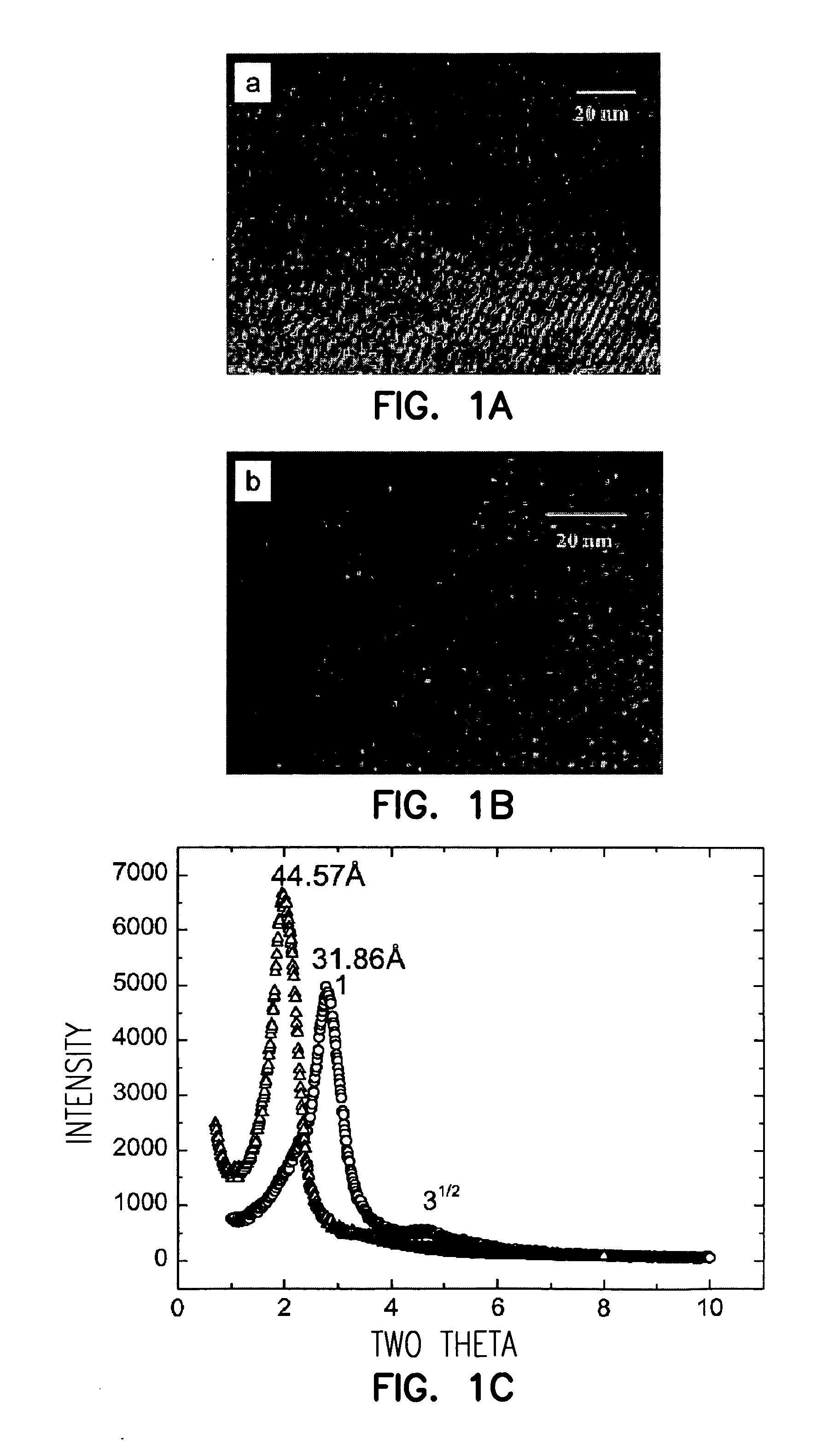
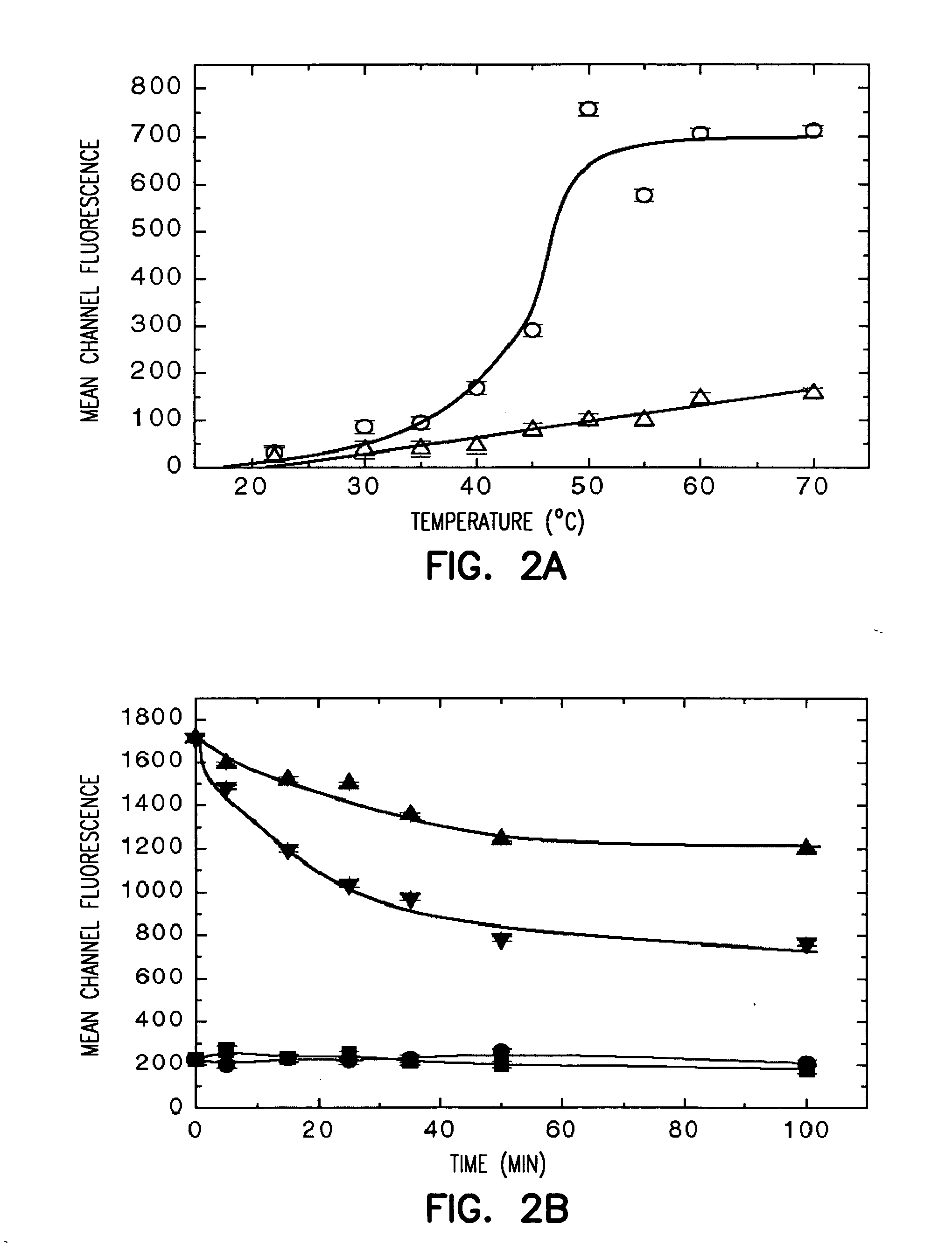
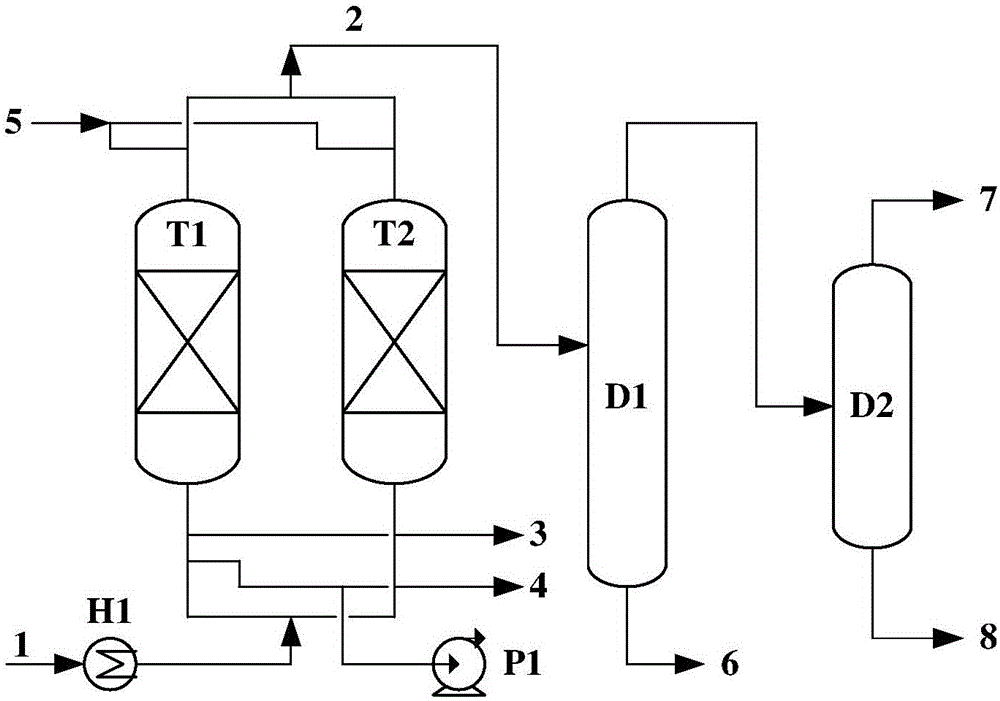
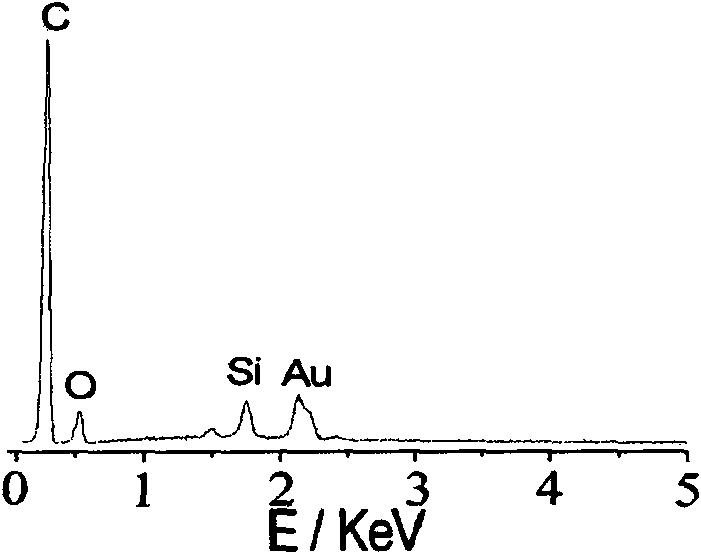
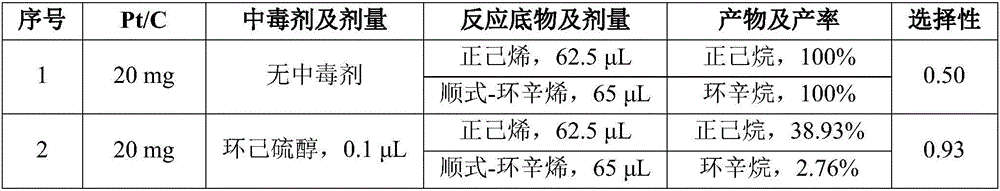
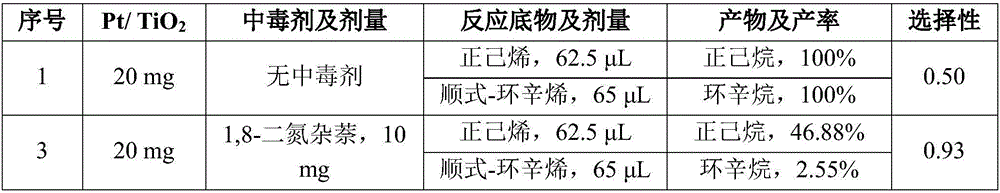
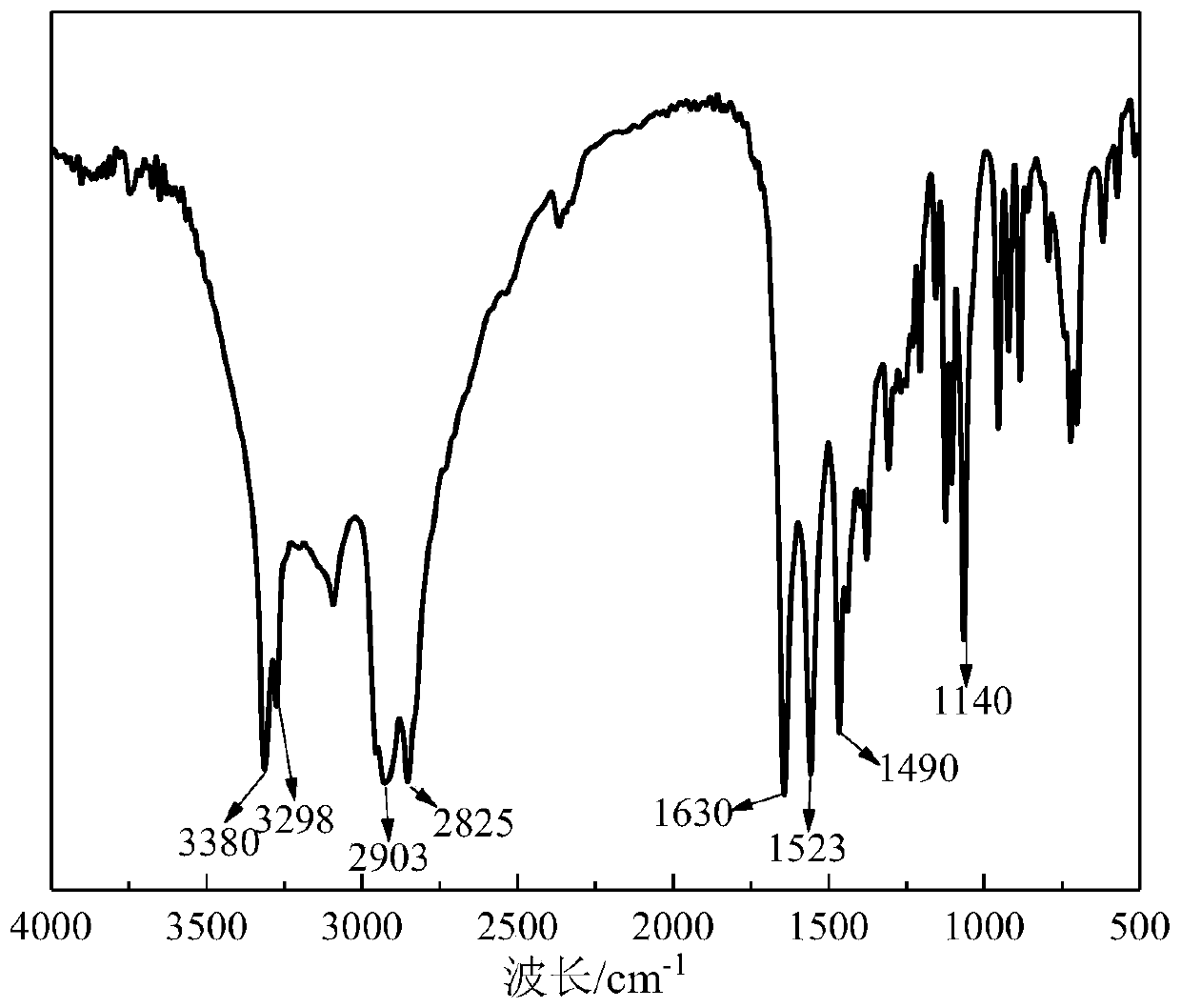
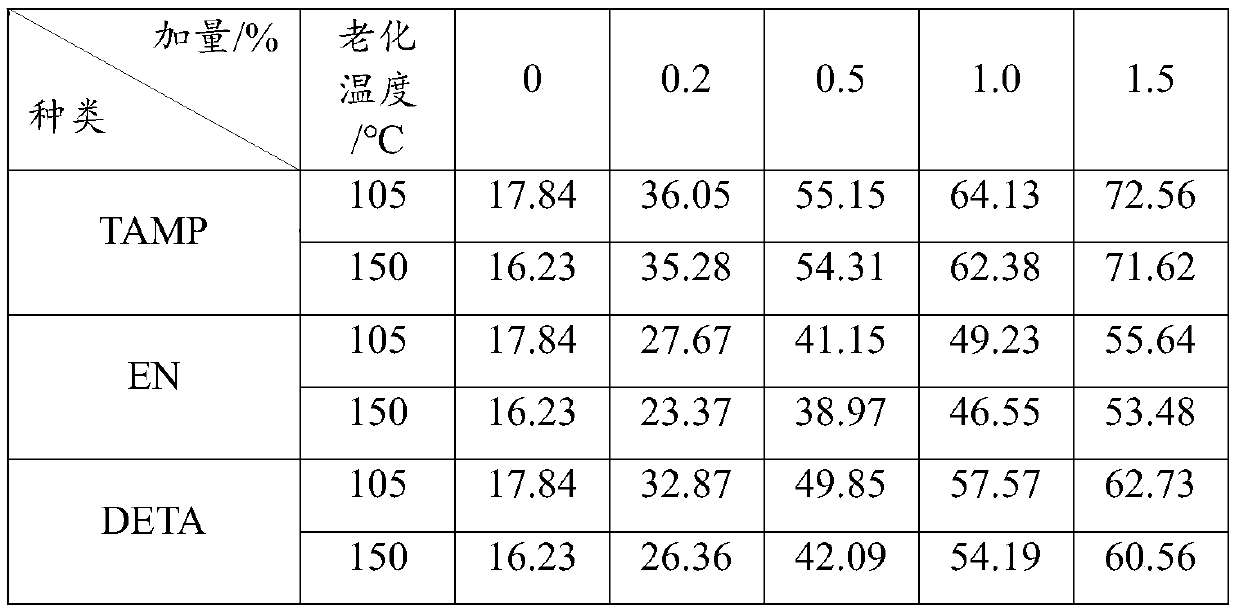
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Molecular dimensions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stimuli responsive mesoporous materials for control of molecular transport
InactiveUS20050013988A1Increase in inter-pore spacingModulating transportSilicaLayered productsStimuli responsiveChemical physics
The present subject matter relates generally to design, synthesis, and characterization of materials with well-defined porous networks of molecular dimensions in which the size and surface energy of the pores can be externally and reversibly controlled to dynamically modulate the adsorption and transport of molecular species.
Owner:FU QIANG +8
Modified compound kieselguhr adsorbing agent for treating industrial wastewater and preparation method
The invention relates to a modified compound kieselguhr adsorbing agent for treating industrial wastewater and a preparation method. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, modifying a diatomite subjected to ore-dressing purification and calcinations by using an organic quaternary ammonium salt, and then uniformly mixing the modified diatomite, attapulgite and de-magnesium silicon residues of serpentine at mass percentage of (60%-75%):(5%-35%):(5%-35%), thereby preparing the modified compound kieselguhr adsorbing agent. In the modified compound kieselguhr adsorbing agent, three porous mineral materials, namely, the diatomite modified by quaternary ammonium salt, the attapulgite and de-magnesium silicon residues of serpentine can give play to individual strengths, can collaboratively match one another and can selectively absorb the organic and inorganic pollutants in different types and molecular dimensions. The modified compound kieselguhr adsorbing agent is fit for treating the industrial wastewater in complex pollutant components and higher concentration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Optimized utilization method for light naphtha
InactiveCN106318459ADistillation purification/separationTreatment with plural serial refining stagesAlkaneNaphtha
The invention discloses an optimized utilization method for light naphtha. According to the method, firstly, the light naphtha passes through an adsorptive separation unit, adsorbed remaining oil rich in iso-alkanes and desorbed oil rich in n-alkanes can be obtained separately, and the desorbed oil can directly serve as an ethylene cracking stock; and the adsorbed remaining oil then passes through a rectifying unit, and a gasoline mixture rich in iso-C6 and high-purity isopentane can be obtained separately. According to the optimized utilization method for the light naphtha, an adsorptive separation-rectifying separation coupled process is adopted, the adsorptive separation unit uses a high-performance adsorbent, and the adsorbent can be used for achieving the distinct partition of the n-alkanes and the iso-alkanes according to molecular dimension difference, so that the selectivity is high, and the regeneration effect is good; and compared with the traditional multi-tower precise rectification, the method has the advantages that the energy consumption is low, and both the product purity and the product yield are relatively high.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM +1
Organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101628204AGood flexibilityNot suitable for breakingSemi-permeable membranesFiltrationPliability
The invention discloses an organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane and a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the field of membrane materials. The preparation method thereof includes three steps, namely the preparation of precursor solution, the filtration preparation of compound mesoporous membrane and the elution of surface active agent in the membrane, namely that the method of filtration is mainly used for assembling inorganic mesoporous materials in pores in a polycarbonate membrane so as to prepare the compound membrane, and the mode of extraction and elution is utilized for eliminating the surface active agent in the compound membrane, thereby obtaining the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane; and the pore diameter of the mesoporous material in the membrane is 3.0nm or 8.0 nm. Compared with the formerly reported inorganic compound mesoporous membrane, the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane has better flexibility, hard breakage and better acid and alkali resistance. Besides, due to the ordering and the nanometer size effect of the pore diameter of the mesoporous structure, the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane can be applied to the fields of molecular dimension selective transfer, membrane separation, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Redox-Flow Batteries Employing Oligomeric Organic Active Materials and Size-Selective Microporous Polymer Membranes
Intermittent energy sources, including solar and wind, require scalable, low-cost, multi-hour energy storage solutions to be effectively incorporated into the grid. Redox-flow batteries offer a solution, but suffer from rapid capacity fade and low Coulombic efficiency due to the high permeability of redox-active species across the battery's membrane. Here we show that active-species crossover can be arrested by scaling the membrane's pore size to molecular dimensions and in turn increasing the size of the active material to be above the membrane's pore-size exclusion limit. When oligomeric redox-active organic molecules were paired with microporous polymer membranes, the rate of active-material crossover was either completely blocked or slowed more than 9,000-fold compared to traditional separators at minimal cost to ionic conductivity. In the case of the latter, this corresponds to an absolute rate of ROM crossover of less than 3 μmol cm−2 day−1 (for a 1.0 M concentration gradient), which exceeds performance targets recently set forth by the battery industry. This strategy was generalizable to both high and low-potential ROMs in a variety of electrolytes, highlighting the importance of macromolecular design in implementing next-generation redox-flow batteries.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
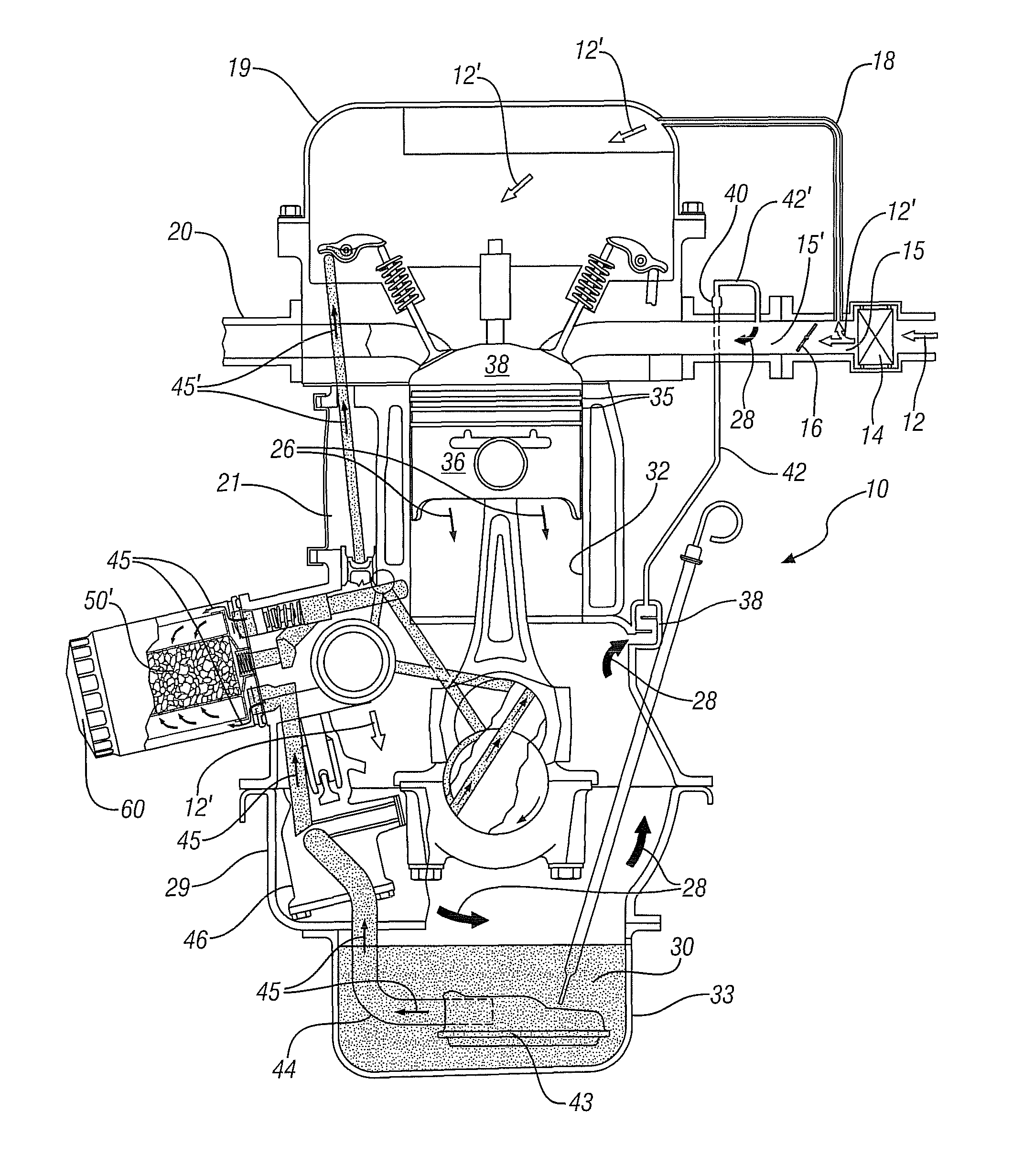
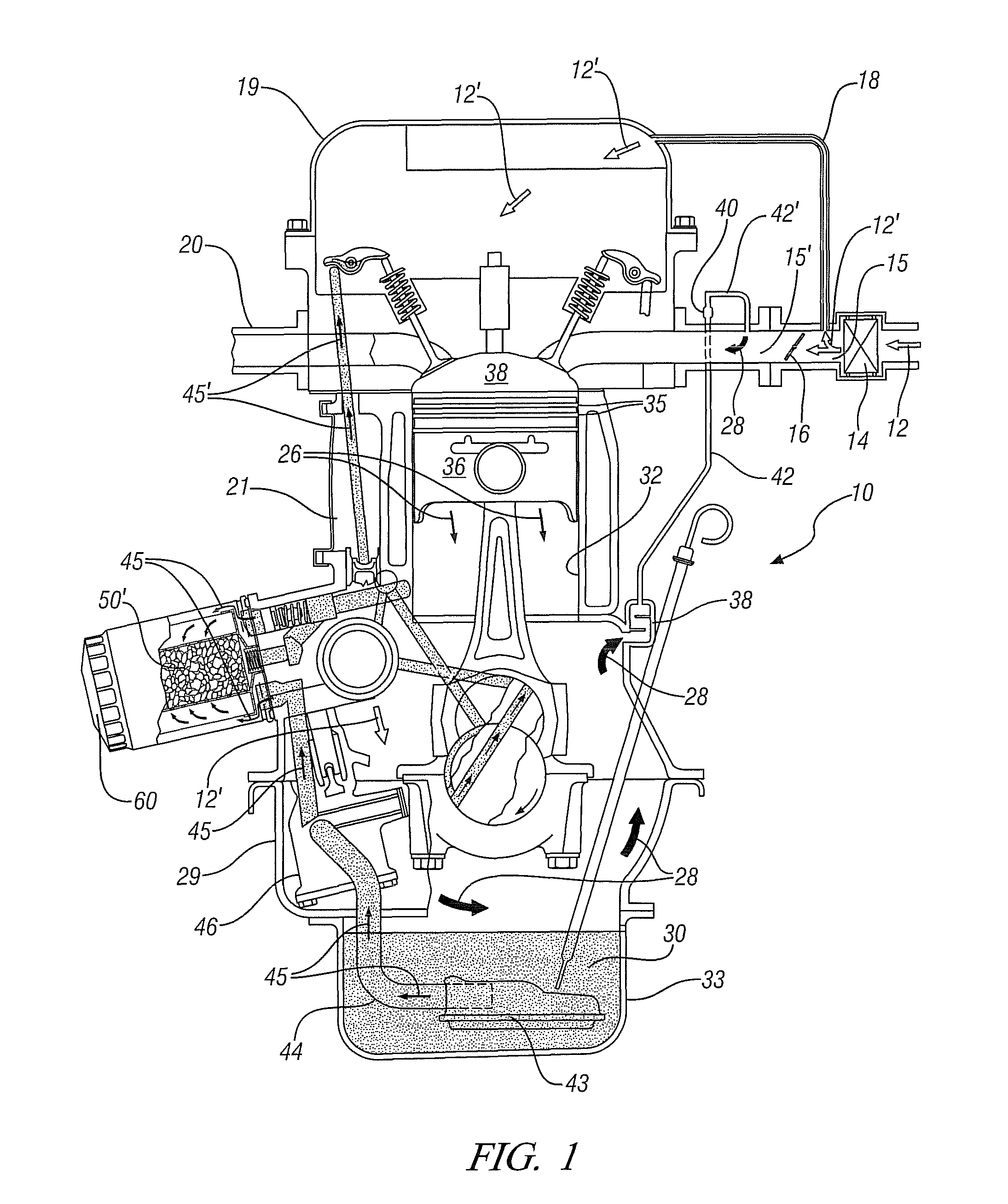
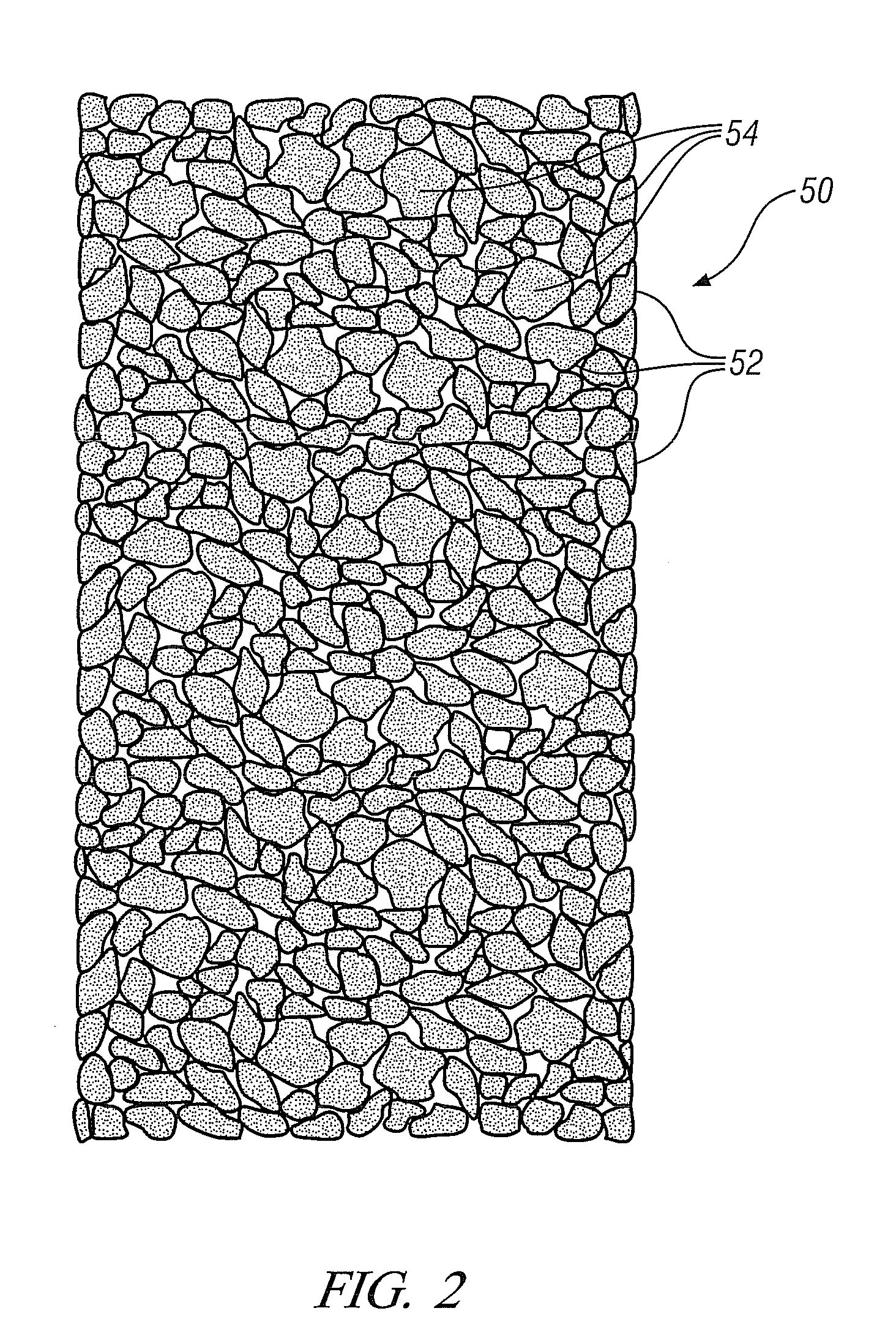
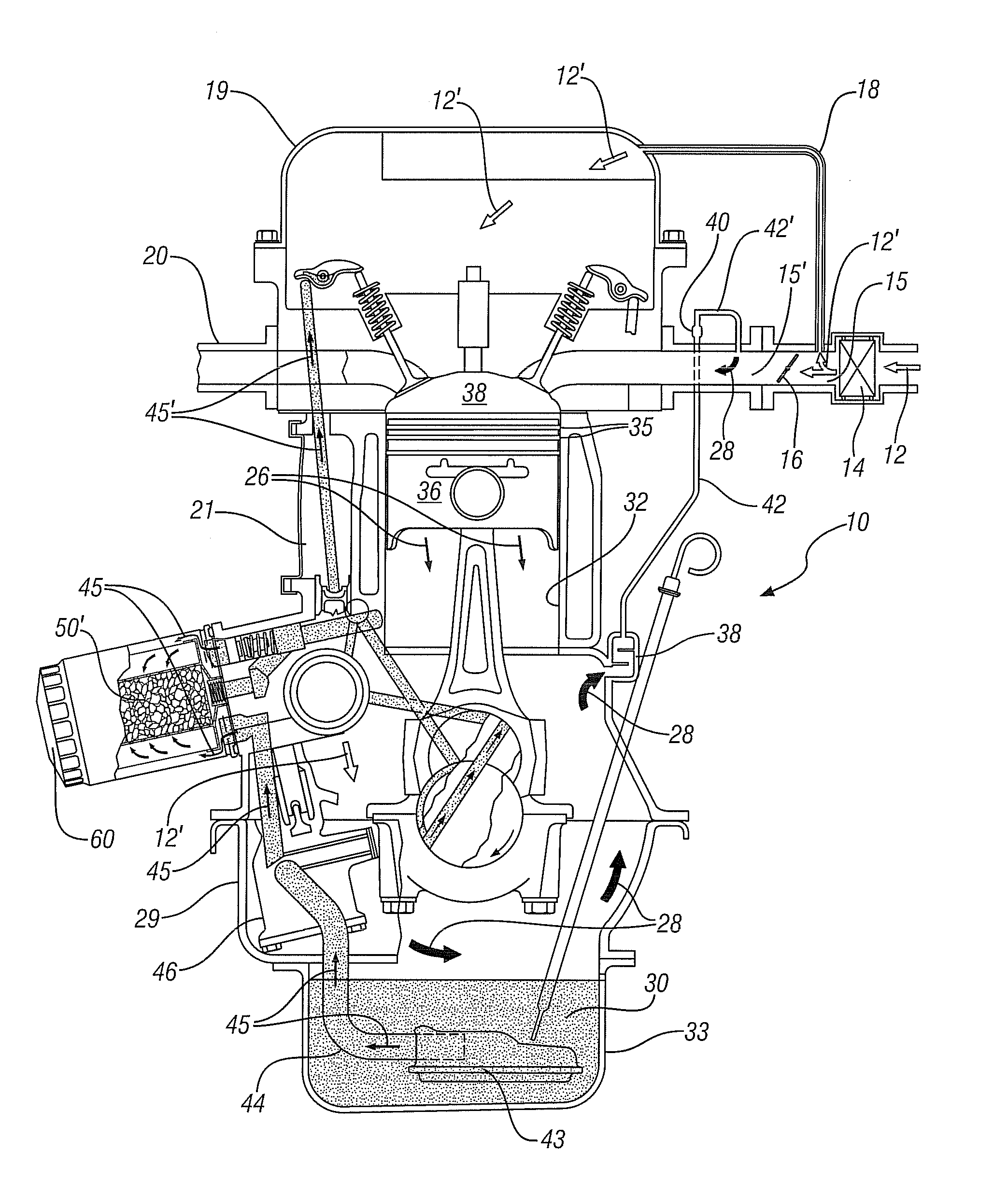
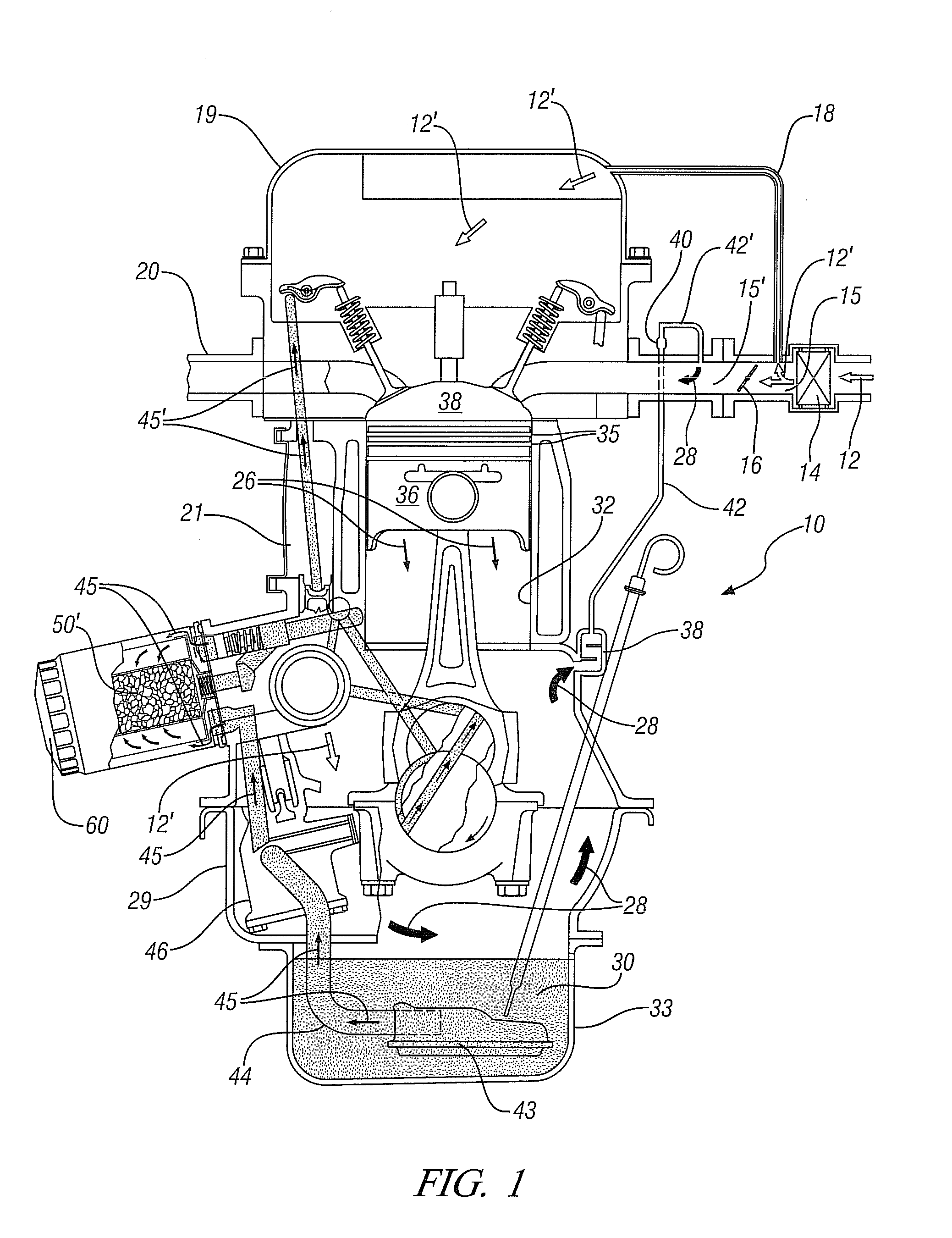
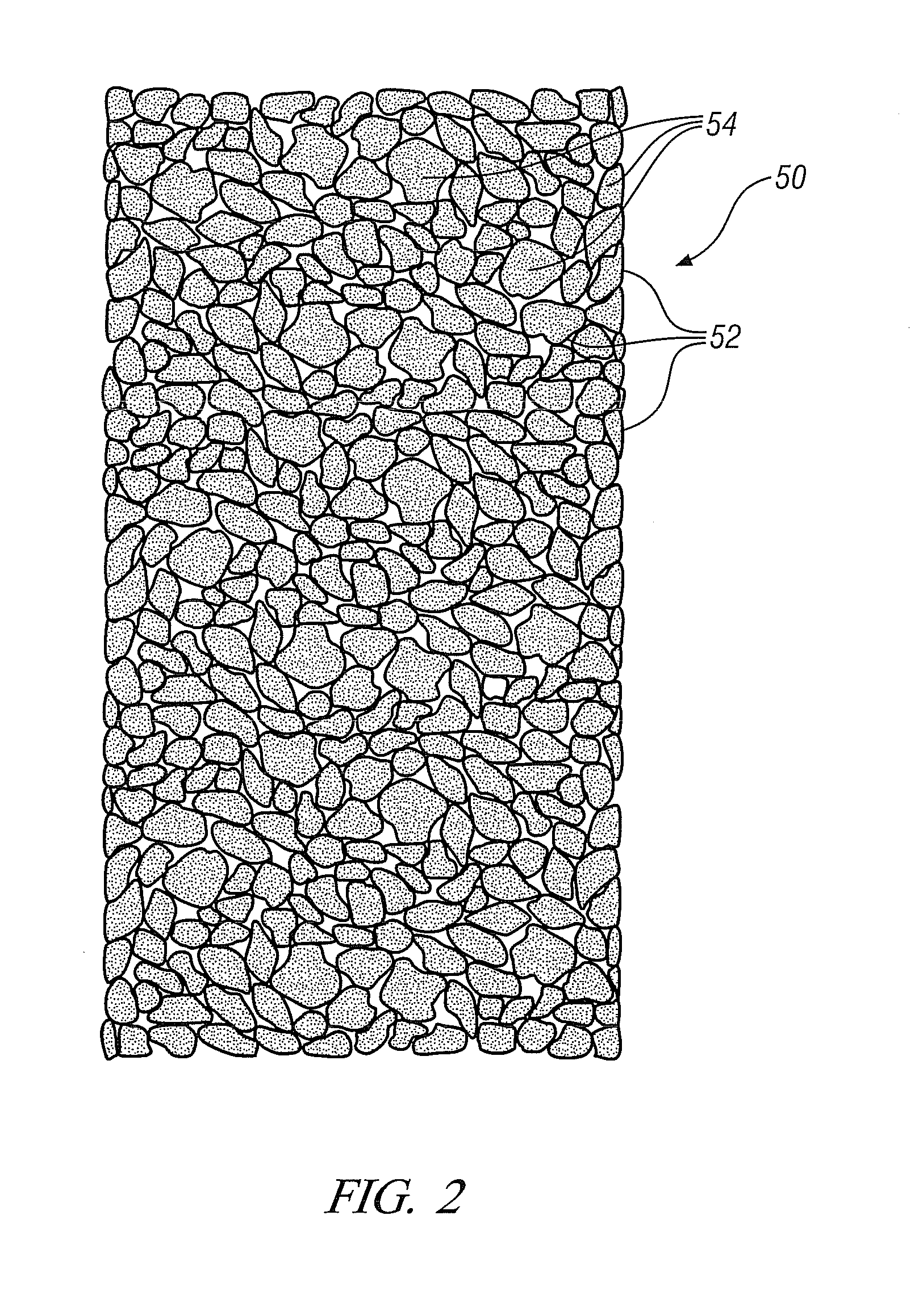
Adsorbent structures for removal of water and fuel contaminants in engine oil
InactiveUS8161953B1Improve the lubrication effectExtensive interactionLubrication of auxillariesIon-exchanger regenerationCombustionAlcohol
Devices and methods for removal of condensed, blow-by contaminants with small molecular dimensions from the circulating lubricating engine oil of internal combustion engines, including automotive engines, with a positive crankcase ventilation system are disclosed. These condensable blow-by contaminants include water, alcohols and hydrocarbons with preponderantly seven or fewer carbon atoms. A macroporous structure comprising alumino-silicate particles with micro-pores is at least partially immersed in the circulating oil. The micro-pores are sized to adsorb the small, condensed, blow-by, contaminant molecules but not the larger oil molecules. The particles may be multi-layered, with an inner layer adapted for adsorption of polar molecules. Adsorption is most extensive at lower oil temperatures and decreases as the oil temperature increases. Thus at low temperatures the contaminant molecules may be adsorbed, removed from the oil and temporarily stored in the micropores. At high temperatures some of the contaminants will desorb and be re-incorporated in the oil. The desorbed contaminants will be carried with the higher temperature oil into the engine crankcase where they may vaporize and be removed by the engine positive crankcase ventilation system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Chromatographic treatment method of industrial wastewater containing paranitroaniline
InactiveCN106430398AEfficient removalEfficient recyclingAmino compound purification/separationSpecific water treatment objectivesP-NitroanilineIndustrial wastewater treatment
The invention relates to a chromatographic treatment method of industrial wastewater containing paranitroaniline and belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment. According to the invention, a multi-performance macroporous adsorption resin combination chromatographic method is adopted, thereby effectively adsorb paranitroaniline in wastewater, paranitroaniline in wastewater can be effectively eliminated and recycled. According to the characteristics of wastewater containing paranitroaniline mother liquid and the molecular dimension and the physicochemical property of paranitroaniline molecules, a nonpolar macroporous adsorption resin D-141, a moderately polar macroporous adsorption resin D-145 and a strongly polar macroporous adsorption resin D-160 are combined to treat the wastewater, thereby obtaining a relatively good treatment process technology.
Owner:赵佳
Rubber anti-aging paint, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107118656AHigh strengthDoes not affect processabilityPretreated surfacesEpoxy resin coatingsPolymer scienceAdditive ingredient
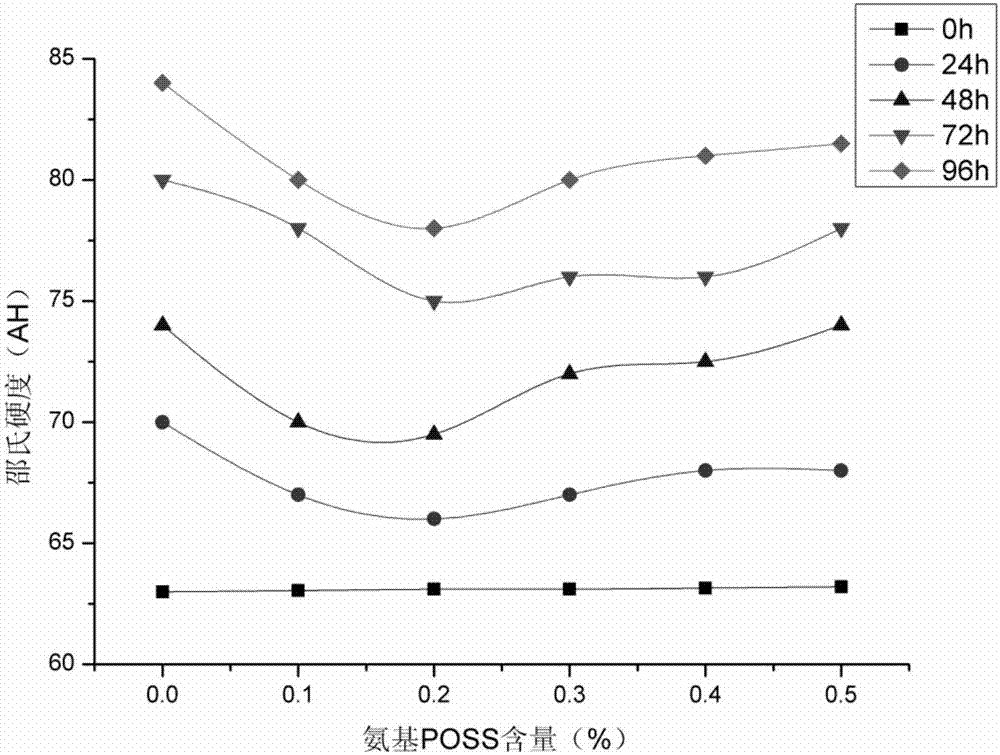
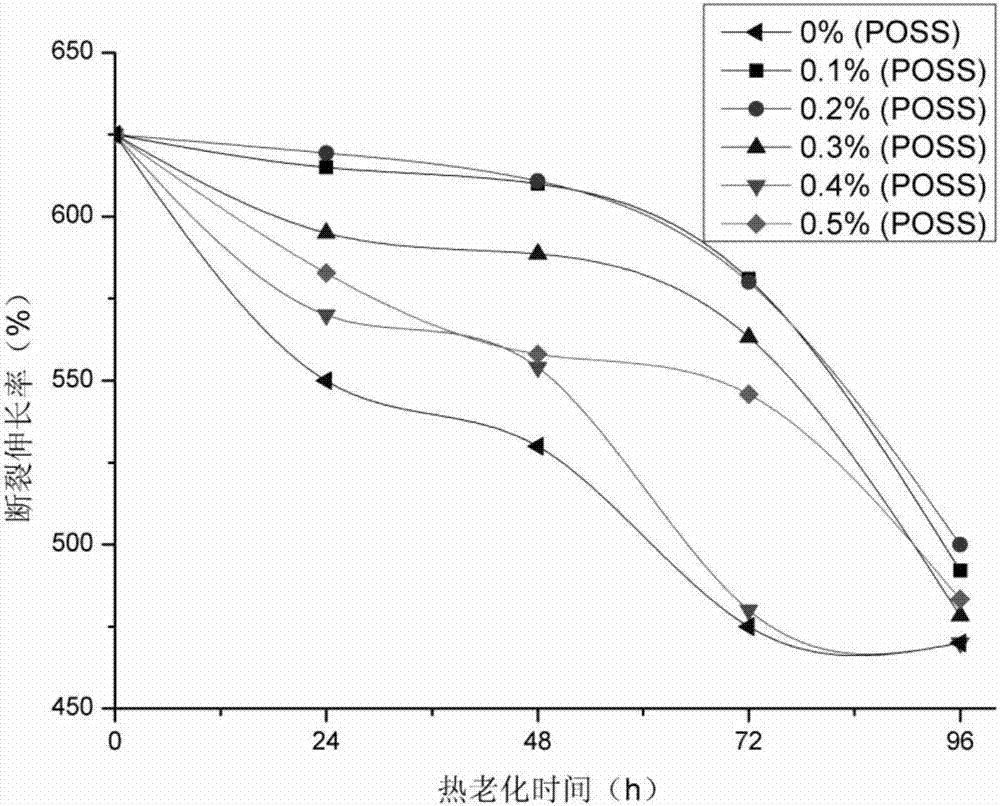
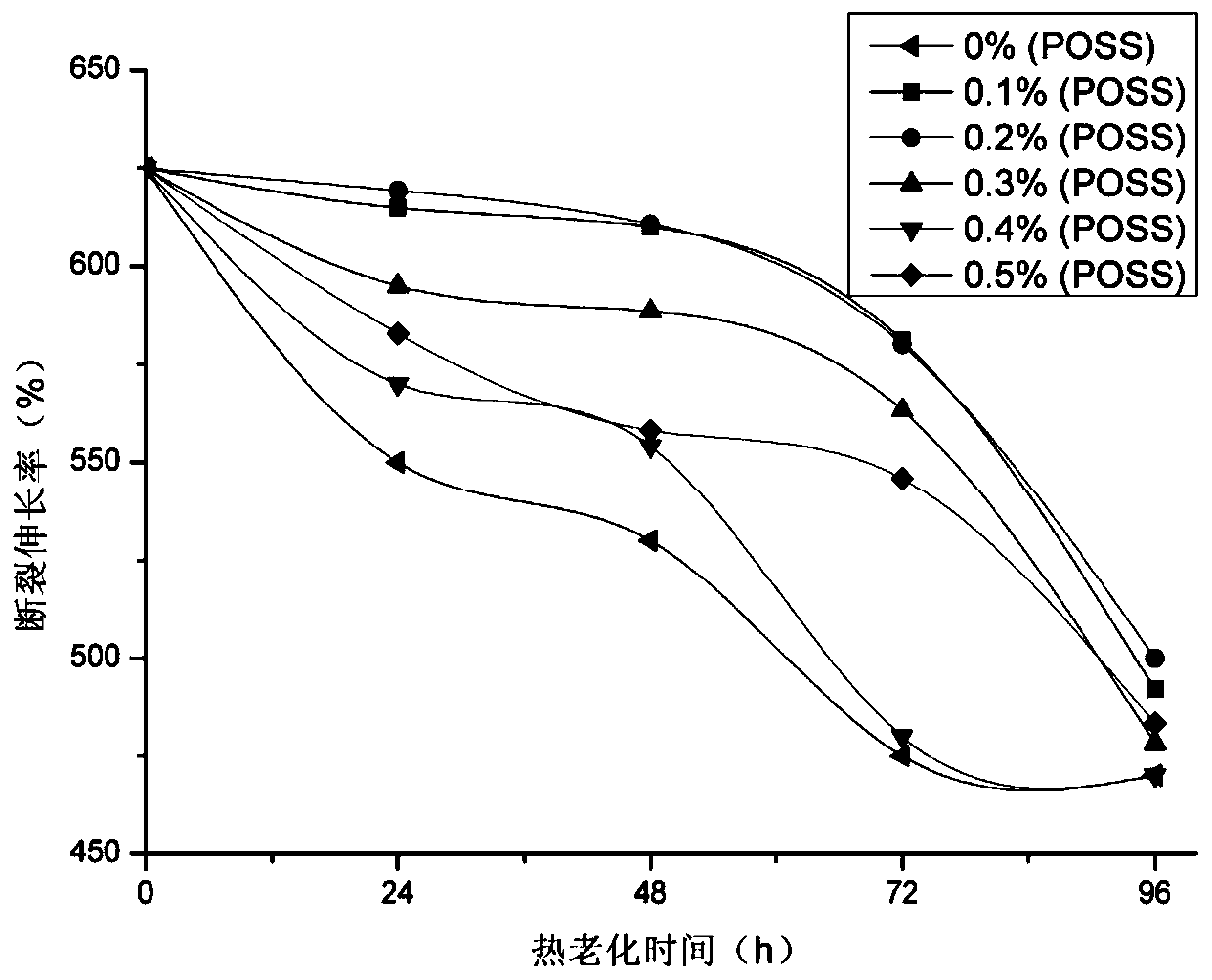
The invention provides rubber anti-aging paint, and a preparation method and application thereof. The rubber anti-aging paint comprises the following ingredients in parts by weight with the total weight being 1000 parts: 200 to 350 parts of resin, 0.2 to 3.5 parts of auxiliary agents, 0 to 5 parts of POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) and 641.5 to 799.8 parts of water. The paint can be used as a rubber coating. The rubber anti-aging paint provided by the invention comprises the POSS; the POSS can improve the intensity of the coating after film forming; through a cage-shaped three-dimensional structure, the self molecular dimension is larger; potential physical cross linking points are formed in the coating; the curing crosslinking of the paint is facilitated, so that the coating inside structure stability is improved; the sealing performance and the thermal stability of the coating are effectively increased. When the addition of the POSS is 0.2 percent, the improvement effect of the coating on the rubber is most obvious; the stretch intensity is 9.2 MPa; the break elongation rate is 620 percent.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Polyamide composite membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108126536AIncrease the degree of cross-linkingReduce thicknessSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisCross-linkPolyamide
The invention provides a polyamide composite membrane which is characterized by comprising a composite membrane body, wherein the composite membrane body comprises non-woven cloth, a porous support layer and a polyamide layer arranged sequentially; the polyamide layer is prepared by an interfacial polymerization reaction of a polyamine solution and a polyacyl chloride solution; and polyamine has astar type molecule structure. Polyamine with the star type molecule structure has the following advantages that: a, more cross-linked structure are easily formed during interfacial polymerization, sothat a nascent membrane structure is more compact; b, due to higher molecular weight and larger molecular dimension, polyamine more difficultly penetrates through the nascent membrane to continue toreact with trimesoyl chloride; and a formed functional layer is thinner; and c, during the subsequent interfacial polymerization with trimesoyl chloride, the original carbon skeleton is not changed todamage the performance of the membrane. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the polyamide composite membrane. The preparation method has the characteristics of simplified technology, easy control of technical parameters, good quality and the like.
Owner:湖南澳维膜科技有限公司
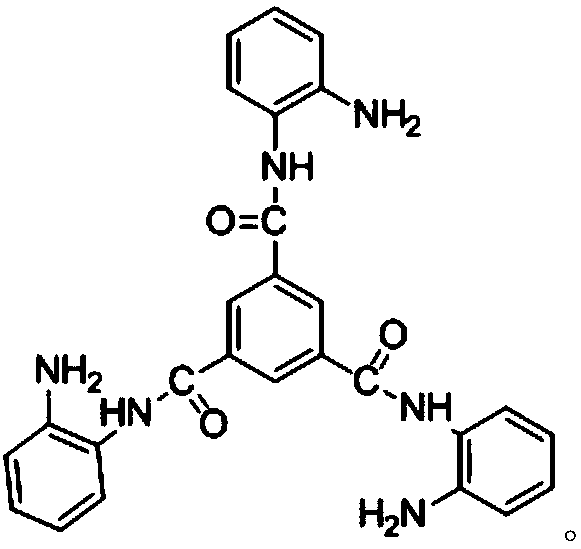
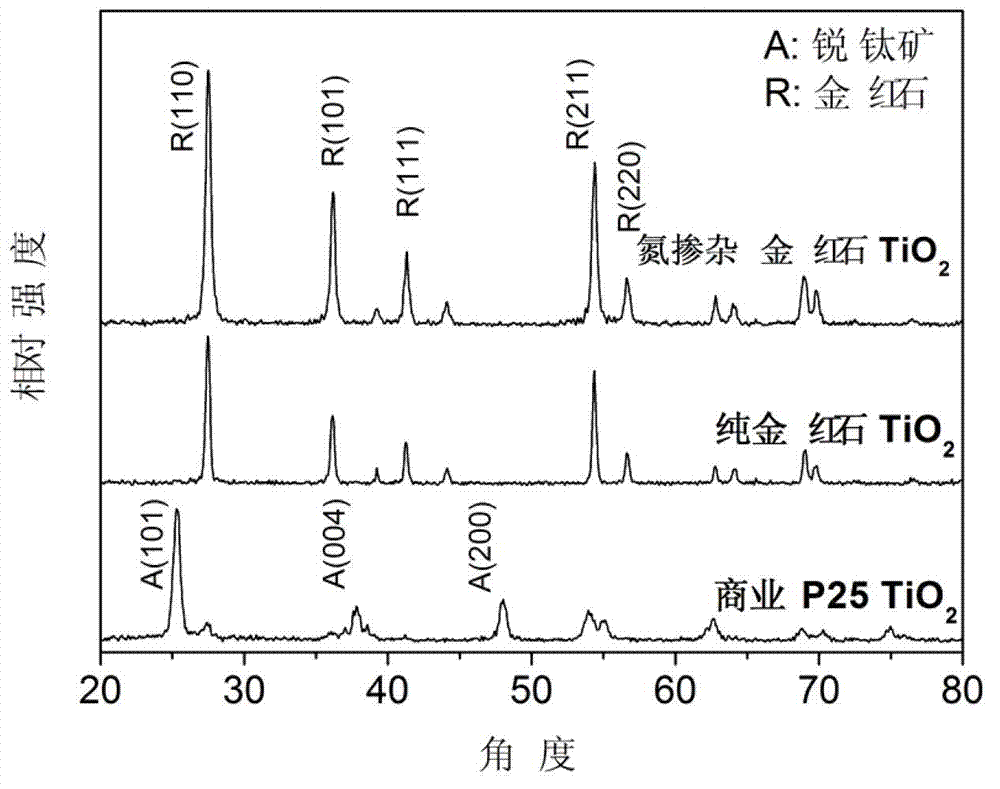
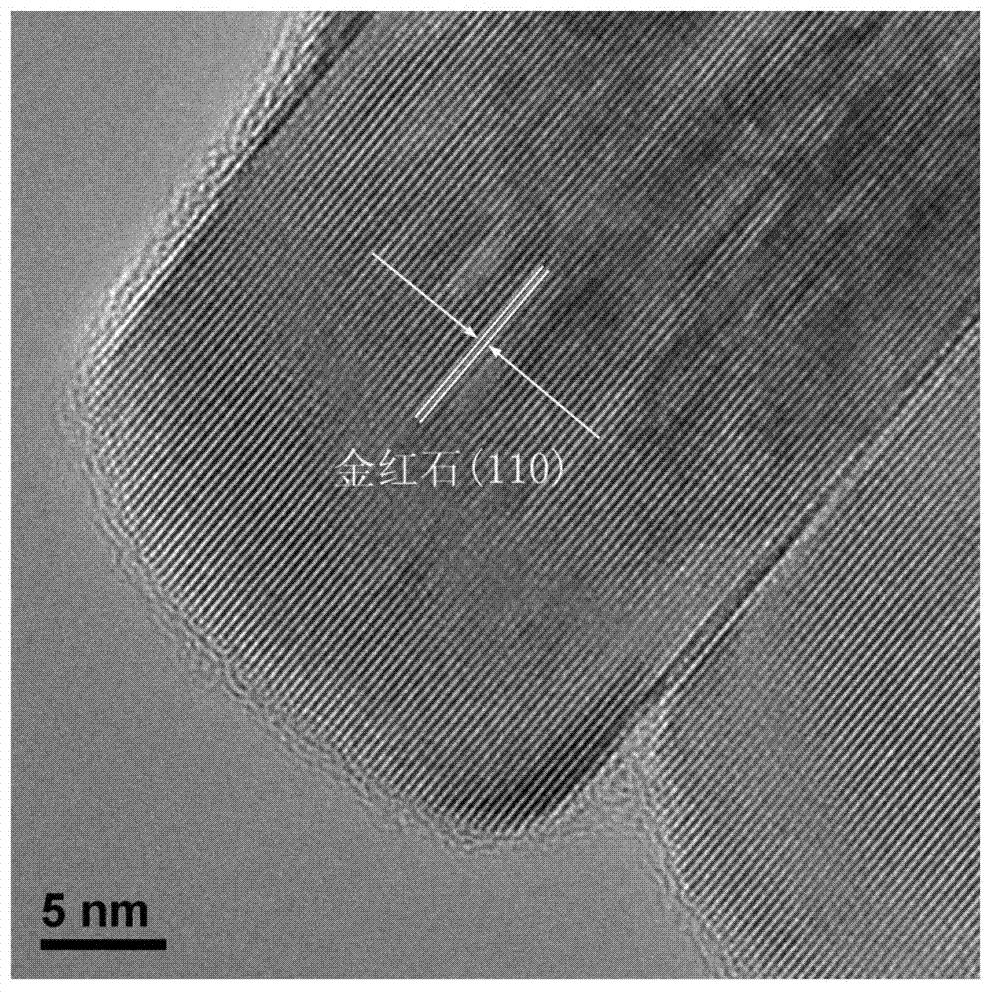
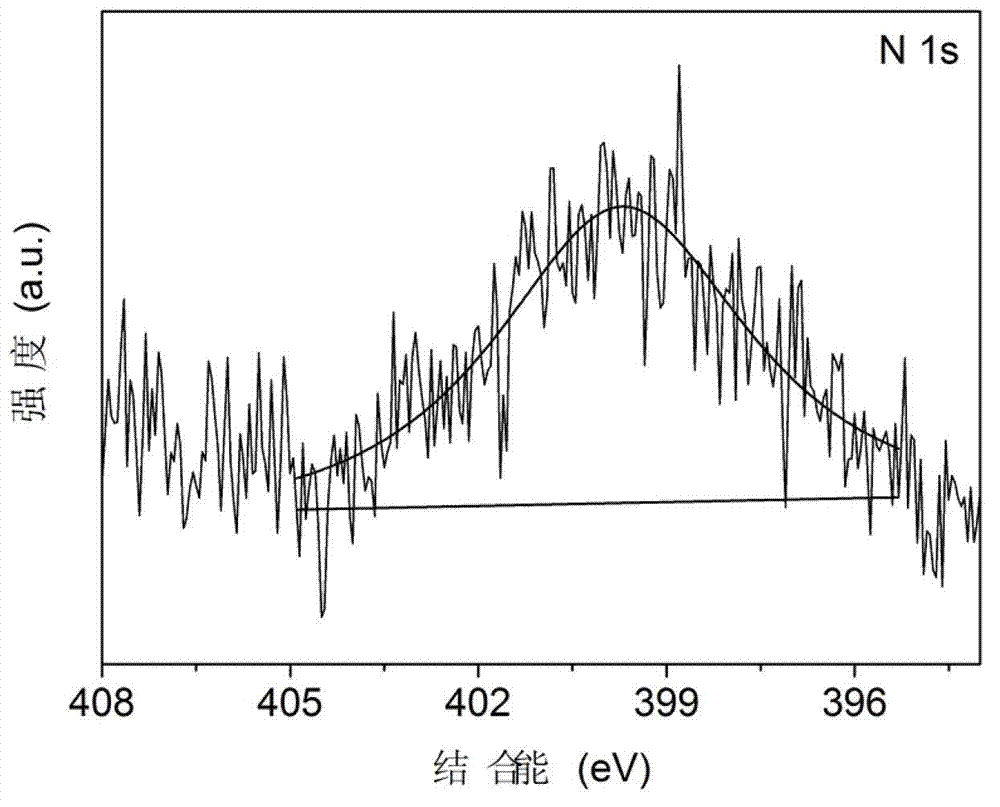
Method for preparing nitrogen-doped rutile TiO2 selective photocatalyst
InactiveCN102962089APhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationTitanium nitrideMethyl orange
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nitrogen-doped rutile TiO2 selective photocatalyst. The method disclosed by the invention comprises a step of mixing titanium nitride with nitric acid and hydrochloric acid to prepare a nitrogen-doped rutile TiO2 nanorod by hydrothermal reaction for selective photodegradation of an organic matter. An experiment confirms that the nitrogen-doped rutile TiO2 nanorod has selective photodegradation effect on methyl orange in a mixed aqueous solution system of methylene blue and the methyl orange, and illustrates that the nitrogen-doped rutile TiO2 nanorod has selective photodegradation capacity on the organic matters with approximate molecular dimensions, and the degradation capacity is from an unsaturated chemical bond formed by surface nitrogen-doped atoms. A new way for achieving selective photodegradation is developed by the invention.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
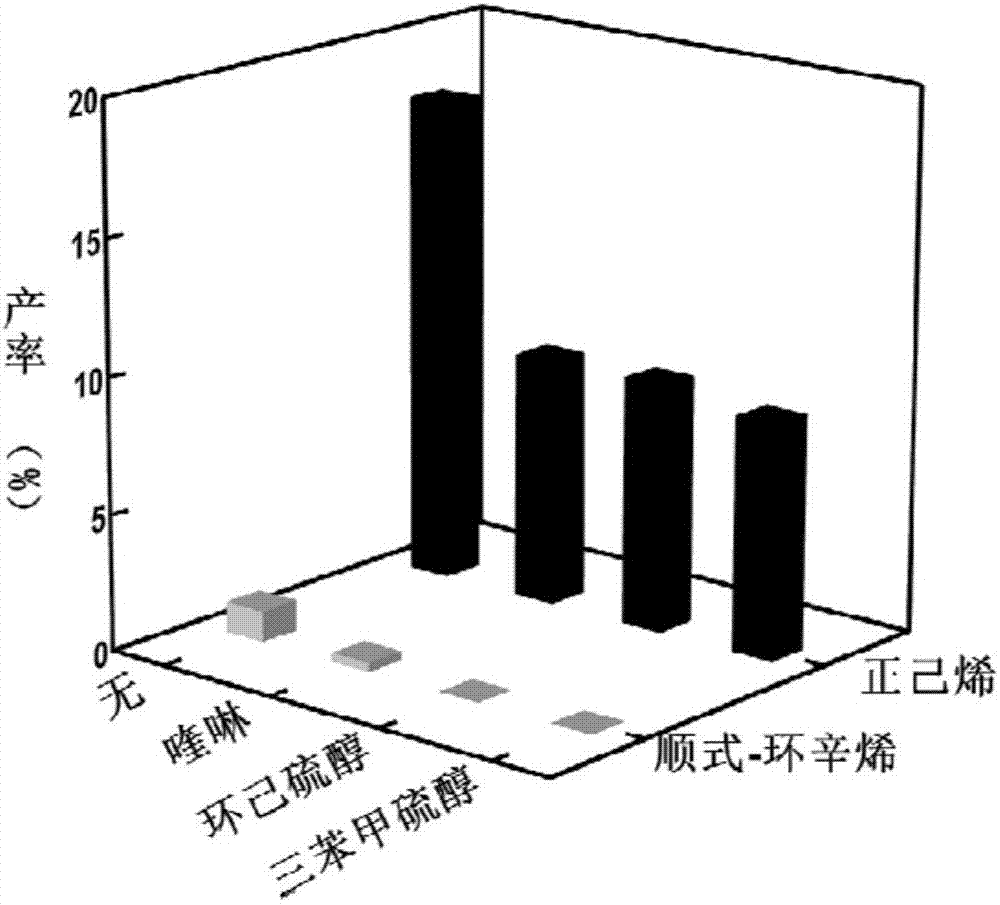
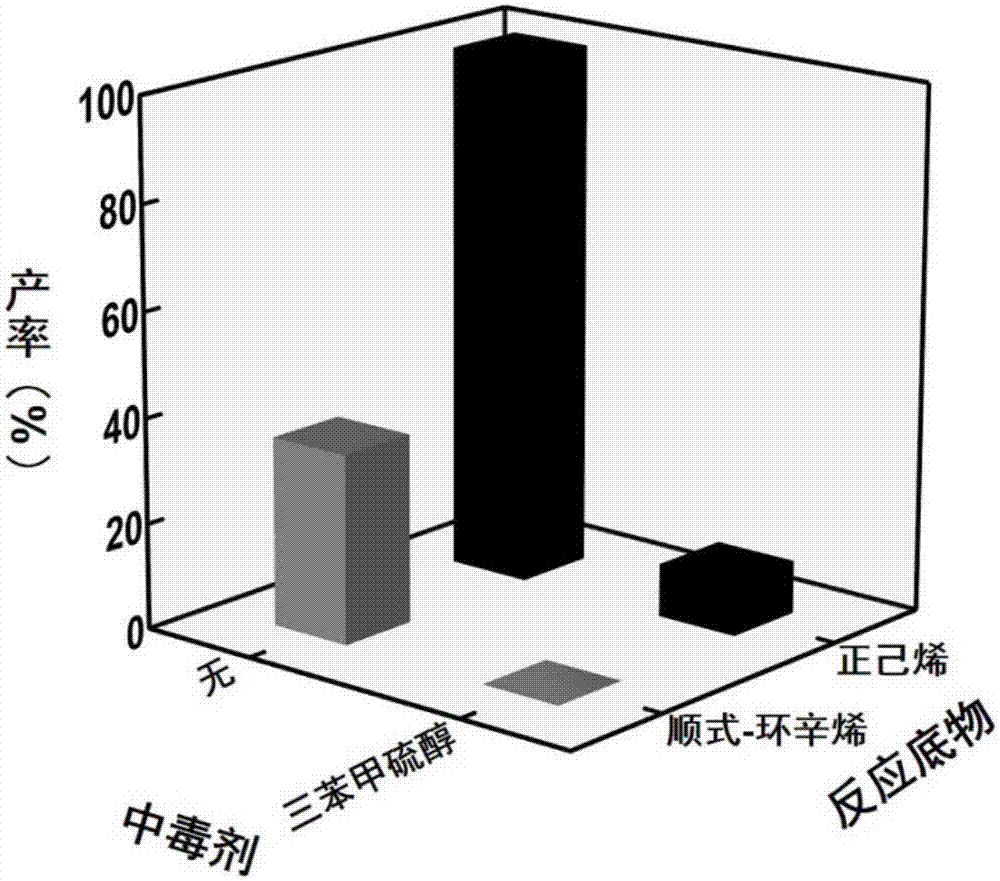
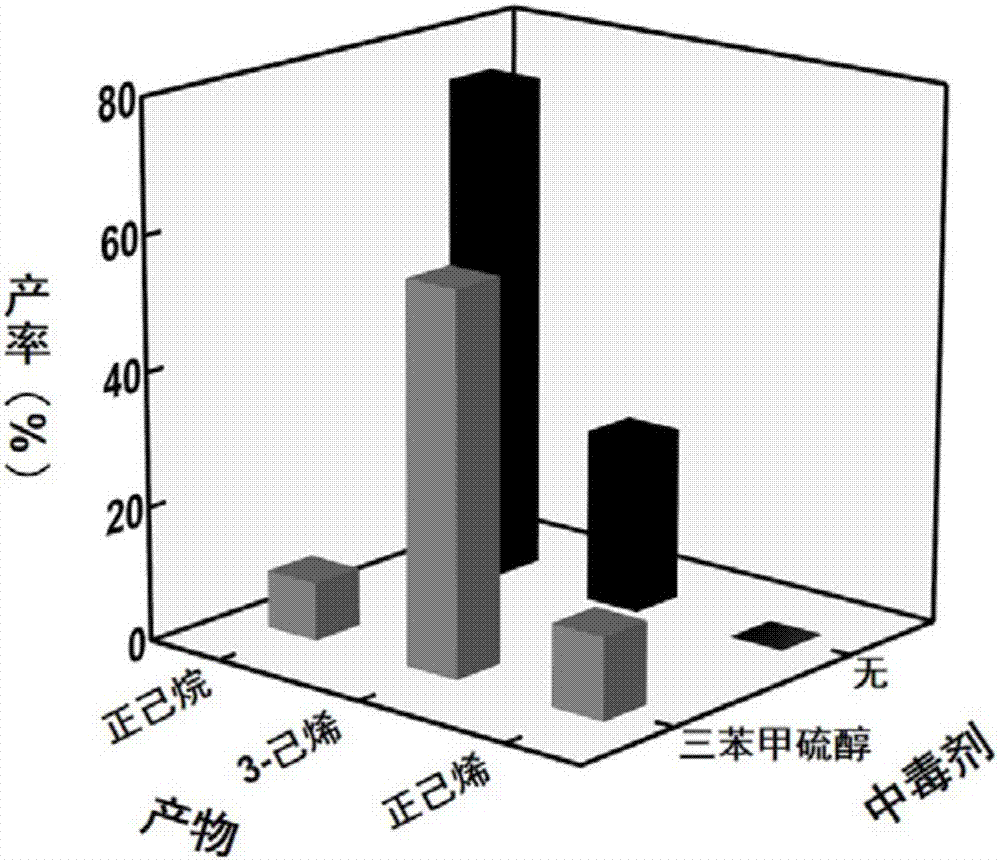
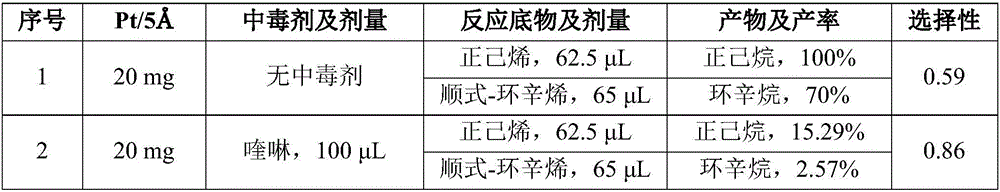
Method for improving catalytic selectivity of metal nanoparticle/porous coordination polymer composite catalyst and application thereof
InactiveCN107344122ACatalytic activity retentionHigh selectivityCatalyst protectionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical reactionMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a method for improving catalytic selectivity of a metal nanoparticle / porous coordination polymer composite catalyst and application thereof. A passivator with the size larger than the hole diameter of porous coordination polymer is utilized to passivate metal nanoparticles compounded on the outer surface of the porous coordination polymer to reduce or inhibit catalytic activity thereof; meanwhile, catalytic activity of the metal nanoparticles in hole channels of the porous coordination polymer is kept; thus, the catalytic selectivity of the metal nanoparticle / porous coordination polymer composite catalyst is improved. A poisoningpassivating effect of the passivator to a metal catalyst is utilized, and a trace of reagents of quinoline, mercaptan and the like are introduced into a catalytic reaction system to passivate a part of metal nanoparticles being unfavorable for selective catalyst in the composite catalyst. When the method is applied to catalytic hydrogenation reaction of olefin, molecular dimension selectivity or chemical reaction locus selectivity can be effectively improved. The method is simple, easy and practicable and provides a novel design idea for further improving the catalytic selectivity of the composite catalyst.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing chlorotoluene
ActiveCN103102243AReduce dosageHigh activityHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationO-chlorotolueneEthyl Chloride
The invention relates to a method of toluene chlorination reaction and particularly relates to a method for preparing chlorotoluene through the toluene chlorination reaction. The method is characterized by adopting a made-to-order macroporous metal chelating resin as a catalyst; and the catalyst is chelated from an iron chloride water solution with the mass concentration of 10% and D418 styrene cation exchange resin with the particle size of 0.5-1.5 millimeters and the aperture of 0.6-1 nanometer at 60 DEG C under the conditions of stirring and ph of 3.5. Thus, electrophilic reaction during toluene chlorination is mainly carried out in a catalyst pore path; because chlorotoluene is smaller than o-chlorotoluene in molecular dimension and has higher diffusion velocity than o-chlorotoluene in a pore path with certain size, more para-position products are obtained; in addition, the method disclosed by the invention has low requirements on temperature and pressure; and the highest content ratio of chlorotoluene to o-chlorotoluene is 4.1:1 under the conditions of 10-80 DEG C and 0.05-0.1 MPa.
Owner:江苏超跃化学有限公司
Grain husk modified activated carbon adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103521184ALow costEfficient desulfurizationOther chemical processesActivated carbonCamellia oleifera
The invention provides a grain husk modified activated carbon adsorbent prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100-120 parts of activated carbon, 40-45 parts of camellia oleifera husks, 30-34 parts of peanut husks, 20-23 parts of sunflower seed husks, 4-5 parts of castor oil plant husks, 12-14 parts of diatomite, 8-10 parts of modified attapulgite and a proper amount of water. Grain such as camellia oleifera husks and the like is carbonized to obtain activated carbon which has different pore diameters and can absorb harmful substances with different molecular dimensions; meanwhile, the novel applications of various grain husks are also developed, the cost is reduced, and the grain husk modified activated carbon adsorbent is environment-friendly and efficient. The modified attapulgite is also added to effectively desulfurize, and jade powder and medical stone powder which are beneficial to the health of a human body are also added, so that the grain husk modified activated carbon adsorbent is healthy and environment-friendly.
Owner:ANHUI PHOENIX INT CO LTD
Method for improving catalytic selectivity of supported catalyst and application thereof
ActiveCN106824268AHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical reactionKinetic diameter
The invention relates to a method for improving the catalytic selectivity of a supported catalyst and application thereof. When a catalyst support is a porous one, a poisoning agent of which the kinetic diameter is greater than the dimension of a support pore and a previously prepared supported catalyst are sufficiently stirred to react; and when the catalyst support is a non-porous one, a poisoning agent of which the kinetic diameter is greater than that of a target selective reactant and the previously prepared supported catalyst are sufficiently stirred to react, thereby obtaining the poisoned supported catalyst. According to the method, the catalytic activity of internal metal nanoparticles is retained by reducing the catalytic activity of metal nanoparticles on the external surface of the support; or the effect of improving the catalytic selectivity of the supported catalyst is achieved by screening the target reactant by means of the poisoning agent. The method can effectively improve molecular dimension selectivity or chemical reaction site selectivity in catalytic hydrogenation reaction of olefin.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent for guar gum fracturing fluid system, preparation method of organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent, and guar gum fracturing fluid system
The invention provides an organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent for a guar gum fracturing fluid system, and belongs to the fields of crosslinking agents for fracturing transformation of a hydrocarbon reservoir. The organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 1-20 parts of inorganic zircon salt, 1-10 parts of inorganic acid, 0-20 parts of polyalcohol amine, 1-20 parts of macromolecule organic acid, 1-20 parts of sodium hydroxide, and 50-90 parts of water. The inorganic zircon salt and the macromolecule organic acid are used to improve the molecular dimension of the organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent through the complex reaction, the mass fraction of a guar gum in the guar gum fracturing fluid system prepared through the provided organic polyacid metal crosslinking agent is low, and better high temperature viscosity is still kept under the condition that the use level of the guar gum is reduced.
Owner:昆山京昆油田化学科技有限公司 +2
Nitrogen-hydrogen mixed plasma cleaning method suitable for substrate circuit
PendingCN109671613AGood removal effectReduce the impactElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSurface cleaning
The invention relates to a nitrogen-hydrogen mixed plasma cleaning method suitable for a substrate circuit. The specific method comprises the following steps of: (1) placing an integrated circuit substrate circuit to be cleaned in a plasma cleaning machine cleaning chamber, and closing a door of the cleaning chamber; (2) injecting the nitrogen-hydrogen mixture gas with a certain proportion; (3) setting parameters of the RF power, the cavity vacuum, and the cleaning time; and (4) starting a cleaning program to perform plasma cleaning, taking out the substrate circuit after the steps are finished, and closing the door of the cleaning chamber. The nitrogen-hydrogen mixed plasma cleaning method has the advantages in that: a chemical reagent is not used in the cleaning process so as to have little influence on operators and the environment; the cleaning process is performed in a vacuum environment, the process gas is little in consumption, and the cost is low; a clamp is configured to perform large-scale cleaning; the removal effect for the molecular dimension-level dirty mark is better than a method of plasma cleaning by employing the nitrogen-hydrogen mixed gas. The nitrogen-hydrogenmixed plasma cleaning method is suitable for surface cleaning prior to welding of thick-film substrate circuits such as alumina and beryllium oxide and thin-film substrate circuits.
Owner:GUIZHOU ZHENHUA FENGGUANG SEMICON
Red organic electroluminescent materials containing naphthylamine group and method for preparing same
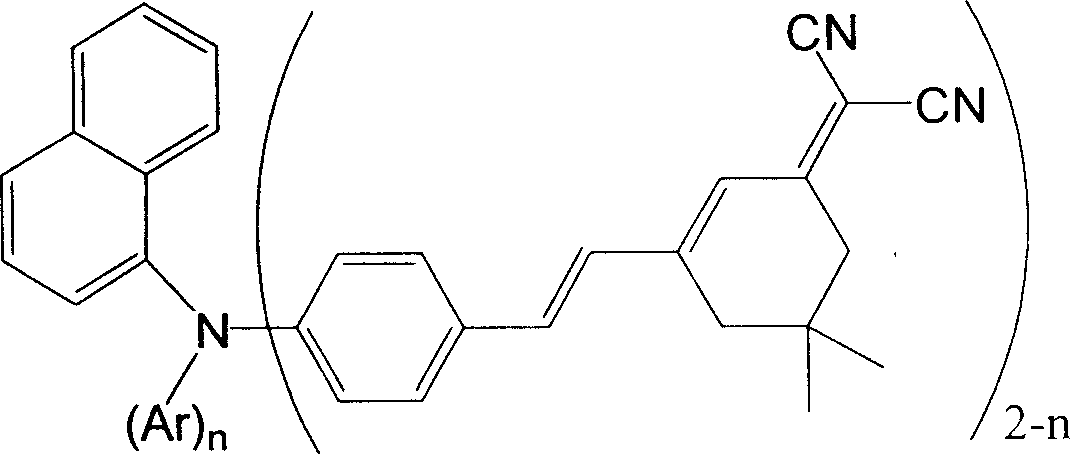
InactiveCN1594494AWith photoelectric conversion functionReduce self-quenchingElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVitrificationThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a red organic electroluminescent materials containing naphthylamine group and method for preparing same, wherein the material has the basic frame of triarylamine, whose extensibility on the three dimensional space and the large rigidity and molecular dimension of the naphthyl can reduce the clustering between the molecules.
Owner:未名光电盐城有限公司
Fish-in-net immobilized enzyme based on rubricyte carrier
InactiveCN101429506AHigh biocatalytic activityAperture controllableOn/in inorganic carrierOn/in biological cellErythrocyte membraneCatalytic effect
The invention relates to a biological / inorganic catalytic reactor with high activity and high stability, namely a fish-in-net immobilized enzyme based on a hematid vector, wherein the catalytic core of the reactor is a biological catalytic material wrapped by hematid; vector hematid is prepared through a method of hypotonicity; a biological material with catalyzing effect is introduced to the vector hematid through a diffusion method; the vector is re-wrapped for subsequent immobilized operation; and the biological-inorganic catalytic reactor is obtained by the immobilized operation, and has a shell made of an inorganic gridding material and the catalytic center made of the biological material wrapped by a hematid membrane. The biological material in the reactor has higher activity and stability, greatly reduces the influence of various organic and inorganic materials in immobilized process on the structure and the activity of the biological material. The reactor can normally construct and execute catalyzing function when the molecular dimension (diameter) of the loaded biological material with catalyzing effect is smaller than 50 nanometers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Acetone-soluble, absorbable, crystalline polyaxial copolymers and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070077382A1Minimum solubilityInherent viscositySuture equipmentsLayered productsSolubilityBlood vessel
High-purity, acetone-soluble, absorbable components of medical devices are designed for optimum interfacing with human blood or the cell lining of a body cavity, and are formed of a crystalline, segmented l-lactide polyaxial copolymer structurally tailored to have certain molecular dimensions, thermal and physicomechanical properties, and solubility characteristics to allow their uses, optimally, as parts of vascular, urological, and post-surgical adhesion prevention devices
Owner:POLY MED
Adsorbent structures for removal of water and fuel contaminants in engine oil
InactiveUS20120103286A1Avoid damageShort lifeIon-exchanger regenerationAluminium silicatesEngineeringAutomotive engine
Devices and methods for removal of condensed, blow-by contaminants with small molecular dimensions from the circulating lubricating engine oil of internal combustion engines, including automotive engines, with a positive crankcase ventilation system are disclosed. These condensable blow-by contaminants include water, alcohols and hydrocarbons with preponderantly seven or fewer carbon atoms. A macroporous structure comprising alumino-silicate particles with micro-pores is at least partially immersed in the circulating oil. The micro-pores are sized to adsorb the small, condensed, blow-by, contaminant molecules but not the larger oil molecules. The particles may be multi-layered, with an inner layer adapted for adsorption of polar molecules. Adsorption is most extensive at lower oil temperatures and decreases as the oil temperature increases. Thus at low temperatures the contaminant molecules may be adsorbed, removed from the oil and temporarily stored in the micropores. At high temperatures some of the contaminants will desorb and be re-incorporated in the oil. The desorbed contaminants will be carried with the higher temperature oil into the engine crankcase where they may vaporize and be removed by the engine positive crankcase ventilation system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
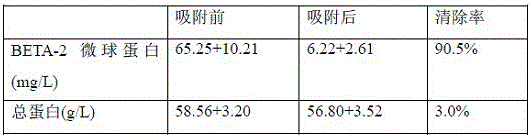
An adsorbent for removing beta-2 microglobulin from blood
ActiveCN104174386BImprove adsorption capacityReduce adsorptionOther chemical processesDialysis systemsBenzeneSorbent
Owner:TIANJIN YOUNASI BIOTECH
Poly-ferrocene graft polymer and preparation method thereof
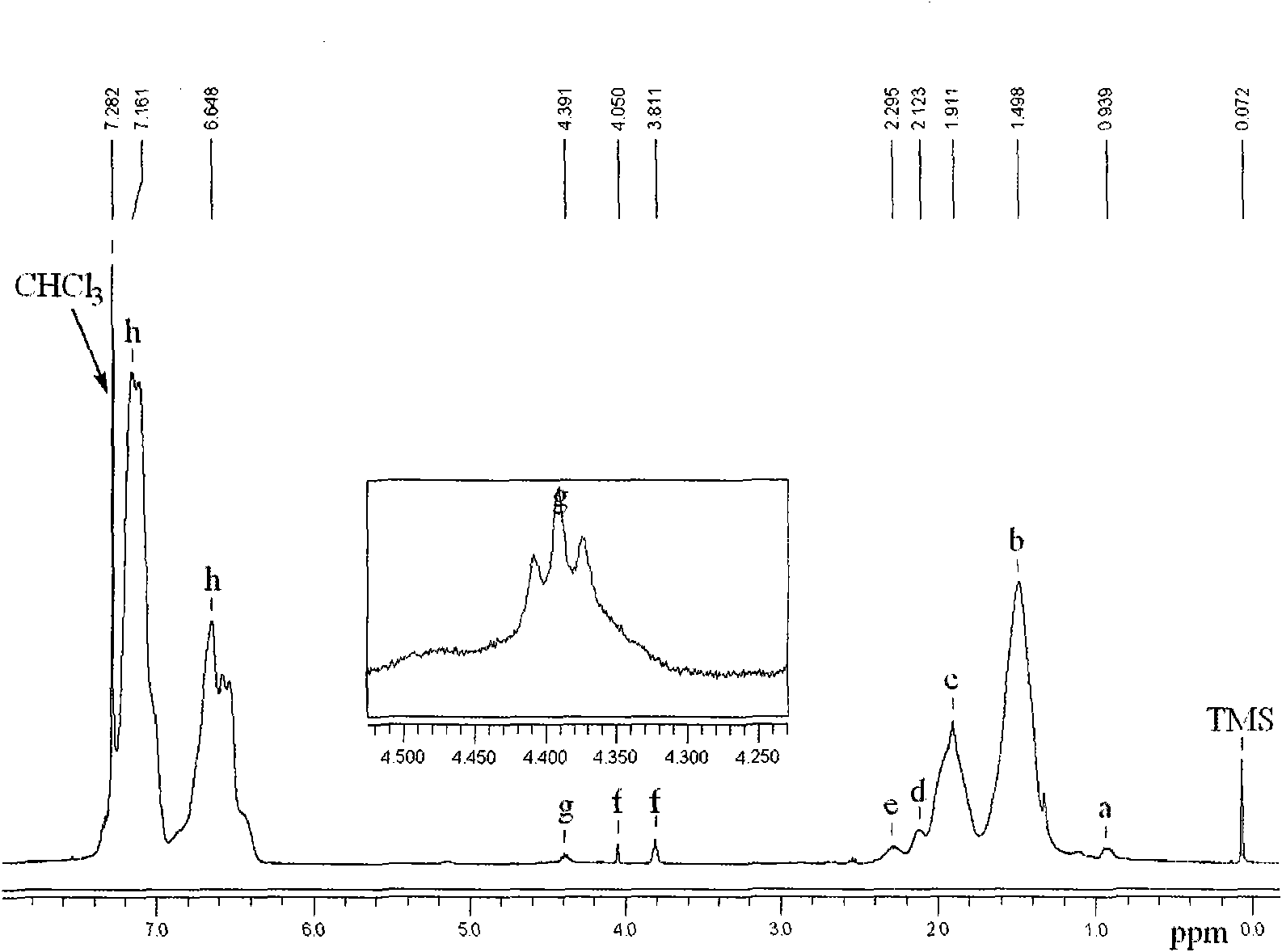
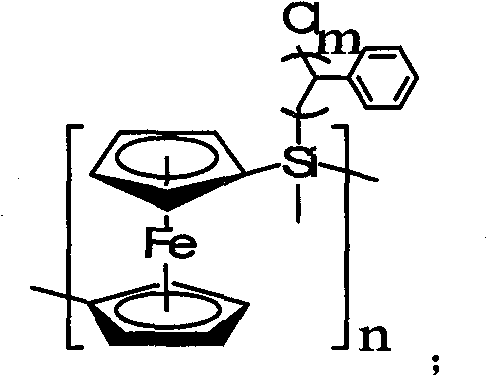
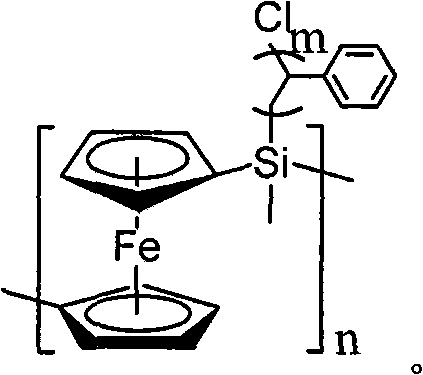
The invention discloses a poly-ferrocene graft polymer and a preparation method thereof. Poly-ferrocene methyl chlorsilane (PFMCS) is used as a macromolecular evocating agent, and styrene (St) is used as a graft monomer. In the presence of a ferrocene-containing poly-ferrocene silane-g-polystyrene (PFS-g-PS) polymer is obtained by atomic transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), purification and drying. In a polymerization process, the ferrocene mass fraction content is regulated in the PFS-g-PS by controlling a polymerization process. The ferrocene in the polymer is evenly distributed into a polystyrene (PS) base body in a molecular dimension, has excellent comprehensive stability and can be used as a precursor for preparing a carbon nano tube and a new material for preparing the carbon nano tube in a one-step method.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of polycarboxylic acid with low sensitivity to silt content for concrete
The invention discloses a preparation method of polycarboxylic acid with low sensitivity to silt content for concrete. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, trimethylsilyl groups are introduced into polycarboxylic acid molecule structures, so that chemical bonding with cement particles can be formed, increase of the molecular dimension is facilitated, the polycarboxylic acid is prevented from being adsorbed by silt with an intercalated structure, the adaptability problem to the cement is improved, and the sensitivity to the silt content change can be reduced; and moreover, by introducing a polyether-ester structure into the polycarboxylic acid molecule structure, the shape and branched structure of long side chains of the polycarboxylic acid in a concrete heterogeneous system can be improved, so that the side chains are expanded and slacked, the peaceability of the concrete is improved, and the sensitivity on the silt content change is reduced.
Owner:KZJ NEW MATERIALS GROUP CO LTD +1
A kind of clay stabilizer for slick water fracturing fluid and preparation method thereof
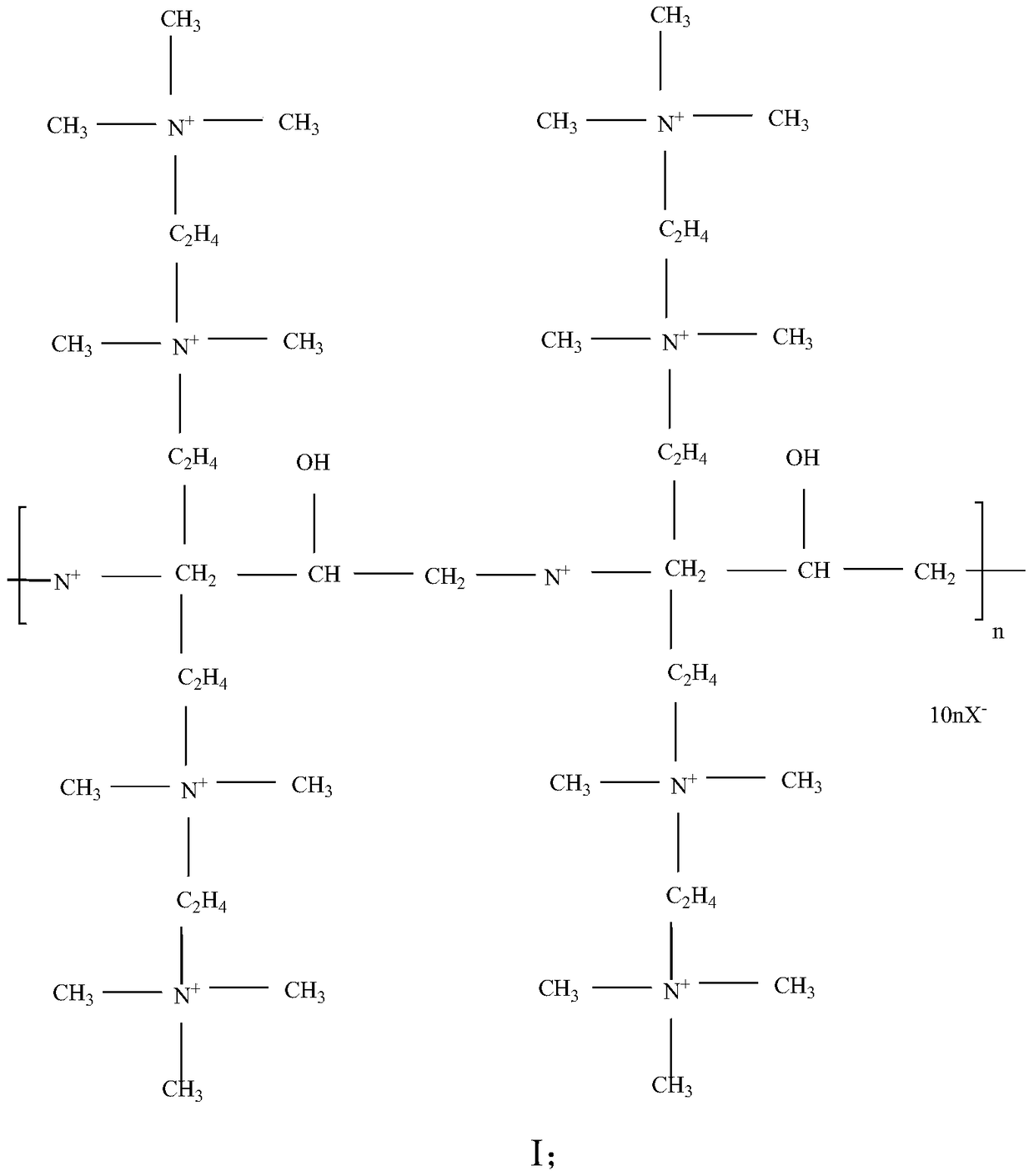
ActiveCN106467735BReduce harmOutstanding Clay Stabilization FunctionOrganic chemistryDrilling compositionDiethylenetriamineFracturing fluid
The invention provides a clay stabilizer used for a slick water fracturing fluid. The clay stabilizer is a quaternary ammonium salt compound. The invention also provides a preparation method of the clay stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: adding reactants 1,1,7,7-tetramethyl diethylenetriamine, 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane and 2-chloroethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride into a solvent to obtain a mixture; heating the mixture to 50-90 DEG C, adding an initiator and reacting for 2-10 h; and finally adding a polymerization inhibitor to stop the reaction. The clay stabilizer has proper molecular dimension. When the clay stabilizer is used in a slick-water fracturing fluid system in shale gas exploitation, clay stabilization function is prominent, and shale reservoir damage is greatly reduced. The product has a good promotion prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of rubber anti-aging coating and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN107118656BHigh strengthDoes not affect processabilityPretreated surfacesEpoxy resin coatingsPolymer scienceAdditive ingredient
The invention provides rubber anti-aging paint, and a preparation method and application thereof. The rubber anti-aging paint comprises the following ingredients in parts by weight with the total weight being 1000 parts: 200 to 350 parts of resin, 0.2 to 3.5 parts of auxiliary agents, 0 to 5 parts of POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) and 641.5 to 799.8 parts of water. The paint can be used as a rubber coating. The rubber anti-aging paint provided by the invention comprises the POSS; the POSS can improve the intensity of the coating after film forming; through a cage-shaped three-dimensional structure, the self molecular dimension is larger; potential physical cross linking points are formed in the coating; the curing crosslinking of the paint is facilitated, so that the coating inside structure stability is improved; the sealing performance and the thermal stability of the coating are effectively increased. When the addition of the POSS is 0.2 percent, the improvement effect of the coating on the rubber is most obvious; the stretch intensity is 9.2 MPa; the break elongation rate is 620 percent.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Red organic electroluminescent materials containing naphthylamine group and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1333040CWith photoelectric conversion functionReduce self-quenchingElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVitrificationThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a red organic electroluminescent materials containing naphthylamine group and method for preparing same, wherein the material has the basic frame of triarylamine, whose extensibility on the three dimensional space and the large rigidity and molecular dimension of the naphthyl can reduce the clustering between the molecules.
Owner:未名光电盐城有限公司
Clay stabilizer used for slick water fracturing fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106467735AReduce harmOutstanding Clay Stabilization FunctionDrilling compositionDiethylenetriamineFracturing fluid
The invention provides a clay stabilizer used for a slick water fracturing fluid. The clay stabilizer is a quaternary ammonium salt compound. The invention also provides a preparation method of the clay stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: adding reactants 1,1,7,7-tetramethyl diethylenetriamine, 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane and 2-chloroethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride into a solvent to obtain a mixture; heating the mixture to 50-90 DEG C, adding an initiator and reacting for 2-10 h; and finally adding a polymerization inhibitor to stop the reaction. The clay stabilizer has proper molecular dimension. When the clay stabilizer is used in a slick-water fracturing fluid system in shale gas exploitation, clay stabilization function is prominent, and shale reservoir damage is greatly reduced. The product has a good promotion prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hyperbranched small molecular intercalation agent with primary amine group as the terminal group and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110003015AGood size controlOptimal Control StructureCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationPreparation by reductive alkylationTrimethylolpropanePhotochemistry
The invention discloses a hyperbranched small molecular intercalation agent with a primary amine group as the terminal group and a preparation method thereof. The molecular structure of the hyperbranched small molecular intercalation agent is as shown in the specification. The hyperbranched small molecular intercalation agent is prepared by using 1,1,1-trimethylolpropane as the raw material and successively through an oxidation reaction and a Leuckart-Wallach reaction. The hyperbranched small molecular intercalation agent has characteristics of controllable molecular dimension and structure, high terminal protonated group density and uniform space distribution, has strong inhibition performance on both hydration pulping effect of bentonite and mud shale, can effectively inhibit hydration swelling and dispersion migration of bentonite and mud shale, and has good temperature-tolerance performance. The temperature-tolerance performance can reach 150 DEG C.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101628204BGood flexibilityNot suitable for breakingSemi-permeable membranesFiltrationInorganic compound
The invention discloses an organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane and a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the field of membrane materials. The preparation method thereof includes three steps, namely the preparation of precursor solution, the filtration preparation of compound mesoporous membrane and the elution of surface active agent in the membrane, namely thatthe method of filtration is mainly used for assembling inorganic mesoporous materials in pores in a polycarbonate membrane so as to prepare the compound membrane, and the mode of extraction and elution is utilized for eliminating the surface active agent in the compound membrane, thereby obtaining the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane; and the pore diameter of the mesoporous materialin the membrane is 3.0nm or 8.0 nm. Compared with the formerly reported inorganic compound mesoporous membrane, the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane has better flexibility, hard breakage and better acid and alkali resistance. Besides, due to the ordering and the nanometer size effect of the pore diameter of the mesoporous structure, the organic-inorganic compound mesoporous membrane can be applied to the fields of molecular dimension selective transfer, membrane separation, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com