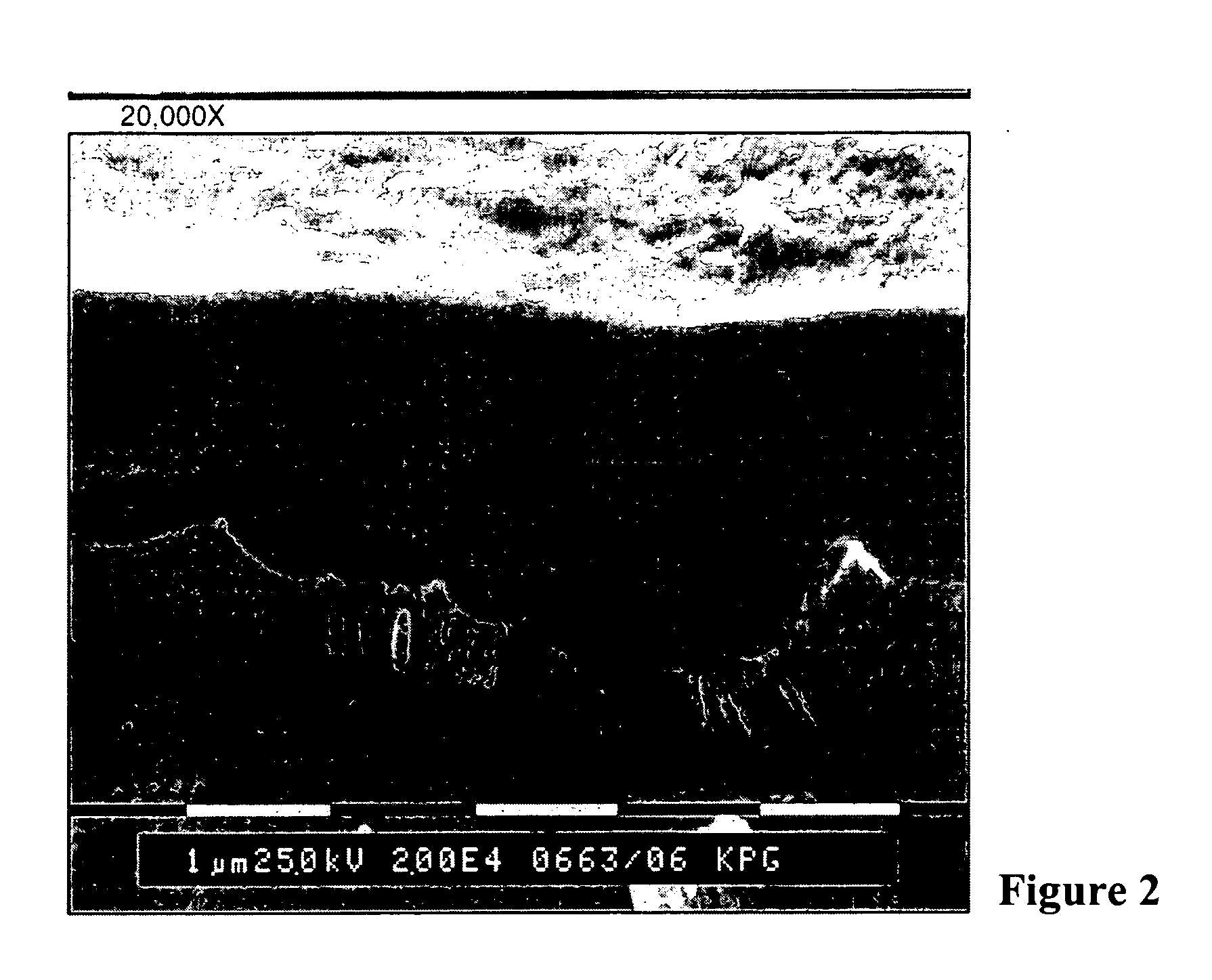
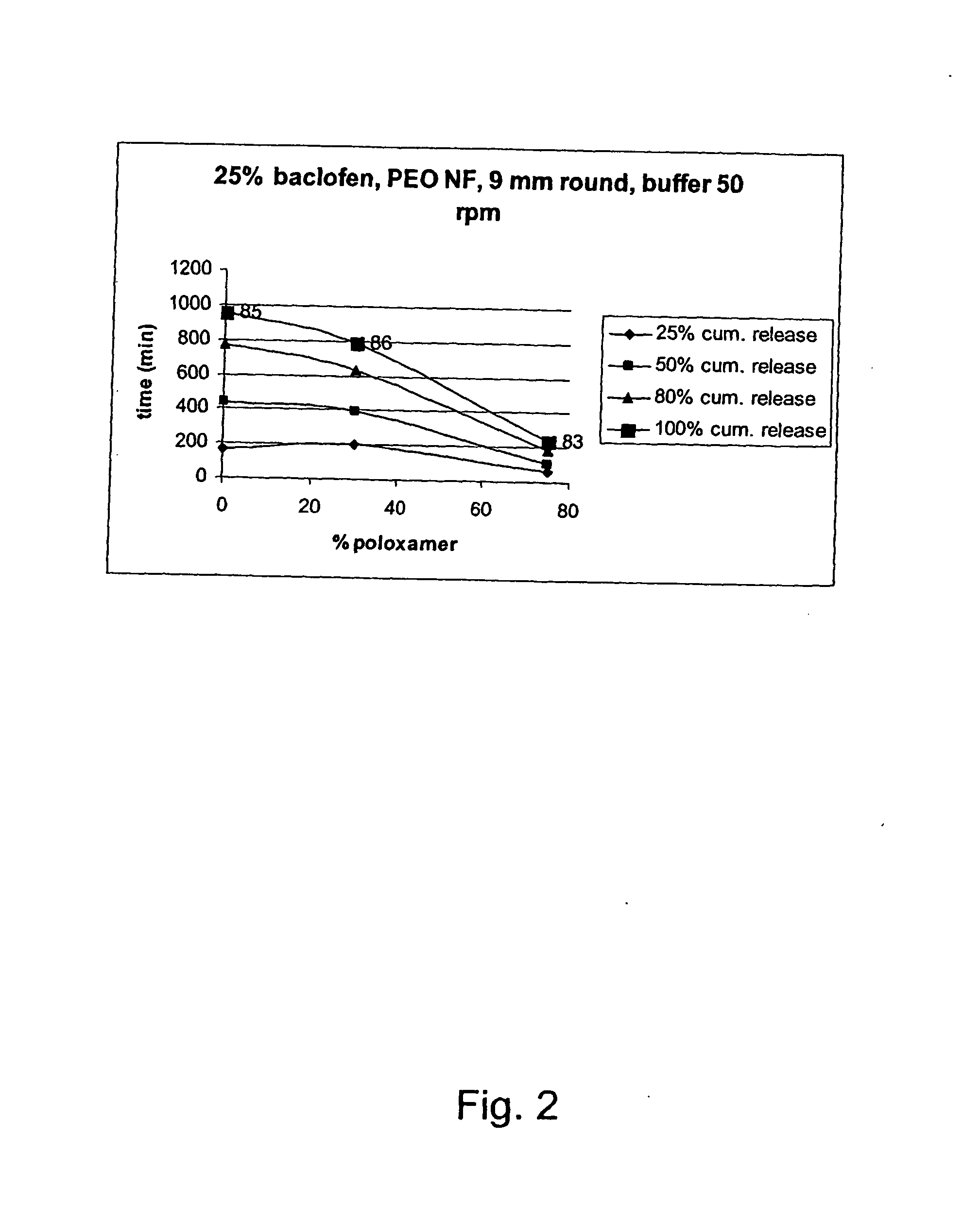
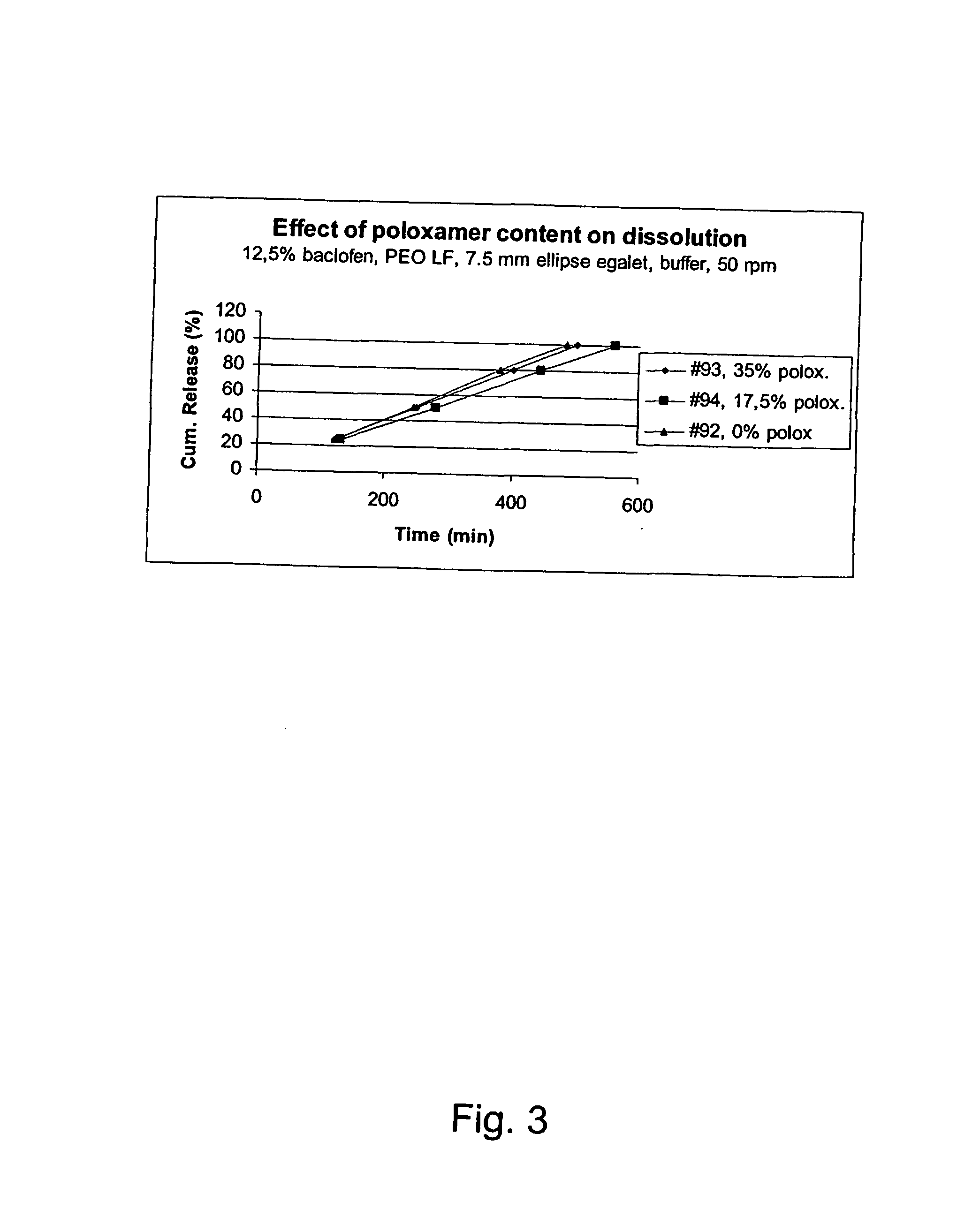
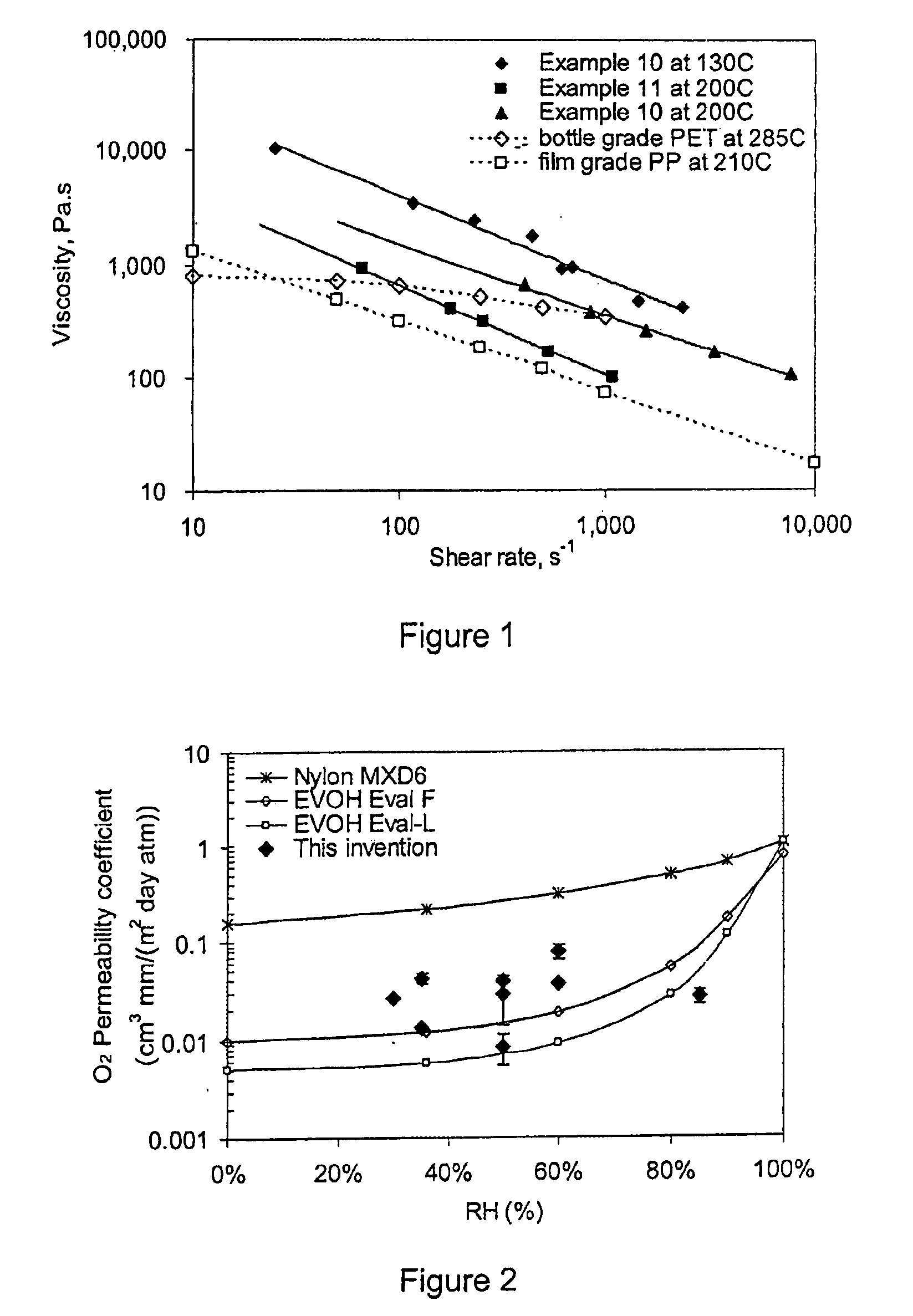
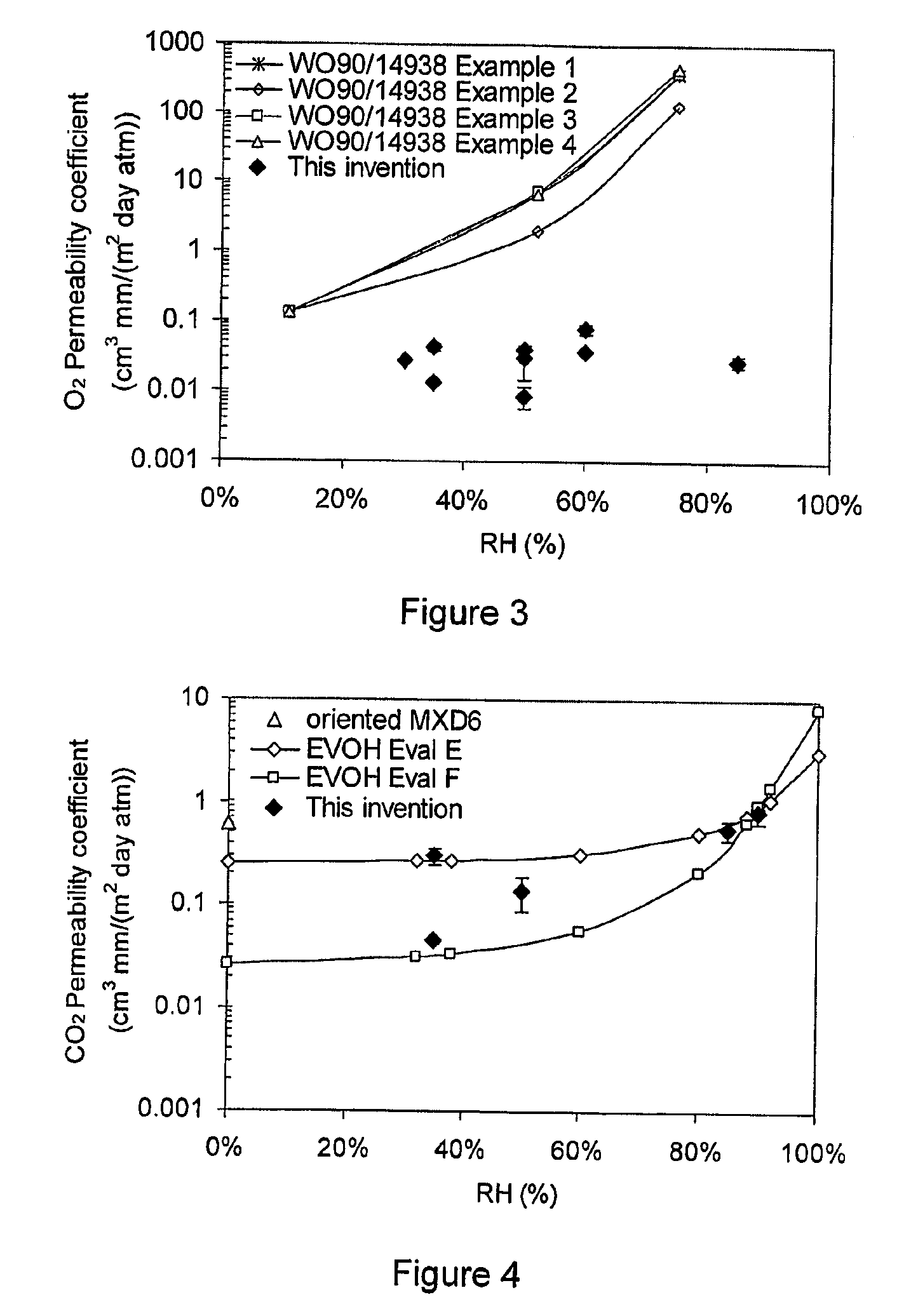
Patents
Literature
2312 results about "Polyethylene oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
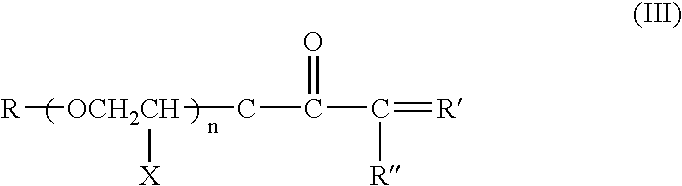
The Polyethylene Oxide (the short name is PEO) (CAS No.: 25322-68-3/68441-17-8) is a new type water soluble resin. It is very popular all over the world. The molecular weight of our Polyethylene Oxide (PEO) is 50000 to 6000000.
On-press developable IR sensitive printing plates using binder resins having polyethylene oxide segments
InactiveUS6899994B2Prevent steppingRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePolyethylene oxide
The present invention relates to a polymerizable coating composition suitable for the manufacture of printing plates developable on-press. The coating composition comprises (i) a polymerizable compound and (ii) a polymeric binder comprising polyethylene oxide segments, wherein the polymeric binder is selected from the group consisting of at least one graft copolymer comprising a main chain polymer and polyethylene oxide side chains, a block copolymer having at least one polyethylene oxide block and at least one non-polyethylene oxide block, and a combination thereof. The invention is also directed to an imageable element comprising a substrate and the polymerizable coating composition.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
Gas sampling line
ActiveUS9861298B2Improve accuracyReduce distortion problemsDispersed particle separationRespiratory organ evaluationGas analysisLine tubing
A gas sampling line having a channel for conducting respiratory gases from a patient respiratory interface to a gas monitor, the gas sampling line comprising, i.a., a gas sampling tube comprised of a polyether block amide material, the polyether segments of which comprise polyethyleneoxide. Use of a tube comprised of a polyether block amide material, the polyether segments of which comprise polyethyleneoxide, for sampling of respiratory gases; and a method for sampling of respiratory gases, the method comprising conducting respiratory gases through such a tube. A gas analysis system for analyzing respiratory gases, comprising a gas sampling line as defined above and a gas monitor connectable to the gas sampling line.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component, which includes polyethylene oxide optionally blended with hydrophilic cellulosic polymers. Desirably, the films also contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent with no more than a 10% variance of the active agent pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent per unit area of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
Gas sampling line
ActiveUS20110237969A1Improve accuracyReduce distortion problemsDispersed particle separationRespiratory organ evaluationGas analysisPolyethylene oxide
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Silicone based membranes for use in implantable glucose sensors
Membrane systems incorporating silicone polymers are described for use in implantable analyte sensors. Some layers of the membrane system may comprise a blend of a silicone polymer with a hydrophilic polymer, for example, a triblock poly(ethylene oxide) -poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) polymer. Such polymeric blends provide for both high oxygen solubility and aqueous analyte solubility.
Owner:DEXCOM
Printing plates using binder resins having polyethylene oxide segments
InactiveUS20050170286A1Prevent steppingRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePolyethylene oxide
The present invention relates to a polymerizable coating composition suitable for the manufacture of printing plates, which may be developable on-press. The coating composition comprises (i) a polymerizable compound and (ii) a polymeric binder comprising polyethylene oxide segments, wherein the polymeric binder is selected from the group consisting of at least one graft copolymer comprising a main chain polymer and polyethylene oxide side chains, a block copolymer having at least one polyethylene oxide block and at least one non-polyethylene oxide block, and a combination thereof. The invention is also directed to an imageable element comprising a substrate and the polymerizable coating composition.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component, which includes polyethylene oxide optionally blended with hydrophilic cellulosic polymers. Desirably, the films also contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent with no more than a 10% variance of the active agent pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent per unit area of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
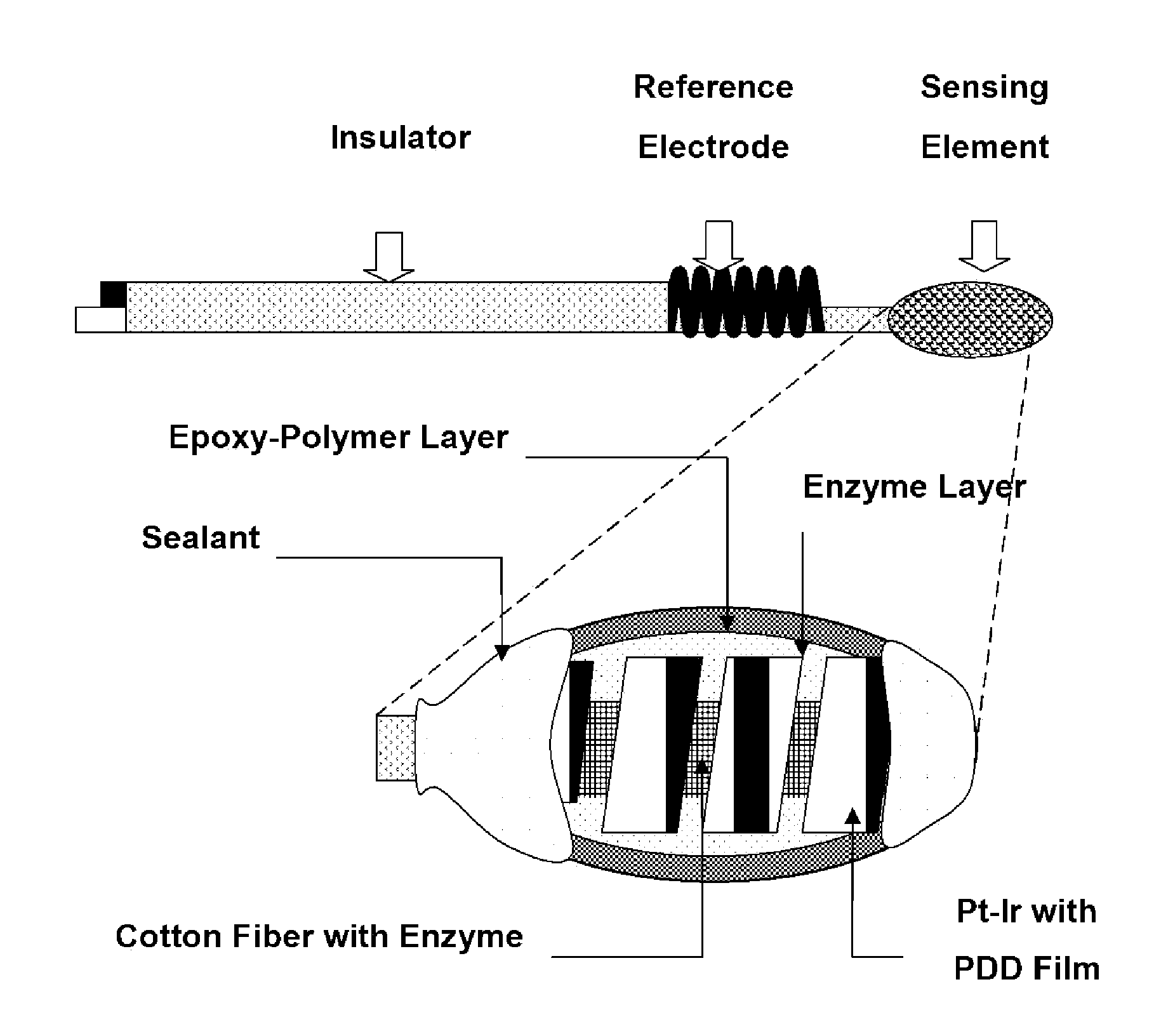
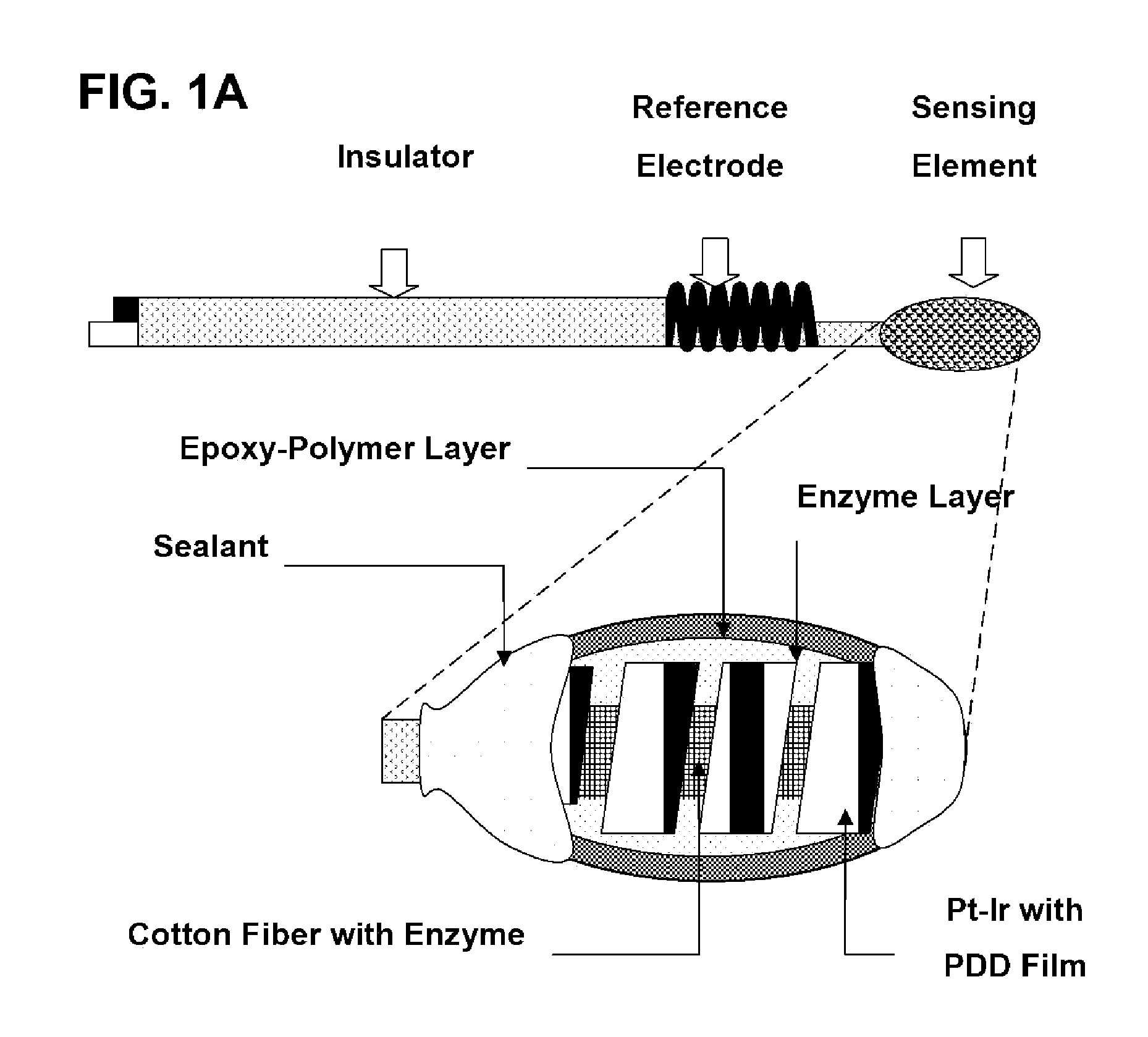
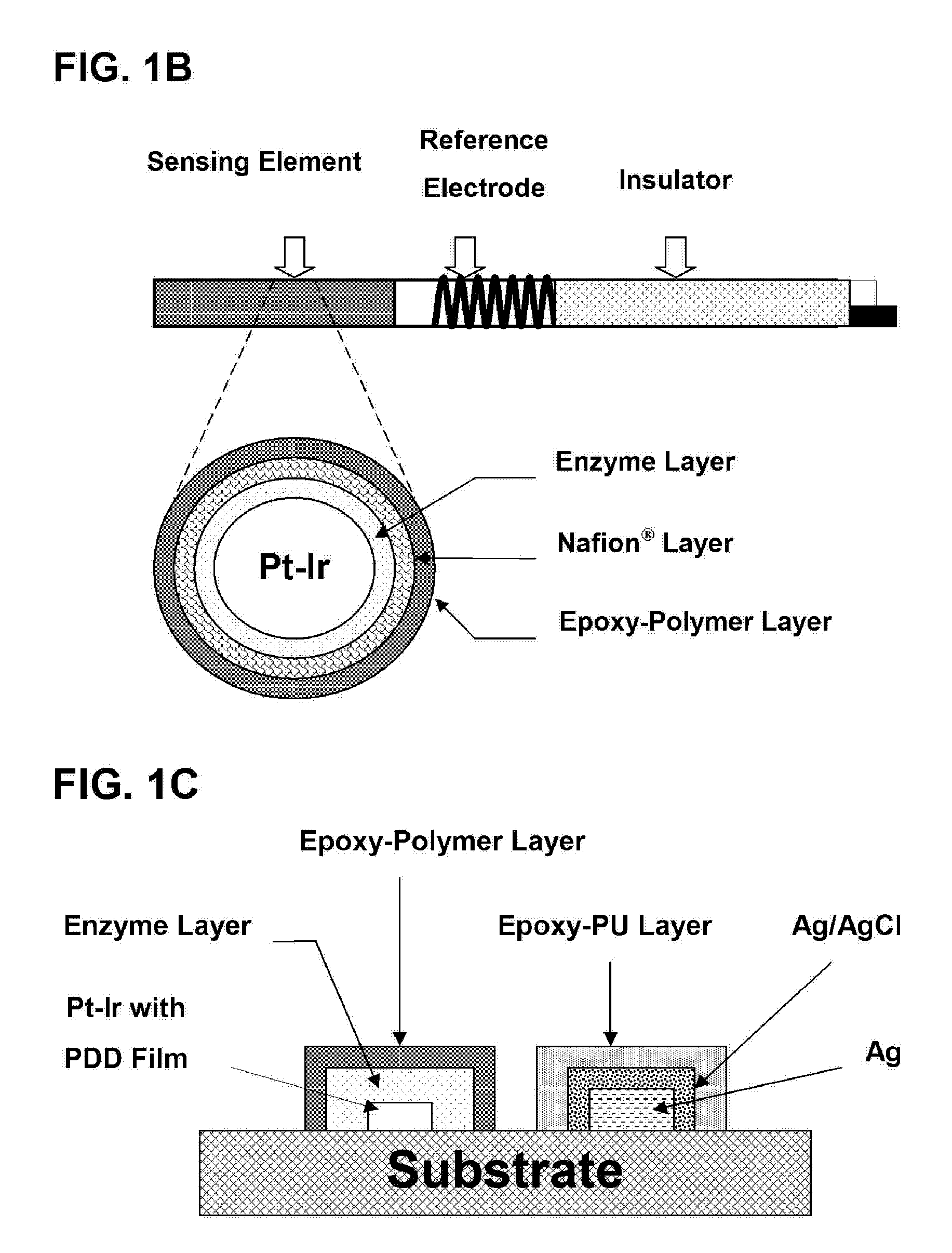
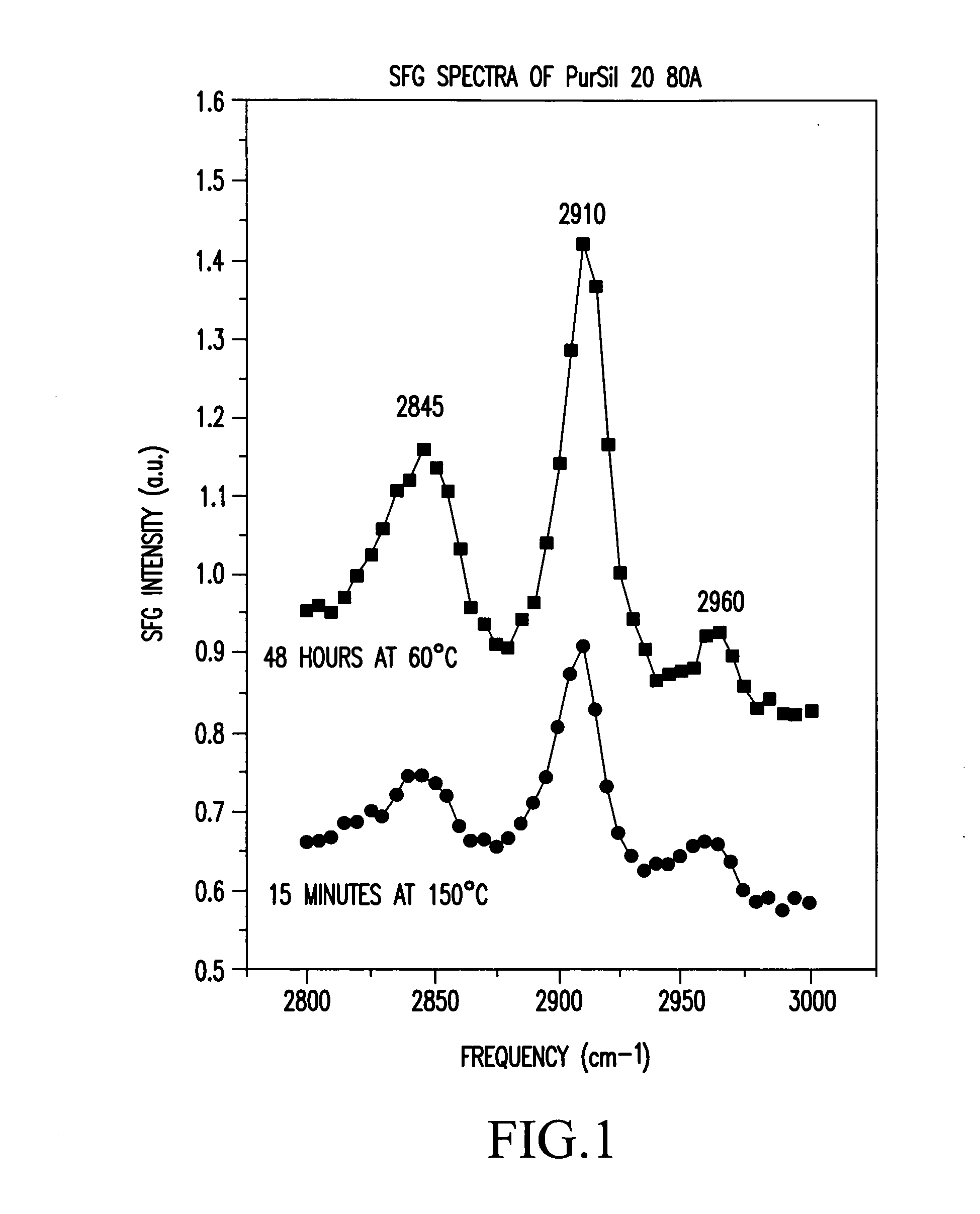
Epoxy Enhanced Polymer Membrane to Increase Durability of Biosensors
ActiveUS20060289307A1Increasing in vivo durabilityImprove long-term stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEpoxyPolyethylene oxide
The present invention provides a polymer membrane enhanced with cured epoxy resin for use as the outer membrane of biosensors. The membrane includes approximately 30-80% epoxy resin adhesives, 10-60% polymer such as poly(vinyl chloride), polycarbonate and polyurethane and 0-30% plasticizers and 5-15% surface modifier reagent such as polyethylene oxide-containing block copolymers. Utilizing the polymer membrane of the present invention, a three-layered sensing element has been developed. This sensing element will be particularly useful for miniaturized biosensors used for in vitro blood measurements or for continuous in vivo monitoring such as implantable biosensors. This element includes an enzyme layer, an interference-eliminating layer and the novel polymer member of the present invention as the outer polymer layer. This novel sensing element shows excellent response characteristics in solutions and has an extremely long lifetime. This technology is particularly useful for improving the lifetime of implantable biosensors.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
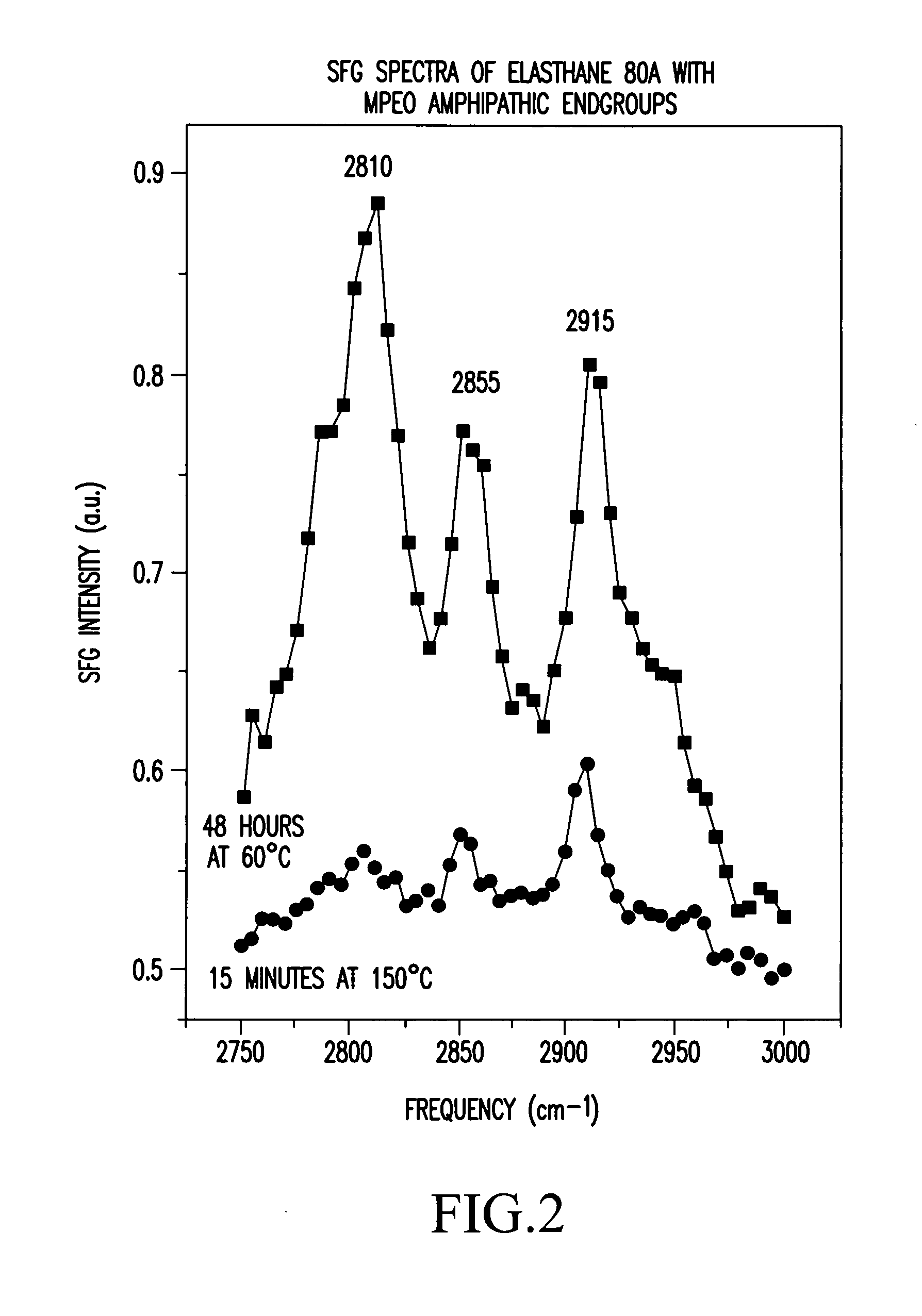
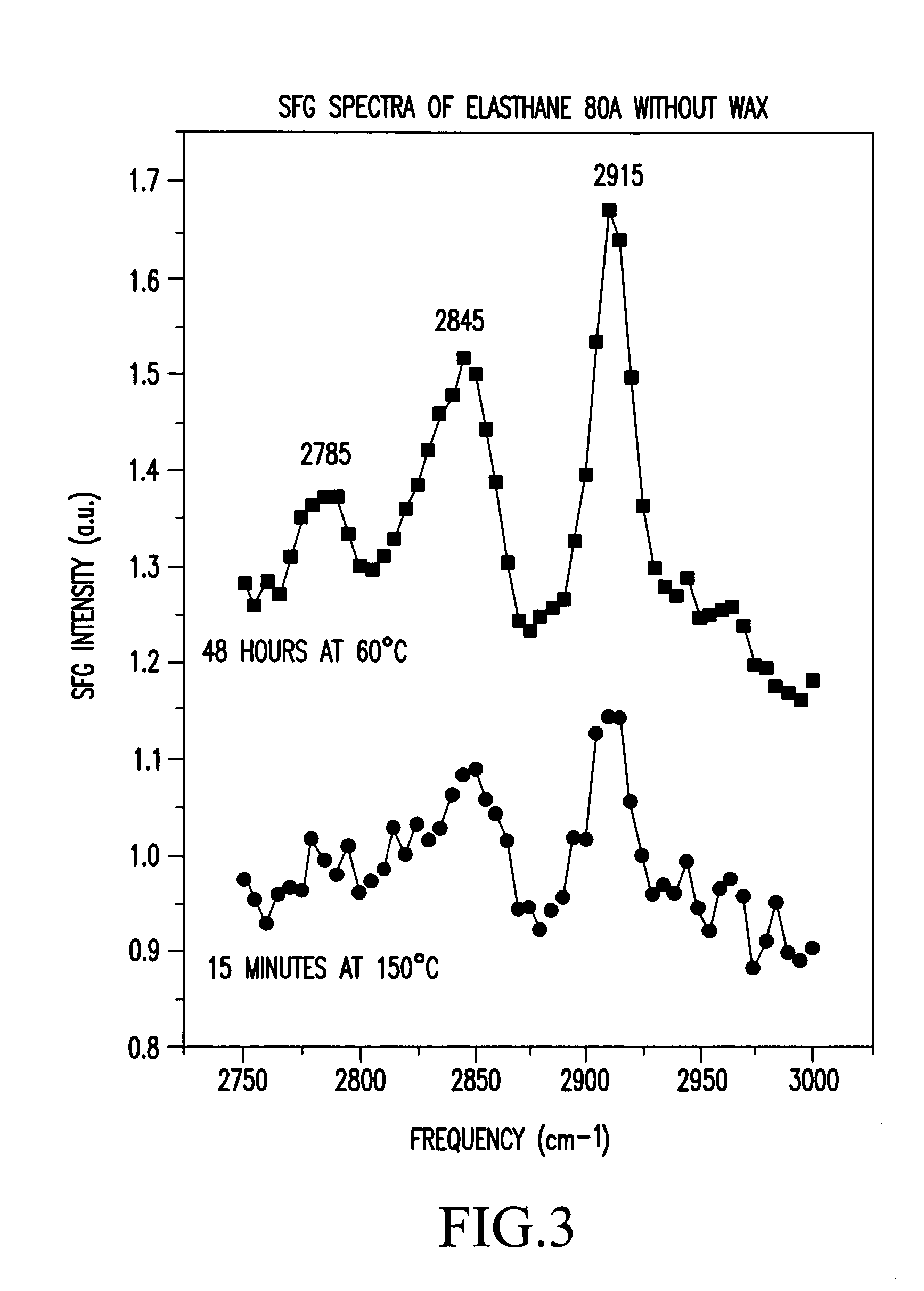
Control of polymer surface molecular architecture via amphipathic endgroups
ActiveUS20050282997A1Promote resultsReduce signal to noise ratioSurgeryCatheterPolymeric surfacePolyethylene oxide
Polymers whose surfaces are modified by endgroups that include amphipathic surface-modifying moieties. An amphipathic endgroup of a polymer molecule is an endgroup that contains at least two moieties of significantly differing composition, such that the amphipathic endgroup spontaneously rearranges its positioning in a polymer body to position the moiety on the surface of the body, depending upon the composition of the medium with which the body is in contact, when that re-positioning causes a reduction in interfacial energy. An example of an amphipathic surface-modifying endgroup is one that has both a hydrophobic moiety and a hydrophilic moiety in a single endgroup. For instance, a hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) terminated with a hydrophilic hydroxyl group is not surface active in air when the surface-modifying endgroup is bonded to a more hydrophobic base polymer. If the hydroxyl group on the oligomeric poly(ethylene oxide) is replaced by a hydrophobic methoxy ether terminus, the poly(ethylene oxide) becomes surface active in air, and allows the poly(ethylene oxide) groups to crystallize in the air-facing surface. In this example, immersion in water destroys the crystallinity as the poly(ethylene oxide) sorbs water and the hydrophobic methoxy group retreats below the surface of the polymer. Also disclosed are methods and articles of manufacture that make use of these polymers.
Owner:THE POLYMER TECH GROUP
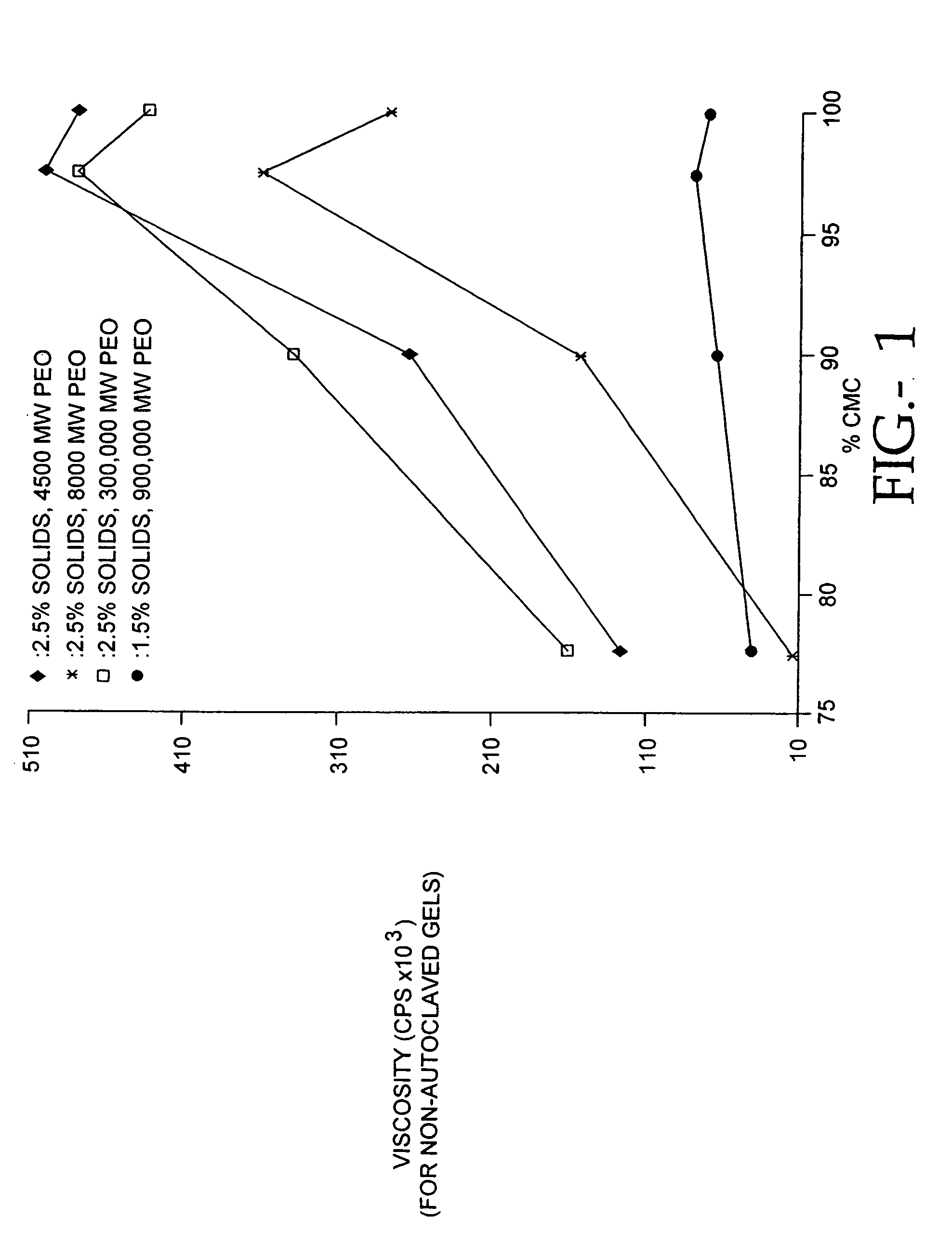
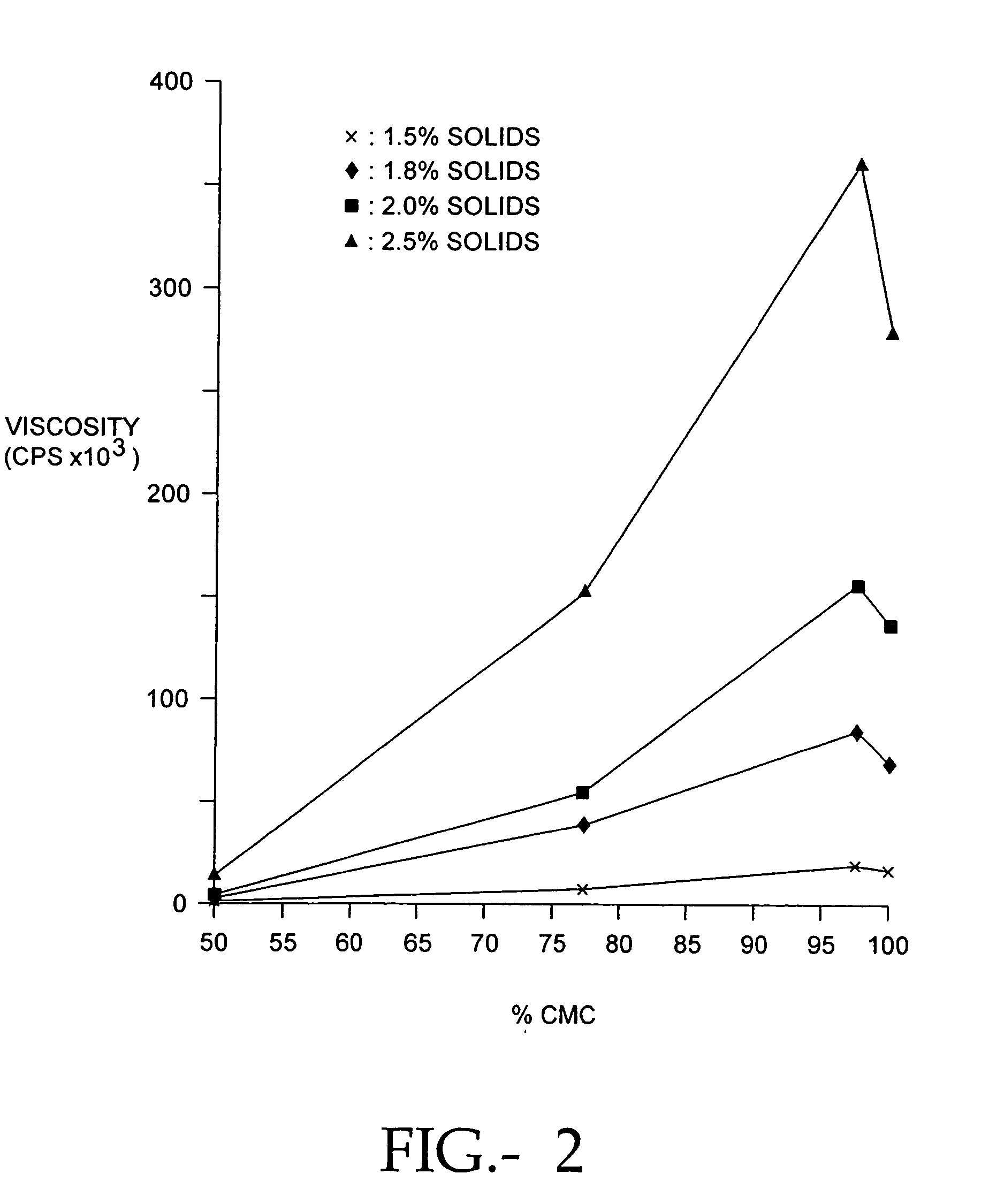
Compositions of polyacids and polyethers and methods for their use as dermal fillers
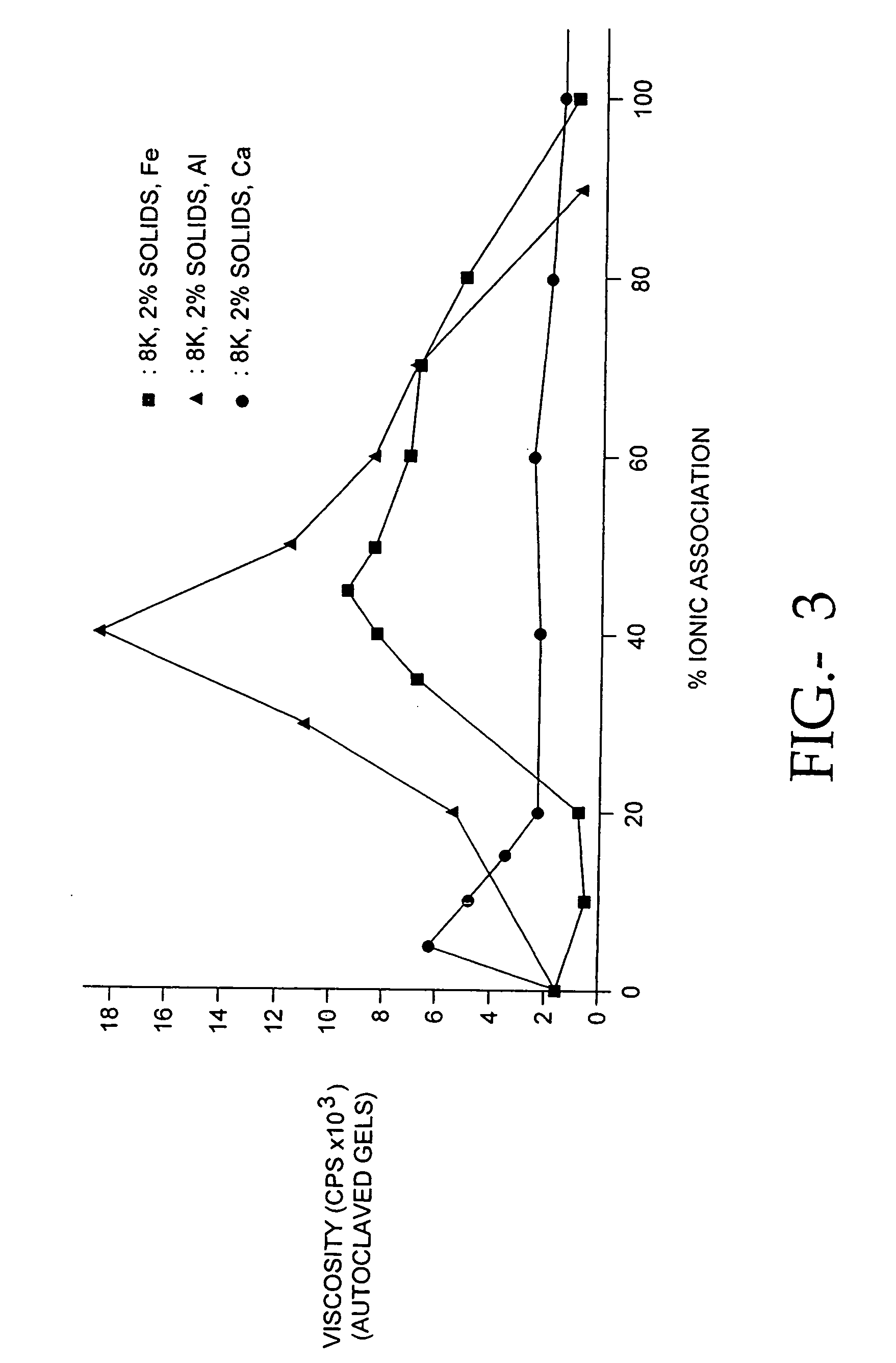
The present invention relates to improved methods for filling the skin for cosmetic or medical purposes. Compositions comprising carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), polyethylene oxide (PEO) and calcium ions can be made and have physical properties that depend on the amounts and types of CMC, PEO, and calcium ions to form ioniclaly cross-linked gels. Compositions can be formed into microspheres, coascervates, gels, or membranes. Gels, microspheres and coascervates can be injected directly into a site for dermal filling. Membranes can be surgically introduced, where they swell to form hydrated gels. After introduction, the dermal filler persists for a period of time and then can disintegrate and be removed from the body.
Owner:FZIOMED
Crosslinkable Graft Polymer Non-Preferentially Wetted by Polystyrene and Polyethylene Oxide
ActiveUS20080318005A1Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsPolyethylene oxidePolymer science
Methods for fabricating a random graft PS-r-PEO copolymer and its use as a neutral wetting layer in the fabrication of sublithographic, nanoscale arrays of elements including openings and linear microchannels utilizing self-assembling block copolymers, and films and devices formed from these methods are provided. In some embodiments, the films can be used as a template or mask to etch openings in an underlying material layer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Bioabsorbable adhesive compounds and compositions
Bioabsorbable compounds which include a polyalkylene oxide backbone with two or more isocyanate substituents are useful as one component adhesives. Absorbable compositions useful as a two component adhesive contain a) a polyethylene oxide having two or more amine substituents with b) a bioabsorbable diisocyanate compound, or alternatively contain a) a polyethylene oxide having two or more isocyanate substituents with b) a bioabsorbable diamine compound, or, alternatively contain a) a bioabsorbable diisocyanate compound and b) a bioabsorbable diamine compound.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Controlled release solid dispersions
InactiveUS20080234352A1Different equipmentInhibition strengthBiocideAnimal repellantsSolubilityPolyethylene oxide
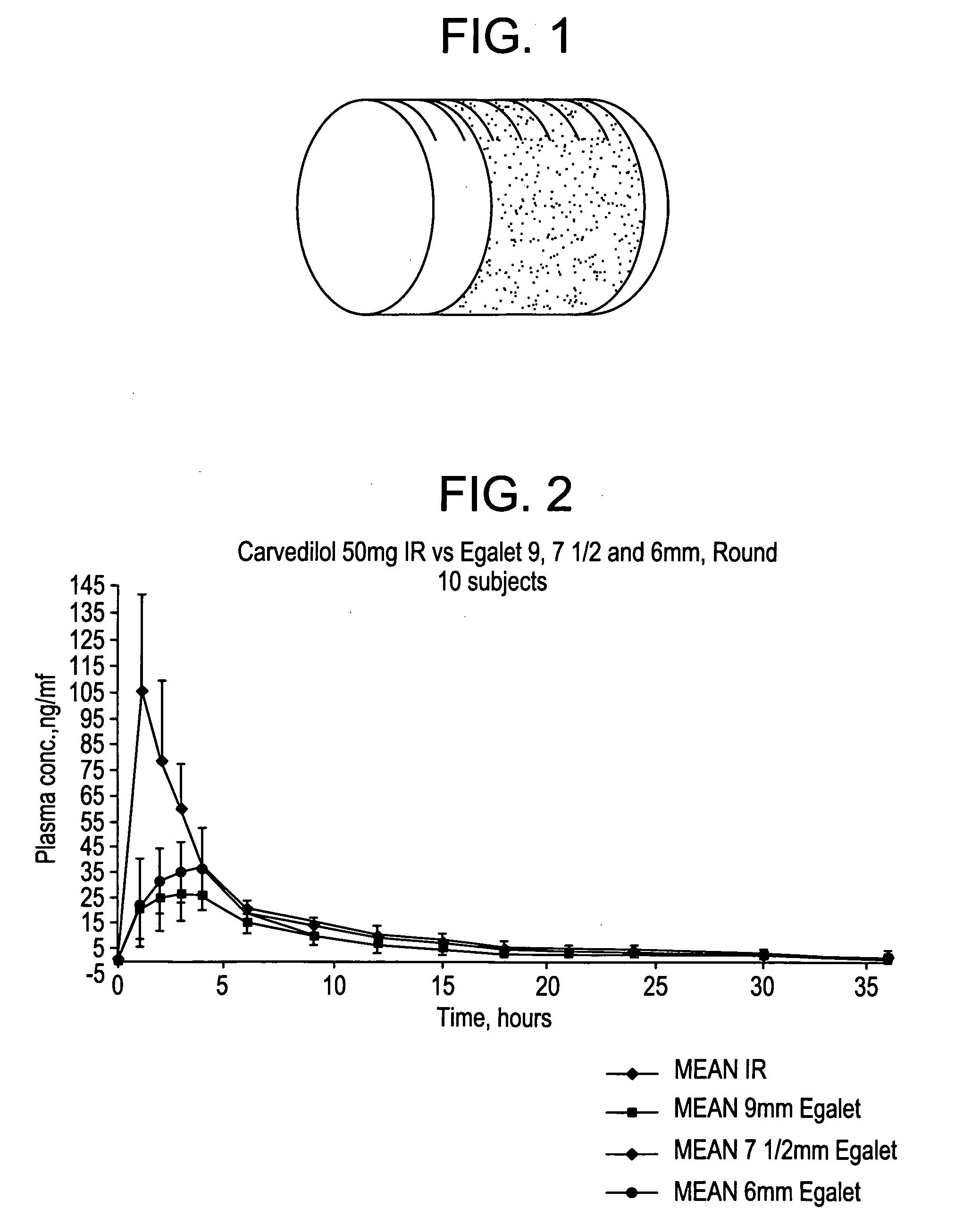
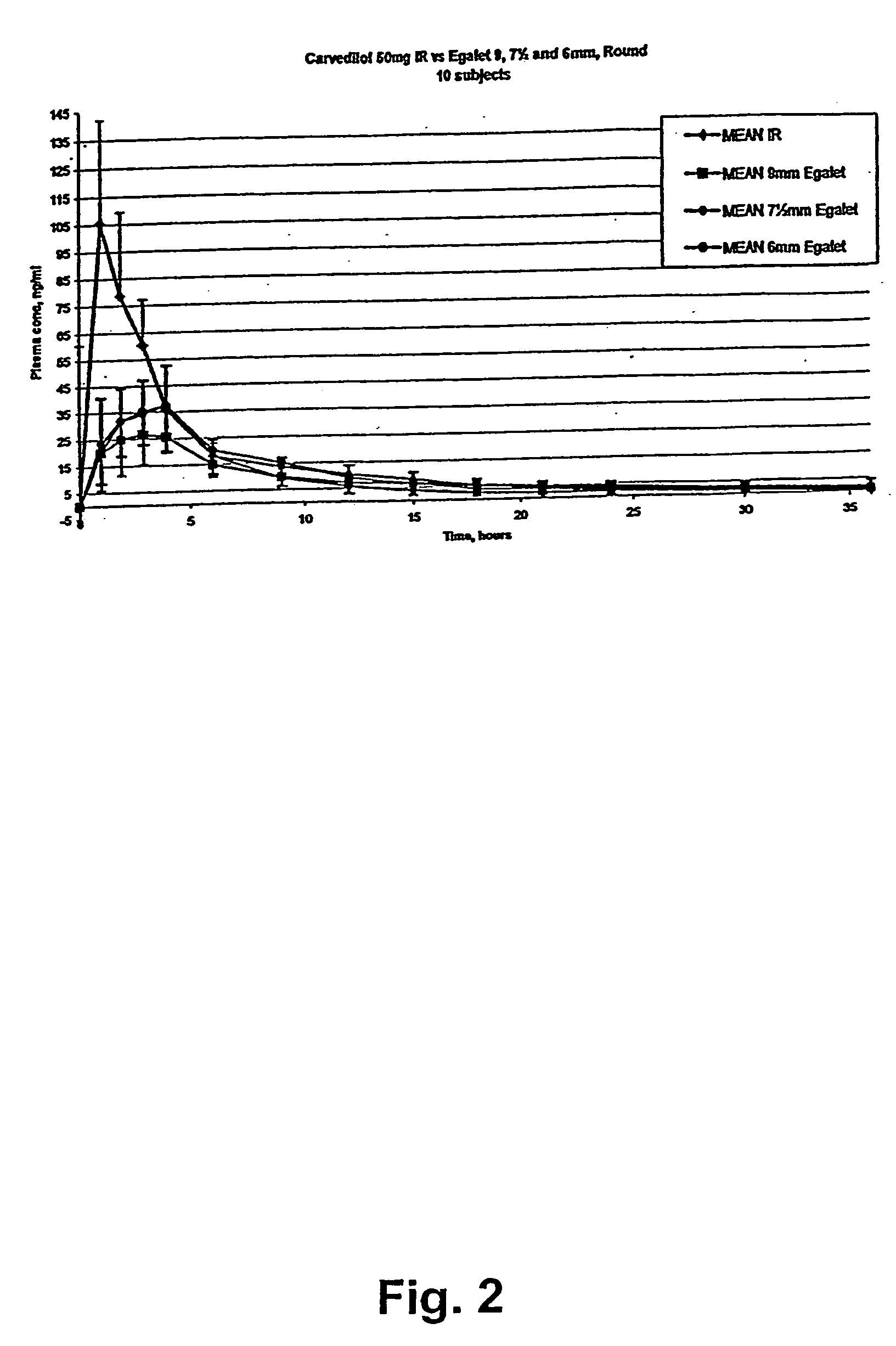
A controlled release pharmaceutical composition for oral use comprising a solid dispersion of i) at least one therapeutically, prophylactically and / or diagnostically active substance, which at least partially is in an amorphous form, ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable polymer that has plasticizing properties, and iii) optionally a stabilizing agent, the at least one active substance having a limited water solubility, and the composition being designed to release the active substance with a substantially zero order release. The polymer is typically a poly ethylene glycol and / or polyethylene oxide having a molecular weight of at least about 20,000 in crystalline and / or amorphous form or a mixture of such polymers, and the active substance is typically carvedilol. The composition may comprise a coated matrix, the coating comprising a first cellulose derivative which is substantially insoluble in the aqueous medium, and at least one of a) a second cellulose derivative which is soluble or dispersible in water, b) a plasticizer, and c) a filler.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Matrix compositions for controlled delivery of drug substances
InactiveUS20070042044A1Improve solubilityImprove oral bioavailabilityBiocidePowder deliveryPolyethylene oxidePEG-PLGA-PEG
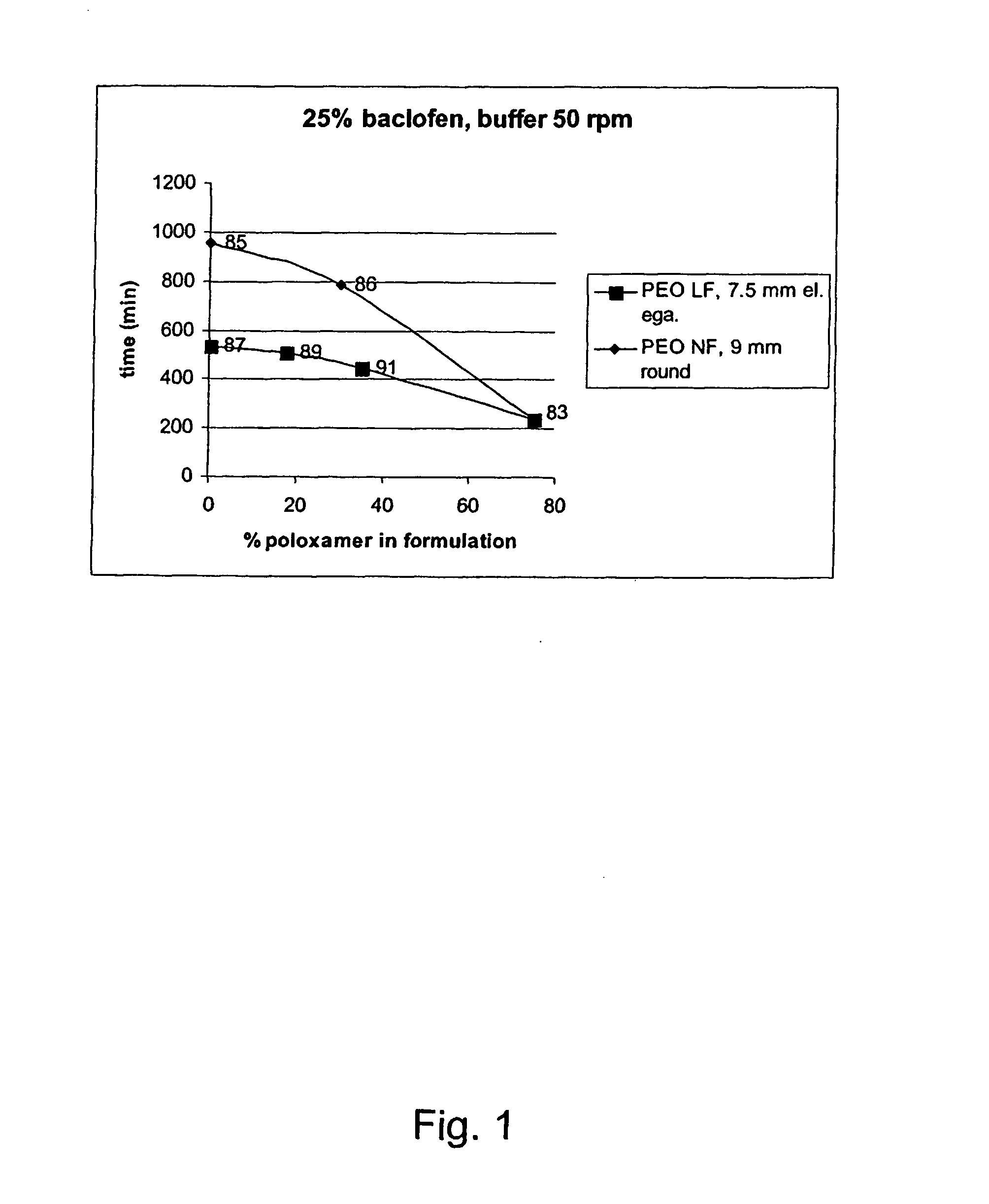
A novel matrix composition for pharmaceutical use. The matrix composition has been designed so that it is especially suitable in those situation where an improved bioavailability is desired and / or in those situation where a slightly or insoluble active substance is employed. Accordingly, a controlled release pharmaceutical composition for oral use is provided in the form of a coated matrix composition, the matrix composition comprising i) a mixture of a first and a second polymer that have plasticizing properties and which have melting points or melting intervals of a temperature of at the most 200° C., the first polymer being selected from the group consisting of polyethylene glycols and polyethylene oxides, and the second polymer being selected form block copolymer of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide including poly(ethylene-glycol-b-(DL-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-b-ethylene glycol (PEG-PLGA PEG), poly((DL-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-g-ethylene glycol) (PLGA-g-PEG), poloxamers and polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide (PEO-PPO), ii) a therapeutically, prophylactically and / or diagnostically active substance, the matrix composition being provided with a coating having at least one opening exposing at one surface of said matrix, wherein the active substance is released with a substantially zero order release.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
Polymer-Based Films and Drug Delivery Systems Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20070281003A1Pharmaceutical product form changeDrying machines with progressive movementsPolyethylene oxideActive agent
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component which includes polyethylene oxide, optionally blended with at least one additional polymer. The films may alternatively contain a polymer component which includes polyvinyl alcohol, optionally blended with at least one additional polymer. The films also may contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent.
Owner:MONOSOL RX
Cyclosporin compositions
A composition is disclosed herein comprising from about 0.001% to about 0.4% cyclosporin A, castor oil, and a surfactant selected from the group consisting of alcohol ethoxylates, alcohols, alkyl glycosides, alkyl polyglycosides, alkylphenol ethoxylates, amine oxides, block polymers, carboxylated alcohol or alkylphenol ethoxylates, carboxylic acids / fatty acids, cellulose derivatives, ethoxylated alcohols, ethoxylated alkylphenols, ethoxylated aryl phenols, ethoxylated fatty acids, ethoxylated fatty acids, ethoxylated fatty esters and oils, fatty alcohols, fatty esters, glycol esters, lanolin-based derivatives, lecithin and lecithin derivatives, lignin and lignin derivatives, methyl esters, monoglycerides and derivatives , phosphalipids, polyacrylic acids, polyethylene glycols, polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide copolymers, polyethylene oxides, polymeric surfactants, polypropylene oxides, propoxylated alcohols, propoxylated alkyl phenols, propoxylated fatty acids, protein-based surfactants, sarcosine derivatives, silicone-based surfactants, sorbitan derivatives, stearates, sucrose and glucose esters and derivatives, and combinations thereof.
Owner:SAINT REGIS MOHAWK TRIBE
Oral Compositions for Treatment of Dry Mouth
An oral care composition for the treatment of dry mouth comprising a polyethylene oxide with a molecular weight from about 200,000 to about 7,000,000, an anti-bacterial agent, and a sensate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
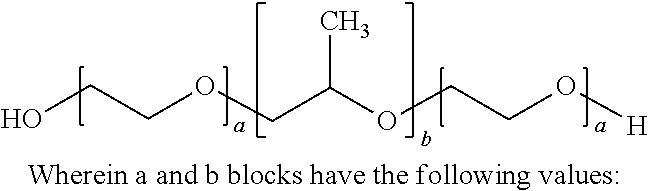
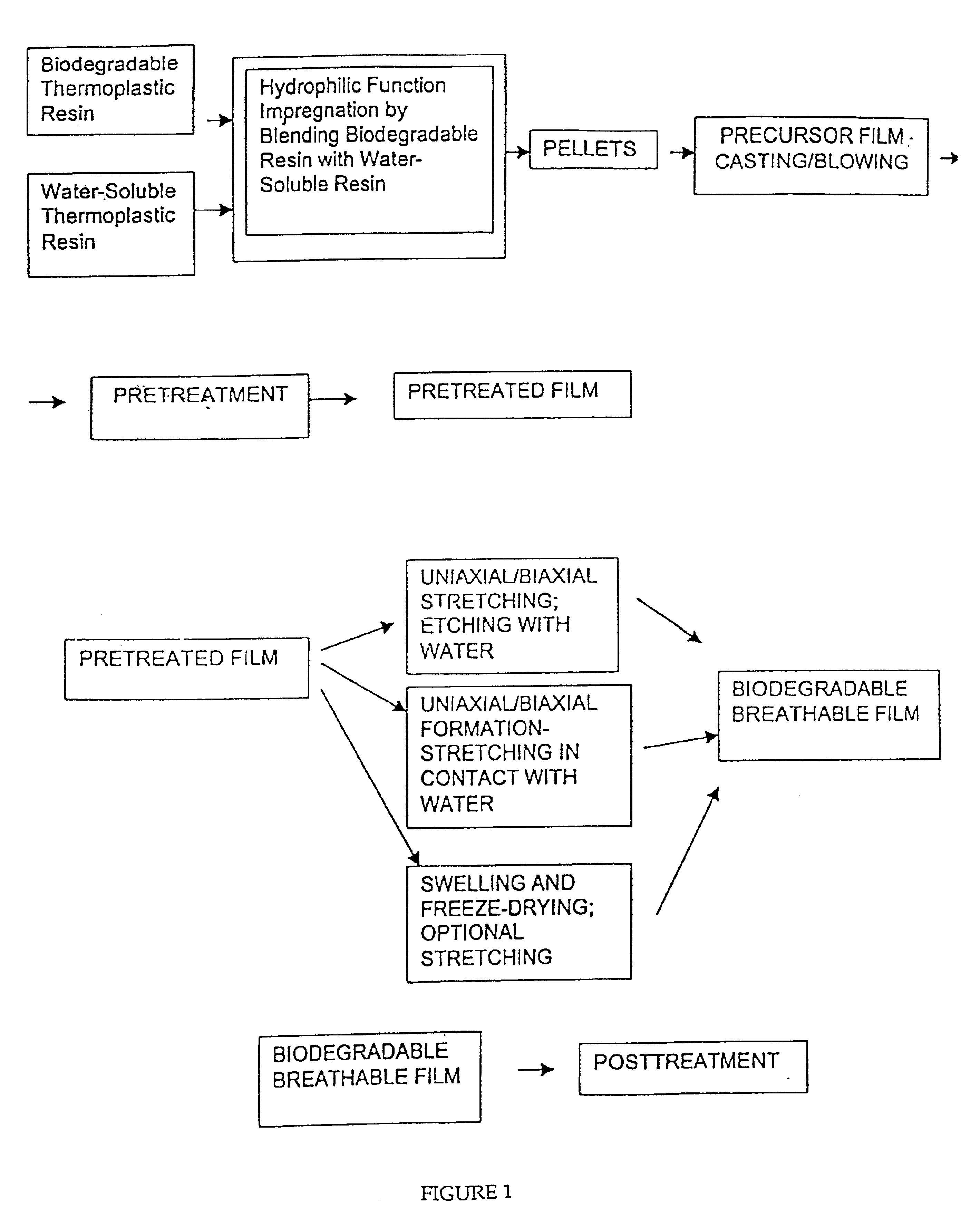
Biodegradable films having enhanced ductility and breathability
InactiveUS6905759B2Improve breathabilityImprove ductilitySynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsPolyethylene oxidePolymer science
The present invention is directed to biodegradable films and biodegradable precursor films having enhanced breathability and ductility. The films contain a biodegradable polymer and a water soluble polymer. The biodegradable polymer is preferably polycaprolactone, and the water soluble polymer is preferably polyethylene oxide. The precursor film of the present invention preferably has a water vapor transmission rate of at least 500 g / 24 hrs / m2. The biodegradable film of the present invention preferably has a water vapor transmission rate of at least 2500 g / 24 hrs / m2.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Polymeric films
ActiveUS20090312462A1Excellent oxygen barrier propertiesSuitable for usePaper coatingDomestic articlesMolten statePolymer science
A polymer composition and its use for thin film packaging applications including on a dry basis: a) from 45 to 90% by weight of starch; b) from 0.1 to 15% by weight of a water soluble polymer selected from polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylacetate, and copolymers of ethylene and vinyl alcohol which have a melting point compatible with the molten state of the starch component; and c) from 5 to 45% by weight of one or more plasticizers having a molecular weight in the range of 50-6000, more preferably 50-2500 and more preferably still 100-400 and desirably selected from the group consisting of sorbitol, glycerol, maltitol, xylitol, mannitol, erythritol, glycerol trioleate, tributyl citrate, acetyl tri-ethyl citrate, glyceryl triacetate, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate, polyethylene oxide, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol or polyethylene glycol.
Owner:PLANTIC TECH
Method for grafting polymer on inorganic material surface
The present invention discloses a method of grafting a polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol which contains amino or hydroxyl at the chain-end by a covalent bond or an ionic bond, or a compound containing glucose units is firstly fixed at the surface of the inorganic materials, so as to have a reductive organic chemical group on the surface; then a high cerium salt and a polymerizable monomer are added, the present invention makes use of the high cerium salt and the reductive organic group on the surface of the inorganic materials to constitute an oxidation-reduction initiation system, so as to initiate the monomer polymerization under the acidic condition, further to graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials. The method of the present invention can graft the polymer on the surface of the inorganic materials easily, which has the advantages of simple reaction process, mild reaction condition and high grafting rate, so the present invention is particularly applicable for the grafting of a water-soluble polymer or a polymer hydrogel thin layer on the surface of the inorganic materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
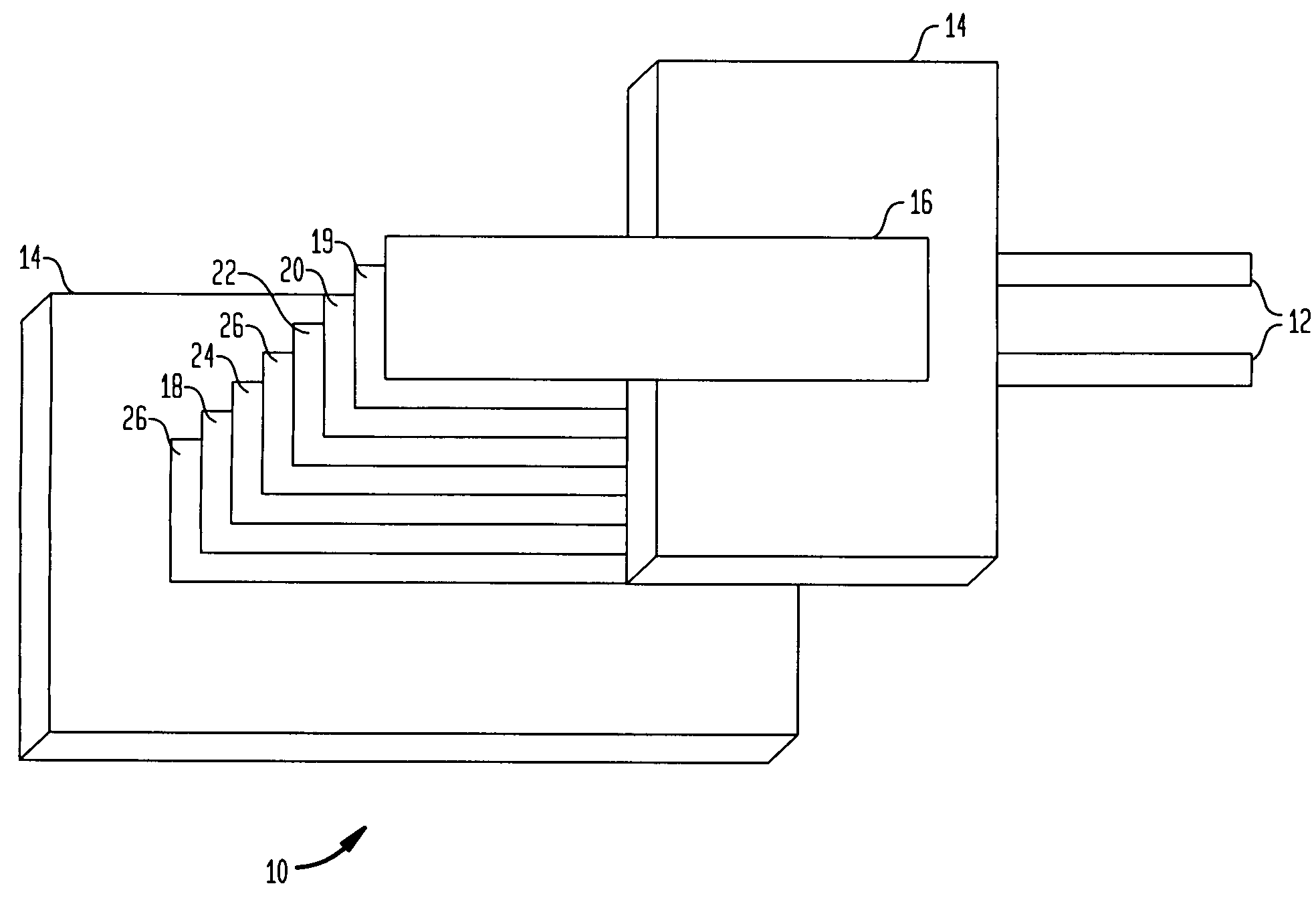
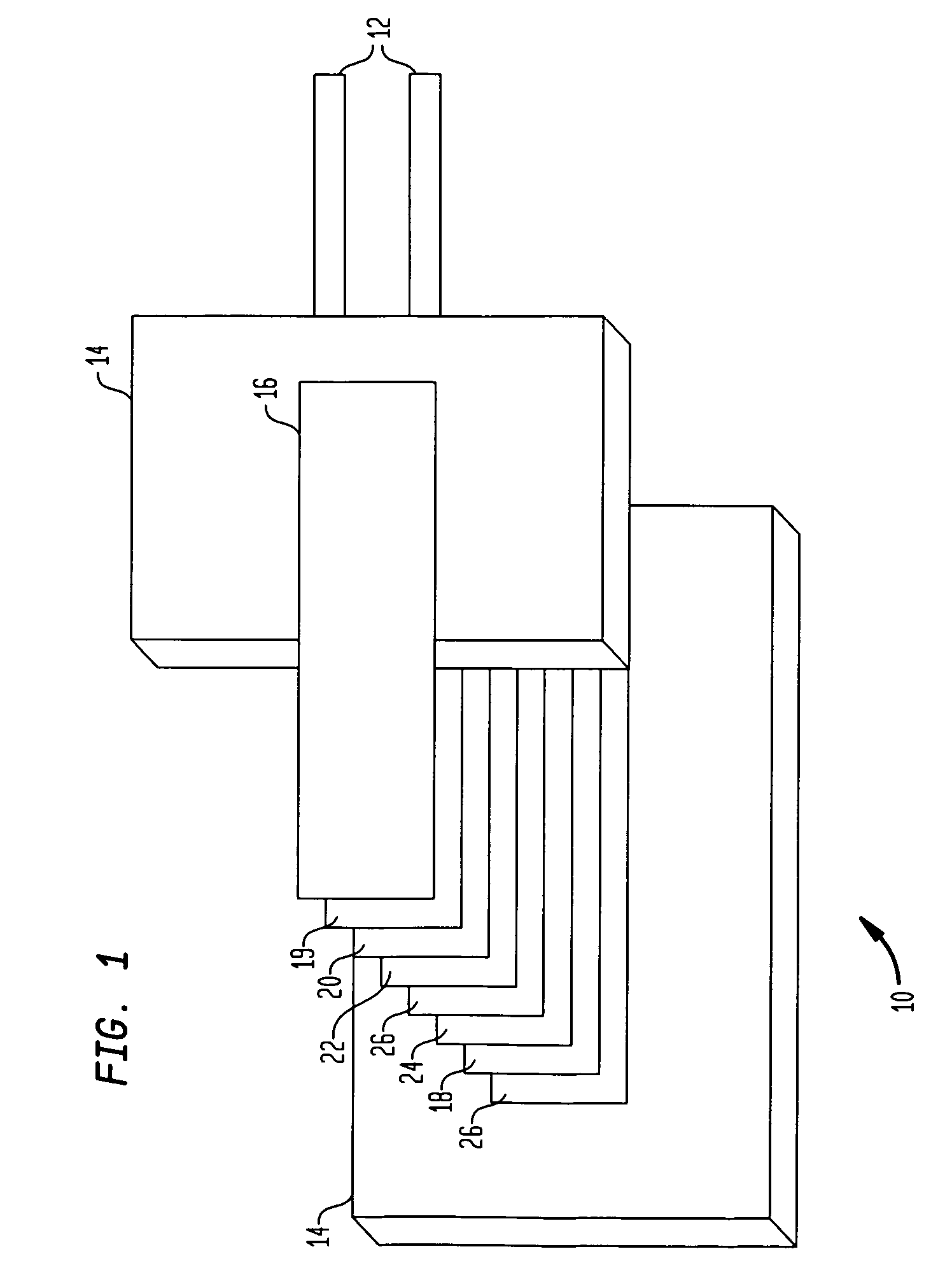
Process for making a nonwoven, porous fabric from polymer composite materials
The present invention is a method for producing a nonwoven fabric from a water modifiable polyolefin-containing film. In order to produce the fabric where polyethylene is the minority constituent, a polymer blend is formed with the polyethylene as the dispersed phase and polyethylene oxide as the continuous phase. In another embodiment wherein the polyethylene is the majority constituent and the polyethylene oxide is the minority constituent of the film, a reactive blend created during processing exhibits an inverse phase morphology so that the polyethylene oxide becomes the continuous phase and the polyethylene becomes the dispersed phase. In either embodiment, the film is then treated with an aqueous solvent to remove the polyethylene oxide to produce the nonwoven, porous fabric. The resulting nonwoven, porous fabric has a silk-like hand and shine ideal for disposable personal hygiene articles, and is flushable through waste water disposal systems.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
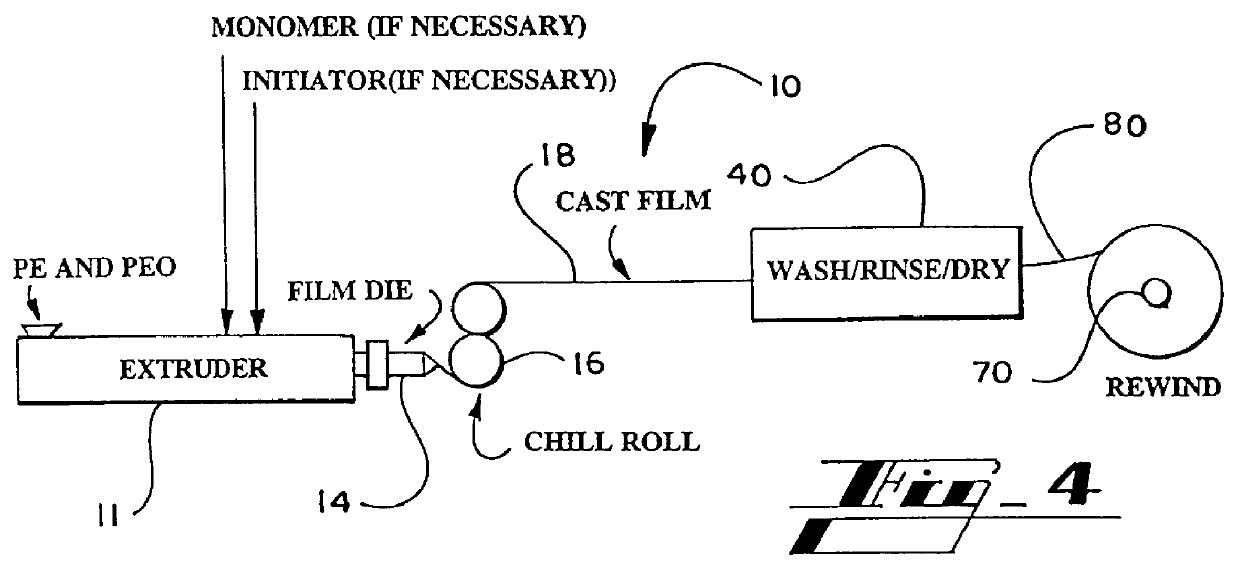
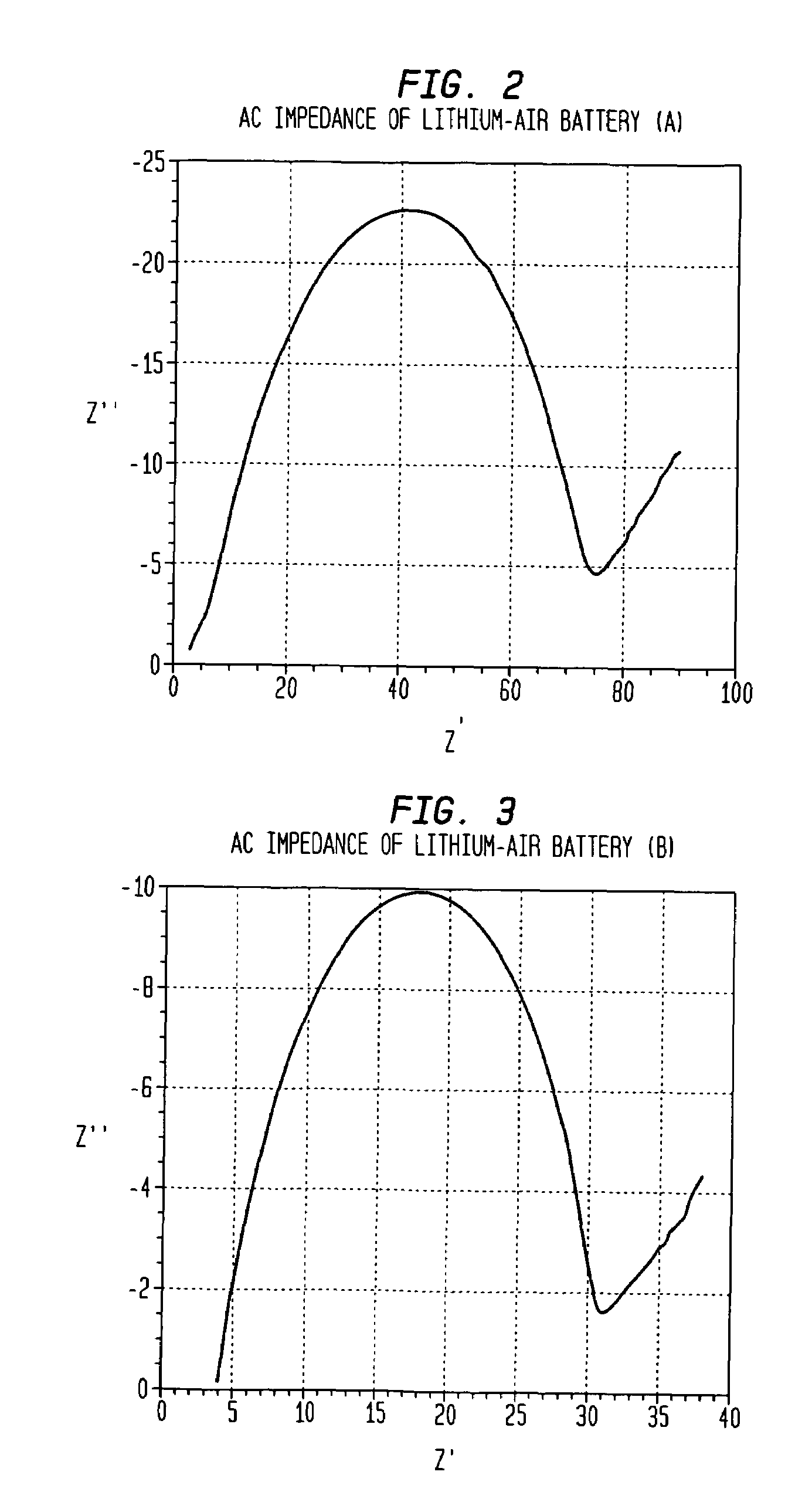
Alkali-hydroxide modified poly-vinylidene fluoride/polyethylene oxide lithium-air battery
InactiveUS7670724B1Reduce passageFuel and secondary cellsCell component detailsPolyethylene oxideMetal foil
A metal-air battery includes a housing having an aperture for the passage of air and a pair of electrodes that extend from the housing. An air cathode may be interconnected with one of the electrodes and an anode may include a metal foil that is interconnected with another of the electrodes. A separator may be interposed between the air cathode and the metal foil and a barrier layer may surround the metal foil. The barrier layer may function to substantially reduce the passage of moisture to the metal foil. A method of making a metal-air battery is also presented.
Owner:ARMY THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY
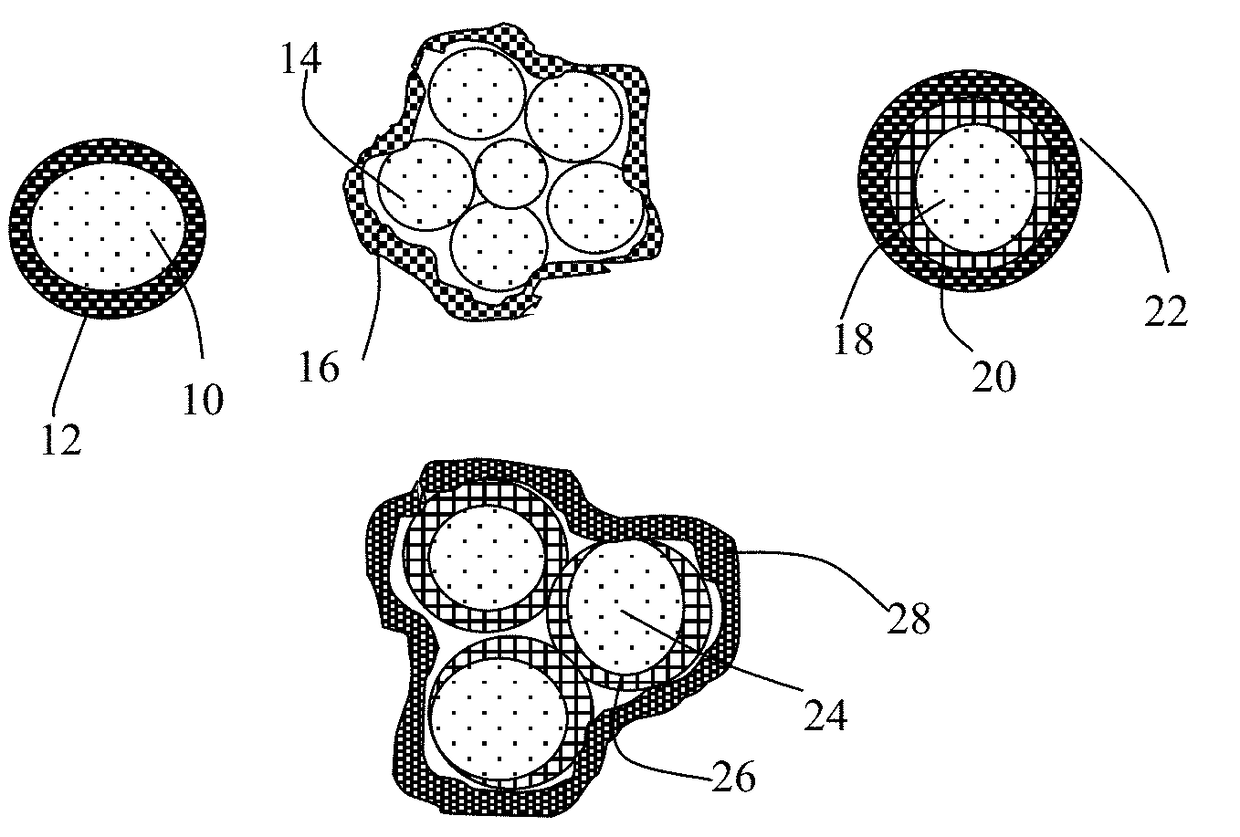
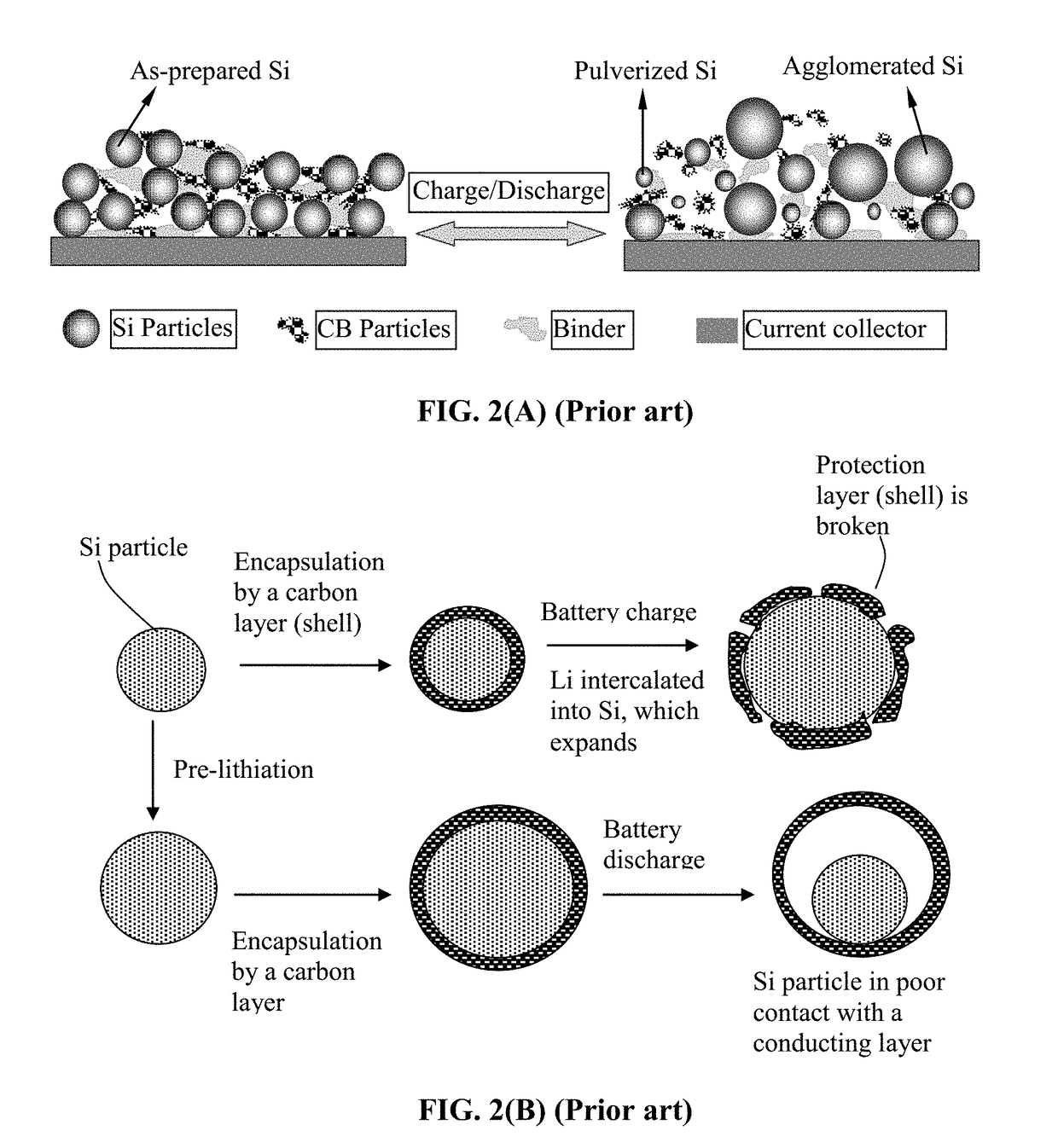
Encapsulated Anode Active Material Particles, Lithium Secondary Batteries Containing Same, and Method of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20180287142A1Improve lithium ion conductivitySolid electrolytesNegative electrodesParticulatesPolyethylene oxide
Provided is particulate of an anode active material for a lithium battery, comprising one or a plurality of anode active material particles being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 5%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm to 10 μm, wherein the polymer contains an ultrahigh molecular weight (UHMW) polymer having a molecular weight from 0.5×106 to 9×106 grams / mole. The UHMW polymer is preferably selected from polyacrylonitrile, polyethylene oxide, polypropylene oxide, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylamide, poly(methyl methacrylate), poly(methyl ether acrylate), a copolymer thereof, a sulfonated derivative thereof, a chemical derivative thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
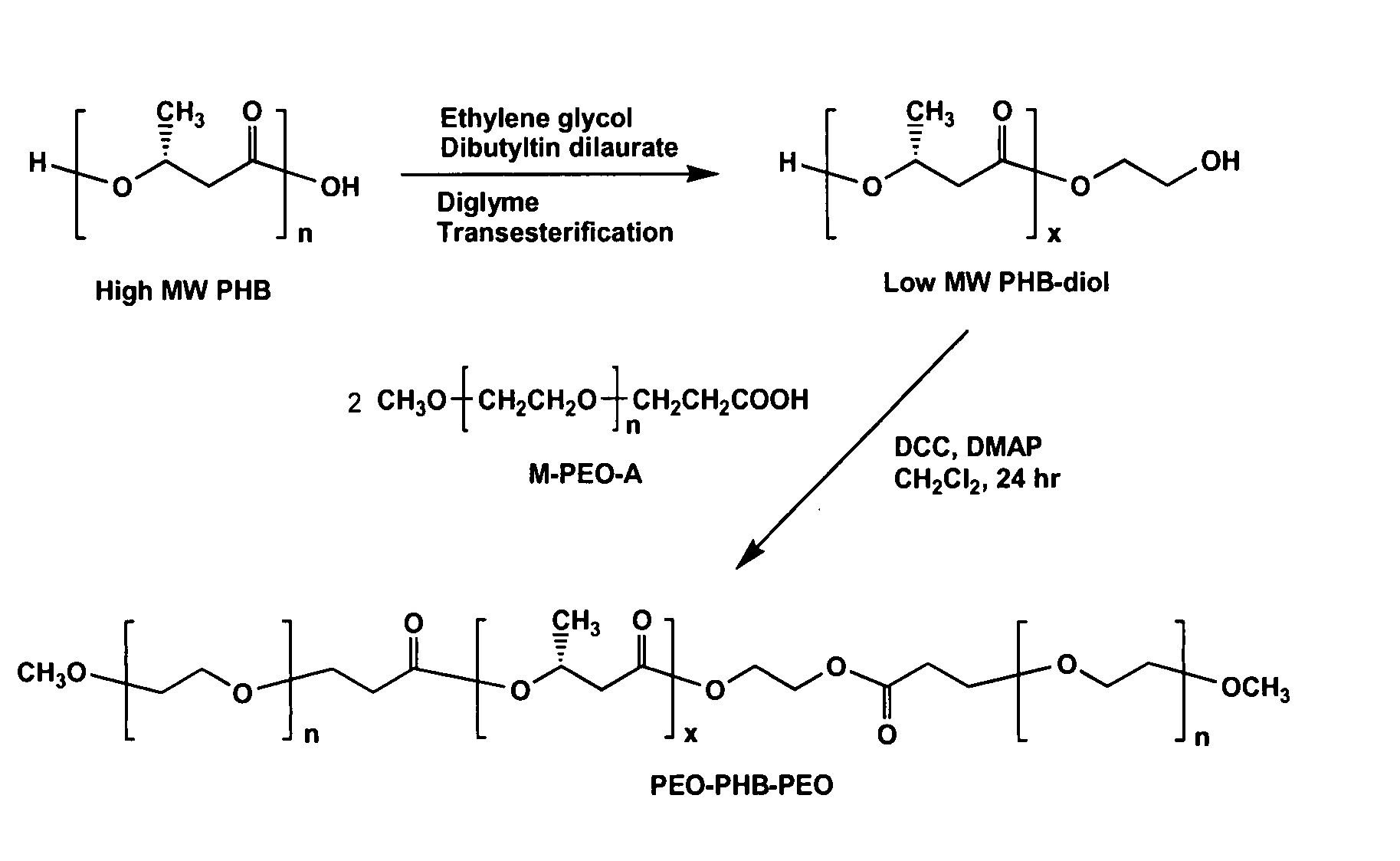
Biodegradable triblock copolymers, synthesis methods therefore, and hydrogels and biomaterials made there from
InactiveUS20080057128A1Interesting propertyVivo degradation ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
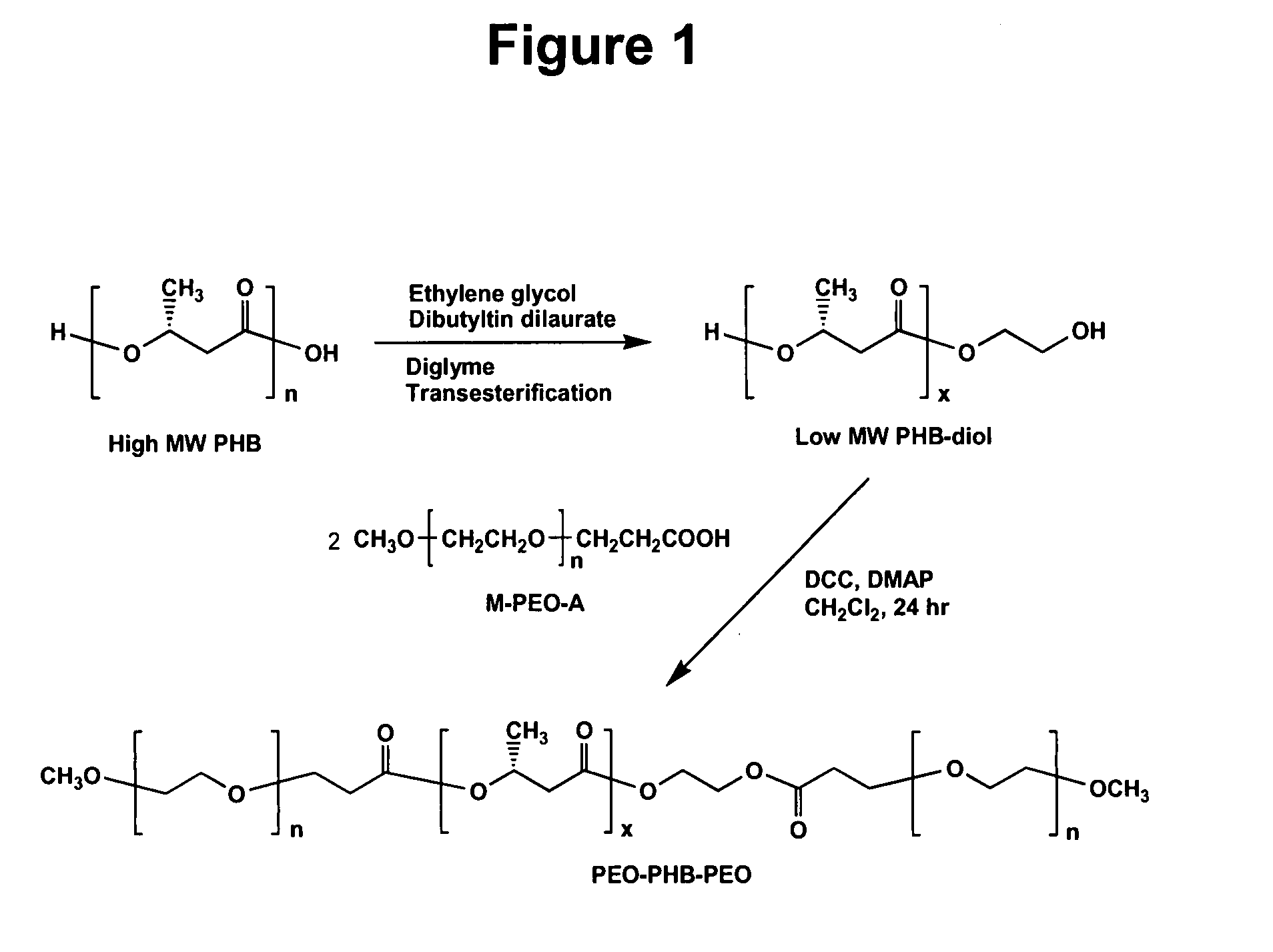
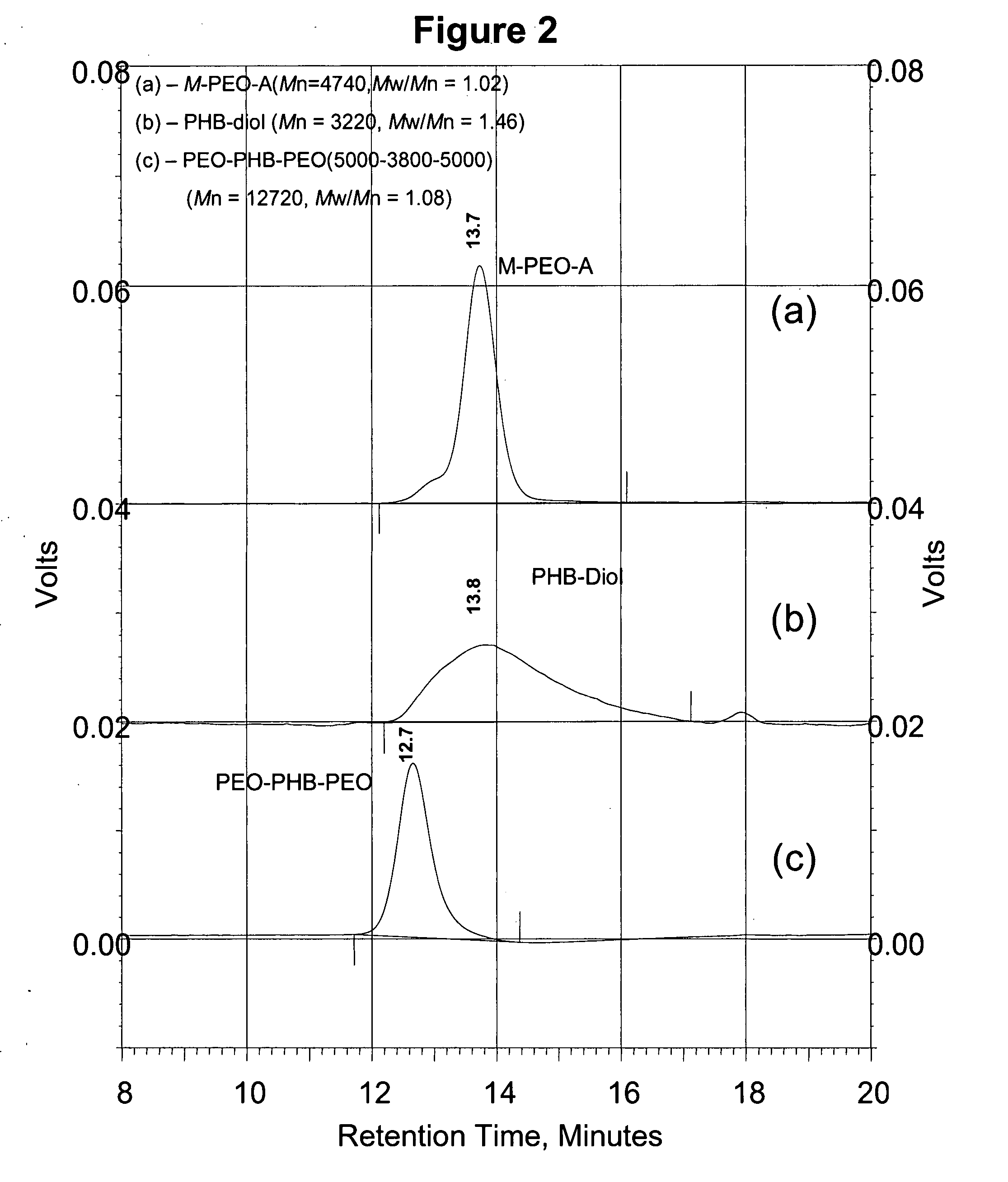
A drug delivery system that includes micelles formed from an amphiphilic copolymer that includes an A polymer block comprising a poly(alkylene oxide) and a B polymer block comprising a poly(hydroxyalkanoate), and a therapeutically effective amount of at least one therapeutic agent intimately contained within the micelles. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, the A polymer block is poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the B polymer block is poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB), and the copolymer is the triblock ABA copolymer PEO-PHB-PEO. A method of synthesizing the amphiphilic triblock copolymer is also provided.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Absorbent article comprising polymeric foam with superabsorbent and intermediates
InactiveUS20150119837A1Improve propertiesOther chemical processesBaby linensPolyolPolyethylene oxide
Absorbent articles are described comprising an absorbent composite. The absorbent composite comprises a first absorbent layer comprising a polymeric foam having an average cell size of at least 100 microns and discrete pieces of superabsorbent polymer dispersed within the polymeric foam; and a second absorbent layer in fluid communication with the first absorbent layer. Favored articles include disposable diapers, feminine hygiene articles, and adult incontinence articles. Also described is a polyurethane foam is described having an average cell size of at least 100 microns. The polyurethane foam is the reaction product of a polyether polyol having polyethylene oxide units and at least one polymeric polyisocyanate that lacks urethane linkages. The polyureth ane foam comprises at least 5 wt-% of discrete pieces of superabsorbent polymer. Also described are various composites comprising the polyurethane foam described herein in combination with another substrate such as a second absorbent layer, a fluid impervious backsheet, and / or a fluid pervious topsheet.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Controlled release solid dispersions
InactiveUS20050019399A1Suitable shelf-lifeImprove solubilityBiocideAnimal repellantsSolubilityPolyethylene oxide
A controlled release pharmaceutical composition for oral use comprising a solid dispersion of: i) at least one therapeutically, prophylactically and / or diagnostically active substance, which at least partially is in an amorphous form, ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable polymer that has plasticizing properties, and iii) optionally, a stabilizing agent, the at least one active substance having a limited water solubility, and the composition being designed to release the active substance with a substantially zero order release. The polymer is typically a polyethylene glycol and / or polyethylene oxide having a molecular weight of at least about 20,000 in crystalline and / or amorphous form or a mixture of such polymers, and the active substance is typically carvedilol. The composition may comprise a coated matrix, the coating comprising a first cellulose derivative which is substantially insoluble in the aqueous medium, and at least one of a) a second cellulose derivative which is soluble or dispersible in water, b) a plasticizer, and c) a filler.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Solid polymer electrolyte and method of preparation
InactiveUS20030180624A1Increased room temperature ionic conductivityLower impedanceSolid electrolytesFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesPolymer science
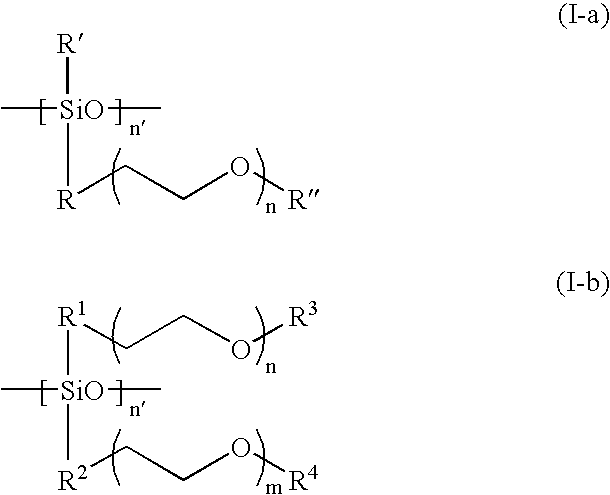
Disclosed is an improved solid electrolyte made of an interpenetrating network type solid polymer comprised of two compatible phases: a crosslinked polymer for mechanical strength and chemical stability, and an ionic conducting phase. The highly branched siloxane polymer of the present invention has one or more poly(ethylene oxide) ("PEO") groups as a side chain. The PEO group is directly grafted to silicon atoms in the siloxane polymer. This kind of branched type siloxane polymer is stably anchored in the network structure and provides continuous conducting paths in all directions throughout the IPN solid polymer electrolyte. Also disclosed is a method of making an electrochemical cell incorporating the electrolyte. A cell made accordingly has an extremely high cycle life and electrochemical stability.
Owner:OH BOOKEUN +3
Membrane which comprises a blend of a polysulphone or a polyether sulphone and polyethylene oxide/polypropylene oxide substituted ethylene diamine
A membrane which can be used in membrane filtration processes and which has a reduced tendency to fouling is a polysulphone or a plyether sulphone and a polyethylene oxide / polypropylene oxide substituted diamine and can be made by a phase inversion process in the presence of pore modifying agents such as an alcohol, glycerol or glycol to give a membrane which has a pore size of 0.1.mu. to 1 micron and is hydrophilic.
Owner:HYDRANAUTICS
Barrier film
InactiveUS20090110942A1Stable mechanical propertiesImprove homogeneityFireproof paintsFibre treatmentMolten statePolyethylene oxide
A barrier composition which is injection mouldable and able to be made into a transparent film or incorporated (by co-extrusion and / or lamination) into multi-layer film products, the composition on dry basis: a) from 45 to 90% by weight of a starch and / or a modified starch selected from starches modified by reaction with a hydroxyl alkyl group, an acetate or a dicarboxylic acid anhydride or a grafting polymer; b) from 4 to 12% by weight of a water soluble polymer selected from polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylacetate, and copolymers of ethylene and vinylalcohol which have a melting point compatible with the molten state of the starch components c) from 5 to 45% by weight of a non-crystallising mixture of sorbitol and at least one other plasticizer selected from glycerol, maltitol, xylitol, mannitol, glycerol trioleate, epoxidised linseed or soybean oil, tributyl citrate, acetyl tri-ethyl citrate, glyceryl triacetate, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate; polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol; d) from 0.3 to 2.5 % by weight of a C12-22 fatty acid or salt; e) from 0.25% to 3% of an emulsifier system having a hydrophilic lipophilic balance value between 2 and 10. The barrier film may be co-injection moulded with polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polylactic acid (PLA) for blow moulding into beverage bottles, with polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) or biodegradable polymers for high gas-barrier containers or closures, or may be co-extruded with polyethylene, polypropylene or polylactic acid for thin film packaging applications or for blow-moulded containers.
Owner:PLANTIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com