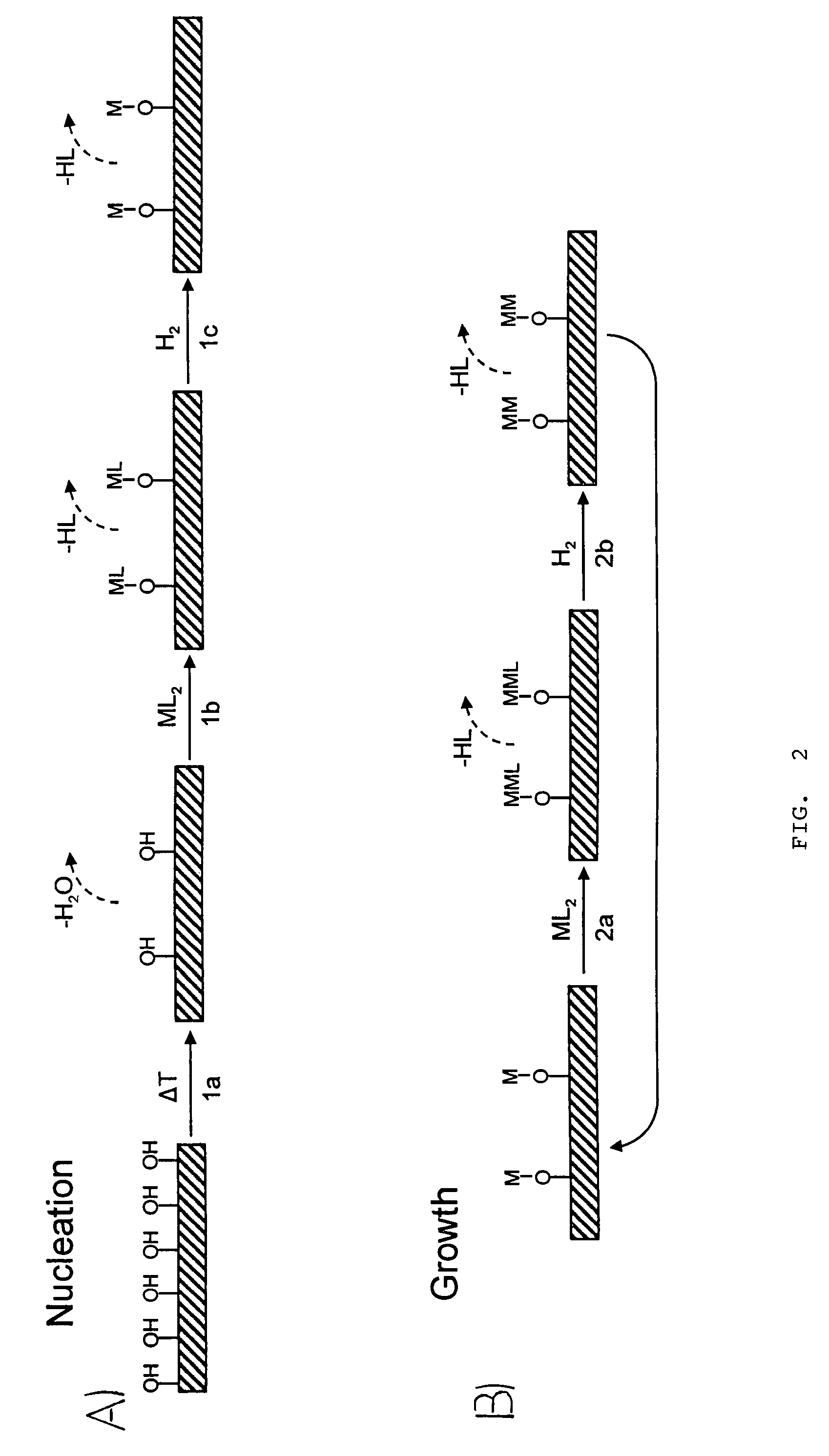
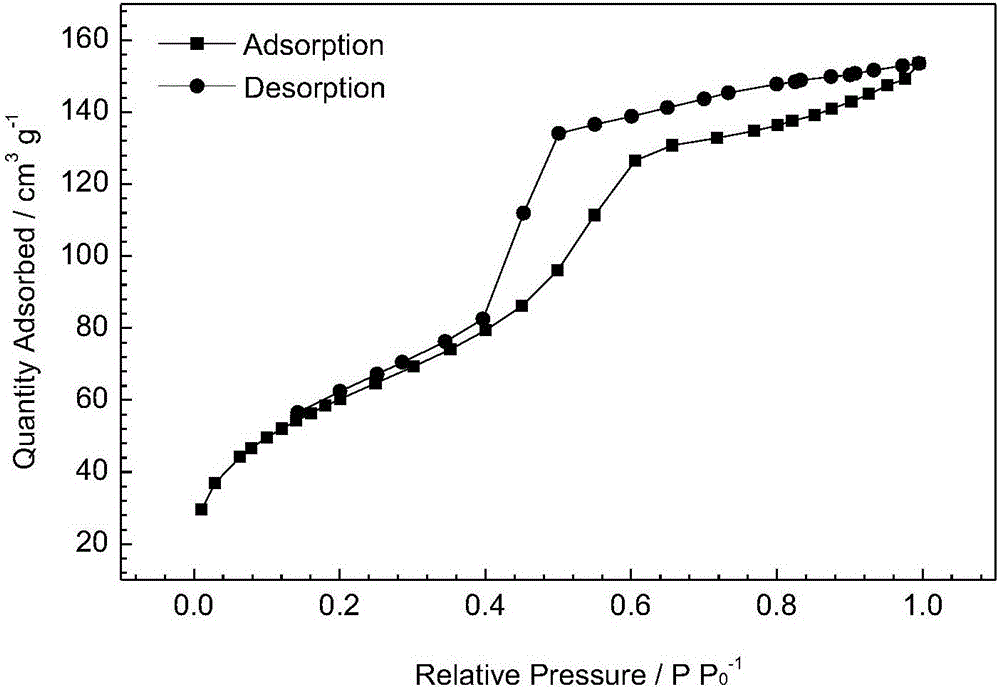
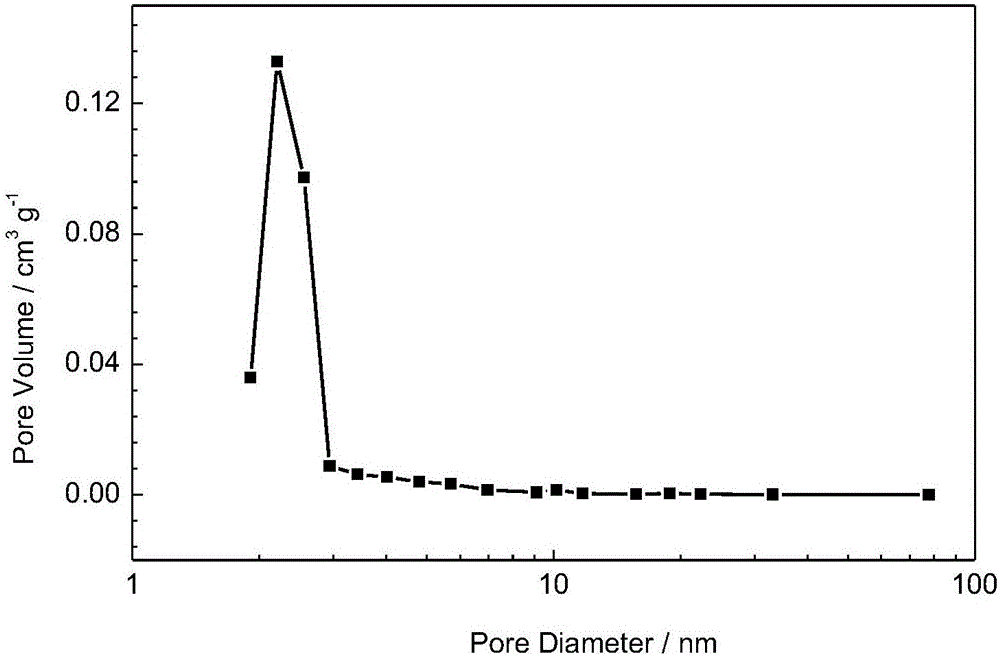
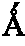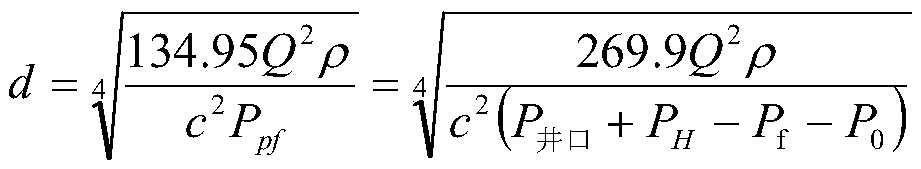Patents
Literature
86 results about "Size selective" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
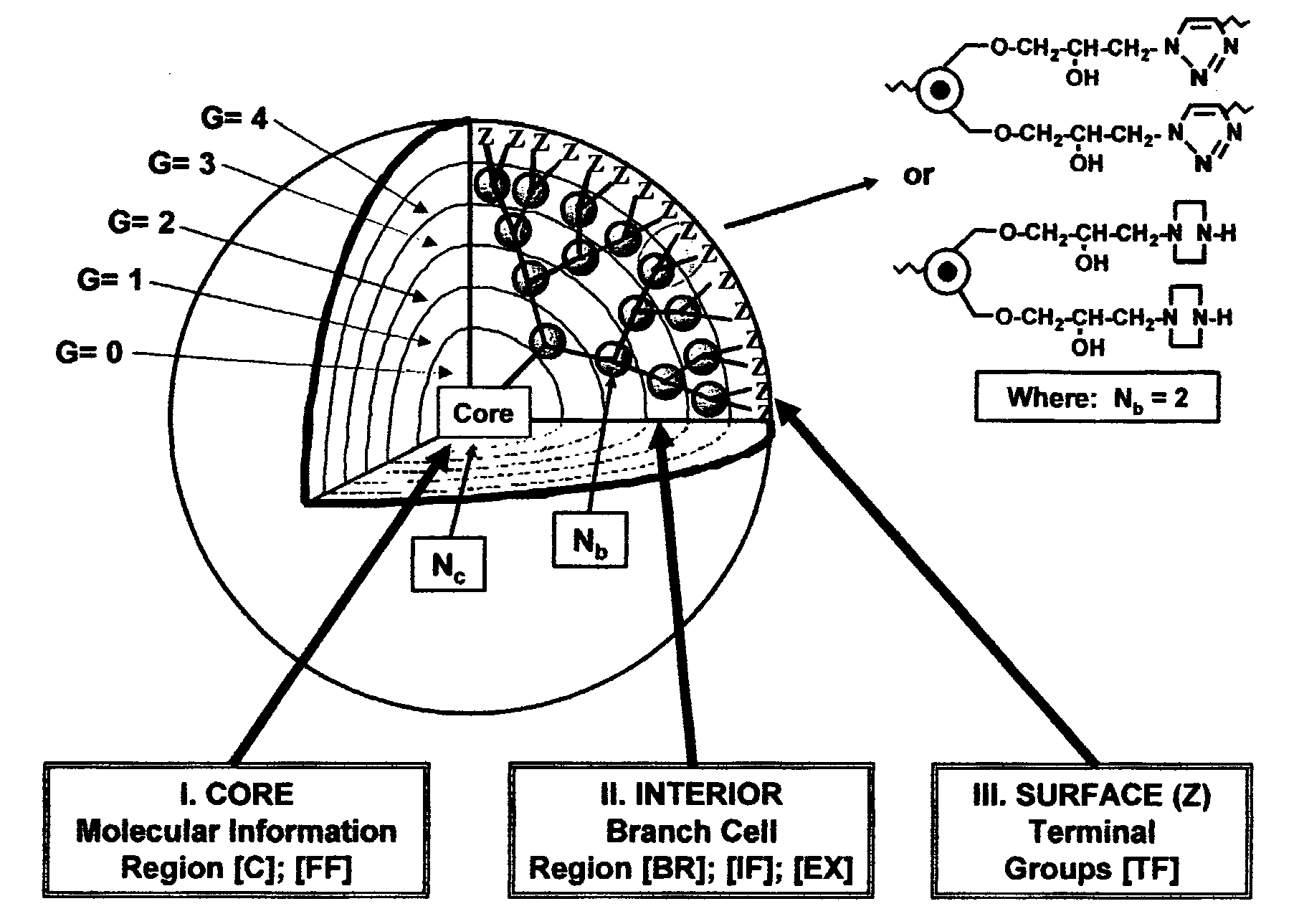
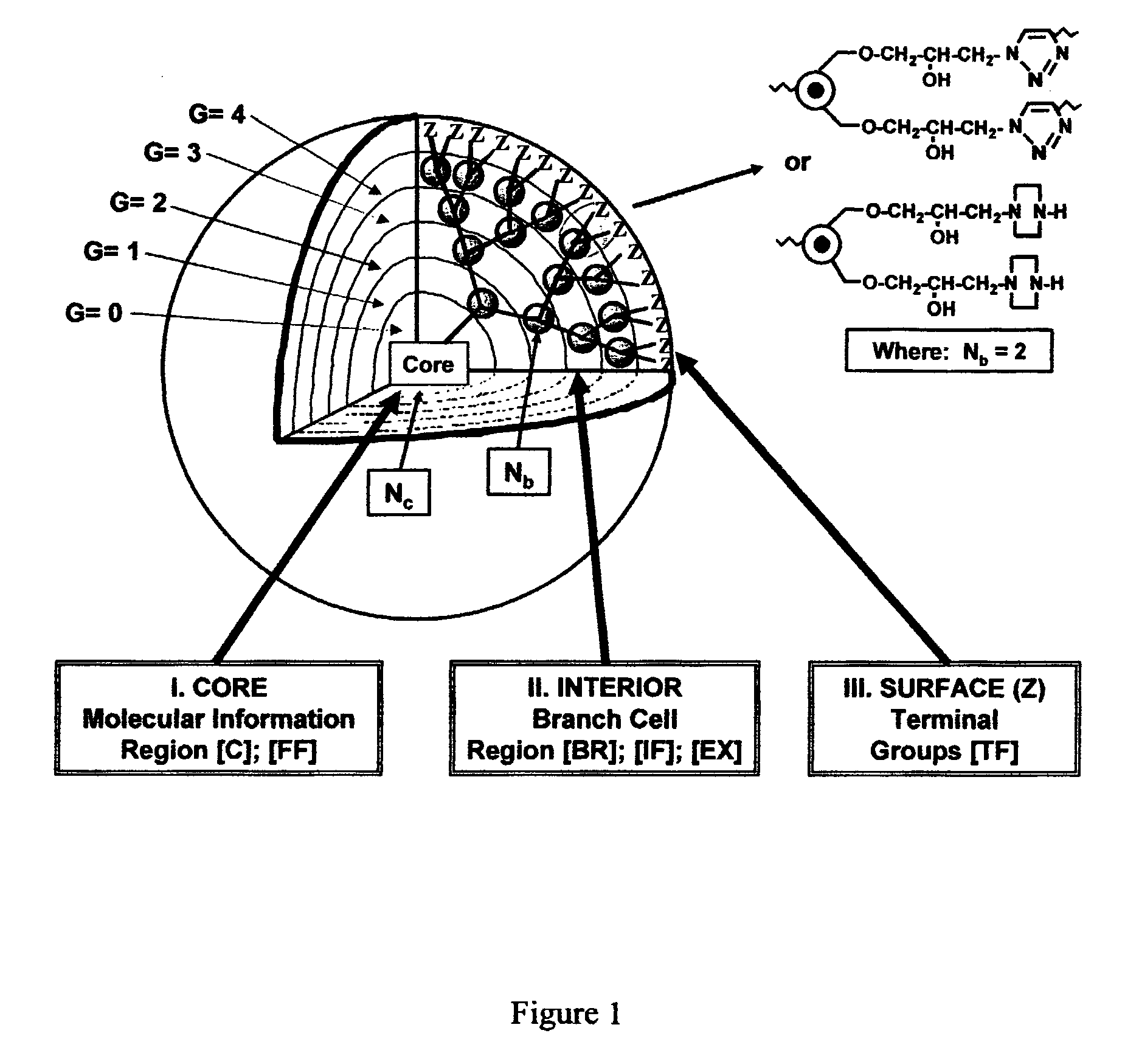
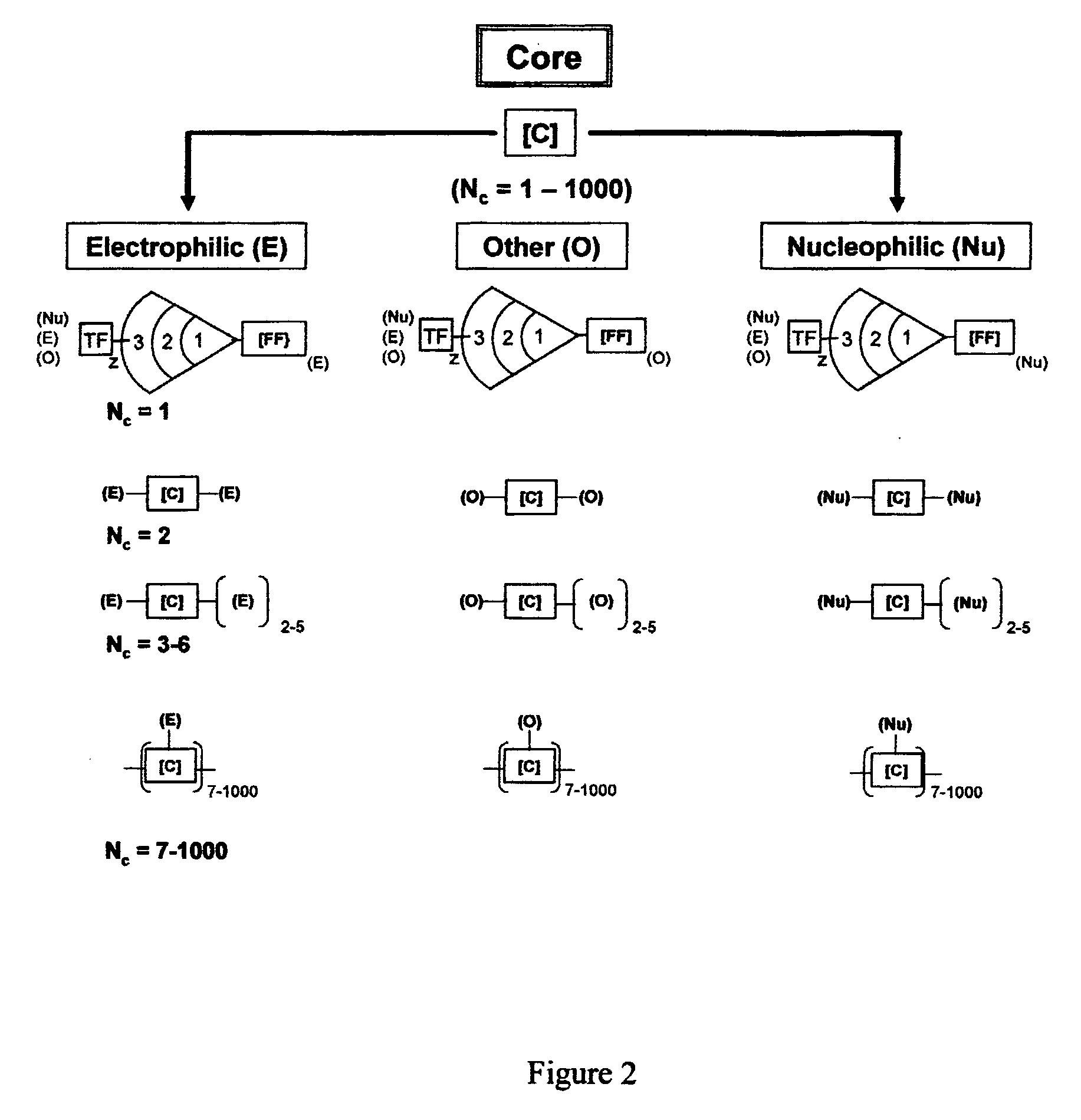
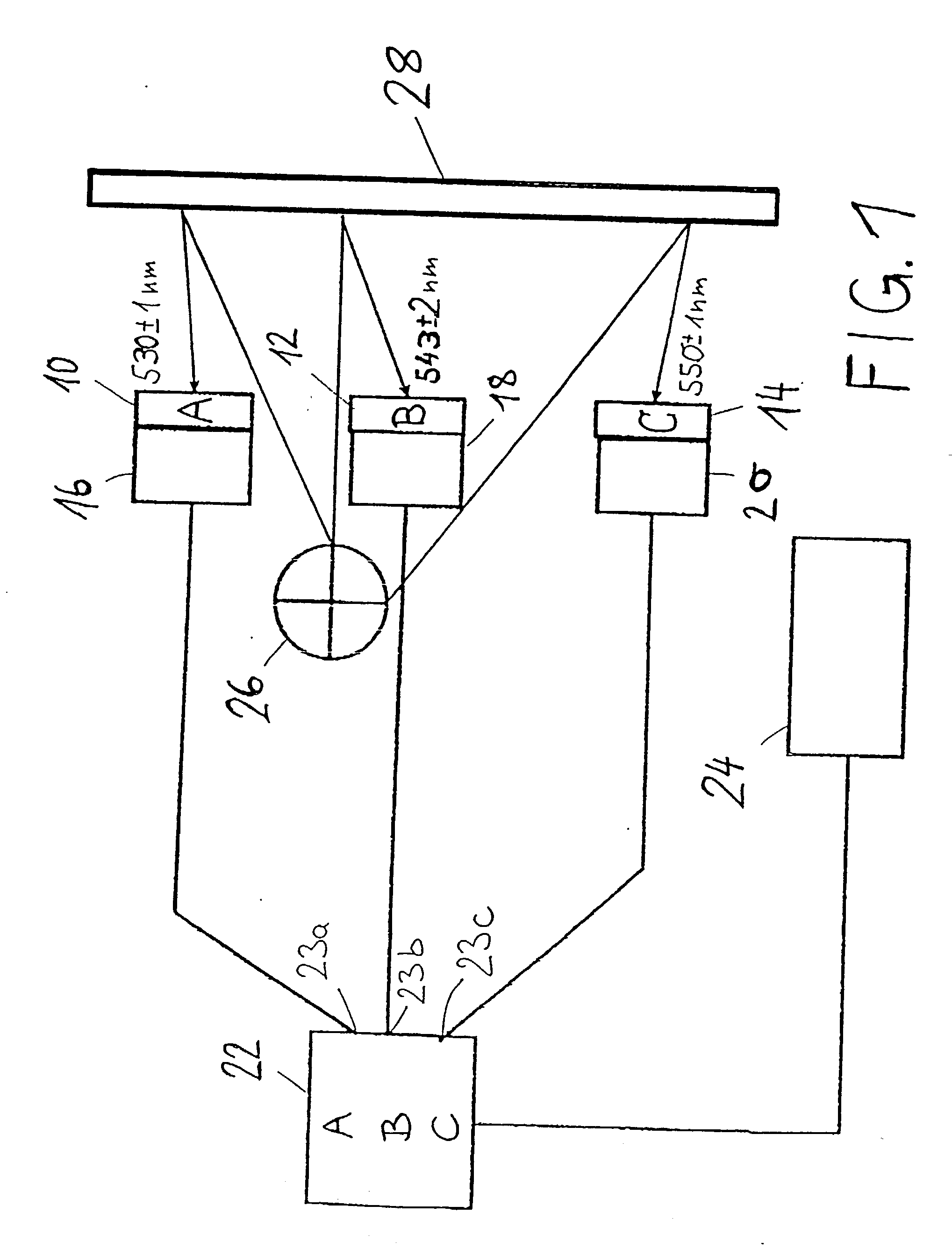
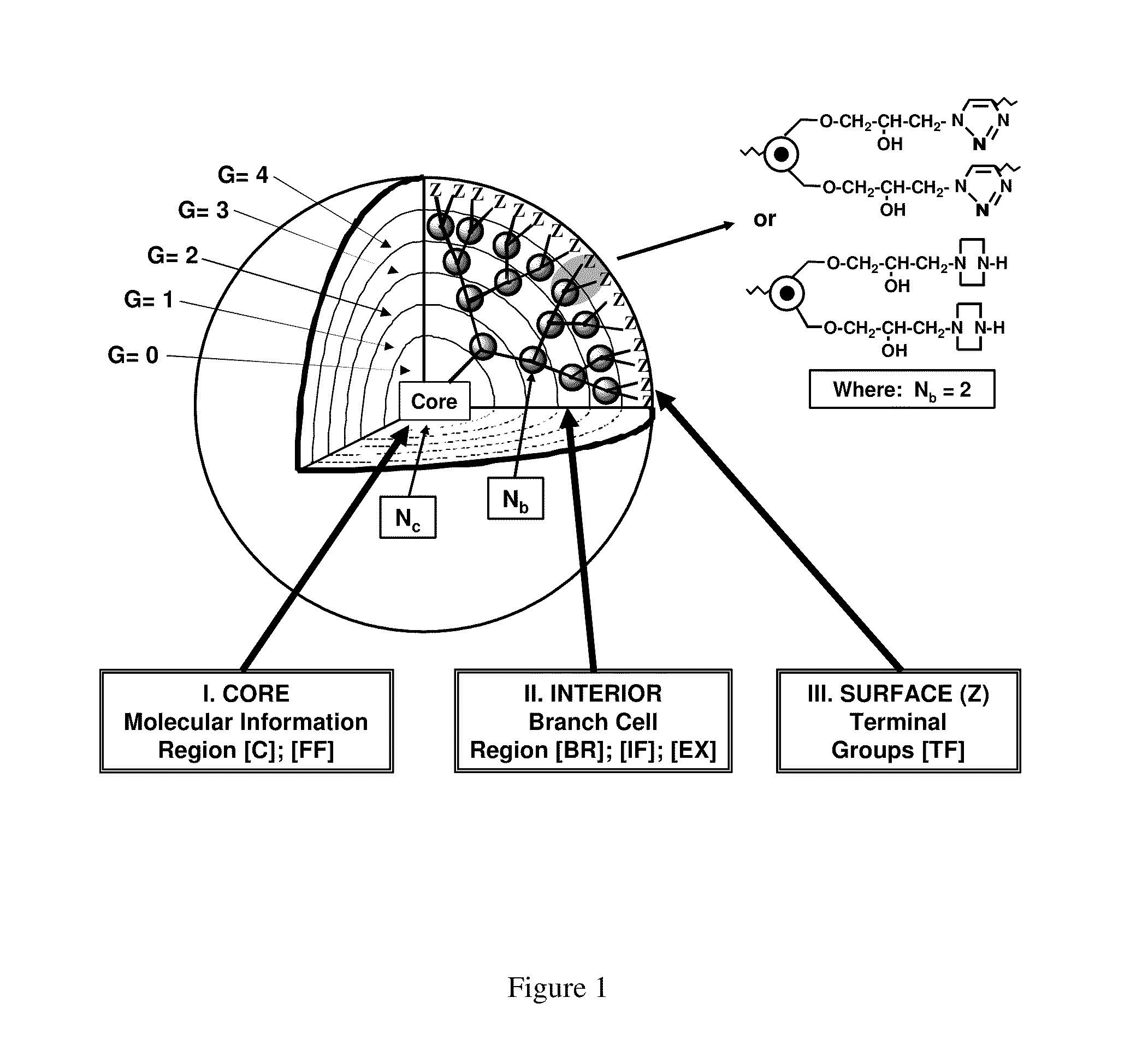
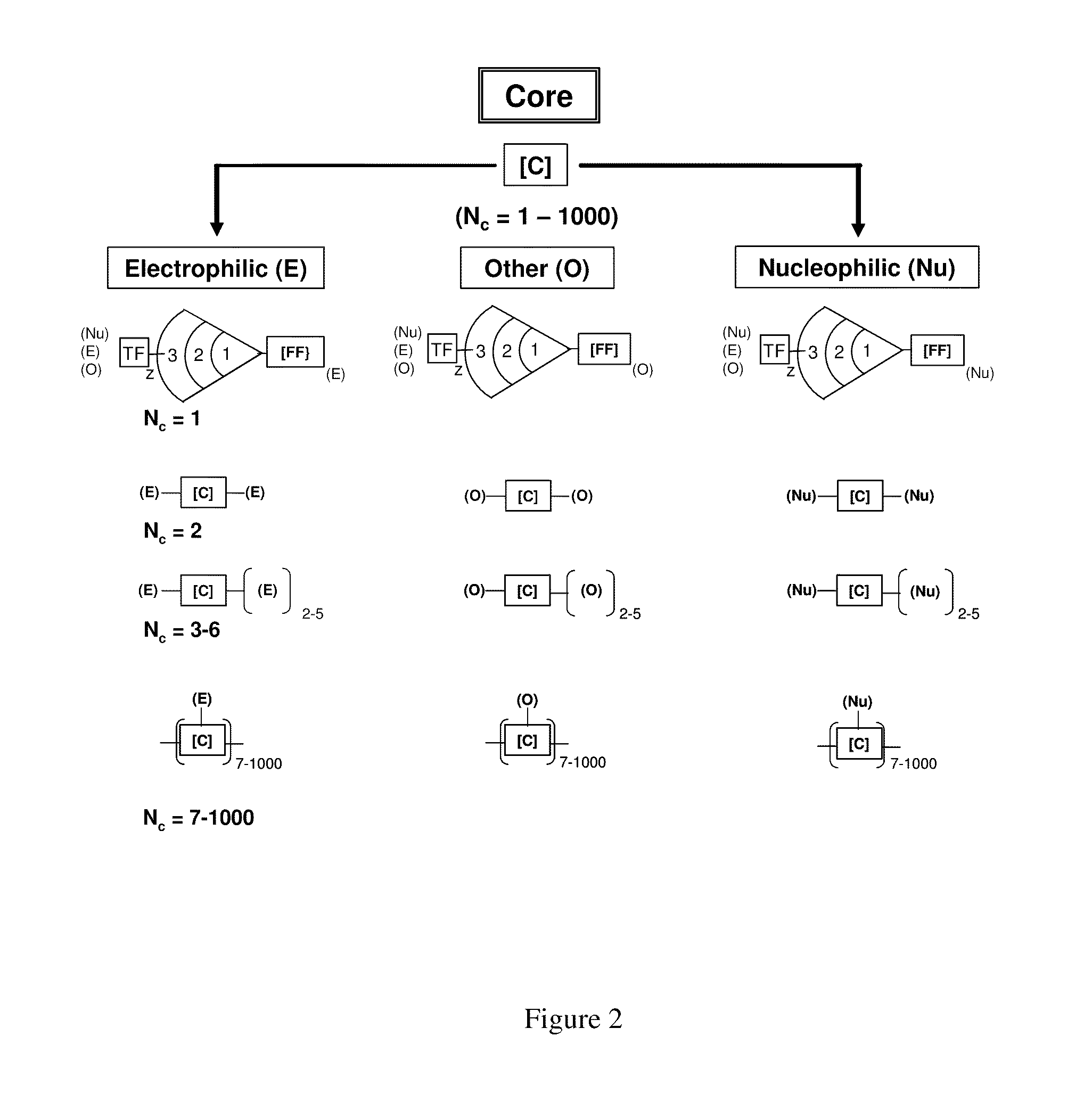
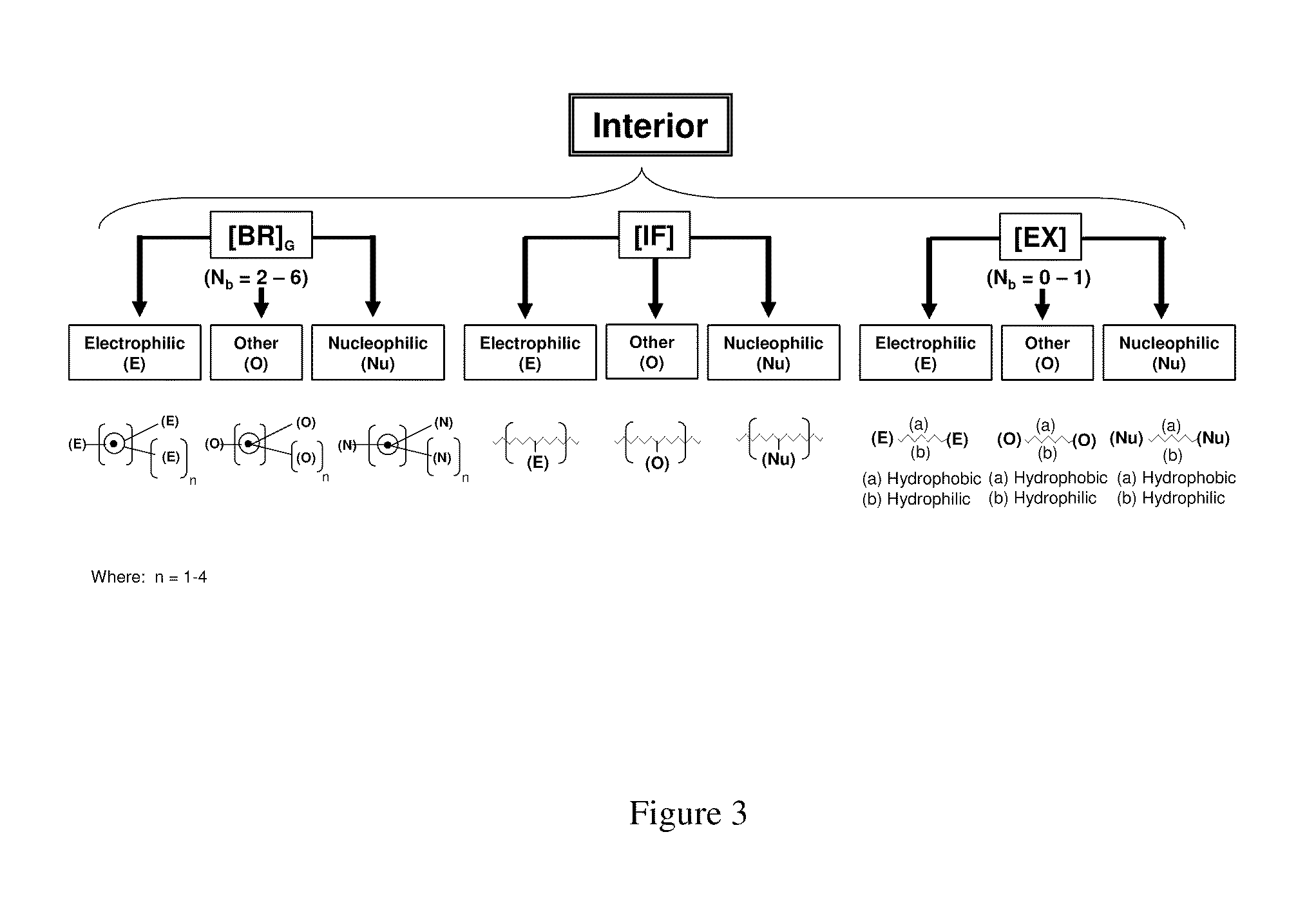
Dendritic Polymers With Enhanced Amplification and Interior Functionality
ActiveUS20070298006A1Reduced responseSizePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkScavenger
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality are disclosed. These dendritic polymers are made by use of fast, reactive ring-opening chemistry (or other fast reactions) combined with the use of branch cell reagents in a controlled way to rapidly and precisely build dendritic structures, generation by generation, with cleaner chemistry, often single products, lower excesses of reagents, lower levels of dilution, higher capacity method, more easily scaled to commercial dimensions, new ranges of materials, and lower cost. The dendritic compositions prepared have novel internal functionality, greater stability (e.g., thermal stability and less or no reverse Michael's reaction), and reach encapsulation surface densities at lower generations. Unexpectedly, these reactions of polyfunctional branch cell reagents with polyfunctional cores do not create cross-linked materials. Such dendritic polymers are useful as demulsifiers for oil / water emulsions, wet strength agents in the manufacture of paper, proton scavengers, polymers, nanoscale monomers, calibration standards for electron microscopy, making size selective membranes, and agents for modifying viscosity in aqueous formulations such as paint. When these dendritic polymers have a carried material associated with their surface and / or interior, then these dendritic polymers have additional properties for carrying materials due to the unique characteristics of the dendritic polymer, such as for drug delivery, transfection, and diagnostics.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
Synthesis of nanoparticles
InactiveUS20030032192A1High sensitivityIncreasing efficiency of collectorOptical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyDopantOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to methods for the preparation of inorganic nanoparticles capable of fluorescence, wherein the nanoparticles consist of a host material that comprises at least one dopant. The synthesis of the invention in organic solvents allows to gain a considerably higher yield compared to the prior art synthesis in water. All kinds of objects can advantageously be marked and reliably authenticated by using an automated method on the basis of a characteristic emission. Further, the size distribution of the prepared nanoparticles is narrower which renders a subsequent size-selected separation process superfluous.
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
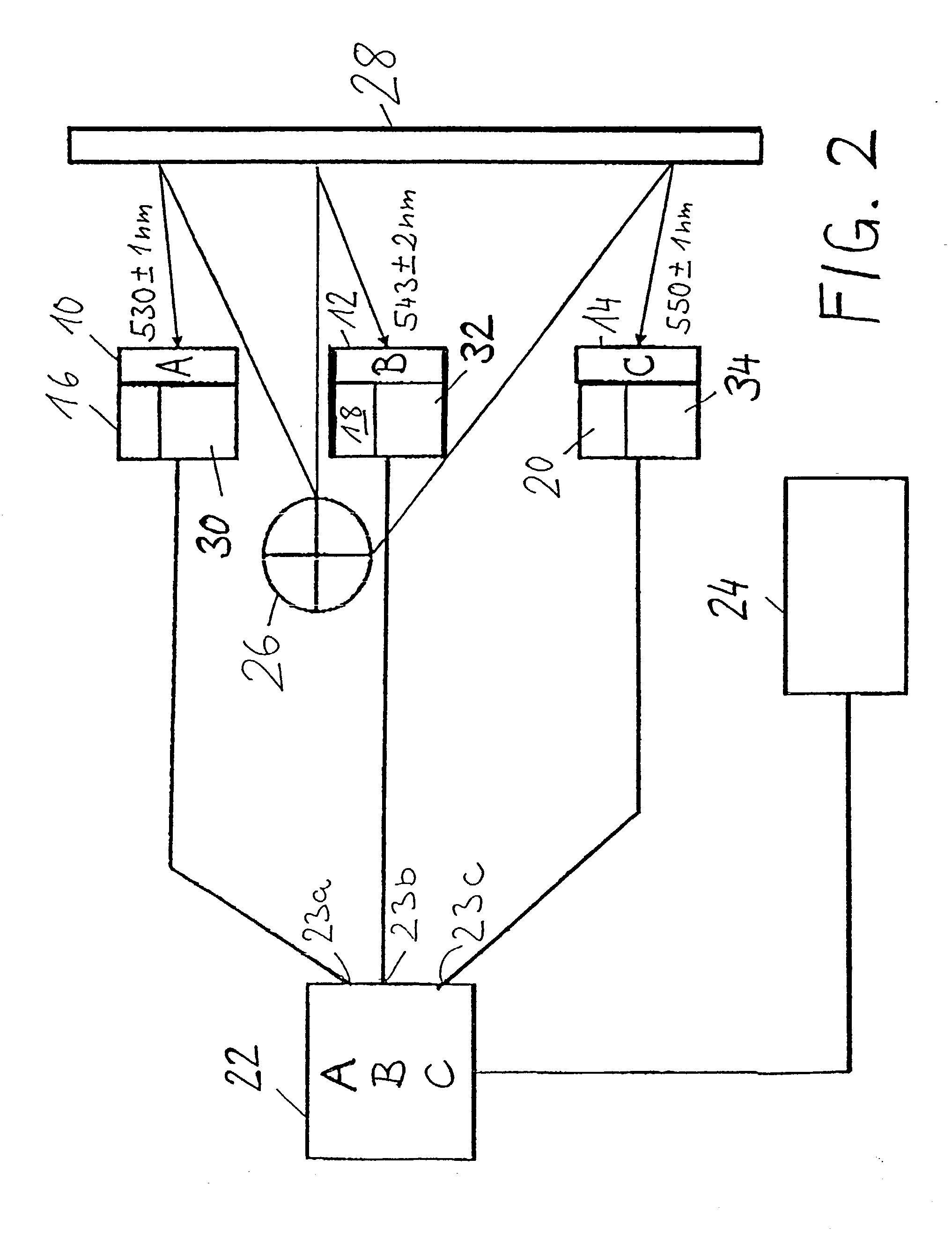
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality
ActiveUS7985424B2Increase productionSimple materialPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsCross-linkChemical reaction
Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality are disclosed. These dendritic polymers are made by use of fast, reactive ring-opening chemistry (or other fast reactions) combined with the use of branch cell reagents in a controlled way to rapidly and precisely build dendritic structures, generation by generation, with cleaner chemistry, often single products, lower excesses of reagents, lower levels of dilution, higher capacity method, more easily scaled to commercial dimensions, new ranges of materials, and lower cost. The dendritic compositions prepared have novel internal functionality, greater stability (e.g., thermal stability and less or no reverse Michael's reaction), and reach encapsulation surface densities at lower generations. Unexpectedly, these reactions of polyfunctional branch cell reagents with polyfunctional cores do not create cross-linked materials. Such dendritic polymers are useful as demulsifiers for oil / water emulsions, wet strength agents in the manufacture of paper, proton scavengers, polymers, nanoscale monomers, calibration standards for electron microscopy, making size selective membranes, and agents for modifying viscosity in aqueous formulations such as paint. When these dendritic polymers have a carried material associated with their surface and / or interior, then these dendritic polymers have additional properties for carrying materials due to the unique characteristics of the dendritic polymer, such as for drug delivery, transfection, and diagnostics.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
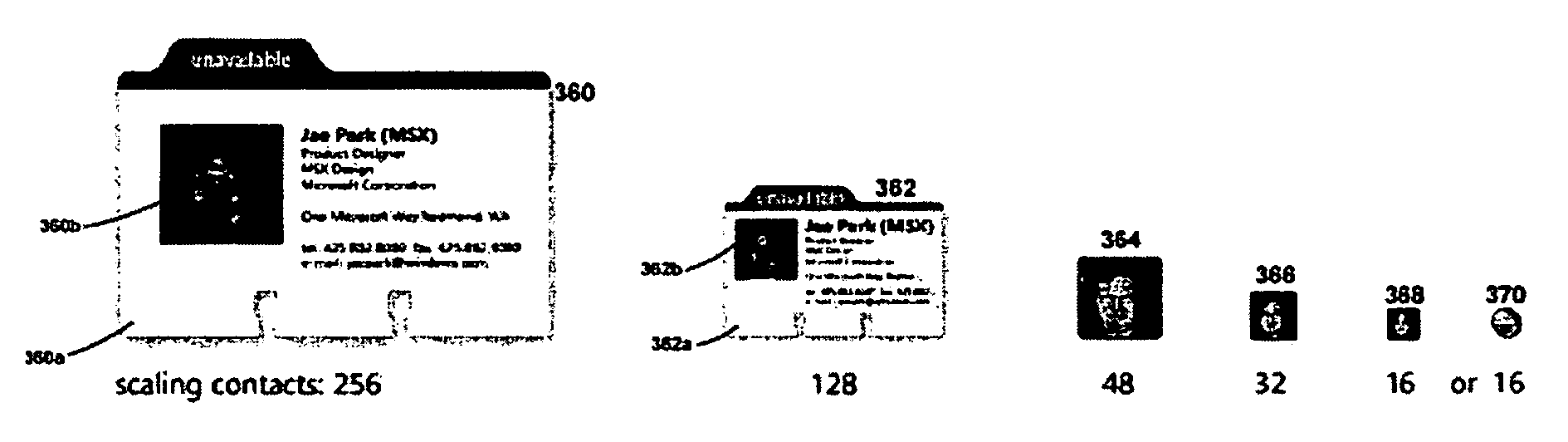
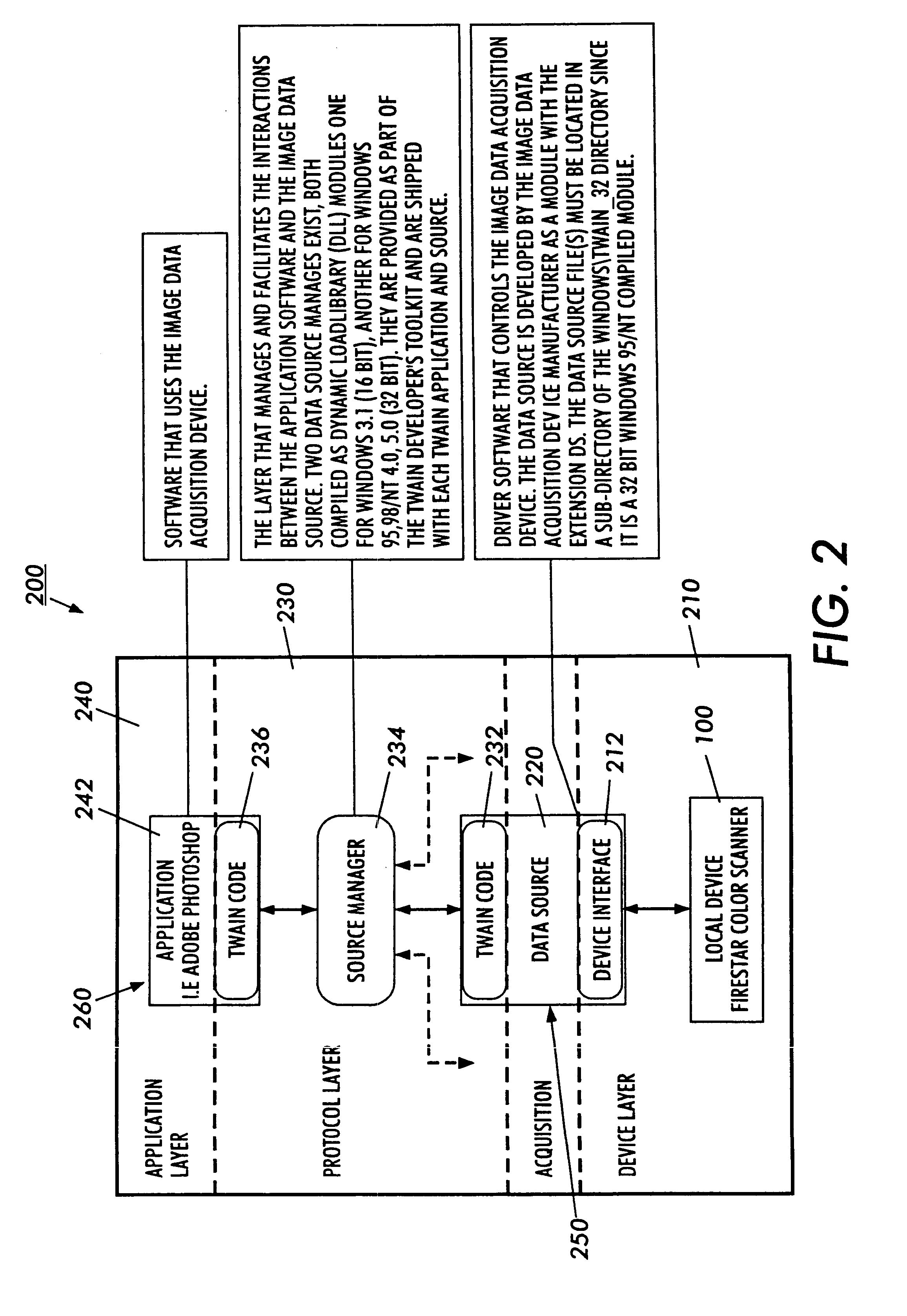
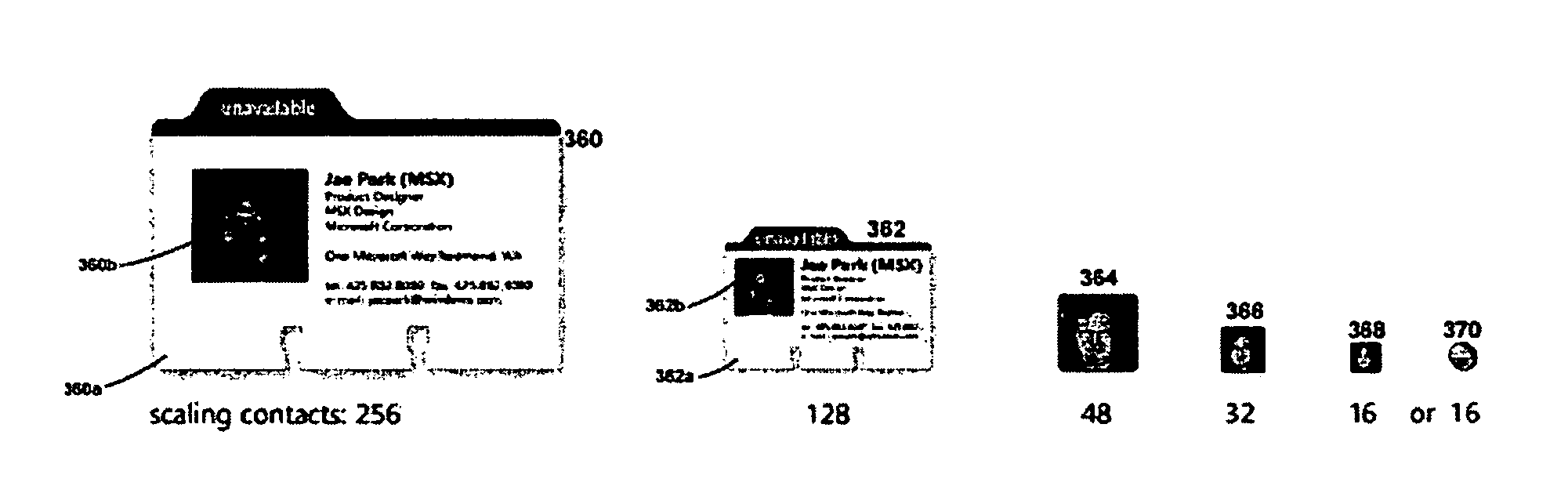
Scaling icons for representing files
ActiveUS20060020899A1Improve the display effectProgram controlSpecial data processing applicationsSize selectiveMinutiae
A method and system are provided for displaying icons in accordance with user preferences. The method includes providing a user with a size selection mechanism for selecting an icon size from a range of sizes. The method additionally includes searching a set of stored resources related to the underlying file and generating the icon in the selected size based upon the stored resources. The method may additionally include selecting an icon type including one of an image icon, a detail icon and a generic icon based on at least one of the user's size selection and the represented file. Furthermore, the icon display system of the invention positions labels and overlays in the vicinity of the icon based upon the selected size of the icon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Size-selective hemoperfusion polymeric adsorbents
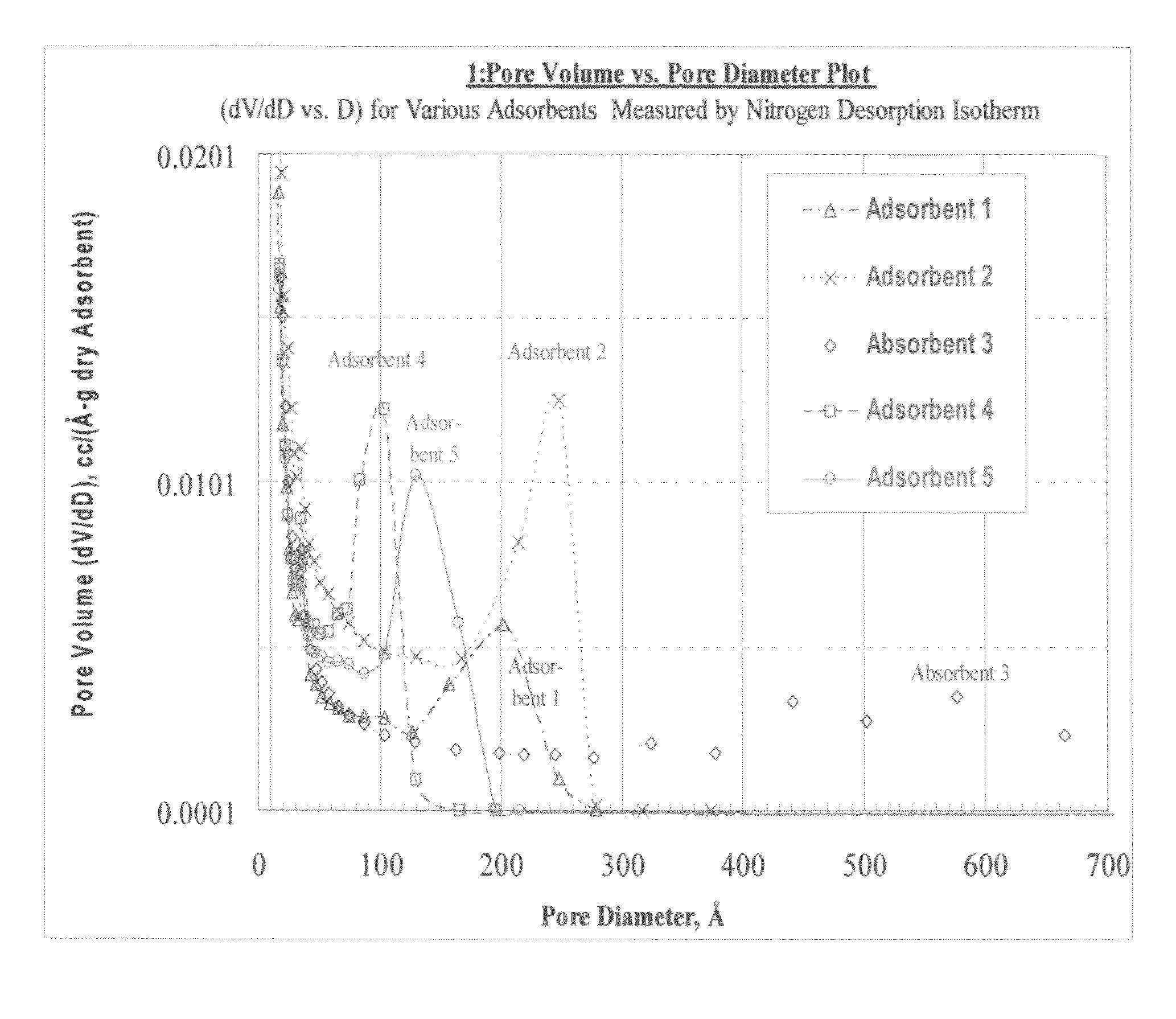
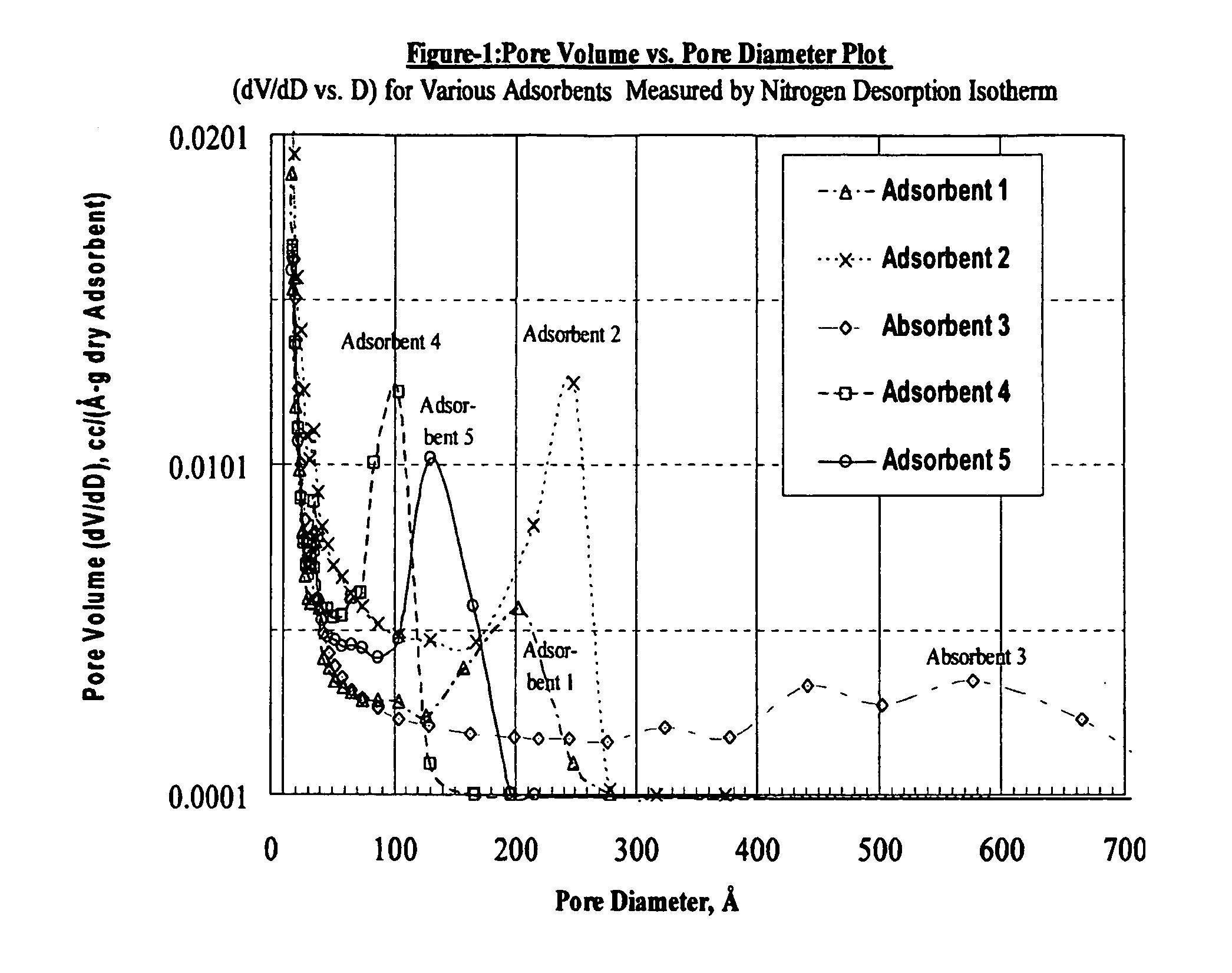
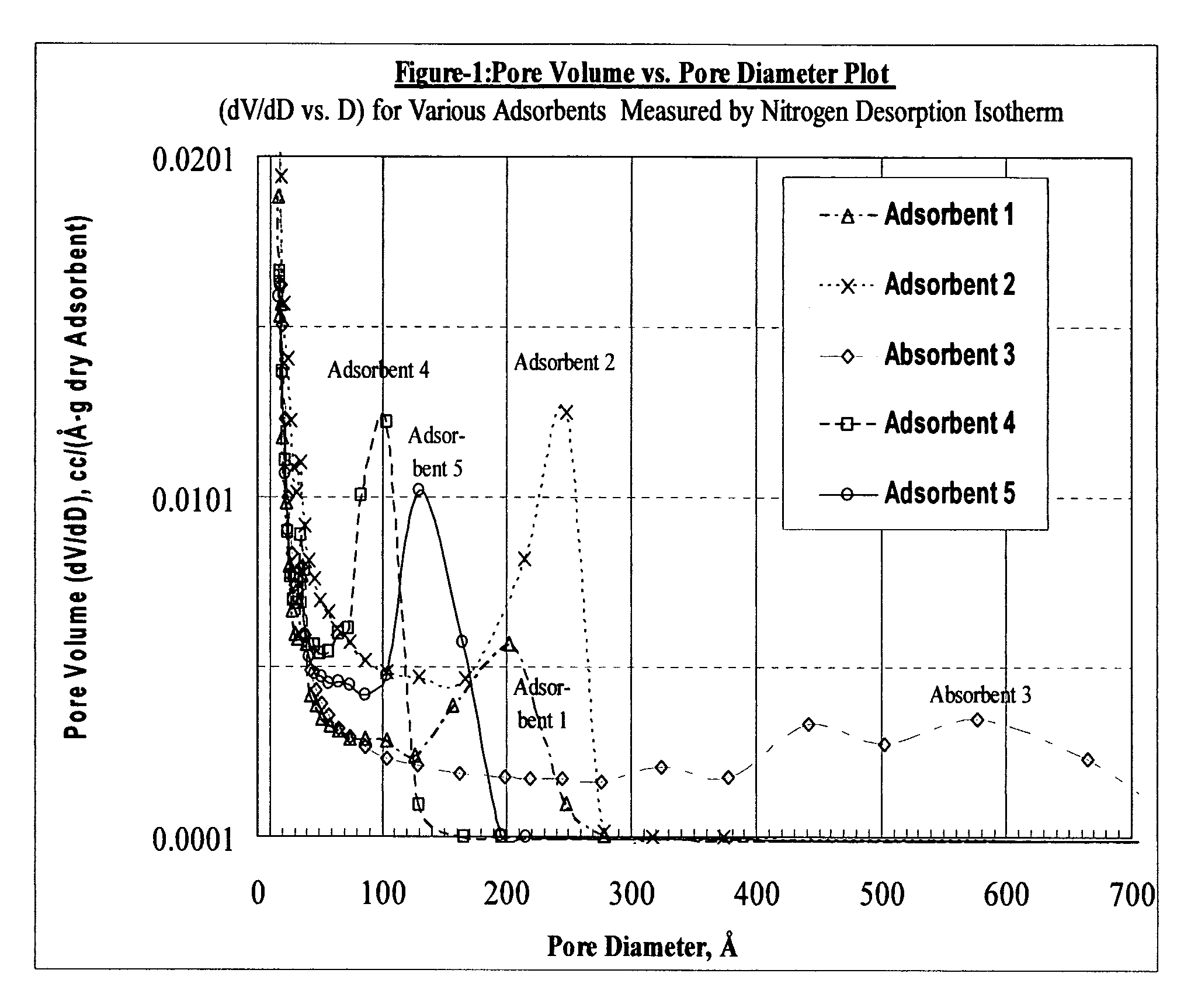
Size-selective hemocompatible porous polymeric adsorbents are provided with a pore structure capable of excluding molecules larger than 50,000 Daltons, but with a pore system that allows good ingress and egress of molecules smaller than 35,000 Daltons. The pore system in these porous polymeric adsorbents is controlled by the method of synthesis so that 98% of the total pore volume is located in pores smaller than 300 Angstroms (Å) in diameter with a working pore size range within 100 to 300 Å in diameter. The porous polymeric adsorbents of this invention are very selective for extracting midsize proteins, such as cytokines and β2-microglobulin, from blood and other physiologic fluids while keeping the components required for good health such as cells, platelets, albumin, hemoglobin, fibrinogen, and other serum proteins intact.
Owner:CYTOSORBENTS CORP
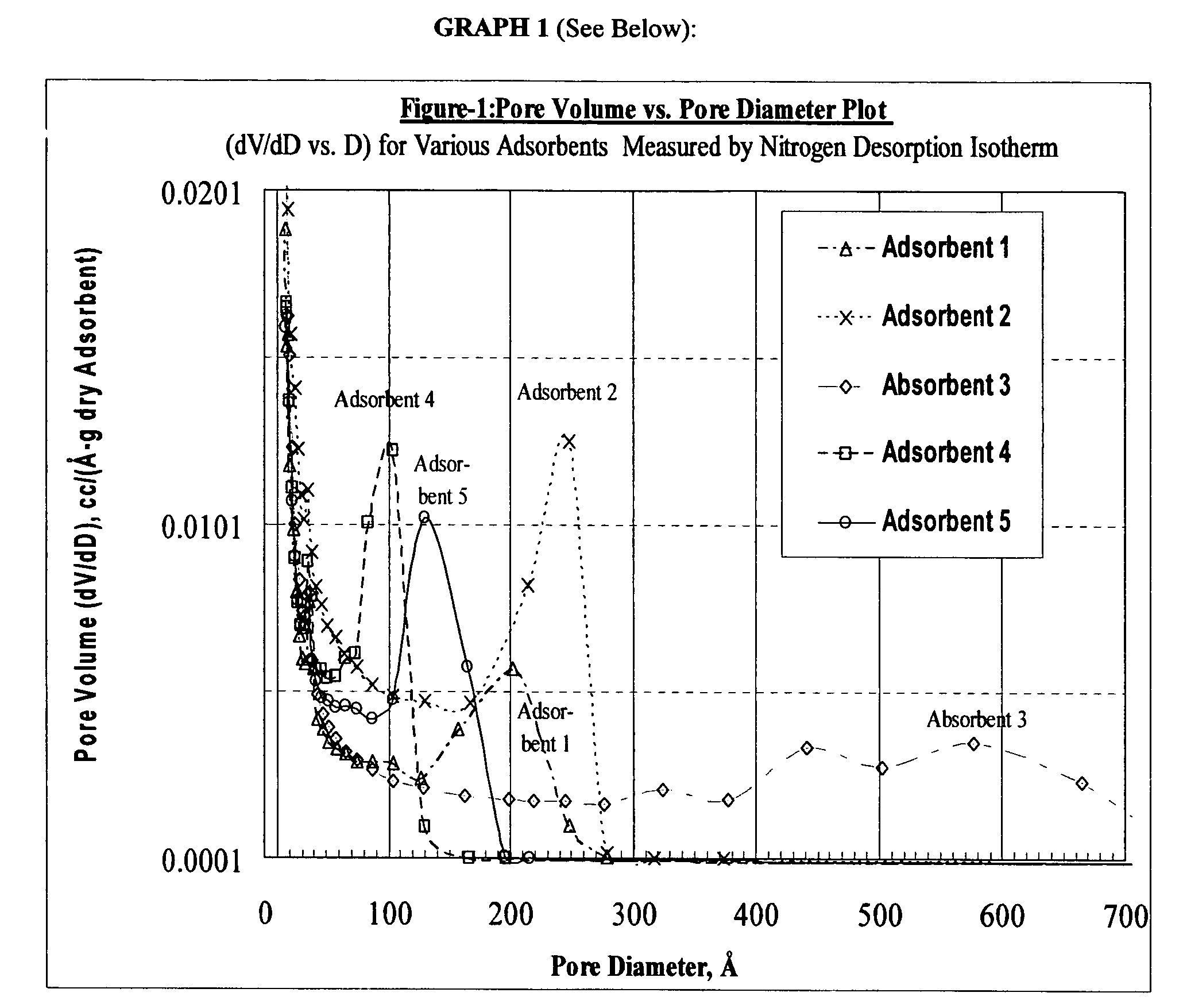
Systems and methods scaling a captured image using predetermined scale information
InactiveUS6741270B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceSize selectiveAlternative methods
Conventionally, text boxes are used to inform an image capture device of the size of an area to which a captured image will need to be scaled, when fitting the captured image into that area of the composite document. In contrast, size selection systems, methods and graphical user interfaces allow the user to select one of a number of predetermined sets of scale dimensions that the captured image is to be scaled to. The size selection systems, methods and graphical user interfaces provide an alternative method for specifying the dimensions that a captured image is to be scaled to. In various exemplary embodiments of the size selection systems, methods and graphical user interfaces, an image size tab of a graphical user interface for an image capture driver includes a scale portion. The scale portion, in addition to having a number of dimension boxes that allow the user to directly input the desired dimensions to which the captured image is to be scaled, also includes a dimension list box. The dimension list box includes predetermined sets of dimensions to which the captured image can be scaled. In various exemplary embodiments, the dimensions list box includes, as the predetermined sets, sets of dimensions for common paper sizes and sets of dimensions for different paper orientations. The predetermined sets of dimensions can also include sets of user-defined dimensions. These user-defined dimensions allow the user to specify the dimensions of an image area of a document that is often used.
Owner:XEROX CORP
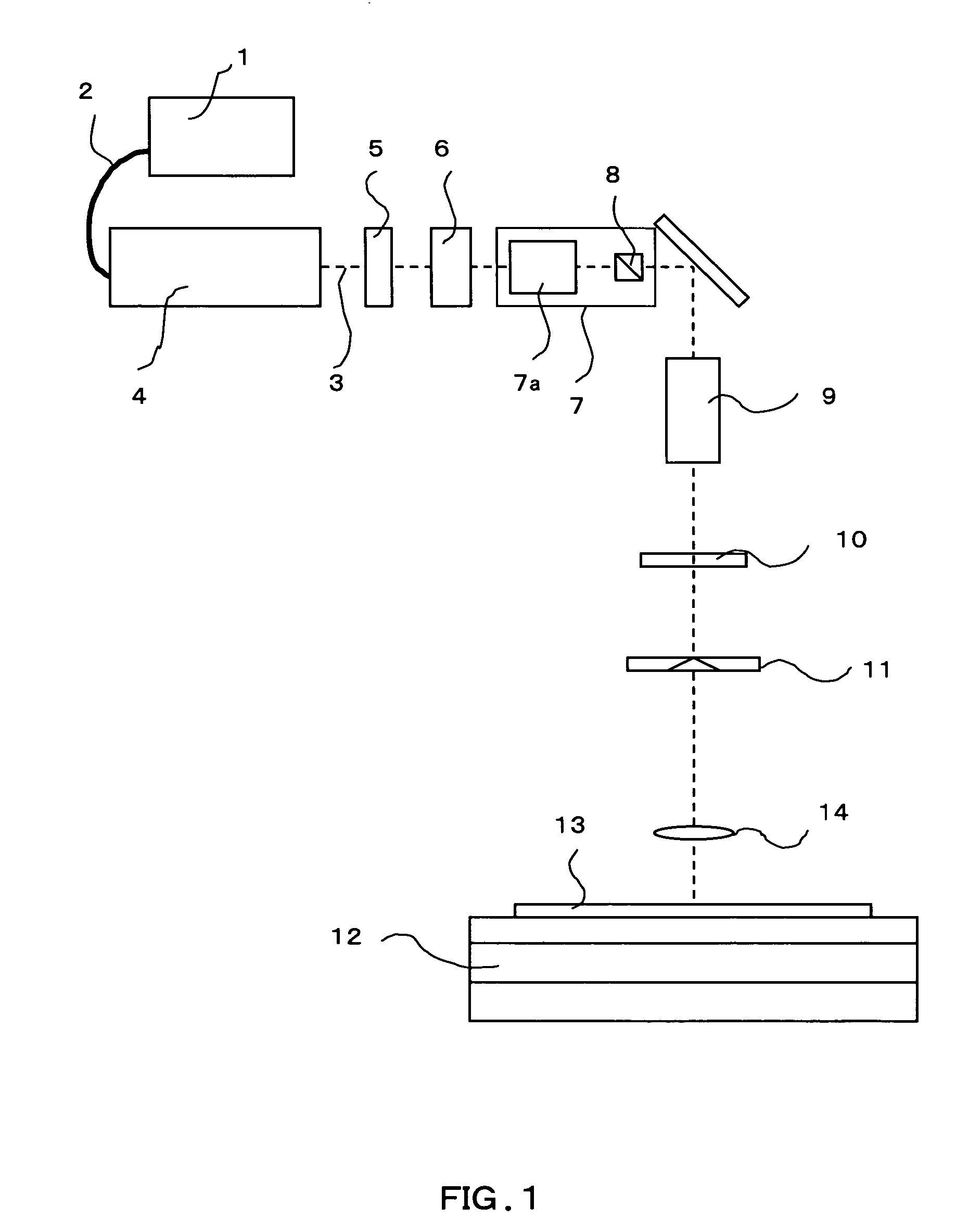
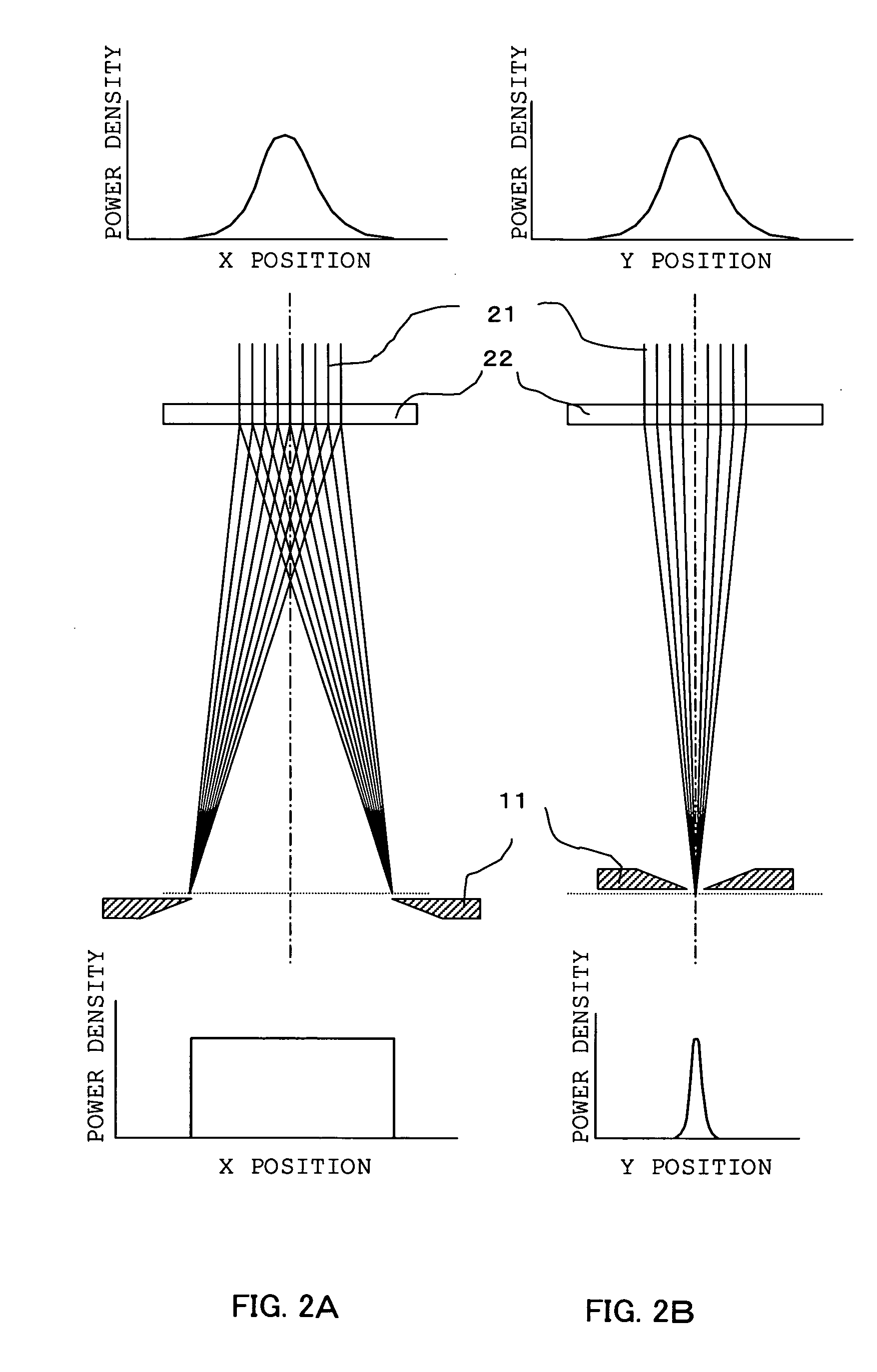
Laser annealing apparatus and annealing method of semiconductor thin film
InactiveUS20050169330A1Improve mobilityKeep energy smallTransistorPolycrystalline material growthBand shapeLight beam
When a laser bean temporally modulated in amplitude by a modulator is shaped into a long and narrow beam by a beam shaper, the scanning-direction size of the long and narrow beam shaped by the beam shaper is selected to be in a range of from 2 to 10 microns, preferably in a range of from 2 to 4 microns and the scanning speed of the beam is selected to be in a range of from 300 to 1000 mm / s, preferably in a range of from 500 to 1000 m / s. As a result, damage of the silicon thin film can be suppressed while energy utilizing efficiency of the laser beam can be improved. Accordingly, laterally grown crystals (belt-like crystals) improved in throughput can be obtained on a required region of a substrate scanned and irradiated with the laser beam.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Intelligent text driven document sizing
InactiveUS20080062437A1Improve image processing capabilitiesDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersSize selectiveMagnification
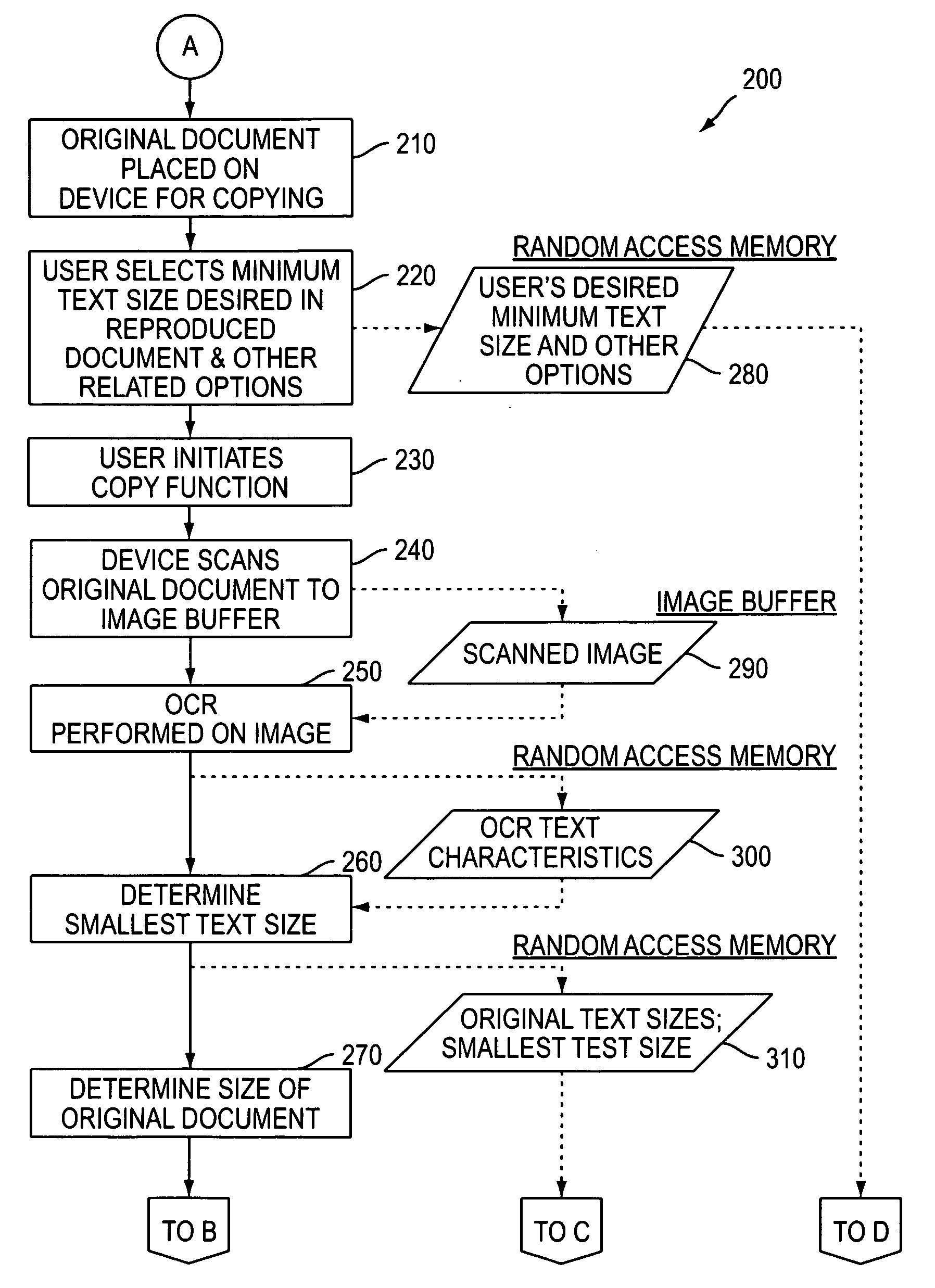
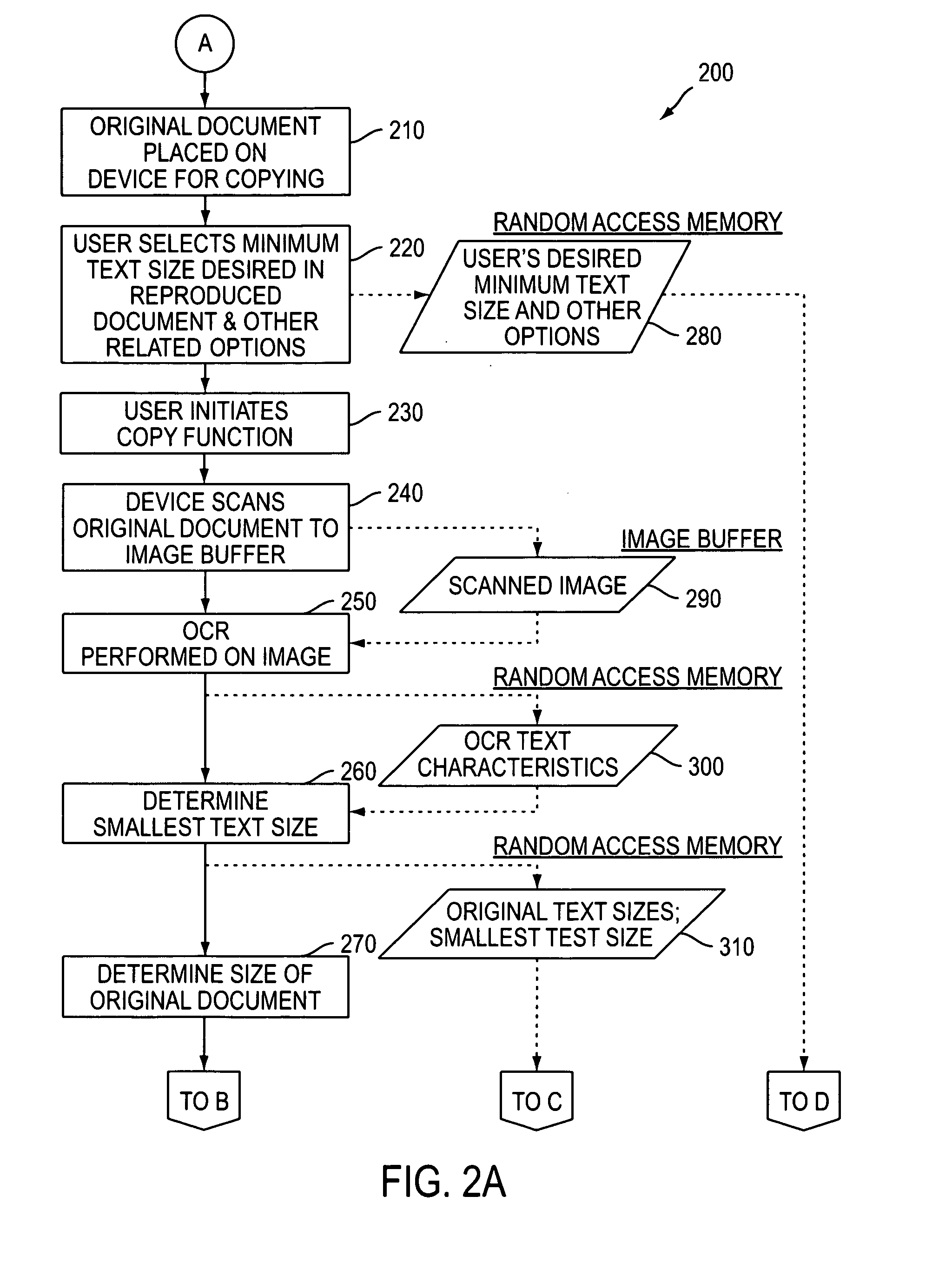
A method for automatically magnifying a copy job to result in a copied text that is not smaller than a user specified minimum size. An original document is automatically scanned and an analysis performed to determine, the smallest text size within the original document. A magnification for rendering the document can then be set. Media size can then be selected appropriately, and an image magnification ratio and output document size selections optimized to create a text size in the resulting rendering document which are as close as possible to a user's minimum text size selection when the user selected minimum text size cannot be achieved.
Owner:XEROX CORP
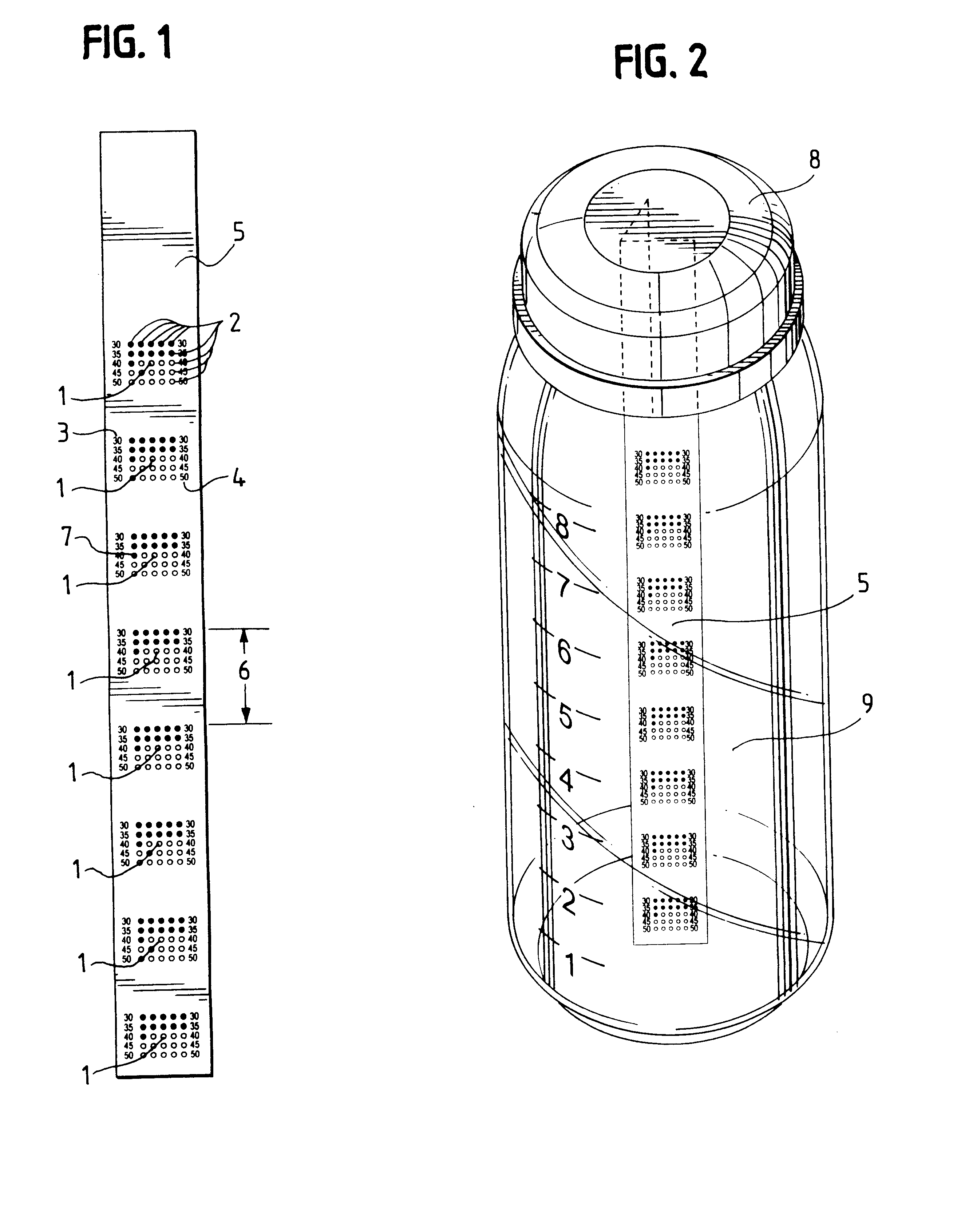
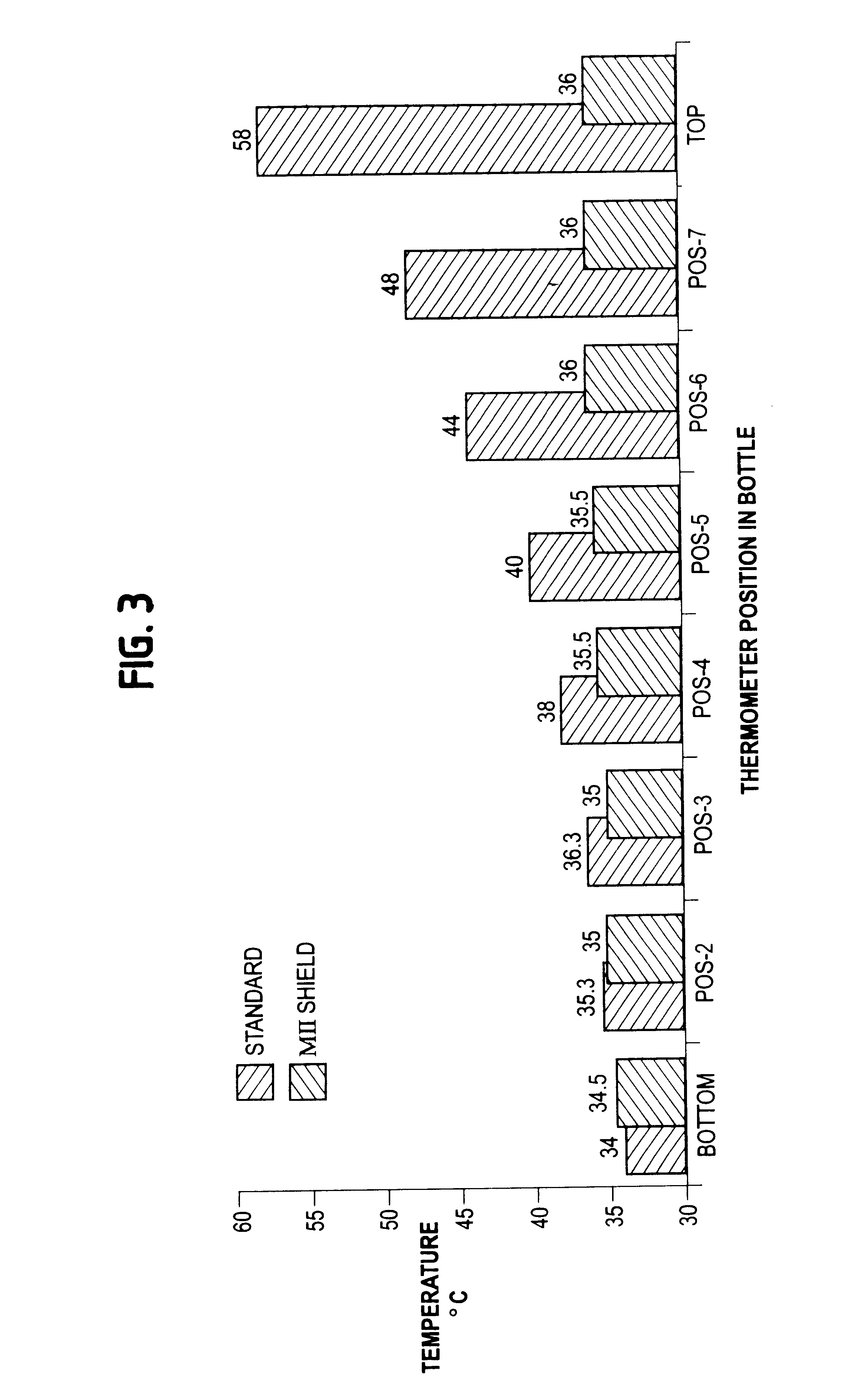
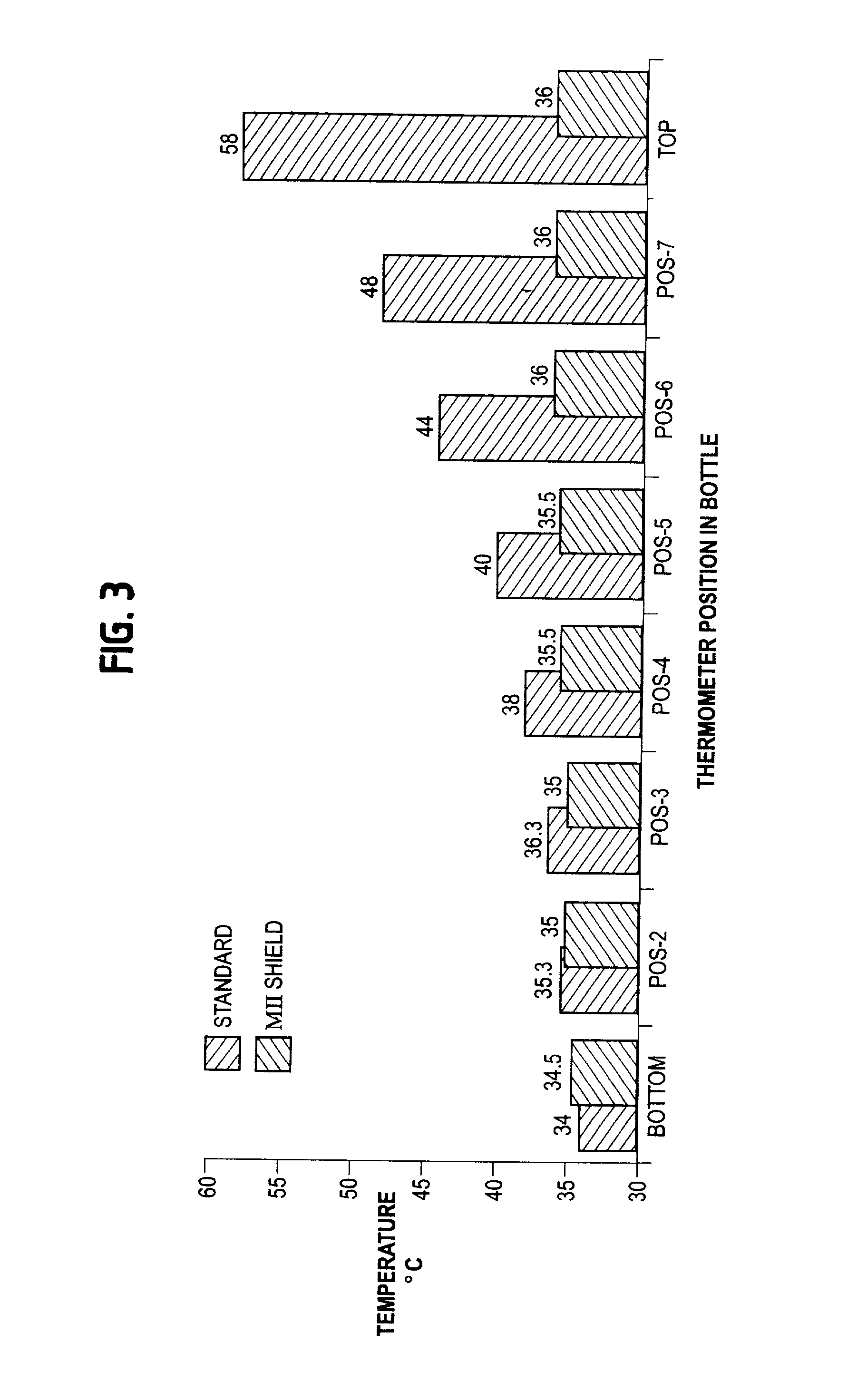
Shielding method for microwave heating of infant formula to a safe and uniform temperature
InactiveUS6410896B2Minimal reflectionMinimize electric field intensityThermometer detailsDough treatmentVertical mixingEngineering
Owner:MEDICAL INDICATORS INC
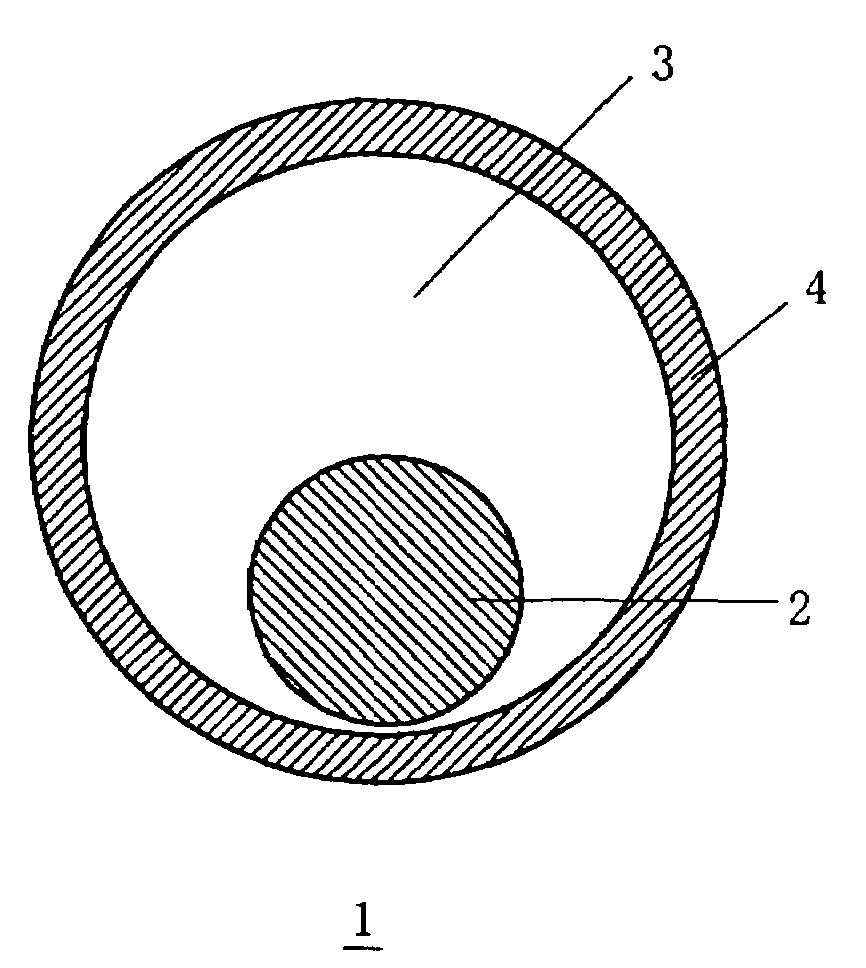
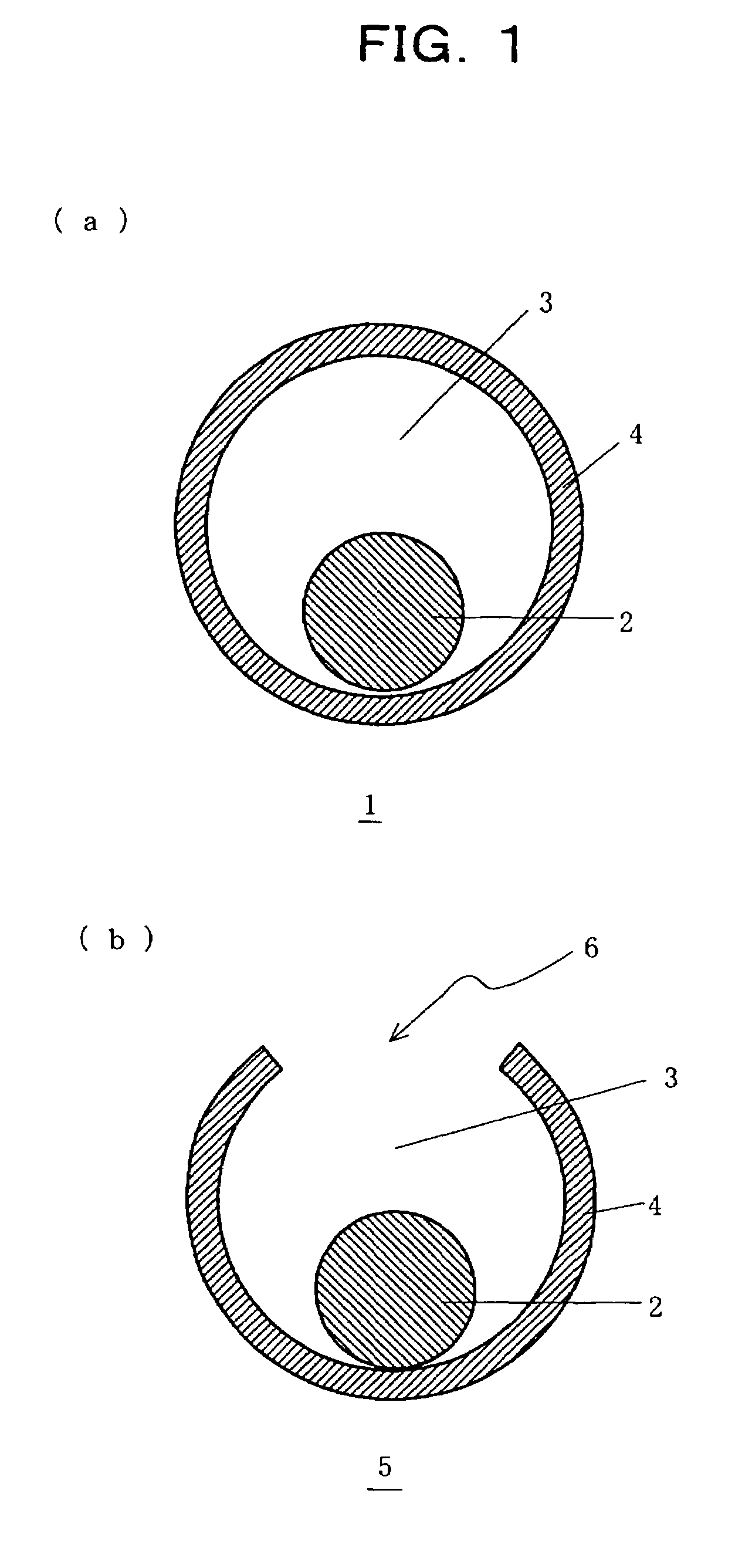
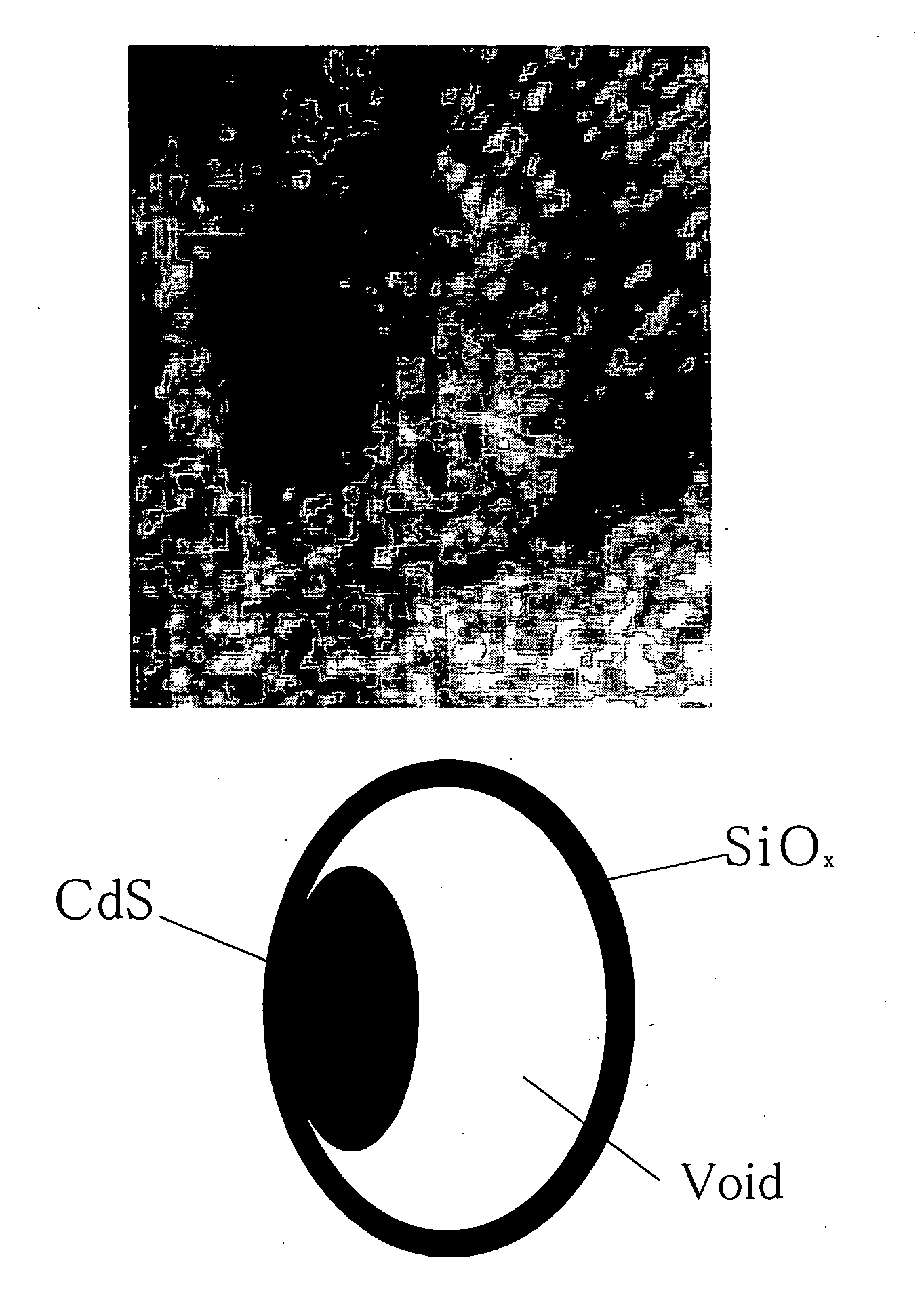
Core-shell structure having controlled cavity inside and structure comprising the core-shell structure as component, and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS7381465B2Reduce the overall diameterMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsNanoparticleSize selective
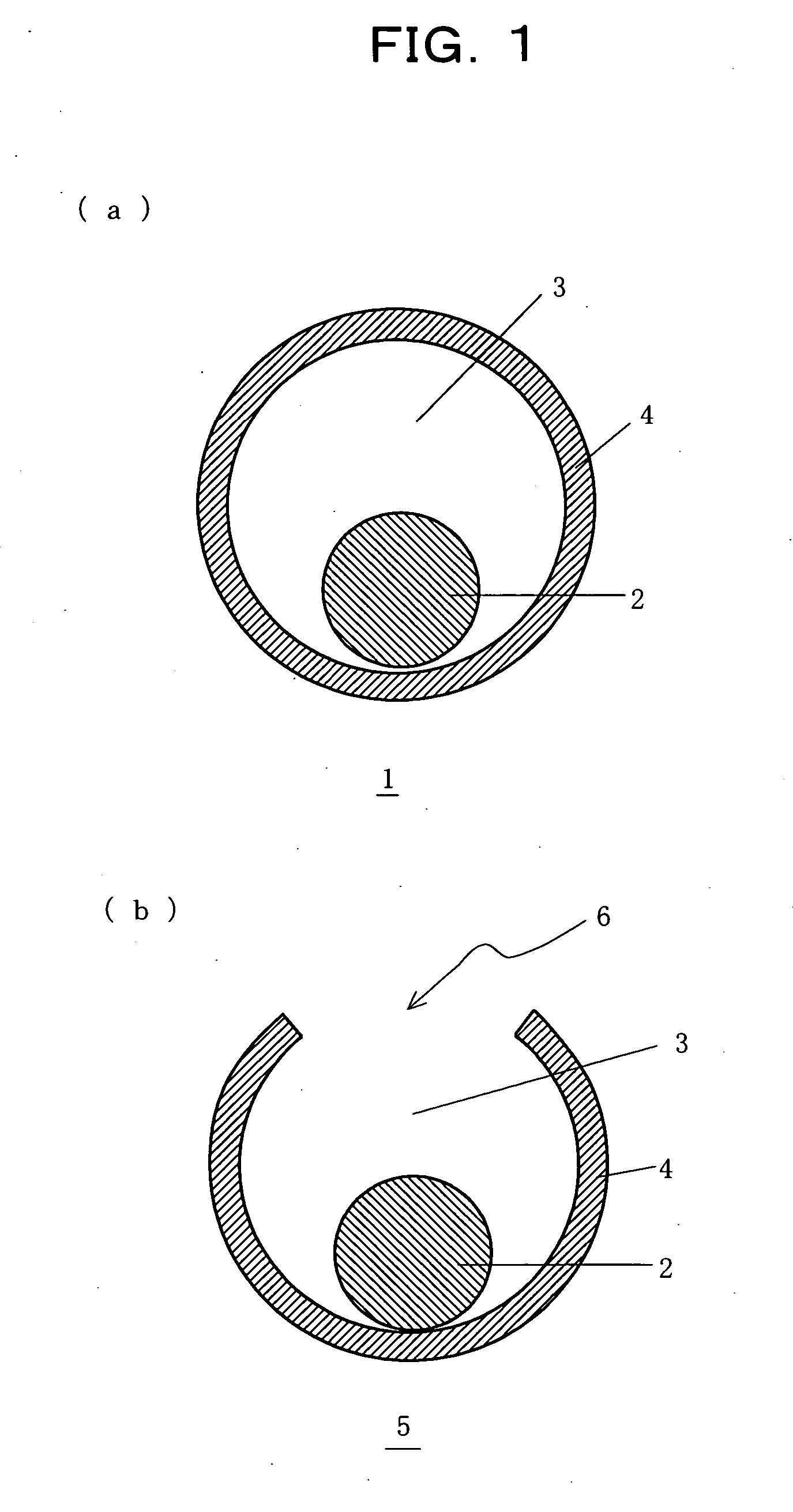
A core-shell structure comprises a core (2) comprising nanoparticles and a shell (4) coating the core (2), and its void space (3) formed by the core (2) and the shell (4) is controlled. A method of preparing the core-shell structure comprises: forming particles comprising a photoetchable semiconductor, metal or polymer and coating the particles with a shell (4) comprising a non-photoetchable semiconductor, metal or polymer, to form a core-shell structure (5); and irradiating the core-shell structure with a light having a controlled wavelength in the photoetching solution to form an adjustable void space inside a shell (3) within the core-shell structure by the size-selective photoetching method. The core-shell structure allows the preparation of a catalyst exhibiting an extremely high efficiency, and can be used as a precursor for preparing a nanomaterial required for a nanodevice.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Preparation method of layered molybdenum sulfide nanosheet molecular separating membrane
InactiveCN103585896ALow costIncrease productionSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMaterials preparationFiltration
The invention discloses a preparation method of a layered molybdenum sulfide nanosheet molecule separating membrane. According to the preparation method, n-butyllithium is taken as an intercalation modular and enters a molybdenum sulfide crystal lattice after long-time stirring; water is added for decomposing n-butyllithium, so that the interlayer distances of a molybdenum sulfide sheet are enlarged; molybdenum sulfide is dispersed into monoatomic layer materials through ultrasonic treatment; redundant impurities are removed through dialysis, and a purified and clean molybdenum sulfide water solution is obtained; the obtained molybdenum sulfide water solution is treated with a vacuum filtration method, and the layered molybdenum sulfide nanosheet molecule separating membrane is obtained; and the thickness of the membrane is adjusted by adjusting the volume of the used molybdenum sulfide water solution. A molecule-selective separation membrane is obtained with a method of stacking the monoatomic layer materials to form the membrane; and the material preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the obtained membrane has size selective separation performance on different molecules.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Shielding method for microwave heating of infant formula to a safe and uniform temperature
InactiveUS20010008238A1Minimize electric field intensityAvoid arcingThermometer detailsDough treatmentVertical mixingSize selective
A shielding method for achieving highly uniform temperatures in liquids during microwave heating by substantially enhancing vertical mixing currents in said liquids, making determinations of final temperature reached in said liquids either by touch or the use of a temperature indicator efficacious, comprising: a electrically conductive shield having very low impedance at microwave frequencies; having, a generally cylindrical shape, and dimensions chosen to accommodate a variety of microwaveable containers. said shield: to be concentric with a microwaveable container, containing a liquid to be heated by microwave radiation; and, to be located so as the top edge of said shield is at or above a vertical level corresponding to the level of the liquid in said container; and, to be of sufficient height as to cover at least 10% of the height of the liquid in said container. In a preferred embodiment, the shield has a height "h", covering between 10% and 90% of the of the liquid contained in the container to be heated; and, a circumference / length "L" covering at least 90% of the circumference of the container to be heated.
Owner:MEDICAL INDICATORS INC
Prediction system and method based on insect body filtration and insect quantity and variety recognition
InactiveCN107333731AEasy to identifyEasy to countImage enhancementImage analysisFiltrationSize selective
The invention discloses a prediction system and method based on insect body filtration and insect quantity and variety recognition, and belongs to the technical fields of agriculture and forestry plant protection and insect condition monitoring. Aiming at the problems of indefiniteness of target insect bodies to be trapped and killed, inaccurate recognition and quantity prediction caused by insect body stacking, inconvenient disassembly and assembly of equipment and complex maintenance in the prior art, the main purpose of the invention is to provide an insect condition prediction device and method. The insect condition prediction device is characterized in that an insect body filter screen cover is arranged at the outer side of an impact plate or is arranged below a trap lamp tube and above an insect receiving hopper; an insect receiving bag has a function of scattering, separating and dropping insects; the insect bodies are transported and photographed through timing control of the movement of a conveyer belt; and finally, all the insect bodies fall into an insect storage bin or even are directly discharged to the outside of the machine. According to the invention, the insect body selective trap and kill and big insect size selective filtration can be made possible; uploaded pictures can have the favorable effects of clear insect body characteristics and a very low overlapping ratio; and meanwhile, the cleanliness inside the device can be kept, thereby effectively reducing the output of extra manpower.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TUOPUYUN AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method of preparing size-selected metal clusters
InactiveUS7713907B2High catalytic efficiencyEasy to produceMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsMetal clustersSize selective
The invention provides a method for depositing catalytic clusters on a surface, the method comprising confining the surface to a controlled atmosphere; contacting the surface with catalyst containing vapor for a first period of time; removing the vapor from the controlled atmosphere; and contacting the surface with a reducing agent for a second period of time so as to produce catalyst-containing nucleation sites.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Preparation method for mesoporous compound film
ActiveCN106731886AMesopore size is continuously adjustableUnique mesopore sizeSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesPolyethylene oxideUltrafiltration
The invention provides a preparation method for a mesoporous compound film. The method comprises the following steps: triggering the alcoholysis reaction of a precursor compound and a structure-directing agent in ethyl alcohol, thereby obtaining a sol; performing surface treatment on a porous film and soaking in the sol; airing the soaked porous film under a room temperature condition and completing a sol-gelling process; cleaning and drying, thereby obtaining the mesoporous compound film. According to the invention, a polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide-polyethylene oxide triblock copolymer, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide or lauryl sodium sulfate is taken as the structure-directing agent, so that the mesoporous size of the prepared mesoporous compound film can be continuously adjusted. The mesoporous compound film prepared according to the invention has a unique mesoporous structure; due to the organic solvent resistance and special porous structure or the capability of further modifying the mesoporous of the compound film, the mesoporous compound film can be applied to the separating purification fields of selective molecule transferring in the solution, the size selective ion transferring and ultrafiltration on a separating and liquid / liquid interface, and the like; the preparation process is simple; the method is environment-friendly.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENIOR TECH MATERIAL
Scaling icons for representing files
InactiveUS7992103B2Improve the display effectProgram controlSpecial data processing applicationsSize selectiveMinutiae
A method and system are provided for displaying icons in accordance with user preferences. The method includes providing a user with a size selection mechanism for selecting an icon size from a range of sizes. The method additionally includes searching a set of stored resources related to the underlying file and generating the icon in the selected size based upon the stored resources. The method may additionally include selecting an icon type including one of an image icon, a detail icon and a generic icon based on at least one of the user's size selection and the represented file. Furthermore, the icon display system of the invention positions labels and overlays in the vicinity of the icon based upon the selected size of the icon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Core-shell structure having controlled cavity inside and structure comprising the core-shell structure as component, and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20050082521A1Reduce the overall diameterMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsNanoparticleSize selective
A core-shell structure comprises a core (2) comprising nanoparticles and a shell (4) coating the core (2), and its void space (3) formed by the core (2) and the shell (4) is controlled. A method of preparing the core-shell structure comprises: forming particles comprising a photoetchable semiconductor, metal or polymer and coating the particles with a shell (4) comprising a non-photoetchable semiconductor, metal or polymer, to form a core-shell structure (5); and irradiating the core-shell structure with a light having a controlled wavelength in the photoetching solution to form an adjustable void space inside a shell (3) within the core-shell structure by the size-selective photoetching method. The core-shell structure allows the preparation of a catalyst exhibiting an extremely high efficiency, and can be used as a precursor for preparing a nanomaterial required for a nanodevice.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Nanoparticles and production thereof
InactiveUS20070065665A1Good repeatabilityReduce variation in propertyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical propertyNanoparticle
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Microwave heating device
A microwave heating device for heating a load by means of microwaves is provided. The microwave heating device (300) comprises a cavity (350) arranged to receive a load to be heated and a feeding structure (325) for feeding microwaves in the cavity. The feeding structure comprises a transmission line (330) for transmitting microwave energy generated by a microwave source (310) and a resonator (320) arranged at the junction between the transmission line and the cavity for operating as a feeding port (320a) of the cavity. The dielectric constant of the material constituting the interior of the resonator and the dimensions of the resonator are selected such that a resonance condition is established in the resonator for the microwaves generated by the source and impedance matching is established between the transmission line, the resonator and the cavity. In addition, the present invention provides a microwave heating device (500) comprising a plurality of feeding ports (525, 525') with reduced crosstalk.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Size-selective polymer system
ActiveUS8211310B2Easy to transportMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesPolymer scienceSize selective
A size-selective hemocompatible porous polymeric adsorbent system is provided, the polymer system comprises at least one polymer with a plurality of pores, and the polymer has at least one transport pore with a diameter from about 250 Angstroms to about 2000 Angstroms, and the polymer has a transport pore volume greater than about 1.8% to about 78% of a capacity pore of volume of the polymer.
Owner:CYTOSORBENTS CORP
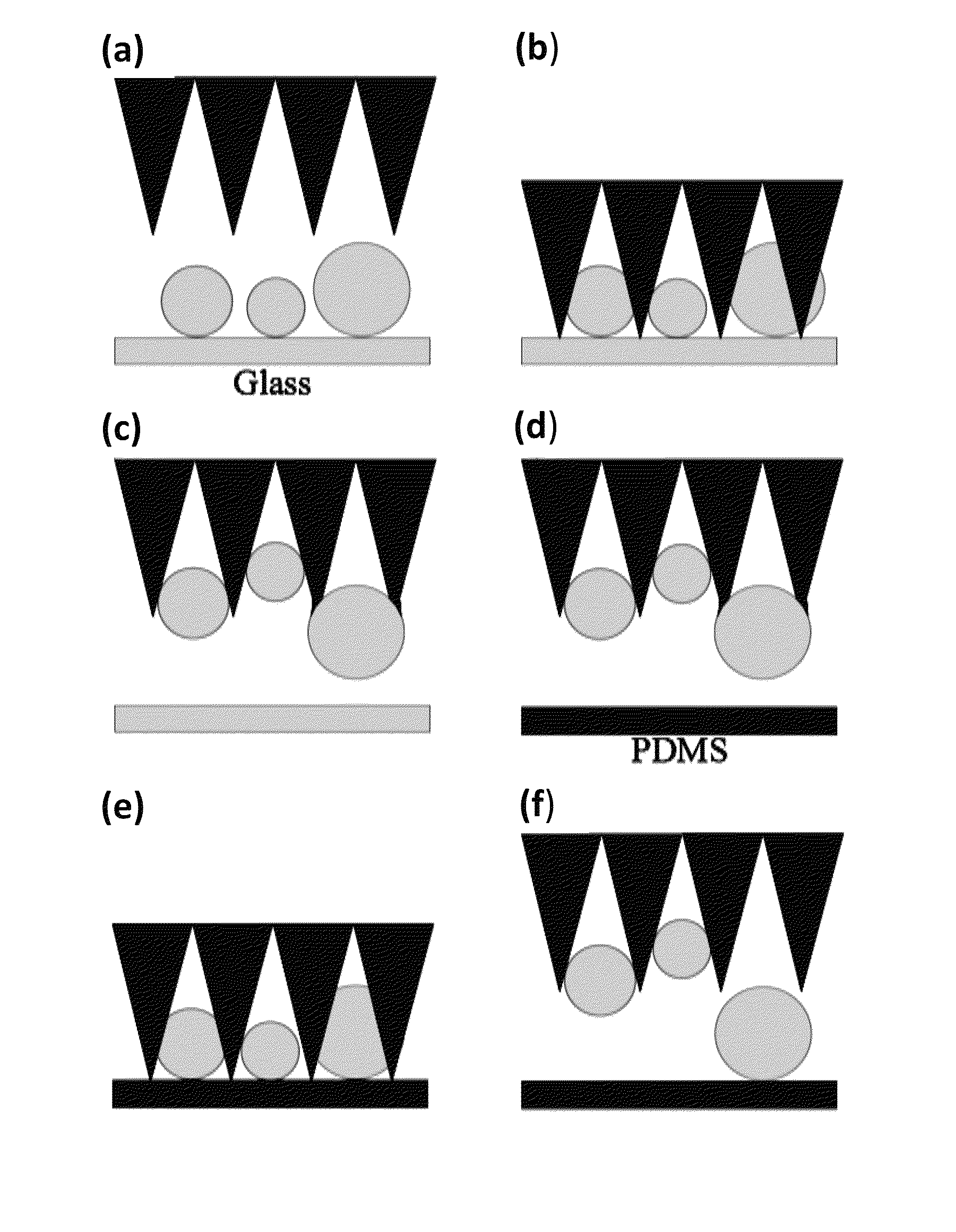
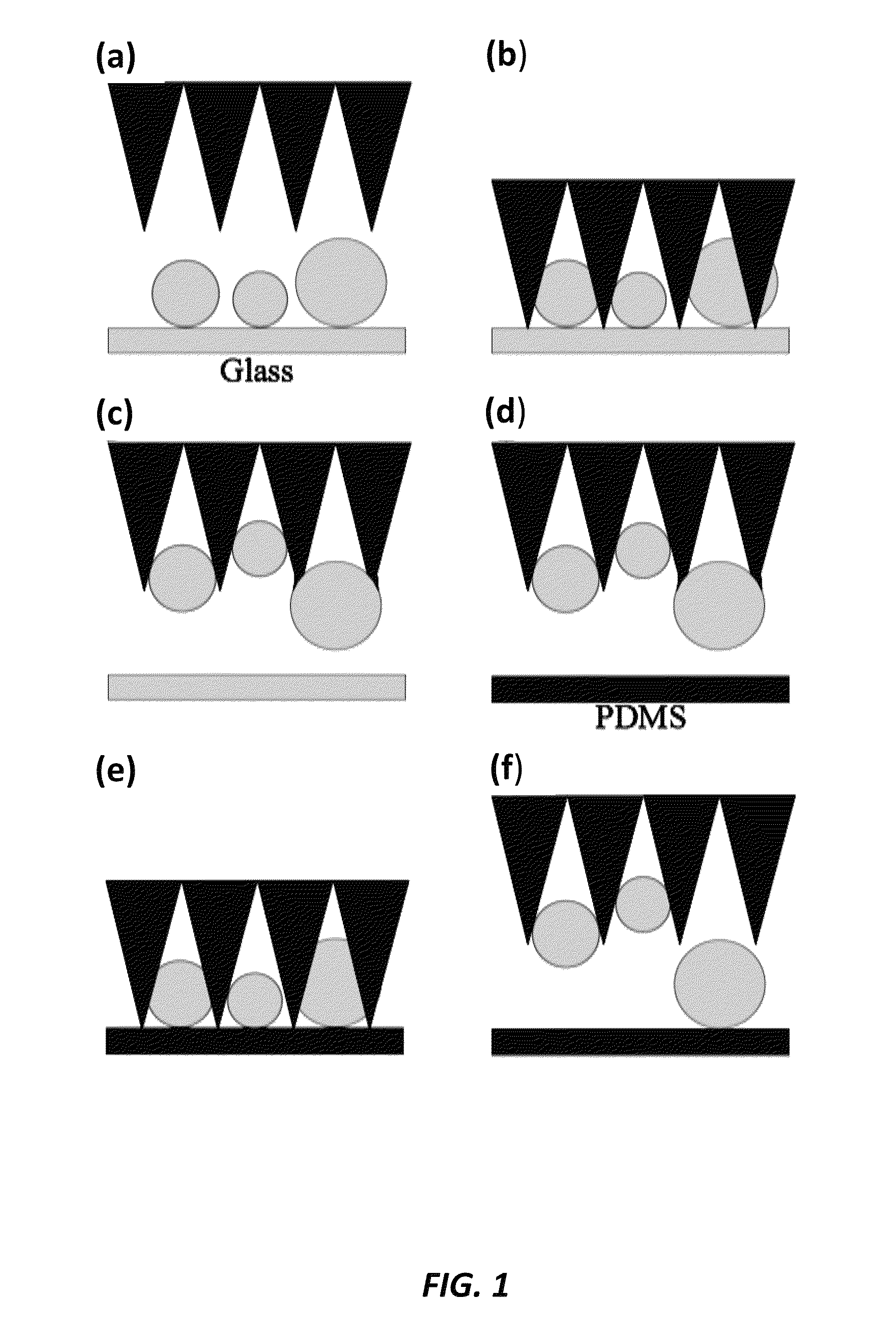
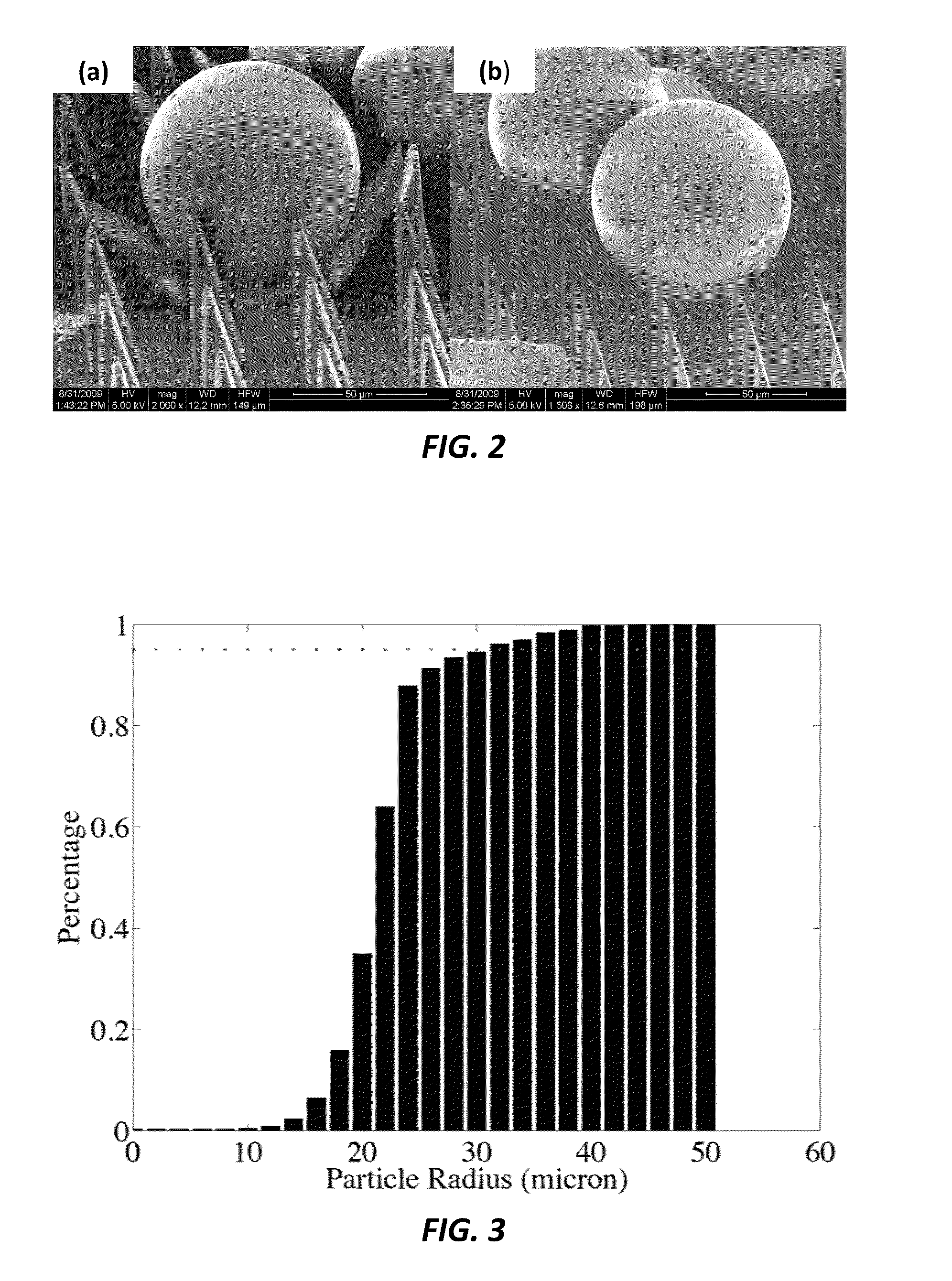
Micro-structure-based adhesives for size-selective particle trapping and sorting
InactiveUS8882996B2Nanostructure manipulationCleaning processes and apparatusParticle trappingMicro structure
A method of separating particles is provided that includes exposing a selective PDMS adhesive to a particle-contaminated surface, where the selective PDMS adhesive captures particles present on the particle-contaminated surface to form a fouled selective PDMS adhesive, and exposing the fouled selective PDMS adhesive to a PDMS transfer sheet, where particles outside of a desired range are transferred over to the PDMS transfer sheet, where the fouled selective PDMS adhesive retains only the particles of a desired range.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Redox-Flow Batteries Employing Oligomeric Organic Active Materials and Size-Selective Microporous Polymer Membranes
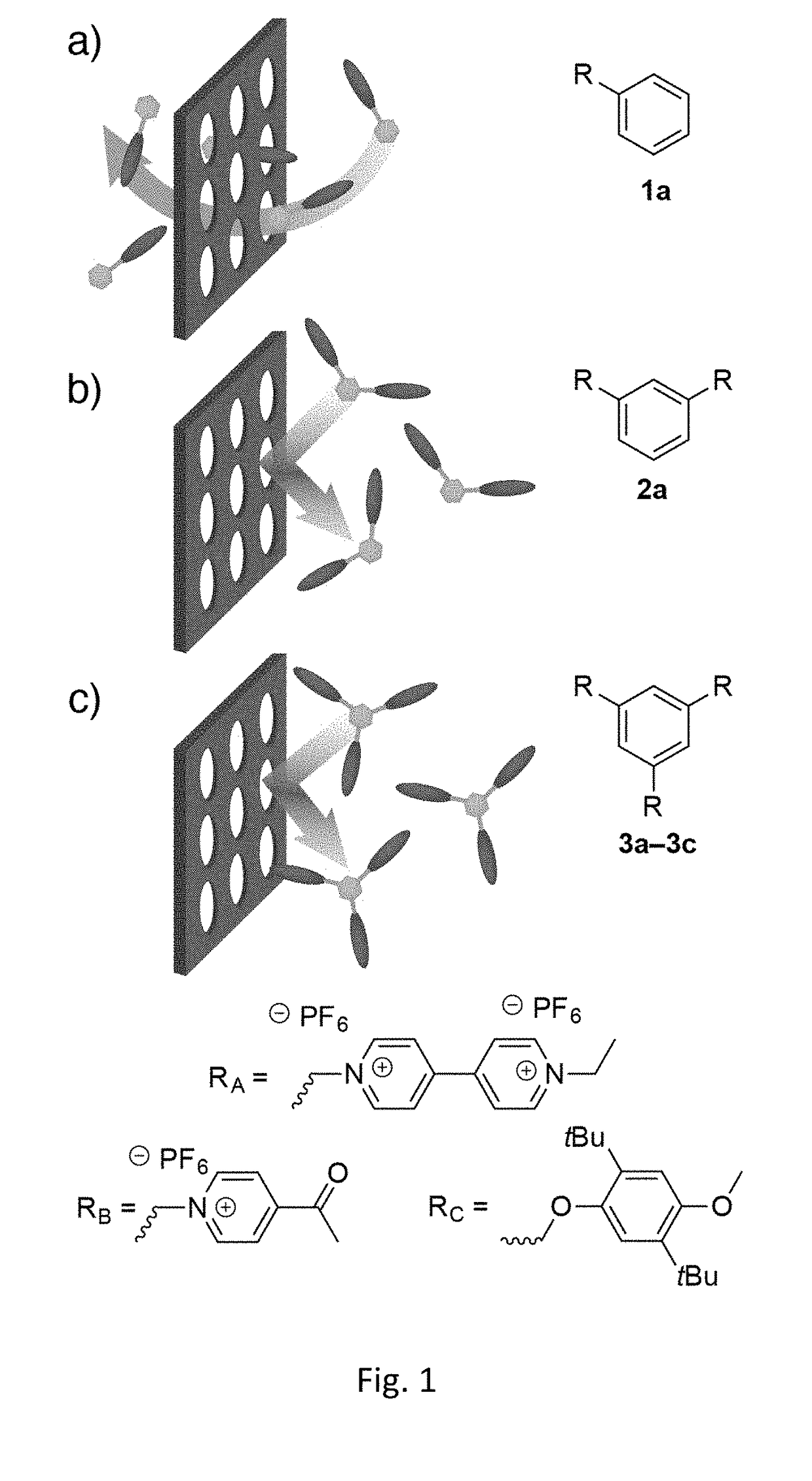
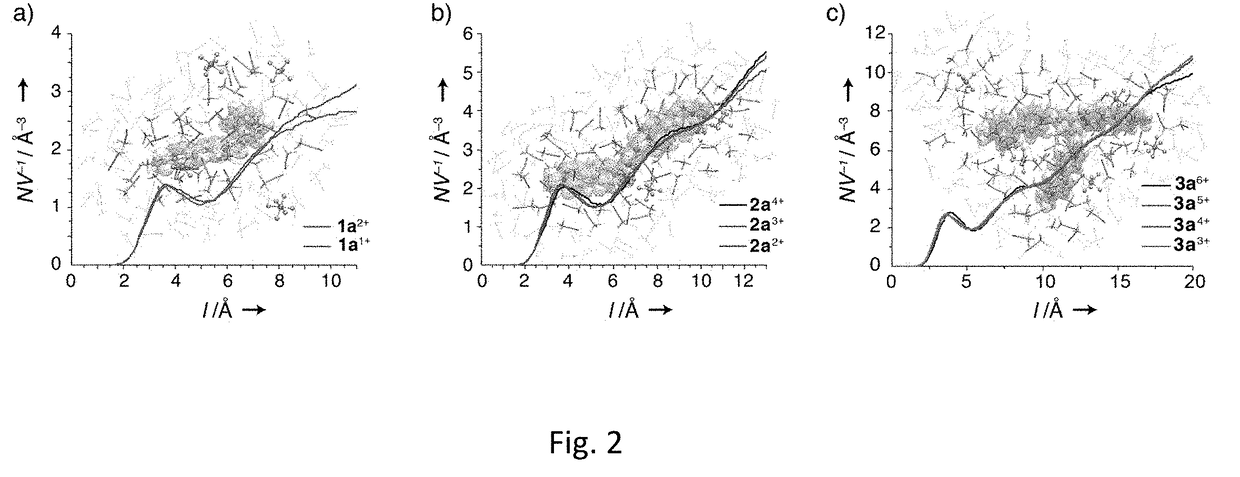
Intermittent energy sources, including solar and wind, require scalable, low-cost, multi-hour energy storage solutions to be effectively incorporated into the grid. Redox-flow batteries offer a solution, but suffer from rapid capacity fade and low Coulombic efficiency due to the high permeability of redox-active species across the battery's membrane. Here we show that active-species crossover can be arrested by scaling the membrane's pore size to molecular dimensions and in turn increasing the size of the active material to be above the membrane's pore-size exclusion limit. When oligomeric redox-active organic molecules were paired with microporous polymer membranes, the rate of active-material crossover was either completely blocked or slowed more than 9,000-fold compared to traditional separators at minimal cost to ionic conductivity. In the case of the latter, this corresponds to an absolute rate of ROM crossover of less than 3 μmol cm−2 day−1 (for a 1.0 M concentration gradient), which exceeds performance targets recently set forth by the battery industry. This strategy was generalizable to both high and low-potential ROMs in a variety of electrolytes, highlighting the importance of macromolecular design in implementing next-generation redox-flow batteries.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Plugging material and plugging method for large leakage casing damage section of oil-water well
InactiveCN110396399AHigh success rate of one-time blockageImprove the blocking effectDrilling compositionSealing/packingSolid phasesSize selective
The invention discloses a plugging material and plugging method for a large leakage casing damage section of an oil-water well. The plugging material comprises a gel system and a resin system, whereina volume ratio of the gel system to the resin system is (4-8):(1-2); and the plugging method comprises the following steps: a leakage pore size is estimated by a deformation formula of a Bernoulli equation to provide a size selection support for a solid phase of the plugging material, leakage reduction operation is performed for multiple times by a strength gel, after leakage is less than 500 L / min, final plugging is performed by using a high-strength modified resin system, and therefore the purpose that the large leakage casing damage section of the oil-water well is successfully plugged atone time is achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Size-selective hemocompatible polymer system
ActiveUS20120238441A1Easy to transportOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationSorbentSize selective
A size-selective hemocompatible porous polymeric adsorbent system is provided, the polymer system comprises at least one crosslinking agent and at least one dispersing agent, and the polymer has a plurality of pores with diameters in the range from about 17 to about 40,000 Angstroms
Owner:CYTOSORBENTS CORP
Method and apparatus for physical separation of different sized nanostructures
InactiveUS8215489B1Easy to adjustIncrease liquid volumeMaterial nanotechnologyReversed direction vortexFractionationSize selective
The present application provides apparatuses and methods for the size-selective fractionation of ligand-capped nanoparticles that utilizes the tunable thermophysical properties of gas-expanded liquids. The nanoparticle size separation processes are based on the controlled reduction of the solvent strength of an organic phase nanoparticle dispersion through increases in concentration of the antisolvent gas, such as CO2, via pressurization. The method of nanomaterial separation contains preparing a vessel having a solvent and dispersed nanoparticles, pressurizing the chamber with a gaseous antisolvent, and causing a first amount of the nanoparticles to precipitate, transporting the solution to a second vessel, pressurizing the second vessel with the gaseous antisolvent and causing further nanoparticles to separate from the solution.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Scroll Wheel Input Device
InactiveUS20080122808A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringSize selective
An objective of the present invention provides a scroll wheel input device that comprises: a scroll wheel providing a longitudinal scrolling and a lateral triggering, wherein the longitudinal scrolling provides a first dimension selection and the lateral triggering provides a second dimension selection; and a plurality of display elements comprising a multiple sets of first dimension display element group. Each of the first dimension display element group comprises at least one second dimension display element, wherein the first dimension selection is made by switching among the different first dimension display element groups via the longitudinal scrolling while the second dimension selection is made by switching among the at least one second dimension display element in the switched first dimension display element group via the lateral triggering.
Owner:HUANG KUO AN
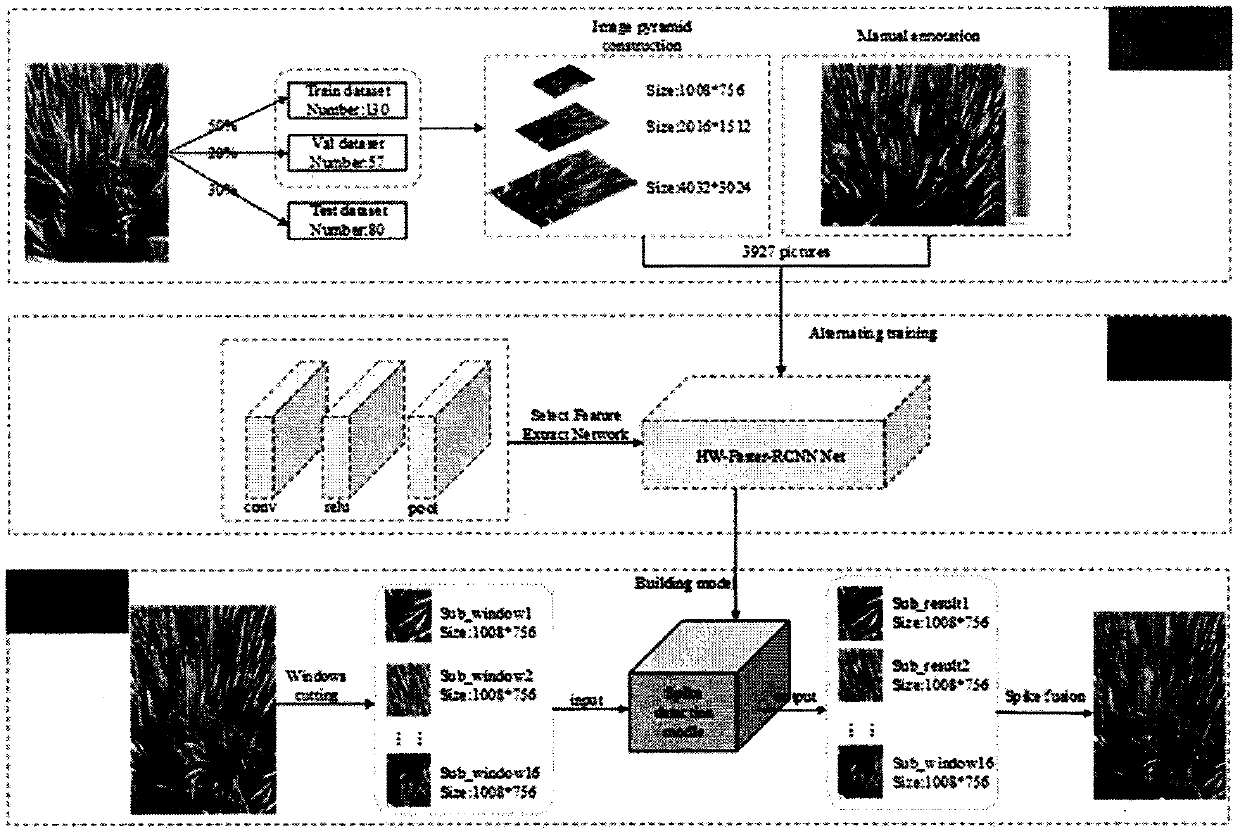
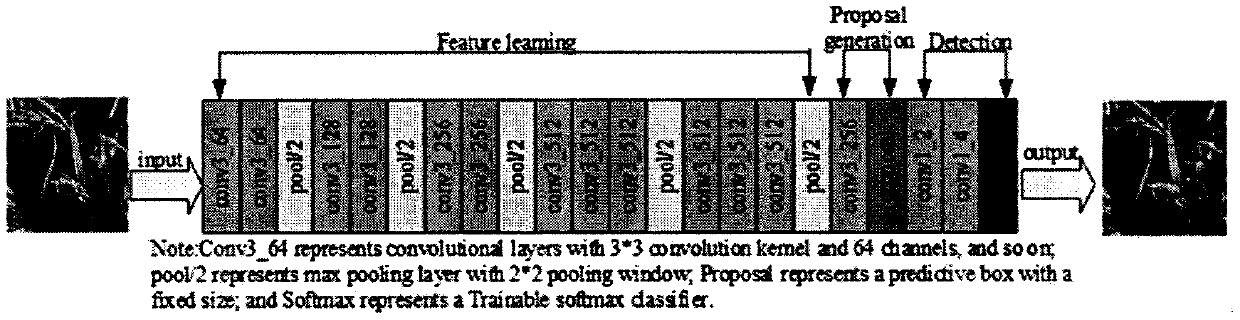
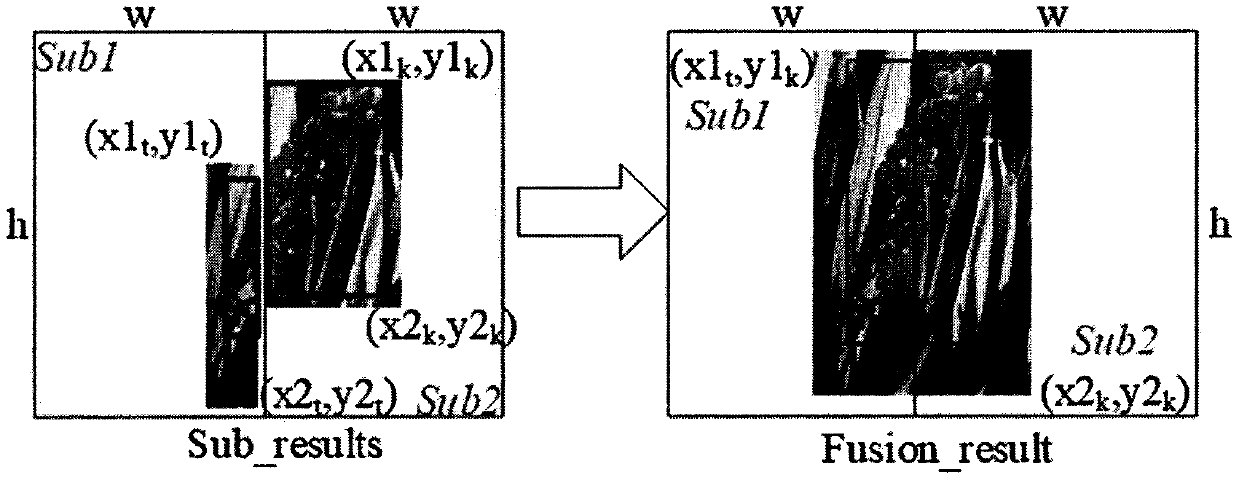
Method for quickly counting rice ear number of field rice by using image pyramid and Fast-RCNN
PendingCN110569747AValid countImprove Counting AccuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setFeature learning
The invention discloses a field rice spike counting algorithm HW-Faster-RCNN based on an image pyramid. The field rice spike counting algorithm HW-Faster-RCNN realizes automatic counting of field riceimages with relatively small rice spike sizes and more than 50 rice spikes. Firstly, the size of a receptive field is analyzed, an appropriate feature learning network is selected, and an appropriateinput image size is calculated according to the rice spike size; secondly, an original image is cut based on the input image size range, and an image pyramid is designed and constructed to increase the relative size of rice ears; then, a mixed window data set is constructed based on the image pyramid, and a rice ear counting model is trained by using an HW-Faster-RCNN network; and finally, the to-be-tested image is segmented, the sub-images are respectively counted by using a rice spike counting model, and a damaged spike fusion algorithm is designed to remove repeated counting. The result shows that the counting accuracy of the small-size rice ears is remarkably improved by selecting the feature learning network and designing the image pyramid according to the ear sizes; the average counting accuracy and the error detection rate of the HW-Faster-RCNN are 87.23% and 4.60% respectively, and the HW-Faster-RCNN can be practically applied to automatic counting of rice ears in a complex field scene.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Aerosol size-selective impactor for reducing particle bounce
InactiveUS20070056389A1Reduce bouncingImprove accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesDispersed particle separationSize selectiveDehydration
An aerosol size-selective impactor for reducing particle bounce includes a main structure, a buffering layer, and a dehydration preventing layer. This main structure with an inlet and an outlet has a central channel and a receiving cavity. There are many nozzles in the inlet. The buffering layer is filled in the receiving cavity. The dehydration preventing layer is coated on the buffering layer for reducing the dehydration of water contained in the buffering layer. So, this invention utilizes the design of the receiving cavity to receive both layers. Its accuracy is high. Its sampling time lasts longer. It can endure vibrations. This invention can yield the particle bounce effect with lower cost. And, its application scope is wide.
Owner:CHUNG SHAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Antenna and mobile terminal
InactiveCN105098353AReduce design difficultySmall sizeAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna equipments with additional functionsSize selectiveMetal
The embodiments of the invention disclose an antenna and a mobile terminal. The antenna comprises a radiation part, wherein the radiation part is made of a nonmetal material and used for dividing a metal rear shell of the mobile terminal into at least two sections; the radiation part comprises a first radiation part and a second radiation part, the second radiation part is arranged at the bottom end of the metal rear shell, the bottom end is far from one end, where components are arranged, of the metal rear shell, and the first radiation part is arranged at the top close to the components; the first radiation part comprises a linear radiator and a curved radiator which are connected with each other, and the curved radiator is used for completely or partially surrounding the components. The limitation to the size selection and the position design of the components on the metal rear shell can be reduced on the premise that the performance of the antenna is ensured.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Size-selective hemoperfusion polymeric adsorbents
Size-selective hemocompatible porous polymeric adsorbents are provided with a pore structure capable of excluding molecules larger than 50,000 Daltons, but with a pore system that allows good ingress and egress of molecules smaller than 35,000 Daltons. The pore system in these porous polymeric adsorbents is controlled by the method of synthesis so that 98% of the total pore volume is located in pores smaller than 300 Angstroms (Å) in diameter with a working pore size range within 100 to 300 Å in diameter. The porous polymeric adsorbents of this invention are very selective for extracting midsize proteins, such as cytokines and β2-microglobulin, from blood and other physiologic fluids while keeping the components required for good health such as cells, platelets, albumin, hemoglobin, fibrinogen, and other serum proteins intact.
Owner:CYTOSORBENTS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com