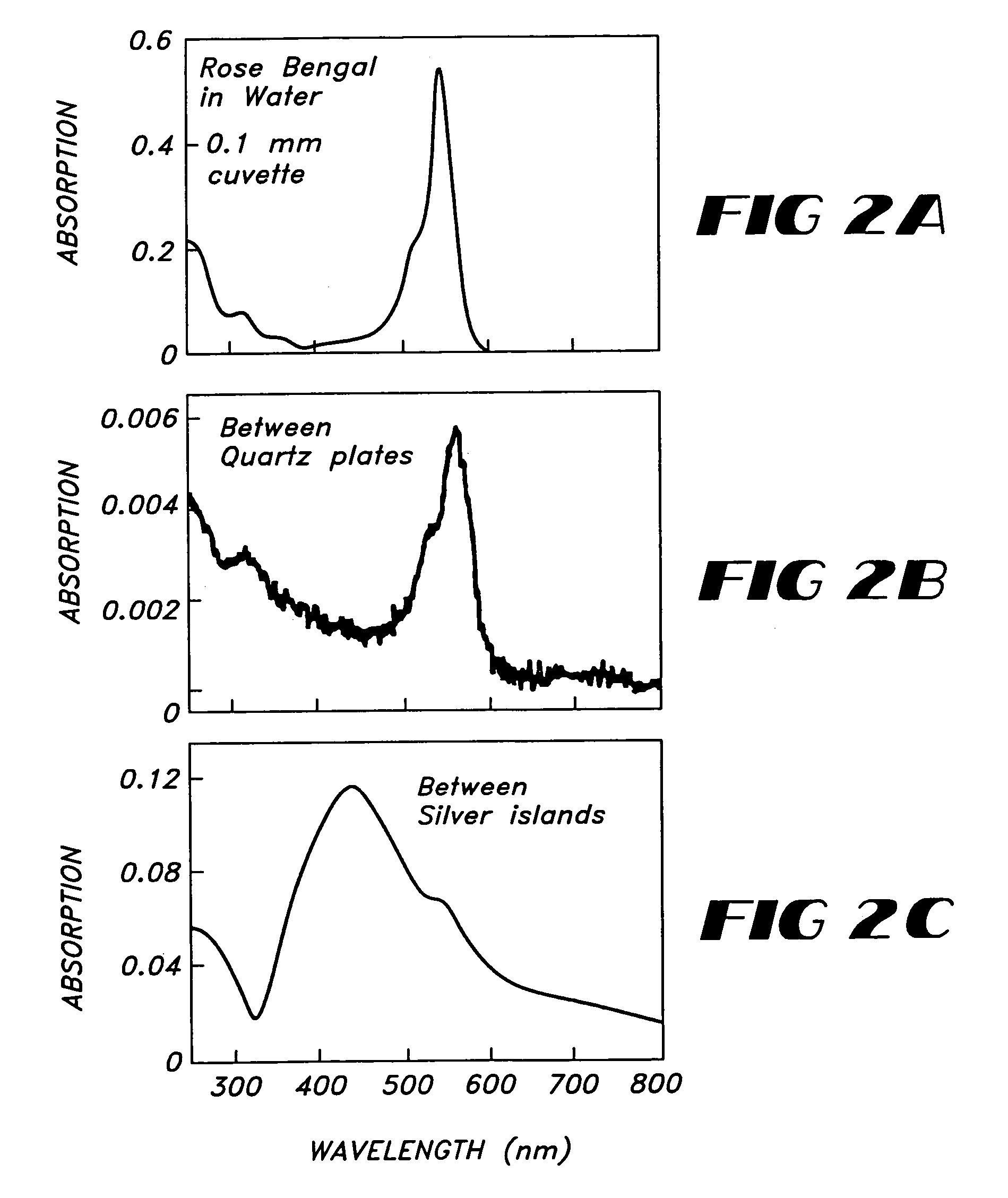
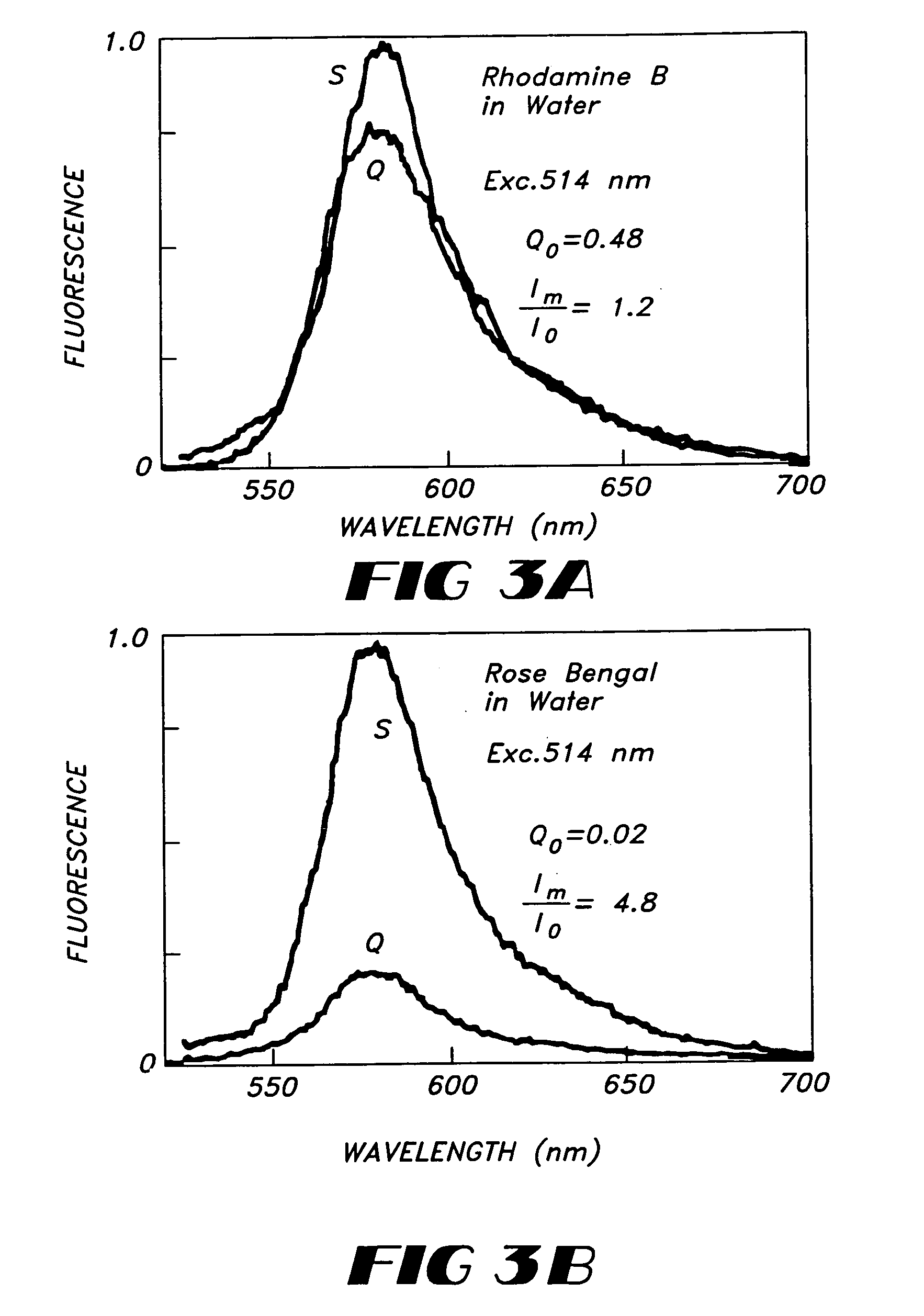
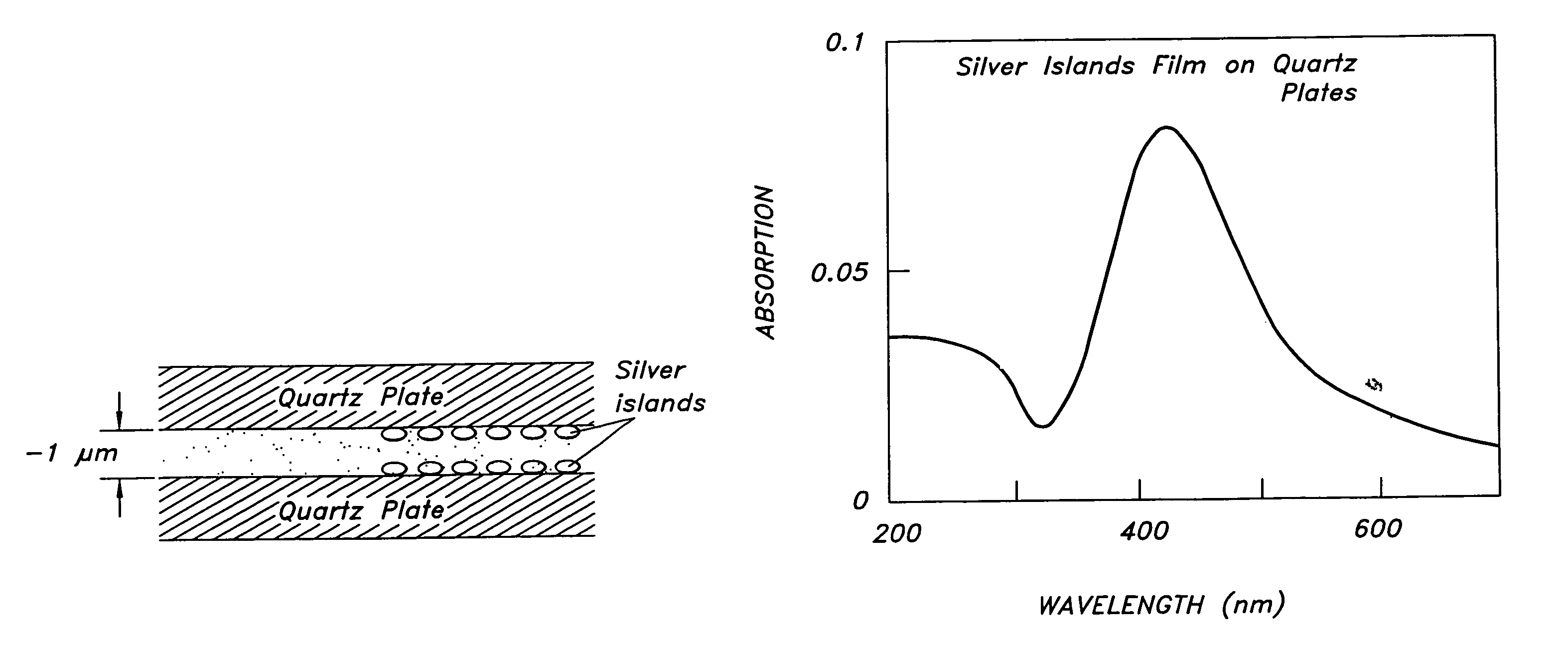
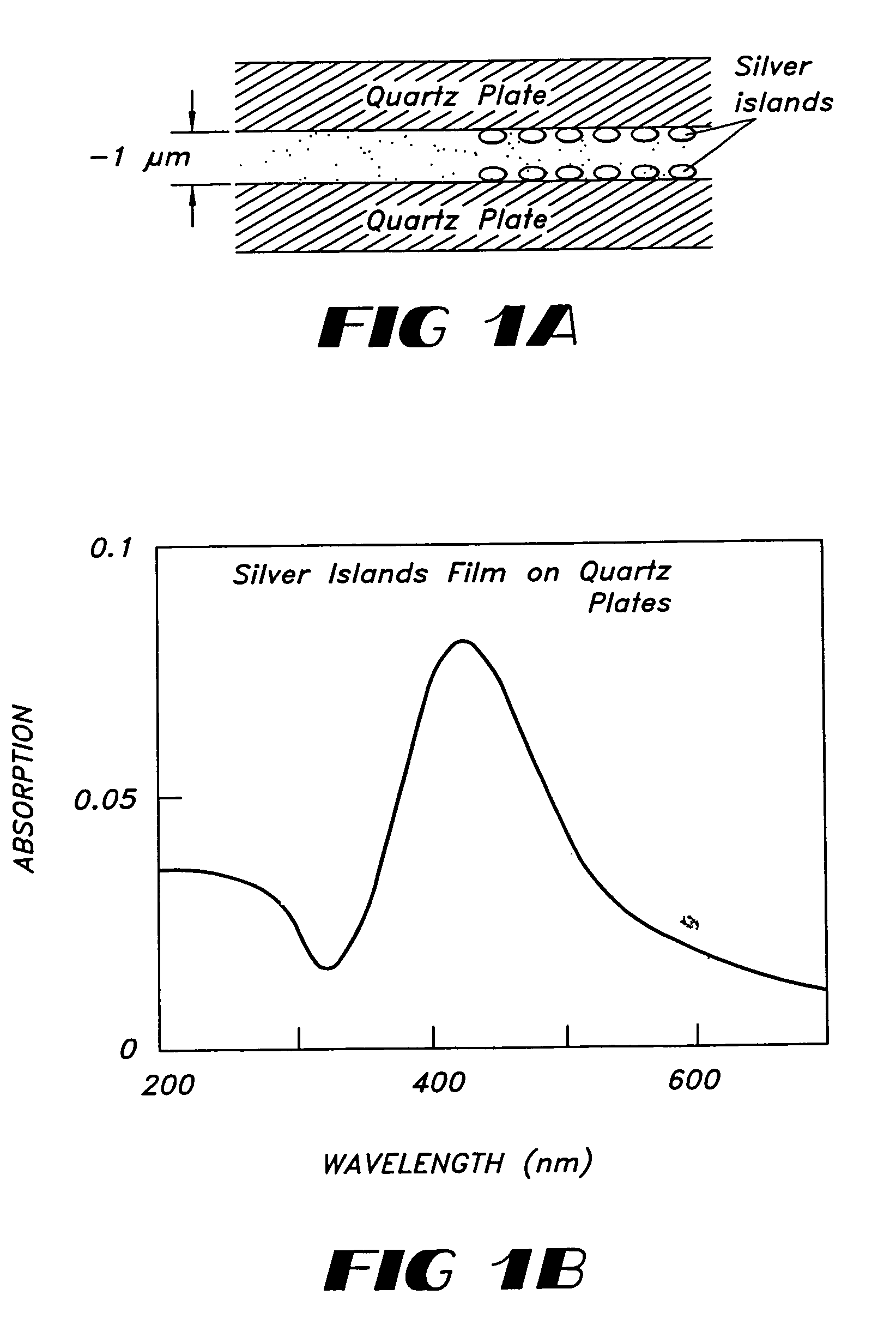
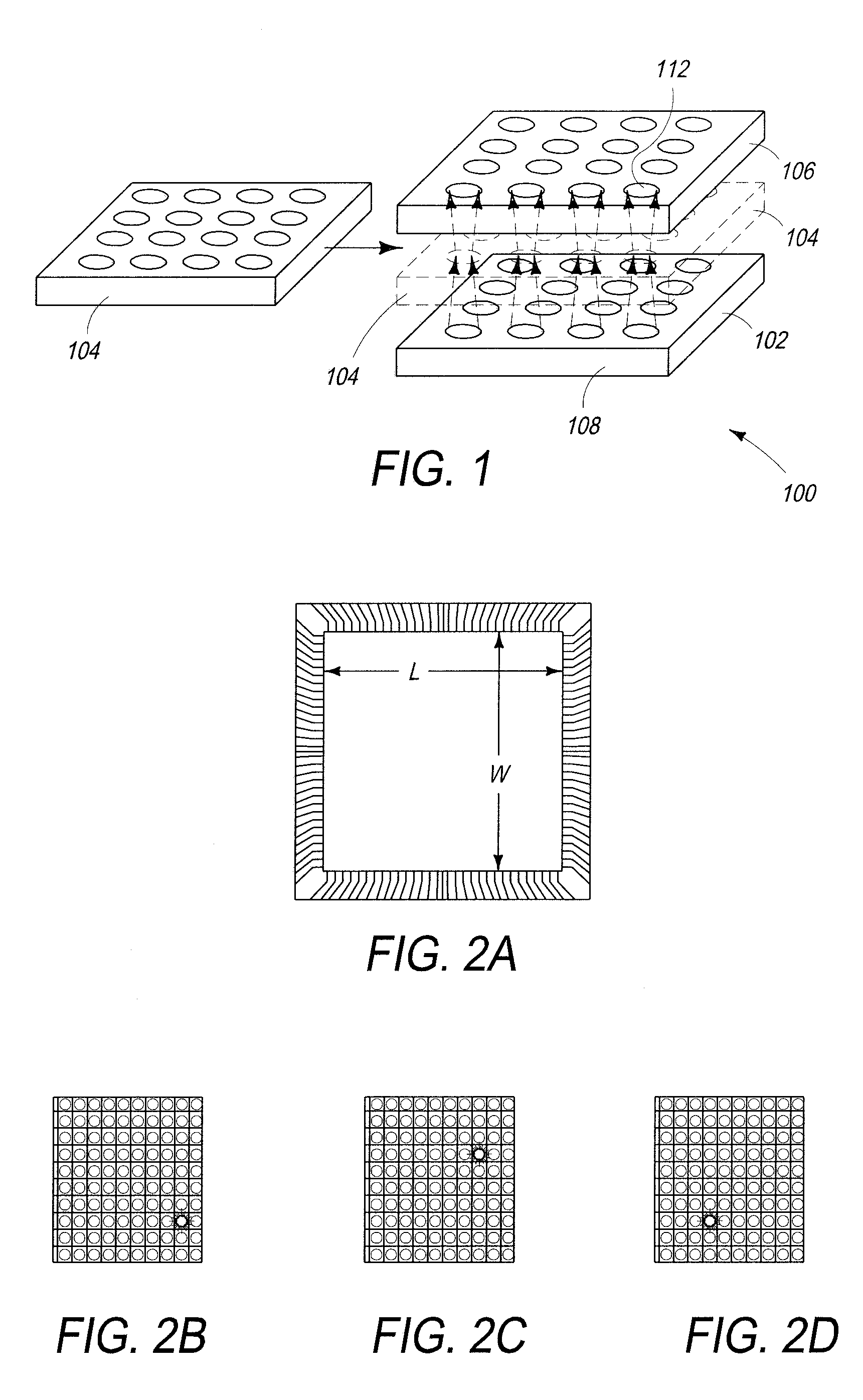
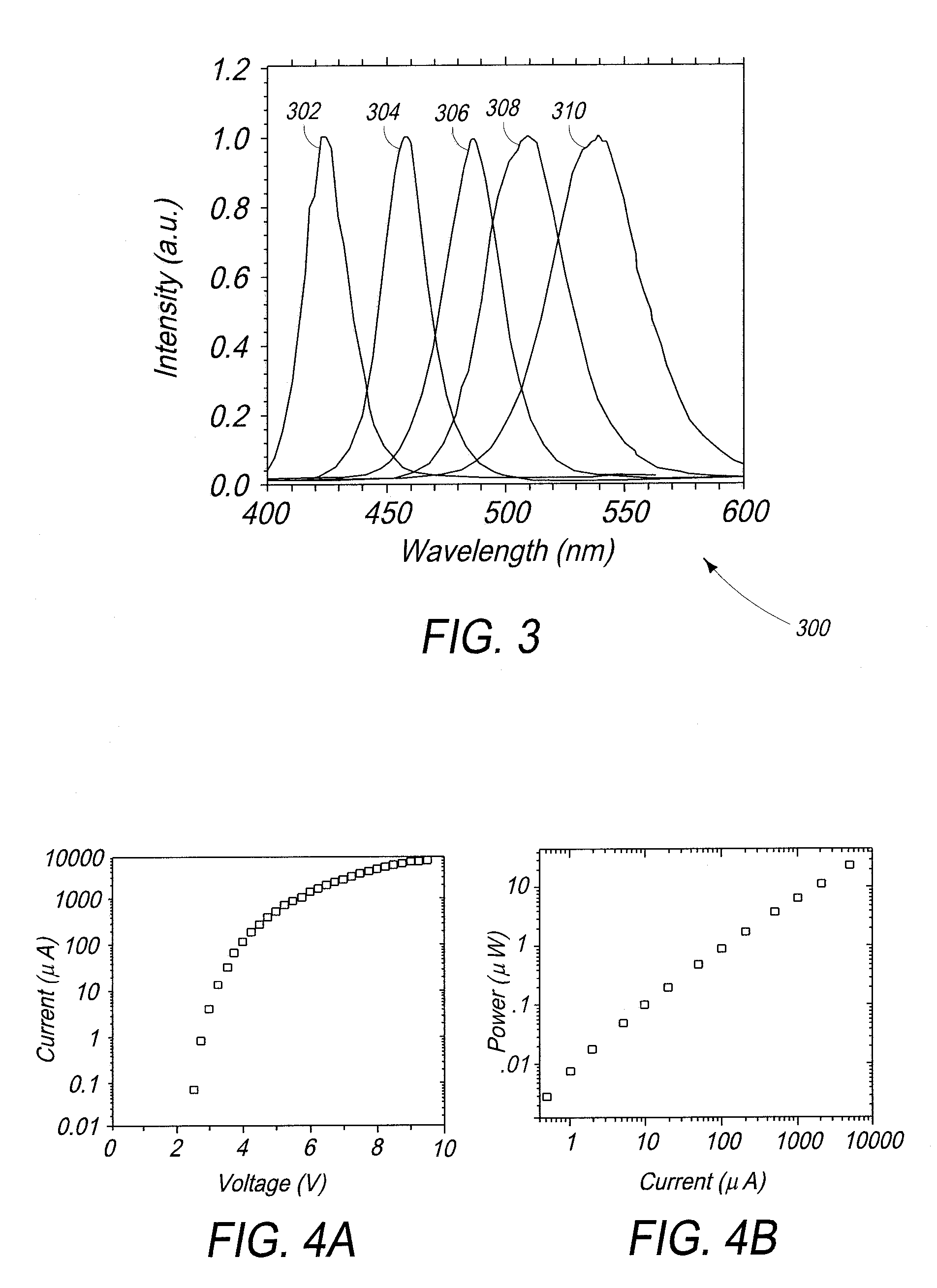
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Intrinsic fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
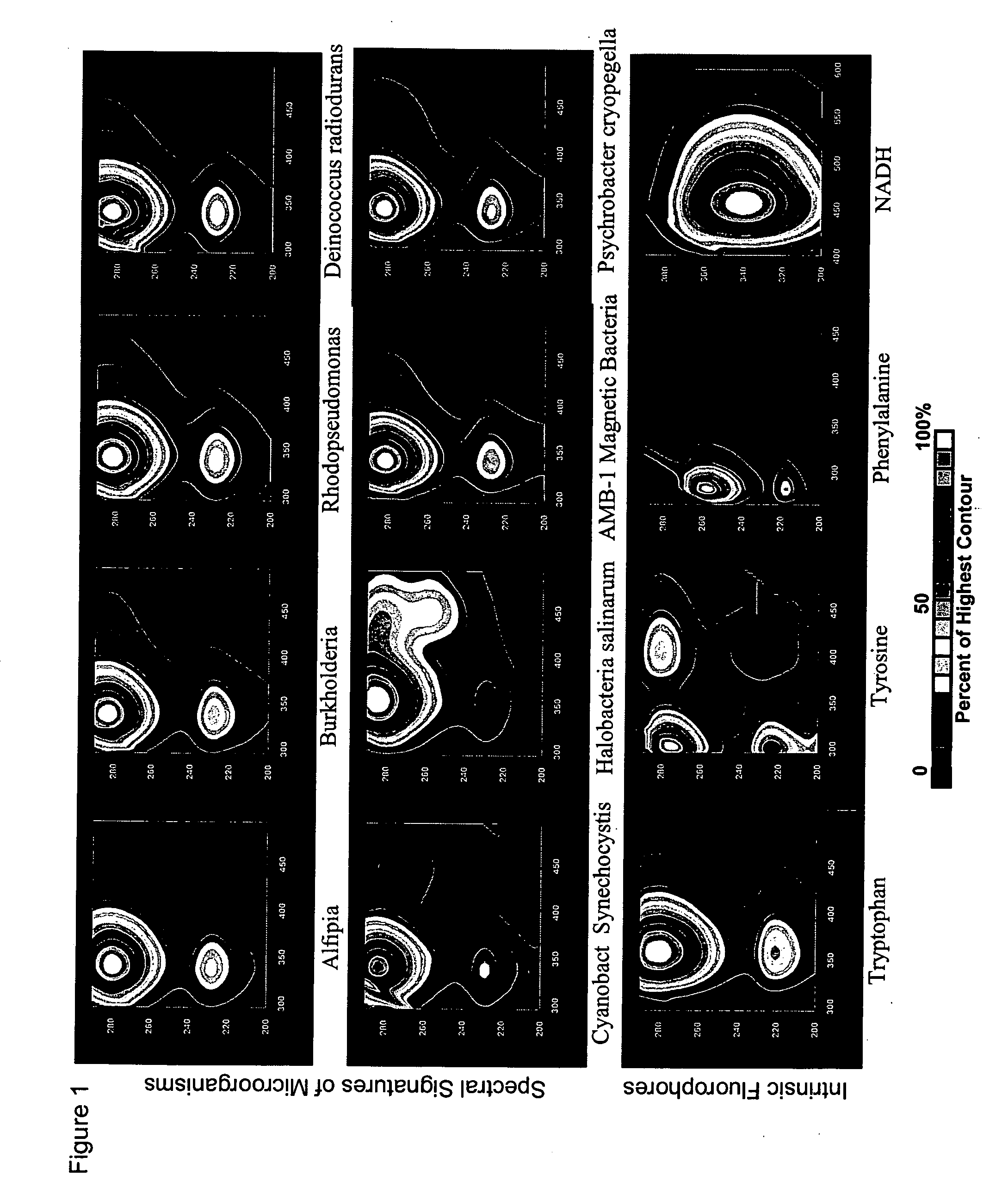
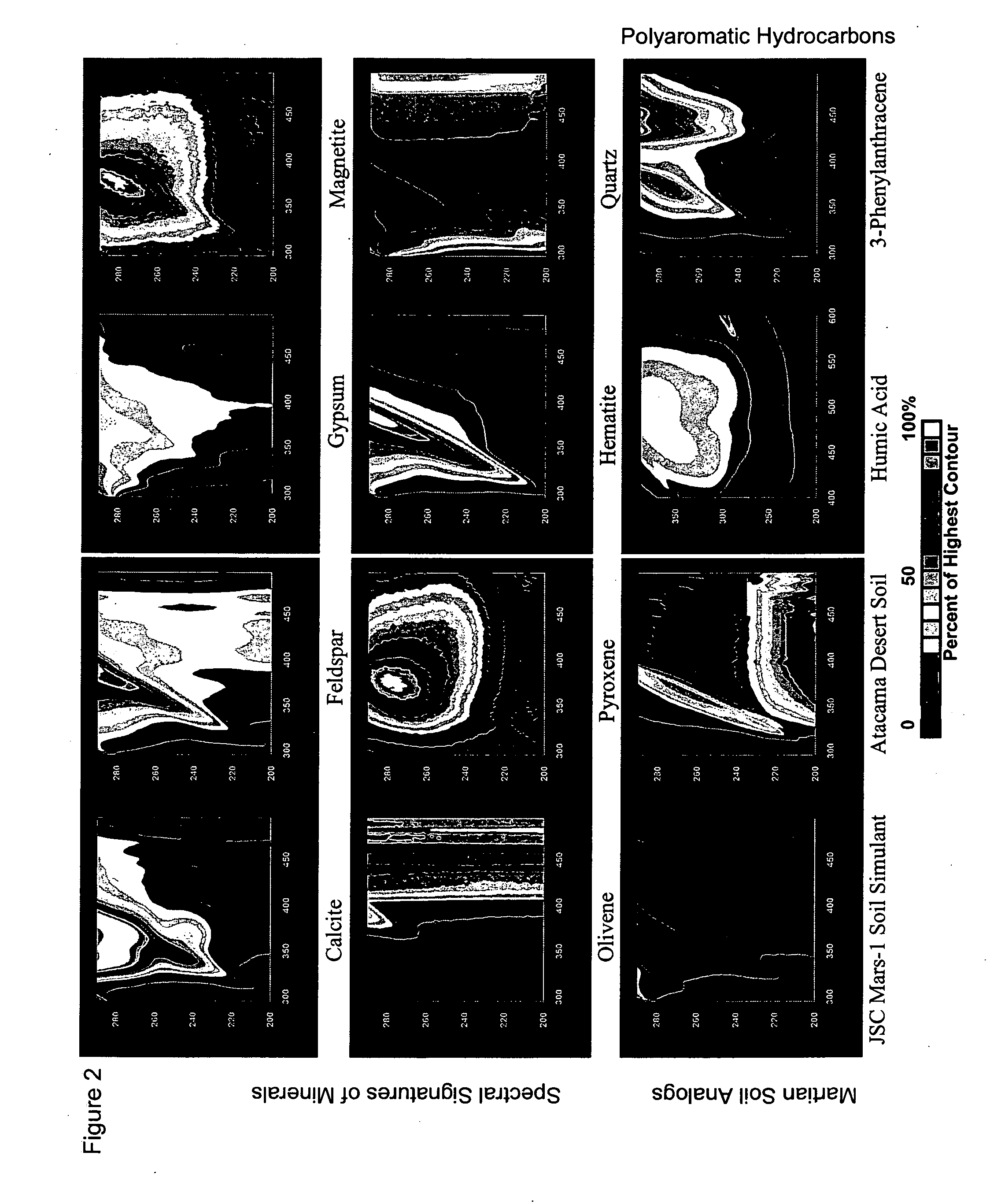
Intrinsic fluorescence is a powerful indicator of protein structure and function. The amount of fluorescence can often give the researcher insight into the protein’s conformational states or activity under different biological conditions including changes in temperature, pH and ion concentration.
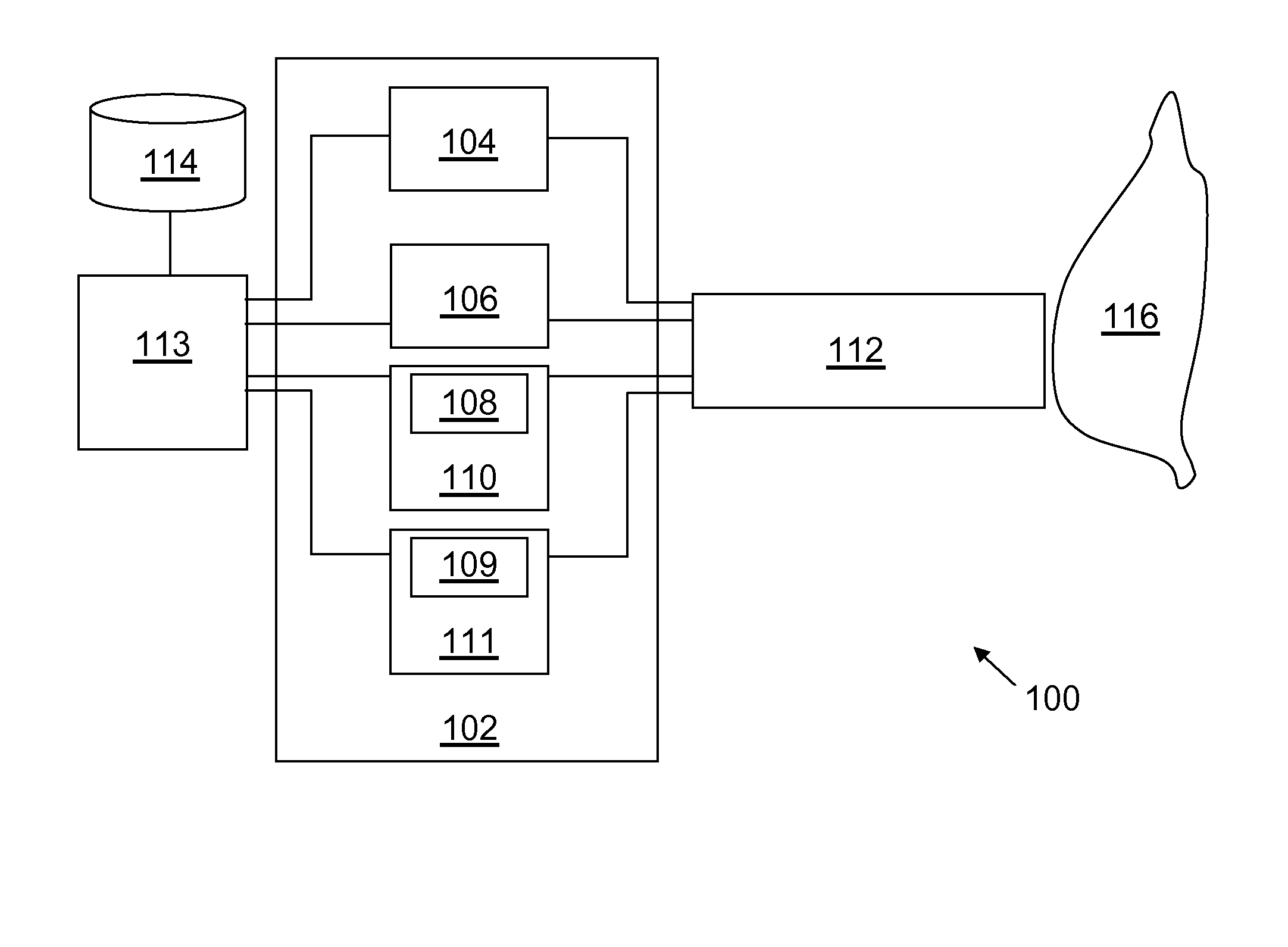
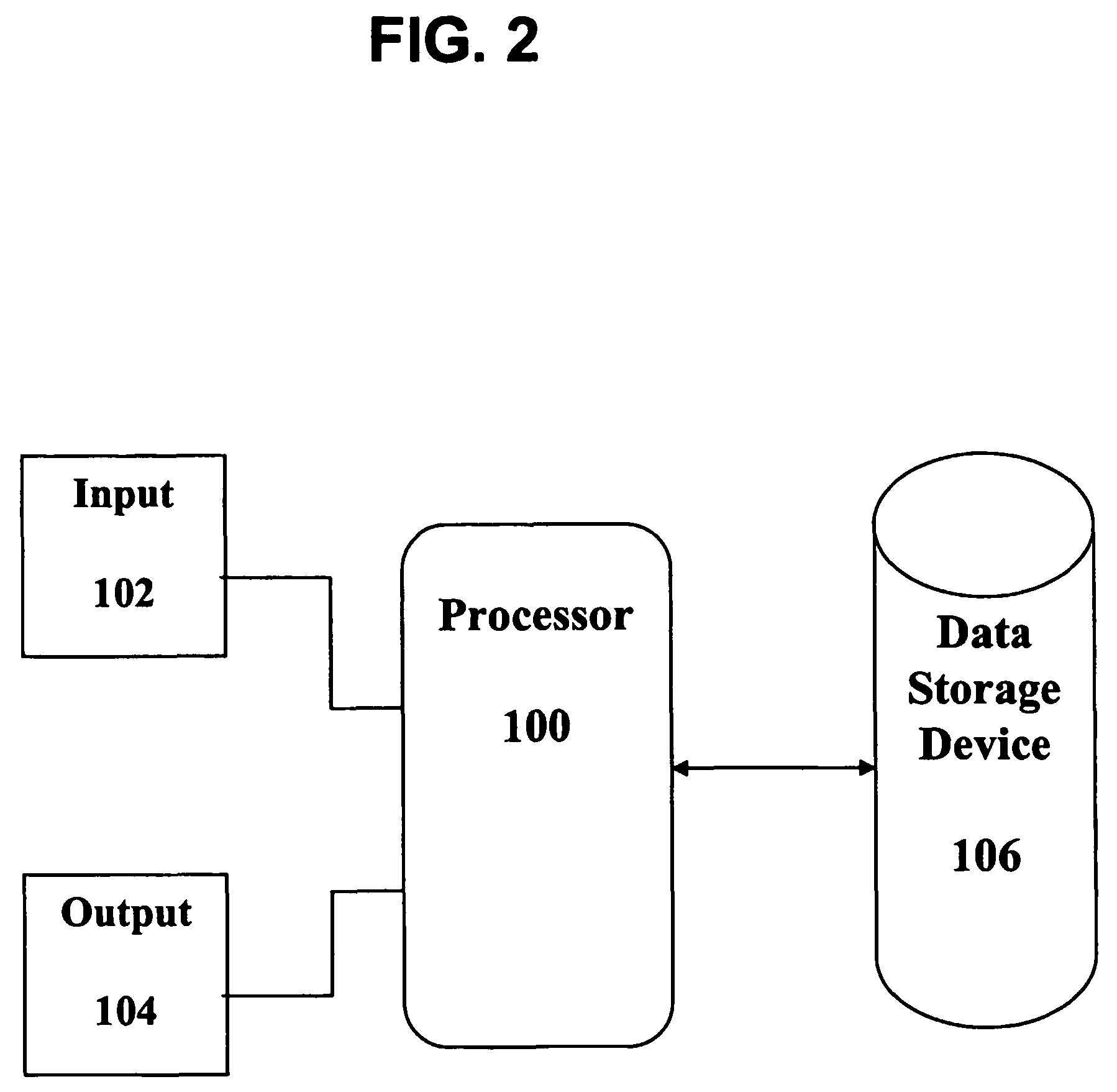
System and method for monitoring an analyte
InactiveUS20070111225A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteFluidics
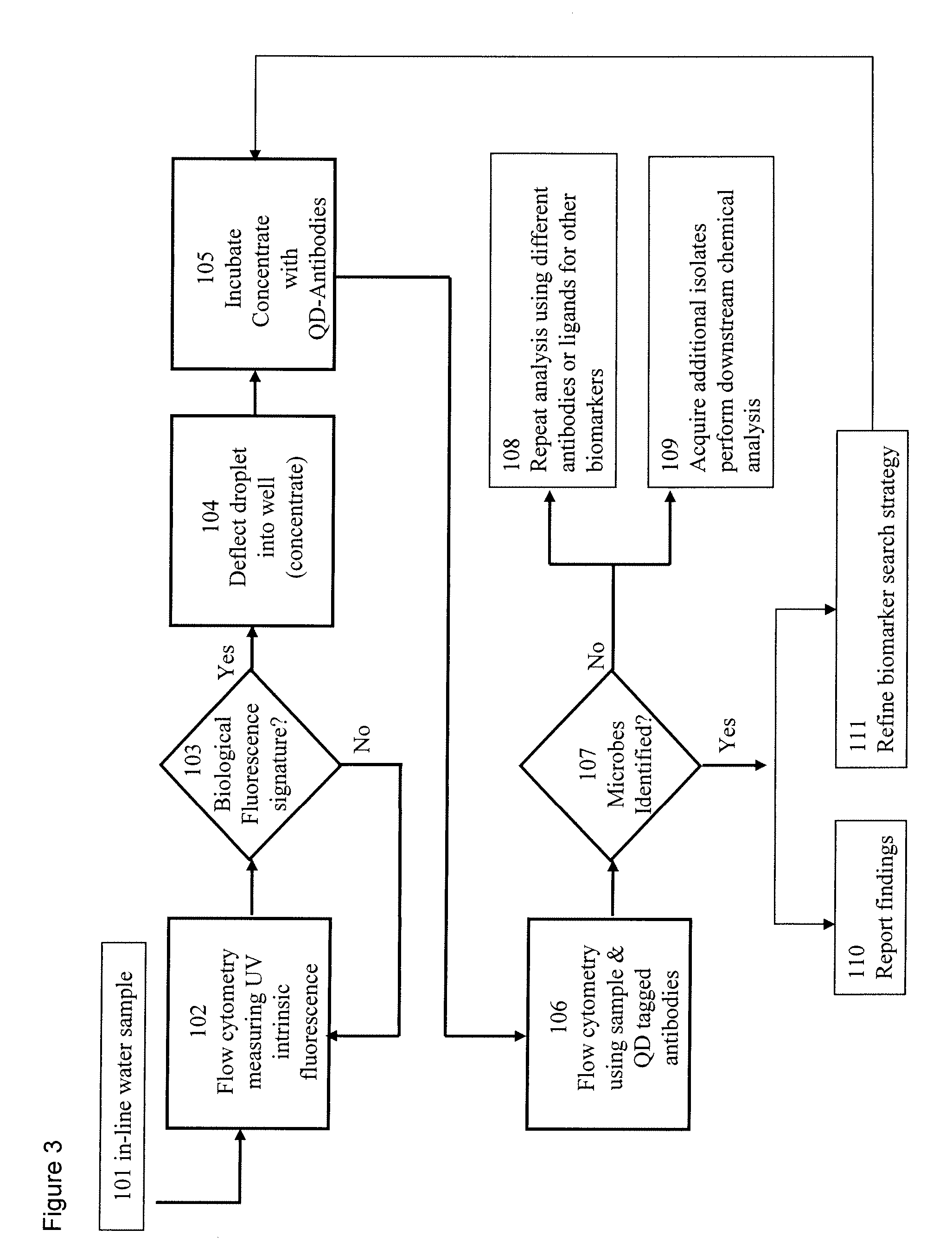
The present invention provides for a monitoring system and method to monitor an analyte, including determining the presence of the analyte and analyzing the analyte; for example, cellular chorography and biological threats. The system and method use a fluidics apparatus (e.g., a flow cytometer), a computer, a probe synthesizer and / or an initial set of fluorophore conjugated probes to monitor the analyte. The fluidics apparatus is adapted to determine the presence of the analyte based on the intrinsic fluorescence of the analyte, and / or to determine the binding of the probes to the analyte in the sample. The binding information is analyzed by the computer by comparing the binding results with a database of information regarding the analyte. The information gained allows the probe synthesizer to synthesize new probes for a subsequent iteration of the process, wherein additional information regarding the analyte is gained with every iteration.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070197894A1Reduce acquisition timeReduce the numberDiagnostics using lightSensorsReal time analysisFunctional change
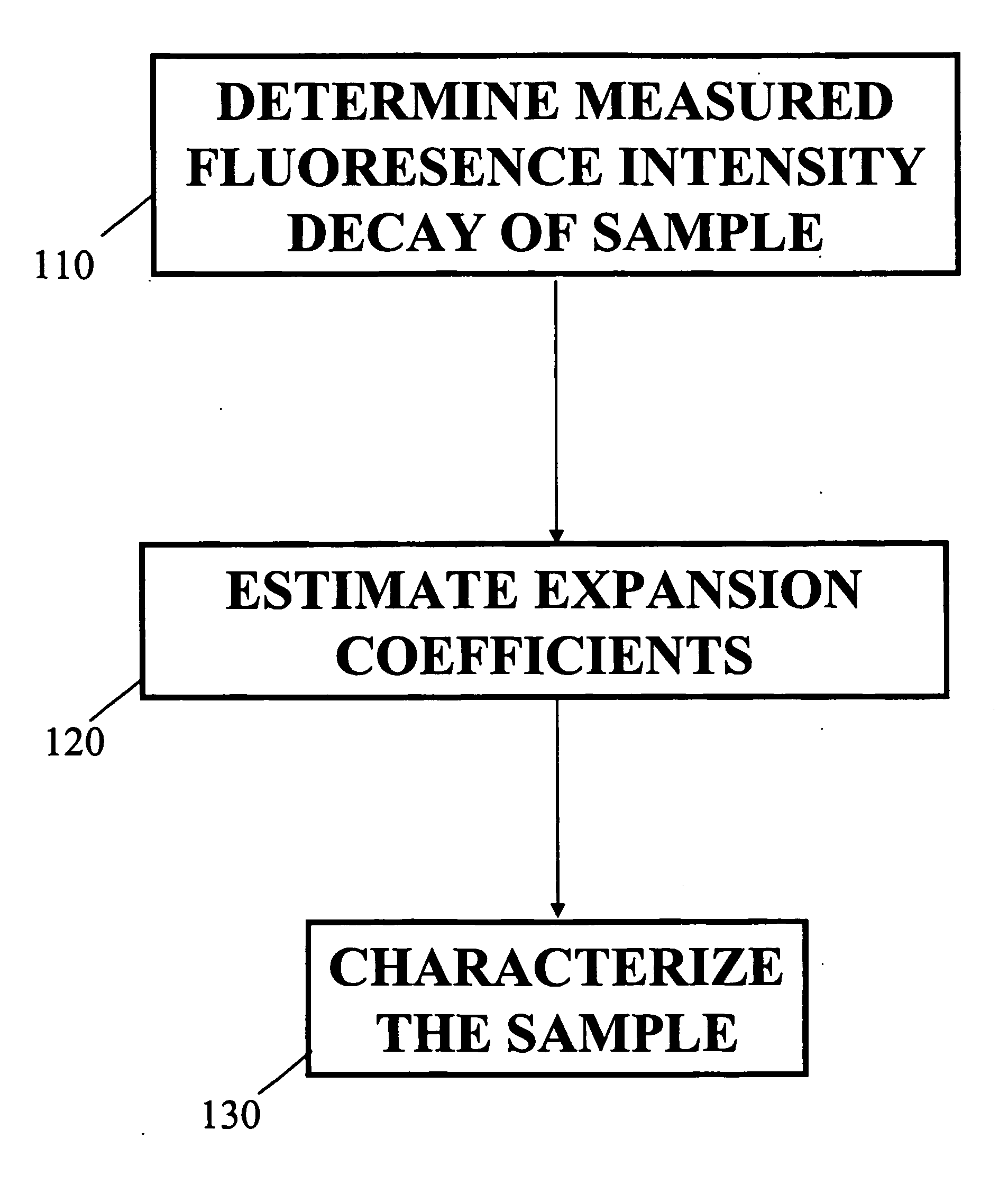
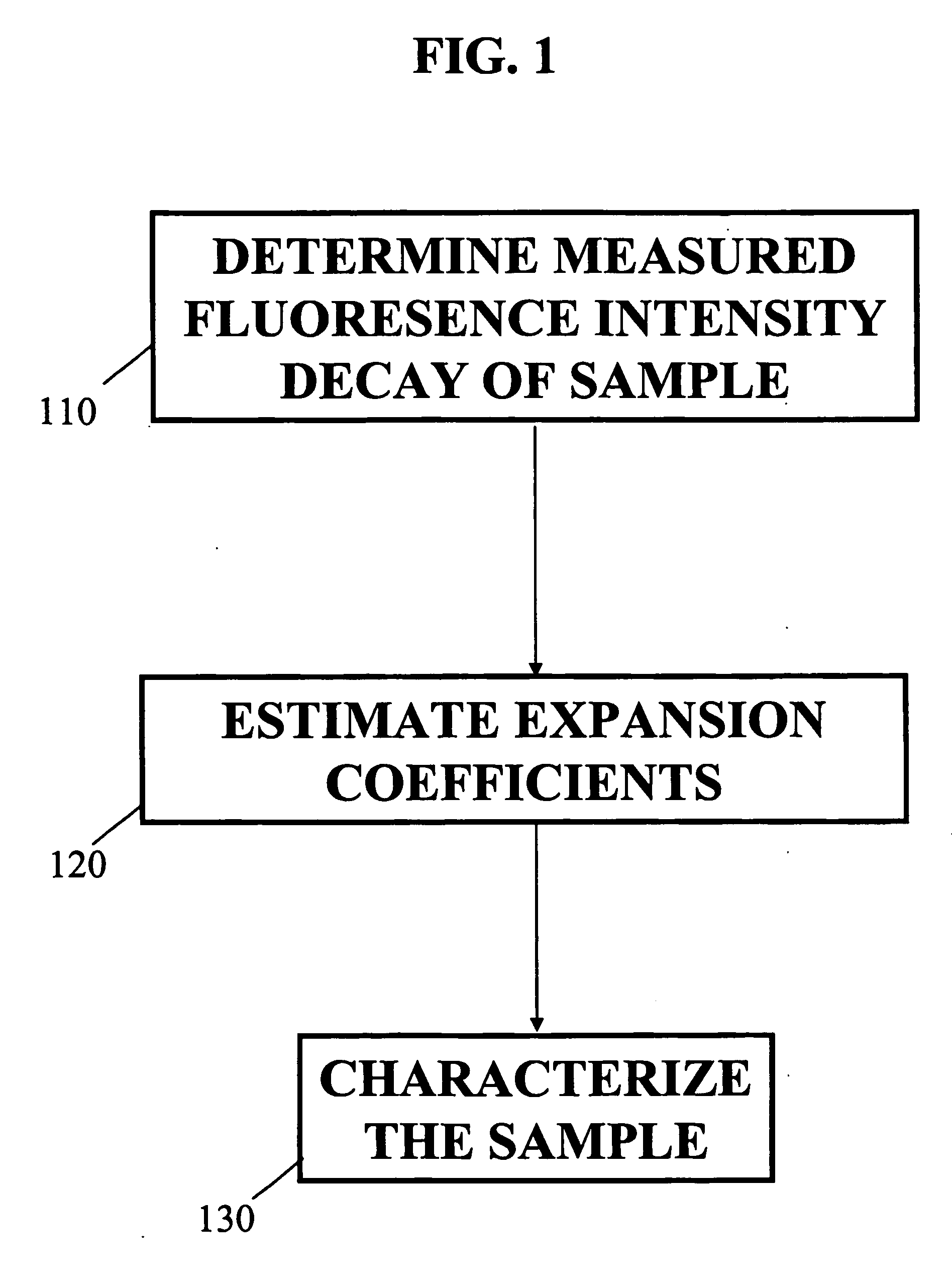
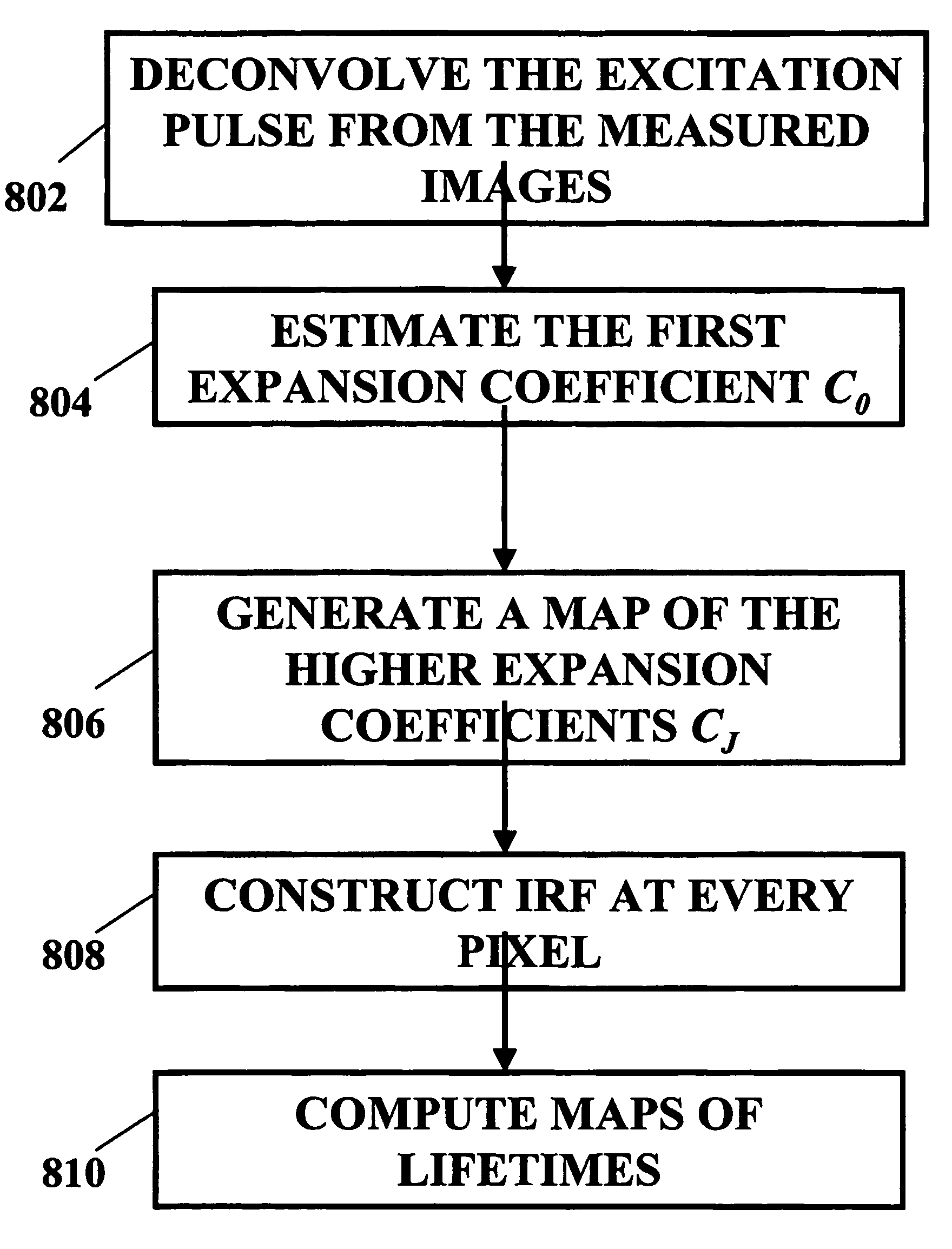
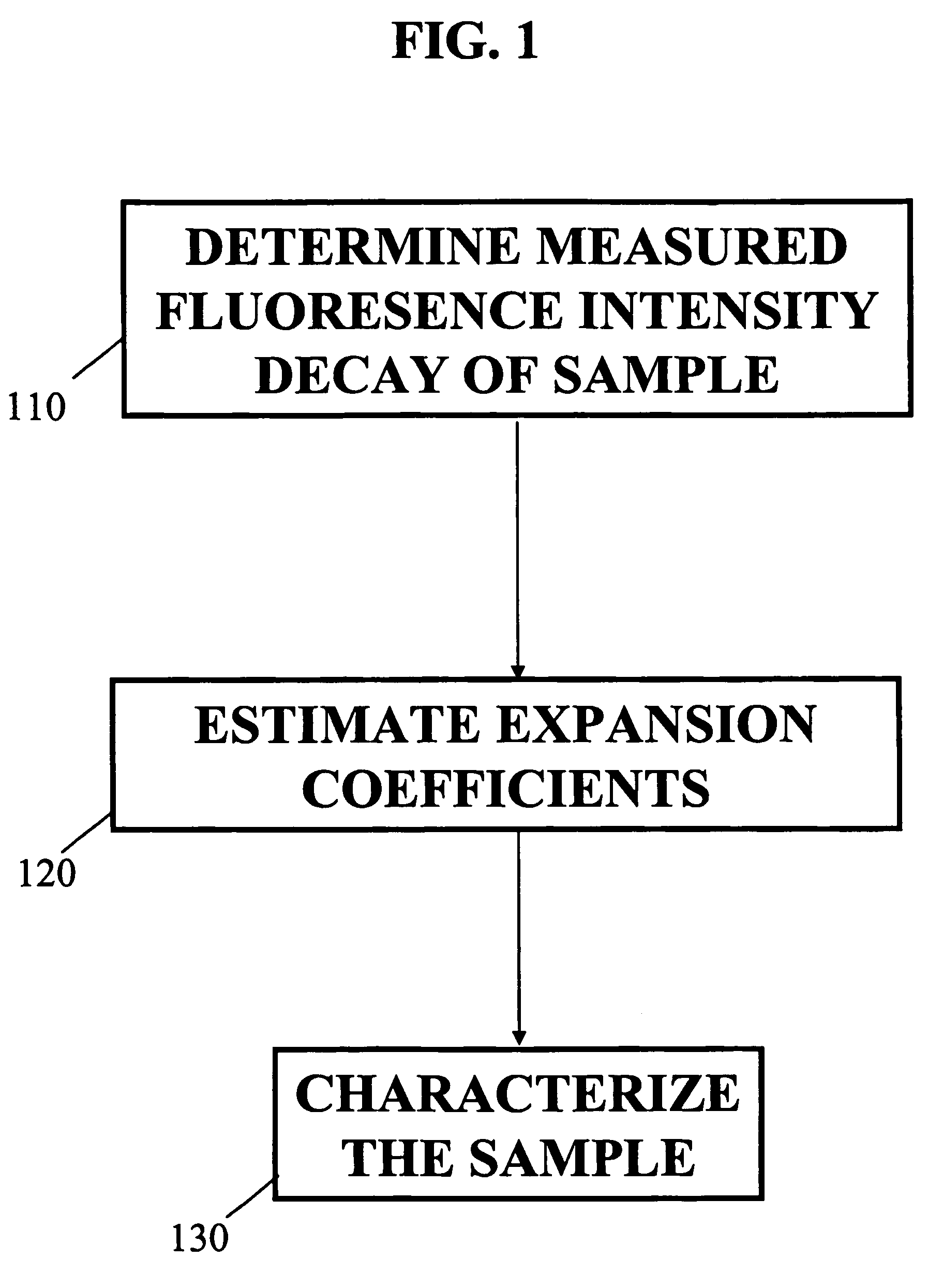
A method and system for analysis of fluorescence emission spectroscopy data and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy data are described. A unique Laguerre expansion can be found for fluorescence intensity decays of arbitrary form with convergence to a correct solution faster than with conventional methods. The Laguerre expansion technique includes expansion coefficients highly correlated with intrinsic fluorescence lifetimes, allowing direct characterization of fluorescence dynamics. For complex systems, conventional analysis of fluorescence intensity decay in terms of discrete exponential components can not readily provide a true representation of underlying fluorescence dynamics. Utilizing the Laguerre expansion technique, an alternative non-parametric method for analysis of time-resolved fluorescence data from various systems is described, facilitating characterization and discrimination of a sample. An ultra-fast method for analysis of fluorescence lifetime imaging is also described, facilitating real-time analysis of compositional and functional changes in samples, at a microscopic or macroscopic level.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Phasor Method to Fluorescence Lifetime Microscopy to Discriminate Metabolic State of Cells in Living Tissue
ActiveUS20120276578A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant Germ CellsPorphyrin
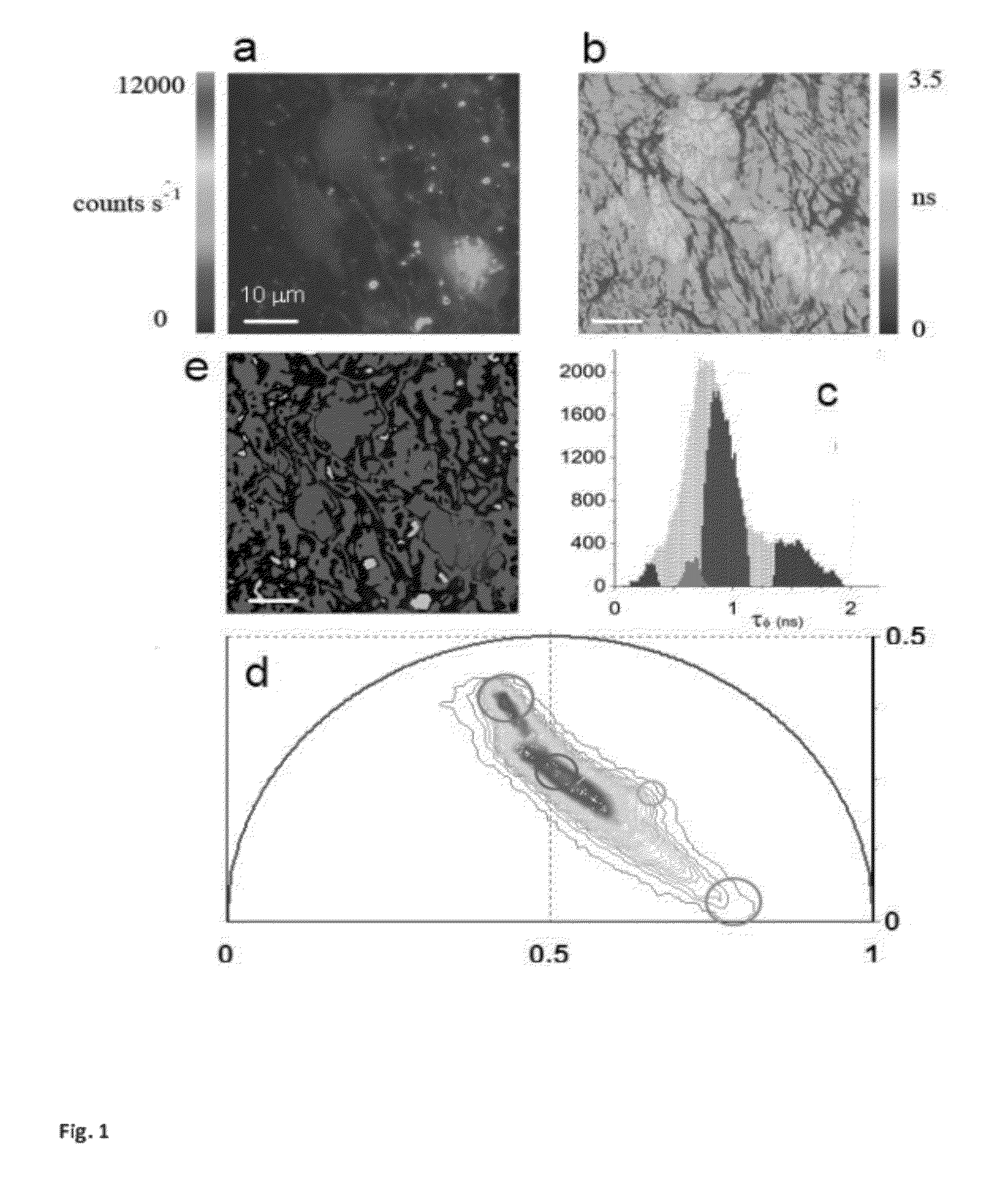
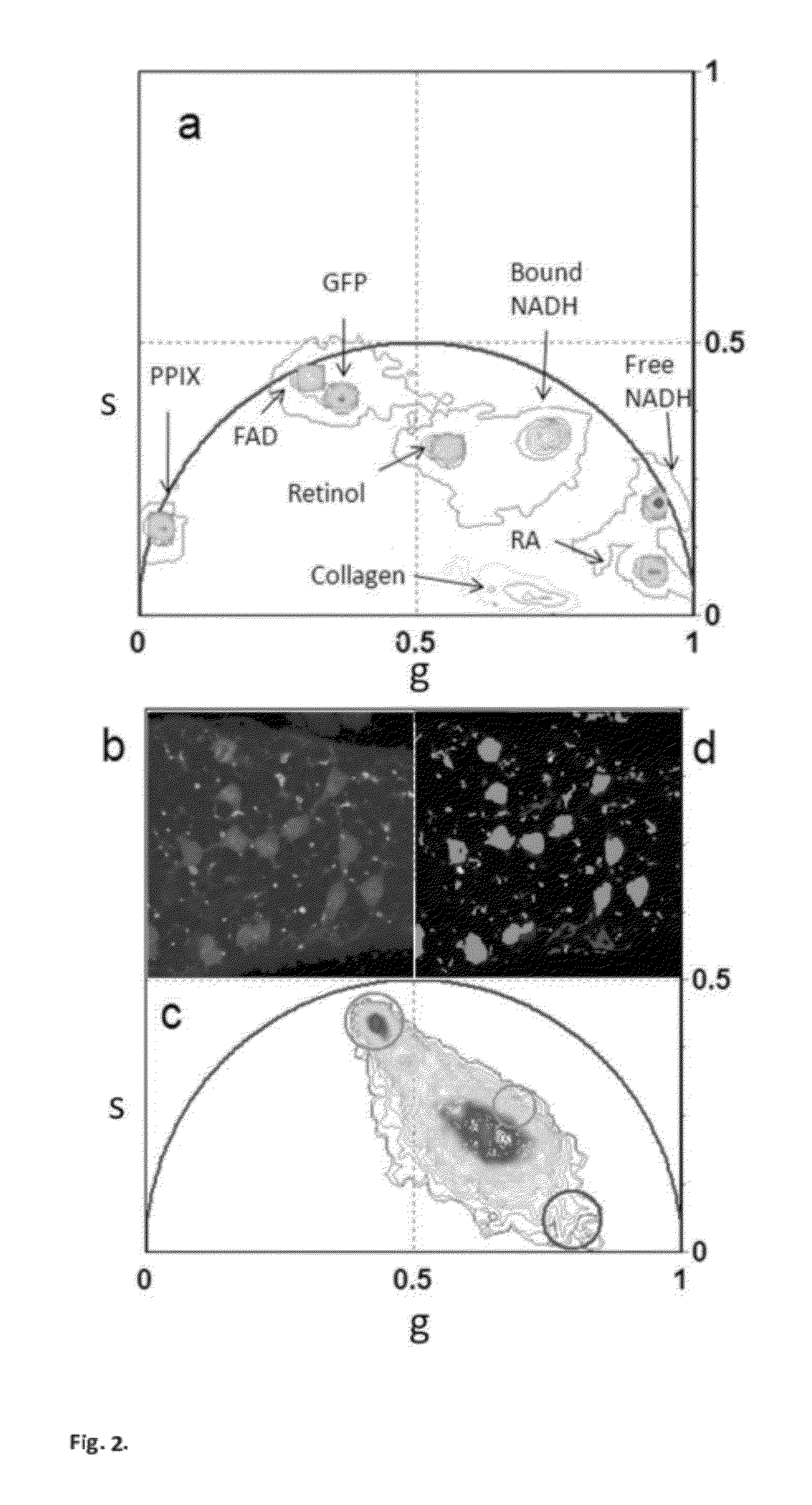
“A label-free imaging method to monitor stem cell metabolism discriminates different states of stem cell as they differentiate in a living tissues. We use intrinsic fluorescence biomarkers and the phasor approach to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). We identify and map intrinsic fluorophores such as collagen, retinol, retinoic acid, flavins, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and porphyrin. We measure the phasor values of germ cells in C. Elegans germ line. Their metabolic fingerprint cluster according to their differentiation state, reflecting changes in FAD concentration and NADH binding during the differentiation pathway. The phasor approach to lifetime imaging provides a label-free, fit-free and sensitive method to identify different metabolic state of cells during differentiation, to sense small changes in the redox state of cells and may identify symmetric and asymmetric divisions and predict cell fate.”
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
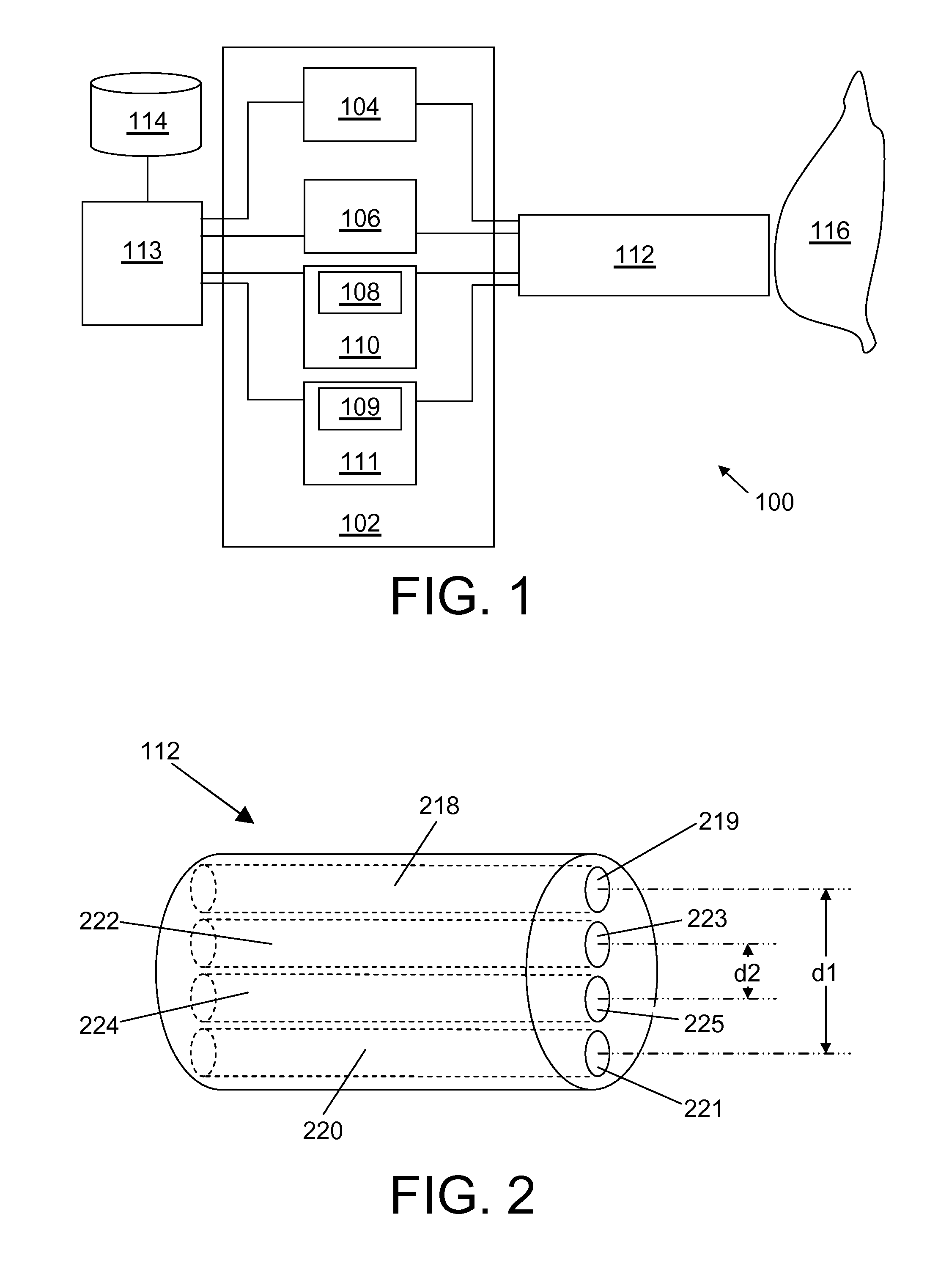
Appratus for optical analysis of an associated tissue sample
InactiveUS20140117256A1Accurate analysisReduce in quantityDiagnostics using spectroscopyPhotometryReflectance spectroscopyOptical detector
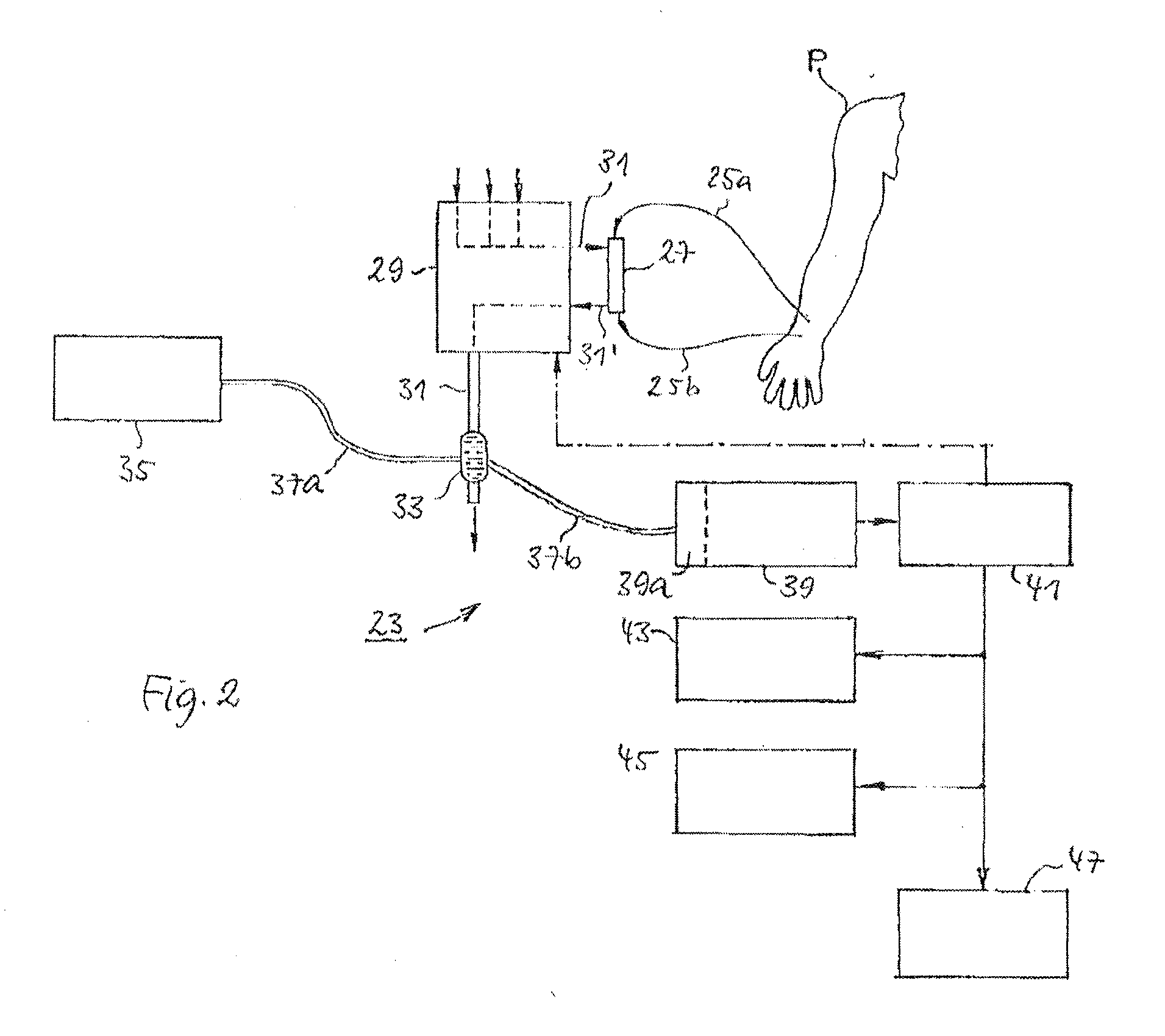
In order to improve fluorescence measurements, there is provided an apparatus and, a method and a computer program for optical analysis of an associated tissue sample, the apparatus comprising a spectrometer comprising an optical detector, a light source, a first light emitter 219 arranged for emitting photons into the associated tissue sample, a first light collector 221 arranged for receiving photons from the associated tissue sample, a second light emitter 223, a second light collector 225, wherein a reflectance spectrum is obtained via the first light emitter 219 and collector 221 and a fluorescence spectrum is obtained via the second light emitter 223 and collector 225, and where a first distance d1 between the first light emitter and collector is larger than a second distance d2 between the second light emitter and collector. By combining the data thus obtained, an intrinsic fluorescence spectrum may be obtained.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Metal-enhanced fluorescence for the label-free detection of interacting biomolecules
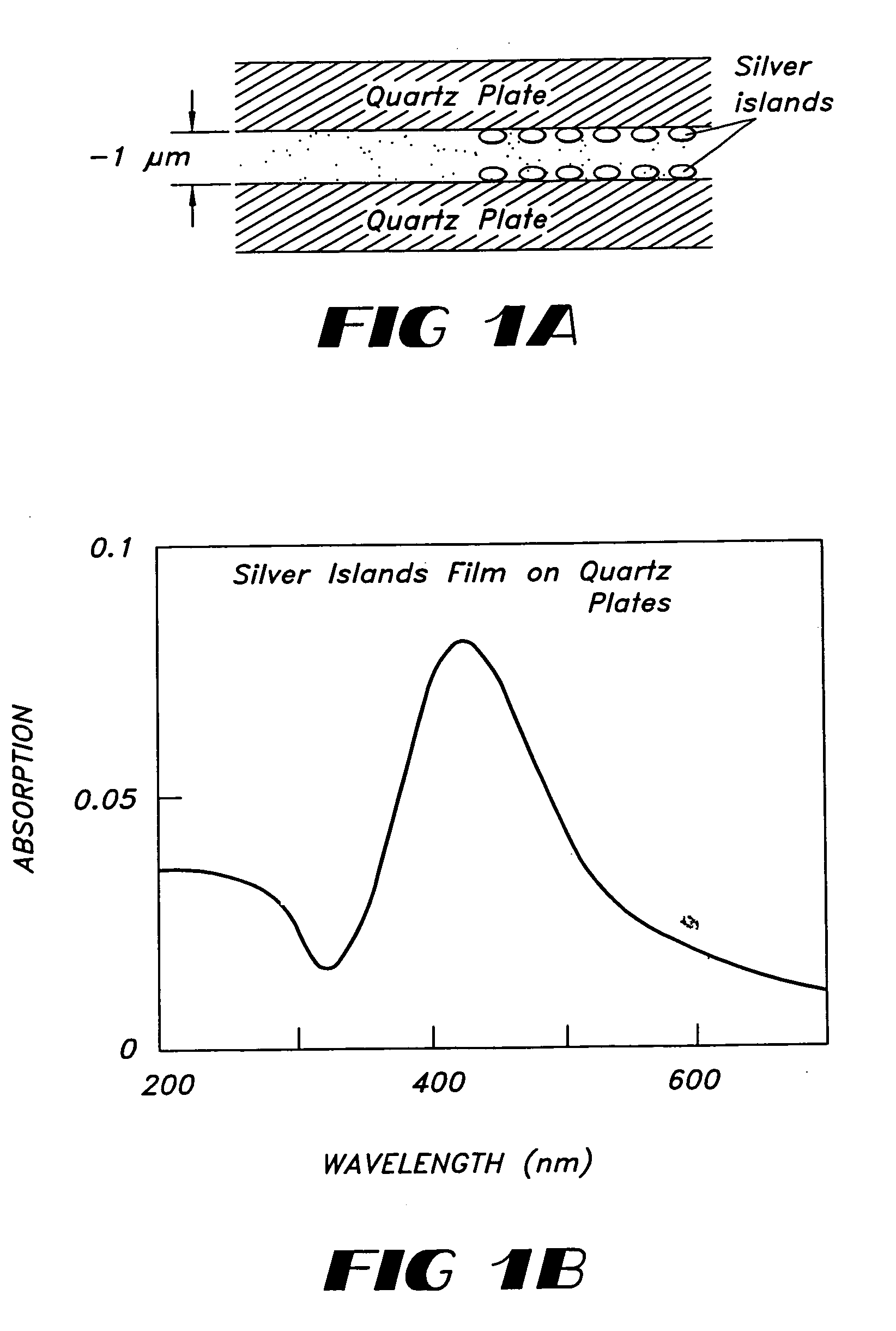
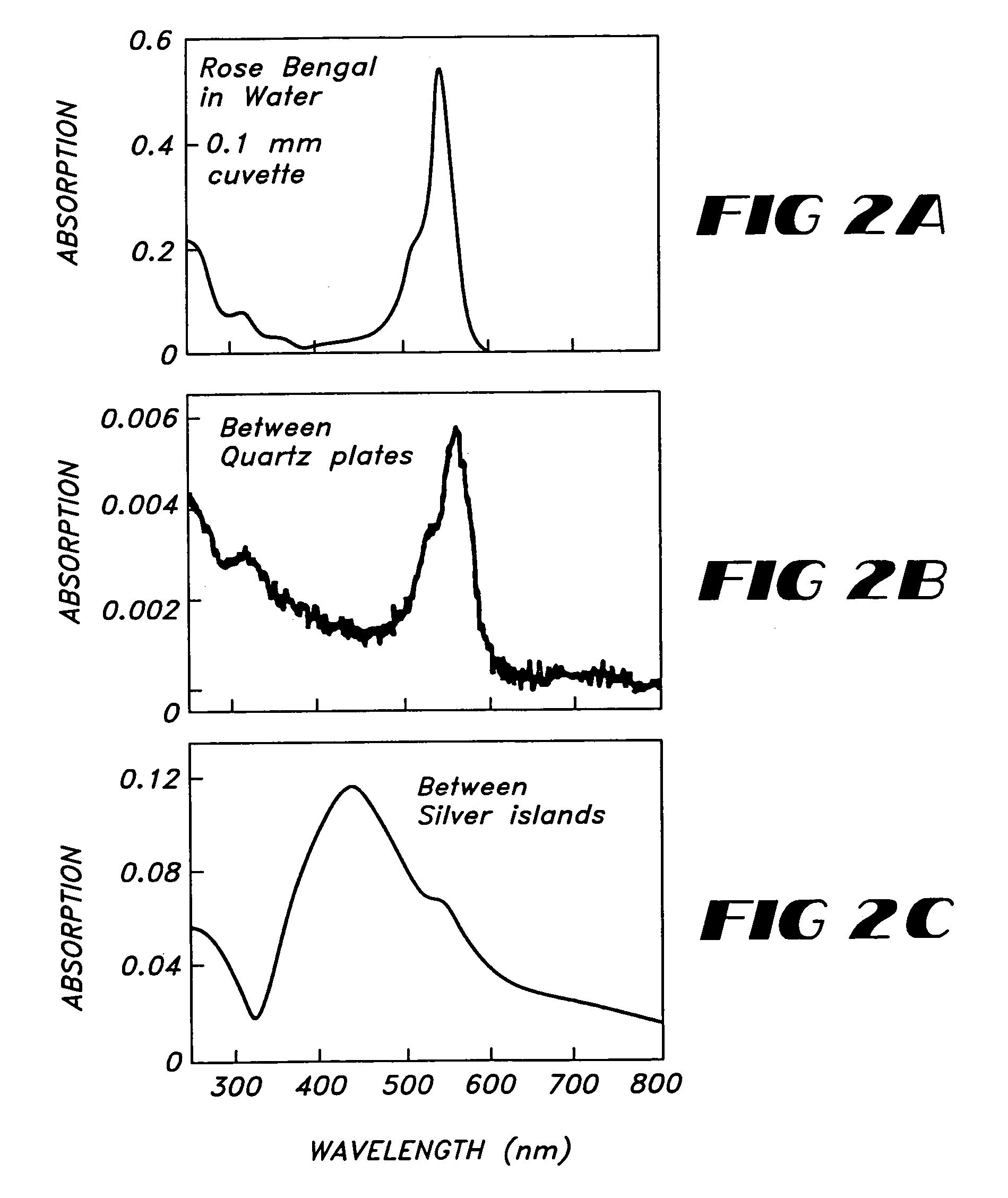
InactiveUS20100035335A1Enhance intrinsic fluorescenceReducing cost and complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanostructured metalElectromagnetic radiation
A method for enhancing fluorescence of a biomolecule includes the step of associating the biomolecule having intrinsic fluorescence with a sensing surface that contains nanostructured metal. Association of the biomolecule with the nanostructured metal enhances its intrinsic fluorescence, which is detected upon exposure to electromagnetic radiation of a suitable wavelength. The sensing surface may include capture or ligand molecule which binds to the biomolecule and sequesters it in proximity to the nanostructured metal, thereby causing its fluorescent signal to be enhanced. The method can be used in label-free bioassays for detection of interacting biomolecules, such as antibody-antigen binding.
Owner:LAKOWICZ JOSEPH R +4
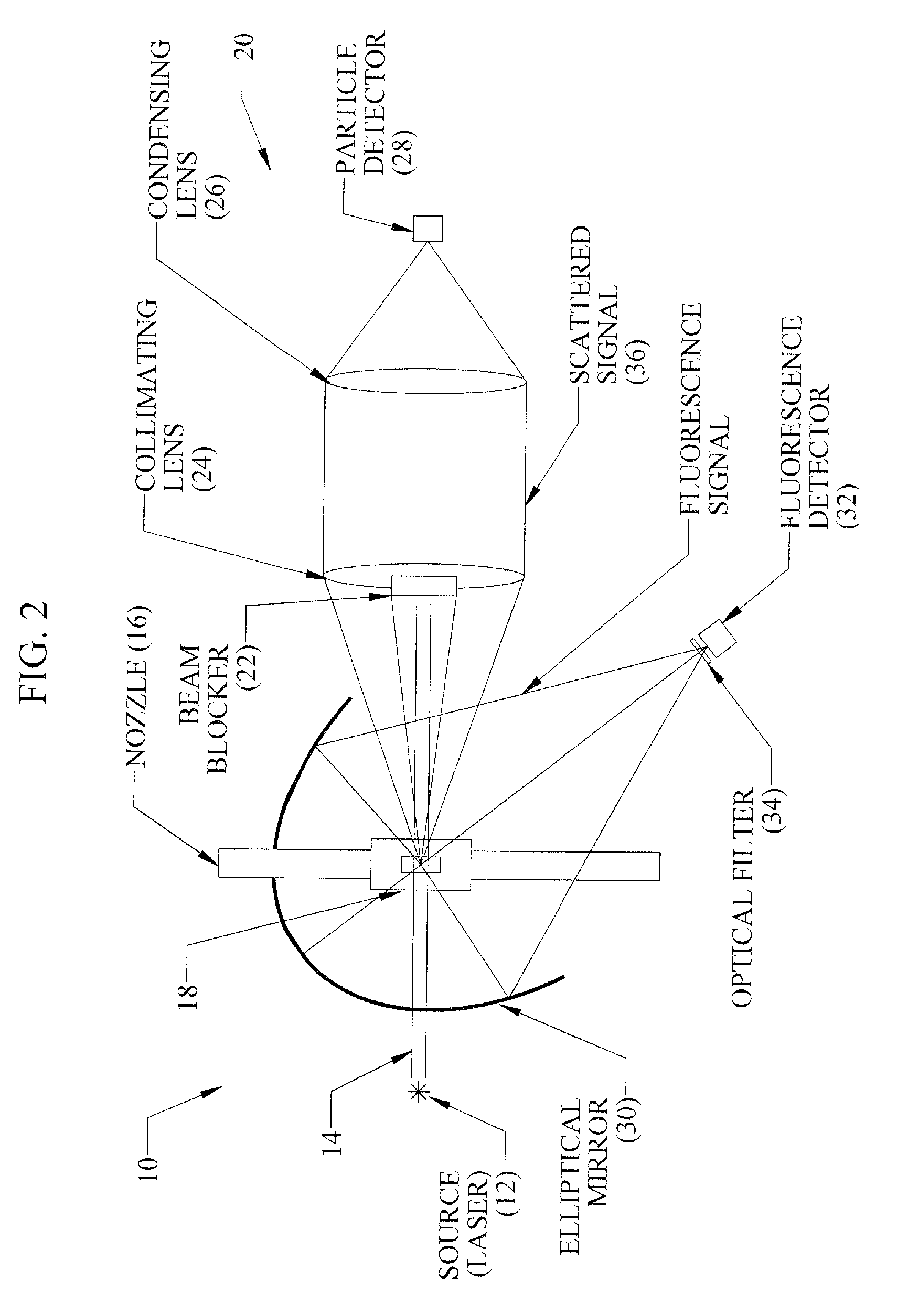
Apparatus and system for characterizing an aerosol particle flow
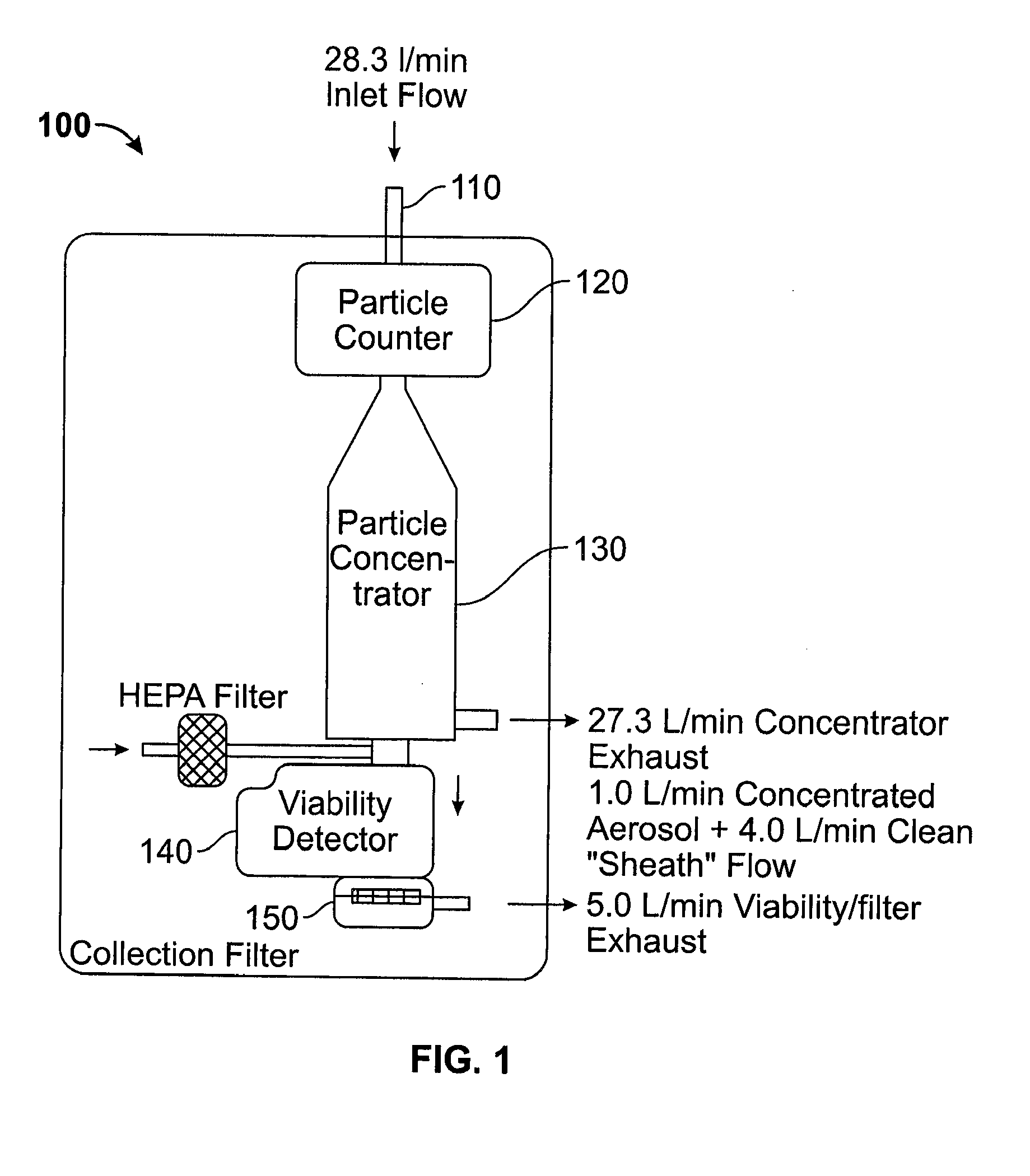
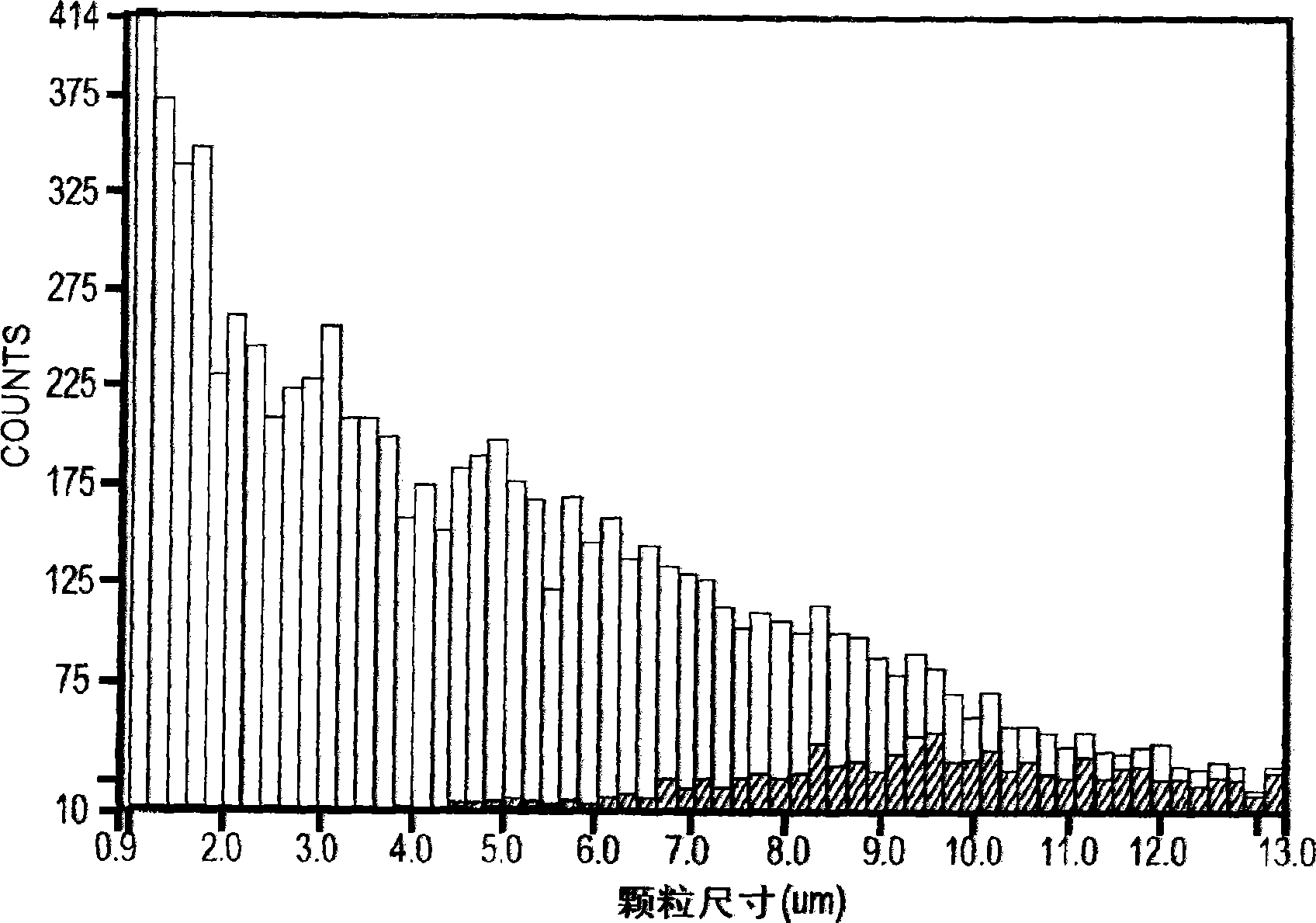
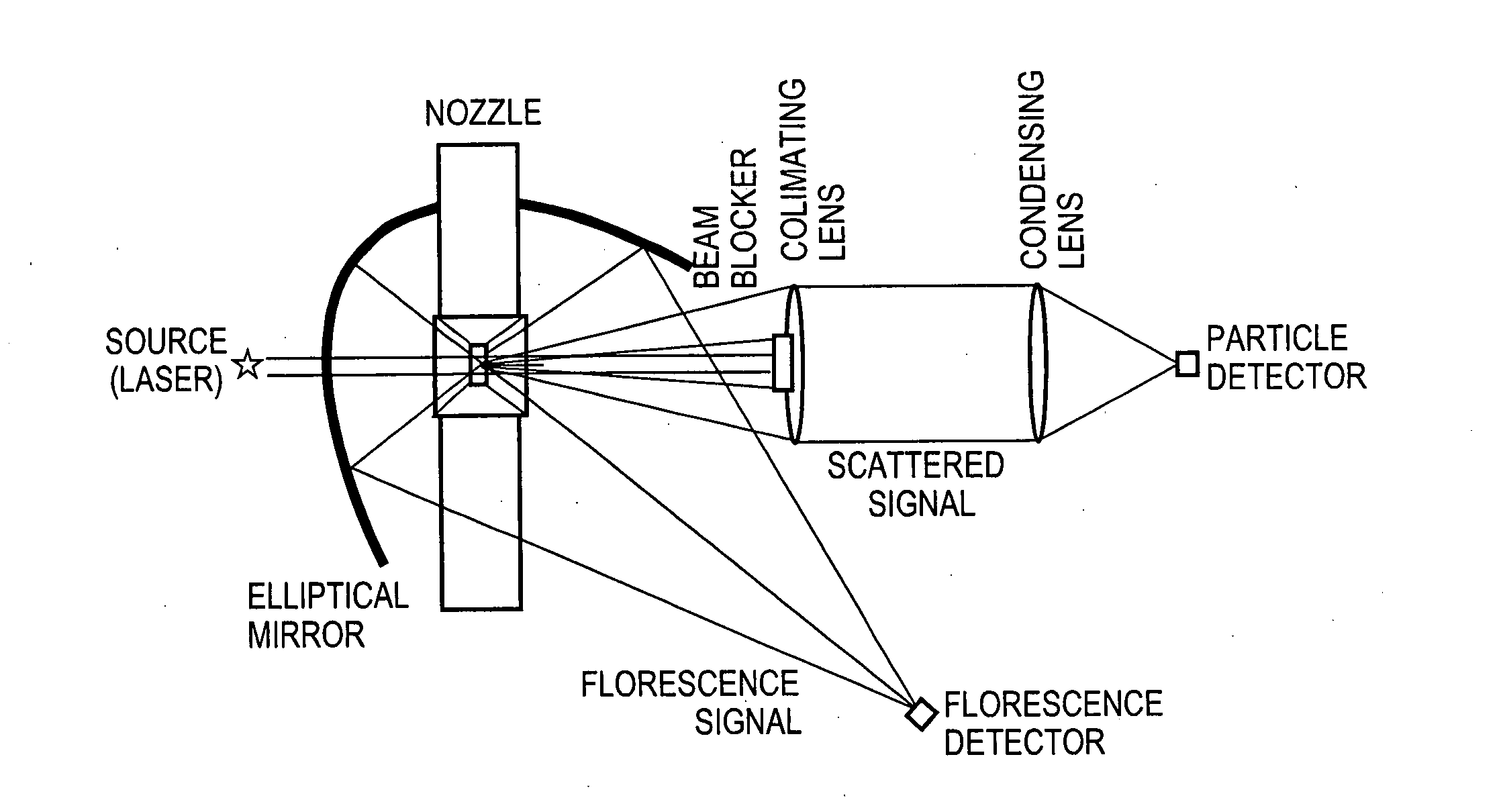
ActiveUS20140354976A1Improving aerosol particle characterizationImprove detection accuracySamplingAnalysis by electrical excitationParticle flowParticle physics
Owner:TSI INC
Method for fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and spectroscopy
ActiveUS7890157B2Diagnostics using lightAnalysis by electrical excitationReal time analysisFunctional change
A method and system for analysis of fluorescence emission spectroscopy data and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy data are described. A unique Laguerre expansion can be found for fluorescence intensity decays of arbitrary form with convergence to a correct solution faster than with conventional methods. The Laguerre expansion technique includes expansion coefficients highly correlated with intrinsic fluorescence lifetimes, allowing direct characterization of fluorescence dynamics. For complex systems, conventional analysis of fluorescence intensity decay in terms of discrete exponential components can not readily provide a true representation of underlying fluorescence dynamics. Utilizing the Laguerre expansion technique, an alternative non-parametric method for analysis of time-resolved fluorescence data from various systems is described, facilitating characterization and discrimination of a sample. An ultra-fast method for analysis of fluorescence lifetime imaging is also described, facilitating real-time analysis of compositional and functional changes in samples, at a microscopic or macroscopic level.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method for the detection of biologic particle contamination
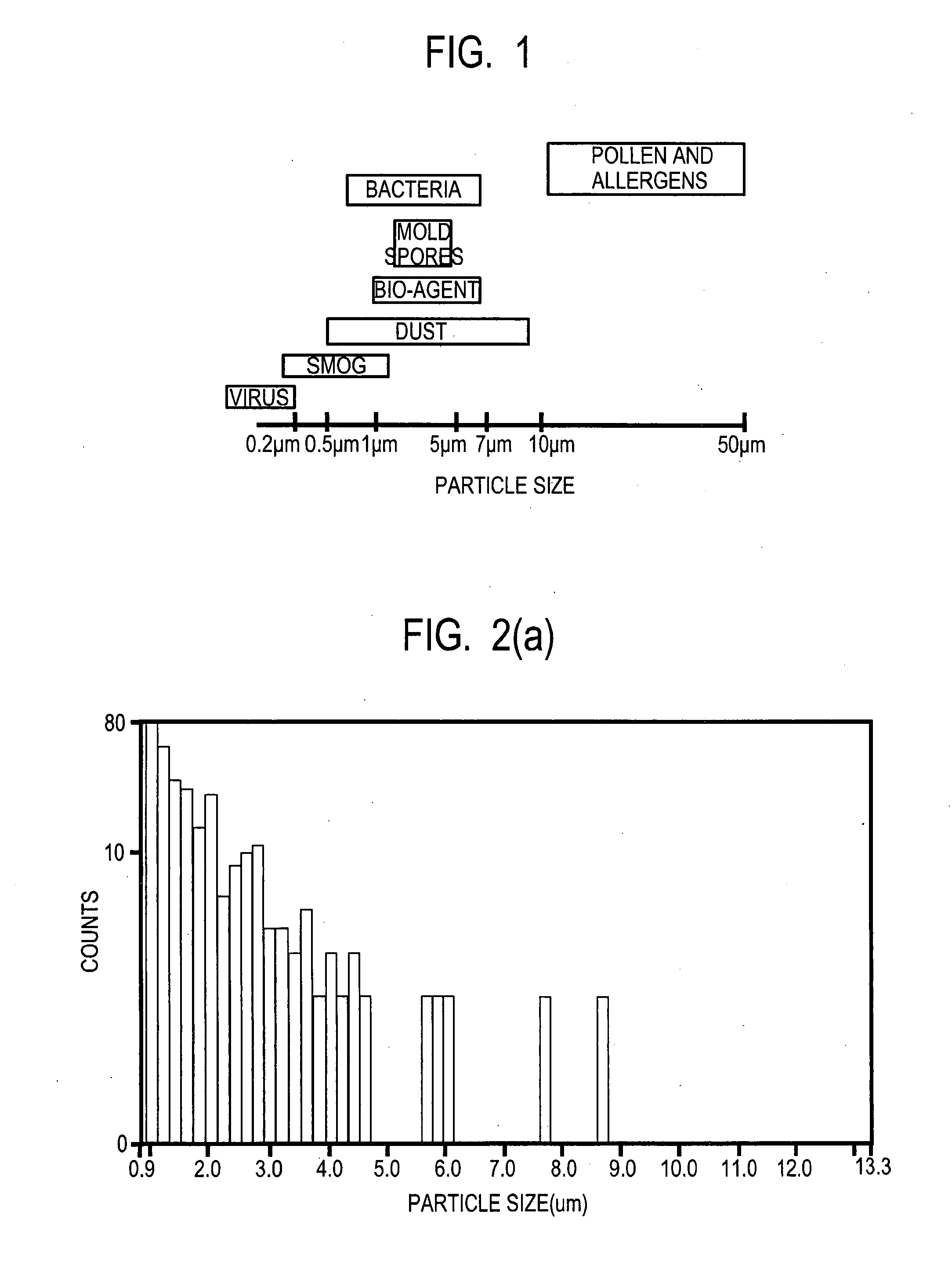
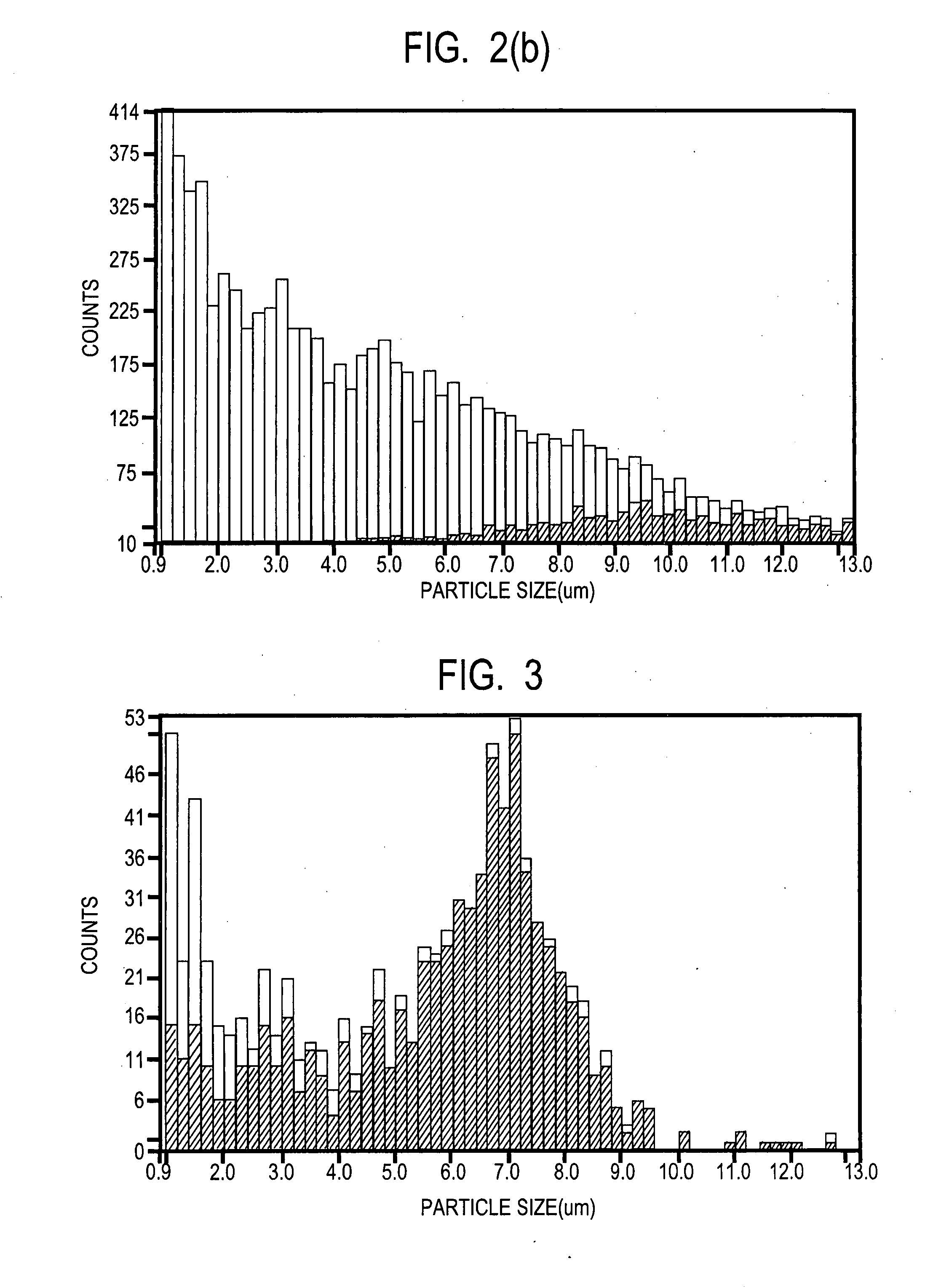
ActiveUS20090242799A1Avoid cleaningReduce dependencePhotometryLuminescent dosimetersClean environmentImaging data
Methods for detecting particles in a fluid, including determining particle size and intrinsic fluorescence of a particle, and time correlating the particle detection data with image data in the vicinity of the detector or detector inlet to identify contamination sources in clean environments are described.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Method and apparatus to detect coronary artery calcification or disease
InactiveUS20120283530A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMedicineArterial calcification
Coronary artery calcification (CAC) occurs at an earlier age in diabetes and is a risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD) in subjects with or without diabetes. One postulated mechanism for the increased CAC is the accelerated accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in the vasculature. As certain collagen AGEs fluoresce, skin intrinsic fluorescence (SIF) can act as a novel maker of collagen AGEs levels. The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for detecting SIF that can be a useful marker of CAD risk and a therapeutic target.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
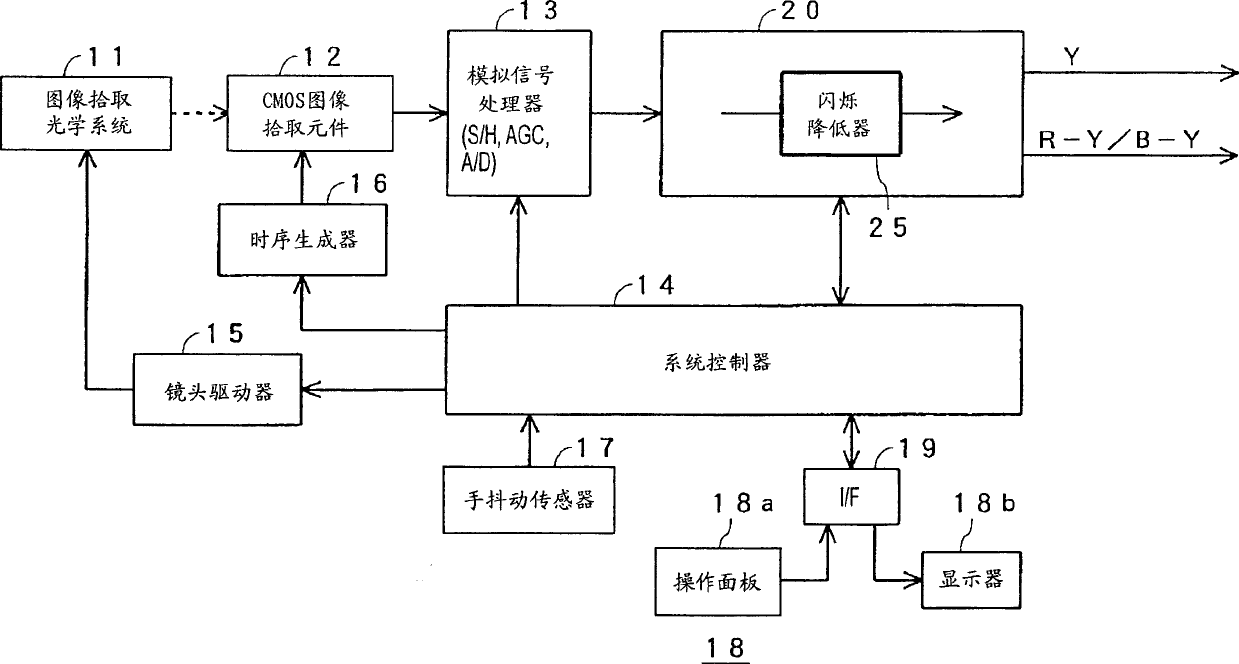
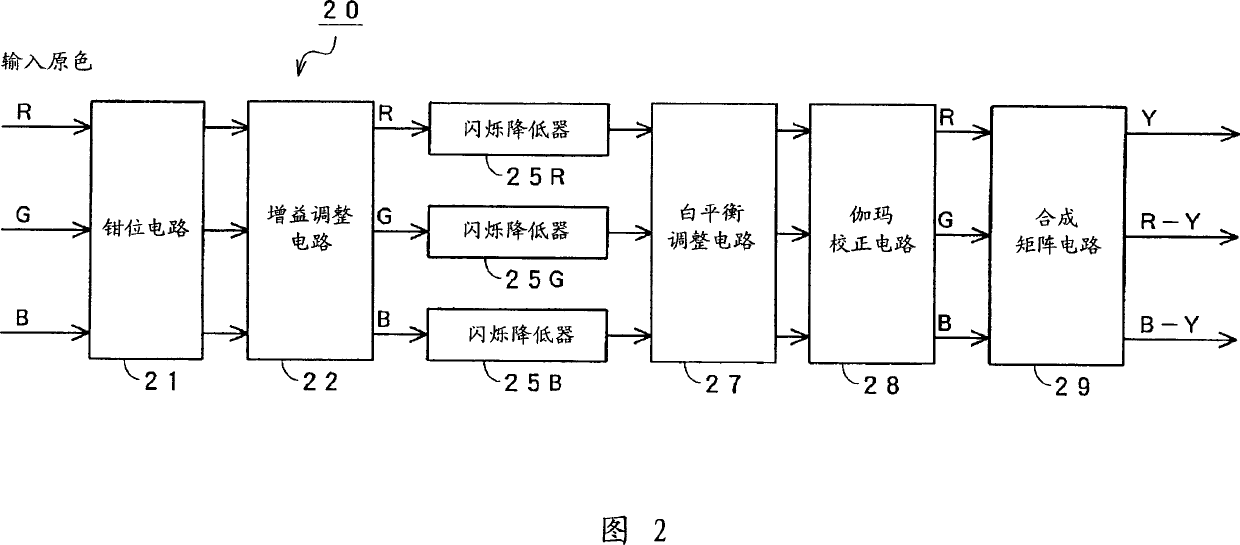
Flicker reduction method, image pickup device, and flicker reduction circuit
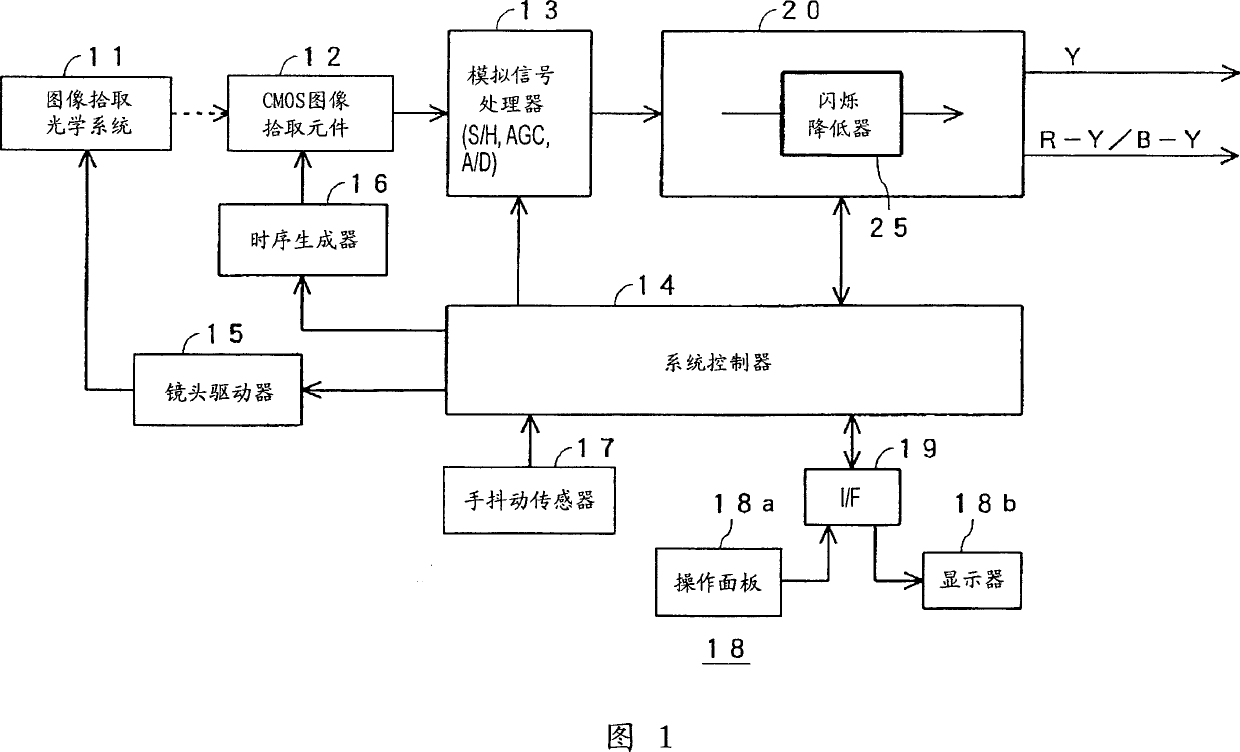
InactiveCN1714565AGood estimateFlicker component reductionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCMOSPhotodetector
On the premise of using only simple signal processing without using a photodetector, it is possible to detect with high accuracy regardless of the subject, video signal level, and type of fluorescent lamp Fluorescent flicker is inherent and reliably substantially reduced. The signal In'(x, y) is an RGB primary color signal including a flicker component or a luminance signal. The signal In'(x, y) is integrated for time over one horizontal period, and the difference value of the integrated value of adjacent fields is normalized by the mean value of the integrated value in three consecutive fields. The normalized difference value gn(y) undergoes discrete Fourier transform to extract the spectrum. From the extracted spectrum, the scintillation coefficient Γn(y) is estimated for the calculation of In'(x, y) / [1+Γn(y)].
Owner:SONY CORP
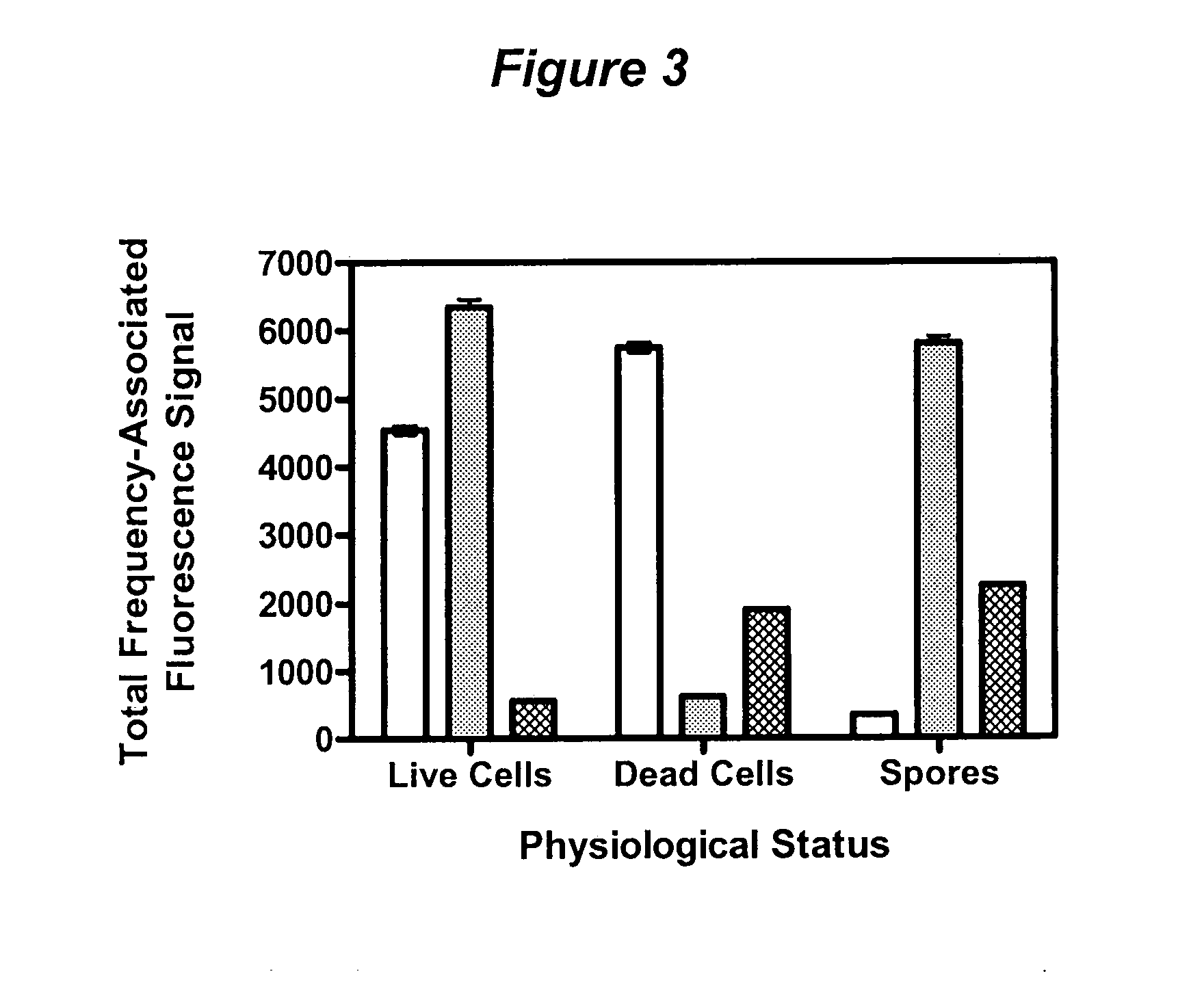
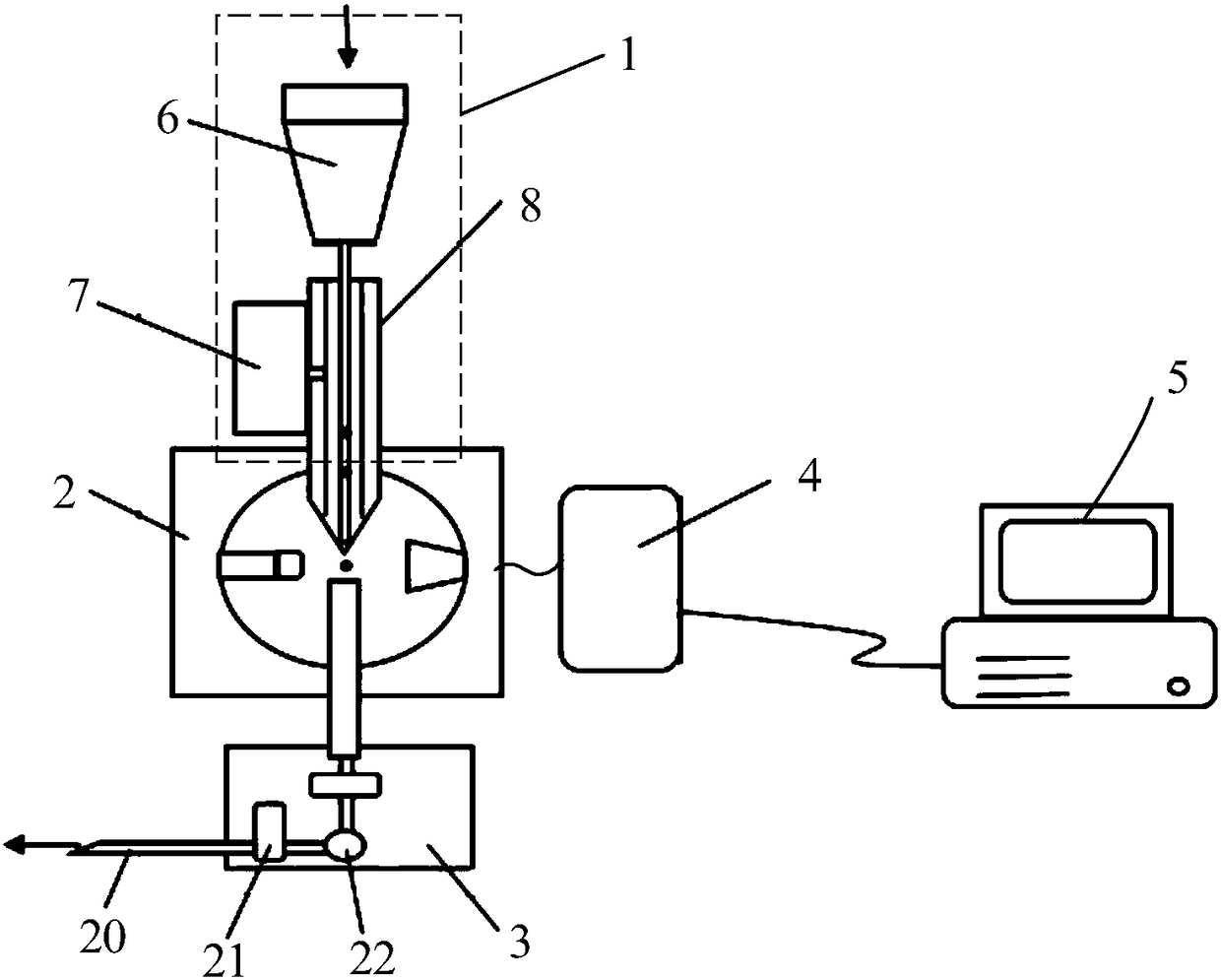
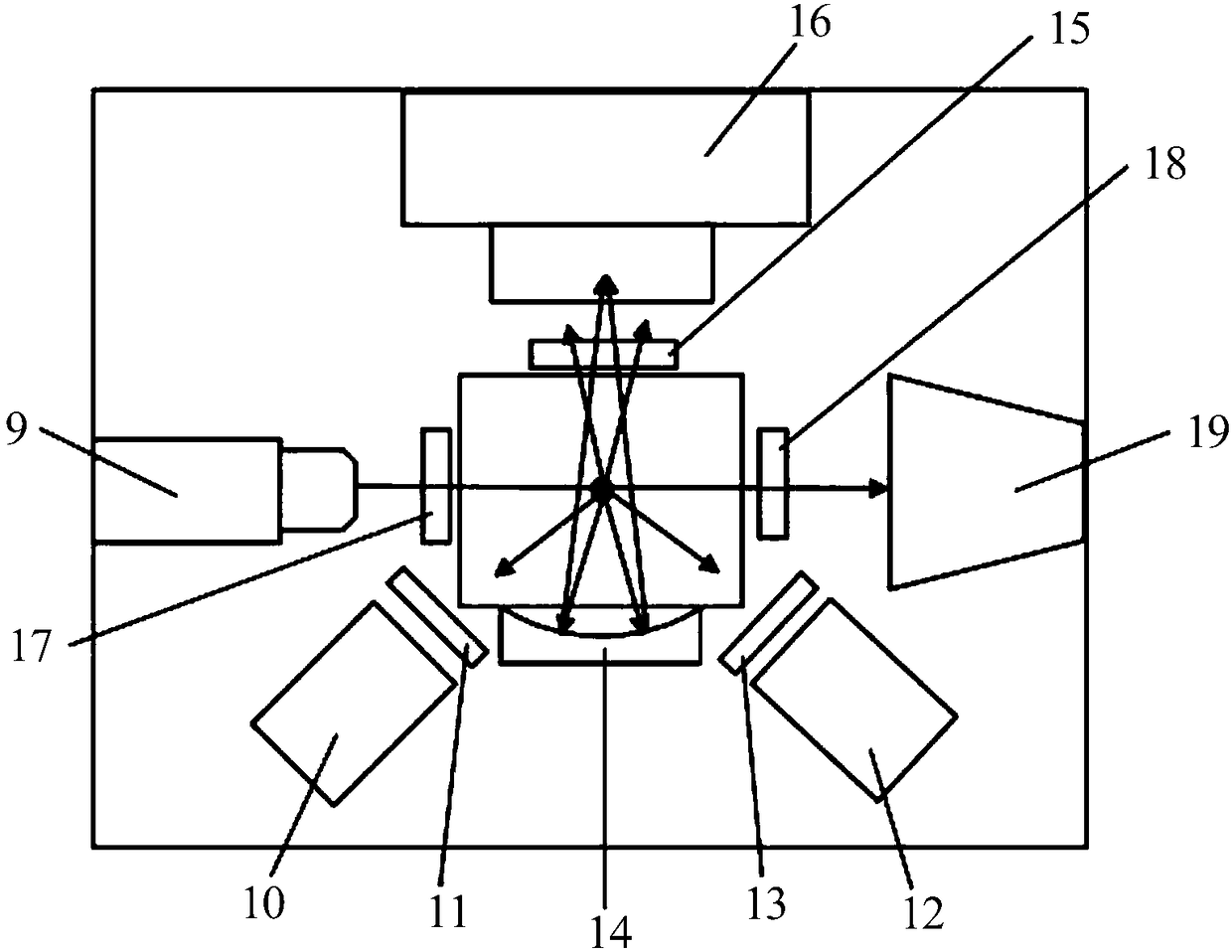
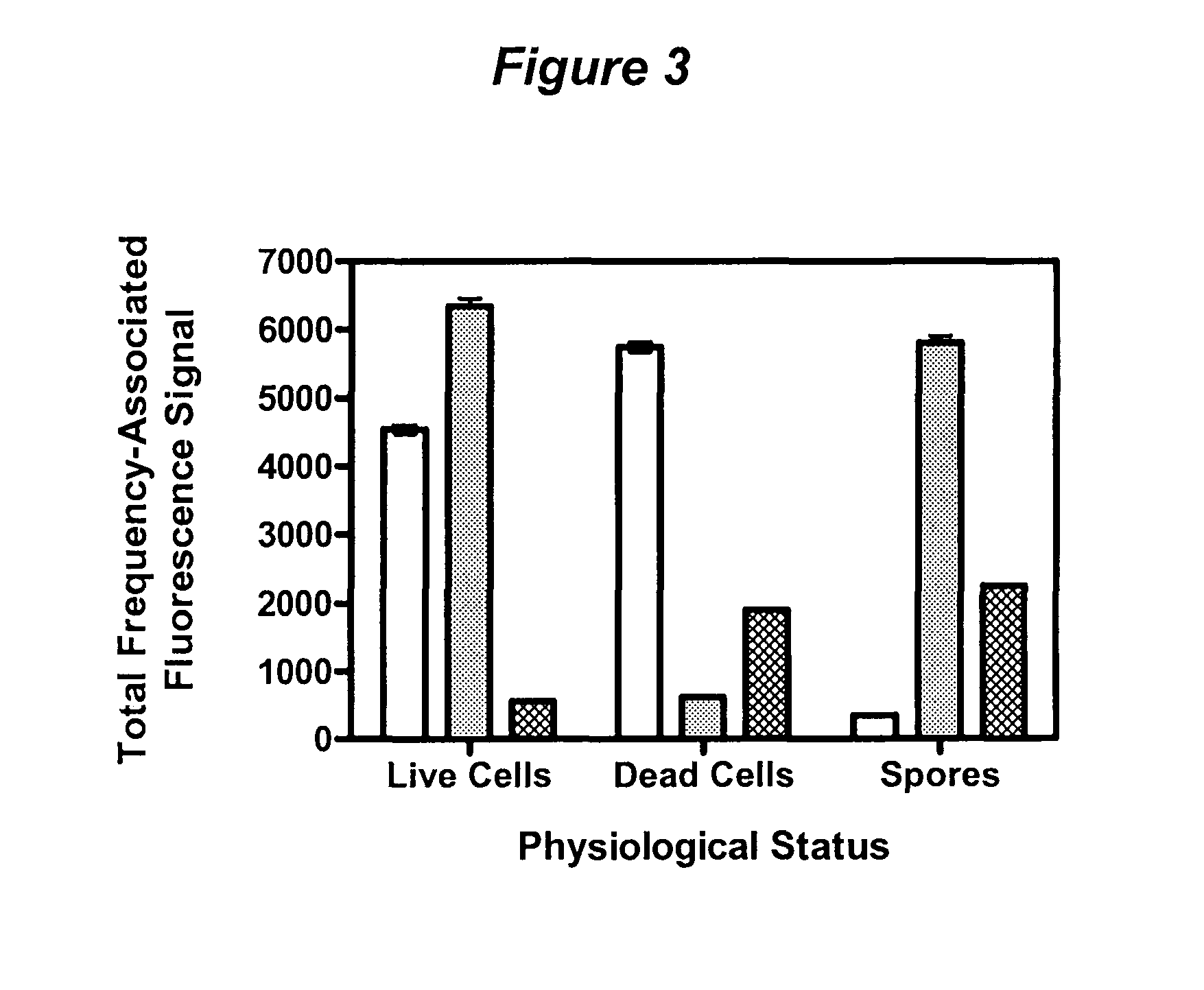
Method and apparatus for detecting the presence of microbes with frequency modulated multi-wavelength intrinsic fluorescence
InactiveUS20080032327A1Reduce riskRapid and inexpensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular componentSpore
Method and apparatus for the detection of microbes in liquids, in air and on non-living surfaces in which samples are exposed to frequency-modulated electromagnetic radiation of specific energies capable of exciting various metabolites, cofactors and cellular and spore components, with the microbial cells to be sampled (and more specifically the excited metabolites, cofactors and / or other cellular components) contained therein emit fluorescence that can be measured that is similarly frequency-modulated provided that the excitation frequencies are longer than the fluorescence lifetime of the excited intrinsic microbial fluorophore. The contribution to the measured signal due to each excitation frequency resulting from microbial intrinsic fluorescence is determined with a method capable of calculating the intensity of each frequency-modulated signal, and the relative total fluorescent signals of the intrinsic microbial components associated with each excitation frequency are required to lie within physiological ranges, with the amplitude of the fluorescence signals used to enumerate the microbe content in the sample.
Owner:MICROBIOSYST
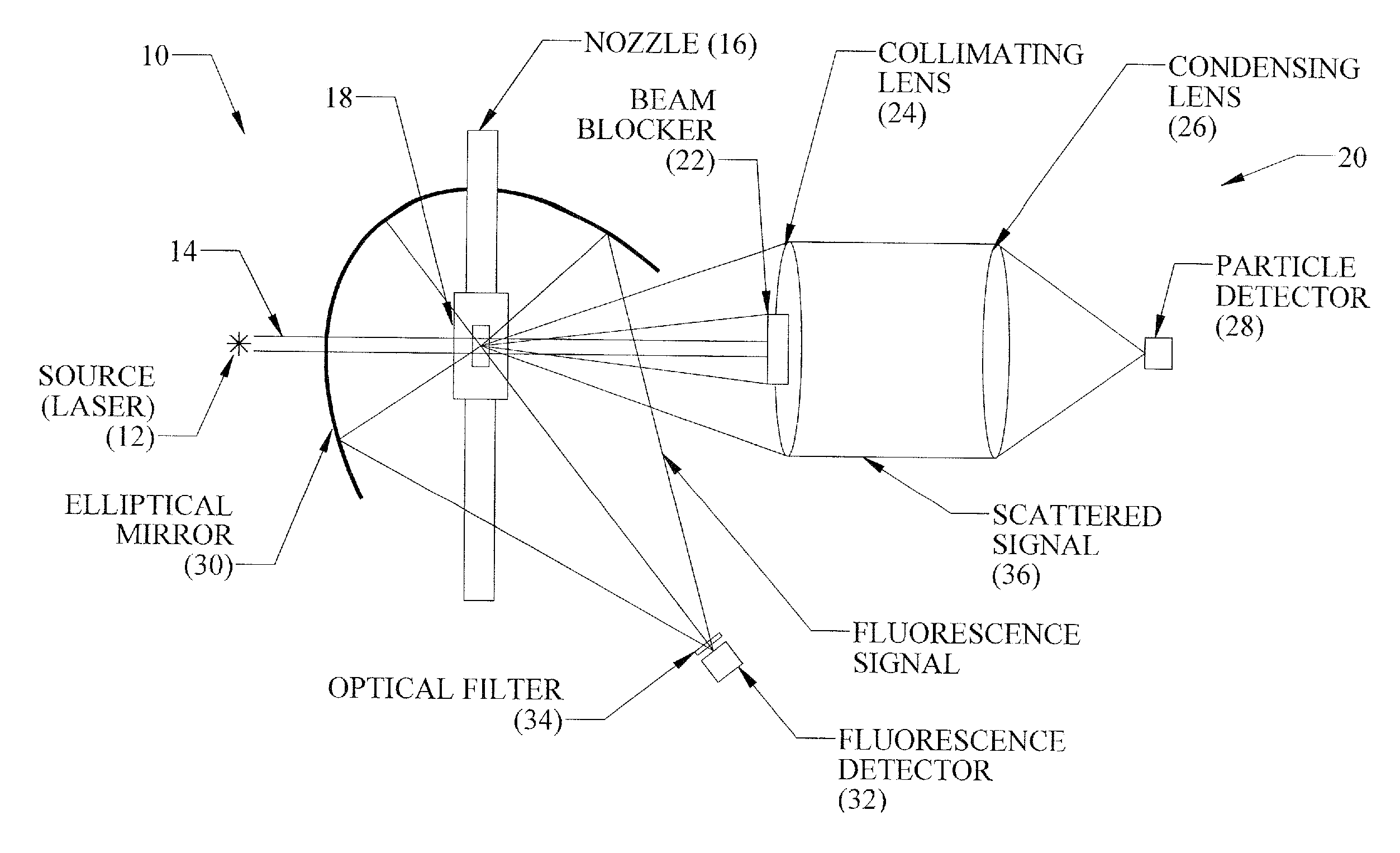
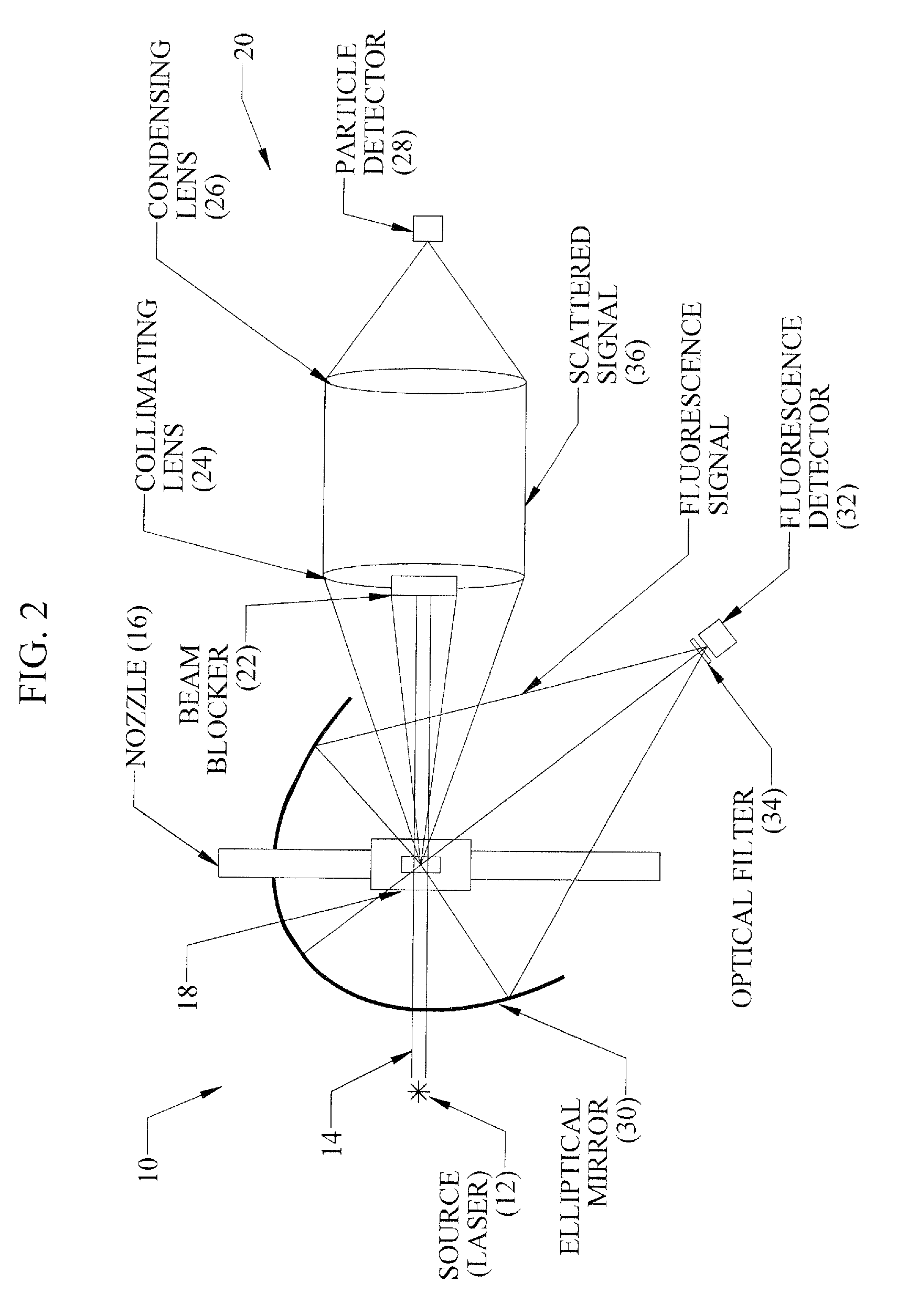
Multichannel fluorescence spectra biological aerosol particle detecting apparatus
InactiveCN108287129AAccurate determination of scattered light signalsAccurate determination of intrinsic fluorescence signalIndividual particle analysisDiffusionFluorescence spectra
The invention discloses a multichannel fluorescence spectra biological aerosol particle detecting apparatus. The apparatus comprises the following components: an aerosol air-flow generation unit for generating aerosol particle gas; a laser detection unit, which is arranged corresponding to the aerosol air-flow generation unit, in order to carry out laser irradiation and detection of partial aerosol particle gas outputted from the aerosol air-flow generation unit, and to obtain diffusion light signals and intrinsic fluorescence signals of the aerosol particles; a total flow controlling and exhausting unit, which is arranged corresponding to the aerosol air-flow generation unit, in order to carry out filtering and discharge of aerosol particles which are outputted from the aerosol air-flow generation unit and do not pass through the laser detection unit and aerosol particles which pass through the laser detection unit; an analyzing unit, which is used for accurately determining classes of the aerosol particles according to the diffusion light signals and the intrinsic fluorescence signals of the aerosol particles.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Apparatus, method and computer program for spectroscopic measurements and analysis
InactiveUS20090040518A1Large changeLess constrainRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationExcitation pulsePopulation
The present invention relates to a spectroscopic method and associated apparatus and computer program for measuring and analysing intensities of fluorescent molecules excited by an energy pulse. The method includes the steps of: a) generating a transient state build-up in the fluorescent molecules by means of an excitation pulse, within which pulse repetitive excitation-emission cycles are induced in the fluorescent molecules between their ground, typically singlet (So) and excited, typically singlet (SO states, resulting also in transition from S] to the transient state, b) relaxation of population of the transient state by transition back to the ground state in a time period following directly after the excitation pulse, c) determination of the transient state population by recording the fluorescence. The invention is characterised by varying pulse characteristics from one sequence of pulses to the next so as to circumvent the need of time-resolution in the detection.
Owner:WIDENGREN JERKER
Pathogen detection by simultaneous size/fluorescence measurement
ActiveCN101479592AAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansAgainst vector-borne diseasesIntrinsic fluorescencePhysics
A method and apparatus for detecting pathogens and particles in a fluid in which particle size and intrinsic fluorescence of a simple particle is determined.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
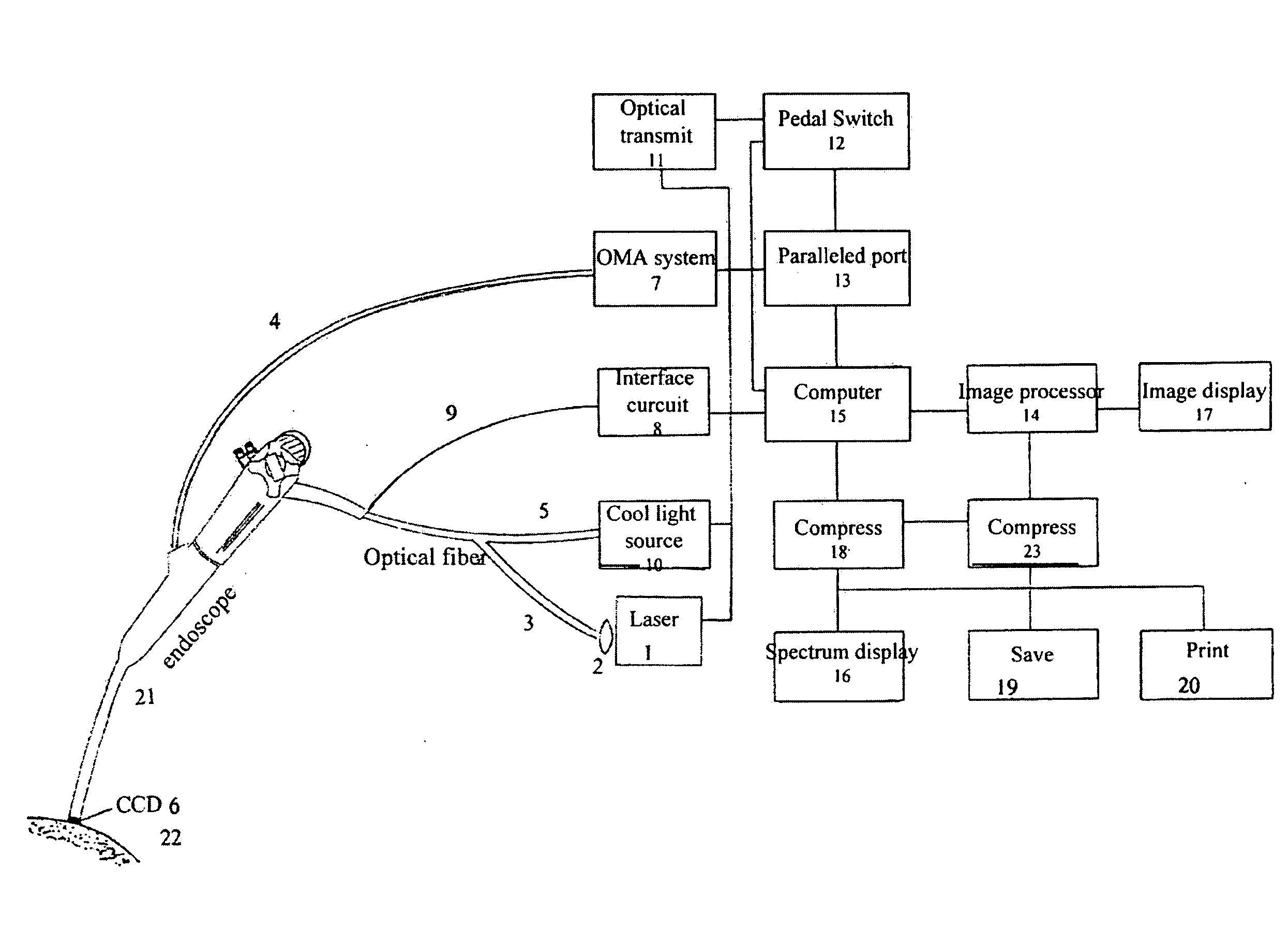
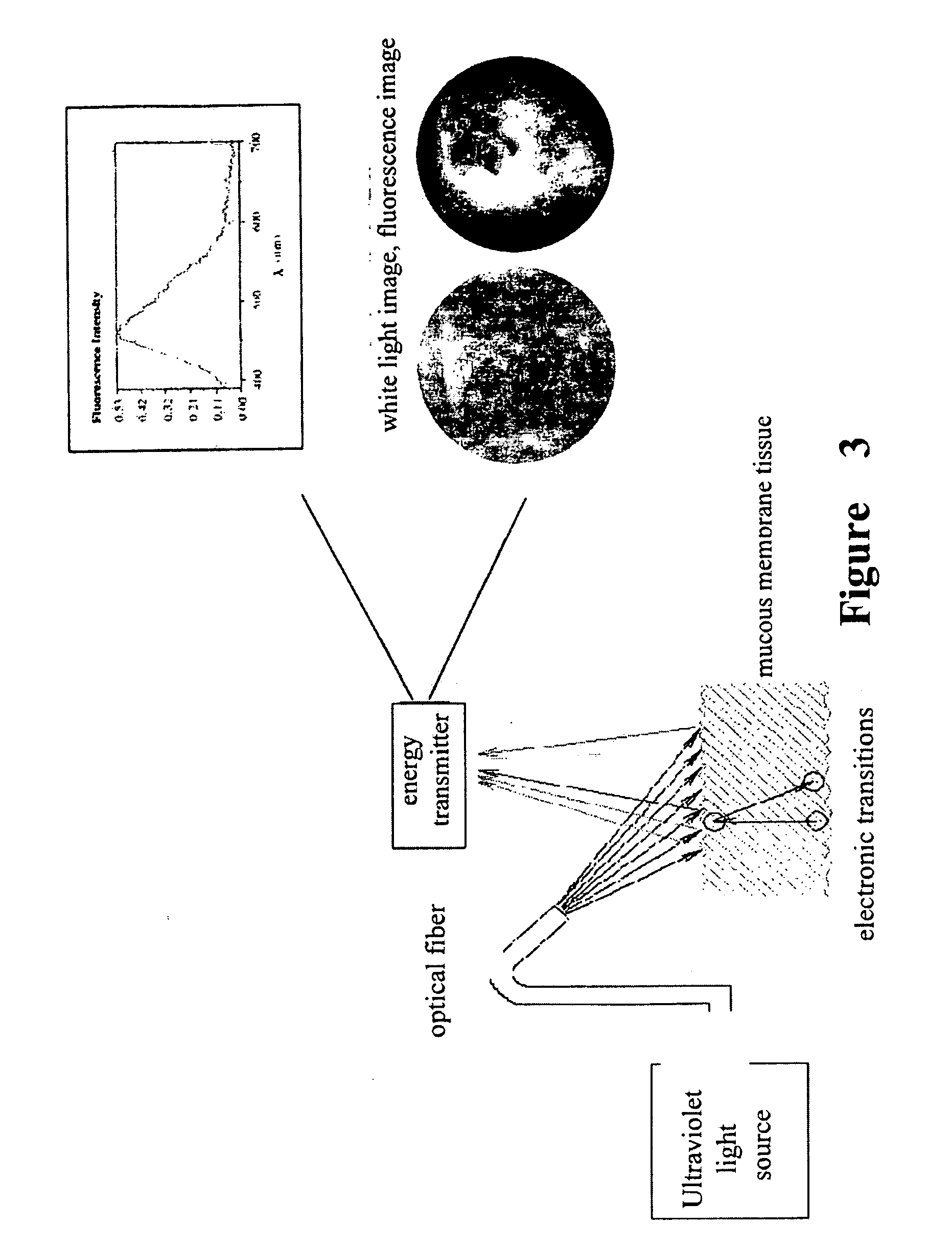
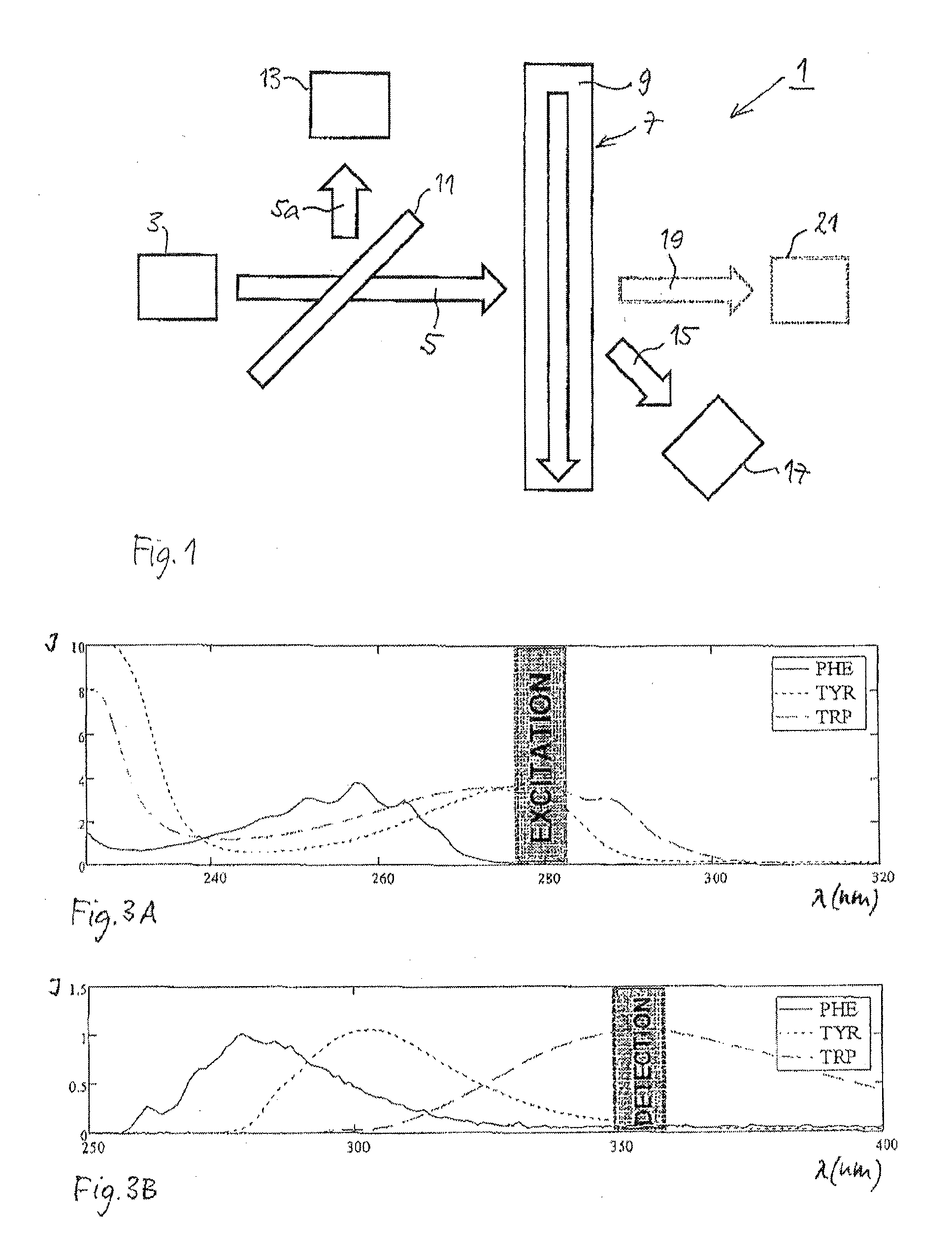
Optical biopsy method for precancerous lesion diagnosis and an endoscope apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20080161699A1High sensitivityStrong specificitySurgeryEndoscopesAbnormal tissue growthForceps
A optical Biopsy method and an apparatus are used in the diagnosis of precancerous lesion for locating the place and determining the level of malignant tumor. The apparatus comprises light source (1, 10) a light channel system, an endoscope (21) and a circuit system. The light sources include an excited light (1) and a cold light source (10). The cold light source and the excited light in the light channel system go through the end of the light guide of the endoscope via optical fiber bundle and irradiate the tested living tissue (22). The white light image signal and the intrinsic fluorescence image signal reflected from the tested living tissue (22) are received by a weak fluorescence CCD (6) that tightly connects to the end of the endoscope (21) and then transmit to the circuit system via a signal wire (9) to produce the image in the display (17). The weak fluorescence signal reflected from the tested living tissue (22) is transmitted to the circuit system via the weak fluorescence fiber bundle (4) protruding from the forceps hole of the endoscope to produce the spectrum image (16).
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENGBIAO SCI & TECH CO LTD
Pathogen detection by simultaneous size/fluorescence measurement
InactiveUS20120120385A1Reduce dependenceReduce the possibilityRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementIntrinsic fluorescencePhysics
A method and apparatus for detecting pathogens and particles in a fluid in which particle size and intrinsic fluorescence of a simple particle is determined.
Owner:BIOVIGILANT SYST
Radiative decay engineering
InactiveUS20050202464A1Enhance intrinsic emissionIncreasing the intrinsic fluorescence of a biomoleculeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsQuantum yieldPhysical chemistry
Compositions and methods for increasing the fluorescence intensity of molecules are provided. In particular, compositions and methods directed to increasing the intrinsic fluorescence of biomolecules and low quantum yield fluorophores are described. The intrinsic fluorescence of biomolecules is increased by positioning a metal particle and a biomolecule at a distance apart sufficient to increase the radiative decay rate of the biomolecule. Methods for the identification of nucleic acids are also provided. The compositions and methods can also be used to increase the emission of any fluorophore, such as the extrinsic probes used to label biomolecules.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Radiative decay engineering
InactiveUS7776528B2Enhance intrinsic emissionIncreasing the intrinsic fluorescence of a biomoleculeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsQuantum yieldPhysical chemistry
Compositions and methods for increasing the fluorescence intensity of molecules are provided. In particular, compositions and methods directed to increasing the intrinsic fluorescence of biomolecules and low quantum yield fluorophores are described. The intrinsic fluorescence of biomolecules is increased by positioning a metal particle and a biomolecule at a distance apart sufficient to increase the radiative decay rate of the biomolecule. Methods for the identification of nucleic acids are also provided. The compositions and methods can also be used to increase the emission of any fluorophore, such as the extrinsic probes used to label biomolecules.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Preparation method of pure yellow fluorescence water-soluble doped zinc selenide quantum dots
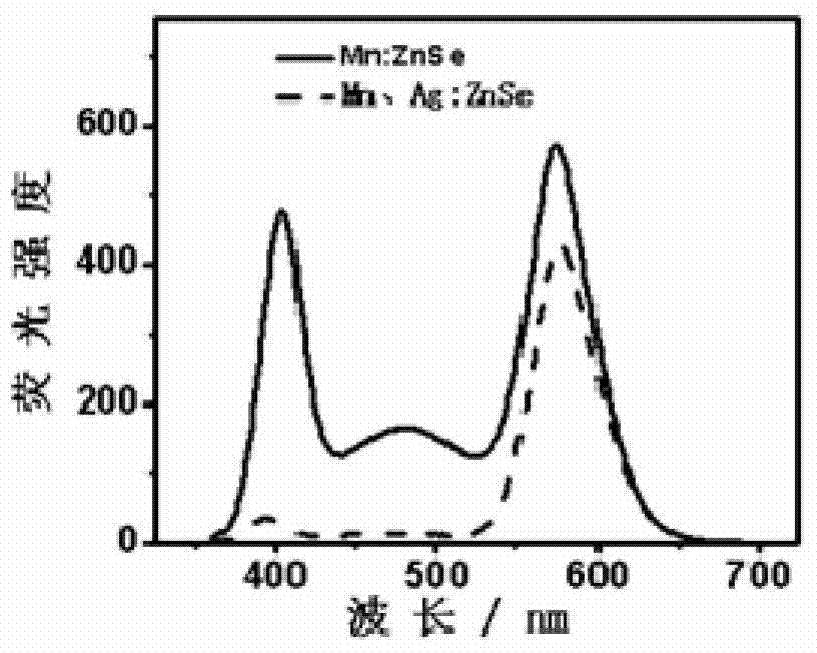
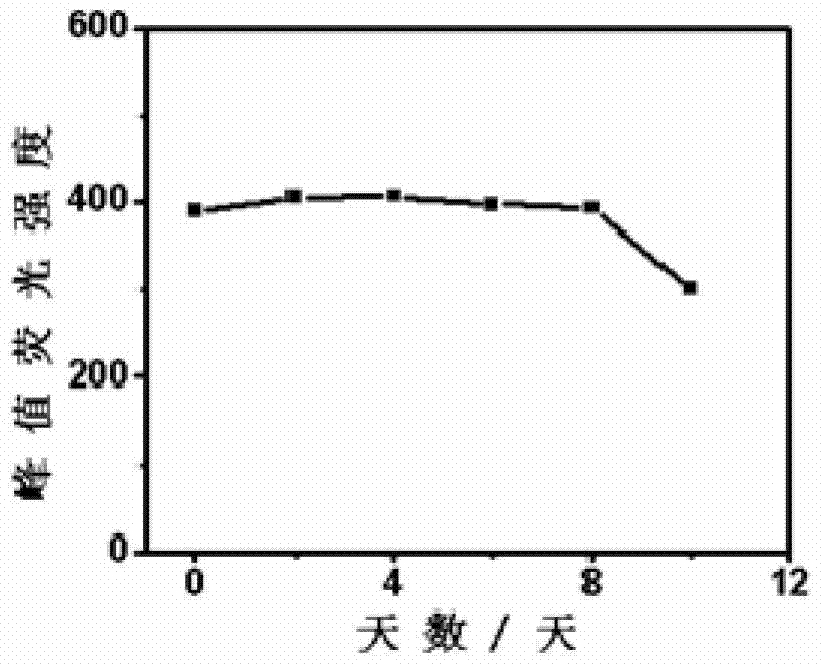
InactiveCN104327847AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityLuminescent compositionsSolubilityZinc selenide
The present invention discloses a preparation method of pure yellow fluorescence water-soluble doped zinc selenide quantum dots, wherein Mn:ZnSe quantum dots are doped with another impurity Ag<+>, such that the intrinsic fluorescence and the defect fluorescence of the ZnSe quantum dots are inhibited while the original intensity of the impurity fluorescence of Mn is maintained so as to prepare the pure Mn yellow fluorescence doped ZnSe quantum dots, and the prepared quantum dots have good water solubility and good fluorescence stability, and only have the one strong Mn fluorescence emission peak. According to the present invention, the one-step synthesis of the pure yellow fluorescence doped ZnSe quantum dots in the aqueous solution is achieved, and the preparation method has advantages of simple operation, good repeatability, green environmental protection, low cost and the like, and can be used for mass production of the quantum dots.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Biological Sensor System
Disclosed is a system using each of the descrete emitters in a III-nitride micro-emitter array as a light source for measuring the properties of independent samples of biological materials deposed on a micro-array using some form of detecting device, e.g, a detector array or charge-coupled device. In embodiments the emitter array produces deep ultraviolet in investigating protein-protein interactions or to detect biological and chemical molecules with high specificity by monitoring changes in a protein's intrinsic fluorescence.
Owner:III N TECH
Method for the detection of biologic particle contamination
ActiveUS8628976B2Avoid cleaningReduce dependenceChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWithdrawing sample devicesClean environmentImaging data
Methods for detecting particles in a fluid, including determining particle size and intrinsic fluorescence of a particle, and time correlating the particle detection data with image data in the vicinity of the detector or detector inlet to identify contamination sources in clean environments are described.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
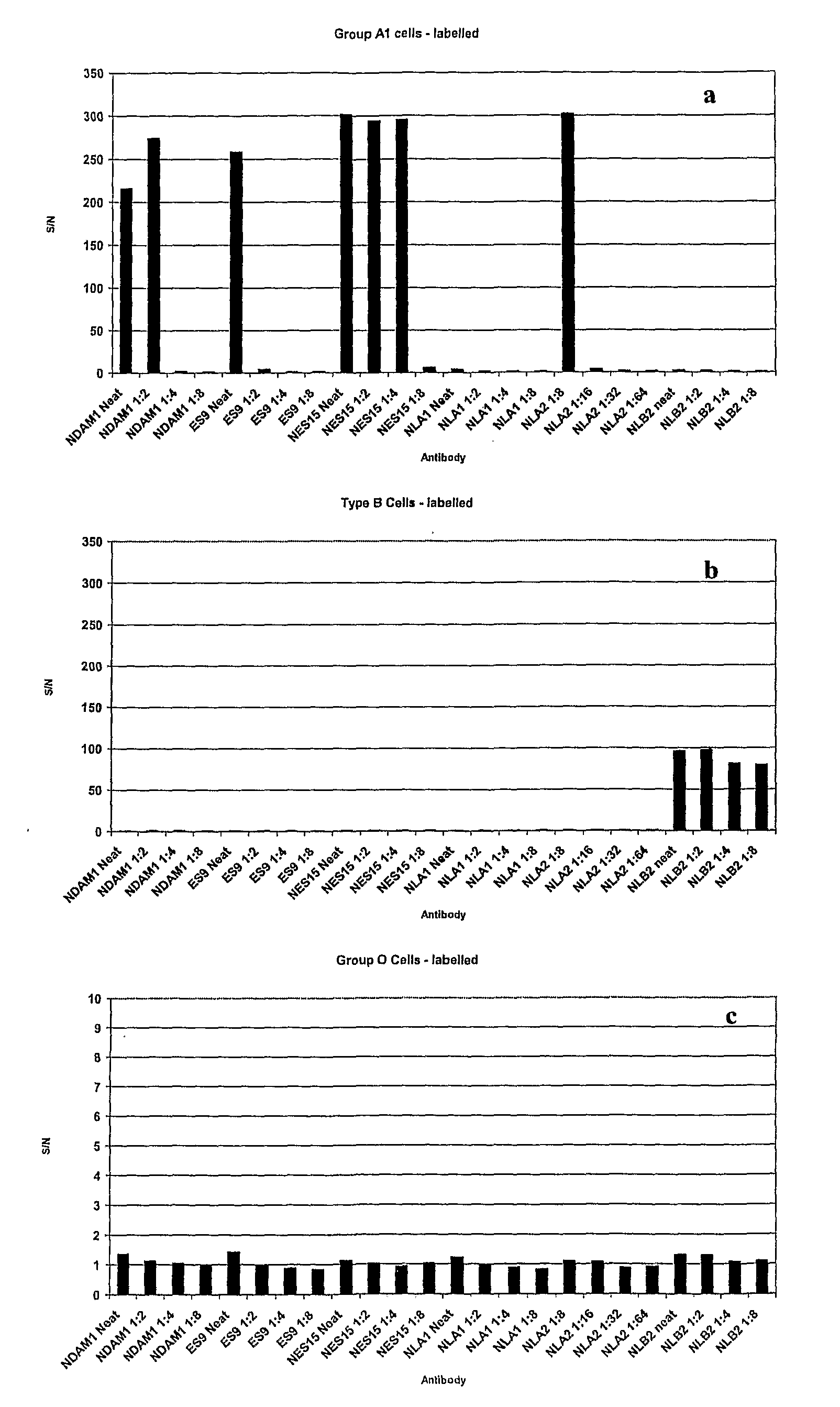
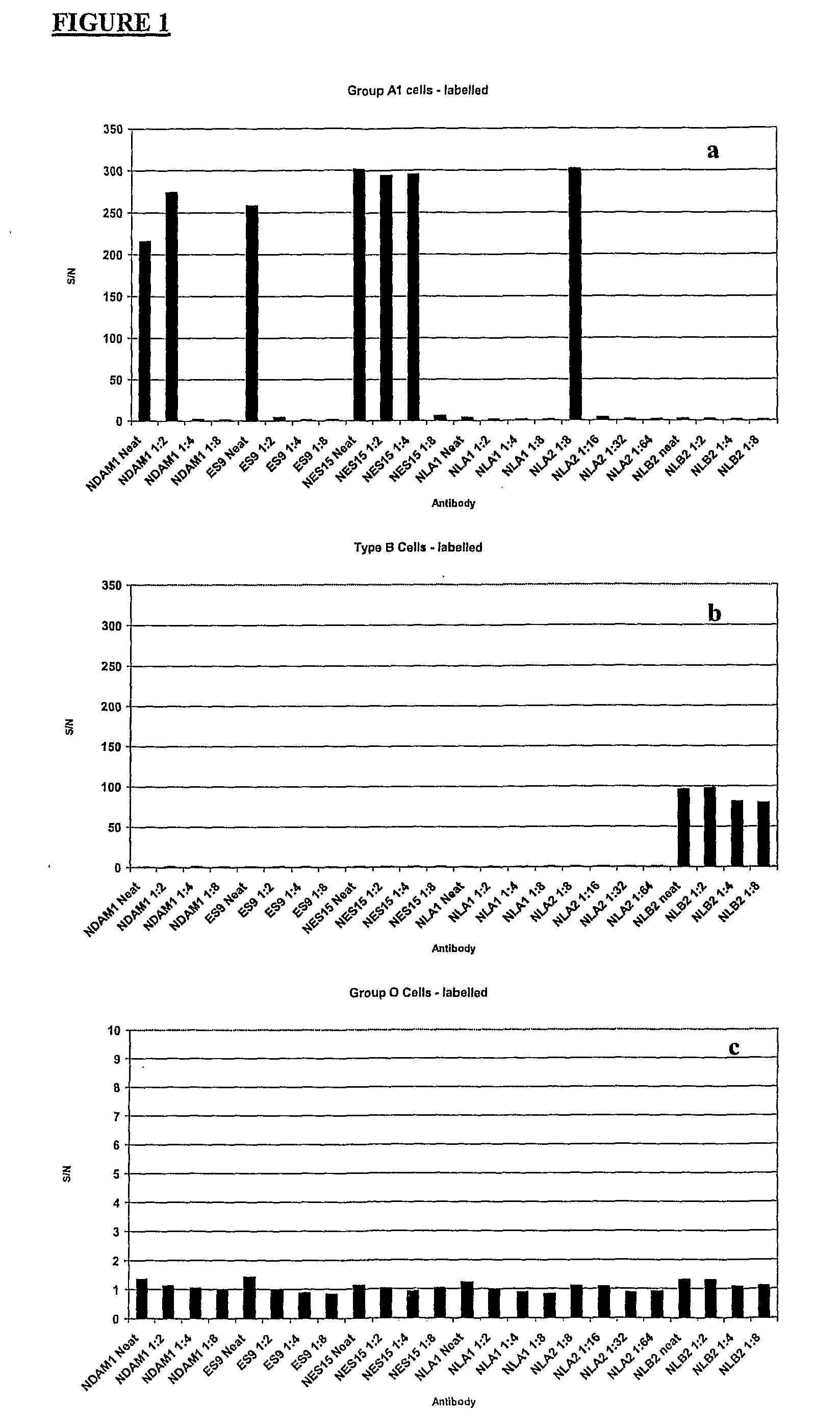
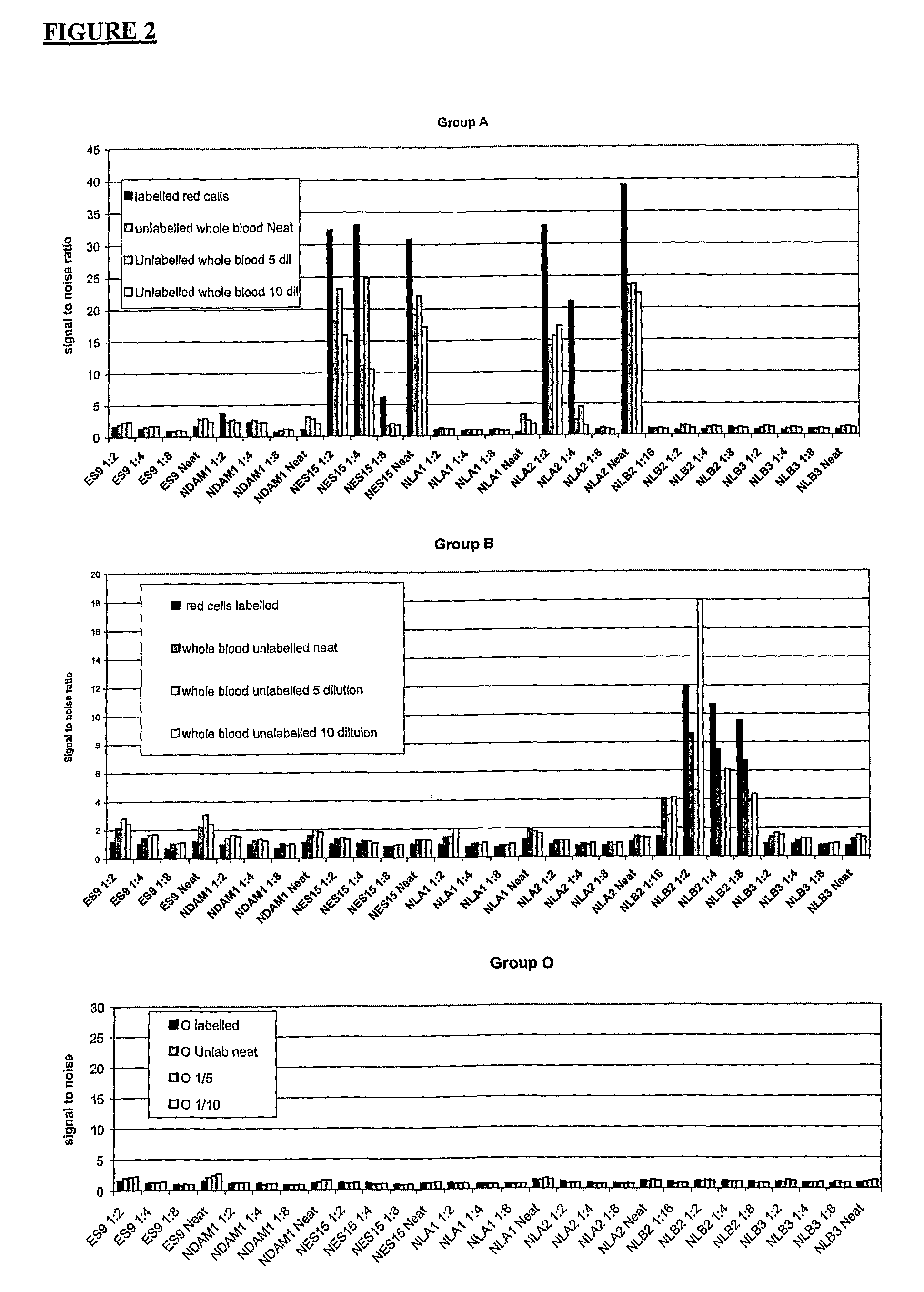
Antigen Detection
InactiveUS20080318798A1Minimise human errorError minimizationLibrary screeningNanosensorsCell Surface AntigensAntigen testing
The present invention relates to methods of detecting specific cell surface antigens present in a sample of cells being tested and in particular blood group antigens, which methods do not employ the addition of extrinsic labels to detect said cell surface antigens. Typically detection is carried out using an intrinsic fluorescence capability of the cells being tested.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH +1
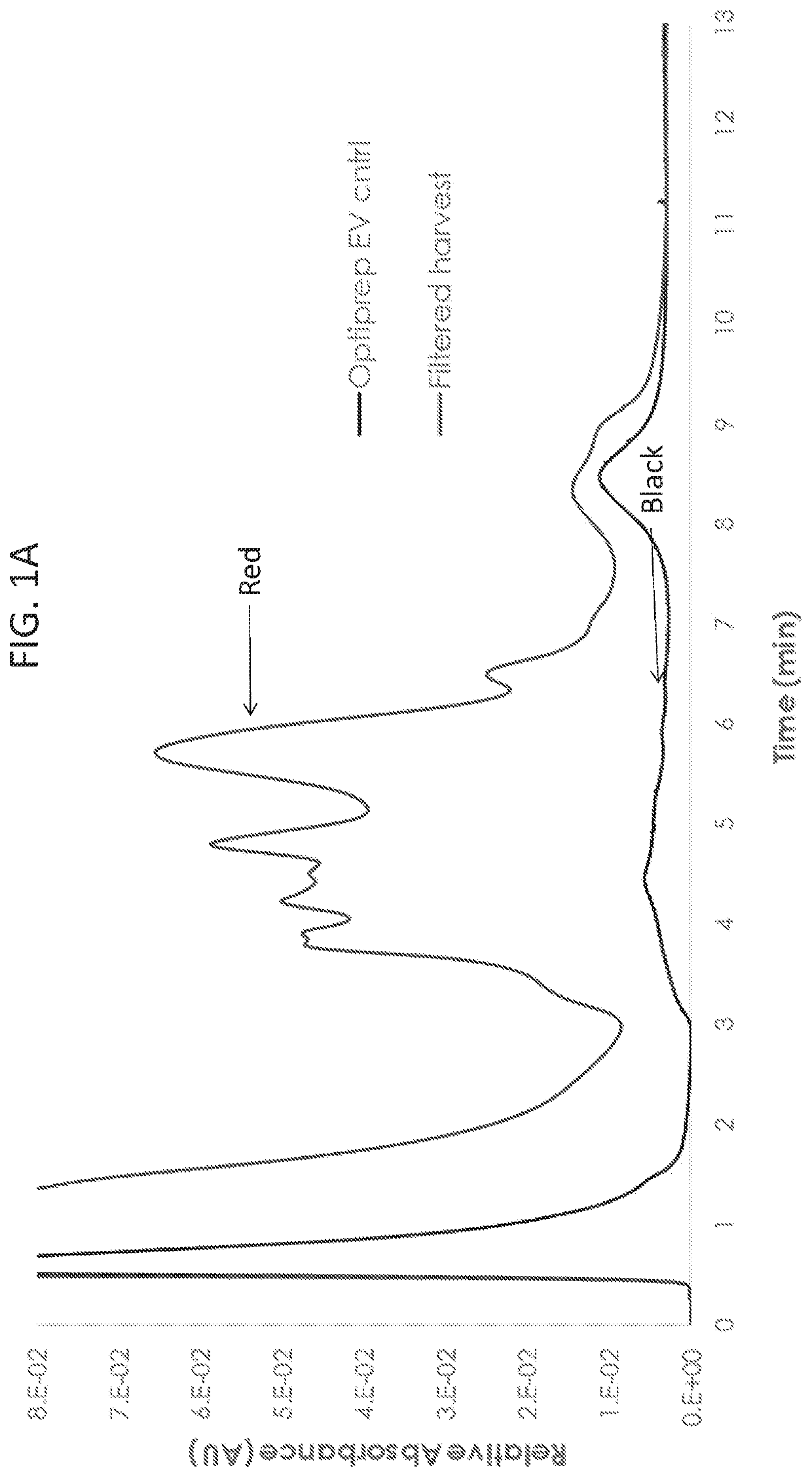
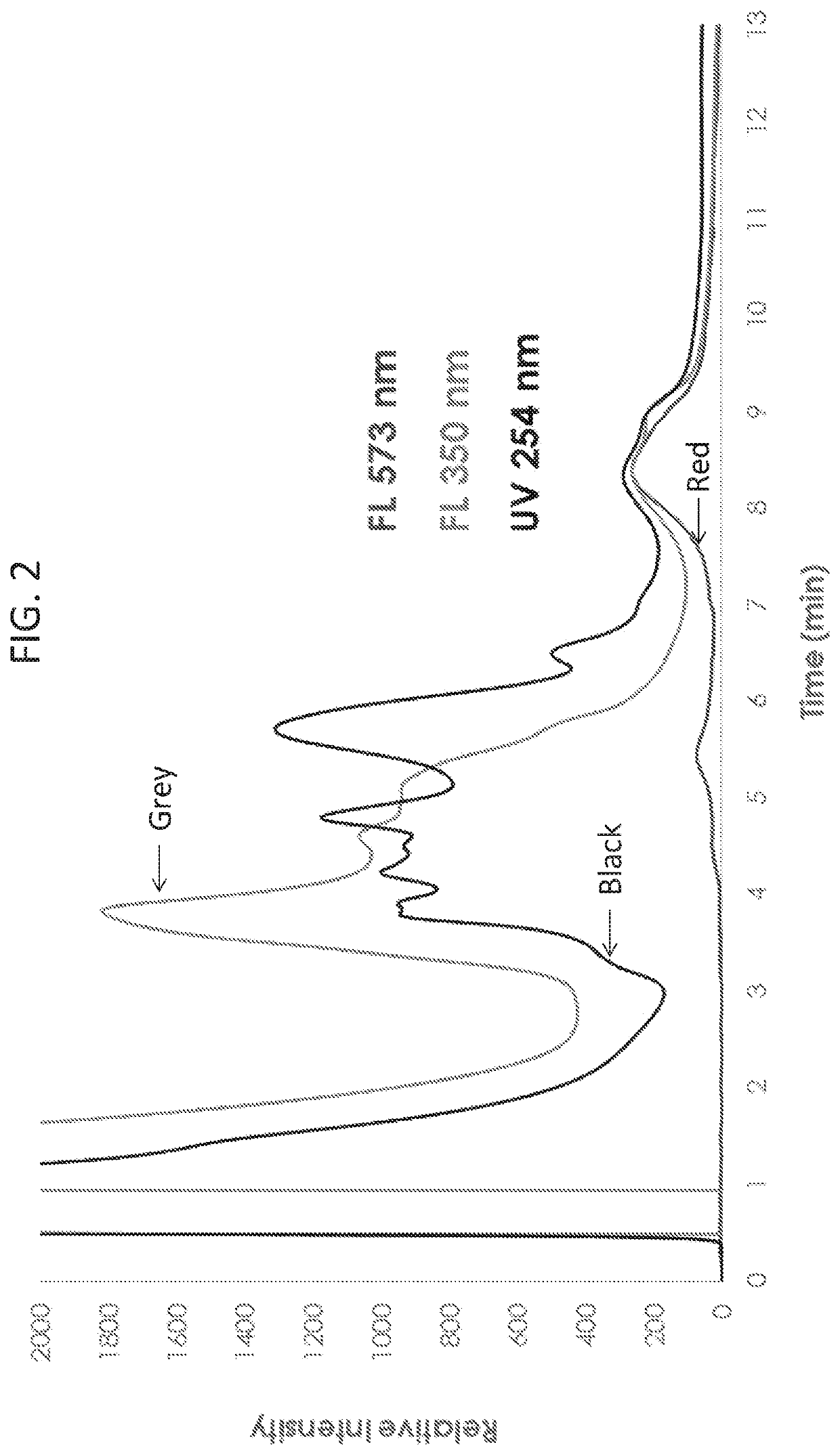
Methods of measuring exosomes using intrinsic fluorescence
InactiveUS20200025685A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellular vesicleExosome
Described herein are novel rapid and reliable methods of detection of extracellular vesicles and quantifying extracellular vesicle concentrations and absolute number from various sources, including raw cell harvest. The methods described herein comprise detection of intrinsic fluorescence of extracellular vesicles in biological samples. Extracellular vesicles analyzed by the methods of this application have a stereotypical elution profile distinct from known contaminants. The methods described herein are a significant improvement over the state of the art and fulfills an unmet need in the field of extracellular vesicle manufacturing and quality control.
Owner:LONZA SALES AG
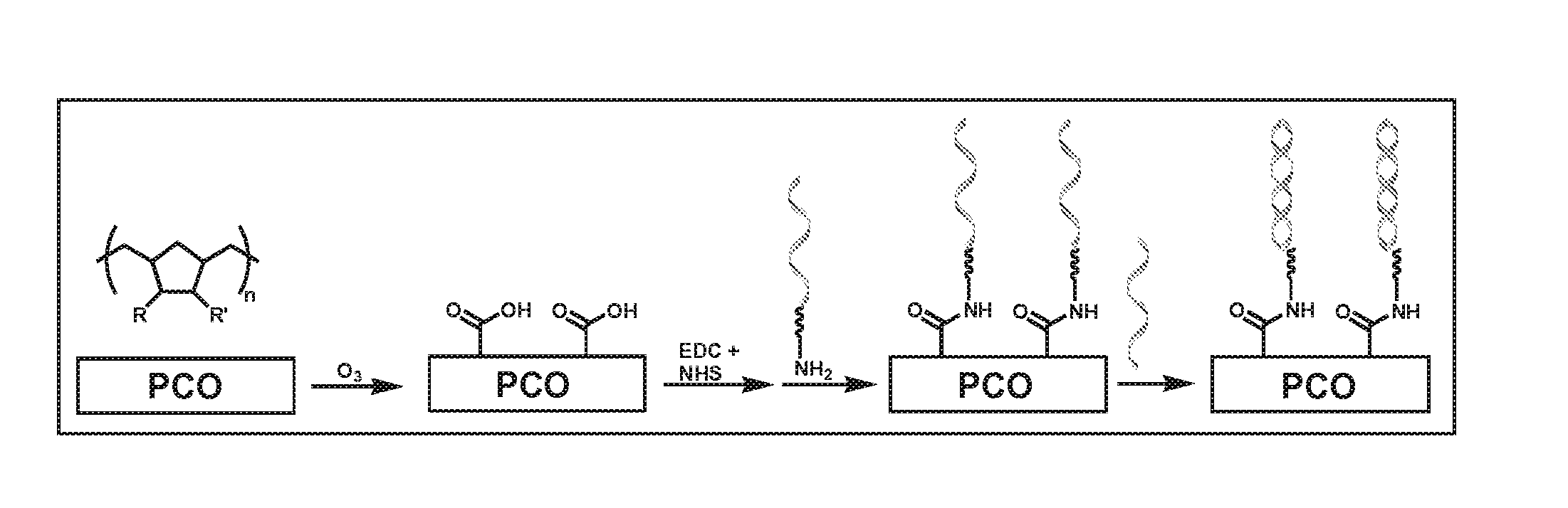
Microdevice for a Fluorescence-based Assay, and a Method for Making the Microdevice
ActiveUS20080124246A1Avoid it happening againChemical analysis using titrationAnalysis by electrical excitationUltravioletFluorophore
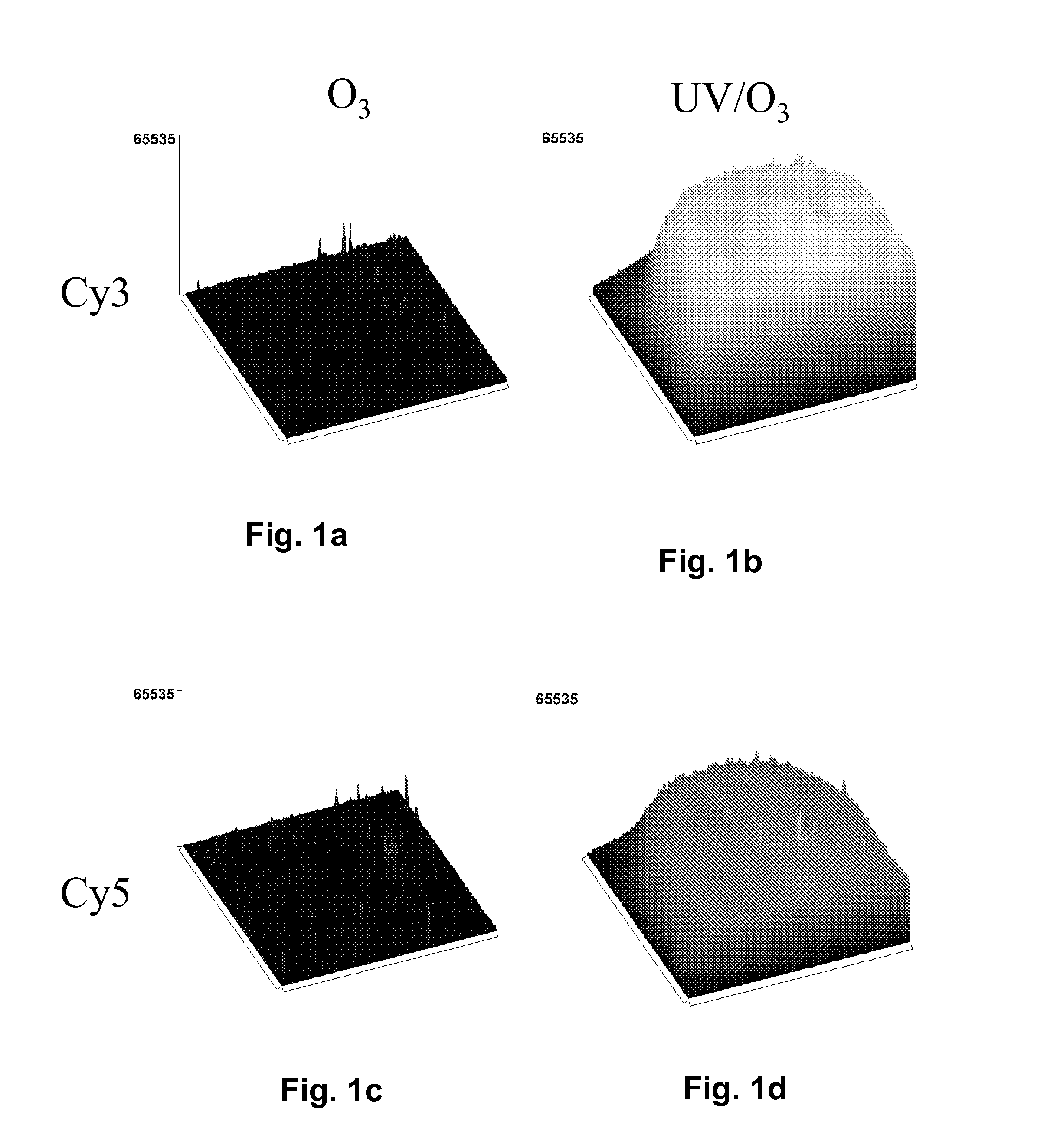
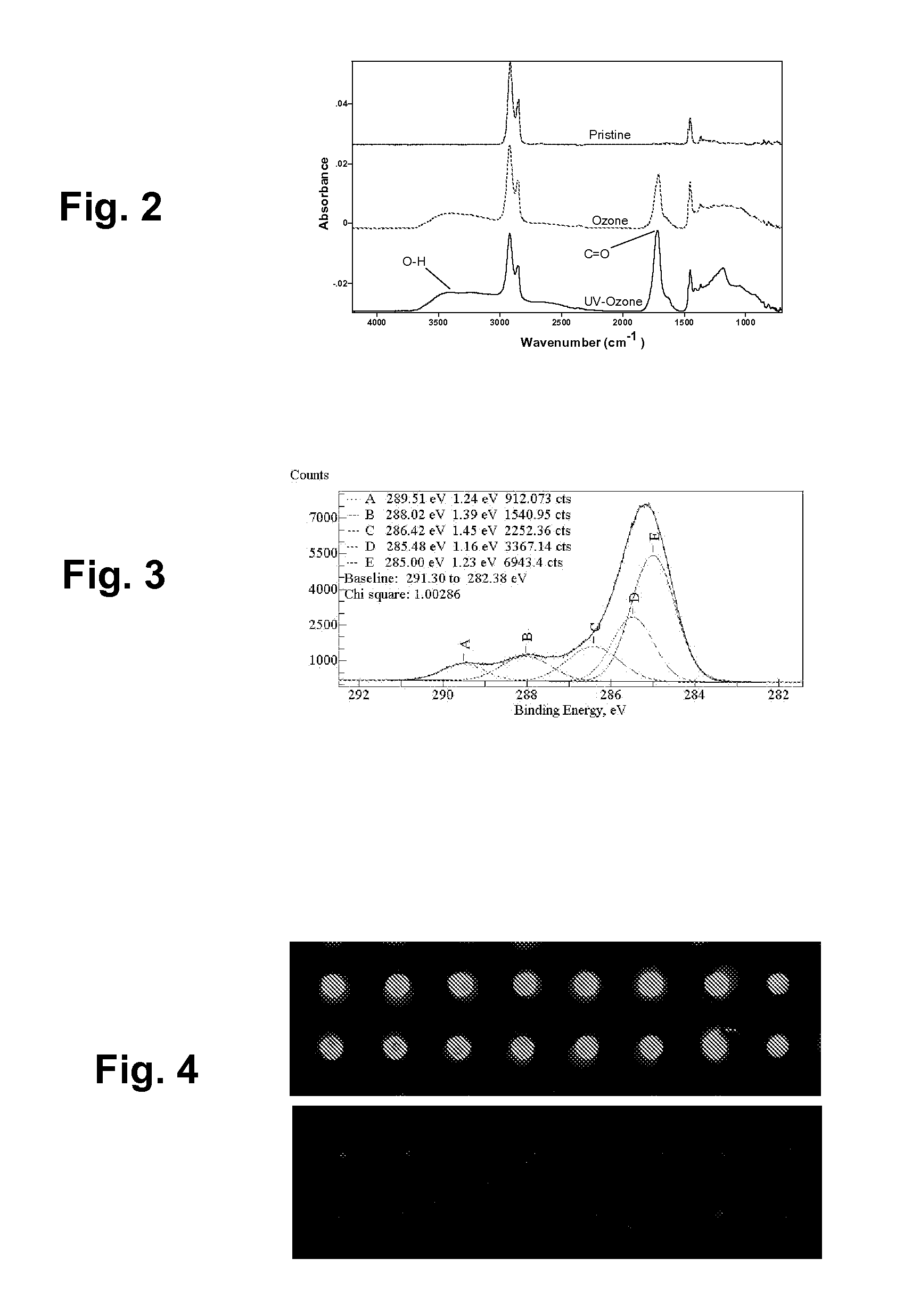
Glass as a substrate for fluorescence-based assays is expensive. Disclosed is a poly(cyclic olefin) alternative to glass that is of comparable sensitivity. More specifically, disclosed is a method of making a microdevice for the immobilization of biomolecules for the purpose of carrying out a fluorescence-based assay, said method comprising providing a substrate comprising a poly(cyclic olefin); protecting the substrate from ultraviolet (UV) light; and subjecting a surface of said UV-protected substrate to ozone oxidation to activate said surface; wherein a content of intrinsic fluorophores on the surface of the substrate remains substantially unchanged after the ozone oxidation. Also disclosed is a microdevice for the immobilization of biomolecules for the purpose of carrying out a fluorescence-based assay, said microdevice comprising a body comprising a poly(cyclic olefin), said body having an ozone-activated surface substantially free of intrinsic fluorophores; wherein said activated surface is substantially free of intrinsic fluorescence during a fluorescence-based assay of said biomolecules bound to said activated surface.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method and apparatus for detecting the presence of microbes with frequency modulated multi-wavelength intrinsic fluorescence
InactiveUS7824883B2Reduce riskRapid and inexpensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular componentSporeling
Method and apparatus for the detection of microbes in liquids, in air and on non-living surfaces in which samples are exposed to frequency-modulated electromagnetic radiation of specific energies capable of exciting various metabolites, cofactors and cellular and spore components, with the microbial cells to be sampled (and more specifically the excited metabolites, cofactors and / or other cellular components) contained therein emit fluorescence that can be measured that is similarly frequency-modulated provided that the excitation frequencies are longer than the fluorescence lifetime of the excited intrinsic microbial fluorophore. The contribution to the measured signal due to each excitation frequency resulting from microbial intrinsic fluorescence is determined with a method capable of calculating the intensity of each frequency-modulated signal, and the relative total fluorescent signals of the intrinsic microbial components associated with each excitation frequency are required to lie within physiological ranges, with the amplitude of the fluorescence signals used to enumerate the microbe content in the sample.
Owner:MICROBIOSYST
Porous silicon dioxide-stabilized noble metal cluster fluorescent material and method for preparing same
The invention provides a porous silicon dioxide-stabilized noble metal cluster fluorescent material and a method for preparing the same, and belongs to the technical field of preparing nano compound materials. The method for preparing the fluorescent material comprises the following steps of: corroding noble metal nano particles into noble metal clusters by a corrosion method, and stabilizing the noble metal clusters by a noble metal cluster stabilizer; performing the in situ stabilization of the noble metal clusters in a porous silicon dioxide structure by the hydrolysis of organic silicate ester, removing organic matters, performing hydrogen reduction to obtain the silicon dioxide-stabilized noble metal clusters, and conveniently preparing the porous silicon dioxide-stabilized noble metal cluster fluorescent material of Au, Ag, Pt, Pd and combination of double noble metals by adjusting the ligand, stabilizer and reaction conditions. Because the silicon dioxide is chemically and electrically inactive, the noble metal clusters show intrinsic fluorescence characteristics. The fluorescent material prepared by the method has stable fluorescence, chemical inertness and biocompatibility and is widely applied to fluorescence imaging and sensing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Detection device and method
InactiveUS20130105371A1Beneficially applicable monitoringBeneficially applicable eventually controllingSemi-permeable membranesPhotometryProtein moleculesIntrinsic fluorescence
Detection device for quantitative detection of predetermined molecules, in particular medium size protein molecules, in a sample liquid with a light source for emitting measurement radiation, a section for irradiating the sample liquid and a light detector for measuring the detection radiation exiting the section for irradiating the sample liquid, as well as an analysis stage located downstream of the light detector for analyzing the detector signal, wherein the light source is designed such that the measurement radiation has a spectral range exciting the intrinsic fluorescence of a molecule to be determined, and the light detector is designed such that at least one spectral range of the detection radiation is measured, in which the molecule emits intrinsic fluorescence radiation.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
Method of determining laser stabilities of optical materials, crystals selected according to said method, and uses of said selected crystals
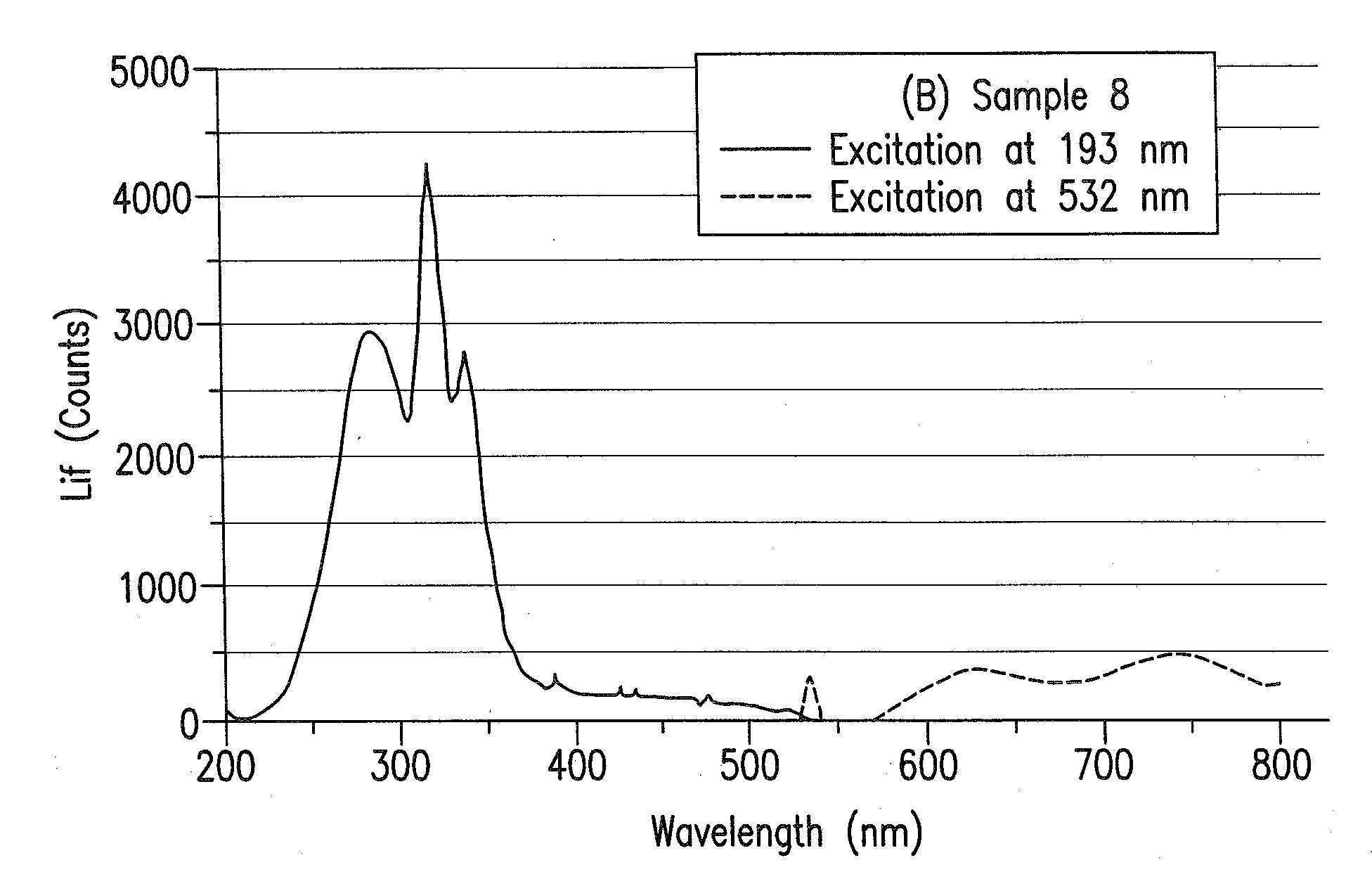
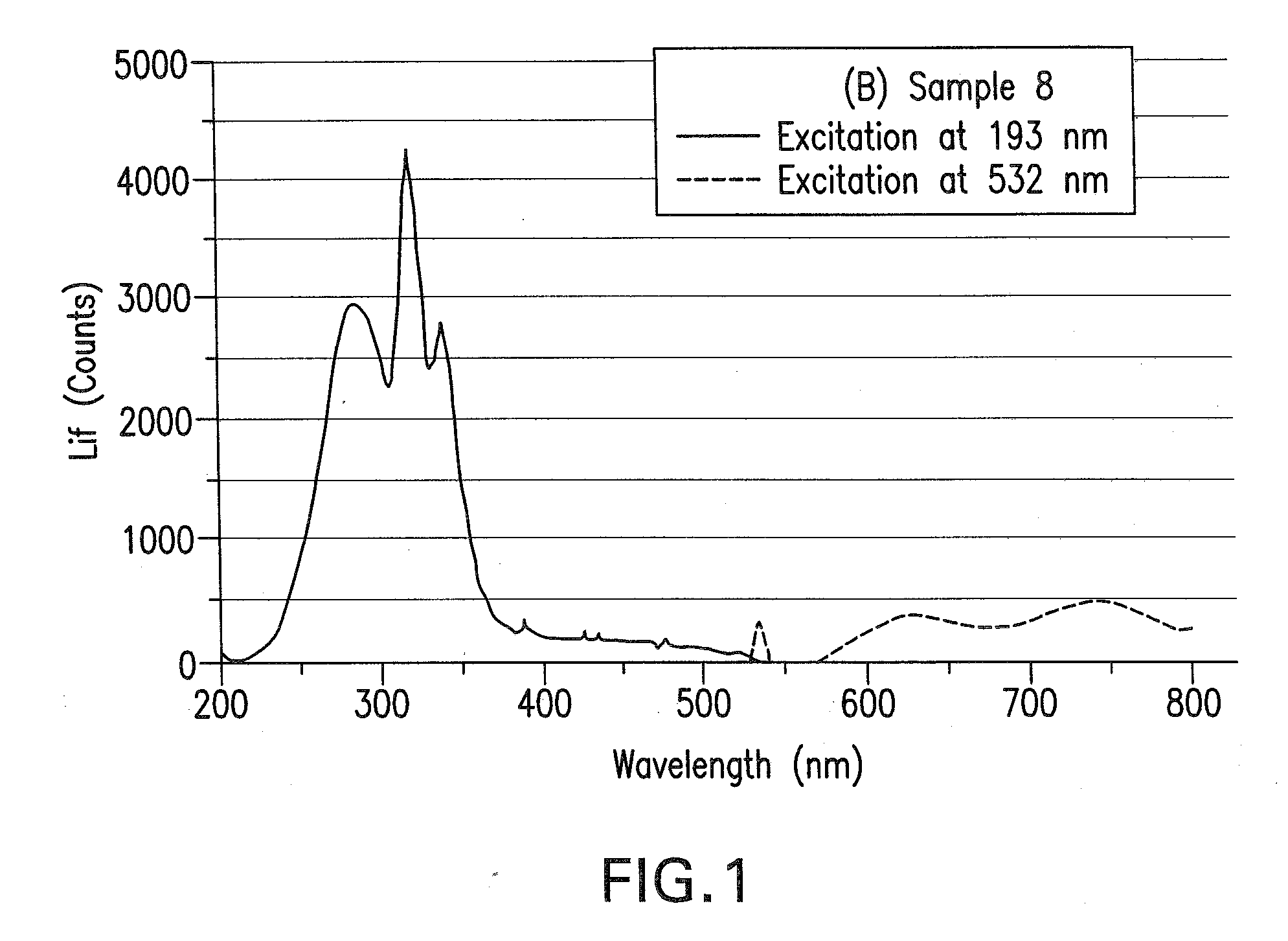
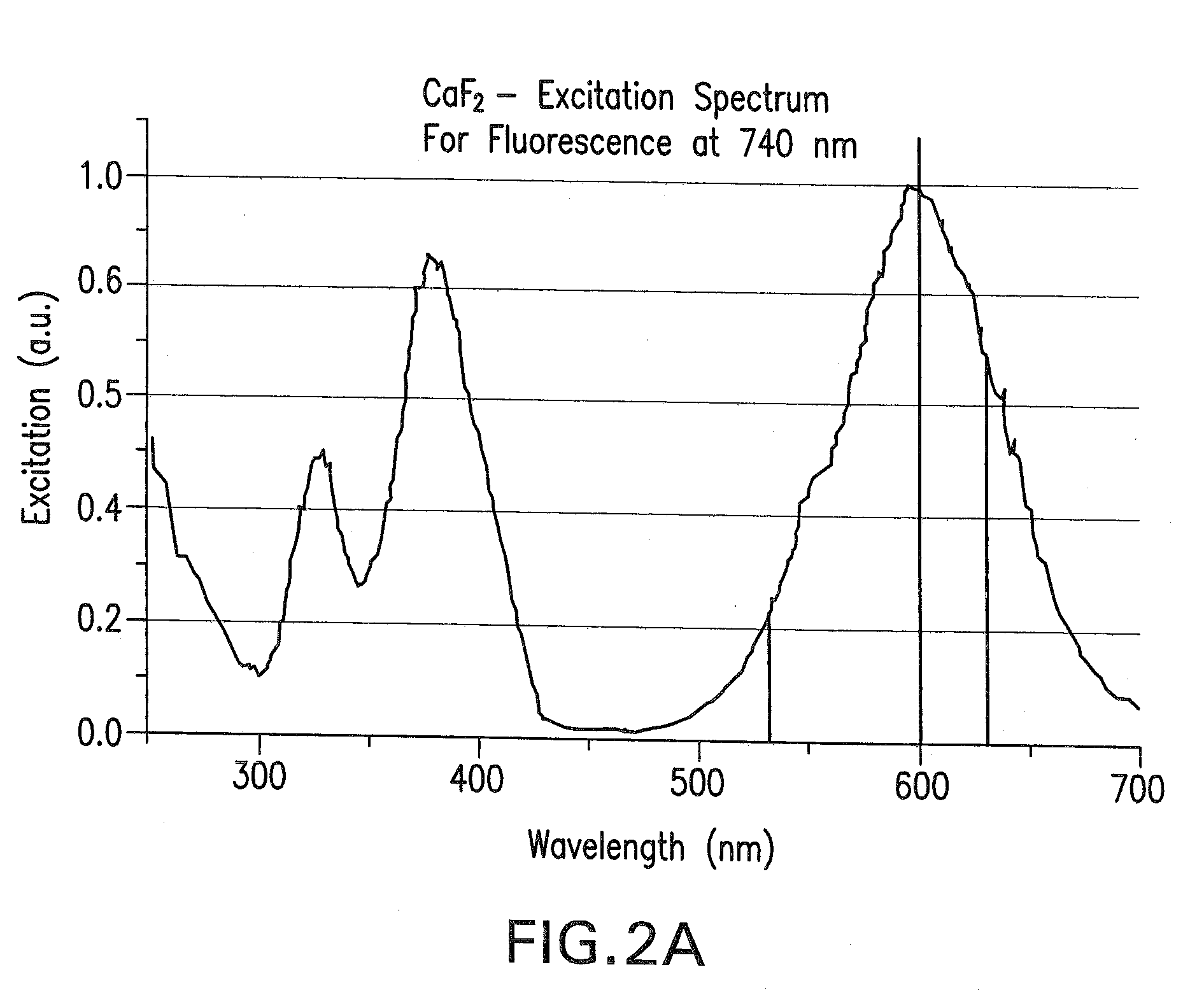
The method determines laser stability of an optical material, which is suitable for making an optical element through which high-energy light passes. The method includes pre-irradiation to produce radiation damage and measurement of the resulting induced non-intrinsic fluorescence. The method is distinguished by excitation of induced fluorescence immediately after pre-irradiation and after at least ten minutes after pre-irradiation with light of a wavelength between 350 and 810 nm, and measurement and quantitative evaluation of fluorescence intensities at wavelengths between 550 nm and 810 nm. Especially laser-stable optical materials, particularly CaF2 crystals, have a normalized difference (Z) of the fluorescence intensities measured at a first time immediately after pre-irradiation and at a second time at least ten minutes after the pre-irradiation, as calculated by the following equation (1):Z=(I2,λ1,λ2−I1,λ1,λ2)I2,λ1,λ2, (1)which is less than 0.3.
Owner:HELLMA MATERIALS
Pyrrolidone derivatives, oligomers and polymers
ActiveUS20190352258A1Small sizeAvoid photobleachingOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOrganic structurePyrrolidinones
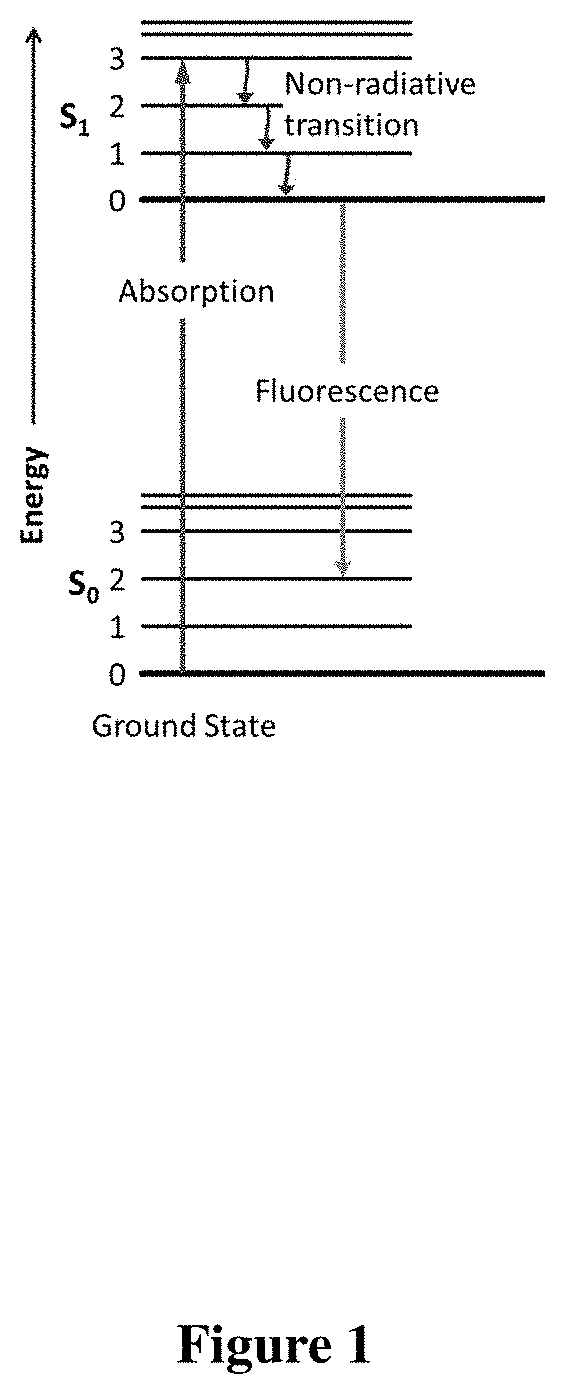
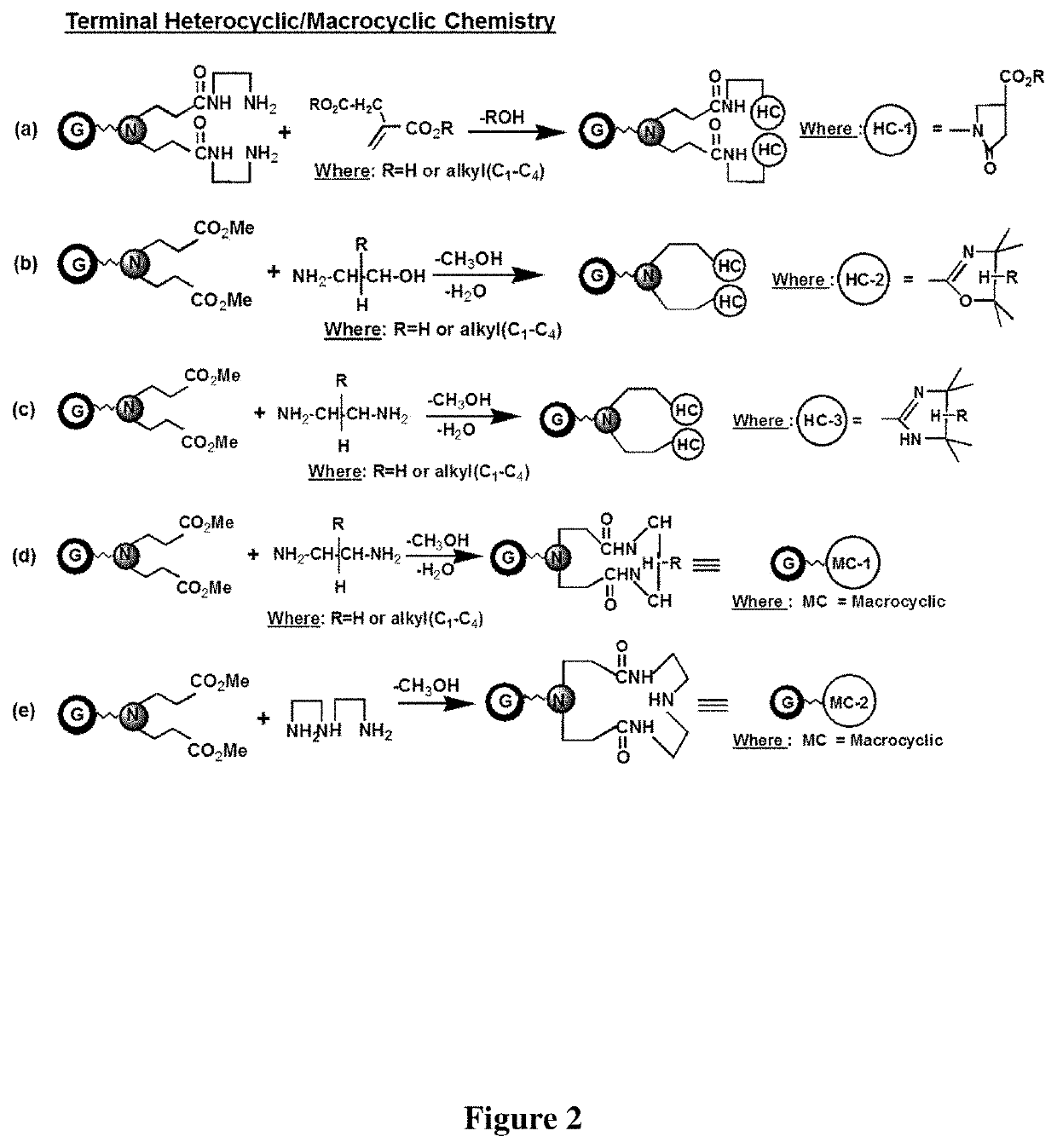
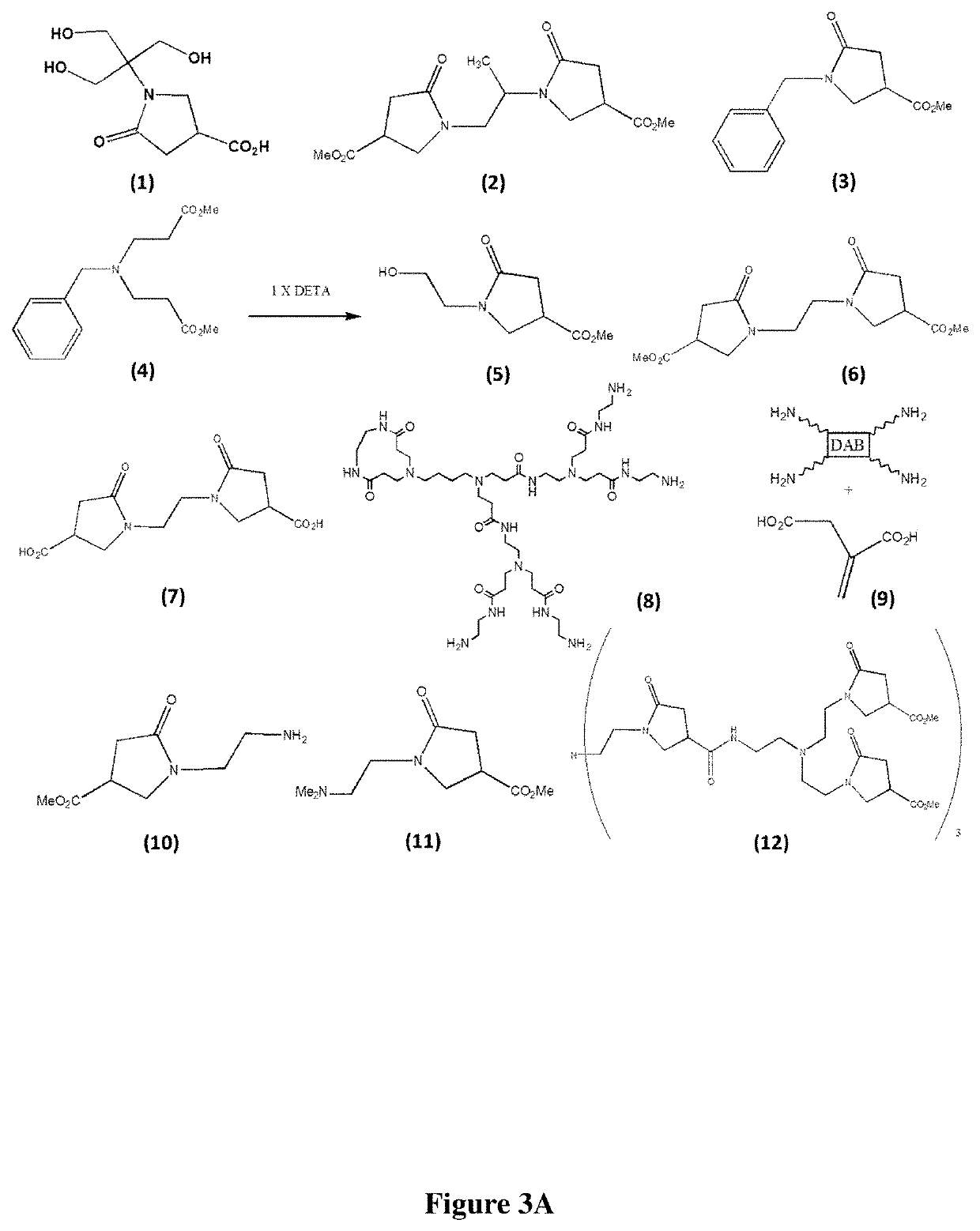
Simple organic structures, organic / inorganic polymers, and other substrates have been made, all of which have at least one pyrrolidone moiety present, and found to exhibit low toxicity, low complement activation features and may be used to reduce protein interactions with drug conjugates while enhancing in vivo residency times for these conjugates when used as an injectable composition; thus these compounds can be used as substitutes for PEG in PEGylation. Surprisingly, these compounds also exhibit unique intrinsic fluorescence (IF) or non-traditional fluorescence (NTF) properties that currently cannot be explained by traditional photochemistry and fluorescence paradigms are described. These compounds have a variety of applications such as in cellular imaging, gene transfection, bio-diagnostics, biosensing, fluorescence directed surgical resections, drug delivery, forensics, environmental diagnostics, mineral / gemstone characterization, counterfeit goods detection, tracer studies related to liquid / water flow, oil field enhancements and diagnostics, prevention of photo-bleaching, and LED display enhancements and others.
Owner:NANOSYNTHONS
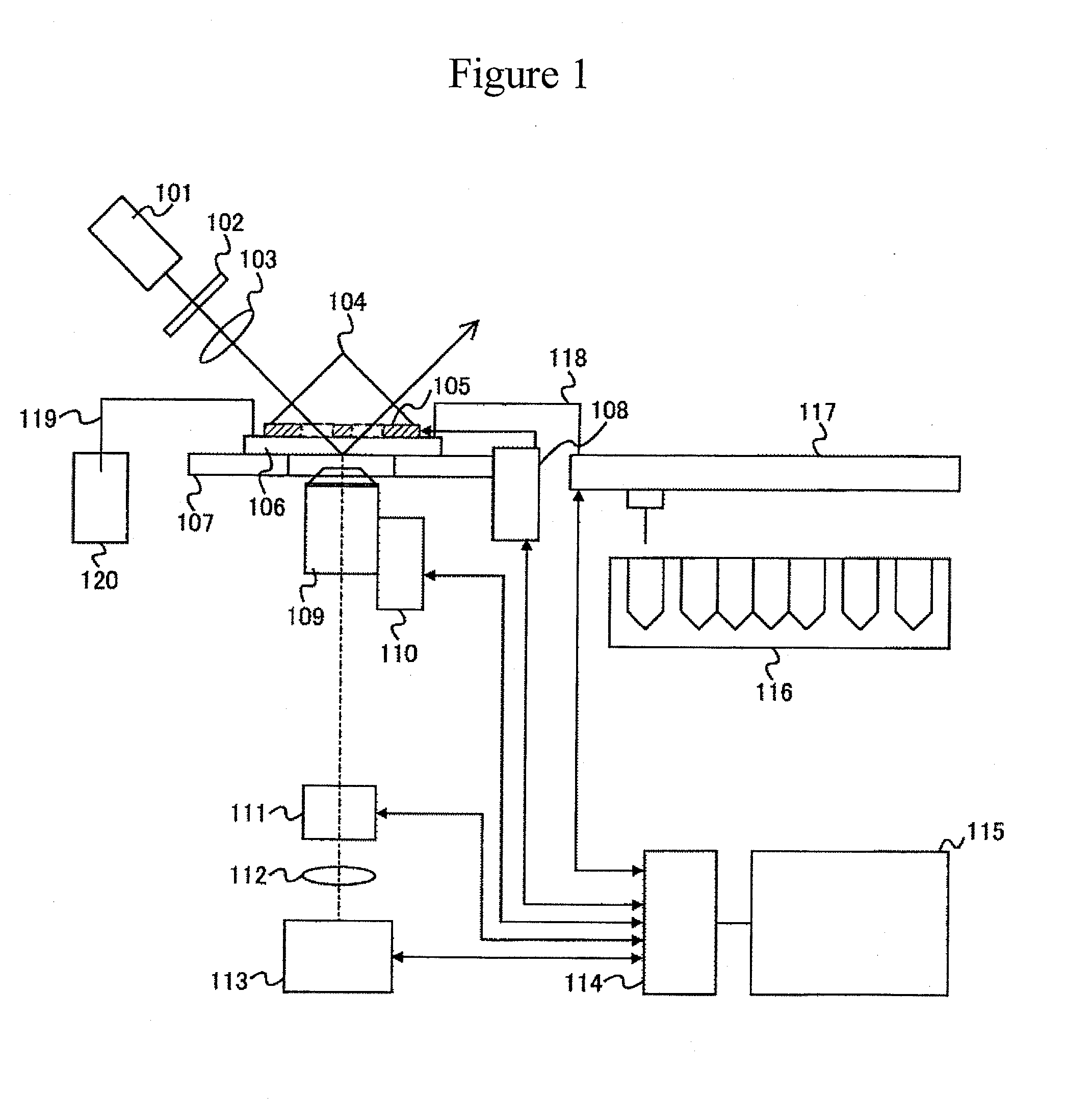
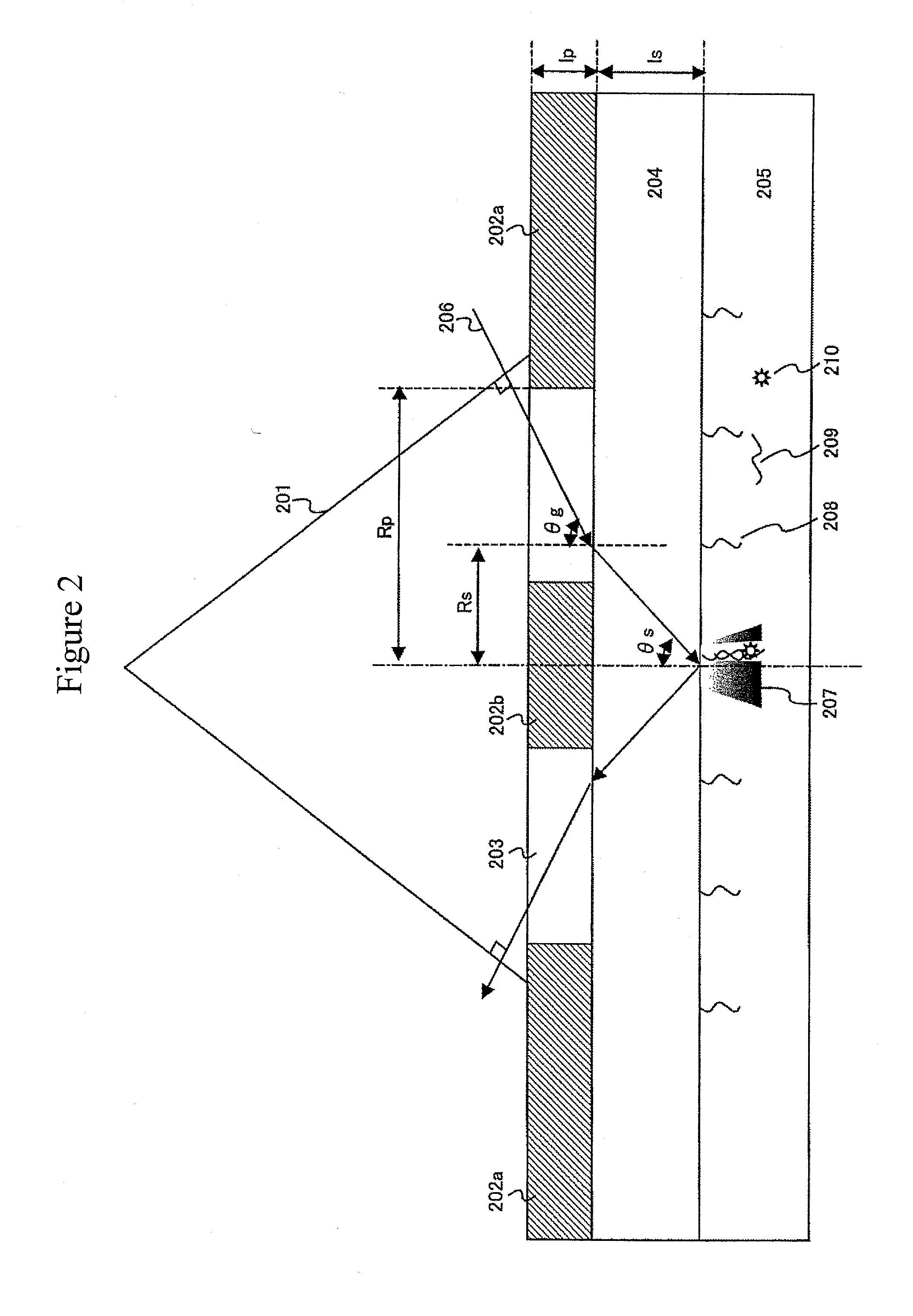
Total internal reflection microscope apparatus and method for analyzing fluorescent sample
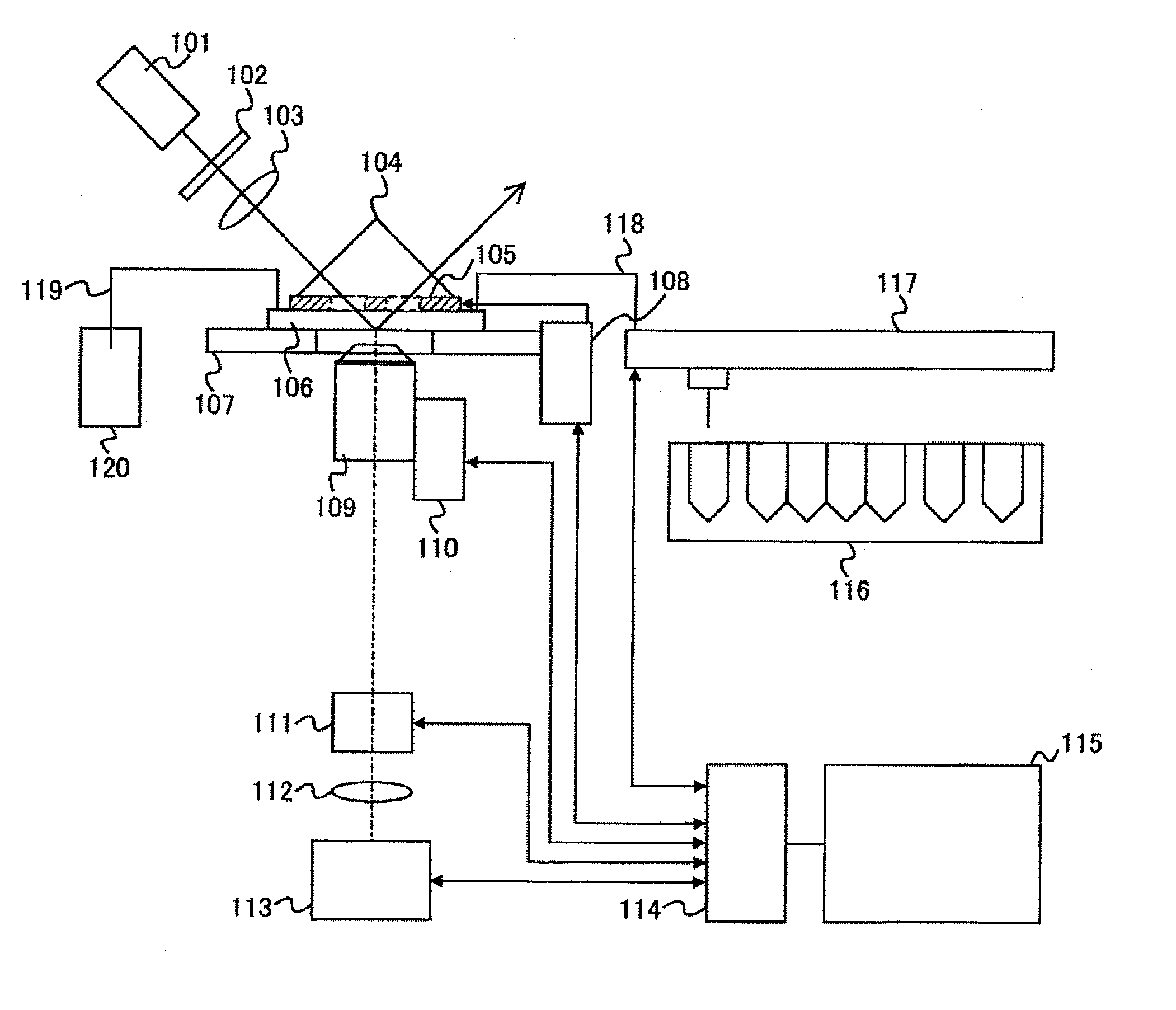
ActiveUS20110284769A1Highly sensitive fluorescence observationImprove accuracyPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersTemperature controlTotal internal reflection
An object of the present invention relates to observation of single molecule fluorescence while temperature of a sample solution is controlled by a temperature controller and intrinsic fluorescence of the temperature controller is avoided, in a total internal reflection microscope. The present invention relates to provision of an opening at areas of the temperature controller through which incident light and reflected light pass, and configuration adopting a material with intrinsic fluorescence lower than that of the other parts, in a total internal reflection microscope including a prism and the temperature controller. The present invention enables intrinsic fluorescence of the temperature controller to be suppressed, which allows highly sensitive fluorescence observation while controlling sample solution temperature with high precision. For instance, this in turn allows the throughput of single molecule DNA sequencing using a total internal reflection microscope to be improved.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com