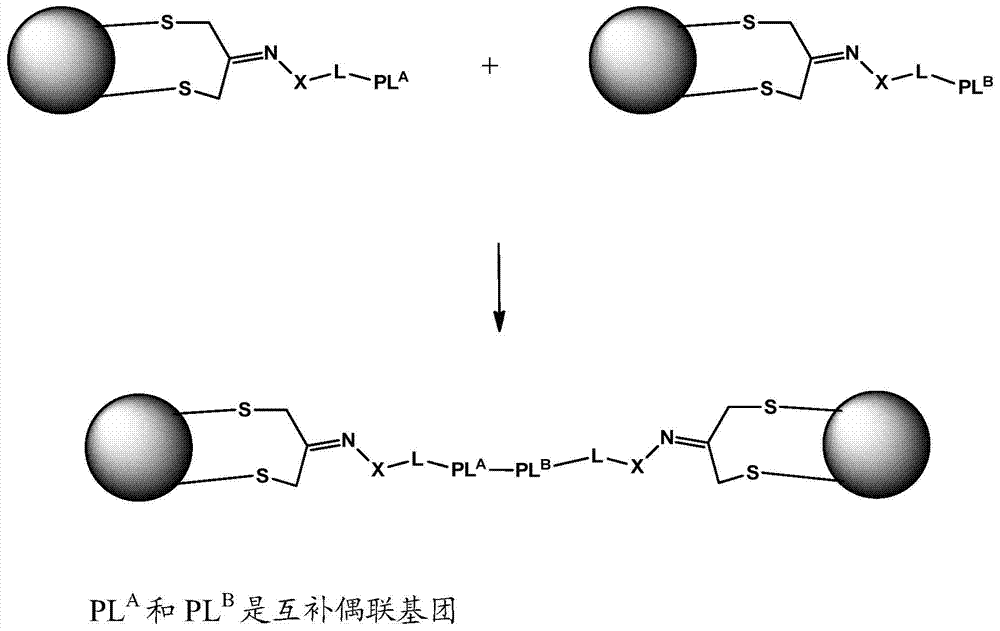
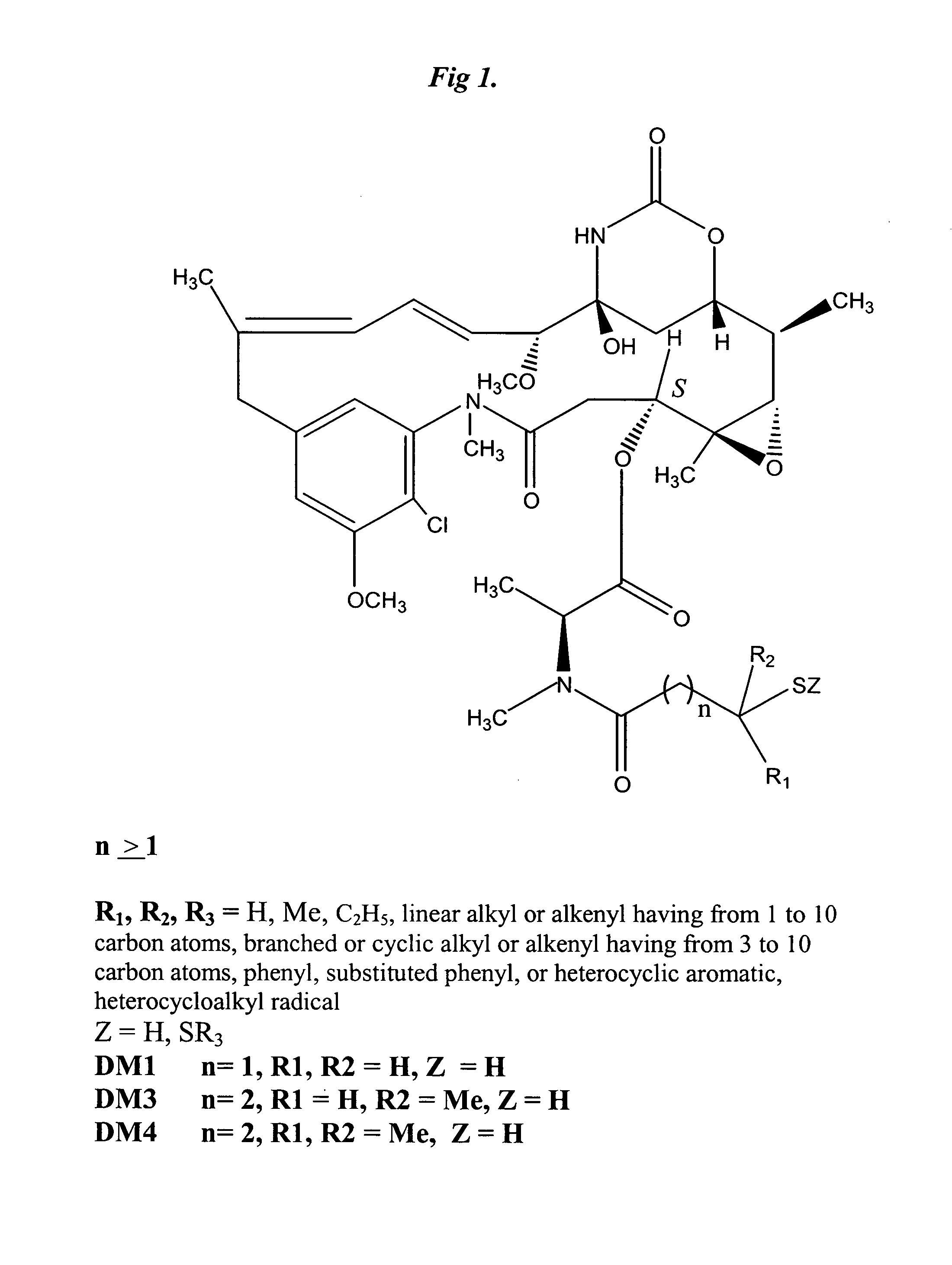
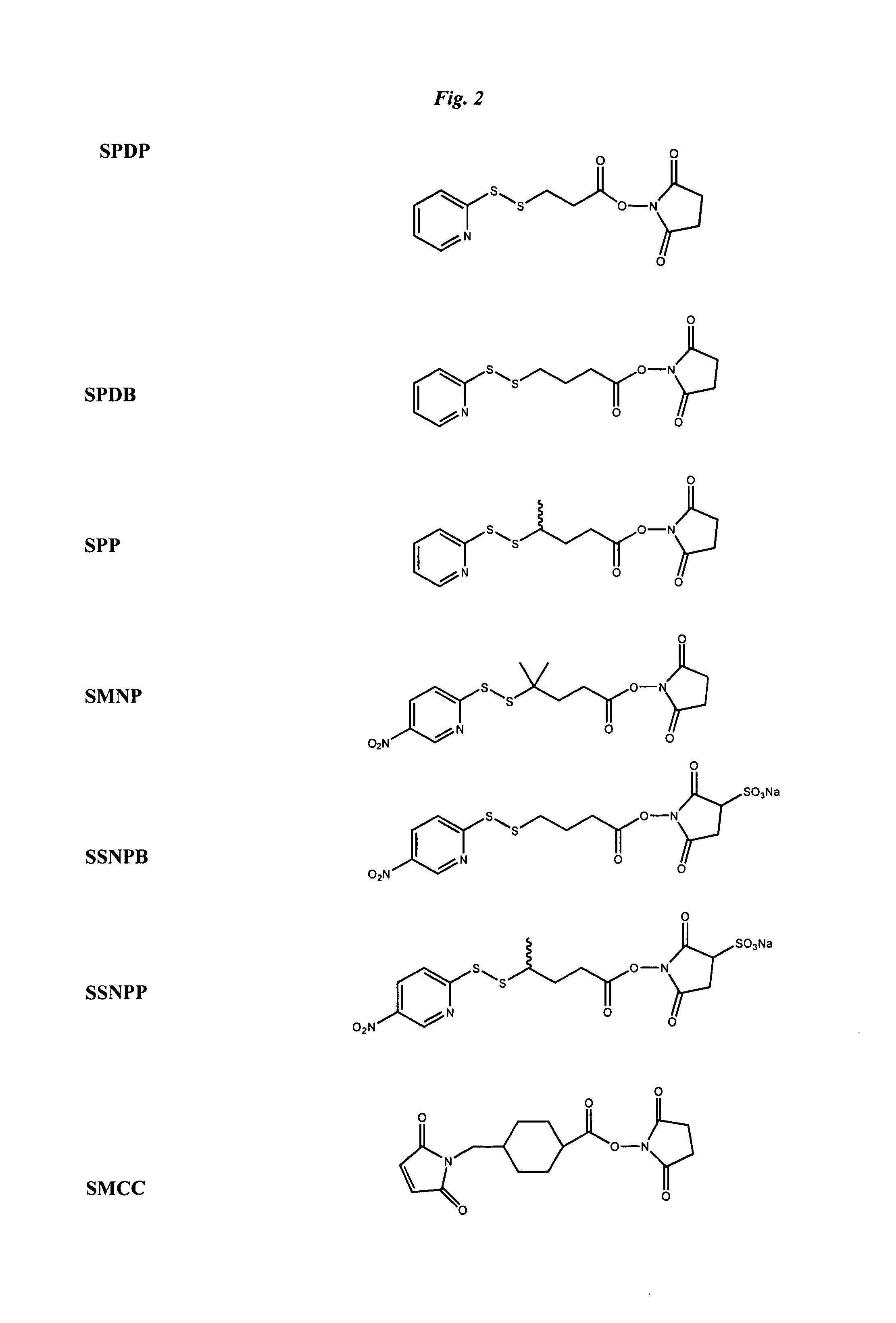
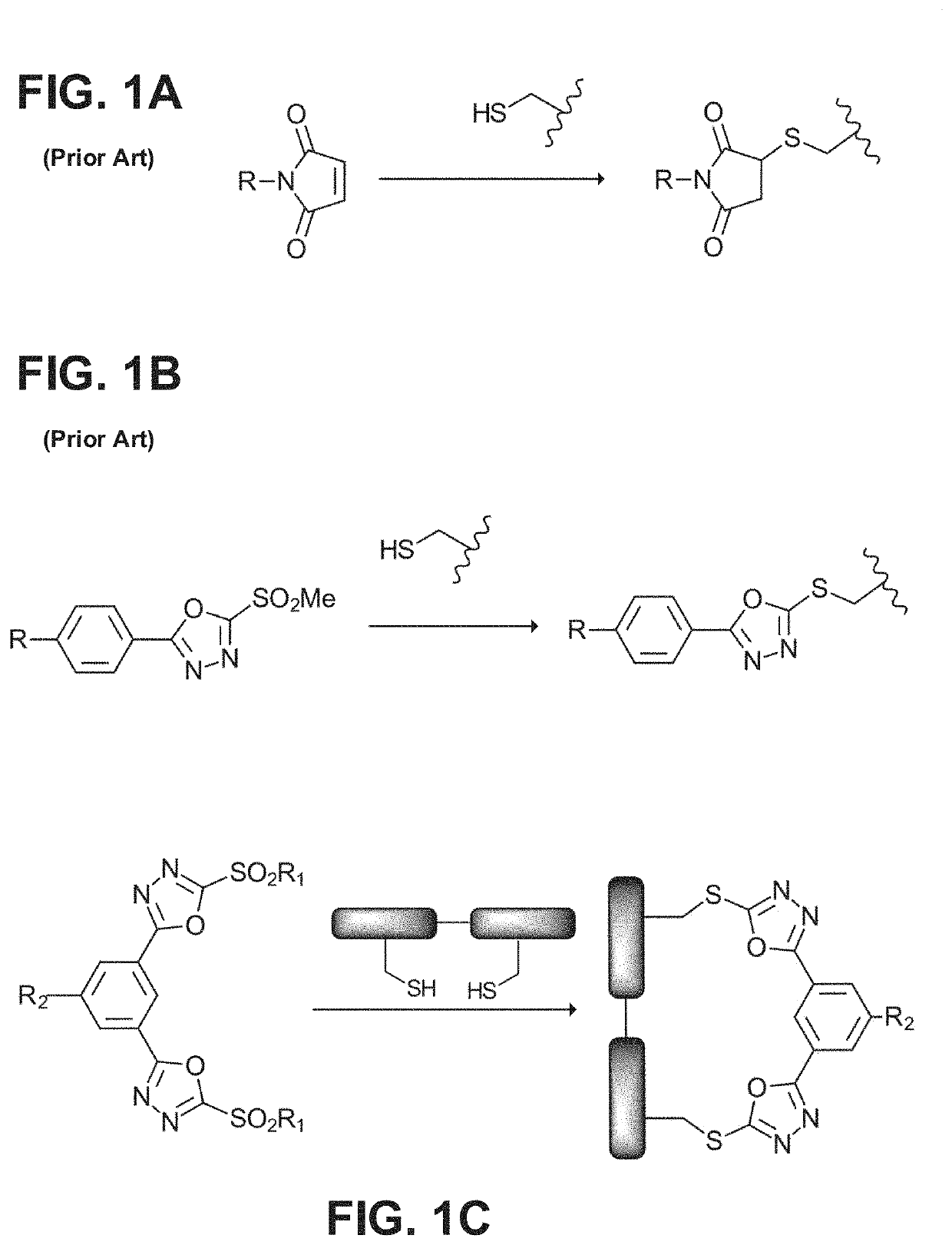
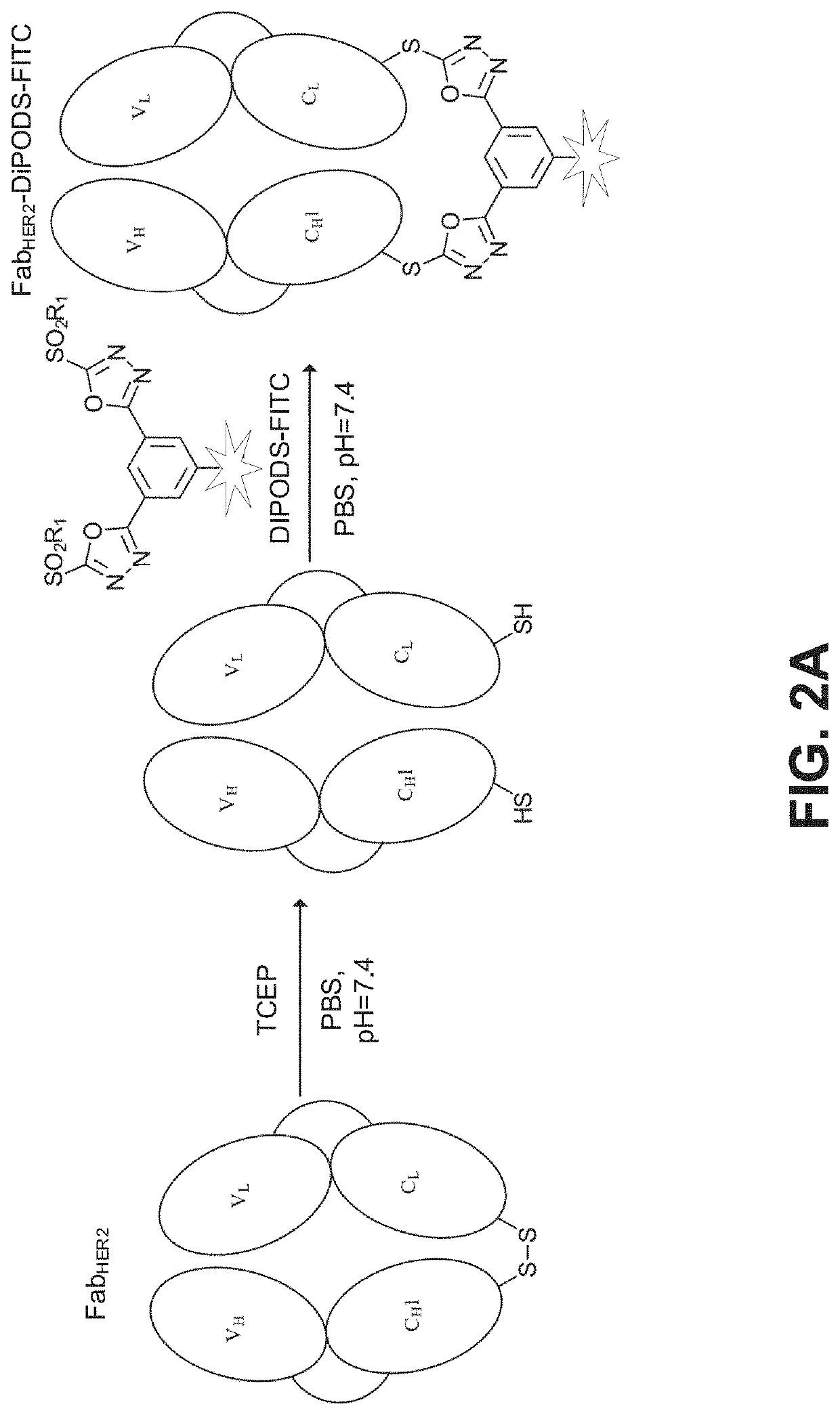
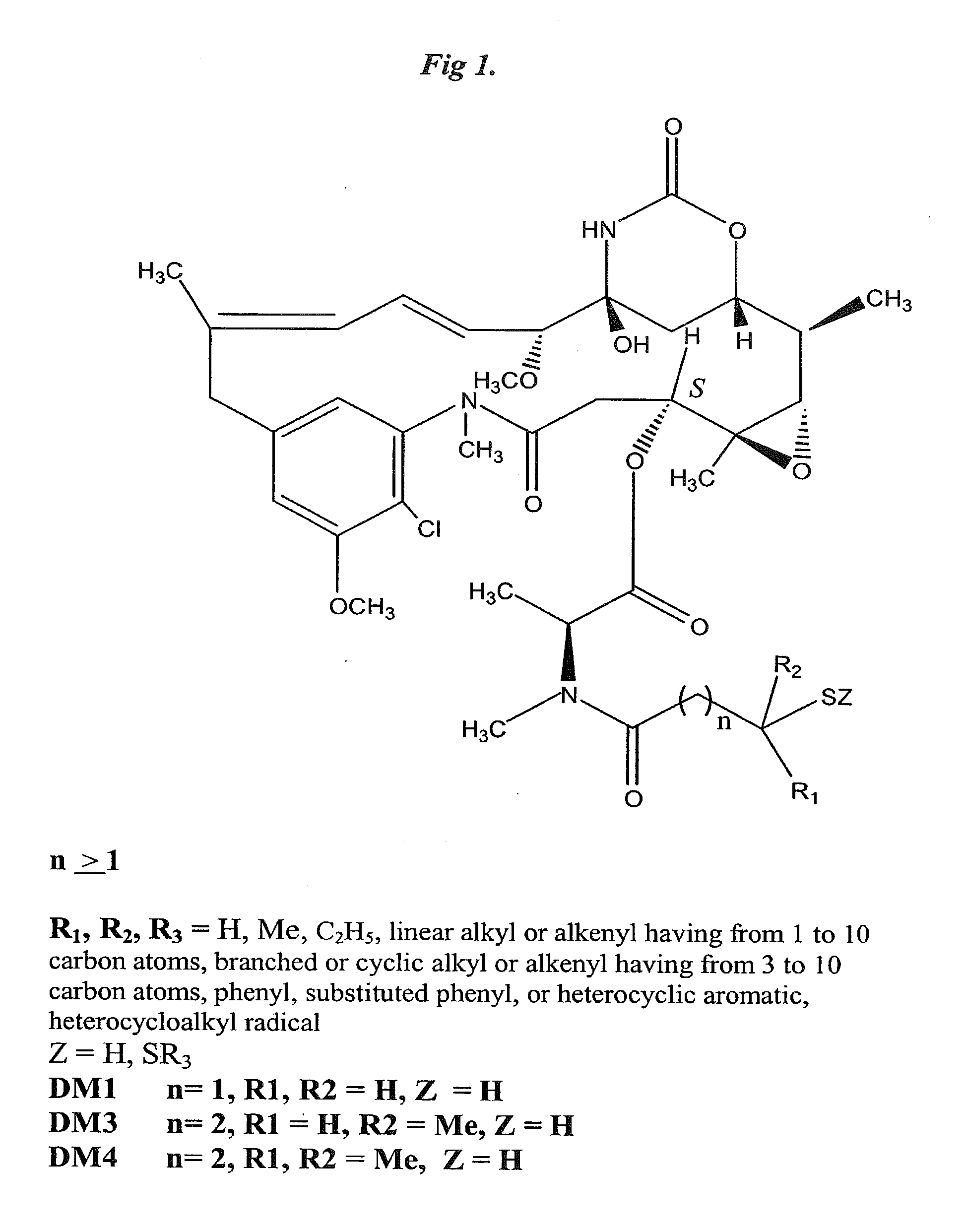
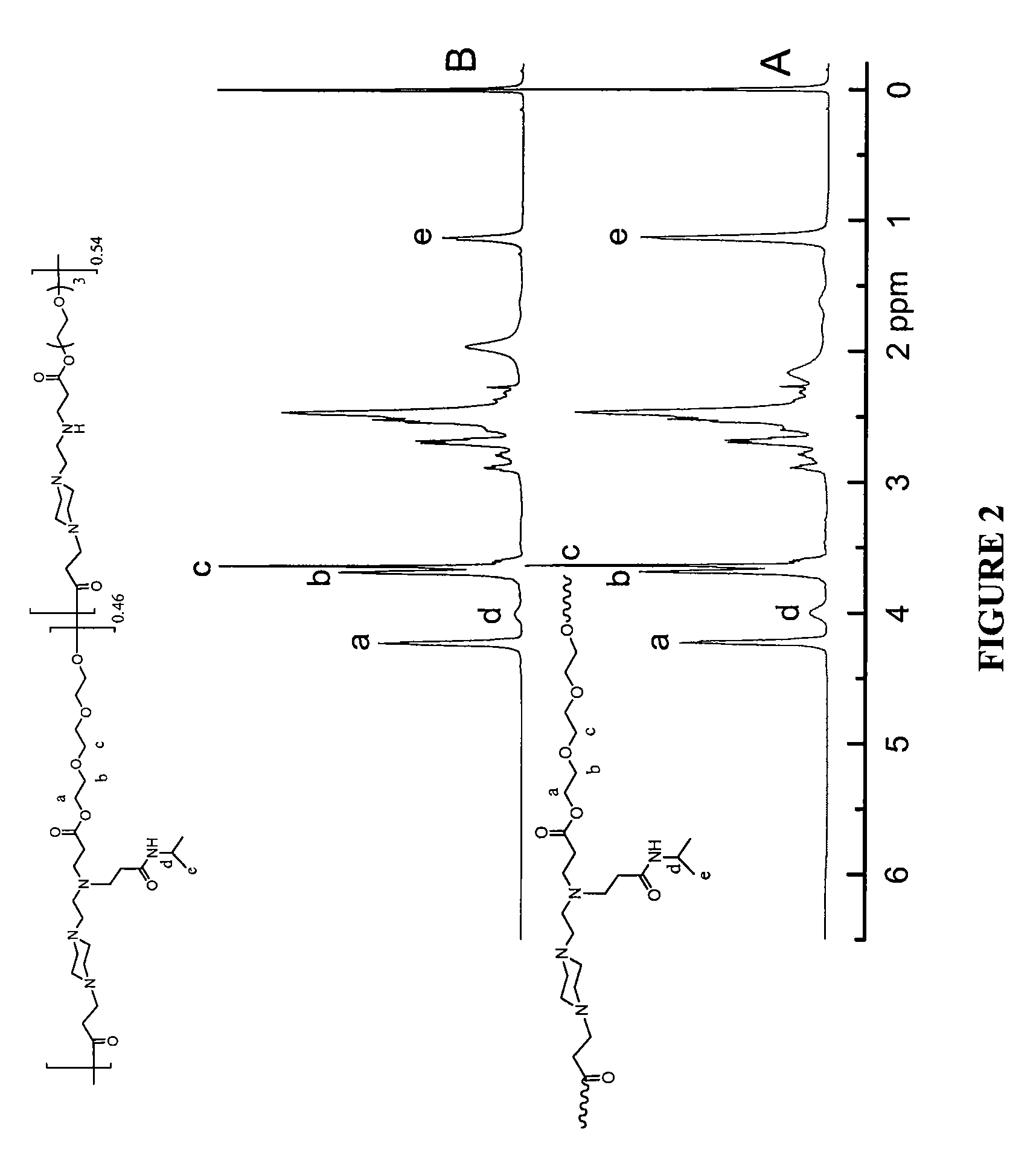
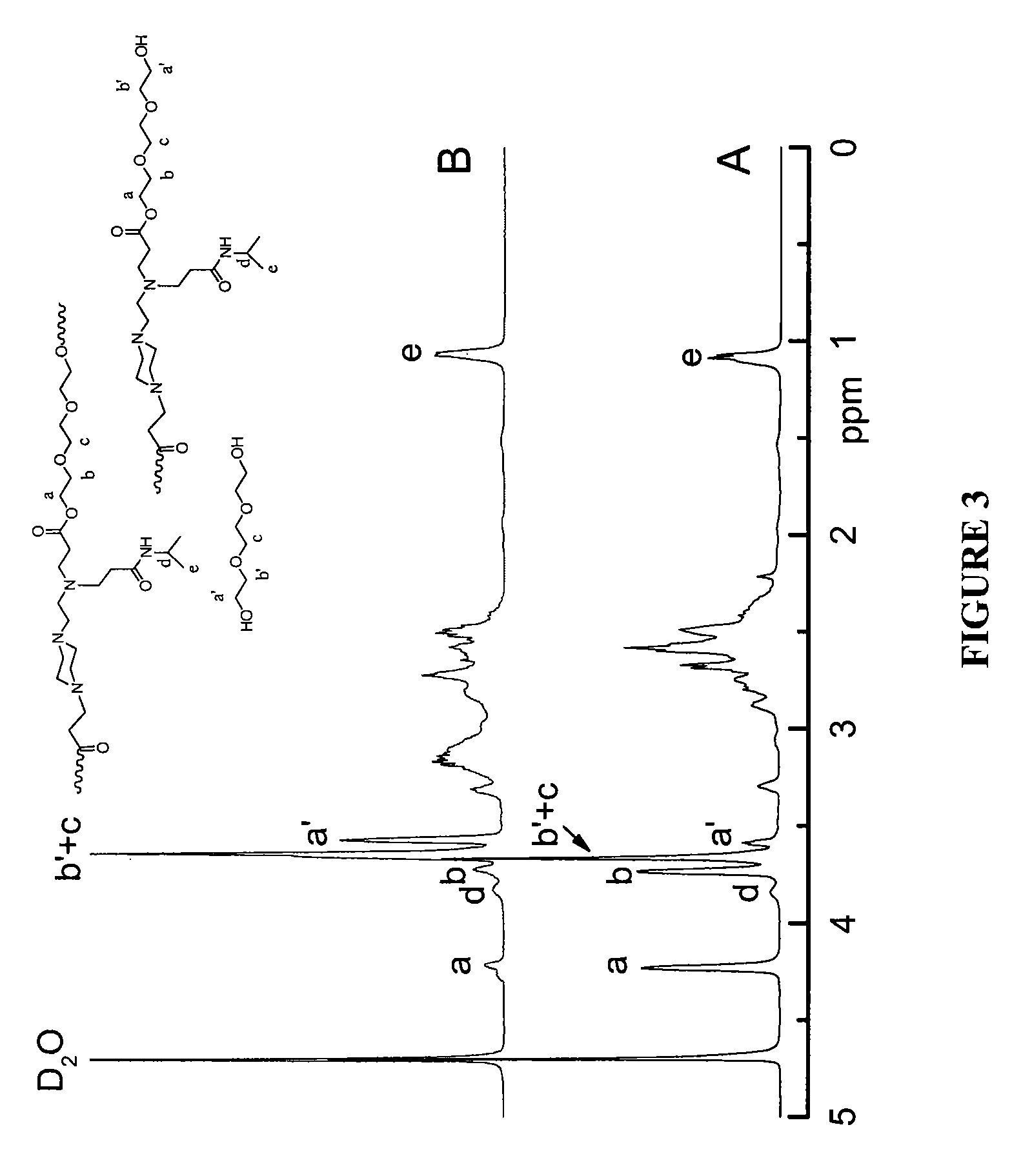
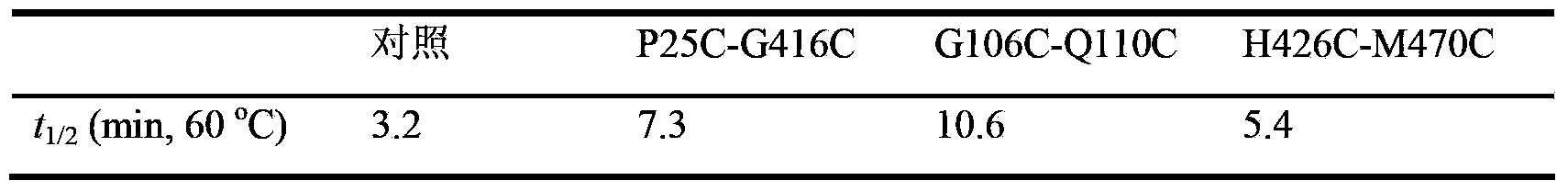Patents
Literature
44 results about "Disulfide Linkage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A disulfide linkage is a covalent bond between 2 sulfide atoms from the thiol group of 2 cysteine residues (S-S). They occur both interstrand and intrastrand.
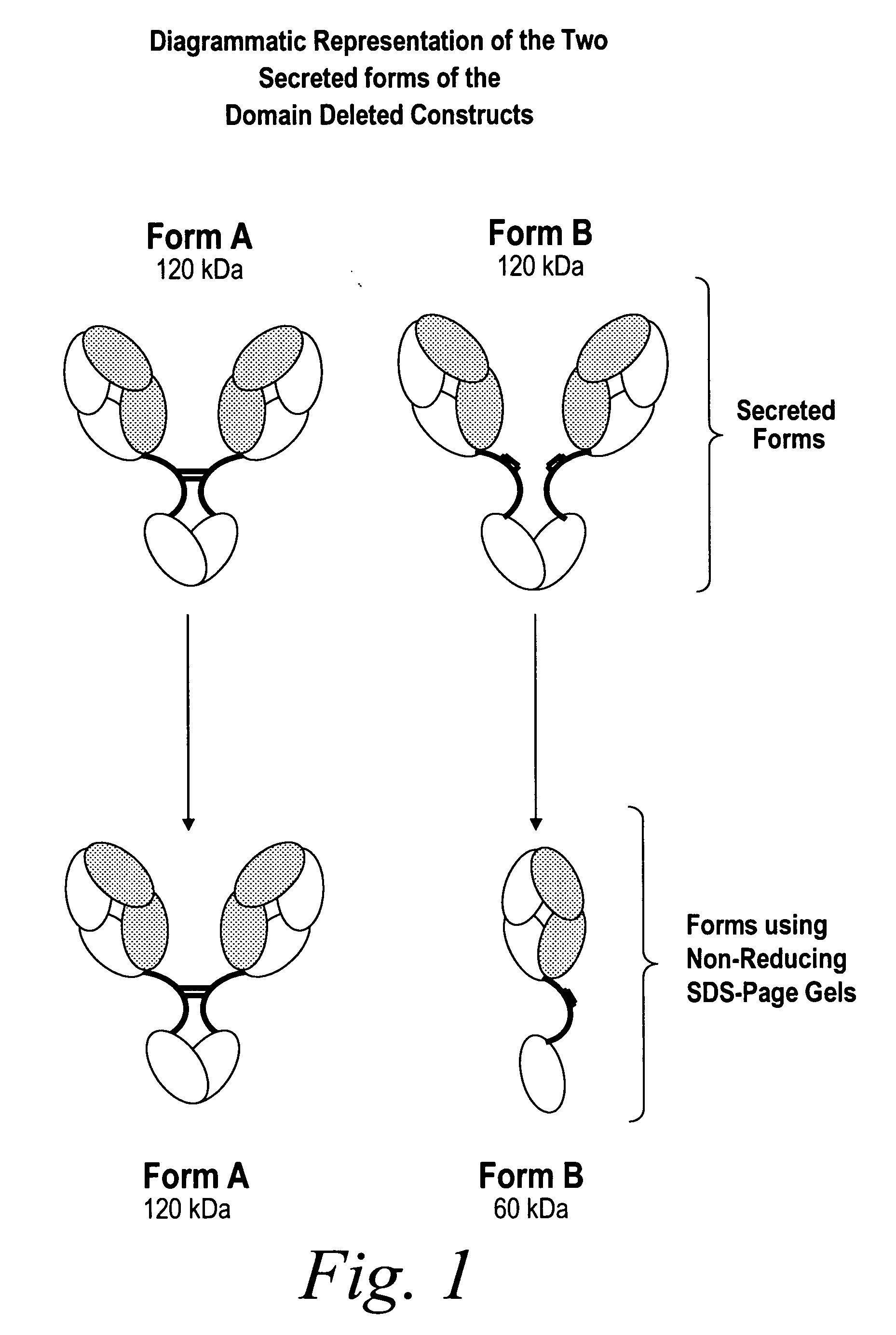
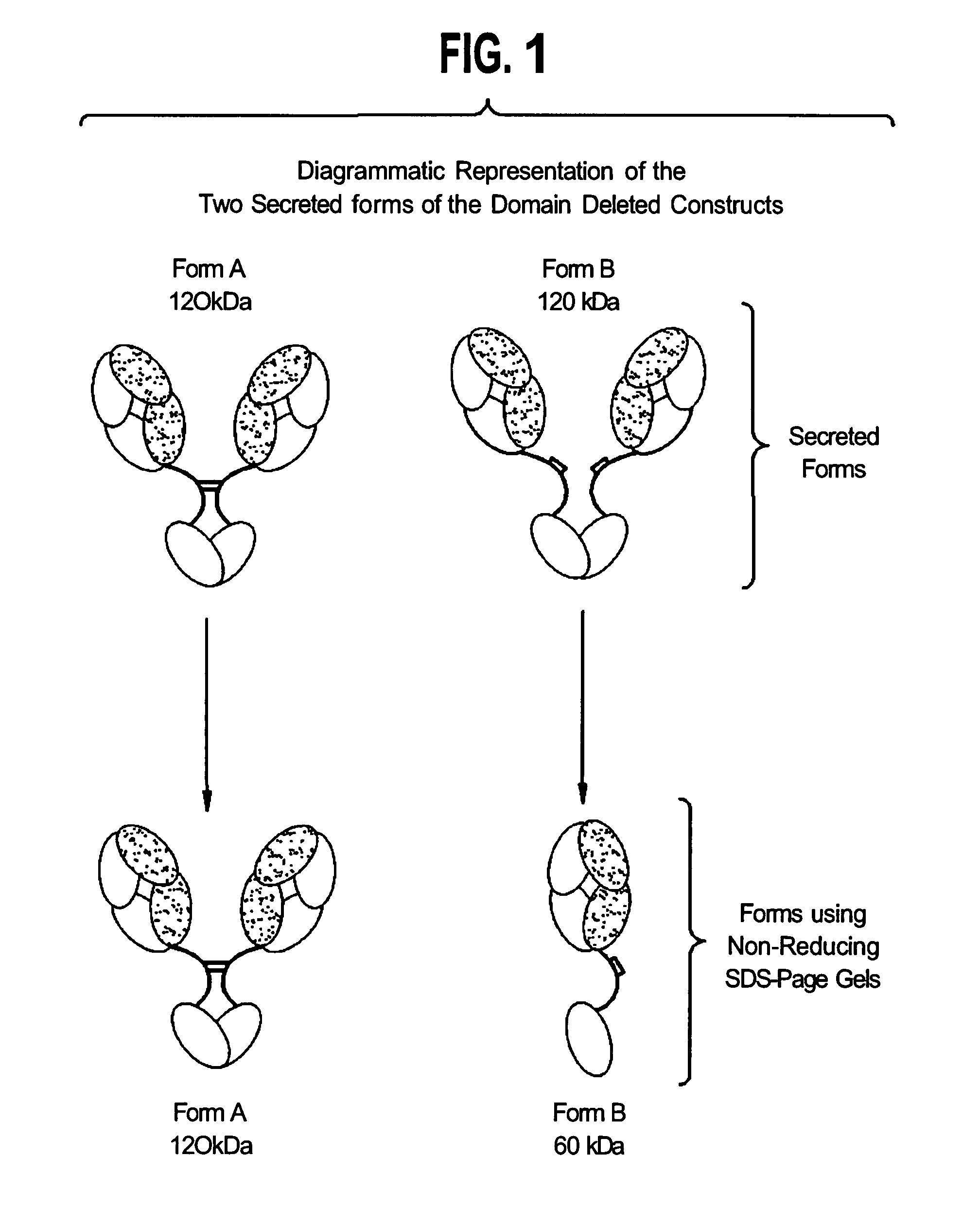
Modified binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
InactiveUS20050163782A1Well formedIncreased formationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide LinkagePeptide
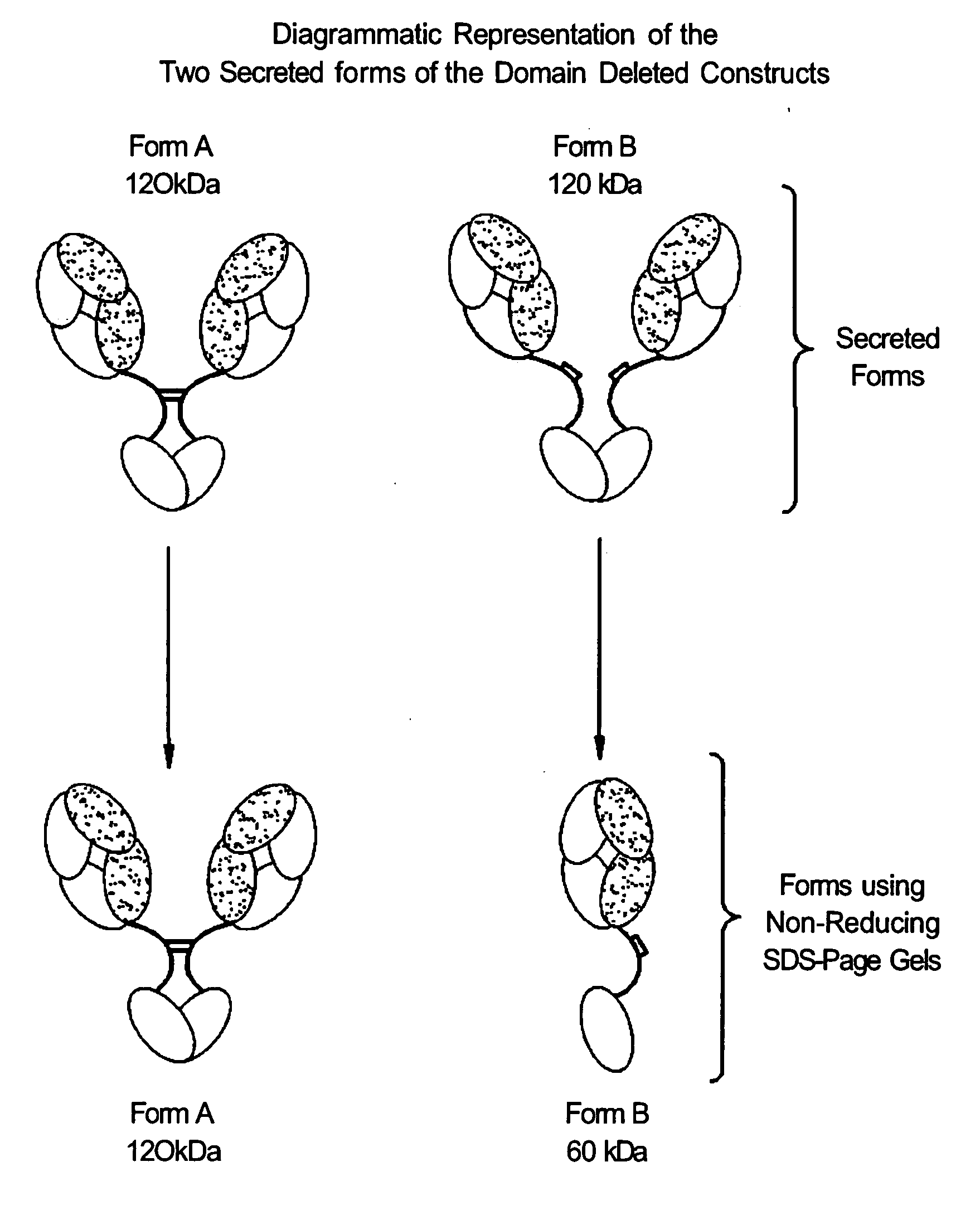
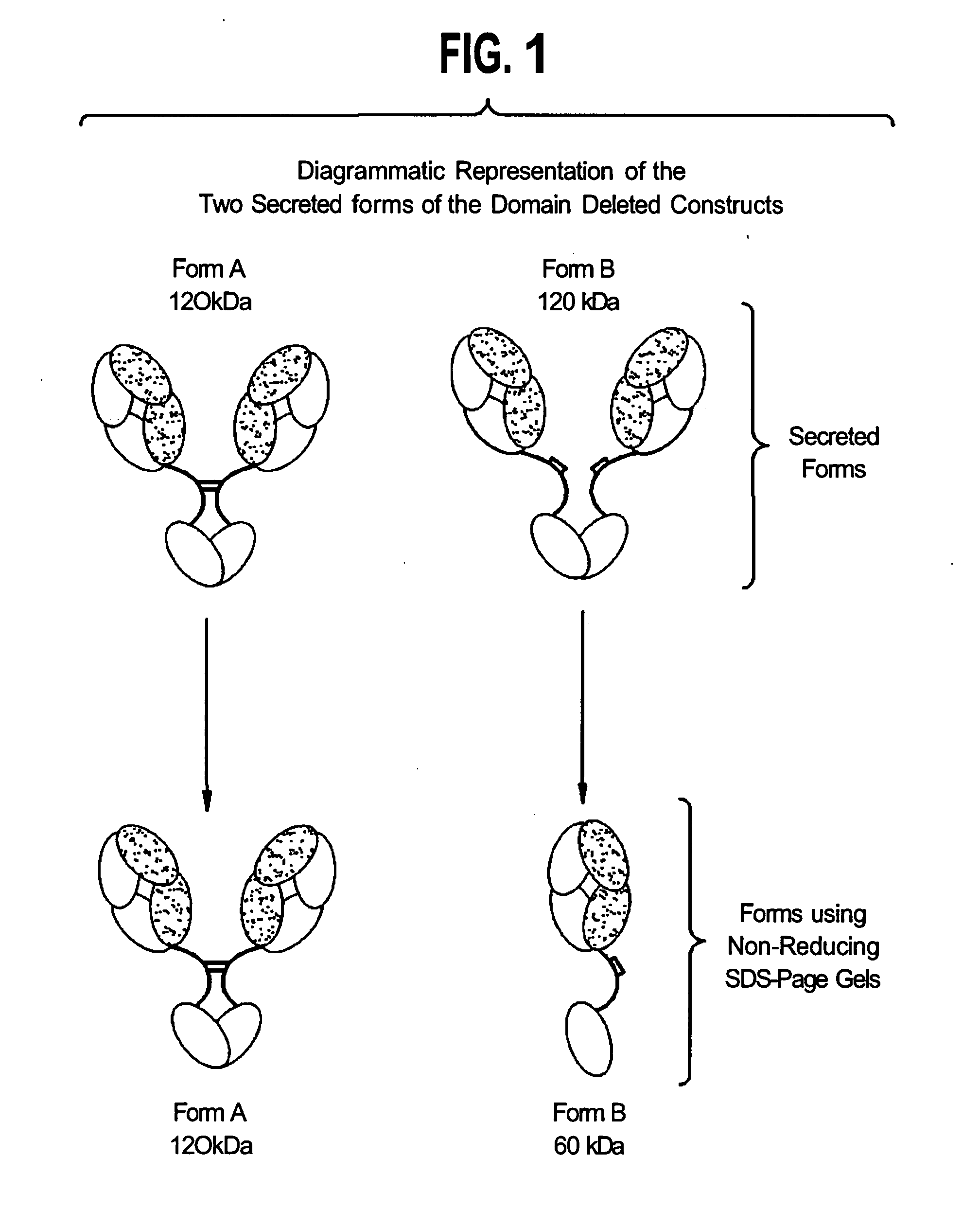
The instant invention describes methods of separating or preferentially synthesizing dimers which are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from dimers which are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from a mixture comprising the two types of polypeptide dimers. These forms can be separated from each other using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. In addition, the invention pertains to connecting peptides that result in the preferential biosynthesis of dimers that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or that are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention also pertains to compositions in which a majority of the dimers are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention still further pertains to novel binding molecules, e.g., comprising connecting peptides of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
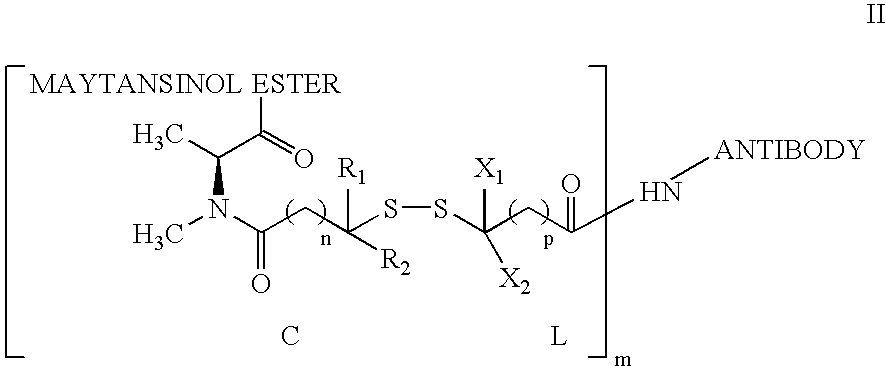
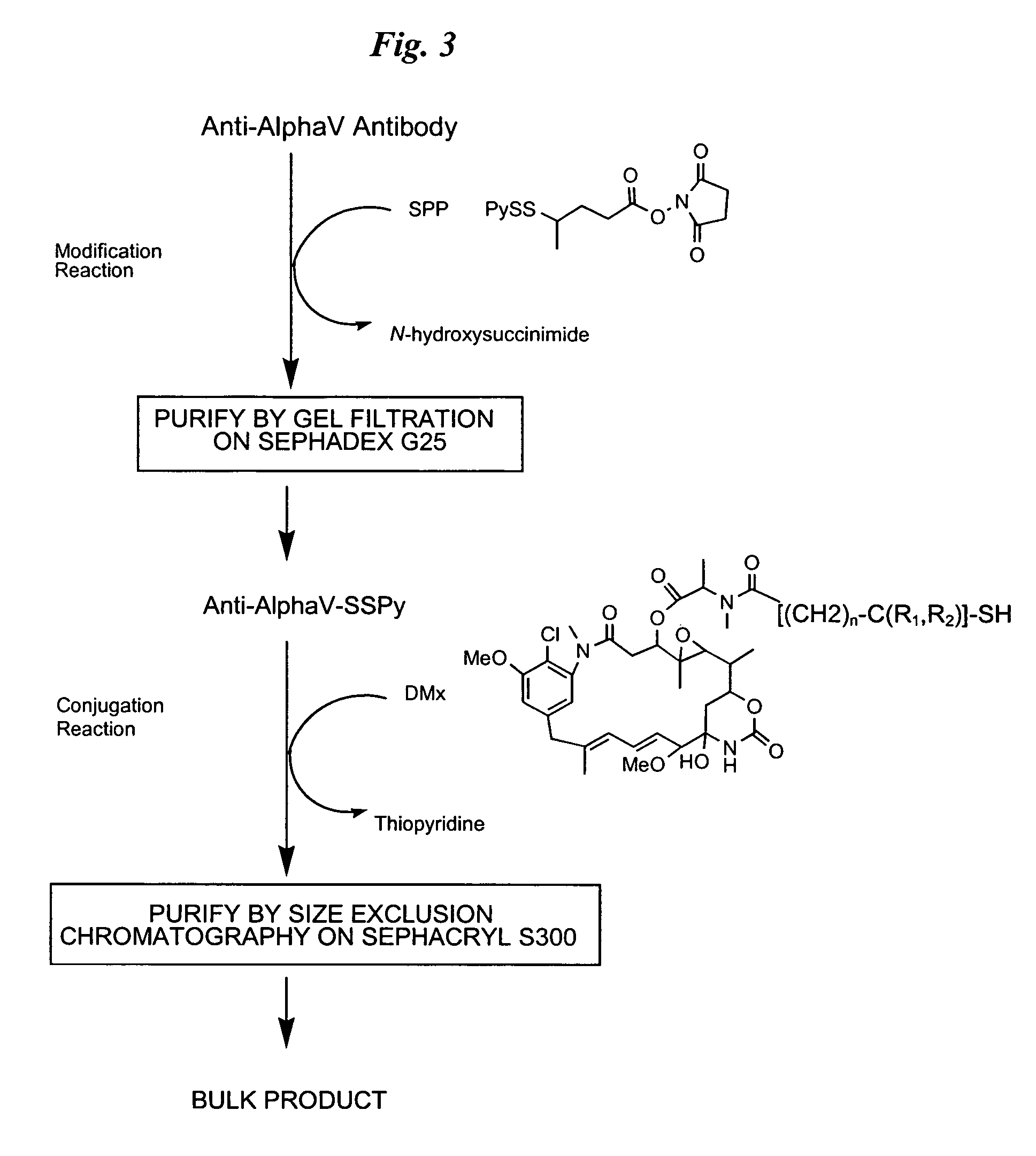
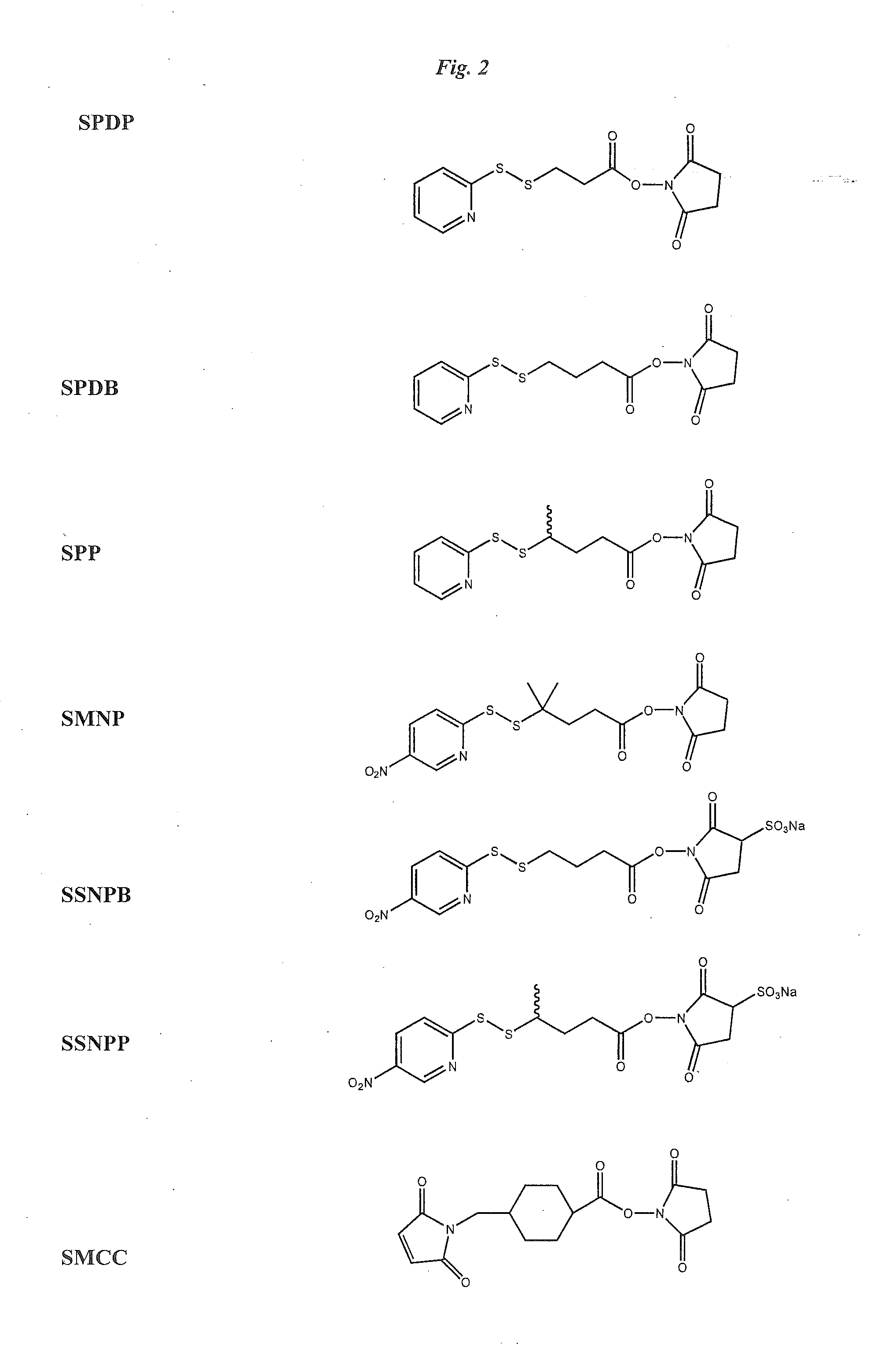
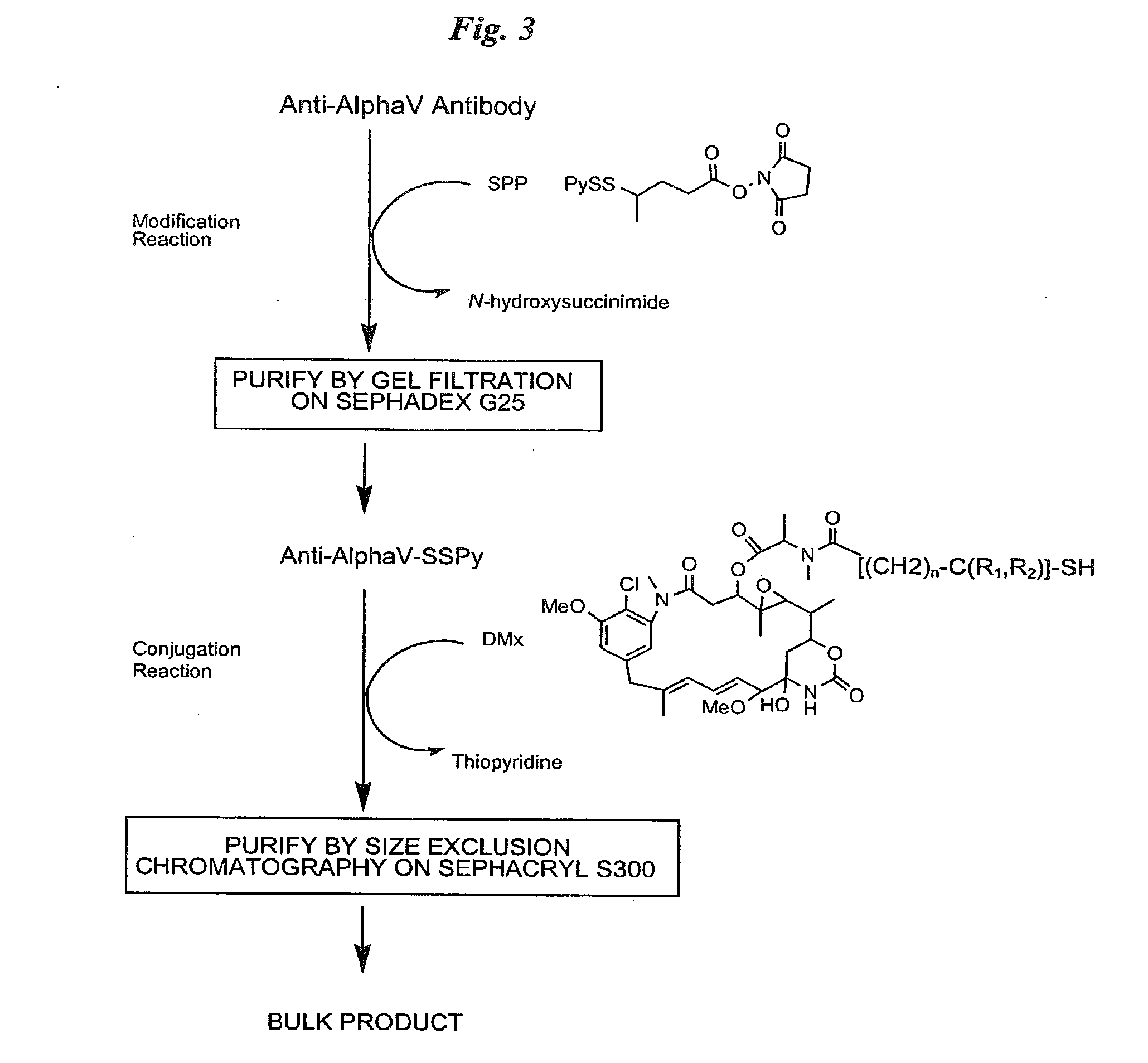
Anti-integrin immunoconjugates, methods and uses
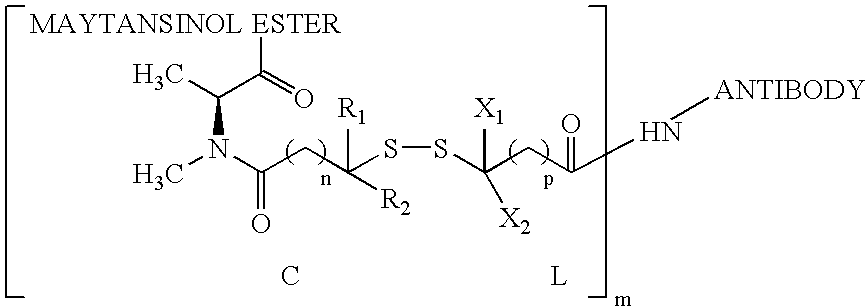
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
Drug Delivery Systems
InactiveUS20140030350A1Rate of drug release is alteredEnhanced drug releaseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCross-linkMicroparticle
The present invention relates to microparticles comprising a gel body, wherein the gel body comprises a synthetic polymer and a drug, wherein the microparticles have an average diameter in the range 40 to 1500 μm, wherein the polymer is cross-linked by groups comprising disulfide linkages and is in the form of a hydrogel.
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Purification and preferential synthesis of binding molecules
ActiveUS20050163783A1Well formedImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide LinkageMedicinal chemistry
The instant invention describes methods of separating or preferentially synthesizing dimers which are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from dimers which are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage from a mixture comprising the two types of polypeptide dimers. These forms can be separated from each other using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. In addition, the invention pertains to connecting peptides that result in the preferential biosynthesis of dimers that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or that are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention also pertains to compositions in which a majority of the dimers are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. The invention still further pertains to novel binding molecules, e.g., comprising connecting peptides of the invention.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
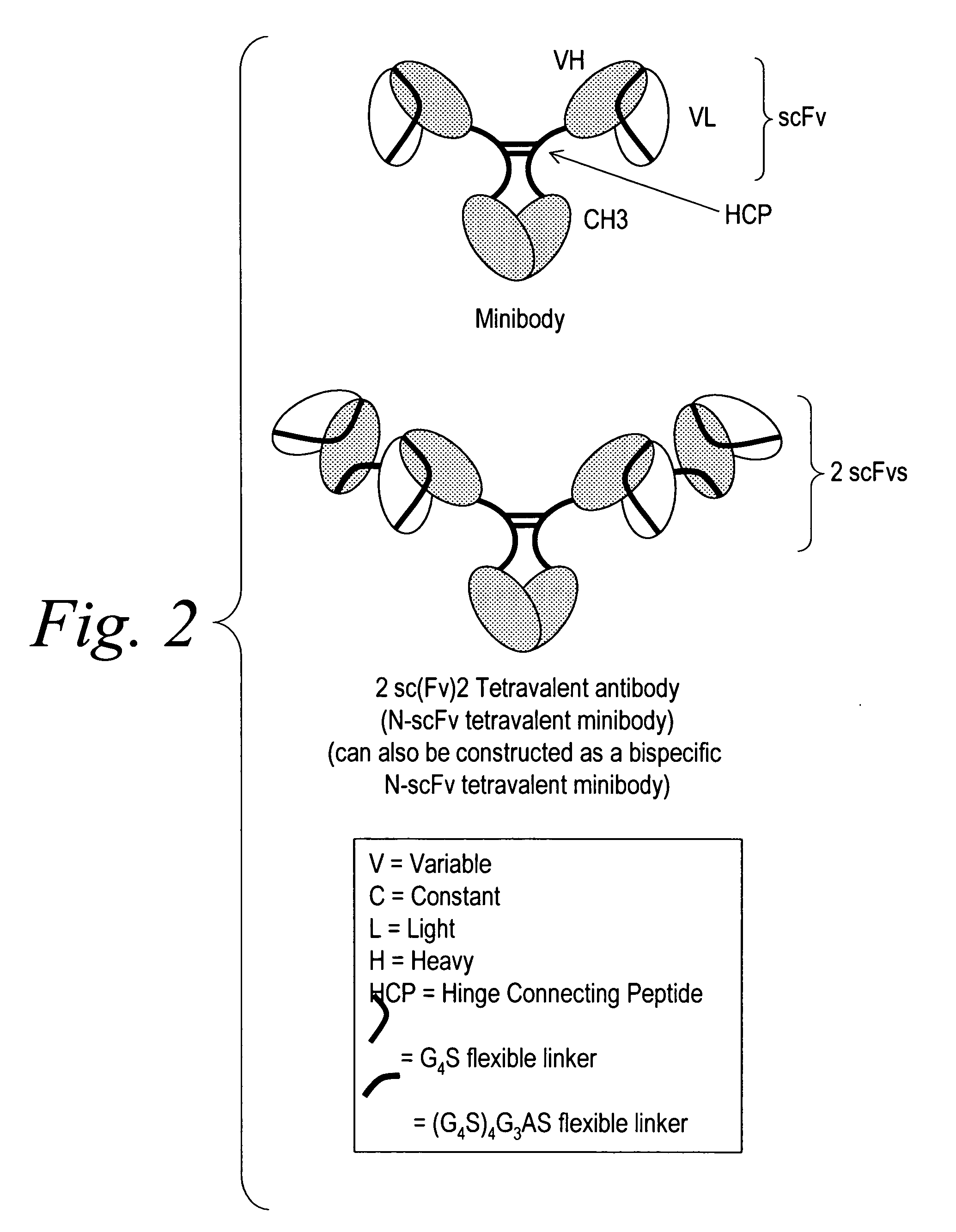
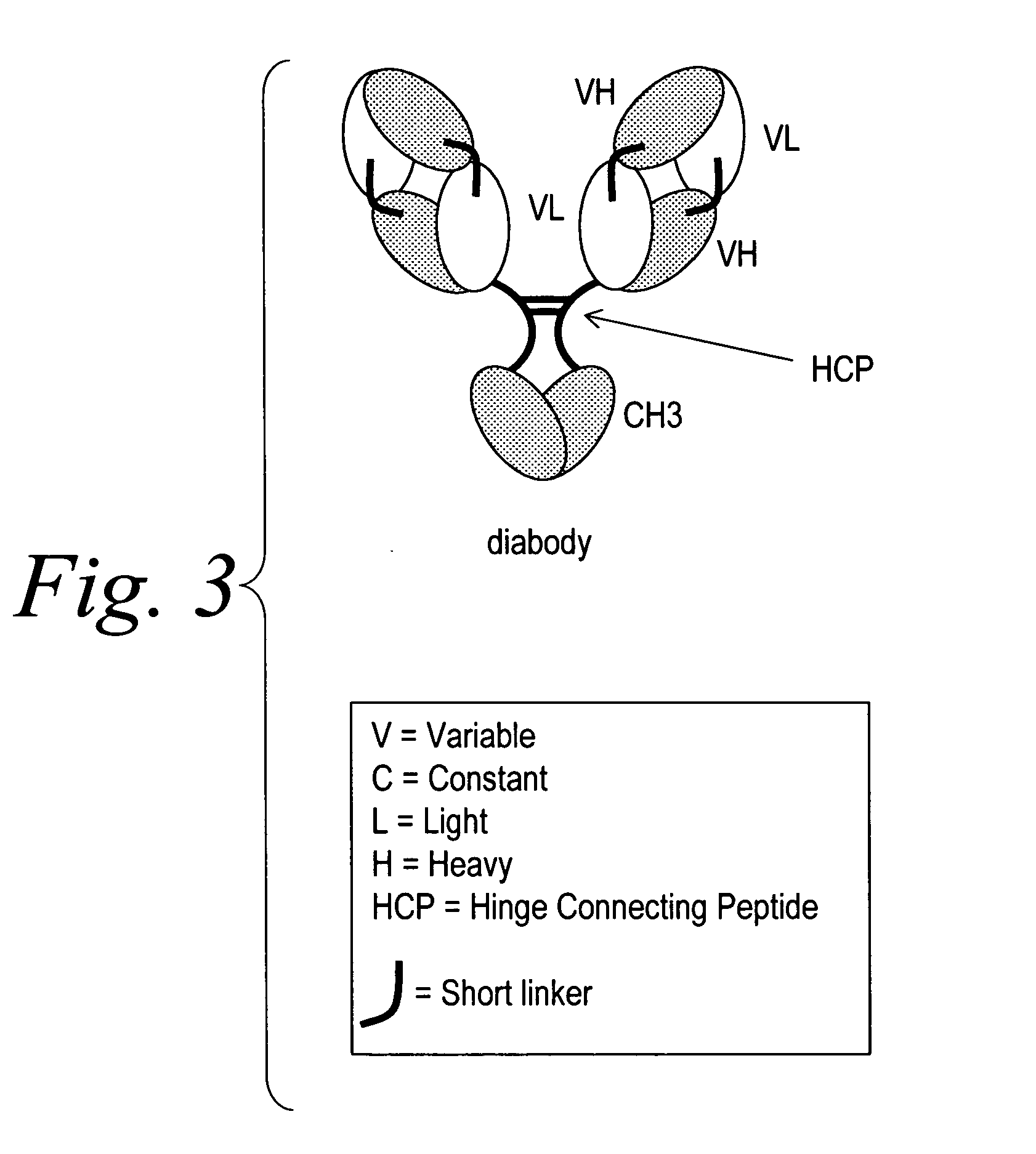
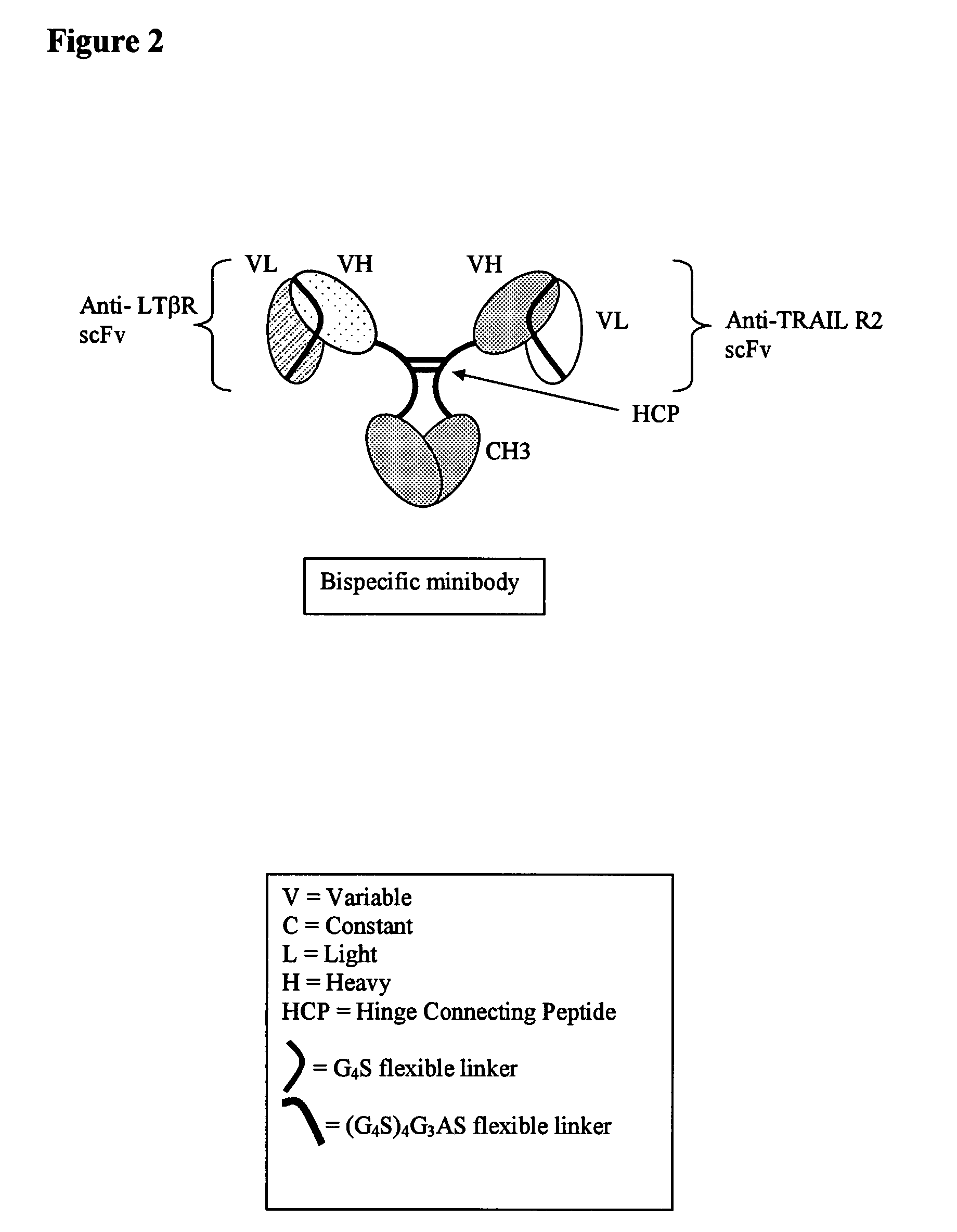
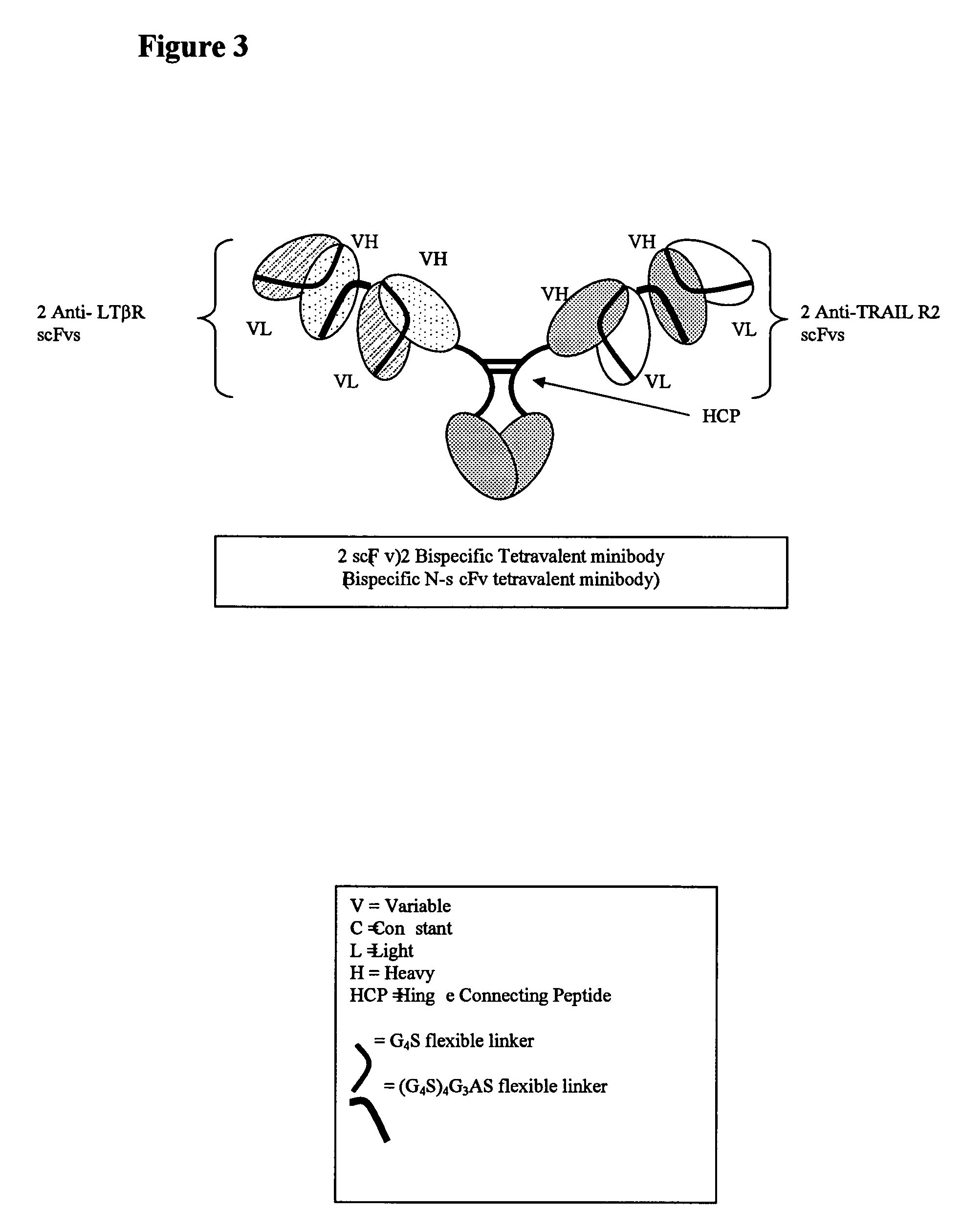
Multispecific binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
ActiveUS20090162380A1Enhance receptor signalingEnhanced signalSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainBinding site
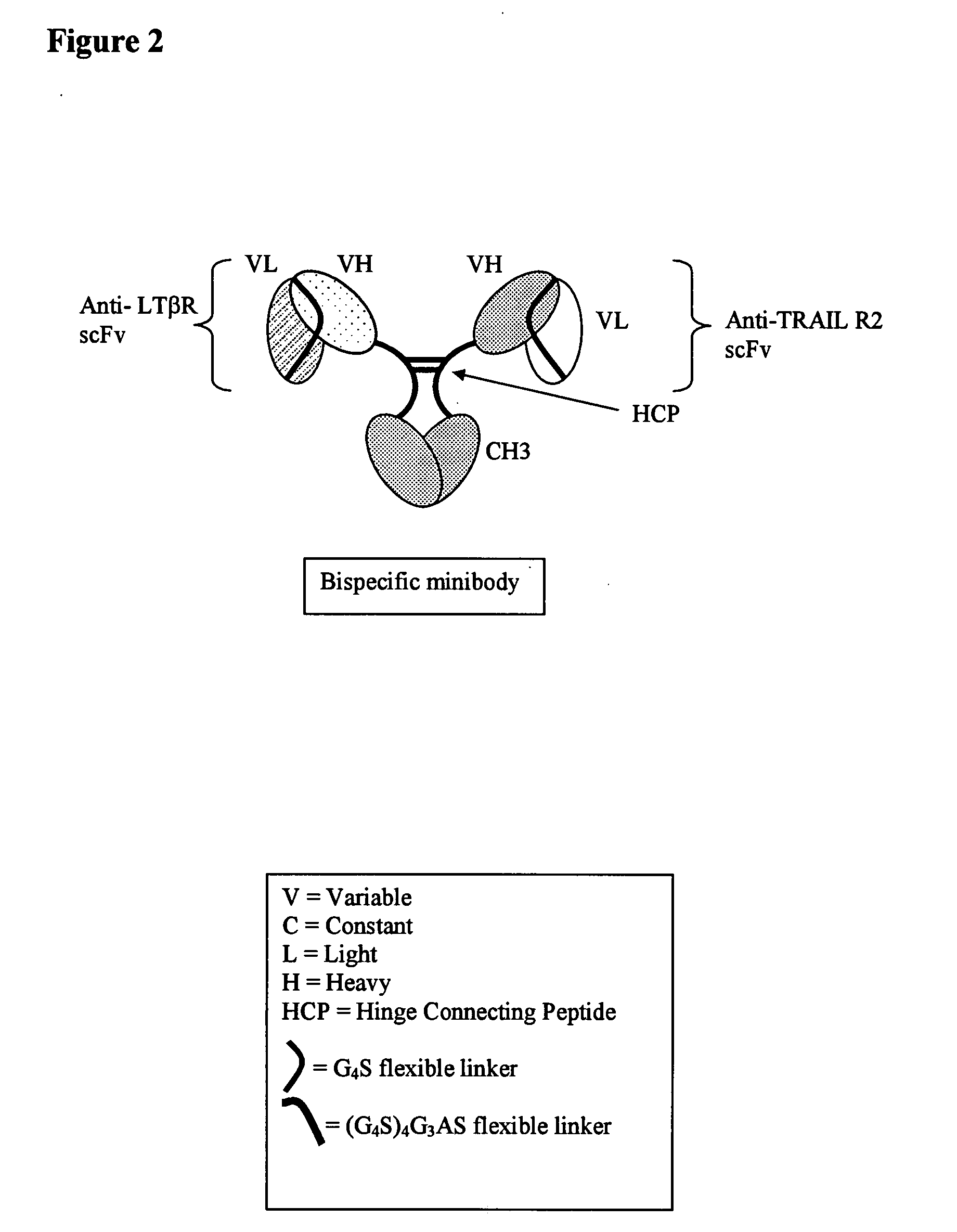
The instant invention describes novel multispecific binding molecules comprising synthetic connecting peptides. The synthetic connecting peptides result in the preferential synthesis of multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. In addition, the invention pertains to compositions in which a majority of the multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chain that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one intrachain disulfide linkage. In a specific embodiment, the invention pertains to compositions comprising multispecific dimeric binding molecules said molecules comprising at least a first binding site specific for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor or a ligand of a TNF receptor family member and at least a second binding site; and at least two polypeptide chains comprising at least one heavy chain portion and a synthetic connecting peptide; wherein greater than about 50% of the dimers comprise polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
Nanometer micelle capable of intelligently releasing medicine as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102391517ASuitable chain complianceImprove biological activityPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyethylene glycolAminolysis
The invention discloses a nanometer micelle capable of intelligently releasing medicine as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The nanometer micelle provided by the invention comprises the components of polyethylene glycol-poly (aspartate-cysteine)-poly (aspartate-diisopropyl ethanediamine). The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, synthesizing PEG-PBLA-N3 and PA-PAsp (DIP); then, taking cuprous bromide / pentamethyldiethylenetriamine as a catalyst system, and synthesizing PEG-PBLA-PAsp (DIP) through a click reaction of PEG-PBLA-N3 and PA-PAsp (DIP); and finally, carrying out an aminolysis reaction on 2-aminoethyl mercaptan to obtain the final polymer PEG-PAsp (MEA)-PAsp (DIP). The nanometer micelle provided by the invention can be used as a hydrophobic medicine carrier. The nanometer micelle is sensitive to pH value, the disulfide bond in the intermediate cross-linking layer is sensitive to a reducing agent, and the nanometer micelle has the characteristic of intelligently releasing medicine.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Multispecific binding molecules comprising connecting peptides
ActiveUS8084026B2High binding affinityImprove localizationHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesDimerHeavy chain
The instant invention describes novel multispecific binding molecules comprising synthetic connecting peptides. The synthetic connecting peptides result in the preferential synthesis of multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage. In addition, the invention pertains to compositions in which a majority of the multispecific binding molecules comprising polypeptide chain that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage or are not linked via at least one intrachain disulfide linkage. In a specific embodiment, the invention pertains to compositions comprising multispecific dimeric binding molecules said molecules comprising at least a first binding site specific for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor or a ligand of a TNF receptor family member and at least a second binding site; and at least two polypeptide chains comprising at least one heavy chain portion and a synthetic connecting peptide; wherein greater than about 50% of the dimers comprise polypeptide chains that are linked via at least one interchain disulfide linkage.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Cloning, expression and application of eimeria tenella protein disulfide isomerase gene
InactiveCN101418309AGenetic material ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliEmoia loyaltiensis
The invention discloses an E.tenella protein disulfide linkage isomerase gene EtPDI (Clone ID is BW1-E06,and the Genbank accession number of is EF552214). The gene is connected with a procaryon expression vector pGEX-4T-2; a procaryon expression recombination plasmid pGEX-4T-EtPDI is constructed and is expressed in a colibacillus system; and most of the expressed recombining protein exists in a soluble form. The recombining protein 4T-EtPDI is purified to carry out SPS-PAGE and is transferred to a PVDF film; and antiserum of E.tenella oocyst oral immunized chicken is used as first resistance and goat anti-chicken IgG is used as second resistance to carry out Western-blot analysis, thereby indicating that the gene has certain antigen. The gene is used for preparing an anti-chicken coccidiosis drug and an anti-chicken coccidiosis vaccine.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Intracellular Molecular Delivery Based On Nanostructure Injectors
InactiveUS20120264108A1High affinityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical LinkageBiotin-streptavidin complex
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Composition for resin
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
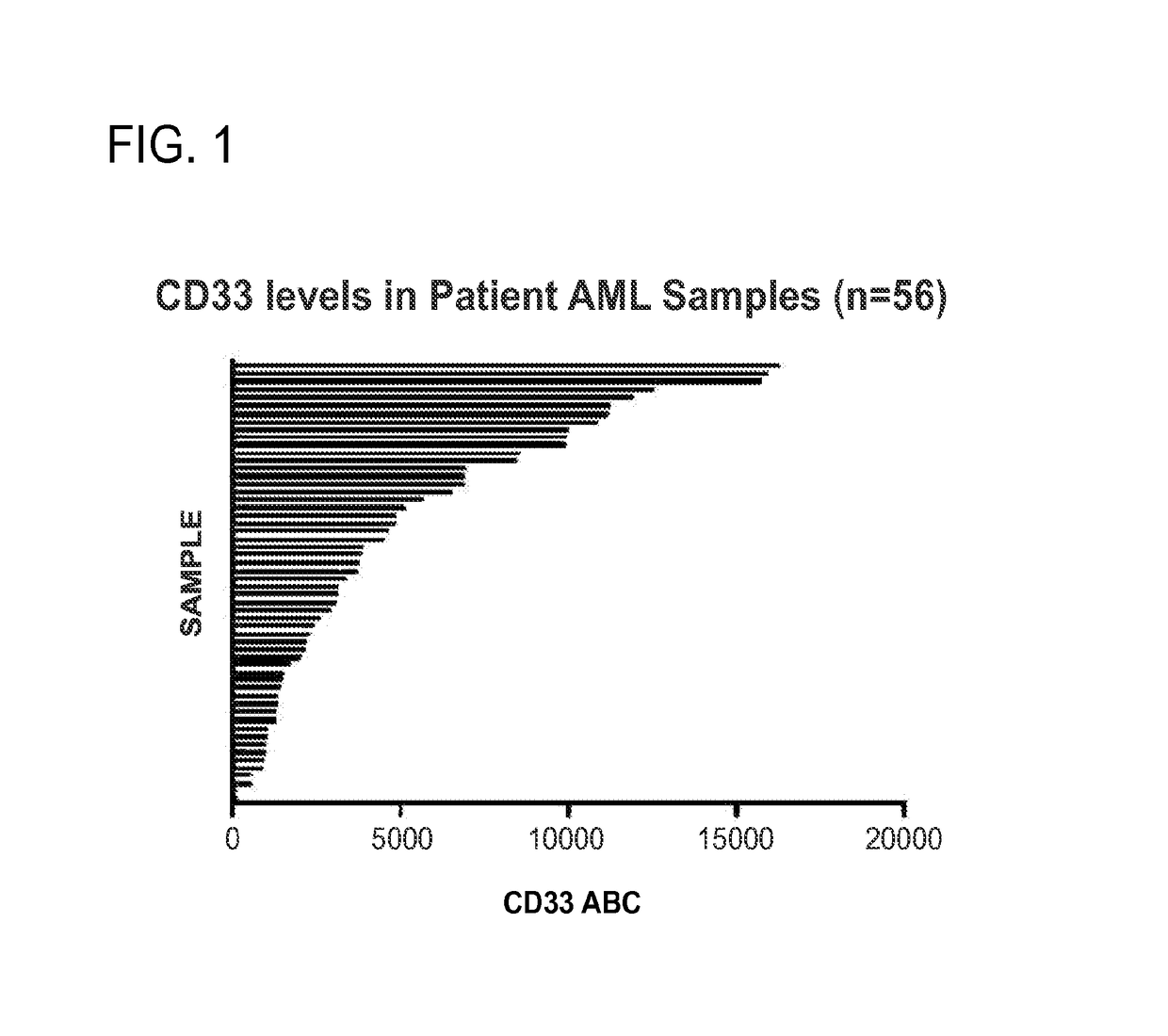
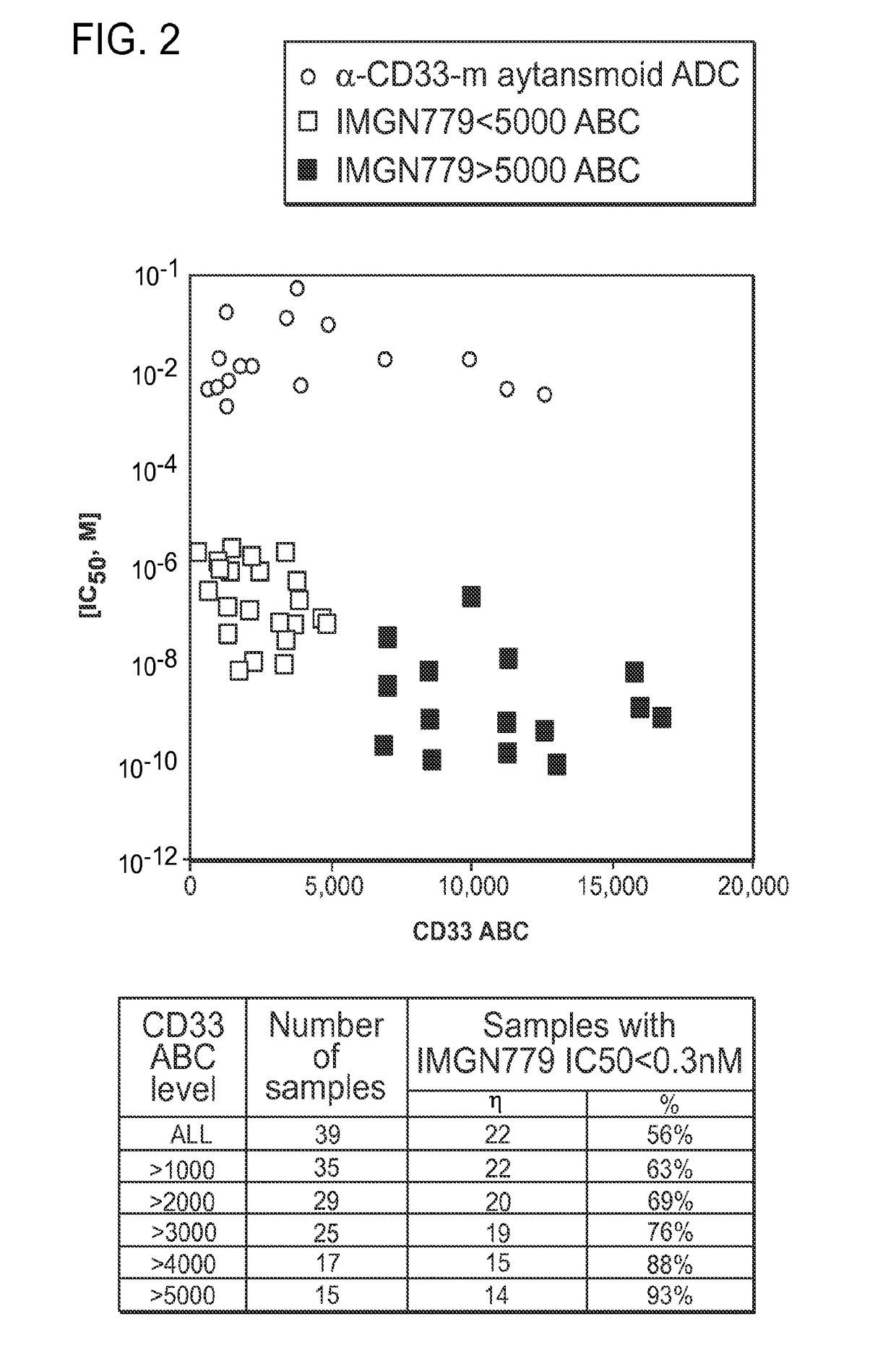
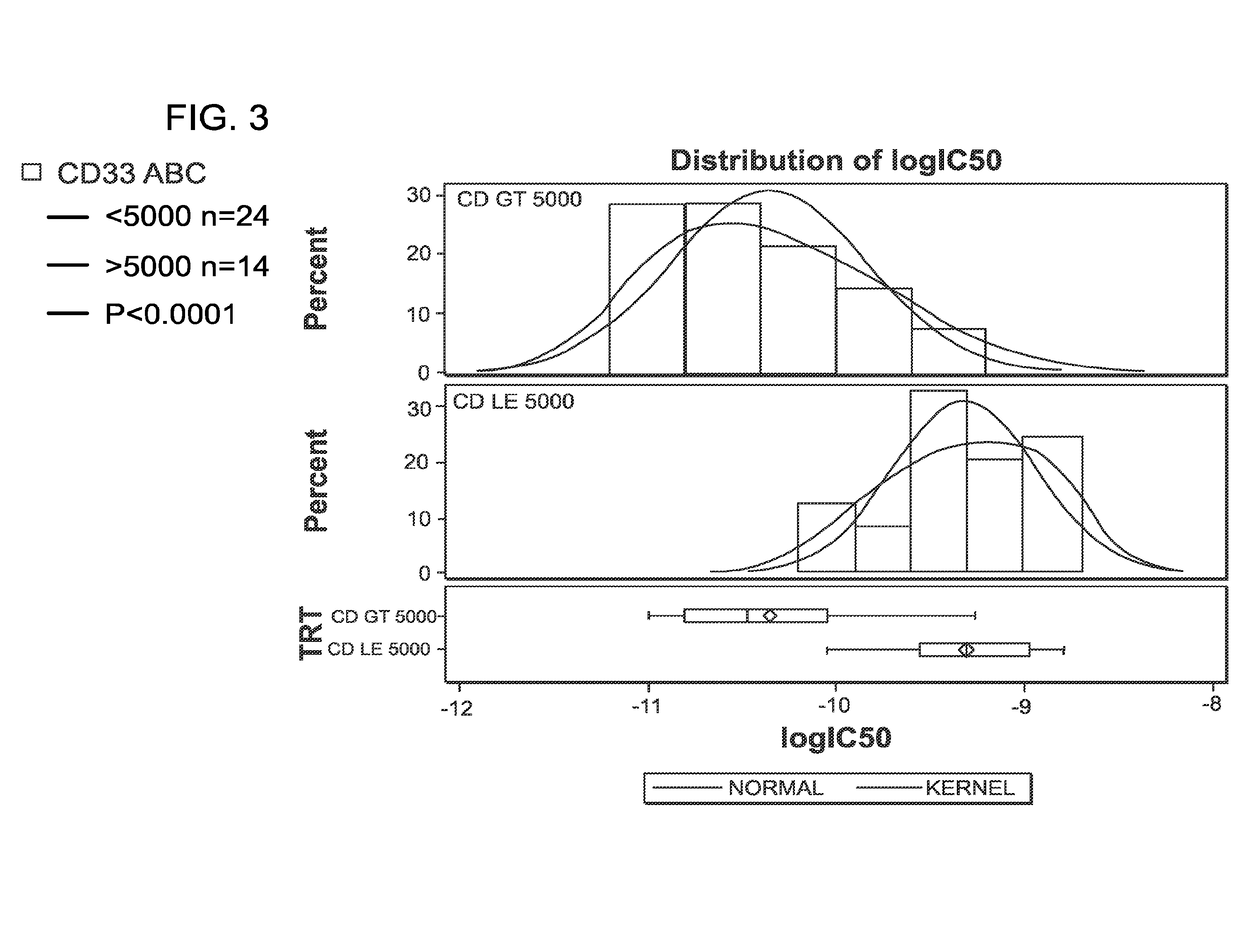
Methods for characterizing and treating acute myeloid leukemia
InactiveUS20170080102A1Reduce probabilityTreating or preventing acute myeloid leukemia relapseOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBenzodiazepineNewly diagnosed
The invention features methods for characterizing and treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (e.g., newly diagnosed, relapsed, and refractory AML) in a subject using immunoconjugates of the invention. In one aspect, the invention generally features a method of treating acute myeloid leukemia in a subject (e.g., a human), the method involving administering an effective amount of an immunoconjugate to a pre-selected subject, where the immunoconjugate contains a humanized or chimeric antibody or fragment conjugated to a cytotoxic benzodiazepine dimer compound via a cleavable disulfide linker.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
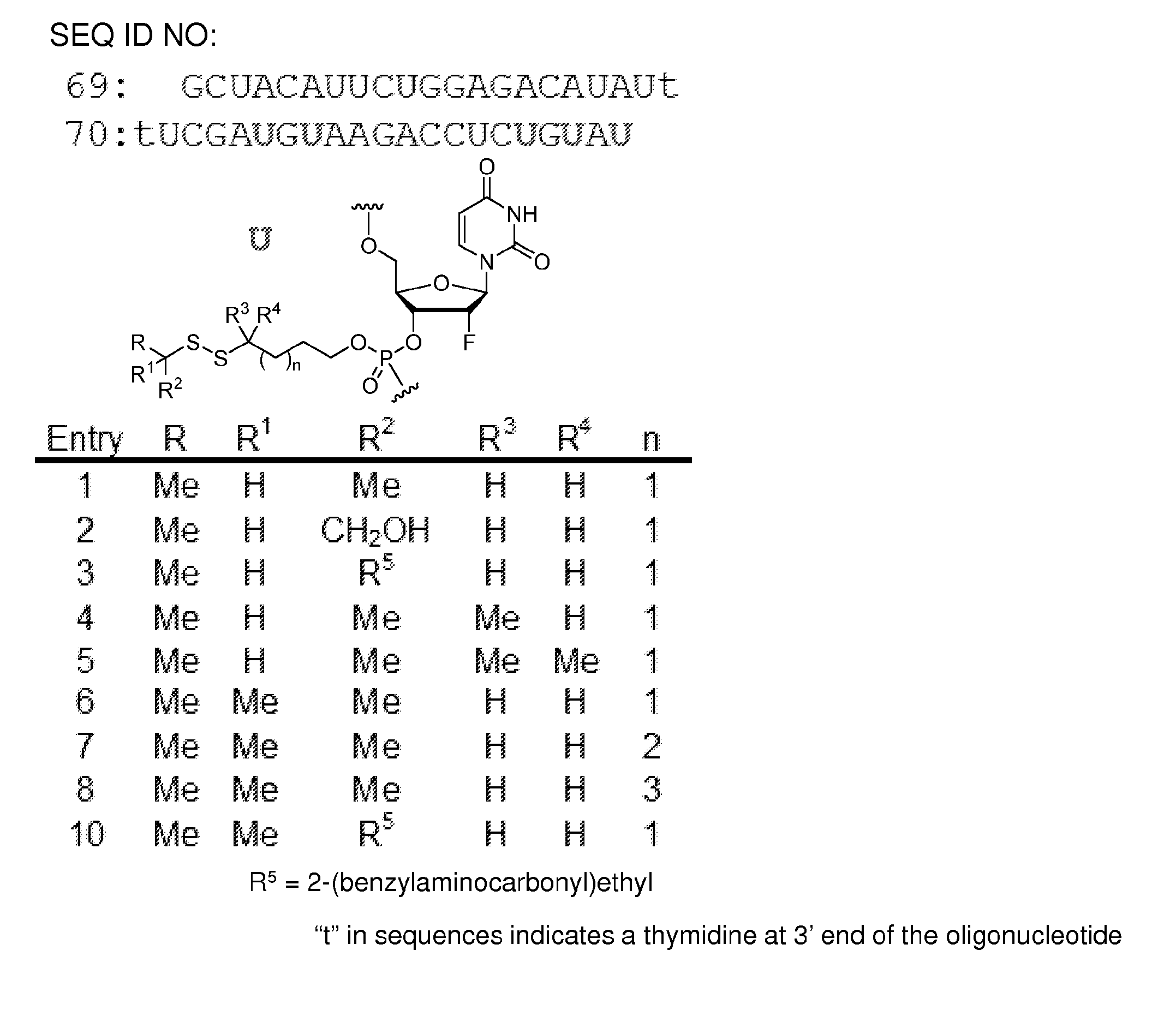
Polynucleotide constructs having disulfide groups
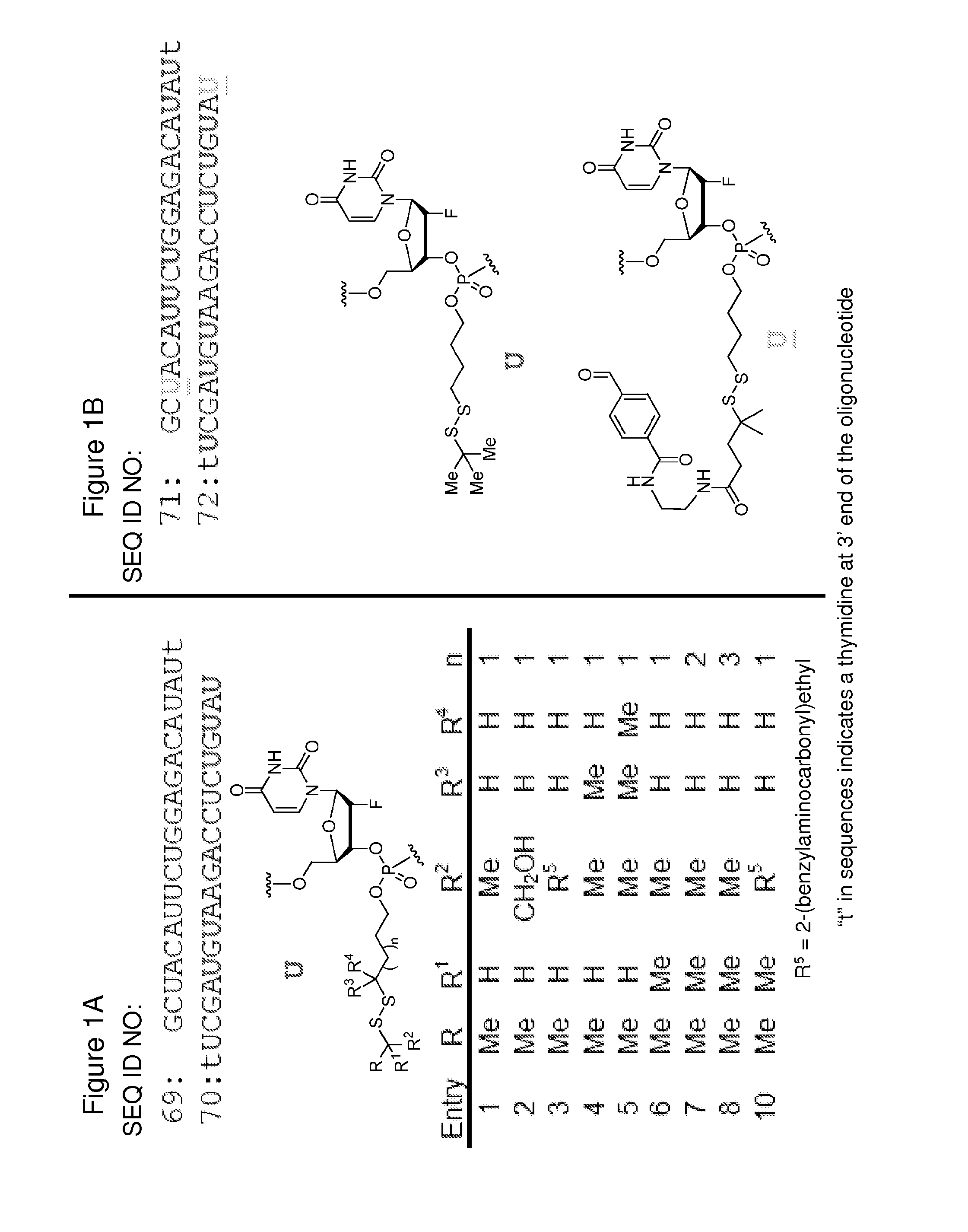
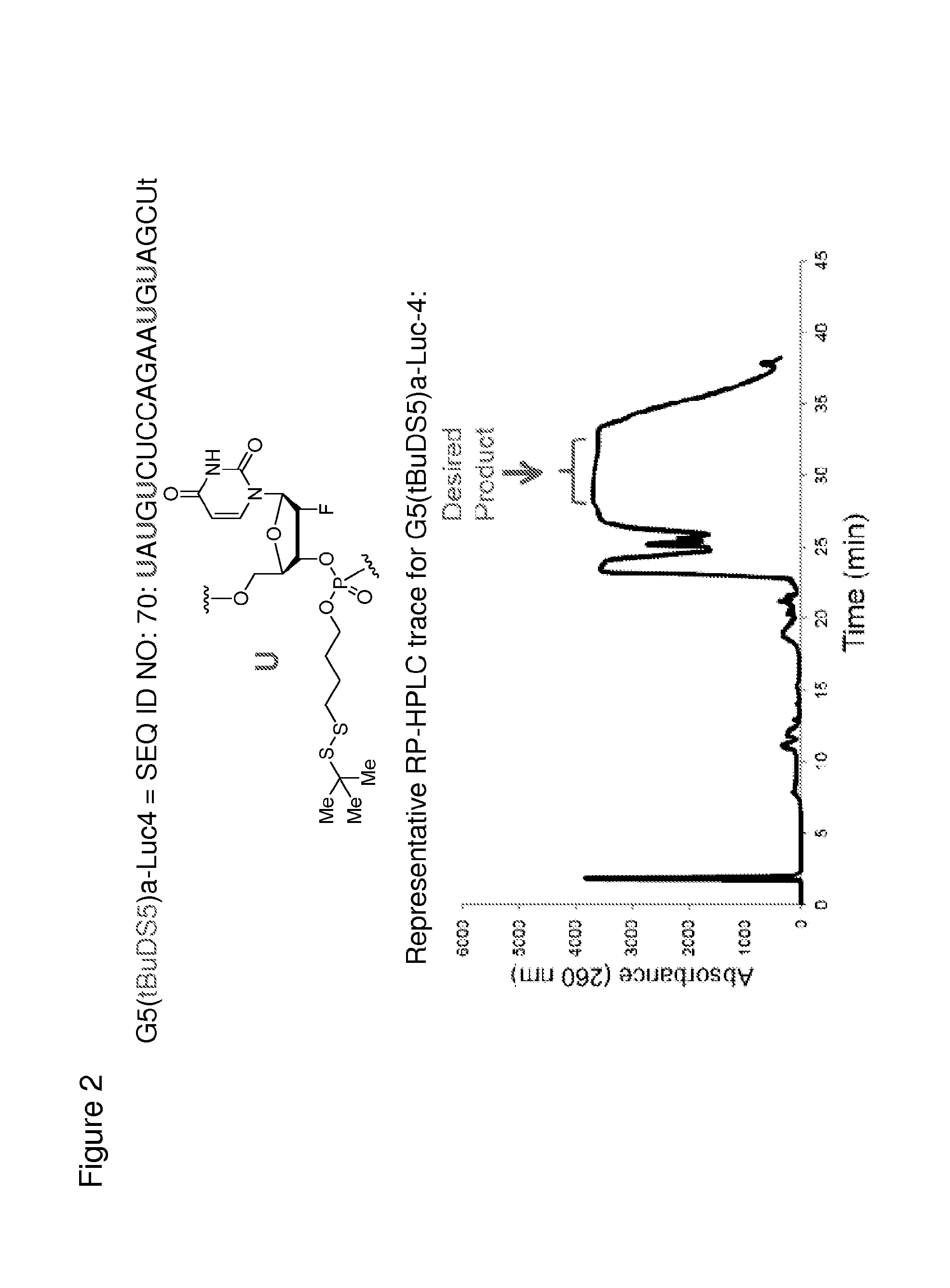
InactiveUS20160257961A1Facilitated releaseSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphatePolynucleotide
The invention features polynucleotide constructs containing one or more components (i) containing a disulfide linkage, where each of the one or more components is attached to an internucleotide bridging group or a terminal group of the polynucleotide construct, and each of the one or more components (i) contains one or more bulky groups proximal to the disulfide group. The invention also features polynucleotide constructs containing one or more components (i) containing a disulfide linkage, where each of the one or more components (i) is attached to an internucleotide bridging group or a terminal group of the polynucleotide construct, and each of the one or more components (i) contains at least 4 atoms in a chain between the disulfide linkage and the phosphorus atom of the internucleotide bridging group or the terminal group; and where the chain does not contain a phosphate, an amide, an ester, or an alkenylene. The invention also features methods of delivering a polynucleotide to a cell using the polynucleotide constructs of the invention.
Owner:BRADSHAW CURT W +8
Exogenous surfactant protein B mimic
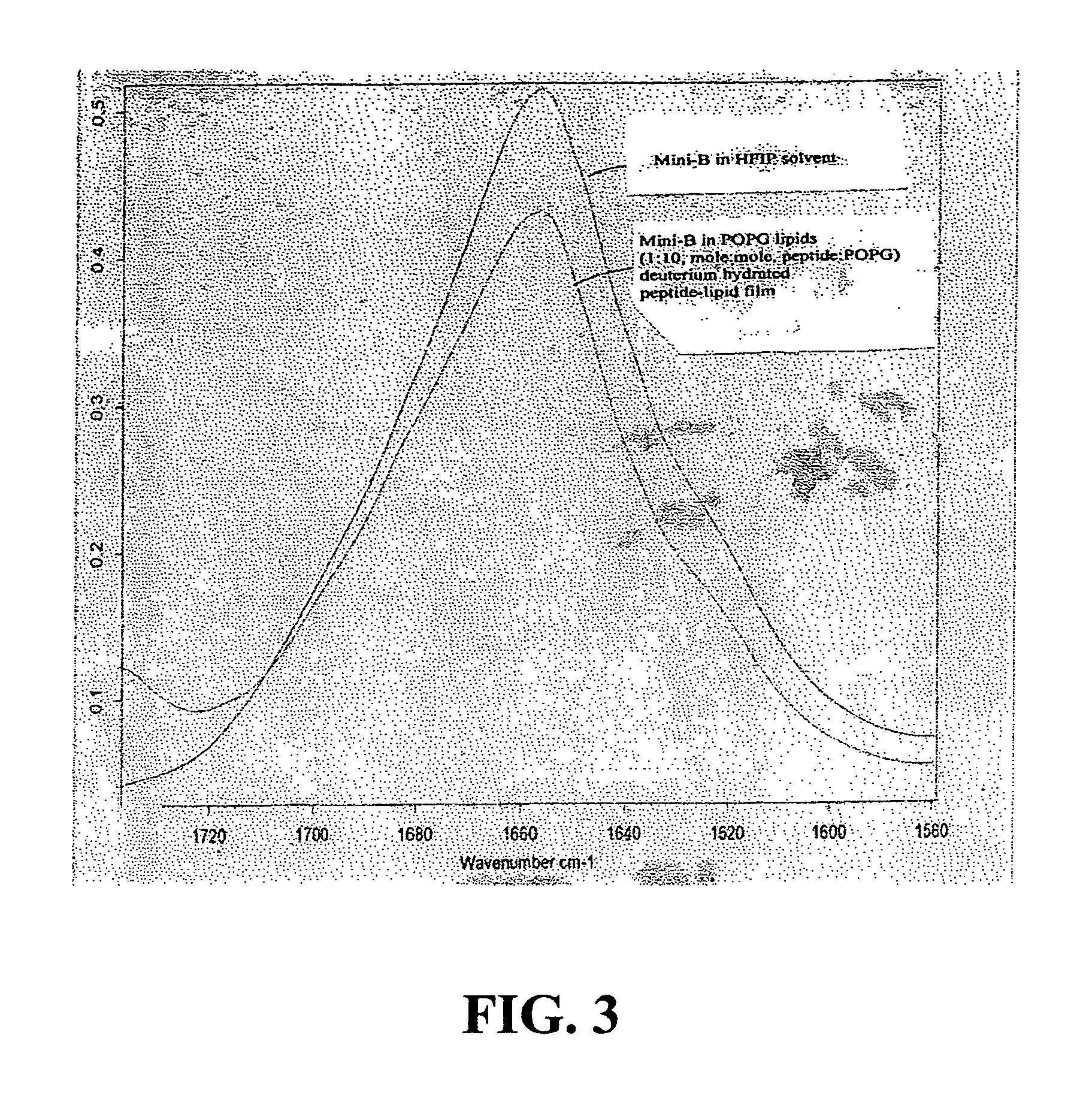
ActiveUS7538090B1Improve compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsAlveolar/pulmonary surfactant peptidesNaturally occurring surfactantsDisulfide Linkage
A composition including a C terminal region having residues corresponding to a peptide identified by PDB ID: 1RG3; an N terminal region having residues corresponding to a peptide identified by PDB ID: 1RG4; and a disulfide linkage between the residues near the C terminal region and the N terminal region. A composition including an exogenous peptide comprising amino acid residues comprising a C terminal region; amino acid residues comprising an N terminal region; a helix-loop-helix conformation between the residues comprising the C terminal region and the residues including the N terminal region; and at least one disulfide linkage between the residues comprising the C terminal region and the residues including N terminal region, wherein the residues including the C terminal region and the residues comprising the N terminal region have an amphiphatic property, and wherein the peptide has an a biological activity comparable to native surfactant protein SP-B. A method including delivering to a body a composition comprising an exogenous peptide having a biological activity comparable to native surfactant protein SP-B. A kit including an exogenous peptide having a biological activity comparable to native surfactant protein SP-B; and a treatment agent different from the peptide.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Thermostable amylase mutant and a preparation method thereof
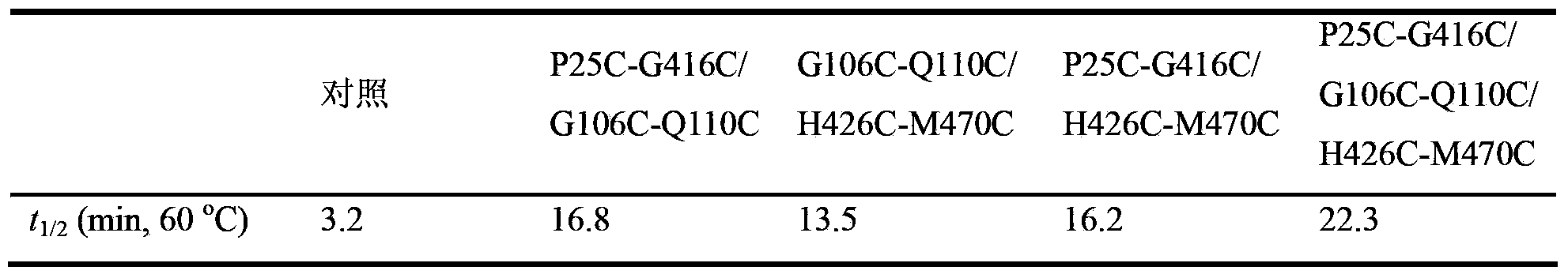
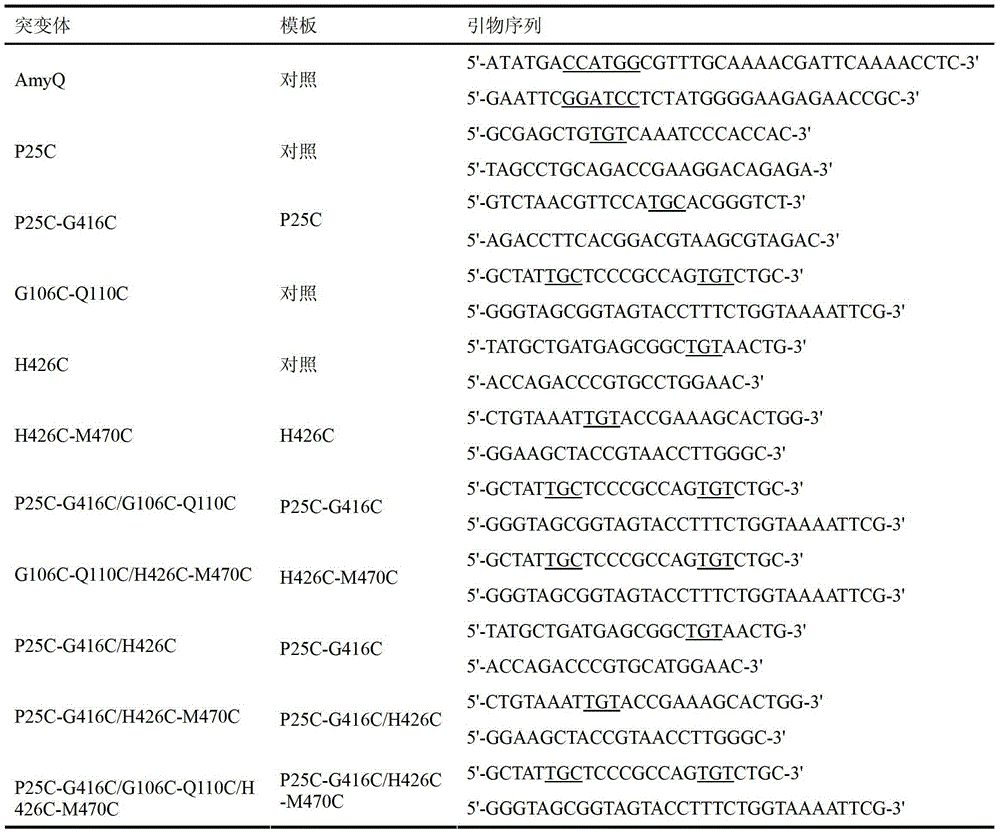
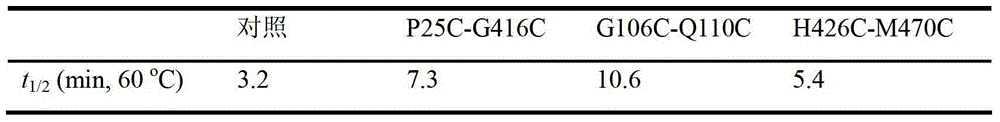
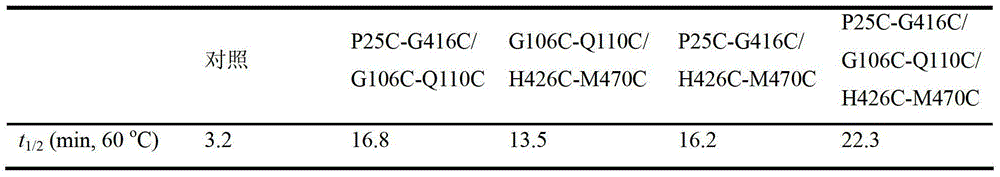
InactiveCN103409392AImprove thermal stabilityEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmylaseBacillus alcalophilus
The invention discloses a thermostable amylase mutant and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to invention, bacillus alcalophilus JN21 (CCTCC NO:M2011231) amylase is used as female parent; molecular biological technique is adopted to conduct site-directed mutagenesis for bacillus alcalophilus amylase sequence; a pair or multiple pairs of disulfide linkages are introduced in amylase catalytic structural domain to obtain amylase mutant with higher thermal stability; under the modification condition, the half-life period of bacillus alcalophilus amylase at 60 DEG C is improved to 22.3 min from 3.2 min of a comparison example (before mutation); by utilizing the strategy, the thermostability of amylase can be obviously improved to provide basis for industrialized production, and the strategy has significant guiding significance for the modification of properties of other enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Polymer/Copper Combination for Targeted Cancer Therapy
ActiveUS20160108160A1Organic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsCancer cellBackbone chain
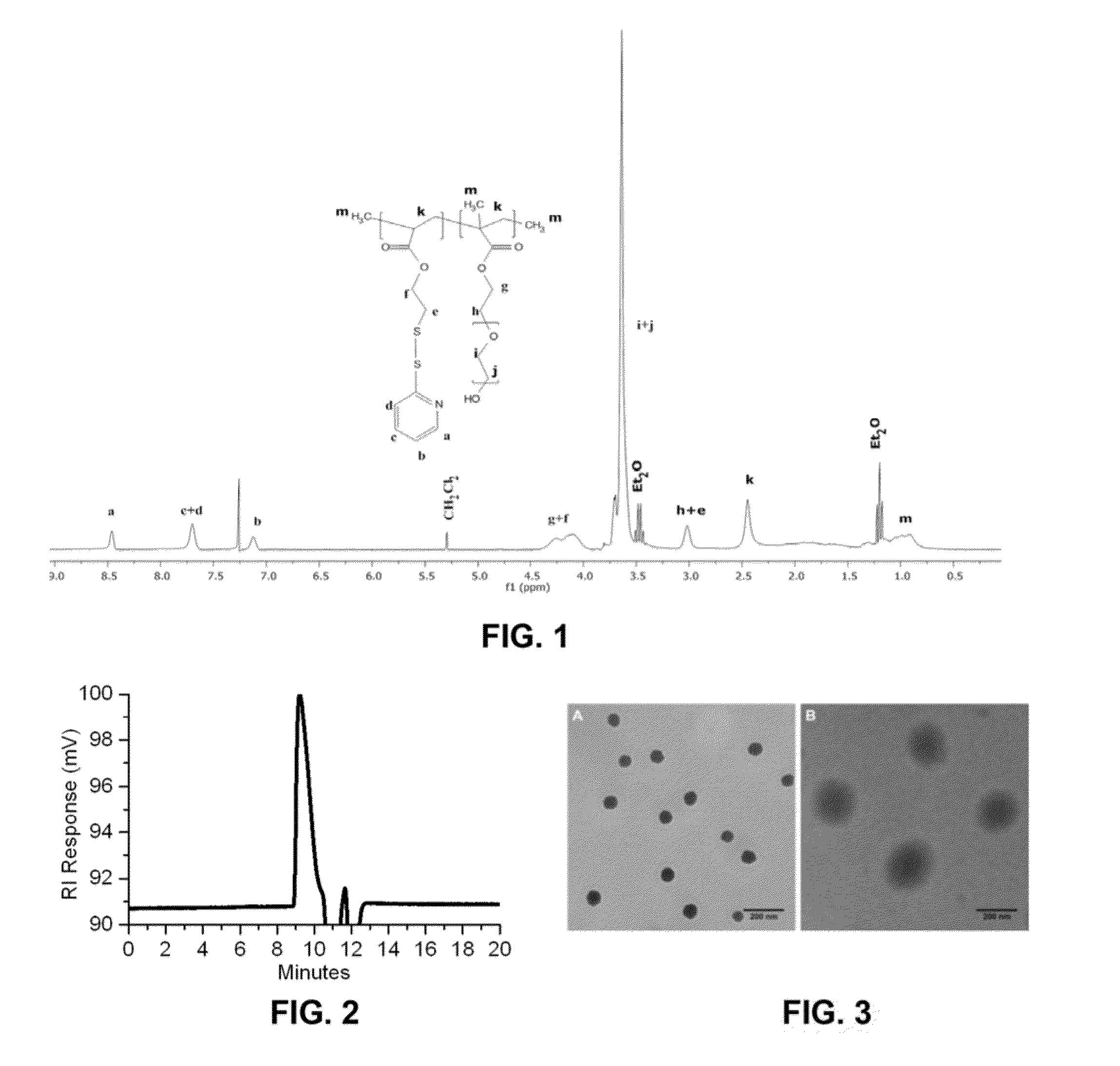
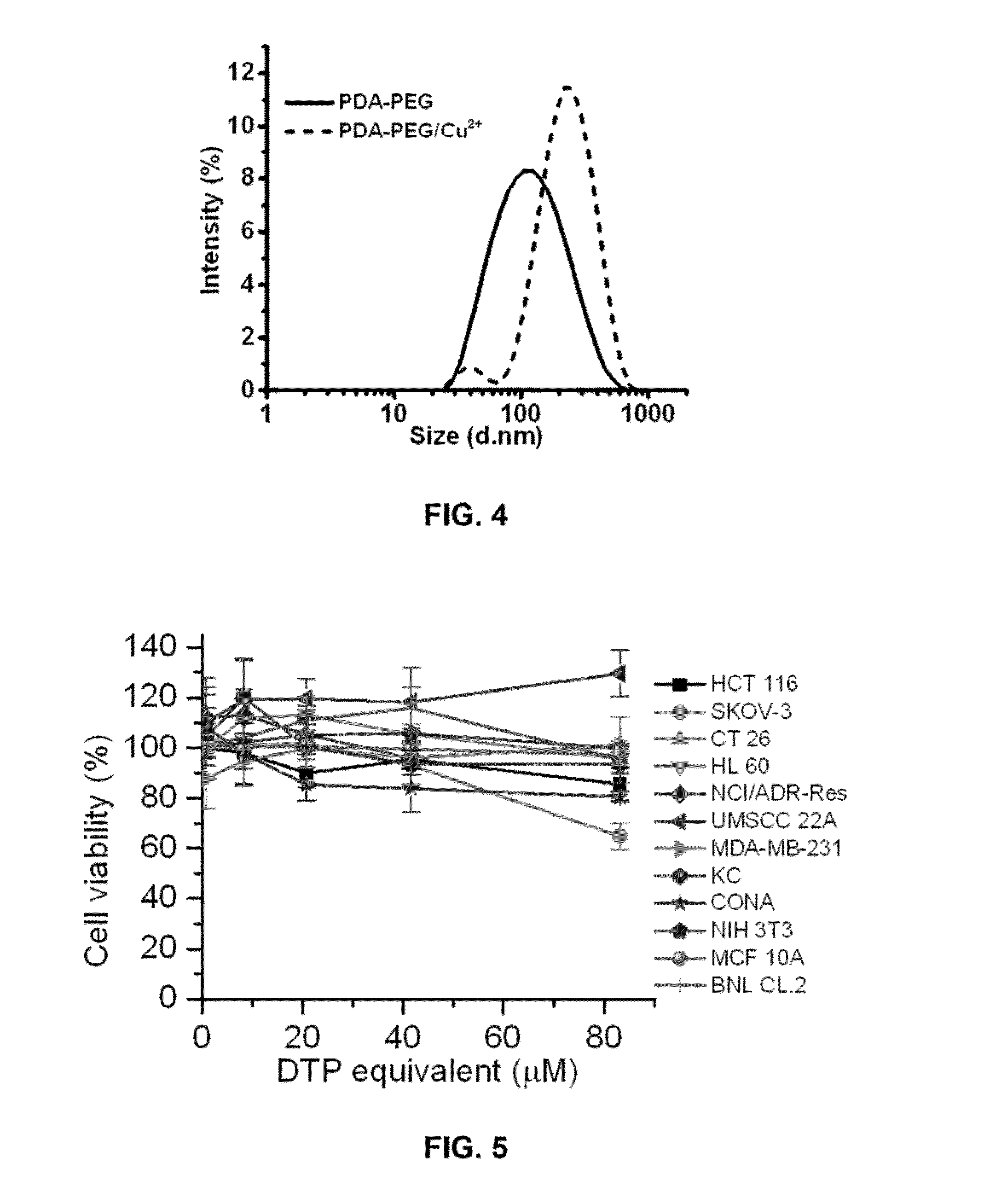
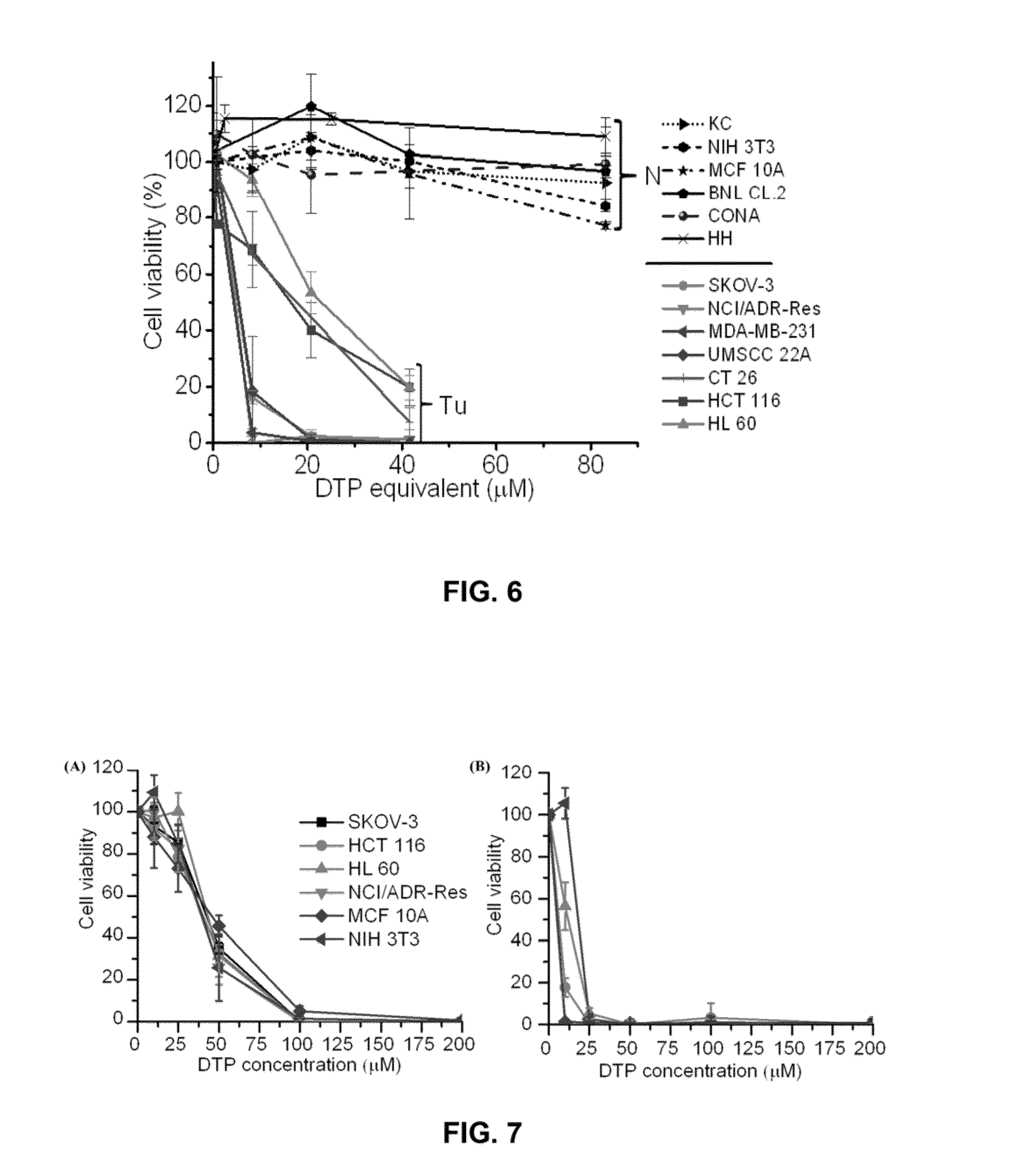
Polymer / copper combination that can selectively target and kill cancer cells are described. Materials can include the reaction product of a biocompatible hydrophilic polymer and pyridine-2-thiol containing monomer. The copolymer reaction product can include pyridine-2-thiol side groups pendant to the backbone via a disulfide linkage. The hydrophilic component can form the polymer backbone and / or can form hydrophilic pendant groups off of the backbone. Copper ions can be associated with the copolymer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
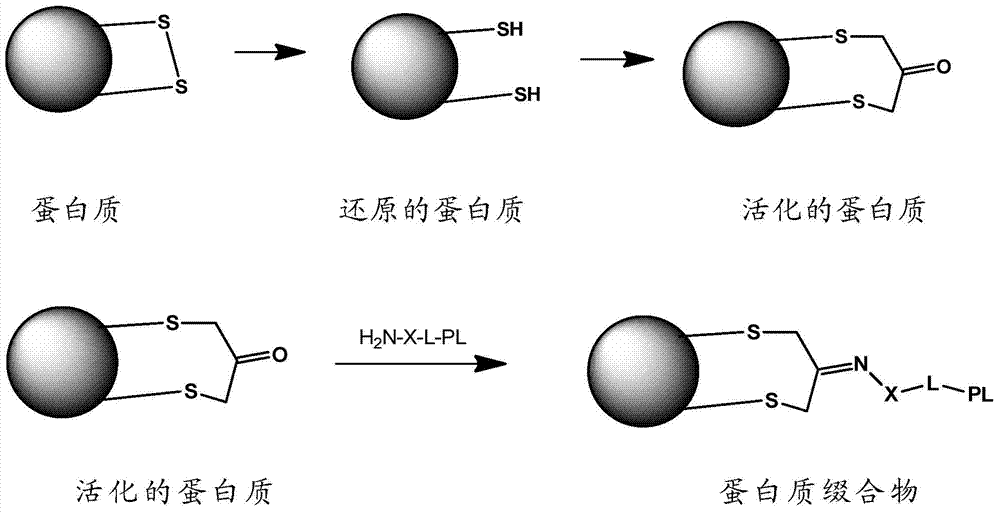
Methods for making conjugates from disulfide-containing proteins
The invention provides methods to prepare protein conjugates from proteins having at least two cysteines. In one embodiment, a protein with a disulfide linkage is reduced to provide two free cysteines for reaction with a 1,3-dihaloacetone or similar reactant, linking the sulfur atoms of the two cysteines together. The ketone inserted between the sulfur atoms is then used to form a Schiff base to an aminated payload molecule, thus conjugating the protein to a payload. In another embodiment, two cysteine residues are tied together by reaction with a 1,3-dihaloacetone or similar reactant. The linkage between the sulfur atoms in each case holds the protein or peptide in a constrained conformation, while also providing a convenient place for attaching a payload with good specificity and efficiency.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Anti-integrin immunoconjugates, methods and uses
InactiveUS8603483B2Effective rate of releaseSenses disorderAntipyreticDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
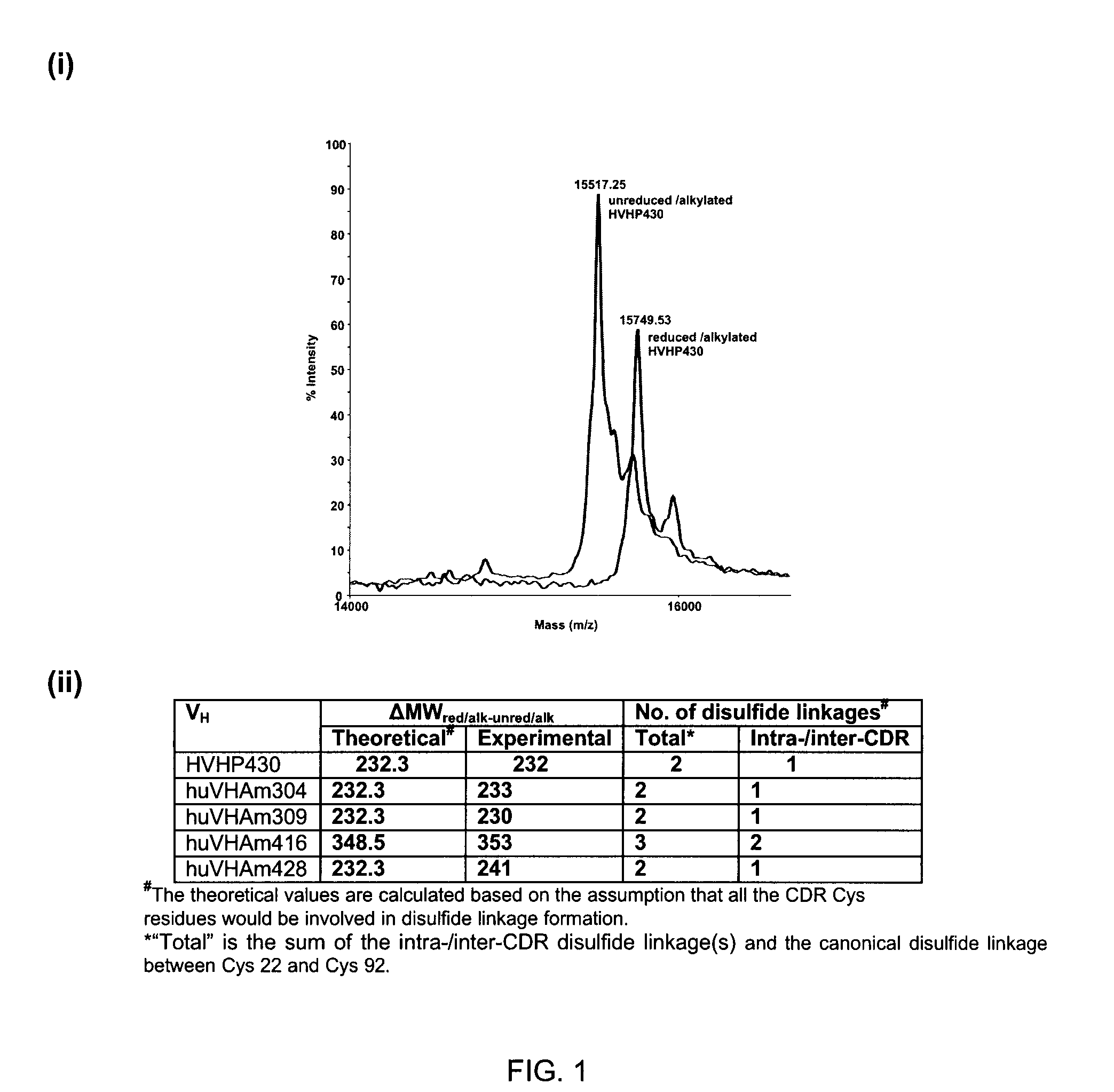
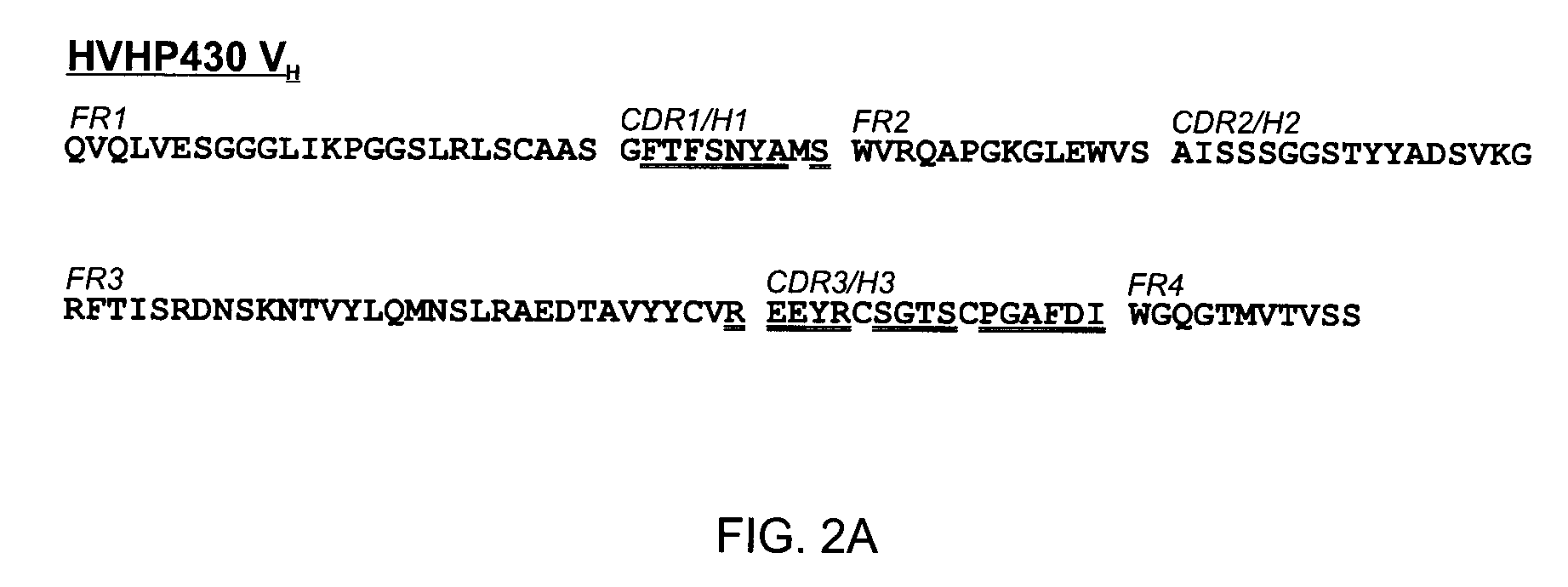
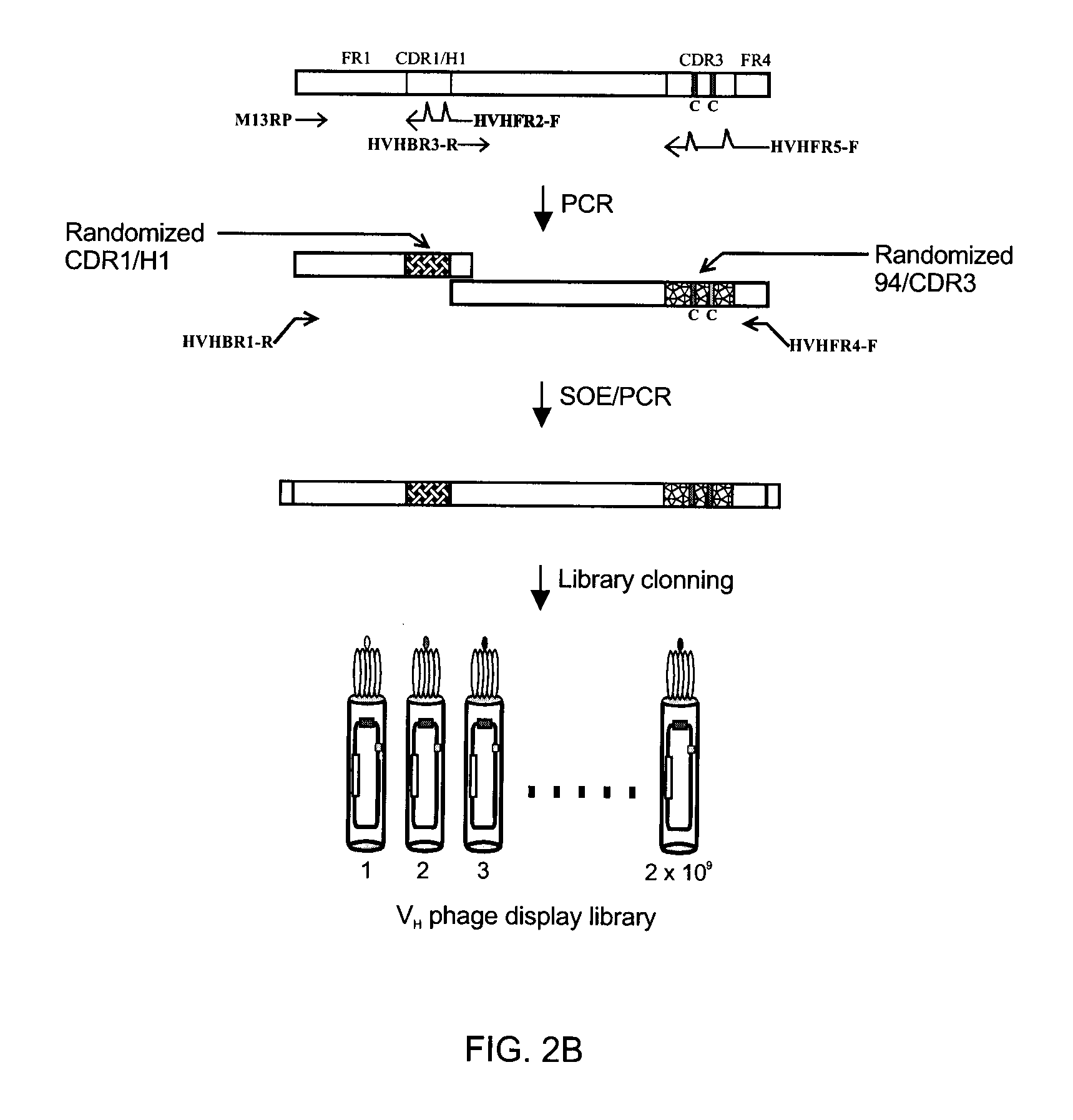
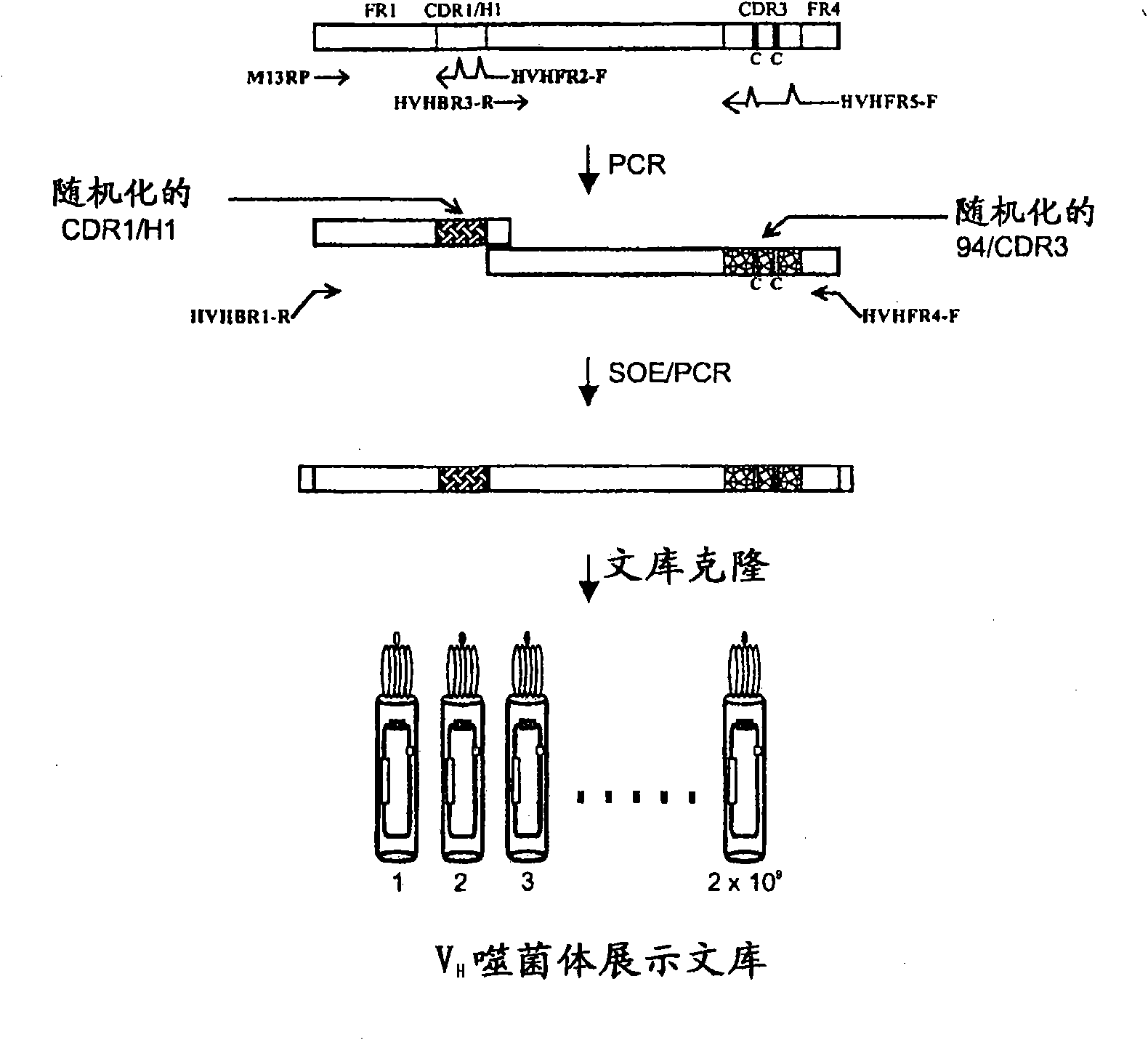
Non-aggregating human vh domains
InactiveUS20110052565A1Rapid antibody expressionFast analysisPeptide librariesSugar derivativesComplementarity determining regionDisulfide Linkage
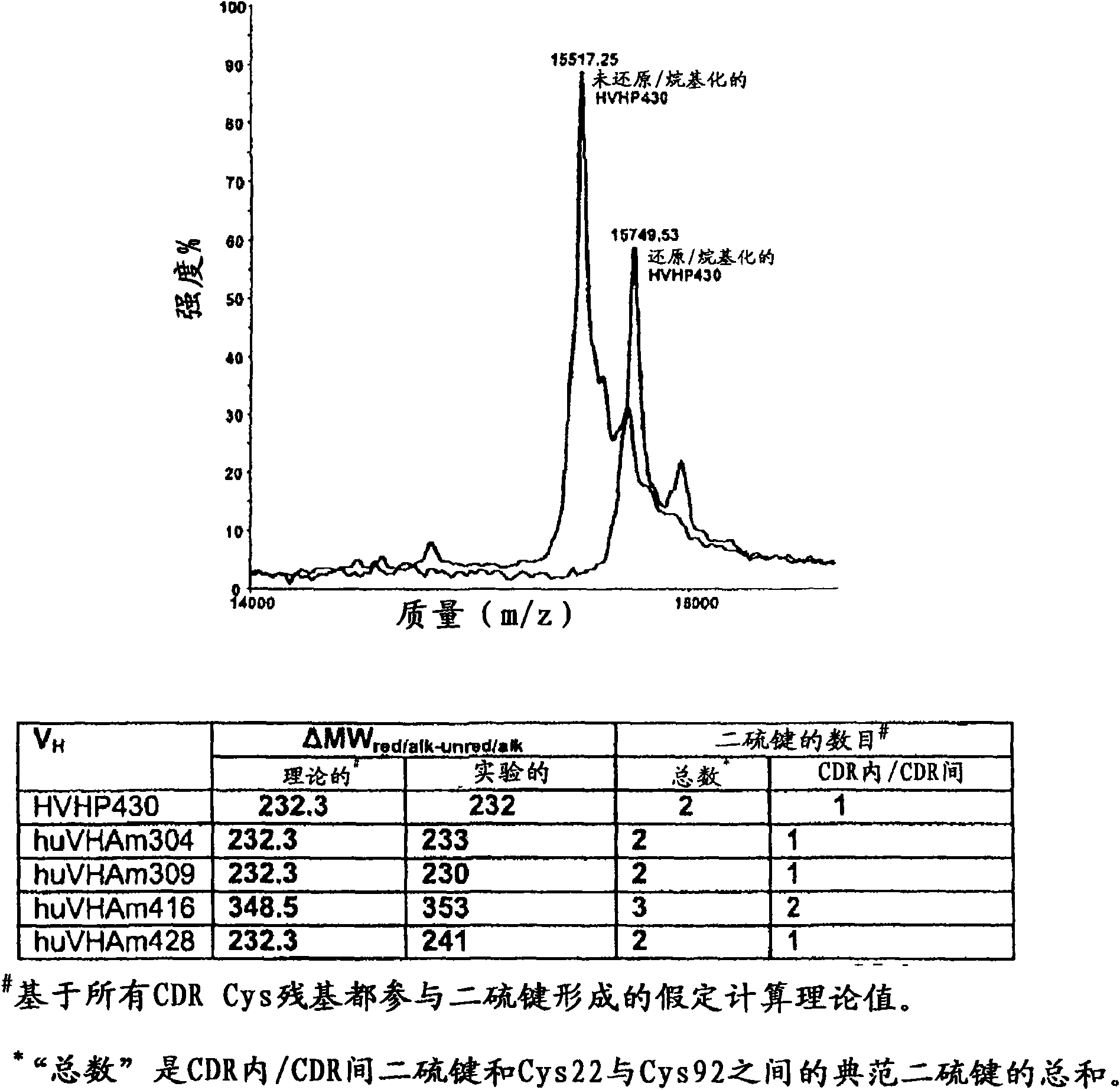
The present invention relates to non-aggregating VH domains or libraries thereof. The VH domains comprise at least one disulfide linkage-forming cysteine in at least one complementarity-determining region (CDR) and an acidic isoelectric point (pI). A method of increasing the power or efficiency of selection of non-aggregating VH domains comprises panning a phagemid-based VH domain phage-display library in combination with a step of selecting non-aggregating phage-VH domains. Compositions of matter comprising the non-aggregating VH domains, as well as methods of use are also provided.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
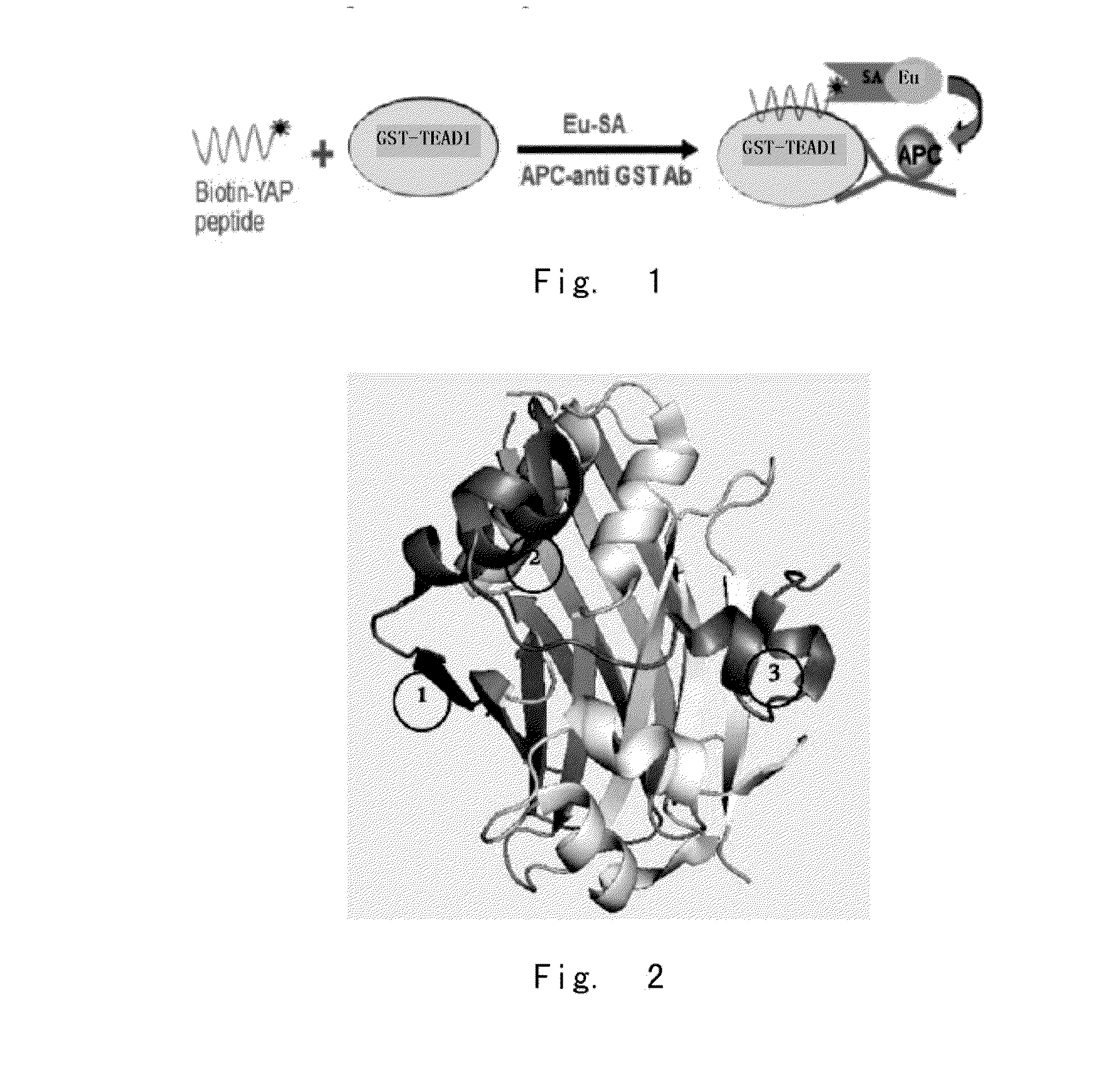
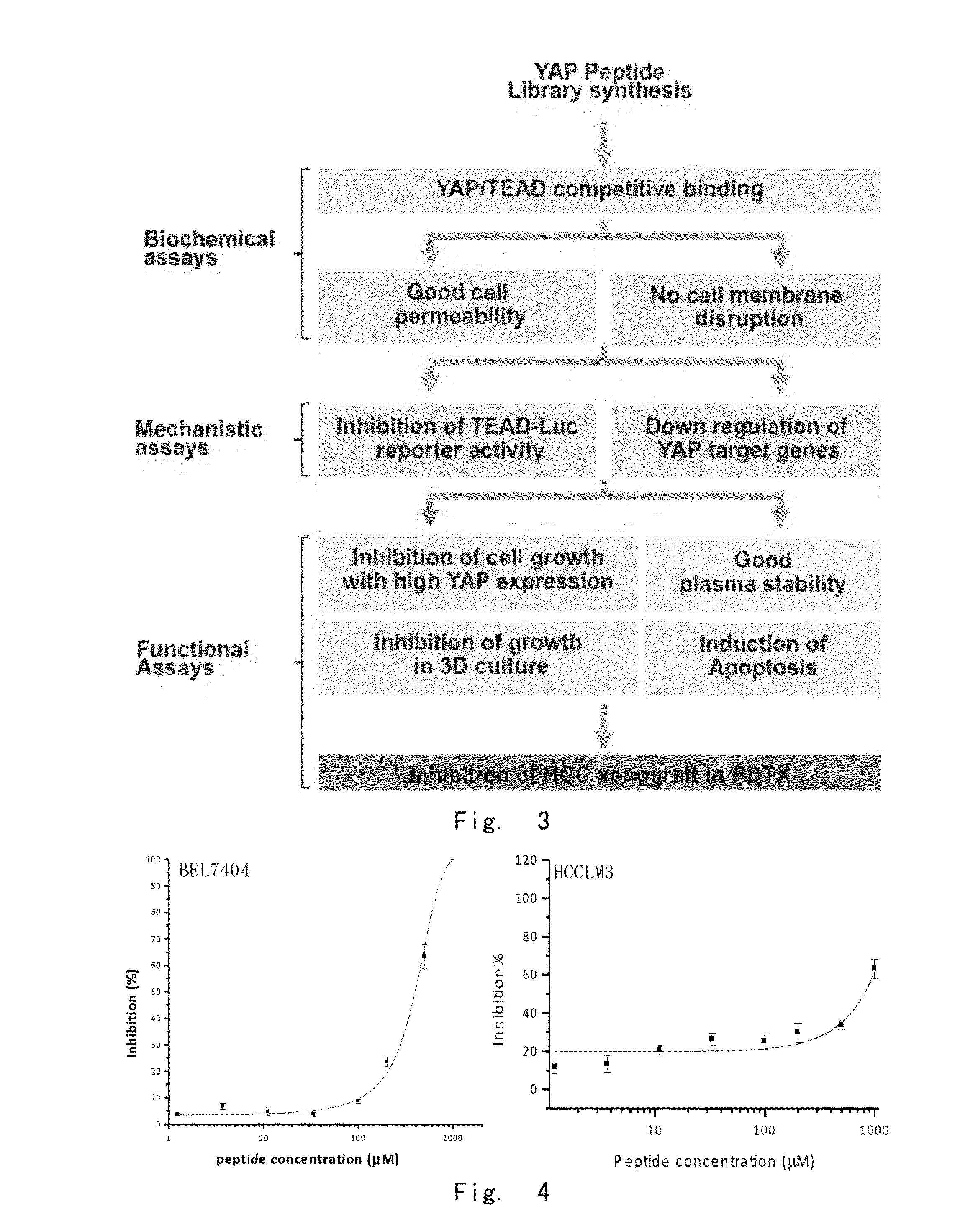
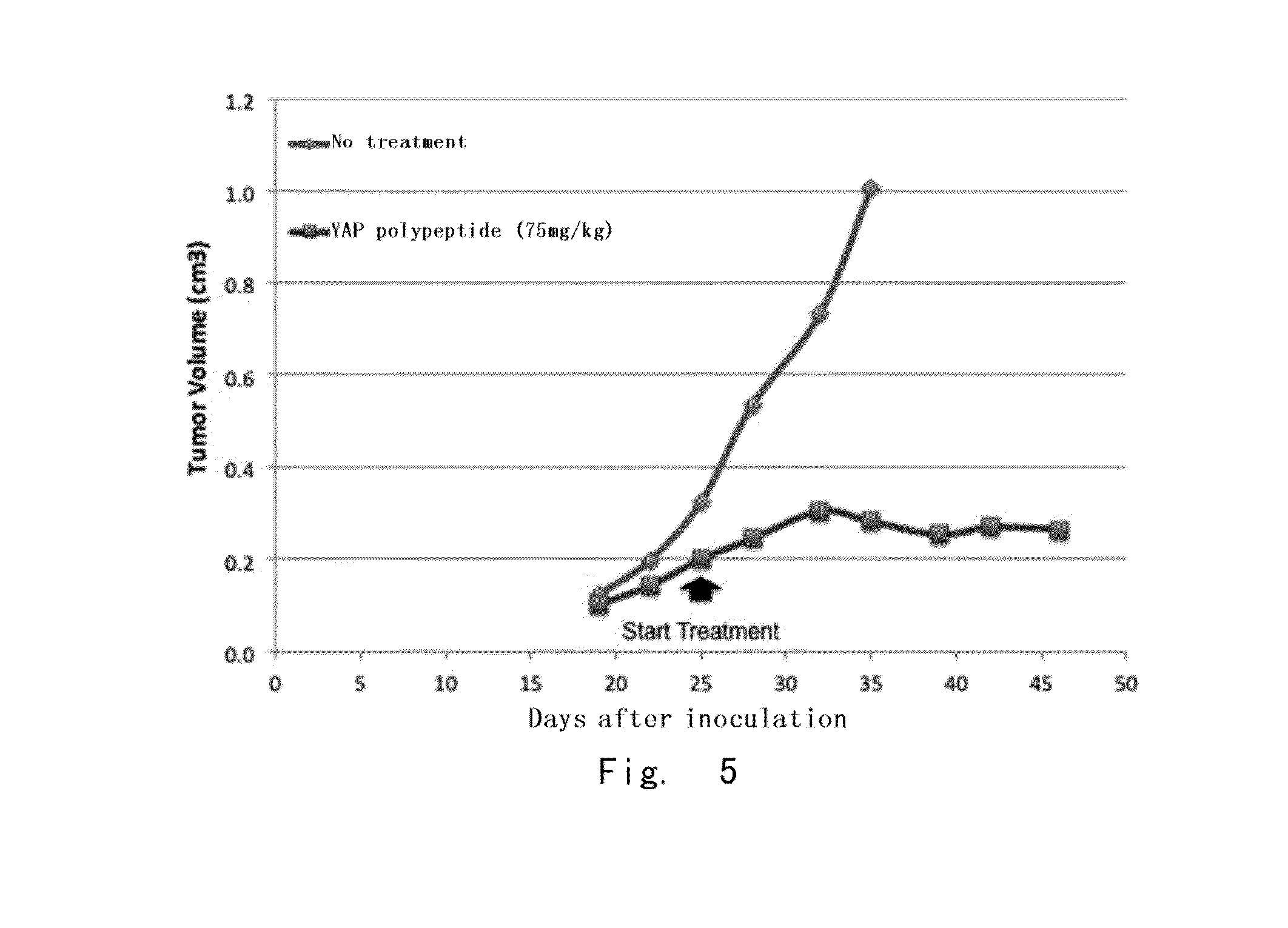
High activity tumour inhibitor and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20170319648A1Prevent tumorGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesBinding siteTherapeutic effect
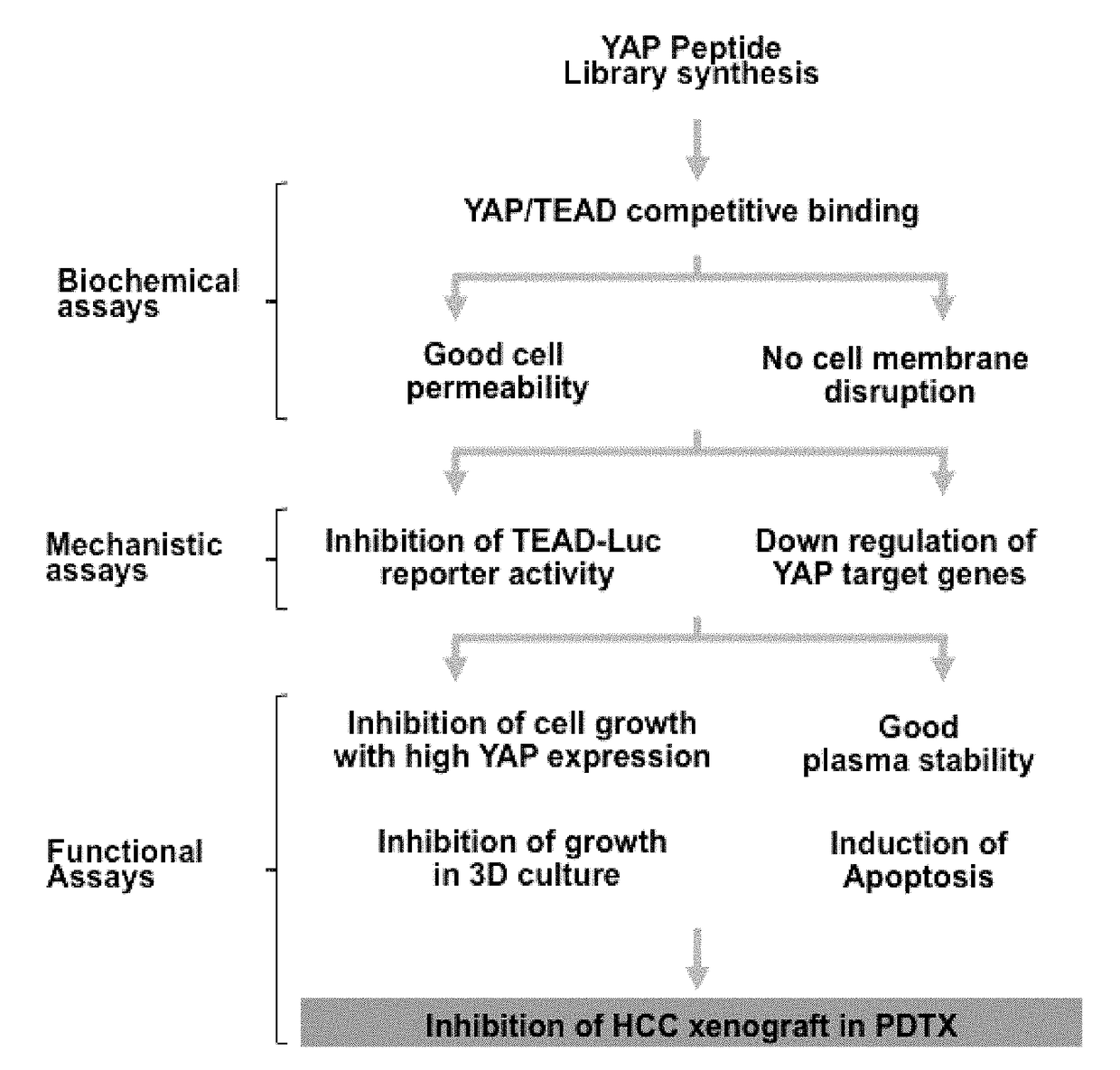
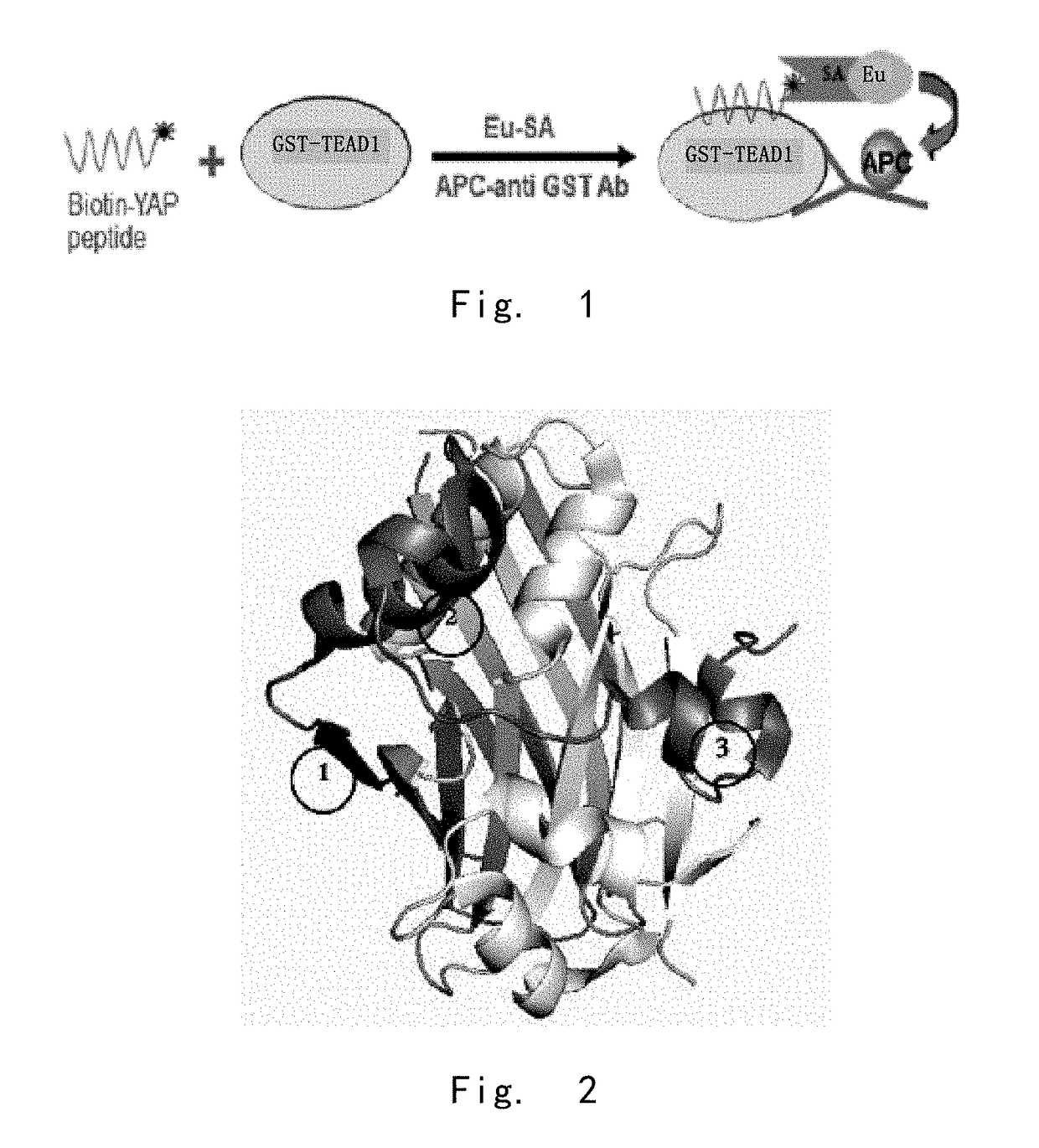
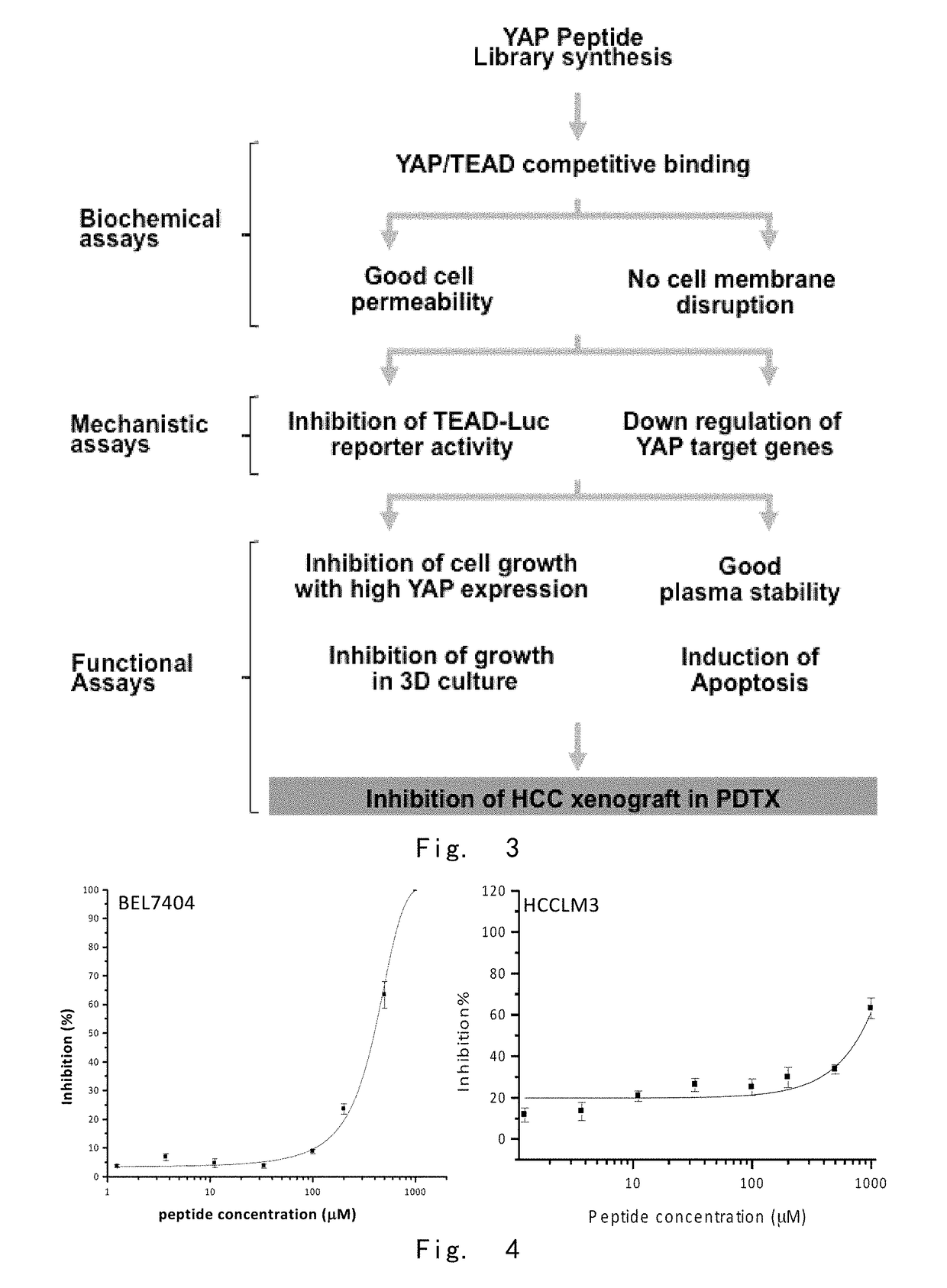
Provided in the present invention are a YAP protein inhibiting polypeptide and application thereof. In particular, the present invention obtains a key binding site of YAP protein and TEAD, screens a polypeptide with best YAP inhibitory activity and modifies the polypeptide, such as adding a disulfide linkage, replacing an amino acid, removing and / or adding (for example, adding a cell-penetrating element), and finally screens and verifies the obtaining of a series of polypeptides with YAP protein activity inhibiting effect and good stability. Experiments show that the polypeptide of the present invention can effectively inhibit the binding activity between YAP protein and TEAD, thus providing good therapeutic effect on digestive tract tumors (especially liver cancer).
Owner:BAO KANG BIOMEDICAL HEALTHCARE
Non-aggregating human VH domains
InactiveCN101939333APeptide librariesLibrary screeningComplementarity determining regionDisulfide Linkage
The present invention relates to non-aggregating VH domains or libraries thereof. The VH domains comprise at least one disulfide linkage-forming cysteine in at least one complementarity-determining region (CDR) and an acidic isoelectric point (pI). A method of increasing the power or efficiency of selection of non-aggregating VH domains comprises panning a phagemid-based VH domain phage-display library in combination with a step of selecting non-aggregating phage-VH domains. Compositions of matter comprising the non-aggregating VH domains, as well as methods of use are also provided.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Yap protein inhibiting polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveUS20160272690A1Prevent tumorGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTreatment effectBinding site
Provided in the present invention are a YAP protein inhibiting polypeptide and application thereof. In particular, the present invention obtains a key binding site of YAP protein and TEAD, screens a polypeptide with best YAP inhibitory activity and modifies the polypeptide, such as adding a disulfide linkage, replacing an amino acid, removing and / or adding (for example, adding a cell-penetrating element), and finally screens and verifies the obtaining of a series of polypeptides with YAP protein activity inhibiting effect and good stability. Experiments show that the polypeptide of the present invention can effectively inhibit the binding activity between YAP protein and TEAD, thus providing good therapeutic effect on digestive tract tumors (especially liver cancer).
Owner:BAO KANG BIOMEDICAL HEALTHCARE
Cysteine peptide-enabled antibodies
PendingCN110248962AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibody fragments
Provided herein are functionalized monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) including antibody fragments covalently linked to a peptide compound through a disulfide linkage. The disulfide linkage is between a cysteine in the Fab region of the antibody or fragment thereof and a thiol moiety of a side chain amino acid of the peptide compound. The covalently formed complexes including provided herein form highly stable and versatile drug delivery and diagnostic compositions.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Synthetic Streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine
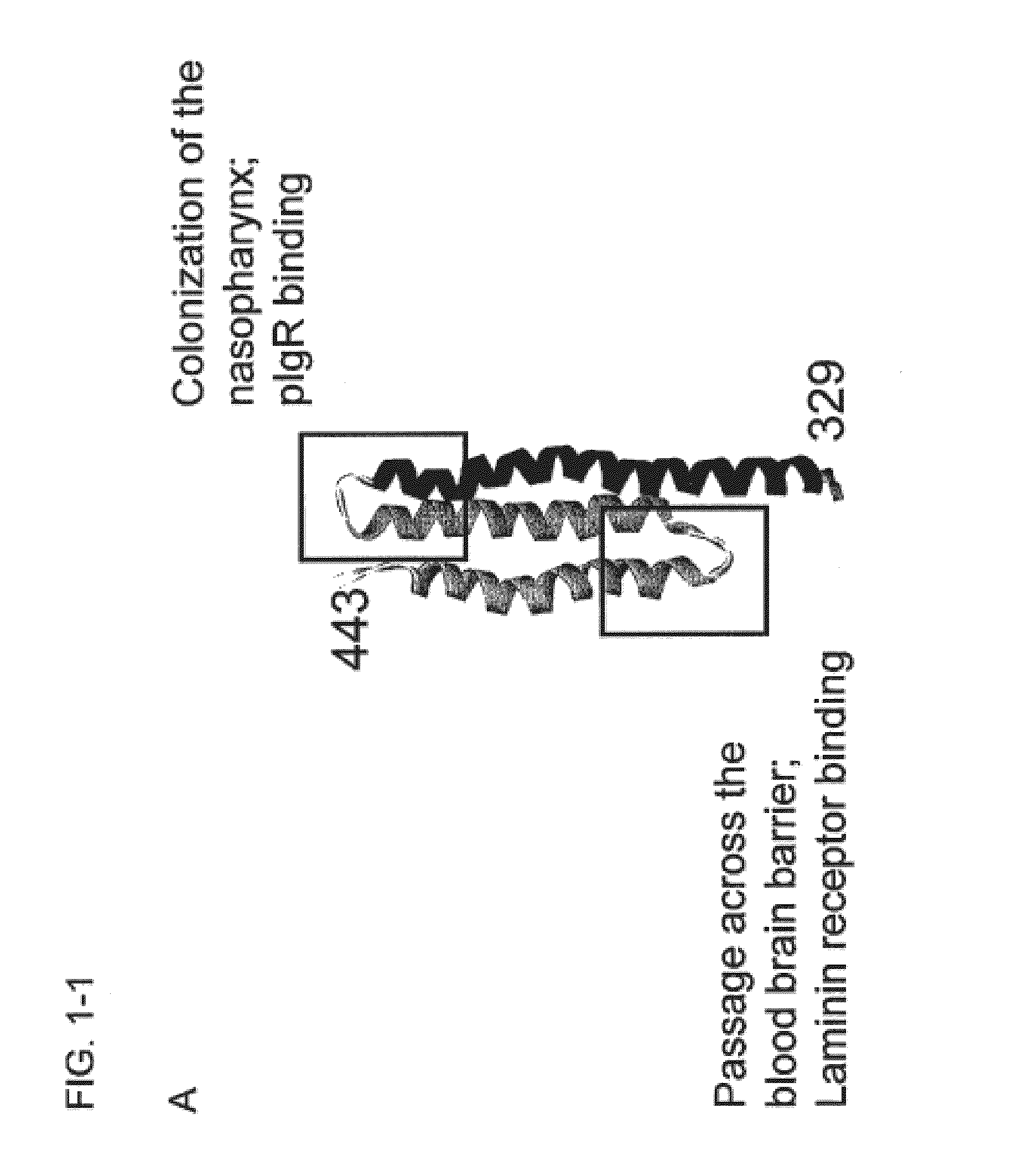
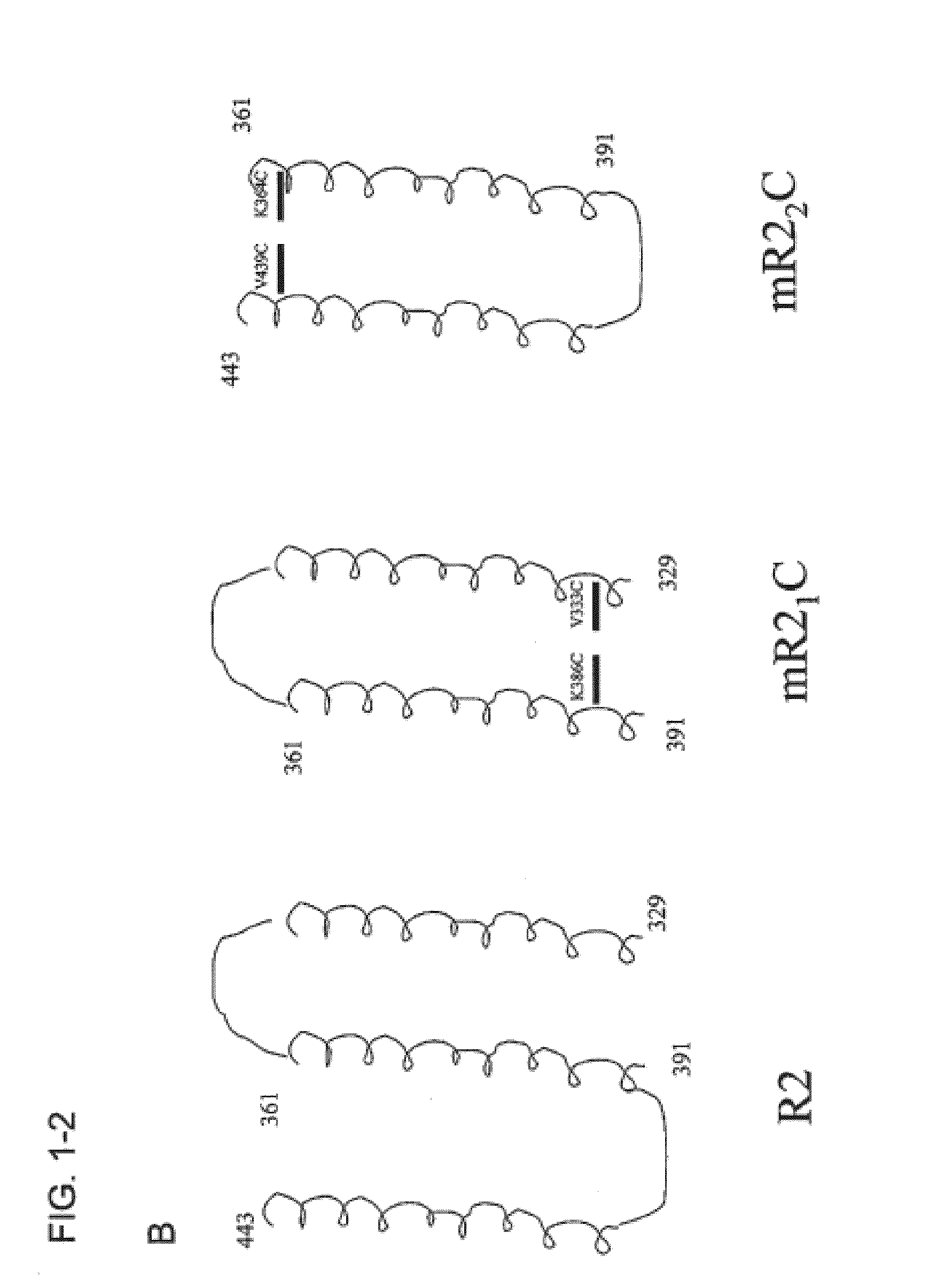
Compositions and methods for preventing and treating pneumococcal infections are provided. Compositions include novel polypeptides comprising an amino acid sequence corresponding to the R2i or R22 domain of CbpA or a consensus sequence of one of these domains, and variants and fragments thereof, wherein the polypeptide is stabilized in a desired conformation, particularly a loop conformation. The polypeptides of the invention may be engineered to comprise a first and a second cysteine residue, thereby resulting in the formation of a disulfide bond that stabilizes the polypeptide in the desired conformation. Alternatively, a polypeptide of the invention may be modified to create a synthetic linkage between a first and second amino acid residue present within the polypeptide, wherein the synthetic linkage stabilizes the polypeptide in the desired conformation. The polypeptides of the invention may further comprise an amino acid sequence for a T cell epitope. Compositions further include isolated nucleic acid molecules that encode the polypeptides of the invention, immunogenic compositions and vaccines comprising the disclosed polypeptides, and antibodies specific for these polypeptides.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Reagent for bioconjugation via irreversible rebridging of disulfide linkages
PendingUS20220024904A1Well formedOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersChemical synthesisSynthon
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Anti-Integrin Immunoconjugates, Methods and Uses
InactiveUS20140093523A1Effective rate of releaseSenses disorderHybrid immunoglobulinsDiseaseCytotoxicity
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein
InactiveCN106432439AEffectively control and prevent lossesLoss control and preventionSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesProtein s antigenViral Vaccine
The invention discloses bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein. Compared with SEQ AAB28458.1, an amino acid sequence of the bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein is characterized in that at least two sites are replaced by cysteines, the replaced cysteines are in disulfide linkage, and improvements such as disulfide linkage, hole filling and single-strand ligation on this basis. The invention further provides a method for preparing the bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein. The bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein and the method for preparing the same have the advantages that technologies and theories of protein crystallography are applied, structural changes of protein in a virus infection and pathopoiesis process are determined, and the key viral protein is subjected to genetic engineering modifications according to structural change results so as to become the antigen protein which is infectious but not pathogenic and capable of causing high-efficiency reaction of animal antigens; the bovine respiratory syncytial virus antigen protein is capable of effectively preventing and treating bovine respiratory syncytial virus infection and is developed into satisfactory viral vaccines on the basis to control and prevent loss brought by virus infection, thereby being of great economic and social significance.
Owner:烟台偌帝生物工程有限公司
Cloning, expression and application of eimeria tenella protein disulfide isomerase gene
InactiveCN101418309BGenetic material ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliEmoia loyaltiensis
The invention discloses an E.tenella protein disulfide linkage isomerase gene EtPDI (Clone ID is BW1-E06,and the Genbank accession number of is EF552214). The gene is connected with a procaryon expression vector pGEX-4T-2; a procaryon expression recombination plasmid pGEX-4T-EtPDI is constructed and is expressed in a colibacillus system; and most of the expressed recombining protein exists in a soluble form. The recombining protein 4T-EtPDI is purified to carry out SPS-PAGE and is transferred to a PVDF film; and antiserum of E.tenella oocyst oral immunized chicken is used as first resistance and goat anti-chicken IgG is used as second resistance to carry out Western-blot analysis, thereby indicating that the gene has certain antigen. The gene is used for preparing an anti-chicken coccidiosis drug and an anti-chicken coccidiosis vaccine.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Stimulus-responsive biodegradable polymers and methods of preparation
There is presently provided a stimulus-responsive polymer comprising a biodegradable polymer backbone and a stimulus-responsive pendant group attached to the biodegradable polymer backbone, wherein the biodegradable polymer backbone comprises a poly(amino ester) or a poly(amido amine), the poly(amido amine) optionally comprising a disulfide linkage in the backbone.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for extracting vegetable butter raft
InactiveCN101508935BAvoid degradationQuality improvementFatty-oils/fats productionLysisCentrifugation
The invention discloses a method for extracting vegetable tallow raft. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the plasma membrane is split to obtain lysis solution; (2) the density gradient centrifugation is carried out on the lysis solution in the step (1) to obtain the plant raft. The method uses dithiothreitol (DTT) to reduce the disulfide linkage, thus causing that the protein is fullydissolved. But phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMS) can effectively prevent the degradation of the protein in the extraction process. The method for extracting the plant raft has the advantages of being fast, simple and practicable and obtaining the tallow raft with higher quality and better repeatability. The method can play important role in the research of the vegetable tallow raft and has veryhigh practical using value.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermostable amylase mutant and a preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN103409392BImprove thermal stabilityEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmylaseBacillus alcalophilus
The invention discloses a thermostable amylase mutant and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to invention, bacillus alcalophilus JN21 (CCTCC NO:M2011231) amylase is used as female parent; molecular biological technique is adopted to conduct site-directed mutagenesis for bacillus alcalophilus amylase sequence; a pair or multiple pairs of disulfide linkages are introduced in amylase catalytic structural domain to obtain amylase mutant with higher thermal stability; under the modification condition, the half-life period of bacillus alcalophilus amylase at 60 DEG C is improved to 22.3 min from 3.2 min of a comparison example (before mutation); by utilizing the strategy, the thermostability of amylase can be obviously improved to provide basis for industrialized production, and the strategy has significant guiding significance for the modification of properties of other enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com