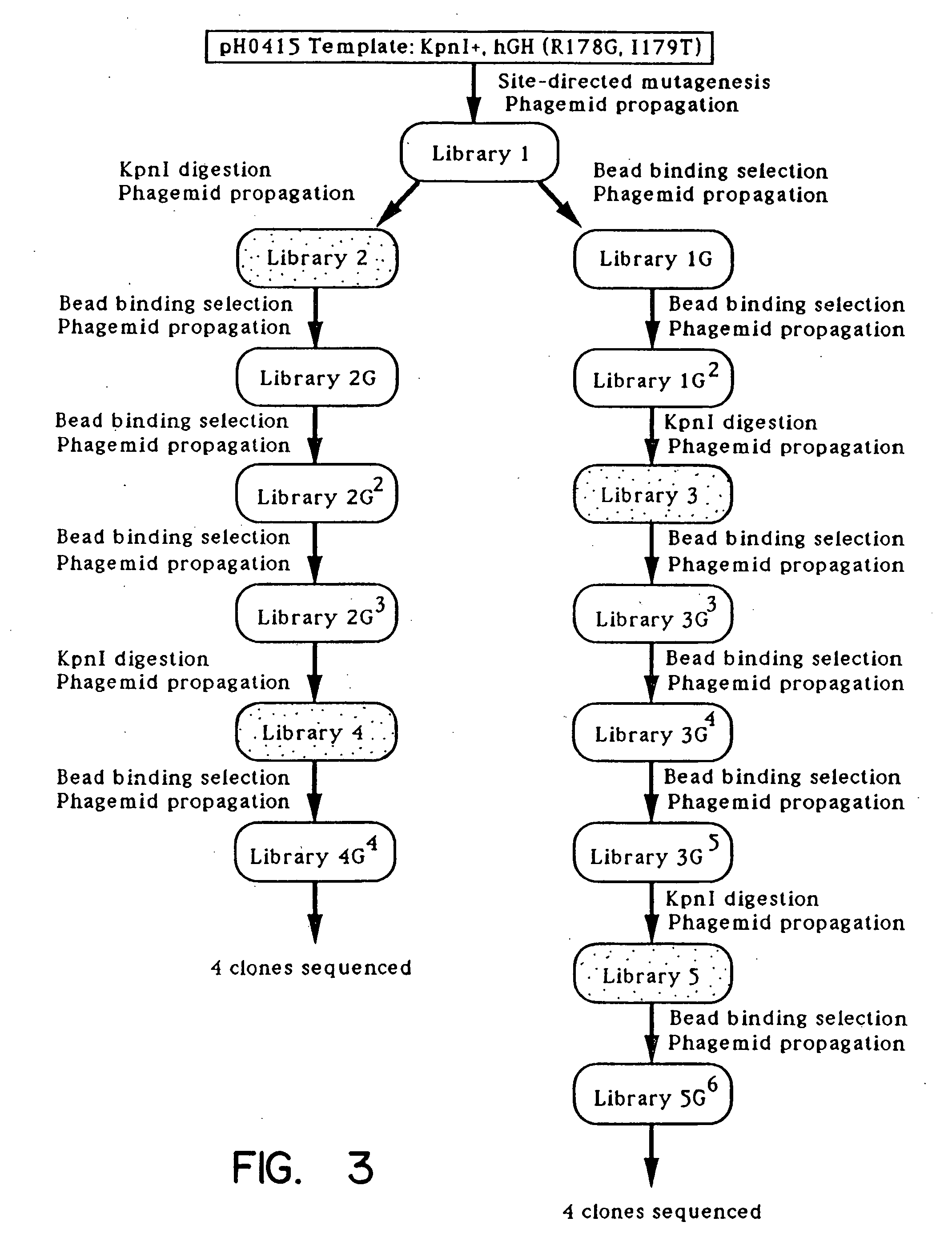
Enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties
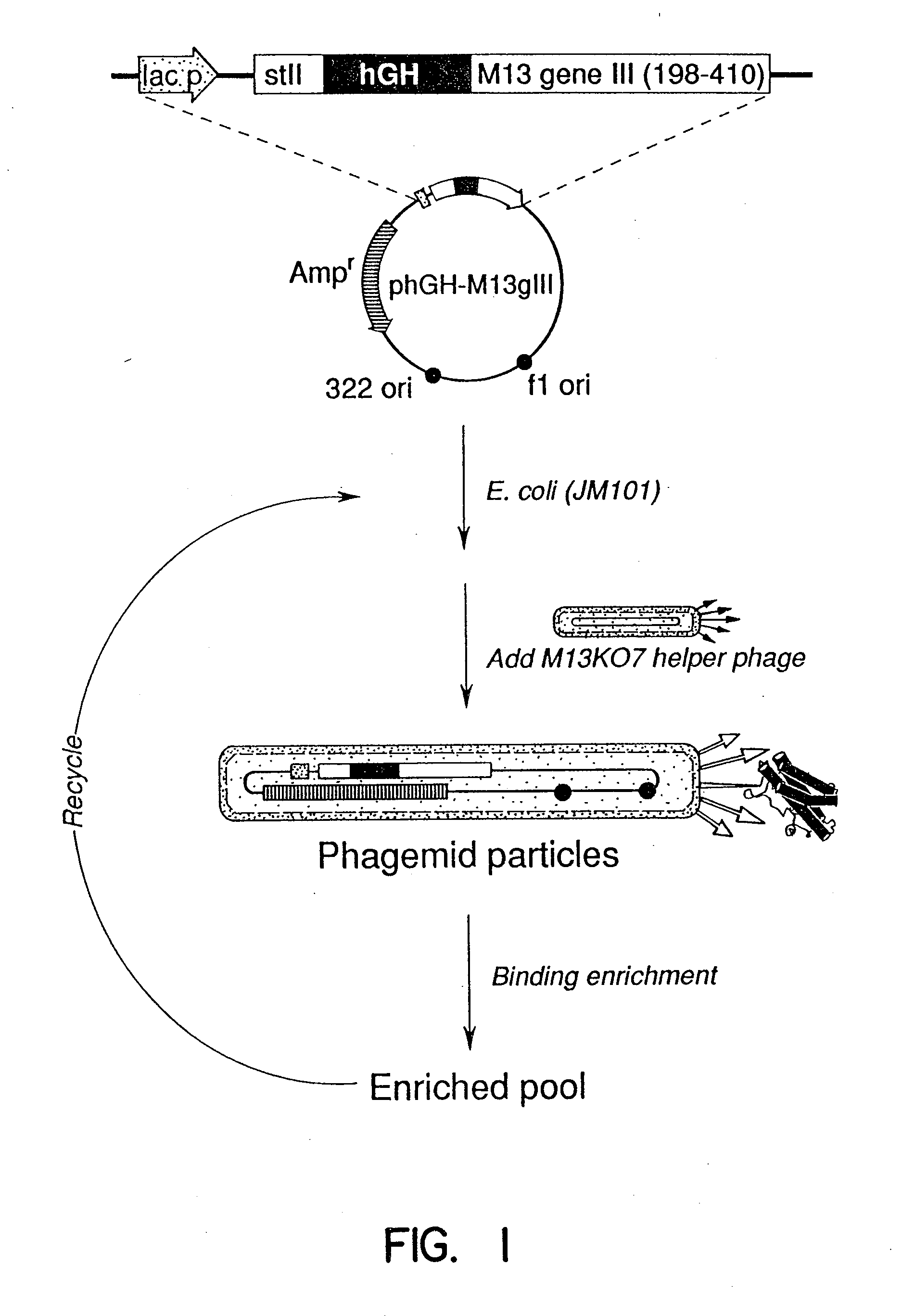
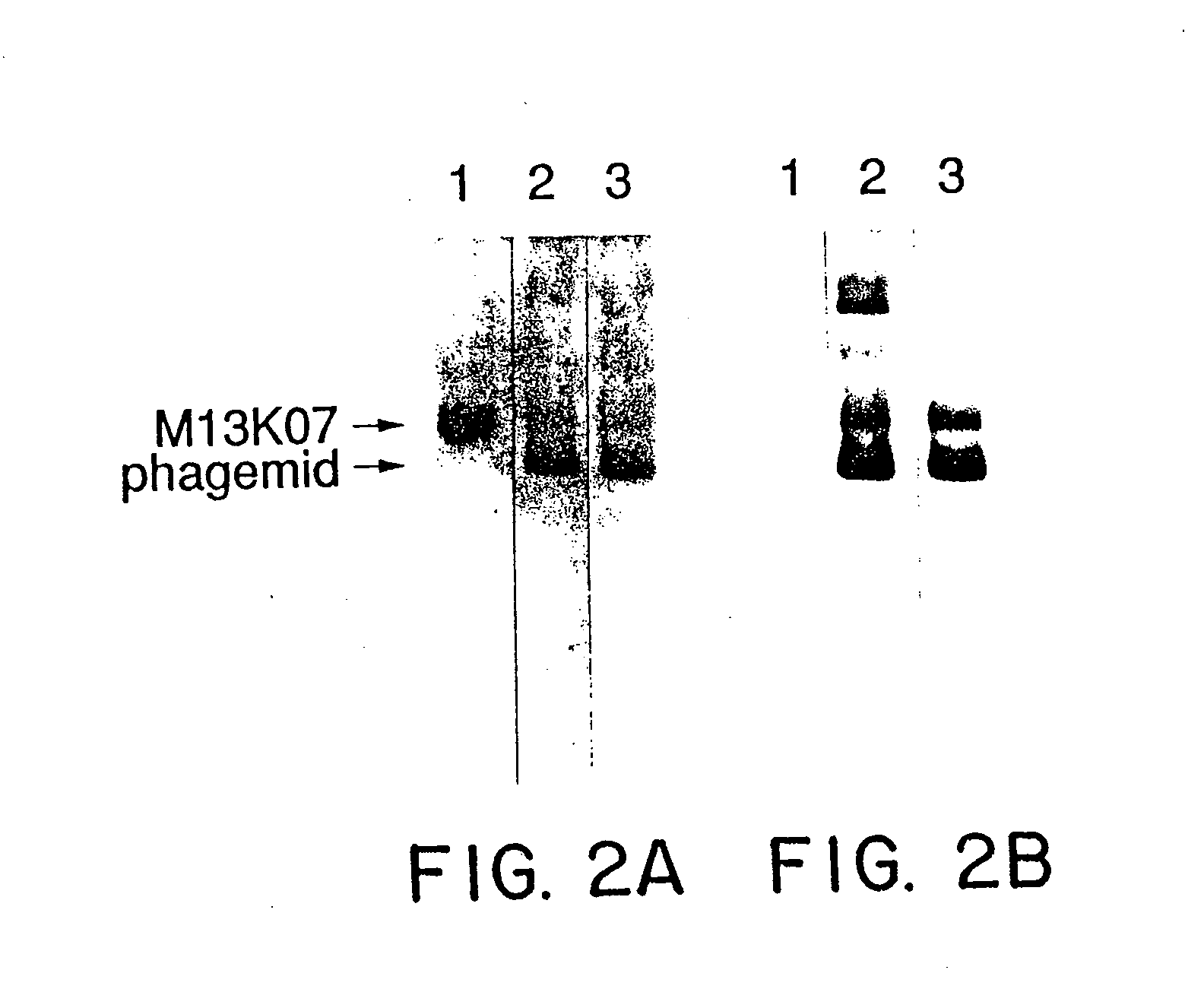
InactiveUS20060115874A1Valid choiceHigh affinity bindingVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsEnrichment methodsAntibody fragments
A method for selecting novel proteins such as growth hormone and antibody fragment variants having altered binding properties for their respective receptor molecules is provided. The method comprises fusing a gene encoding a protein of interest to the carboxy terminal domain of the gene III coat protein of the filamentous phage M13. The gene fusion is mutated to form a library of structurally related fusion proteins that are expressed in low quantity on the surface of a phagemid particle. Biological selection and screening are employed to identify novel ligands useful as drug candidates. Disclosed are preferred phagemid expression vectors and selected human growth hormone variants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
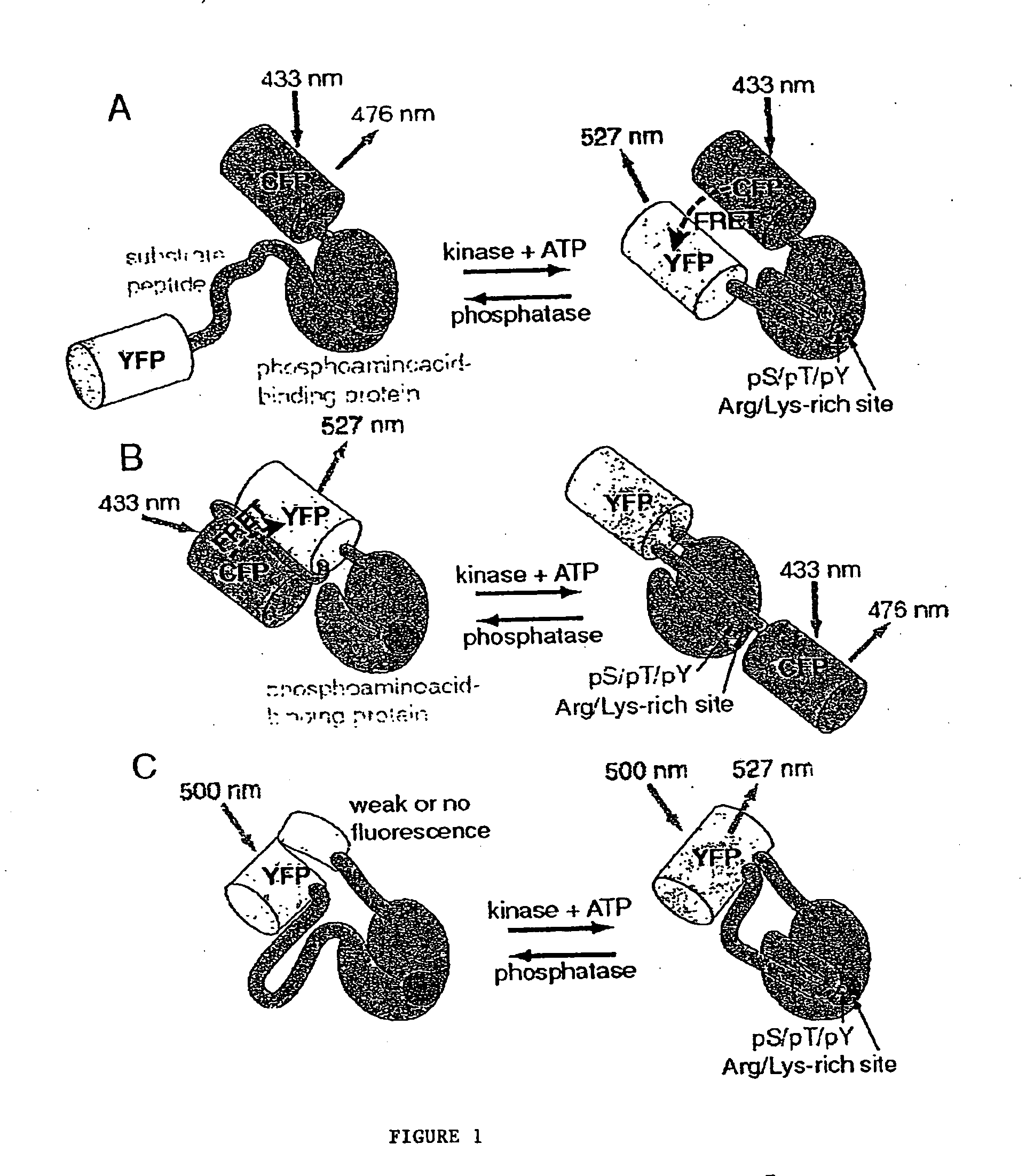
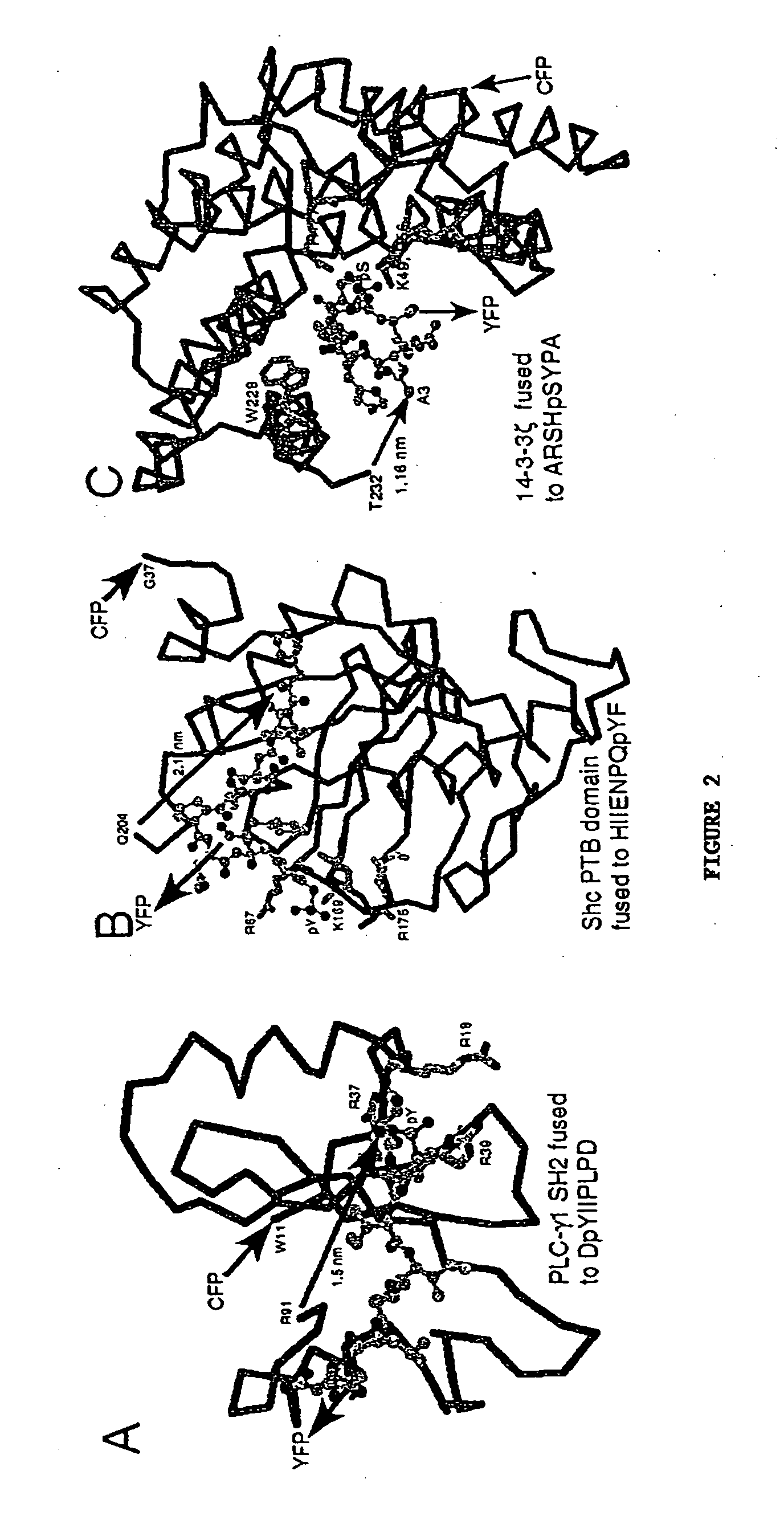
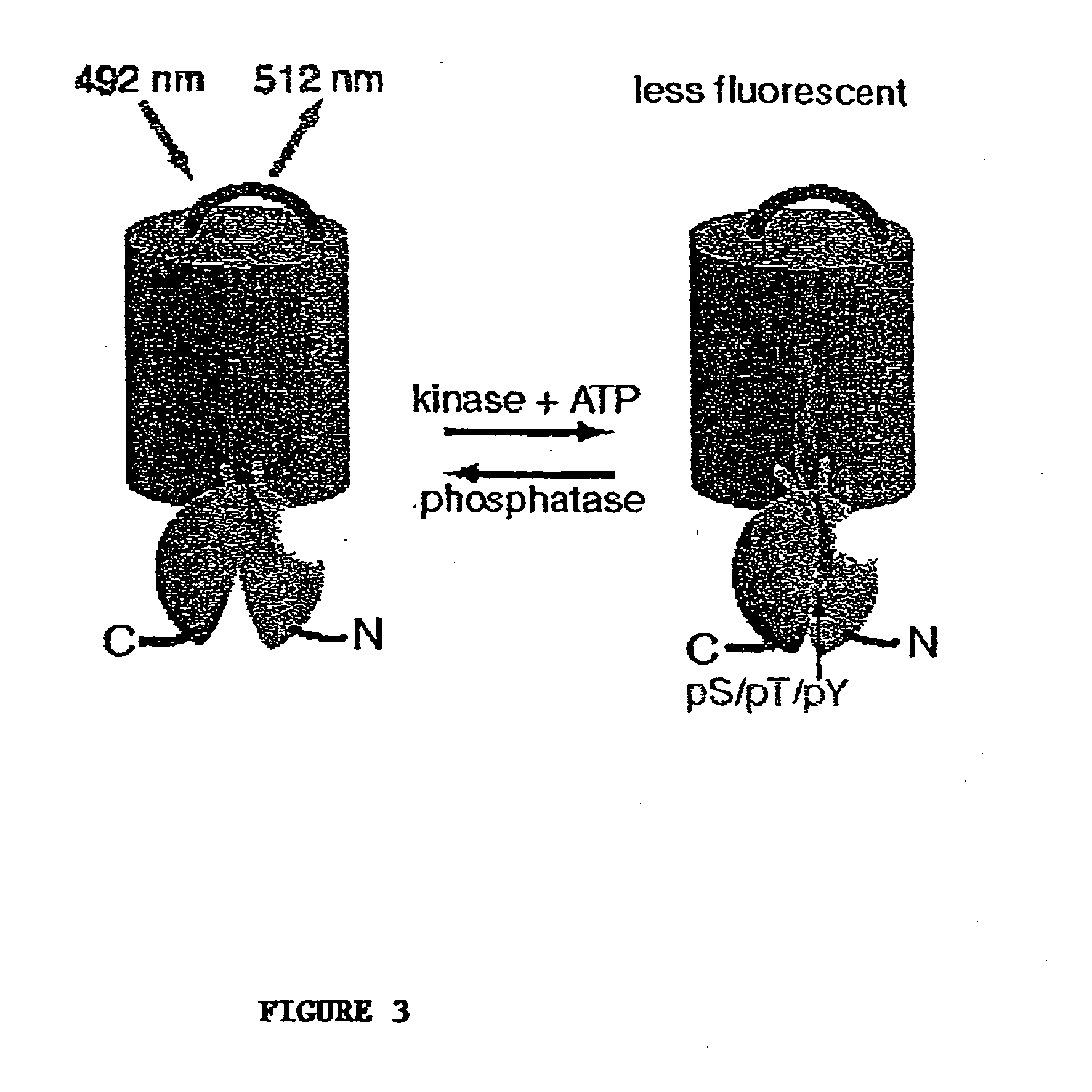
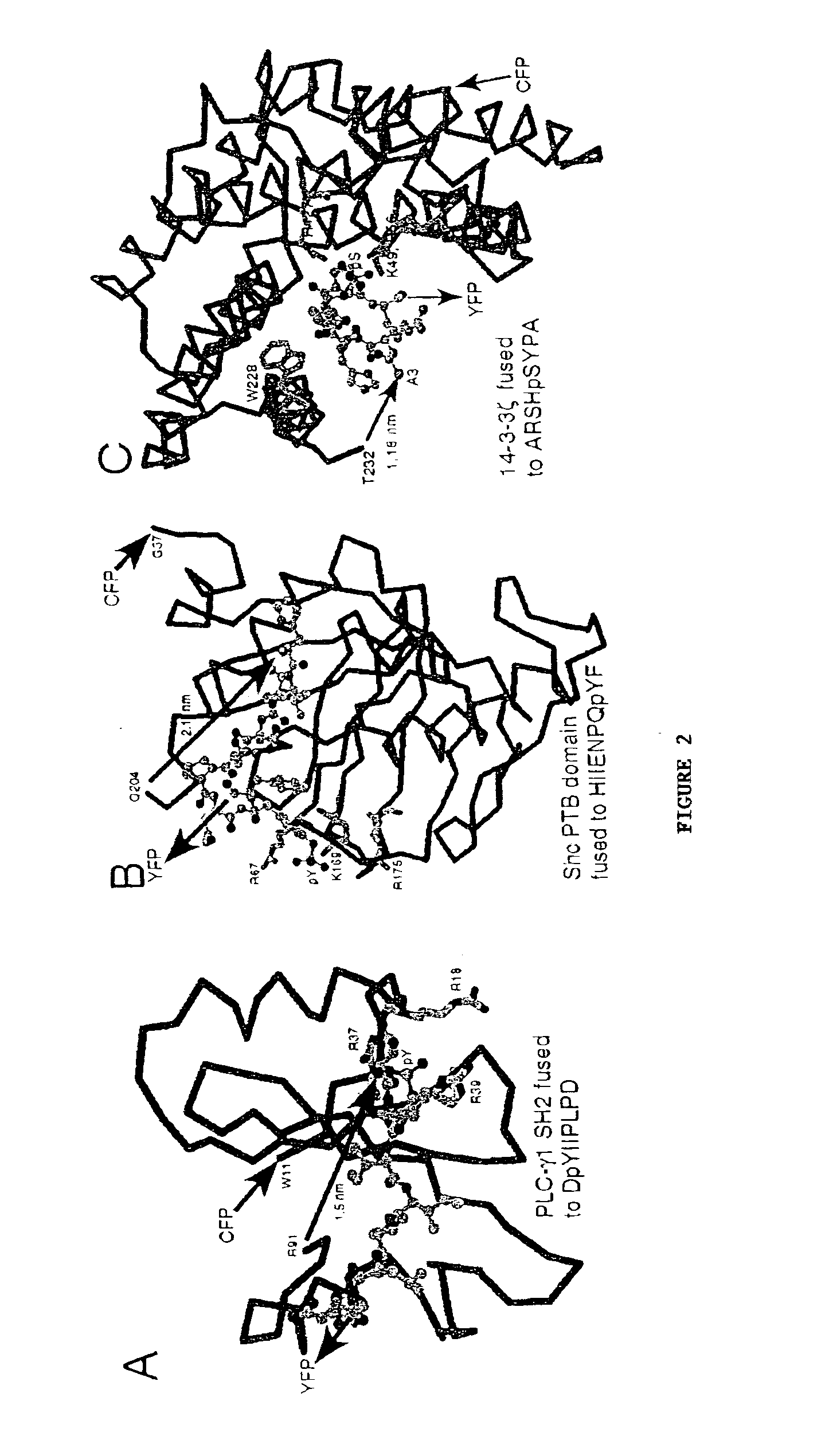
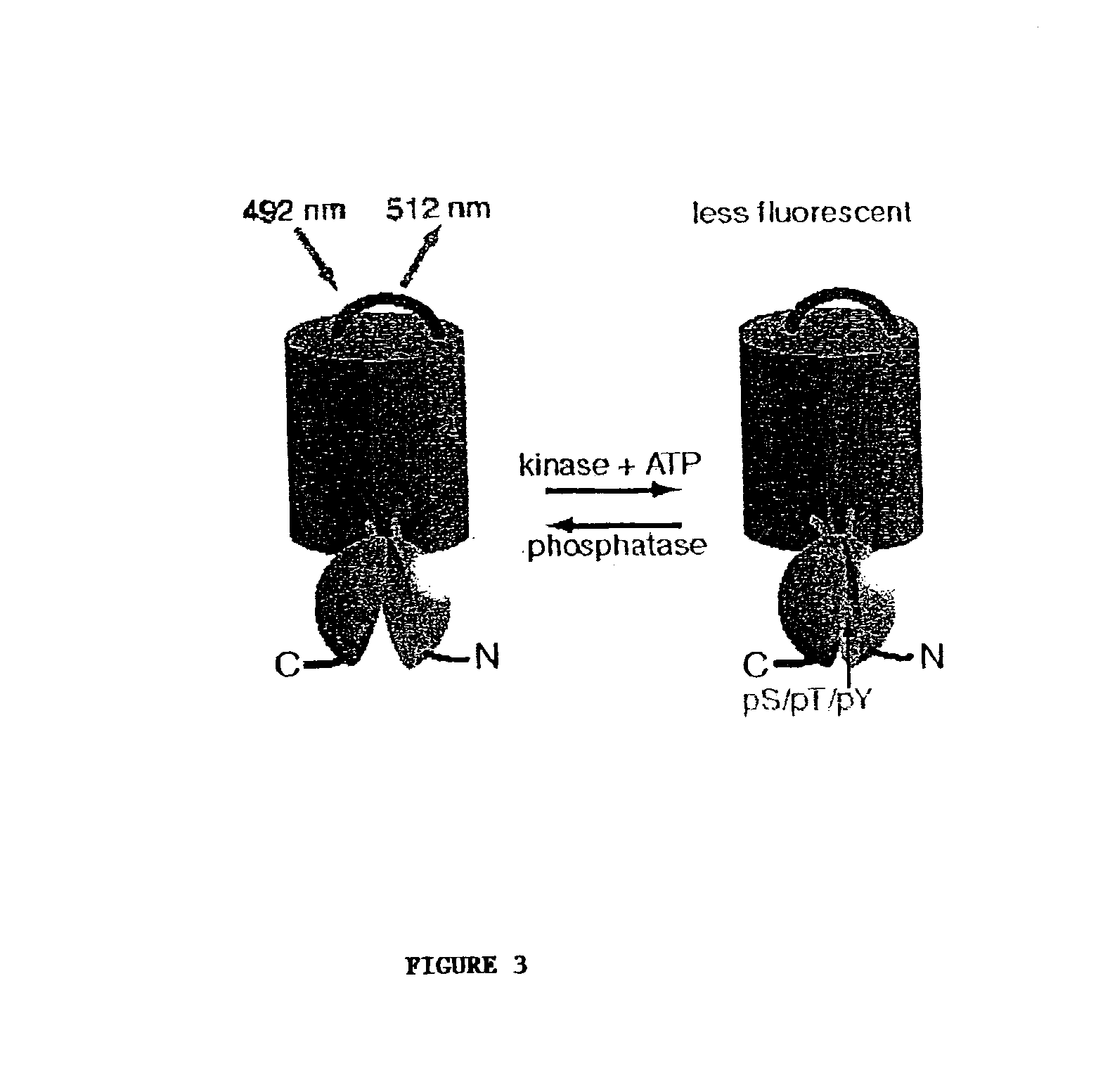
Emission ratiometric indicators of phosphorylation by C-kinase
InactiveUS20050026234A1Facilitate its translocationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideFluorophore
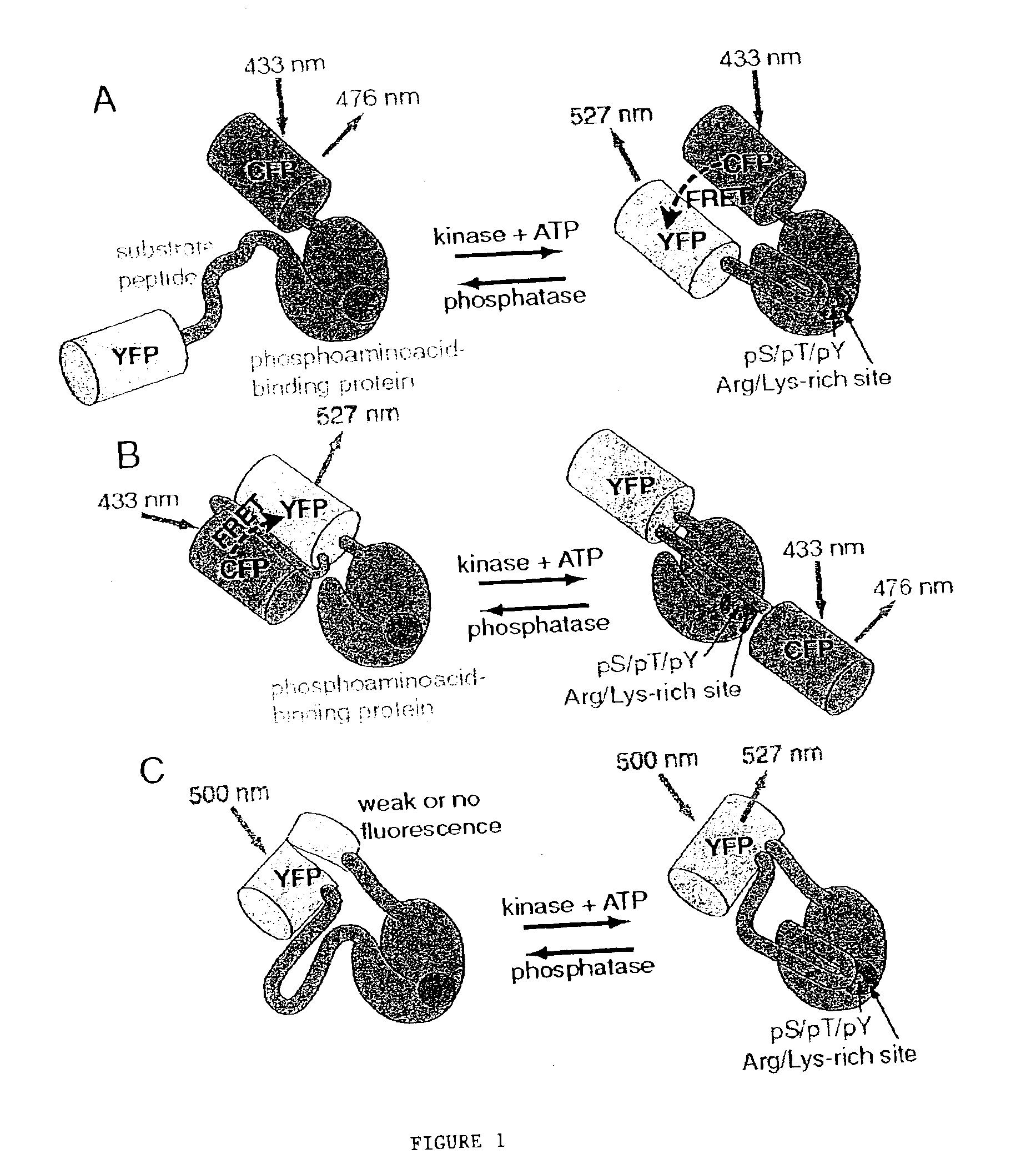
A chimeric phosphorylation indicator (CPI) as provided herein can contain a donor molecule, a phosphorylatable domain, a phosphoaminoacid binding domain (PAABD), and an acceptor molecule. Where the phosphorylatable domain is phosphorylatable by protein kinase C (PKC), the CPI is a c-kinase activity reporter (CKAR). Donor and acceptor molecules may be, independently, fluorescent proteins such as non-oligomerizing fluorescent proteins. A CPI can contain a phosphorylatable polypeptide and a fluorescent protein; the phosphorylatable polypeptide may be contained within the sequence of the fluorescent protein, or the fluorescent protein may be contained within the sequence of the phosphorylatable polypeptide. The spatiotemporal properties of the PKC signal pathway may be tested with CKAR, calcium-sensing fluorophores and FRET-based translocation assays. Polynucleotides encoding such CPIs, and kits containing the indicators and / or the polynucleotides, are provided. A method of using the chimeric phosphorylation indicators to detect a kinase or phosphatase in a sample is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Haemopoietin receptor and genetic sequences encoding same
InactiveUS6911530B1Avoid interactionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAgonistFhit gene
The present invention relates generally to a novel haemopoietin receptor or components or part thereof and to genetic sequences encoding same. The receptor molecules and their components and / or parts and the genetic sequences encoding same of the present invention are useful in the development of a wide range of agonists, antagonists, therapeutics and diagnostic reagents based on ligand interaction with its receptor.
Owner:AMRAD OPERATIONS PTY LTD
Targeted biocides
InactiveUS20050014932A1Sure easyPrevent relapseBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInnate immune systemReceptor molecule
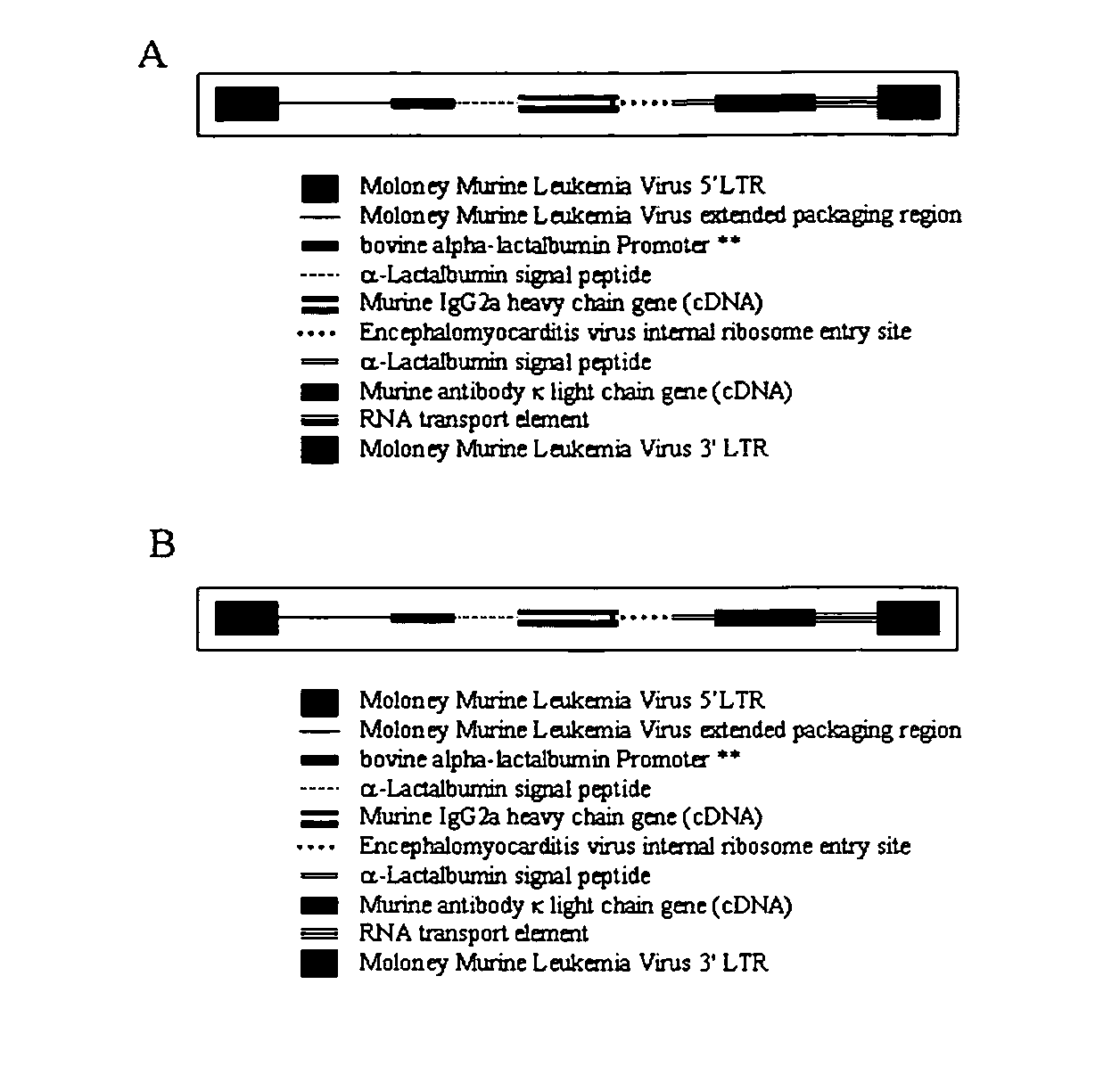
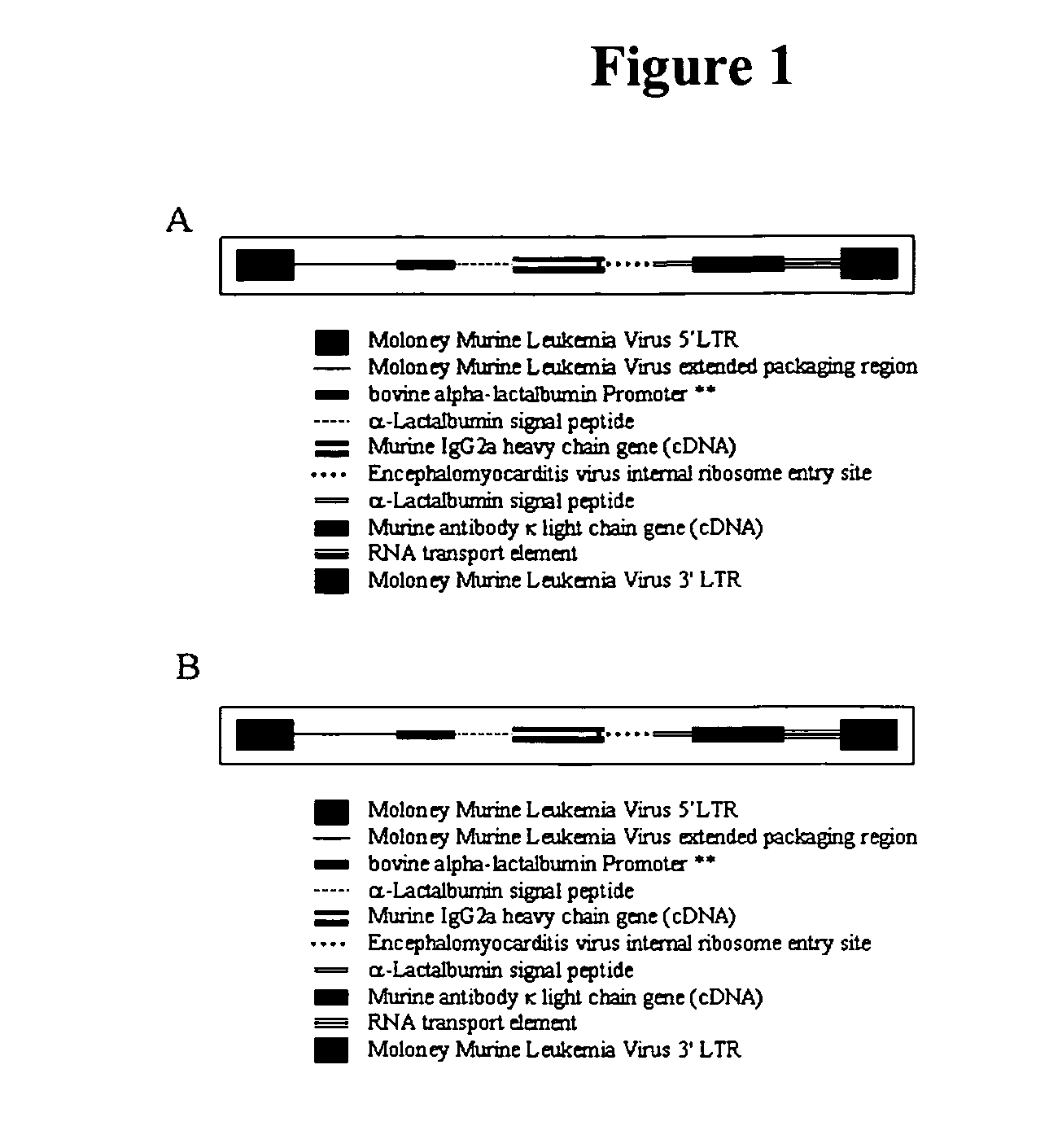
The present invention relates to retroviral constructs that encode novel monoclonal antibodies, novel fusion proteins, and chimeric monoclonal antibodies and to methods of using and producing the same. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of producing a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule (e.g., immunoglobulin or innate immune system receptor molecule) and a biocide (e.g., bactericidal enzymes) in transgenic animals (e.g., bovines) and in cell cultures. The present invention also relates to therapeutic and prophylactic methods of using a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule and a biocide in health care (e.g., human and veterinary), agriculture (e.g., animal and plant production), and food processing (e.g., beef carcass processing). The present invention also relates to methods of using a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule and a biocide in various diagnostic applications in number of diverse fields such as agriculture, medicine, and national defense.
Owner:IOGENETICS
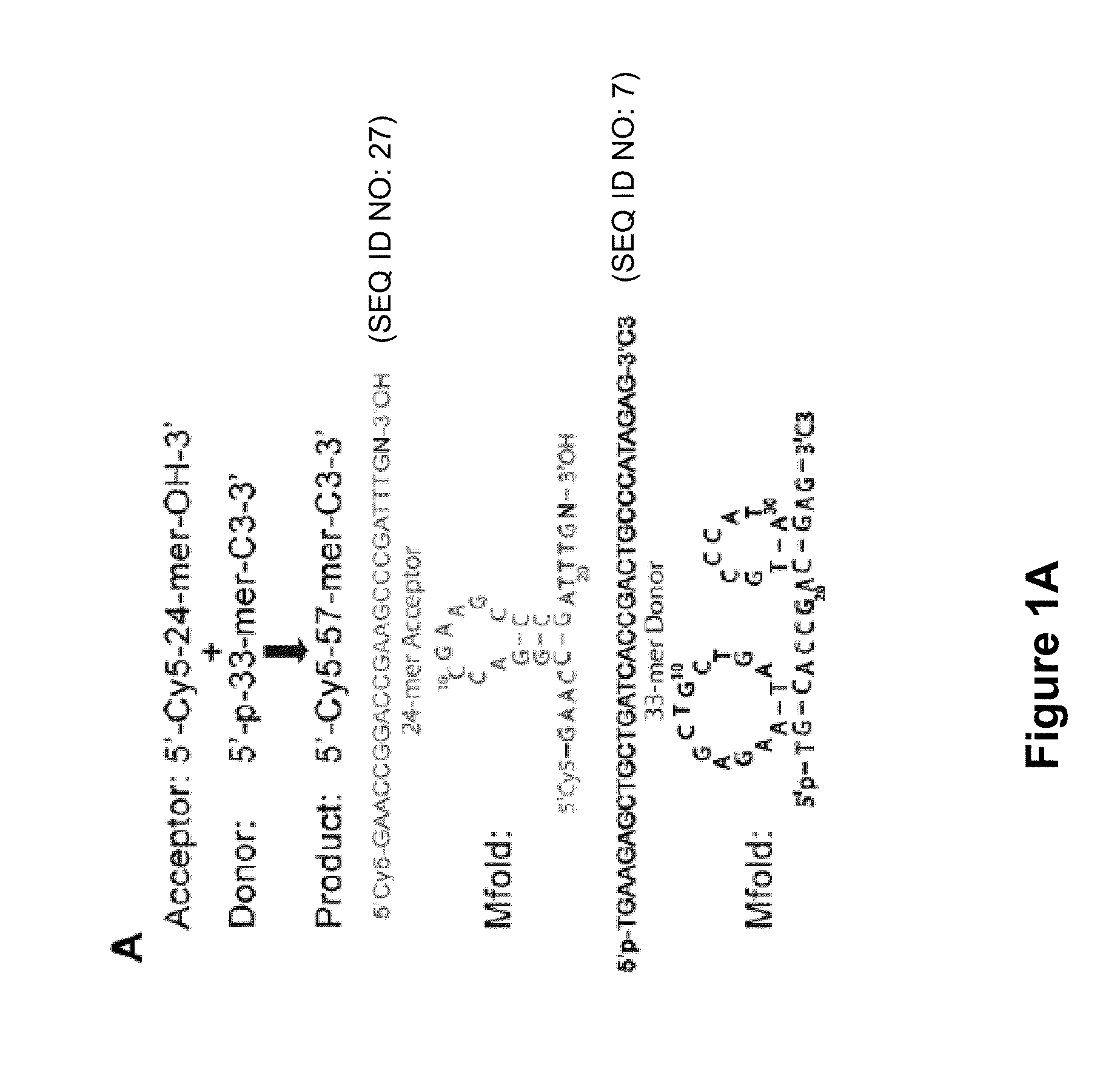
Low Sequence Bias Single-Stranded DNA Ligation
The invention provides compositions and methods for ligating single stranded nucleic acids wherein the ligation is based on fast, efficient, and low-sequence bias hybridization of an acceptor molecule with a donor molecule. In one embodiment, the structure of the donor molecule comprises a stem-loop intramolecular nucleotide base pairing (i.e., hairpin) and a 3′-overhang region such that the overhang is able to hybridize to nucleotides present in the 3′ end of the acceptor molecule.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
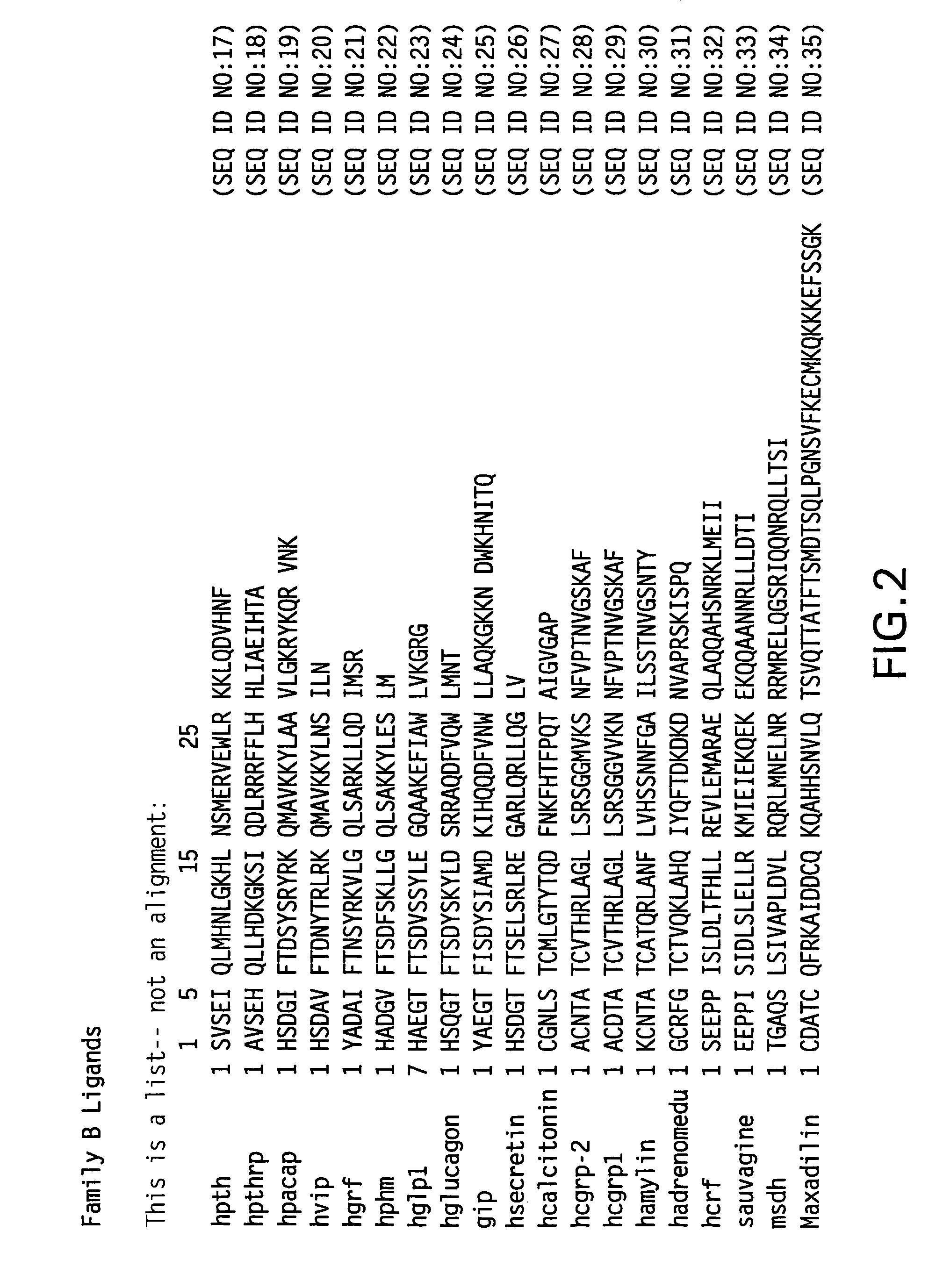
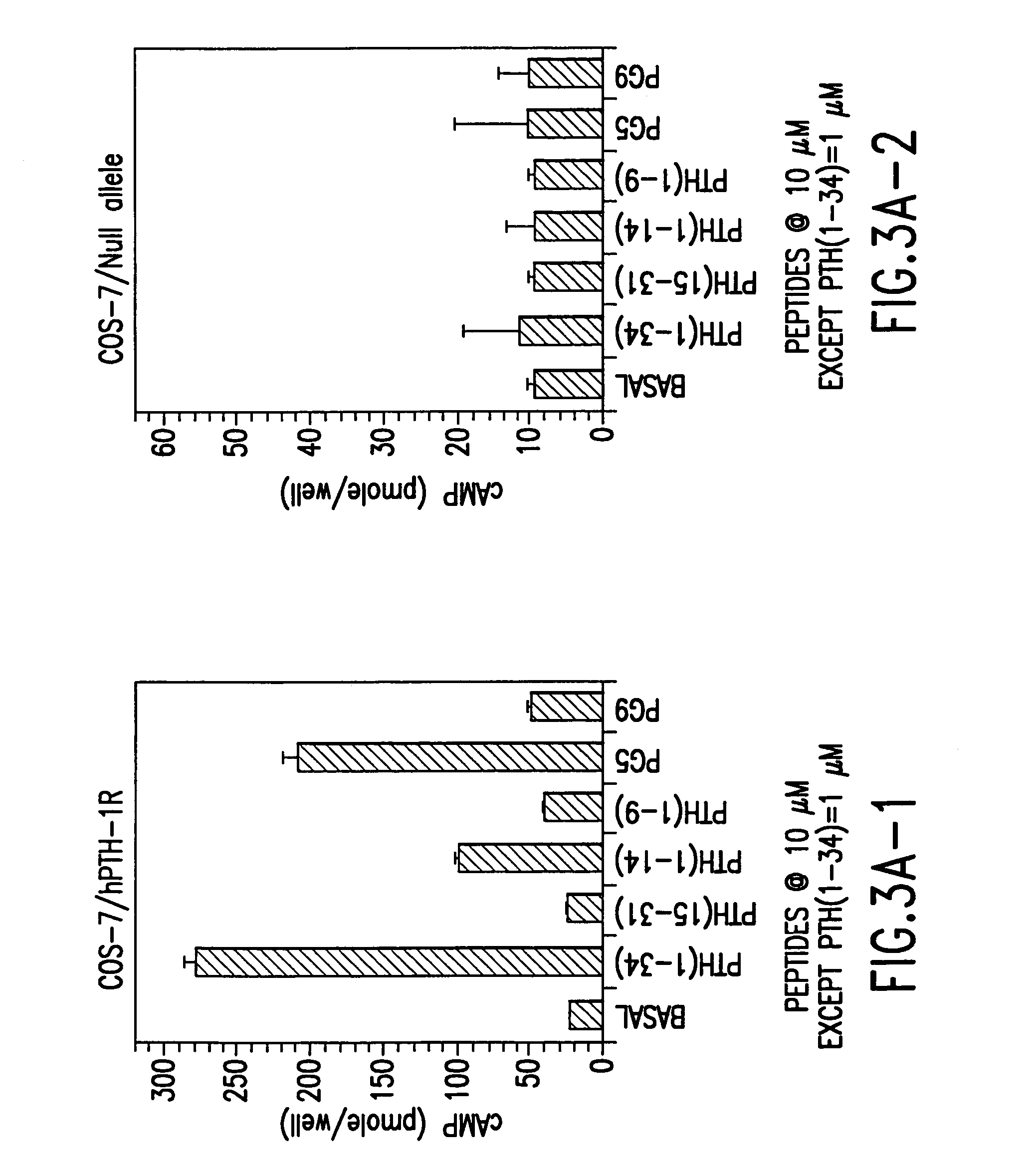
PTH functional domain conjugate peptides, derivatives thereof and novel tethered ligand-receptor molecules
InactiveUS7057012B1Improve efficacyHigh potencyPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAgonist drugsPharmaceutical drug
Novel parathyroid hormone (PTH) peptides and analogs thereof of the PTH(1–34) fragment are disclosed that combine the N-terminal signaling domain (residues 1–9) and the C-terminal binding domain (residues 15–31) via a linker. Nucleic acid molecules and peptides for PTH(1–9)-(Gly)5-PTH(15–31) (PG5) and (1–9)-(Gly)7-PTH(15–31) and a novel PTH receptor are disclosed. Additionally, methods of screening for PTH agonists, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment are disclosed.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
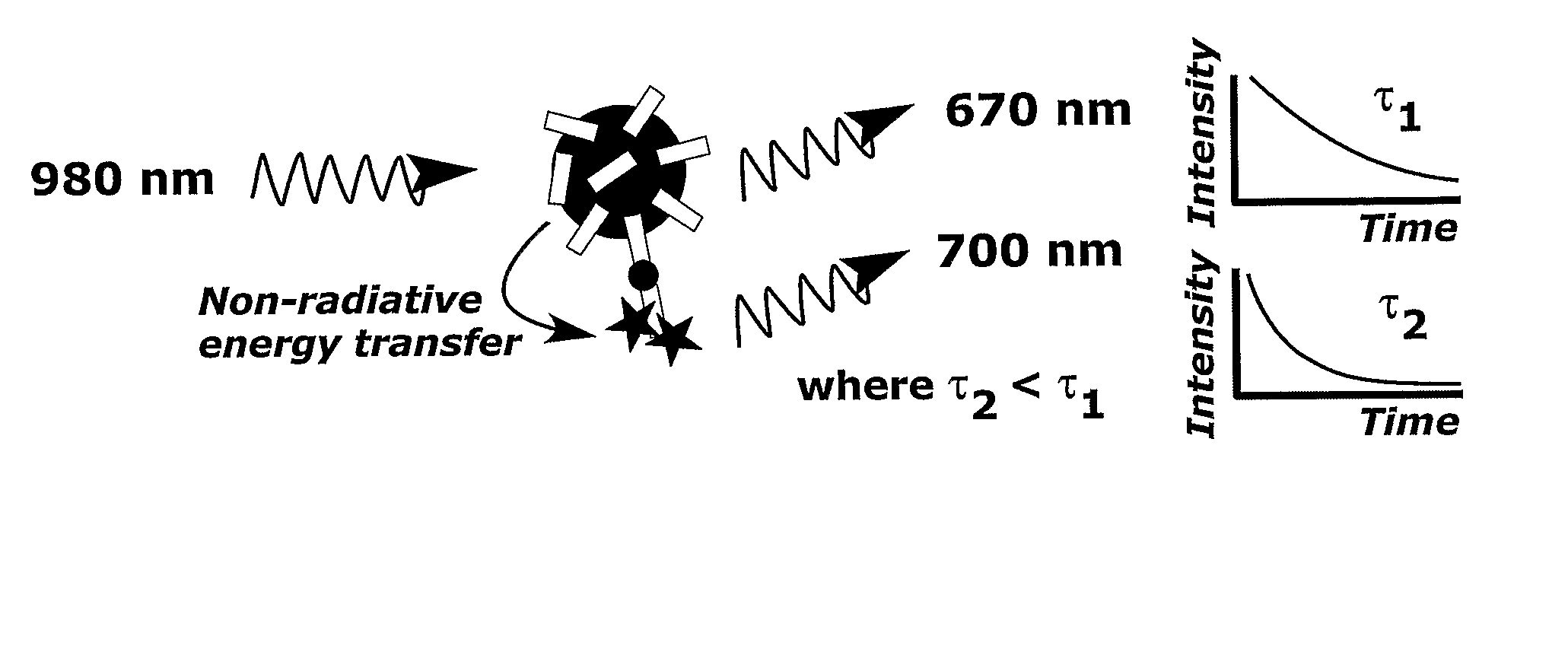
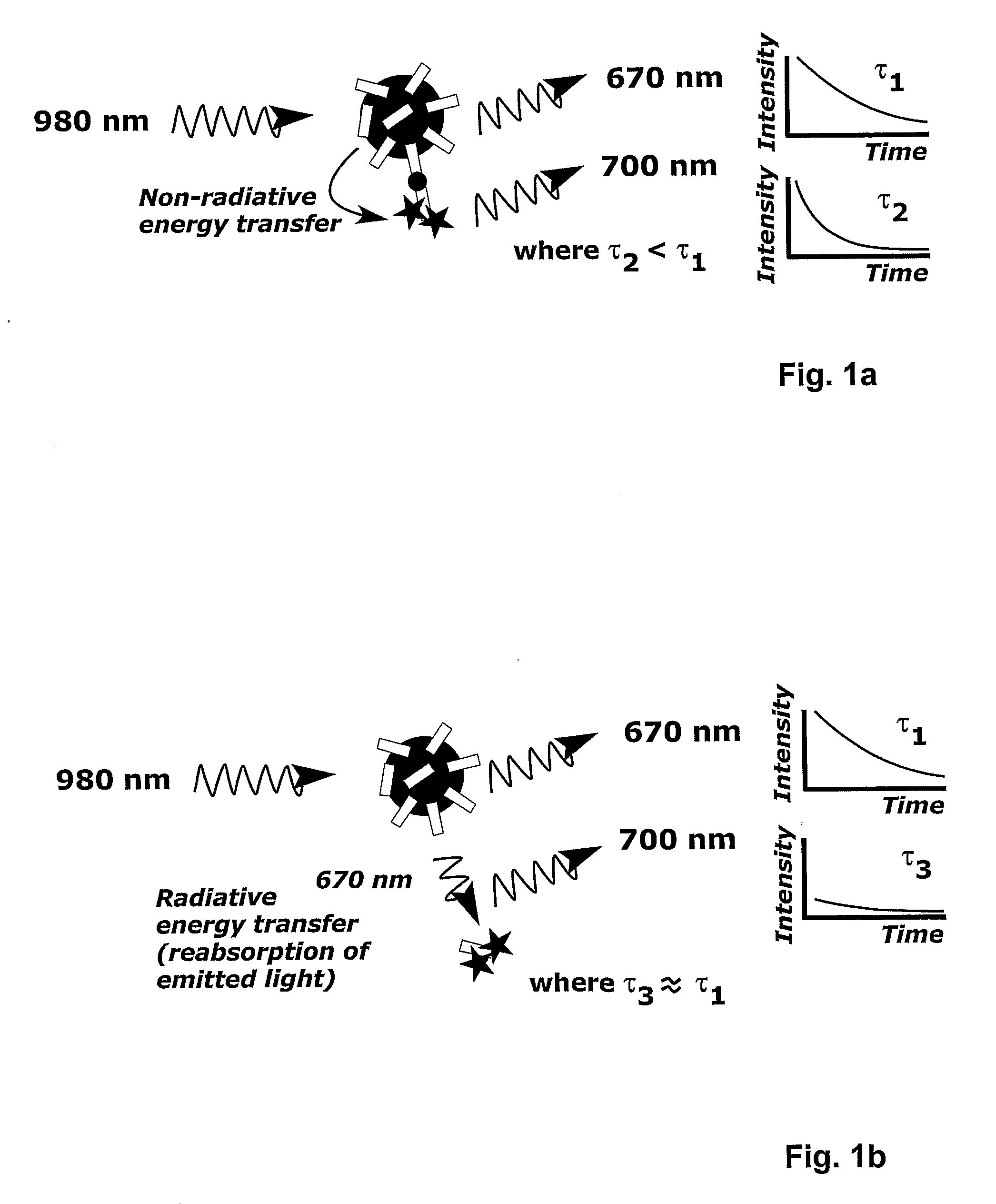
Correction Method and Measurement Device For Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence Measurement
This invention relates to a method to correct for error in an anti-Stokes photoluminescence measurement in a Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay. The method comprises the steps of exciting anti-Stokes photoluminescent molecules, ions, phosphors, chelates, or particles, i.e. donors of the assay, with one wavelength or multiple wavelengths of light wherein the wavelength or wavelengths are greater than that of an emission wavelength of acceptor molecules in the assay; measuring emission light signal at a wavelength, which is the emission wavelength of the acceptor molecules in the Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay, and which differs from the emission wavelength of the anti-Stokes photoluminescent donor in at least two different time windows; a first time window within the time window defined by the excitation light pulse, i.e. within the time window opening when the excitation light pulse is switched on and closing when the excitation light pulse is switched off, and a second time window to follow the first time window not at all overlapping with the time window defined by the excitation pulse; and correcting the emission light signal measured, comprising signals originating from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer, within the first time window by estimating the ratio of the signals from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer or the signal originating from radiative energy transfer using at least one emission light signal measured in the second time window. This invention also relates to the use of a device according to the method of the invention, a system for carrying out the method and a software product for the system.
Owner:HIDEX
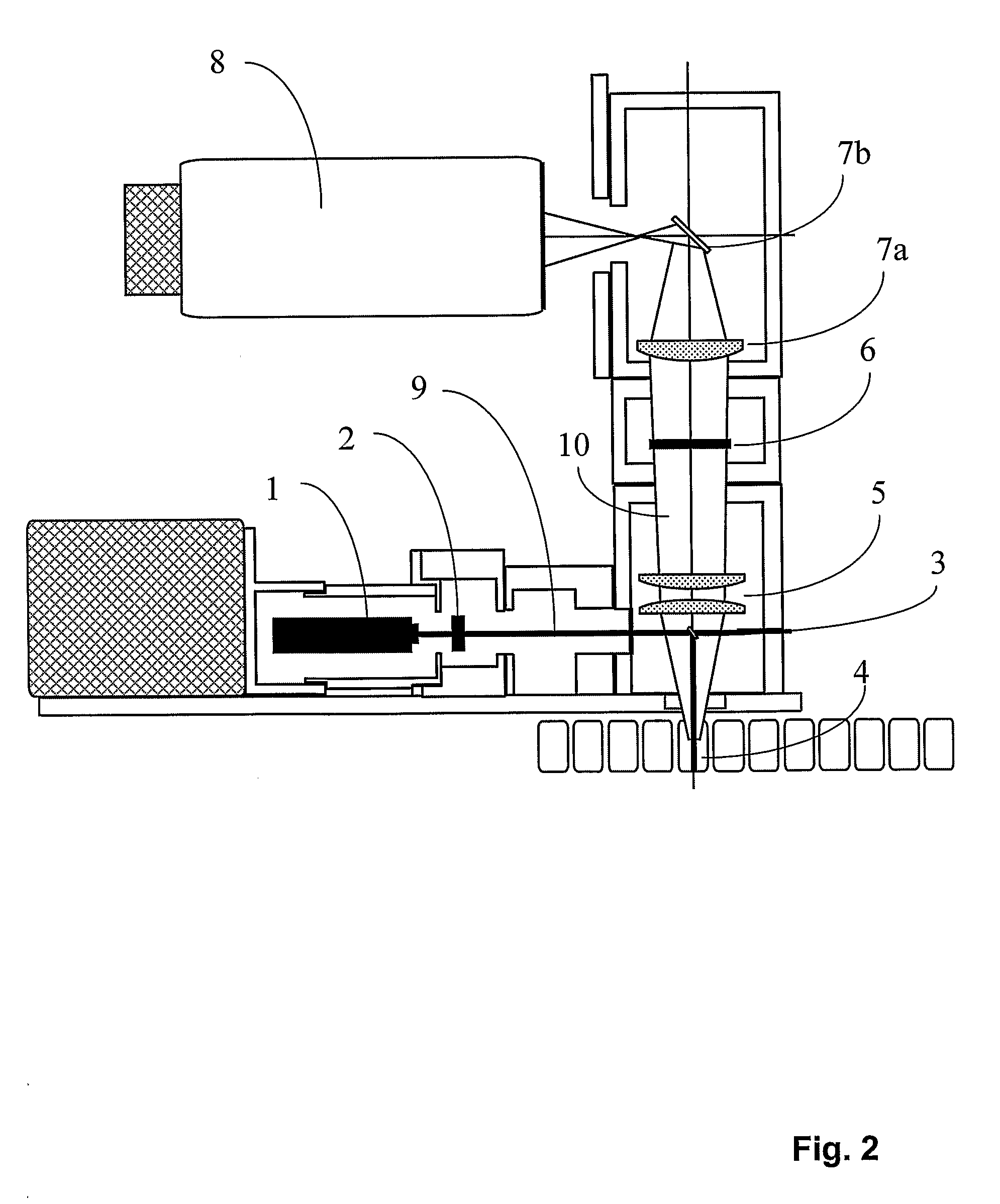
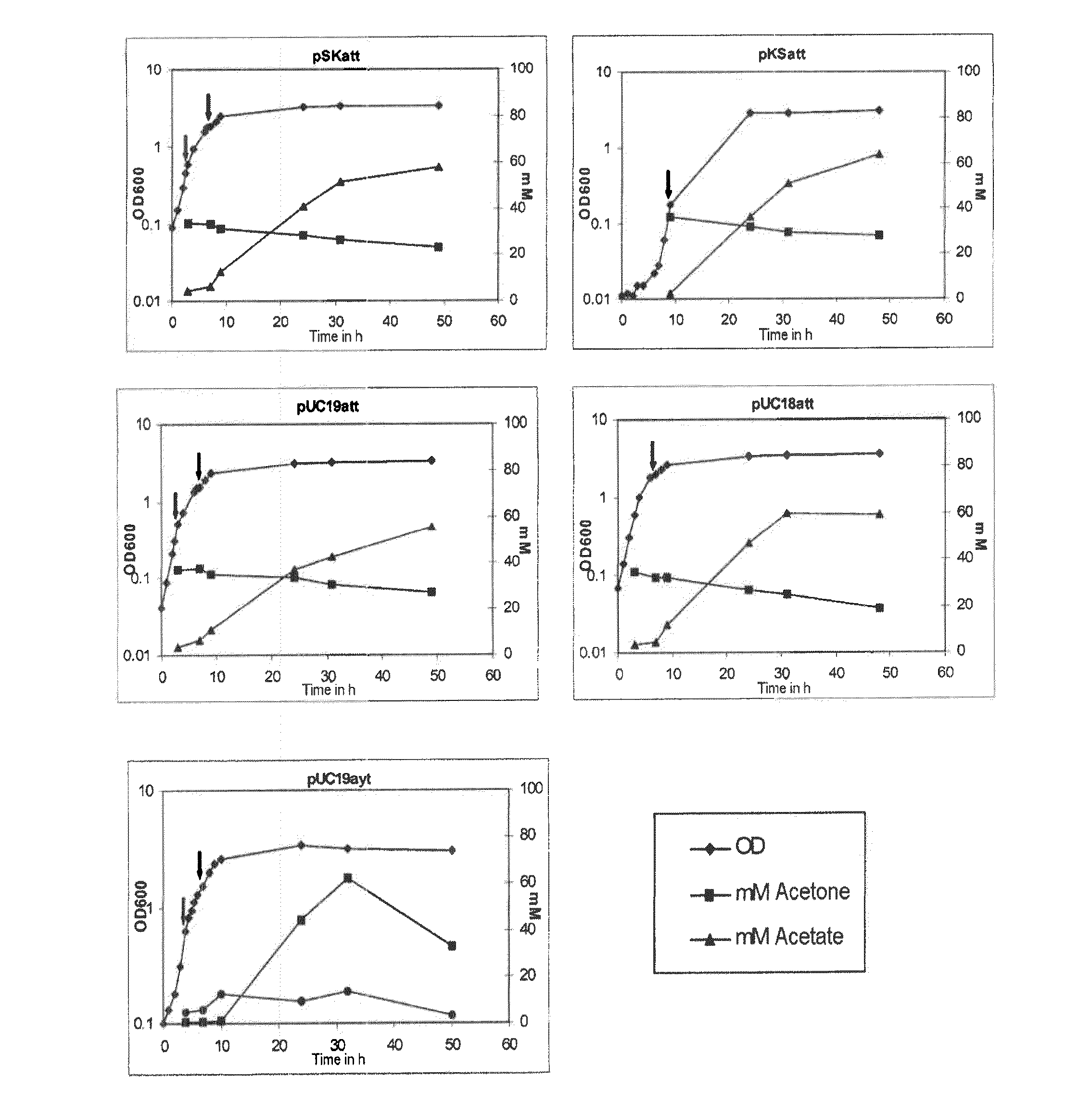
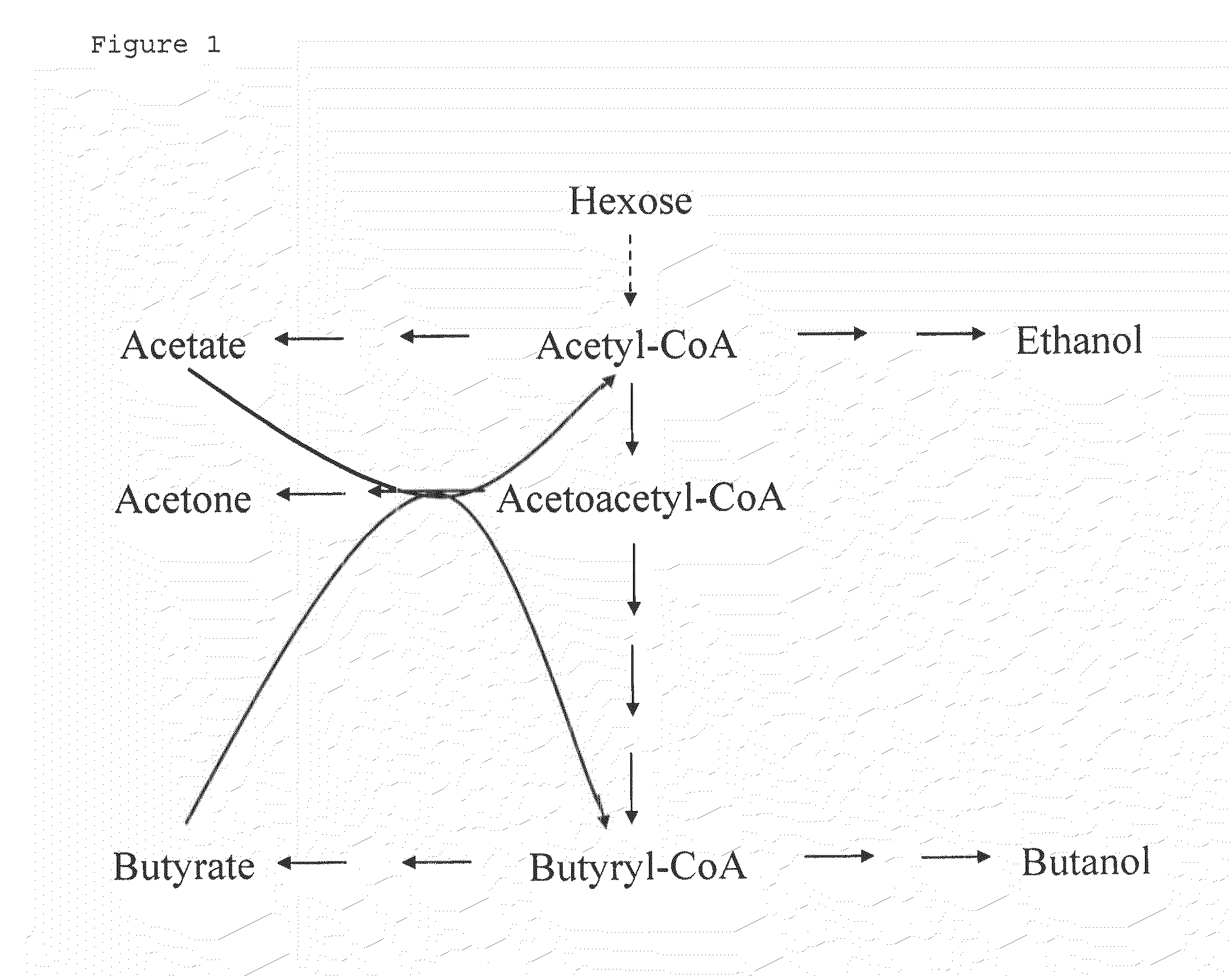
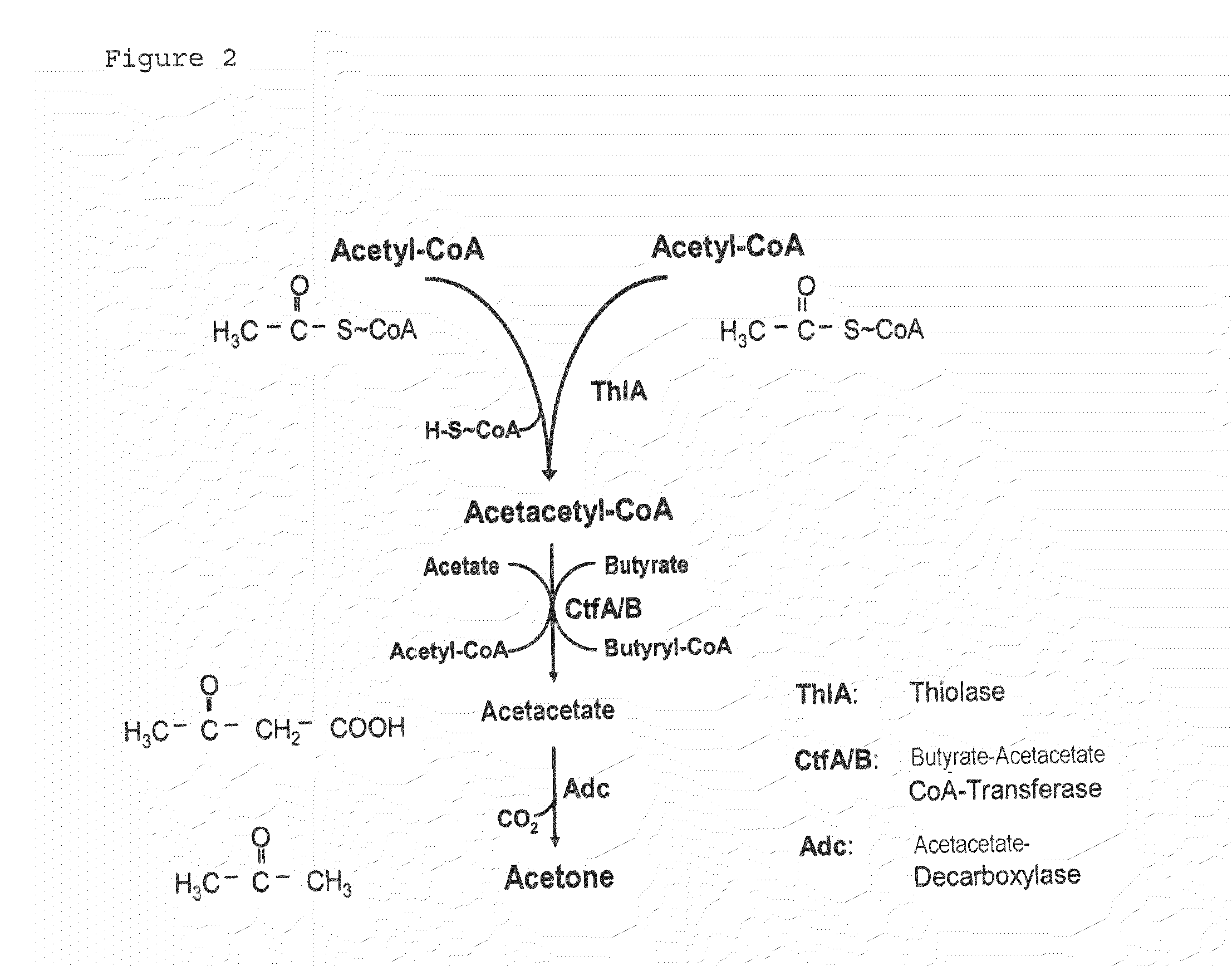
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Intrabody-mediated control of immune reactions
InactiveUS20060034834A1Inhibit expressionVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesPlatelet
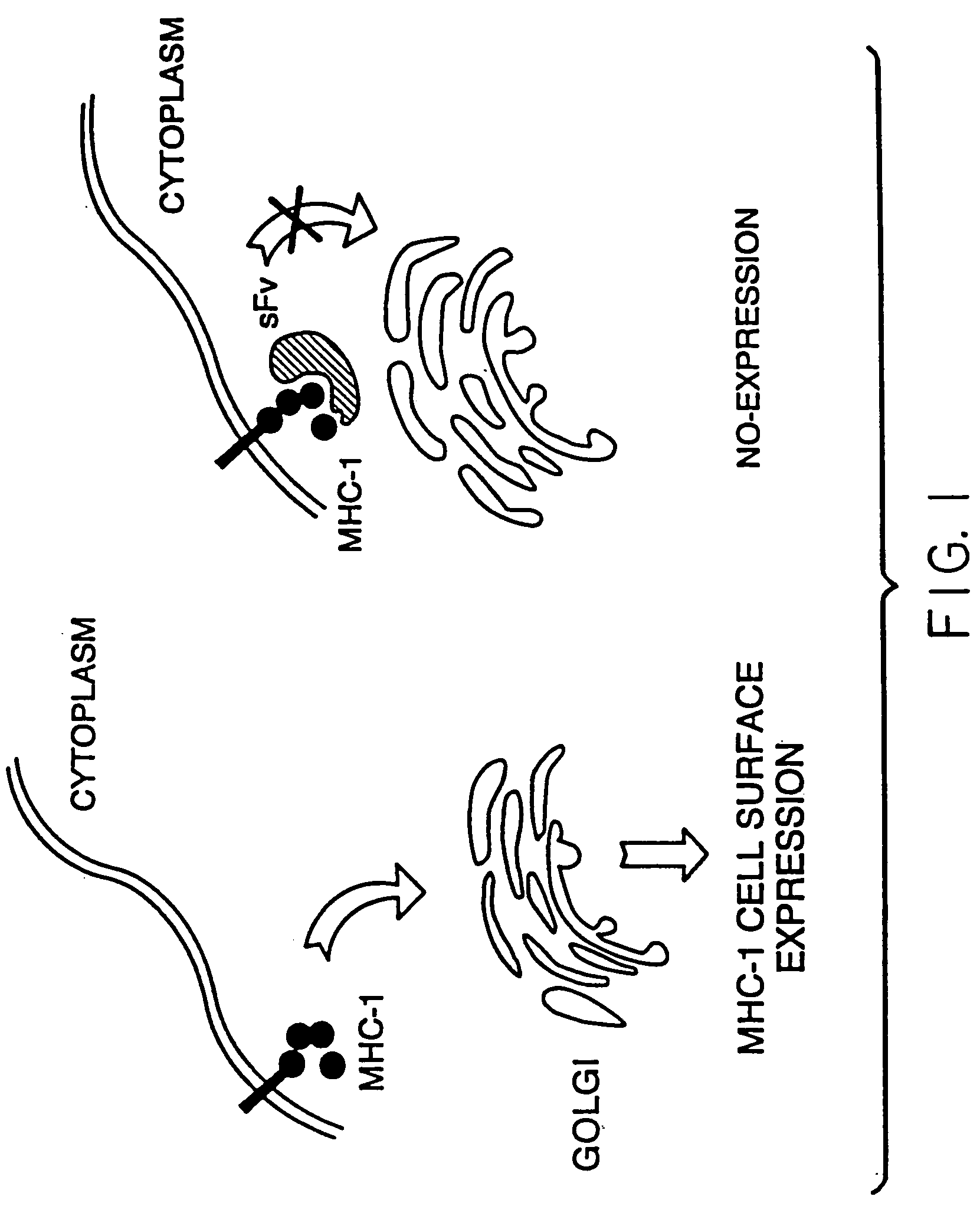
The present invention is directed to methods of altering the regulation of the immune system, e.g., by selectively targeting individual or classes of immunomodulatory receptor molecules (IRMs) on cells comprising transducing the cells with an intracellularly expressed antibody, or intrabody, against the IRMs. In a preferred embodiment the intrabody comprises a single chain antibody against an IRM, e.g, MHC-1 molecules.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Emission ratiometric indicators of phosphorylation
InactiveUS6900304B2Facilitate its translocationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFungiPhosphoamino AcidsNucleotide
A chimeric phosphorylation indicator is provided. A chimeric phosphorylation indicator can contain a donor molecule, a phosphorylatable domain, a phosphoaminoacid binding domain (PAABD), and an acceptor molecule. A chimeric phosphorylation indicator also can contain a phosphorylatable polypeptide and a fluorescent protein, wherein the phosphorylatable polypeptide is contained within the sequence of the fluorescent protein, or wherein the fluorescent protein is contained within the sequence of the phosphorylatable polypeptide. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding such chimeric phosphorylation indicators, as well as kits containing the indicators or the polynucleotides. In addition, a method of using the chimeric phosphorylation indicators to detect a kinase or phosphatase in a sample is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of reversibly staining a target cell
ActiveUS20140295458A1Antibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReceptor moleculeMolecular biology
The present invention relates to methods of reversibly staining a target cell. The invention also relates to methods of isolating a target cell or a target cell population that is defined by the presence of at least one common specific receptor molecule. The invention also provides kits that can be used to carry out the methods of the invention.
Owner:IBA LIFESCIENCES GMBH
Methods and compositions for DNA manipulation
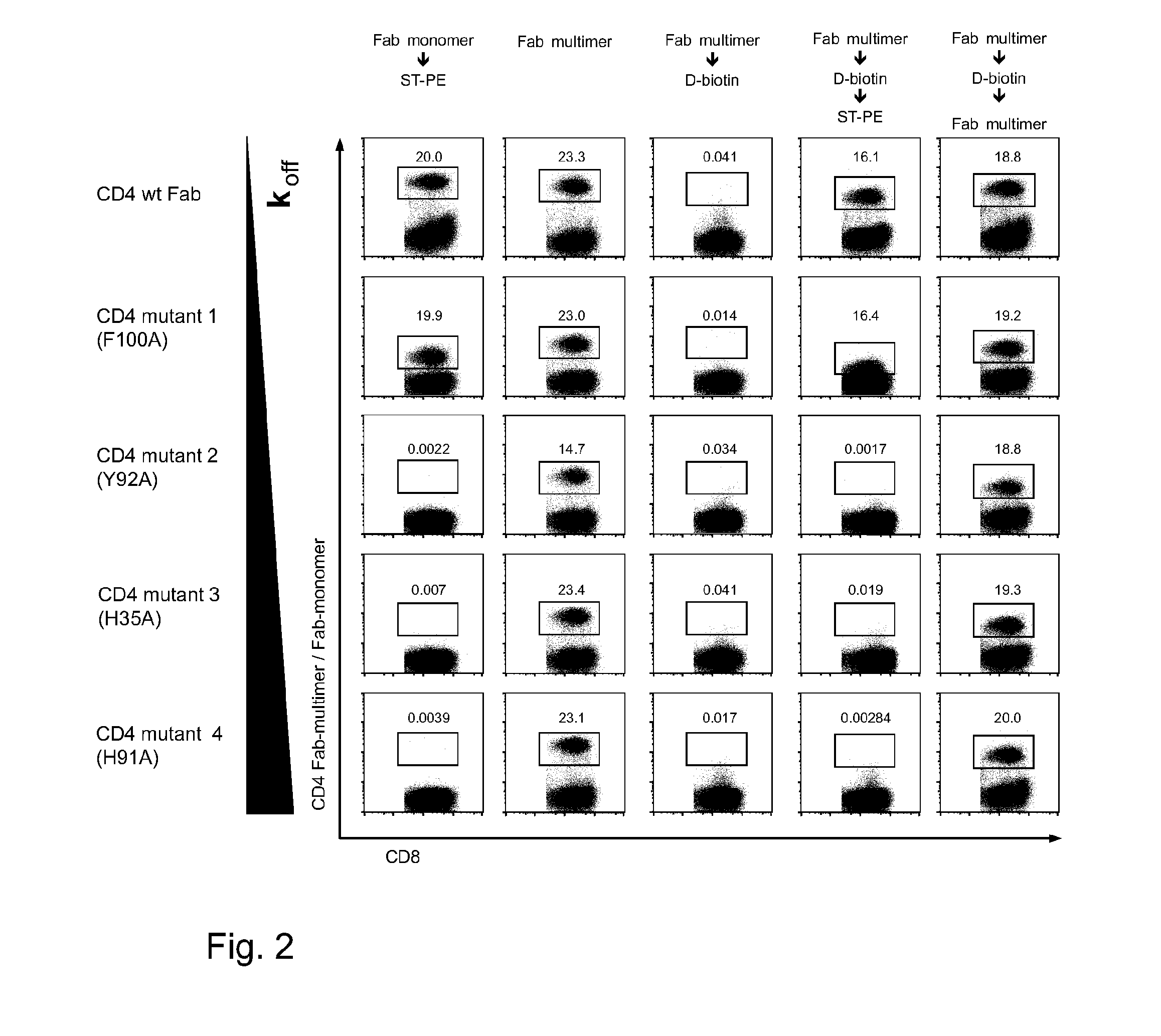
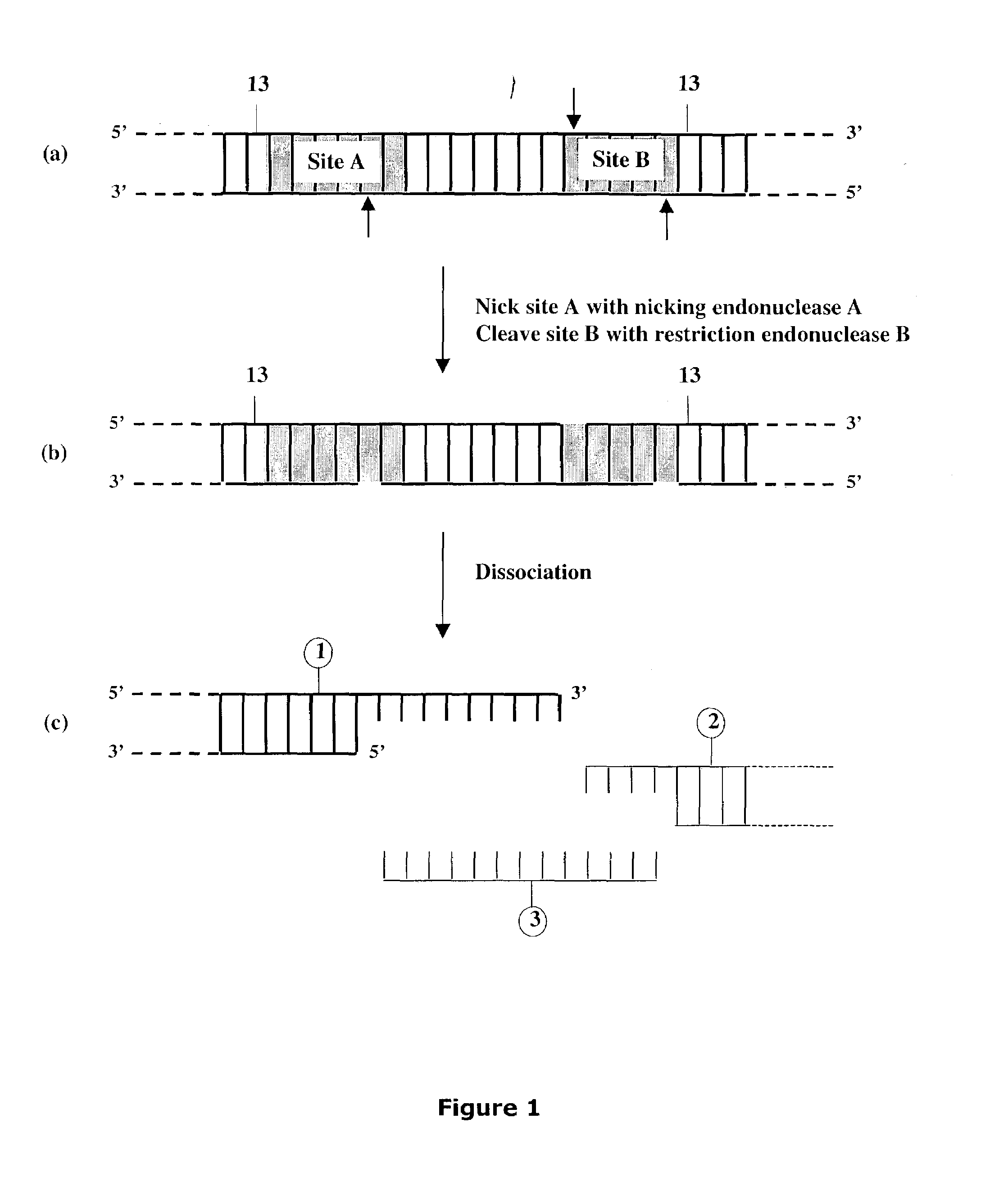
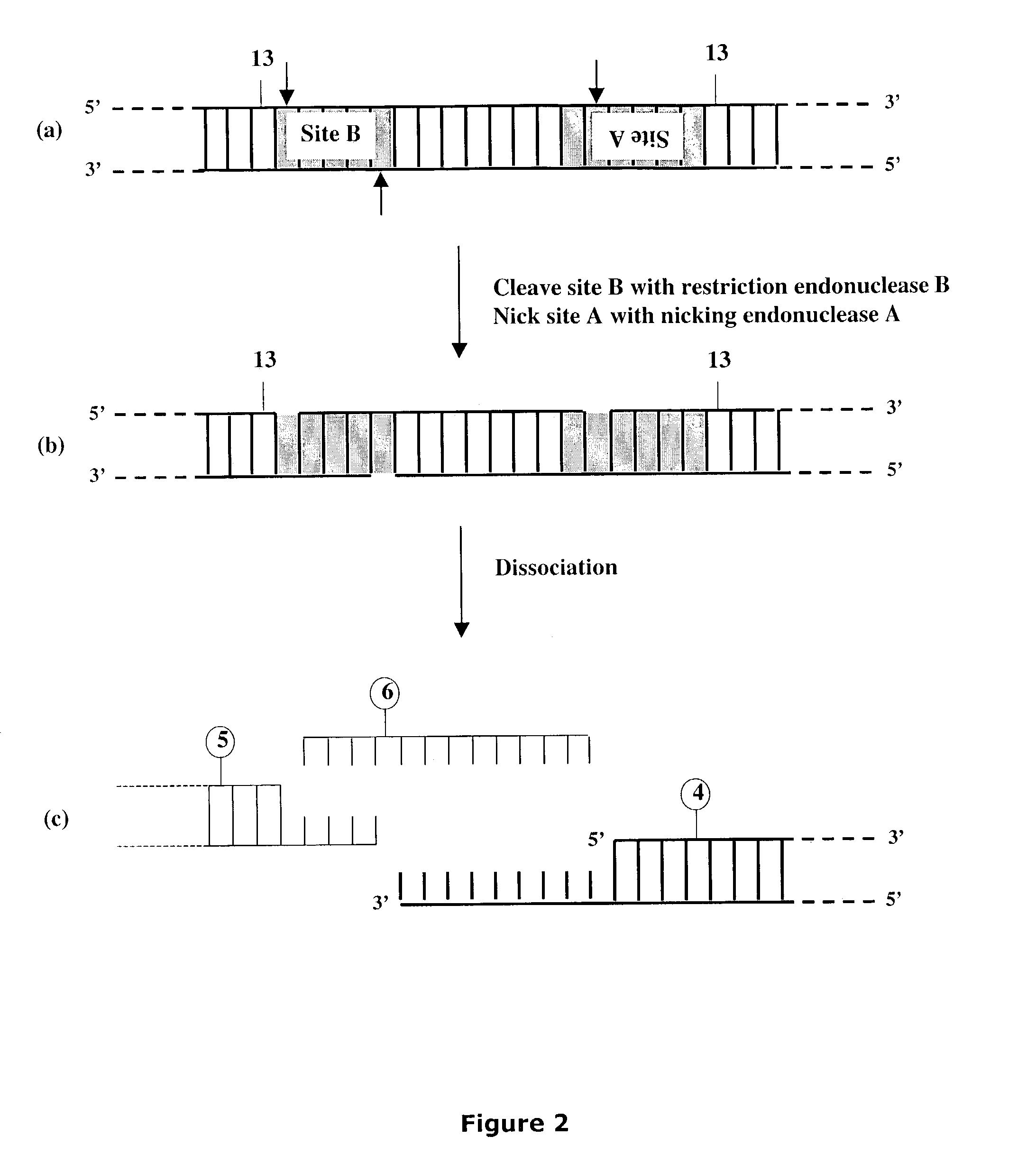
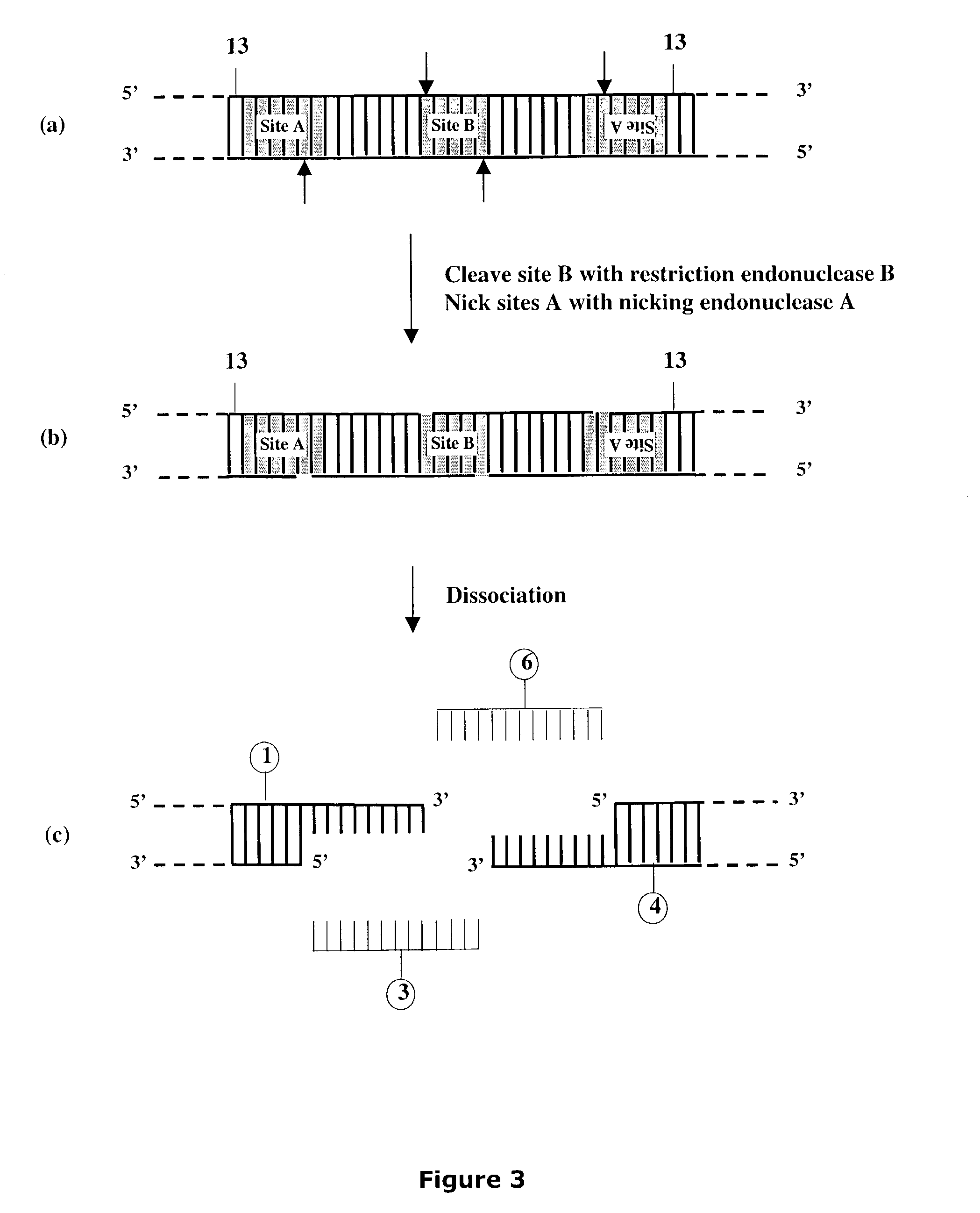
Methods and compositions are provided for generating a single-stranded extension on a polynucleotide molecule, the single-stranded extension having a desired length and sequence composition. Methods for forming single-stranded extensions include: the use of a cassette containing at least one nicking site and at least one restriction site at a predetermined distance from each other and in a predetermined orientation; or primer-dependent amplification which introduces into a polynucleotide molecule, a modified nucleotide which is excised to create a nick using a nicking agent. The methods and compositions provided can be used to manipulate a DNA sequence including introducing site specific mutations into a polynucleotide molecule and for cloning any polynucleotide molecule or set of joined polynucleotide molecules in a recipient molecule such as a vector of choice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Detecting interactions at biomimetic interfaces with liquid crystals
InactiveUS7125592B2Liquid crystal compositionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCrystallographyReceptor molecule
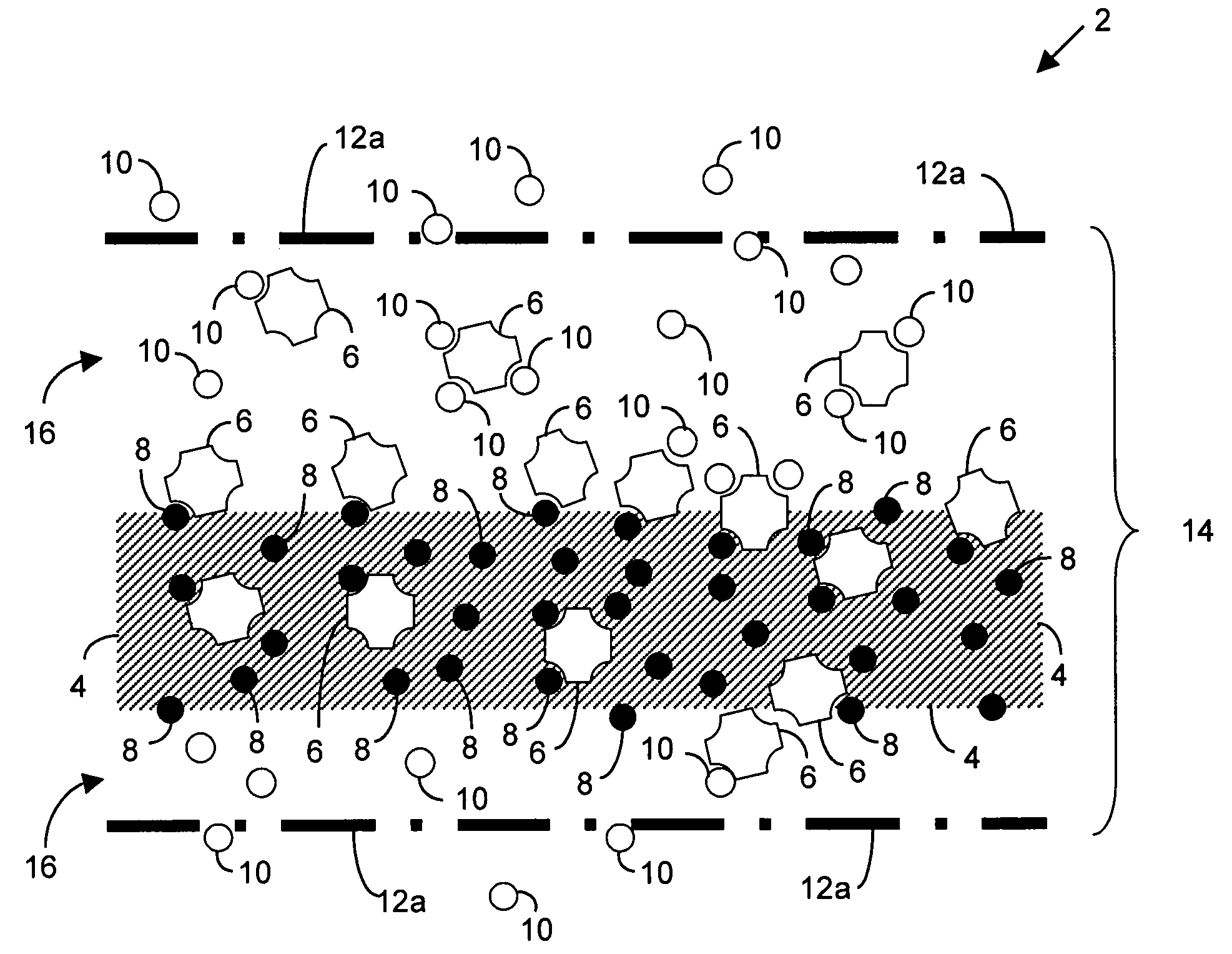
A method of forming a liquid crystal device, includes: contacting an aqueous solution comprising a surfactant and a receptor molecule with a top surface of a liquid crystal. The liquid crystal is in a holding compartment of a substrate, and the receptor molecule is adsorbed on the top surface of the liquid crystal forming an interface between the liquid crystal and the aqueous solution. The receptor molecule is different than the surfactant. A method of detecting a compound in a flowing stream includes passing an aqueous solution over a top surface of a liquid crystal in a holding compartment of a substrate. The method also includes determining whether a change in the orientation of the liquid crystal occurs as the aqueous solution is passed over the top surface of the liquid crystal. A change in the orientation of the liquid crystal indicates the presence of the compound in the flowing stream.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties
InactiveUS20080038717A1Integrity of the rigid secondary structuresPreserve integrityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatotropic hormoneAntibody fragments
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Surfaces comprising a hydrophilic spacer, covalently bonded to hydrogels
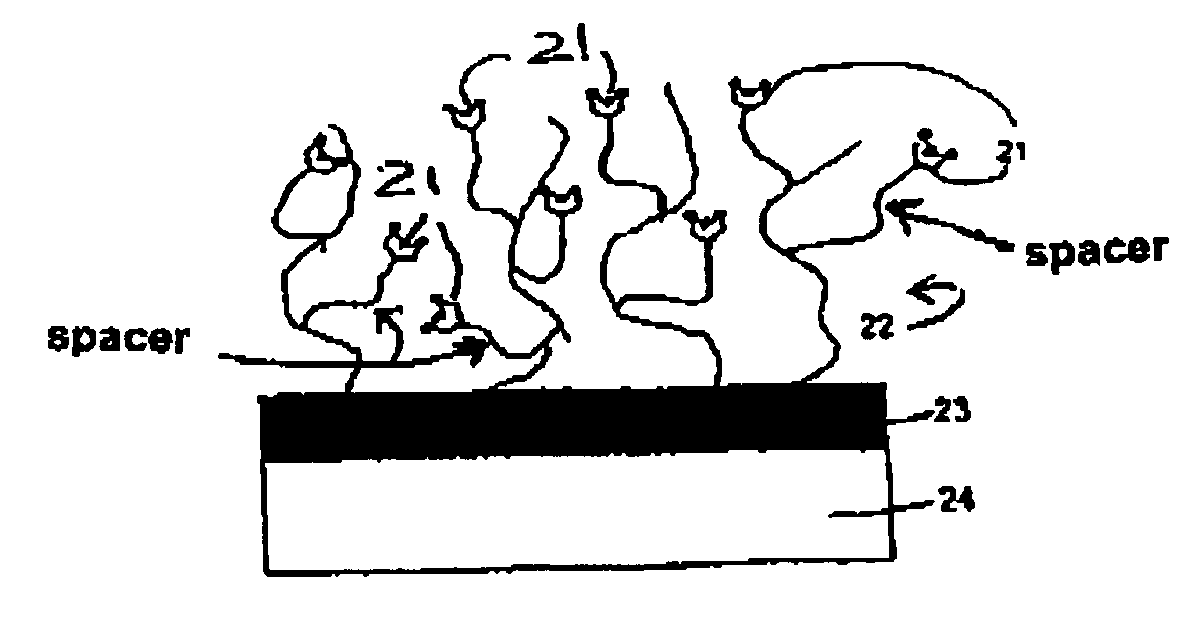
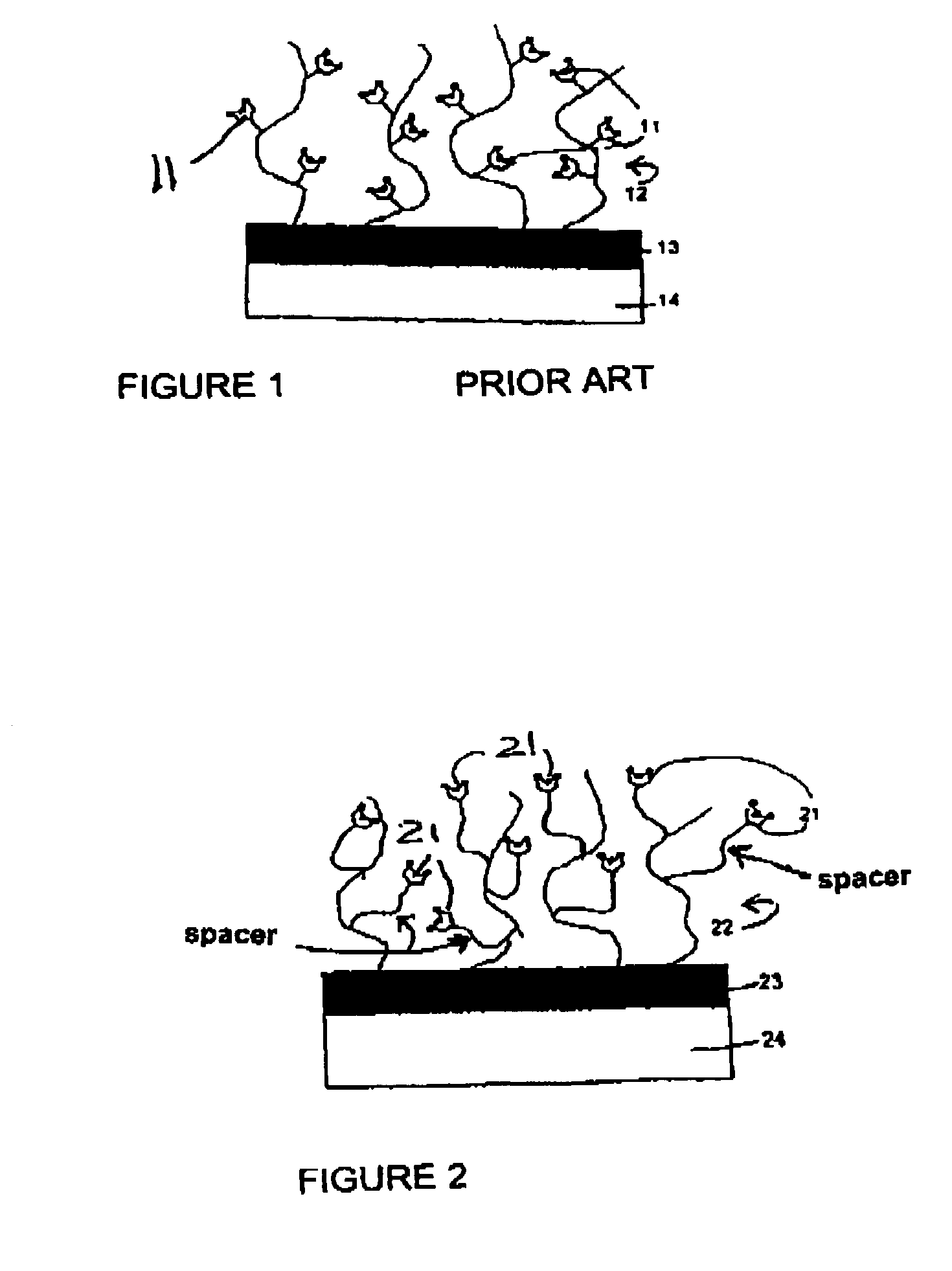
InactiveUS7229840B1Improved binding behaviorImprove accessibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhosphoric acidChain length
The object with the funtionalized hydrogel surface for detection of analyte molecules is obtainable by a process including (1) providing a hydrogel layer on a base surface; (2) bonding organic molecules to the hydrogel layer, each including a chain of atoms with a chain length of at least 8 atoms and a terminal group, which is an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, or a derivative thereof, and (3) reacting the terminal group with a receptor molecule that contains at least three groups, each of which is an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, a sulfonic acid group, a phosphoric acid group, a phosphonic acid group, or a derivative thereof. The receptor molecule can be a protein and the hydrogel can include a water-swellable organic polymer. A method of detecting analyte molecules, for example by surface resonance spectroscopy, is also part of the invention.
Owner:HOFMANN ANDREAS
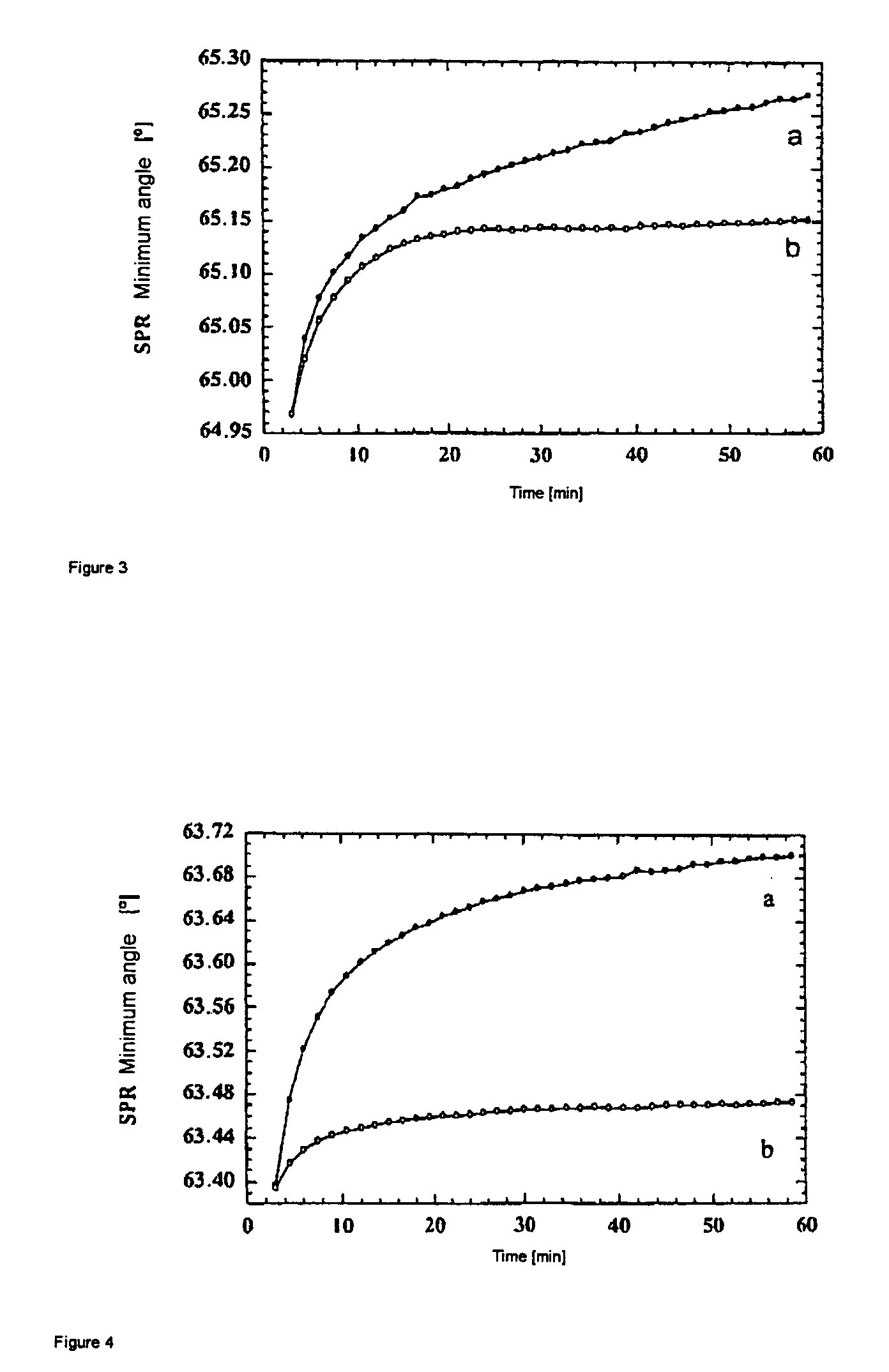
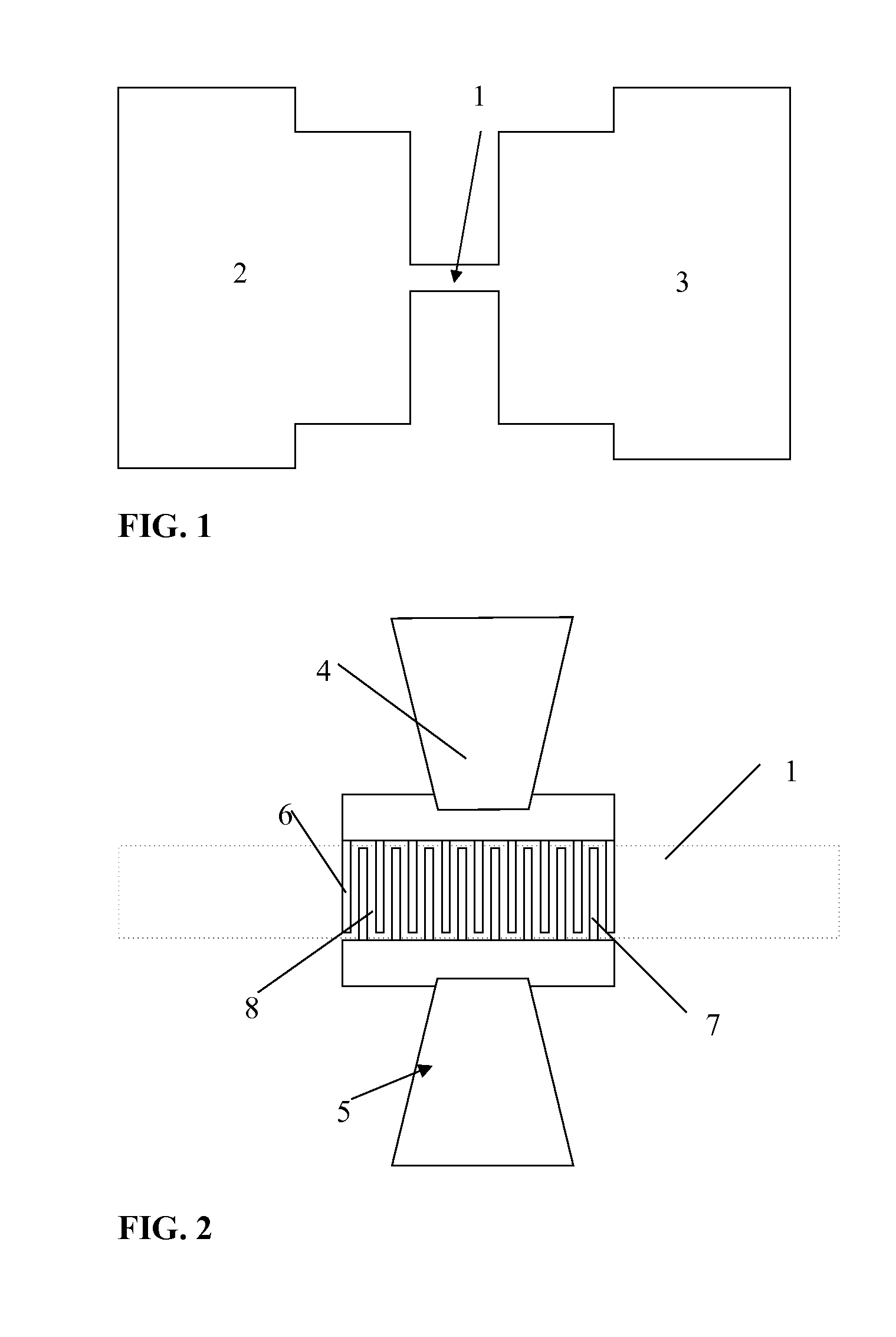
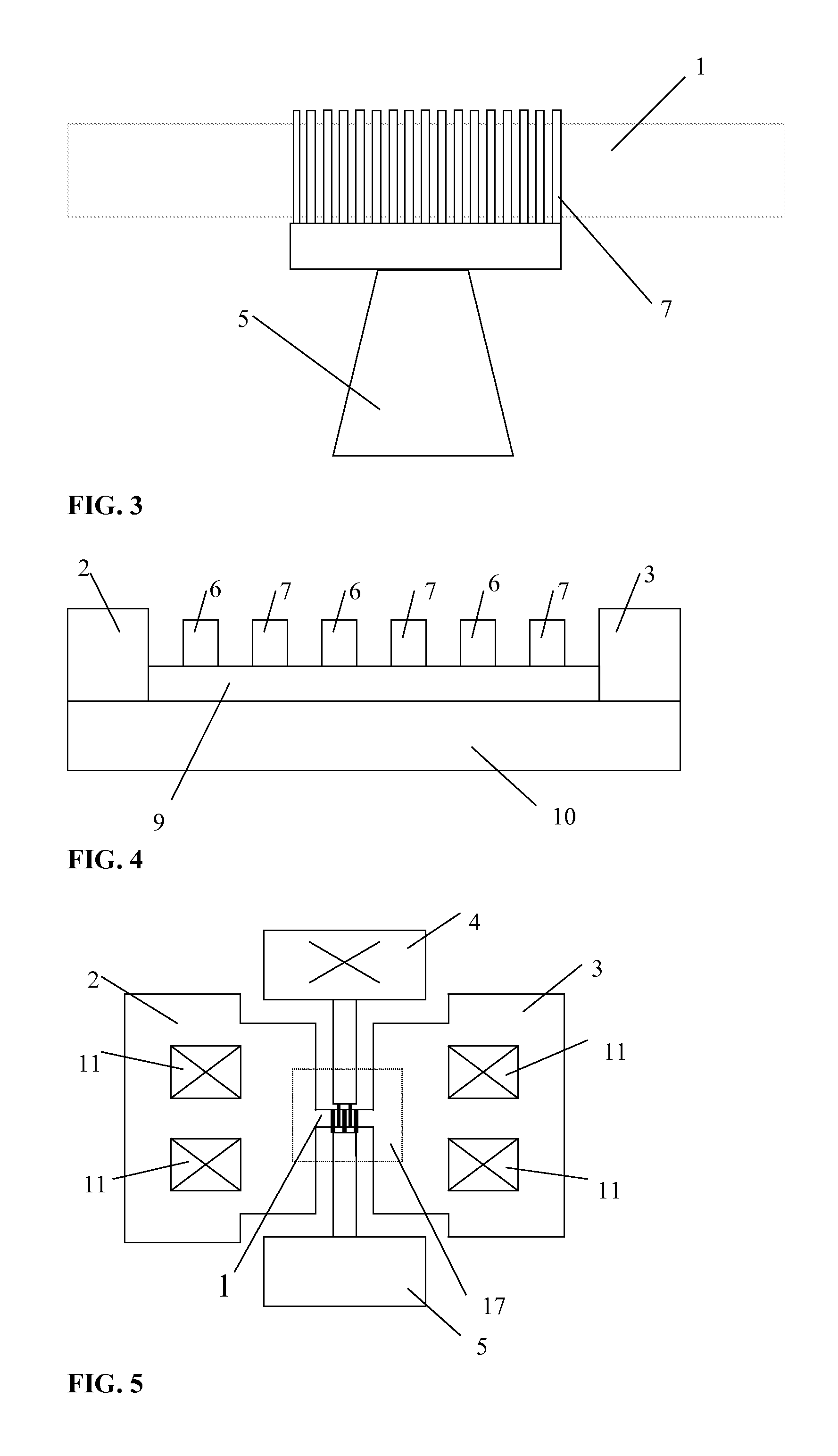
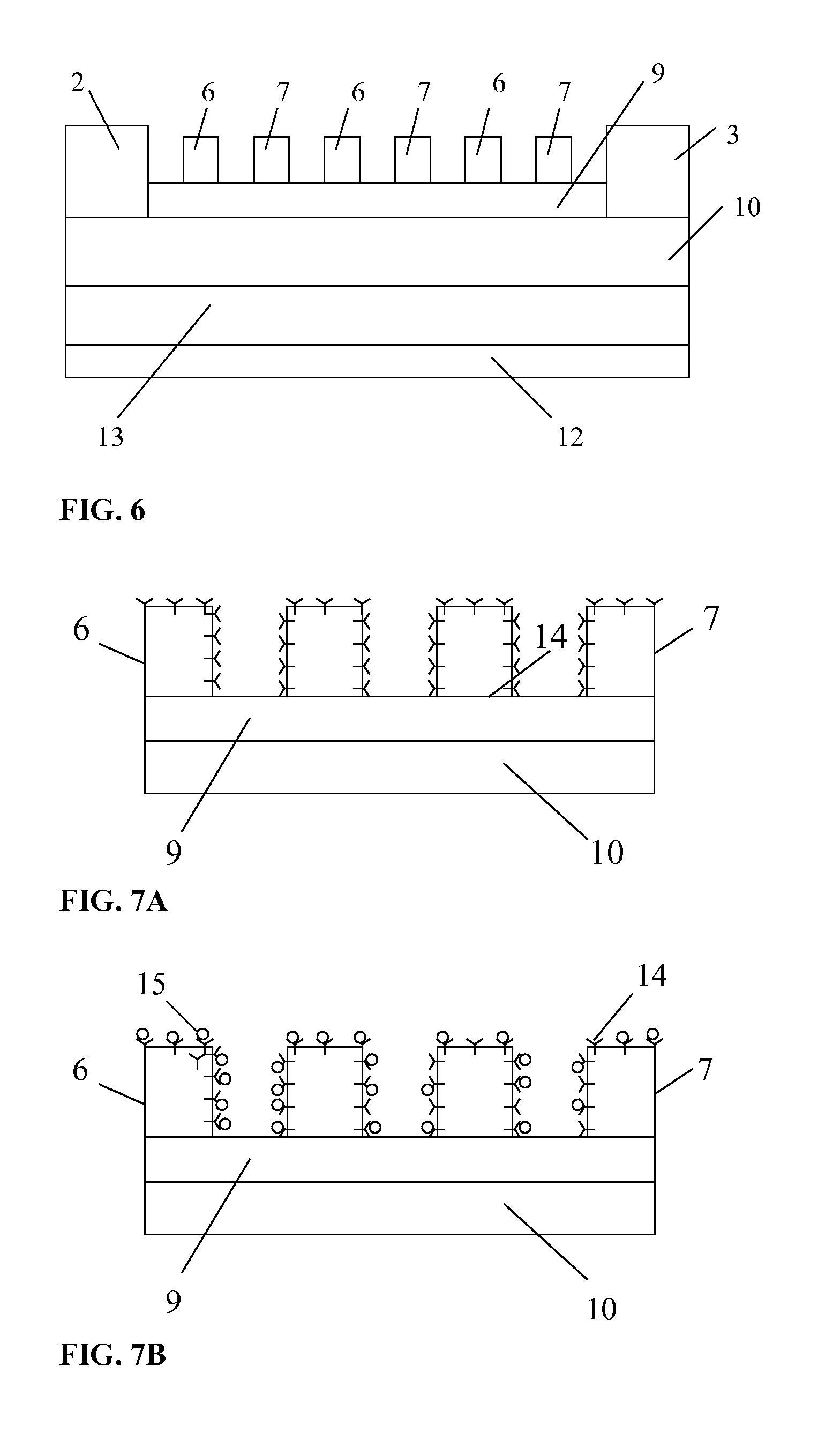
Method and device for high sensitivity and quantitative detection of chemical/biological molecules
InactiveUS20100273672A1Rapid and direct analysisMiniaturizationLibrary screeningMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMOSFETEngineering
A sensor for detecting the presence of predetermined chemical / biological molecules, the sensor having a MOSFET device (2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13), the gate having an array of nanoscale fingers (6,7), and on fingers or in spaces between the fingers, chemical / biological receptor molecules (15) suitable for selectively binding with the predetermined chemical / biological molecules, the sensor also having circuitry (4, 5, 11, 12) for measuring a change in a change in drain current of the FET caused by the predetermined chemical / biological molecules becoming bound to the receptor molecules. Sensitivity and reliability can be increased compared to capacitive sensors.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN +1
Targeted biocides
The present invention relates to retroviral constructs that encode novel monoclonal antibodies, novel fusion proteins, and chimeric monoclonal antibodies and to methods of using and producing the same. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of producing a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule (e.g., immunoglobulin or innate immune system receptor molecule) and a biocide (e.g., bactericidal enzyme) in transgenic animals (e.g., bovines) and in cell cultures. The present invention also relates to therapeutic and prophylactic methods of using a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule and a biocide in health care (e.g., human and veterinary), agriculture (e.g., animal and plant production), and food processing (e.g., beef carcass processing). The present invention also relates to methods of using a fusion protein comprising a microorganism targeting molecule and a biocide in various diagnostic applications in number of diverse fields such as agriculture, medicine, and national defense.
Owner:IOGENETICS +1
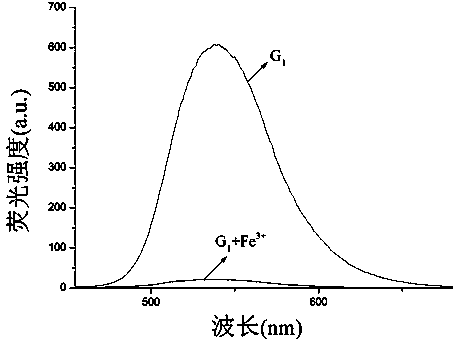
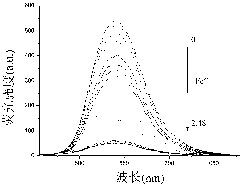
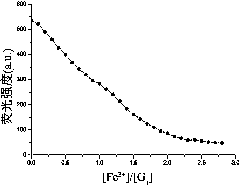
Naphthyl-based phenazine receptor molecule, test paper and synthesis thereof, and application of receptor molecule in identification of Fe<3+> and H2PO4<->
InactiveCN103992324AOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorInorganic saltsChemical physics
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a receptor molecule used for identifying H2PO4<-> and Fe<3+>. The receptor molecule treats a naphthalene ring as a fluorescence signal report group, uses an oxygen atom in a hydroxy group and nitrogen atoms in an imidazolyl group as binding sites of Fe<3+>, and has a strong complexing ability on Fe<3+>, H2PO4<-> and Fe<3+> can form Fe(H2PO4)3 inorganic salt, so Fe<3+> and H2PO4<-> can be continuously fluorescently identified. Results of fluorescence titration experiments show that the receptor has a high detection sensitivity to each of Fe<3+> and H2PO4<->, and the lowest detectable limits reach 0.29ppm and 0.19ppm respectively. The invention also relates to a receptor molecule supported colorimetric test paper. The colorimetric test paper can conveniently and fast fluorescently detect Fe<3+> and H2PO4<->, and has a very good application prospect in the detection fields of Fe<3+> and H2PO4<->.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Colorimetric sensor using polydiacetylene supramolecule
ActiveUS20070275371A1Organic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody antigen reactionsDiacetylene
There is provided a polydiacetylene supramolecule comprising diacetylene molecules, capable of immobilizing a receptor molecule having a thiol group. Since the polydiacetylene supramolecule has a receptor immobilized thereon having a thiol group, for example, an antibody, and thus shows color transition when reacting with a sample, an antigen can be detected through specific color transition of the polydiacetylene when employing in a receptor-ligand reaction, for example, an antibody-antigen reaction.
Owner:SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY
Methods for delivering biologically active molecules into cells
InactiveUS6974698B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotin-binding proteinsCultured cell
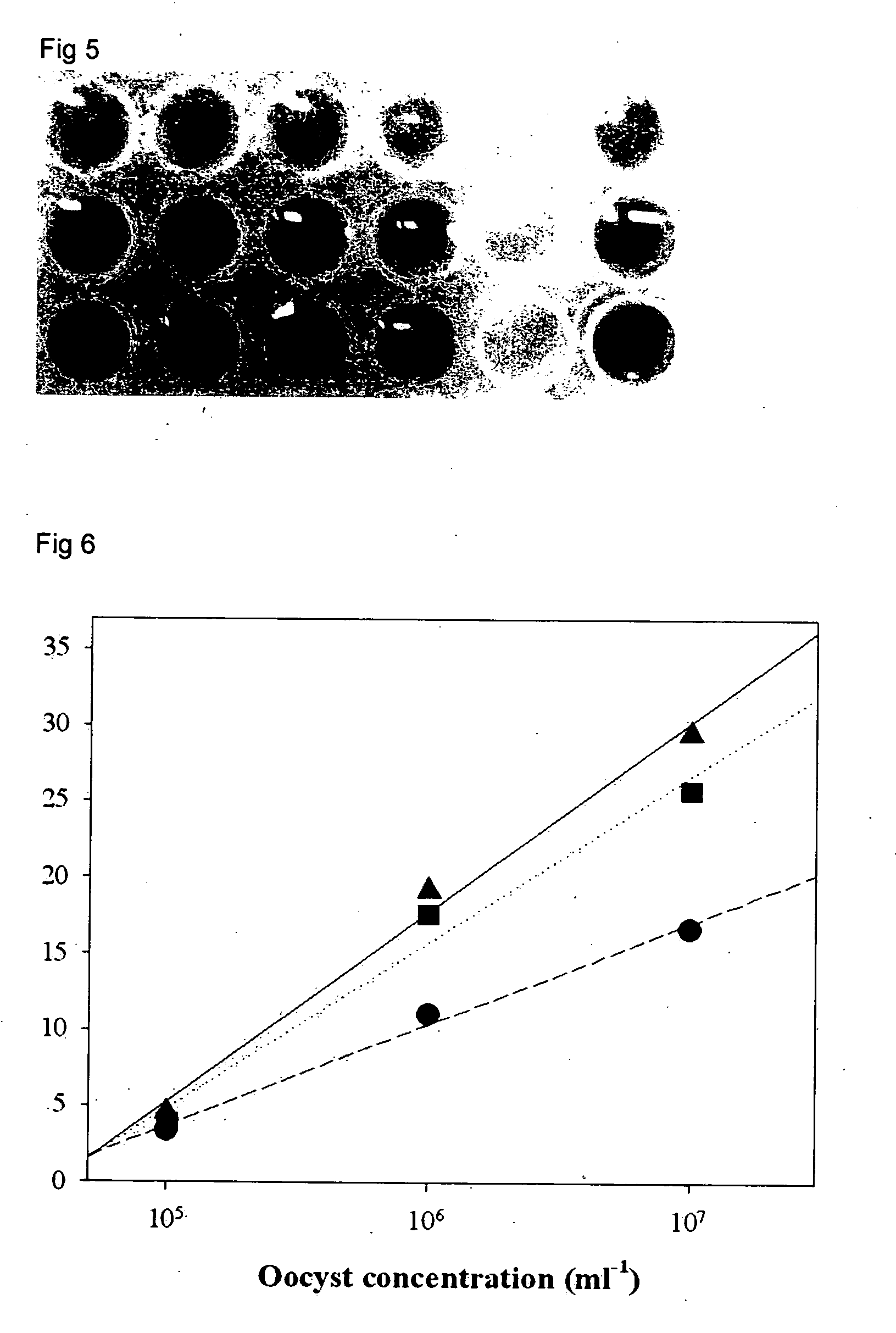
Methods for delivering a biologically active molecule into a cell by linking a molecule to the cell surface, wherein the molecule can act as a surface receptor, then complexing the biologically active molecule with a ligand for the surface receptor, and finally contacting the biologically active molecule-ligand complex with the cell surface are disclosed. Delivery of any biologically active molecule, e.g. proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, hormones, nucleic acids, and oligonucleotides, is contemplated. The use of biotin or biotinylated antibodies as the surface receptor is disclosed. The use of PEI and PEI-avidin conjugates complexed with oligonucleotides for delivery into a directly or indirectly biotinylated cell surface, along with the PEI-avidin-nucleic acid compositions, are disclosed. Primary and cultured cells with a covalently linked surface receptor molecule, such as biotin, on their surfaces are also disclosed.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Novel hemopoietin receptor protein, nr12
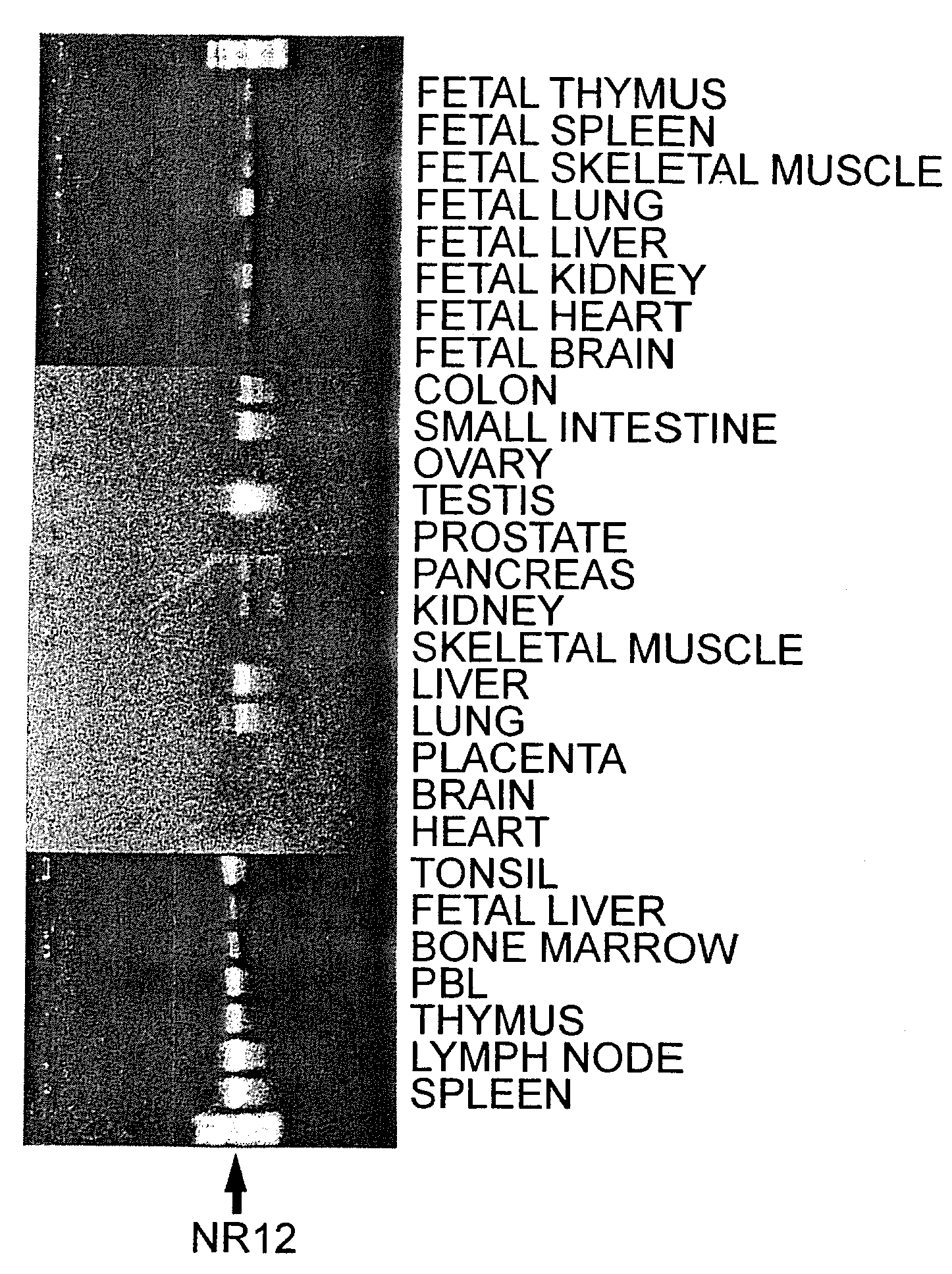
InactiveUS20090105458A1Increased durabilityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseHematopoietic factor
A novel hemopoietin receptor gene (NR12) was successfully isolated by extracting motifs conserved among the amino acid sequences of known hemopoietin receptors and by using the predicted sequence. The NR12 gene encodes two forms of proteins, a transmembrane type and a soluble type. The expression of the NR12 gene was detected in tissues containing hematopoietic cells. NR12 is a novel hemopoietin receptor molecule involved in the regulation of immune system and hematopoiesis in vivo. Thus, NR12 is useful in the search for novel hematopoietic factors that functionally bind to the NR12 receptor, and in the development of therapeutic drugs for diseases associated with immunity or hematopoiesis.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Detecting interactions at biomimetic interfaces with liquid crystals
InactiveUS20070104612A1Liquid crystal compositionsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCrystallographyReceptor molecule
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Measuring cellular metabolism of immobilized cells
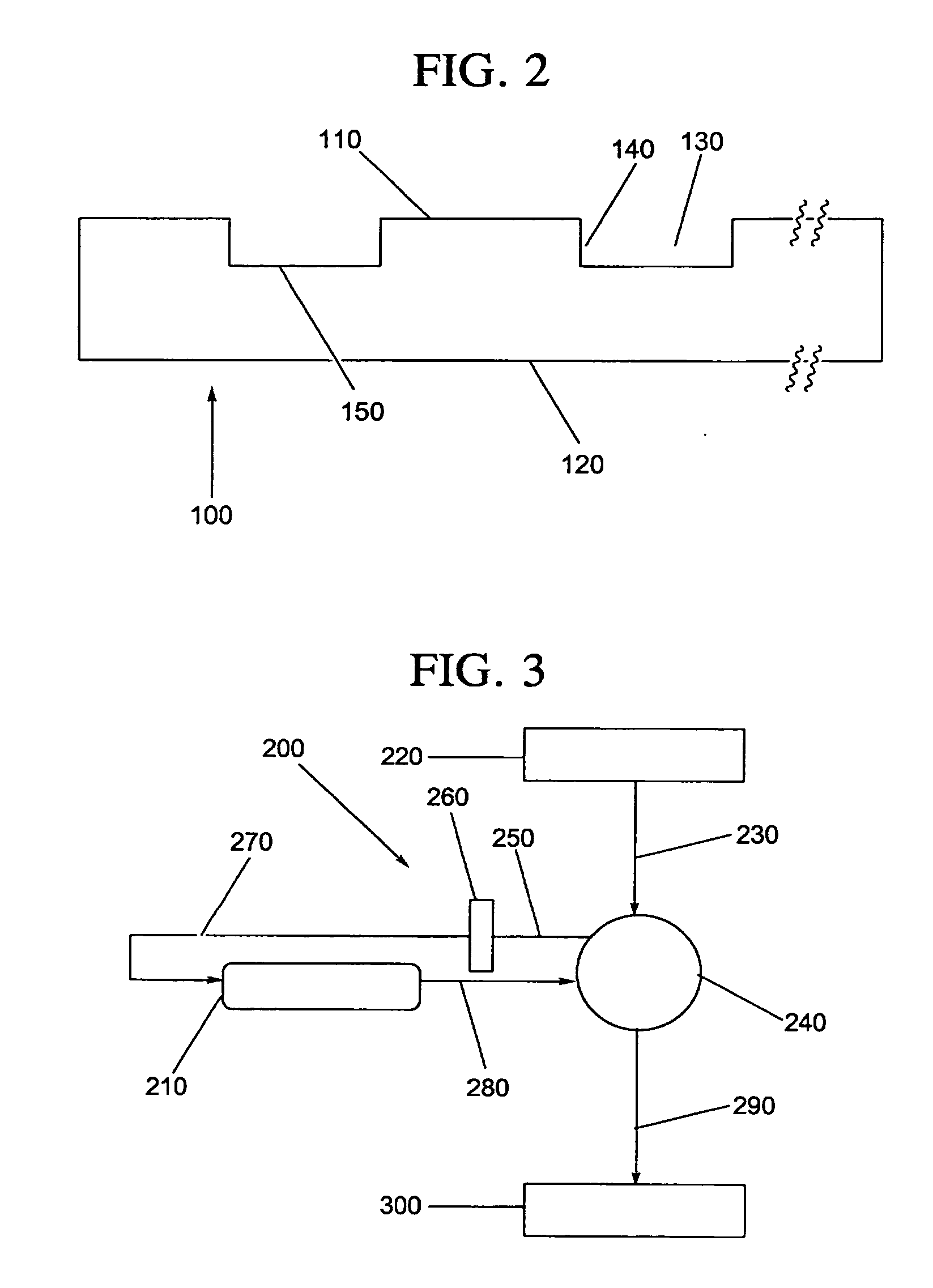
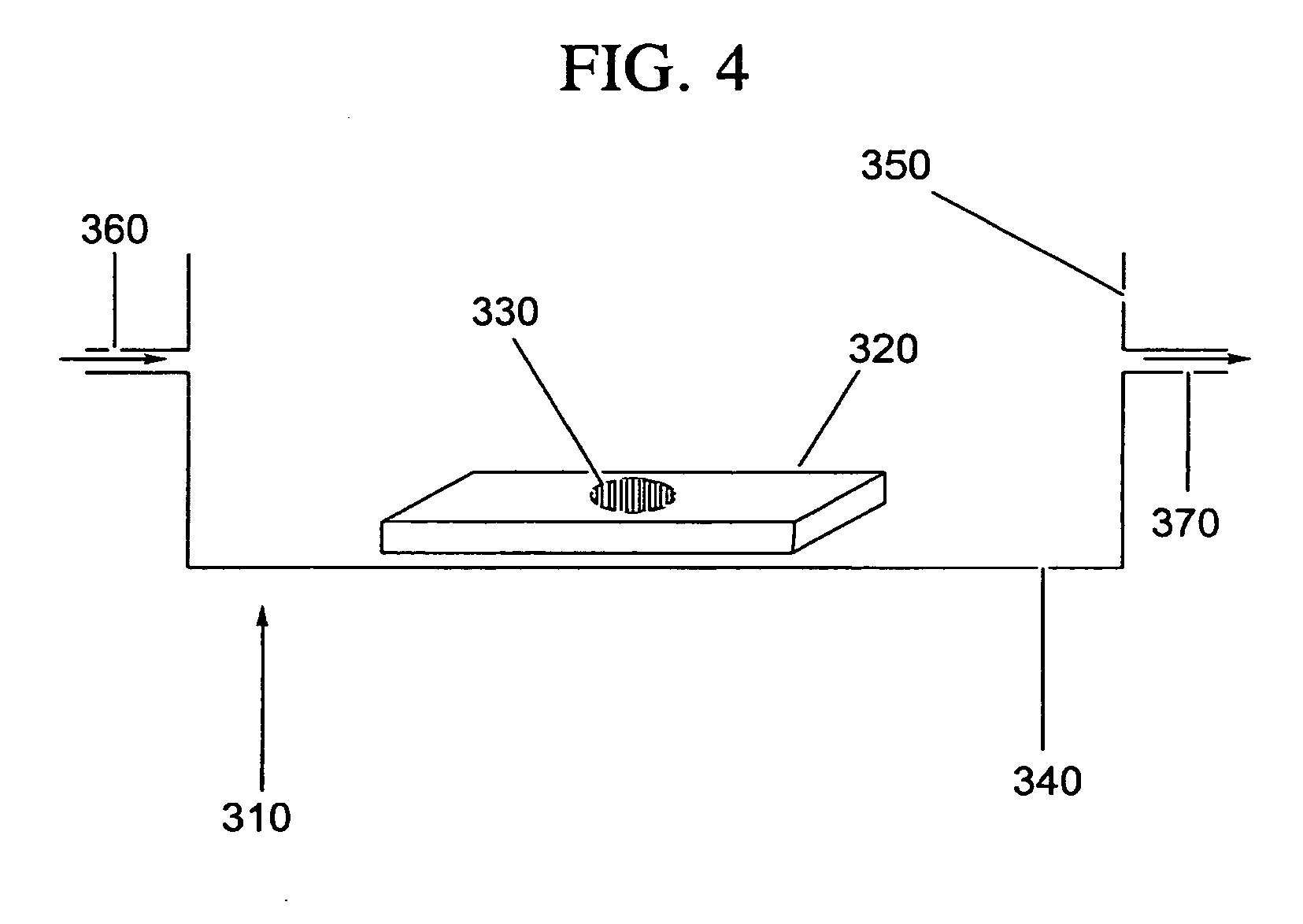
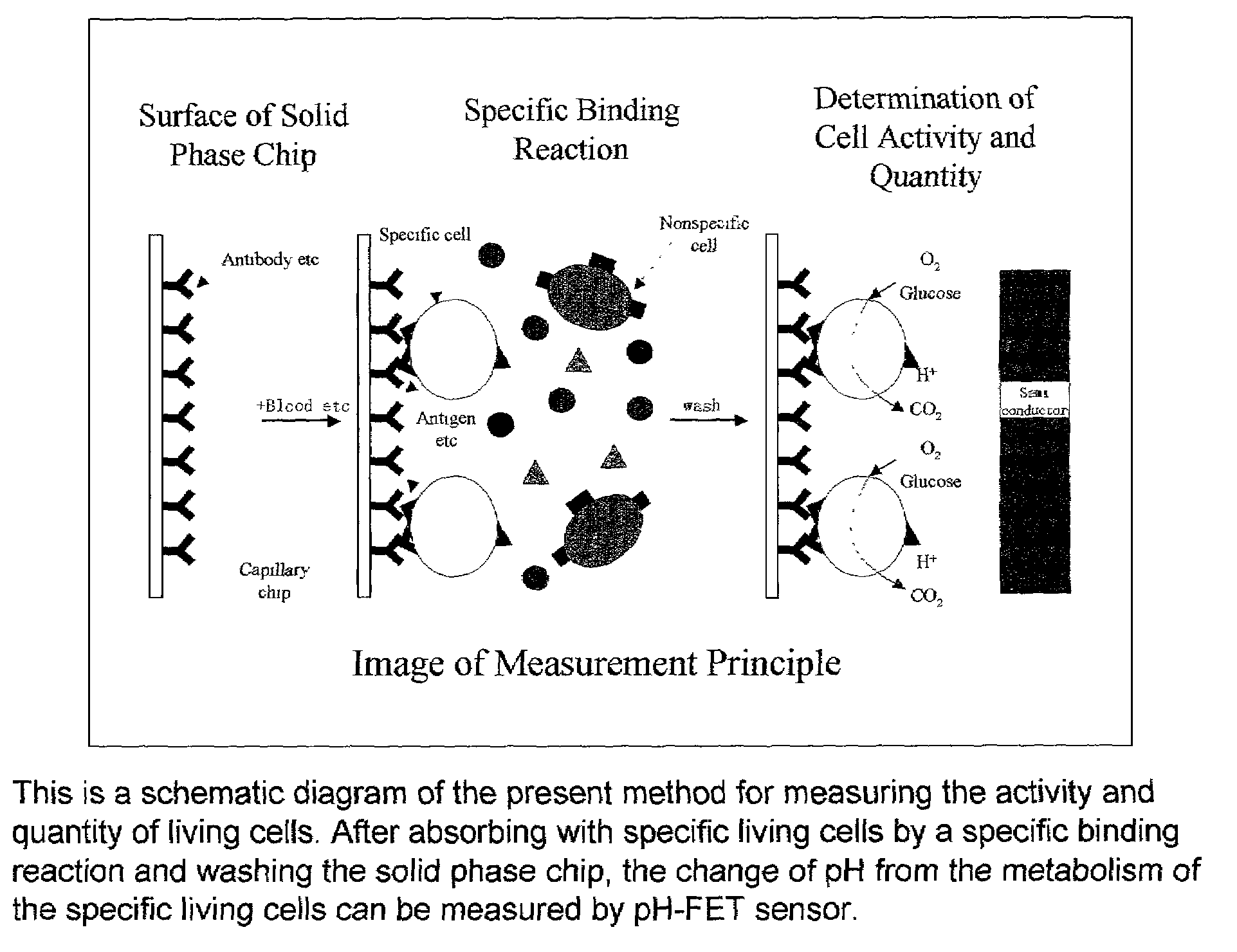
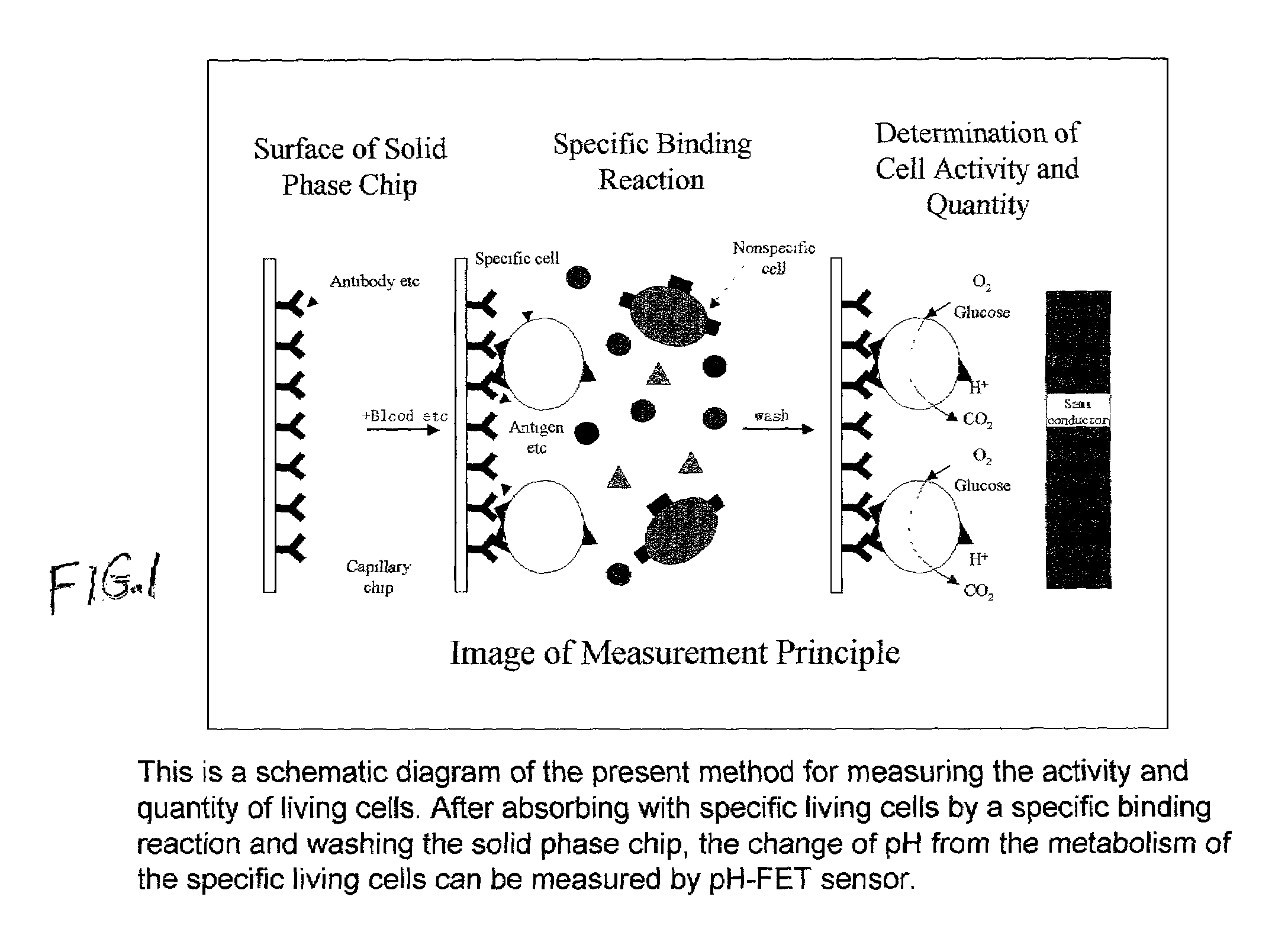
InactiveUS7141369B2Easily and accuratelyMeasure quickly and accuratelyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReceptor moleculeSolid phases
This invention uses a receptor molecule such as an antibody etc immobilized to a chip for a solid phase, and a sensor such as a pH electrode or an oxygen electrode or a glucose electrode for a search device. After immobilizing specific living cells by a bio-specific recognition reaction (a special immunity bond reaction) and washing the solid phase chip, one can measure the change of pH or oxygen consumption or glucose consumption from the metabolism of the specific living cells in substrate solution. This makes it possible to measure the activity and quantity of living cells specifically, accurately and quickly.
Owner:SEMIBIO HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com