Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
A cement-based material and microbial repairing technology, which is applied to the repairing method of cement-based material cracks and the culture solution and repairing nutrient solution, uses microorganisms to deposit calcium carbonate to repair the field of cement-based material cracks, and can solve problems that affect the normal use of materials and induce macroscopic effects. Cracks, limiting the scope of application, etc., to achieve the effects of good volume stability and durability, low cost, and outstanding environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Utilize microorganism to repair the crack method of cement-based material
Embodiment 1-1
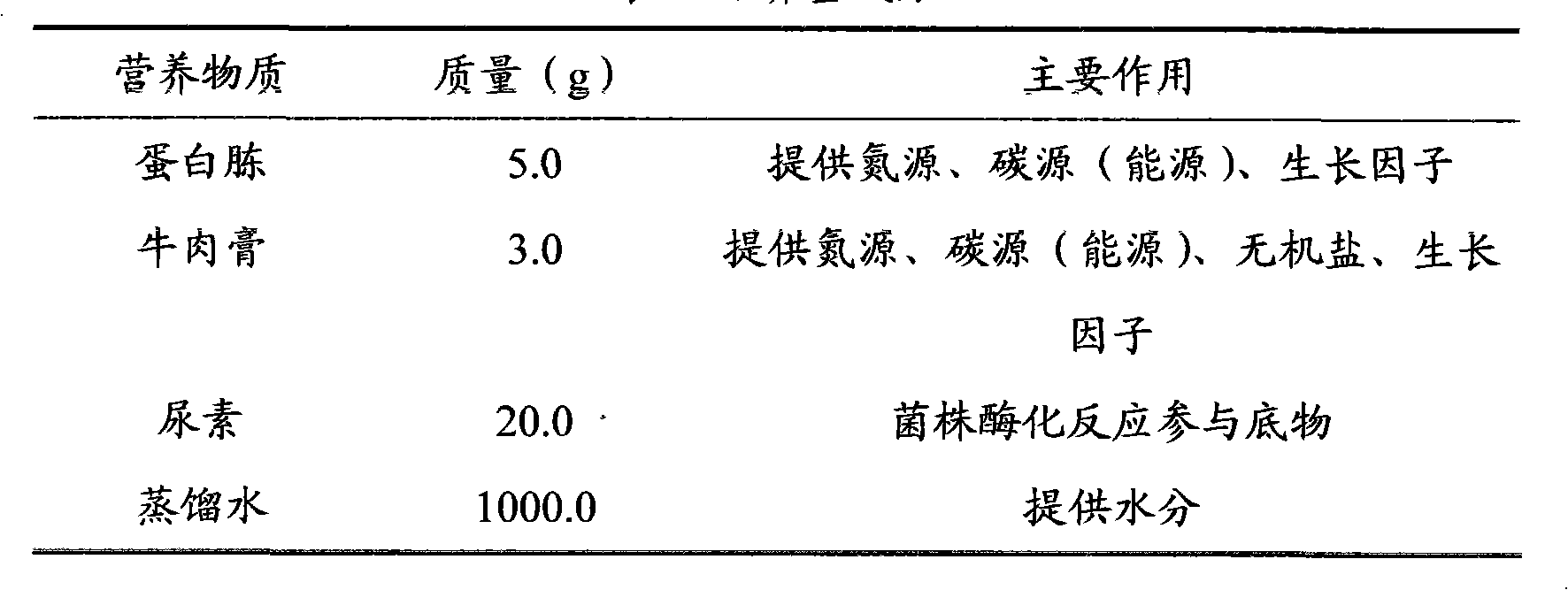
[0032]Example 1-1 A method of using microorganisms to repair cracks in cement-based materials, inoculating the bacterial strain Bacillus pasteurii on a medium containing a urea-containing substrate, performing shaking culture at 25°C, and taking out the culture after 16 hours Centrifuge the bacterial solution at 5000rpm for 5min, remove the supernatant, collect the cells of the strain with the culture medium, measure the OD value of the transmittance of the concentrated bacterial solution with a UV-visible light spectrophotometer, and collect it according to the linear calibration curve between the OD value and the concentration of the bacterial solution. The cell concentration of the strain was controlled at 2×10 9 within the range, then add 8 standard sand, urea, and Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O mixture, mix it and mix it into a slurry, inject it into cement stone cracks with a width of 1 mm and a depth of 50 mm, inject 1 repairing nutrient solution into the cracks of cement stone e...
Embodiment 1-2
[0033] Embodiment 1-2 A method for repairing cracks in cement-based materials by using microorganisms, which is characterized in that the bacterial strain Bacillus pasteurii is inoculated onto a medium containing a urea-containing substrate, and cultured with shaking at 37°C for 24 hours Afterwards, take out the cultured bacteria solution, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 8min, remove the supernatant, collect the strain cells with the culture solution, measure the OD value of the light transmittance of the concentrated bacteria solution with a UV-visible light spectrophotometer, according to the linear calibration curve between the OD value and the concentration of the bacteria solution Control the cell concentration of the collected strains at 2×10 11 within the range of cell / mL, then add 12 g of standard sand, urea, and Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O mixture, mix it and mix it into a slurry, inject it into cement stone cracks with a width of 5 mm and a depth of 1 mm, inject 4 mL of repairing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com