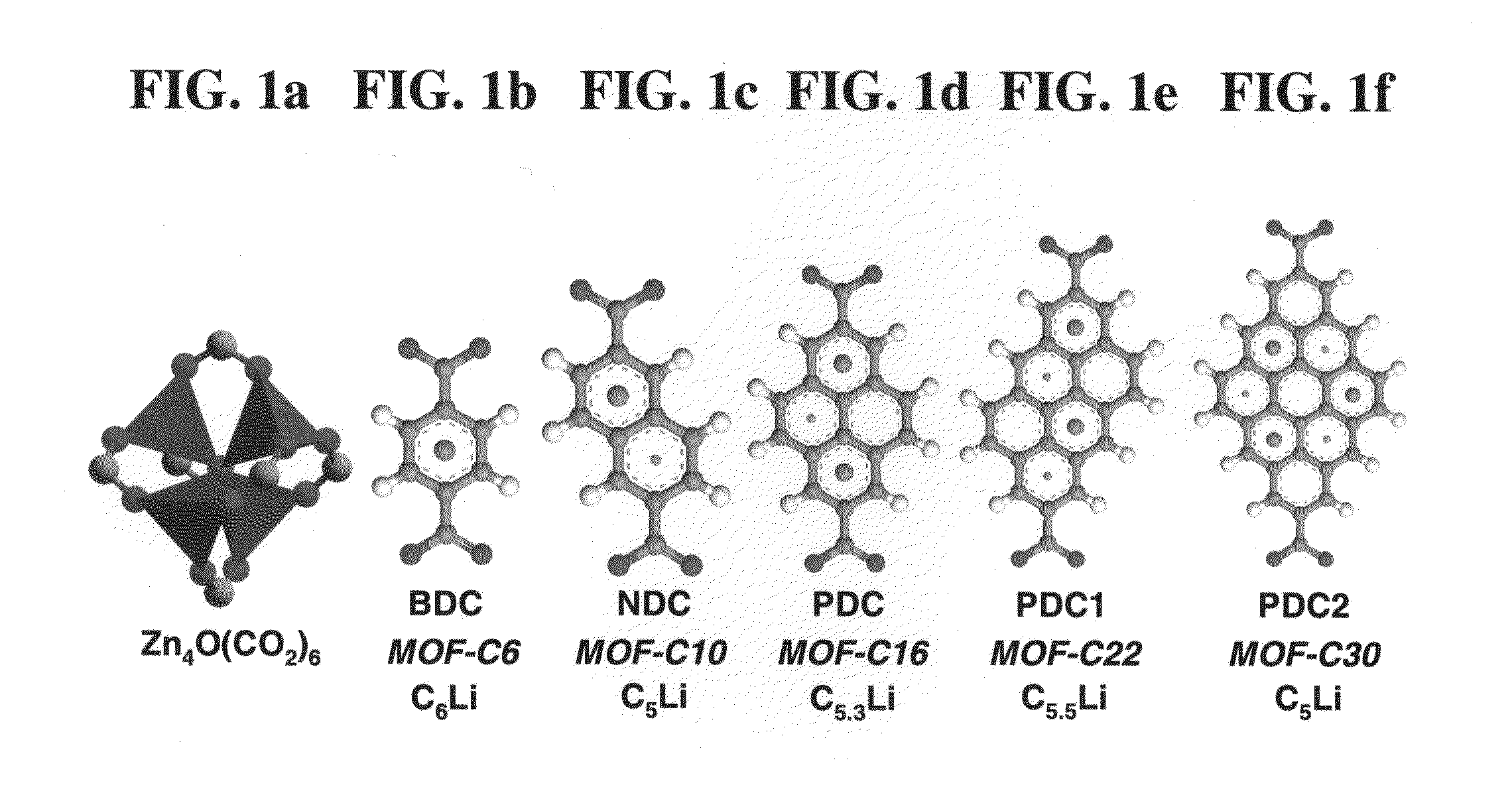
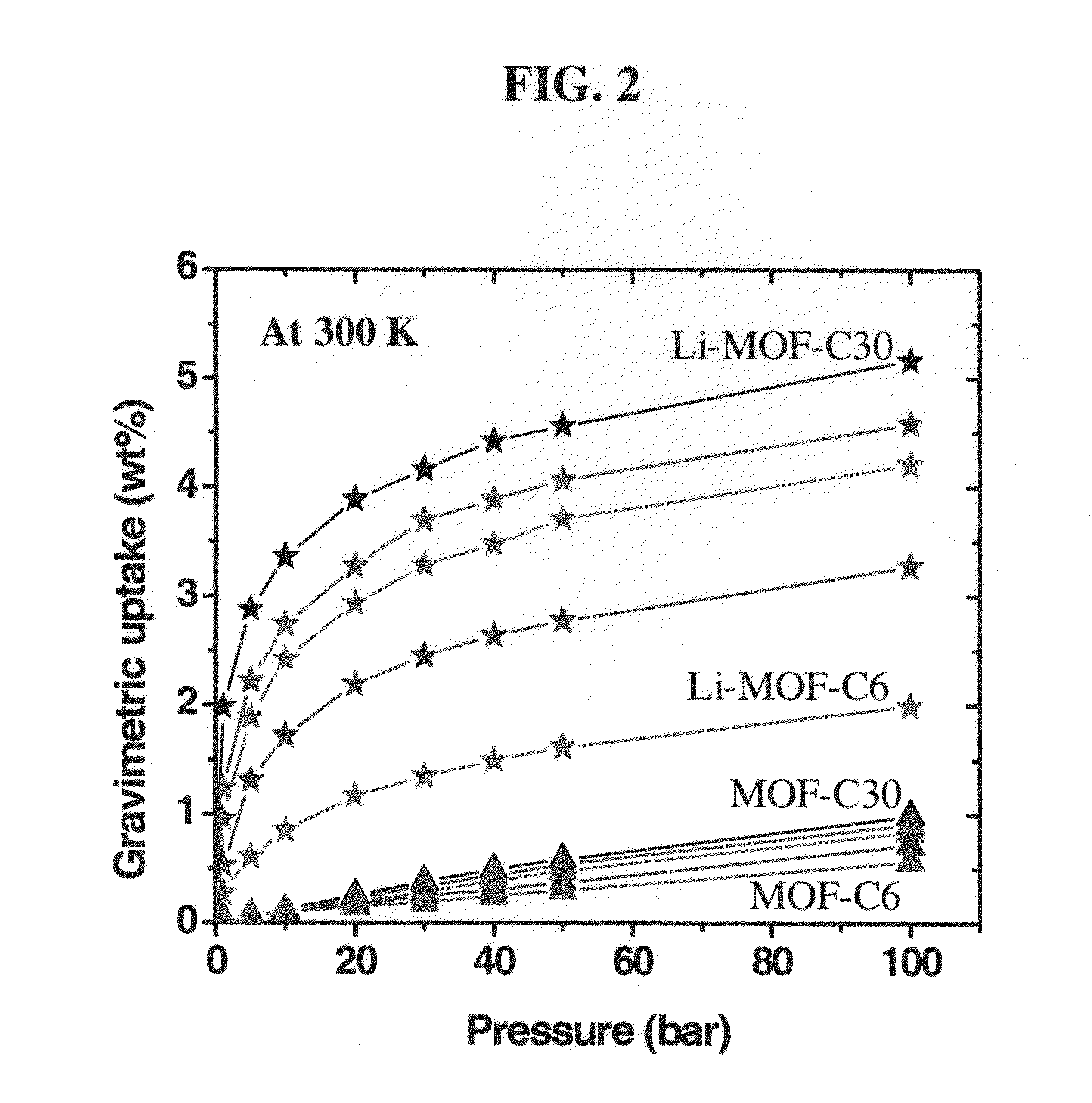
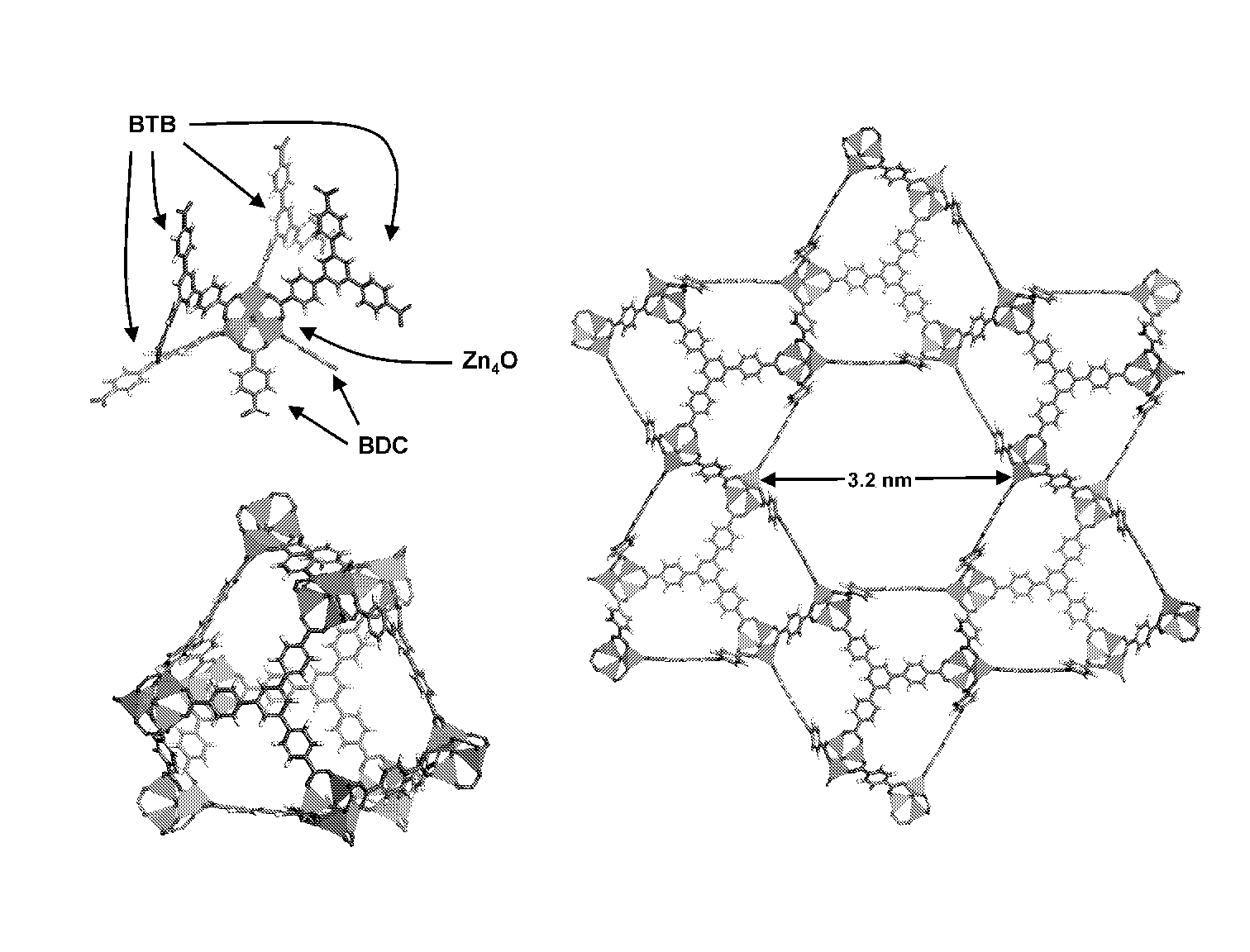
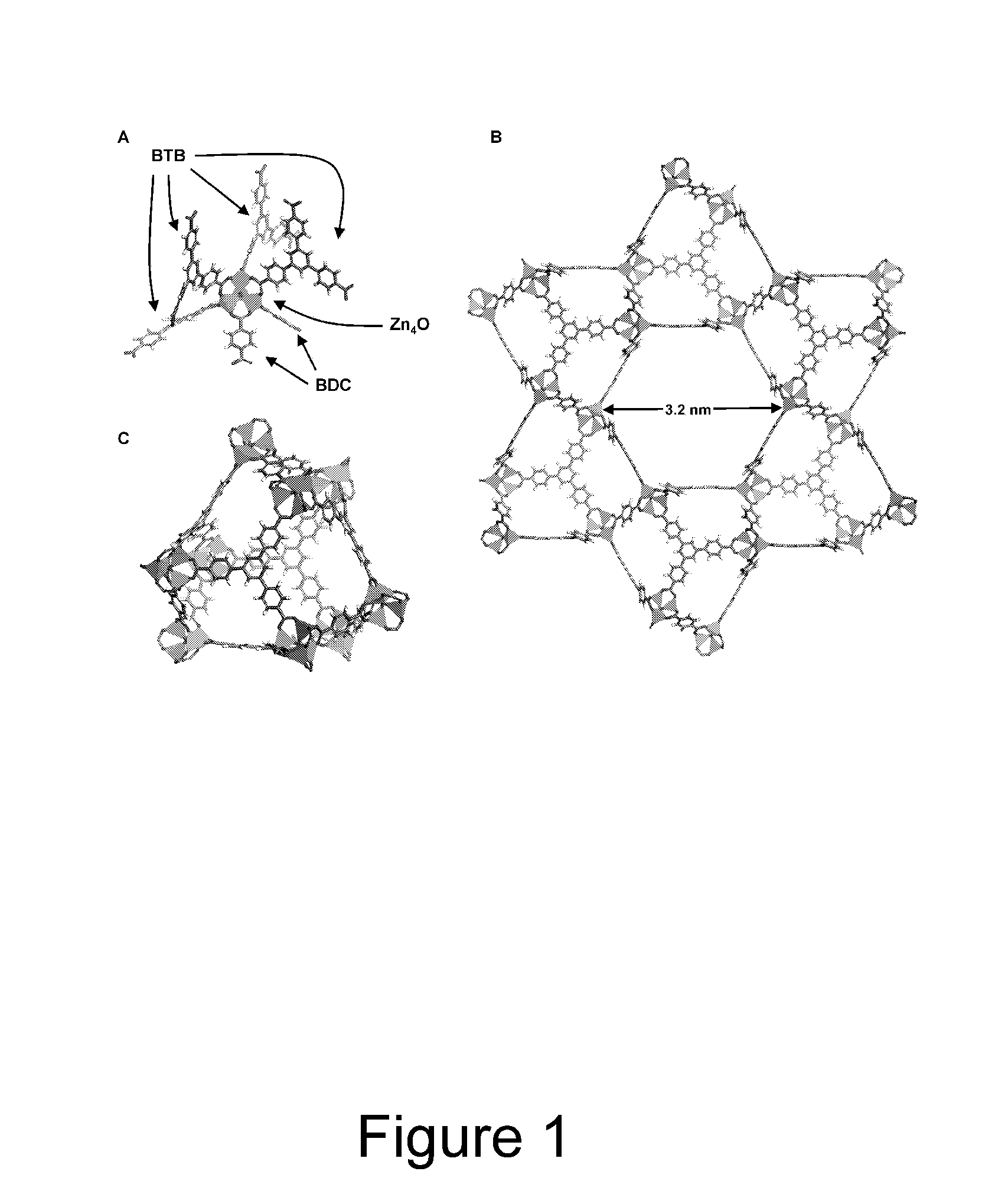
Patents
Literature
244 results about "Metal clusters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
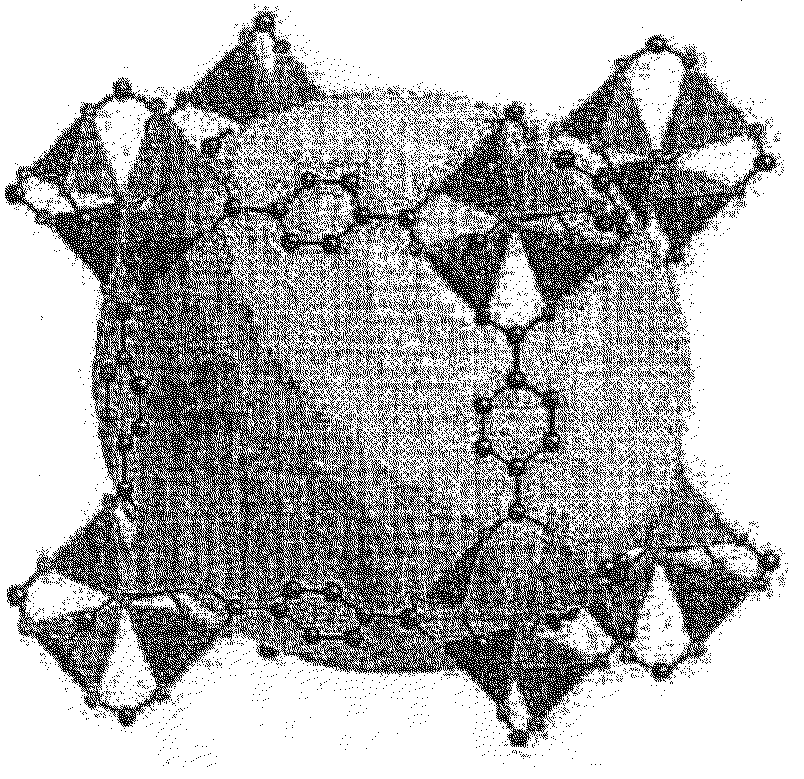
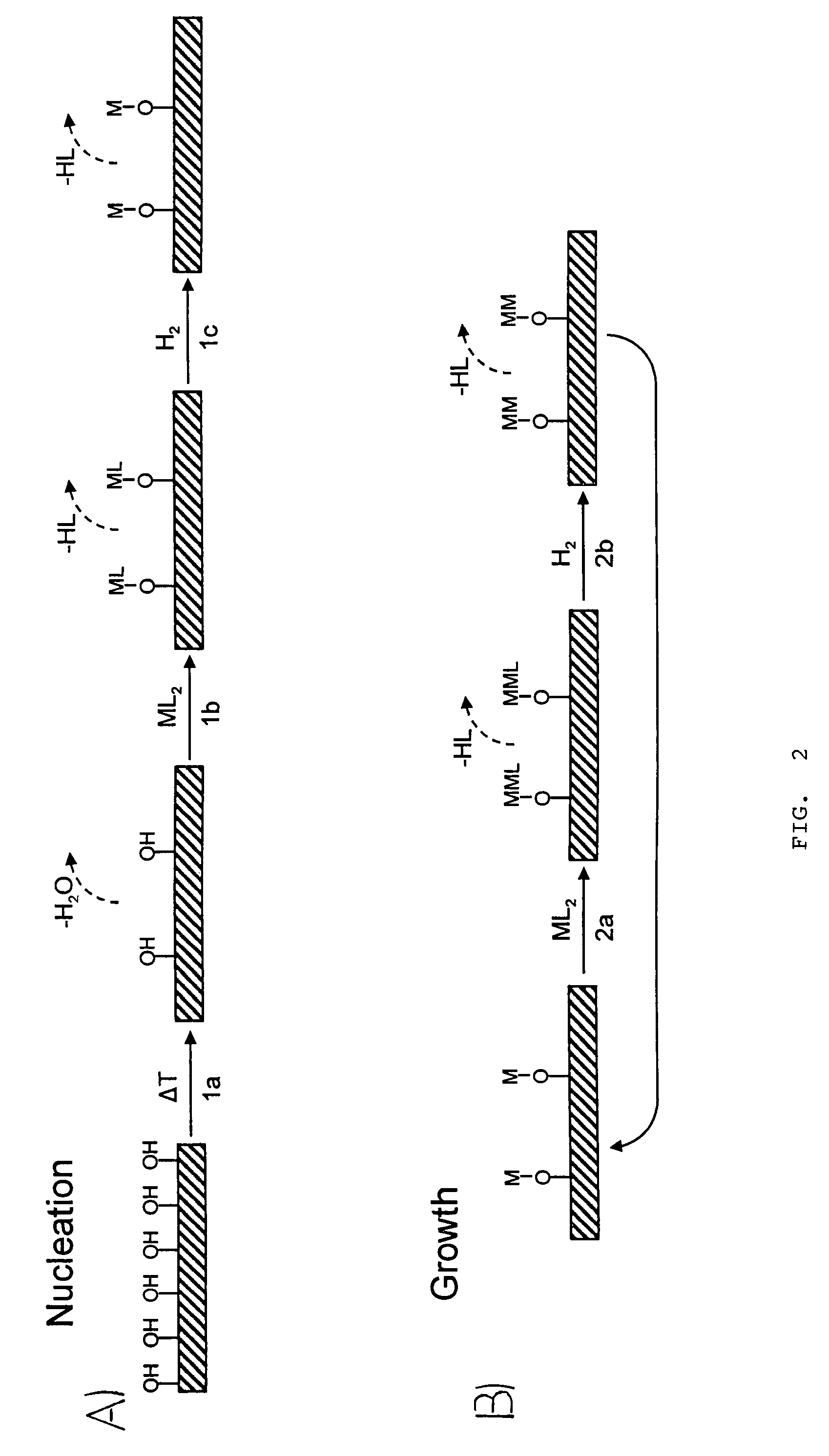
Metal cluster compounds can form a variety of arrays, including triangular, tetrahedral, and octahedral arrays. For many d-block clusters there is a strong correlation between their structure and the number of valence electrons (from the metal atoms and the ligands).
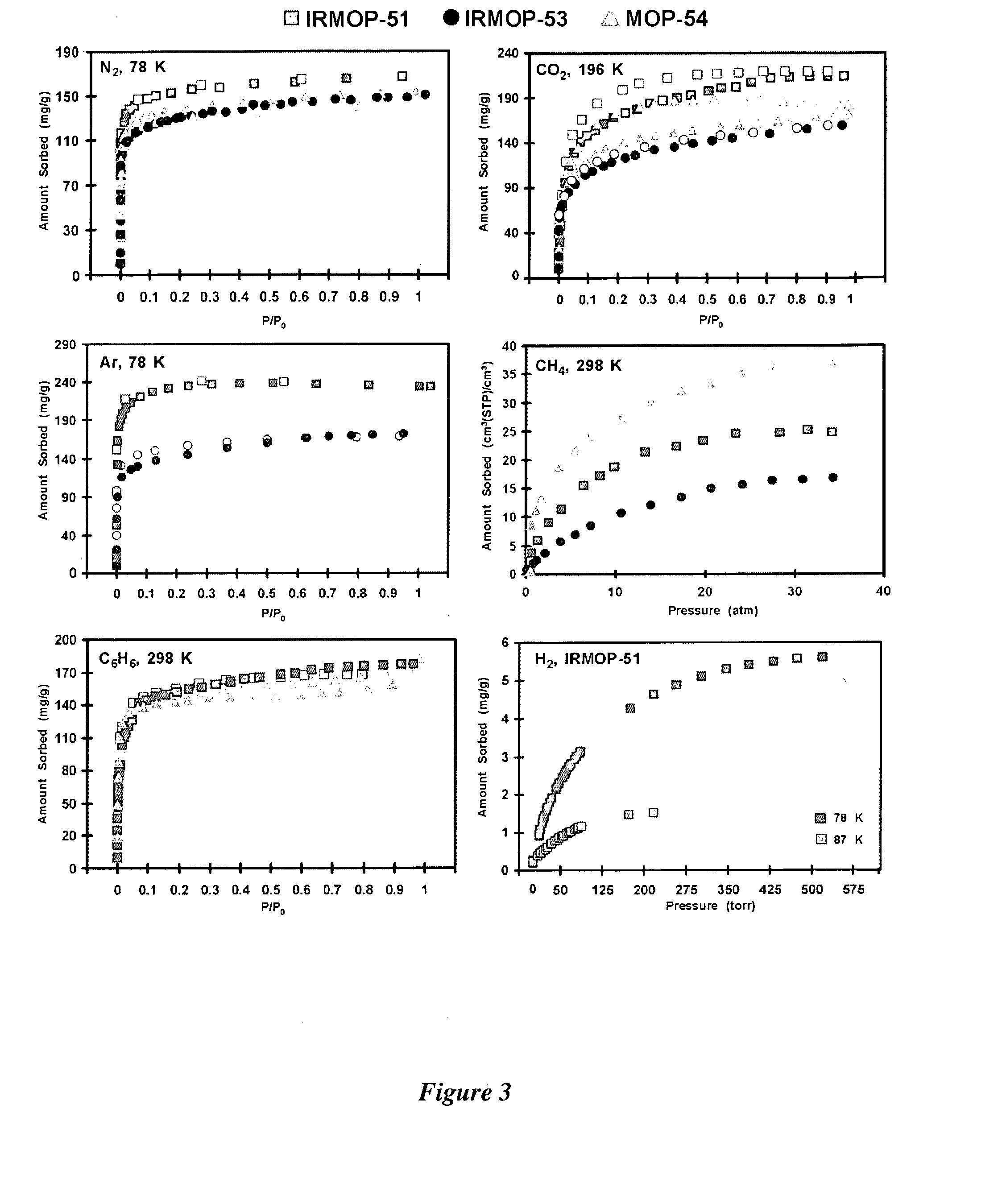
High gas adsorption in a microporous metal-organic framework with open-metal sites
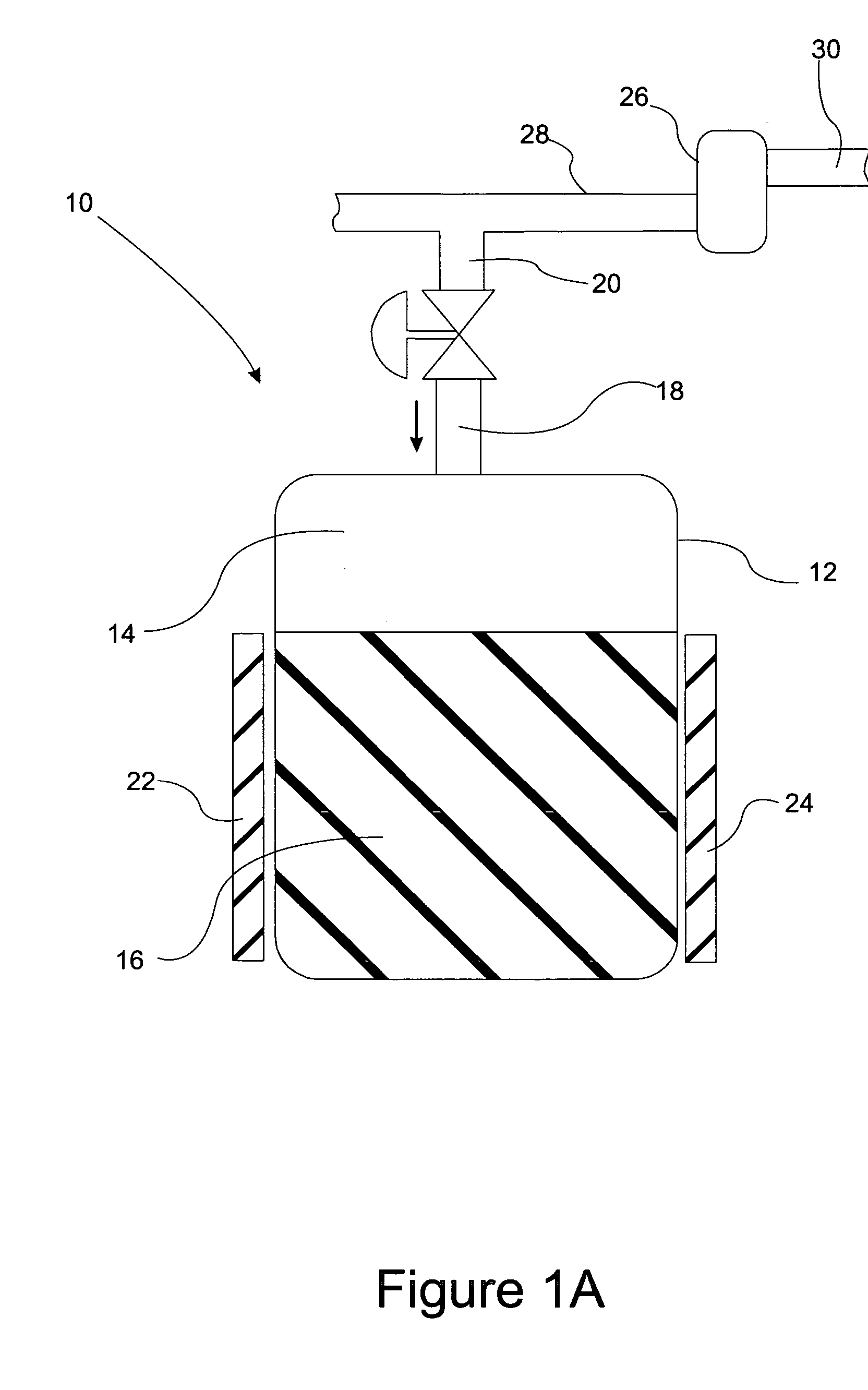
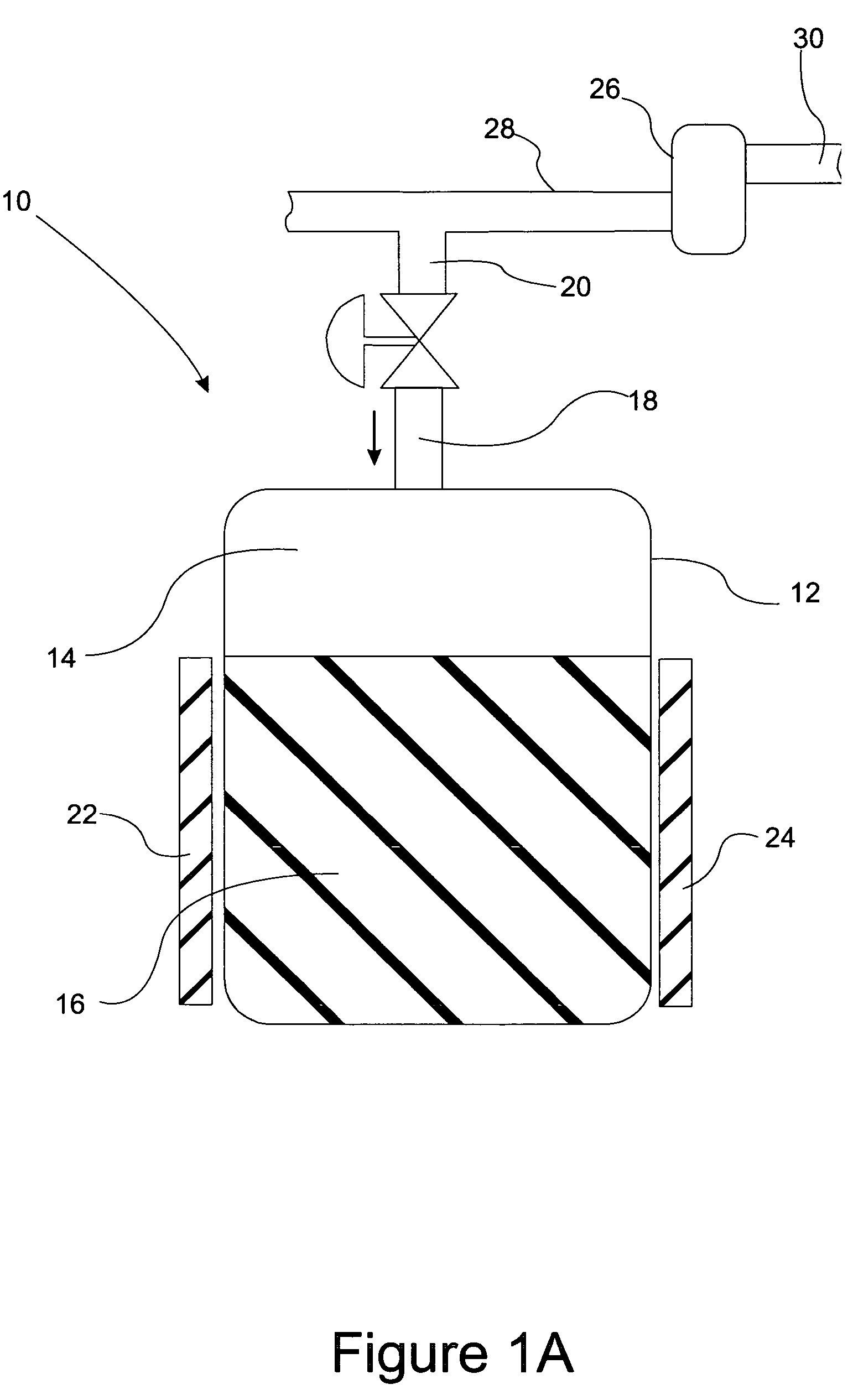
A gas storage material contains a metal-organic framework that includes a plurality of metal clusters and a plurality of charged multidentate linking ligands that connect adjacent metal clusters. Each metal cluster includes one or more metal ions and at least one open metal site. The metal-organic framework includes one or more sites for storing molecular hydrogen. A hydrogen storage system using the hydrogen storage material is provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Methods of chemically derivatizing single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6841139B2Increase resistanceHigh yieldMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentFiberLithium
This invention is directed to making chemical derivatives of carbon nanotubes and to uses for the derivatized nanotubes, including making arrays as a basis for synthesis of carbon fibers. In one embodiment, this invention also provides a method for preparing single wall carbon nanotubes having substituents attached to the side wall of the nanotube by reacting single wall carbon nanotubes with fluorine gas and recovering fluorine derivatized carbon nanotubes, then reacting fluorine derivatized carbon nanotubes with a nucleophile. Some of the fluorine substituents are replaced by nucleophilic substitution. If desired, the remaining fluorine can be completely or partially eliminated to produce single wall carbon nanotubes having substituents attached to the side wall of the nanotube. The substituents will, of course, be dependent on the nucleophile, and preferred nucleophiles include alkyl lithium species such as methyl lithium. Alternatively, fluorine may be fully or partially removed from fluorine derivatized carbon nanotubes by reacting the fluorine derivatized carbon nanotubes with various amounts of hydrazine, substituted hydrazine or alkyl amine. The present invention also provides seed materials for growth of single wall carbon nanotubes comprising a plurality of single wall carbon nanotubes or short tubular molecules having a catalyst precursor moiety covalently bound or physisorbed on the outer surface of the sidewall to provide the optimum metal cluster size under conditions that result in migration of the metal moiety to the tube end.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Chemically modifying single wall carbon nanotubes to facilitate dispersal in solvents
InactiveUS6875412B2High yieldIncrease resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationFiberCarbon fibers
Owner:RICE UNIV
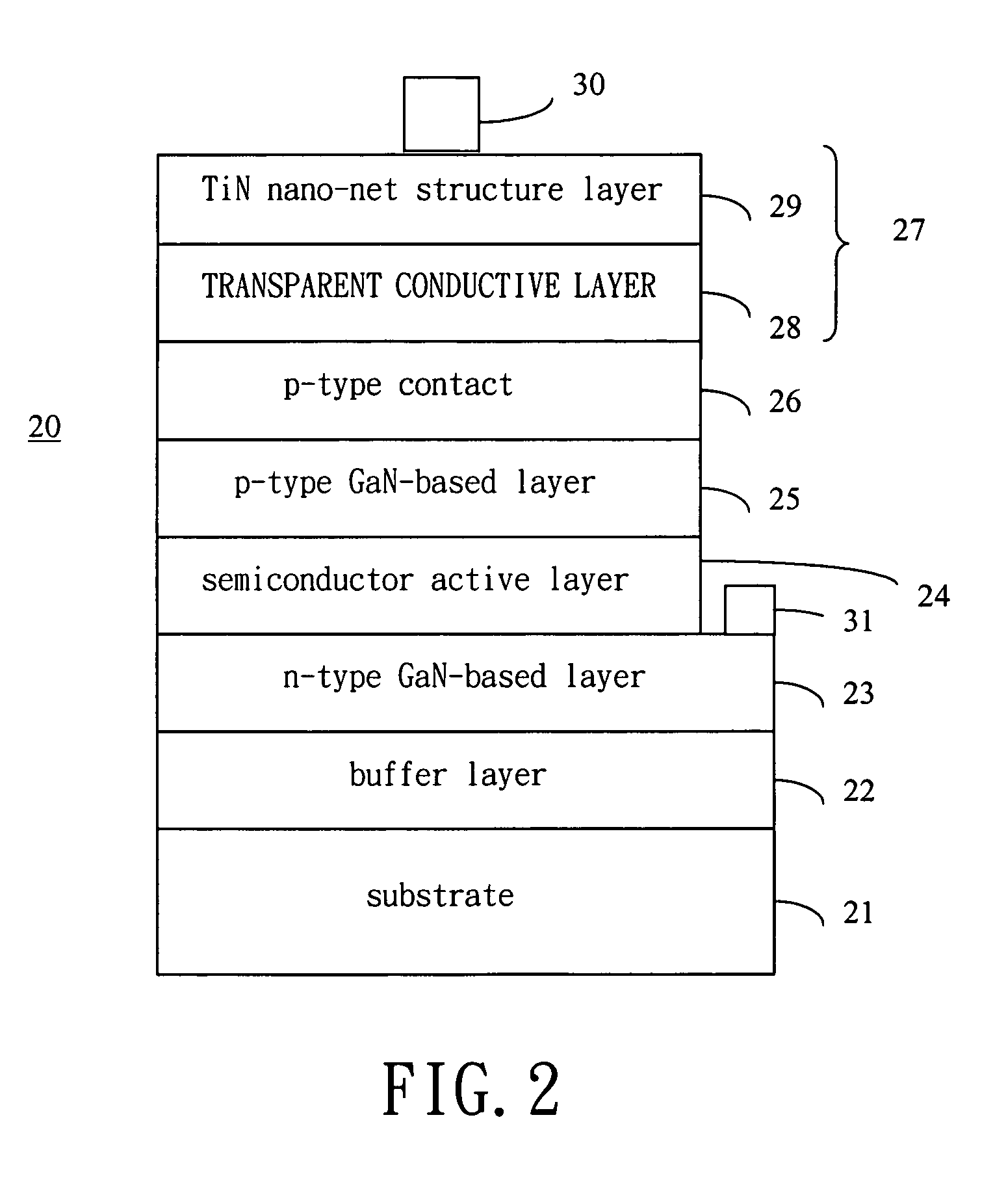
Fabrication method of nitride-based semiconductors and nitride-based semiconductor fabricated thereby
ActiveUS6844569B1Reduce dislocationReduce stressPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyMetal clusters
The present invention relates to a fabrication method of nitride-based semiconductors and a nitride-based semiconductor fabricated thereby. In the fabrication method of the invention, a self-organizing metal layer is formed on a sapphire substrate. The sapphire substrate having the self-organizing metal layer is heated so that self-organizing metal coalesces into nanoscale clusters to irregularly expose an upper surface of the sapphire substrate. Exposed portions of the sapphire substrate is plasma etched using the self-organized metal clusters as a mask to form a nanoscale uneven structure on the sapphire substrate. A resultant structure is wet etched to remove the self-organized metal clusters. The nanoscale uneven structure formed on the sapphire substrate decreases the stress and resultant dislocation between the sapphire substrate and a nitride-based semiconductor layer as well as increases the quantum efficiency between the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High gas adsorption metal-organic framework
A gas storage material contains a metal-organic framework that includes a plurality of metal clusters and a plurality of charged multidentate linking ligands that connect adjacent metal clusters. Each metal cluster includes one or more metal ions and at least one open metal site. The metal-organic framework includes one or more sites for storing molecular hydrogen. A hydrogen storage system using the hydrogen storage material is provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
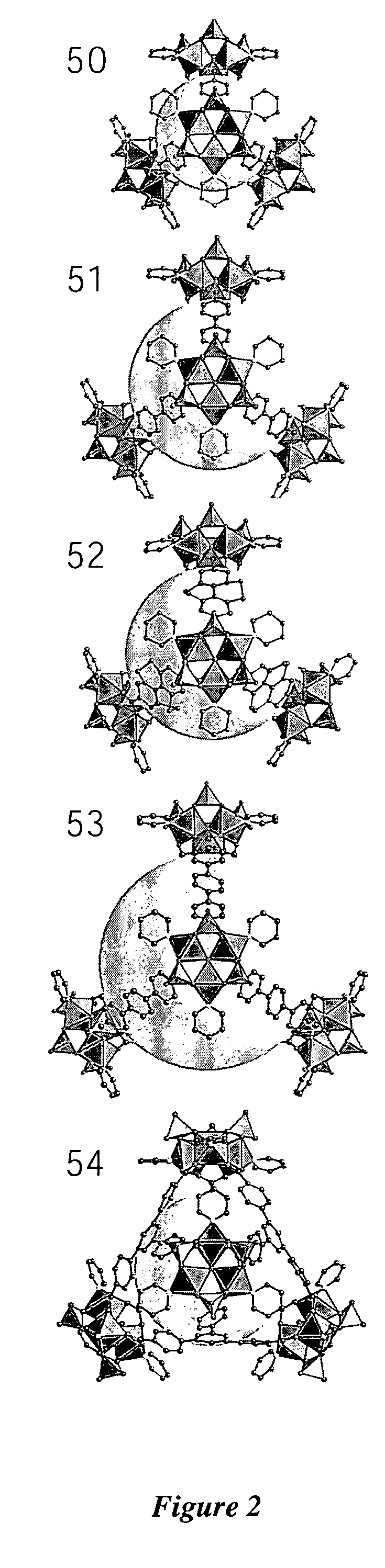
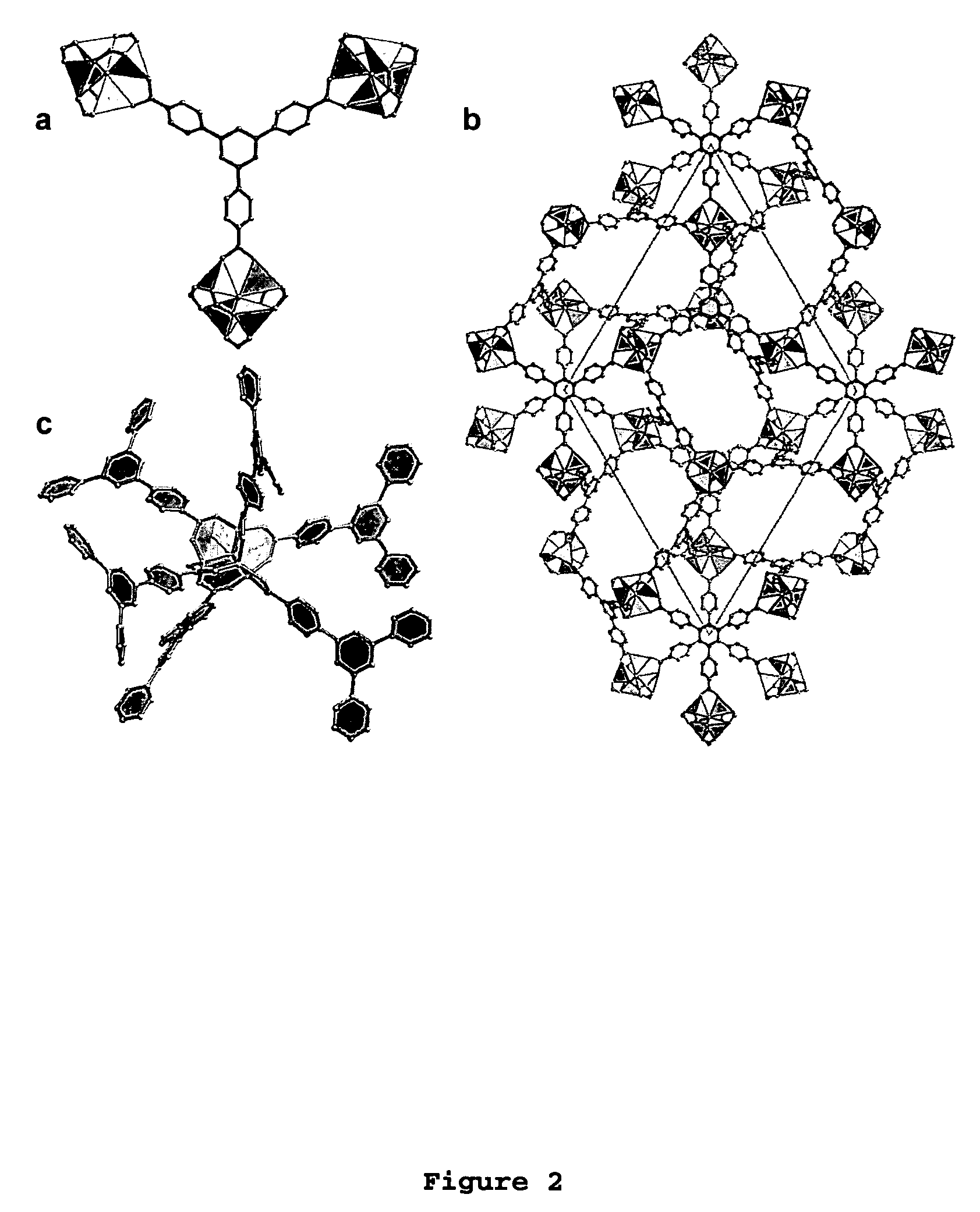
Metal-organic polyhedra
InactiveUS20050124819A1Iron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesMetal clustersCounterion
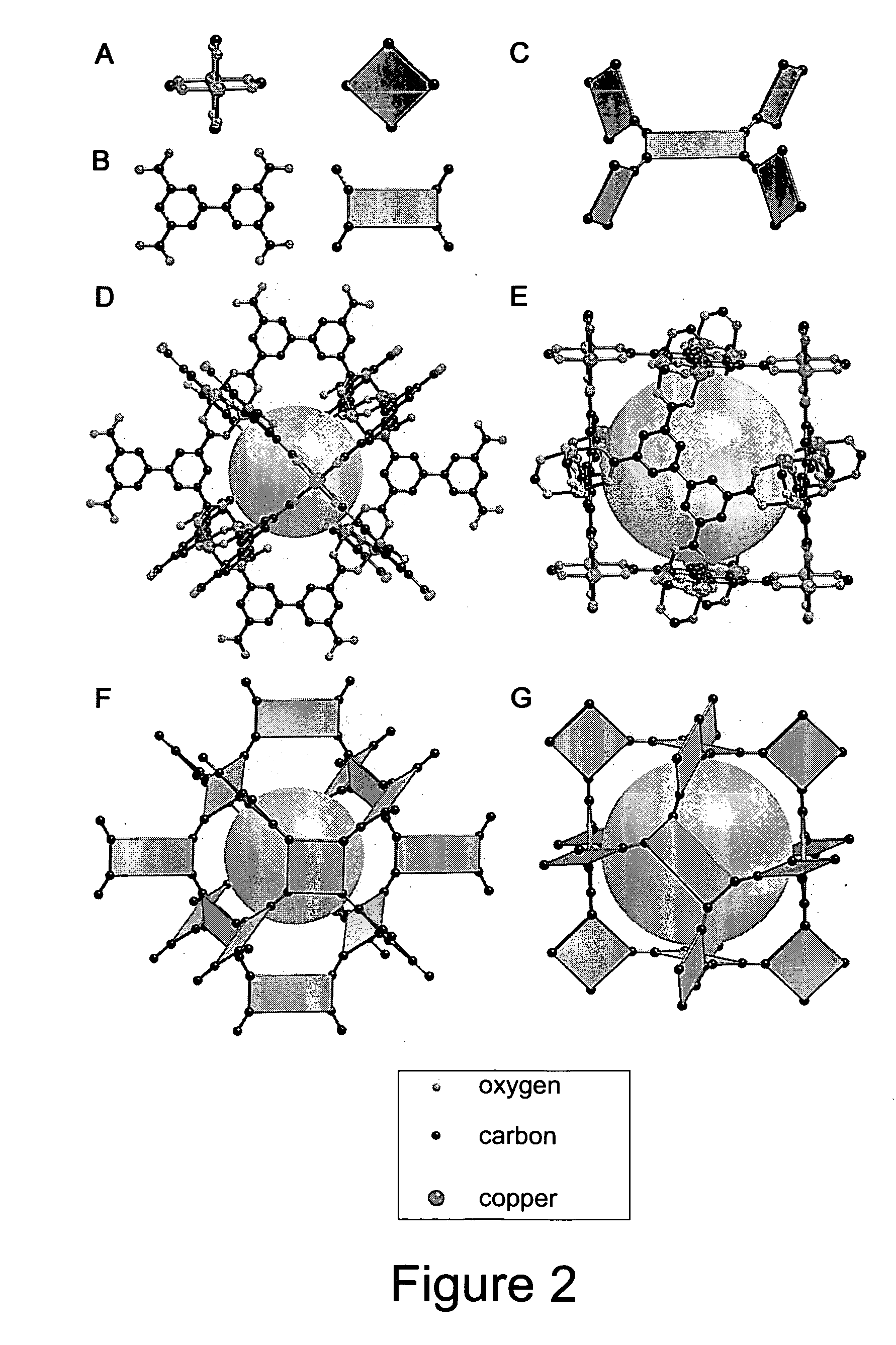
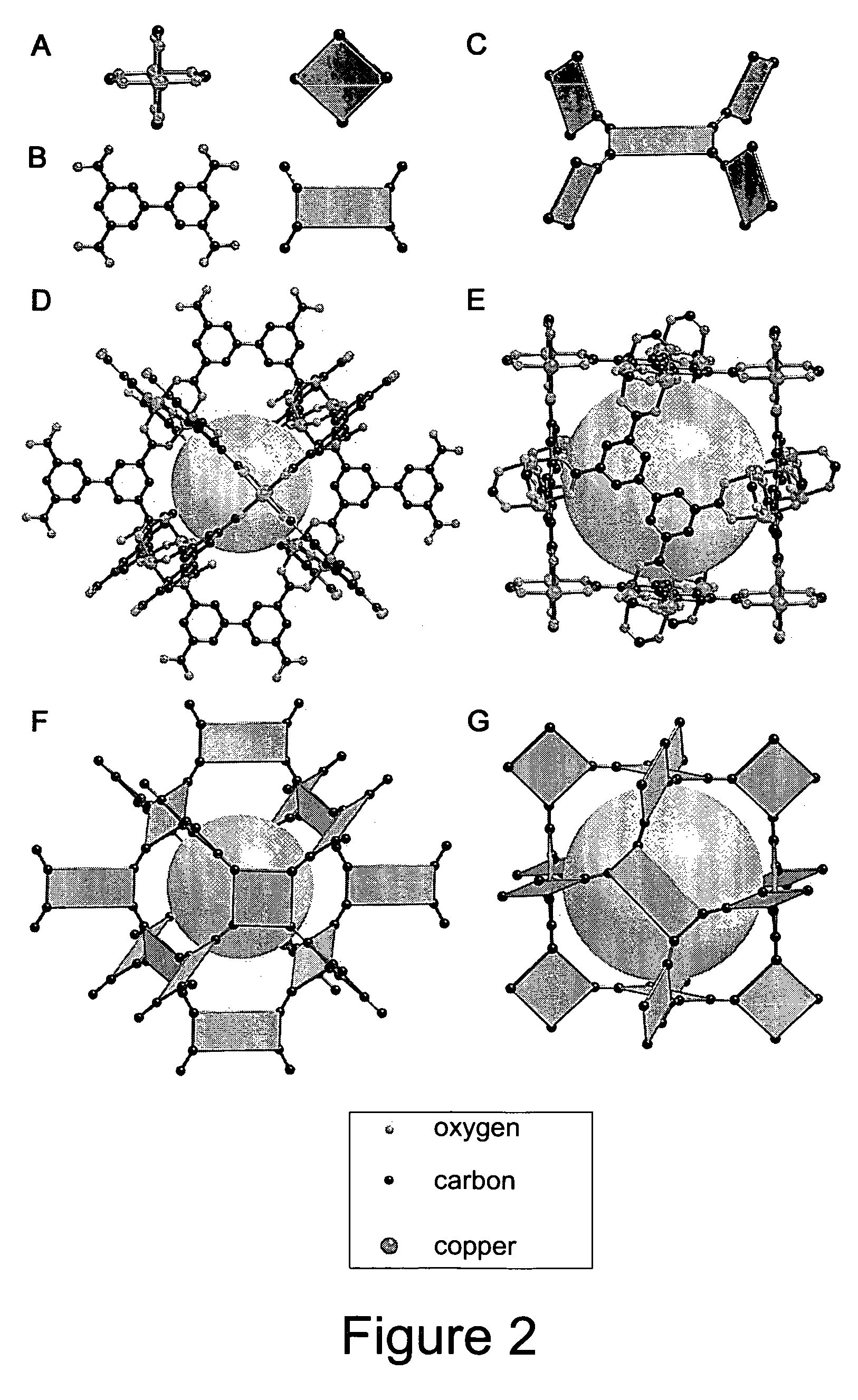
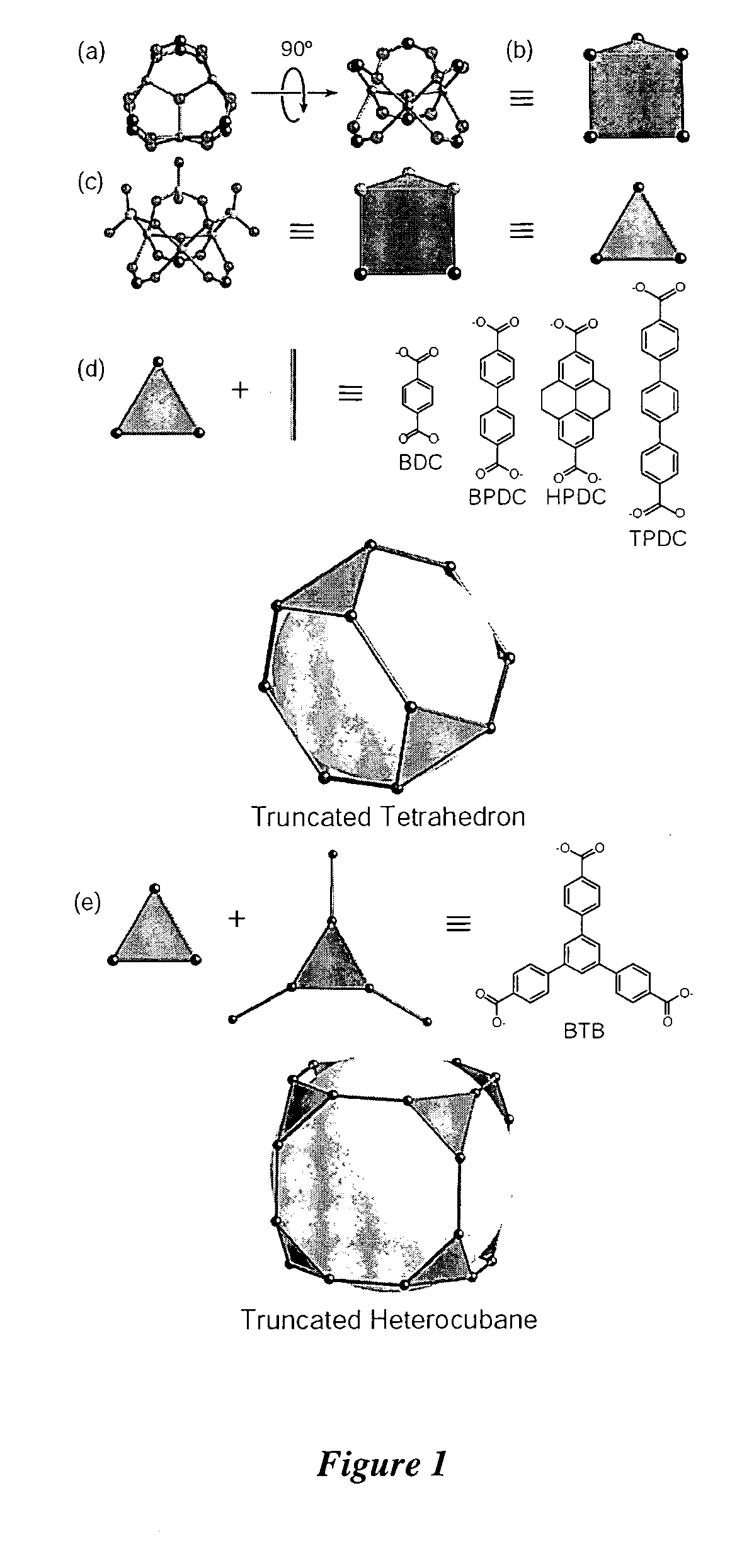
The present invention provides porous metal-organic polyhedra. The porous metal-organic polyhedra of the present invention comprises a plurality of metal clusters each of which have two or more metal ions, and a sufficient number of capping ligands to inhibit polymerization of the metal organic polyhedra. The porous metal-organic polyhedra further includes a plurality of multidentate linking ligands that connect adjacent metal clusters into a geometrical shape describable as a polyhedral with metal clusters positioned at one or more vertices of the polyhedron. The present invention also provides a method of making the porous metal-organic polyhedra in which a solution comprising a solvent, one or more ions, and a counterions that complexes to the porous metal-organic polyhedra as a capping ligand to inhibit polymerization of the metal organic polyhedra, with a multidentate linking ligand.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
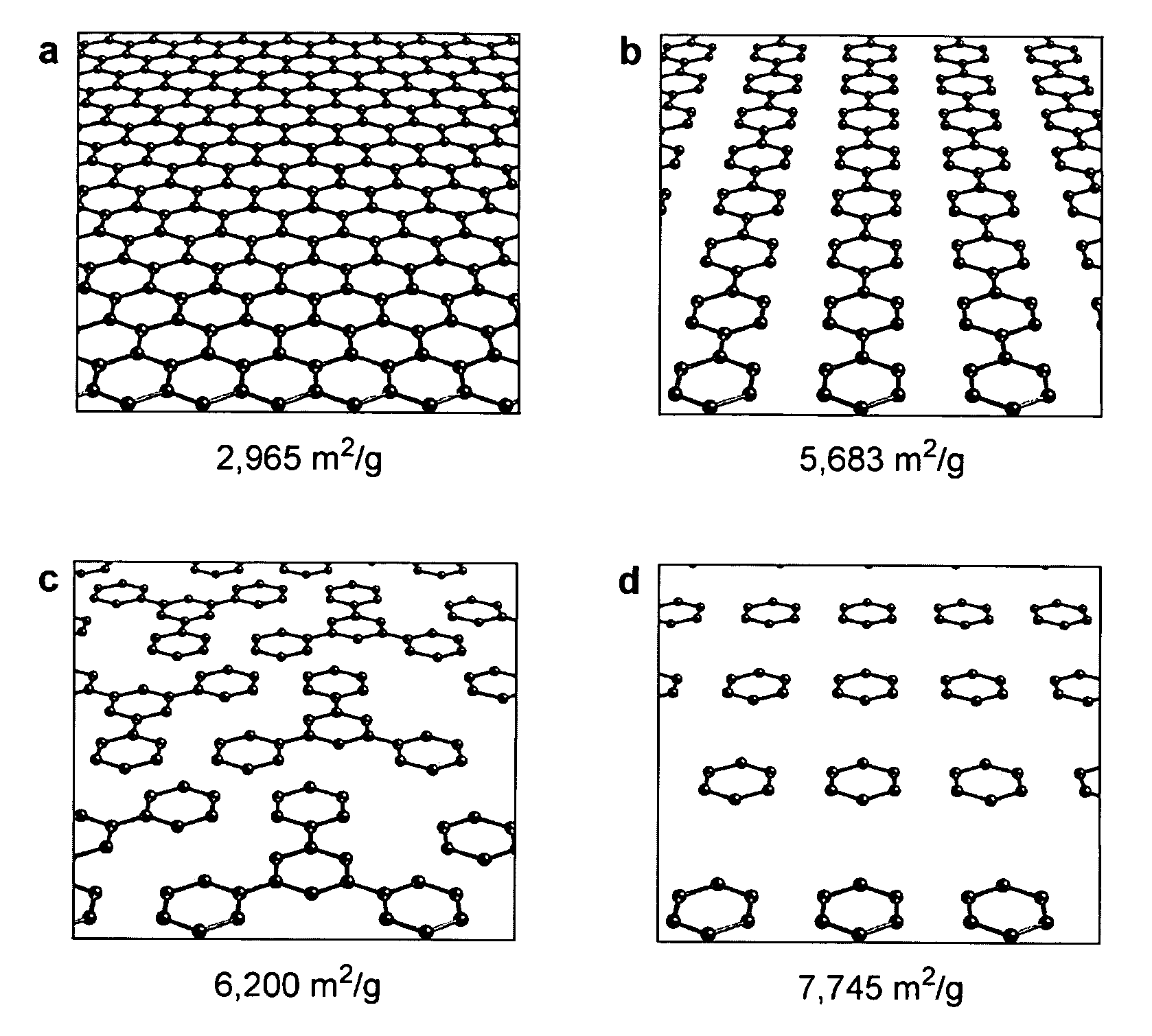
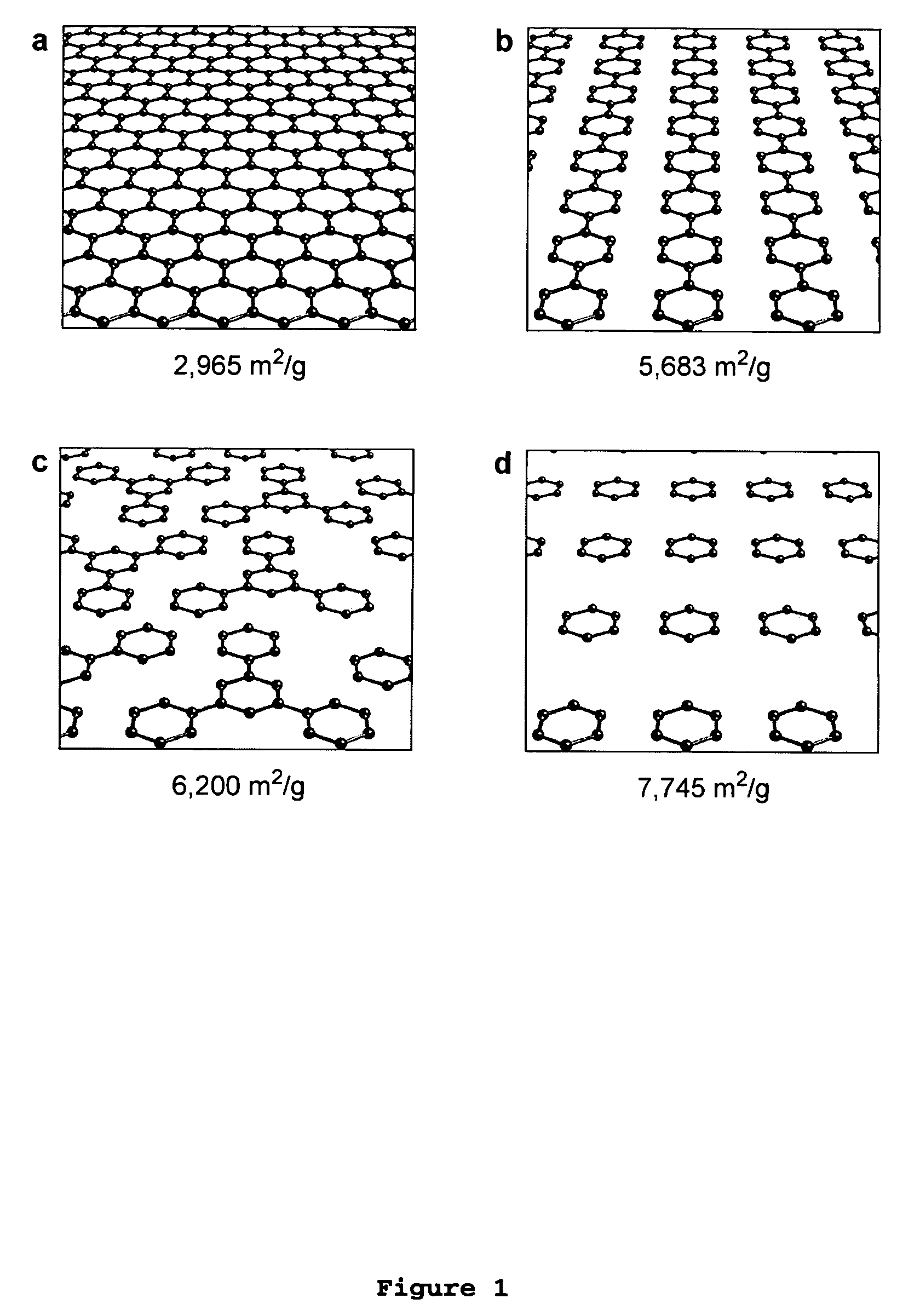
Implementation of a strategy for achieving extraordinary levels of surface area and porosity in crystals
InactiveUS7652132B2Large specific surface areaIncrease the number ofGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMetal clustersPorosity
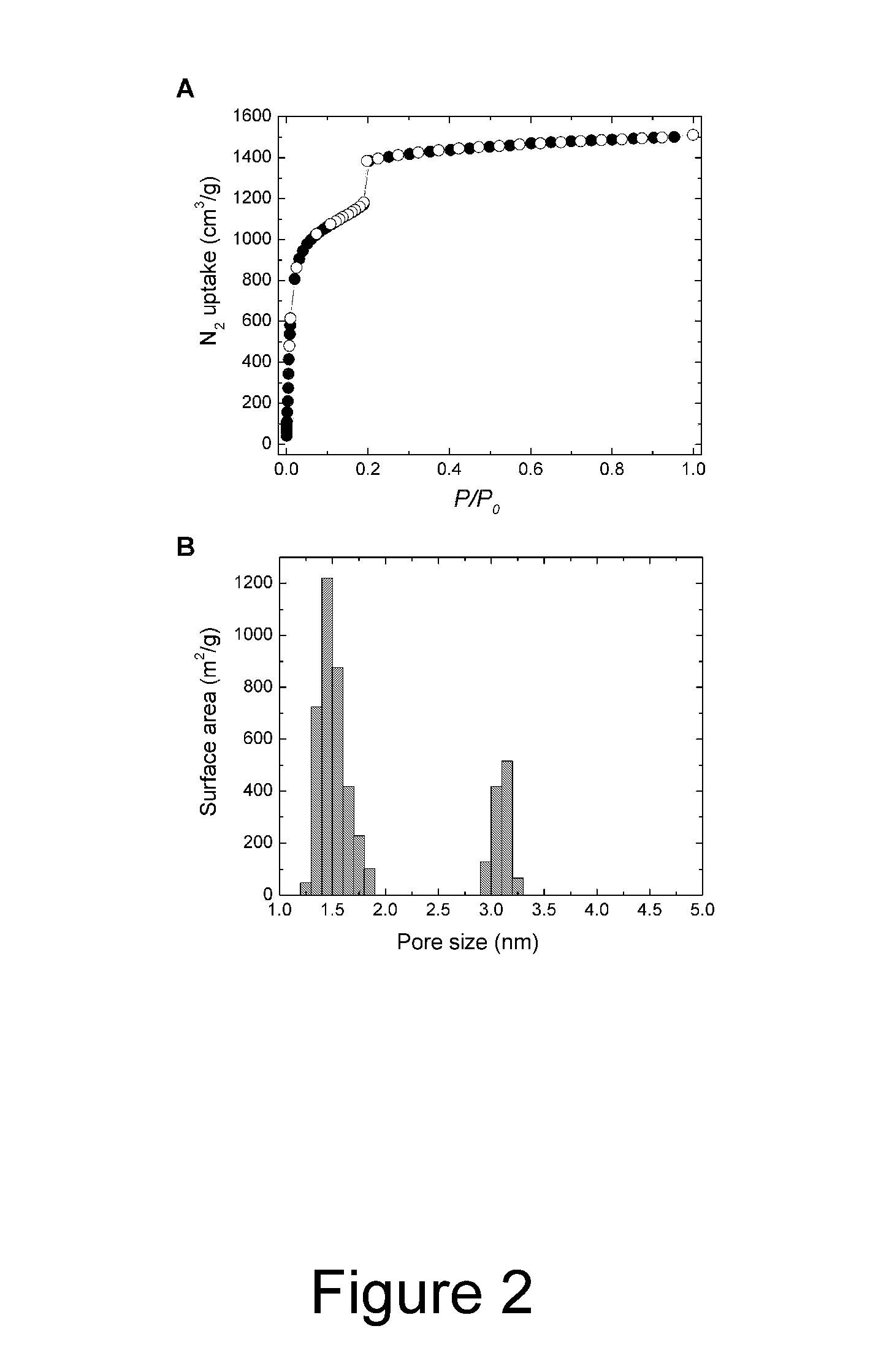
The present invention provides a metal-organic framework (“MOF”) comprising a plurality of metal clusters and a plurality of multidentate linking ligands. Each metal of the plurality of metal clusters comprises one or more metal ions. Each ligand of the plurality of multidentate linking ligands connects adjacent metal clusters. The present invention also provides a method of forming the metal-organic framework. The method of the invention comprises combining a solution comprising one or metal ions with a multidentate linking ligand having a sufficient number of accessible sites for atomic or molecular adsorption that the surface area of the resulting metal-organic framework is greater than 2,900 m2 / g.
Owner:MICHIGAN UNIV OF RGT
Cigarette filter using intermetallic compounds
A filter such as a cigarette filter having a metal reagent which selectively binds with a gaseous component of a gas stream such as tobacco smoke. The metal reagent comprises nanometer or micrometer size clusters of a transition metal or alloy containing a transition metal. The transition metal can be incorporated in an intermetallic compound such as titanium aluminide or iron aluminide. The metal clusters can be incorporated in or on a support material such as silica gel, porous carbon or a zeolite. The metal reagent can remove the gaseous component by selectively binding to unsaturated hydrocarbons such as 1,3-butadiene. The binding can occur by insertion of a metal atom of the metal reagent into a C—H bond or a C—C bond of the gaseous component.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Carbon nanotube pastes and methods of use
Dispersable pastes comprising single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) in water or in an organic solvent are prepared. The method of preparing the dispersable pastes comprises in general the following steps: a) removal of the catalyst used during the synthesis of SWNT; b) while the SWNT are still wet, addition of the appropriate amount of solvent, in a solvent / SWNT ratio which preferably varies between 30:1 and 100:1, depending on the desired viscosity of the paste; and c) high-energy horn sonication with a dismembrator probe. The resulting pastes are suitable for easy redispersion in solvents and incorporation in various matrices such as polymers. They are also suitable to be impregnated with metal precursors such as noble metal compounds for example, Pt. Appropriate drying and thermal treatments of the impregnated material produce metal-SWNT composites in which small metal clusters can be uniformly dispersed over the nanotube surface. These metal-SWNT composites may find applications as catalysts as well as electrodes for fuel cells, batteries, and capacitors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Poly metal cluster water purifying material and its preparing method and use
ActiveCN1821108AEfficient removalQuick removalWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processRare earthHigh activity
The present invention relates to polynary metal cluster as water purifying material and its preparation process and use. The water purifying material is prepared with porous material in 50-99 wt%, and two or more metals of Ag, Cu, Zn and RE in 1-50 wt%. The preparation process includes: selecting metal source; adding the metal source directly or after being compounded into water solution into the porous material to form combined body; and introducing reductant after roasting. Water to be purified is made to flow through the water purifying material or mixed with the water purifying material for purifying. The water purifying material has great specific surface area, high activity and high homogeneity, and may be used to eliminate water soluble heavy metal ion, micro organic pollutant, residual chlorine and sterilizing side product in high effect.
Owner:广州净易环保科技有限公司
Carbon nanotube pastes and methods of use
Dispersable pastes comprising single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) in water or in an organic solvent are prepared. The method of preparing the dispersable pastes comprises in general the following steps: a) removal of the catalyst used during the synthesis of SWNT; b) while the SWNT are still wet, addition of the appropriate amount of solvent, in a solvent / SWNT ratio which preferably varies between 30:1 and 100:1, depending on the desired viscosity of the paste; and c) high-energy horn sonication with a dismembrator probe.The resulting pastes are suitable for easy redispersion in solvents and incorporation in various matrices such as polymers. They are also suitable to be impregnated with metal precursors such as noble metal compounds for example, Pt. Appropriate drying and thermal treatments of the impregnated material produce metal-SWNT composites in which small metal clusters can be uniformly dispersed over the nanotube surface. These metal-SWNT composites may find applications as catalysts as well as electrodes for fuel cells, batteries, and capacitors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Surface modification of nanosensor platforms to increase sensitivity and reproducibility
InactiveUS20100256344A1Increasing nanosensor sensitivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMetal clustersHydroquinone Compound
The present invention relates to various methods of sensitizing and modifying nanosensor platforms. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of increasing sensitivity by inhibiting oxidation of one or more 1,4-hydroquinone (HQ) molecules, functionalizing the nanosensor by using one or more diazonium molecules, creating one or more oxidized carbon groups on the nanosensor, and / or depositing one or more metal clusters on the nanosensor.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
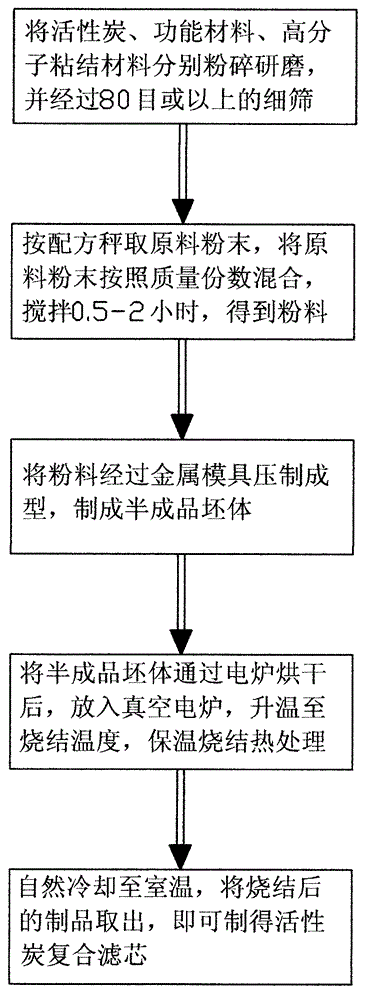
Method for preparing active carbon composite filter core
ActiveCN103143204AImprove rigidityStrong ability to remove pollutionOther chemical processesFiltration separationActivated carbonMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a method for preparing an active carbon composite filter core. The used material of the active carbon composite filter core mainly includes active carbon and a macromolecule binding material. A part of specific functional materials, for example, natural molecular sieve zeolite, nano metal cluster, porous natural diatomite and the like are added according to difference of water source quality and difference of purification demands. The product can be obtained by mixing, stirring, pressing, molding and high-temperature sintering the material. The active carbon powder and the functional material are taken as materials; the macromolecule binding material is added to mix and then pressed and molded through the metal die; the active carbon composite filter core with strong rigidity can be prepared in a high-temperature sintering manner; the products with various shapes and sizes can be processed; and the preparation method is simple and feasible, easily available in raw materials, low in cost, strong in pollution removing capacity, long in service life, and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU NANENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCAL DEV CO LTD +1
Mesh-adjustable molecular sieve
InactiveUS20080184881A1Group 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOther chemical processesMetal clustersMolecular sieve
Metal-organic framework-based molecular sieves comprising pores with a temperature-adjustable pore opening. The temperature-adjustable pore size molecular sieves comprise a plurality of metal clusters bound with a plurality of amphiphilic ligands, each ligand comprising a functionalized hydrophobic moiety and a functionalized hydrophilic moiety, and wherein the metal clusters and amphiphilic ligand hydrophilic moieties form a metal cluster layer, the metal cluster layer forming at least one hydrophilic pore. On each side of the metal cluster layer, a plurality of associated amphiphilic ligand hydrophobic moieties cooperate with the metal cluster layer to form a tri-layer and a plurality of tri-layers are held in proximity with each other to form at least one hydrophobic chamber. The hydrophobic moieties form temperature-adjustable pore size hydrophobic pores. When adjusted to a pre-selected temperature the temperature-adjustable pore openings allow for the passage of molecules having a size less than the size of the pre-selected temperature-adjustable pore opening.
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERSITY
Coordination Polymer Crystal With Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks and Preparation Method Thereof
ActiveUS20100174047A1Low efficiencyInhibition releaseLithium organic compoundsReversible hydrogen uptakeSimple Organic CompoundsMetal clusters
Disclosed is a coordination polymer crystal with porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), in which, while a crystal state of the coordination polymer crystal is maintained, an additional material selected from the group consisting of an organic compound, a metal cluster, and an organometallic compound is chemically bonded to the coordination polymer crystal. Therefore it is possible easily adsorb and store more guest molecules regardless of a change in an ambient temperature or pressure due to the chemically bonded additional material.
Owner:INSILICO CO LTD
Gallium nitride based light emitting device and the fabricating method for the same
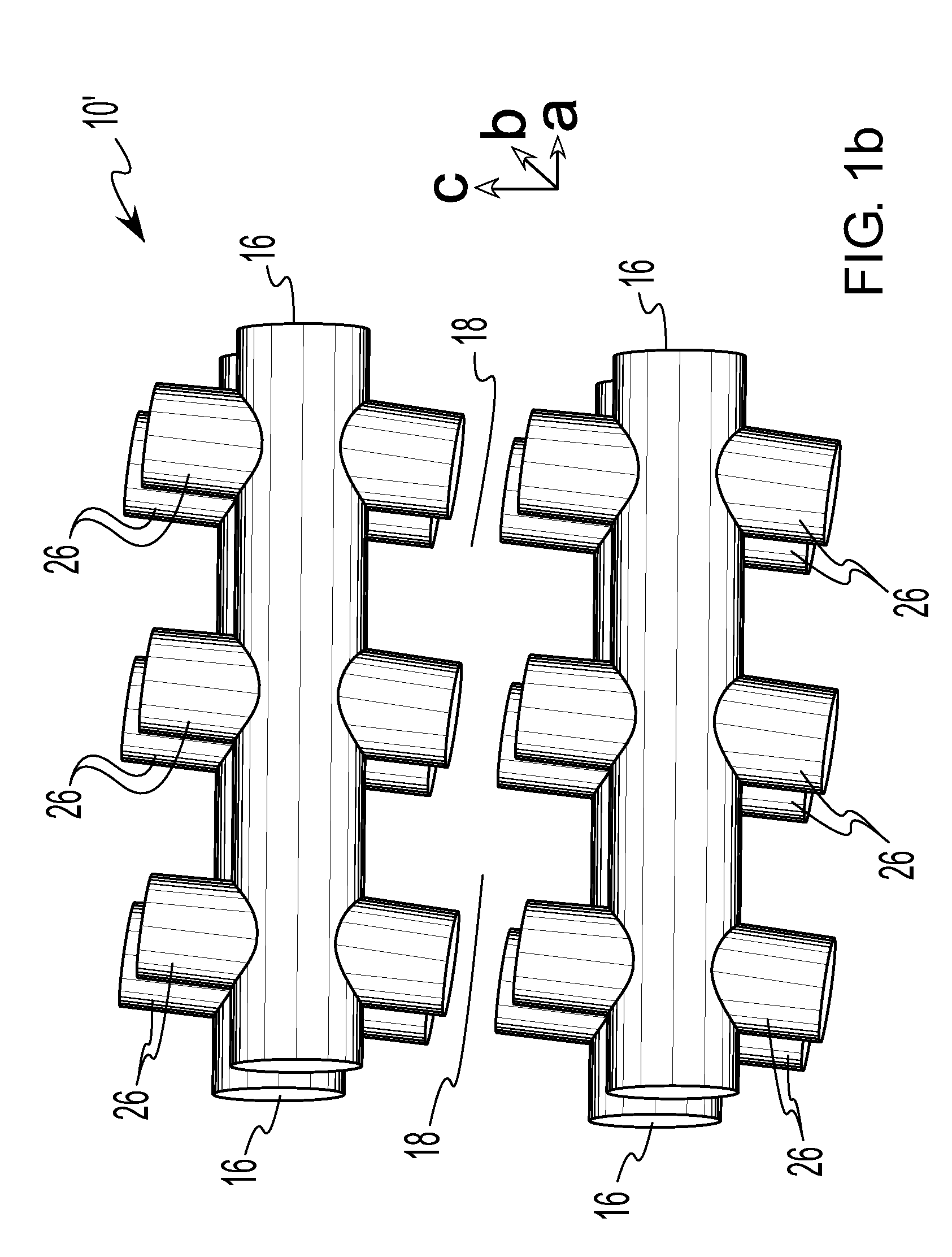
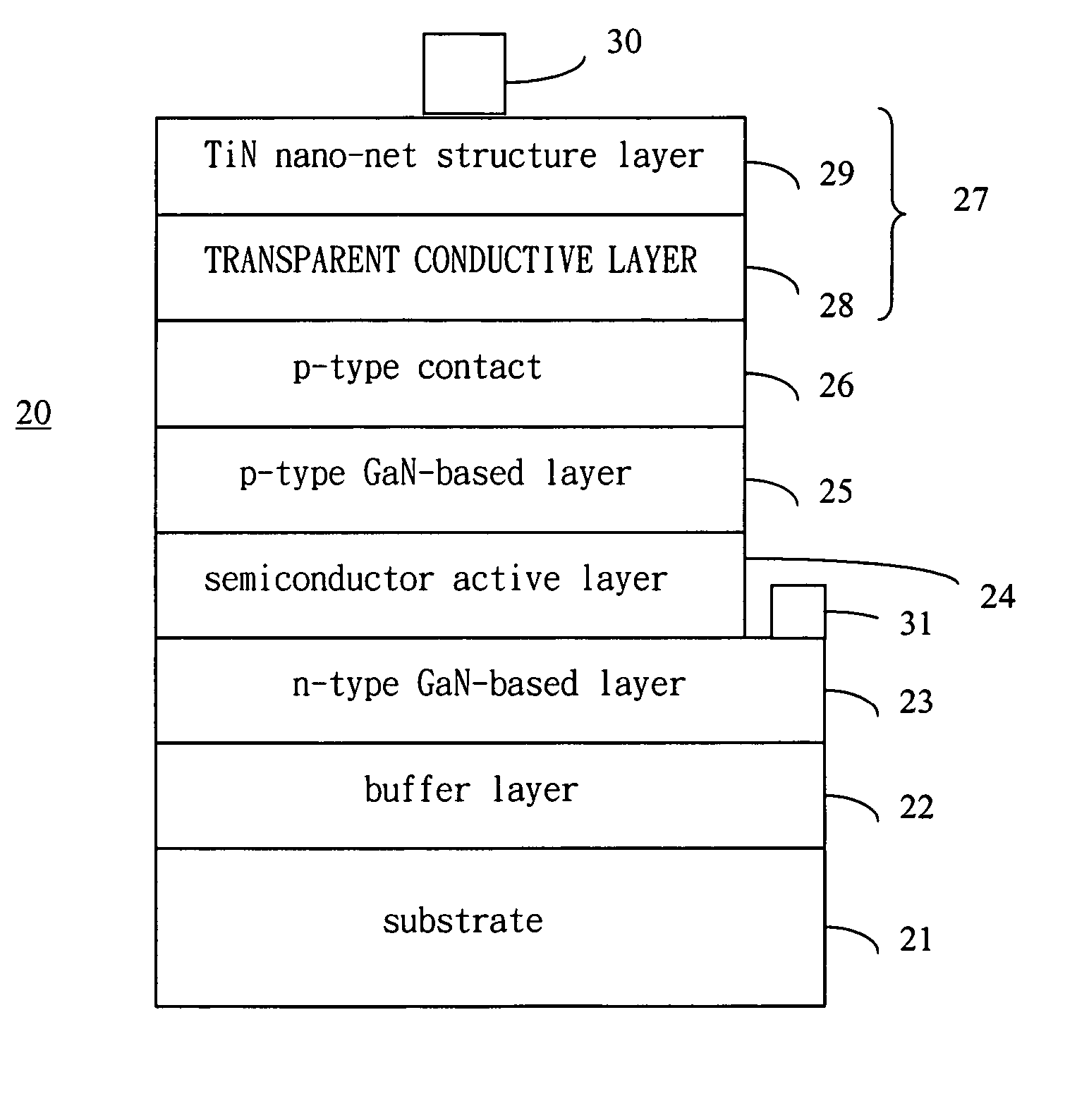
InactiveUS20050263779A1Improve light extraction efficiencyImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesMicro structureMetal clusters
A GaN-based light-emitting device and the fabricating method for the same are described. The light-emitting device is a light-emitting body with a light extraction layer thereon. The light-emitting body has some GaN-based layers and is capable of emitting a light when energy is applied. The light extraction layer is a double layered structure having a current spreading layer and a micro-structure layer, or a single layered structure without the current spreading layer. The micro-structure layer is a TiN layer with a nano-net structure obtained by nitridation of a Ti layer or a Pt layer with metal clusters thereon obtained by annealing of a Pt layer.
Owner:SEMILEDS OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrode material surface coating method and application thereof
InactiveCN106099047ANovel and ideal encapsulation technologyIncrease coverageCell electrodesMetal clustersMetal-organic framework
The invention provides an electrode material surface coating method and application thereof. The method includes steps: (1) enabling in-situ growth of a metal organic skeleton on the surface of an electrode material; (2) subjecting the metal organic skeleton coated electrode material to heat treatment to obtain an oxide coated electrode material. Since the metal organic skeleton material with appropriate morphologic size and target ion metal clusters is designed as a precursor and converted into nanometer oxide after heat treatment, effective coating of the electrode material with the metal oxide and regulation of structure and coating amount of the metal oxide can be realized, more surface coating substances and structures difficult to realize by traditional methods can be introduced, and the electrode material surface coating method is a novel electrode material surface coating means.
Owner:SHENZHEN CITY BATTERY NANOMETER TECH
Doped metal organic frameworks for reversible H2 storage at ambient temperature
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are provided. An exemplary MOF includes a plurality of metal clusters, at least one linking ligand, and at least one dopant. Doped MOFs according to embodiments of the present invention have significantly increased H2 uptake capacity, and some embodiments meet the 2010 DOE H2 storage target of 6 wt % at a temperature ranging from −30 to 80° C. and a pressure less than or equal to 100 bar.
Owner:GODDARD WILLIAM A +1
Porous coordination copolymers and methods for their production
ActiveUS20090062409A1Solve problemsOther chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal clustersCopolymer
A coordination polymer includes a plurality of metal atoms or metal clusters linked together by a plurality of organic linking ligands. Each linking ligand comprises a residue of a negatively charged polydentate ligand. Characteristically, the plurality of multidentate ligands include a first linking ligand having first hydrocarbon backbone and a second ligand having a second hydrocarbon backbone. The first hydrocarbon backbone is different than the second hydrocarbon backbone.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Air purification system
An air purification system that comprises a substrate, and at least one layer of photocatalysts. The at least one layer of photocatalysts further comprise a plurality of metal clusters.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Coordination polymer crystal with porous metal-organic frameworks and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS8093350B2Low efficiencyInhibition releaseLithium organic compoundsReversible hydrogen uptakeMetal clustersSimple Organic Compounds
Disclosed is a coordination polymer crystal with porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), in which, while a crystal state of the coordination polymer crystal is maintained, an additional material selected from the group consisting of an organic compound, a metal cluster, and an organometallic compound is chemically bonded to the coordination polymer crystal. Therefore it is possible easily adsorb and store more guest molecules regardless of a change in an ambient temperature or pressure due to the chemically bonded additional material.
Owner:INSILICO CO LTD
Method of preparing size-selected metal clusters
InactiveUS7713907B2High catalytic efficiencyEasy to produceMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsMetal clustersSize selective
The invention provides a method for depositing catalytic clusters on a surface, the method comprising confining the surface to a controlled atmosphere; contacting the surface with catalyst containing vapor for a first period of time; removing the vapor from the controlled atmosphere; and contacting the surface with a reducing agent for a second period of time so as to produce catalyst-containing nucleation sites.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method for preparing water-soluble glowing metal clusters of platinum, gold, silver and copper and application
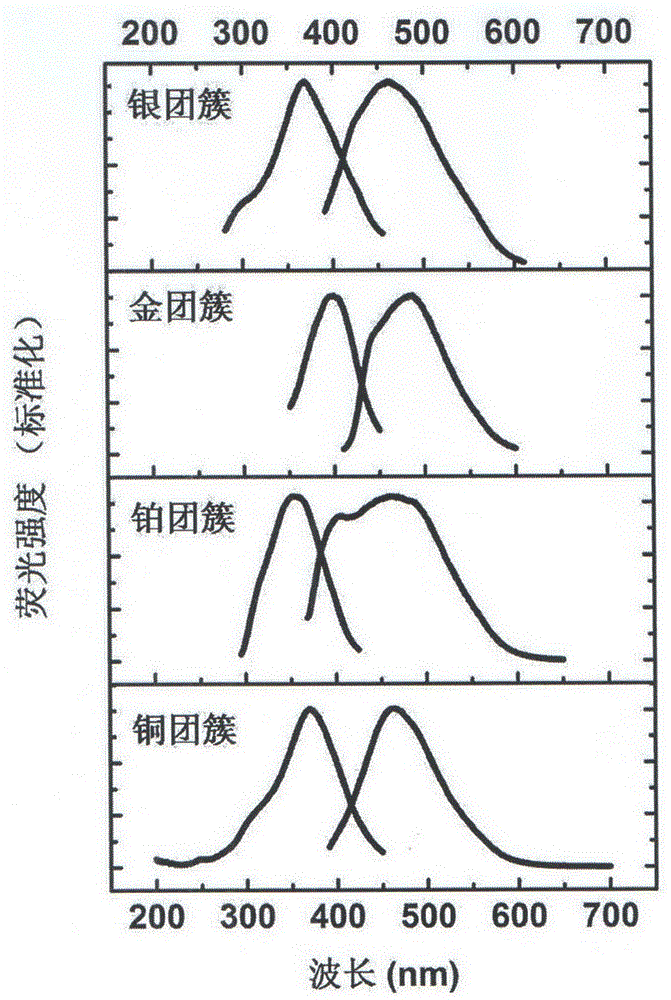
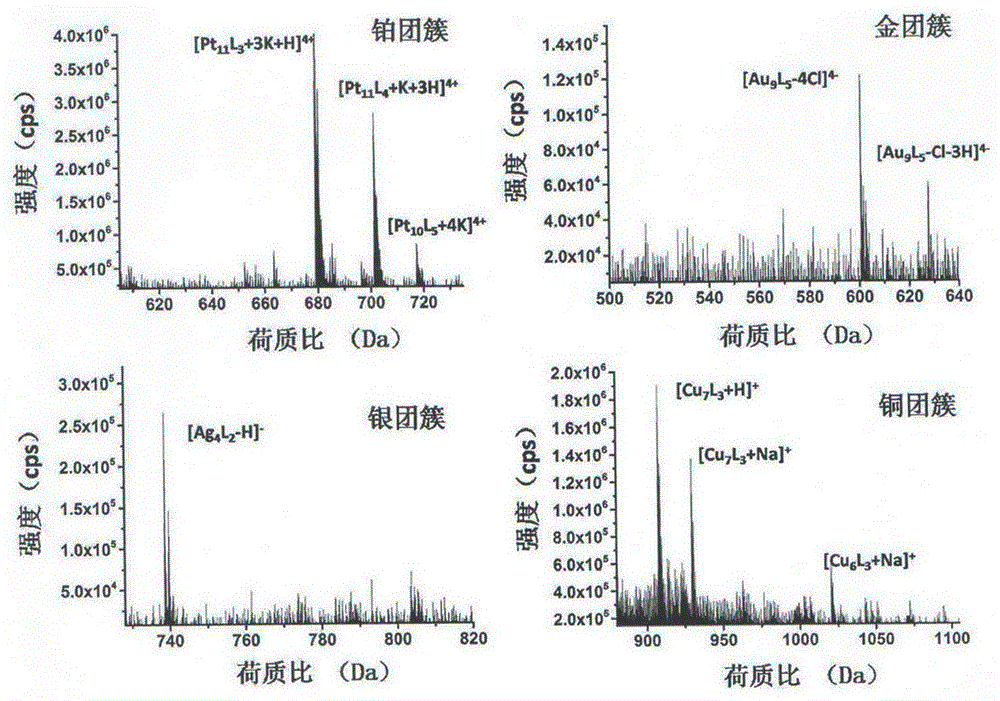
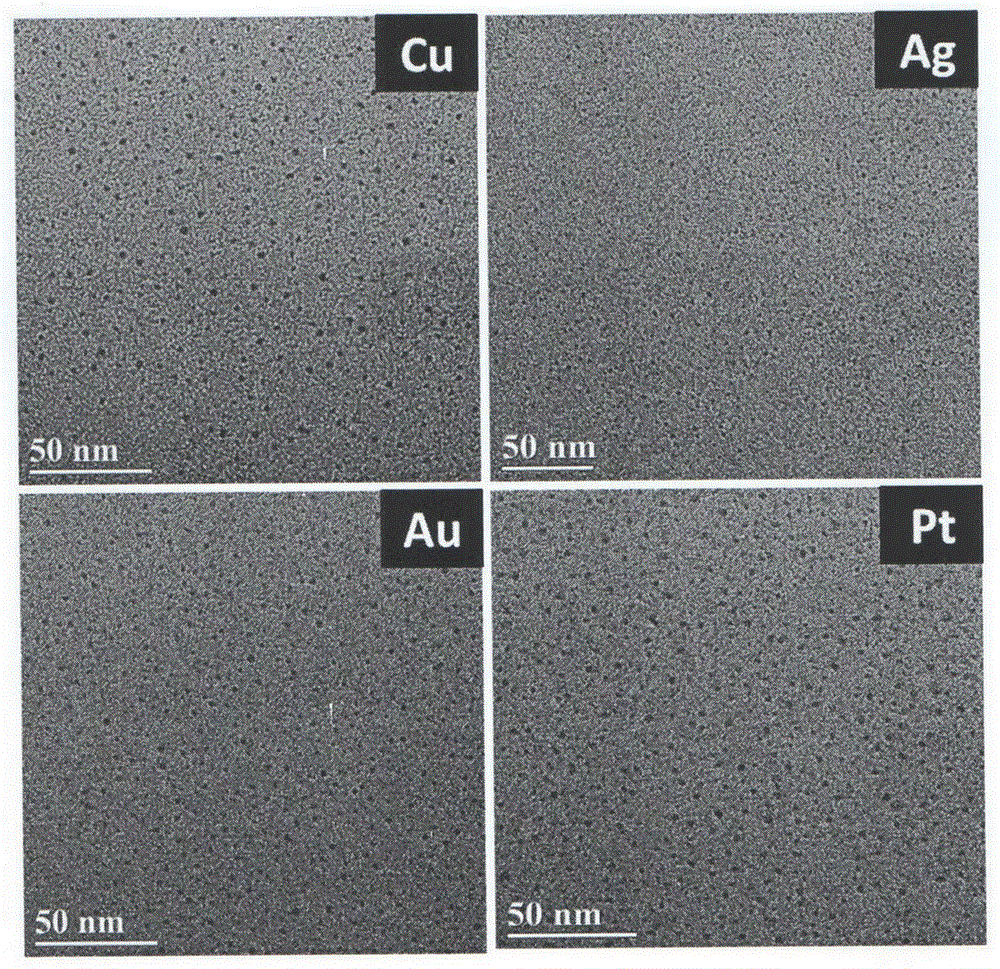
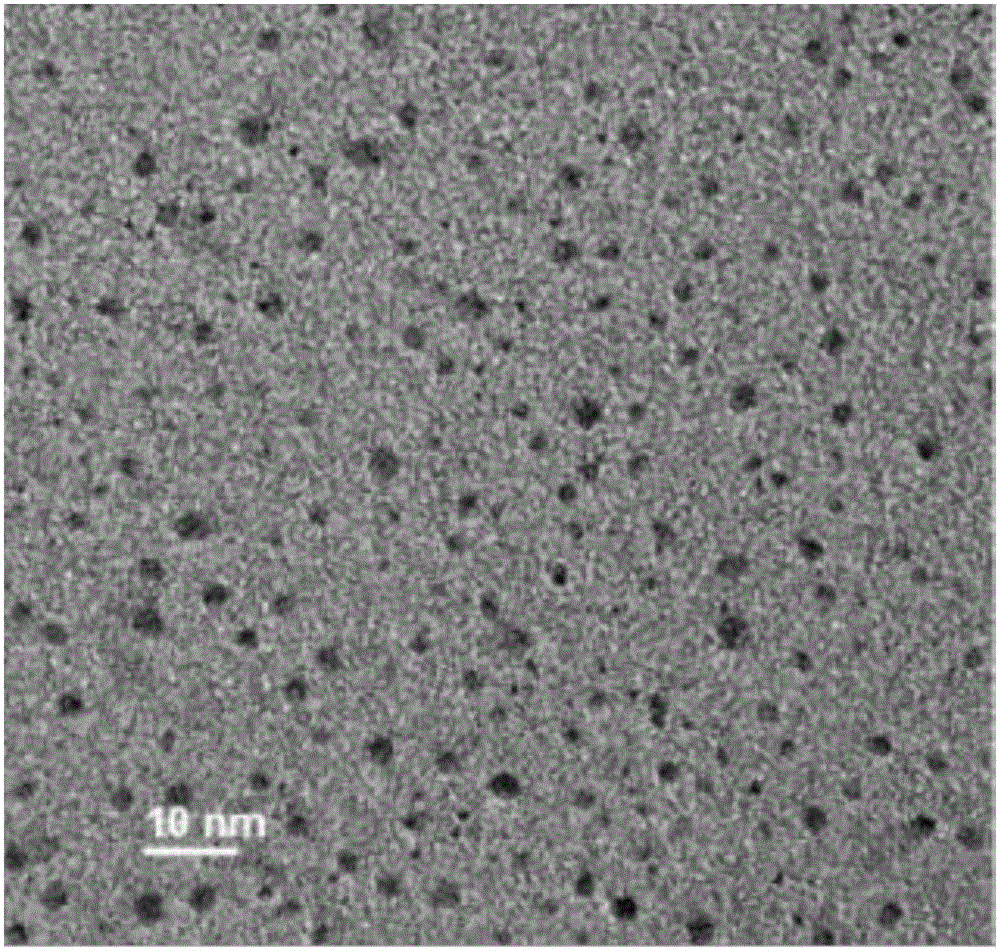
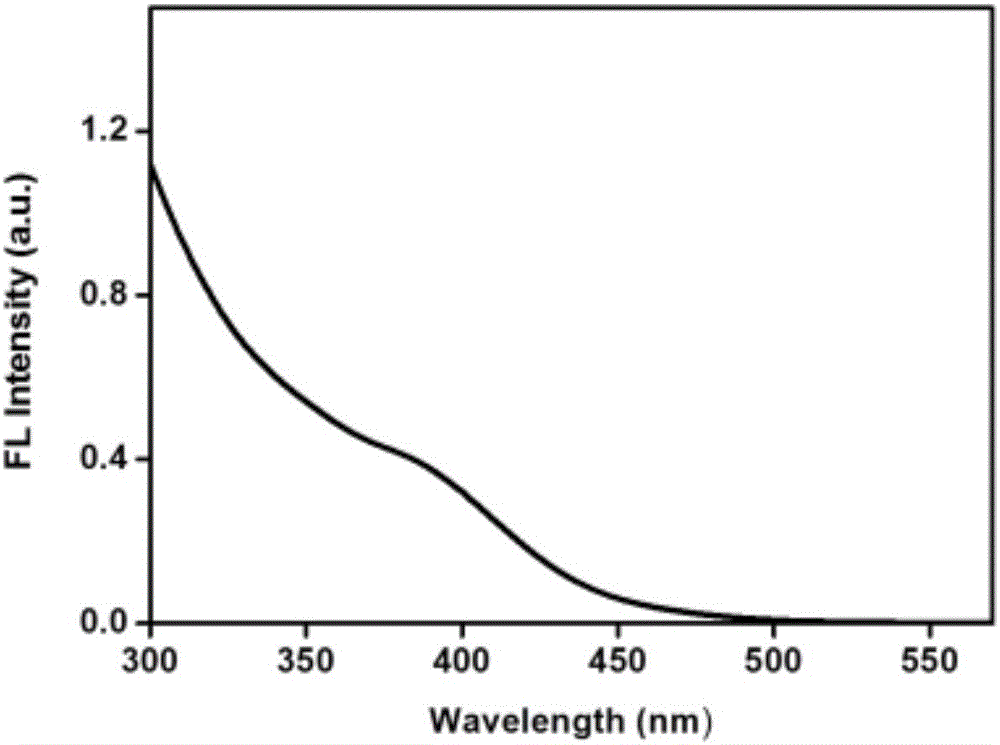
InactiveCN105965028AGentle and rapid size distributionUniform size distributionNanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsPlatinumMetal clusters
The invention relates to a method and application for preparing water-soluble luminescent metal clusters of platinum, gold, silver and copper. This method uses the biomolecule histidine as a stabilizer and ascorbic acid as a reducing agent to prepare four metal clusters with photoluminescent properties of platinum, gold, silver and copper. This method is non-toxic and harmless, and the conditions are mild and fast. , the size distribution of the generated metal clusters is uniform, the particle size is 1-2 nm, and it has good luminous efficiency. The luminous efficiencies of metal platinum, gold, silver, and copper clusters prepared by the method of the present invention are 2.93%, 13.1%, 6.97%, and 8.26%, respectively, and have high selective response to aqueous phase iron ions, and the fluorescence intensity will decrease. Significantly decreased with the increase of iron ion concentration. The linear response ranges to iron ion concentration are 0.05-110μmol / L, 5-125μmol / L, 2.5-500μmol / L and 0.5-100μmol / L, respectively. It can be used as a high-sensitivity fluorescent probe for iron ions in the field of biological detection. It has good application prospect in iron ion detection sensor.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Air purification system
ActiveUS20090246091A1Large specific surface areaReduce mass transfer resistanceGas treatmentDispersed particle separationMetal clustersEngineering
An air purification system that comprises a substrate, and at least one layer of photocatalysts. The at least one layer of photocatalysts further comprise a plurality of metal clusters.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Method for crystallizing amorphous silicon and fabricating thin film transistor using crystallized silicon
InactiveUS20020086470A1Increase the rate of crystallizationReduce the temperatureTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal clustersAmorphous silicon
A method of crystallizing amorphous silicon includes forming an amorphous silicon layer over a substrate, forming a plurality of metal clusters on the amorphous silicon layer, and simultaneously applying a thermal treatment, an electric field, and a magnetic field to crystallize the amorphous silicon layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
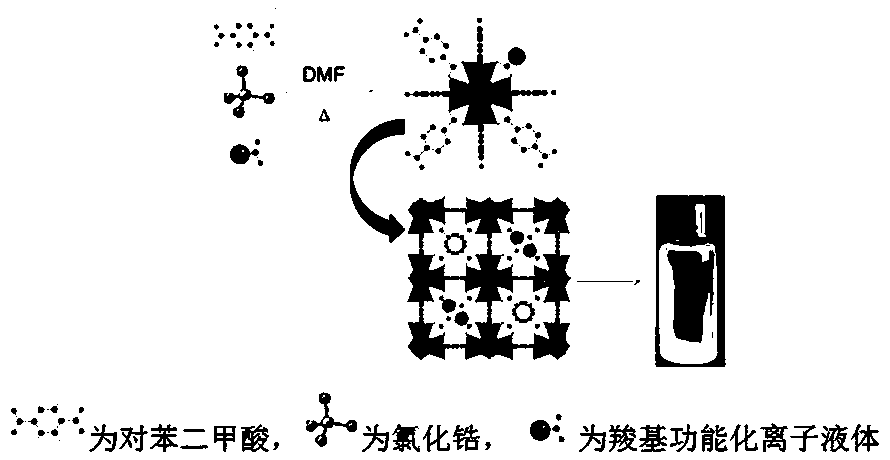
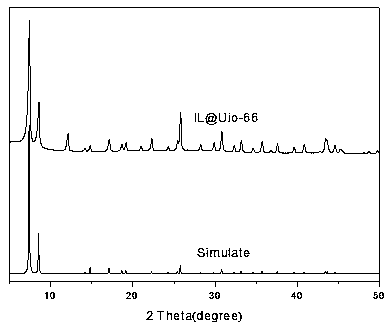
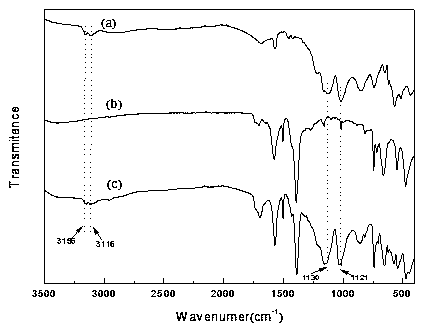
Uio-66 in-situ immobilized carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid composite material as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN108816287AHigh catalytic activityImprove physical stabilityFatty acid esterificationOther chemical processesMetal-organic frameworkIonic liquid
The invention belongs to the technical fields of light-industry and chemical materials, and provides a Uio-66 in-situ immobilized carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid composite material as well as preparation and an application thereof. The composite material uses a metal organic skeleton material Uio-66 as a carrier and a carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid as an active component, carboxyl of the carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid and a zirconium metal cluster are subjected to coordination bonding while the Uio-66 is synthesized, the carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid is immobilized in aUio-66 pore cage in situ, and therefore the composite material is prepared. The composite material provided by the invention has the characteristics of high catalytic activity, a quick mass transferspeed, good selectivity, easy recovery and separation, environmental friendliness, and broad industrialized application prospects in addition to good physical stability and chemical stability; the composite material prepared by the method has a very good effect as a catalyst of an esterification reaction and transesterification reaction of various acids and alcohols; and the composite material hasan obvious adsorption effect on heavy metal ions contained in a liquid as an adsorbent.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
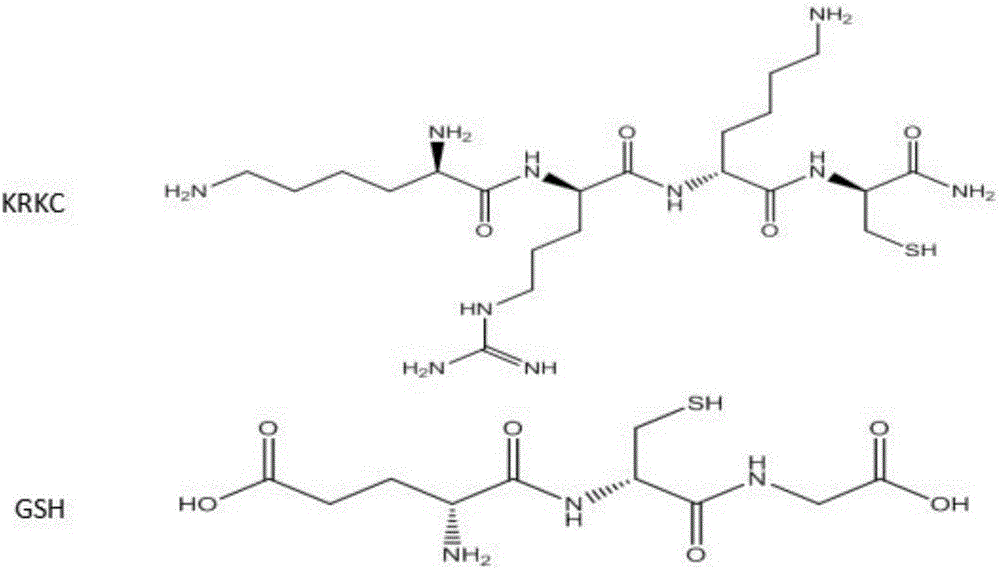
Polypeptide-modified gold nanocluster and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106085420AThe synthesis method is simpleEasy to operateTransportation and packagingMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantum yieldBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional biological nanometer materials, and concretely relates to a polypeptide-modified gold nanocluster and a preparation method thereof. Two polypeptides KRKC and GSH are employed ad stabilizing agents for modification during hydrothermal preparation, a red fluorogold nanocluster with targeting marking effect on cell nucleolus by designing polypeptide sequence for guaranteeing stability of metal clusters, and has the particle size within the scope of 1.5-2.8 nm and the average particle size of 1.9 nm, the gold nanocluster has an obvious absorption peak near 400 nm, when a laser of 400 nm is used to irradiate the gold nanocluster, relatively strong fluorescence emission is generated at the region of 500-750 nm, the emission peak is near 586 nm, and the fluorescent quantum yield of the gold nanocluster is 7%. The method is simple, strong in operability and low in cost, the material is stabilized by the polypeptides, has good biocompatibility, and is low in toxicity, good in stability, long in emission wavelength and beneficial for obtaining relatively good nucleolus imaging effect by employing the polypeptides as the stabilizing agents.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Catalyst for removing dioxin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106732544ALower activation energyIncrease the efficiency of dioxin removalHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsDispersed particle separationMetal clustersActivation energy
The invention relates to a catalyst for removing dioxin. The catalyst comprises carriers, active ingredients and an auxiliary material, the carriers are TiO2 and montmorillonite, and the active ingredients are VOx, CeOx, MnOx and WOx; the mass sum of the carriers and the active ingredients is 100%, and the catalyst comprises 80-90% of TiO2, 1-10% of montmorillonite, 0.3-0.9% of VOx, 1-3% of MnOx, 0.6-1.2% of CeOx and 3-5% of WOx. According to the catalyst for removing the dioxin and the preparation method thereof, the VOx, the CeOx, the MnOx and the WOx serve as the active ingredients, a polybasic metal cluster is formed, the activation energy required by a reaction is reduced, the efficiency of dioxin removal is improved, the montmorillonite of high quality is added, and therefore the mechanical properties such as the abrasive resistance and compressive strength of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TUNA ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Supported catalysts with controlled metal cluster size
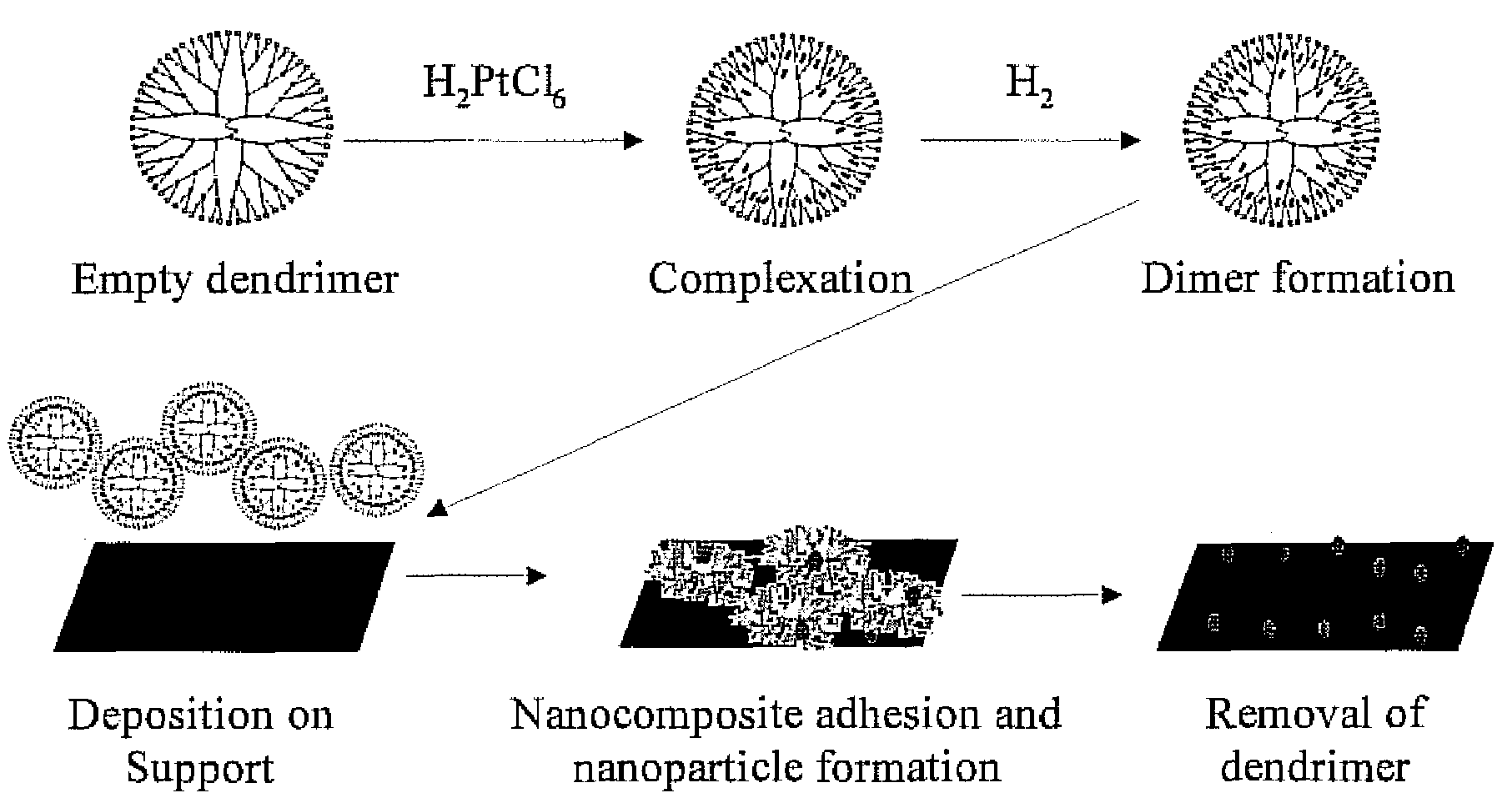
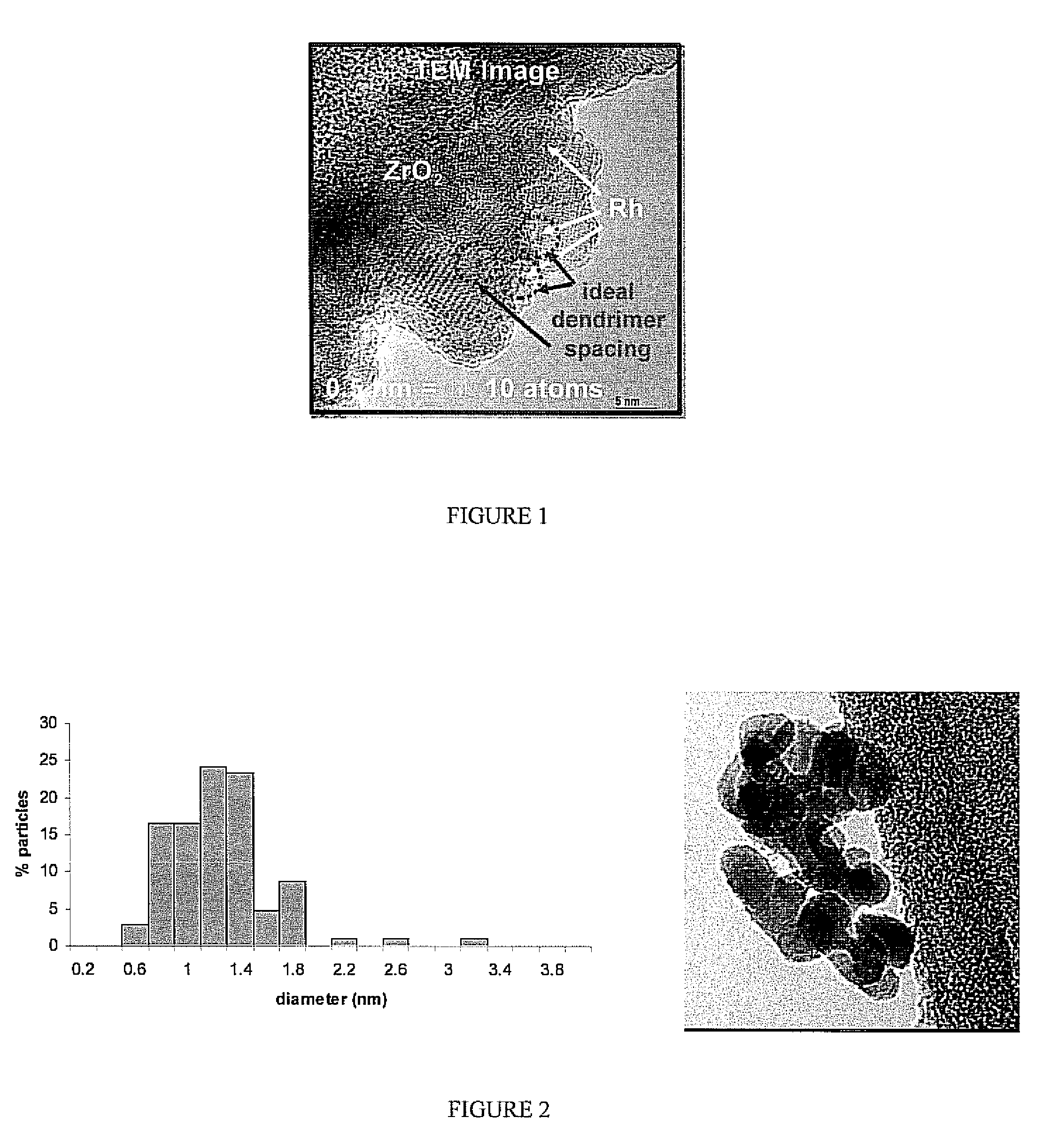
ActiveUS7582586B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationDendrimerSolvent
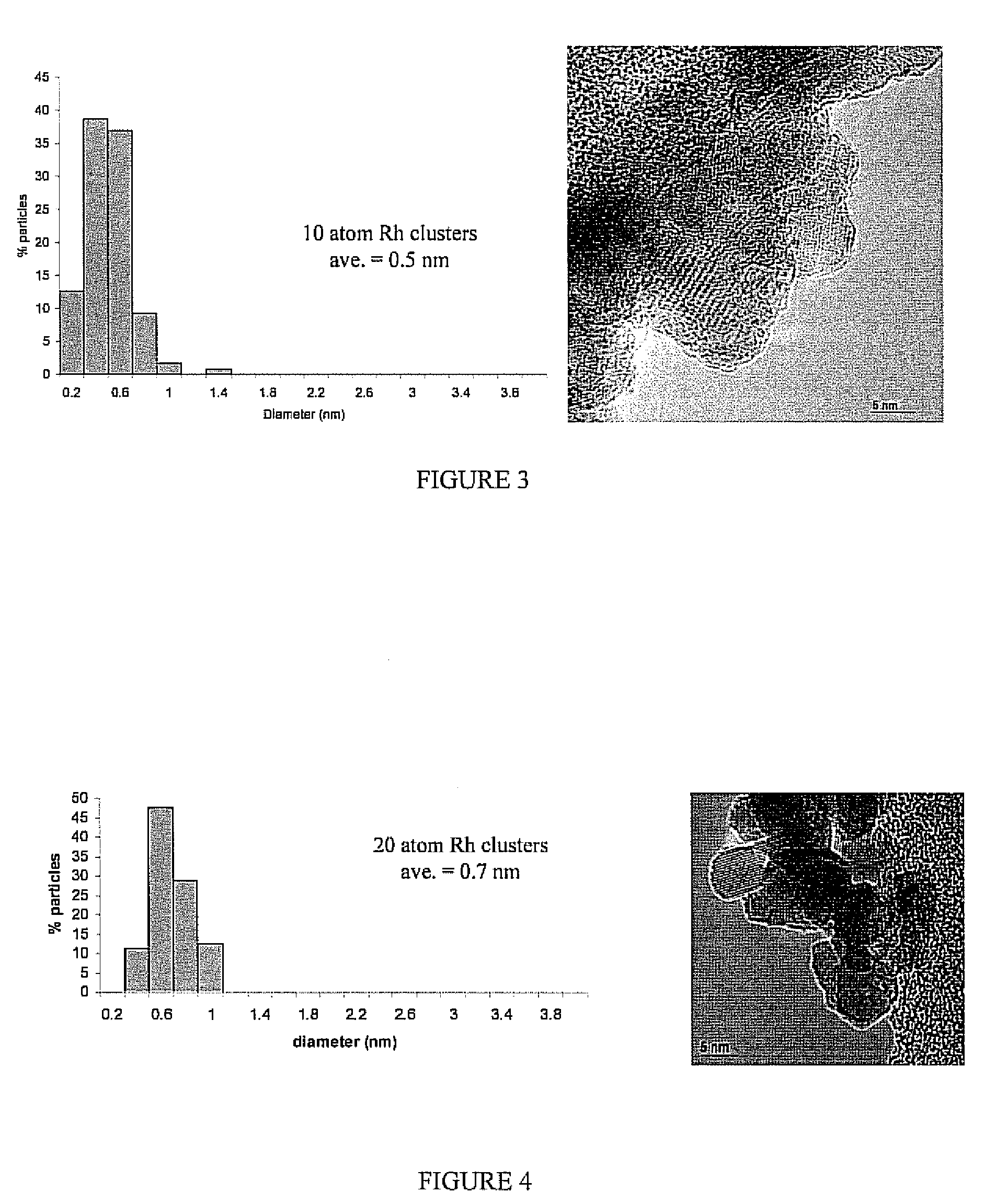
There is disclosed a process for producing a catalyst. The process includes the steps of: a) combining a dendrimer polymer and metal salt in solution forming a metal ion complex; b) exposing the metal ion complex to a reducing environment forming a dendrimer metal nanocomposite; c) depositing the dendrimer metal nanocomposite onto a catalyst support material; d) removing a solvent from the dendrimer metal nanocomposite forming metal clusters; and e) removing the dendrimer polymer forming a catalyst. Additionally, there is disclosed a catalyst having a catalytic metal deposited on a substrate. The catalytic metal is formed in clusters having a size of from 2 to 150 atoms. In another aspect, the clusters may have a spacing of from 2 to 100 nanometers between adjacent metal clusters. Further, in another aspect, the metal clusters which comprise the catalyst have a size distribution in which 70% of the clusters are within 0.6 nm of the average diameter and 99% of the particles are within 1.5 nm of the average diameter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA +1
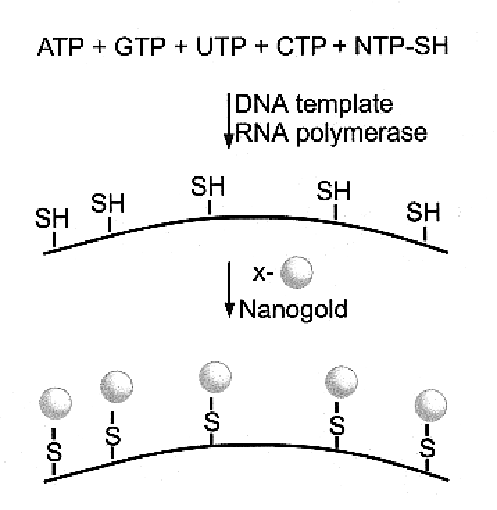
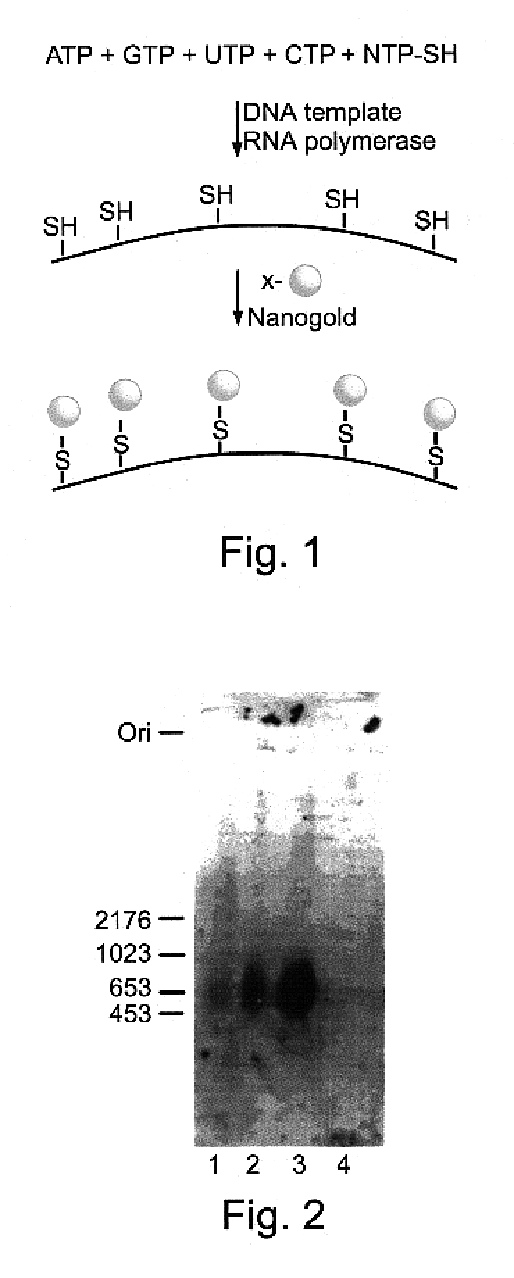
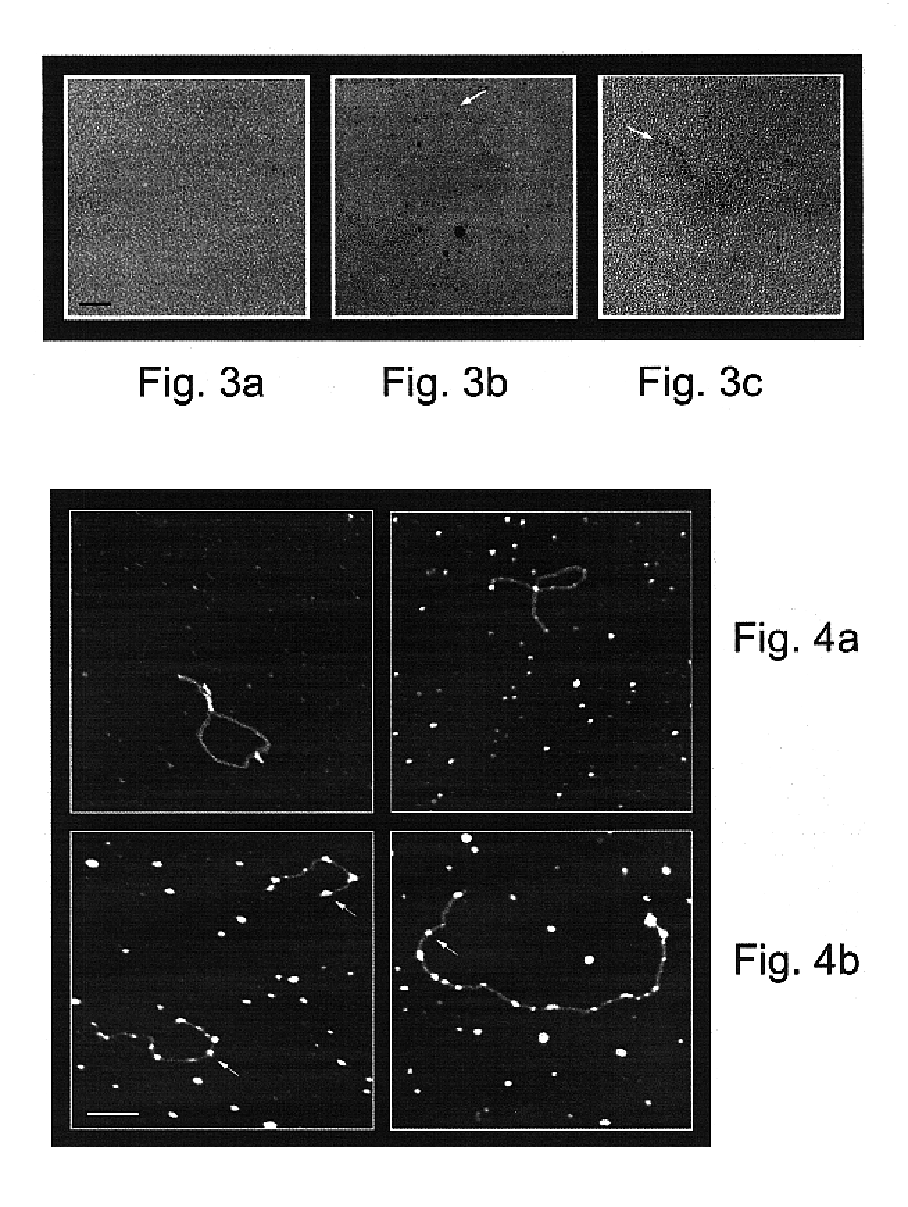
Metal cluster containing nucleotides and nucleic acids, and intermediates therefor
Nucleotides including a sugar moiety, a pyrimidine or purine base and a terminal thiol group at a side chain covalently linked to pyrimidine or purine base of the nucleotide, and optionally further including a metal cluster covalently linked through the terminal thiol group at said side chain to the pyrimidine or purine base of the nucleotide, and nucleic acids incorporating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com