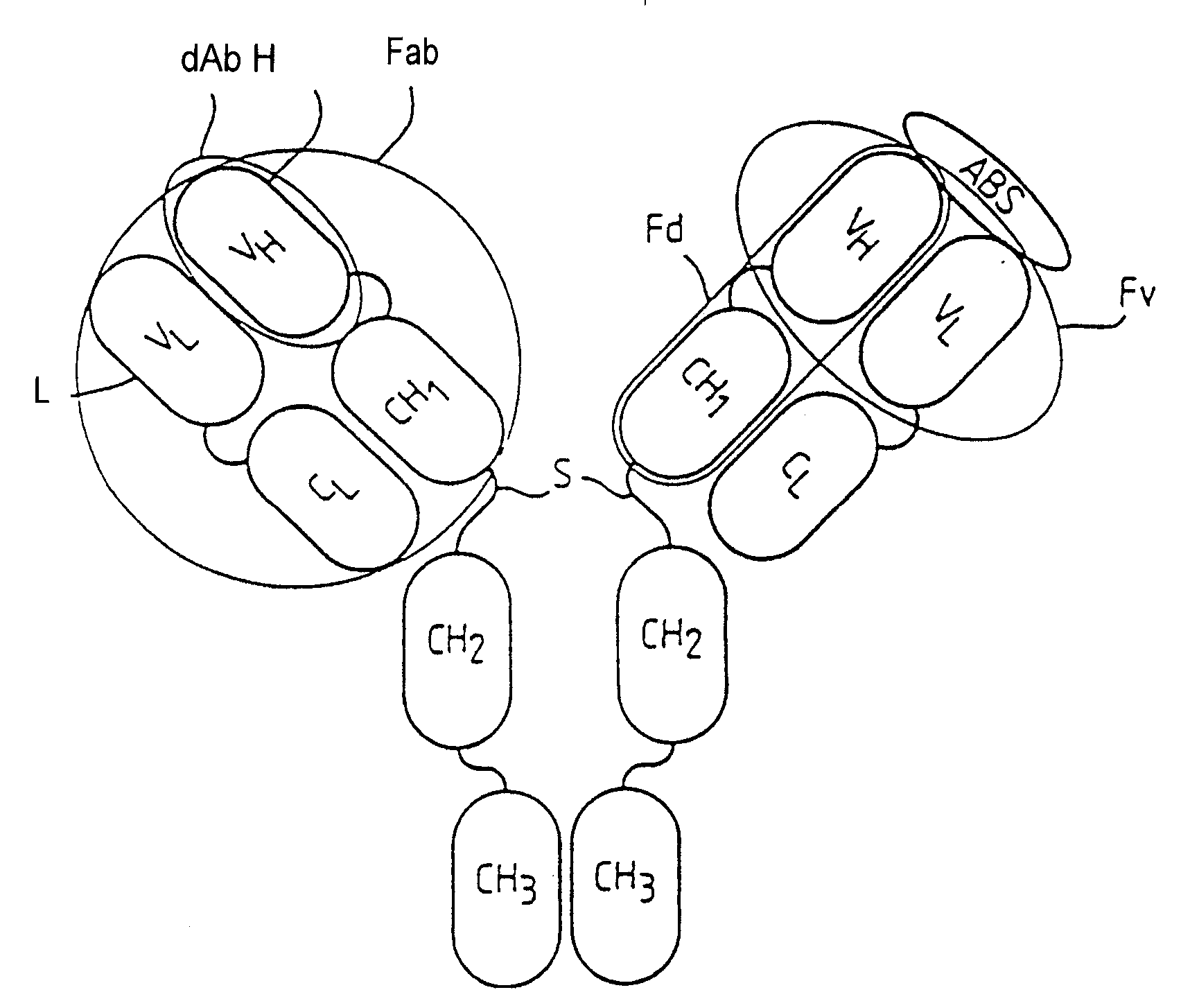
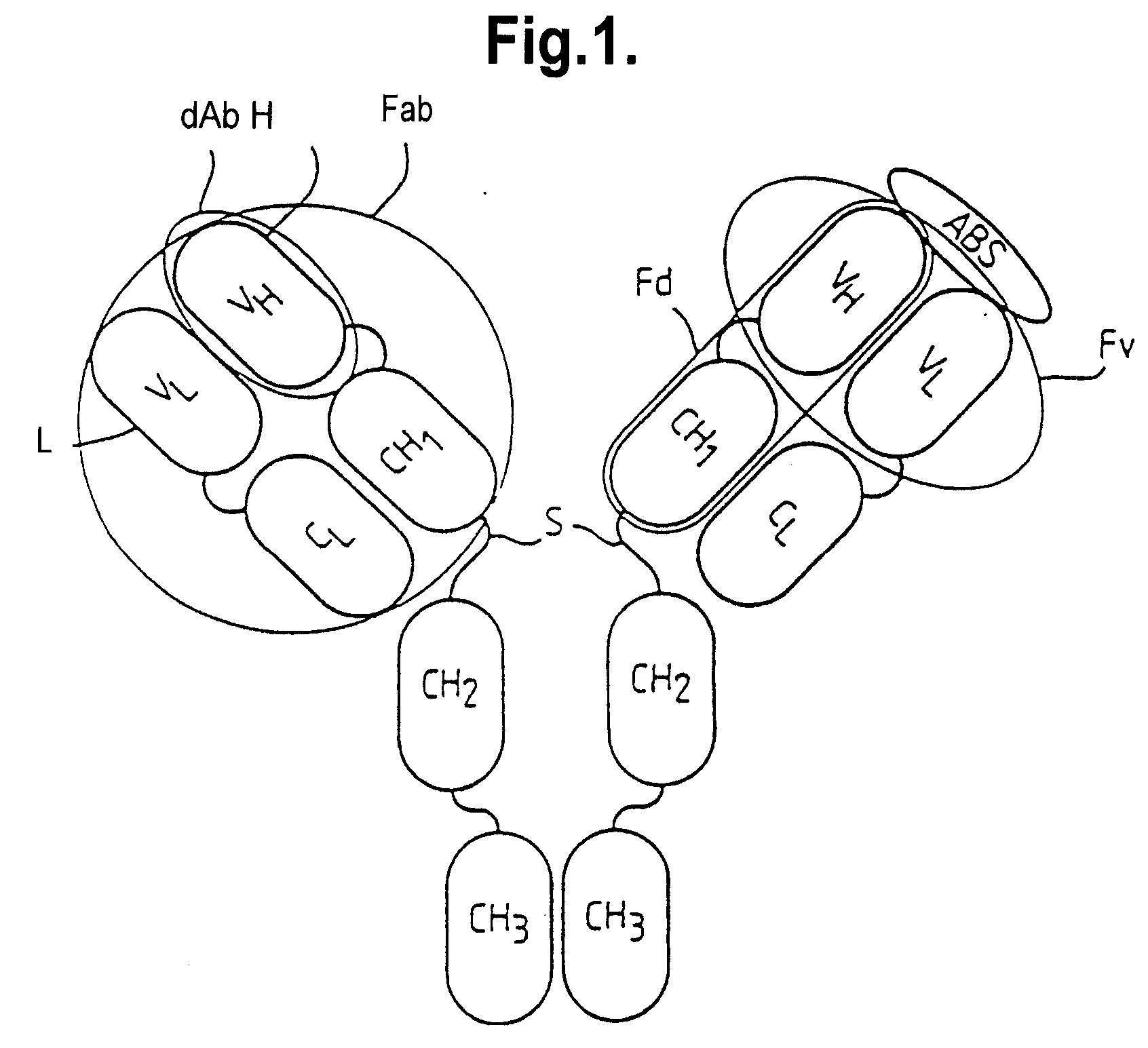
Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs
a specific binding and member technology, applied in the field of methods for producing members of specific binding pairs, can solve the problems of low antibody yield, difficult establishment of immortal antibody-producing human cell lines, and many limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design of Insertion Point Linkers and Construction of Vectors
[0295] The vector fd-tet has two BstEII restriction sites flanking the tetracycline resistance gene (FIG. 3). Since the strategy for inserting the VH fragments was to ligate them into a newly inserted BstEII site within gene III, it was advantageous to delete the original BstEII sites from fd-tet. This was achieved by digesting fd-tet with the restriction enzyme BstEII, filling-in the 5′ overhangs and re-ligating to generate the vector fdTδBst. Digestion of fd-tet with BstEII (0.5 units / μl) was carried out in 1×KGB buffer (100 mM potassium glutamate, 23 mM Tris-acetate (pH 7.5), 10 mM magnesium acetate, 50 μg / ml bovine serum albumin, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol (Sambrook, J., et al., 1989, supra.) with DNA at a concentration of 25 ng / μl. The 5′ overhang was filled in, using 2×KGB buffer, 250 μM each dNTP's (Pharmacia Ltd., Pharmacia House, Midsummer Boulevard, Milton Keynes, Bucks., UK.) and Klenow Fragment (Amersham Internati...
example 2
Insertion of Immunoglobulin Fv Domain into Phage
[0302] The plasmid scFv D1.3 myc (gift from g. Winter and A. Griffiths) contains VH and VL sequences from the antibody D1.3 fused via a peptide linker sequence to form a single chain Fv version of antibody D1.3. The sequence of the scFv and surrounding sequences in scFvD1.3 myc is shown in FIG. 5.
[0303] The D1.3 antibody is directed against hen egg lysozyme (Harper, M. et al., 1987, Molec. Immunol. 24, 97-108) and the scFv form expressed in E. coli has the same specificity (A. Griffiths and G. Winter personal Communication).
[0304] Digestion of scFv D1.3 myc with Pstl and Xhol (these restriction sites are shown on FIG. 5), excises a fragment of 693 bp which encodes the bulk of the scFv. Ligation of this fragment into fdTPs / Xh cleaved with Pst1 and Xhol gave rise to the construct fdTscFvD1.3 encoding the gene III signal peptide and first amino acid fused to the complete D1.3 scFv, followed by the mature gene III protein from amino ac...
example 3
Insertion of Immunoglobulin VH Domain into Phage Antibody
[0309] The VH fragment from D1.3 was generated from the plasmid pSW1-VHD1.3-TAG1 (Ward, E. S. et al., 1989 supra.).
[0310] Digestion of this plasmid with Pst1 and BstEII generates the fragment shown between positions 113 and 432 in FIG. 5. Cloning of this fragment into the Pst1 and BstEII sites of fdTPs / Bs gave rise to the construct fdTVHD1.3 which encodes a fusion protein with a complete VH domain inserted between the first and third amino acids of the mature gene III protein (amino acid two has been deleted).
[0311] The methods used were exactly as in example 2 except that the vector used was fdTPs / Bs digested with Pst1 and BstEII.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight retention | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com