Preparation of pharmaceutical compositions
a technology of compositions and pharmaceuticals, applied in the field of cyclosporins, can solve the problems of ineffective oral therapy, variable and incomplete absorption of gi tract, failure of graft rejection and failure,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
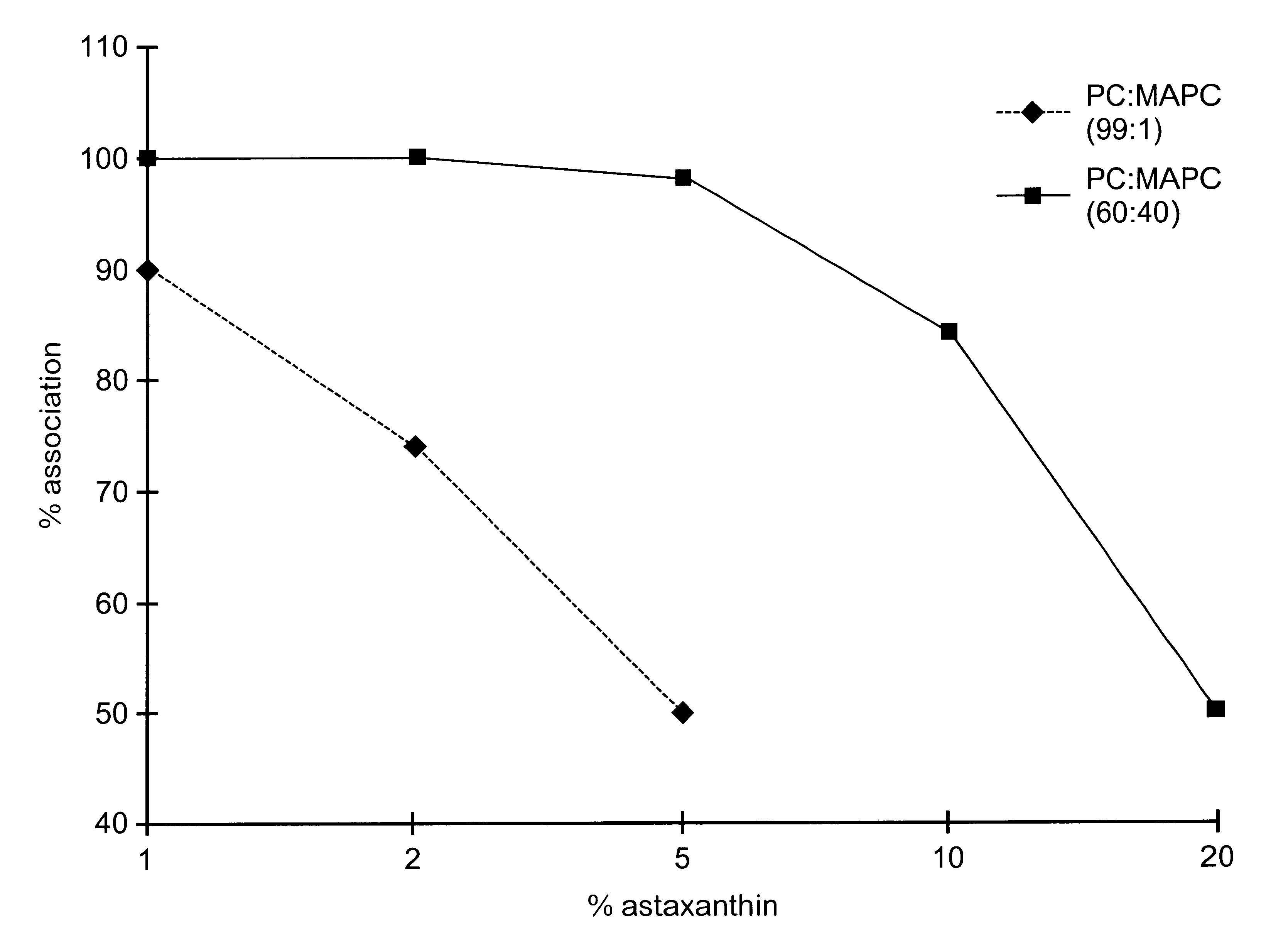
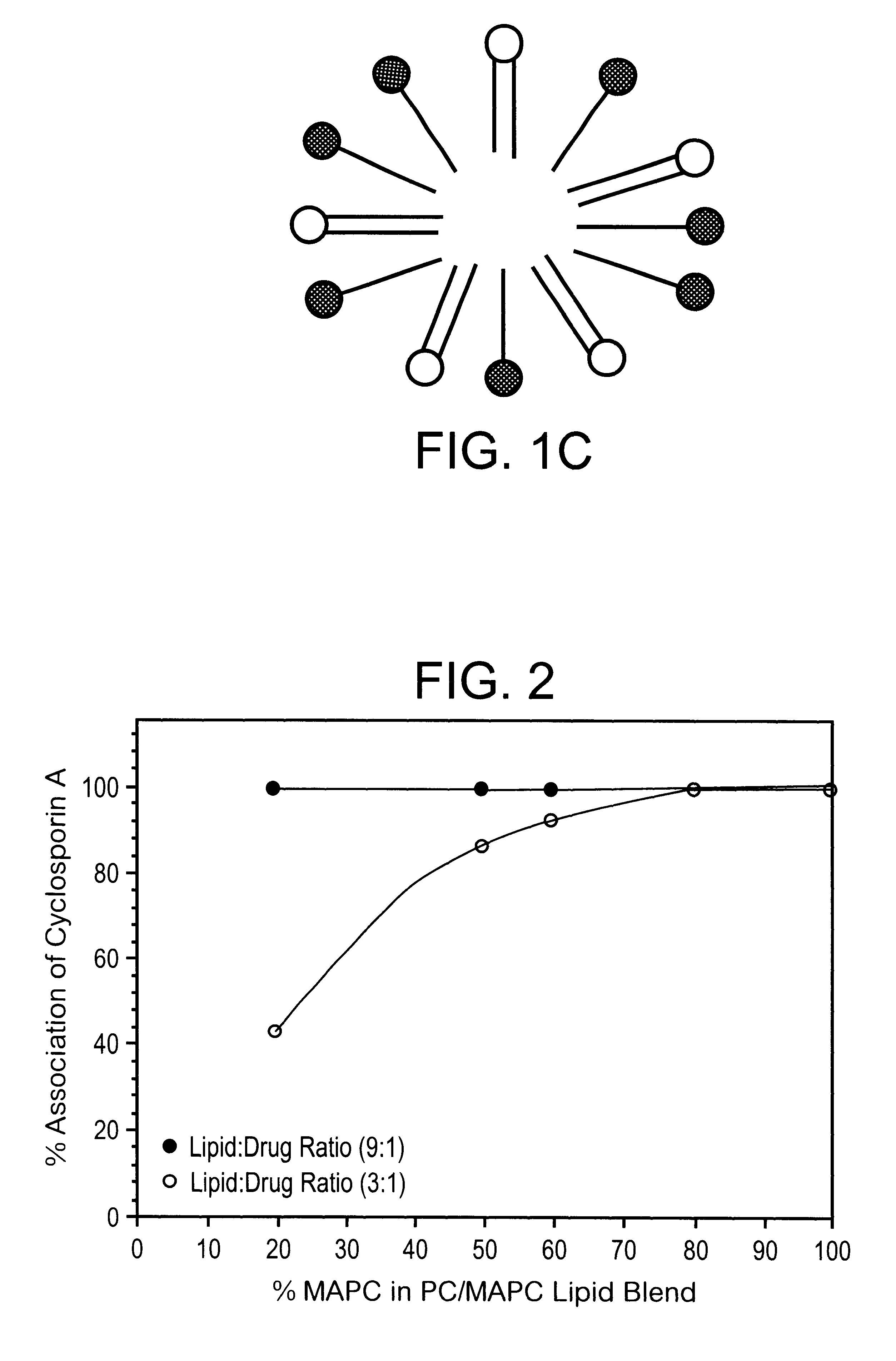
A mixture of 100 g PC, MAPC and CyA in the molar ratios 28:2:1 was dissolved in 75 g of ethanol in a closed container to obtain a homogenous solution, as in Example 1. The required ratio of PC / MAPC in the blend was obtained by adding pure PC to the blend used in Example 1. The resultant lipid composition following removal of the ethanol was a viscous paste. A small quantity of glycerol was mixed in with the paste-like material and worked in, to turn it into a less viscous gel. This CyA lipid composition was filled into soft gelatine capsules. Each capsule contained 50 mg of CyA in association with the lipid.
example 3
A mixture of 100 g of PC, MAPC and CyA in the molar ratios 5:5:1 was dissolved in 100 g of ethanol in a closed container as described in Example 1. The mixture of lipid was obtained by blending PC and PC / MAPC mixtures as in Example 2. The resultant lipid composition following removal of the ethanol was a soft wax. A small quantity of triglyceride (miglyol) was blended into the composition to lower its viscosity and facilitate filling into gelatine capsules. In practice, it was often found to be more convenient to add excipients of this type to the ethanolic solution of the components prior to solvent removal.
example 4
A composition containing 100 g PC, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidyl inositol, MAPC, and CyA in the molar ratios 10:7:3.5:1:1 was dissolved in 75 g of ethanol under gentle heat, with stirring, as in Example 1 until no crystals of CyA could be detected. The ethanol was removed under vacuum until a clear gel was obtained. The resultant CyA lipid mixture obtained contained >5% ethanol. This was filled into gelatine capsules each containing 50 mg CyA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| w/w | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com