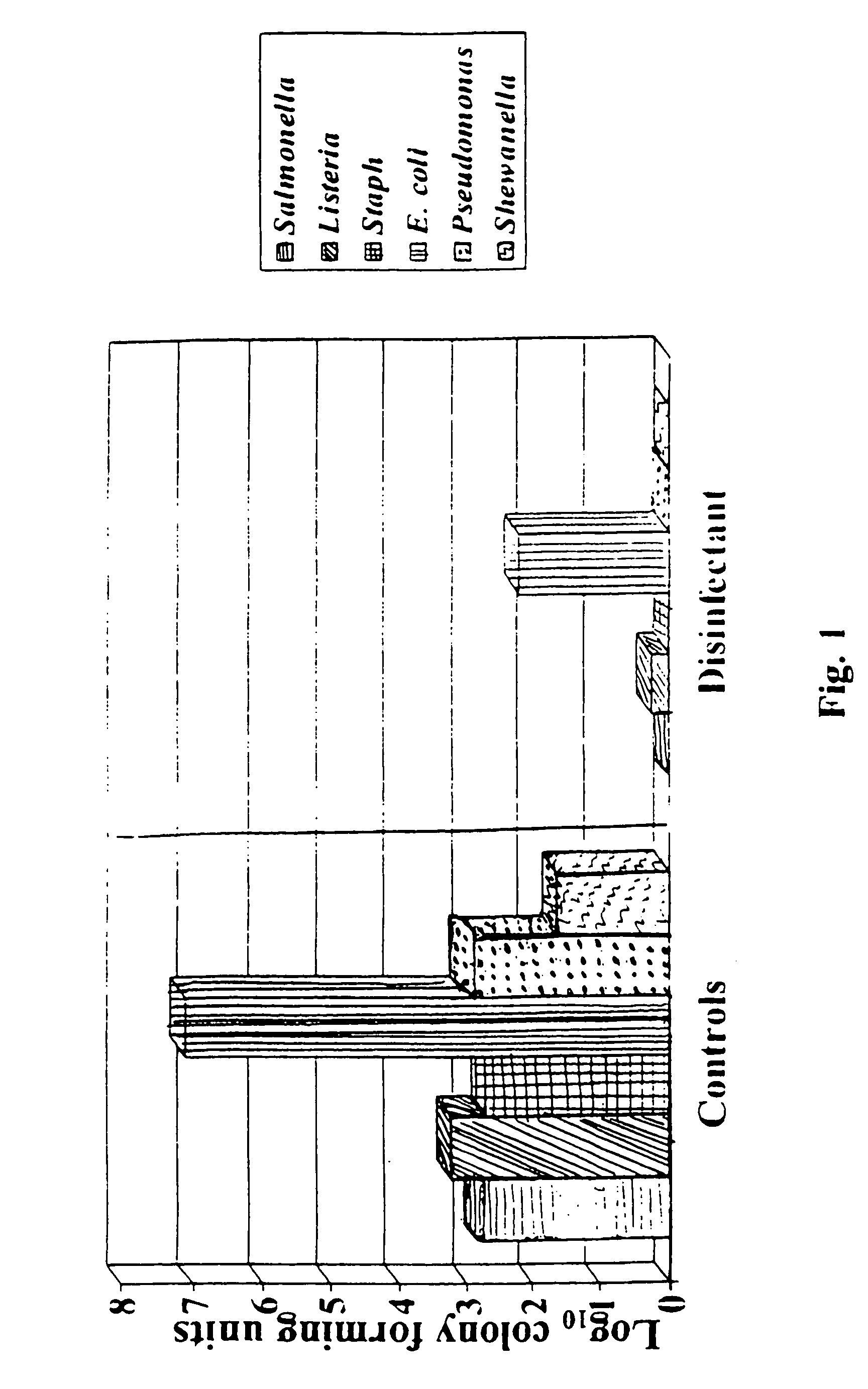
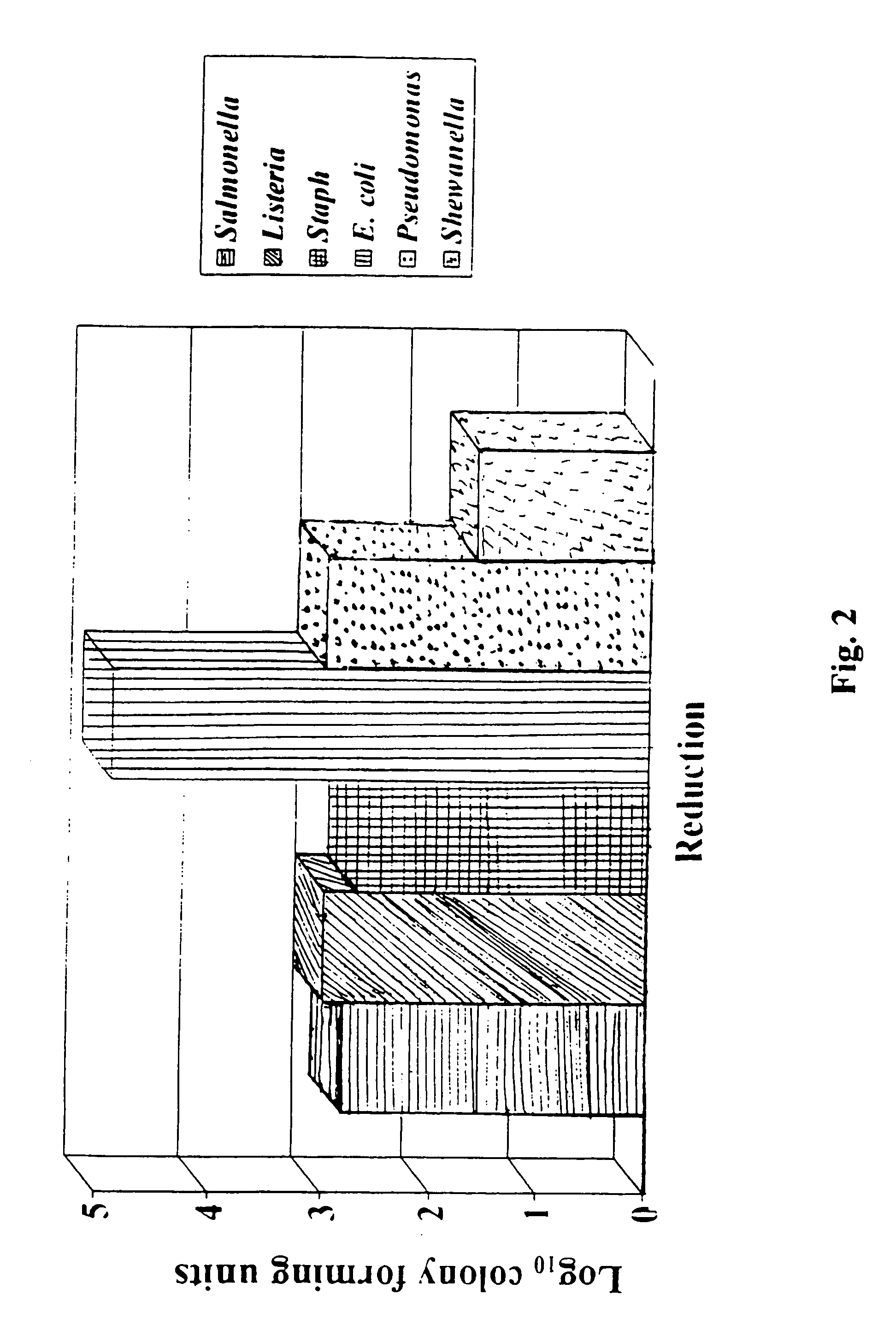
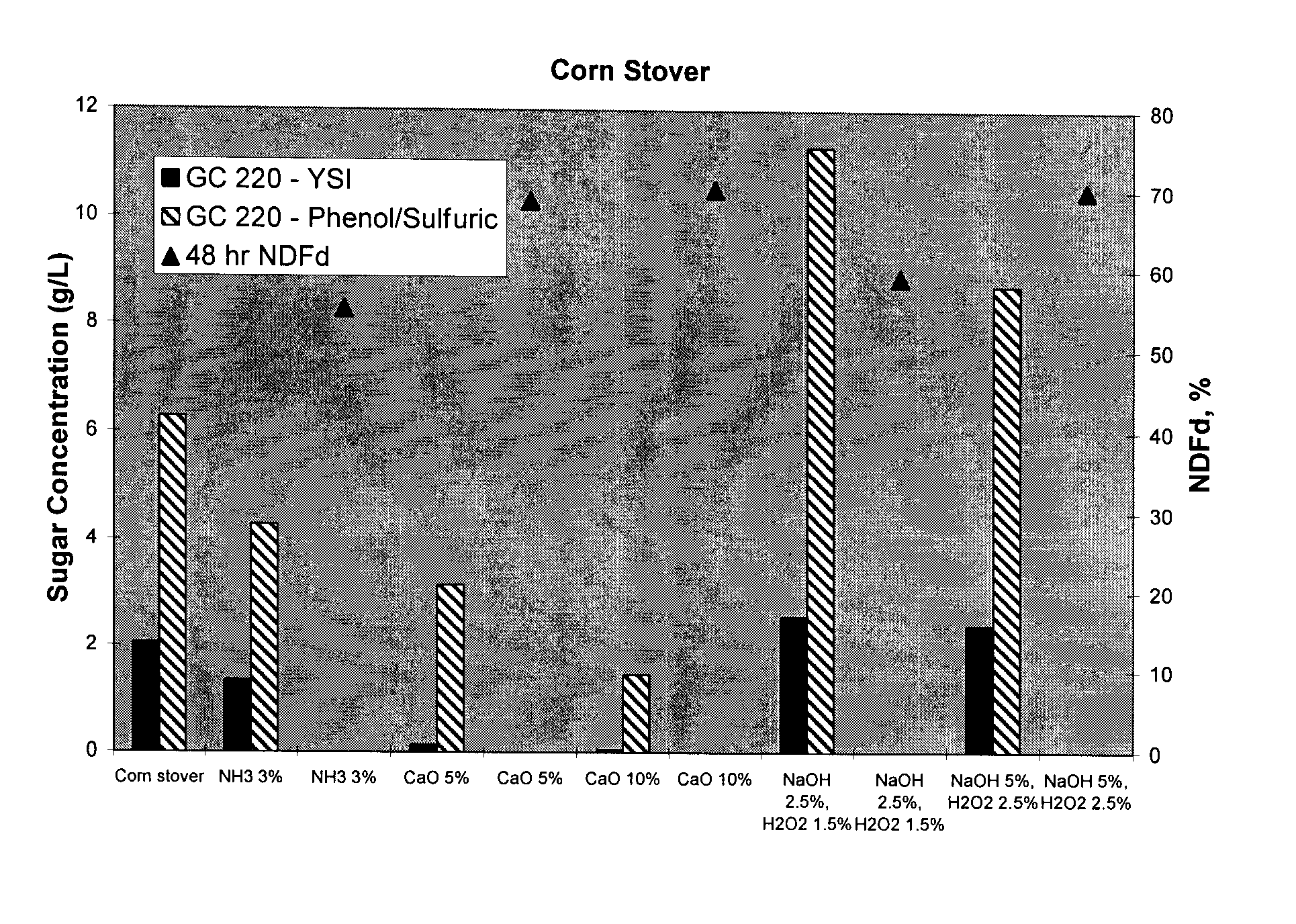
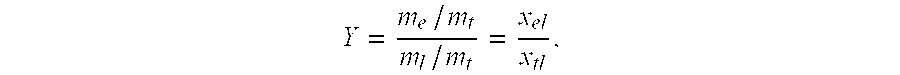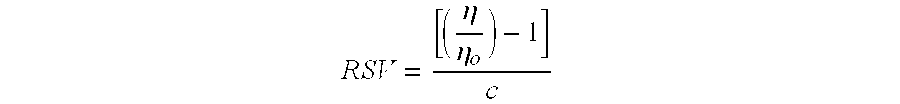Patents
Literature
460results about "Meat/fish preservation using acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
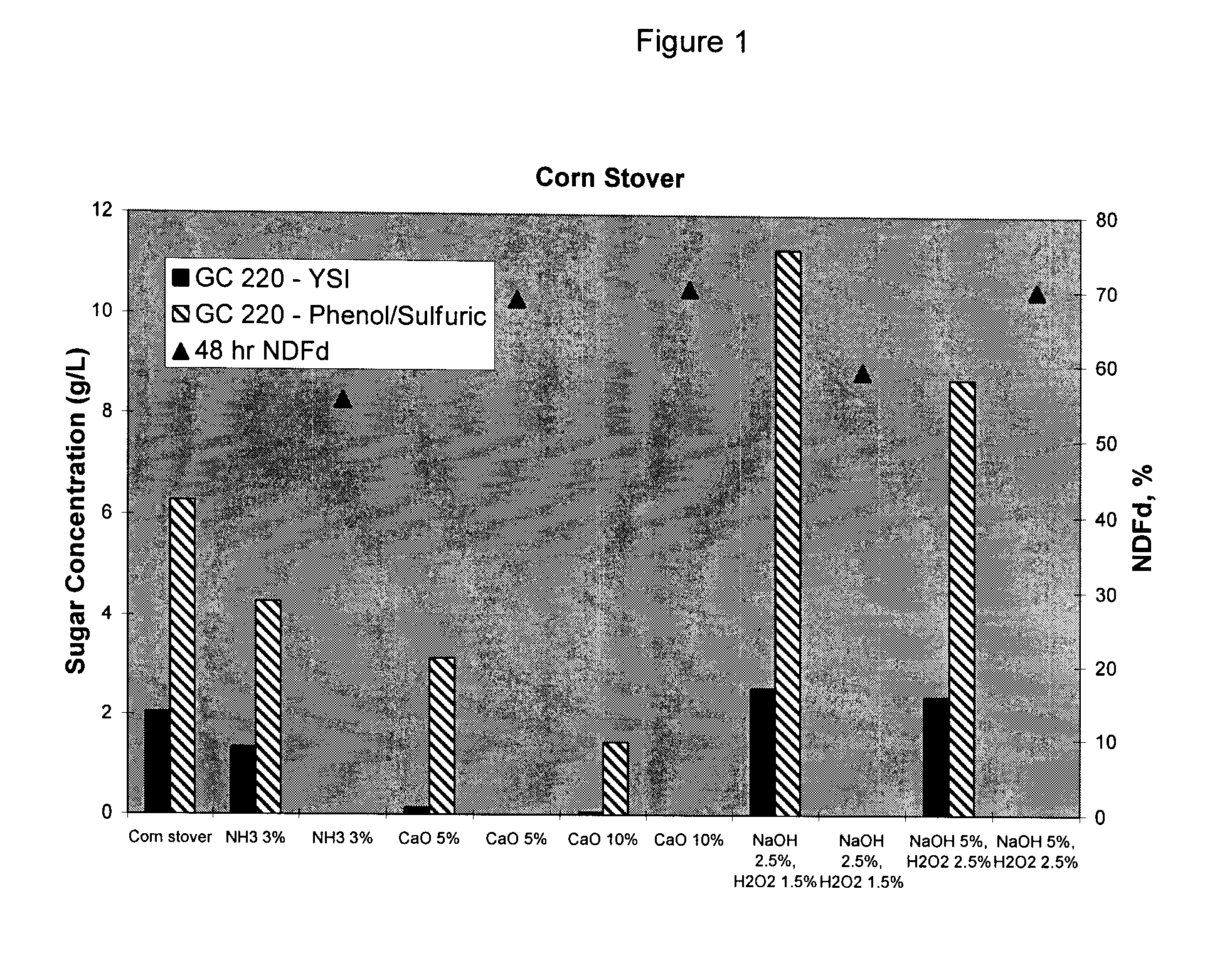
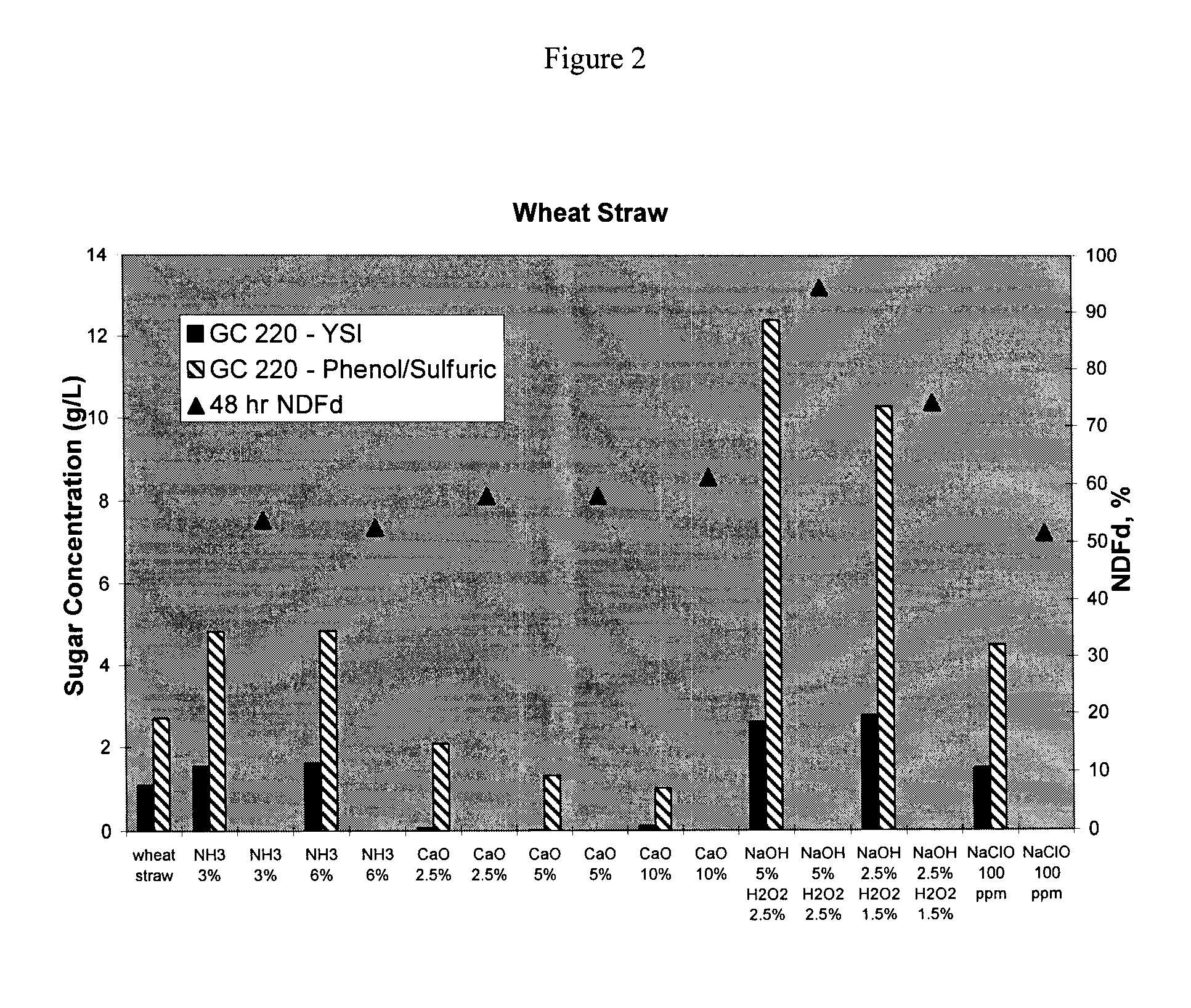
Treatment of biomass to obtain fermentable sugars
InactiveUS20070031918A1Toxic reductionReduce needBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationFermentable sugarCompound (substance)
Biomass is pretreated using a low concentration of aqueous ammonia at high biomass concentration. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Use
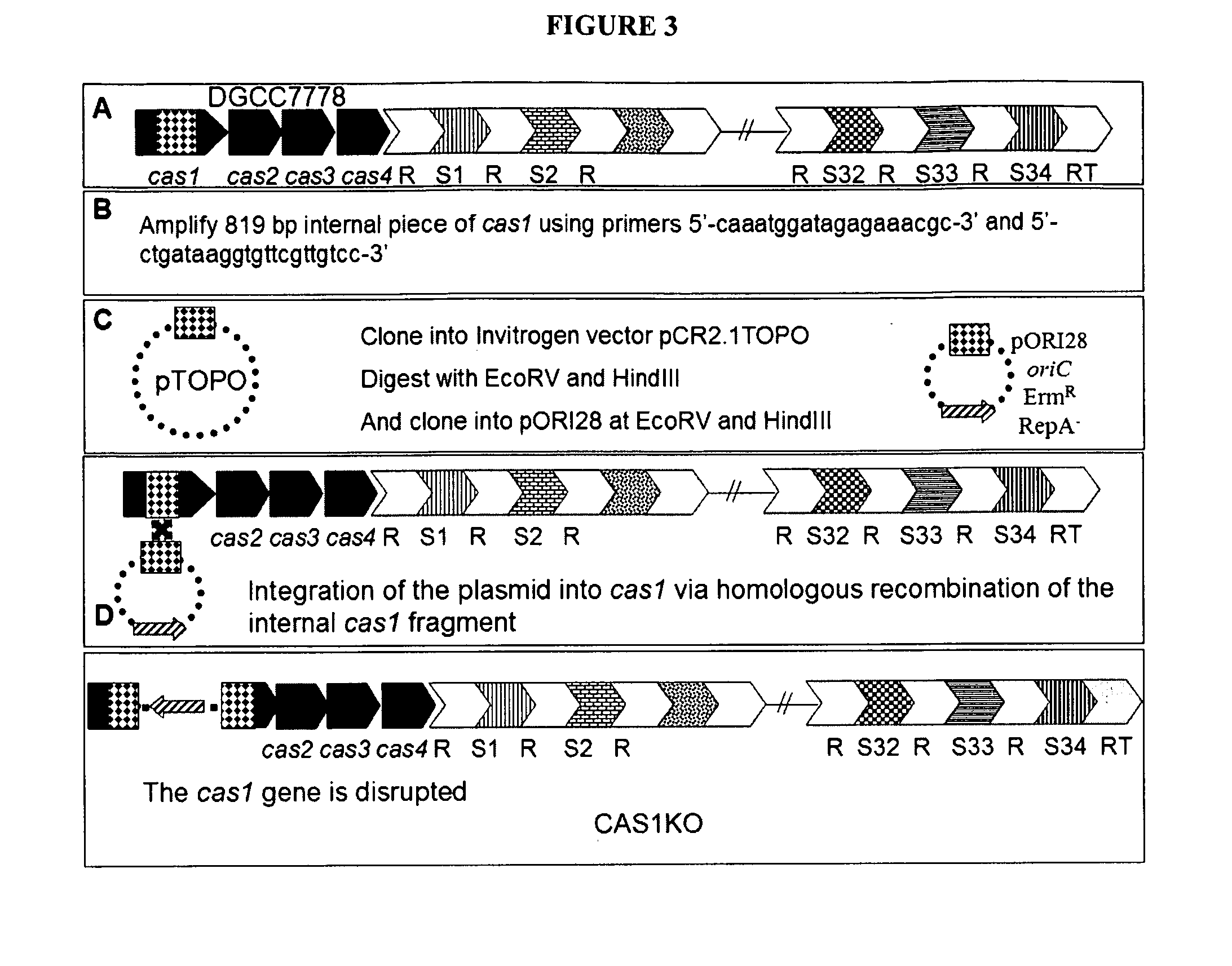
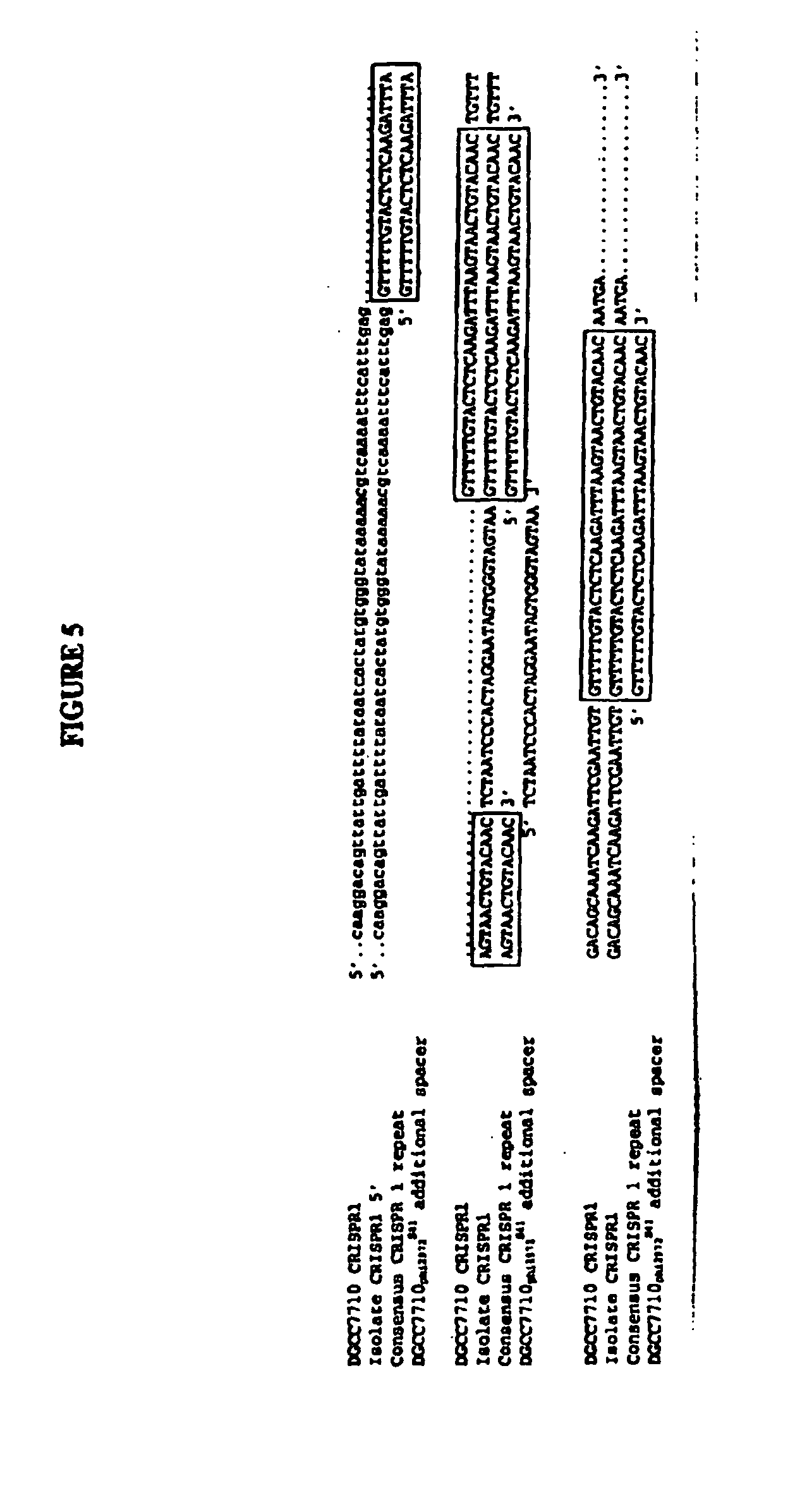
ActiveUS20130011828A1Modulate the resistance of a cellBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneBioinformatics
The present invention relates to the use of one or more cas genes for modulating resistance in a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
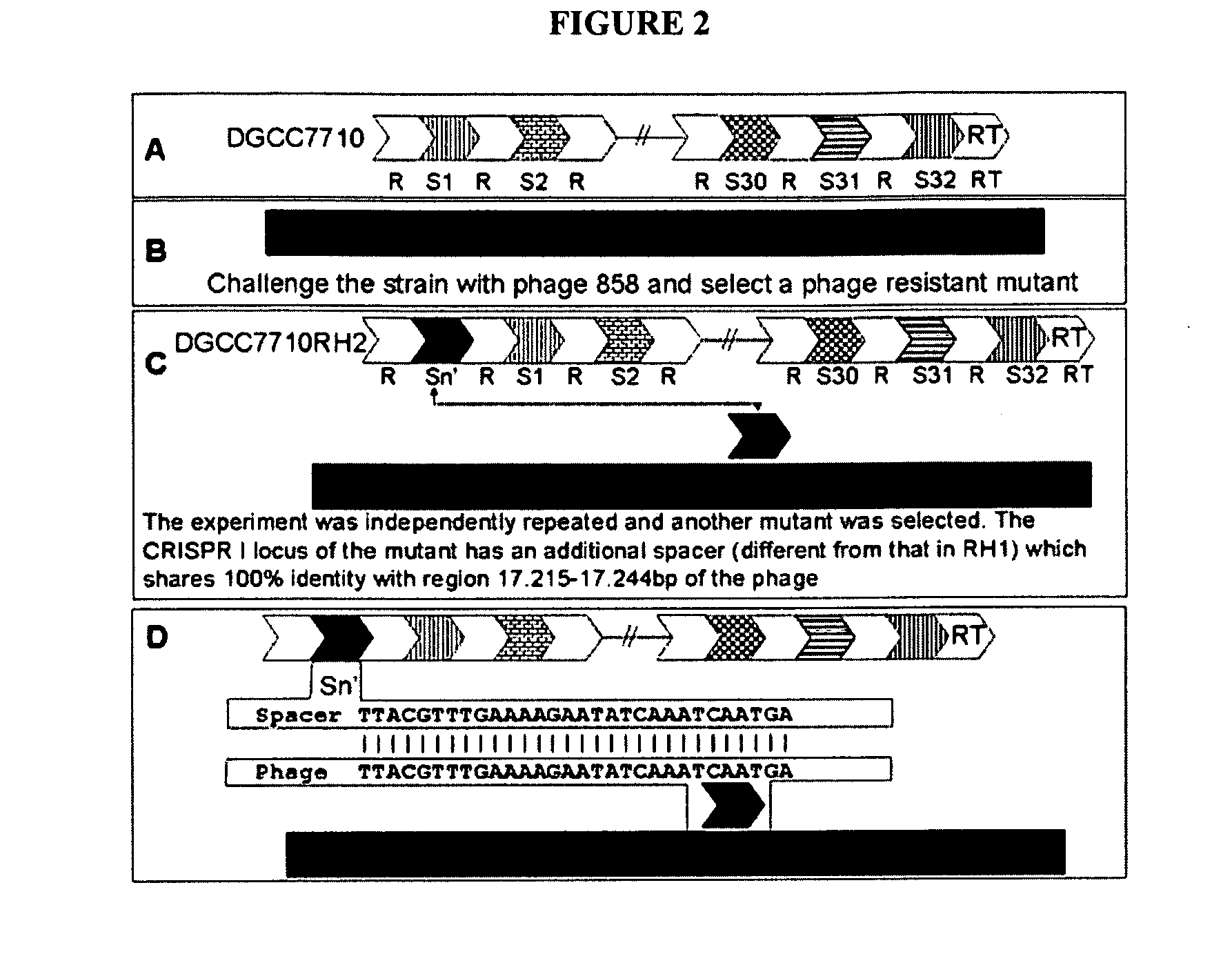
Cultures with Improved Phage Resistance
InactiveUS20110002889A1Reduced degree of homologyReduce decreaseBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsBacteriophage
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the use of one or more cas genes or proteins for modulating the resistance of a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions that find use in the development and use of strain combinations and starter culture rotations. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides methods for labelling and / or identifying bacteria. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods for the use of CRISPR loci to determine the potential virulence of a phage against a cell and the use of CRISPR-cas to modulate the genetic sequence of a phage for increased virulence level. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions for the development and use of phages as biocontrol agents.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Biomass hydrolysate and uses and production thereof
The present invention includes a palatable, stable composition comprising a biomass hydrolysate emulsion for incorporation, into, or used as, nutritional products, cosmetic products or pharmaceutical products. Preferred sources for biomass are microbial sources, plant sources and animal sources. The present invention also provides methods for making such compositions, specifically, a method for producing a product comprising a nutrient, particularly a long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, comprising hydrolyzing a biomass comprising the nutrient and emulsifying the hydrolyzed biomass. Such compositions and methods are useful, for example, for increasing intake of nutrients such as omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids having 18 or more carbons.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
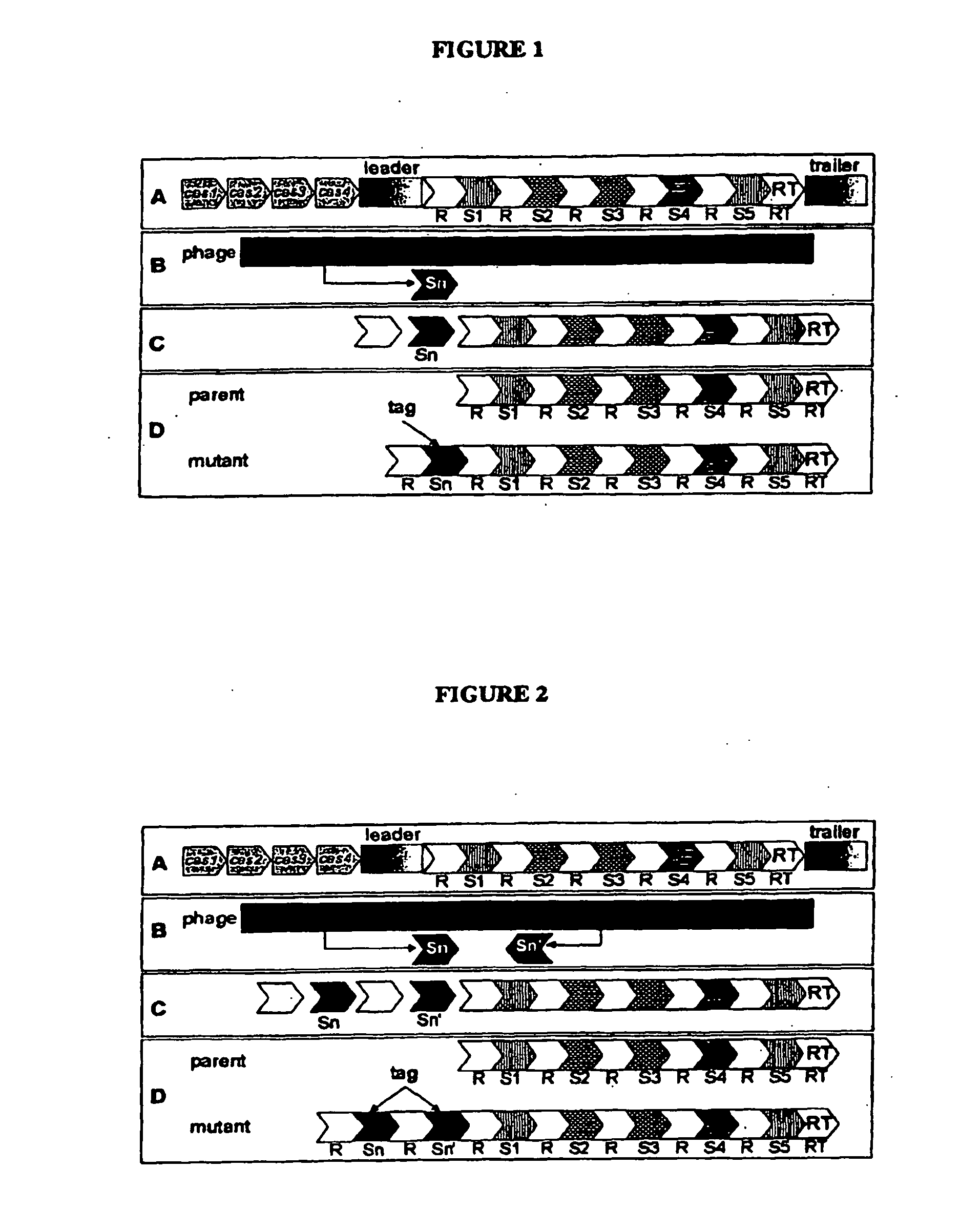
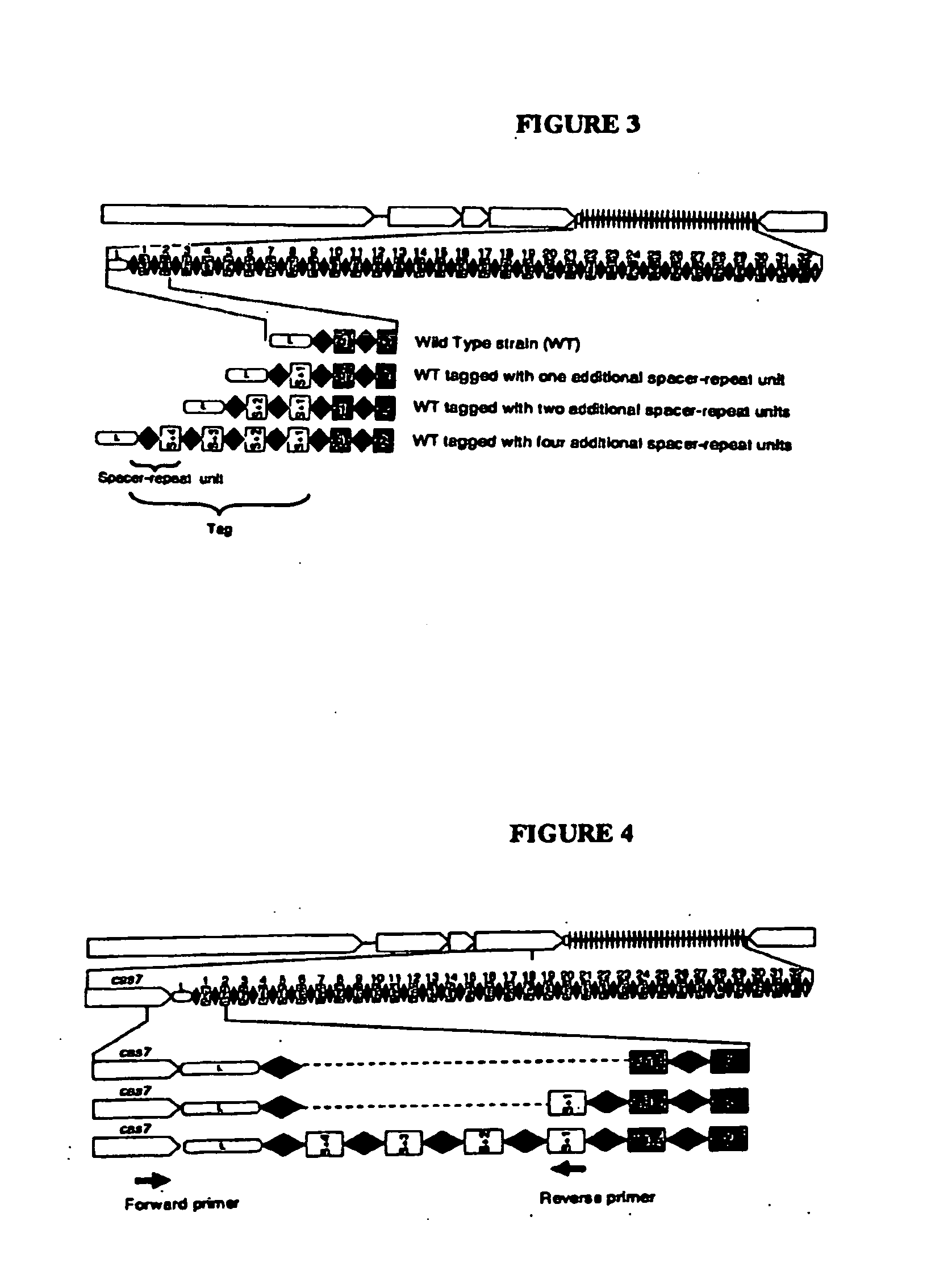
Tagged Microorganisms and Methods of Tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Integration of alternative feedstreams for biomass treatment and utilization
InactiveUS20070037259A1High solid contentBiological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationHigh concentrationDry weight
The present invention provides a method for treating biomass composed of integrated feedstocks to produce fermentable sugars. One aspect of the methods described herein includes a pretreatment step wherein biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream and the resulting integrated feedstock, at relatively high concentrations, is treated with a low concentration of ammonia relative to the dry weight of biomass. In another aspect, a high solids concentration of pretreated biomass is integrated with an alternative feedstream for saccharifiaction.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
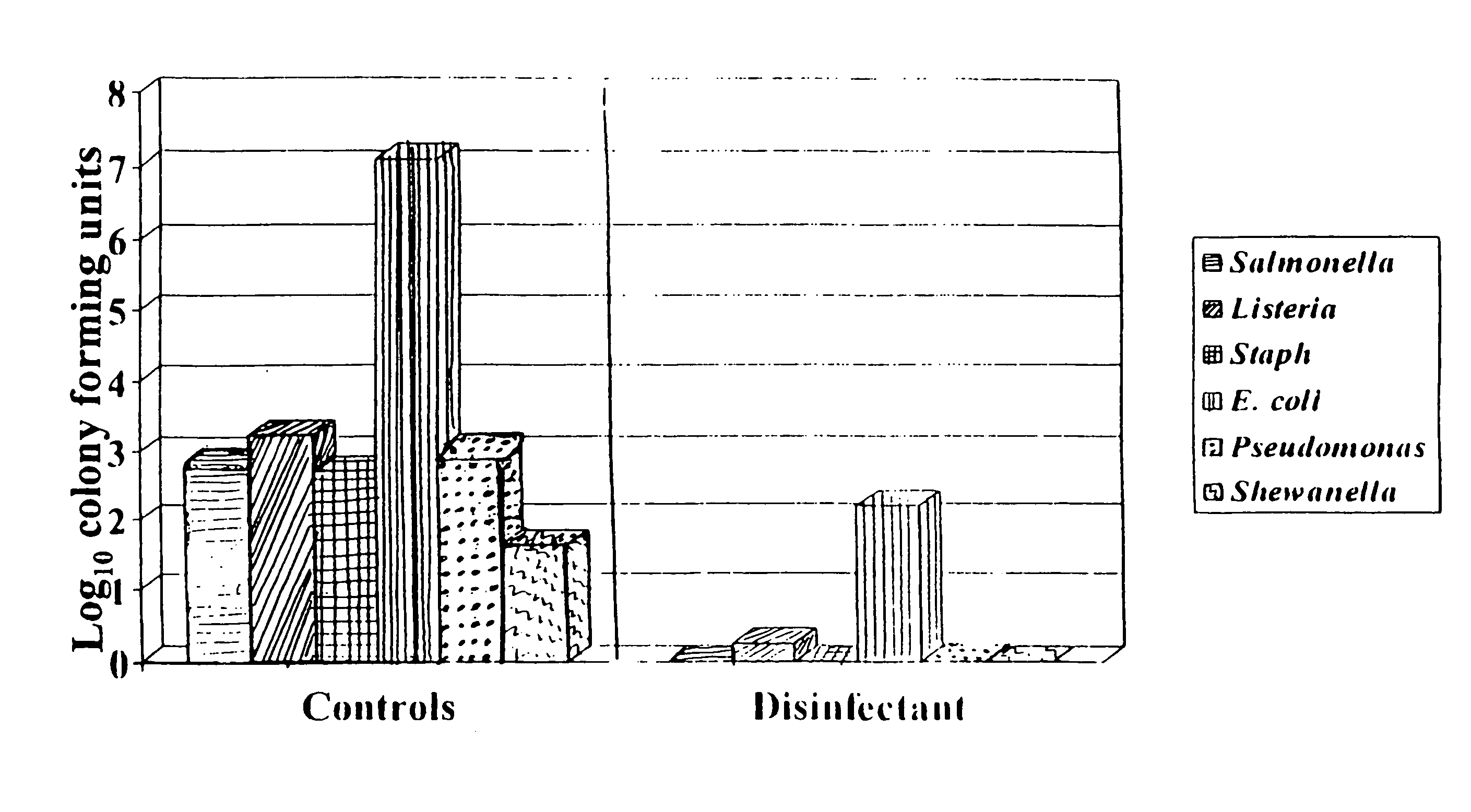
Treatment of meat products
InactiveUS6113963AReduce microbial countPrevent browningBiocideDough treatmentCarboxylic acidNuclear chemistry
Described is a method of sanitizing meat product using aqueous streams having an antimicrobial composition added to the stream. Preferably, the antimicrobial composition includes a mixture of one or more carboxylic acids having up to 18 carbon atoms and one or more peroxycarboxylic acids having up to 12 carbon atoms, preferably a mixture of a C.sub.2-4 peroxycarboxylic acid and a C.sub.8-12 peroxycarboxylic acid.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Natamycin dosage form, method for preparing same and use thereof
InactiveUS20050042341A1Sustained releaseReduce releaseDough treatmentEggs preservation by coatingFood productsDosage form
The present invention relates to a novel natamycin dosage form for the food industry, and more particularly to microcapsules where natamycin is encapsulated within a physiologically acceptable shell to provide a protected natamycin product. The present invention relates also to novel processes for preparing the capsules according to the invention, as well as to the use of the capsules of the present invention. The invention further relates to food products containing natamycin in encapsulated form.
Owner:AS DE DANSKE SUKKERFABRIKKER
Enrichment of process feedstock
InactiveUS20110124034A1Fit for consumptionUnicellular algaeBiomass after-treatmentMicroorganismBiofuel
The subject invention relates to novel methods for treating microbial biomass and uses thereof. In particular, this invention provides methods for production of lipids using ionic liquid solutions, and subsequent uses of biomass components in food, biofuels, and as chemical precursors. Further, this invention provides methods for recovering the ionic liquids using an antisolvent, thus enables subsequent reuse of the ionic liquids In addition, this invention provides practical methods for determining the lipid content of a biomass and screening potential lipid-producing microbial classes. This invention also provides a method of chemical dewatering the lipid-rich algae cells by ionic liquids with its subsequent reuse.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
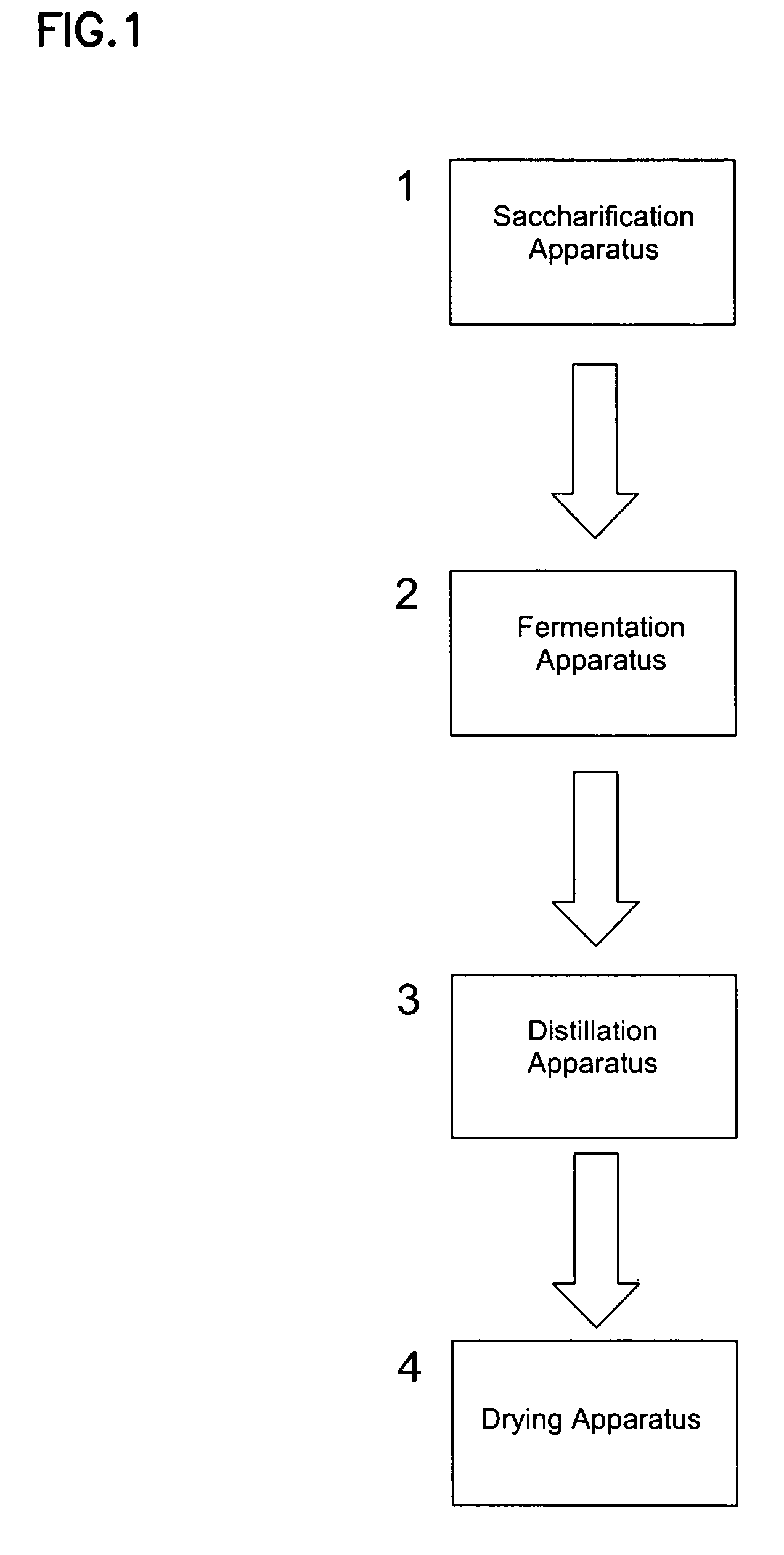
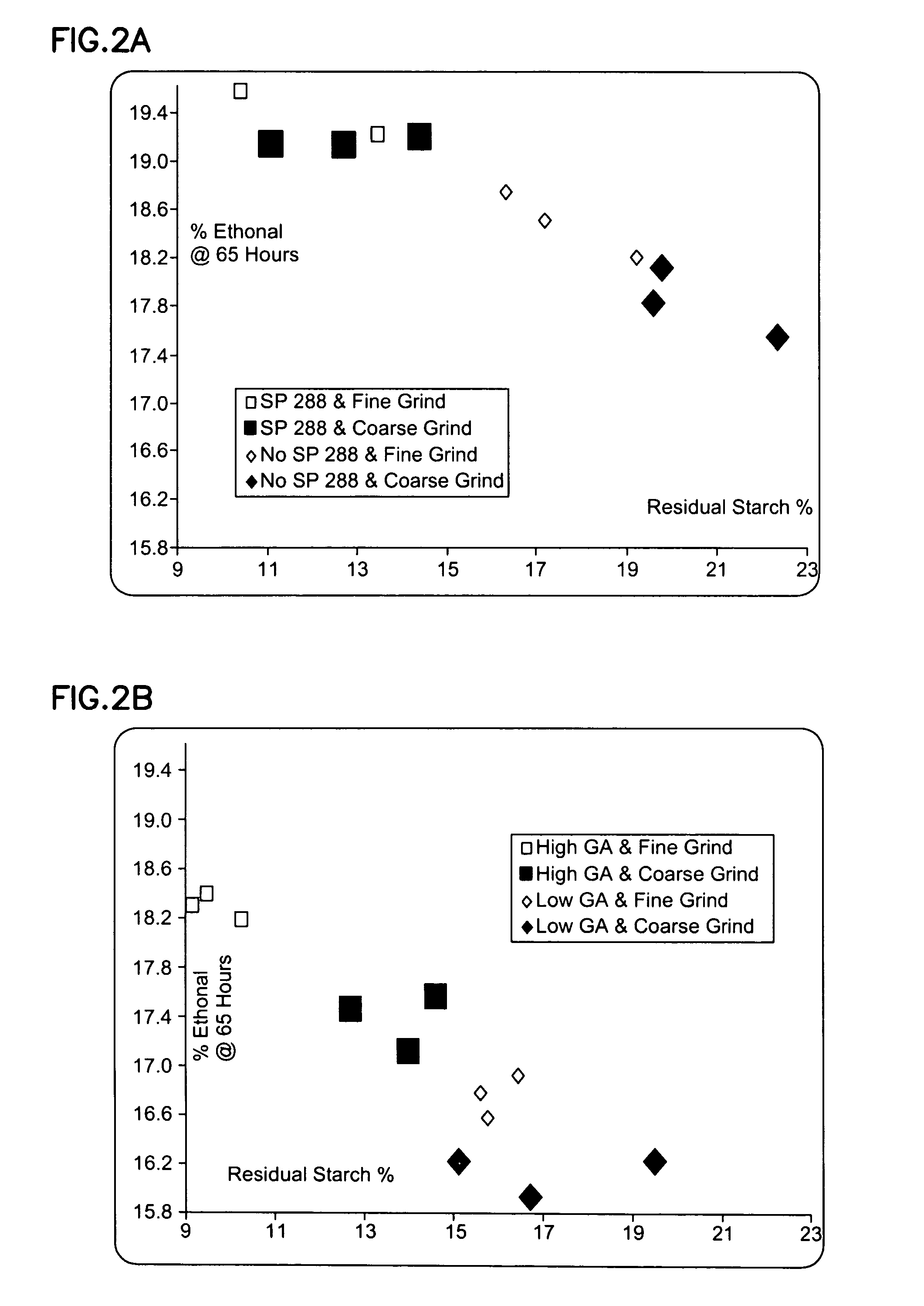
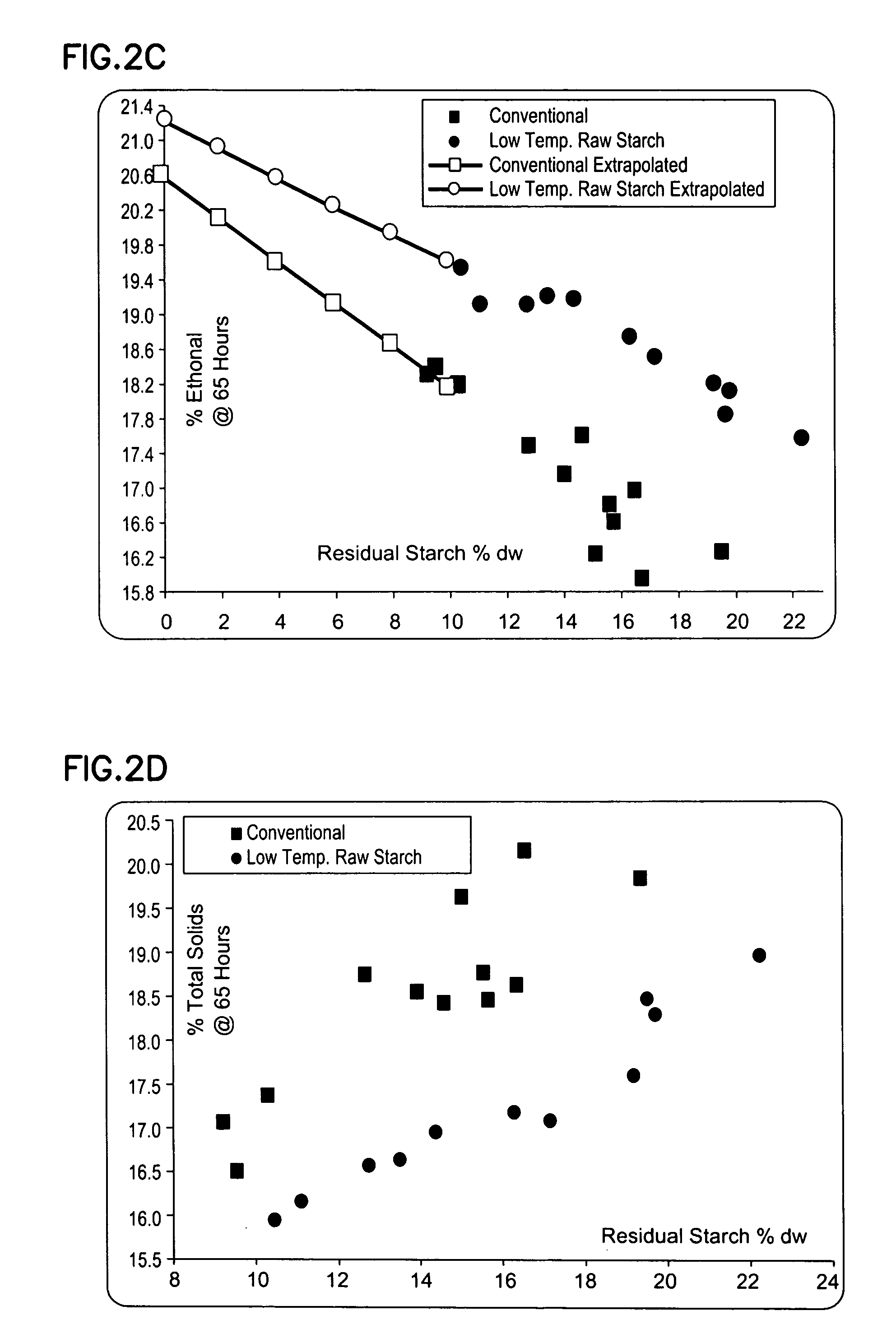
Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and selecting plant material
ActiveUS20070178567A1Improve the level ofDough treatmentWort preparationHigh alcohol beerStarch production
The present invention relates to methods for producing high levels of alcohol during fermentation of plant material, and to the high alcohol beer produced. The method can include selecting plant material. Selecting can include excluding plant material that has been exposed to high temperatures or that has had high moisture content.
Owner:POET RES INC
Labiatae herb extracts and hop extracts for extending the color life and inhibiting the growth of microorganisms in fresh meat, fish and poultry
InactiveUS20040131709A1Good colorDecreases color lifeBiocideUnknown materialsHops extractMicroorganism
Compositions comprising a Labiatae herb extract and a hop extract containing beta acids and methods of using them to extend the color life and retard the growth of microorganisms in fresh meat, fish and poultry stored in an atmosphere that contains 20% or more oxygen.
Owner:KALSEC
Method for increasing the tenderness of a meat product
A method for preserving a food product, such as meat, including the steps of inoculating meat with an effective amount of euhygienic non-pathogenic, non-spoilage bacteria in order to competitively inhibit the growth of undesired pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Edible films that incorporate and / or cover euhygenic bacteria on the food product are used to ensure competitive inhibition of undesired spoilage and pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SWIFT BEEF +1
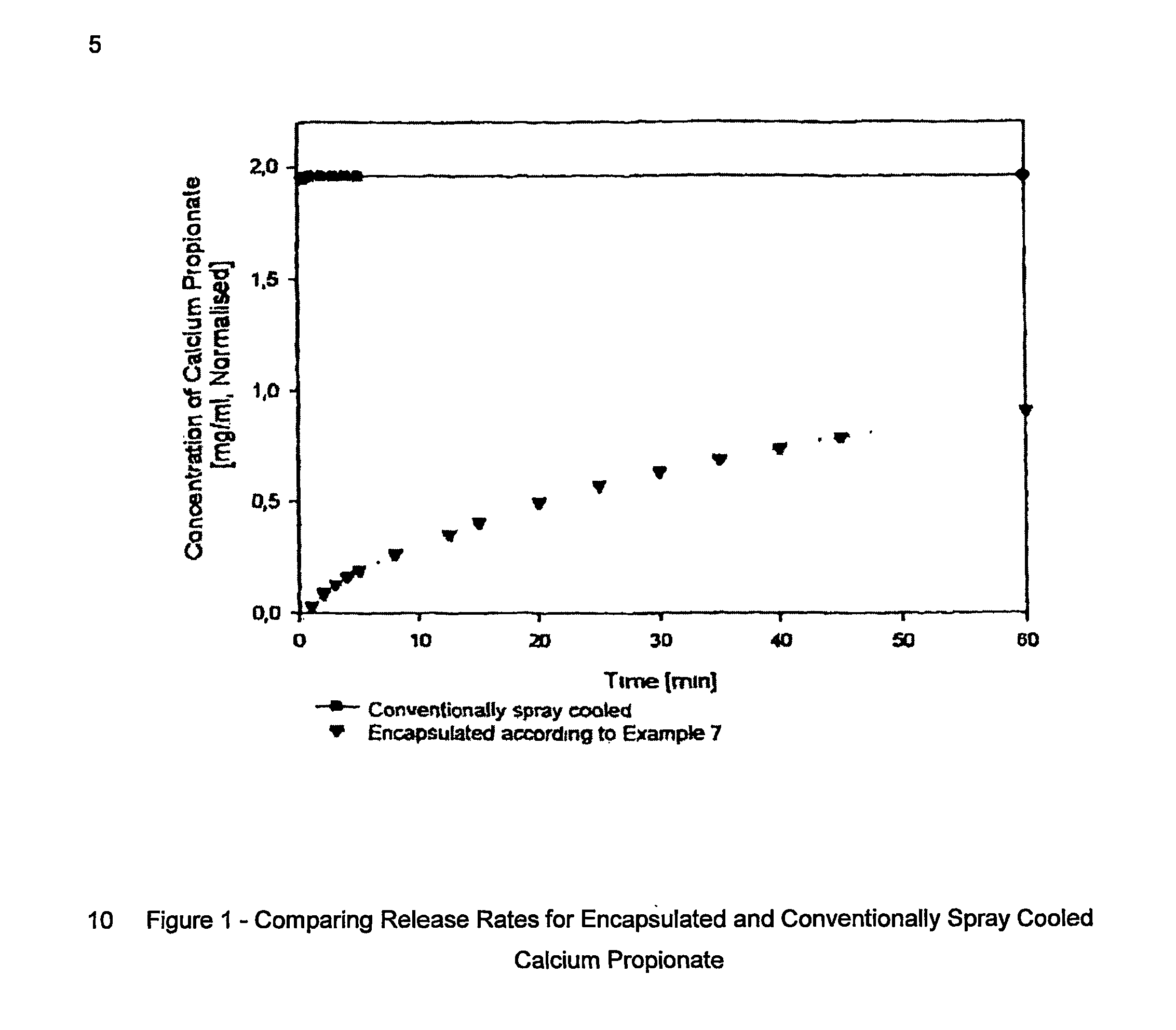
Microcapsules
InactiveUS20070042184A1Increase release rateControl releaseBiocideEggs preservation by coatingBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTActive ingredient
The present invention relates to microcapsules, and more particularly to microcapsules where an aqueous bead or beads comprising the active ingredient is encapsulated in or by a hydrophobic shell matrix. The present invention relates also to novel methods for preparing the microcapsules according to the invention, as well as to the use of the microcapsules of the present invention. A microcapsule of the present invention comprises a solidified hydrophobic shell matrix, an encapsulated aqueous bead or beads which is / are encapsulated in or by the solidified hydrophobic shell matrix, and an active ingredient or active ingredients dissolved or incorporated in the encapsulated aqueous bead or beads.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
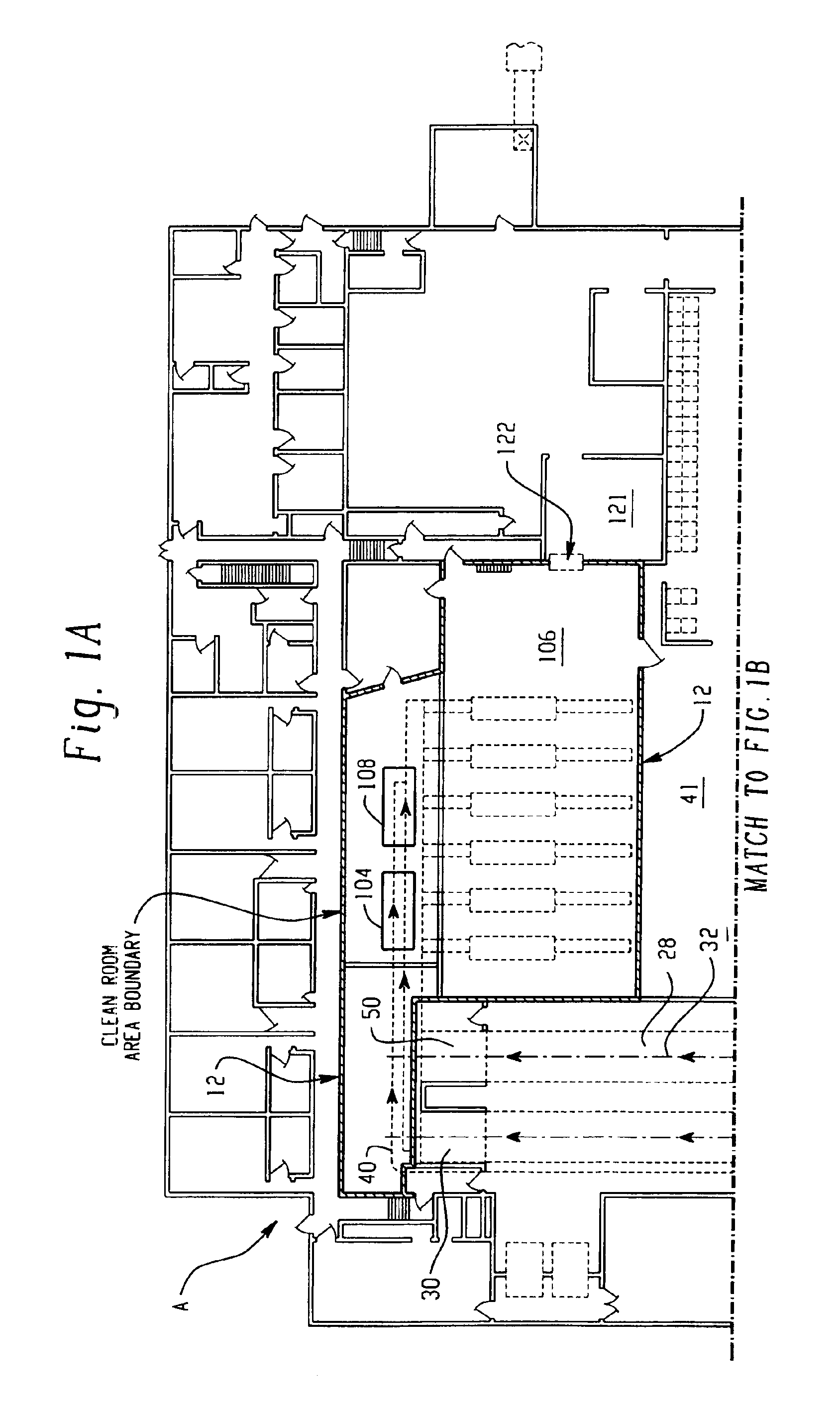
System for handling processed meat and poultry products
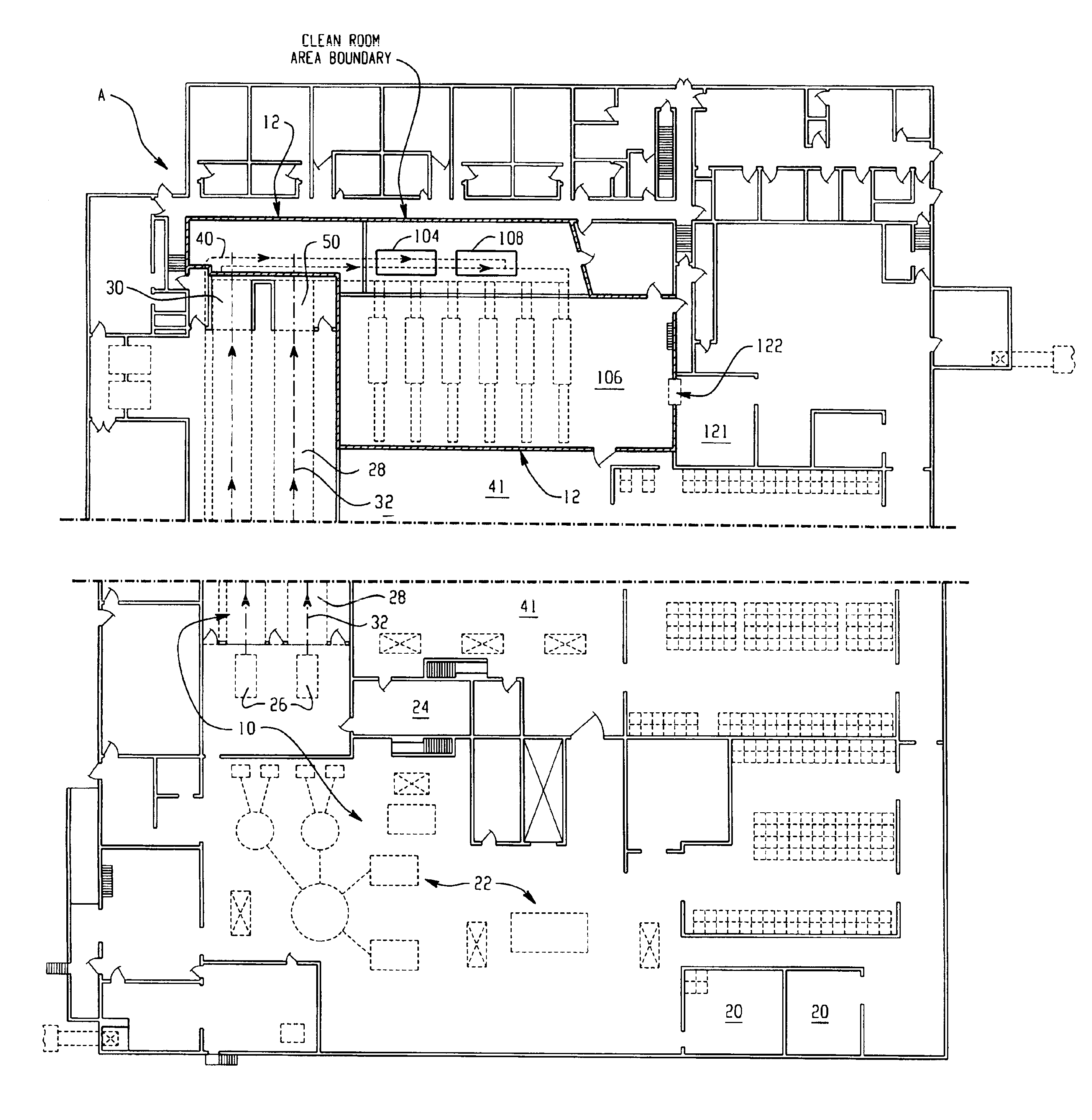
InactiveUS6964788B2Apparent advantageObvious advantagesMeat/fish preservation using liquidsSausage casingsPathogenic microorganismPoultry product
Food products, such as precooked meats, sausages, and the like are microbially decontaminated in their cooking packages to remove surface microorganism contamination from the packages. The cooking packages are removed and the food products optionally subjected to further processing, such as slicing, and then packaged in aseptic packaging. The microbial decontamination step, further processing and packaging are carried out in a clean room which is maintained to a high level of sterilization or disinfection to minimize or eliminate contamination of the food products with pathogenic microorganisms such as Listeria Monocytogenes. The food products thus leave the packaging plant with a much higher assurance of food safety than is found in a conventional packaging plant.
Owner:STERIS CORP
Algal culture production, harvesting , and processing
InactiveUS20110138682A1Maintaining culture selectivityLoss of selectivityAlgae productsUnicellular algaeAlgaenanLipid formation
Materials and methods are provided for growing algae while maintaining culture selectivity. Algae that can be grown include, for example, green algae such as those of the genus Scenedesmus. Lipid obtained from the algae can be used to produce biofuels such as biodiesel or polyunsaturated fatty acids such as omega-3 fatty acids. Feedstocks such as animal feed and aquaculture feed can also be produced as can phytonutrients such as asataxanthin and beta-carotene.
Owner:AQUATIC ENERGY LLC
Method of processing waste product into fuel
InactiveUS20050142250A1Efficient conversionControlled and adjustable resistanceMilk preparationSolid fuelsWaste streamWaste product
Fuels used may be derived from existing waste streams such as animal wastes and streams of discarded or unwanted animal byproducts generated at animal slaughterhouses. A method of processing organic waste products into fuel includes homogenizing the waste products. The waste products are heated and pressurized. Water is removed from the waste products. Selected constituent of the waste products are separated from the waste products into a waste stream. The waste stream is blended with a fuel to form a bio-fuel mixture.
Owner:STONE MICHAEL
Composition based on fish oil
InactiveUS6020020AEfficient dosingFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteDough treatmentFish oilOleic Acid Triglyceride
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 05025 Sec. 371 Date May 26, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 26, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 19601 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 5, 1997Fish oil concentrates, having: < / =40% of long chain poly unsaturated fatty acids <20% of saturated fatty acids (C14-C18) <15% oleic acid <12% C16:1-fatty acid and with a weight-ratio: can be obtained by a process involving the following steps subjecting a fish oil to an enzymic conversion removing free fatty acids or esters from conversion-product subjecting product of above to enzymic hydrolysis, using specific lipase or partial glyceride-specific lipase wash and dry product re-esterify dried product.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Method for treating a food processing facility
A method for preserving a food product, such as meat, comprising the steps of inoculating meat with an effective amount of euhygienic non-pathogenic, non-spoilage bacteria in order to competitively inhibit the growth of undesired pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Edible films that incorporate and / or cover euhygenic bacteria on the food product are used to ensure competitive inhibition of undesired spoilage and pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SWIFT BEEF +1
Engineered comestible meat
ActiveUS20130029008A1Increased formationArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingMyocyteBiology
Provided are engineered meat products formed as a plurality of at least partially fused layers, wherein each layer comprises at least partially fused multicellular bodies comprising non-human myocytes and wherein the engineered meat is comestible. Also provided are multicellular bodies comprising a plurality of non-human myocytes that are adhered and / or cohered to one another; wherein the multicellular bodies are arranged adjacently on a nutrient-permeable support substrate and maintained in culture to allow the multicellular bodies to at least partially fuse to form a substantially planar layer for use in formation of engineered meat. Further described herein are methods of forming engineered meat utilizing said layers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
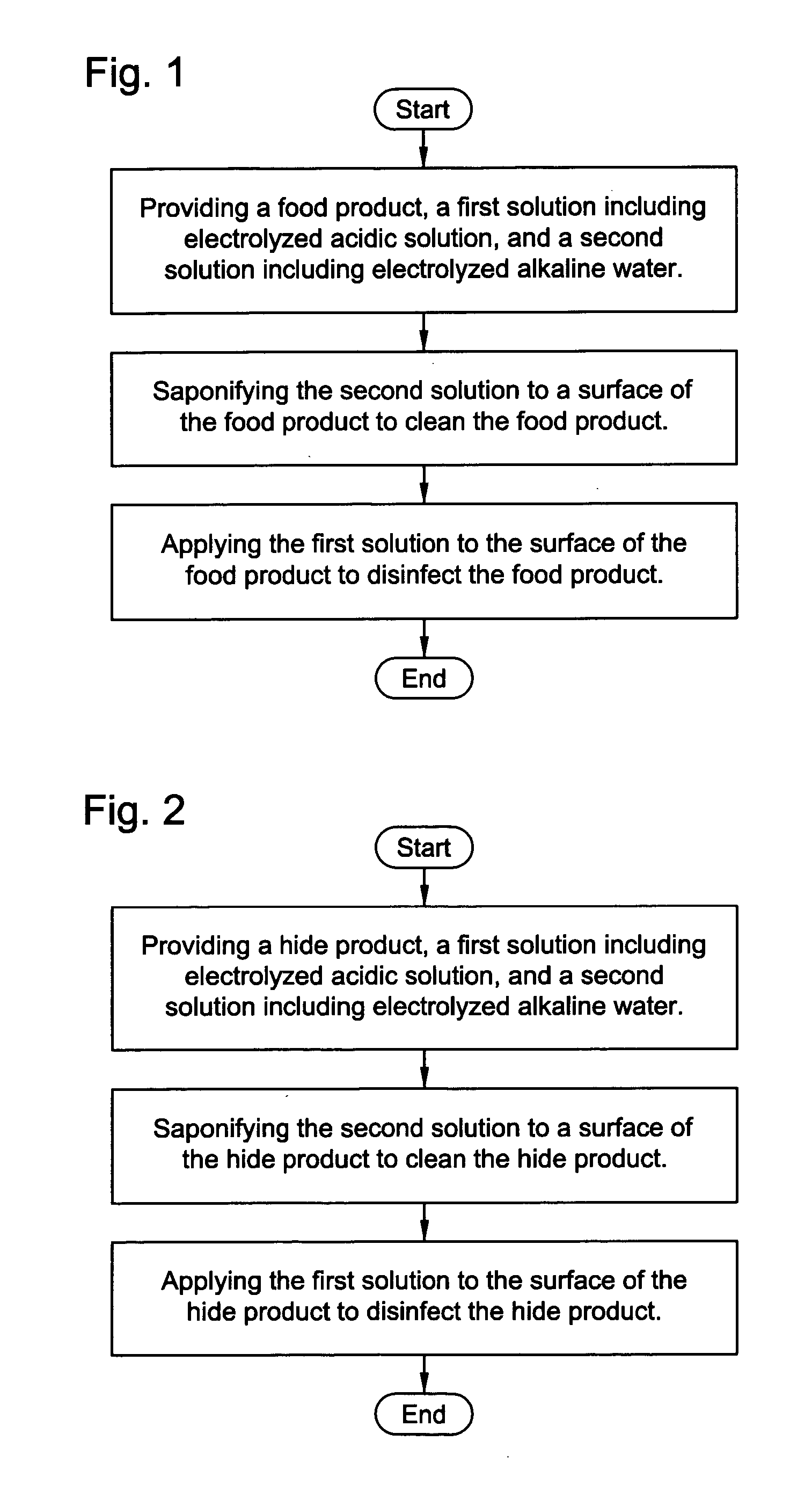
Electrolyzed water treatment for meat and hide
InactiveUS20050244556A1Electrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityElectrolysisIndividual animal
Owner:ELECTRIC AQUAGENICS UNLMITED
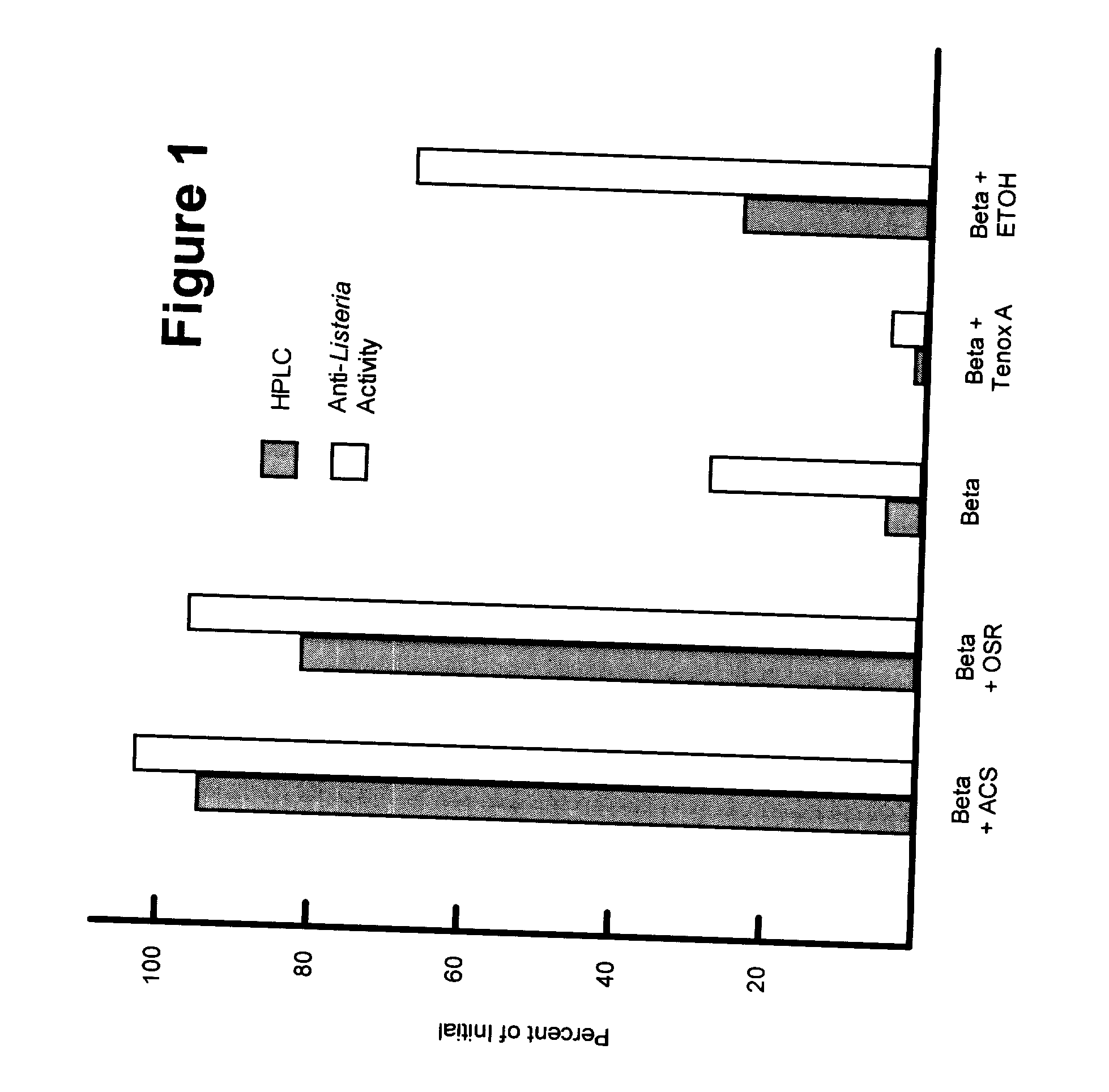
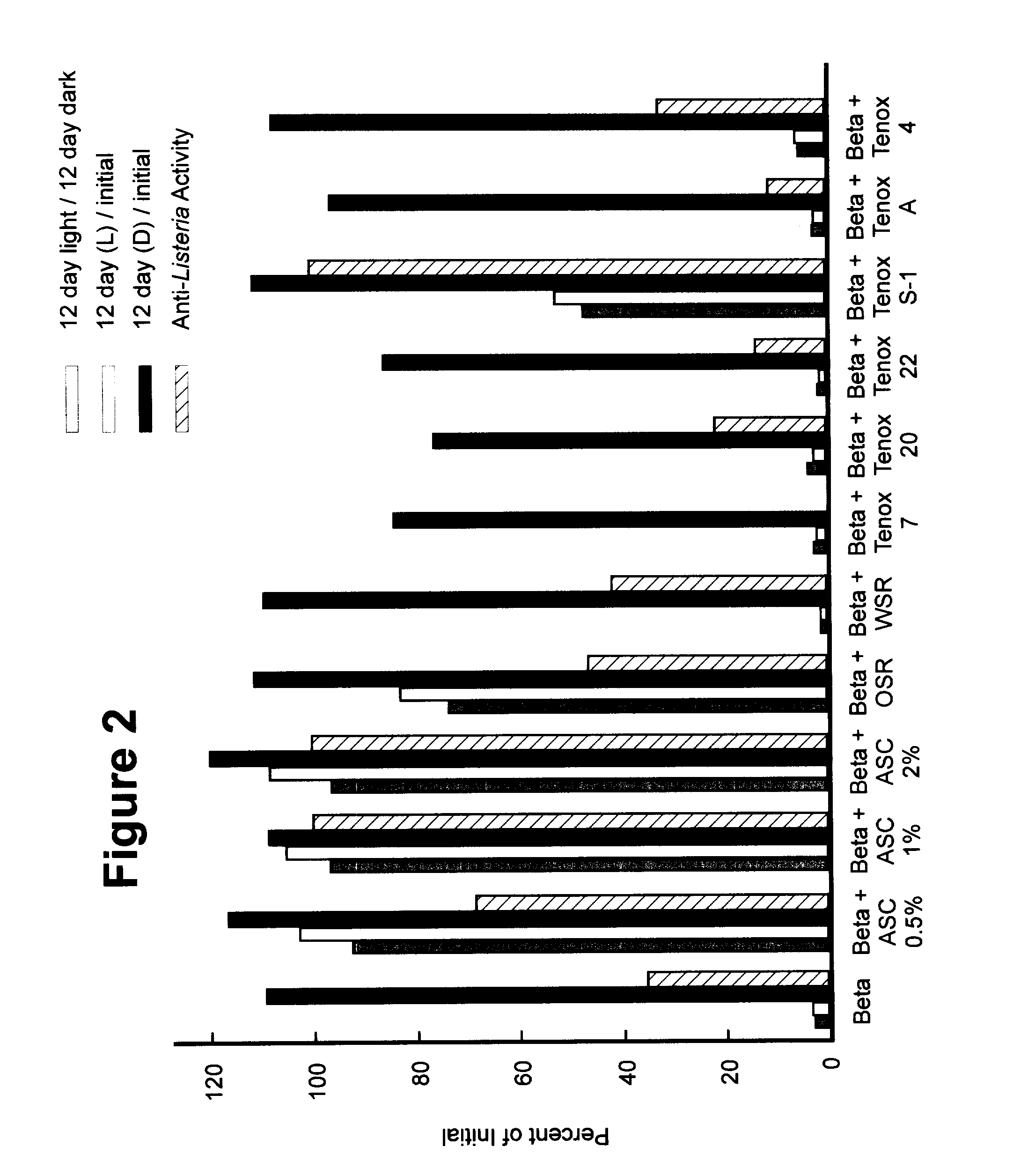
Hop beta acid compositions for use in food products
InactiveUS20040175480A1Easy to optimizeImprove stabilityMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood gradeAlcohol
Hop beta acids are improved with respect to their antibacterial properties, especially their anti-Listeria properties. Enhancement in this regard is especially useful for the treatment of food products which are susceptible to bacterial contamination. This can be especially important when the hop beta acids are to be used in surface application onto the food products. The hop beta acids are rendered more effective by combining them with a food grade acid, a potassium ion source, and an optional antioxidant in a carrier solvent such as, for example, a food grade alcohols or a food grade glycol. The improved hop beta acid compositions of this invention provide increase stability, higher hop beta acid concentrations, and / or higher anti-Listeria activities.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS INC
Production method of bacon
InactiveCN101380117AKeep the traditional flavorKeep the flavorMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood preparationChemistryCeramic
The invention discloses a method for preparing preserved pork. The method comprises the steps of preparing semi-finished pork of raw material, preparing spices, rolling in vacuum, curing and fermenting, fire-curing, packaging in vacuum and fermenting by adding distillery yeast in the semi-finished pork of the raw material; the cypress smoke for fire-curing is firstly absorbed by ceramics and red porcelain, and filtered by a wet cloth layer, and the cured semi-finished pork is fire-cured. The traditional preserved pork has special flavor and taste, the residual harmful substances of the smoke stains are perfectly controlled, and therefore, the preserved pork is clean, sanitary, healthy, special in flavor and convenient for eating. If the pork is added with spices such as preserved black beans or citronella grass for processing and fermentation, the product has amaroidal sweet flavor and special fragrance of the preserved black beans or the fresh grass fragrance of the citronella grass. The special fragrance increases appetite and promotes absorption. The citronella grass can purify, revivify the emotion and relieve depression. The method adopts reasonable raw materials and proportioning of the raw materials, and reasonable adding sequence of the raw materials in the process reflects the fragrance of the product.
Owner:冉伟
Compositions for improving flavor and safety of marinated meat products
A composition for improving the flavor and juiciness of marinated meats and inhibiting growth of pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms and a process for making the composition are described. Lemon juice and vinegar are neutralized, concentrated and blended with non-neutralized lemon juice and non-neutralized vinegar in appropriate proportions to achieve the desired water binding and antimicrobial effects.
Owner:KERRY GRP SERVICES INT
Antimicrobial composition for pre-harvest and post-harvest treatment of plants and animals
ActiveUS7192618B2Minimize growth and spreadReduce Microbial ContaminationHeavy metal active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationFood additiveDisinfectant
Owner:CMS TECH INC +1
Method of dewatering grain stillage solids
ActiveUS20050079270A1Improve throughputShorten the timeBy-product recoveryFood processingAcryditeSodium methacrylate
A method of dewatering corn stillage solids comprising adding to the solids an effective coagulating and flocculating amount of an anionic copolymer comprising acrylic acid sodium salt, methacrylic acid sodium salt or 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt to form a mixture of water and coagulated and flocculated solids; and separating the water from the coagulated and flocculated solids using a dewatering device.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Method of Preparing More Digestible Animal Feed
InactiveUS20080220125A1Improve nutritional qualityImprove practicalityConfectioneryAnimal feeding stuffAdditive ingredientCarbohydrate moiety
Disclosed herein are methods of treating an edible fiber source to make an animal feed with increased digestible energy. An exemplary method includes hydrolyzing the edible fiber source with an inorganic fiber hydrolyzing agent in a twin screw mixer that shears the edible fiber to a size of between 0.5 to 25 mm. The hydrolysis in the mixer occurs at pressure of about 14 psig or higher with a temperature about 100° C. to 110° C. The inorganic hydrolysis liberates a first portion of soluble carbohydrates from the edible fiber source. The inorganically hydrolyzed material is also treated (before or after) with a fiber degrading enzyme to solubilize a second portion of carbohydrates. The dually hydrolyzed material is dried to form an animal feed or feed ingredient having a soluble and insoluble carbohydrate fraction with the amount of soluble carbohydrate being at least 45% wt / wt of the total carbohydrates obtained from the edible fiber source.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Method for producing chlorella fermented food
InactiveUS7914832B2Production is suppressedReduce flavorTea extractionAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyLactobacillus
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a chlorella fermented food in which a flavor and odor that are peculiar to algae are reduced while production of pheophorbide is suppressed. The method for producing a chlorella fermented food according to the present invention can be achieved by using a chlorella negative in coliform bacteria count, and having a content of free pheophorbide equal to or less than 18 mg % and a viable general bacteria count equal to or less than 8000 cfu / mL, or using a chlorella subjected to a heat sterilization treatment to ferment the chlorella with a baker's yeast. The baker's yeast is blended with the chlorella at a ratio of preferably 0.1 to 15% by weight. Further, the fermentation treatment is preferably carried out in the presence of glucose and a lactic acid bacterium.
Owner:KYOTO EIYO +1
Engineered comestible meat
Provided are engineered meat products formed as a plurality of at least partially fused layers, wherein each layer comprises at least partially fused multicellular bodies comprising non-human myocytes and wherein the engineered meat is comestible. Also provided are multicellular bodies comprising a plurality of non-human myocytes that are adhered and / or cohered to one another; wherein the multicellular bodies are arranged adjacently on a nutrient-permeable support substrate and maintained in culture to allow the multicellular bodies to at least partially fuse to form a substantially planar layer for use in formation of engineered meat. Further described herein are methods of forming engineered meat utilizing said layers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com