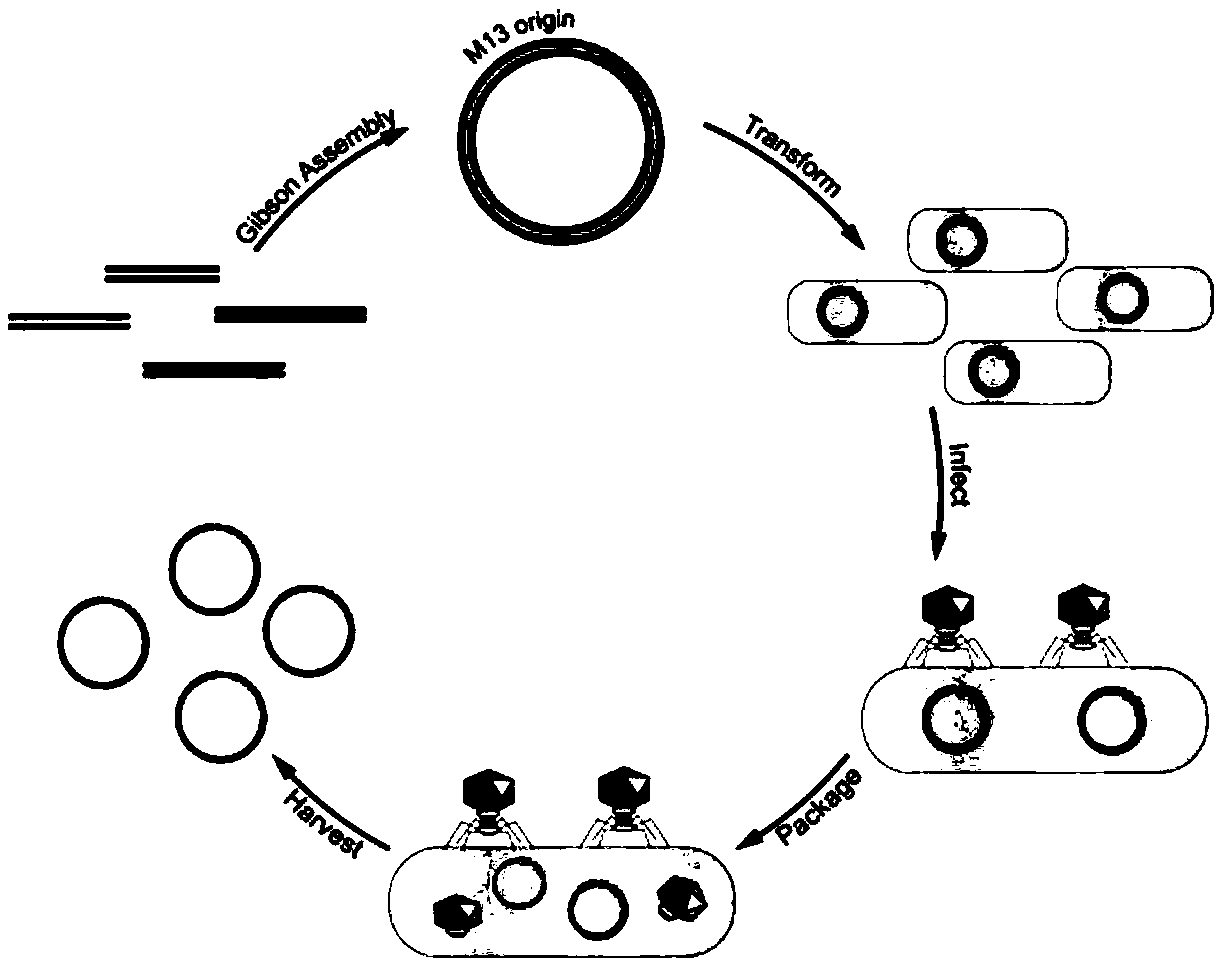
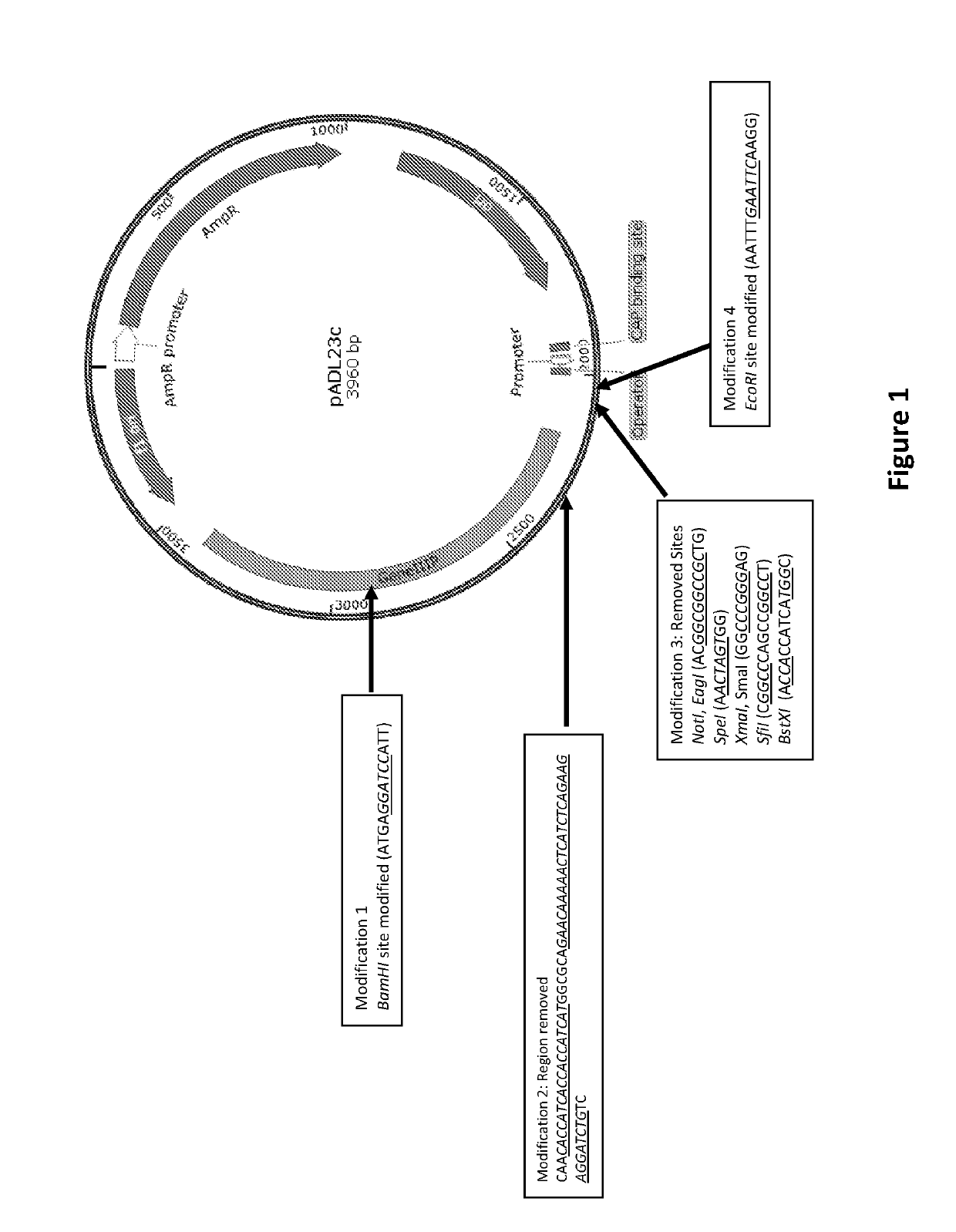
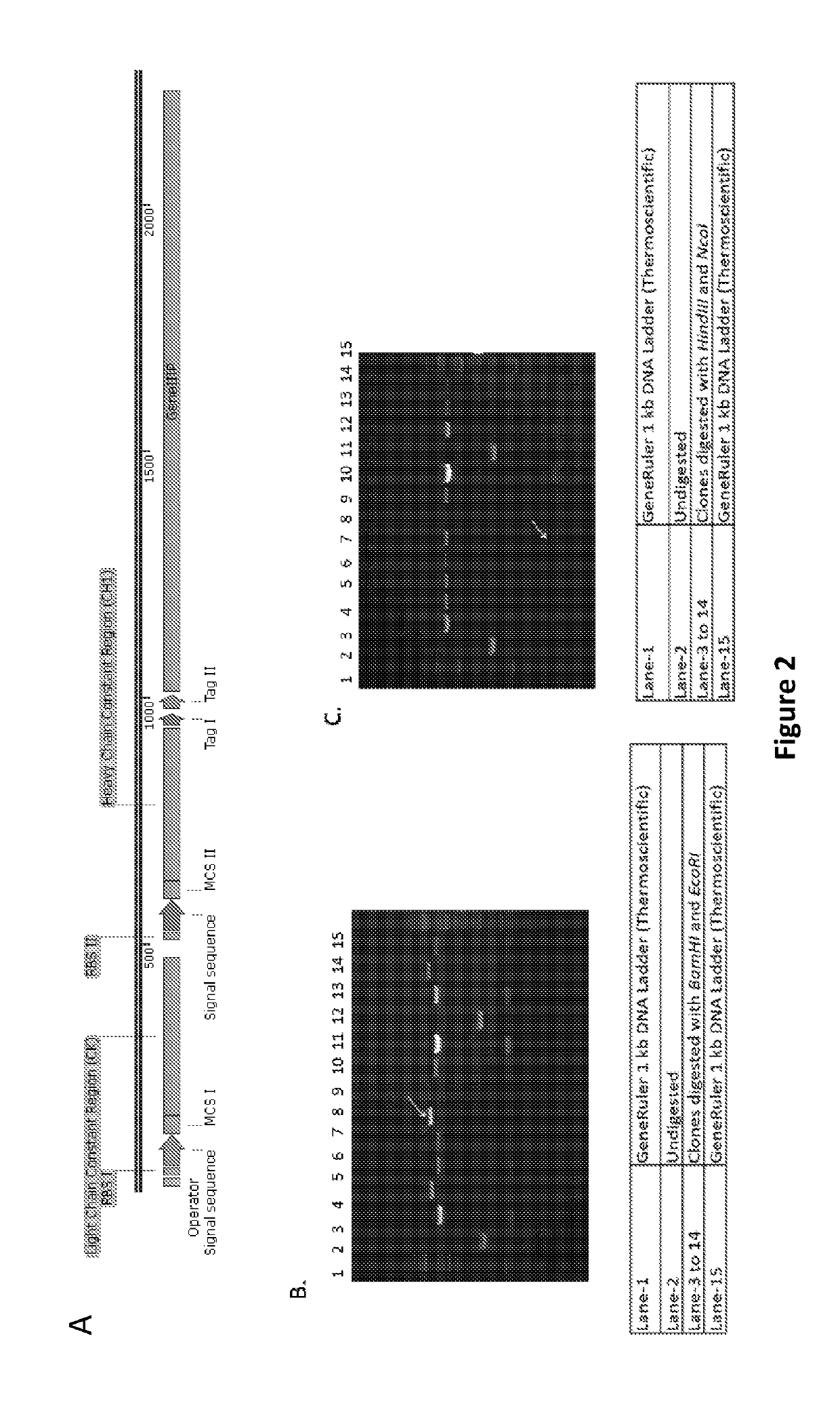
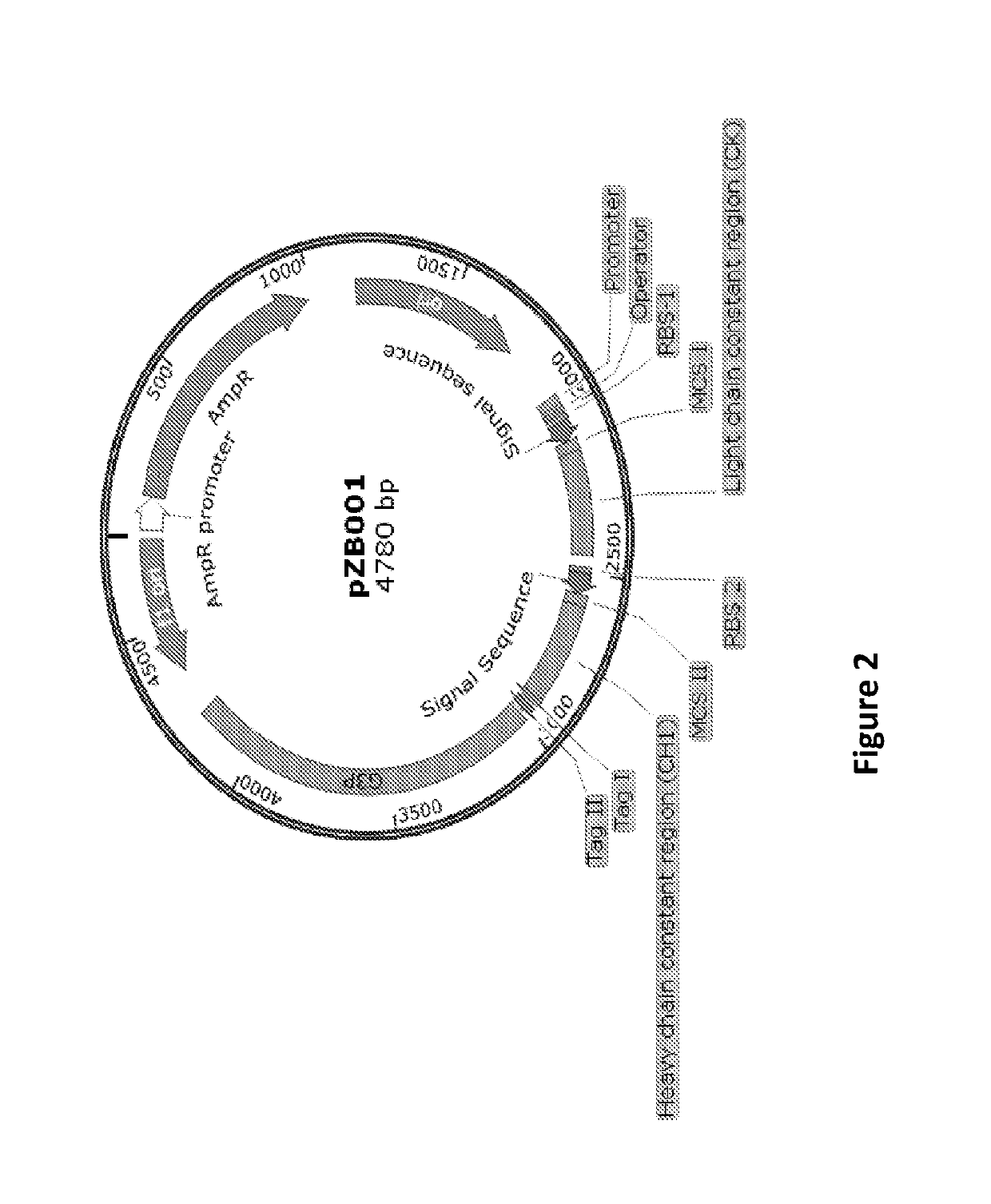
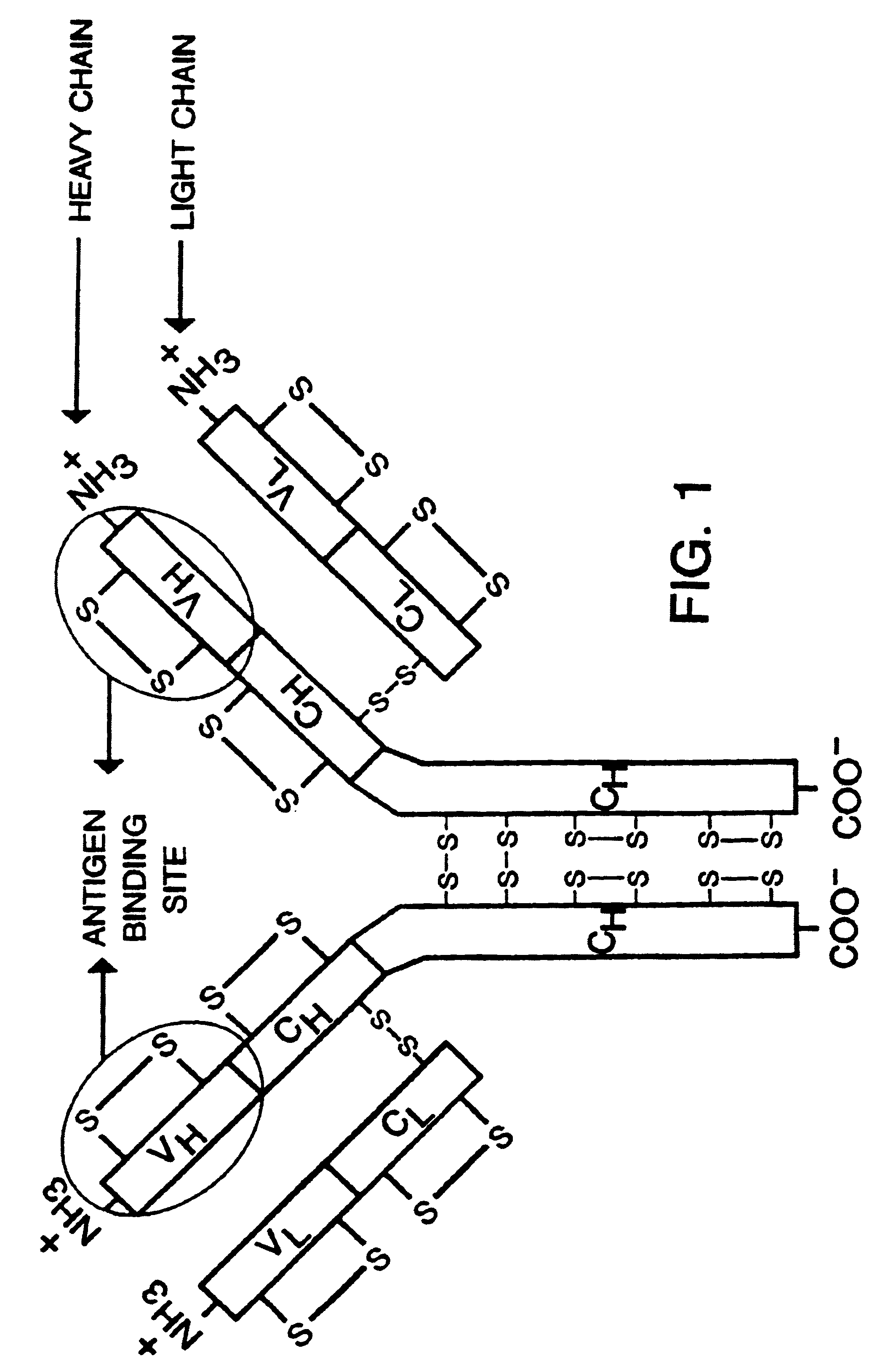
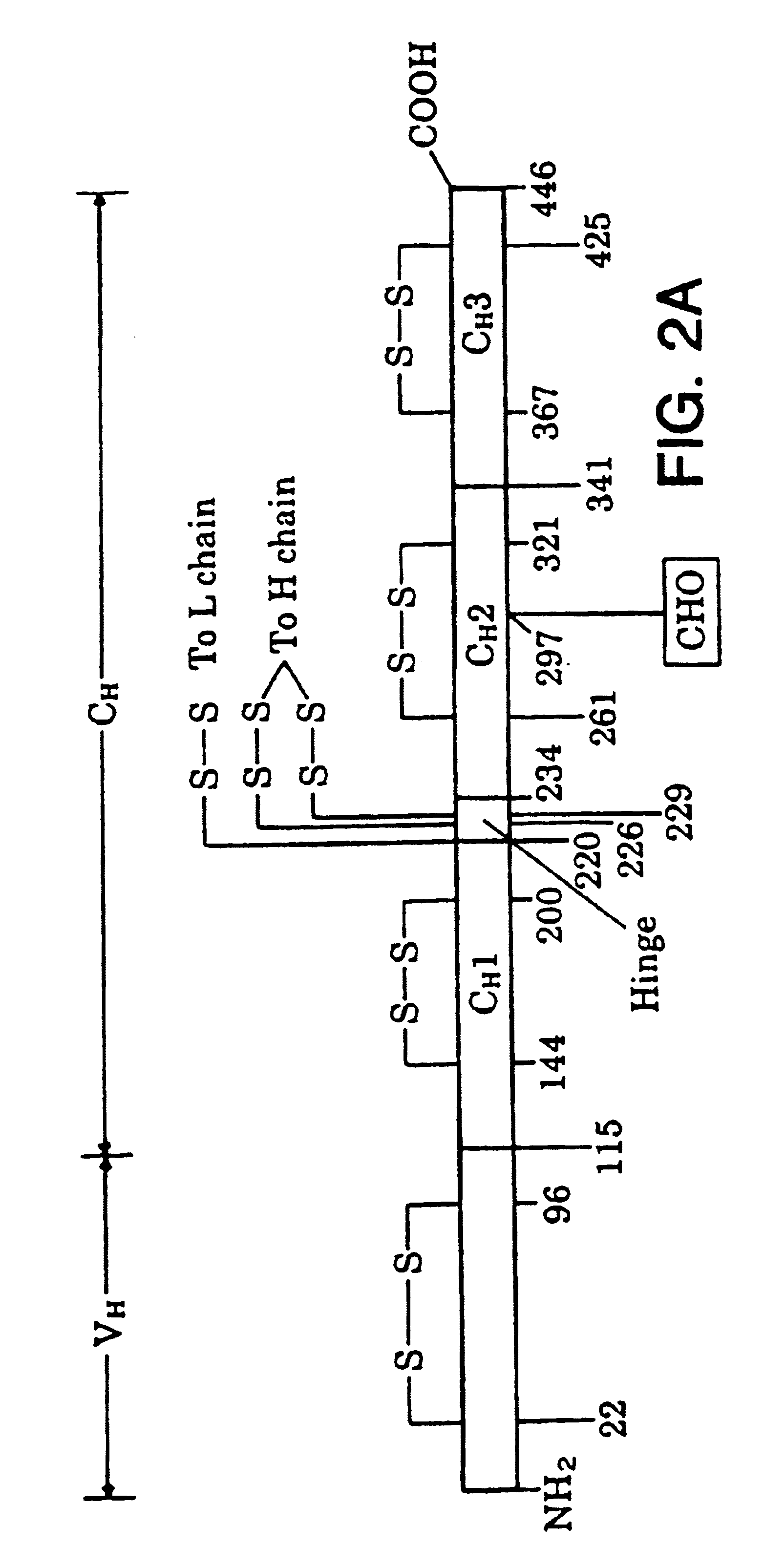
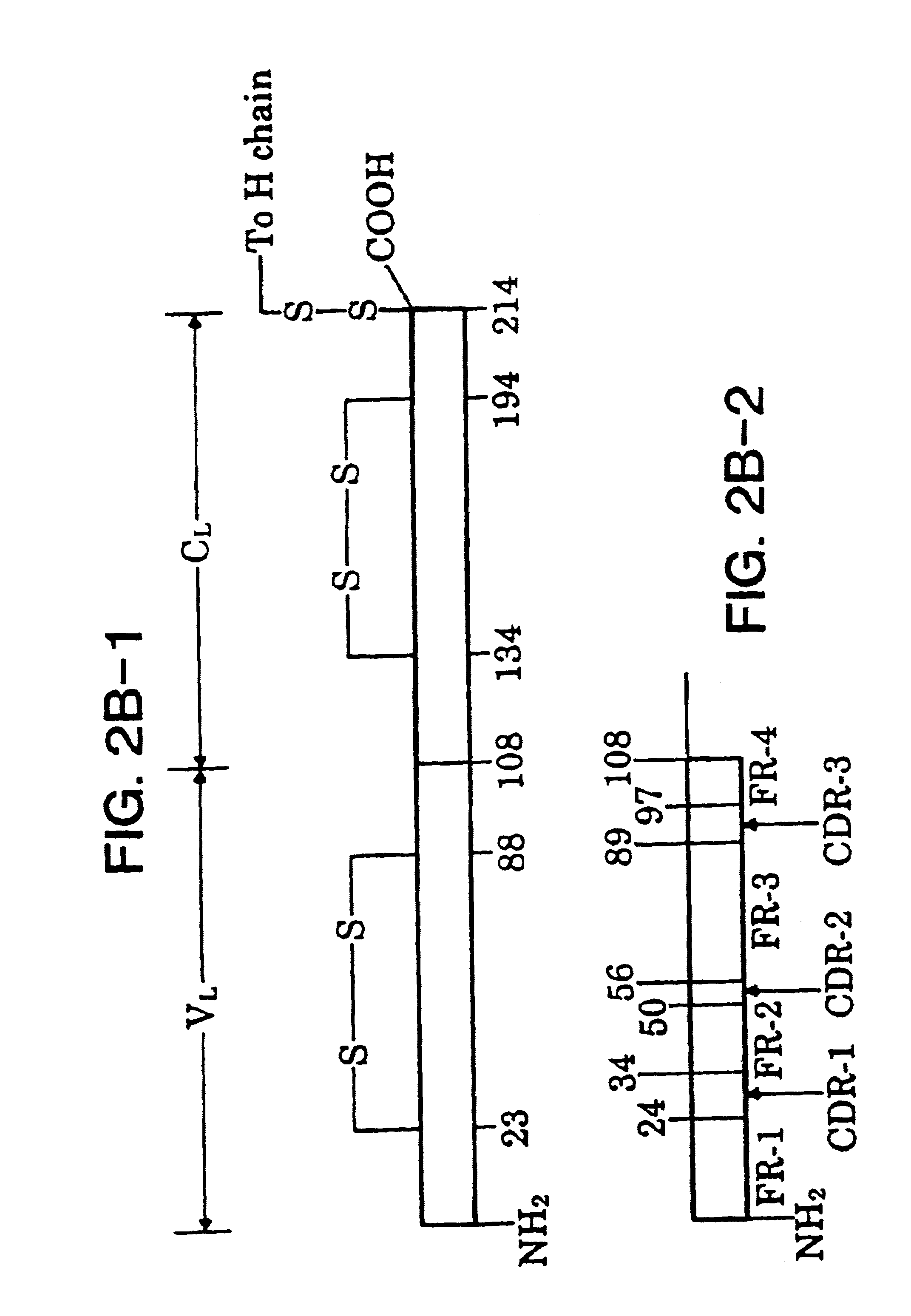
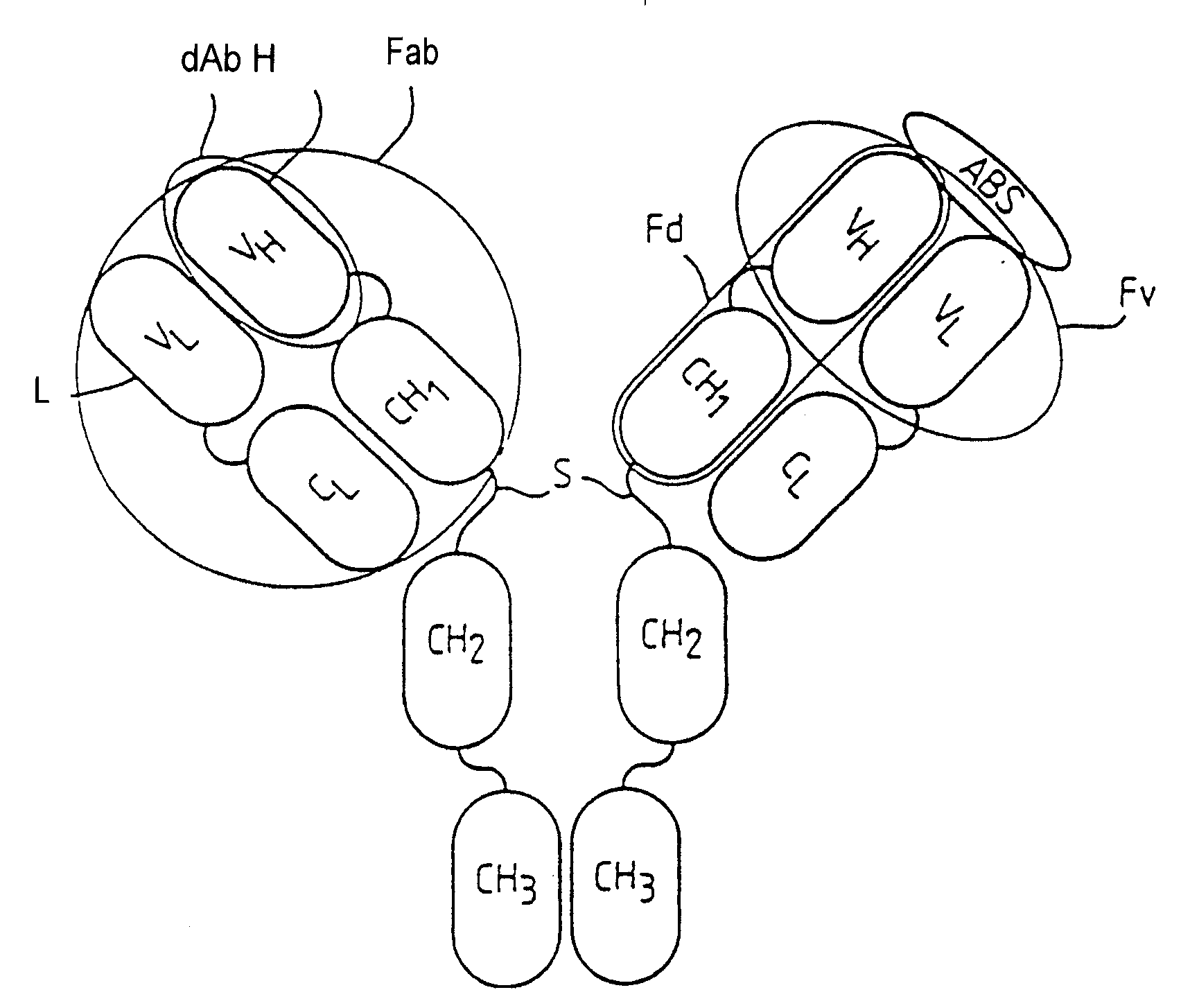
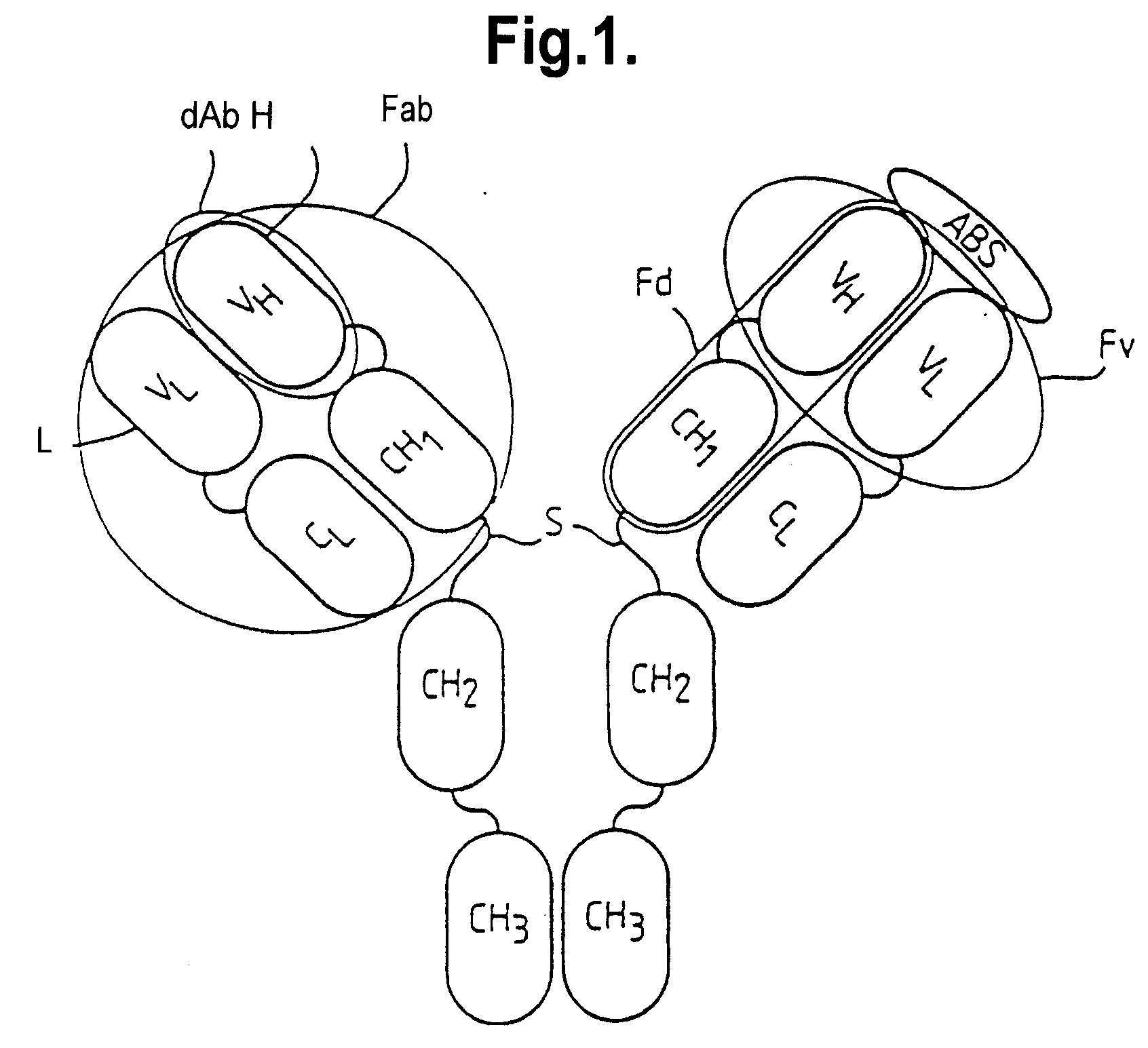
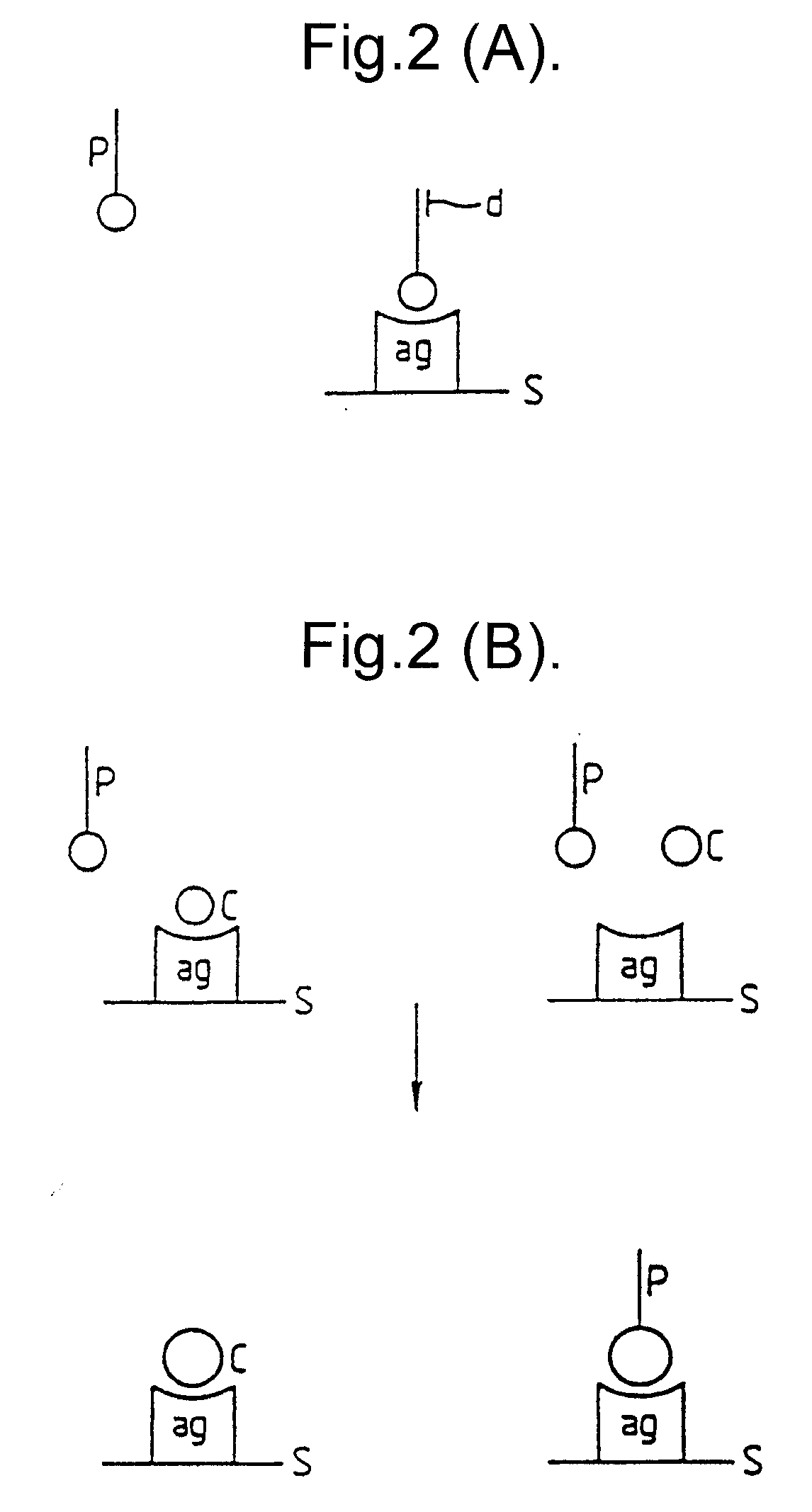
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Phagemid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
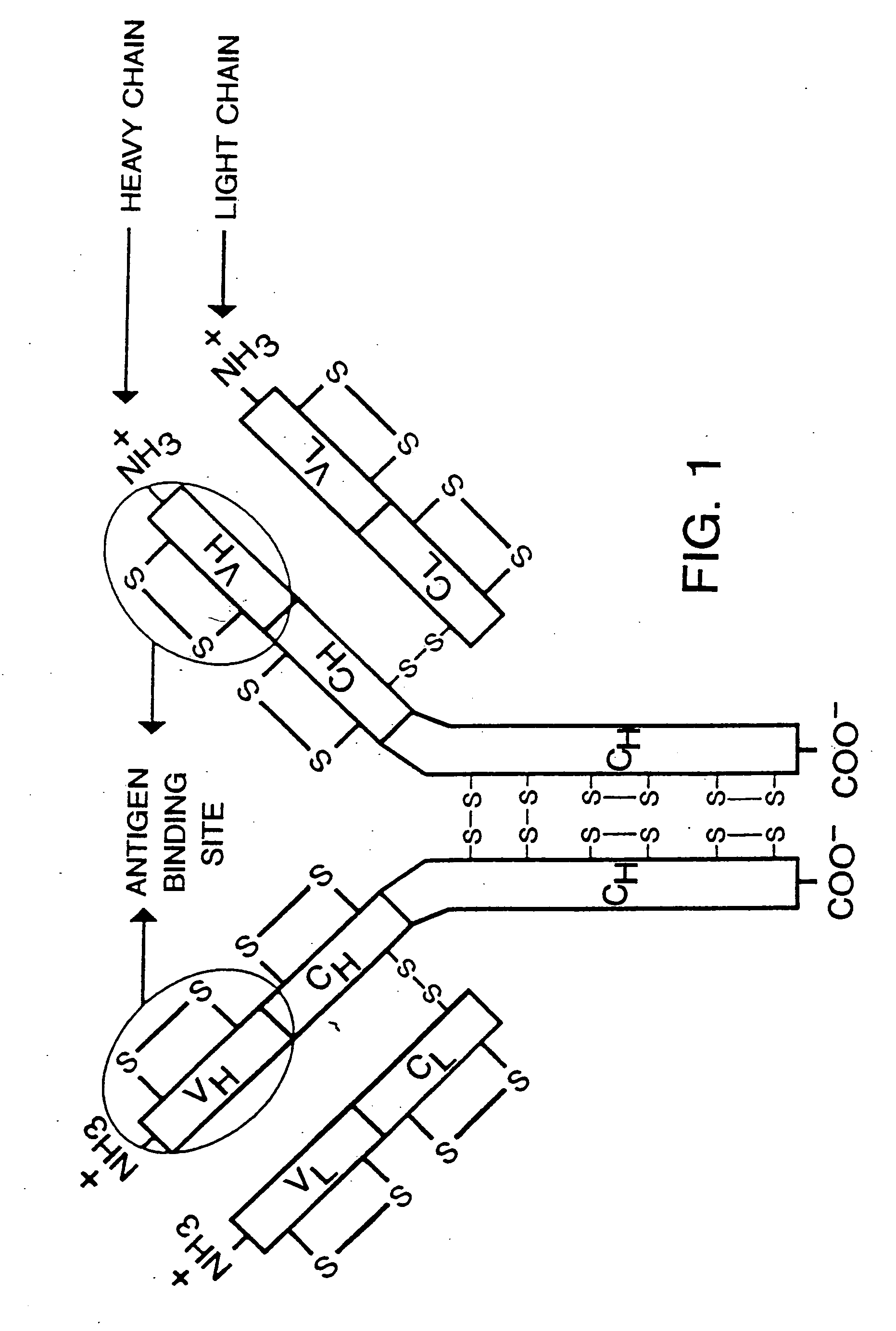
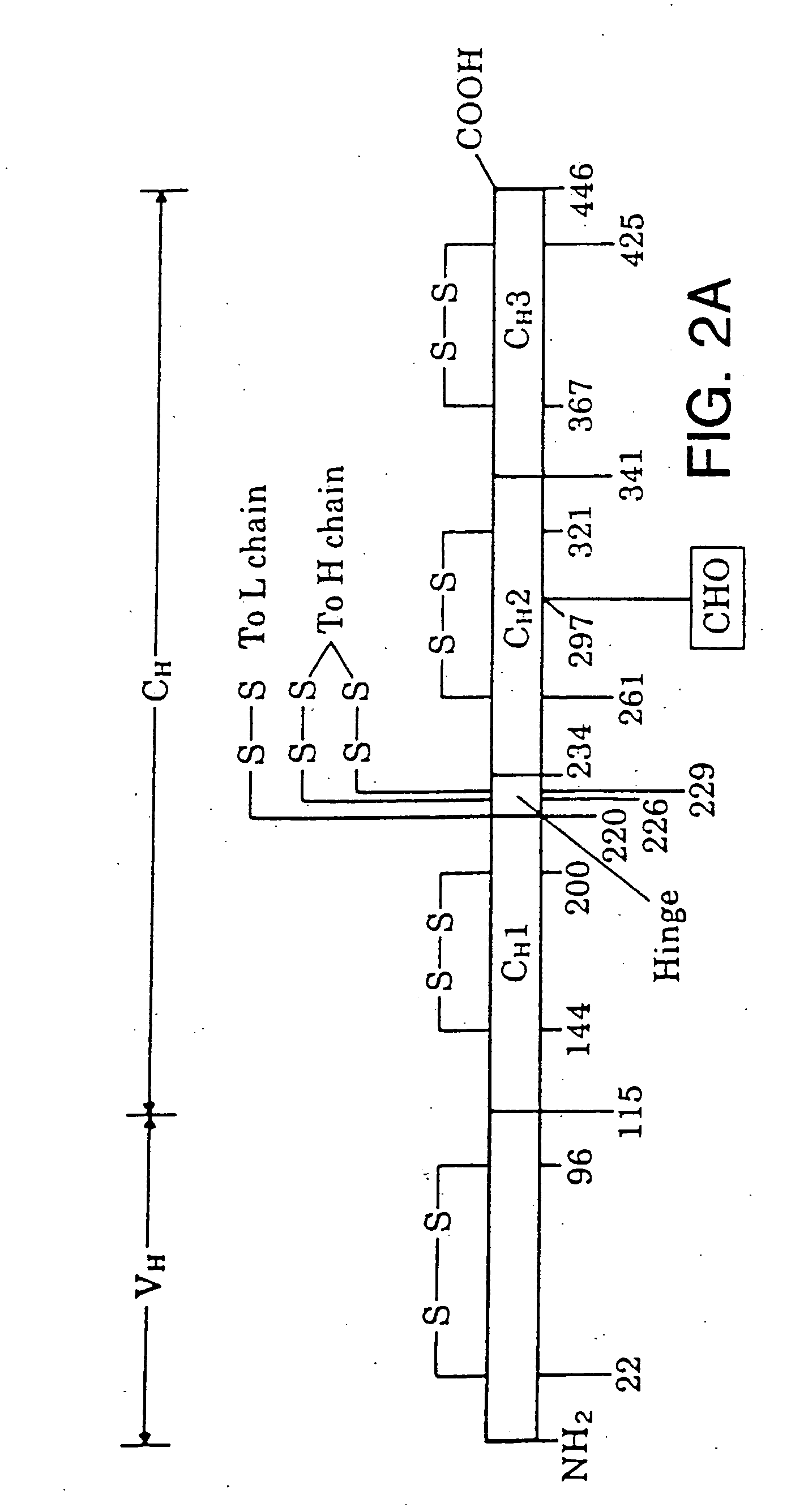
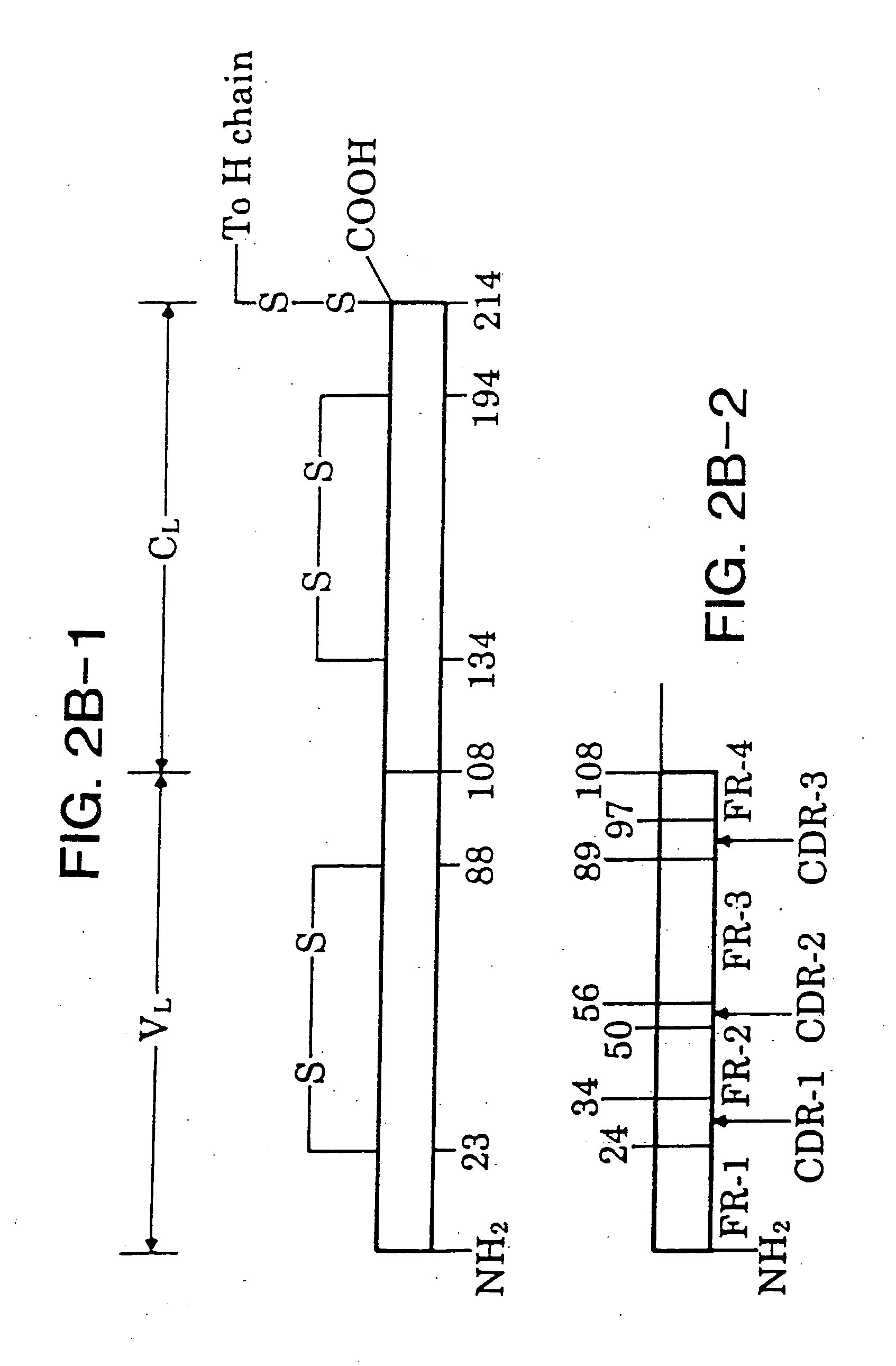
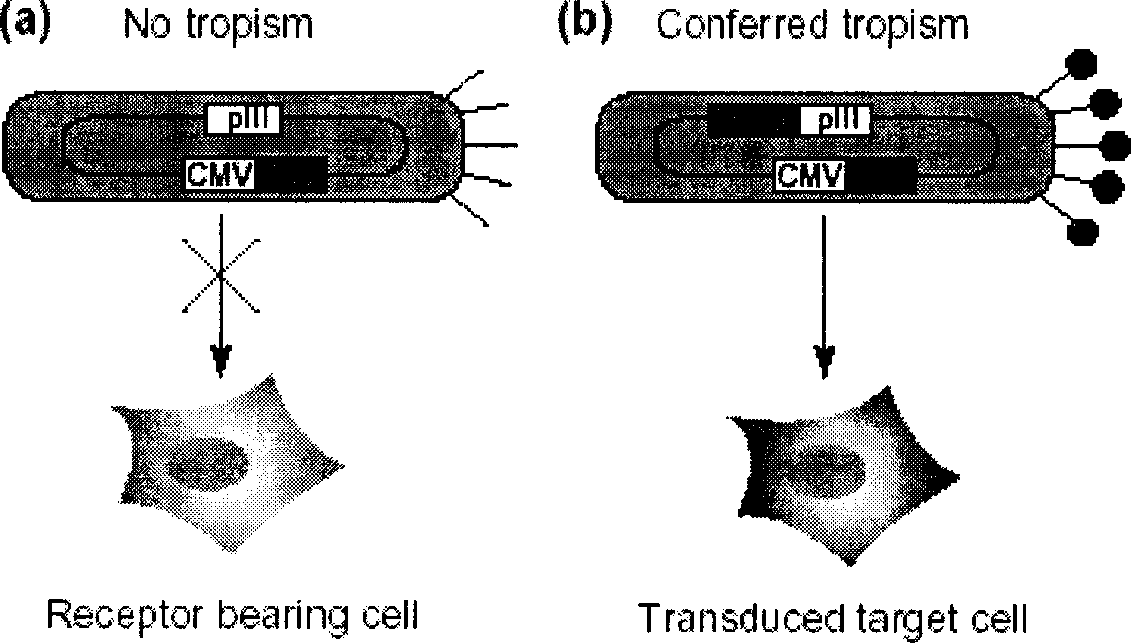
A phagemid or phasmid is a DNA-based cloning vector, which has both bacteriophage and plasmid properties. These vectors carry, in addition to the origin of plasmid replication, an origin of replication derived from bacteriophage. Unlike commonly used plasmids, phagemid vectors differ by having the ability to be packaged into the capsid of a bacteriophage, due to their having a genetic sequence that signals for packaging. Phagemids are used in a variety of biotechnology applications; for example, they can be used in a molecular biology technique called "Phage Display".
Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs
InactiveUS7063943B1Simple procedureSpeedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFree formGenetic diversity
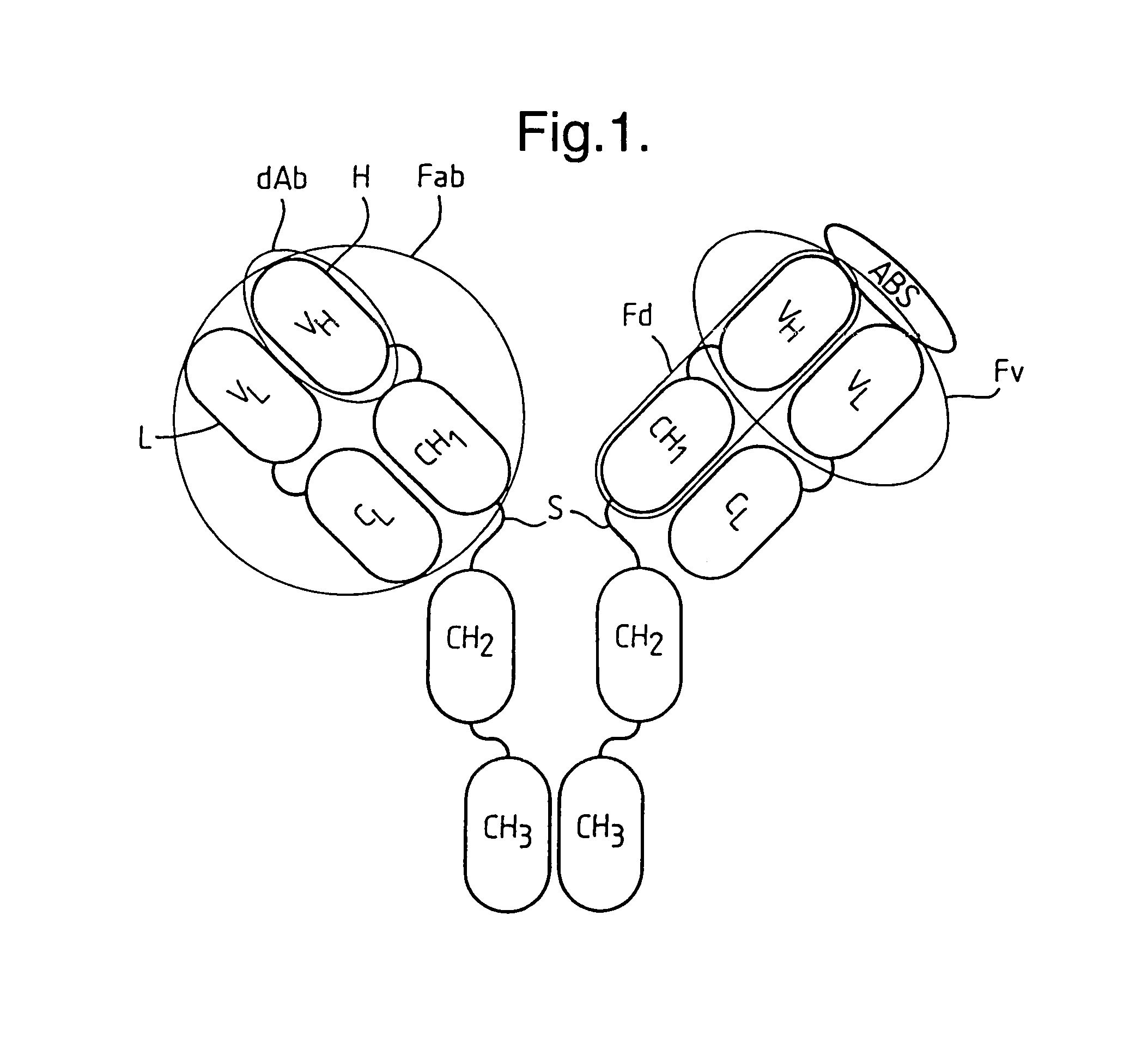
A member of a specific binding pair (sbp) is identified by expressing DNA encoding a genetically diverse population of such sbp members in recombinant host cells in which the sbp members are displayed in functional form at the surface of a secreted recombinant genetic display package (rgdp) containing DNA encoding the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof, by virtue of the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof being expressed as a fusion with a capsid component of the rgdp. The displayed sbps may be selected by affinity with a complementary sbp member, and the DNA recovered from selected rgdps for expression of the selected sbp members. Antibody sbp members may be thus obtained, with the different chains thereof expressed, one fused to the capsid component and the other in free form for association with the fusion partner polypeptide. A phagemid may be used as an expression vector, with said capsid fusion helping to package the phagemid DNA. Using this method libraries of DNA encoding respective chains of such multimeric sbp members may be combined, thereby obtaining a much greater genetic diversity in the sbp members than could easily be obtained by conventional methods.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Improving sequence-specific antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair
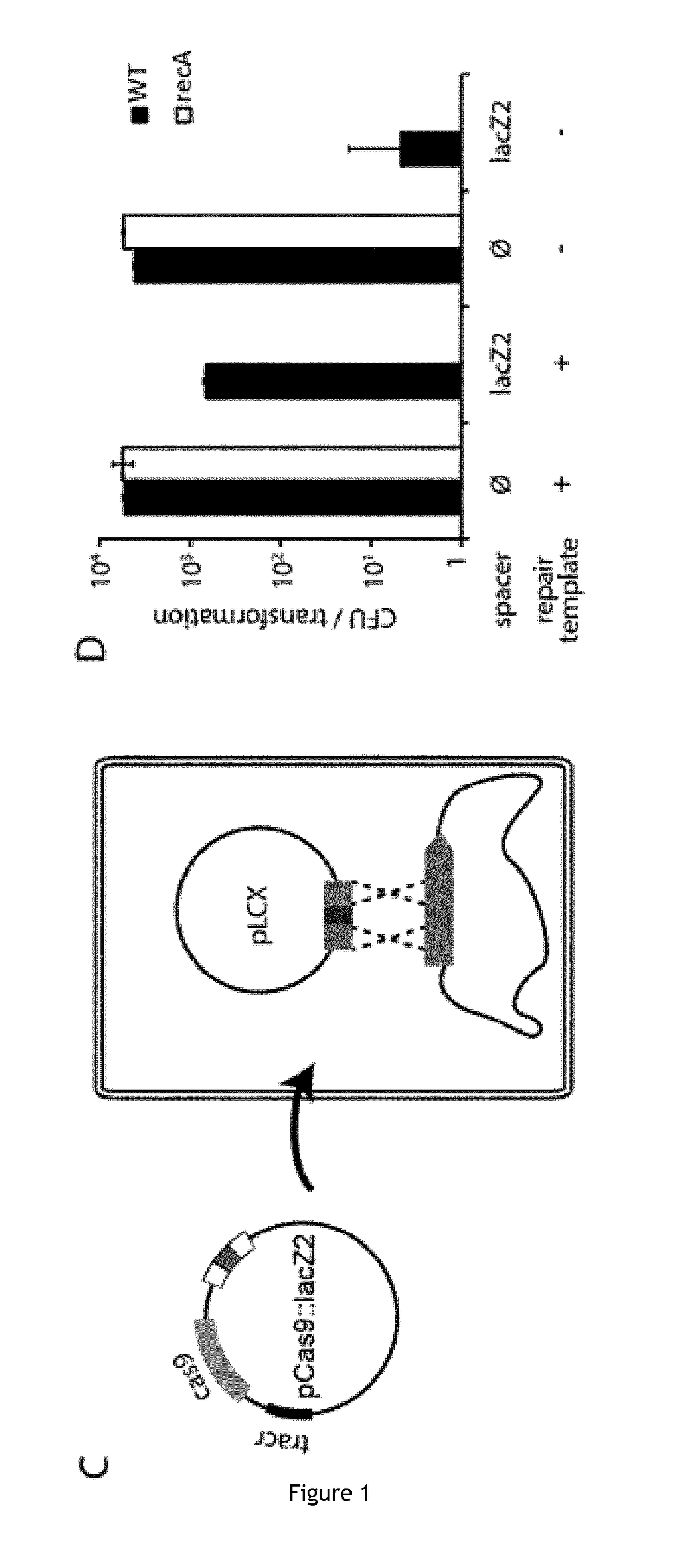
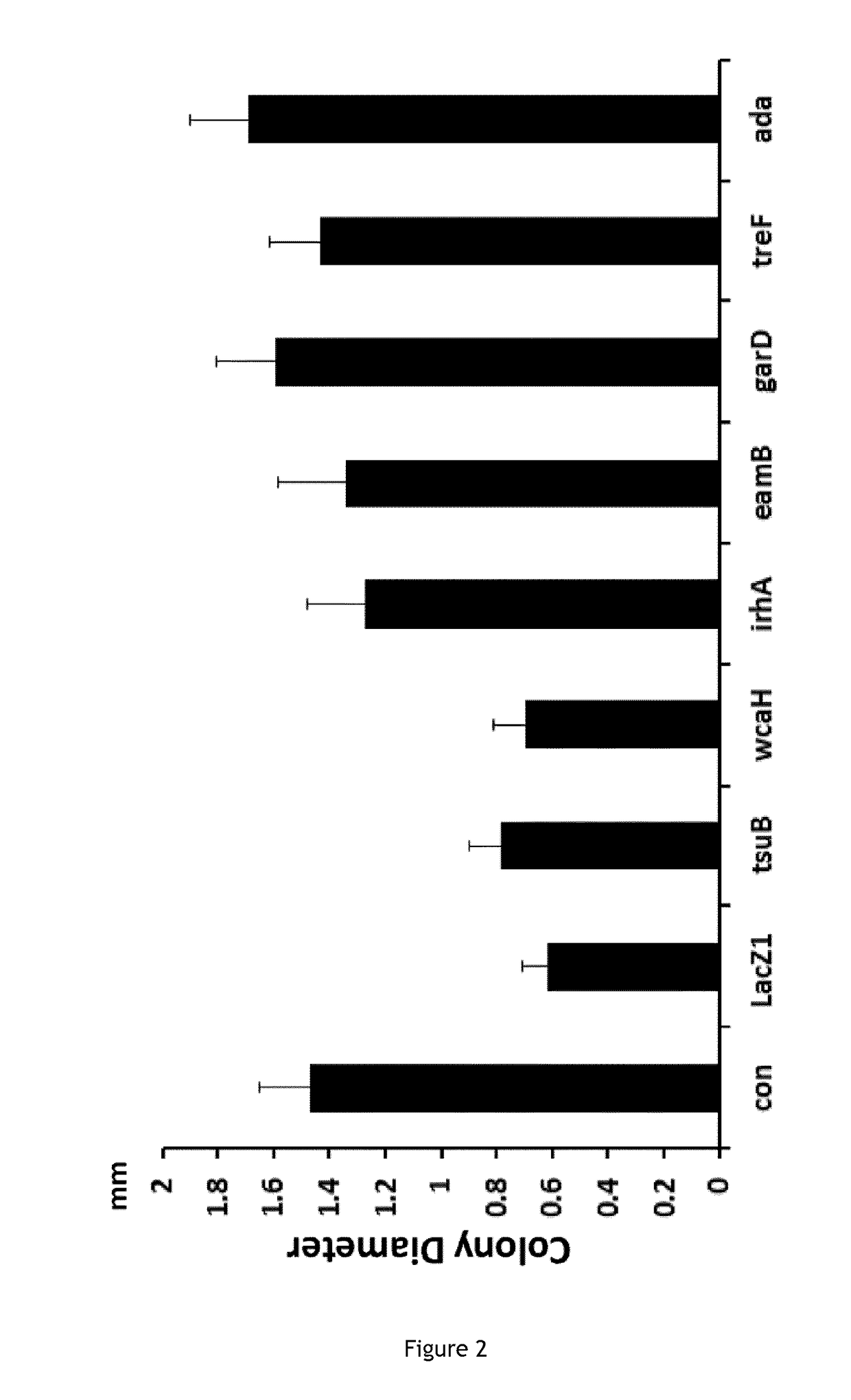
The invention relates to the improvement of endonuclease-based antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair of double-strand break(s) (DSB(s)) in prokaryotic cells. In this respect, the invention especially concerns a method involving blocking DNA repair after a nucleic acid has been submitted to DSB, in particular by a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) associated programmable double-strand endonuclease. The invention particularly relates to the use of an exogenous molecule that inhibits DNA repair, preferably a protein that binds to the ends of the double-stranded break to block DSB repair. The invention also relates to vectors, particularly phagemids and plasmids, comprising nucleic acids encoding nucleases and Gam proteins, and a pharmaceutical composition and a product containing these vectors and their application.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties
InactiveUS20060115874A1Valid choiceHigh affinity bindingVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsEnrichment methodsAntibody fragments
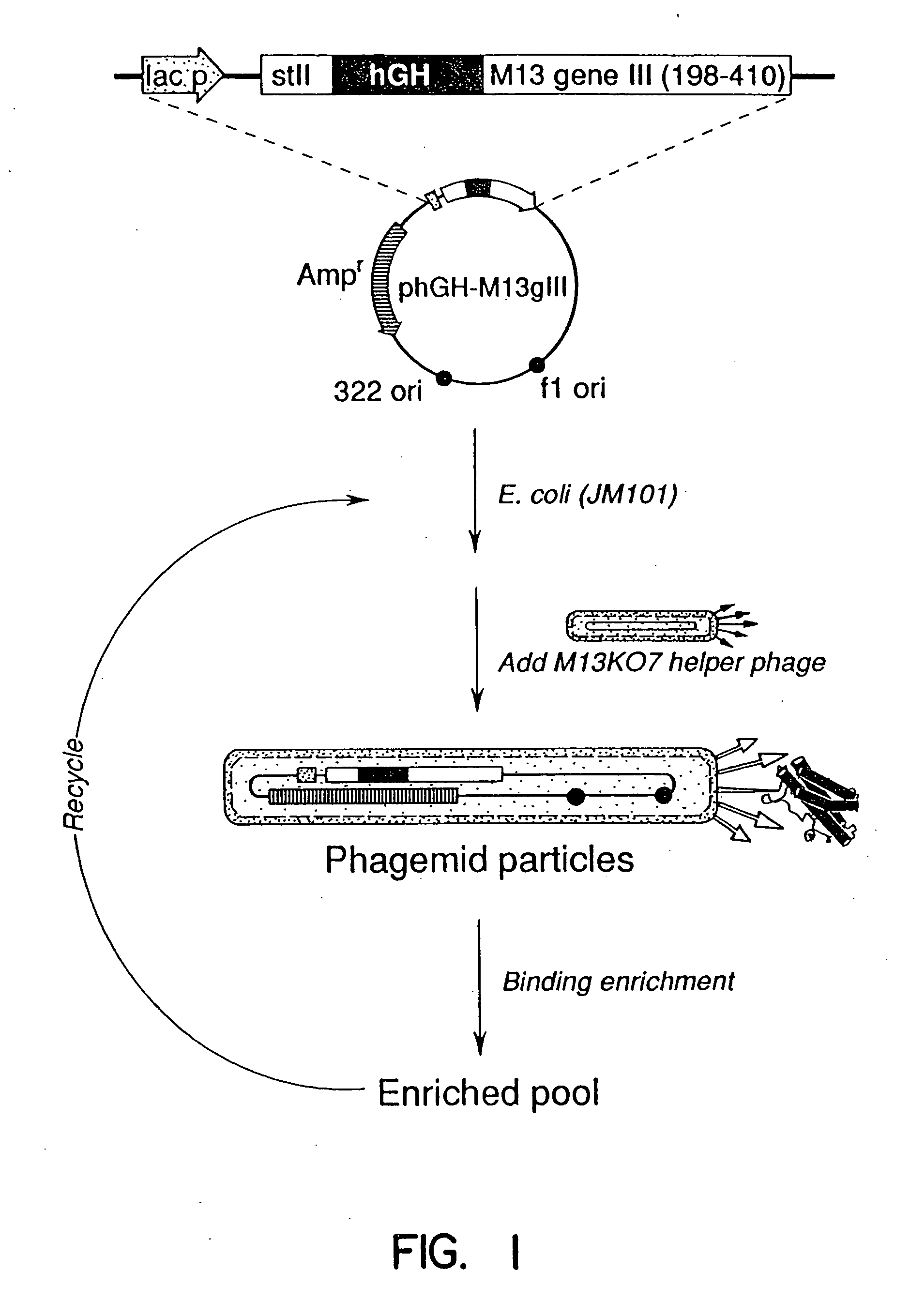
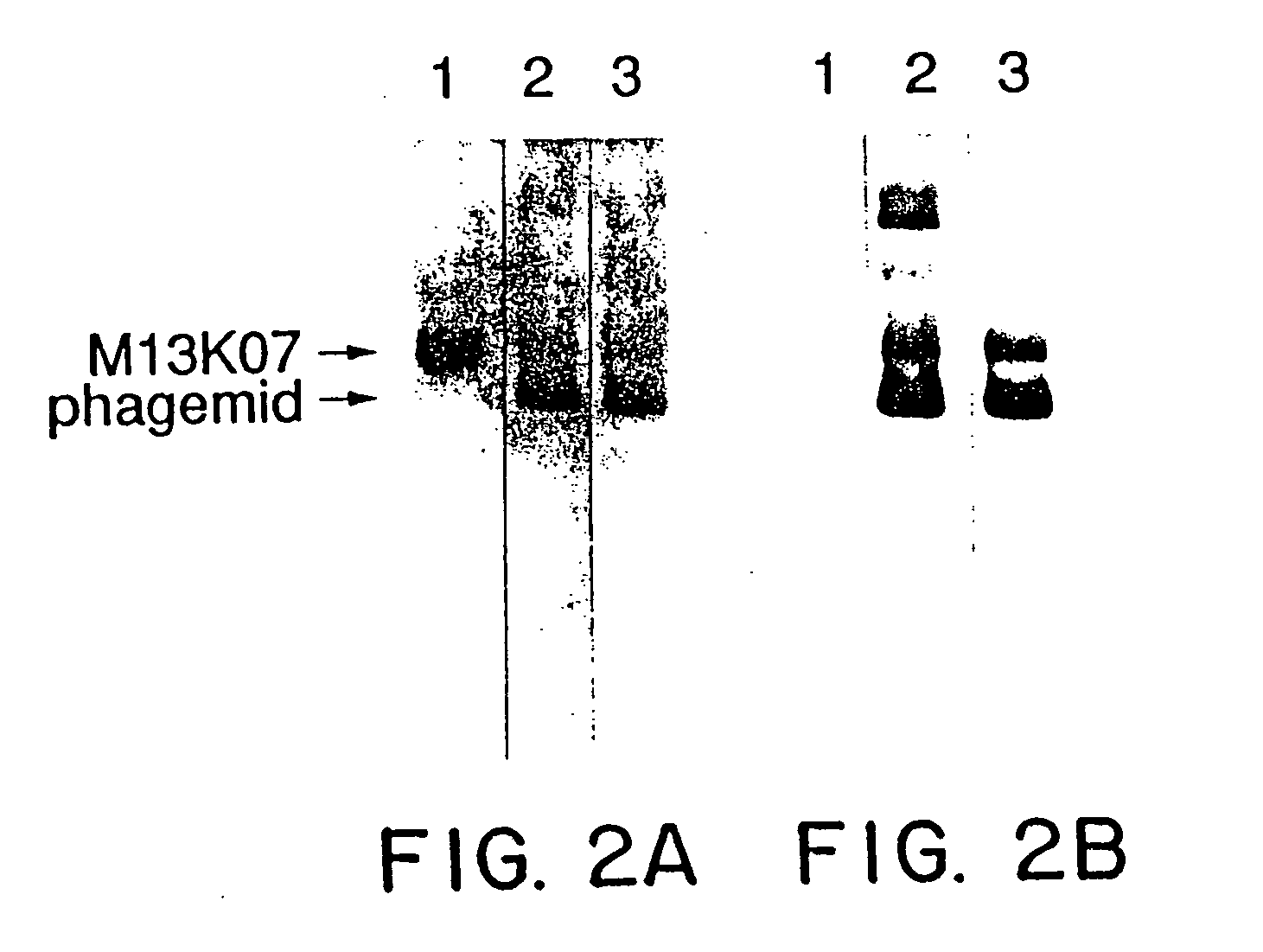
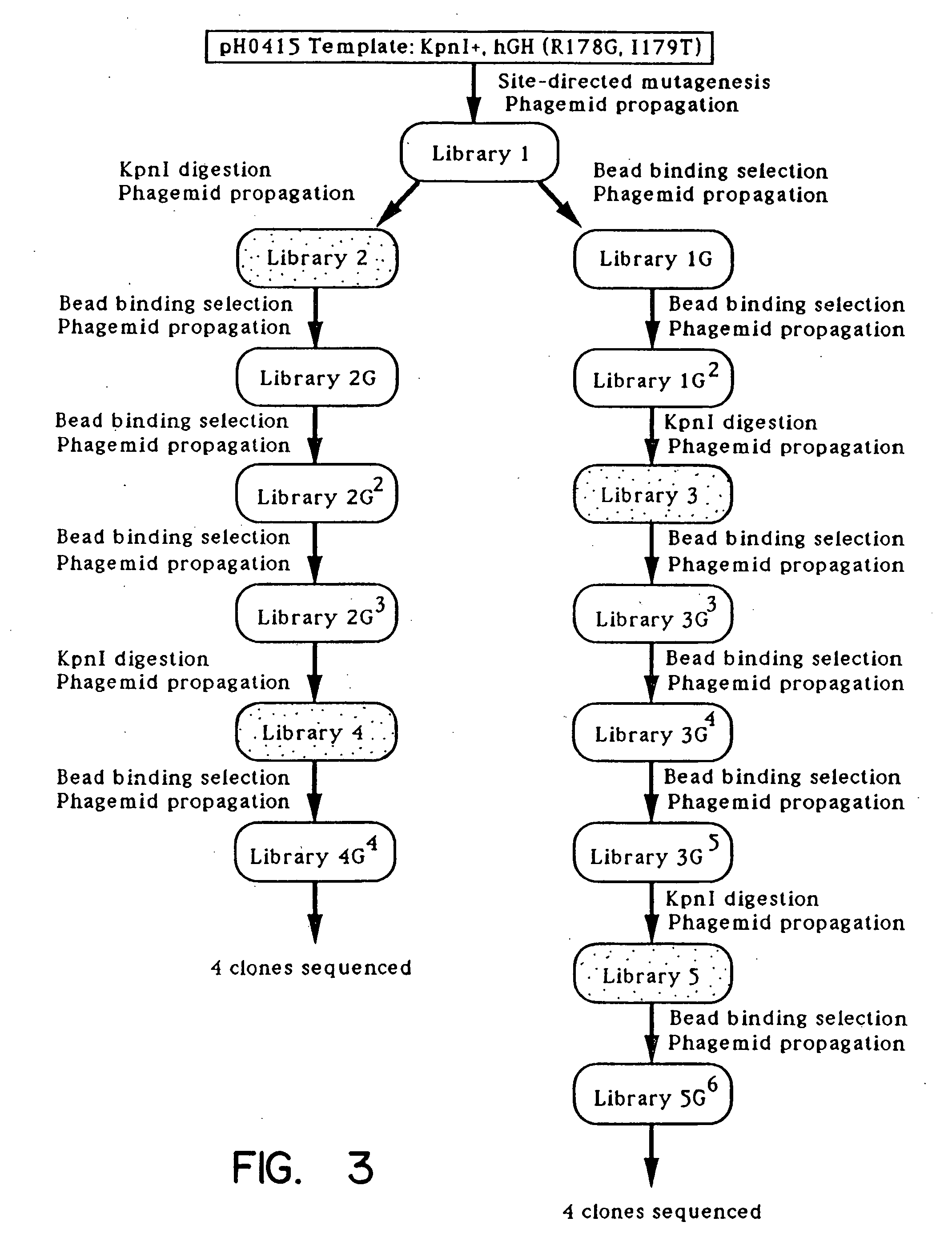
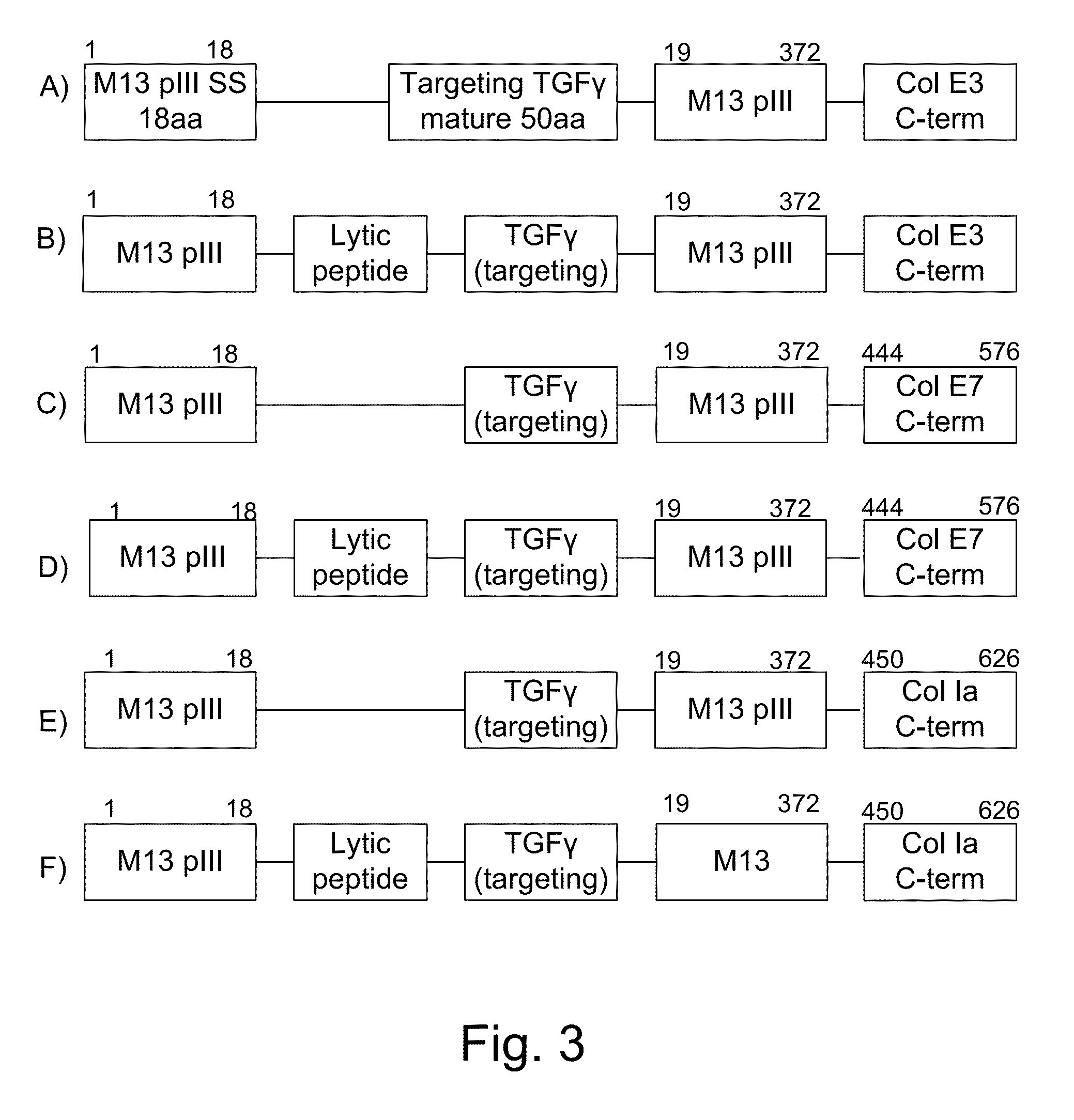
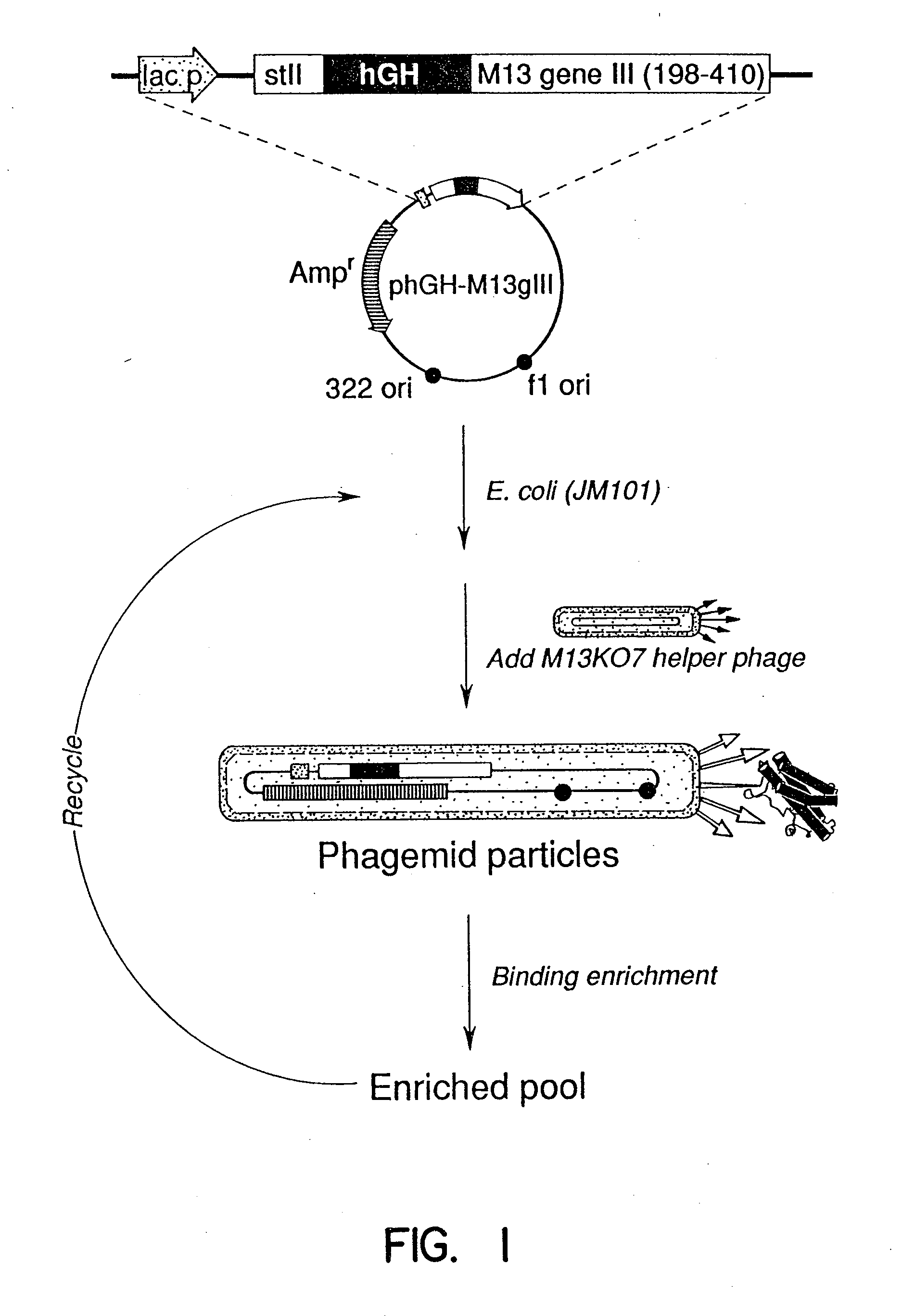
A method for selecting novel proteins such as growth hormone and antibody fragment variants having altered binding properties for their respective receptor molecules is provided. The method comprises fusing a gene encoding a protein of interest to the carboxy terminal domain of the gene III coat protein of the filamentous phage M13. The gene fusion is mutated to form a library of structurally related fusion proteins that are expressed in low quantity on the surface of a phagemid particle. Biological selection and screening are employed to identify novel ligands useful as drug candidates. Disclosed are preferred phagemid expression vectors and selected human growth hormone variants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs
InactiveUS7662557B2Simple procedureSpeedImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic diversityDna encoding
A member of a specific binding pair (sbp) is identified by expressing DNA encoding a genetically diverse population of such sbp members in recombinant host cells in which the sbp members are displayed in functional form at the surface of a secreted recombinant genetic display package (rgdp) containing DNA encoding the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof, by virtue of the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof being expressed as a fusion with a capsid component of the rgdp. The displayed sbps may be selected by affinity with a complementary sbp member, and the DNA recovered from selected rgdps for expression of the selected sbp members. A phagemid may be used as an expression vector, with said capsid fusion helping to package the phagemid DNA.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Phage Display Using Cotranslational Translocation of Fusion Polypeptides
ActiveUS20110118146A1Difficult to displayAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganism librariesSignal recognition particleCDNA library
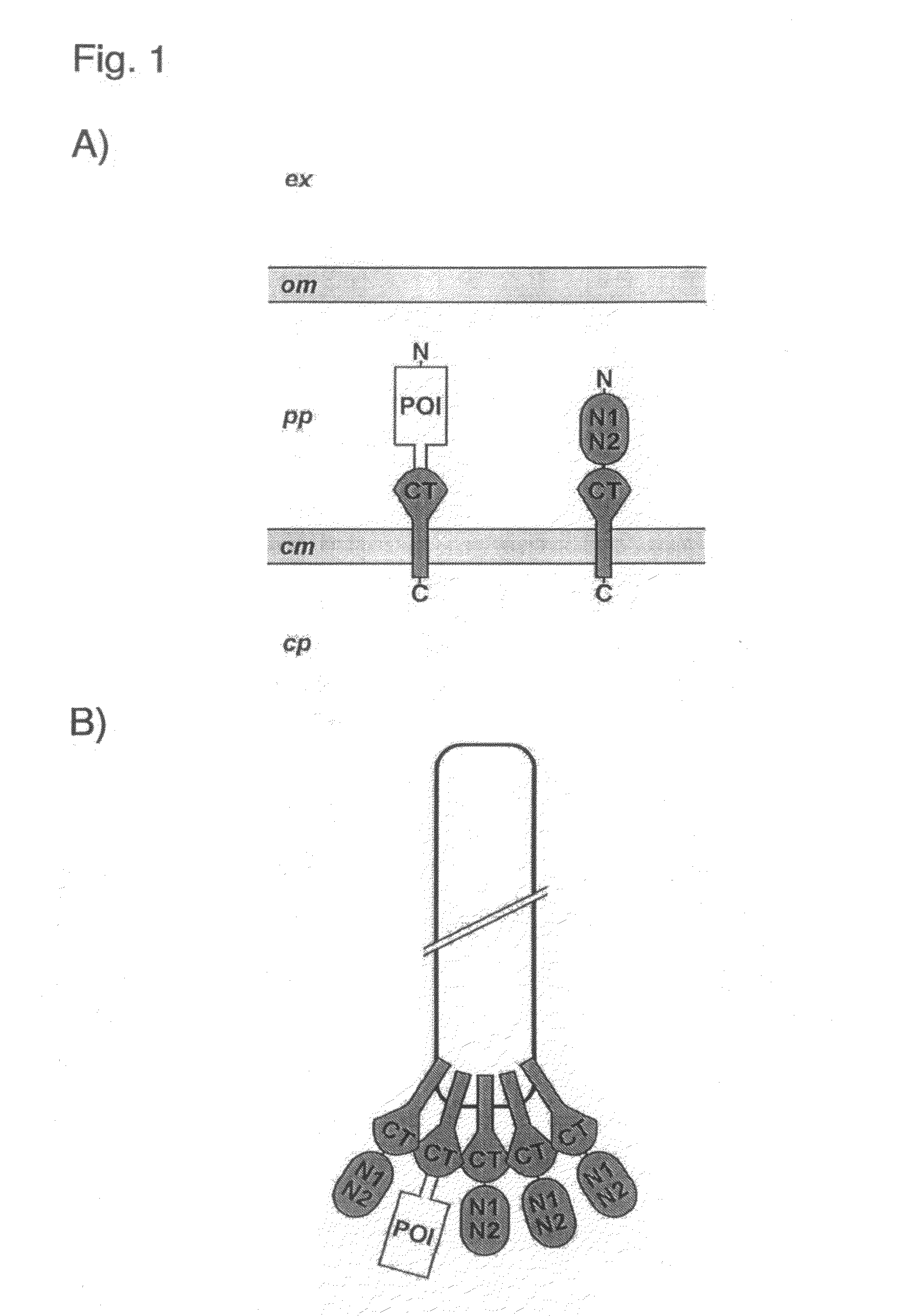
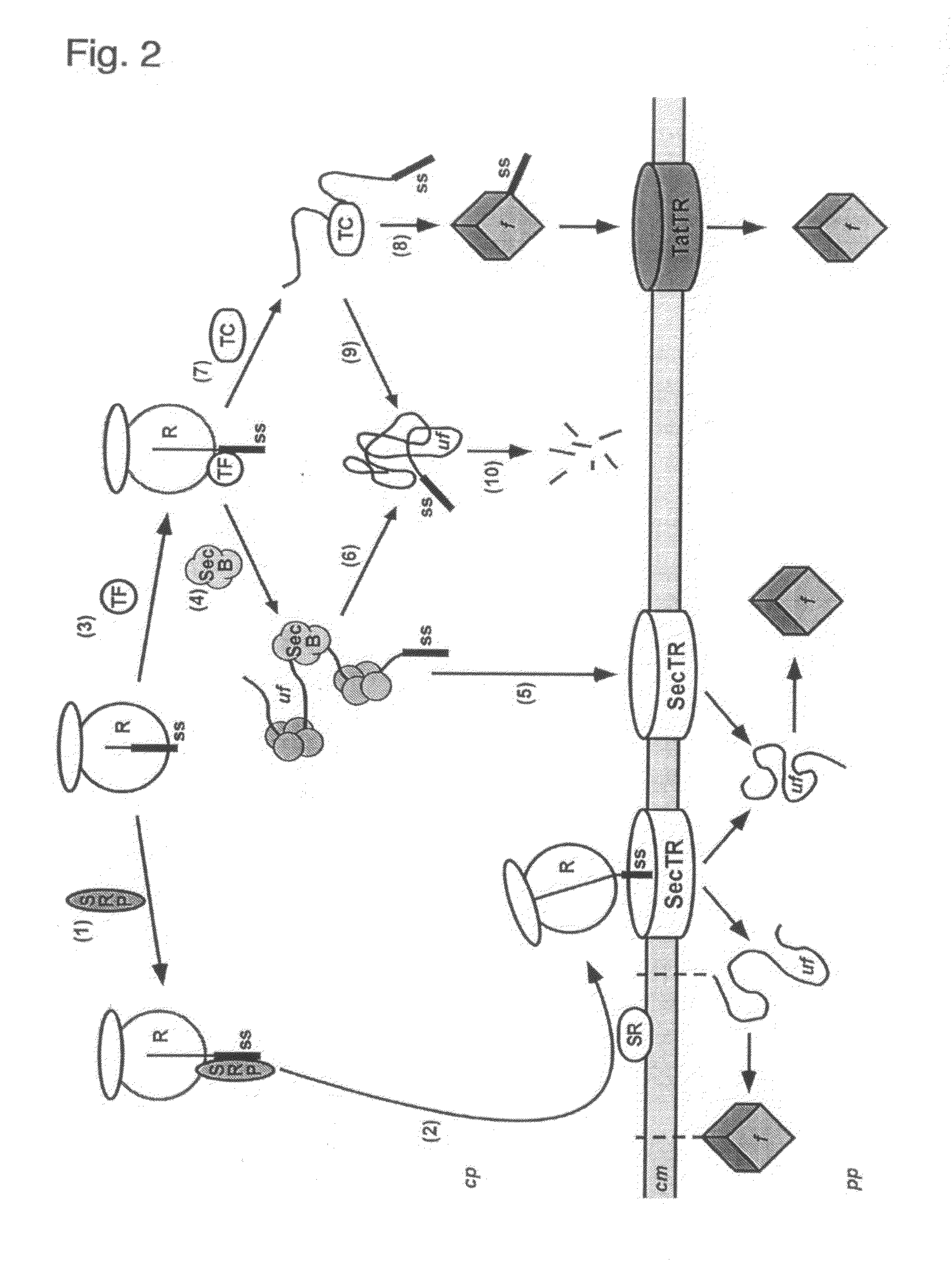
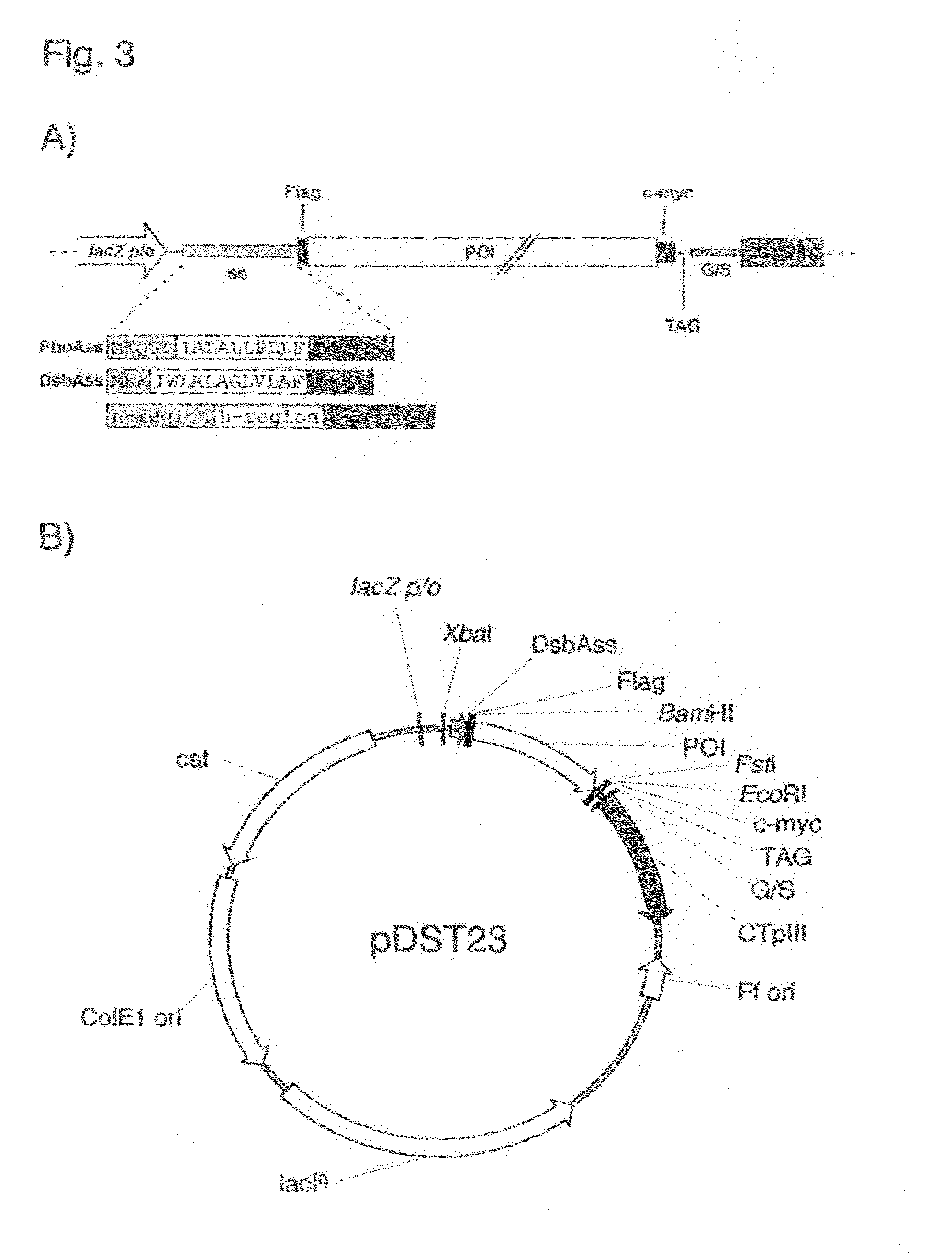
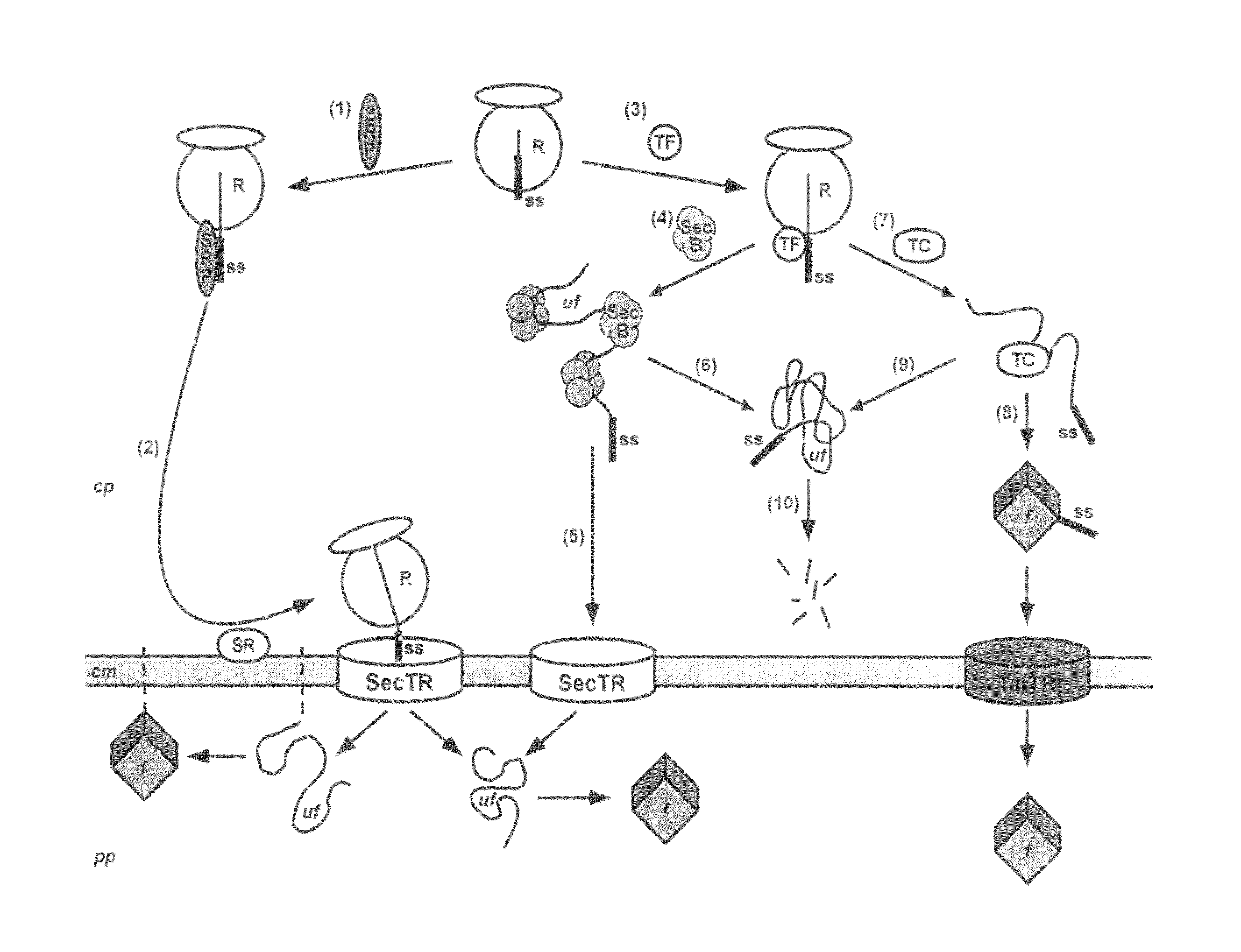
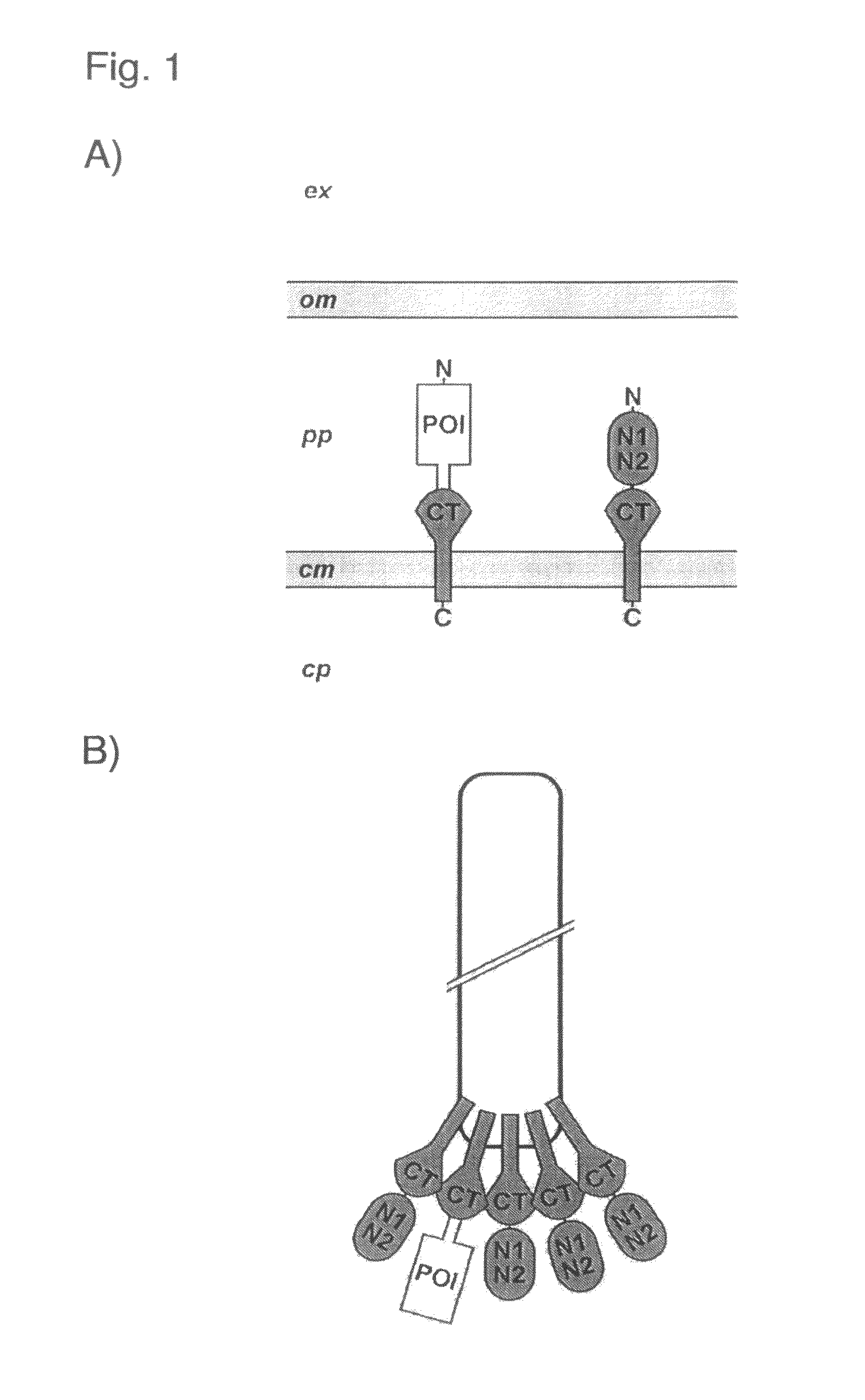
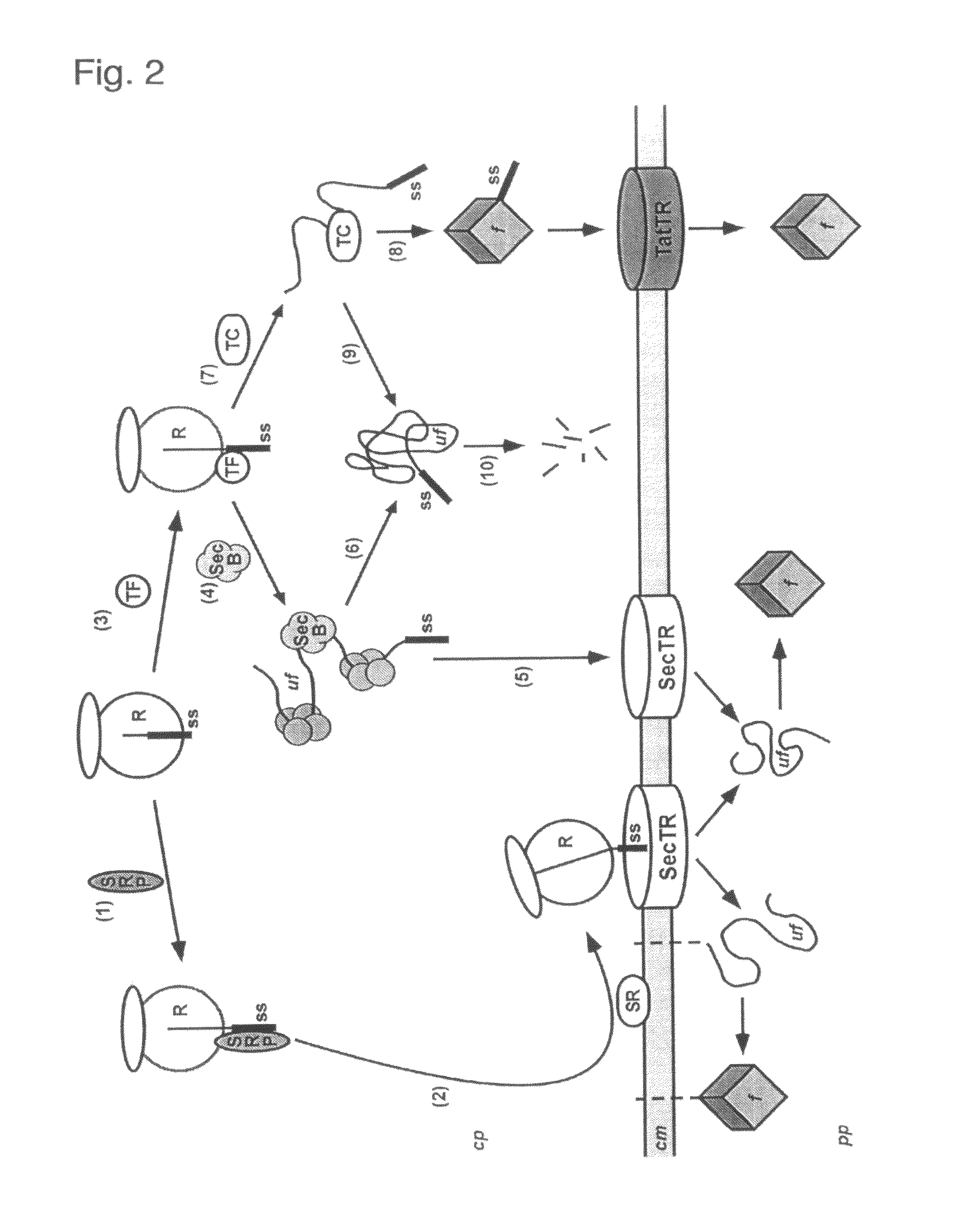
The present invention relates to a filamentous phage display method wherein the polypeptides of interest displayed on the phage particle are cotranslationally translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-negative bacteria based on the signal recognition particle pathway. This method is particularly suitable for polypeptides, which are known to be difficult to display on phages, and for proteins of cDNA libraries and other combinatorial libraries, in particular when derived from very fast folding, stable protein scaffolds. The invention further relates to phage or phagemid vectors useful in the method comprising a gene construct coding for a fusion polypeptide comprising the polypeptide to be displayed on the phage particle and an N-terminal signal sequence promoting cotranslational translocation.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
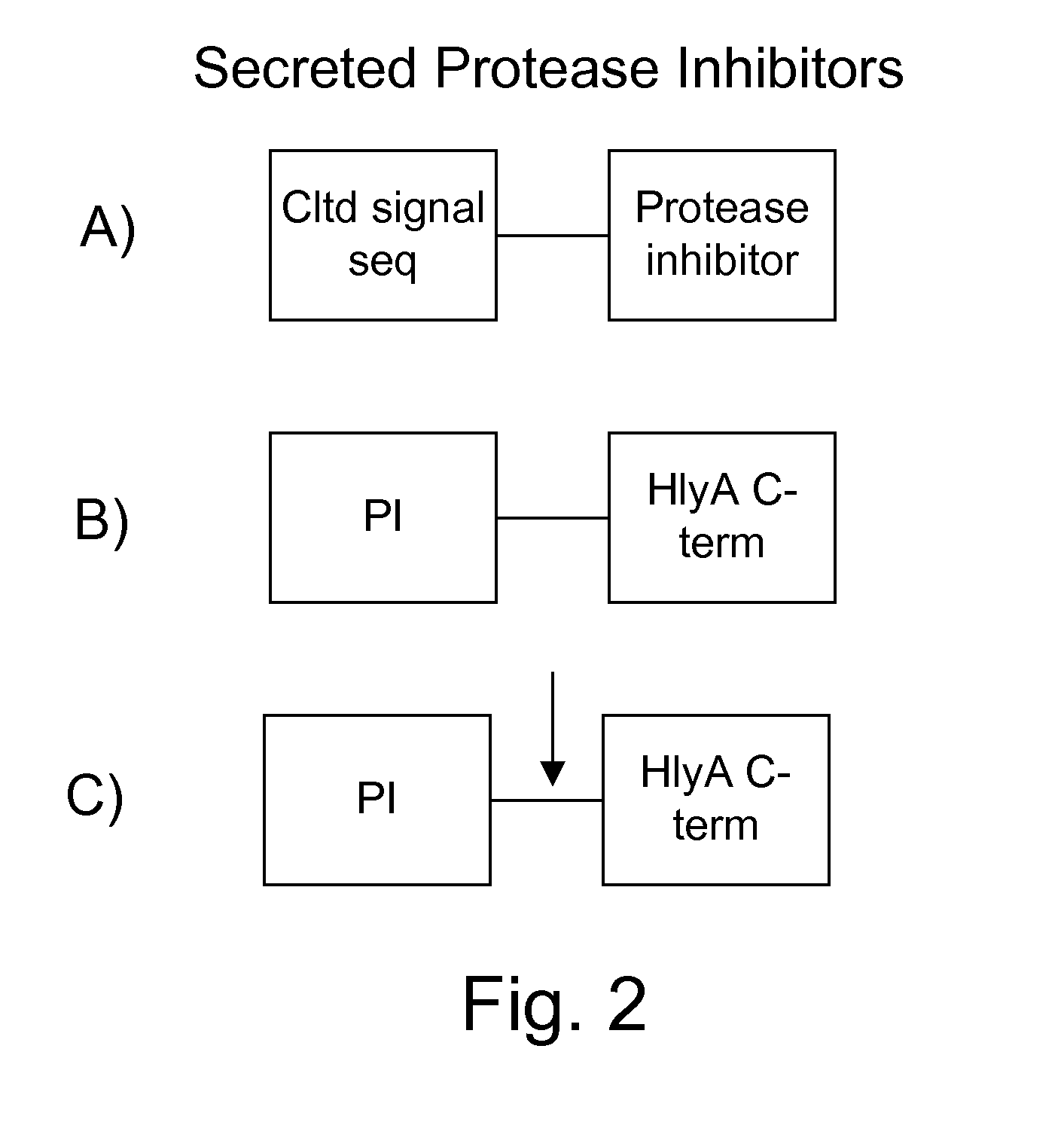
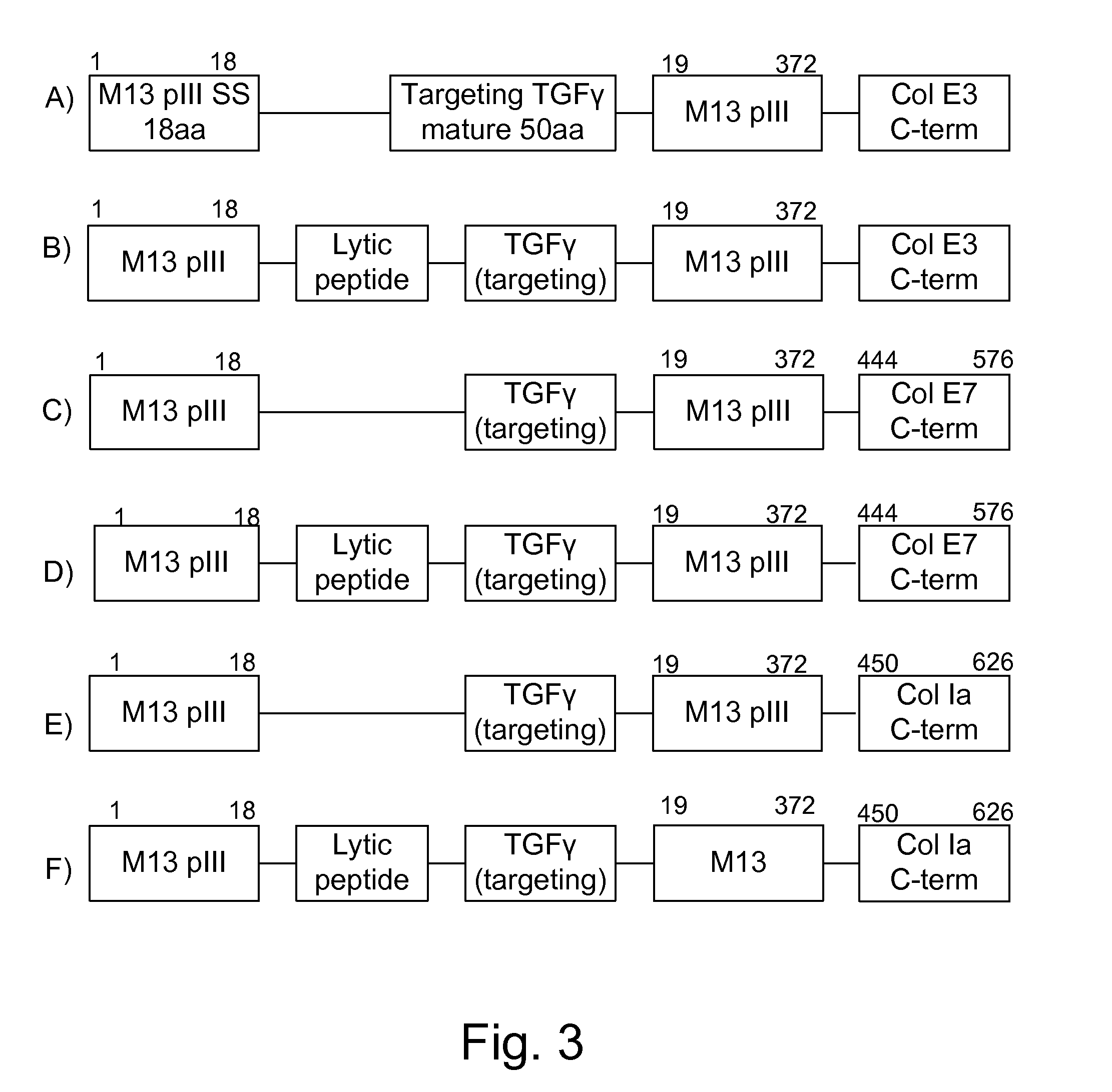
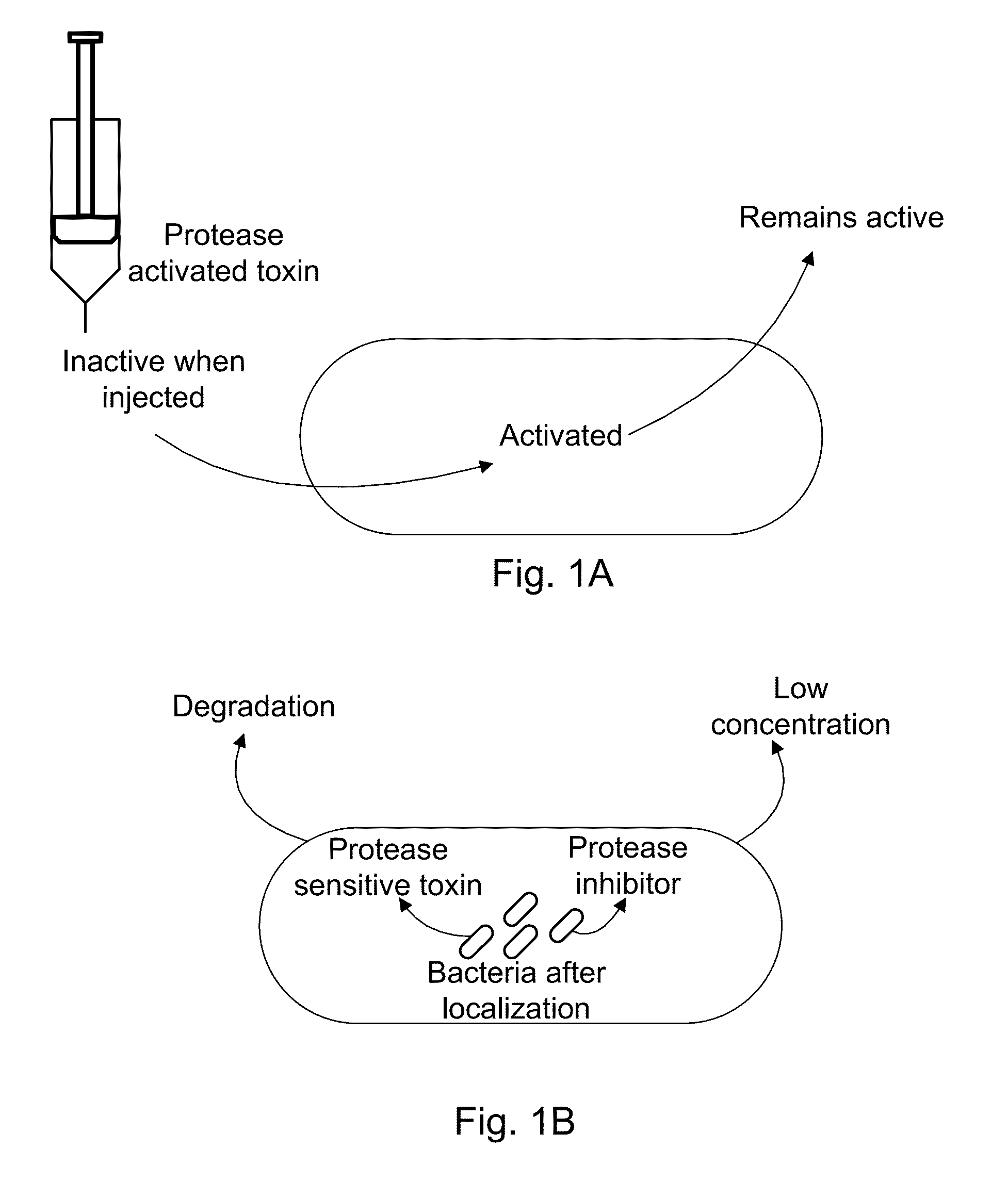
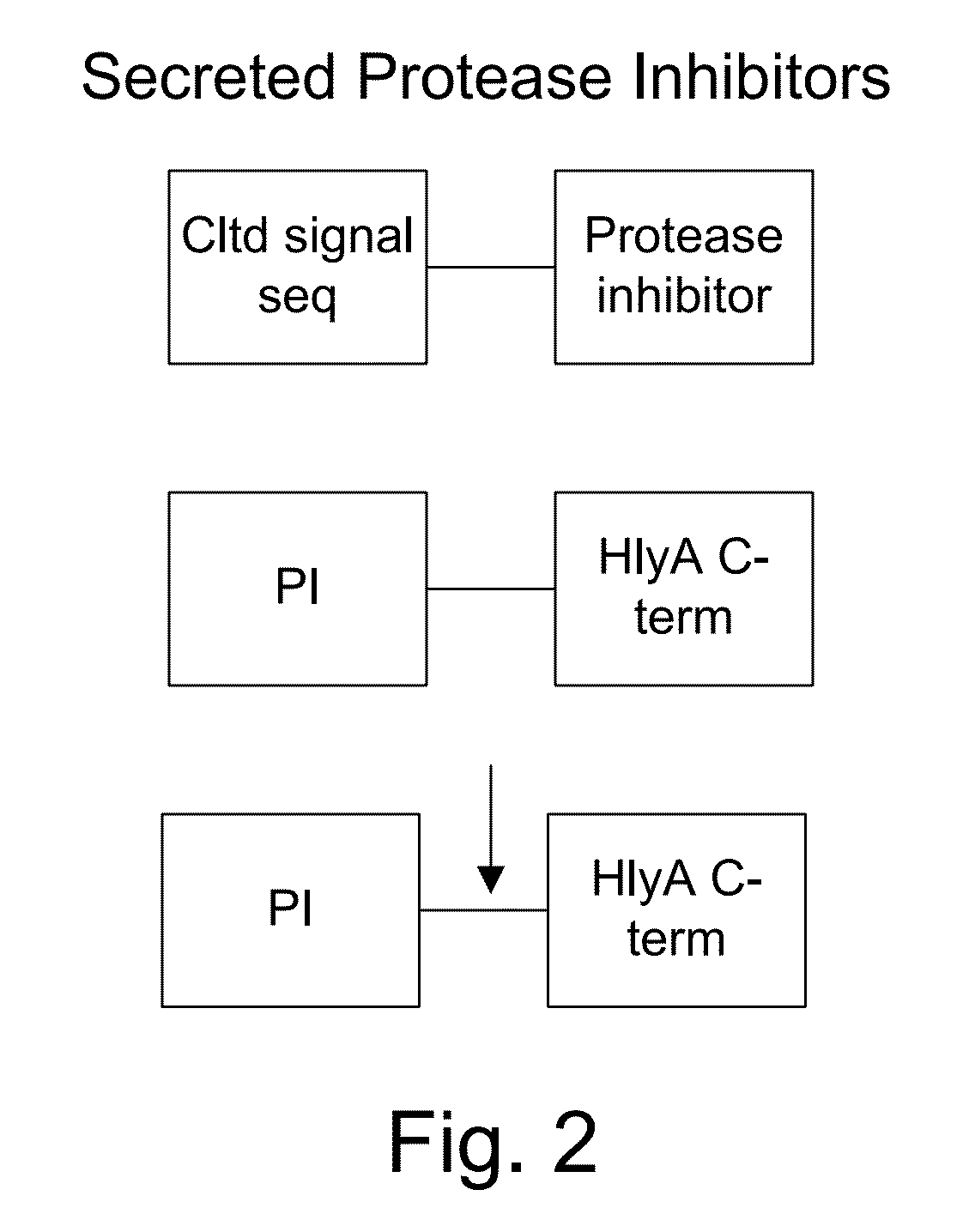
Protease sensitivity expression system
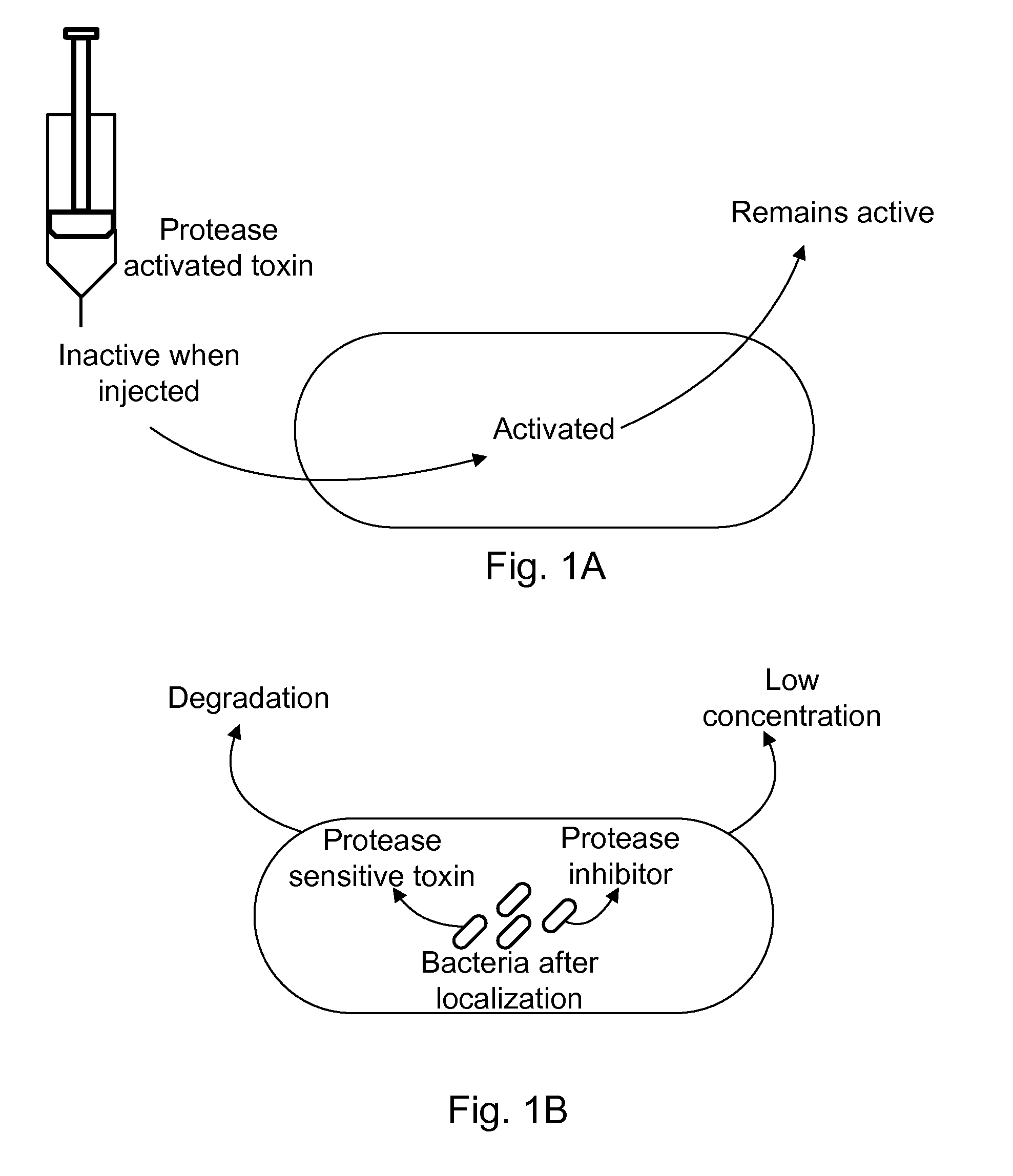
The present invention uses co-expression of protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents that results in their localized production within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. Inactivation is also accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic construct for proteases, preferably those that are under-expressed within the target tissue yet present in non-target tissues within the body, resulting in therapeutic activity within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria are also described. The chimeric proteins include chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells and cells of the immune system. Novel combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria capable of delivering phage / phagemids expression cassettes for DNA and RNA-based therapeutics are also described.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system and method improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins and phage and phagemids delivered by bacteria
The present invention uses co-expression of protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents that results in their localized production within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. Inactivation is also accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic construct for proteases, preferably those that are under-expressed within the target tissue yet present in non-target tissues within the body, resulting in therapeutic activity within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria are also described. The chimeric proteins include chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells and cells of the immune system. Novel combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria capable of delivering phage / phagemids expression cassettes for DNA and RNA-based therapeutics are also described.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties
InactiveUS20080038717A1Integrity of the rigid secondary structuresPreserve integrityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatotropic hormoneAntibody fragments
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Microbial production of pure single stranded nucleic acids
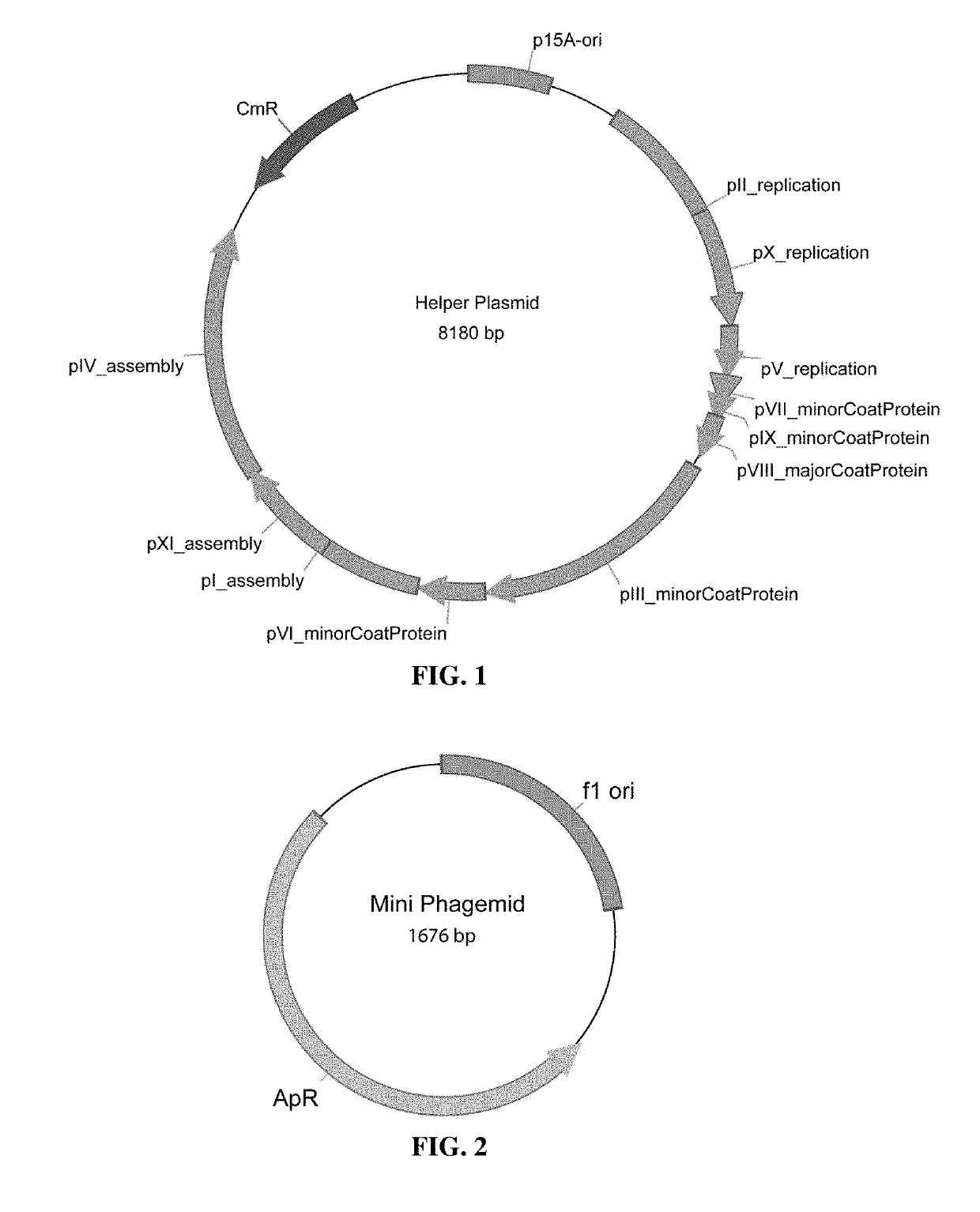
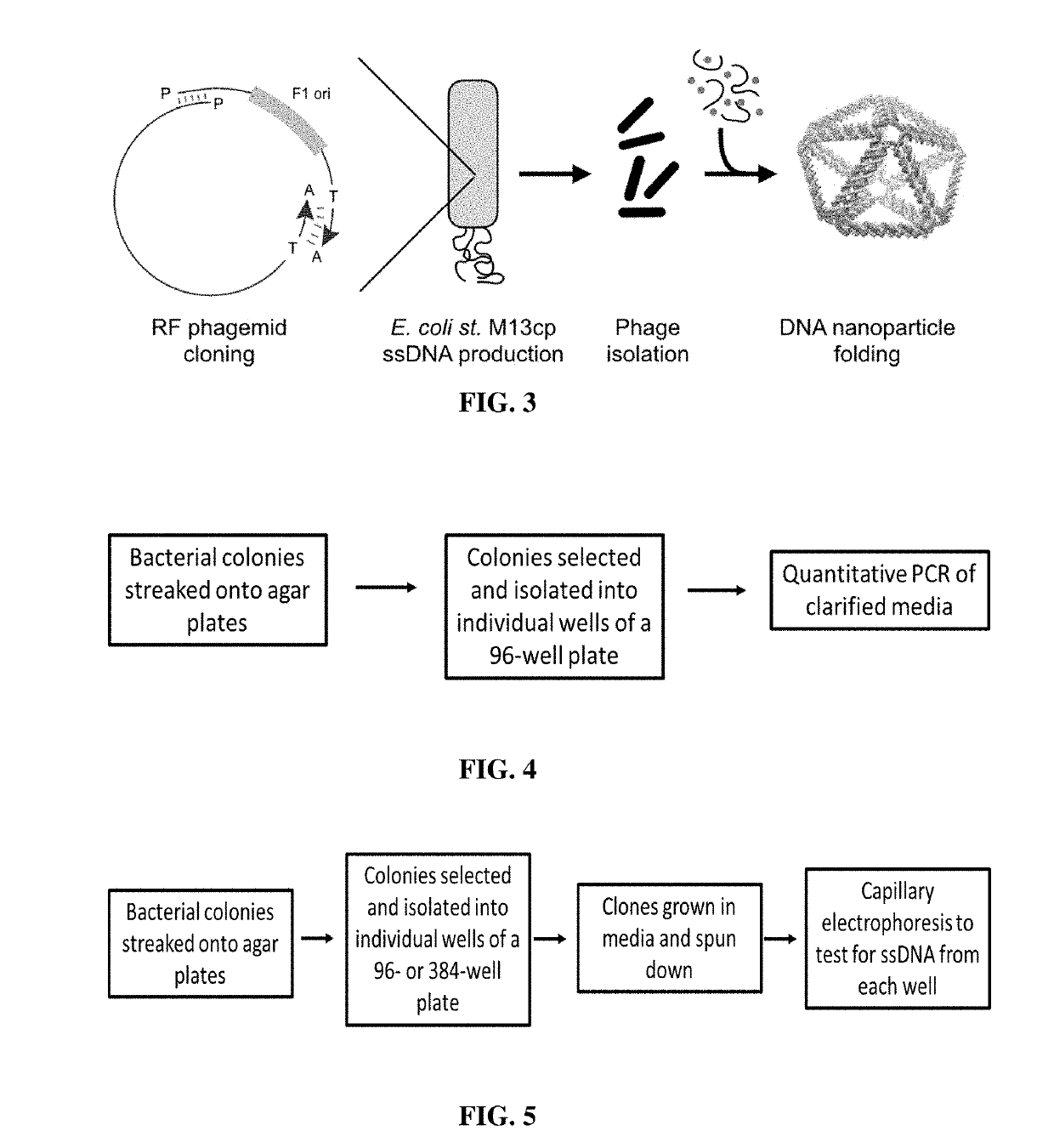
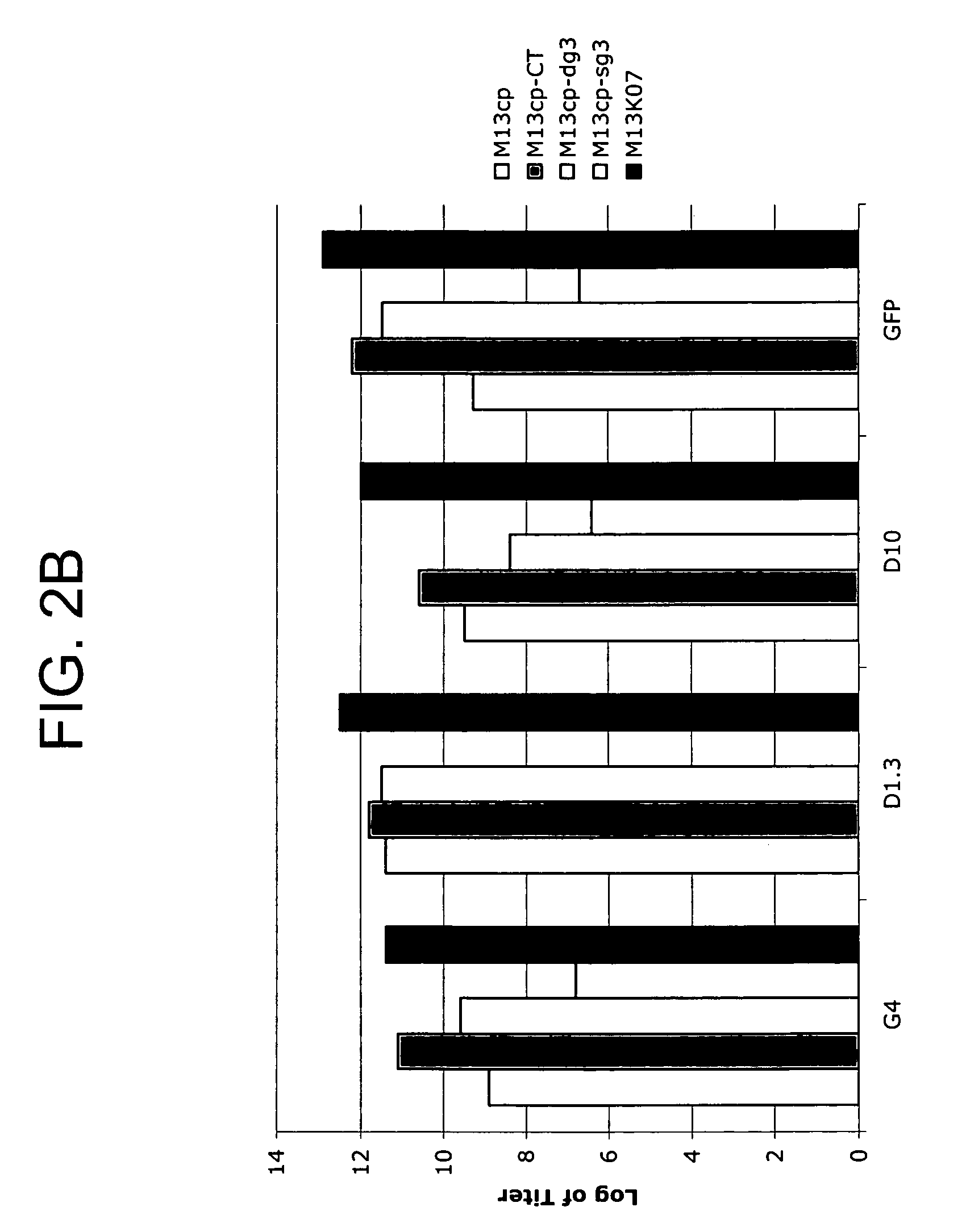
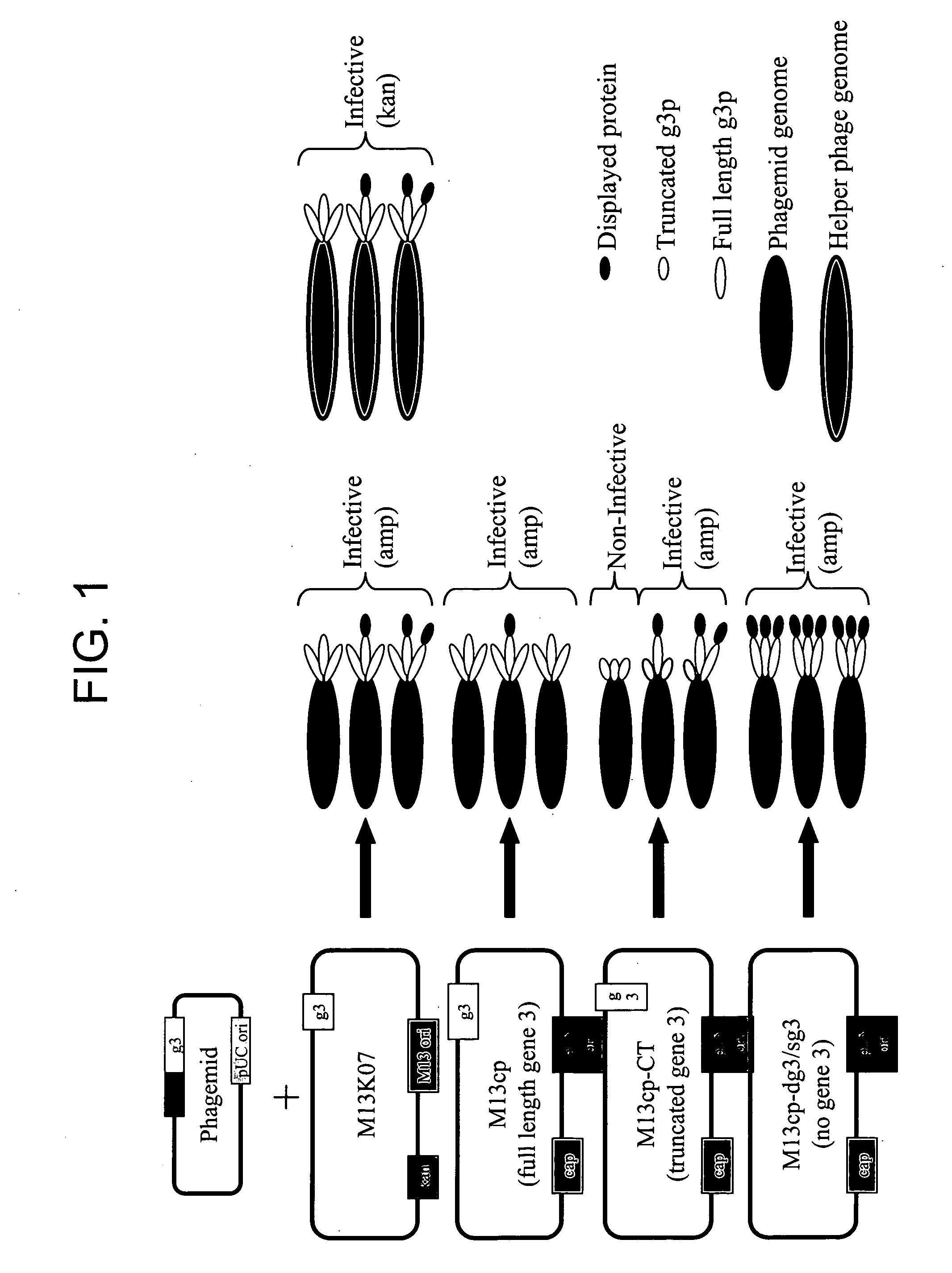
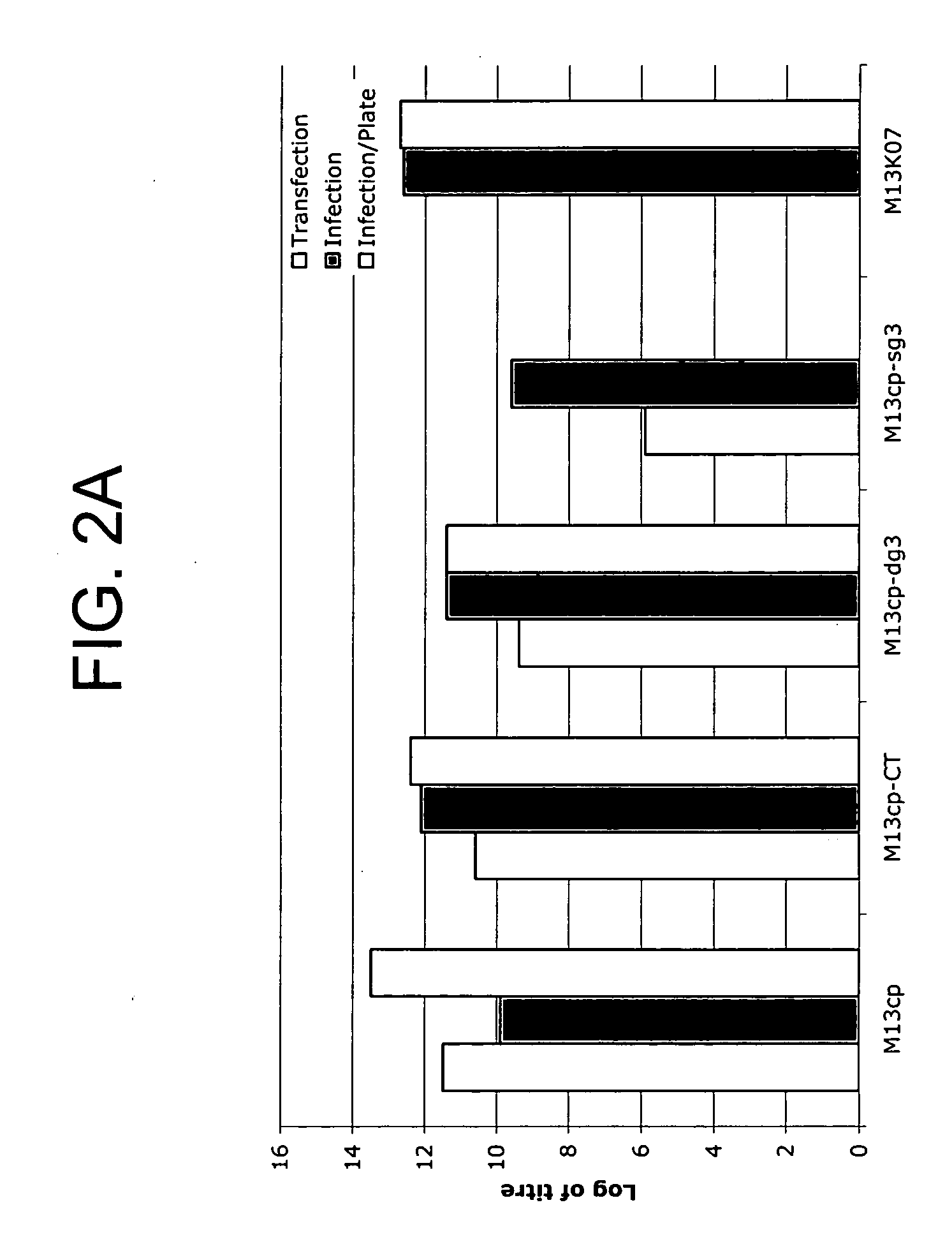
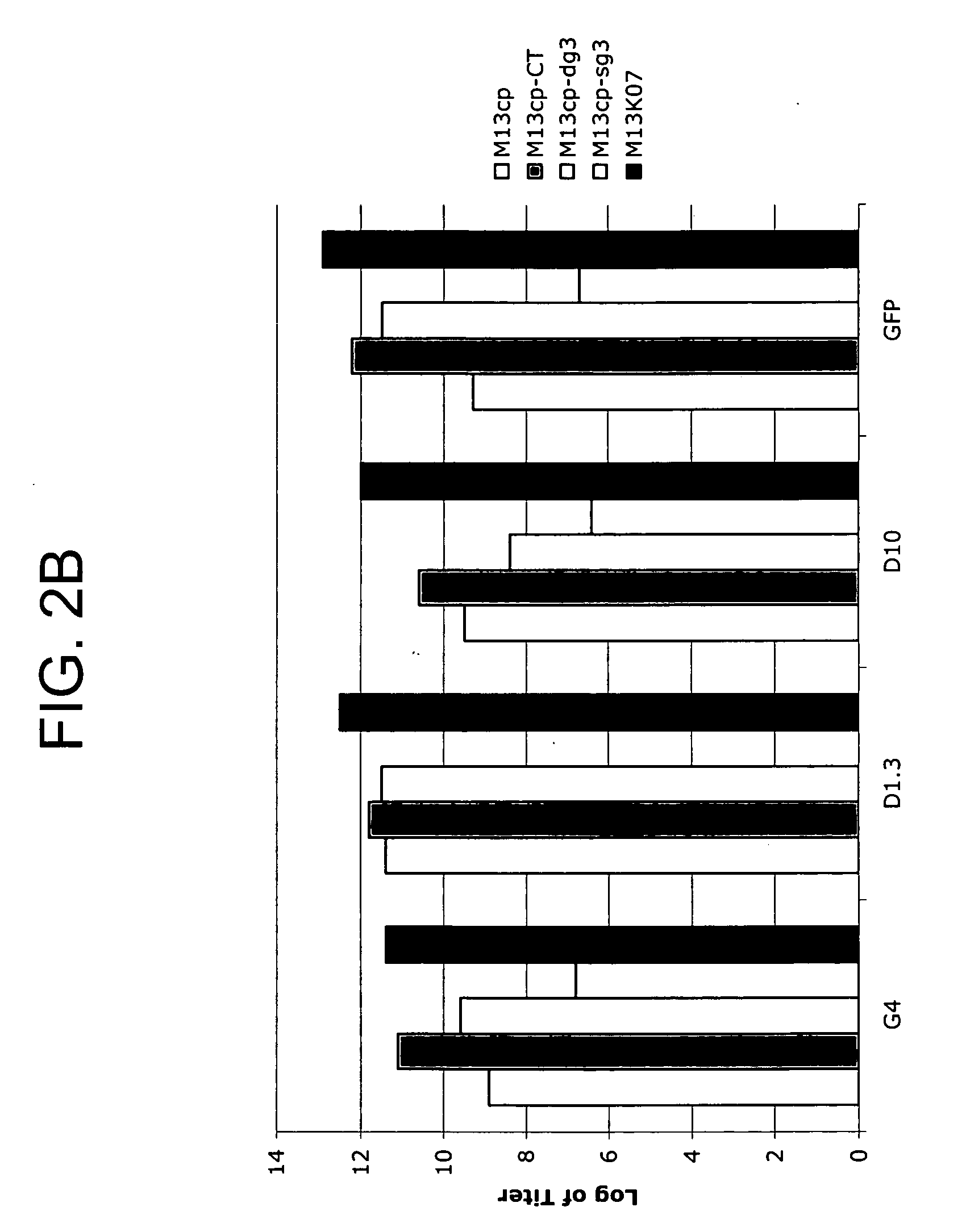
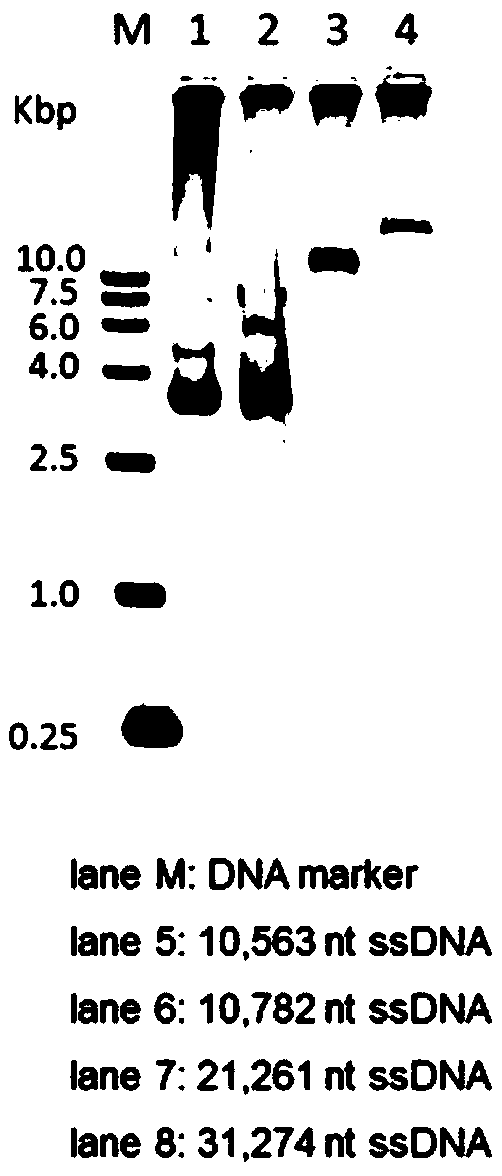
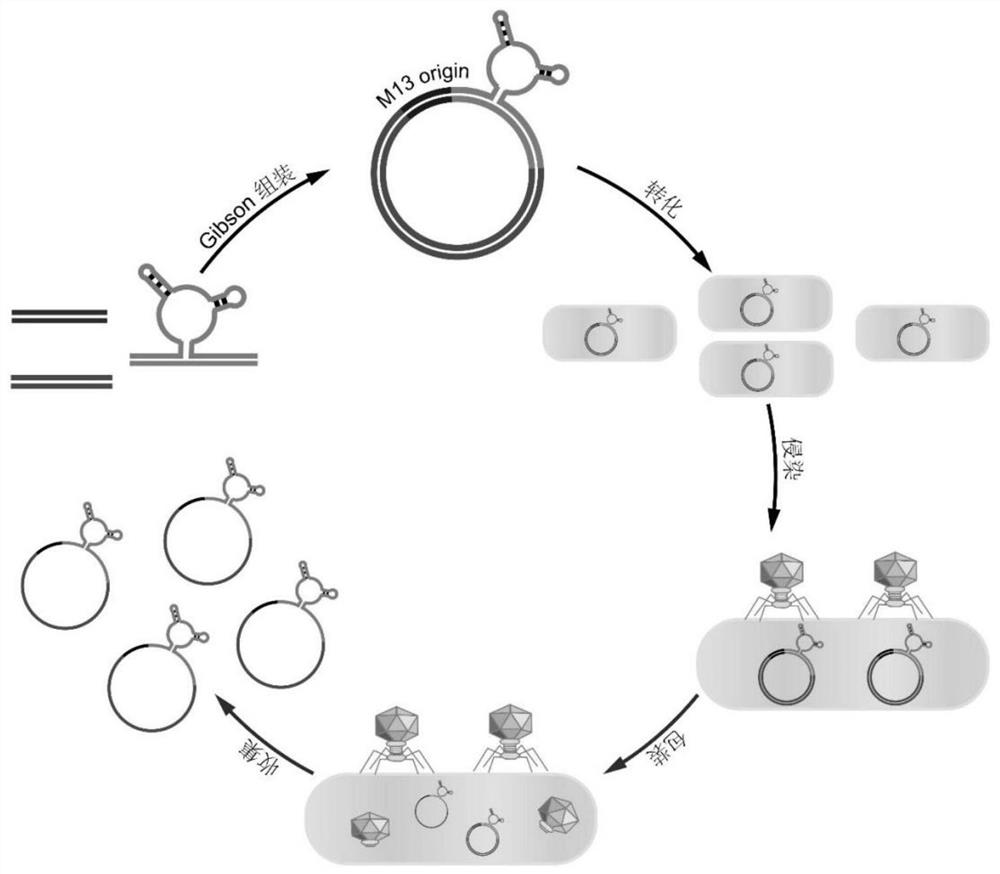
Methods and compositions for bacterial production of pure single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) composed of custom sequence and size have been developed. The methods enable scalability and bio-orthogonality in applications of scaffolded DNA origami, offering one-step purification of large quantities of pure ssDNA amendable for immediate folding of DNA nanoparticles. The methods produce pure ssDNA directly from bacteria. In some embodiments the E. coli helper strain M13cp combined with a phagemid carrying only an f1 -origin allows for, without the need for additional purification from contaminating dsDNA. This system is useful for generalized circular ssDNA synthesis, and here is applied to the assembly of DNA nanoparticles folded both in vitro and direct from phage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Phage display using cotranslational translocation of fusion polypeptides
ActiveUS8846577B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganism librariesSignal recognition particleCDNA library
The present invention relates to a filamentous phage display method wherein the polypeptides of interest displayed on the phage particle are cotranslationally translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-negative bacteria based on the signal recognition particle pathway. This method is particularly suitable for polypeptides, which are known to be difficult to display on phages, and for proteins of cDNA libraries and other combinatorial libraries, in particular when derived from very fast folding, stable protein scaffolds. The invention further relates to phage or phagemid vectors useful in the method comprising a gene construct coding for a fusion polypeptide comprising the polypeptide to be displayed on the phage particle and an N-terminal signal sequence promoting cotranslational translocation.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Bacteria carrying bacteriophage and protease inhibitors for the treatment of disorders and methods of treatment
ActiveUS9593339B1Increase productivityGreat transcriptionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesBiology
The present invention uses co-expression of protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents including phage and phagemids delivering peptides, therapeutic antibodies, DNA and RNA-based therapeutics that results in treating inflammation of a variety of disorders including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease. The invention also provides bacteria that inhibit the growth of intestinal parasites such as worms, and deliver siRNA or miRNA that have specific anti-parasitic effects that results in the reduction or elimination of the parasite.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Single-chain antibody of broad-spectrum anti-p21ras protein and preparation method thereof
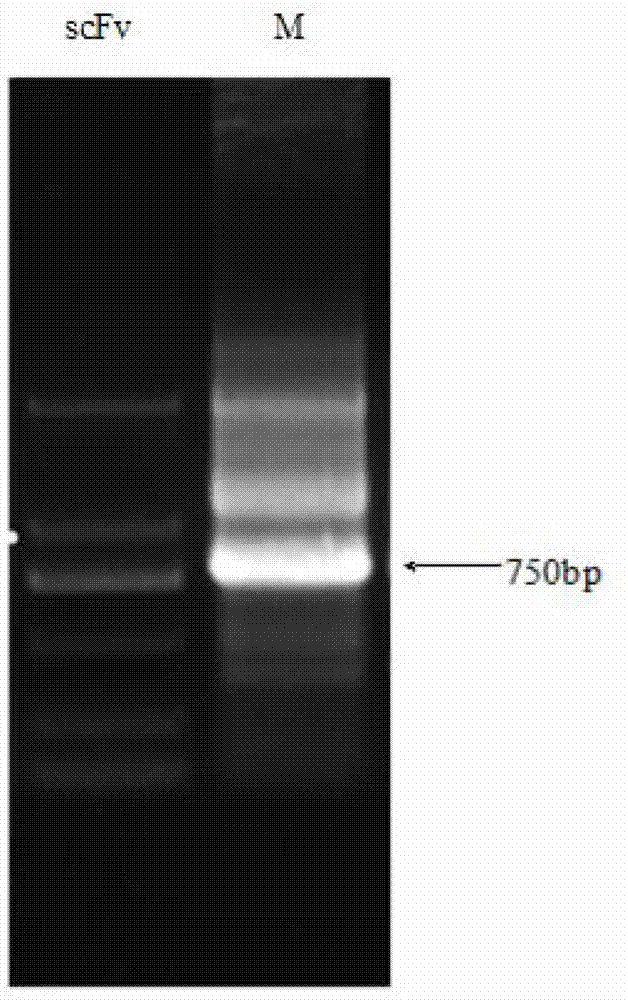
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody of broad-spectrum anti-p21ras protein and a preparation method thereof. The gene segment of the single-chain antibody is constructed by connecting light and heavy chain variable region gene segments of monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strains of the broad-spectrum anti-p21ras protein through flexible oligonucleotide linkers; the gene segment of the single-chain antibody is connected with a phagemid expression vector to construct recombinant phagemid; the recombinant phagemid is converted into amber inhibiting colon bacillus TG1 to perform fusion expression; the positive recombinant phagemid is identified by using indirect ELISA screening through phage library exhibition; the positive recombinant phagemid is converted into non-amber inhibiting colon bacillus BL21 (DE3) to perform soluble expression of the single-chain antibody; indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immune cell and tissue chemical experiments prove that the single-chain antibody for the soluble expression has strong binding specificity with three p21ras proteins of H-ras, K-ras and N-ras and high affinity; and the single-chain antibody is used for constructing small molecular antibodies such as intracellular antigens and the like and used for diagnosis and research of ras gene related tumors.
Owner:成都军区昆明总医院
Plasmids and packaging cell lines for use in phage display
The invention relates to a novel phagemid display system for packaging phagemid DNA into phagemid particles which completely avoids the use of helper phage. The system of the invention incorporates the use of bacterial packaging cell lines which have been transformed with helper plasmids containing all required phage proteins but not the packaging signals. The absence of packaging signals in these helper plasmids prevents their DNA from being packaged in the bacterial cell, which provides a number of significant advantages over the use of both standard and modified helper phage. Packaged phagemids expressing a protein or peptide of interest, in fusion with a phage coat protein such as g3p, are generated simply by transfecting phagemid into the packaging cell line.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Canine parvovirus single-domain antibody, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103665152ARealize large-scale preparationBiologically activeImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a canine parvovirus single-domain antibody, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The canine parvovirus single-domain antibody has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQIDNO.1. The preparation method comprises the steps: immunizing an alpaca by a canine parvovirus inactivated vaccine, and taking peripheral blood to obtain alpaca anti-canine parvovirus serum; extracting RNA in the peripheral blood, and carrying out reverse transcription to generate cDNA; utilizing specific primers for amplification, and purifying a VHH fragment; connecting the VHH fragment with a phagemid vector, transforming TG1, and constructing a canine parvovirus single-domain antibody library; and enriching the antibody library by utilizing a canine parvovirus structural protein VP2, introducing into an expression bacterial strain E.coil HB2151, and utilizing IPTG to induce the canine parvovirus single-domain antibody VHH having the biological activity to be expressed. The prepared canine parvovirus single-domain antibody has the detection activity of 15 [mu]g / ml and the detection sensitivity of 250 ng / ml, and can be used as drugs applied for treating dogs with canine parvovirus disease.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Plasmids and packaging cell lines for use in phage display
ActiveUS20070128728A1Simplified generationEliminate needBacteriaFermentationEukaryotic plasmidsCoat protein
The invention relates to a novel phagemid display system for packaging phagemid DNA into phagemid particles which completely avoids the use of helper phage. The system of the invention incorporates the use of bacterial packaging cell lines which have been transformed with helper plasmids containing all required phage proteins but not the packaging signals. The absence of packaging signals in these helper plasmids prevents their DNA from being packaged in the bacterial cell, which provides a number of significant advantages over the use of both standard and modified helper phage. Packaged phagemids expressing a protein or peptide of interest, in fusion with a phage coat protein such as g3p, are generated simply by transfecting phagemid into the packaging cell line.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Heterodimeric receptor libraries using phagemids
Filamentous phage comprising a matrix of cpVIII proteins encapsulating a genome encoding first and second polypeptides of an antogenously assembling receptor, such as an antibody, and a receptor comprised of the first and second polypeptides surface-integrated into the matrix via a filamentous phage coat protein membrane anchor domain fused to at least one of the polypeptides.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for preparing phase granule for displaying polypeptide
InactiveCN1884555AHigh level of presentationViruses/bacteriophagesHybrid peptidesPeptide displayCoat protein
This invention involves the phagemid in molecule biology field and medicine field. It is a preparation method of display peptide's phagemid. This method adopts the gene group plasmid of assistant phage fusion protein of coding foreign peptide and pIII coat protein, to co-transformation or successive-transformation F factor positive Isolates together with phagemid, so to obtain phagemid that display foreign peptide. The phagemid prepared by this method has high foreign peptide display level, and it is not necessarily prepare assistant phage so to simplified the process of preparation of assistant phage.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Antibody like protein
ActiveUS20160090400A1High throughput screeningPeptide librariesBacteriaADAMTS ProteinsNucleic acid sequencing
A general method and recombinant nucleic acid sequences, by means which the method selects a recombinant protein containing an FHA domain for binding a target molecule from a library proteins with a high-throughput method of creating protein variations within the FHA domain in non-conserved or non-structural sequences of the FHA scaffold, and the library may also be in the form of a phagemid or phage library wherein the ALP nucleic acid sequence is inserted into a vector capable of allowing the vector and expressed ALP protein from being virally packaged, and the recombinant nucleic acid sequences which are randomly mutated at varying non-conserved or non-structural FHA domain sequences.
Owner:IDEA ORCHARD LLC
Method for preparing PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) nanoantibody by immunizing alpacas with PD-L1 antigen
InactiveCN110256564ADifficult to identifyEvade captureMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSequence signalAntigen
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibodies and discloses a method for preparing PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) nanoantibody by immunizing alpacas with a PD-L1 antigen. The method comprises: designing two synthetic primers, amplifying by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to obtain sufficient target products for enzyme digestion, linking target fragments to a vector, converting, and carrying out screening and cloning; carrying out protein verifying and expressing; constructing an antibody library; displaying a VHH antibody library through an M13 bacteriophage display system which is composed of a pMECS phagemid vector, E. coli TG1 and an M13KO7 helper phage. In the phasmid vector pMECS, a sequence before a Pst I enzyme digestion site is a coding sequence for part of amino acids in first frame regions of pelB secretory signal peptides and antibodies; the pelB signal peptides can guide subsequent polypeptides secreted to periplasmic cavities; a sequence after a Not I enzyme digestion site is a coding sequence for HA and 6*His tags; the method is suitable for purification or detection of fusion proteins.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
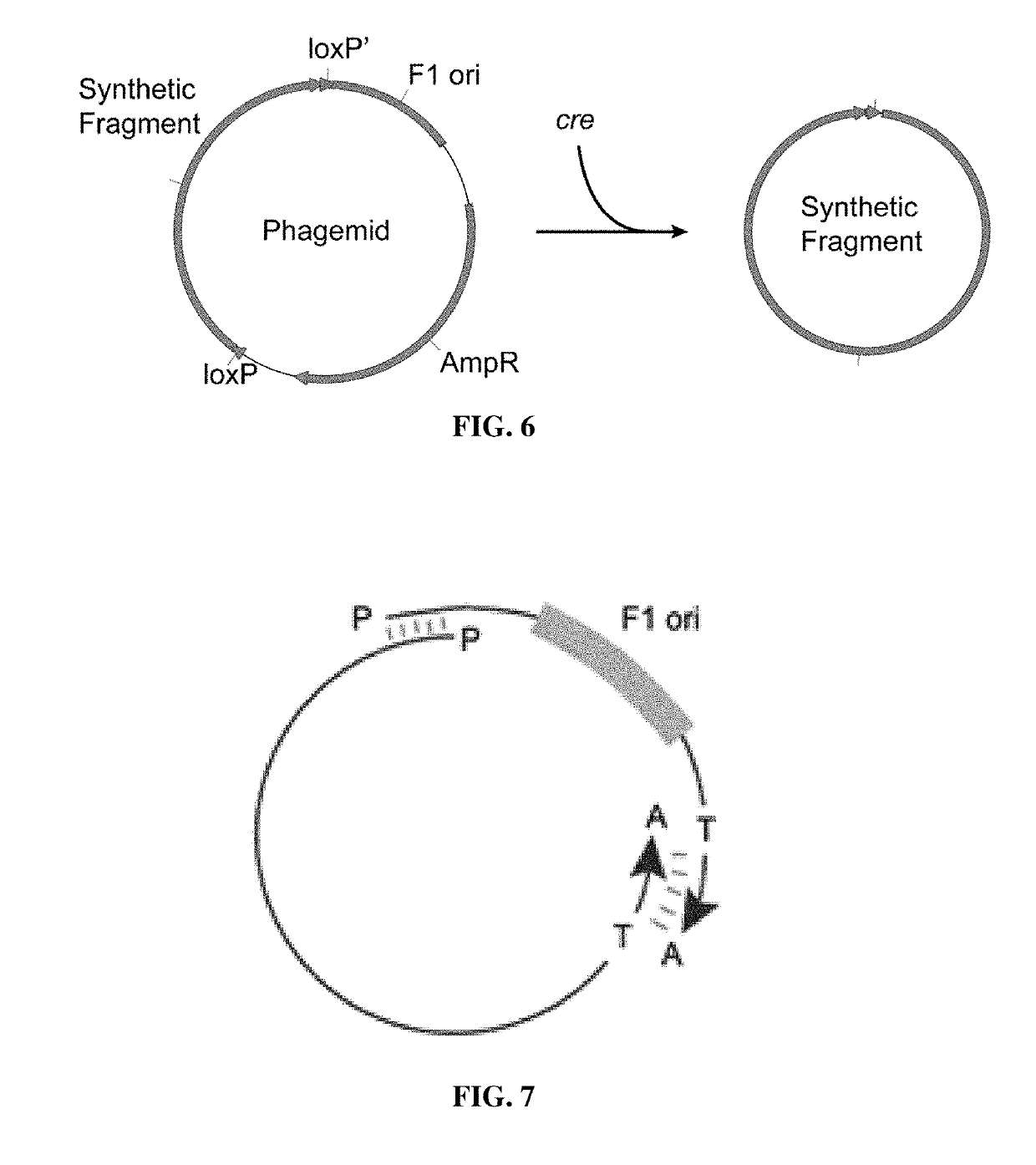
Preparation method of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA to DNA origami
The invention discloses a preparation method of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application of the sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to DNA origami. The preparation method of the sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA, disclosed by the invention, comprises the following steps: (1) designing and synthesizing circular double-stranded recombinant phagemid; (2) transforming escherichia coli through the recombinant phagemid and infecting through helper phage to prepare the circular single-stranded DNA with a corresponding form; (3) assembling different origami structures by taking prepared the ssDNA as a framework chain respectively, and carrying out characterization through atomic force microscope imaging. According to the method disclosed by the invention, aiming at the certain specific DNA, various types of single-stranded DNAs with different base sequences and lengths can be designed according to application requirements, so that customization is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Lipopolysaccharide conjugated protein and monoclonal antibody and preparation method and usage
InactiveCN101081863AReduce sensitivityReduce Excessive Inflammatory ResponseAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticPhage antibodiesAntigen
The present invention discloses one kind of lipopolysaccharide bindin and its monoclonal antibody, preparation process and use. Through extracting NH-LBP coding cDNA segment from human liver cell, preparing NH-LBP protein with insect sf21 cell, establishing humanized phage antibody base with pComb3H phagemid and screening with NH-LBP as antigen, anti-NH-LBP humanized monoclonal antibodies, Fab antibody and dsFv antibody are prepared. The Fab antibody and the dsFv antibody can combine specifically with the N end of complete human lipopolysaccharide bindin and inhibit the combination between LBP and LPS competively to lower the LPS sensitivity of body, lower LPS caused excessive inflammatory reaction, promote the degradation of LPS in body and prevent diffused blood coagulation inside capillary vessel and multiple organ failure.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Non-aggregating human vh domains
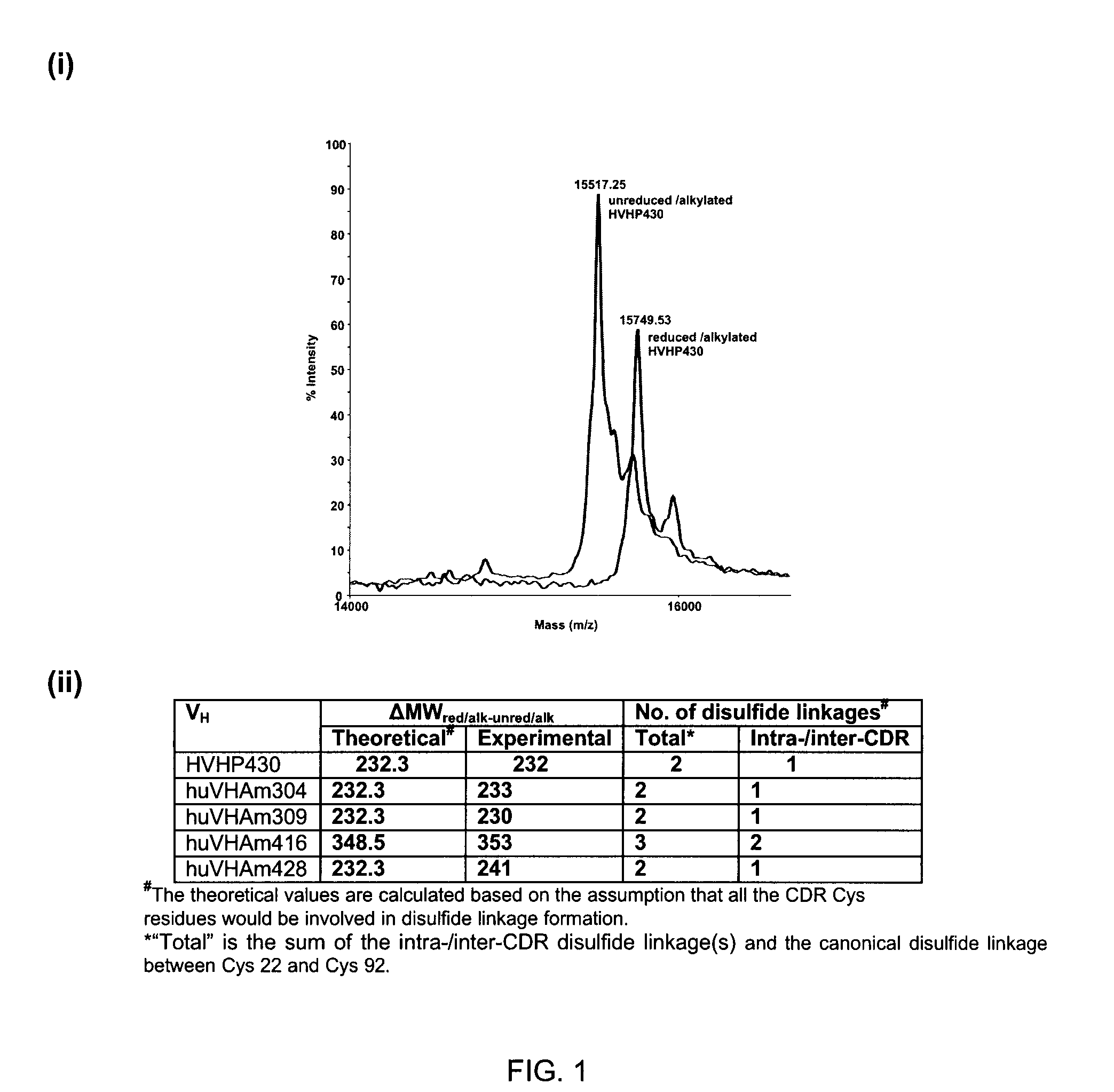
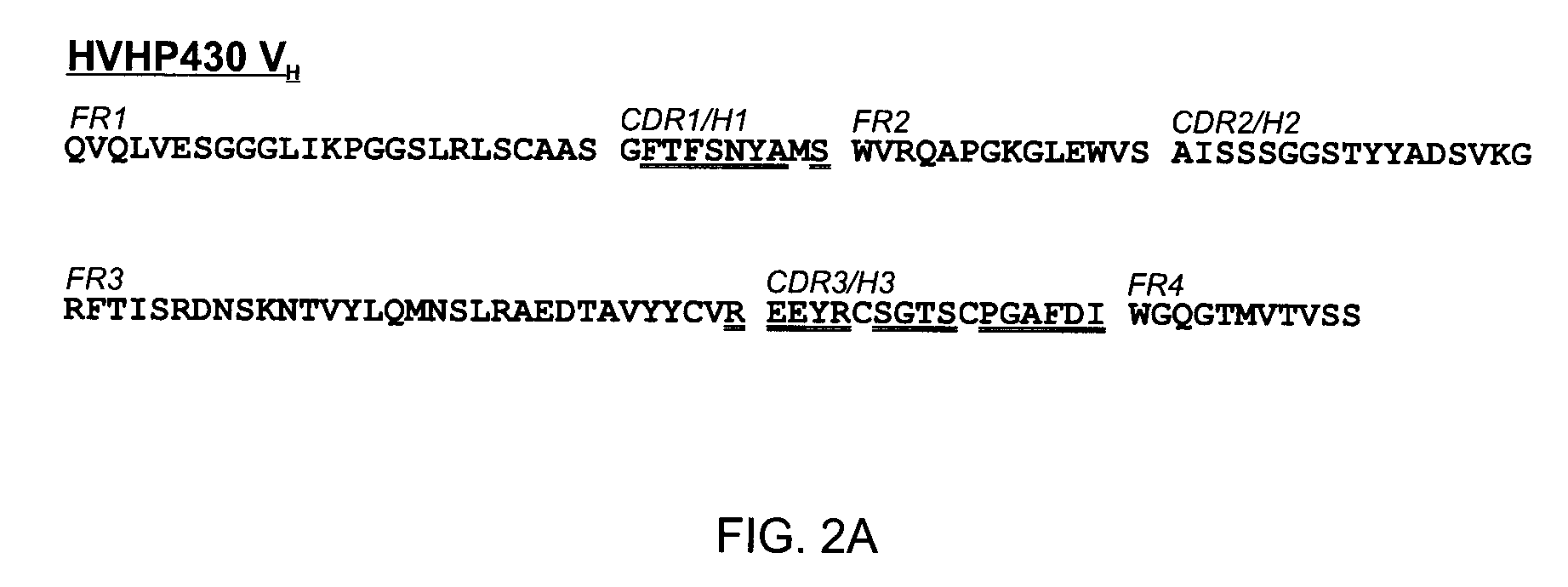
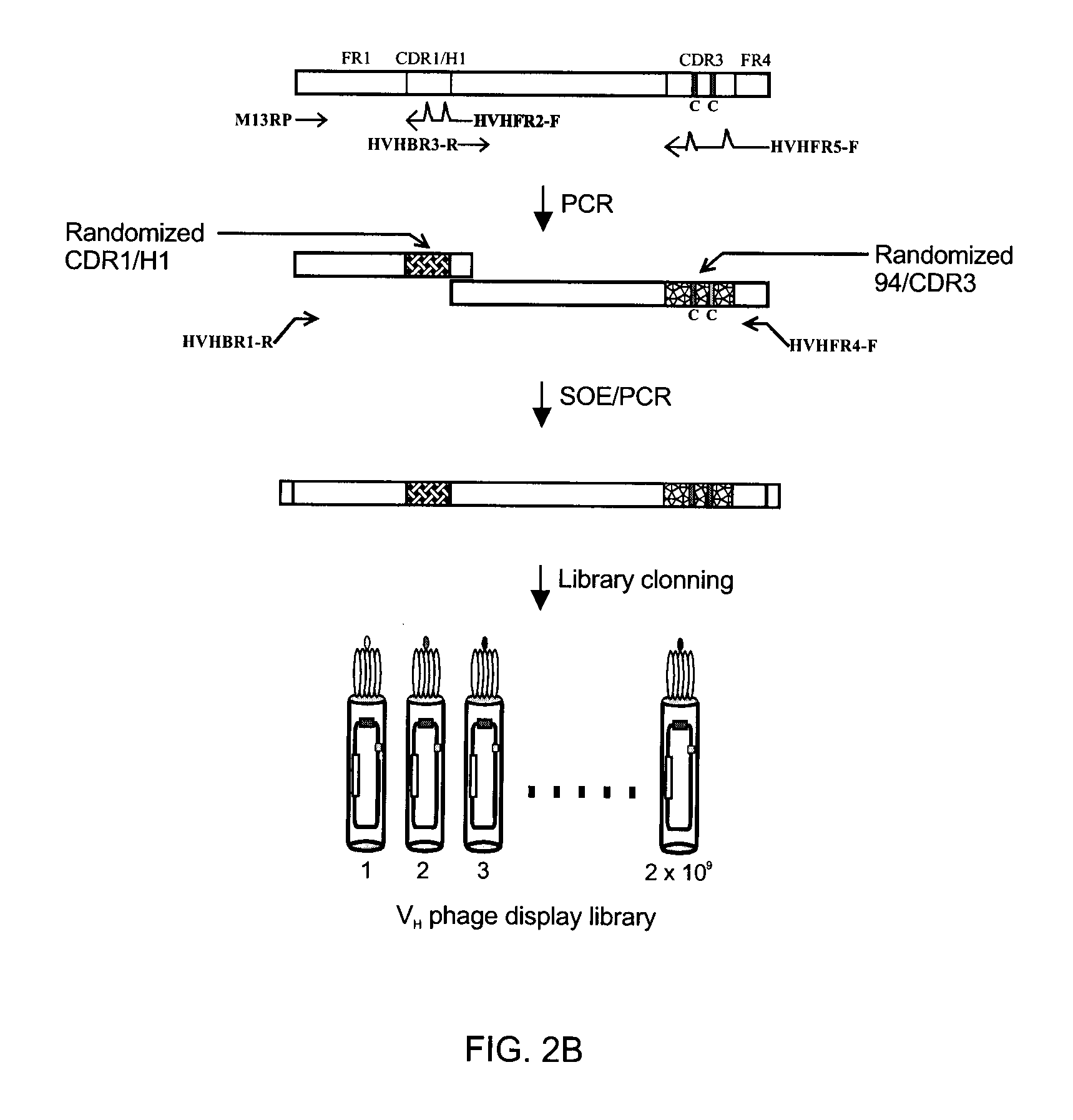
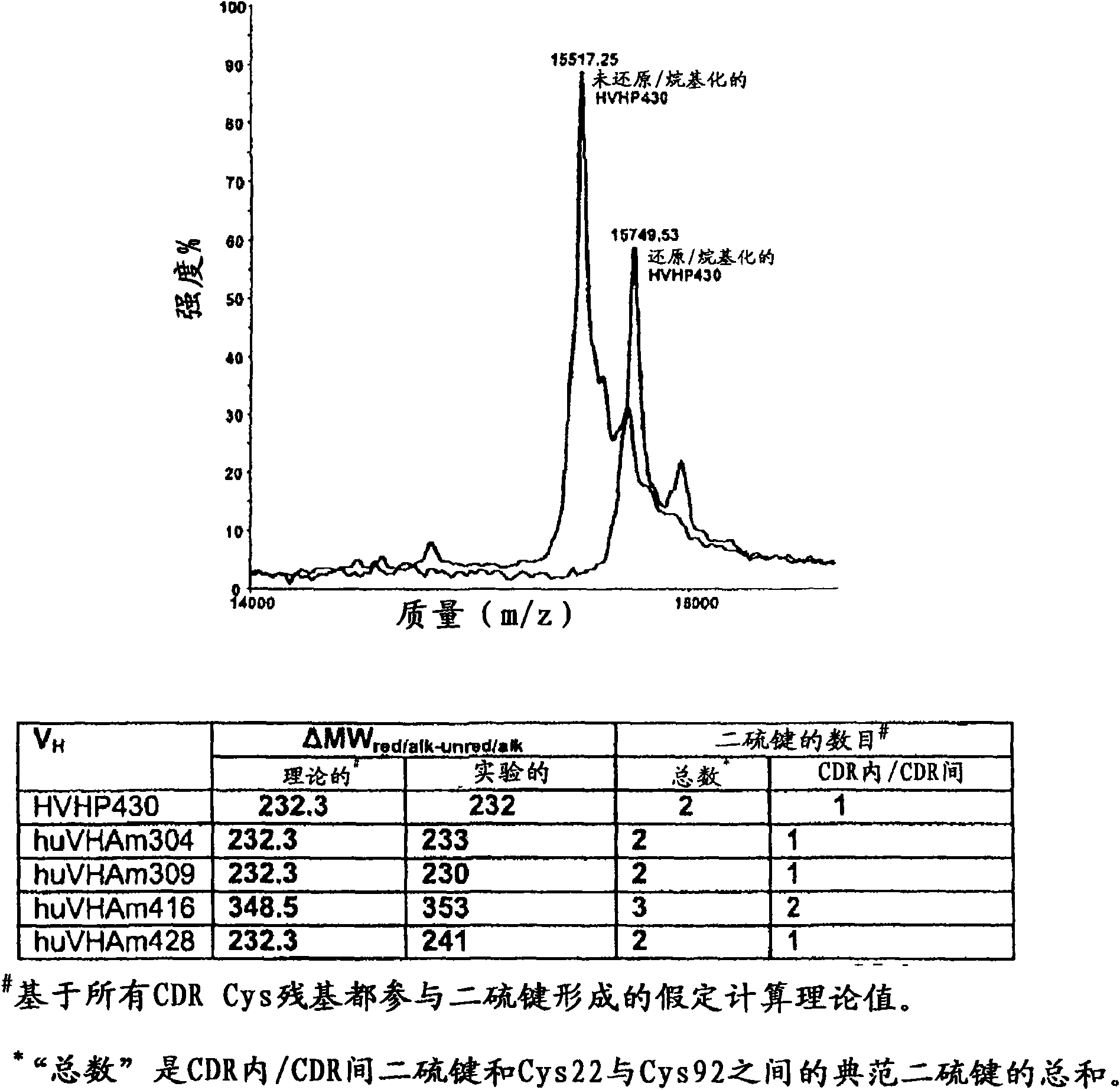
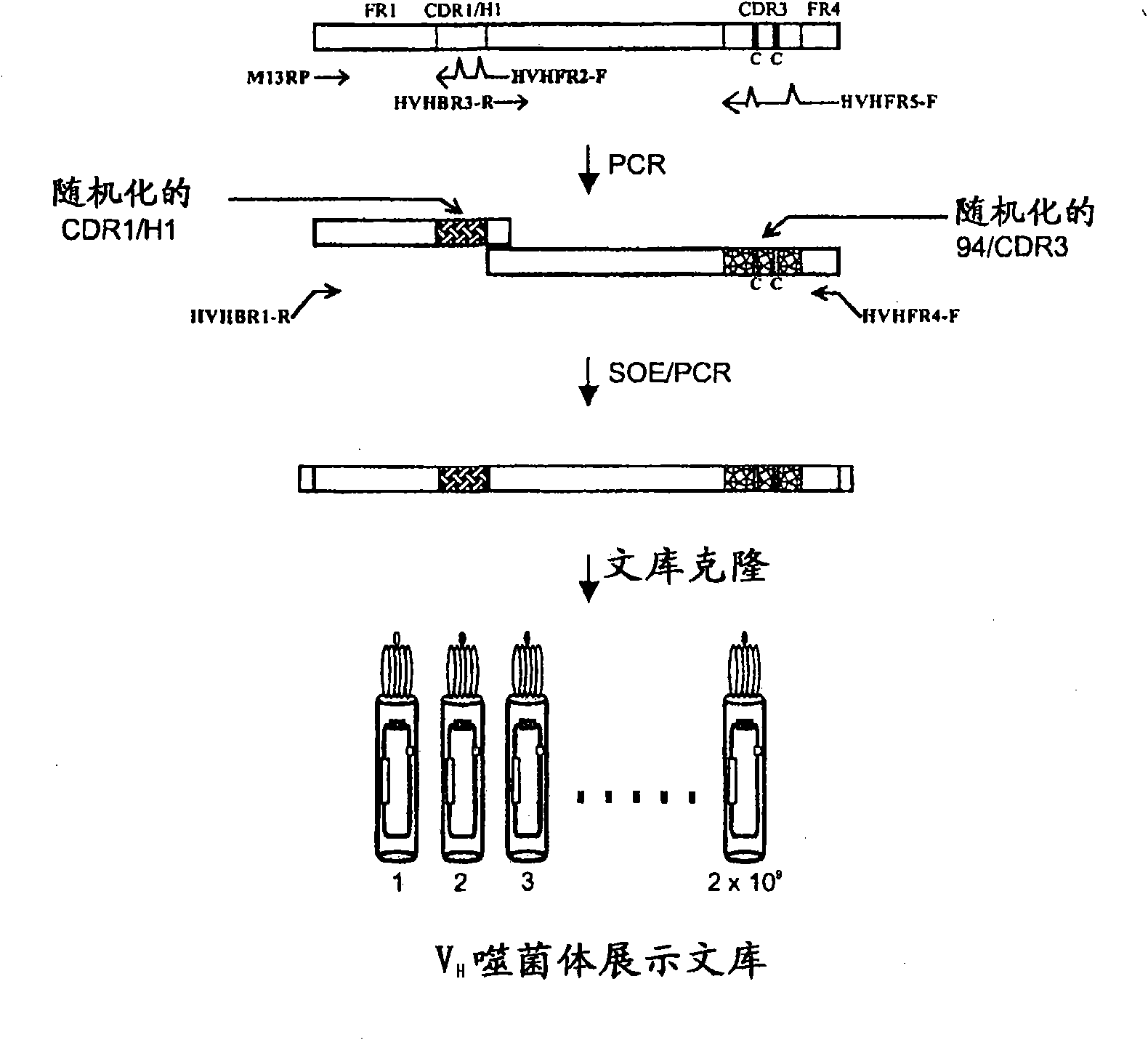
InactiveUS20110052565A1Rapid antibody expressionFast analysisPeptide librariesSugar derivativesComplementarity determining regionDisulfide Linkage
The present invention relates to non-aggregating VH domains or libraries thereof. The VH domains comprise at least one disulfide linkage-forming cysteine in at least one complementarity-determining region (CDR) and an acidic isoelectric point (pI). A method of increasing the power or efficiency of selection of non-aggregating VH domains comprises panning a phagemid-based VH domain phage-display library in combination with a step of selecting non-aggregating phage-VH domains. Compositions of matter comprising the non-aggregating VH domains, as well as methods of use are also provided.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Antibody gene for resisting pyrethriods pesticide scFv (Single Chain Fragment Variable) and application of antibody gene
The invention relates to an antibody gene for resisting pyrethriods pesticide scFv (Single Chain Fragment Variable), and particularly relates to construction of a pyrethriods pesticide antibody library, screening and sequence determination of a specific single-chain antibody gene and preparation of a specific phage display chain antibody. The antibody gene comprises nucleotide sequences of a coding heavy chain variable region (116 amino acids), a flexible chaining region (15 amino acids) and a light chain variable region (107 amino acids), shown as a SEQ ID No. 1 and a SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table; and the antibody which is displayed on the surface of phage is prepared in a host cell by using phagemid. The antibody can be normally expressed and folded on the surface of the phage and can be used for well identifying pyrethriods antigens. Compared with a conventional antibody, the antibody has the advantages of high stability, convenient preparation and important potential application value.
Owner:天津市明大百诚科技有限公司
Non-aggregating human VH domains
InactiveCN101939333APeptide librariesLibrary screeningComplementarity determining regionDisulfide Linkage
The present invention relates to non-aggregating VH domains or libraries thereof. The VH domains comprise at least one disulfide linkage-forming cysteine in at least one complementarity-determining region (CDR) and an acidic isoelectric point (pI). A method of increasing the power or efficiency of selection of non-aggregating VH domains comprises panning a phagemid-based VH domain phage-display library in combination with a step of selecting non-aggregating phage-VH domains. Compositions of matter comprising the non-aggregating VH domains, as well as methods of use are also provided.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Improved bacteriophage expression carrrier
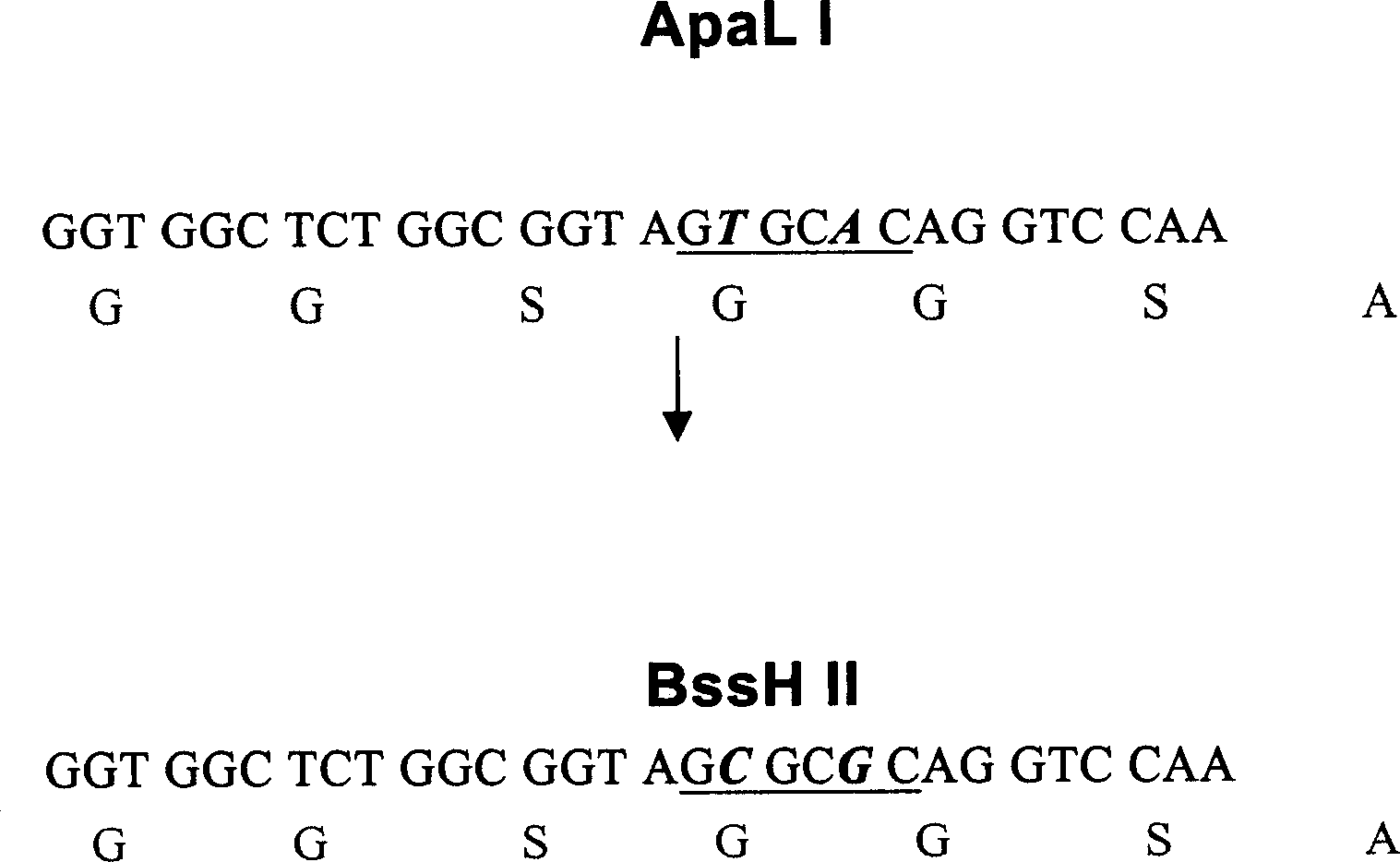
An improved expression carrier pHEN2 used to screen the phagemid in single-chain antibody by phage display method features that the enzyme severing site ApaL1 in its multiple enzyme severing sites is removed or replaced by BssH II, so more products coded by the light-chain gene of human immunoglobulin can be effectively inserted in single-chain antibody library to ensure its diversity and high volume.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
Preparation method for circular single-stranded DNA integrated with aptamer and applications of circular single-stranded DNA integrated with aptamer in DNA origami
PendingCN113278607AEfficient preparationAvoid cross sacrificeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAptamerEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a preparation method for circular single-stranded DNA integrated with aptamer and applications of the circular single-stranded DNA integrated with aptamer in DNA origami, and belongs to the field of DNA nanotechnologies and biological application. The preparation method mainly includes the following steps: (1.1) constructing circular double-stranded recombinant phagemid including an aptamer sequence; and (1.2) converting the constructed circular double-stranded recombinant phagemid into competent escherichia coli cells; and extracting the circular single-stranded DNA integrated with aptamer. Through the preparation method, a user defined skeleton chain sequence can be designed and produced, so as to add various function sequences at a user defined position. Problems of poor efficiency and stability of structural functionalization of traditional DNA origami can be broken through.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Expression vector for constructing high-quality bacteriophage antibody library
ActiveCN102094035AImprove connection efficiencyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansViruses/bacteriophagesAgricultural scienceHeavy chain
The invention discloses an expression vector for constructing a high-quality bacteriophage antibody library. The vector disclosed by the invention is prepared by the following steps: 1) inserting coding genes of a light-chain region SacB in multiple cloning sites of pDF to obtain an intermediate vector PSBX; 2) mutating BssHII enzyme cutting sites of the intermediate vector PSBX obtained in the step 1) into BglII enzyme cutting sites to obtain an intermediate vector PSGX; and 3) inserting coding genes of a heavy-chain region SacB in Nhe I and Nco I enzyme cutting sites of the intermediate vector PSGX obtained in the step 2) to obtain a vector pDF-D-SacB. Experiment disclosed by the invention proves that the obtained phagemid vector pDF-D-SacB containing suicide genes is applicable to the construction of a high-capacity bacteriophage antibody library.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Vectors for cloning and expression of proteins, methods and applications thereof
The present disclosure relates to vectors for cloning and expressing genetic material including but not limiting to antibody gene or parts thereof and methods of generating said vectors. Said vectors express the antibody genes in different formats such as Fab or scFv as a part of intertransfer system, intratransfer system or direct cloning and expression in individual display systems. In particular, phage display technology is used to clone and screen potential antibody genes in phagemid which is followed by the transfer of said genes to yeast vector for further screening and identification of lead molecules against antigens. The present vectors have numerous advantages including uniquely designed inserts / expression cassettes resulting in efficient and smooth transfer of clonal population from phage to yeast vectors resulting in efficient library preparation and identification of lead molecules.
Owner:ZUMUTOR BIOLOGICS
Heterodimeric receptor libraries using phagemids
Filamentous phage comprising a matrix of cpVIII proteins encapsulating a genome encoding first and second polypeptides of an antogenously assembling receptor, such as an antibody, and a receptor comprised of the first and second polypeptides surface-integrated into the matrix via a filamentous phage coat protein membrane anchor domain fused to at least one of the polypeptides.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs
InactiveUS20070148774A1Simple procedureSpeedImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensBacteriaGenetic diversityFree form
A member of a specific binding pair (sbp) is identified by expressing DNA encoding a genetically diverse population of such sbp members in recombinant host cells in which the sbp members are displayed in functional form at the surface of a secreted recombinant genetic display package (rgdp) containing DNA encoding the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof, by virtue of the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof being expressed as a fusion with a capsid component of the rgdp. The displayed sbps may be selected by affinity with a complementary sbp member, and the DNA recovered from selected rgdps for expression of the selected sbp members. Antibody sbp members may be thus obtained, with the different chains thereof expressed, one fused to the capsid component and the other in free form for association with the fusion partner polypeptide. A phagemid may be used as an expression vector, with said capsid fusion helping to package the phagemid DNA. Using this method libraries of DNA encoding respective chains of such multimeric sbp members may be combined, thereby obtaining a much greater genetic diversity in the sbp members than could easily be obtained by conventional methods.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com