Cysteine peptide-enabled antibodies
A technology of amino acid and phenylalanine, applied in the direction of peptide, specific peptide, anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0179] For the preparation of suitable antibodies of the invention and uses according to the invention, e.g. recombinant, monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, a number of techniques known in the art can be used (see, e.g., Kohler & Milstein, Nature 256:495-497 (1975); People such as Kozbor, Immunology Today 4:72 (1983); People such as Cole, pages 77-96 in Monoclonal Antibodies and Cancer Therapy, Alan R. Liss, Inc. (1985); Coligan, Current Protocols in Immunology (1991); Harlow & Lane, Antibodies, A Laboratory Manual (1988); and Goding, Monoclonal Antibodies: Principles and Practice (2nd Edition, 1986)). Genes encoding the heavy and light chains of an antibody of interest can be cloned from cells, for example, genes encoding monoclonal antibodies can be cloned from hybridomas and used to produce recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Gene libraries encoding the heavy and light chains of monoclonal antibodies can also be prepared from hybridomas or plasma cells. Random combination...
Embodiment 1
[0378] Example 1: Cys-Meditope
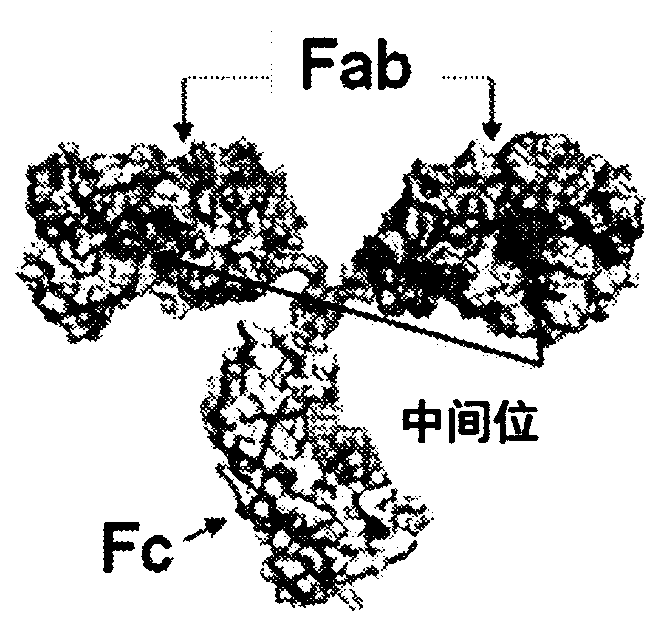
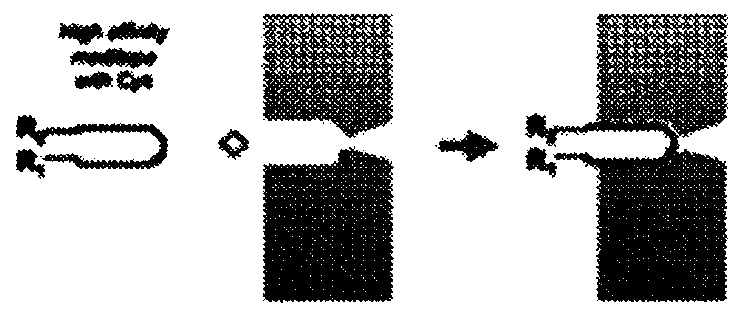
[0379]In some cases, it is desirable to add functionality to monoclonal antibodies through covalent linkages. To achieve this, Applicants used a meditope / meside-enabled Fab (meFab) interaction to generate a disulfide bond ( figure 1 with Figure 2A ).
[0380] Based on careful examination of the meditope-meFab interaction and the previous observation that the cysteine (Cys) introduced at K208 by site-directed mutagenesis was not oxidized, Applicants' meditope-enabled monoclonal antibody to trastuzumab Cys was introduced at position 175 of alanine (Ala) in (memAb)V2(I83E). In addition, Applicants synthesized a linear meditope (SEQ. ID NO: 4) in which X is diphenylalanine and the serine (Ser) at position 6 is replaced by Cys. Applicants hypothesize that the Ala175Cys mutation in the memAb heavy chain and the Ser6Cys mutation in the meditope bring the sulfur groups into close proximity, promoting disulfide bond formation ( Figure 2A ).
...
Embodiment 2
[0395] Example 2: Stable site-specific modification of disulfide-conjugated monoclonal antibodies using meditope peptide-assisted
[0396] The high specificity and favorable pharmacological properties of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have generated significant interest in reengineering such molecules to enhance their therapeutic and diagnostic potential. Herein, applicants use high-affinity interactions between meditope peptides and meditope-enabled mAbs (memAbs) to drive rapid, efficient and robust site-specific formation of disulfide bonds. Applicants use this meditope, peptide-assisted conjugation technology (mPACT) platform to attach fluorescent dyes, cytotoxins, or "click" chemistry to memAbs and meFabs. More importantly, Applicants developed genetically encoded meditope-tagged biologics to generate stable bifunctional Fabs and mAbs. This includes conjugation of bacterially expressed fluorescent proteins, Nanobodies and Affibodies to memAbs and meFabs containing N-, C- or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com