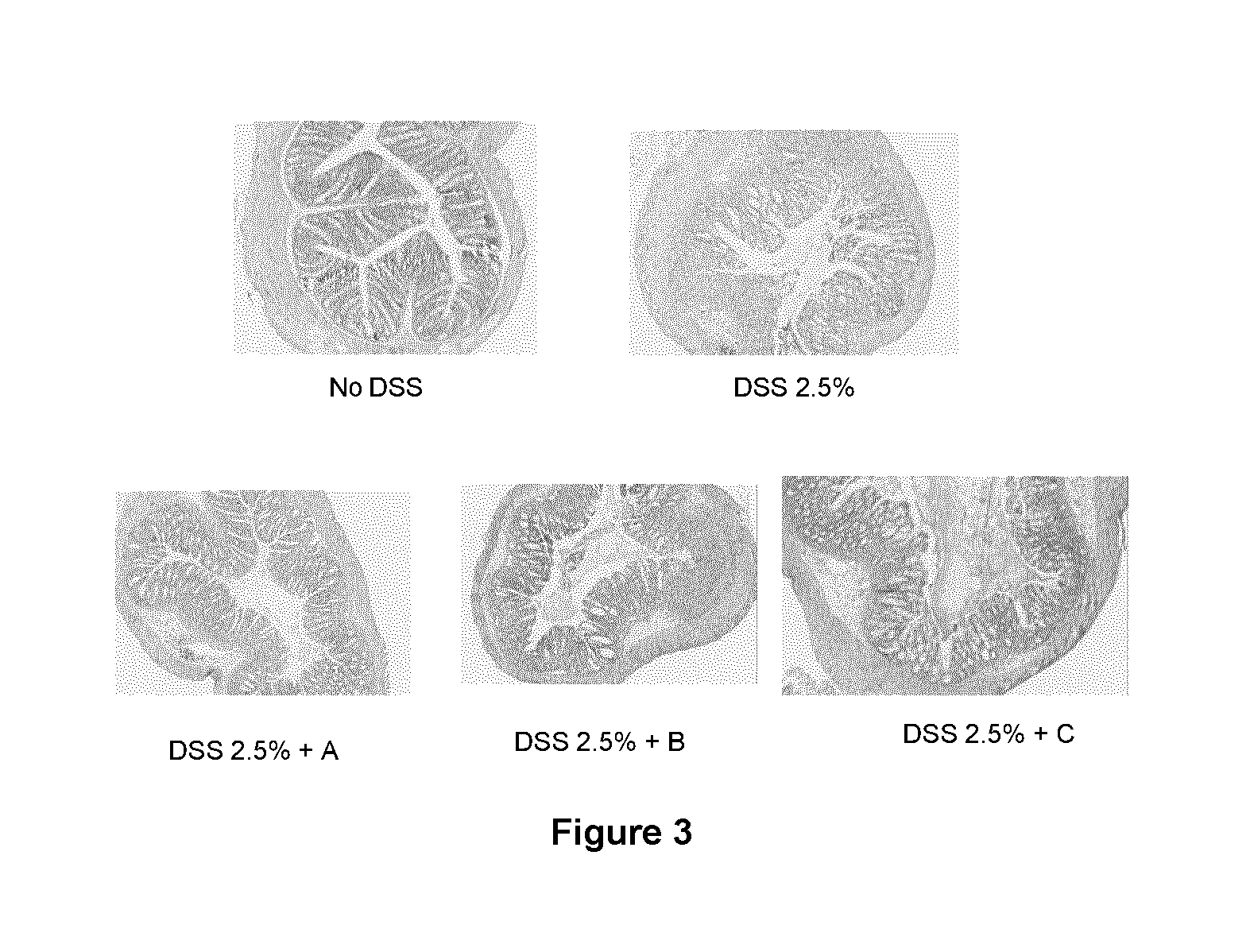
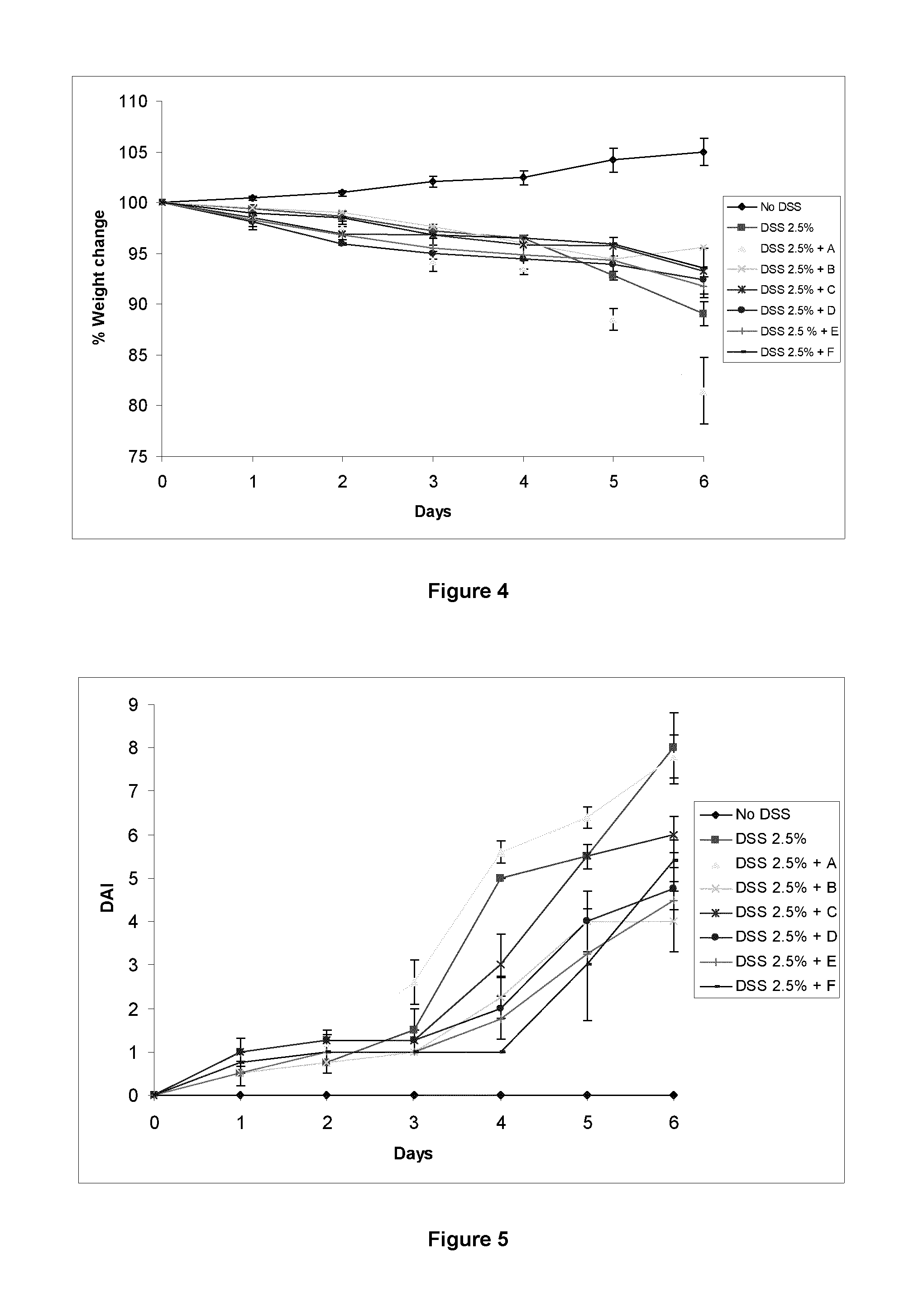
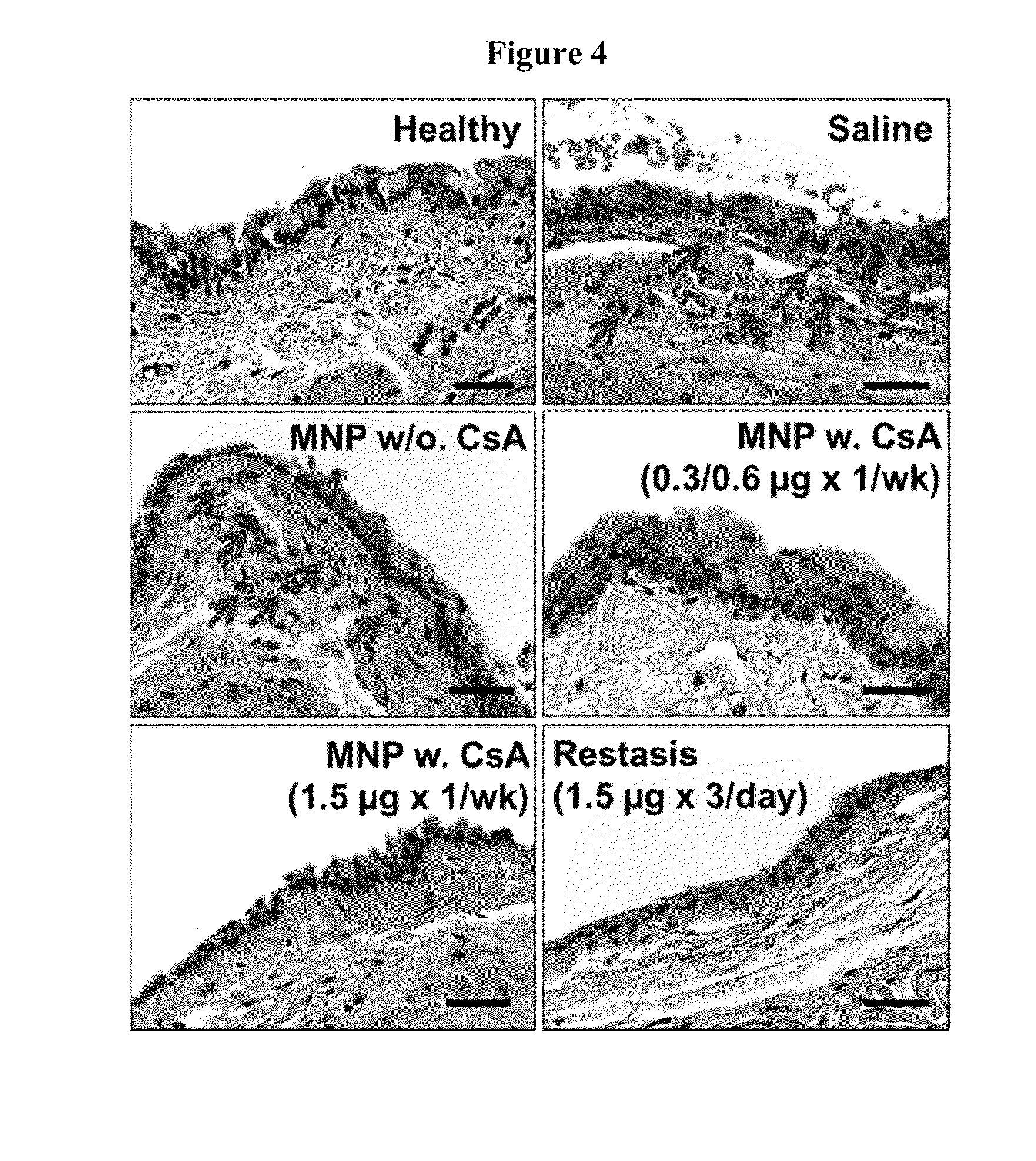
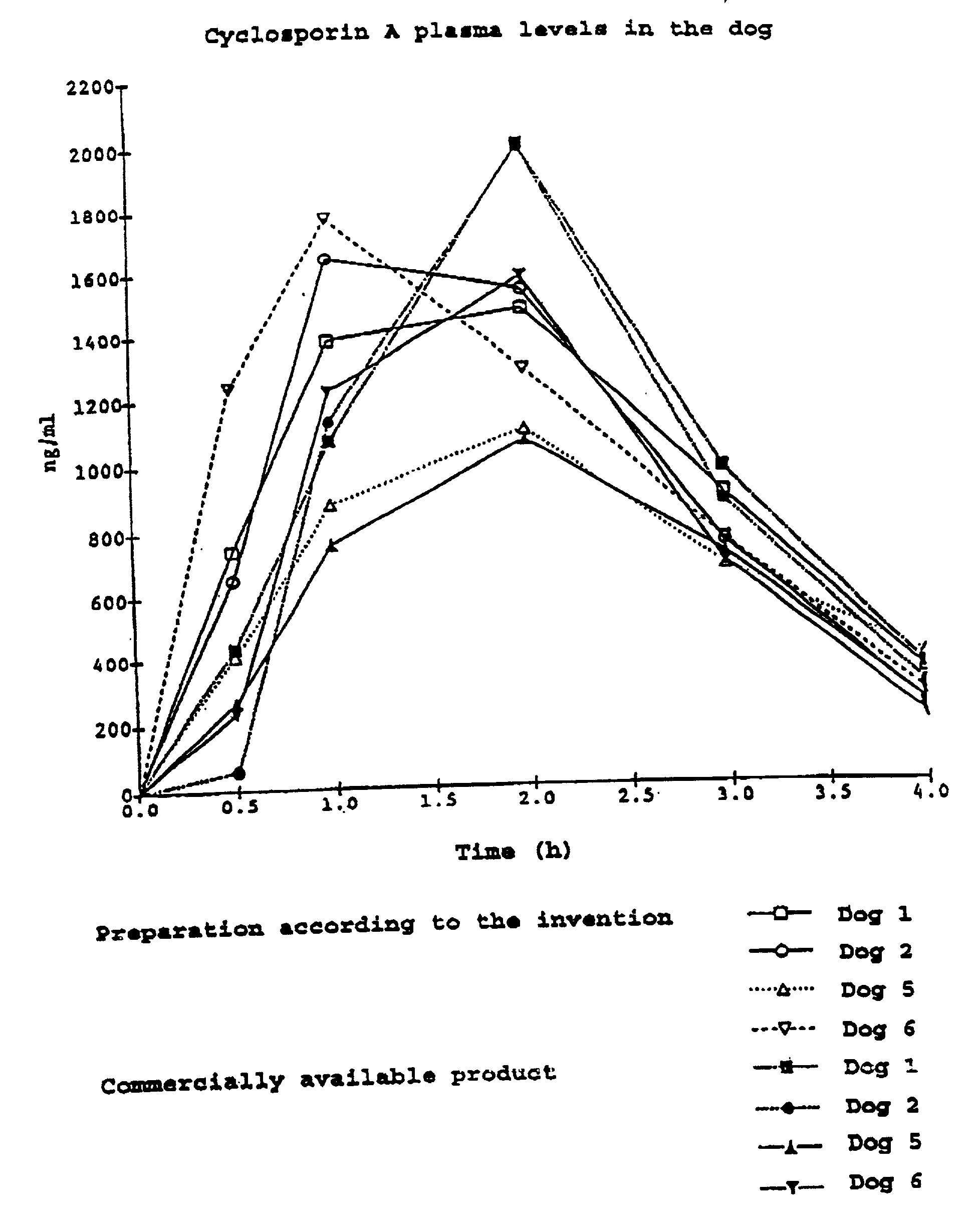
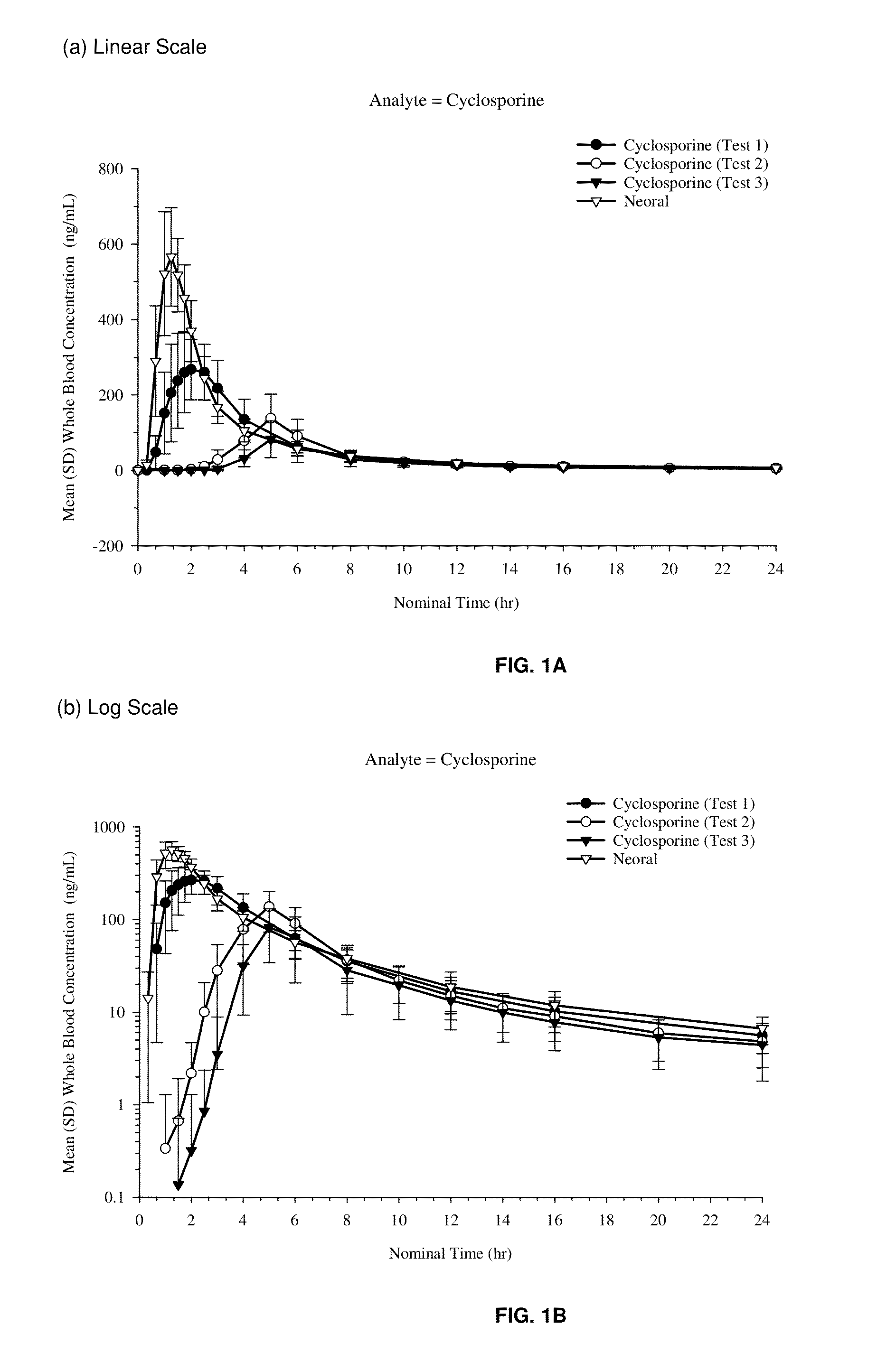
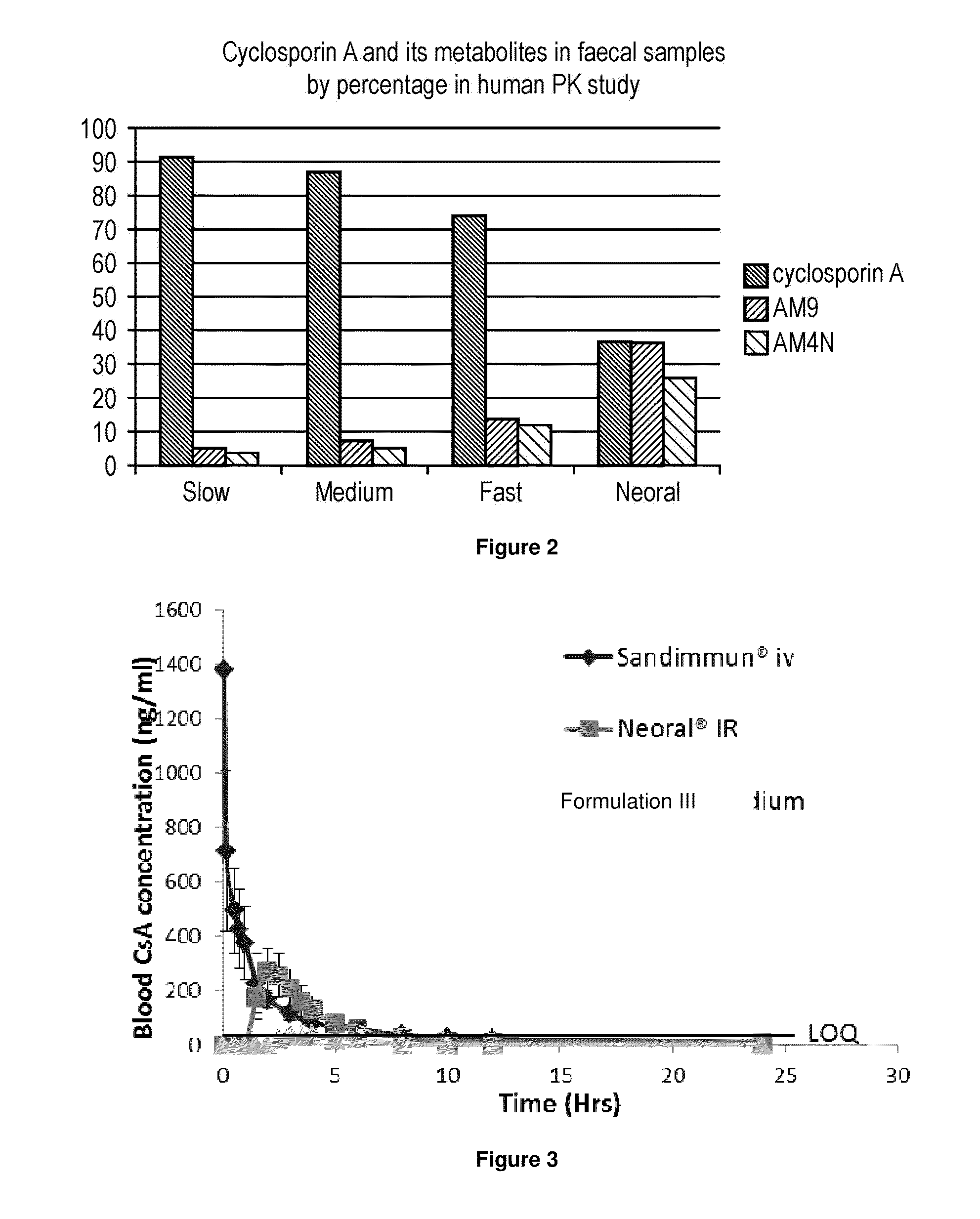
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Cyclosporin a" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composition and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6187756B1Increased formationPromote activationBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsDiseaseGlial fibrillary acidic protein
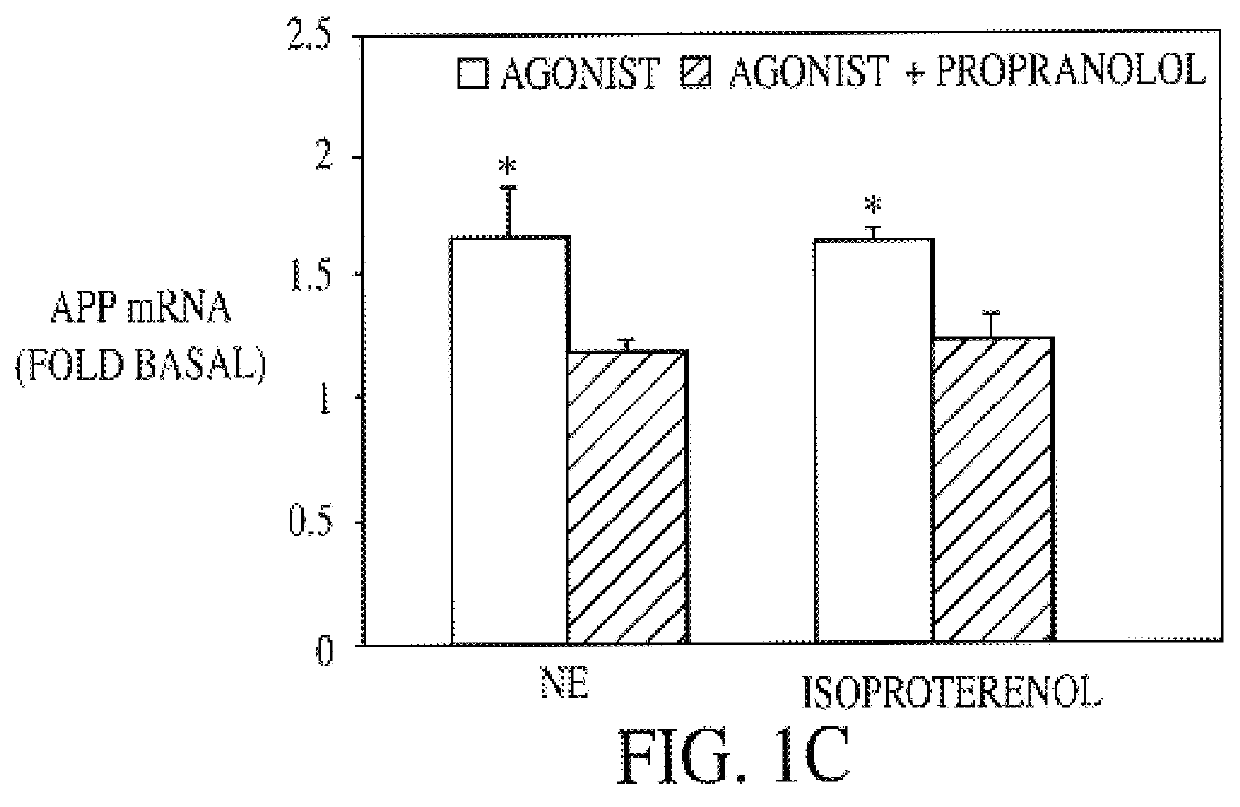
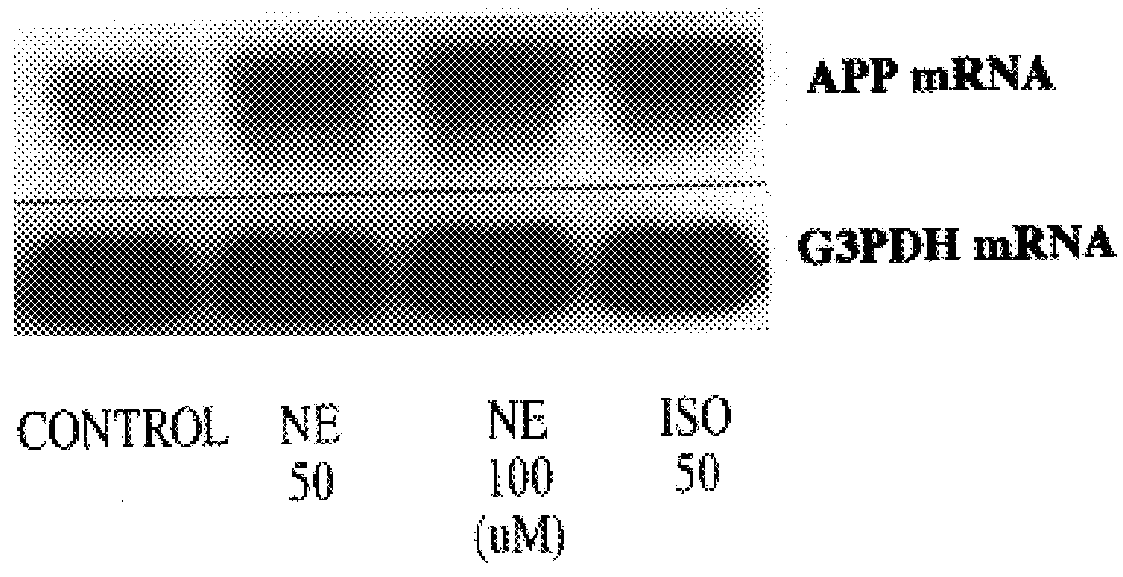
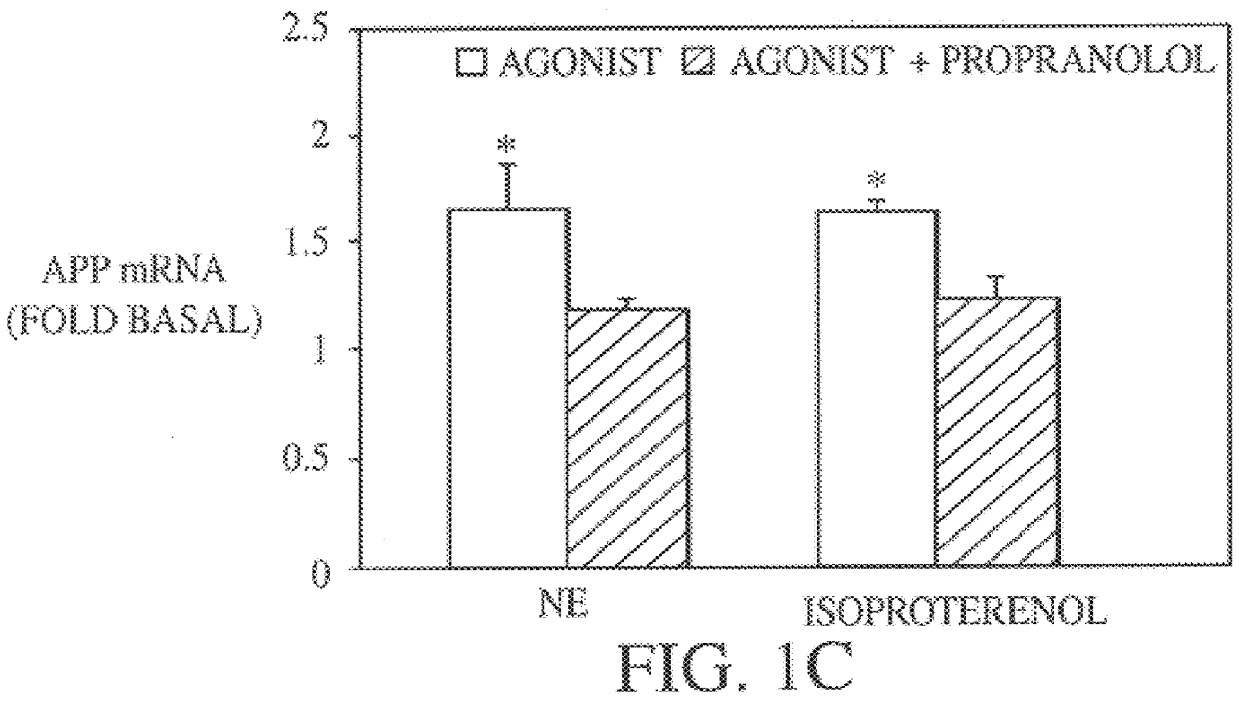
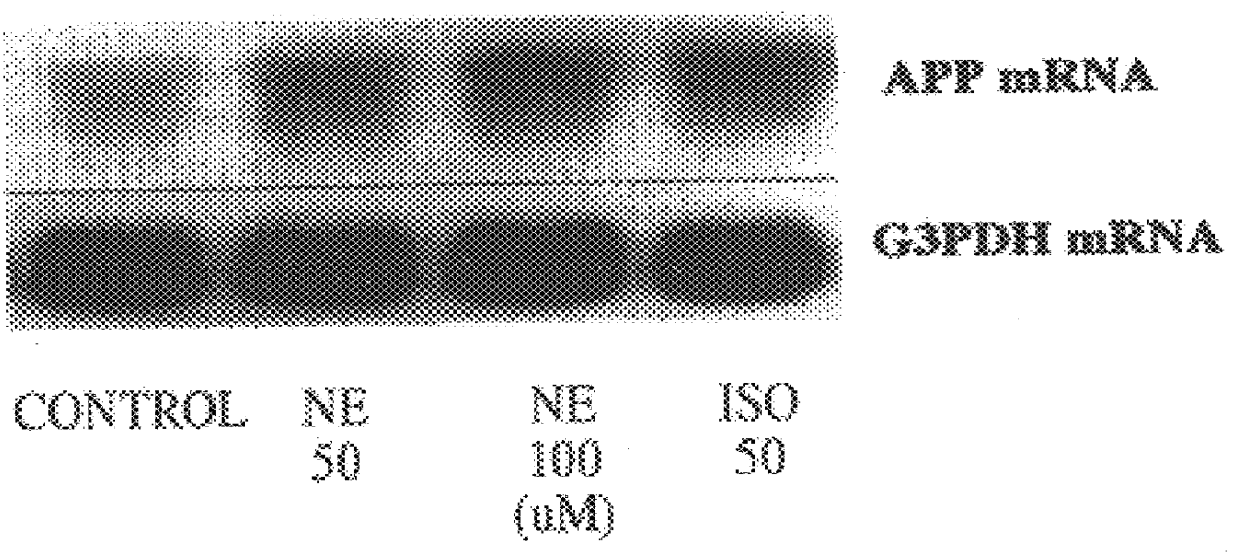
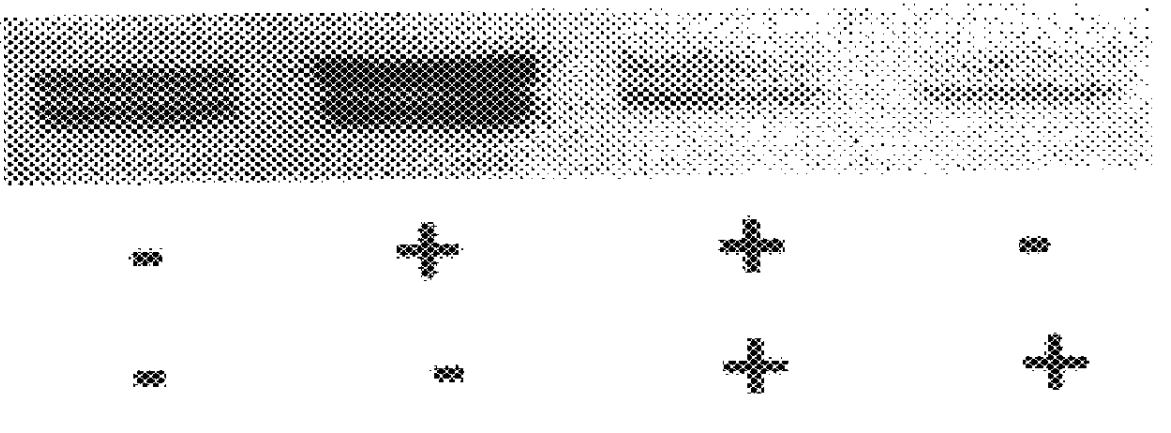
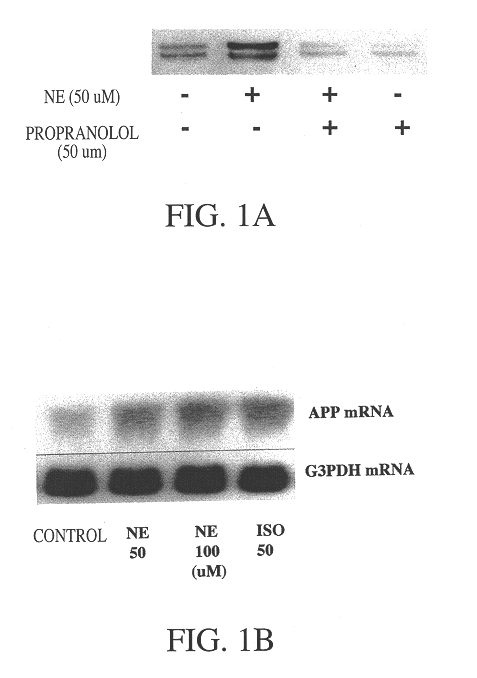
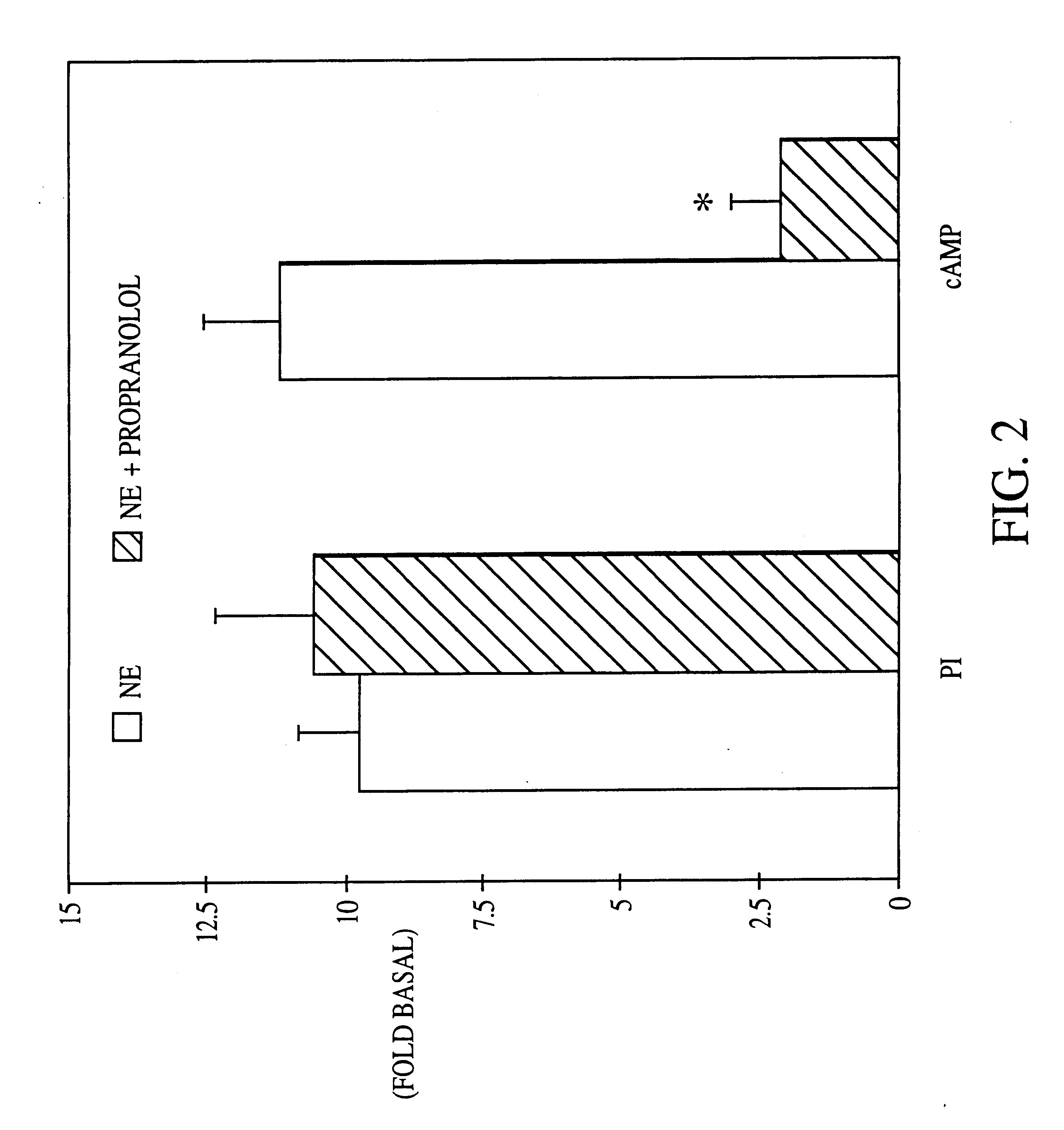
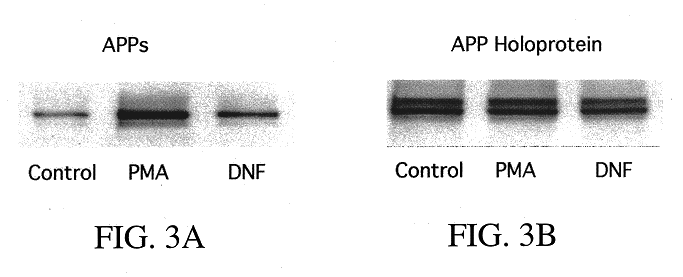
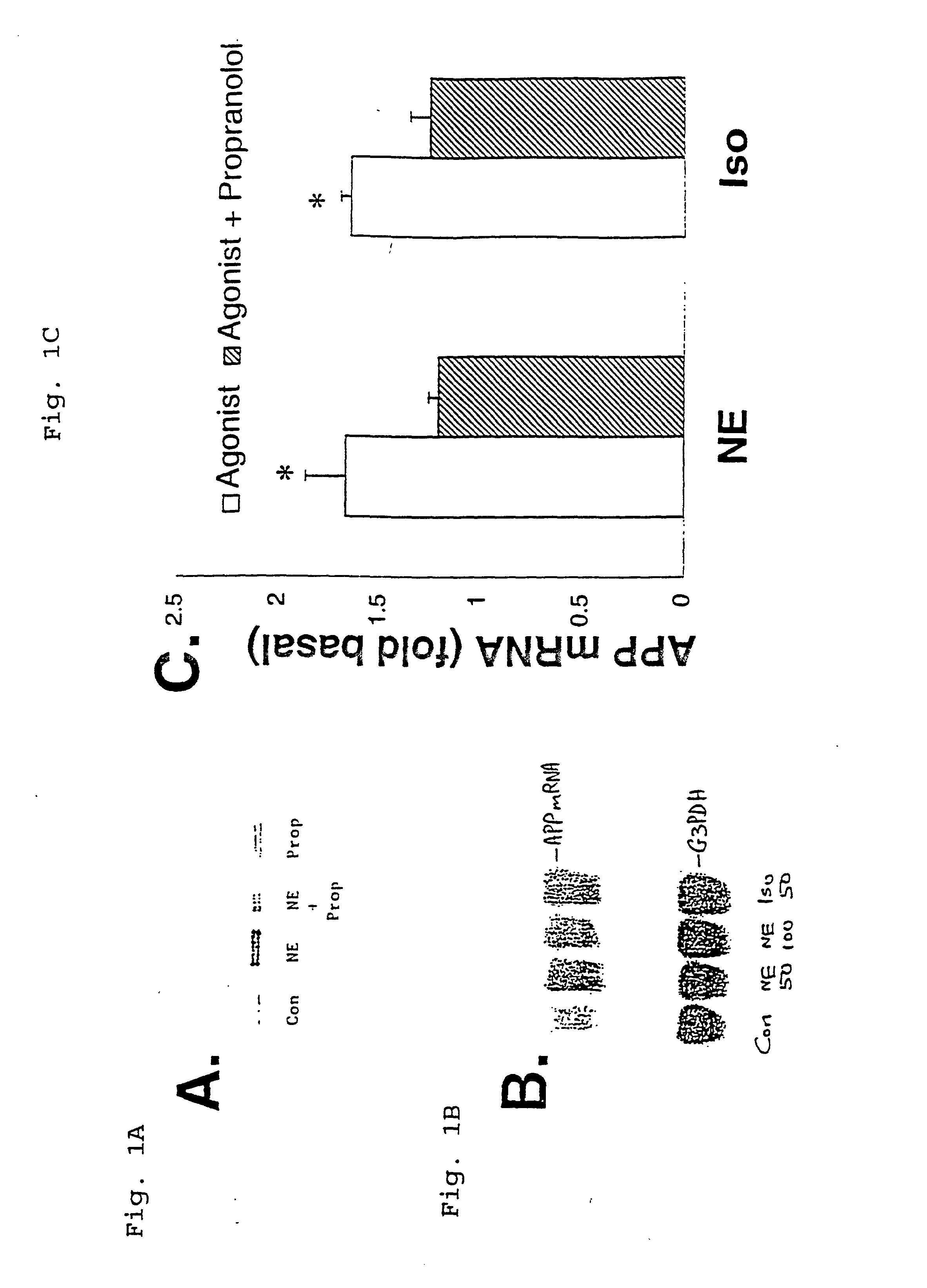
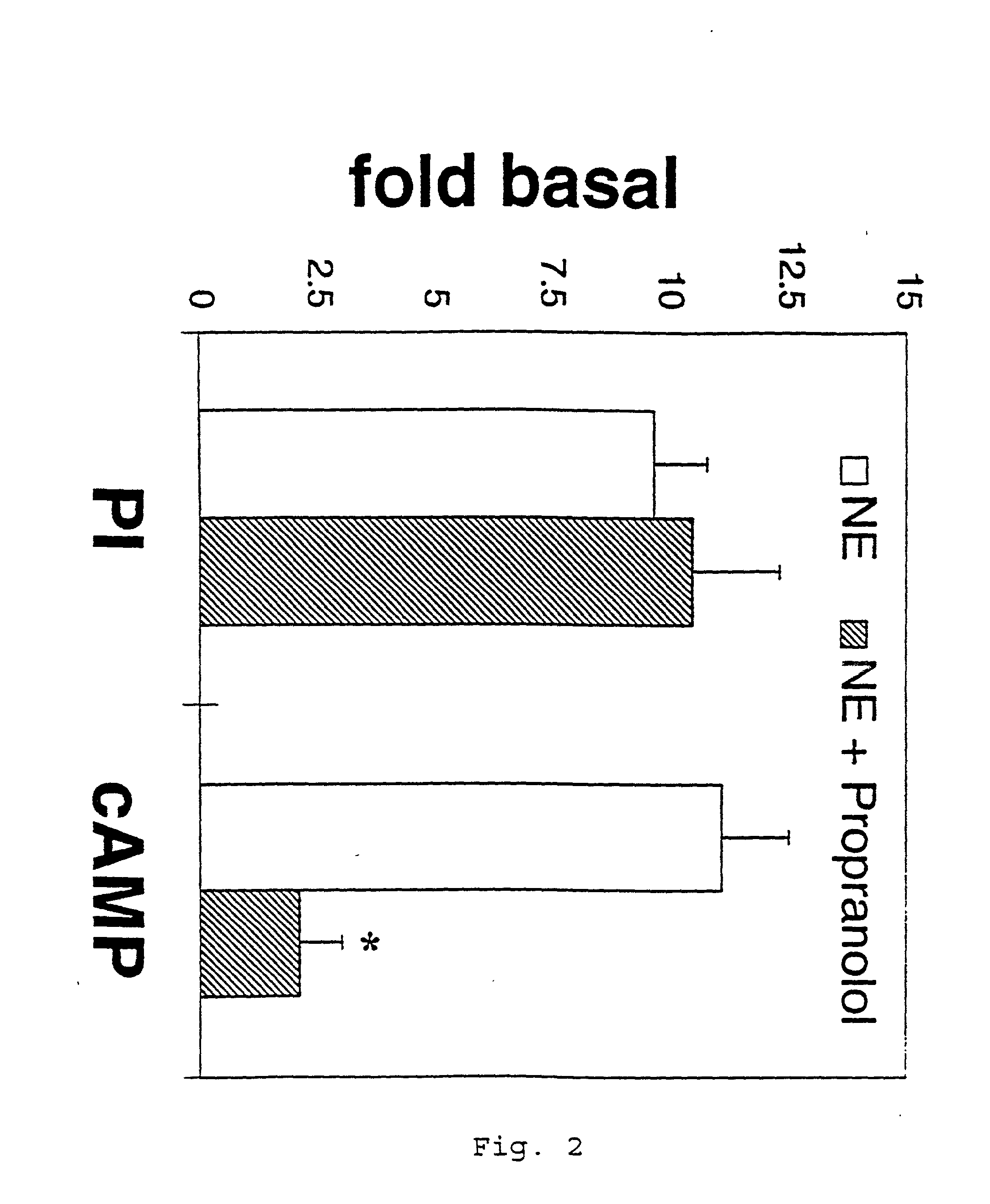
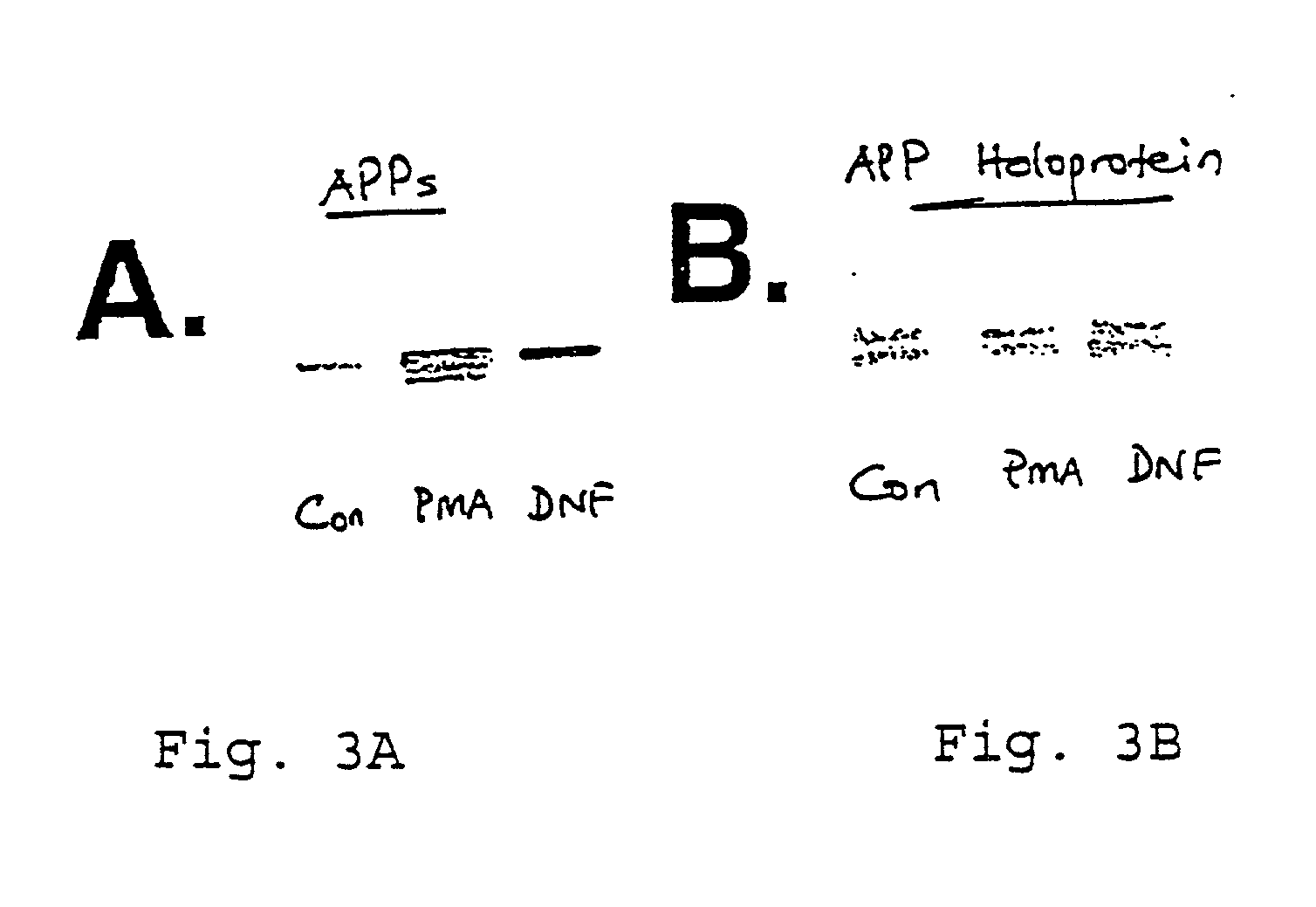
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, forskolin, or nicotine ditartrate is inhibited by immunosuppressants or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6043224AIncreased formationPromote activationBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta -adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta -adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta -adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta -adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, forskolin, or nicotine ditartrate is inhibited by immunosuppressants or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Pharmaceutical composition containing cyclosporin A
InactiveUS6022852AImprove solubilityInhibit synthesisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAlpha-tocomonoenolTocopherol
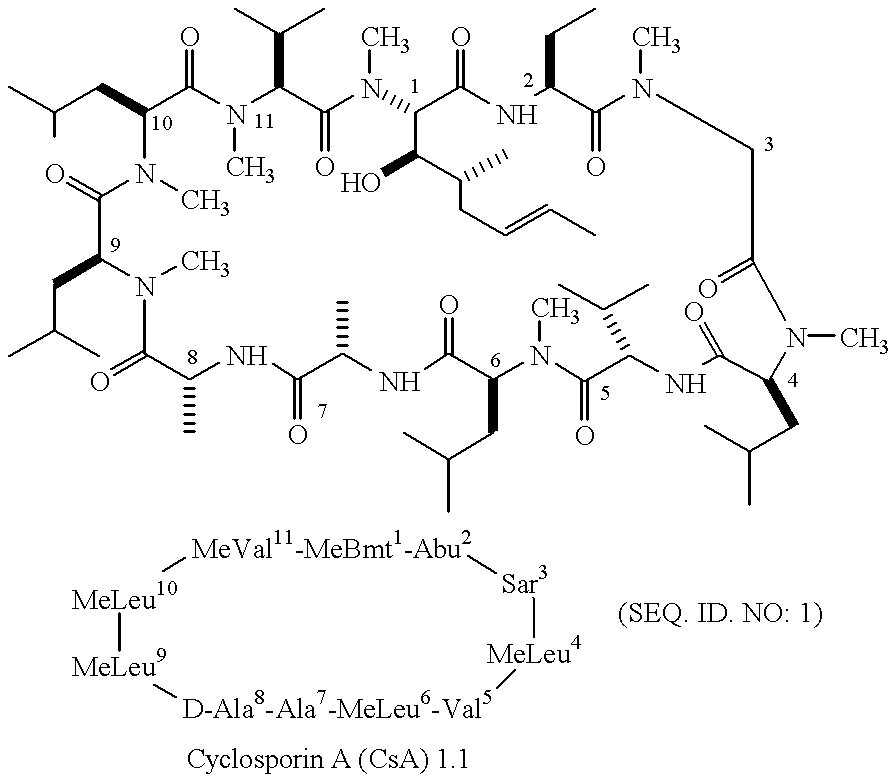
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition consisting of or containing cyclosporin A and alpha -tocopherol or one of the derivatives thereof.
Owner:HEXAL AG
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6469055B2Increased formationPromote activationBiocideNervous disorderGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, or forskolin is inhibited by immunosuppressants, immunophilin ligands, or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20020052407A1Prevent APP over-expressionInhibit overexpressionBiocideNervous disorderGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, or forskolin is inhibited by immunosuppressants, immunophilin ligands, or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Immunomodulatory compositions
InactiveUS20130243873A1Promote dissolutionFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHydralazineDopamine hydroxylase inhibitor
Immunomodulator formulations for use in the treatment of disease of the GI tract. The formulations comprise a hydroxylase inhibitor and / or an immunosuppressant. Exemplary formulations comprise hydralazine as a hydroxylase inhibitor and / or cyclosporin A as an immunosuppressant.
Owner:SIGMOID PHARM LIMITED
Preparation of pharmaceutical compositions
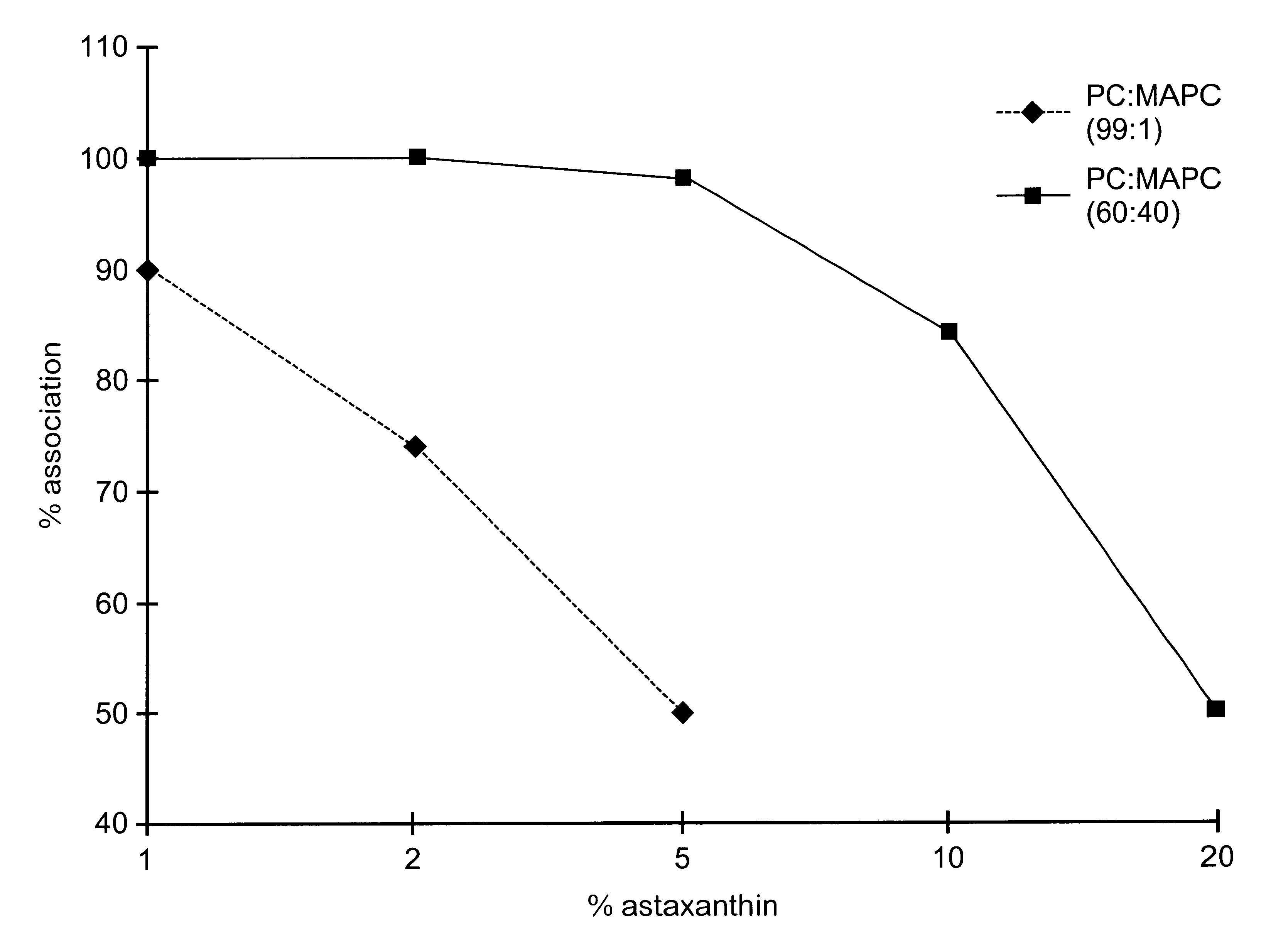
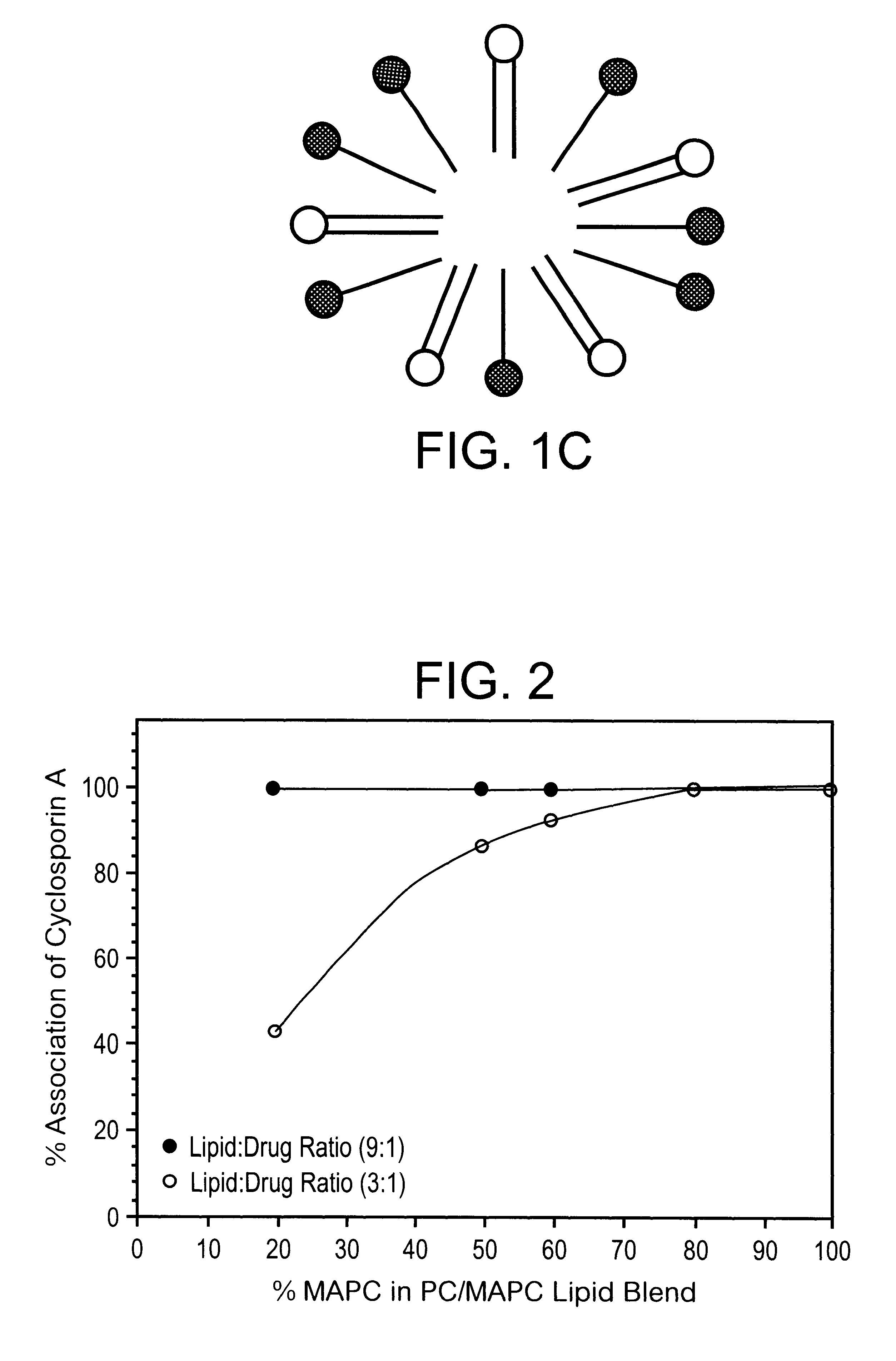
A substantially homogeneous composition for human administration comprises a biologically active lipophilic compound dissolved in or associated with at least one micelle-forming lipid. For example, cyclosporin A is dissolved or dispersed in the mixture of PC and MAPC. The composition may be made by dissolving the lipid material in ethanol, adding the lipophilic compound to the ethanol and removing the ethanol, after which the composition may be formulated for human oral administration.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS
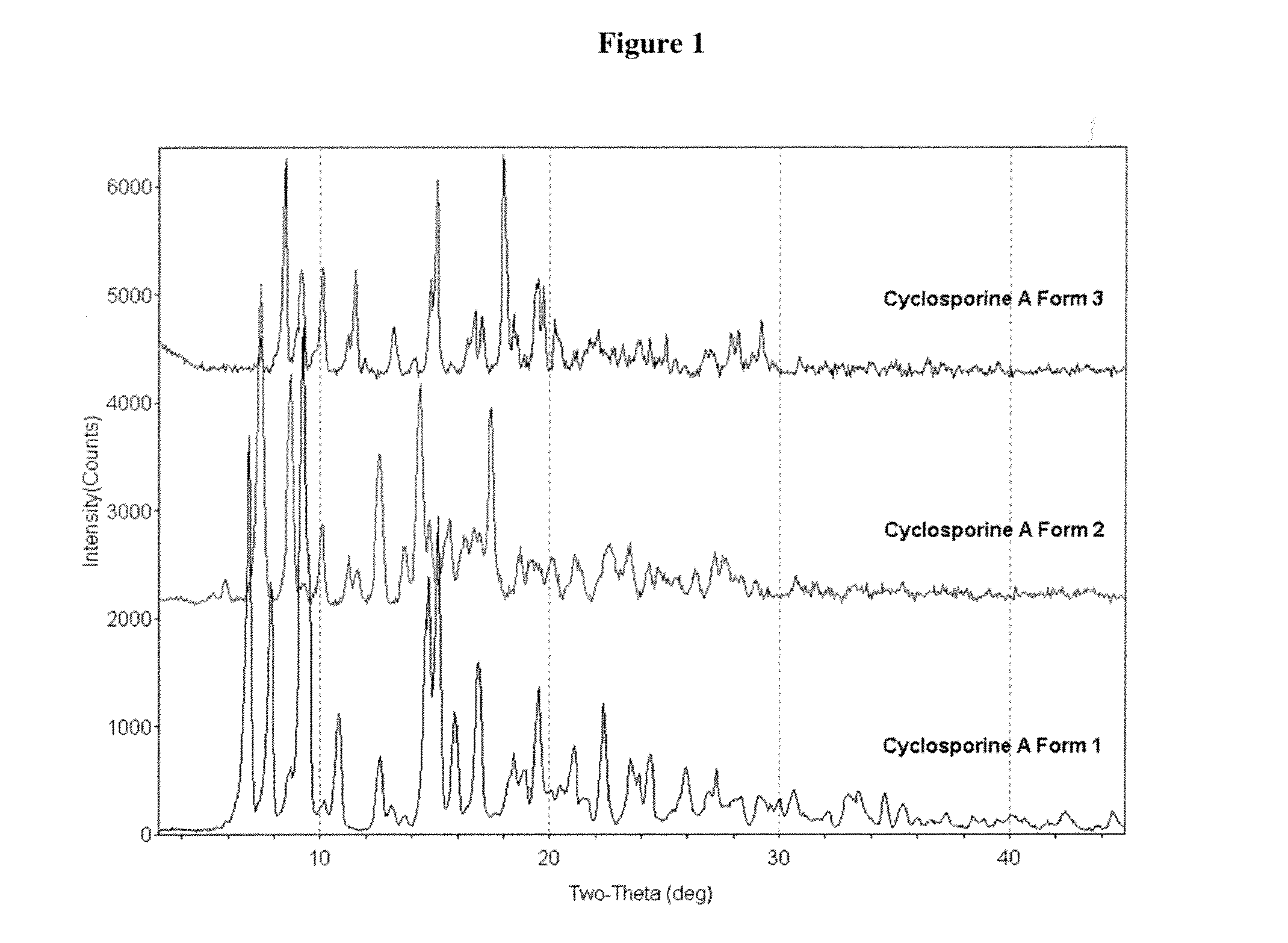
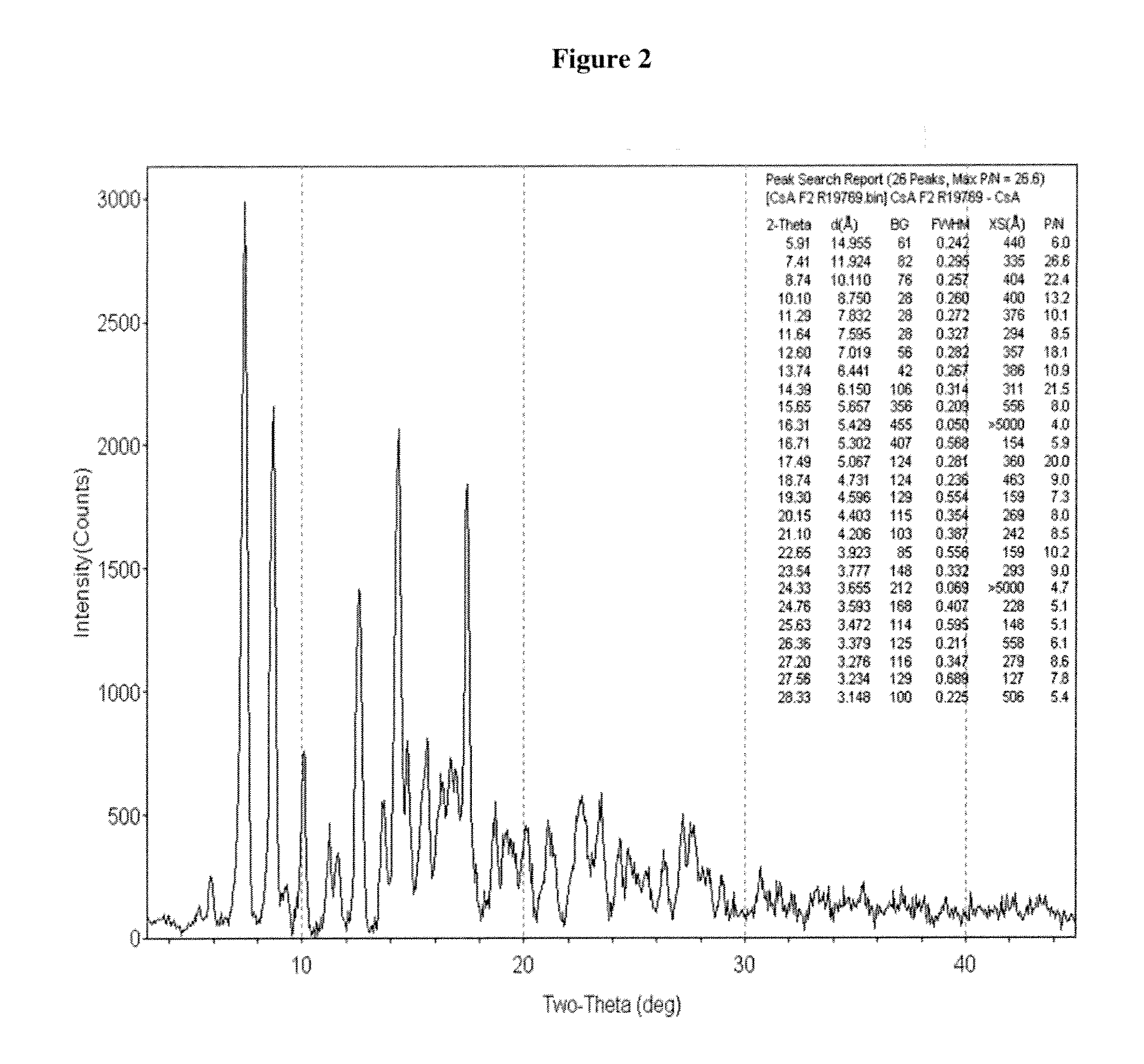
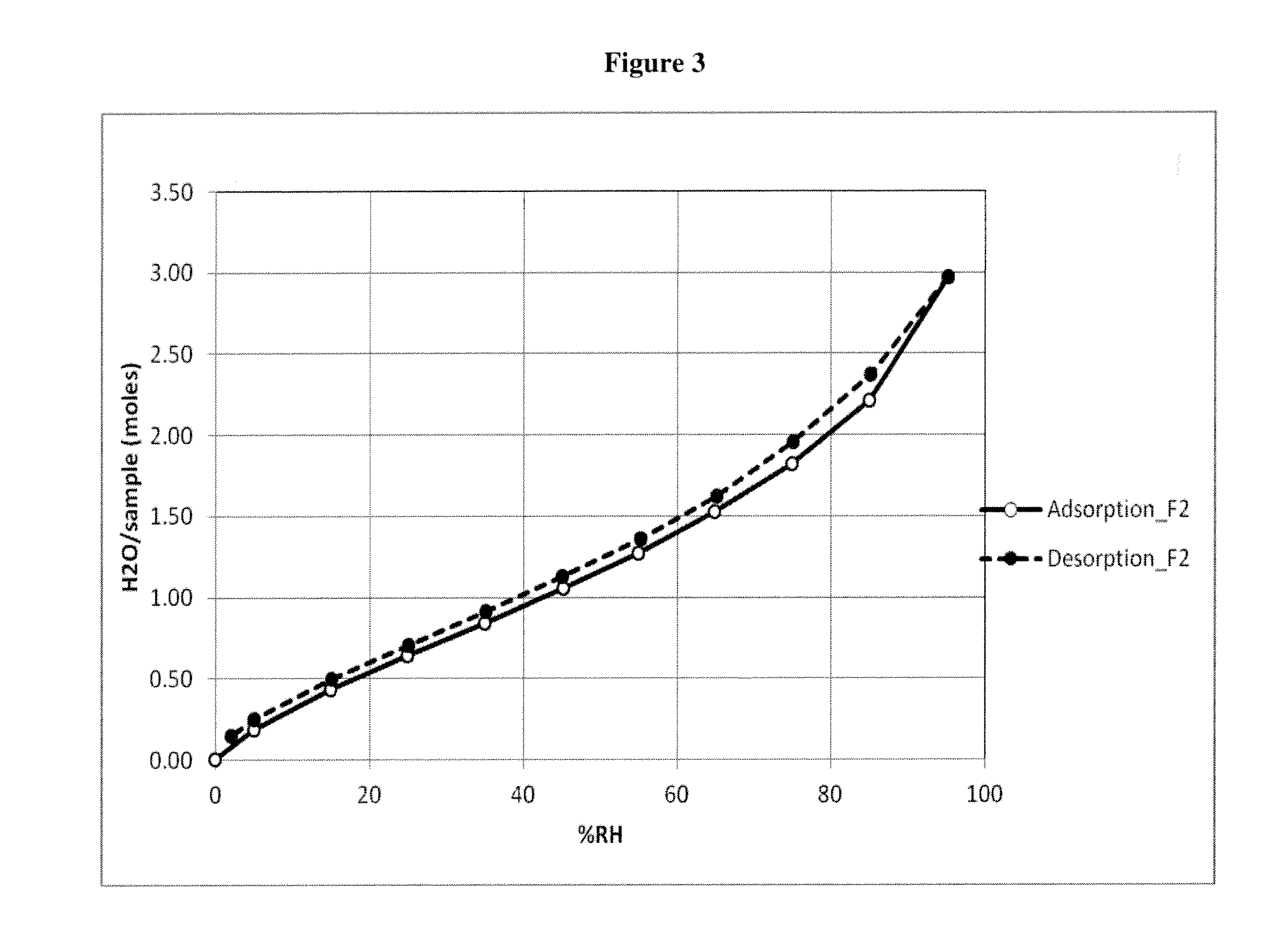
Crystalline form of cyclosporine a, methods of preparation, and methods for use thereof
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compositions and methods for hair growth
InactiveUS20120129789A1Promote growthPrevent graying of hair or loss of melanin or pigmentOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsHair growthScalp
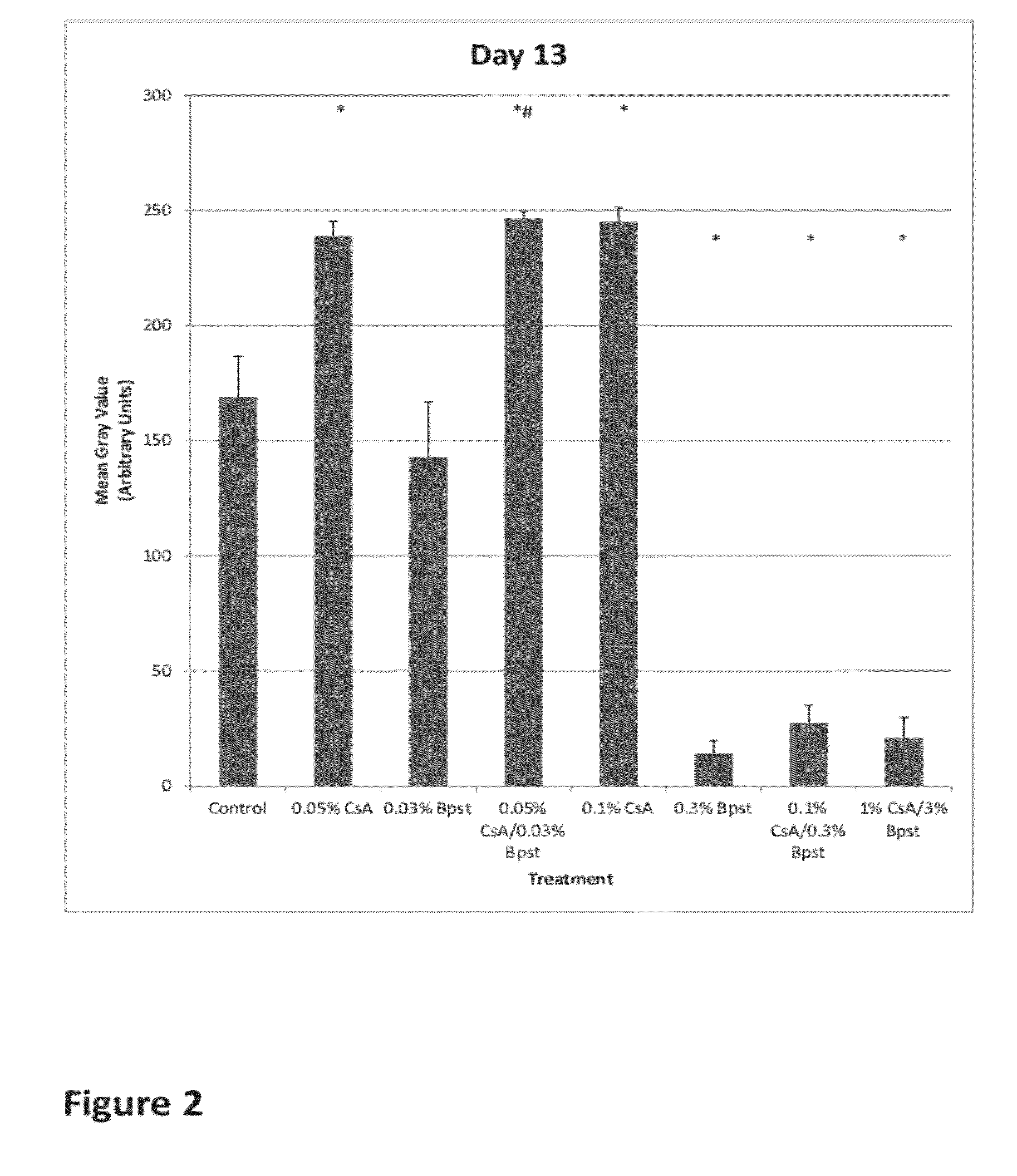
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods comprising the use of bimatoprost and cyclosporine, used concurrently and in combination, to grow hair and for the treatment of all types of hair loss conditions such as but not limited to alopecia areata. The present invention is also directed to compositions containing bimatoprost and cyclosporine A to grow hair on the scalp and other areas of the body and methods of administration of the compositions.
Owner:YOELIN STEVEN
Cyclosporin a conjugates and uses therefor
InactiveUS6316405B1Highly effective to treat or prevent neurological disordersAct synergisticallyNervous disorderMetabolism disorderAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisAmyloid
Disclosed are conjugates of Abeta-binding peptides and CsA analogs and conjugates of Abeta-binding peptides and FK506 Binding Peptide inhibitors. These conjugates chemically induce dimerization of either cyclophilin or FK506 Binding Peptide with Abeta peptide, a major component of amyloid plaques found in neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The conjugates are useful in the treatment of neurological diseases involving the formation of amyloid plaques because they inhibit and / or prevent the aggregation and deposition of Abeta peptide into plaques.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Treatment of ocular disease
InactiveUS7354574B2Without substantial ocular toxicityHindering progressSenses disorderMetabolism disorderDiabetic retinopathyDisease
A method and article to treat ocular disease with Cyclosporin A alone or with compounds related to Cyclosporin A for intraocular injection or implantation. Treatment does not result in ocular toxicity and encompasses age related macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, and retinopathy such as diabetic retinopathy.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A DR
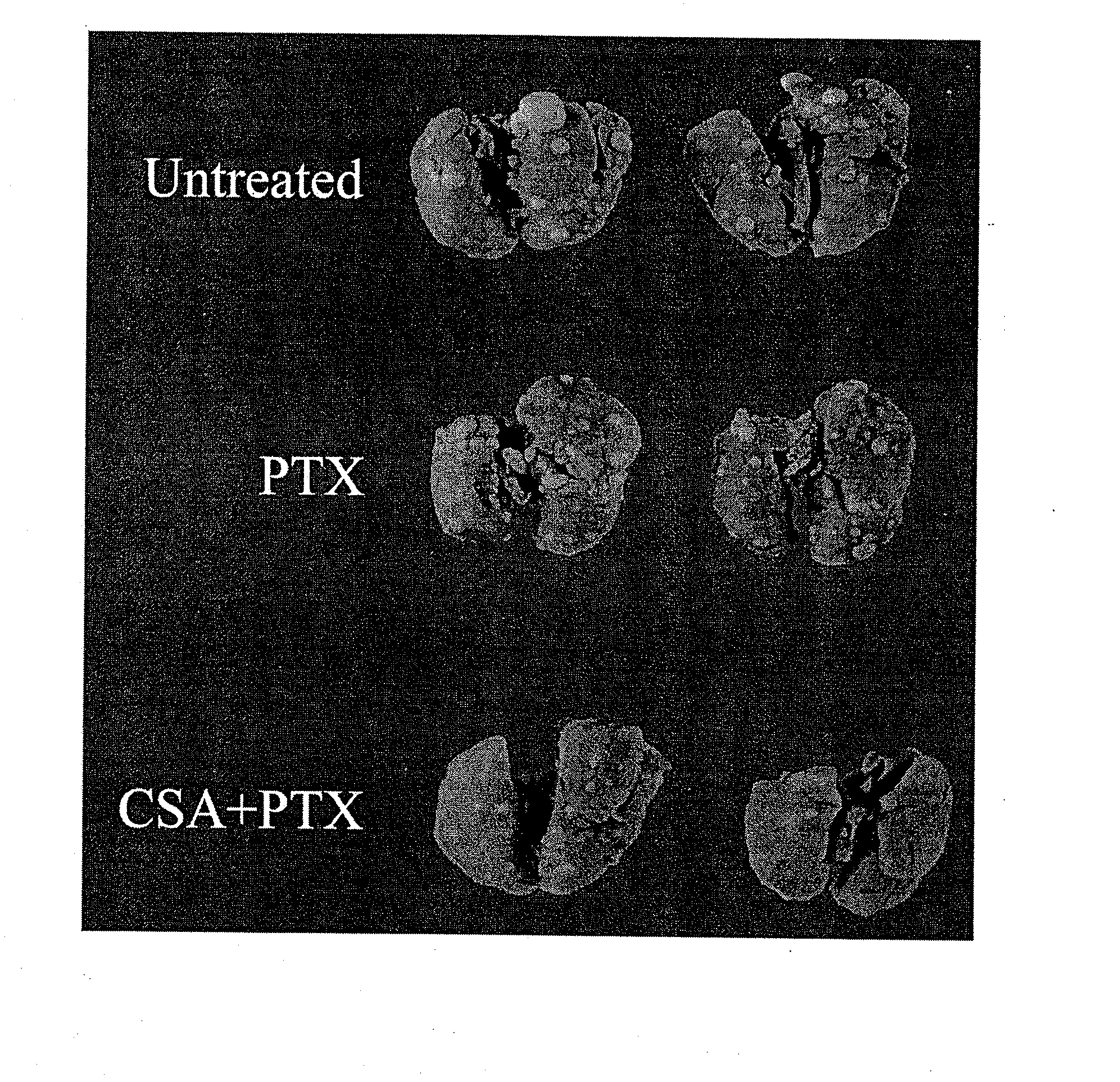
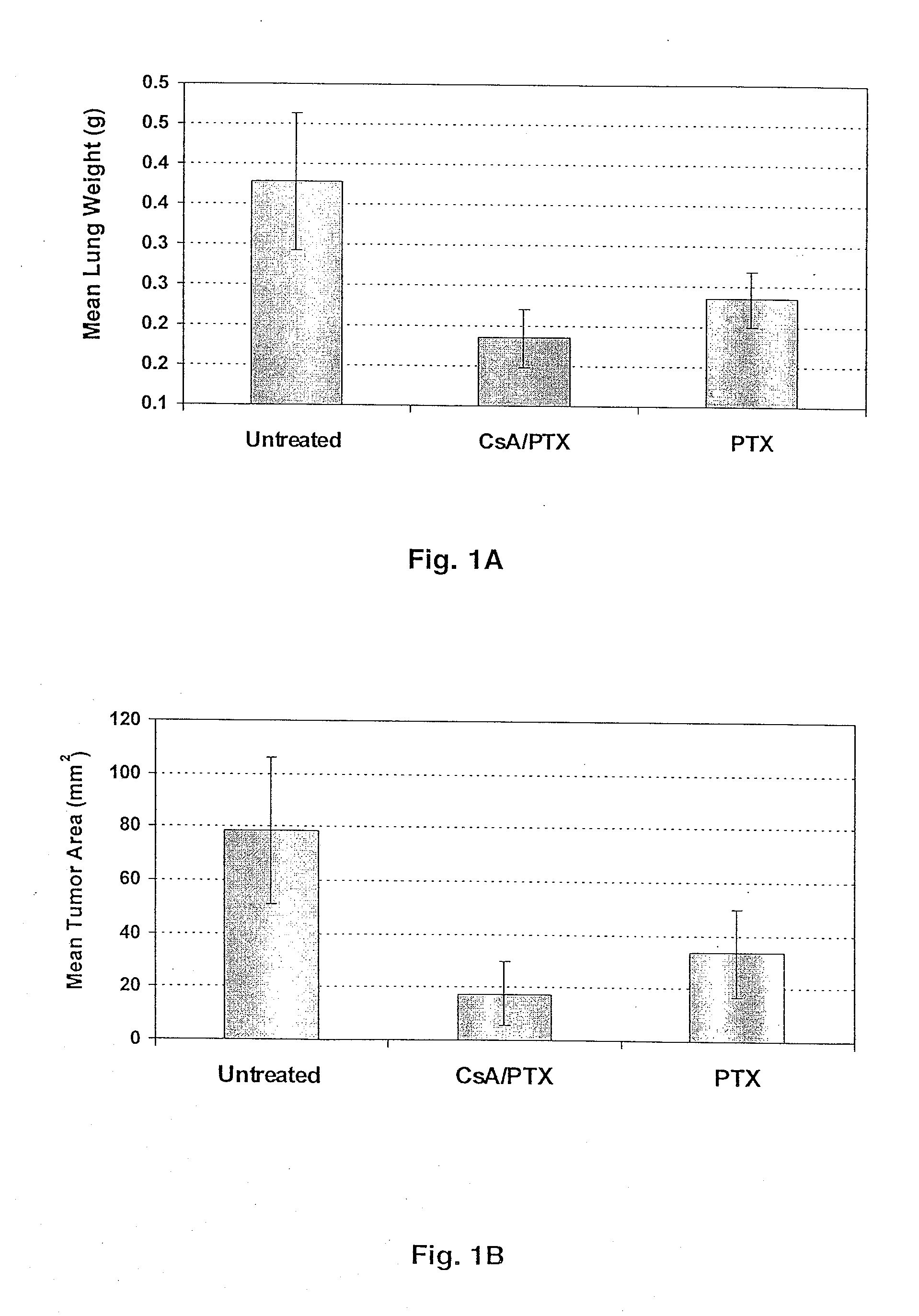
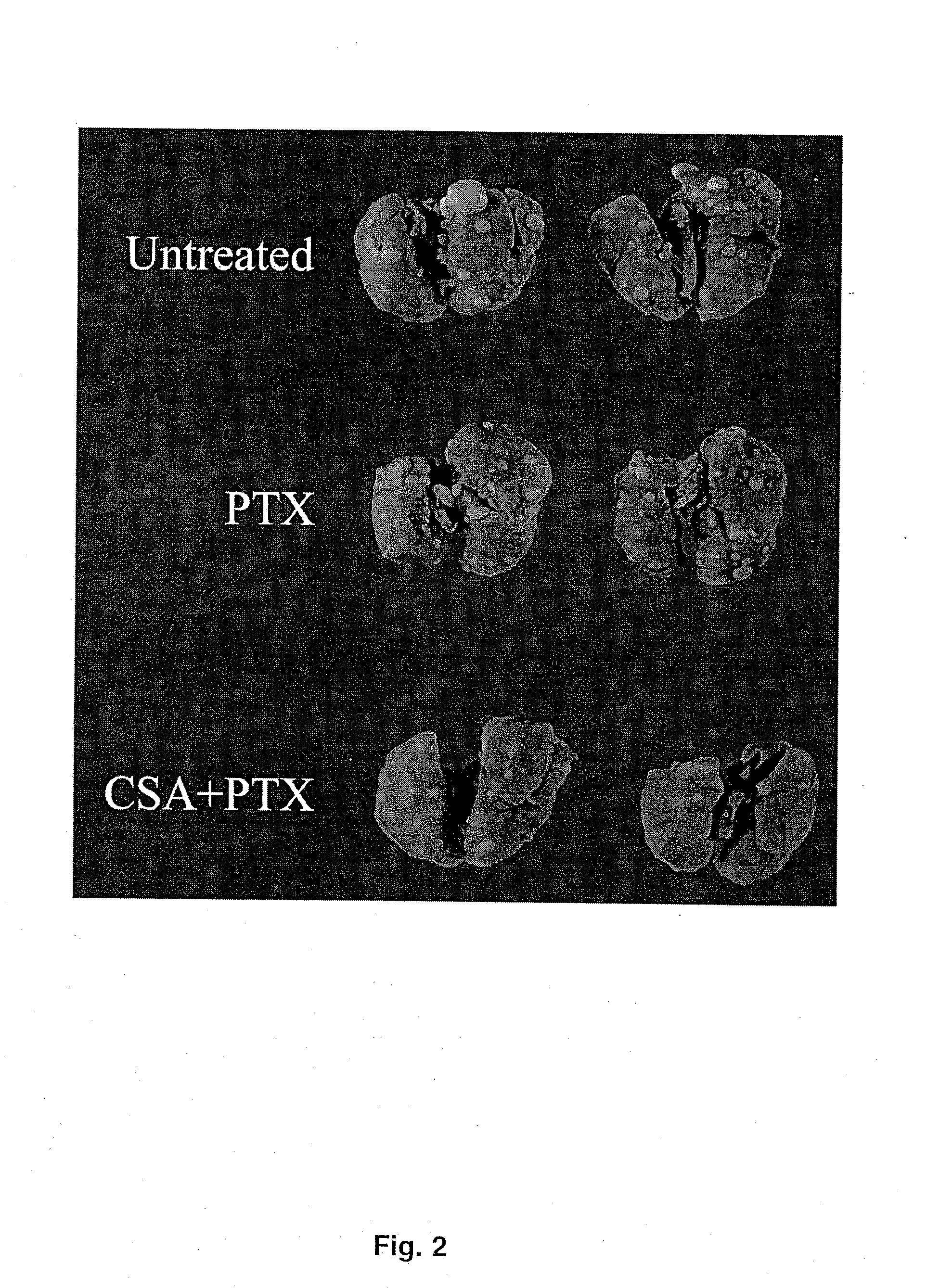
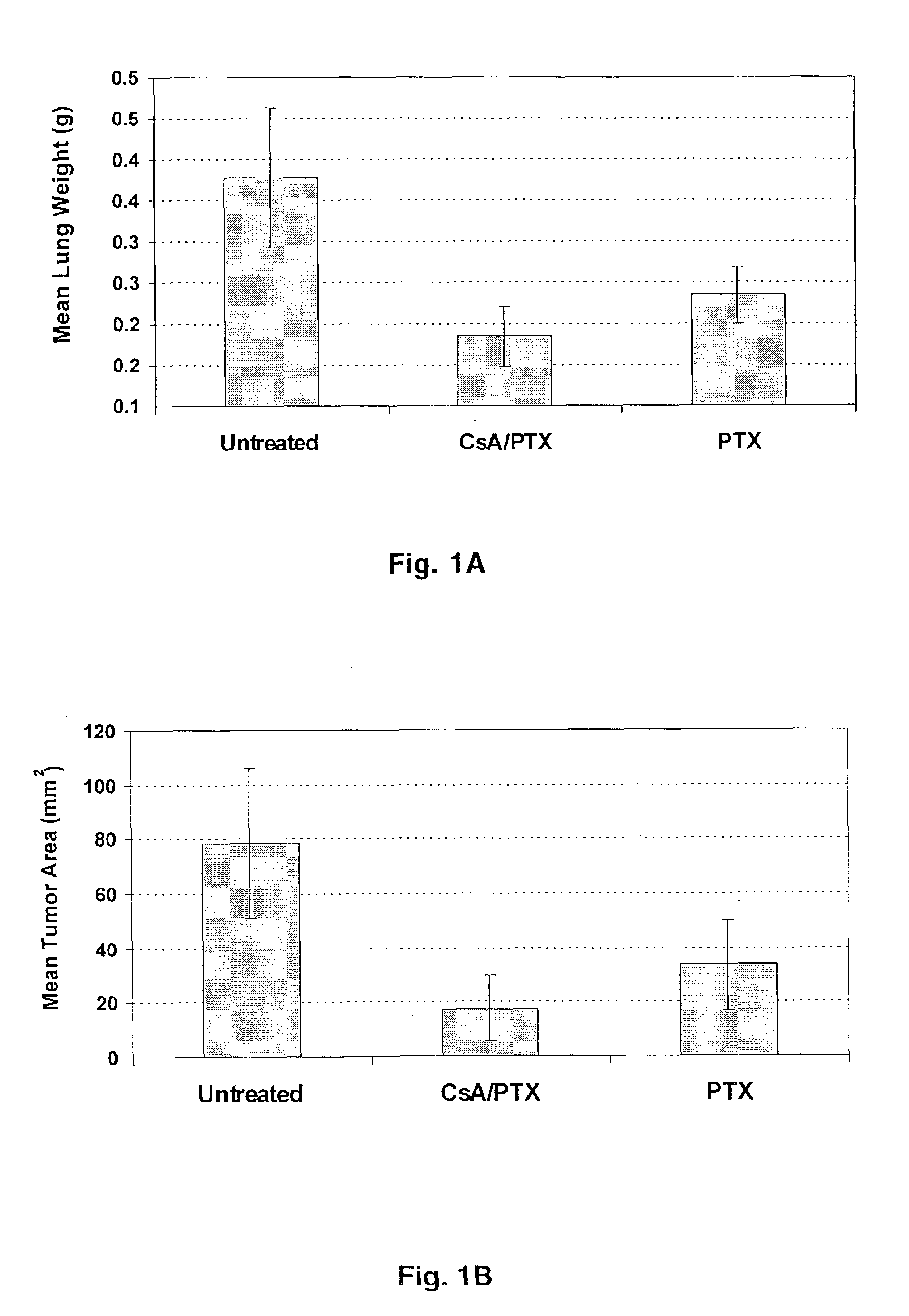
Aerosol Drug Inhibition of Lung Cancer
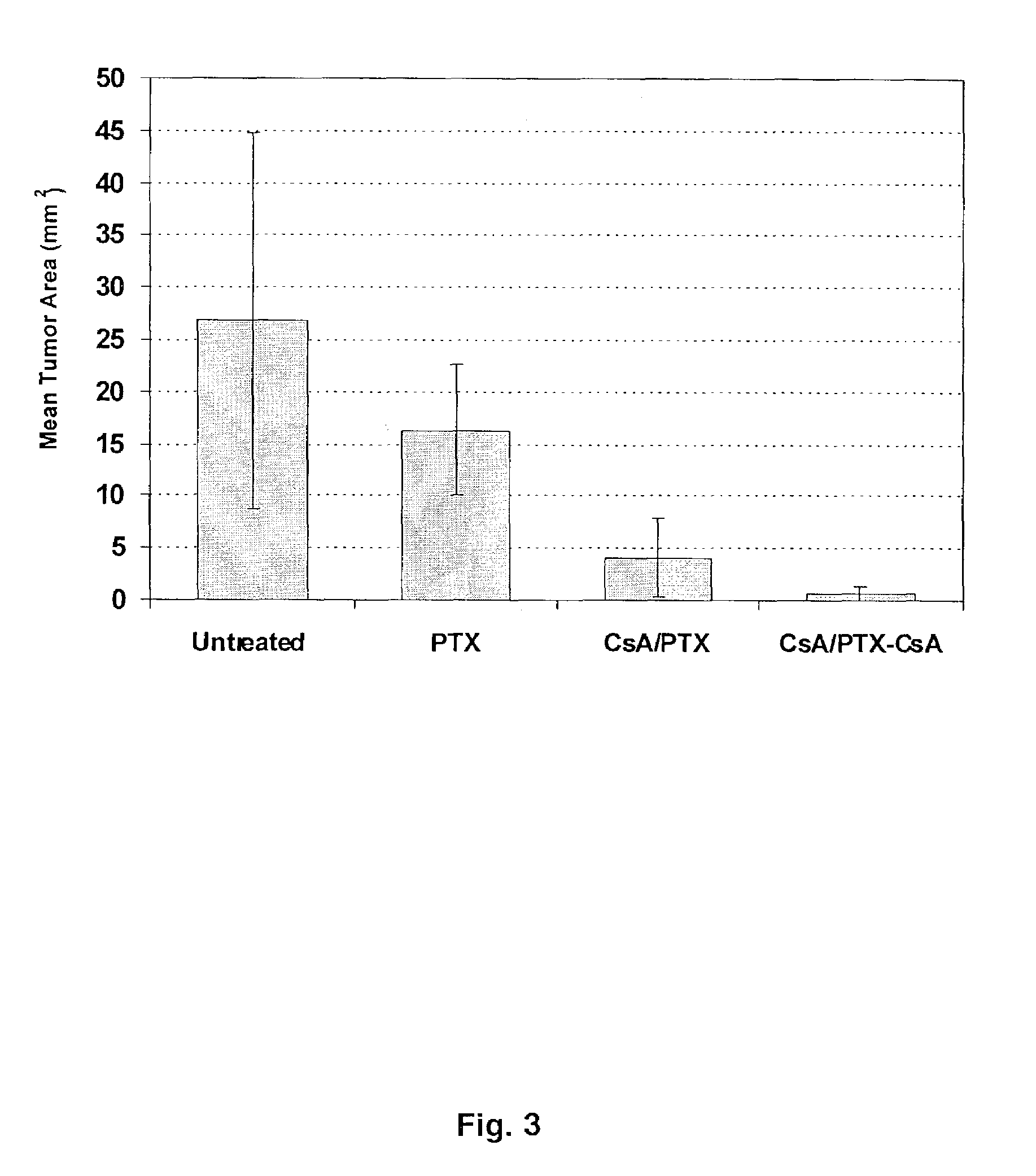
The present invention provides a method of inhibiting growth of lung metastases in an individual comprising the steps of administering a dose of a lipid-drug enhancer liposomal complex and, in sequence, administering a dose of a lipid-anticancer drug liposomal complex. Furthermore, the lipid-drug enhancer liposomal complex may be administered in a continuing dose with the lipid-anticancer drug liposomal complex whereby both liposomal complexes are mixed in the nebulizer. Methods of inhibiting growth of lung metastases in an individual by the sequential administration via aerosolization of a dilauroylphosphatidylcholine-cyclosporin A liposomal complex and a dilauroylphosphatidylcholine-paclitaxel liposomal complex are also provided.
Owner:KNIGHT J VERNON +2
Aerosol drug inhibition of lung metastases
The present invention provides a method of inhibiting growth of lung metastases in an individual comprising the steps of administering a dose of a lipid-drug enhancer liposomal complex and, in sequence, administering a dose of a lipid-anticancer drug liposomal complex. Furthermore, the lipid-drug enhancer liposomal complex may be administered in a continuing dose with the lipid-anticancer drug liposomal complex whereby both liposomal complexes are mixed in the nebulizer. Methods of inhibiting growth of lung metastases in an individual by the sequential administration via aerosolization of a dilauroylphosphatidylcholine-cyclosporin A liposomal complex and a dilauroylphosphatidylcholine-paclitaxel liposomal complex are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
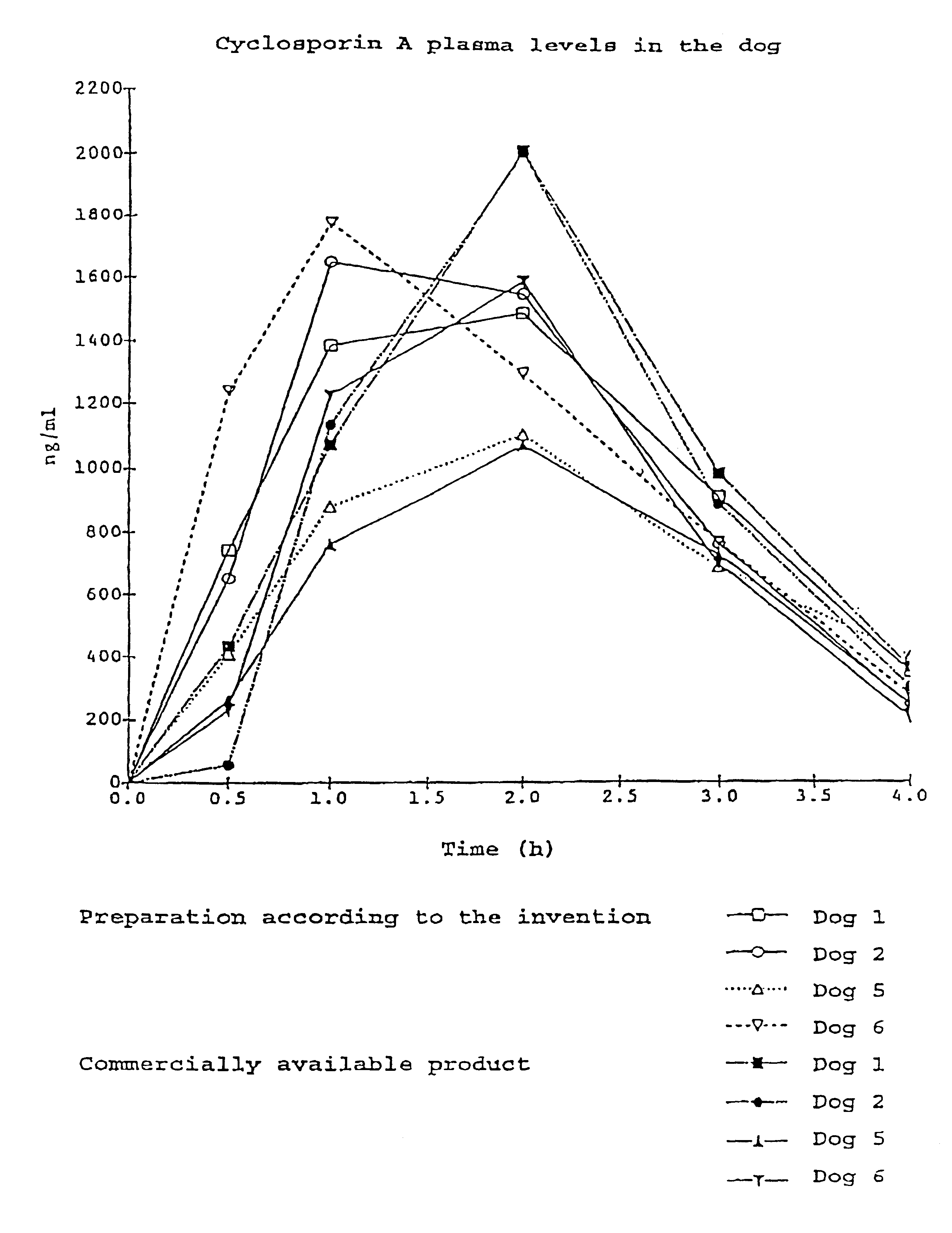
Pharmaceutical preparation with cyclosporin A
InactiveUS6696413B2Reduce impactPromote permeationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsVegetable oilAlcohol
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical preparation which consists of or contains cyclosporin A, an emulsifying alpha-tocopherol derivative, an ethoxylation product of vegetable oils, fatty acids or fats as a further emulsifier and a pharmaceutically customary alcohol.
Owner:HEXAL AG
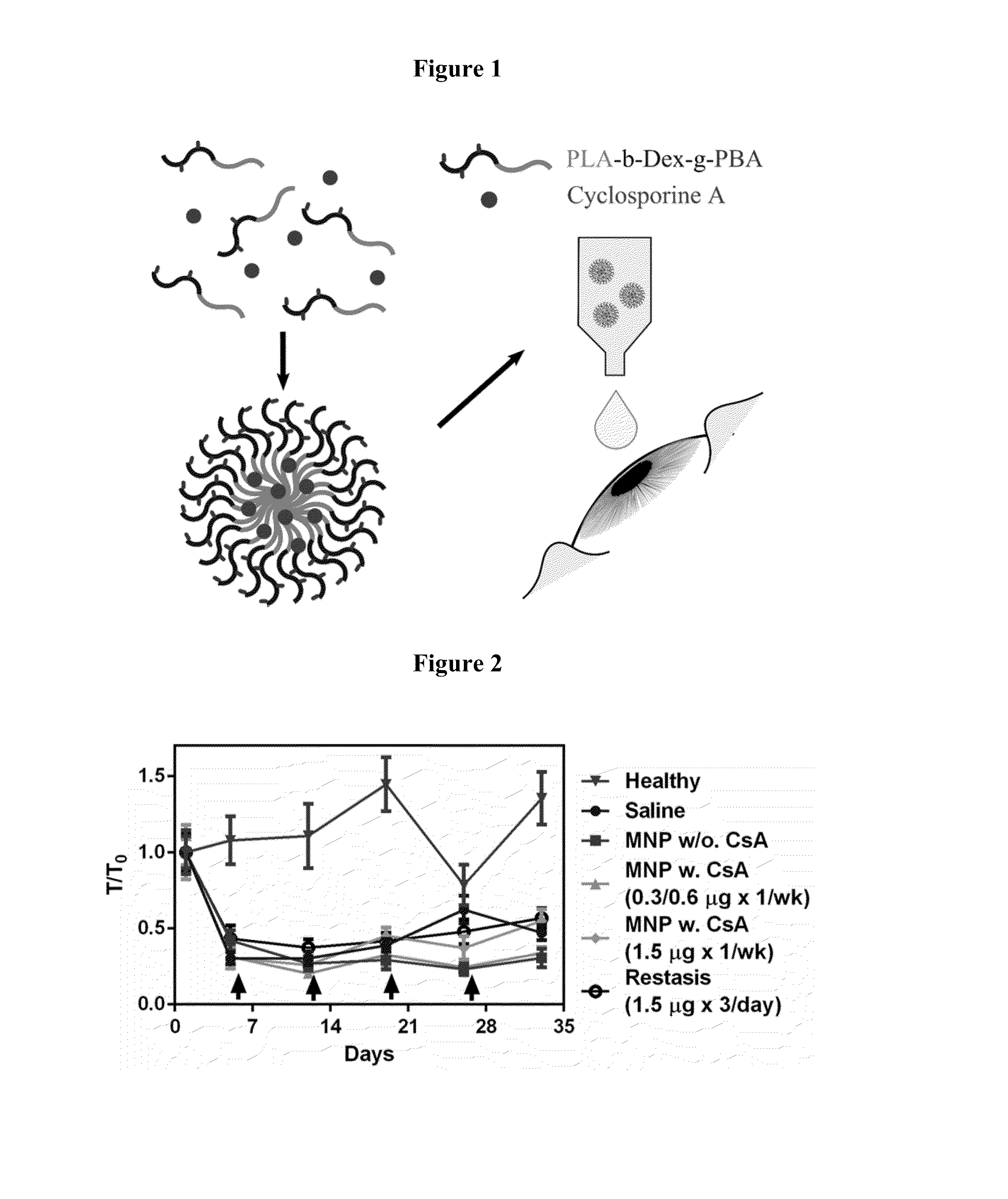
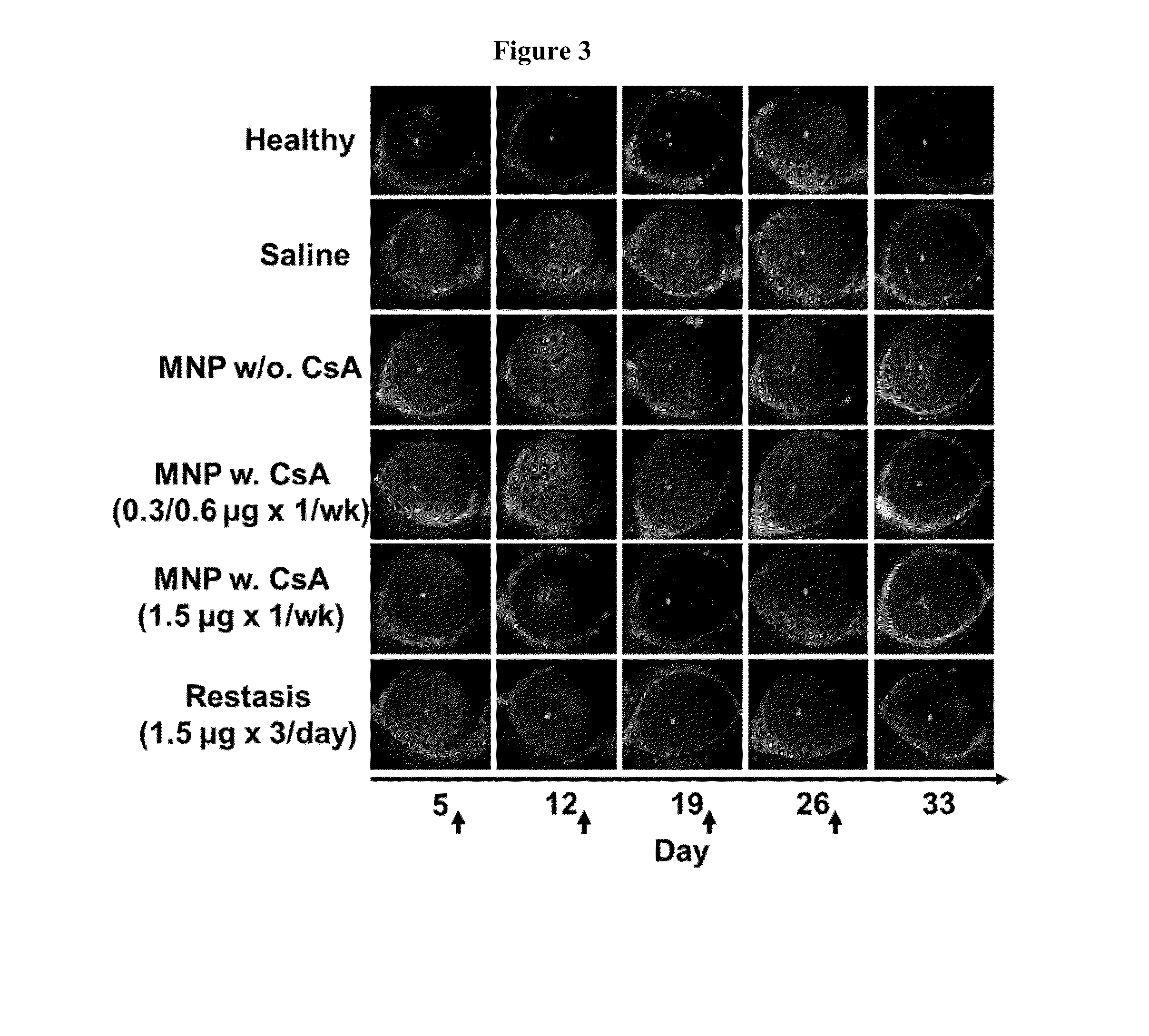
Mucoadhesive nanoparticle composition comprising immunosuppresant and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160243189A1Powder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsDiseaseParticle composition
Disclosed is a mucoadhesive nanoparticle delivery system for delivering an immunosuppressant, such as cyclosporine A, to a mucosal site for treatment of a disease or condition involving inflammation or excess immune activity. The system comprises nanoparticles formed from a plurality of linear amphiphilic block copolymers, each having a hydrophobic block comprising polylactide (PLA) and a hydrophilic block comprising dextran. The nanoparticles are surface-functionalized with a mucosal targeting moiety, such as a phenylboronic acid derivative, for targeted delivery and enhanced retention at the mucosal site. Pharmaceutical compositions, methods, and uses thereof comprising the mucoadhesive nanoparticle delivery system are disclosed. The compositions can be administered in an effective amount for treating the disease or condition while substantially preserving or restoring the function and / or integrity of the mucosal lining. The composition may be formulated as an aqueous suspension for administration to an anterior surface of the eye in the treatment of dry eye syndrome.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
Methods to measure immunosuppressive tacrolimus, sirolimus, and cyclosporin a complexes in a blood sample
The present invention provides methods, diagnostic assays, and diagnostic kits based on said methods, to determine levels of immunosuppressive complexes containing immunosuppressive drugs tacrolimus, sirolimus and cyclosporine A separately and in combination, formed in the blood of a drug-treated patient or in a patient candidate to immunosuppressive drug therapy. These methods, assays and kits are especially useful when using automated systems.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Pharmaceutical preparation with cyclosporin a
InactiveUS20010014665A1Reduce nephrotoxicityReduce impactOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAlcoholVegetable oil
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical preparation which consists of or contains cyclosporin A, an emulsifying .alpha.-tocopherol derivative, an ethoxylation product of vegetable oils, fatty acids or fats as a further emulsifier and a pharmaceutically customary alcohol.
Owner:HEXAL AG
Methods for Treating Severe Atopic Dermatitis by Administering an IL-4R Inhibitor
ActiveUS20180078603A1Reduce dependenceReduce the amount requiredPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsWhole bodySevere atopic dermatitis
The present invention provides methods for treating moderate-to-severe or severe atopic dermatitis (AD). The methods of the present invention comprise administering to a subject in need thereof one or more doses of an interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) inhibitor such as an anti-IL-4R antibody. In certain embodiments, the methods of the present invention are used to treat severe AD in a patient whose disease is not controlled with systemic therapy (e.g., cyclosporine A) or when such therapy is inadvisable.
Owner:SANOFI BIOTECH SAS +1
Self-micro emulsifying soft capsule of cyclosporine A and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101130059AOvercoming low bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityCyclic peptide ingredientsCapsule deliveryWater insolubleTG - Triglyceride
The invention relates to a self micro emulsifying soft capsule with cyclosporin A and the preparing method. The preparing method comprises the following steps: heating and dissolving cyclosporin A, absolute ethyl alcohol, methyl ethylene glycol, polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, span 80 and medium chain fatty acid triglyceride in the homogenized emulsified pan; making soft capsule; and getting the product by treating the surface with alcohol and drying. The disintegrated self micro emulsifying soft capsule is dispersed into the transparent microemulsion, and the determined result indicates that the grain diameter of microemulsion is uniform. The invention has the easy getting solvent, the low price and the simple technology, which is fit for the large scale industry production, overcomes the low bioavailability of cyclosporin A , reduces the enormous difference of bioavailability among the individual, improves the digestion of the water-insoluble medicine, and improves bioavailability of the medicine.
Owner:无锡曙辉药业有限公司
Formulations
InactiveUS20150132374A1Low systemic blood exposureHigh peak levelAntipyreticAnalgesicsOral medicationWhole body
A modified release composition comprising cyclosporin A for oral administration. The composition may comprise a core and a modified release coating, wherein the core comprises a hydrogel-forming polymer matrix and cyclosporin A. The composition may be in the form of a minibead. The compositions provide a pharmacokinetic profile and dissolution profile which provides release of cyclosporin A in the lower GI tract whilst minimising systemic exposure. Also disclosed are uses of the composition in the treatment of conditions affecting the lower GI tract, particularly the colon.
Owner:SUBLIMITY THERAPEUTICS LTD
Gene therapy by cell specific targeting
InactiveUS6982082B1Selectively inhibiting proliferationPrevent proliferationBiocideCyclosporinsCell specificDisease
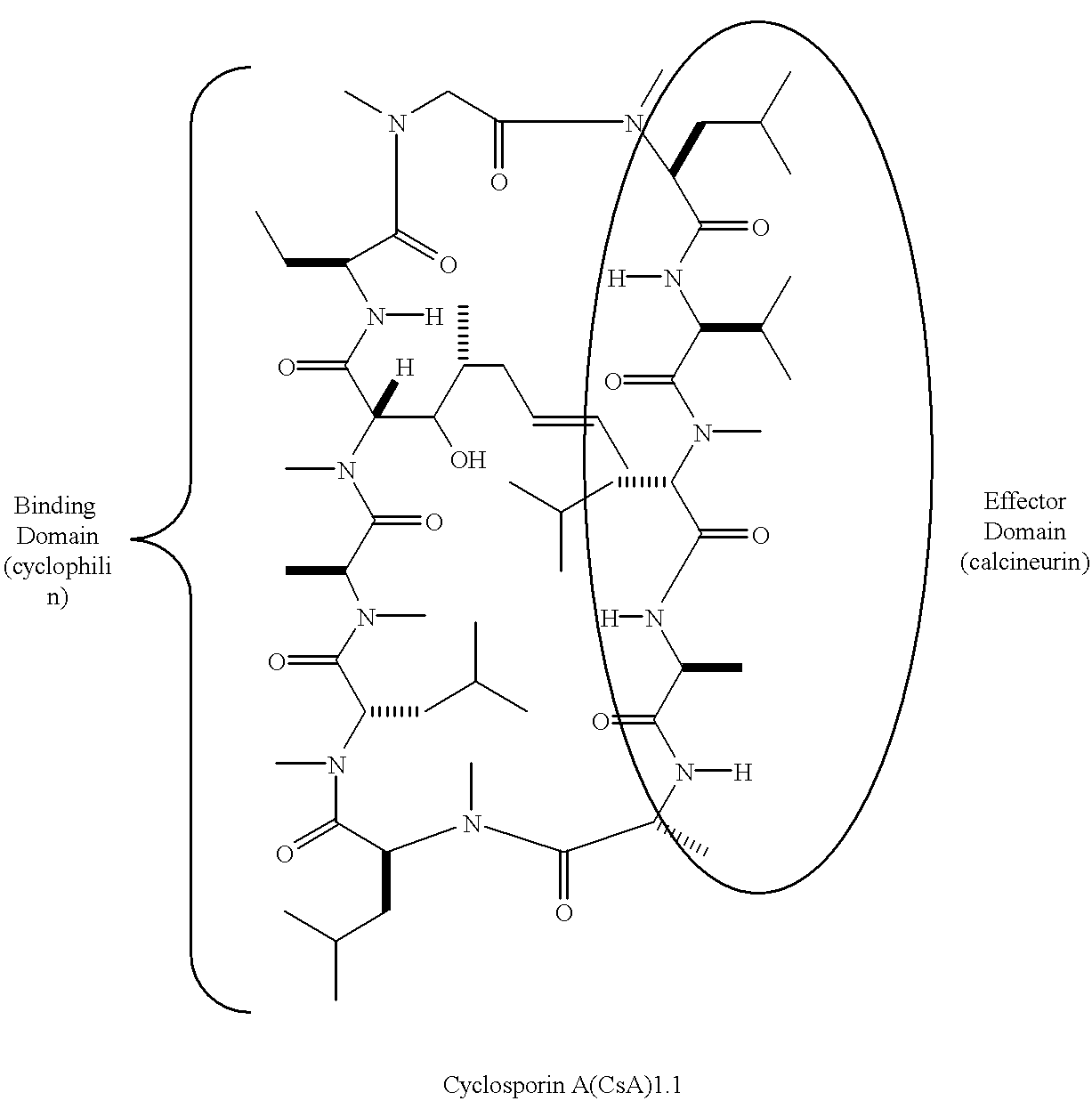
This invention is directed to a modified cyclosporin A and to a modified, genetically engineered version of its receptor, cyclophilin. This invention is further directed to a method for treating host versus graft disease following blood marrow transplantation by transfecting stem cells so that after introduction into a patient the stem cells will express the modified cyclophilin, and, as necessary, administer the modified cyclosporin A to the patient.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
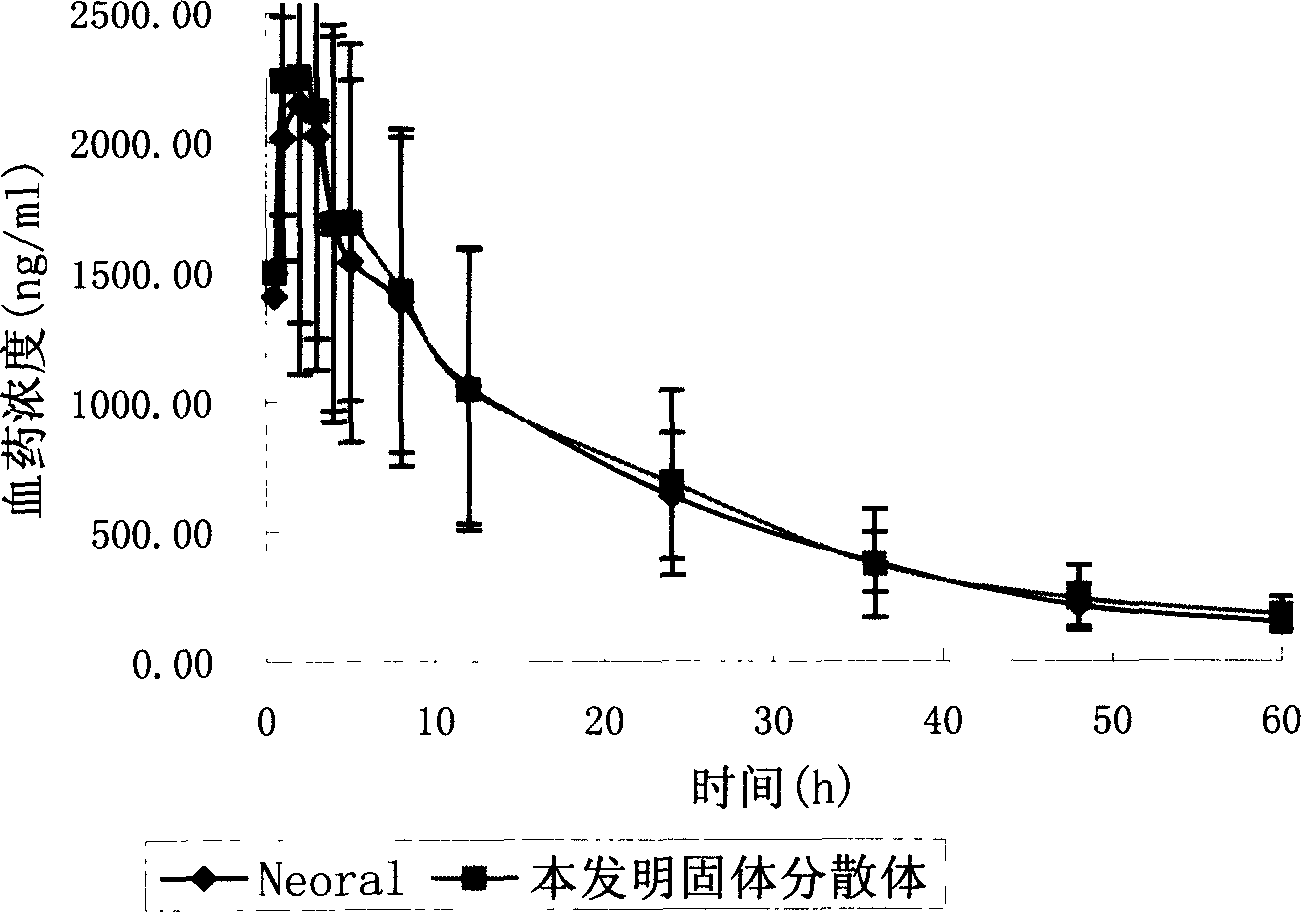
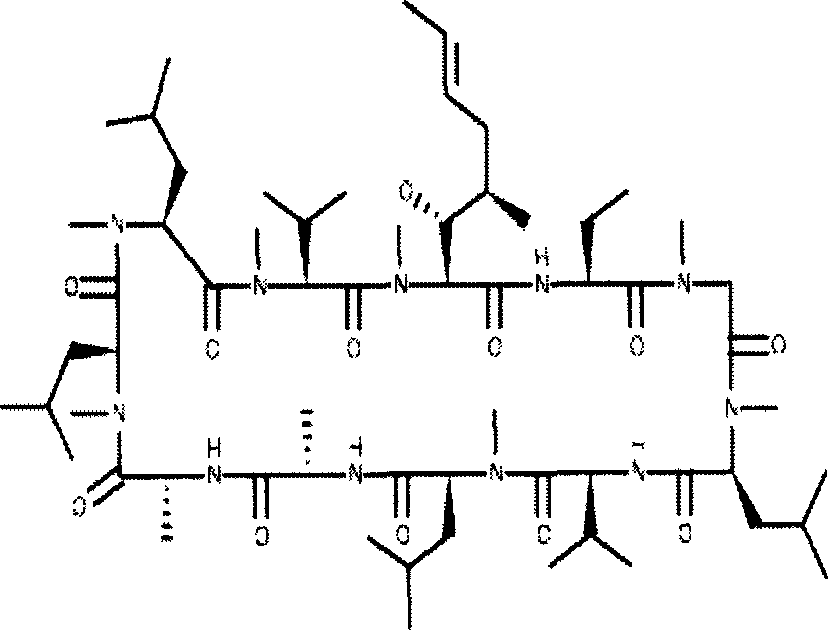
Cyclosporin A dispersion solid and its preparation method
InactiveCN1559606AIncrease dissolution ratePowder deliverySuppositories deliverySolubilityCaplet Dosage Form
A dispersing solid (capsule, tablet, particle, suppository and dripping pill) of cyclosporin A is prepared from cyclosporin A and carrier by solvent method, solvent fusion method, etc. It has high solubility of easy absorption.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Apparatus for Improved Immunosuppressant Drug Monitoring
InactiveUS20140299765A1Easy to separateComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationEverolimusMass analyzer
A liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry system includes: a source of a first mobile phase solvent consisting essentially of water plus 10 mM ammonium formate plus 0.05% formic acid; a source of a second mobile phase solvent consisting essentially of methanol plus 10 mM ammonium formate plus 0.05% formic acid; a chromatography column comprising a length of 30 mm or less of a stationary phase comprising an 8-carbon alkyl chain material bonded to 2.6 μm diameter particles having solid silica cores surrounded by porous silica outer layers; an electrospray ion source of a mass spectrometer fluidically coupled to the chromatography column so as to generate ions therefrom; a mass analyzer of the mass spectrometer operable to quantitatively detect the ions; and a programmable processor electronically coupled to the mass analyzer and comprising instructions operable to determine, based on the ion detection, a concentration of everolimus, sirolimus, tacrolimus, or cyclosporin A.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Cyclosporin A semisolid skeleton capsule and its preparation method
A capsule of cyclosporin A and semi-solid skeleton is proportionally prepared from cyclosporin A, oil phase, emulsifier, emulsifying aid, and semi-solid carrier through fusing them except cyclosporin A in water bath at 60 deg.C, stirring, adding cyclosporin A, stirring for full dissolving, cooling and loading it in capsules.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Stable cyclosporine containing ophthalmic emulsion for treating dry eyes
ActiveUS20120093894A1Relieve dry eye symptomsEfficiently relievedBiocideSenses disorderVegetable oilSide chain
Disclosed herein are stable oil-in-water emulsion ophthalmic topical liquid compositions having an average particle size less than 1 μm including at least one plant-derived oil other than castor oil wherein the oil comprises only aliphatic side chains free of polar pendent groups. The oil-in-water emulsion ophthalmic topical liquid compositions also include a hydrophilic surfactant having an HLB value between approximately 10 and 14, a vegetable oil-derived hydrophobic non-co-block surfactant having unsaturated side chains that contain less than four oxygen atoms having an HLB value between approximately 4 and 6 and is a liquid at room temperature. The oil-in-water emulsion ophthalmic topical liquid compositions disclosed herein can further include an amount of cyclosporine A or polyphenol in an amount effective to relieve dry eye symptoms.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method for preparing cyclosporine A
ActiveCN102086226ASignificant concentration and enrichmentLess effective removalPeptide preparation methodsImmunological disordersElutionSolvent
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical technology and provides an industrialized method for preparing high-purity cyclosporine A. According to the method, the cyclosporine A is obtained through extraction by utilizing fermentation liquid, chromatography by utilizing a nonpolar macroporous absorption resin, silica gel column chromatography, crystallization and purification. In the invention, isoconcentration elution is adopted without complicated intermediary steps of dissolvent substitution processes; the process is easy to operate and is suitable for industrialized production; the purity of products is greater than 98.5; and the yield is above 65%.
Owner:鲁南新时代生物技术有限公司
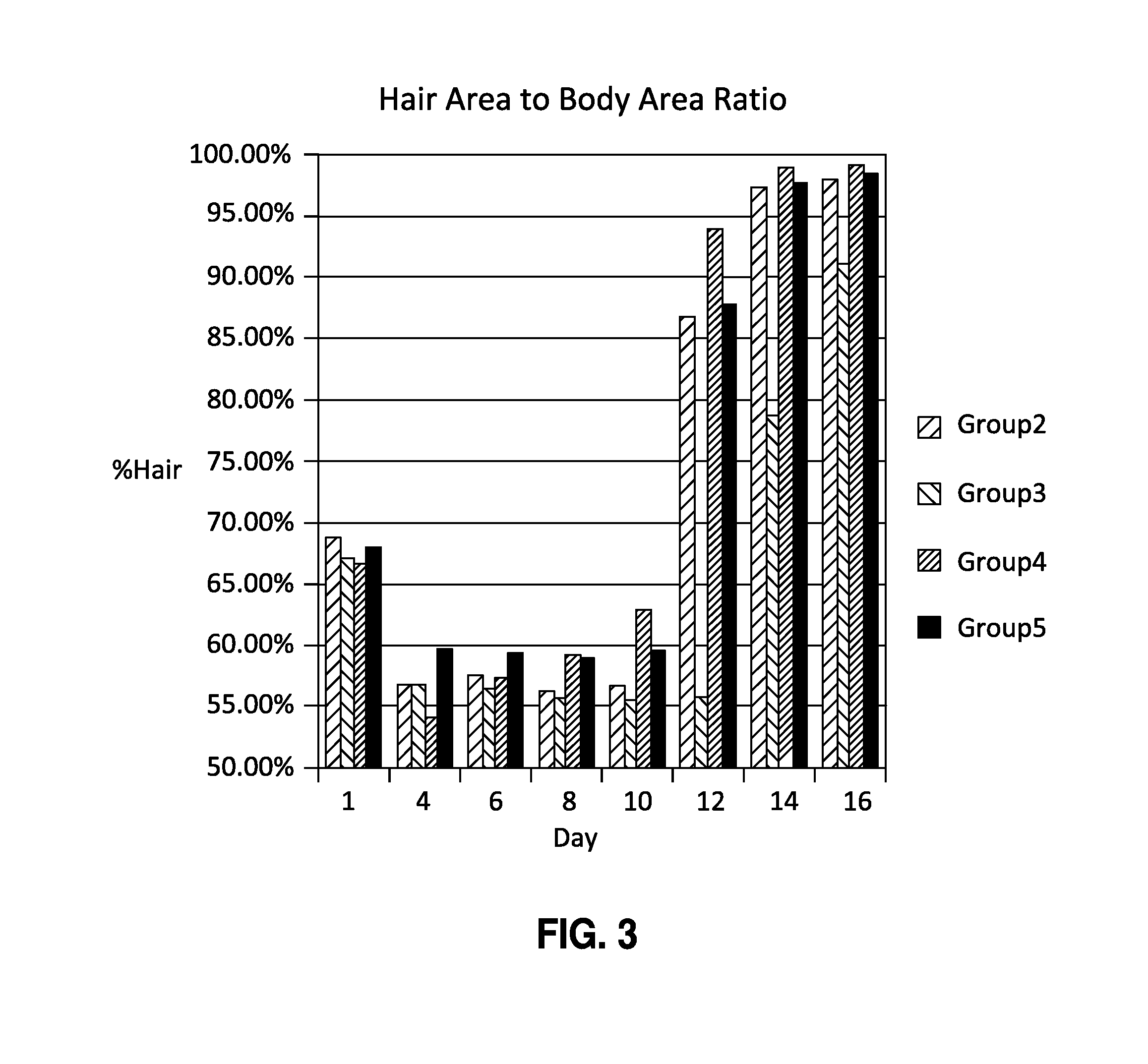
Compositions and methods for hair growth
InactiveUS20150164765A1Promote growthPrevent graying of hair or loss of melanin or pigmentCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsHair streamsHair growth
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods comprising the use of bimatoprost and cyclosporine, used concurrently and in combination, to grow hair and for the treatment of all types of hair loss conditions such as but not limited toalopecia areata. The present invention is also directed to compositions containing bimatoprost and cyclosporine A to grow hair on the scalp and other areas of the body and methods of administration of the compositions.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Methods to measure immunosuppressive tacrolimus, sirolimus, and cyclosporin A complexes in a blood sample
The present invention provides methods, diagnostic assays, and diagnostic kits based on said methods, to determine levels of immunosuppressive complexes containing immunosuppressive drugs tacrolimus, sirolimus and cyclosporine A separately and in combination, formed in the blood of a drug-treated patient or in a patient candidate to immunosuppressive drug therapy. These methods, assays and kits are especially useful when using automated systems.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
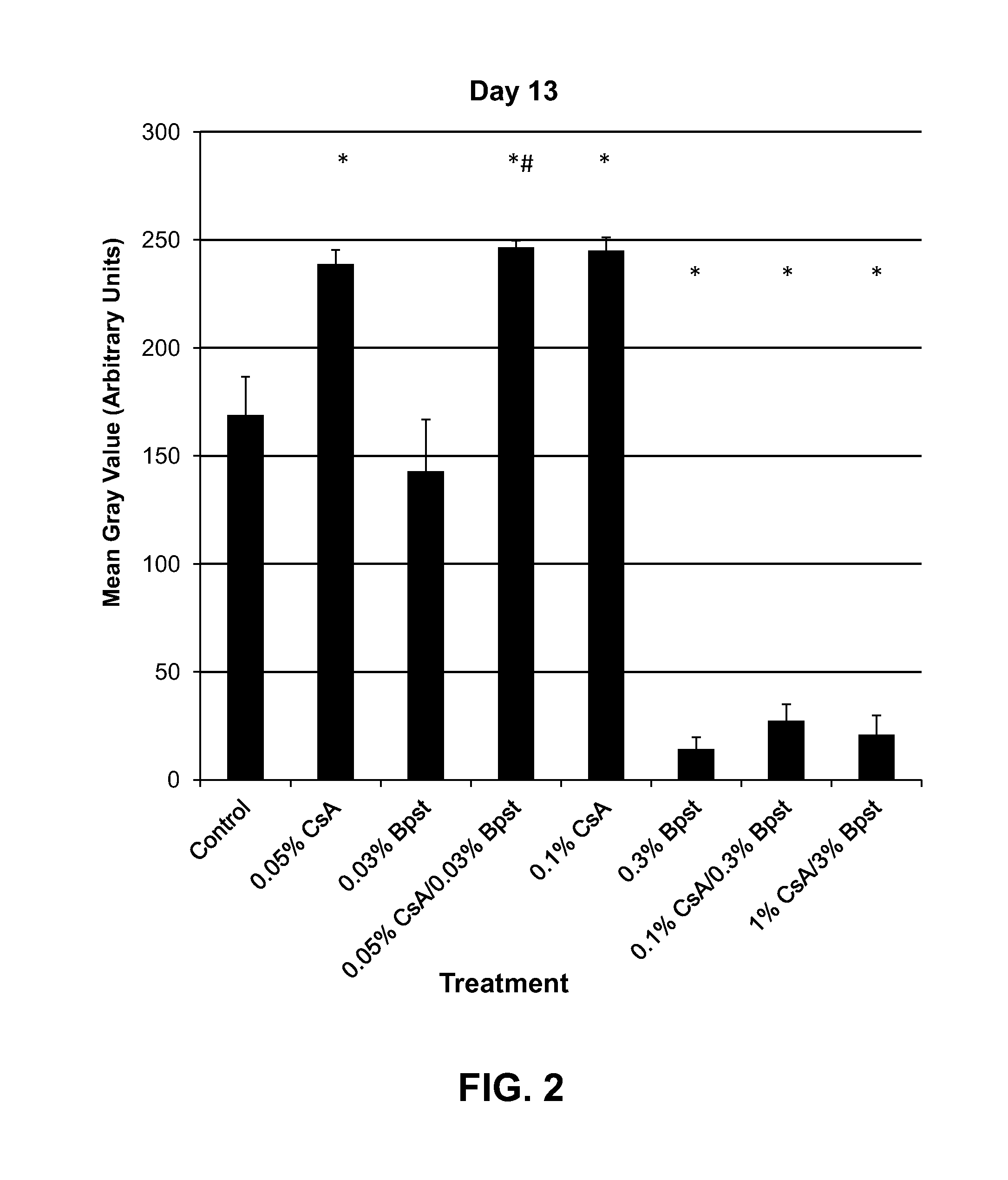
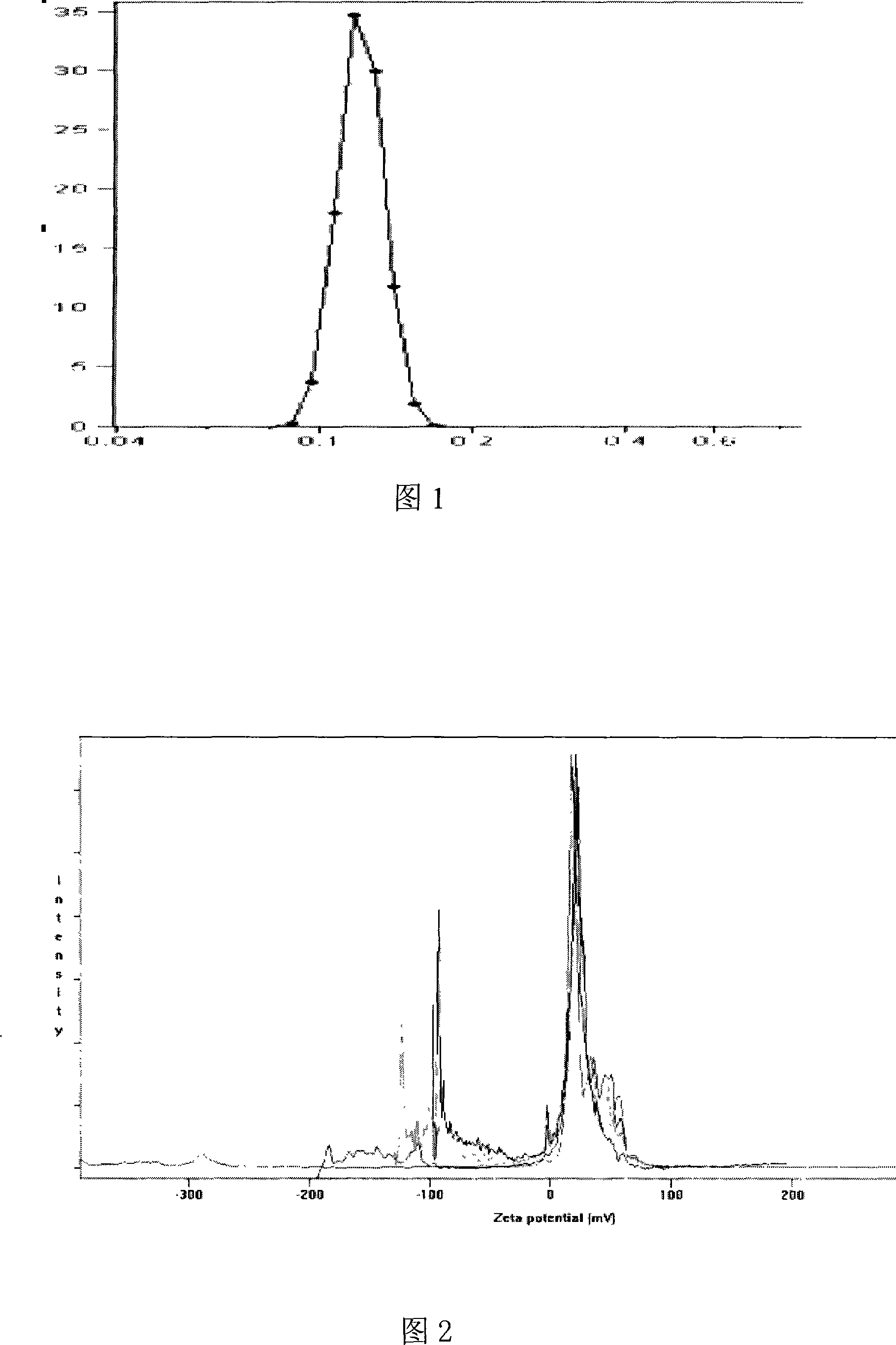
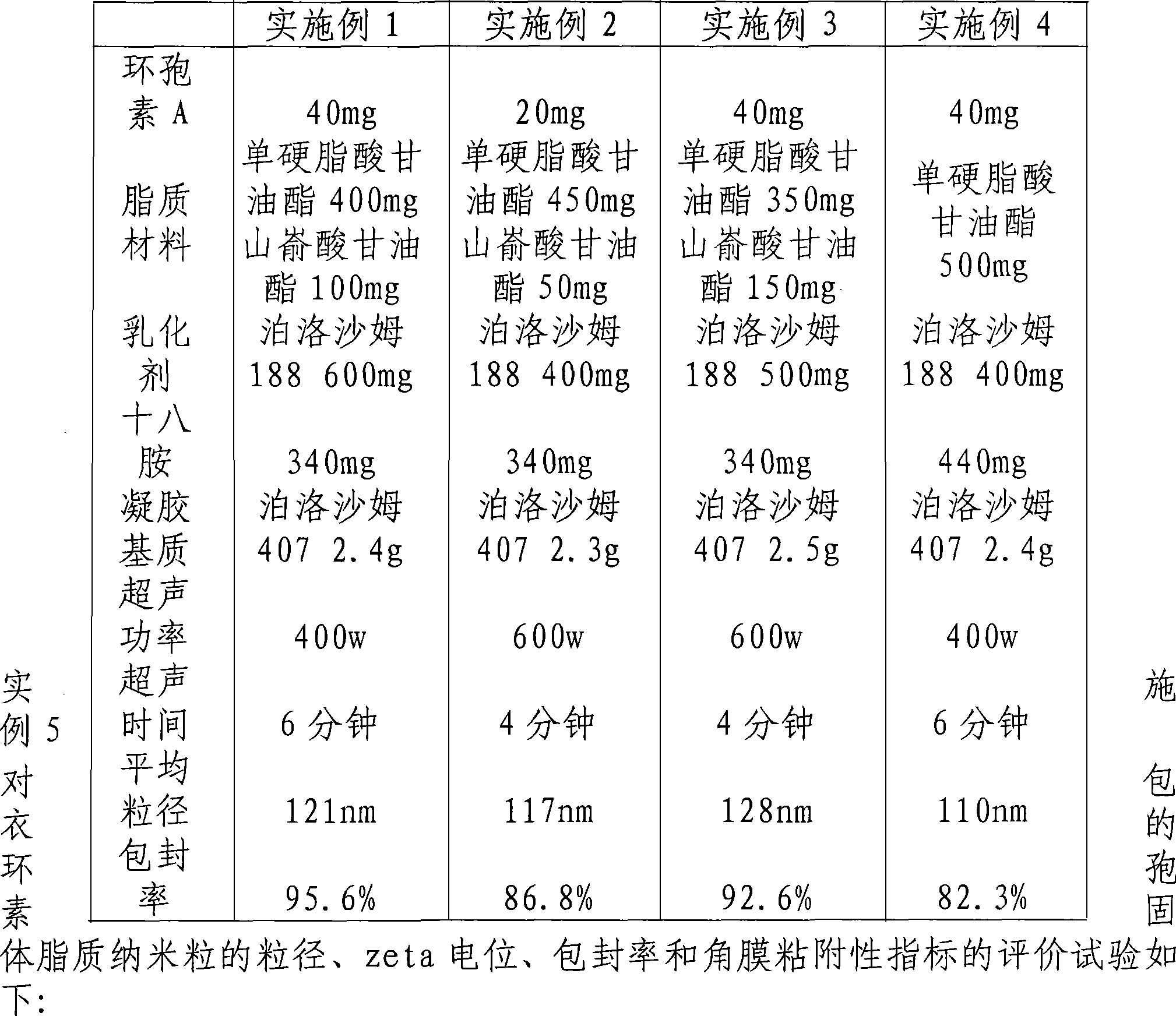
Solid lipid nanometer particle in-situ gel rubber preparations of biological adherent cyclosporine A and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101181227AImprove stabilityReduce dosageCyclic peptide ingredientsImmunological disordersLipid formationZeta potential
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Cyclosporin a compositions
InactiveUS20070219127A1Stable and long-term shelf-livesLong shelf-livesPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseCiclosporin
A composition comprising cyclosporin A and a nonaqueous, physiologically acceptable liquid carrier, said composition being suitable for topical administration to an eye of a mammal is disclosed herein. Methods of treating disease related thereto are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com