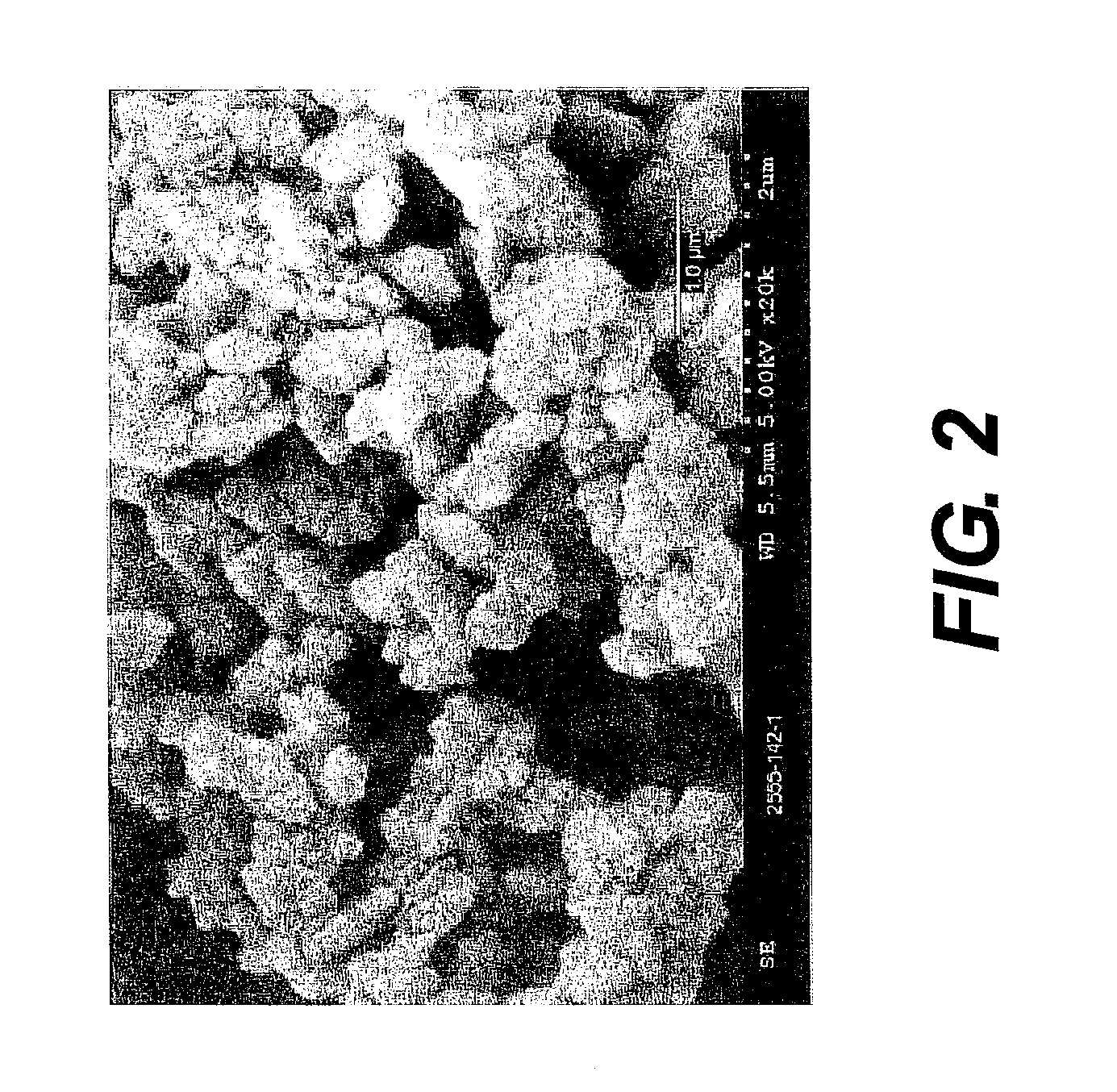
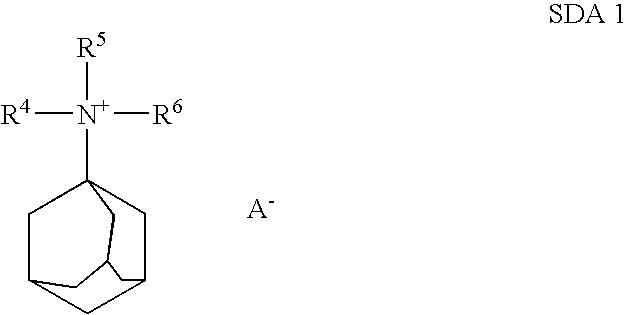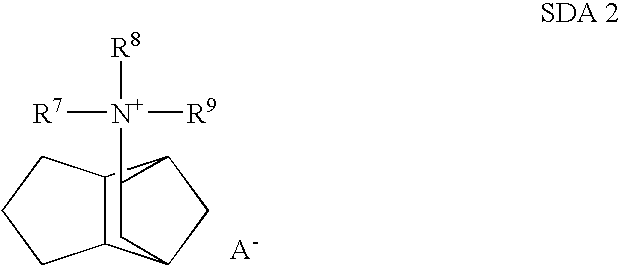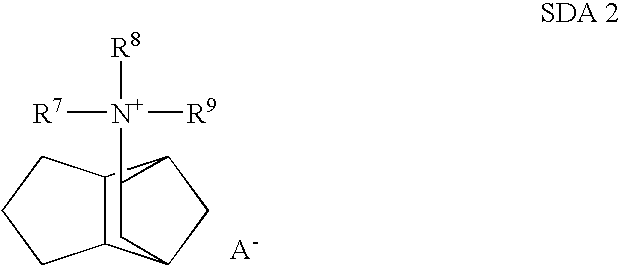Patents
Literature
231 results about "Organic structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of fabricating organic thin film transistors
InactiveUS20120122275A1Suppresses and eliminates adverse effectSuppress and eliminate degradationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic structureSemiconductor materials
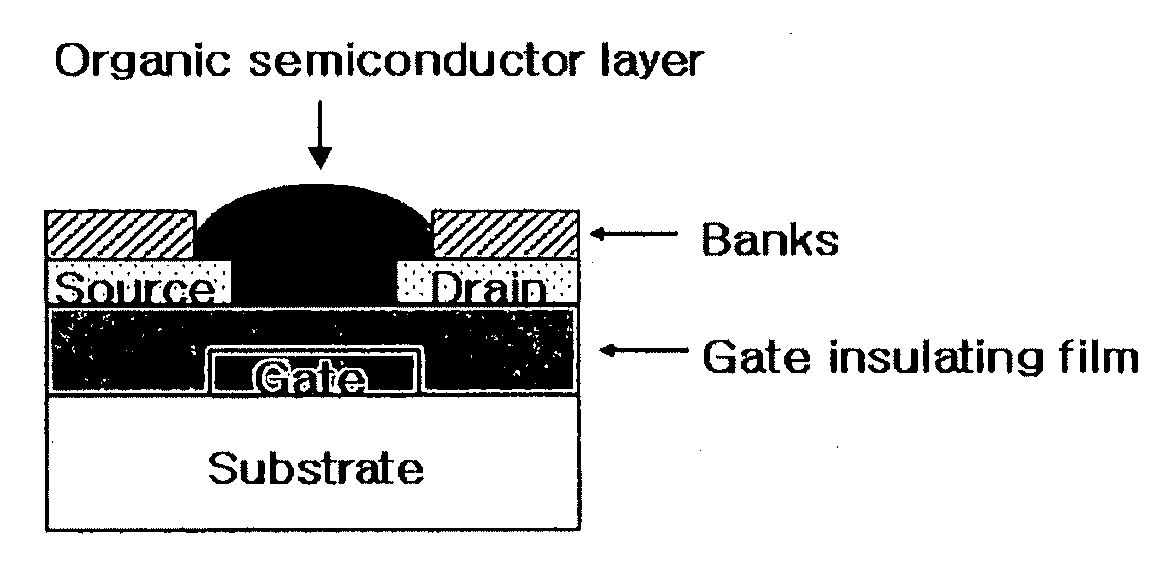
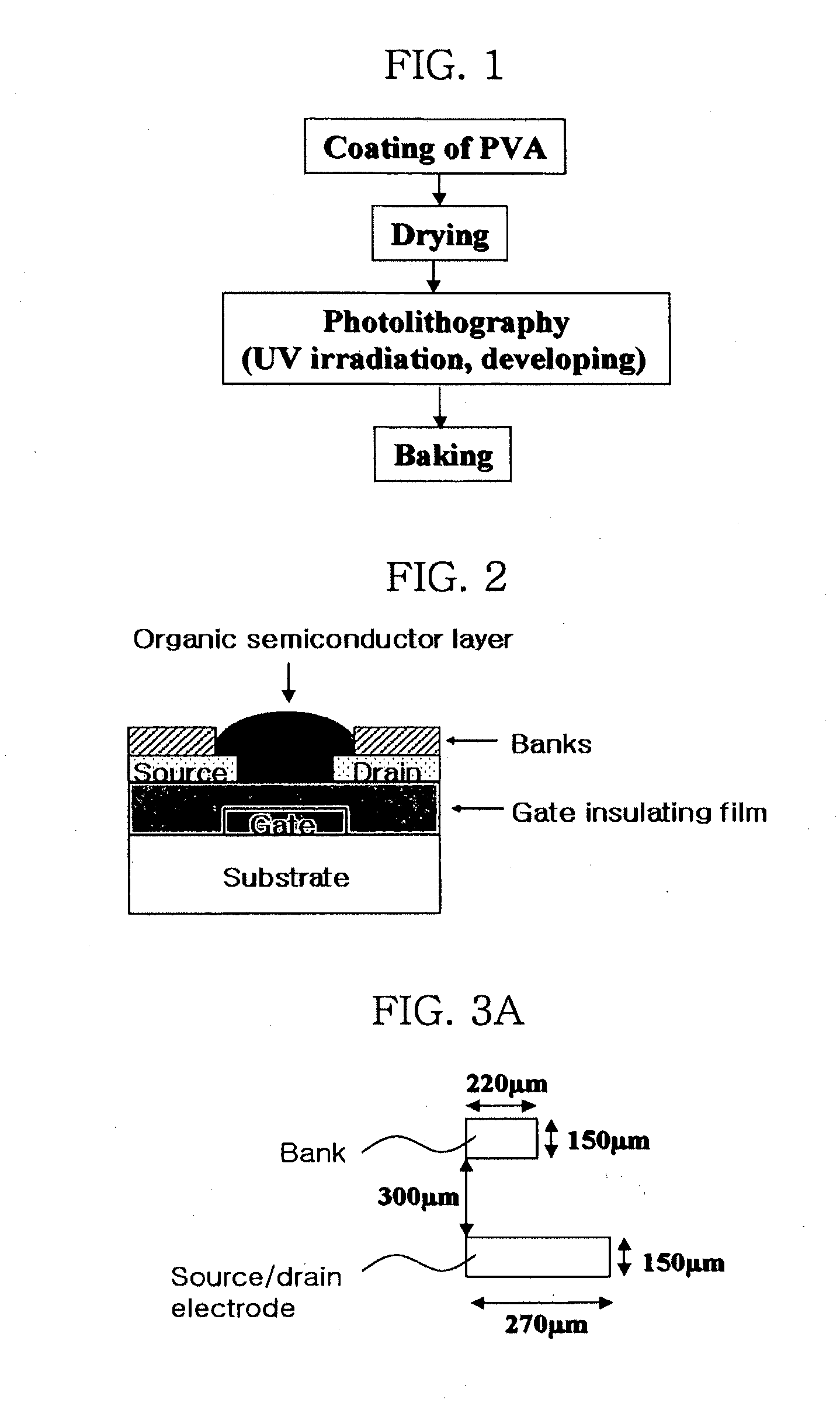
Disclosed is a method for forming banks during the fabrication of electronic devices incorporating an organic semiconductor material that includes preparing an aqueous coating composition having at least a water-soluble polymer, a UV curing agent and a water-soluble fluorine compound. This coating composition is applied to a substrate, exposed using UV radiation and then developed using an aqueous developing composition to form the bank pattern. Because the coating composition can be developed using an aqueous composition rather than an organic solvent or solvent system, the method tends to preserve the integrity of other organic structures present on the substrate. Further, the incorporation of the fluorine compound in the aqueous solution provides a degree of control over the contact angles exhibited on the surface of the bank pattern and thereby can avoid or reduce subsequent surface treatments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20050084712A1Lower energy barrierLow voltage driveDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic structureSimple Organic Compounds
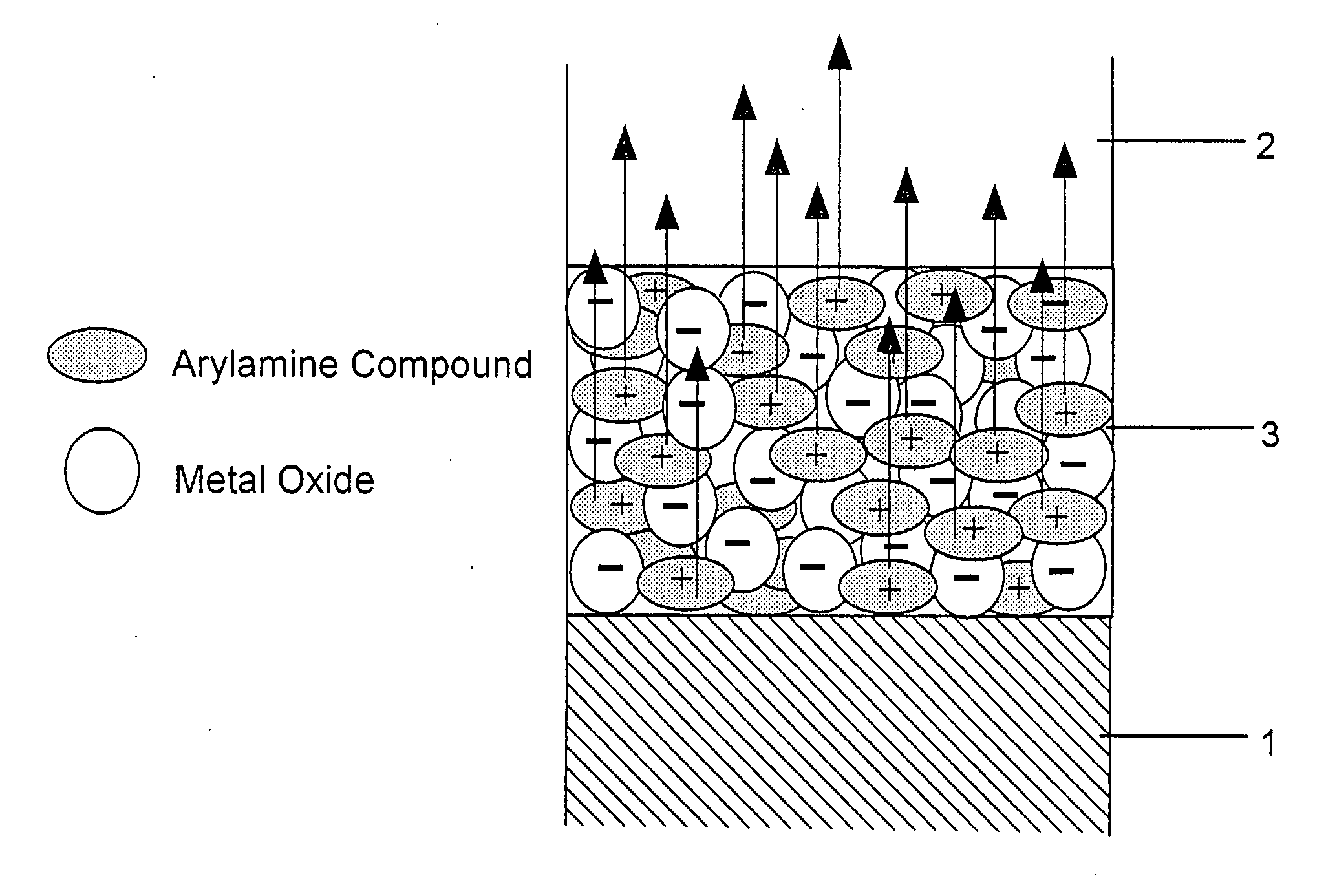
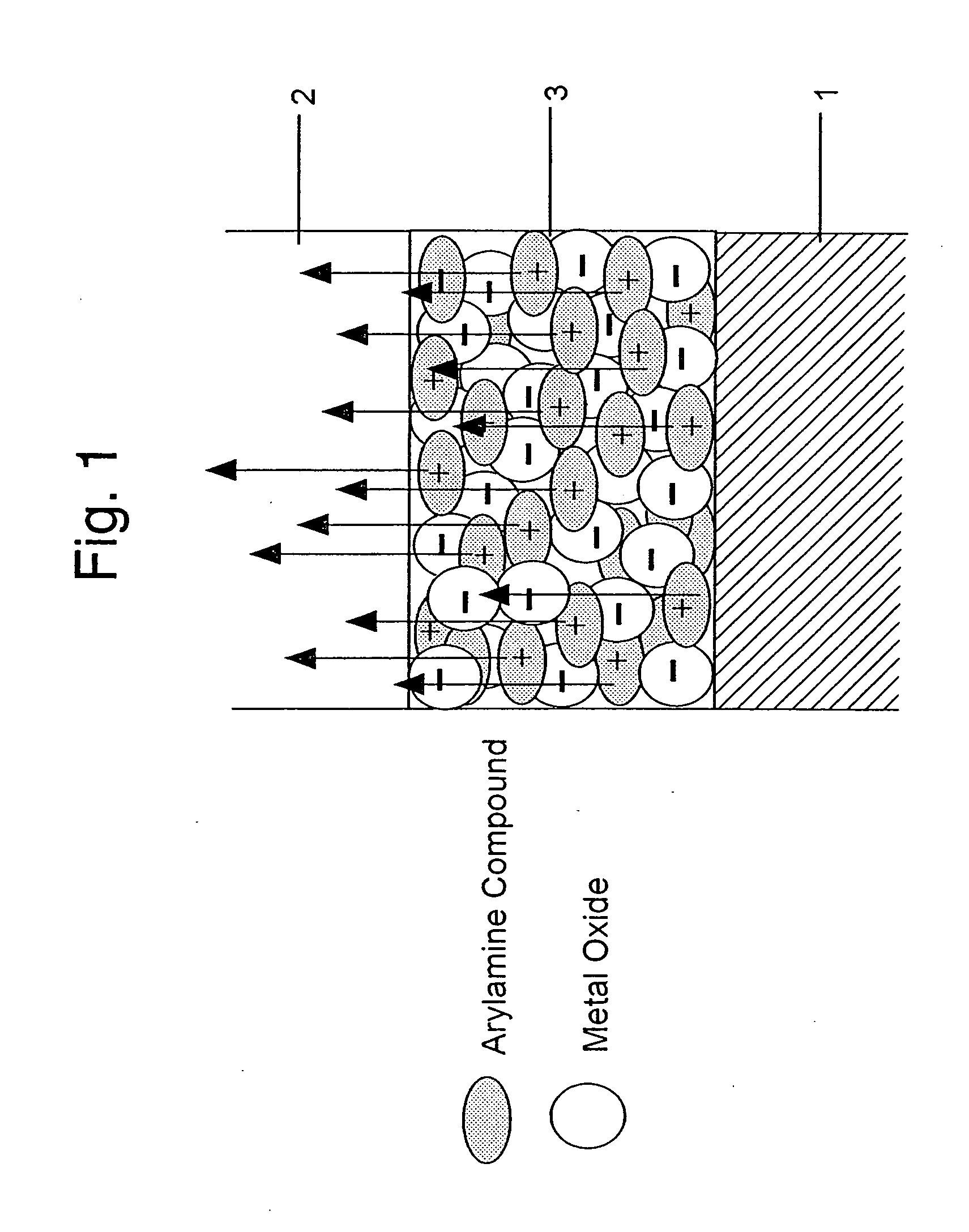
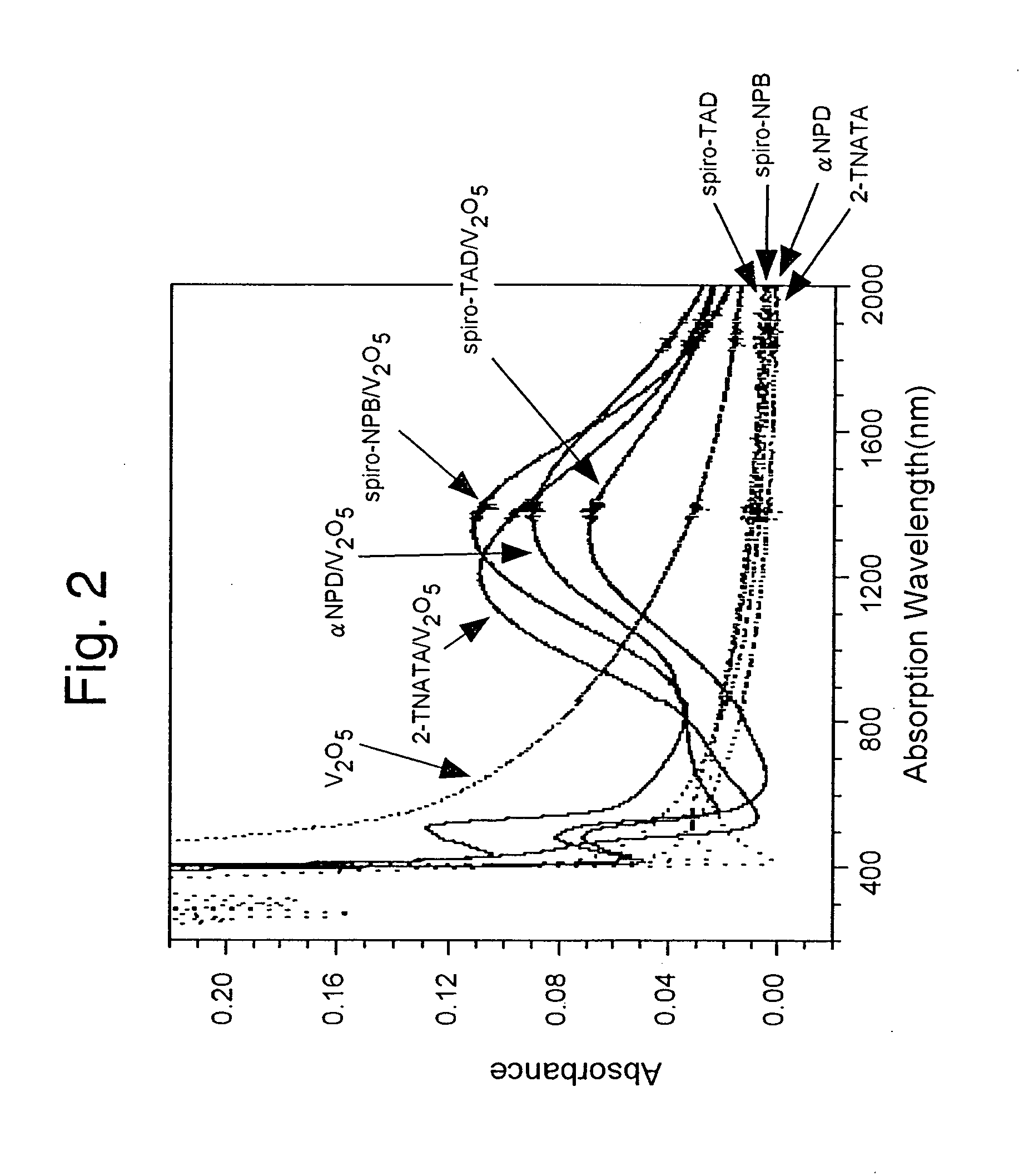
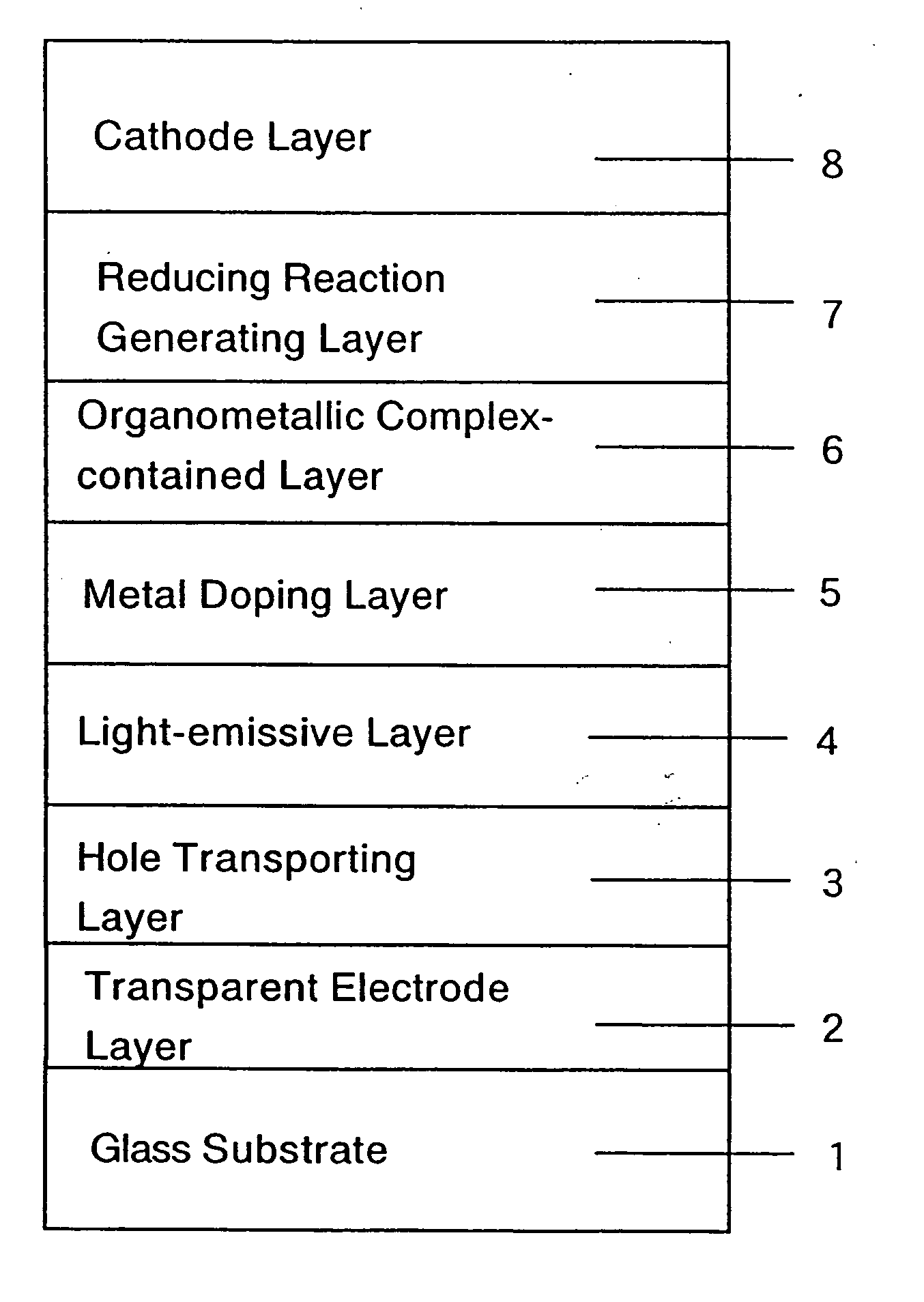
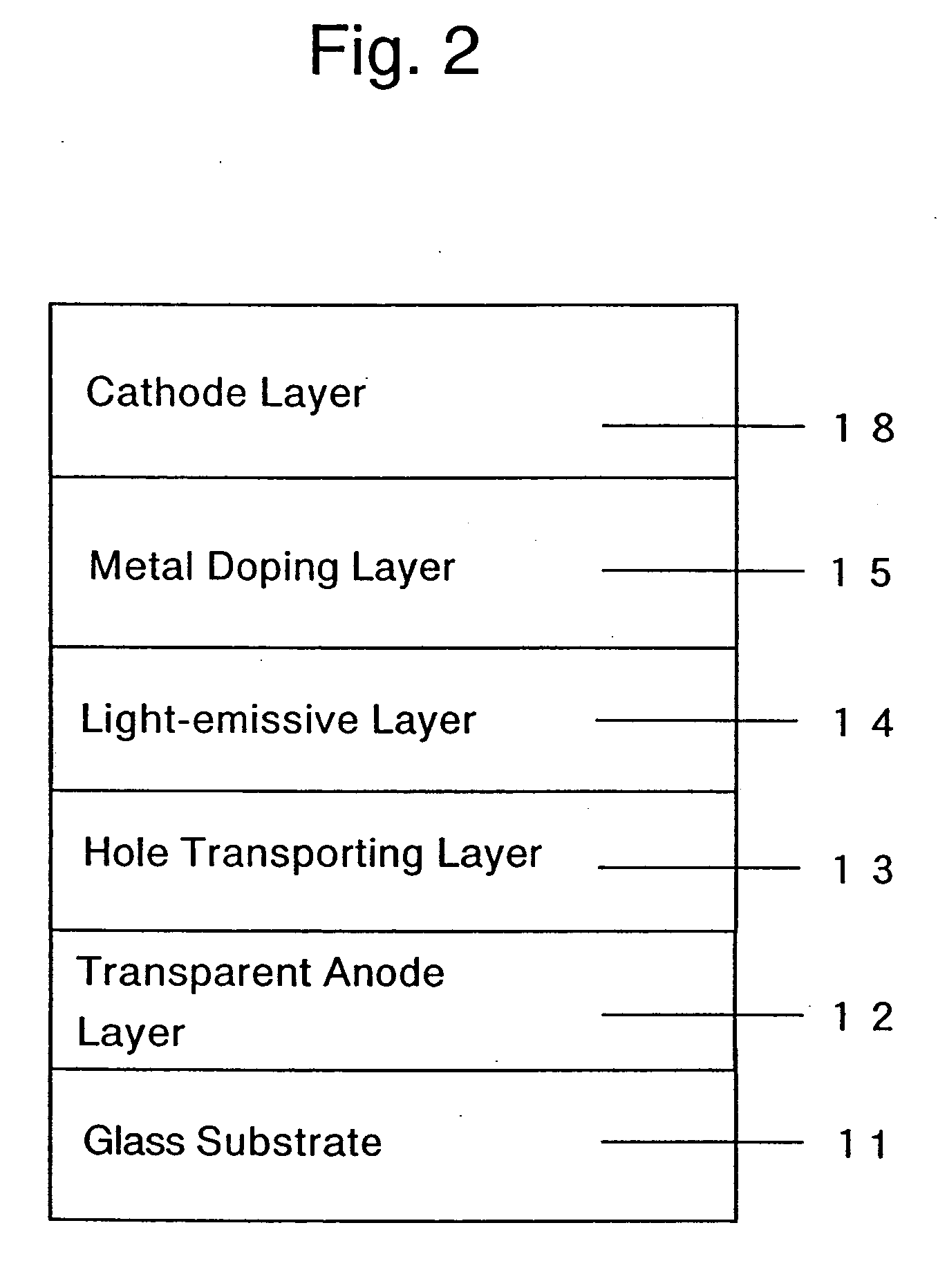
An organic electroluminescent device includes an anode electrode layer; a cathode electrode layer opposed to the anode electrode layer; a hole injection layer provided adjacent to the anode electrode layer an organic structure including at least one light-emissive layer_or at least one light-emissive unit having at least one light-emissive layer; between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer. At least one of the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer is transparent. The hole injection layer includes a mixed layer of a metal oxide and an organic compound. The mixed layer is formed upon co-deposition of the metal oxide and the organic compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Organic semiconductor element
InactiveUS7420203B2Improve reliabilityHigh yieldFinal product manufactureElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic structureOrganic semiconductor
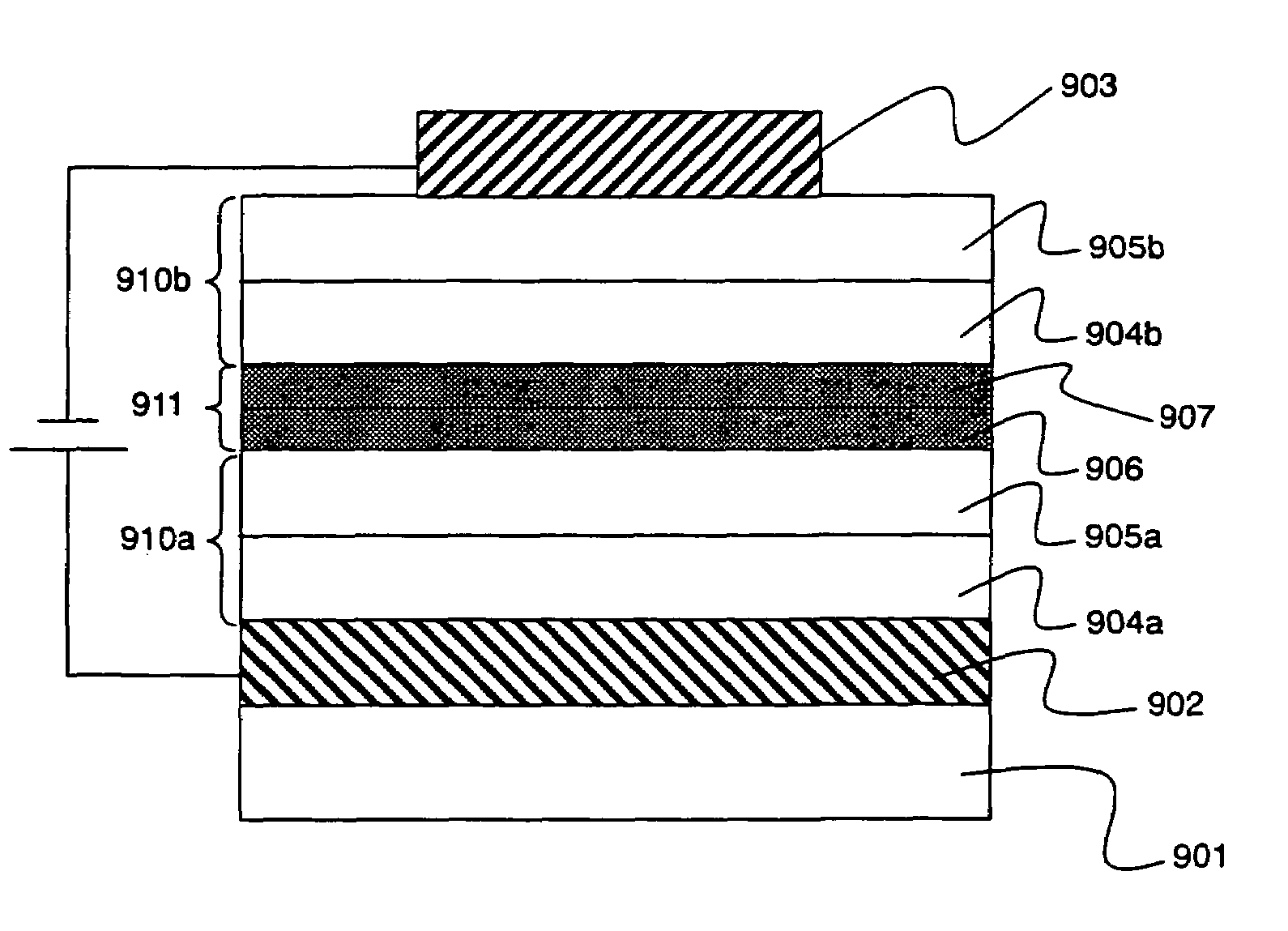
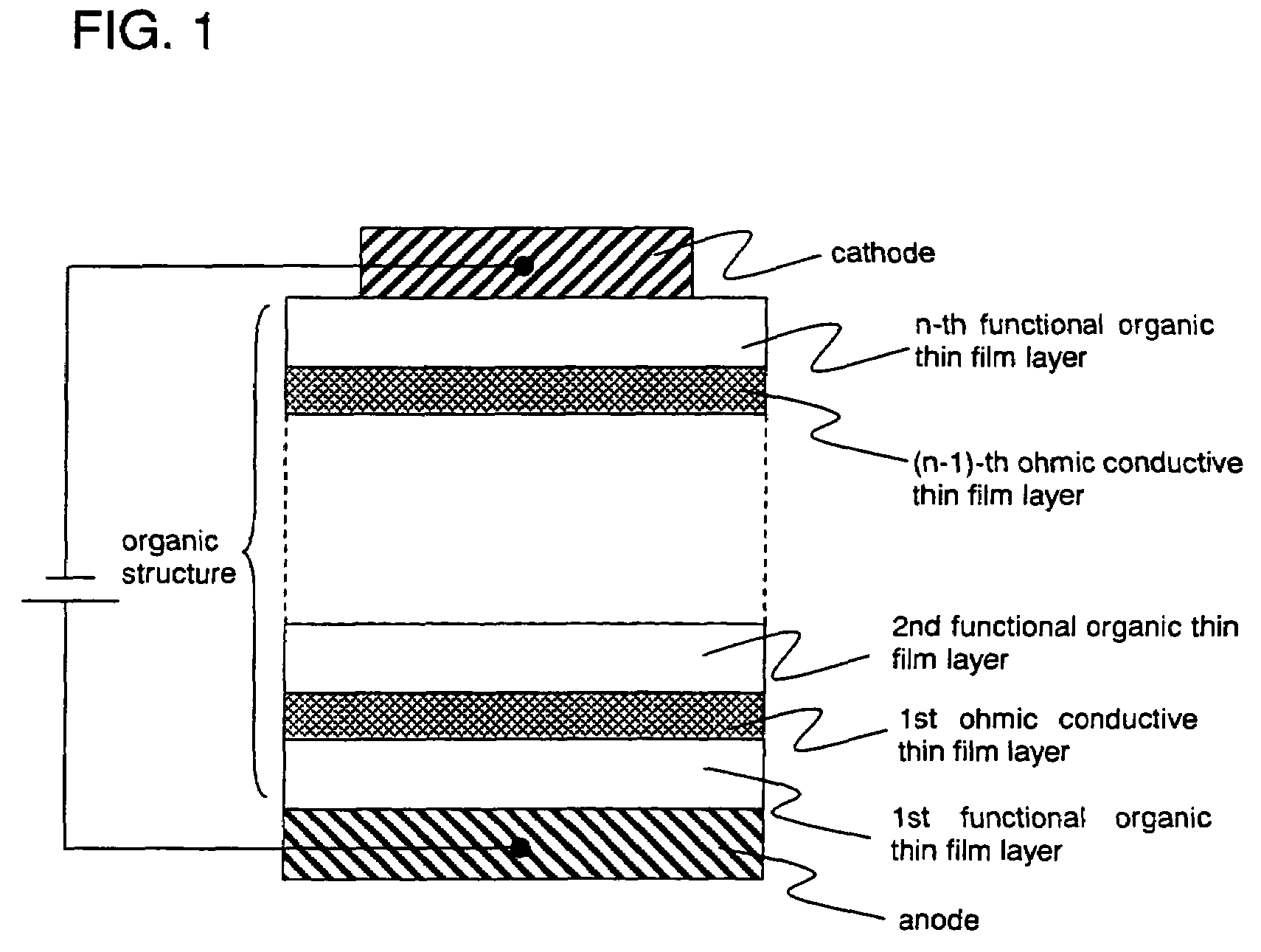
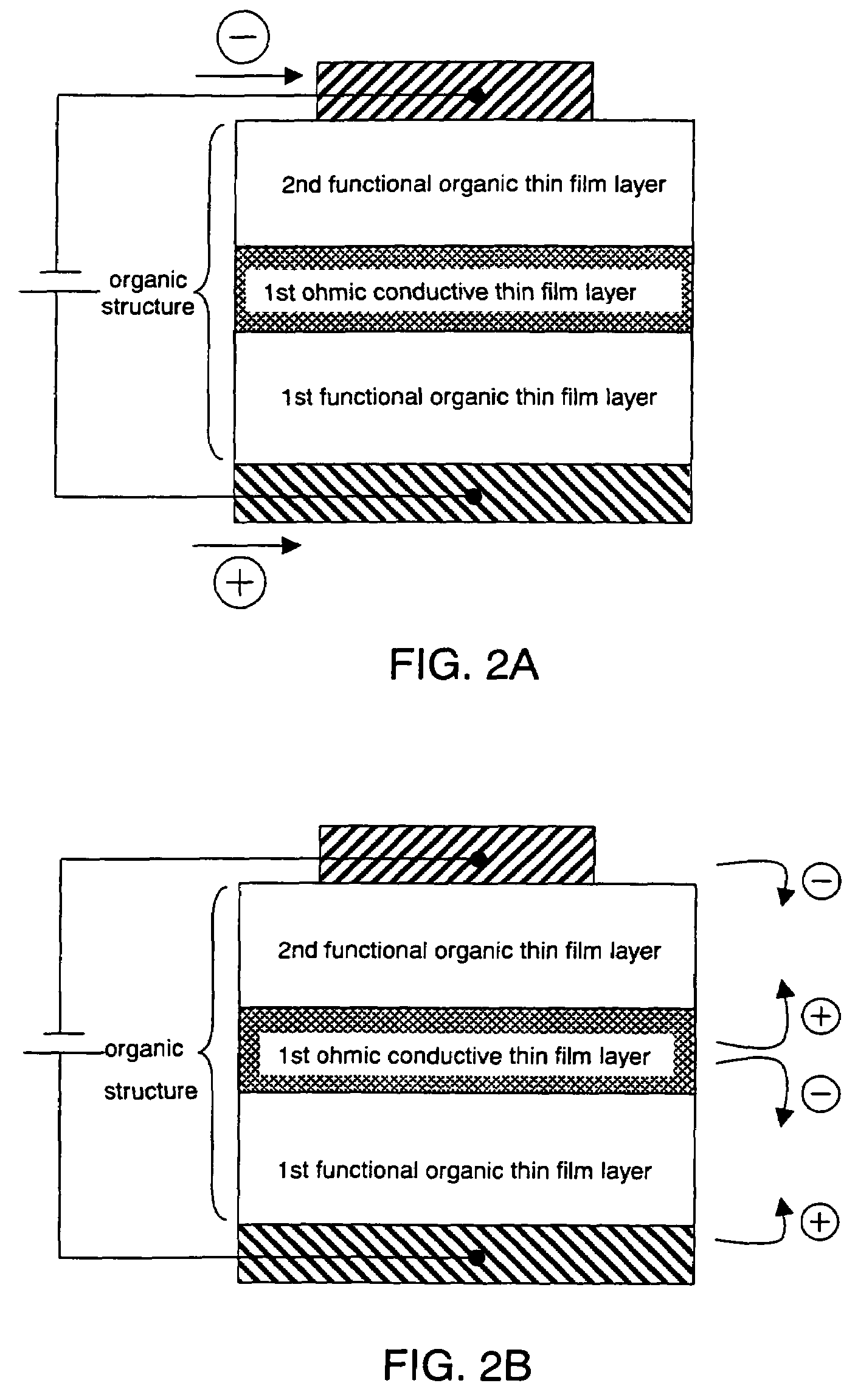
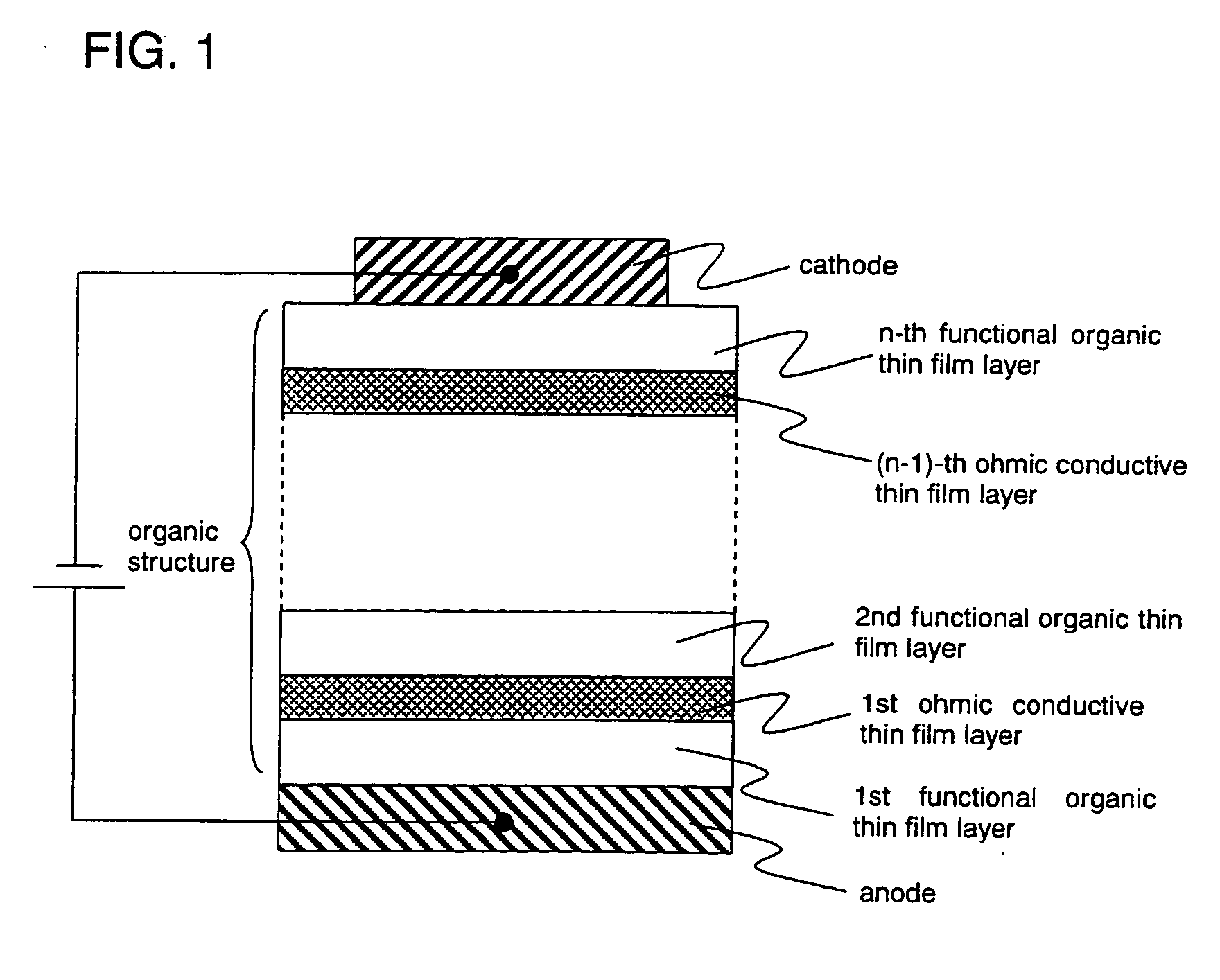
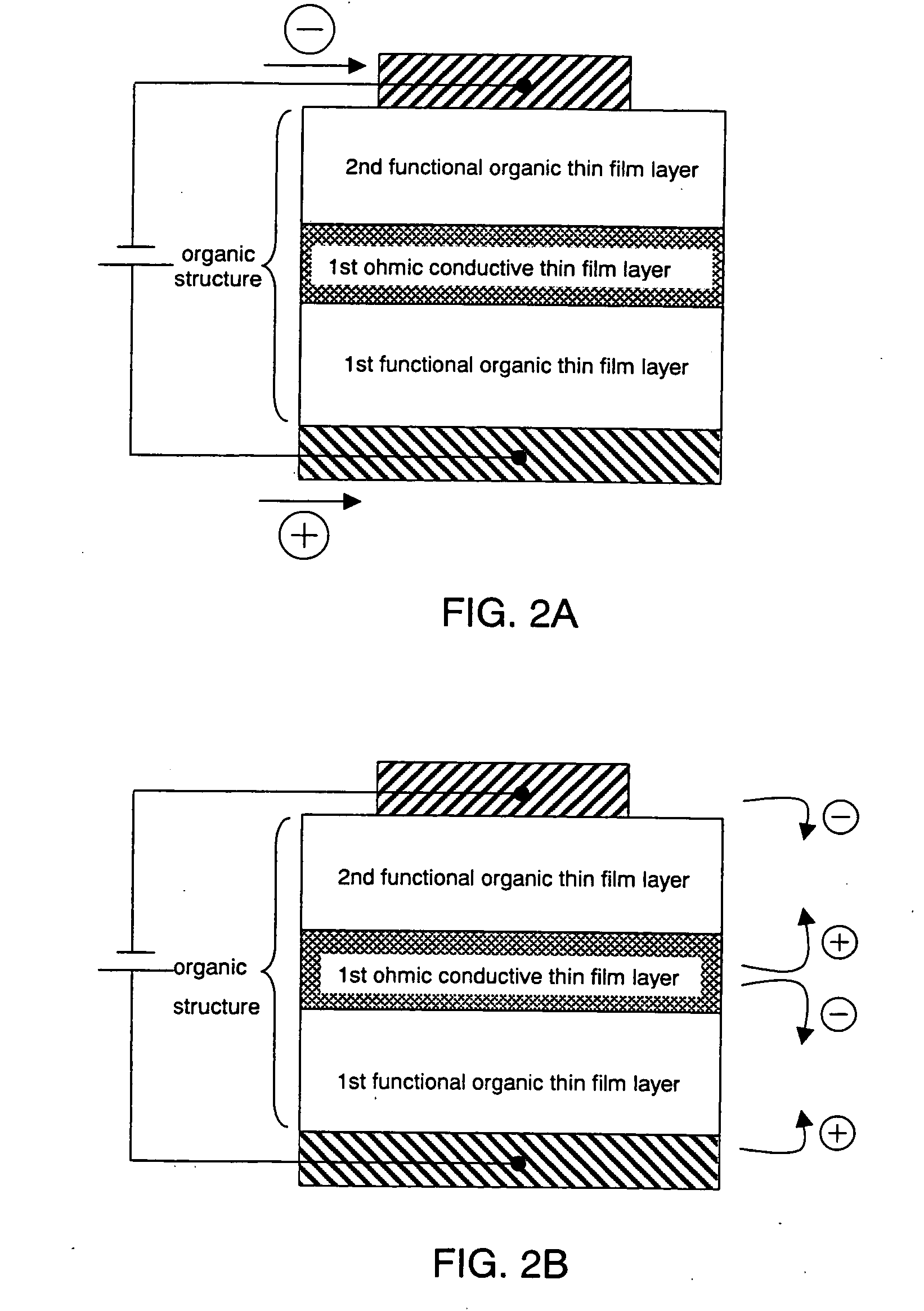
By introducing new concepts into a structure of a conventional organic semiconductor element and without using a conventional ultra thin film, an organic semiconductor element is provided which is more reliable and has higher yield. Further, efficiency is improved particularly in a photoelectronic device using an organic semiconductor. Between an anode and a cathode, there is provided an organic structure including alternately laminated organic thin film layer (functional organic thin film layer) realizing various functions by making an SCLC flow, and a conductive thin film layer (ohmic conductive thin film layer) imbued with a dark conductivity by doping it with an acceptor and a donor, or by the like method.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device and production process thereof
ActiveUS20050084713A1Stable device propertyIncrease the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic structureAlkaline earth metal
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
Orthogonal Procesing of Organic Materials Used in Electronic and Electrical Devices
ActiveUS20110159252A1Avoid damageImprove throughputOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsOrganic structureMethacrylate
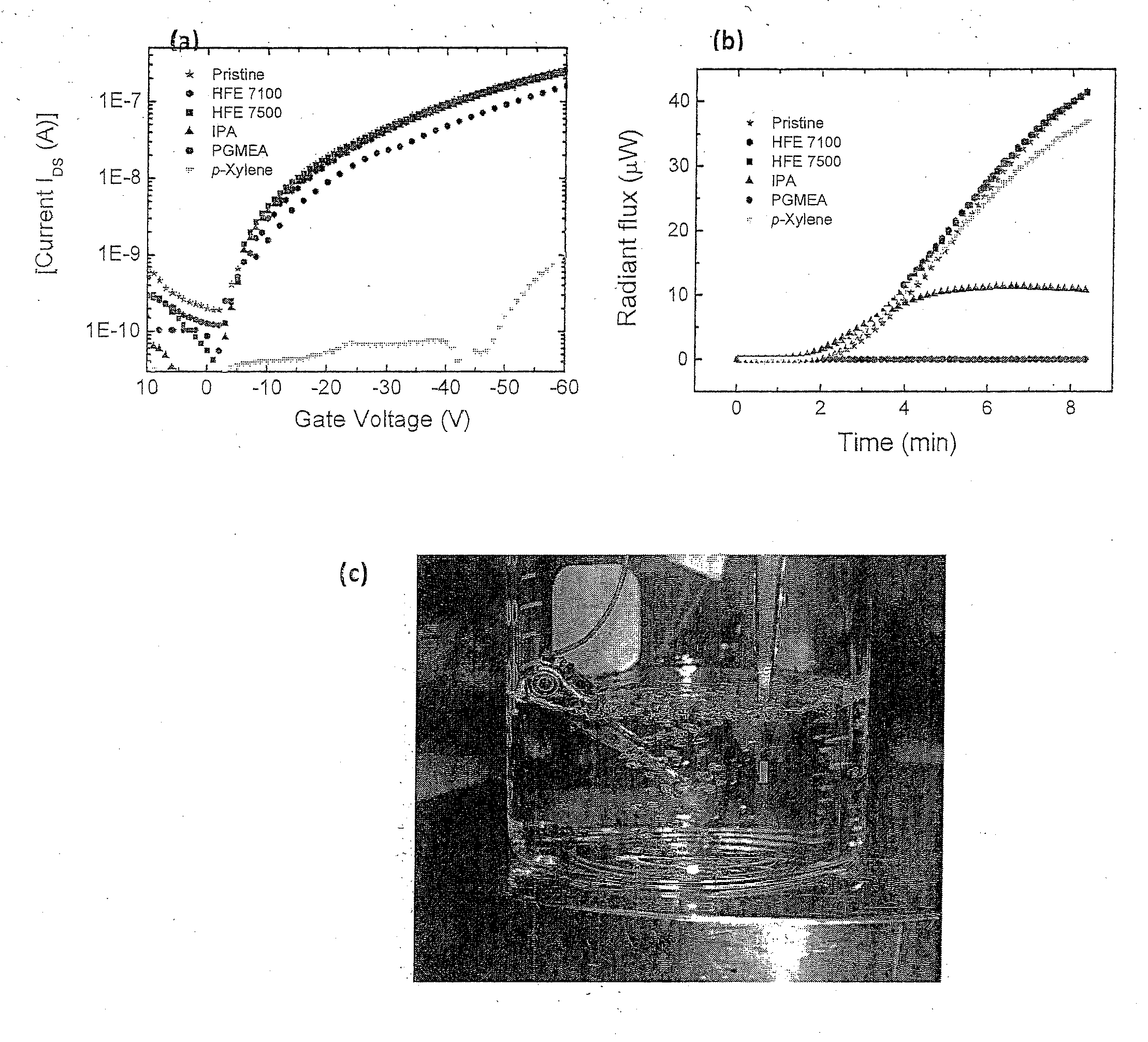
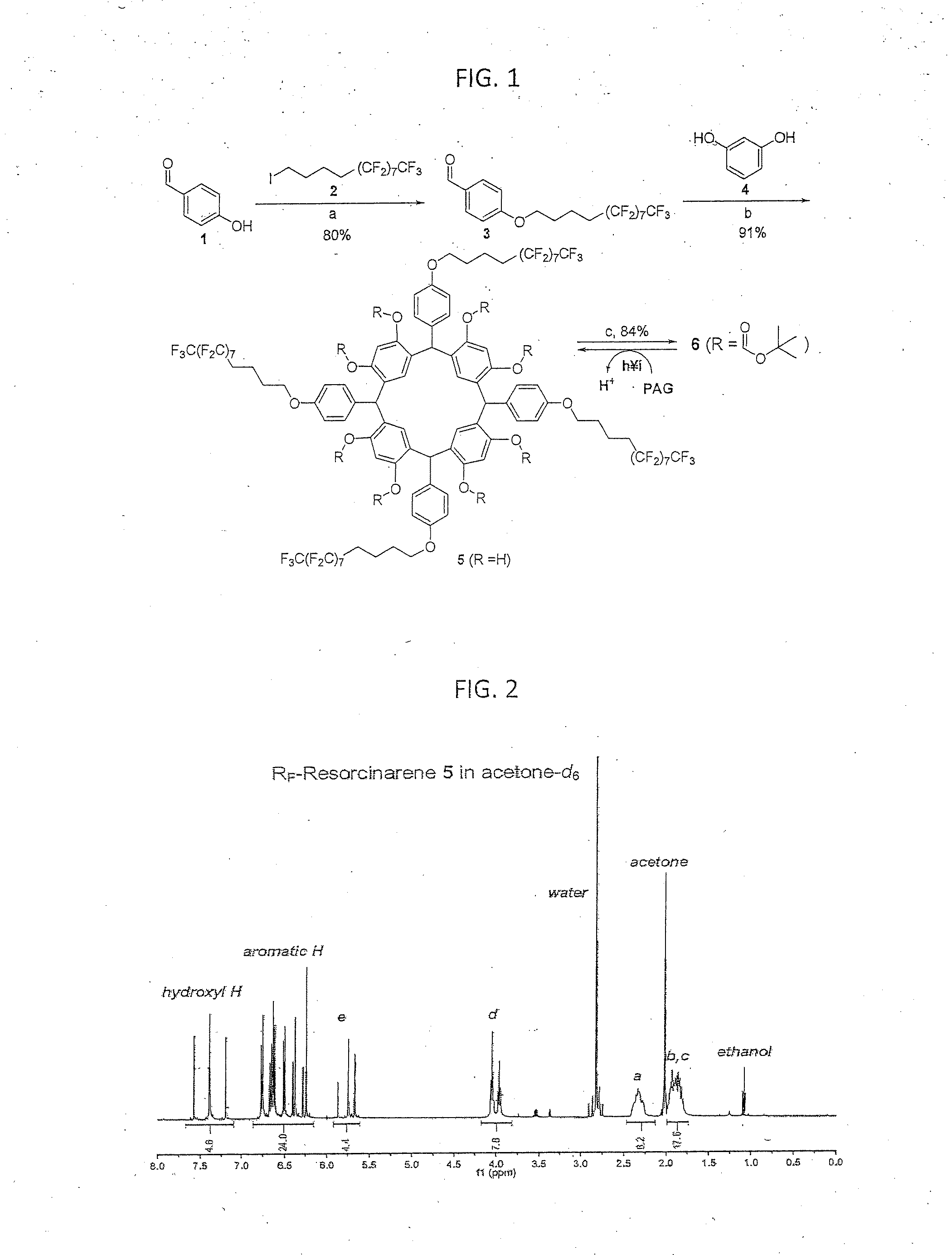
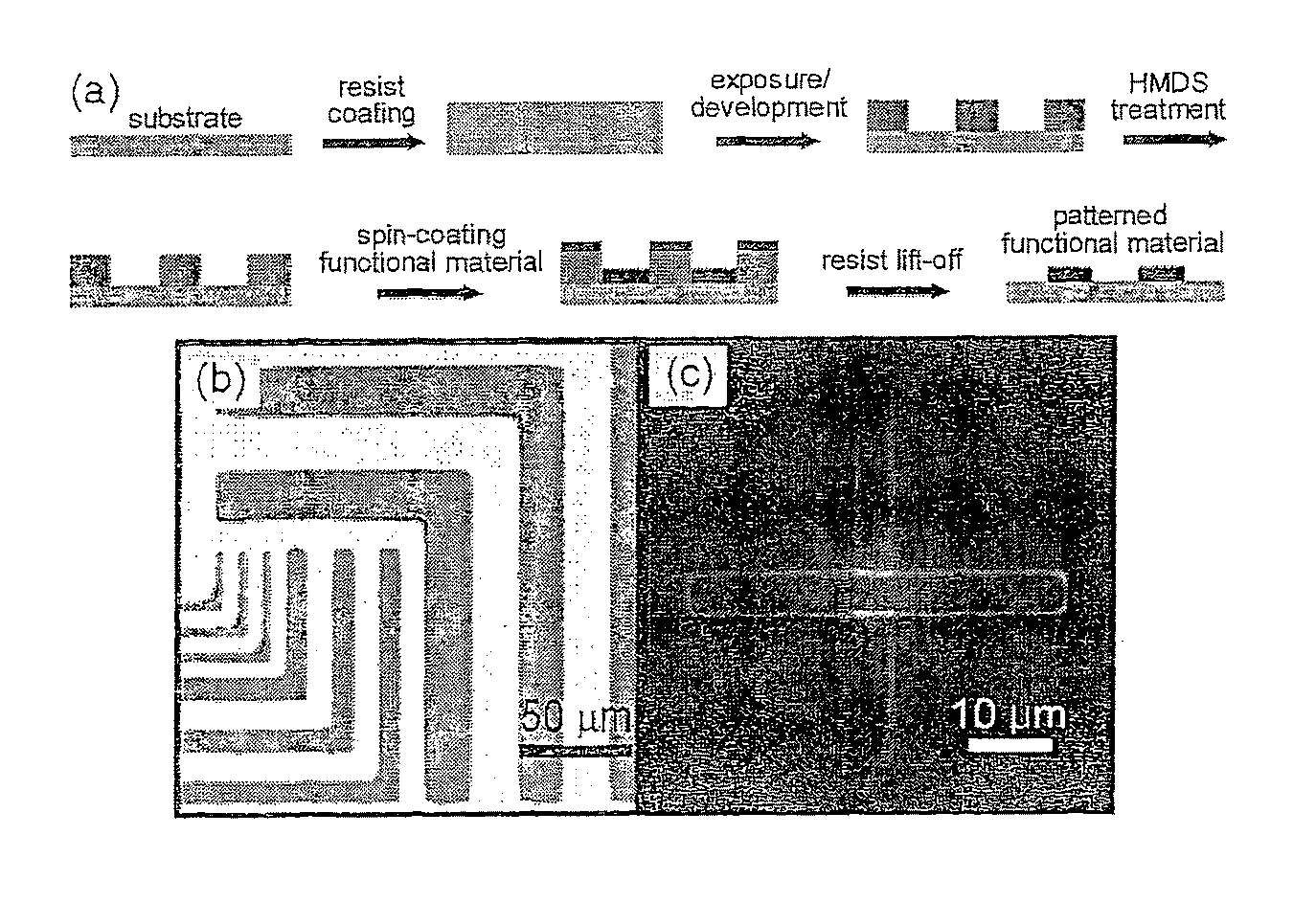
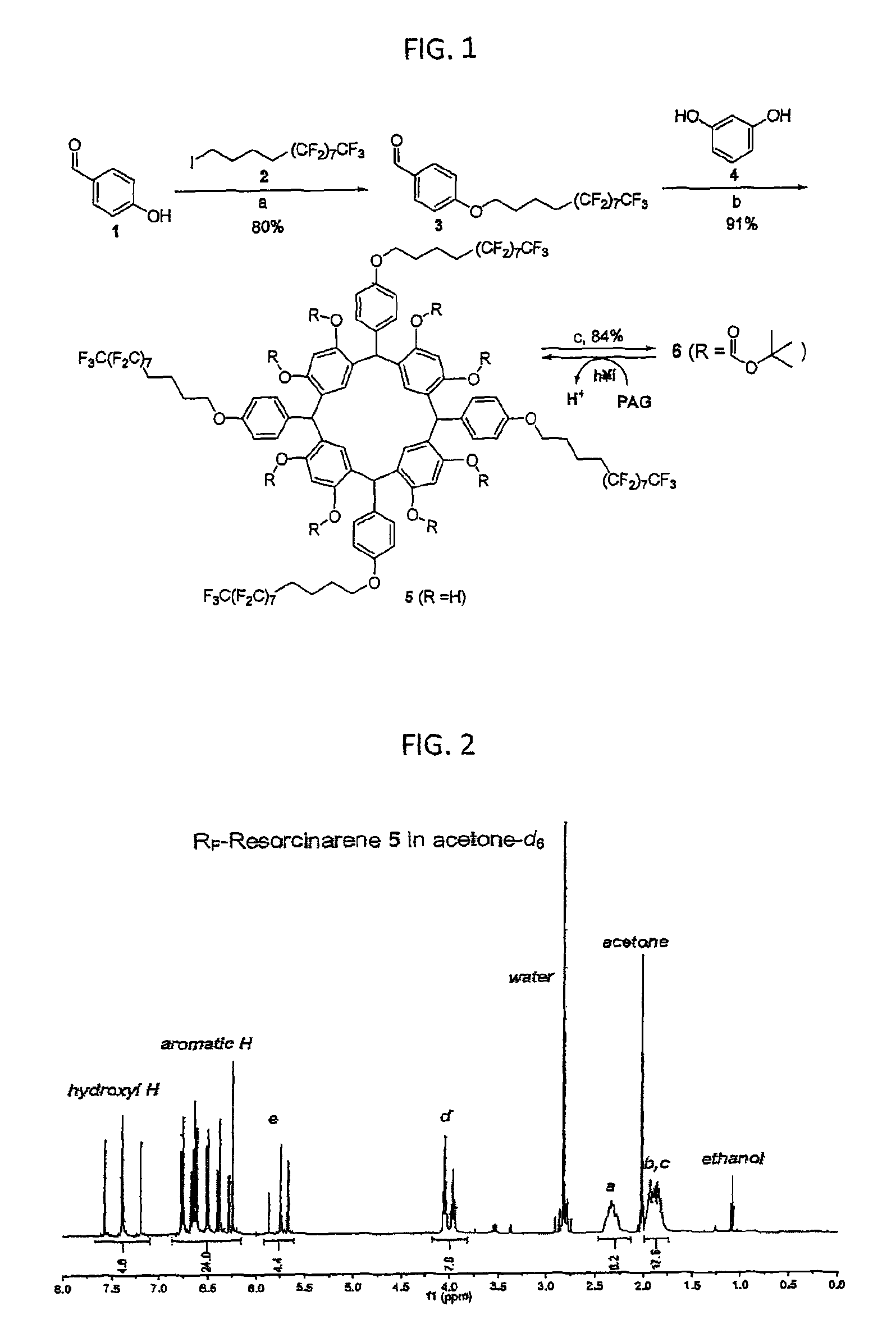
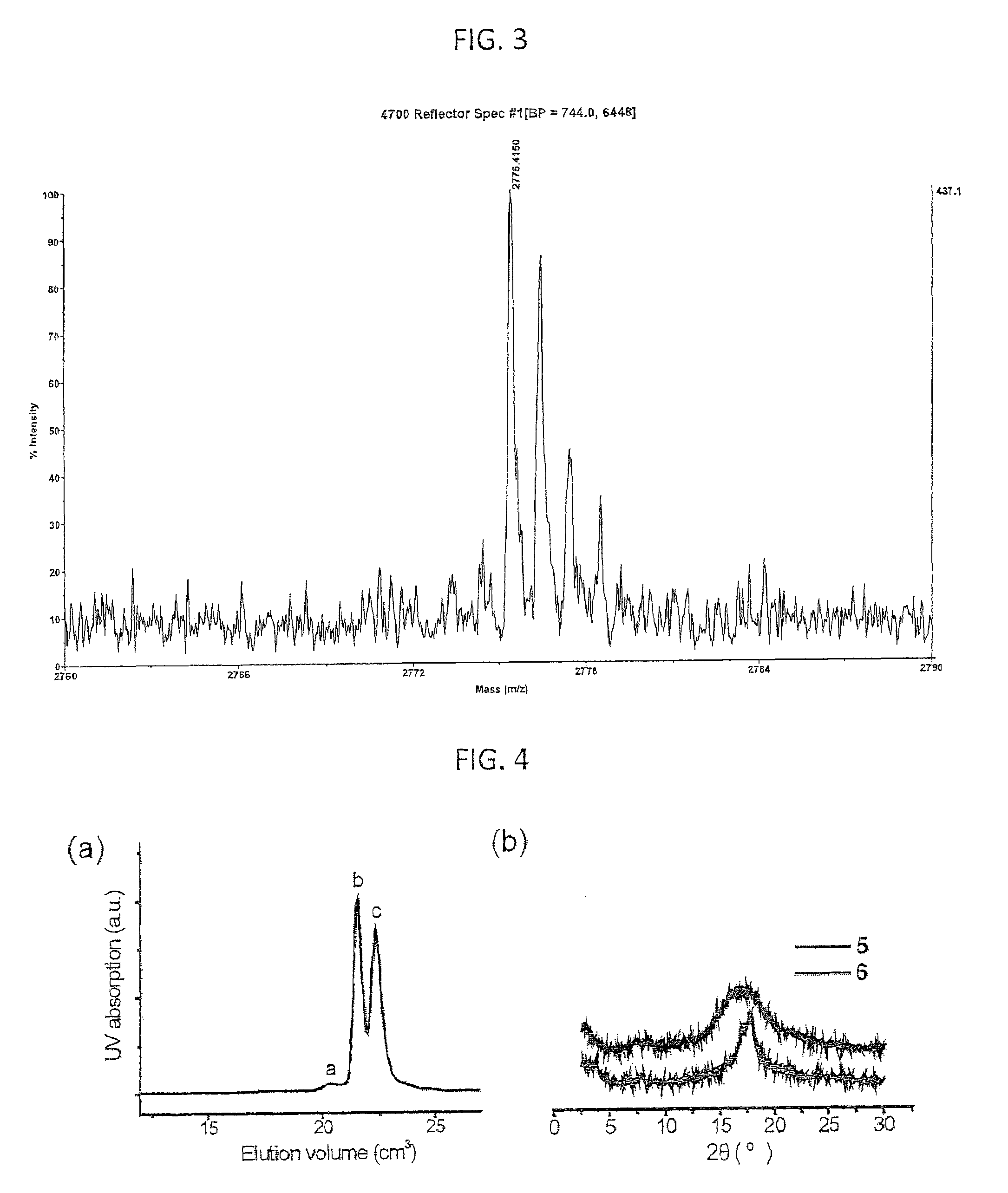
An orthogonal process for photolithographic patterning organic structures is disclosed. The disclosed process utilizes fluorinated solvents or supercritical CO2 as the solvent so that the performance of the organic conductors and semiconductors would not be adversely affected by other aggressive solvent. One disclosed method may also utilize a fluorinated photoresist together with the HFE solvent, but other fluorinated solvents can be used. In one embodiment, the fluorinated photoresist is a resorcinarene, but various fluorinated polymer photoresists and fluorinated molecular glass photoresists can be used as well. For example, a copolymer perfluorodecyl methacrylate (FDMA) and 2-nitrobenzyl methacrylate (NBMA) is a suitable orthogonal fluorinated photoresist for use with fluorinated solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide in a photolithography process. The combination of the fluorinated photoresist and the fluorinated solvent provides a robust, orthogonal process that is yet to be achieved by methods or devices known in the art.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Organic semiconductor element
InactiveUS20060091797A1Improve reliabilityHigh yieldDischarge tube luminescnet screensFinal product manufactureOrganic structureOrganic semiconductor
By introducing new concepts into a structure of a conventional organic semiconductor element and without using a conventional ultra thin film, an organic semiconductor element is provided which is more reliable and has higher yield. Further, efficiency is improved particularly in a photoelectronic device using an organic semiconductor. Between an anode and a cathode, there is provided an organic structure including alternately laminated organic thin film layer (functional organic thin film layer) realizing various functions by making an SCLC flow, and a conductive thin film layer (ohmic conductive thin film layer) imbued with a dark conductivity by doping it with an acceptor and a donor, or by the like method.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Inverter with dual-gate organic thin-film transistor
InactiveUS20070272948A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic structureOrganic semiconductor
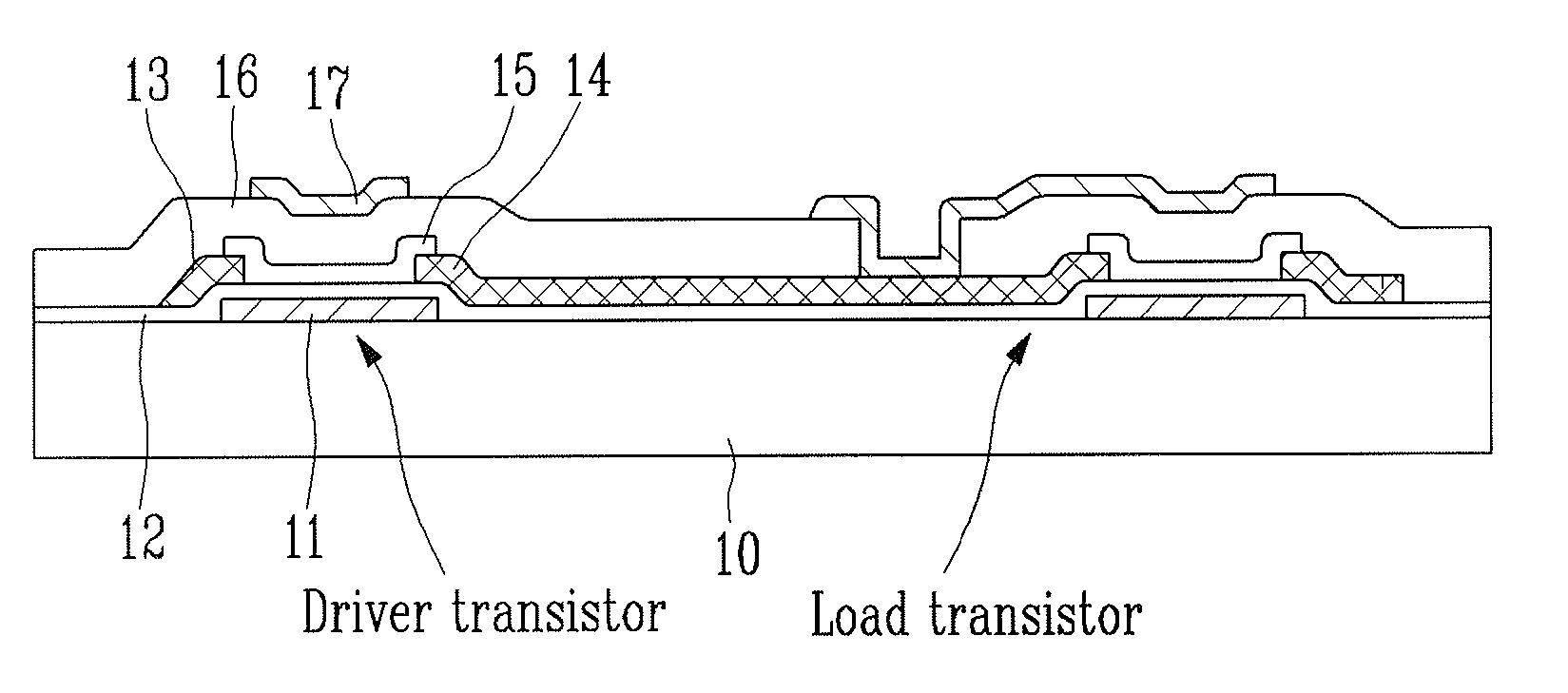
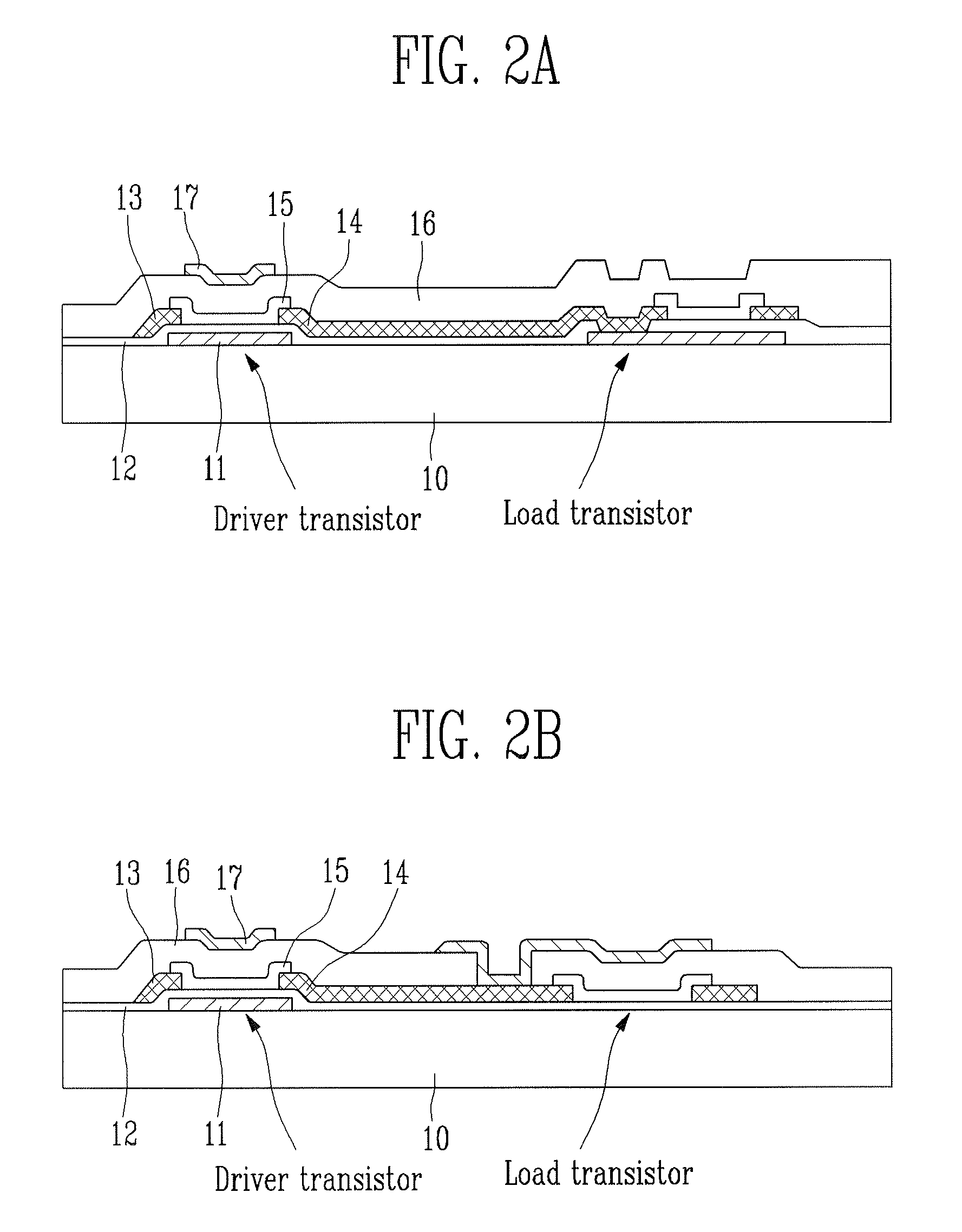
Provided is an inverter having a new structure capable of easily controlling a threshold voltage according to position in fabricating an inverter circuit on a plastic substrate using an organic semiconductor. A driver transistor is formed with a dual-gate structure and a positive bias voltage is applied to the top gate of the driver transistor so that a body effect appears in the organic semiconductor. Accordingly, the threshold voltage is shifted to a negative zone due to positive potential applied to the top gate of the driver transistor so that the driver transistor acts as an enhancement type transistor. A dual-gate organic structure may be applied to a load transistor rather than the driver transistor, or a p-type dual-gate organic transistor structure may be applied to both the driver transistor and the load transistor. Lifespan of the device can be increased, reliability of the device can be improved, and an organic inverter can be provided in which characteristics of organic electronic elements are easily adjusted according to circuit design even after the organic electronic elements are fabricated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
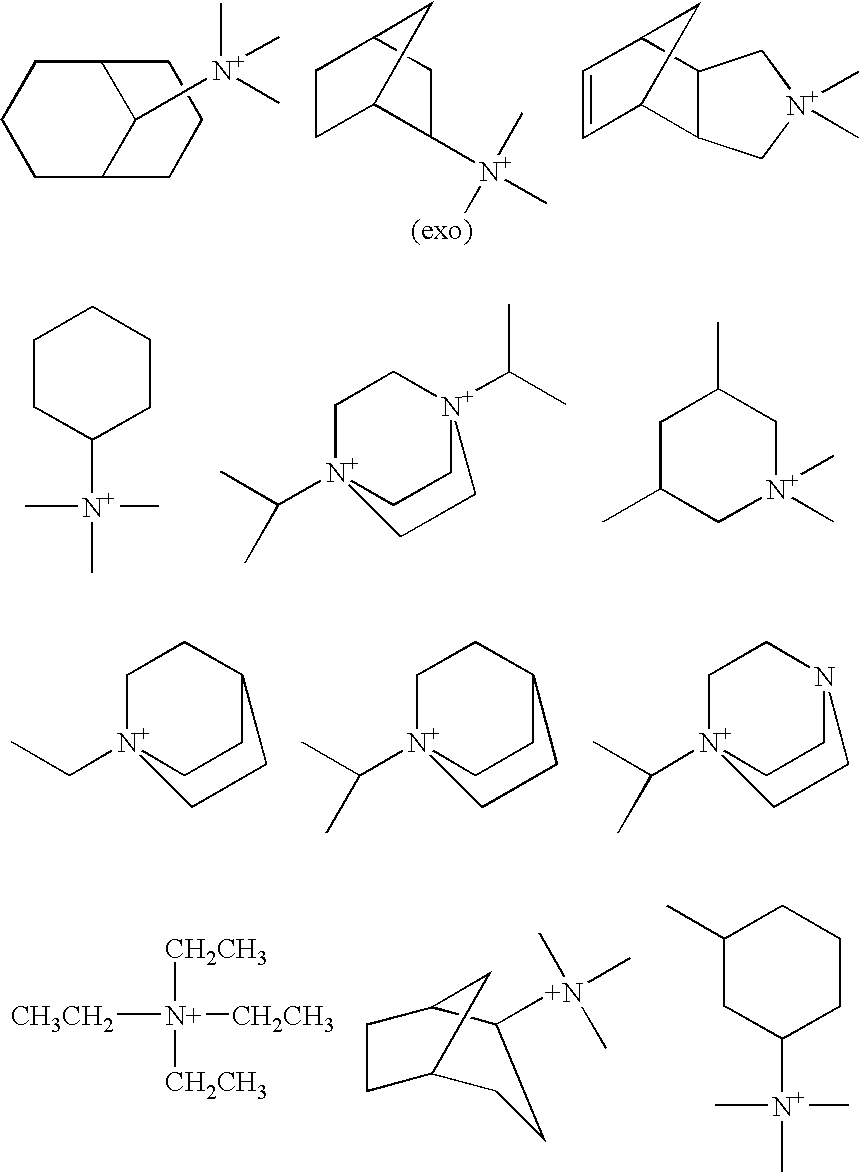
Preparation of Molecular Sieves Using a Structure Directing Agent and An N, N, N-Triakyl Benzyl Quaternary Ammonium Cation
Crystalline molecular sieves are prepared using a mixture comprising an organic structure directing agent capable of forming the molecular-sieve and an N,N,N-trialkyl benzyl quaternary ammonium cation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
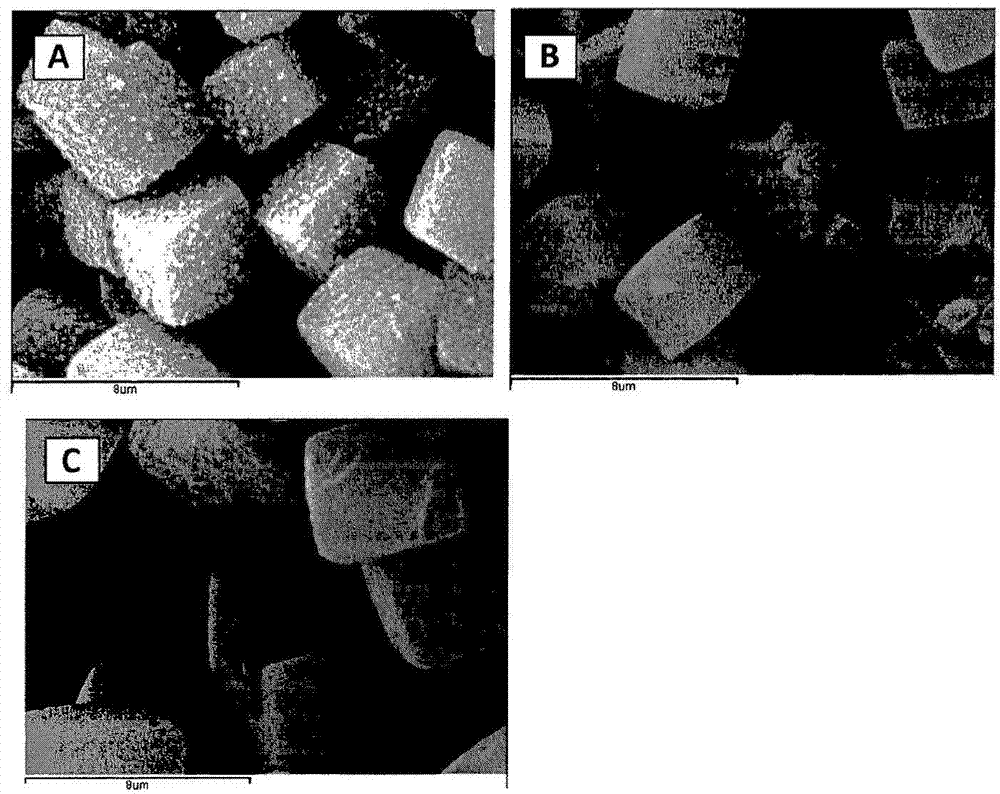
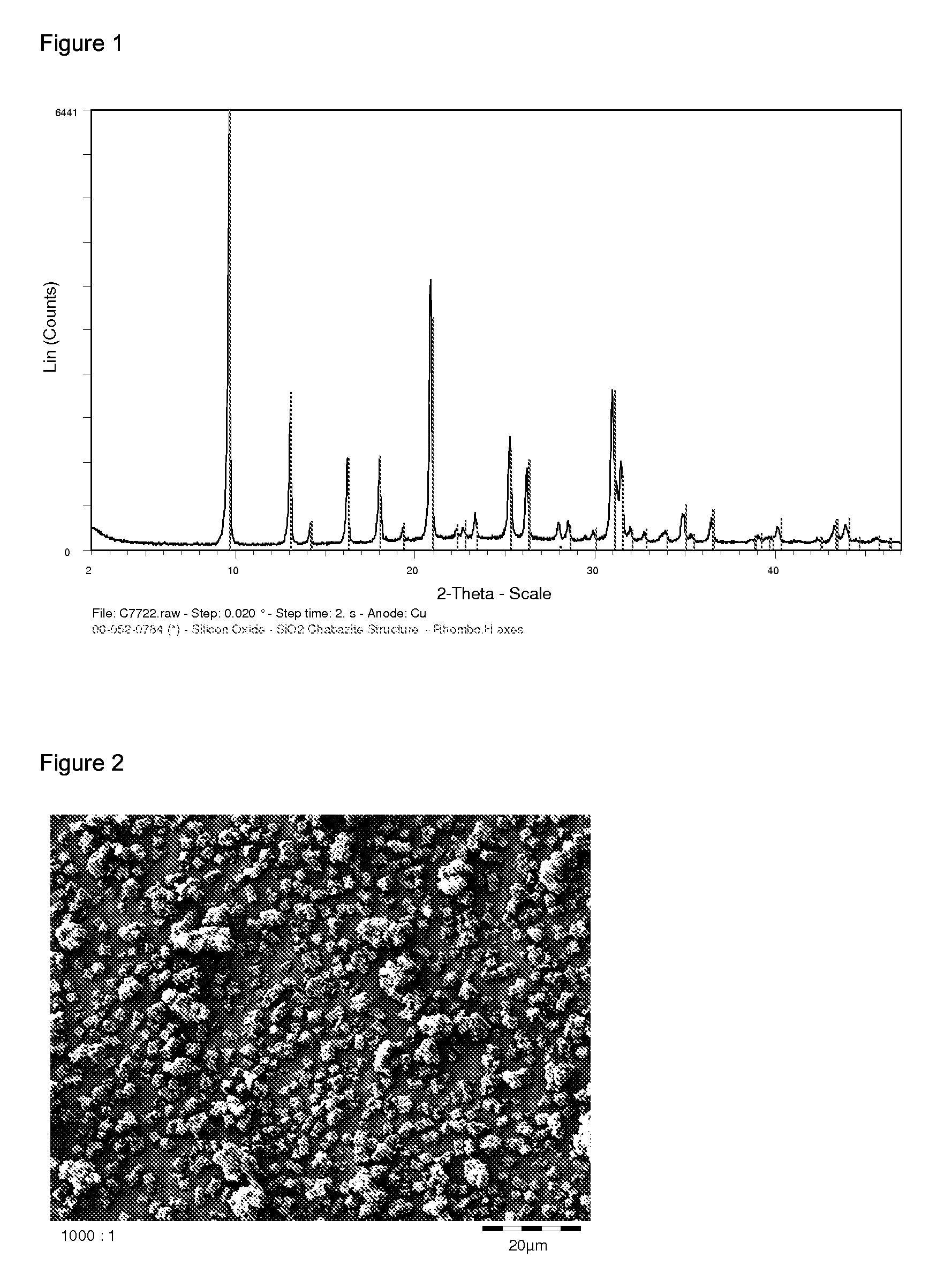
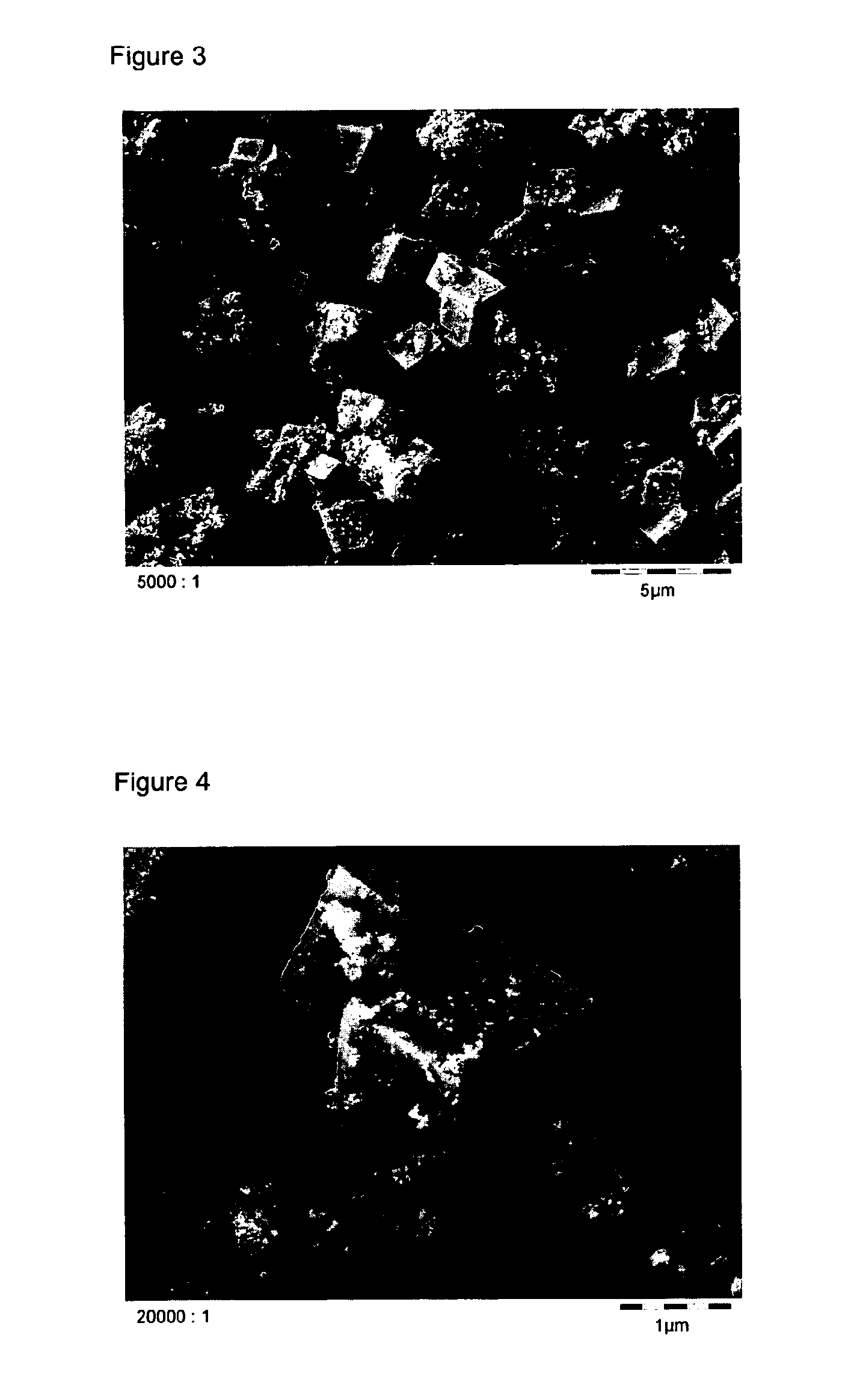
Large crystal, organic-free chabazite, methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20120269719A1SAR of the product may be increasedAluminium compoundsGas treatmentOrganic structureCrystalline materials
Owner:PQ CORP (US)
Method for preparing molecular sieve-multielement oxide composite integrally extruded denitration catalyst
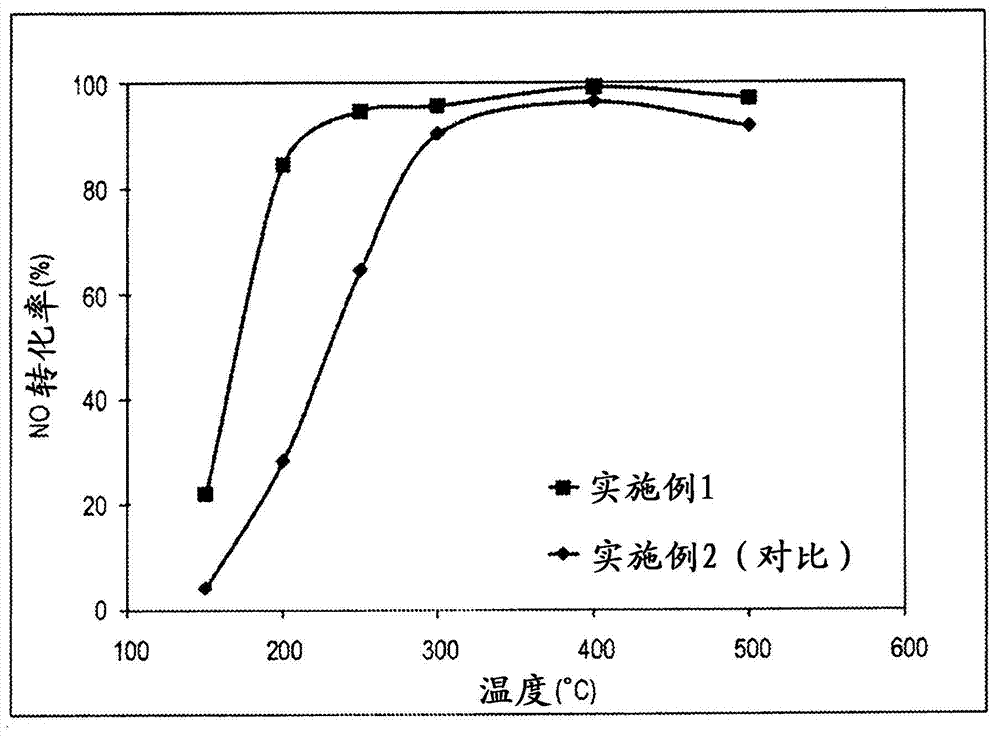
ActiveUS20190046962A1Wide operating temperature rangeImprove efficiencyGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic structureMolecular sieve
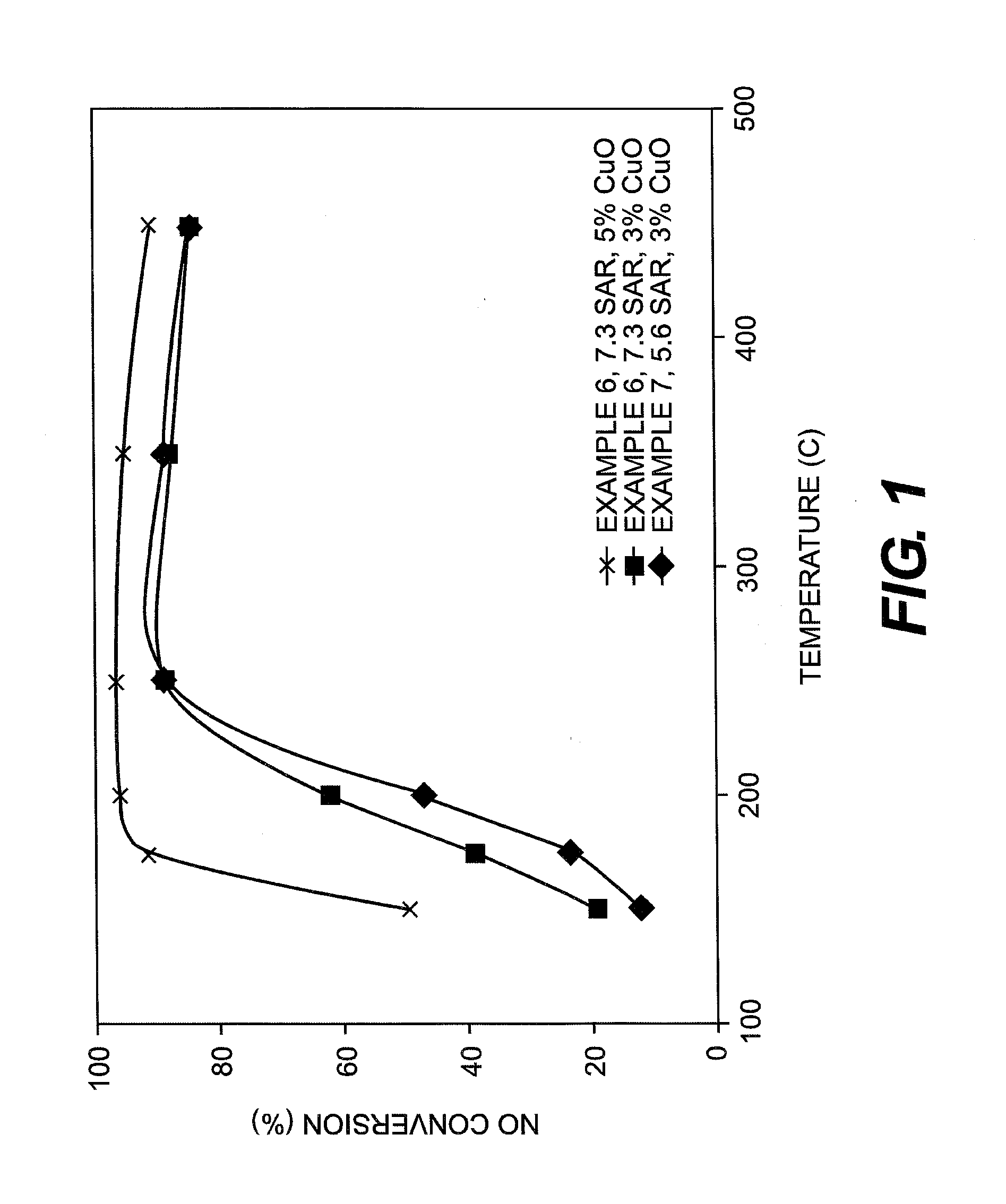
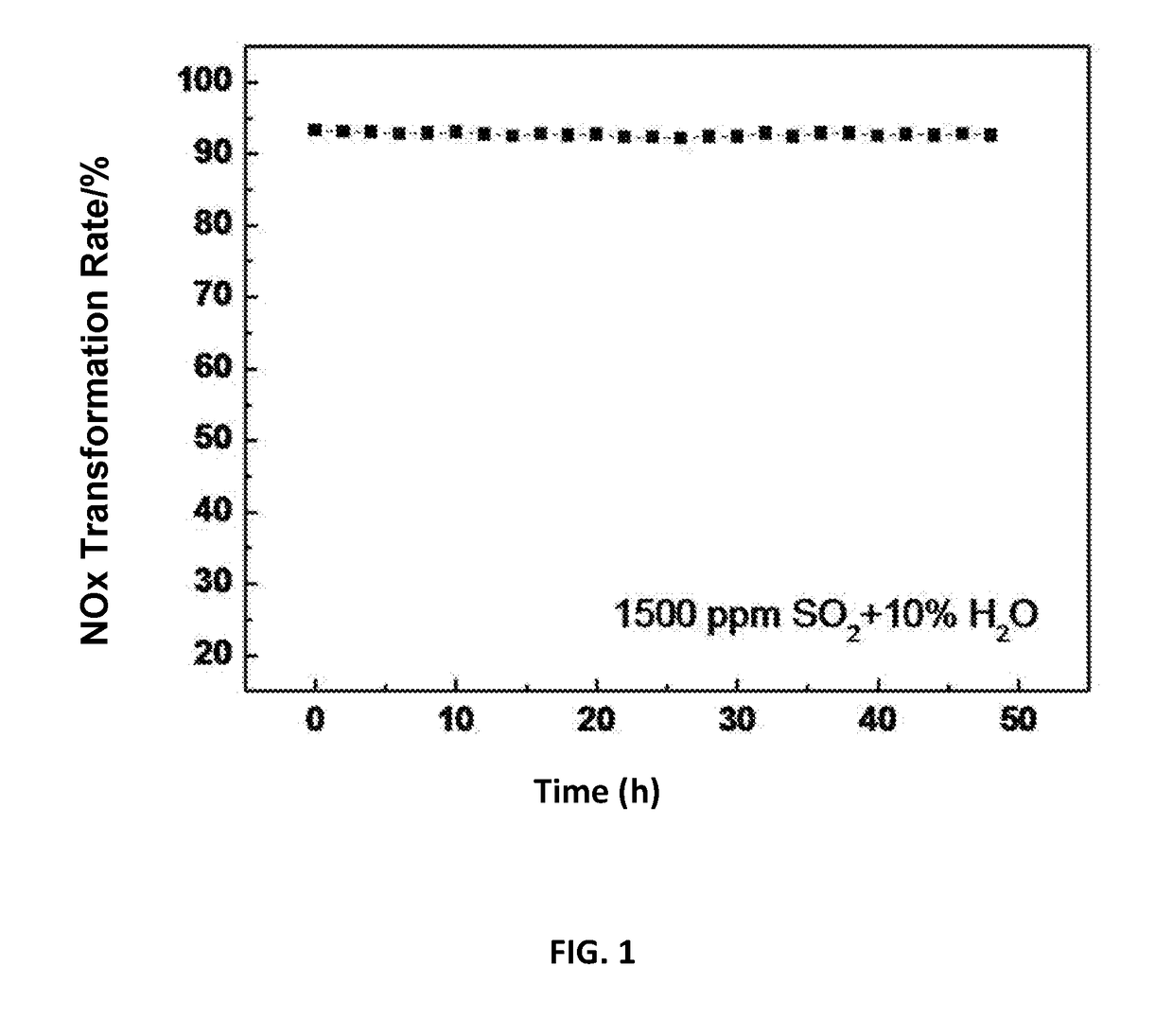
Disclosed is a preparation method for a molecular sieve-multiple oxide composite integral extrusion type denitration catalyst, belonging to the technical fields of atmosphere pollution control and environment-friendly catalytic materials. The preparation method comprises: constructing an organic structure coating on the surface of a metal ion-exchanged molecular sieves and synchronously adding multiple oxide components, thus obtaining an ion-exchanged molecular sieve-multiple oxide composite denitration catalyst active component; and then mixing, kneading into paste, staling, carrying out integral extrusion forming, drying, and calcining, thus obtaining the integral extrusion type denitration catalyst. The molecular sieve-multiple oxide composite integral extraction type denitration catalyst has a denitration efficiency more than 80% at the temperature ranging from 250° C. to 420° C. in the presence of 10% steam and 500 ppm sulfuric dioxide. According to the present invention, the application field of metal-loaded molecular sieve denitration catalysts is widened, and thus the metal-loaded molecular sieve denitration catalysts can be widely applied to the flue gas denitration of stationary sources.
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Method and device for utilizing high value through pyrolysis and gasification of coal
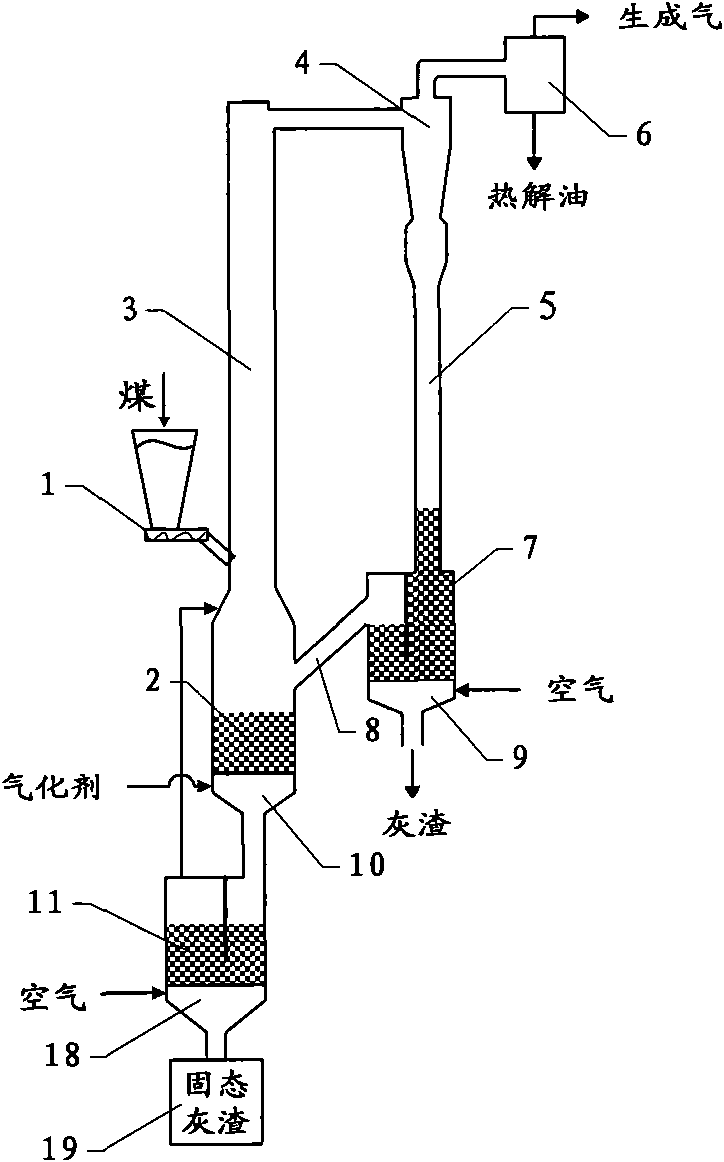
ActiveCN101781583ARealize joint productionFast pyrolysisLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCombined combustion mitigationOrganic structureFluidized bed
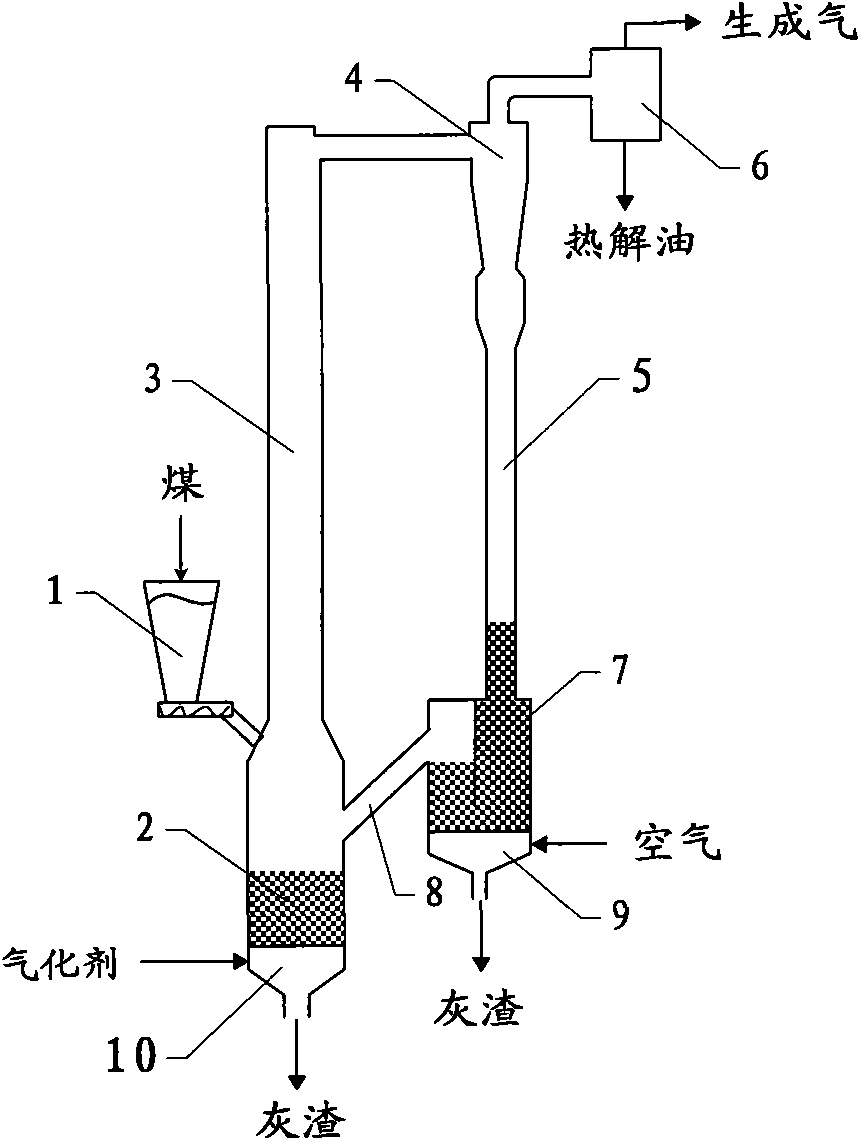
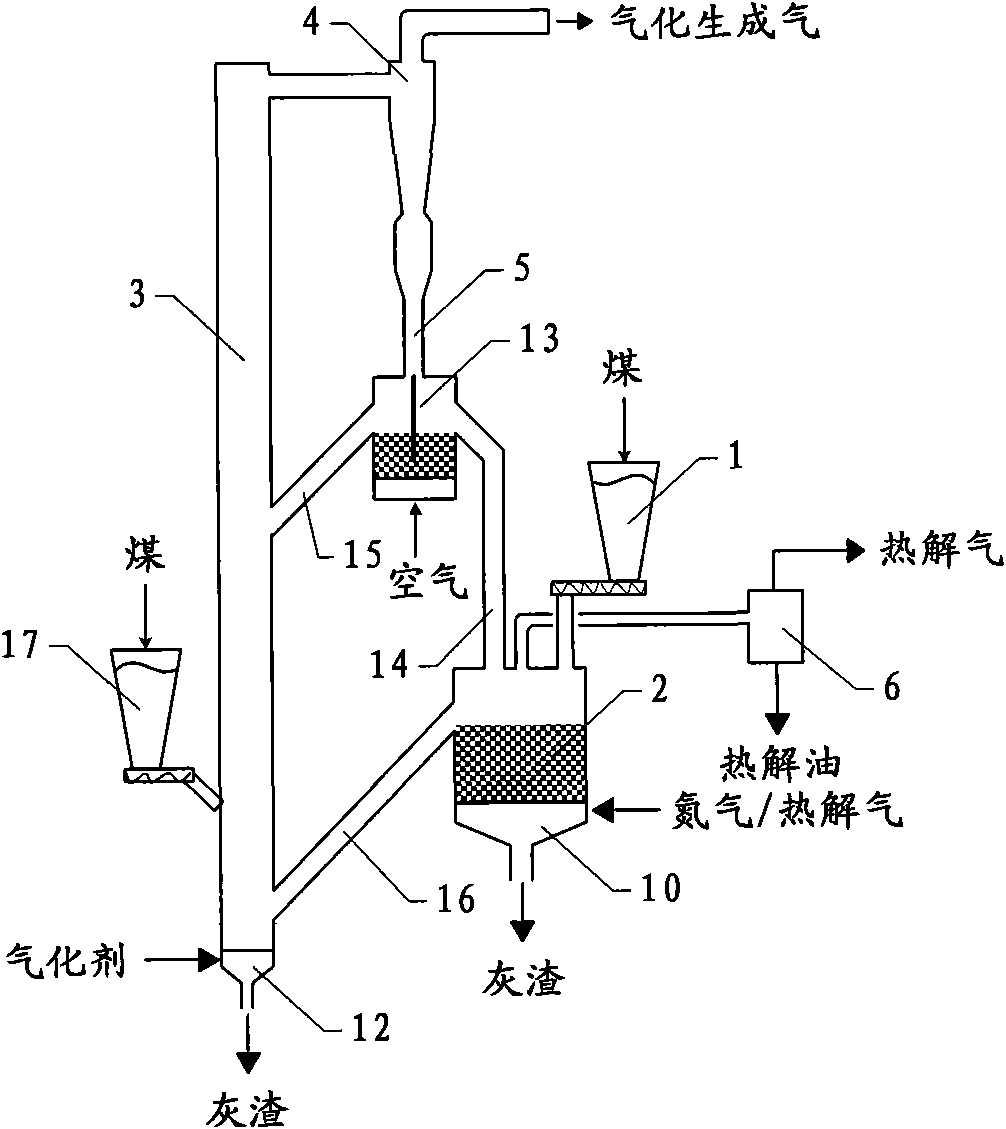
The invention relates to a method and a device for utilizing high value through pyrolysis and gasification of coal. The pyrolysis and gasification processes of the coal are separated in a mode of coupling a dilute phase conveying bed and a dense phase fluidized bed; and the coal is partially or wholly pyrolyzed before gasification, and co-production of pyrolysis gas, gasification generated gas and pyrolysis oil is realized. The dilute phase conveying bed and the dense phase fluidized bed can be coupled in two modes, namely upper-lower coupling and left-right coupling, and are applied to treating the coal in wide particle diameter distribution. High-value organic structures in the coal can be extracted before the gasification of the coal, and the utilization value of the coal is improved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Orthogonal processing of organic materials used in electronic and electrical devices
ActiveUS8846301B2Avoid damageImprove throughputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMethacrylateOrganic structure
An orthogonal process for photolithographic patterning organic structures is disclosed. The disclosed process utilizes fluorinated solvents or supercritical CO2 as the solvent so that the performance of the organic conductors and semiconductors would not be adversely affected by other aggressive solvent. One disclosed method may also utilize a fluorinated photoresist together with the HFE solvent, but other fluorinated solvents can be used. In one embodiment, the fluorinated photoresist is a resorcinarene, but various fluorinated polymer photoresists and fluorinated molecular glass photoresists can be used as well. For example, a copolymer perfluorodecyl methacrylate (FDMA) and 2-nitrobenzyl methacrylate (NBMA) is a suitable orthogonal fluorinated photoresist for use with fluorinated solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide in a photolithography process. The combination of the fluorinated photoresist and the fluorinated solvent provides a robust, orthogonal process that is yet to be achieved by methods or devices known in the art.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Color organic EL display and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060017383A1Good coating performanceMinimum pin holeIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic structureDecomposition
A color organic EL display includes: a substrate; a color filter layer disposed on the substrate; a gas barrier layer disposed on the color filter layer; and an organic EL structural body disposed on the gas barrier layer. The substrate and the color filter layer provide an underlayer of the gas barrier layer. The underlayer is a degassed underlayer. The gas barrier layer is provided by an atomic layer deposition method at a temperature equal to or lower than a decomposition starting temperature of the color filter layer.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Process for preparation of an EUO-structural-type zeolite, the zeolite that is obtained and its use as catalyst for isomerization of C8-aromatic compounds
InactiveUS6616910B2High yieldLower ratioHydrocarbon by isomerisationAluminium compoundsOrganic structureIsomerization
This invention relates to a process for synthesis of an EUO-structural-type zeolite that comprises at least one element X that is selected from among silicon and germanium and at least one element T that is selected from among aluminum, iron, gallium, boron, titanium, vanadium, zirconium, molybdenum, arsenic, antimony, chromium and manganese, whereby said process is carried out in the presence of an organic structuring agent that is derived from dibenzyldimethylammonium (DBDMA) or its precursors and in the presence of nuclei of at least one zeolitic material of the same structure as the zeolite that is to be synthesized. The zeolite that is thus obtained has an X / T ratio of between 5 and 50. It is used in particular as a catalyst, for example in a process for isomerization of aromatic compounds with 8 carbon atoms per molecule.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Preparation of molecular sieves using a structure directing agent and an N,N,N-trialkyl benzyl quaternary ammonium cation
Crystalline molecular sieves are prepared using a mixture comprising an organic structure directing agent capable of forming the molecular sieve, and an N,N,N-trialkyl benzyl quaternary ammonium cation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
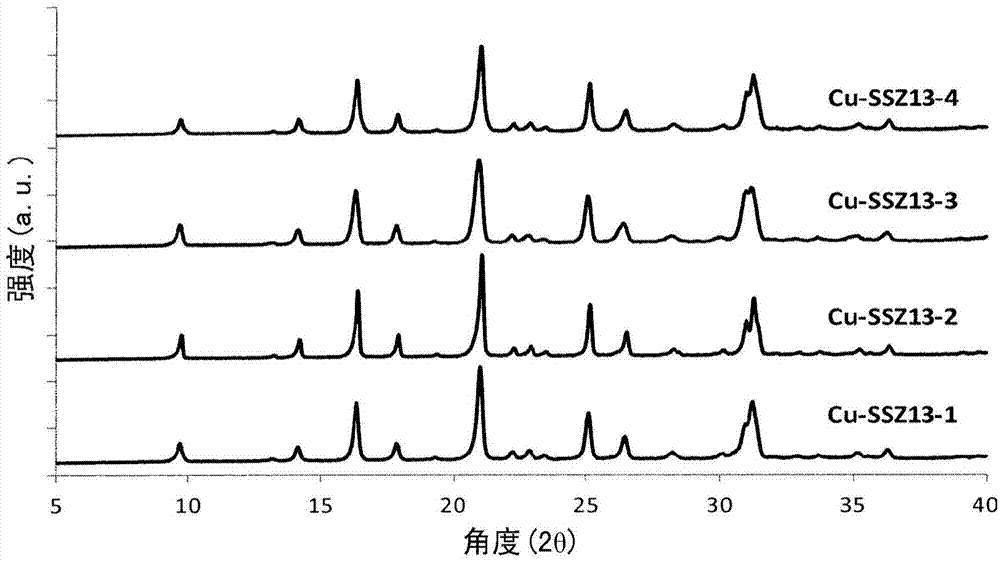
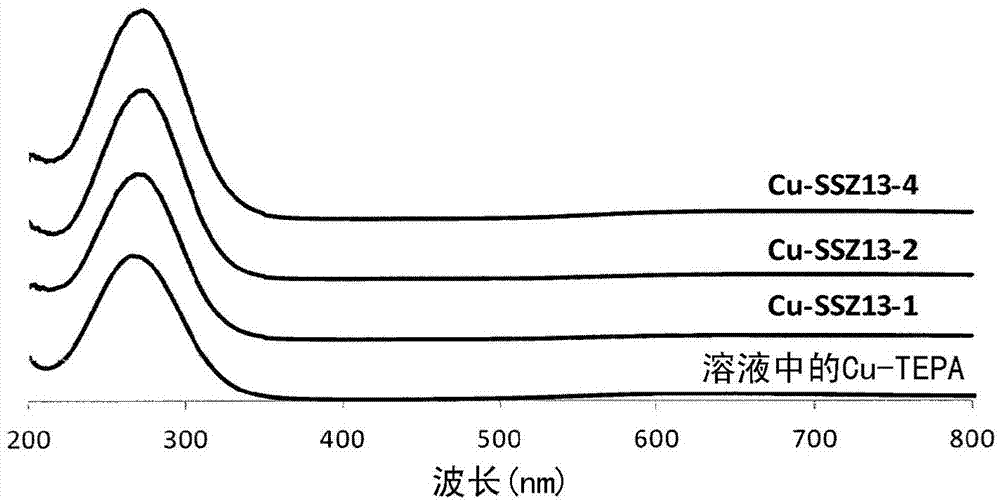
One-pot method for the synthesis of cu-ssz-13, the compound obtained by the method and use thereof
Process for the direct synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 from a synthesis mixture comprising water, at least one silicon source, at least one Al source, at least one Cu source, at least one polyamine for complexing with Cu, and a single organic structure directing agent. A Cu containing molecular sieve having the framework structure of SSZ-13, obtainable by the process and use of the Cu containing molecular sieve.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Process for the preparation of zeolites having CHA structure
ActiveUS8883119B2Nitrous oxide captureAluminium compoundsTetramethylammonium hydroxideOrganic structure
A process for the preparation of zeolites having CHA framework structure and a composition comprising the molar ratio (n Si02):X203, wherein X is a trivalent element, and wherein n is at least 10, the process comprising (i) preparation of an aqueous solution containing at least one source for X203, wherein X is selected from Al, B, Ga, and a mixture of two or more, and at least one source for Si02, at least one organic structure directing agent (SDA) other than Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH), acting as a template for the CHA structure, and Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH), wherein the SDA or mixtures thereof are employed in such amounts that the aqueous solution in (i) exhibits a molar ratio of SDA:TMAOH of 0.01 to 5; (ii) hydrothermal crystallization of the aqueous solution according to (i); wherein the aqueous solution of (i) contains copper in an amount less than 0.005 Cu:((n O2):X2O3) where n is in the range of 10 to 50.
Owner:BASF AG
Preparation method and application of hierarchical porous ZSM-5 molecular sieve
InactiveCN108658093AReduce dosageEasy to separateMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystOrganic structureN octane
The invention provides a preparation method for a hierarchical porous ZSM-5 molecular sieve. According to the preparation method for the hierarchical porous ZSM-5 molecular sieve, in a synthesis system of a silicon source, an aluminum source, an organic structure directing agent and deionized water, a proper amount of cationic surfactant cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide is added to serve as a softtemplate agent, full stirring and uniform mixing are carried out so as to form molecular sieve synthesis sol-gel, then the sol-gel is dried so as to obtain dry glue, and then the hierarchical porousZSM-5 molecular sieve is prepared by using a dry glue conversion method. The preparation method for the hierarchical porous ZSM-5 molecular sieve has the advantages of being mild in preparation conditions, simple, convenient to use, high in efficiency, free of emission of synthetic waste liquid, environmentally friendly and capable of realizing industrial production, the good catalytic performanceis realized in the reaction of preparing the low-carbon olefins through catalytic cracking of n-octane, and therefore, remarkable environmental benefits and economic benefits can be achieved, and theindustrial production prospect is good.
Owner:SHENYANG NORMAL UNIV
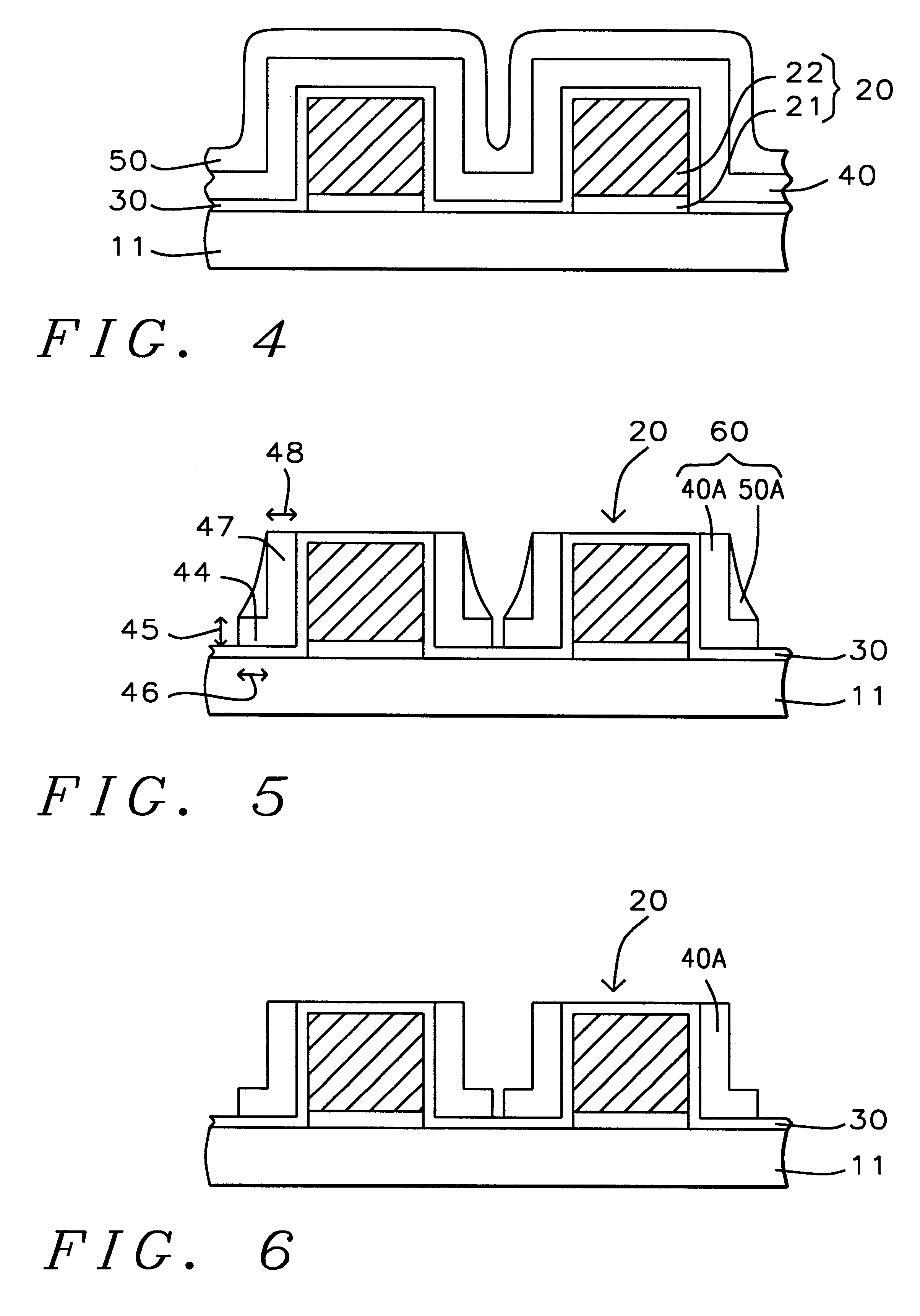
Method for forming an L-shaped spacer with a disposable organic top coating
InactiveUS6294480B1Reduce sensitivityExcellent gap fillingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic structureDielectric
A method for forming an L-shaped spacer using a sacrificial organic top coating. A semiconductor structure is provided having a gate structure thereon. A liner oxide layer is formed on the gate structure. A dielectric spacer layer is formed on the liner oxide layer. In the preferred embodiment, the dielectric spacer layer comprises a silicon nitride layer or a silicon oxynitride layer. A sacrificial organic layer is formed on the dielectric spacer layer. The sacrificial organic layer and the dielectric spacer layer are anisotropically etched to form spacers comprising a triangle-shaped sacrificial organic structure and an L-shaped dielectric spacer. The triangle-shaped sacrificial organic structure is removed leaving an L-shaped dielectric spacer.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
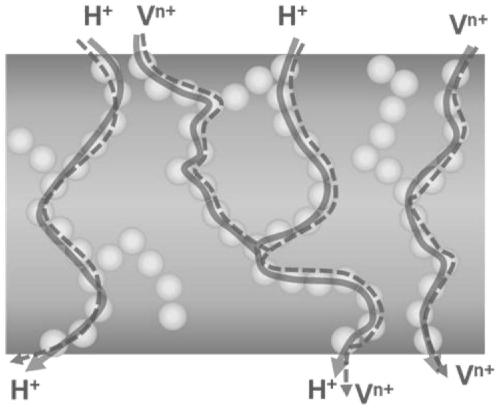
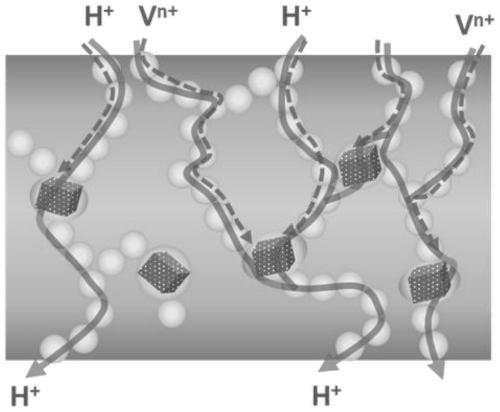
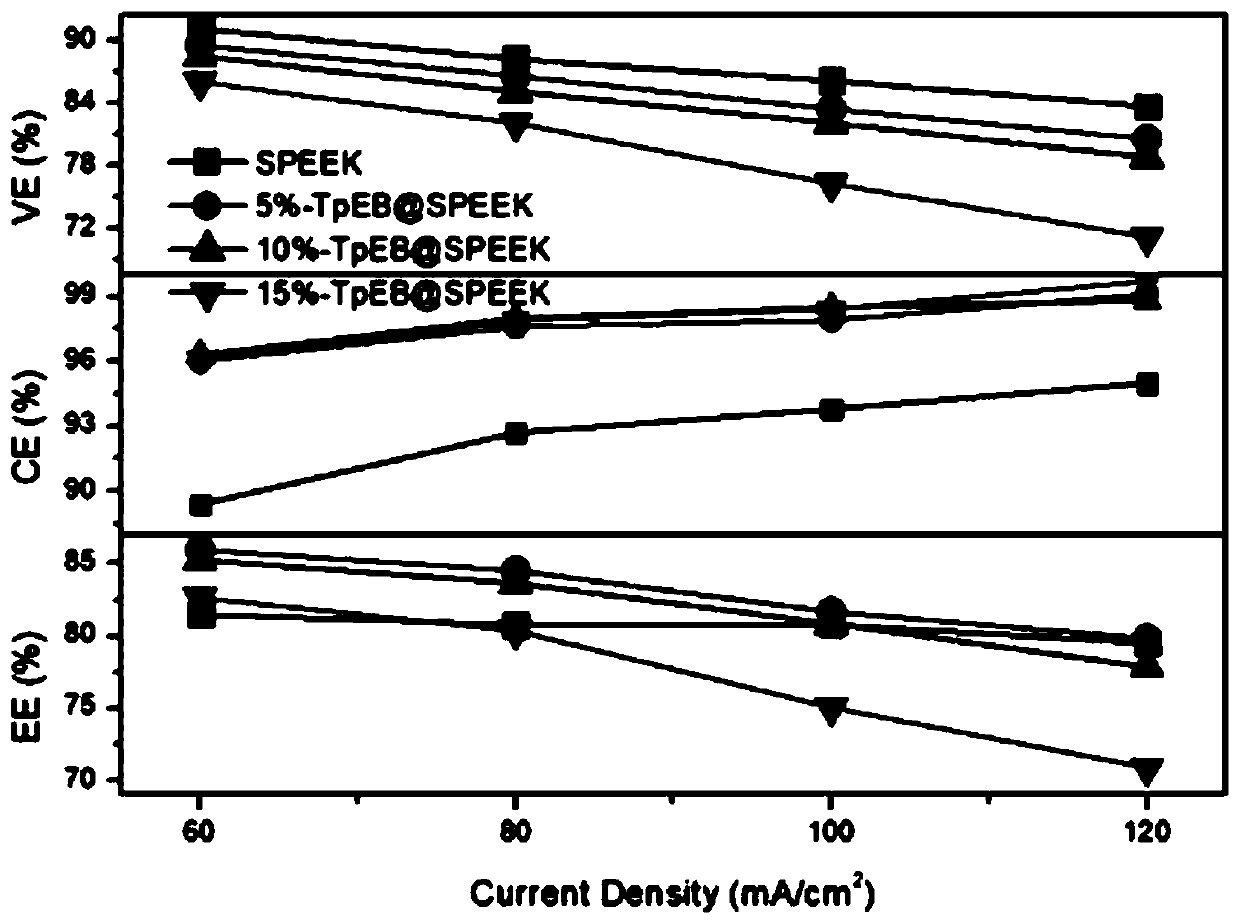
Mixed matrix type cation exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110336052AInhibit water swellingImprove tensile propertiesRegenerative fuel cellsOrganic structureFunctional modification
The invention relates to a mixed matrix type cation exchange membrane and a preparation method thereof. The cation exchange membrane takes a sulfonated modified polymer material as a substrate and isdoped with Schiff base type covalent organic framework materials loaded with different functional groups. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: sequentially performing monomer preparation and polymerization of a covalent organic framework material, sulfonation modification of a polymer, uniform mixing of the covalent organic framework material and a sulfonated polymer, and flow-spreading film formation; and finally, performing acid treatment to obtain the cation exchange membrane. The covalent organic framework material can effectively improve the vanadium resistance of themembrane based on the rigid porous structure; the organic porous structure of the covalent organic framework and the different functional modifications can partially compensate the loss of membrane proton conductivity caused by the introduction of particles; the rigid framework can obviously inhibit the swelling in the membrane and can improve the tensile strength of the membrane; COFs is composedof organic structures and can promote compatibility between sulfonated polymers and covalent organic framework materials; and moreover, the polymer as the substrate can improve the film forming performance of the covalent organic framework material, so that the covalent organic framework material has the better mechanical strength.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing trace amount of toxic pollutants in water by enzyme-loading magnetic particle reinforced flocculation
ActiveCN103708673AHigh selectivityGood removal effectWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsOrganic structureTreatment effect
The invention relates to a method for removing a trace amount of toxic pollutants in water by enzyme-loading magnetic particle reinforced flocculation. The method comprises the following steps that 1, enzyme-loading magnetic particles are used, an enzymatic cross-coupling polymerization reaction is controlled so that a trace amount of toxic pollutants enter into an organic macro-molecule structure by covalent binding, and after the reaction, the hydrophobicity and molecular weight of the organic structure are improved; 2, the enzyme-loading magnetic particles are subjected to magnetic recovery; and 3, the recovered enzyme-loading magnetic particles are added with a flocculating agent, and the pollutants obtained by enzymatic polymerization are easily precipitated and removed by coacervation / flocculation processes such as double electrode layer compression, adsorption electrical neutralization and precipitation net-capturing and thus a trace amount of the toxic pollutants in water are removed by enzyme-loading magnetic particle reinforced flocculation. The method has good selectivity and good treatment effects on low-concentration toxic pollutants, realizes recovery and use of an enzyme, has a low cost and a wide application range and is suitable for treatment on natural water, drinking water and waste water containing low-concentration toxic pollutants.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hydrophilic zeolite coating
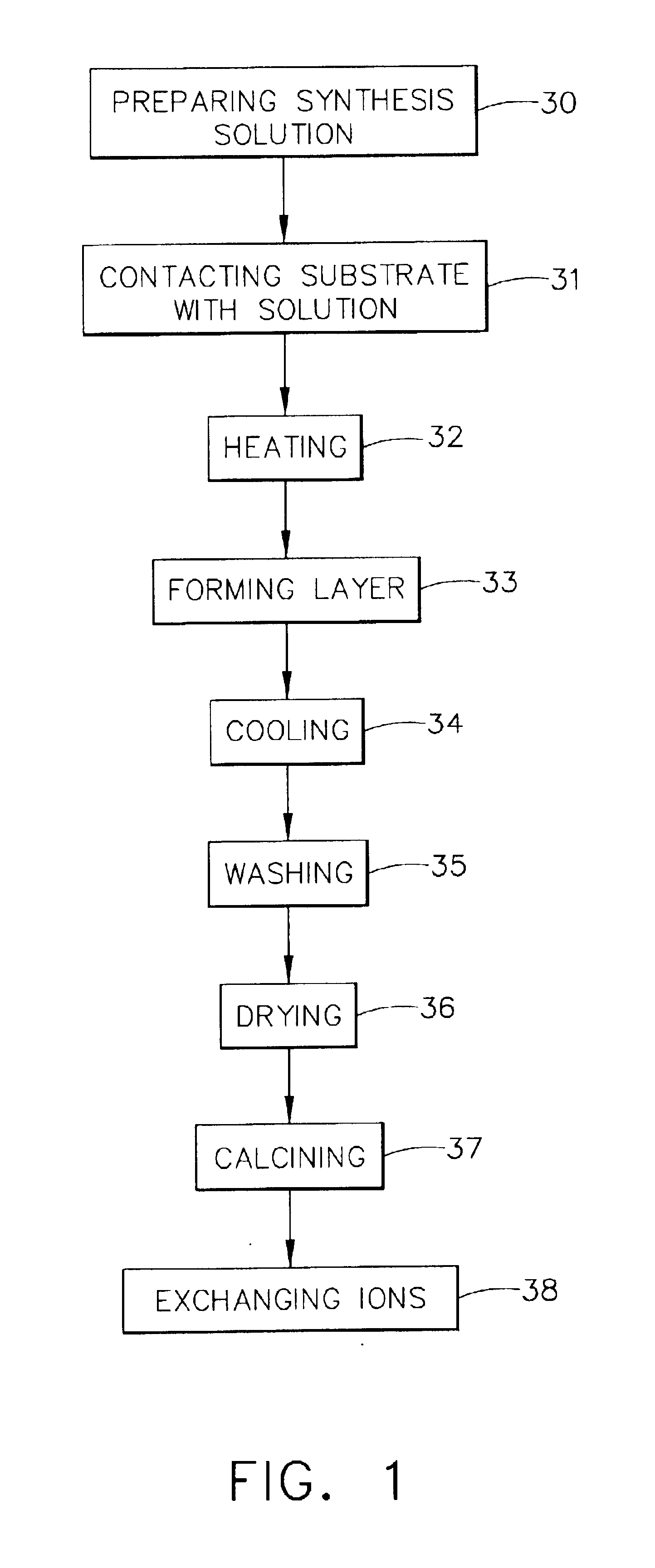
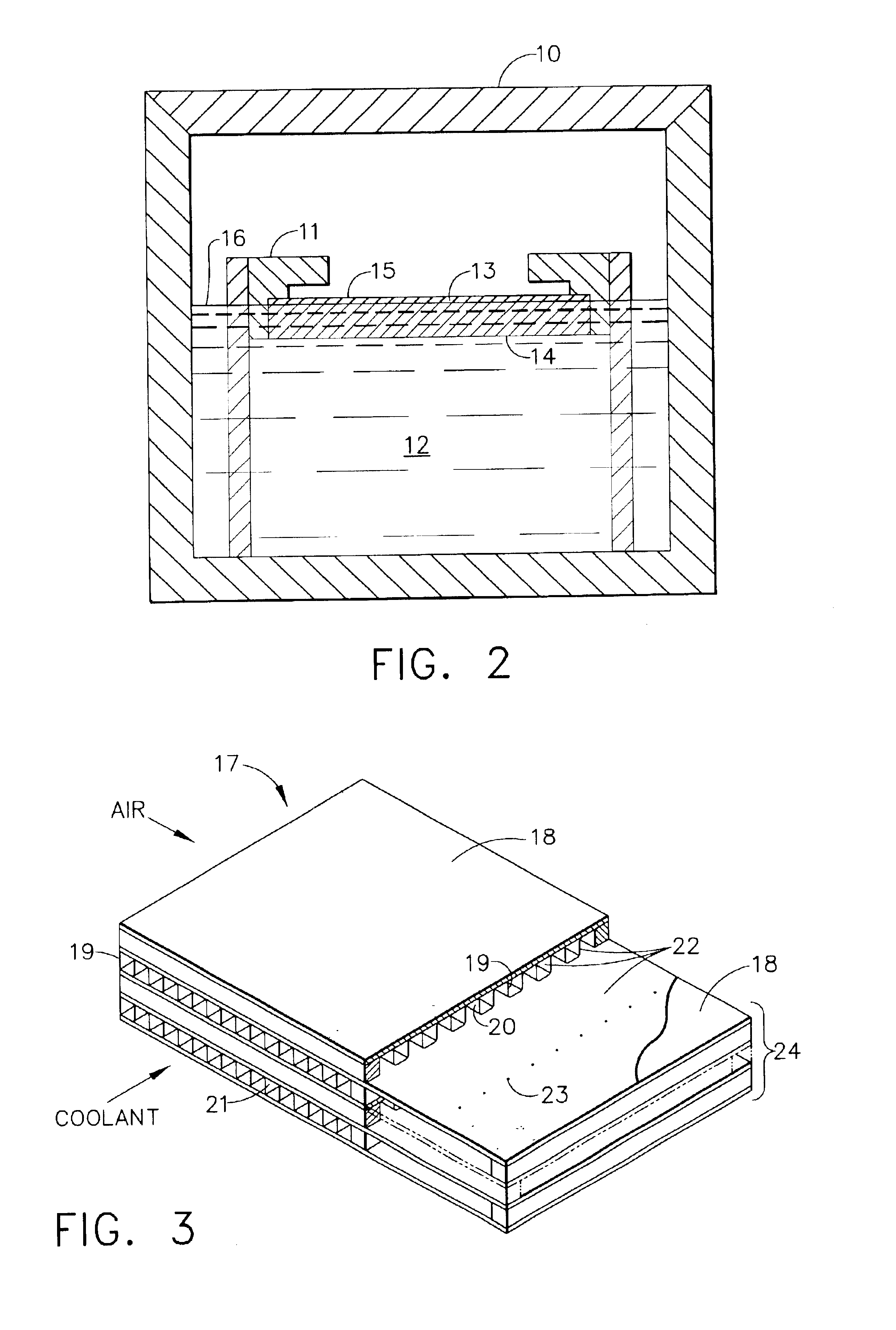
A hydrophilic coating can be optionally corrosion resistant and / or microbial resistant for a substrate such as a heat exchanger. The coating is provided by a zeolite layer that can be formed from a synthesis solution comprising a structure directing agent, a base, a silicon source, an aluminum source, and a solvent. In one preferred embodiment, the synthesis solution comprises tetrapropylammonium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, aluminum oxide, tetraethylorthosilicate, and water. The layer is characterized by a zeolite MFI structure and by a composition having the formula of Mn / m[AlnSi(96-n)O192], or [AlnSi(96-n)O192].4[(CH3CH2CH2)4N—OH] wherein M is a metal ion of valence m+ (e.g., Na+) and 27>n>=0. After formation of the coating, the organic structure directing agent can be left intact inside the zeolite coating to make the coating corrosion resistant. Alternatively, and after removal of the organic structure directing agent, a biocidal metal ion can be incorporated into the coating by an ion exchange process to render the coating microbial resistant. A hydrophilic coating that is also corrosion resistant and microbial resistant can be made by a zeolite coating with two sub-layers—the bottom sub-layer being corrosion resistant and the top sub-layer being microbial resistant.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
SYNTHESIS OF HIGH SILICA ZEOLITE VIA INTERZEOLITE TRANSFORMATION WITHOUT OSDAs
ActiveUS20160023912A1Low costLess equipment intensiveMolecular sieve catalystsPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteOrganic structureCost effectiveness
Provided is a method for preparing a zeolite having a Si / Al ratio of at least 10 by interzeolite transformation in the absence of an organic structure directing agent. The method is more cost effective and less equipment intensive as it eliminates the costly organic structure directing agent and the waste treatment at the plant.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Preparation method of nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve
InactiveCN108793185AHigh crystallinityLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteOrganic structureCrystallinity
The invention belongs to the technical field of synthesis of zeolite molecular sieves, aims at providing a preparation method of a green and simple nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve, and in particular relates to a method for preparing the nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve through adding a high molecular polymer, a silicon source, an aluminum source, an organic structure directing agent and de-ionized water intoa synthesis process and uniformly mixing to form sol-gel of a molecular sieve synthetic precursor, and then preparing the sol-gel into dry glue, and utilizing a water steam assisted crystallization method. According to the method provided by the invention, the prepared nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve has the characteristics of relatively high crystallization degree, the crystal size capable of being regulated to be between 10 and 100nm, a mesoporous-micropore composite multi-grade structure, relatively great specific surface area and the like. According to the preparation method of the nano ZSM-5molecular sieve, provided by the invention, the technical defects that the nano molecular sieve is difficult to separate and collect from a mother solution, a lot of synthetic waste liquid is discharged and the like are avoided, and the synthesis efficiency also can be improved; the preparation method is a simple and efficient, and environment-friendly synthetic route and has a certain industrialized application prospect.
Owner:SHENYANG NORMAL UNIV
Catalytic pyrolysis using UZM-44 aluminosilicate zeolite
ActiveUS8609911B1Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic pyrolysisOrganic structure
A new family of aluminosilicate zeolites designated UZM-44 has been synthesized. These zeolites are represented by the empirical formula.NanMmk+TtAl1-xExSiyOz where “n” is the mole ratio of Na to (Al+E), M represents a metal or metals from zinc, Group 1, Group 2, Group 3 and or the lanthanide series of the periodic table, “m” is the mole ratio of M to (Al+E), “k” is the average charge of the metal or metals M, T is the organic structure directing agent or agents, and E is a framework element such as gallium. The process involves contacting a carbonaceous biomass feedstock with UZM-44 at pyrolysis conditions to produce pyrolysis gases comprising hydrocarbons. The catalyst catalyzes a deoxygenation reaction converting oxygenated hydrocarbons into hydrocarbons and removing the oxygen as carbon oxides and water. A portion of the pyrolysis gases is condensed to produce low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UOP LLC
Aassociation drying Method for preparing dehydrated vegetable and fruit
InactiveCN101156623AReduce qualityImprove qualityFruits/vegetable preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentFruits/vegetable preservation by dehydrationOrganic structureFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a dehydrating and drying method for the top-grade vegetable and fruit. After being sliced, the vegetable and the fruit are placed in a microwave vacuum dryer for being dried, the exerting microwave power density is between 0.5 w / g and 1.2 w / g (watt / gram), the vacuum rate is between 2.5KPa and 4.5KPa (remaining pressure), the materials to be dried can do reciprocating movement along with the drying dish in the microwave vacuum dryer. After being dehydrated by about 40-50 percent of the total moisture by the microwave vacuum drying, the materials are taken out and positioned on a stainless steel dish and then are positioned in a freezing dryer, and are frozen and sublimed dry under 25 DEG C below zero, the drying time is about 7-10 hours, and the moisture is lowered to the safe moisture of 6-7 percent. The preserving of the color, the scent, the taste, and the nutritious components of the dehydrated vegetable and fruit which are produced by the invention are quite approximate to that of the single freezing dried products, the volume is 60-70 percent of the volume of the single freezing dried products, the appearance and the organic structure are approximate too, the drying cost is low, and the energy can be saved by 40 percent above.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
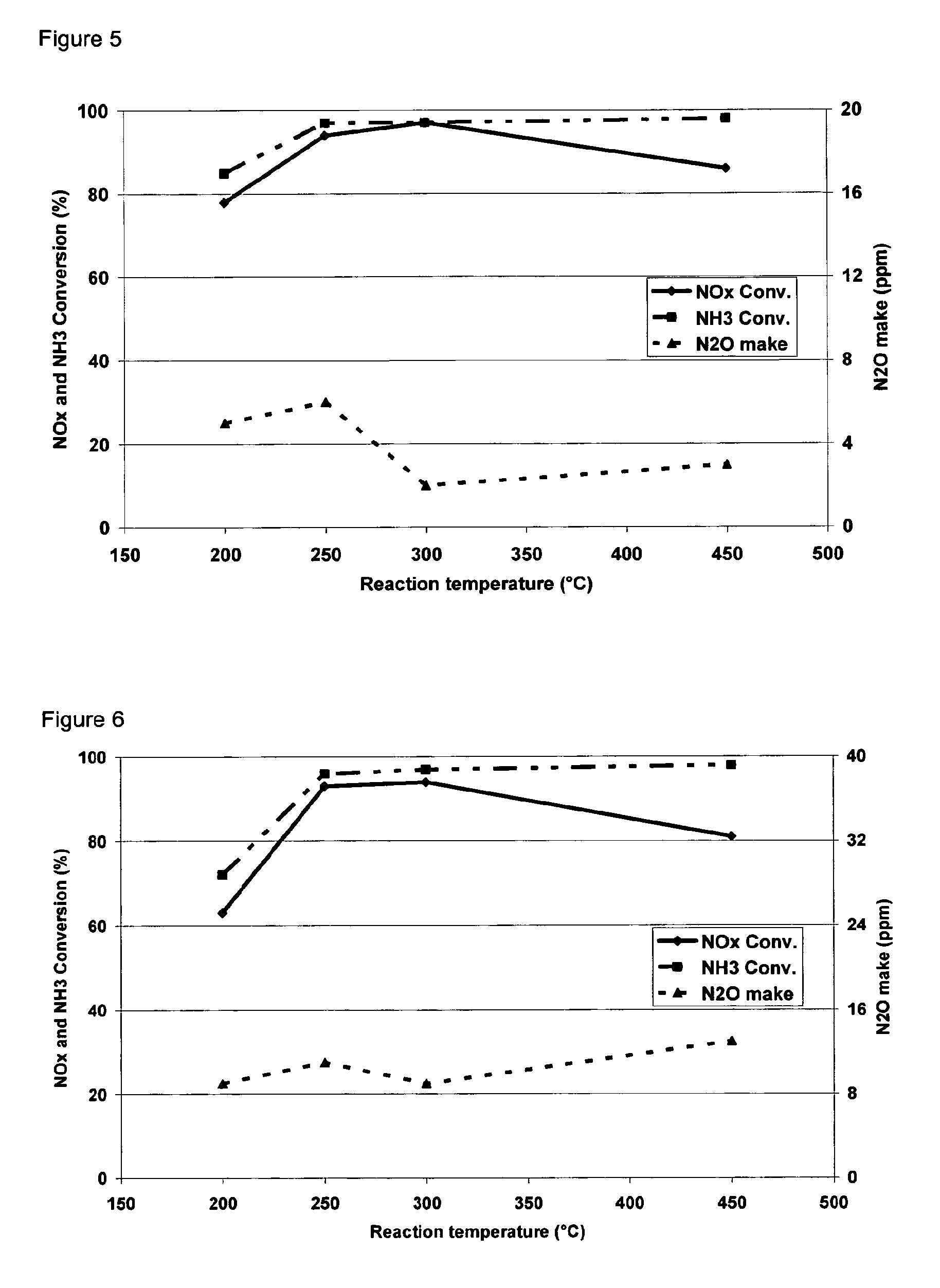
Novel metal-containing zeolite beta for NOx reduction and methods of making the same
ActiveCN102971065AMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationOrganic structureNitrogen oxide
There is disclosed an organic-free, metal-containing zeolite Beta with a silica-to-alumina ratio (SAR) ranging from 5 and 20, and a metal content of at least 0.5 wt.%. There is also disclosed a method of making such a zeolite beta without organic structure directing agent (SDA). The metal, which may comprise Fe or Cu, can be found in amounts ranging from 1-10 wt.%. A method of selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases using the disclosed zeolite is also disclosed.
Owner:ECOVYST CATALYST TECH LLC
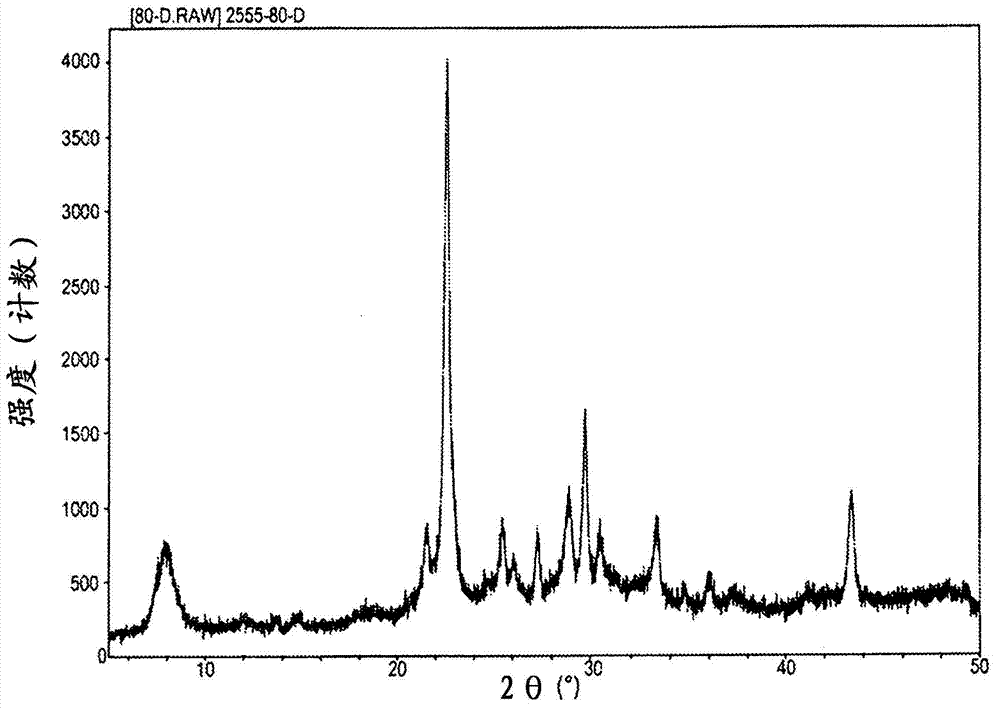
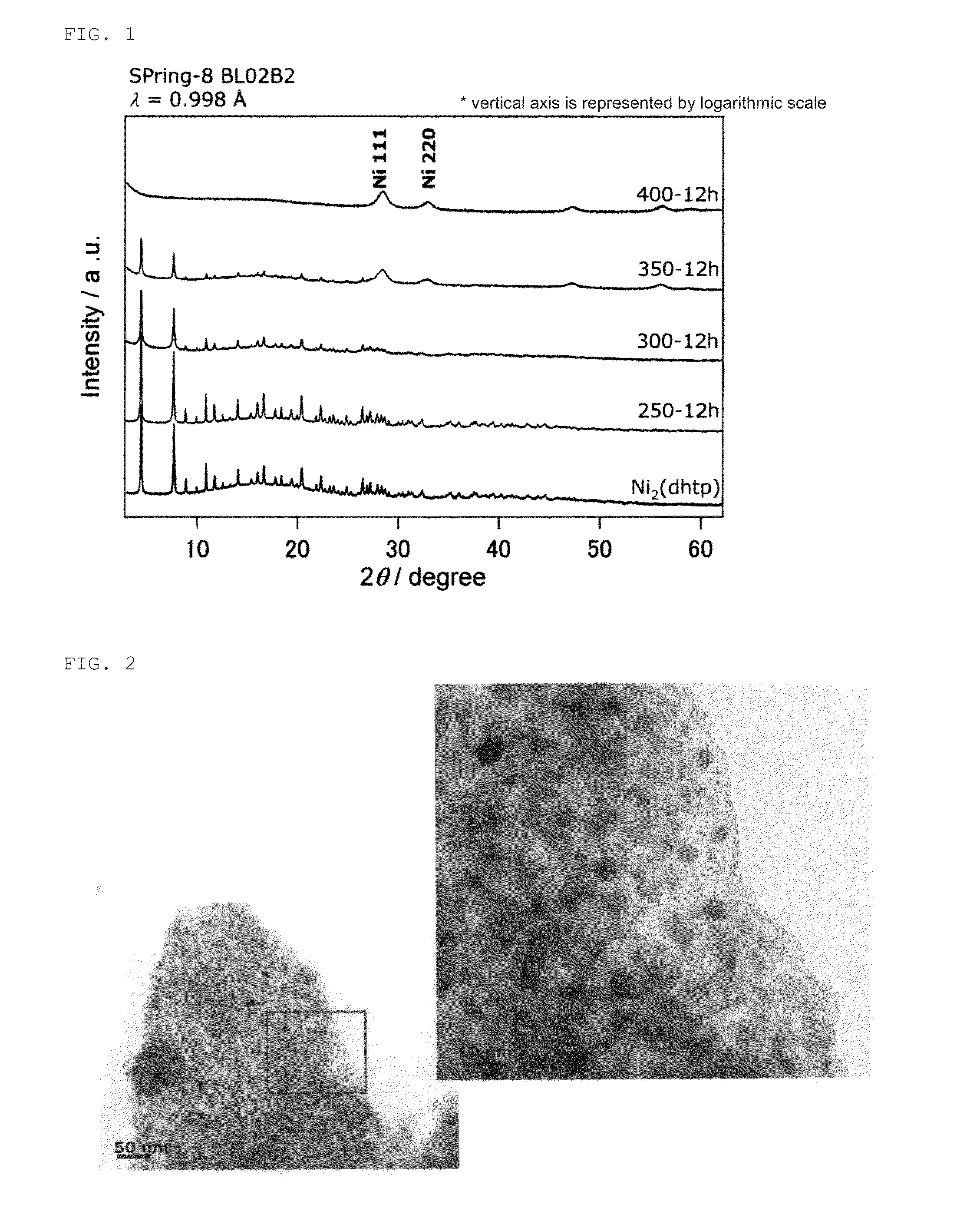
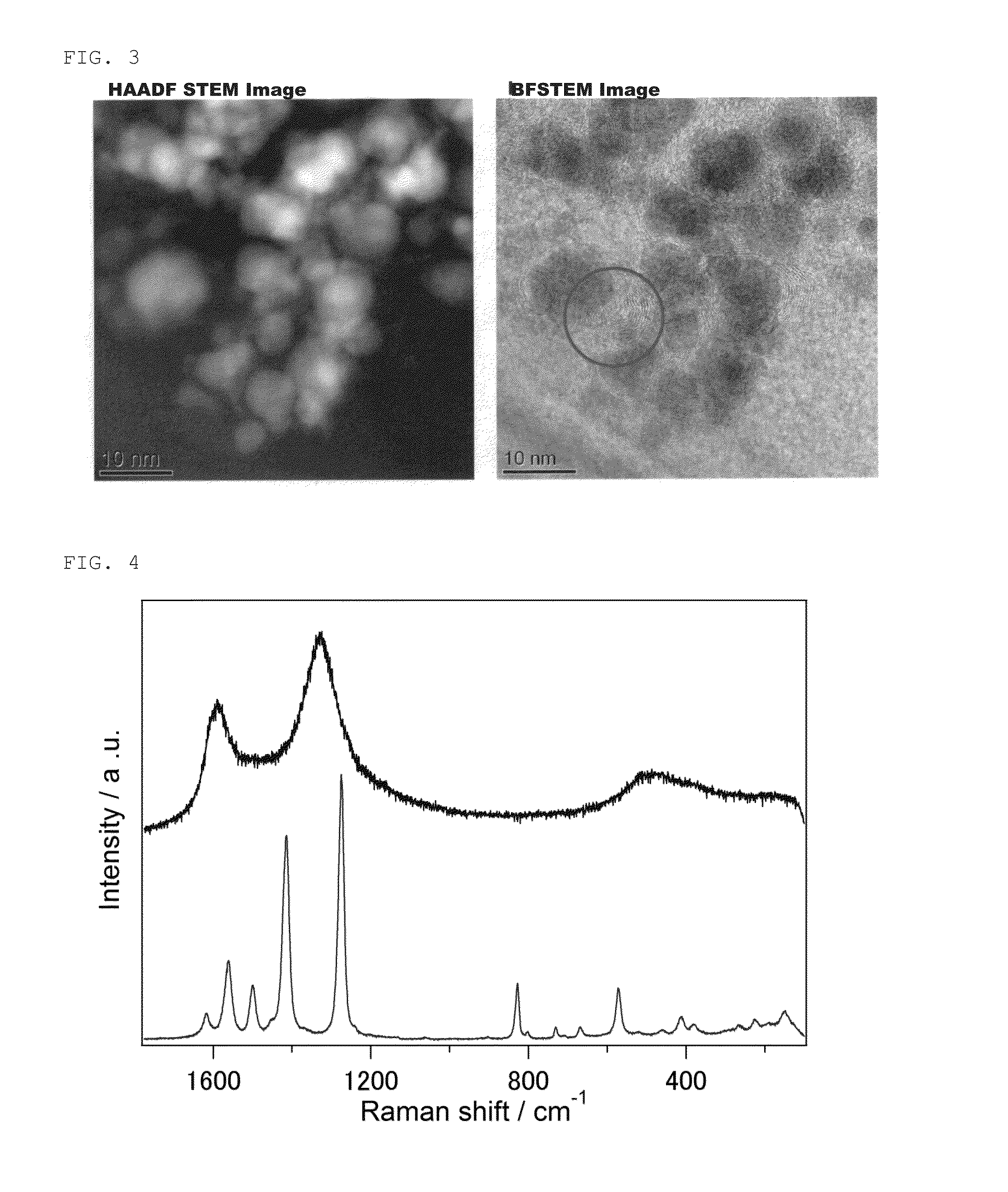
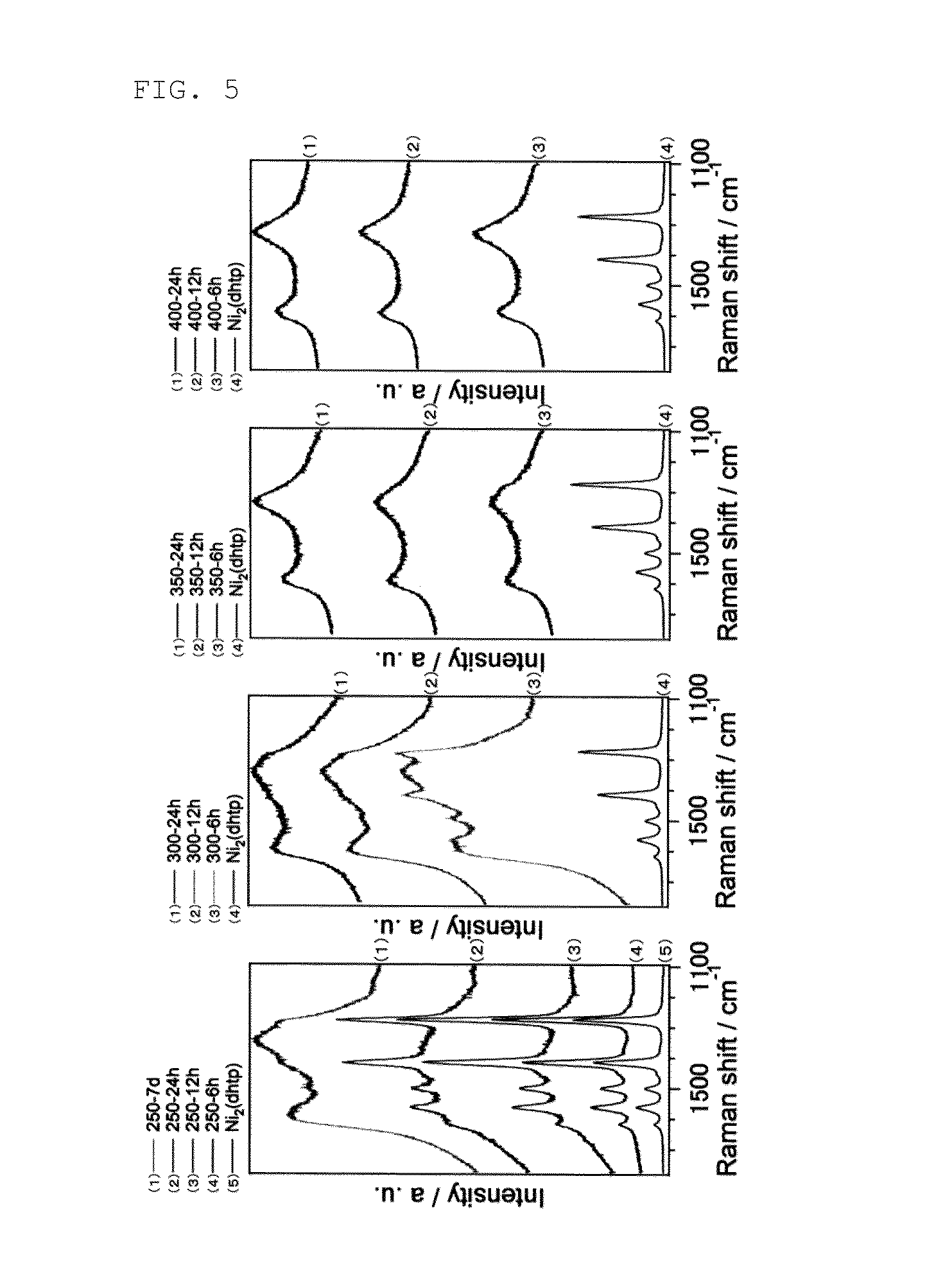
Metal nanoparticle complex and method for producing same
InactiveCN104640908AHigh activityMetal Nanoparticle DispersionMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingOrganic structurePorous Coordination Polymers
The present invention provides a metal nanoparticle complex characterized by having such a structure that metal nanoparticles are dispersed in an organic structure, wherein the organic structure comprises a structure of a porous coordination polymer (PCP) containing both a metal and a polyvalent ligand capable of reducing the metal or a structure of a metal-organic framework (MOF) and carbon.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
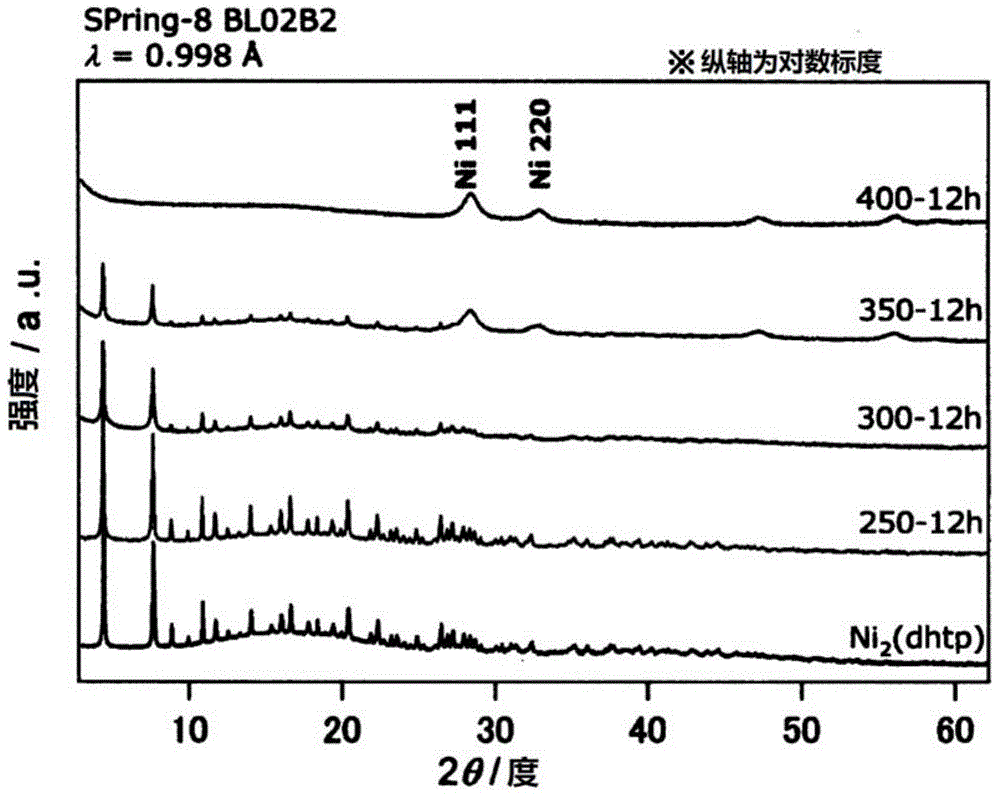
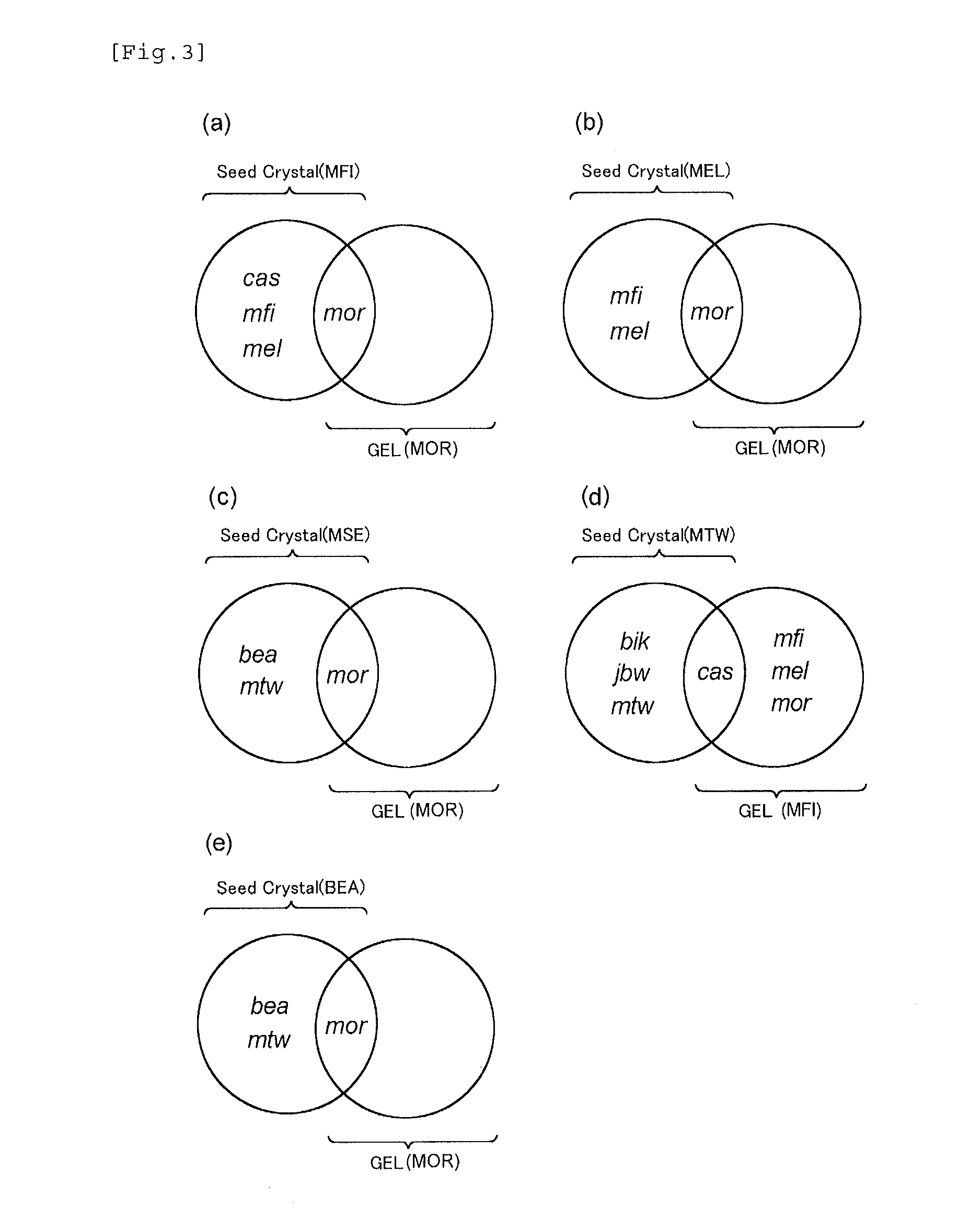
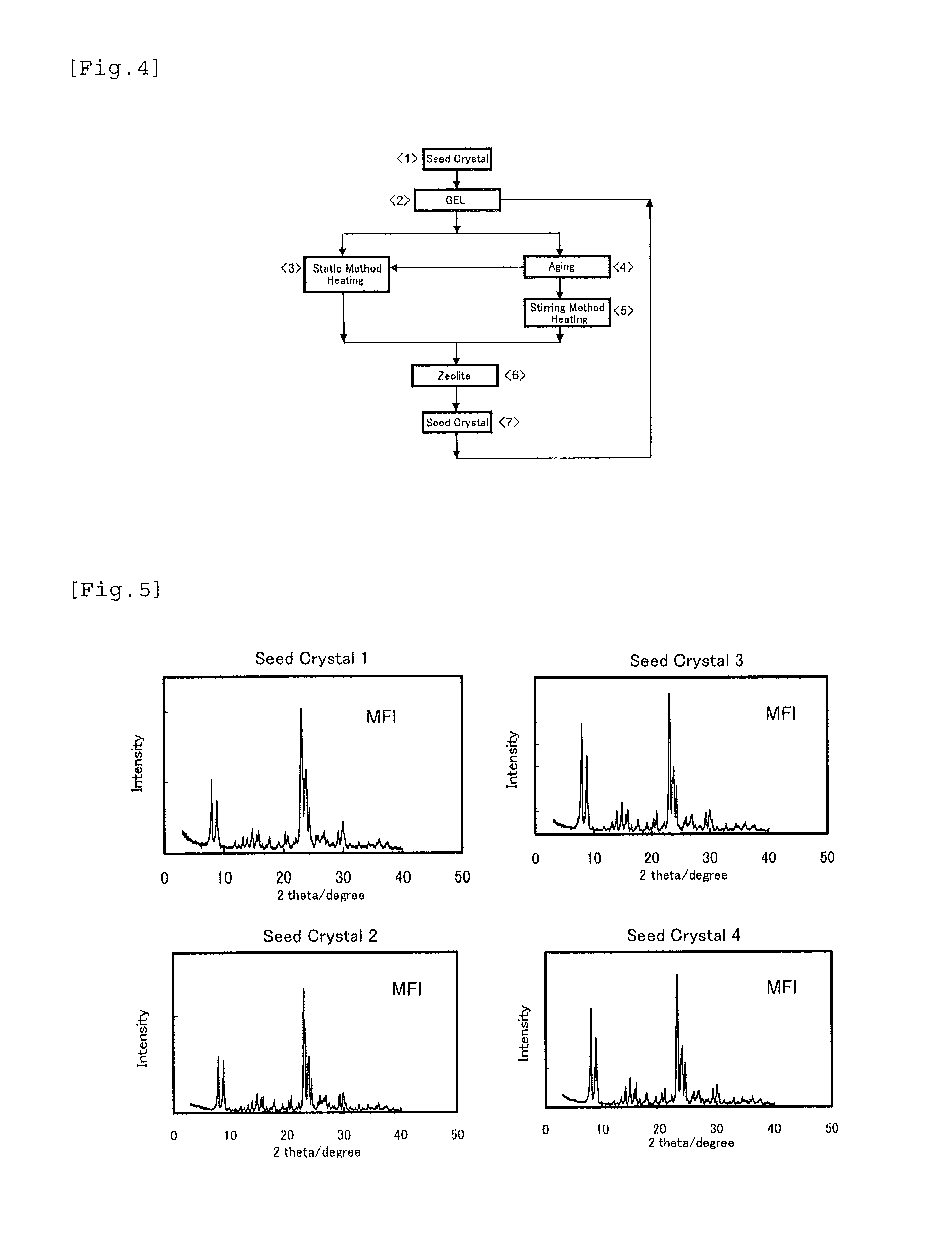
Zeolite production method
ActiveUS20130156690A1Readily and inexpensively produceEfficient productionFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthOrganic structureBuilding unit
Disclosed is a method for readily and inexpensively producing zeolite without using an organic structure-directing agent (organic SDA). Specifically disclosed is a method whereby a gel containing a silica source, an alumina source, an alkaline source and water is reacted with zeolite seed crystals, to produce a zeolite with the same kind of skeletal structure as the zeolite. The gel used is a gel of a composition whereby, when a zeolite is synthesized from this gel only, the synthesized zeolite comprises at least one of the kinds of composite building units of the target zeolite.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD +1
Metal nanoparticle complex and method for producing same
InactiveUS20150231622A1High activityEvenly dispersedMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic structurePorous Coordination Polymers
The present invention provides a metal nanoparticle composite having a structure, in which metal nanoparticles are dispersed in an organic structure, the organic structure including: a structure of a porous coordination polymer (PCP) or metal-organic framework (MOF) containing a metal and a polyvalent ligand capable of reducing the metal; and carbon.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com